Vision. Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. How rods work H 3 C CH 3. Protein opsin. 11-cis-retinal. Opsin. Rhodopsin.
|
|
|
- Geraldine Gaines
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C C C 3 C 3 ow rods work
2 Geometric Isomers of Cyclic Compounds Important in carbohydrate chemistry. Two substituents on the same side (face) of the ring are cis to each other. 3 C C 3 Cis-1,2-dimethylcyclopropane (bp 37ºC) Two substituents on the opposite side (face) of the ring are trans to each other. 3 C C 3 Trans-1,2-dimethylcyclopropane (bp 28ºC)
3 Chemical Properties of Alkenes Addition reactions to the double bond. Addition of symmetrical reagents. X X X X Addition of unsymmetrical reagents. X Y X Y
4 Addition of Symmetrical Reagents 1. Addition of 2 : ydrogenation Ni catalyst Conversion of alkene to alkane. 2. Addition of alogens: alogenation Cl 2 and Br 2 add rapidly to carbon-carbon double bonds. No catalyst is needed. Cl Cl Cl Cl Br Br Br Br I 2 does not add (unreactive). F 2 reacts explosively.
5 Addition of Unsymmetrical Reagents 1. Addition of Cl. Cl Cl Chloroalkane 2. Addition of Br. Br Br Bromoalkane 3. Addition of conc. 2 SO 4. O O S O O O O S O O Alkyl hydrogen sulfate (very polar) Concentrated sulfuric acid dissolves alkenes.
6 Addition of Unsymmetrical Reagents 4. Addition of 2 O: ydration. O catalyst O Water does not add in the absence of an acid catalyst.
7 Addition of Unsymmetrical Reagents Unsymmetrical reagents add selectively to unsymmetrical double bonds. C 3 C 3 C 2 C C 2 Cl 1-chloro-2-methylbutane C 3 C 3 C 2 C C 2 Cl 2-methyl-1-butene C 3 Unsymmetrical alkene C 3 C 2 C Cl C 2 2-chloro-2-methylbutane (major product) Two possible products Note: The products are constitutional isomers.
8 Markovnikov's Rule When an unsymmetrical reactant of the type G adds to an unsymmetrical alkene, the adds to the carbon atom of the double bond that has the greater number of hydrogens. C 3 C C 3 C 3 catalyst C 2 O C 3 CC 3 2-methyl-1-propene O tert-butanol (major product) C 3 C C 2 2 SO 4 C 3 CC 3 1-propene OSO 3 isopropyl hydrogen sulfate (major product) Note: The chemical basis for Markovnikov's Rule is the mechanism for addition (see later).
9 Markovnikov's Rule Markovnikov's Rule does not apply to symmetrical alkenes. i.e. Symmetrical alkenes do not add G selectively. Cl Cl cyclohexene 1-chlorocyclohexane
10 Chemical Basis of Markovnikov's Rule Mechanism of addition of G to alkenes. 2-methyl-1-propene C 3 C 3 C C 2 Cl 3 o Carbocation 1 o Carbocation C 3 C C 3 C 2 C 3 C C 3 C 2 Cl Cl C 3 C 3 C 3 C C 2 C 3 C C 2 Cl 2-chloro-2-methylpropane (major product) Markovnikov Product Cl 1-chloro-2-methylpropane
11 Chemical Basis of Markovnikov's Rule The more stable carbocation preferentially forms. Order of stability of carbocations: R R C 3 < R C 2 < R C Methyl Carbocation LEAST STABLE 1 o Carbocation 2 o Carbocation < R C R 3 o Carbocation MOST STABLE Alkyl groups stabilize the positive charge on the carbocation by electron donation through the σ-bond.
12 Addition of 2 O to Alkenes Mechanism 2-methyl-1-propene C 3 C 3 C C 2 2 O 3 o Carbocation 1 o Carbocation C 3 C C 3 C 2 C 3 C C 3 C 2 2 O 2 O C 3 C 3 C 3 C C 2 C 3 C C 2 O 2 O 2 C 3 C 3 C 3 C C 2 C 3 C C 2 O tert-butanol (major product) O
13 Aromatic Compounds C 3 O Benzene Toluene Benzaldehyde Naphthalene Anthracene Biphenyl Benzene and structural relatives. Aromatic hydrocarbons are found in coal and petroleum.
14 Benzene C C C C C C Does not undergo usual alkene reactions Reacts with Br 2 to give substitution product NOT addition product Br 2 Br Br Br Br Addition Product Substitution Product
15 Benzene as a relatively small heat of hydrogenation. Compare 2 Pt catalyst hydrog Cyclohexene -118 kj/mol 2 Pt catalyst hydrog Cyclohexadiene -230 kj/mol Expect 2 Pt catalyst hydrog Benzene Actual -356 kj/mol 2 Pt catalyst hydrog Benzene -206 kj/mol
16 Benzene Structure Planar molecule, hexagonal shape. All C-C bonds are same length. All C-C-C bond angles are 120 o. Resonance hybrid of two equivalent forms. All six carbon atoms are sp 2 hybridized. p-orbital on each carbon atom perpindicular to plane of ring.
17 Nomenclature Continued There are also a large number of common (or "trivial") names for arenes which are in common usage. Many of these are acceptable "parents" with regard to nomenclature. When one of these is used as the parent chain, the substituent is position #1, by definition.
18 Carcinogenicity of Benzopyrene O Benzo[a]pyrene O O N Base pair O O O "Ultimate Carcinogen" Partial metabolism of of benzopyrene in in mammals in in series of of enzