Graphenes Aromatic Giants
|
|
|
- Anne Caitlin Baker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ivan Gutman and Boris Furtula Graphenes Aromatic Giants Ivan Gutman and Boris Furtula Ivan Gutman is Professor of Physical Chemistry at the Faculty of Science, Kragujevac, Serbia. Among his interests are mathematical methods in chemistry and the theory of polycyclic aromatic compounds. Boris Furtula is secretary of the journal MATCH Communications in Mathematical and in Computer Chemistry. Keywords Graphenes, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, polyphenyls, condensed benzenes. Recently, extremely large benzenoid hydrocarbons have been synthesized. These compounds resemble graphite in many ways, and have been named graphenes. Because of their nonstandard properties, graphenes have already found numerous applications, especially as special-purpose materials in electronics. In this article we outline the basic chemical facts on graphenes. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (often abbreviated as PAH) are an important class of organic compounds. Students learn about them in any course on organic chemistry. The best known representatives are benzene (which, in fact, is cyclic, not polycyclic), naphthalene, anthracene, phenanthrene and pyrene. Today about 1000 such compounds are known, whereas the number of possible isomers is significantly greater. For instance, there are only 15 stable benzenoid hydrocarbons with 5 six-membered rings, whereas the number of such species with 10 and 14 rings is and , respectively [1,2]. There are only 12 benzenoid isomers with formula C 22 H 14 (which have all been obtained experimentally), but there are 777 and possible C 36 H 20 and C 46 H 24 isomers, respectively. The number of benzenoid isomers with formula C 62 H 34 is calculated to be Evidently, only a minute fraction of these possible isomers will ever be synthesized in the laboratory. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are among the most stable organic compounds [3]. The main sources are tar and pitch [4], especially coal-tar. Coal-tar is a by-product in the manufacturing process of coke, and is produced in millions of tons annually. The molecules of PAH consist of condensed six-membered 1238 Appeared in Vol.13, No.8, pp , 2008.
2 Graphenes Aromatic Giants 1 2 (benzene) rings. Until recently it was believed [5] that their chemical investigations are limited to compounds with not more than 15 rings. The reason for this is based on the fact that large PAHs are practically insoluble in water or organic solvents, which makes their purification and chemical characterization nearly impossible. This is especially the problem when separation of isomers (which are very numerous) is needed. Figure 1. Two large graphenes, both with 114 carbon atoms: 1 = C 114 H 30 ; 2 = C 114 H 34. Recently, these problems were overcome by Klausa Müllen (working at the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research in Mainz, Germany). He discovered a chemical reaction (see Figure 4a) by means of which PAHs of unprecedentedly large size can be obtained, with just a single isomer each! In addition to this, Müllen discovered a laboratory trick (which is outlined in Figure 6) by means of which these compounds can be converted into easily soluble forms. The formulas of a few largest (obtained so far) PAHs are shown in Figures 1 3. Synthesis of Graphenes The synthesis of graphenes, elaborated by Müllen and coworkers, [6,7] consists of two phases. In the first, by standard methods of organic chemistry, one obtains polyphenyls compounds having a large number of benzene rings connected by single carbon- PAHs of unprecedentedly large size can be obtained, with just a single isomer each! 1239
3 Ivan Gutman and Boris Furtula Figure 2 (top). Two still bigger graphenes, both with 132 carbons atoms: 3 = C 132 H 34, 4 = C 132 H 42. Figure 3 (bottom). The two biggest graphenes synthesized so far:: 5 = C 186 H 46, 6 = C 222 H 40. It is worth noting that compound 6 contains only 1.48% hydrogen, whereas the rest is carbon. carbon bonds. A typical reaction of this kind is shown in Figure 4a. The six-membered rings in polyphenyls (for instance, in the polyphenyl 7 shown in Figure 4a) have a complicated spatial arrangement, and do not lie in a single plane. In the second phase, 1240
4 Graphenes Aromatic Giants the polyphenyl is treated with a mild oxidizing agent. Müllen discovered that if one uses iron(iii)-chloride, FeCl 3, as an oxidant, then the polyphenyl is transformed into a graphene in a single chemical reaction. This reaction runs fast and with very high yield. Figure 4b shows how graphene 6 is obtained from polyphenyl 7. It is worth noting that in this way a non-planar Figure 4a. The first phase of synthesis of graphene: Polyphenyl 7 is obtained by standard procedures. Br Br TMS [Pd] TMS TMS [F] O Dieis- Alder [CO]
5 Ivan Gutman and Boris Furtula [Ox] 7 6 Figure 4b. The second phase of synthesis of graphene: By a single-step oxidation of the polyphenyl 7, graphene 6 is gained in high yield. FeCl 3 is used as the oxidizing agent. polyphenyl is transformed into a graphene, whose molecules are almost perfectly planar, that is all atoms of the graphene molecule lie in the same plane. In Figure 5 is shown another, but in essence very similar, synthesis of a graphene [6,7]. For this synthesis it is characteristic that first a mixture of several isomeric polyphenyls is obtained, all yielding (by oxidation) the same end product. We leave to the readers to recognize how great an advantage this is for a successful and efficient laboratory synthesis. Soluble Graphite The problem of low solubility of graphenes has been resolved by Müllen in an ingenious manner. The problem of low solubility of graphenes has been resolved by Müllen in an ingenious manner. The readers of this article may think that this was something obvious and very easy. However, the fact is that nobody came up with such an idea prior to Müllen. The idea is the following [6,7]: By minor modifications of the synthesis procedure, using compounds with appropriate side groups as starting reactants, one arrives at graphenes to which these side groups are attached. These side groups may be long hydrocarbon chains (as in compound 11 in Figure 6) or methoxy groups (as in compound 12) or 1242
6 Graphenes Aromatic Giants O + D-A 8 + [Ox] any other substituent. 10 Thanks to the side groups, the substituted graphenes become easily soluble in organic solvents. Then it is much easier to work with them. We illustrate this by a simple example. If a drop of a dilute solution of a graphene (for instance, in ether) is put on some surface (for instance, of an insulating plastic), and if the solvent is evaporated, then an extremely thin layer of graphene is obtained, whose electrical behaviour is similar to that of graphite. Graphenes, same as graphite, possess easily movable electrons (so-called -electrons) that are responsible for their characteristic electric properties. However, instead of being true conductors (like graphite), graphenes are semiconductors. This feature is of great value in electrical engineering (for instance, for designing transistors), because the semiconducting properties of graphenes 9 Figure 5. Another example of how a graphene is obtained. In the first phase a mixture of isomeric polyphenyls 8 9 is obtained. In the second phase, this mixture is oxidized (in a one-step reaction) into a unique end product the graphene
7 Ivan Gutman and Boris Furtula Figure 6. Graphenes with side groups. Thanks to these substituents the graphenes become easily soluble in organic solvents (for instance, 11 is soluble in ether, and 12 in alcohol). There are also watersoluble graphenes. Such solutions have many, especially electric, properties similar to graphite and are called liquid graphite or soluble graphite
8 Graphenes Aromatic Giants depend on the size and shape of the aromatic core of the molecule, as well as on the nature of its side groups. All these structural details a chemist can modify according to the customer s wish. Substituted graphenes, known as soluble graphite or liquid graphite have become highly valued materials in electronics. Nowadays these compounds are used in various high-tech devices, mainly in those in which light and electricity are interconverted (photo cells, solar cells, light detectors, lightemitting diodes, colour photocopying). Details of these applications are not easy to get because these are usually treated as industrial secrets. In particular, in the two extensive, recently published review articles [6,7], the technical applications of graphenes are mentioned in only a few lines, without saying anything concrete. Substituted graphenes, known as soluble graphite or liquid graphite, have become highly valued materials in electronics. In 2010 the Nobel Prize for physics was given to Andre Gein and Koustantin Novoselov, for their ground breaking experiments regarding the two-dimensional material graphene. Suggested Reading [1] J Brunvoll, B N Cyvin and S J Cyvin, Benzenoid chemical isomers and their enumeration, Topics in Current Chemistry, Vol.162, p.181, [2] G Brinkmann, C Grothaus and I Gutman, Fusenes and benzenoids with perfect matchings, Journal of Mathematical Chemistry, Vol.42, p.909, [3] I Gutman and S J Cyvin, Introduction to the Theory of Benzenoid Hydrocarbons, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, [4] J R Kershaw, The chemical composition of coal-tar pitch, Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds, Vol.3, p.185, [5] J C Fetzer and W R Biggs, A review of the large polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds Vol.4, p.3, [6] M D Watson, A Fechtenkötter, K Müllen, Big is beautiful Aromaticity revisited from the viewpoint of macromolecular and supramolecular benzene chemistry, Chemical Reviews, Vol.101, p.1267, [7] J Wu, A Pisula and K Müllen, Graphenes as potential material for electronics, Chemical Reviews, Vol.107, p.718, [8] T M Figueira-Dharte, K Müllen, Pyrene based materials for organic electronics, Chemical Reviews, Vol.111, p.7260, Address for Correspondence Ivan Gutman and Boris Furtula Faculty of Scienc University of Kragujevac Kragujevac P. O. Box 60, Serbia gutman@kg.ac.yu 1245
RELATION BETWEEN WIENER INDEX AND SPECTRAL RADIUS
 Kragujevac J. Sci. 30 (2008) 57-64. UDC 541.61 57 RELATION BETWEEN WIENER INDEX AND SPECTRAL RADIUS Slavko Radenković and Ivan Gutman Faculty of Science, P. O. Box 60, 34000 Kragujevac, Republic of Serbia
Kragujevac J. Sci. 30 (2008) 57-64. UDC 541.61 57 RELATION BETWEEN WIENER INDEX AND SPECTRAL RADIUS Slavko Radenković and Ivan Gutman Faculty of Science, P. O. Box 60, 34000 Kragujevac, Republic of Serbia
Chemistry 11. Unit 10 Organic Chemistry Part III Unsaturated and aromatic hydrocarbons
 Chemistry 11 Unit 10 Organic Chemistry Part III Unsaturated and aromatic hydrocarbons 2 1. Unsaturated hydrocarbons So far, we have studied the hydrocarbons in which atoms are connected exclusively by
Chemistry 11 Unit 10 Organic Chemistry Part III Unsaturated and aromatic hydrocarbons 2 1. Unsaturated hydrocarbons So far, we have studied the hydrocarbons in which atoms are connected exclusively by
Chapter 21: Hydrocarbons Section 21.3 Alkenes and Alkynes
 Section 21.1 Introduction to Hydrocarbons Section 1 Objectives: Explain the terms organic compound and organic chemistry. Section 21.2 Alkanes Chapter 21: Hydrocarbons Section 21.3 Alkenes and Alkynes
Section 21.1 Introduction to Hydrocarbons Section 1 Objectives: Explain the terms organic compound and organic chemistry. Section 21.2 Alkanes Chapter 21: Hydrocarbons Section 21.3 Alkenes and Alkynes
Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes & Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes & Aromatic Compounds Chapter Outline 13.1 Alkenes and Alkynes 13.2 Nomenclature of Alkenes and Alkynes 13.3 Cis Trans Isomers 13.4 Alkenes in Food and Medicine 13.6 Reactions
Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes & Aromatic Compounds Chapter Outline 13.1 Alkenes and Alkynes 13.2 Nomenclature of Alkenes and Alkynes 13.3 Cis Trans Isomers 13.4 Alkenes in Food and Medicine 13.6 Reactions
Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry The study of carbon compounds constitutes a separate branch of chemistry known as organic chemistry The
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry The study of carbon compounds constitutes a separate branch of chemistry known as organic chemistry The
BIOB111 - Tutorial activities for session 8
 BIOB111 - Tutorial activities for session 8 General topics for week 4 Session 8 Physical and chemical properties and examples of these functional groups (methyl, ethyl in the alkyl family, alkenes and
BIOB111 - Tutorial activities for session 8 General topics for week 4 Session 8 Physical and chemical properties and examples of these functional groups (methyl, ethyl in the alkyl family, alkenes and
Seminar_3. 1. Substituded derivatives of benzene and their nomenclature
 1. Substituded derivatives of benzene and their nomenclature 2. Reactions of arenes. Electrophilic aromatic substitutions 3. Activating substituents. Orientation in the aromatic ring Seminar_3 TEST - Aromatic
1. Substituded derivatives of benzene and their nomenclature 2. Reactions of arenes. Electrophilic aromatic substitutions 3. Activating substituents. Orientation in the aromatic ring Seminar_3 TEST - Aromatic
HISTORY OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 ISTORY OF ORGANI EMISTRY In the early days of chemistry, scientists classified chemical substances into 2 groups: 1. Inorganic: those that were composed of minerals, such as rocks and nonliving matter.
ISTORY OF ORGANI EMISTRY In the early days of chemistry, scientists classified chemical substances into 2 groups: 1. Inorganic: those that were composed of minerals, such as rocks and nonliving matter.
On benzenoid systems with a minimal number of inlets
 J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 78 (9) 1351 1357 (2013) UDC 547.53+547.535:544.112: JSCS 4502 548.1.023:548.115 Original scientific paper On benzenoid systems with a minimal number of inlets ROBERTO CRUZ 1, IVAN GUTMAN
J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 78 (9) 1351 1357 (2013) UDC 547.53+547.535:544.112: JSCS 4502 548.1.023:548.115 Original scientific paper On benzenoid systems with a minimal number of inlets ROBERTO CRUZ 1, IVAN GUTMAN
Electron content of rings of fully benzenoid hydrocarbons
 J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 70 (10) 1199 1204 (2005) UDC 547.53:537.12 JSCS 3357 Original scientific paper Electron content of rings of fully benzenoid hydrocarbons IVAN GUTMAN 1,*#, BORIS FURTULA 1, SVETLANA
J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 70 (10) 1199 1204 (2005) UDC 547.53:537.12 JSCS 3357 Original scientific paper Electron content of rings of fully benzenoid hydrocarbons IVAN GUTMAN 1,*#, BORIS FURTULA 1, SVETLANA
Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds. Discovery of Benzene
 Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C: ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized in 1834 by Eilhard Mitscherlich who determined molecular formula to
Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C: ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized in 1834 by Eilhard Mitscherlich who determined molecular formula to
FIBONACCI NUMBERS AND ALGEBRAIC STRUCTURE COUNT OF SOME NON-BENZENOID CONJUGATED POLYMERS
 FIBONACCI NUMBERS AND ALGEBRAIC STRUCTURE COUNT OF SOME NON-BENZENOID CONJUGATED POLYMERS Olga Bodroza-Pantid Institute of Mathematics, University of Novi Sad, Novi Sad, Yugoslavia Ivan Gutmaii Faculty
FIBONACCI NUMBERS AND ALGEBRAIC STRUCTURE COUNT OF SOME NON-BENZENOID CONJUGATED POLYMERS Olga Bodroza-Pantid Institute of Mathematics, University of Novi Sad, Novi Sad, Yugoslavia Ivan Gutmaii Faculty
Chapter 6: Chemical Bonding
 Chapter 6: Chemical Bonding Learning Objectives Describe the formation of ions by electron loss/gain to obtain the electronic configuration of a noble gas. Describe the formation of ionic bonds between
Chapter 6: Chemical Bonding Learning Objectives Describe the formation of ions by electron loss/gain to obtain the electronic configuration of a noble gas. Describe the formation of ionic bonds between
Chem 1075 Chapter 19 Organic Chemistry Lecture Outline
 Chem 1075 Chapter 19 Organic Chemistry Lecture Outline Slide 2 Introduction Organic chemistry is the study of and its compounds. The major sources of carbon are the fossil fuels: petroleum, natural gas,
Chem 1075 Chapter 19 Organic Chemistry Lecture Outline Slide 2 Introduction Organic chemistry is the study of and its compounds. The major sources of carbon are the fossil fuels: petroleum, natural gas,
Solutions and Organic Chemistry
 Adult Basic Education Science Chemistry 2102C Solutions and Organic Chemistry Prerequisites: Chemistry 1102 Chemistry 2102A Chemistry 2102B Credit Value: 1 Chemistry Concentration Chemistry 1102 Chemistry
Adult Basic Education Science Chemistry 2102C Solutions and Organic Chemistry Prerequisites: Chemistry 1102 Chemistry 2102A Chemistry 2102B Credit Value: 1 Chemistry Concentration Chemistry 1102 Chemistry
Aliphatic Hydrocarbons Anthracite alkanes arene alkenes aromatic compounds alkyl group asymmetric carbon Alkynes benzene 1a
 Aliphatic Hydrocarbons Anthracite alkanes arene alkenes aromatic compounds alkyl group asymmetric carbon Alkynes benzene 1a Hard coal, which is high in carbon content any straight-chain or branched-chain
Aliphatic Hydrocarbons Anthracite alkanes arene alkenes aromatic compounds alkyl group asymmetric carbon Alkynes benzene 1a Hard coal, which is high in carbon content any straight-chain or branched-chain
WHAT CHEMISTS COULD NOT SEE WITHOUT MATHEMATICS Dependence of total π-electron energy on molecular structure
 Xjenza 2005; 0, p. 3-7 3 Invited Article WHAT CHEMIT COULD NOT EE WITHOUT MATHEMATIC Dependence of total -electron energy on molecular structure Ivan Gutman Faculty of cience, University of Kragujevac,
Xjenza 2005; 0, p. 3-7 3 Invited Article WHAT CHEMIT COULD NOT EE WITHOUT MATHEMATIC Dependence of total -electron energy on molecular structure Ivan Gutman Faculty of cience, University of Kragujevac,
I Write the reference number of the correct answer in the Answer Sheet below.
 (2016) Nationality No. CHEMISTRY Name (Please print full name, underlining family name) Marks I Write the reference number of the correct answer in the Answer Sheet below. (1) Which of the atoms 1) to
(2016) Nationality No. CHEMISTRY Name (Please print full name, underlining family name) Marks I Write the reference number of the correct answer in the Answer Sheet below. (1) Which of the atoms 1) to
Organic Chemistry Worksheets
 Highlight the single longest, continuous carbon-carbon chain. Note the alkyl branches that are connected to the root chain. Count the carbons in the root chain, starting from the end closest to the alkyl
Highlight the single longest, continuous carbon-carbon chain. Note the alkyl branches that are connected to the root chain. Count the carbons in the root chain, starting from the end closest to the alkyl
CHEM 112 Name: (Last) (First). Section No.: VISUALIZING ORGANIC REACTIONS THROUGH USE OF MOLECULAR MODELS
 CHEM 112 Name: (Last) (First). Section No.: VISUALIZING ORGANIC REACTIONS THROUGH USE OF MOLECULAR MODELS 1) HYDROCARBONS: a. Saturated Hydrocarbons: Construct a model for propane, C 3 H 8, using black
CHEM 112 Name: (Last) (First). Section No.: VISUALIZING ORGANIC REACTIONS THROUGH USE OF MOLECULAR MODELS 1) HYDROCARBONS: a. Saturated Hydrocarbons: Construct a model for propane, C 3 H 8, using black
Benzene and aromaticity
 aromaticity The word "benzene" derives historically from "gum benzoin", sometimes called "benjamin" (i.e., benzoin resin), an aromatic resin known to European pharmacists and perfumers since the 15th century
aromaticity The word "benzene" derives historically from "gum benzoin", sometimes called "benjamin" (i.e., benzoin resin), an aromatic resin known to European pharmacists and perfumers since the 15th century
Same theme covered in Combined but extra content Extra parts atomic symbols (first 20, Group 1 and Group 7)
 Co-teaching document new ELC Science 5960 and Foundation Level GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy (8464) Chemistry: Component 3 Elements, mixtures and compounds ELC Outcomes Summary of content covered in ELC
Co-teaching document new ELC Science 5960 and Foundation Level GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy (8464) Chemistry: Component 3 Elements, mixtures and compounds ELC Outcomes Summary of content covered in ELC
Also note here that the product is always a six membered ring with a double bond in it.
 Diels Alder Class 1 March 3, 2011 I want to talk in some detail over the next few classes about Diels Alder reactions. I am sure that most of you have heard of Diels Alder reactions before, but we will
Diels Alder Class 1 March 3, 2011 I want to talk in some detail over the next few classes about Diels Alder reactions. I am sure that most of you have heard of Diels Alder reactions before, but we will
YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan
 YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes 1 1. The particulate nature of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. Describe the structure of solids,
YEAR 10- Chemistry Term 1 plan 2016-2017 Week Topic Learning outcomes 1 1. The particulate nature of matter State the distinguishing properties of solids, liquids and gases. Describe the structure of solids,
Organic Chemistry. Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon.
 Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon. In this chapter we will discuss the structural features of organic molecules, nomenclature, and a
Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon. In this chapter we will discuss the structural features of organic molecules, nomenclature, and a
Chemistry 1110 Exam 4 Study Guide
 Chapter 10 Chemistry 1110 Exam 4 Study Guide 10.1 Know that unstable nuclei can undergo radioactive decay. Identify alpha particles, beta particles, and/or gamma rays based on physical properties such
Chapter 10 Chemistry 1110 Exam 4 Study Guide 10.1 Know that unstable nuclei can undergo radioactive decay. Identify alpha particles, beta particles, and/or gamma rays based on physical properties such
554 Chapter 10 Liquids and Solids
 554 Chapter 10 Liquids and Solids above 7376 kpa, CO 2 is a supercritical fluid, with properties of both gas and liquid. Like a gas, it penetrates deep into the coffee beans; like a liquid, it effectively
554 Chapter 10 Liquids and Solids above 7376 kpa, CO 2 is a supercritical fluid, with properties of both gas and liquid. Like a gas, it penetrates deep into the coffee beans; like a liquid, it effectively
Chapter 16. Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C:H ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized in 1834 by Eilhard Mitscherlich who determined molecular formula to
Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C:H ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized in 1834 by Eilhard Mitscherlich who determined molecular formula to
3. What number would be used to indicate the double bond position in the IUPAC name for CH 3 CH 2 CH=CH CH 3 a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d.
 Chapter 2 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Name a difference between a saturated and an unsaturated hydrocarbon. a. Saturated hydrocarbons are composed of only carbon and hydrogen, and unsaturated
Chapter 2 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Name a difference between a saturated and an unsaturated hydrocarbon. a. Saturated hydrocarbons are composed of only carbon and hydrogen, and unsaturated
ALGEBRAIC STRUCTURE COUNT OF ANGULAR HEXAGONAL-SQUARE CHAINS
 ALGEBRAIC STRUCTURE COUNT OF ANGULAR HEXAGONAL-SQUARE CHAINS Olga Bodroža-Pantić Department of Mathematics and Informatics, Faculty of Sciences, Trg D. Obradovića 4, University of Novi Sad, 21000 Novi
ALGEBRAIC STRUCTURE COUNT OF ANGULAR HEXAGONAL-SQUARE CHAINS Olga Bodroža-Pantić Department of Mathematics and Informatics, Faculty of Sciences, Trg D. Obradovića 4, University of Novi Sad, 21000 Novi
OCR A GCSE Chemistry. Topic 2: Elements, compounds and mixtures. Properties of materials. Notes.
 OCR A GCSE Chemistry Topic 2: Elements, compounds and mixtures Properties of materials Notes C2.3a recall that carbon can form four covalent bonds C2.3b explain that the vast array of natural and synthetic
OCR A GCSE Chemistry Topic 2: Elements, compounds and mixtures Properties of materials Notes C2.3a recall that carbon can form four covalent bonds C2.3b explain that the vast array of natural and synthetic
WHAT CHEMISTS COULD NOT SEE WITHOUT MATHEMATICS - DEPENDENCE OF TOTAL π-electron ENERGY ON MOLECULAR STRUCTURE
 57 Kragujevac J. ci. 27 (2005) 57-66. WHAT CHEMIT COULD NOT EE WITHOUT MATHEMATIC - DEPENDENCE OF TOTAL π-electron ENERGY ON MOLECULAR TRUCTURE Ivan Gutman Faculty of cience, P. O. Box 60, 34000 Kragujevac,
57 Kragujevac J. ci. 27 (2005) 57-66. WHAT CHEMIT COULD NOT EE WITHOUT MATHEMATIC - DEPENDENCE OF TOTAL π-electron ENERGY ON MOLECULAR TRUCTURE Ivan Gutman Faculty of cience, P. O. Box 60, 34000 Kragujevac,
17B: Distilling Aromatic Hydrocarbons
 Chapter 17 17B: Distilling Aromatic Hydrocarbons Key Question: How are aromatic compounds isolated? What do they have in common? Aromatic hydrocarbon molecules were originally discovered in spices and
Chapter 17 17B: Distilling Aromatic Hydrocarbons Key Question: How are aromatic compounds isolated? What do they have in common? Aromatic hydrocarbon molecules were originally discovered in spices and
ACID-BASE EXTRACTION
 ACID-BASE EXTRACTION An acid-base extraction is a type of liquid-liquid extraction. It typically involves different solubility levels in water and an organic solvent. The organic solvent may be any carbon-based
ACID-BASE EXTRACTION An acid-base extraction is a type of liquid-liquid extraction. It typically involves different solubility levels in water and an organic solvent. The organic solvent may be any carbon-based
2. A triple Diels-Alder reaction followed by a triple retro Diels Alder reaction give this interesting product:
 Lecture 8 October 6, 2011 Last time we talked a lot about highly reactive dienes, especially those developed by the group of Sam Danishefsky. One more example of an interesting diene is isobenzofuran:
Lecture 8 October 6, 2011 Last time we talked a lot about highly reactive dienes, especially those developed by the group of Sam Danishefsky. One more example of an interesting diene is isobenzofuran:
Organic Chemistry. A. Introduction
 Organic Chemistry A. Introduction 1. Organic chemistry is defined as the chemistry of CARBON compounds. There are a huge number of organic compounds. This results from the fact that carbon forms chains
Organic Chemistry A. Introduction 1. Organic chemistry is defined as the chemistry of CARBON compounds. There are a huge number of organic compounds. This results from the fact that carbon forms chains
Assignment Isomers, Nomenclature, Polymers
 Assignment Isomers, Nomenclature, Polymers Anne-Marie Guirguis K /20 T /26 A /20 C /11 Total St. Francis Xavier SCH4U1 April 14 2017 Multiple Choice [Knowledge 20] Select the letter of the best answer
Assignment Isomers, Nomenclature, Polymers Anne-Marie Guirguis K /20 T /26 A /20 C /11 Total St. Francis Xavier SCH4U1 April 14 2017 Multiple Choice [Knowledge 20] Select the letter of the best answer
Organic Chemistry, 7 L. G. Wade, Jr. 2010, Prentice Hall
 Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds 2010, Prentice Hall Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C:H ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized
Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 16 Aromatic Compounds 2010, Prentice Hall Discovery of Benzene Isolated in 1825 by Michael Faraday who determined C:H ratio to be 1:1. Synthesized
EFFECT OF BENZOCYCLOBUTADIENO-ANNELATION ON CYCLIC CONJUGATION IN PERYLENE. Ivan Gutman and Beba Stojanovska
 Macedonian Journal of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Vol. 30, No. 2, pp. 235 240 (2011) MJCCA9 585 ISSN 1857-5552 Received: March 4, 2011 UDC: 547.6 Accepted: May 5, 2011 Original scientific paper
Macedonian Journal of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Vol. 30, No. 2, pp. 235 240 (2011) MJCCA9 585 ISSN 1857-5552 Received: March 4, 2011 UDC: 547.6 Accepted: May 5, 2011 Original scientific paper
BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
 BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS The discovery of benzene: 1825 - Michael Faraday, empirical formula of C 1834 - Eilhard Mitscherlich synthesized benzin from gum benzoin, empirical formula C Aromatic The
BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS The discovery of benzene: 1825 - Michael Faraday, empirical formula of C 1834 - Eilhard Mitscherlich synthesized benzin from gum benzoin, empirical formula C Aromatic The
AQA Chemistry Checklist
 Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
Topic 1. Atomic structure Video: Atoms, elements, compounds, mixtures Use the names and symbols of the first 20 elements in the periodic table, the elements in Groups 1 and 7, and other elements in this
12/27/2010. Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds
 Nomenclature of Benzene Derivatives Benzene is the parent name for some monosubstituted benzenes; the substituent name is added as a prefix Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds For other monosubstituted benzenes,
Nomenclature of Benzene Derivatives Benzene is the parent name for some monosubstituted benzenes; the substituent name is added as a prefix Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds For other monosubstituted benzenes,
General Chemistry (Third Quarter)
 General Chemistry (Third Quarter) This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence
General Chemistry (Third Quarter) This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence
4.2.1 Chemical bonds, ionic, covalent and metallic
 4.2 Bonding, structure, and the properties of matter Chemists use theories of structure and bonding to explain the physical and chemical properties of materials. Analysis of structures shows that atoms
4.2 Bonding, structure, and the properties of matter Chemists use theories of structure and bonding to explain the physical and chemical properties of materials. Analysis of structures shows that atoms
Hexagonal Chains with Segments of Equal Lengths Having Distinct Sizes and the Same Wiener Index
 MATCH Communications in Mathematical and in Computer Chemistry MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 78 (2017) 121-132 ISSN 0340-6253 Hexagonal Chains with Segments of Equal Lengths Having Distinct Sizes and
MATCH Communications in Mathematical and in Computer Chemistry MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 78 (2017) 121-132 ISSN 0340-6253 Hexagonal Chains with Segments of Equal Lengths Having Distinct Sizes and
Chapter 12: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
 Chapter 12: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS contain carbon-carbon multiple bonds. Alkenes C=C double bonds Alkynes triple bonds Aromatics benzene rings 1 2 NAMING ALKENES Step 1: Name
Chapter 12: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS contain carbon-carbon multiple bonds. Alkenes C=C double bonds Alkynes triple bonds Aromatics benzene rings 1 2 NAMING ALKENES Step 1: Name
4. AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
 BOOKS 1) Organic Chemistry Structure and Function, K. Peter C. Vollhardt, Neil Schore, 6th Edition 2) Organic Chemistry, T. W. Graham Solomons, Craig B. Fryhle 3) Organic Chemistry: A Short Course, H.
BOOKS 1) Organic Chemistry Structure and Function, K. Peter C. Vollhardt, Neil Schore, 6th Edition 2) Organic Chemistry, T. W. Graham Solomons, Craig B. Fryhle 3) Organic Chemistry: A Short Course, H.
Chapter 9. Organic Chemistry: The Infinite Variety of Carbon Compounds. Organic Chemistry
 Chapter 9 Organic Chemistry: The Infinite Variety of Carbon Compounds Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is defined as the chemistry of carbon compounds. Of tens of millions of known chemical compounds,
Chapter 9 Organic Chemistry: The Infinite Variety of Carbon Compounds Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is defined as the chemistry of carbon compounds. Of tens of millions of known chemical compounds,
Wiener Index of Degree Splitting Graph of some Hydrocarbons
 Wiener Index of Degree Splitting Graph of some carbons K. Thilakam A. Sumathi PG and Research Department of Mathematics Department of Mathematics Seethalakshmi Ramaswami College Seethalakshmi Ramaswami
Wiener Index of Degree Splitting Graph of some carbons K. Thilakam A. Sumathi PG and Research Department of Mathematics Department of Mathematics Seethalakshmi Ramaswami College Seethalakshmi Ramaswami
Chapter 22. Organic and Biological Molecules
 Chapter 22 Organic and Biological Molecules The Bonding of Carbon Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon. Because carbon can form single, double, and triple bonds, the following
Chapter 22 Organic and Biological Molecules The Bonding of Carbon Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon. Because carbon can form single, double, and triple bonds, the following
PELLISSIPPI STATE TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE MASTER SYLLABUS APPLIED ORGANIC CHEMISTRY W/ LAB CHT 2210
 PELLISSIPPI STATE TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE MASTER SYLLABUS APPLIED ORGANIC CHEMISTRY W/ LAB CHT 2210 Class Hours: 3.0 Credit Hours: 4.0 Laboratory Hours: 3.0 Date Revised: Fall 2001 NOTE: This course
PELLISSIPPI STATE TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE MASTER SYLLABUS APPLIED ORGANIC CHEMISTRY W/ LAB CHT 2210 Class Hours: 3.0 Credit Hours: 4.0 Laboratory Hours: 3.0 Date Revised: Fall 2001 NOTE: This course
Index. C 60 buckminsterfullerene 87 C 60 buckminsterfullerene formation process
 Index acetone 64 aluminum 64 65 arc-discharged carbon 25 argon ion laser 43 aromaticity 2D 99 3D 89 90, 98 planar 89 spherical 90 astronomy 113, 125, 127, 131 atoms chlorine 107 108 titanium 161 162 benzene
Index acetone 64 aluminum 64 65 arc-discharged carbon 25 argon ion laser 43 aromaticity 2D 99 3D 89 90, 98 planar 89 spherical 90 astronomy 113, 125, 127, 131 atoms chlorine 107 108 titanium 161 162 benzene
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
 Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry Organic Chemistry The chemistry of carbon compounds. Carbon has the ability to form long chains. Without this property, large biomolecules such as proteins,
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry Organic Chemistry The chemistry of carbon compounds. Carbon has the ability to form long chains. Without this property, large biomolecules such as proteins,
NH 2. 8 (c) (ii) This diamine is then reacted with benzene-l,4-dicarboxylic acid to form Kevlar. Draw the repeating unit of Kevlar.
 Polymers 8 (c) Isomer Y is used in the production of the polymer Kevlar. Y is first reduced to the diamine shown below. 20 Areas outside the will not be scanned for marking 2 N N 2 8 (c) (i) Identify a
Polymers 8 (c) Isomer Y is used in the production of the polymer Kevlar. Y is first reduced to the diamine shown below. 20 Areas outside the will not be scanned for marking 2 N N 2 8 (c) (i) Identify a
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones Based on Material Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette
 Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones Based on Material Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Chapter 16 Aldehydes and Ketones Based on Material Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Semiconductor Polymer
 Semiconductor Polymer Organic Semiconductor for Flexible Electronics Introduction: An organic semiconductor is an organic compound that possesses similar properties to inorganic semiconductors with hole
Semiconductor Polymer Organic Semiconductor for Flexible Electronics Introduction: An organic semiconductor is an organic compound that possesses similar properties to inorganic semiconductors with hole
Molecular Geometry: VSEPR model stand for valence-shell electron-pair repulsion and predicts the 3D shape of molecules that are formed in bonding.
 Molecular Geometry: VSEPR model stand for valence-shell electron-pair repulsion and predicts the 3D shape of molecules that are formed in bonding. Sigma and Pi Bonds: All single bonds are sigma(σ), that
Molecular Geometry: VSEPR model stand for valence-shell electron-pair repulsion and predicts the 3D shape of molecules that are formed in bonding. Sigma and Pi Bonds: All single bonds are sigma(σ), that
Organic Chemistry. Introduction to Organic Chemistry
 Organic Chemistry Introduction to Organic Chemistry What is Organic Chemistry? Organic Chemistry is the study of carbon containing compounds Organic compound Is molecular compound of carbon Is made up
Organic Chemistry Introduction to Organic Chemistry What is Organic Chemistry? Organic Chemistry is the study of carbon containing compounds Organic compound Is molecular compound of carbon Is made up
Benzene a remarkable compound. Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds. Some proposed structures for C 6 H 6. Dimethyl substituted benzenes are called xylenes
 Benzene a remarkable compound Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds Discovered by Faraday 1825 Formula C 6 H 6 Highly unsaturated, but remarkably stable Whole new class of benzene derivatives called aromatic compounds
Benzene a remarkable compound Chapter 14 Aromatic Compounds Discovered by Faraday 1825 Formula C 6 H 6 Highly unsaturated, but remarkably stable Whole new class of benzene derivatives called aromatic compounds
Dependence of the total -electron energy on a large number of non-bonding molecular orbitals
 J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 69 (10) 777 782 (2004) UDC 54 724+537.872:519.17:54 12 JSCS 3204 Original scientific paper Dependence of the total -electron energy on a large number of non-bonding molecular orbitals
J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 69 (10) 777 782 (2004) UDC 54 724+537.872:519.17:54 12 JSCS 3204 Original scientific paper Dependence of the total -electron energy on a large number of non-bonding molecular orbitals
Electronegativity Scale F > O > Cl, N > Br > C, H
 Organic Chem Chapter 12 Alkanes Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds. Carbon has several properties that are worth discussing: Tetravalent Always forms 4 bonds Can form multiple bonds (double
Organic Chem Chapter 12 Alkanes Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds. Carbon has several properties that are worth discussing: Tetravalent Always forms 4 bonds Can form multiple bonds (double
Topic 10 Organic Chemistry. Ms. Kiely IB Chemistry (SL) Coral Gables Senior High School
 Topic 10 Organic Chemistry Ms. Kiely IB Chemistry (SL) Coral Gables Senior High School -Alkanes: have low reactivity and undergo free radical substitution. -Alkenes: are more reactive than alkanes, since
Topic 10 Organic Chemistry Ms. Kiely IB Chemistry (SL) Coral Gables Senior High School -Alkanes: have low reactivity and undergo free radical substitution. -Alkenes: are more reactive than alkanes, since
UNIT 4 REVISION CHECKLIST CHEM 4 AS Chemistry
 UNIT 4 REVISION CHECKLIST CHEM 4 AS Chemistry Topic 4.1 Kinetics a) Define the terms: rate of a reaction, rate constant, order of reaction and overall order of reaction b) Deduce the orders of reaction
UNIT 4 REVISION CHECKLIST CHEM 4 AS Chemistry Topic 4.1 Kinetics a) Define the terms: rate of a reaction, rate constant, order of reaction and overall order of reaction b) Deduce the orders of reaction
Nucleic Acid Derivatised Pyrrolidone By: Robert B. Login
 ucleic Acid Derivatised Pyrrolidone By: Robert B. Login Templated polymer synthesis is a growing technology with many recent references illustrating for example how employing ucleic acid bases attached
ucleic Acid Derivatised Pyrrolidone By: Robert B. Login Templated polymer synthesis is a growing technology with many recent references illustrating for example how employing ucleic acid bases attached
Benzenes & Aromatic Compounds
 Benzenes & Aromatic Compounds 1 Structure of Benzene H H C C C H C 6 H 6 H C C C H H A cyclic conjugate molecule Benzene is a colourless odourless liquid, boiling at 80 o C and melting at 5 o C. It is
Benzenes & Aromatic Compounds 1 Structure of Benzene H H C C C H C 6 H 6 H C C C H H A cyclic conjugate molecule Benzene is a colourless odourless liquid, boiling at 80 o C and melting at 5 o C. It is
Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes Based on Material Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette
 Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes Based on Material Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes Based on Material Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Cherry Hill Tuition A Level Chemistry OCR (A) Paper 12
 herry ill Tuition A Level hemistry OR (A) Paper 12 ADVANED SUBSIDIARY GE EMISTRY A hains, Energy and Resources F322 *F318530611* andidates answer on the question paper. OR Supplied Materials: Data Sheet
herry ill Tuition A Level hemistry OR (A) Paper 12 ADVANED SUBSIDIARY GE EMISTRY A hains, Energy and Resources F322 *F318530611* andidates answer on the question paper. OR Supplied Materials: Data Sheet
Chapter 15: Benzene & Aromaticity
 Chapter 15: Benzene & Aromaticity Learning Objective & Key Concepts 1. Sources and nomenclature of aromatic compounds. 2. Introduction to Huckel 4n+2 rule and aromaticity stability and reactivity, 3. Introduction
Chapter 15: Benzene & Aromaticity Learning Objective & Key Concepts 1. Sources and nomenclature of aromatic compounds. 2. Introduction to Huckel 4n+2 rule and aromaticity stability and reactivity, 3. Introduction
Experiment 10: Molecular Models
 B hemistry 162 Laboratory Manual Name Section Experiment 10: Molecular Models Modeling the shape of small organic molecules Previously we have considered molecules and ions for which one chemical formula
B hemistry 162 Laboratory Manual Name Section Experiment 10: Molecular Models Modeling the shape of small organic molecules Previously we have considered molecules and ions for which one chemical formula
Tar measurement by the Solid Phase Adsorption (SPA) method
 Tar measurement by the Solid Phase Adsorption (SPA) method A.J. Grootjes Presented at the 19th European Biomass Conference and Exhibition (EU BC&E), ICC Berlin, Germany (Conference 6-10 June 2011 - Exhibition
Tar measurement by the Solid Phase Adsorption (SPA) method A.J. Grootjes Presented at the 19th European Biomass Conference and Exhibition (EU BC&E), ICC Berlin, Germany (Conference 6-10 June 2011 - Exhibition
Clar number of catacondensed benzenoid hydrocarbons
 Clar number of catacondensed benzenoid hydrocarbons Sandi Klavžar a,, Petra Žigert a, Ivan Gutman b, a Department of Mathematics, PEF, University of Maribor, Koroška 160, 2000 Maribor, Slovenia b Faculty
Clar number of catacondensed benzenoid hydrocarbons Sandi Klavžar a,, Petra Žigert a, Ivan Gutman b, a Department of Mathematics, PEF, University of Maribor, Koroška 160, 2000 Maribor, Slovenia b Faculty
AGS Chemistry 2007 Correlated to: Prentice Hall Chemistry (Wilbraham) including AGS Differentiated Instruction Strategies
 - including AGS Differentiated Instruction 1-1 Chemistry 1-1 Chemistry and the Nature of Science Page 3: ELL/ESL Strategy; Page 4: Science ; Pages 5, 6: Applications-Global ; Pages 5, 7: Learning Styles-
- including AGS Differentiated Instruction 1-1 Chemistry 1-1 Chemistry and the Nature of Science Page 3: ELL/ESL Strategy; Page 4: Science ; Pages 5, 6: Applications-Global ; Pages 5, 7: Learning Styles-
Exp #08: ORGANIC MOLECULES Introductory Chemistry
 Exp #08: ORGANIC MOLECULES Introductory Chemistry Chem 10 De Anza College Name: Student ID: Goals Explore different ways organic molecules are represented and understood. Distinguish between structural
Exp #08: ORGANIC MOLECULES Introductory Chemistry Chem 10 De Anza College Name: Student ID: Goals Explore different ways organic molecules are represented and understood. Distinguish between structural
The Fundamental Laws of Chemistry
 The Fundamental Laws of Chemistry As we have discussed, matter can be classified into different categories based on directly observable properties, be they physical or chemical. Heterogeneous systems contain
The Fundamental Laws of Chemistry As we have discussed, matter can be classified into different categories based on directly observable properties, be they physical or chemical. Heterogeneous systems contain
Review Topic 8: Phases of Matter and Mixtures
 Name: Score: 24 / 24 points (100%) Review Topic 8: Phases of Matter and Mixtures Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. C 1. Soda water is a solution
Name: Score: 24 / 24 points (100%) Review Topic 8: Phases of Matter and Mixtures Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. C 1. Soda water is a solution
Time Allowed: 60 minutes MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC AND BIOCHEMISTRY QUIZ 5 Time Allowed: 60 minutes MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What is the IUPAC name
INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC AND BIOCHEMISTRY QUIZ 5 Time Allowed: 60 minutes MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What is the IUPAC name
2. a) R N and L N so R L or L R 2.
 1. Use the formulae on the Some Key Equations and Definitions for Chromatography sheet. a) 0.74 (remember that w b = 1.70 x w ½ ) b) 5 c) 0.893 (α always refers to two adjacent peaks) d) 1.0x10 3 e) 0.1
1. Use the formulae on the Some Key Equations and Definitions for Chromatography sheet. a) 0.74 (remember that w b = 1.70 x w ½ ) b) 5 c) 0.893 (α always refers to two adjacent peaks) d) 1.0x10 3 e) 0.1
Benzene and its Isomers
 Gopalpur Nagendrappa Benzene and its Isomers How many Structures can we raw for C 6? Gopalpur Nagendrappa Gopalpur Nagendrappa teaches organic chemistry at Bangalore University. His work includes organic
Gopalpur Nagendrappa Benzene and its Isomers How many Structures can we raw for C 6? Gopalpur Nagendrappa Gopalpur Nagendrappa teaches organic chemistry at Bangalore University. His work includes organic
CHAPTER 3 HW SOLUTIONS: INTERMOLECULAR FORCES
 APTER 3 W SLUTINS: INTERMLEULAR FRES ENERGY DIAGRAMS 1. Label and answer questions about the following energy diagram. Energy * I * I * small E a3 a. ow many steps are in the overall reaction? 3 b. Label
APTER 3 W SLUTINS: INTERMLEULAR FRES ENERGY DIAGRAMS 1. Label and answer questions about the following energy diagram. Energy * I * I * small E a3 a. ow many steps are in the overall reaction? 3 b. Label
Chemistry 2.5 AS WORKBOOK. Working to Excellence Working to Excellence
 Chemistry 2.5 AS 91165 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds WORKBOOK Working to Excellence Working to Excellence CONTENTS 1. Writing Excellence answers to Cis-Trans
Chemistry 2.5 AS 91165 Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds WORKBOOK Working to Excellence Working to Excellence CONTENTS 1. Writing Excellence answers to Cis-Trans
[2]... [1]
![[2]... [1] [2]... [1]](/thumbs/75/71765689.jpg) 1 Carbon and silicon are elements in Group IV. Both elements have macromolecular structures. (a) Diamond and graphite are two forms of the element carbon. (i) Explain why diamond is a very hard substance....
1 Carbon and silicon are elements in Group IV. Both elements have macromolecular structures. (a) Diamond and graphite are two forms of the element carbon. (i) Explain why diamond is a very hard substance....
Review Chemistry Paper 1
 Atomic Structure Topic Define an atom and element. Use scientific conventions to identify chemical symbols Identify elements by chemical symbols Define compound Use chemical formulae to show different
Atomic Structure Topic Define an atom and element. Use scientific conventions to identify chemical symbols Identify elements by chemical symbols Define compound Use chemical formulae to show different
AMINES. 3. Secondary When two hydrogen atoms are replaced by two alkyl or aryl groups.
 AMINES Amine may be regarded as derivative of ammonia formed by replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms by corresponding number of alkyl or aryl group CLASSIFICATION 1. Ammonia 2. Primary amine 3. Secondary
AMINES Amine may be regarded as derivative of ammonia formed by replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms by corresponding number of alkyl or aryl group CLASSIFICATION 1. Ammonia 2. Primary amine 3. Secondary
1. What is the letter of the alphabet in parentheses that follows EXAM I in the title above? a. a b. b c. c d. d e. e
 HEM 102, EXAM I ( a ) 1. What is the letter of the alphabet in parentheses that follows EXAM I in the title above? a. a b. b c. c d. d e. e 2. Which compound has the most constitutional isomers? a. 2 H
HEM 102, EXAM I ( a ) 1. What is the letter of the alphabet in parentheses that follows EXAM I in the title above? a. a b. b c. c d. d e. e 2. Which compound has the most constitutional isomers? a. 2 H
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change
 CHEMISTRY Matter and Change CHAPTER 21 Table Of Contents Section Section Chapter 21: Hydrocarbons Section 21.3 Alkenes and Alkynes Section Section 21.5 Aromatic Hydrocarbons Explainthe terms organic compound
CHEMISTRY Matter and Change CHAPTER 21 Table Of Contents Section Section Chapter 21: Hydrocarbons Section 21.3 Alkenes and Alkynes Section Section 21.5 Aromatic Hydrocarbons Explainthe terms organic compound
KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II
 KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II Course Objectives: 1) To introduce the chemistry of alcohols and ethers. 2) To study the chemistry of functional groups. 3) To learn the chemistry of aromatic compounds and
KOT 222 Organic Chemistry II Course Objectives: 1) To introduce the chemistry of alcohols and ethers. 2) To study the chemistry of functional groups. 3) To learn the chemistry of aromatic compounds and
Mixtures and Solutions: The Sugar in the Tea by Emily Sohn and Joseph Brennan
 Readers Mixtures and Solutions: The Sugar in the Tea by Emily Sohn and Joseph Brennan Science Objective This book introduces children to some basics of chemistry as they explore the atoms and molecules
Readers Mixtures and Solutions: The Sugar in the Tea by Emily Sohn and Joseph Brennan Science Objective This book introduces children to some basics of chemistry as they explore the atoms and molecules
ORGANIC - EGE 5E CH. 2 - COVALENT BONDING AND CHEMICAL REACTIVITY
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: HYBRID ORBITAL THEORY The Aufbau Principle states that electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy. If carbon has only two unfilled orbitals, why does it like to
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: HYBRID ORBITAL THEORY The Aufbau Principle states that electrons fill orbitals in order of increasing energy. If carbon has only two unfilled orbitals, why does it like to
4 States of matter. N Goalby chemrevise.org 1. Ideal Gas Equation
 4 States of matter Ideal Gas Equation The ideal gas equation applies to all gases and mixtures of gases. If a mixture of gases is used the value n will be the total moles of all gases in the mixture. The
4 States of matter Ideal Gas Equation The ideal gas equation applies to all gases and mixtures of gases. If a mixture of gases is used the value n will be the total moles of all gases in the mixture. The
LECTURE #13 Tues., Oct.18, Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, , 7.10, 2, Sections
 CEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #13 Tues., Oct.18, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSGNED READNGS: TODAY S CLASS: Sections 4.1 4.6 NEXT CLASS: rest of Ch.4 http://artsandscience.concordia.ca/facstaff/p-r/rogers
CEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #13 Tues., Oct.18, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSGNED READNGS: TODAY S CLASS: Sections 4.1 4.6 NEXT CLASS: rest of Ch.4 http://artsandscience.concordia.ca/facstaff/p-r/rogers
PCB Chemistry 101. Presented by Valerie Tillinghast O Reilly, Talbot & Okun Associates, Inc.
 PCB Chemistry 101 Presented by Valerie Tillinghast O Reilly, Talbot & Okun Associates, Inc. Short History of PCBs Reports indicate that PCBs were first synthesized by chemists in 1881 but significant commercial
PCB Chemistry 101 Presented by Valerie Tillinghast O Reilly, Talbot & Okun Associates, Inc. Short History of PCBs Reports indicate that PCBs were first synthesized by chemists in 1881 but significant commercial
Vision. Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. How rods work H 3 C CH 3. Protein opsin. 11-cis-retinal. Opsin. Rhodopsin.
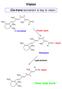 Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
Aromatic Compounds I
 2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 1 Aromatic Compounds I Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 16 in Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition, L.
2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 1 Aromatic Compounds I Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 16 in Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition, L.
On π-electron configuration of cyclopenta-derivatives of benzenoid hydrocarbons
 Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 49, July 010, pp. 853-860 On π-electron configuration of cyclopenta-derivatives of benzenoid hydrocarbons Ivan Gutman*, Jelena Đurđević, Dušan Bašić & Dragana Rašović Faculty
Indian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 49, July 010, pp. 853-860 On π-electron configuration of cyclopenta-derivatives of benzenoid hydrocarbons Ivan Gutman*, Jelena Đurđević, Dušan Bašić & Dragana Rašović Faculty
4.2 Bonding, structure, and the properties of matter
 4.2 Bonding, structure, and the properties of matter Chemists use theories of structure and bonding to explain the physical and chemical properties of materials. Analysis of structures shows that atoms
4.2 Bonding, structure, and the properties of matter Chemists use theories of structure and bonding to explain the physical and chemical properties of materials. Analysis of structures shows that atoms
Chemistry 2202 Course Outline
 Chemistry 2202 Course Outline Unit 1 Stoichiometry Chemistry is a qualitative and quantitative science. Students have generally been studying chemistry in a qualitative sense. In this introduction to the
Chemistry 2202 Course Outline Unit 1 Stoichiometry Chemistry is a qualitative and quantitative science. Students have generally been studying chemistry in a qualitative sense. In this introduction to the
Worksheet 1.1. Chapter 1: Quantitative chemistry glossary
 Worksheet 1.1 Chapter 1: Quantitative chemistry glossary Amount The number of moles of a substance present in a sample. Aqueous solution A solution with water as the solvent. Atmosphere The unit atmosphere
Worksheet 1.1 Chapter 1: Quantitative chemistry glossary Amount The number of moles of a substance present in a sample. Aqueous solution A solution with water as the solvent. Atmosphere The unit atmosphere
Calculating the hyper Wiener index of benzenoid hydrocarbons
 Calculating the hyper Wiener index of benzenoid hydrocarbons Petra Žigert1, Sandi Klavžar 1 and Ivan Gutman 2 1 Department of Mathematics, PEF, University of Maribor, Koroška 160, 2000 Maribor, Slovenia
Calculating the hyper Wiener index of benzenoid hydrocarbons Petra Žigert1, Sandi Klavžar 1 and Ivan Gutman 2 1 Department of Mathematics, PEF, University of Maribor, Koroška 160, 2000 Maribor, Slovenia
Personalised Learning Checklists AQA Trilogy Chemistry Paper 1
 AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 Topics T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are Describe what elements and compounds are State
AQA TRILOGY Chemistry (8464) from 2016 Topics T5.1 Atomic structure and the periodic table State that everything is made of atoms and recall what they are Describe what elements and compounds are State
Benzene and Aromatic Compounds. Chapter 15 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry
 Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Chapter 15 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Background Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Four degrees of unsaturation. It
Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Chapter 15 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Background Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Four degrees of unsaturation. It
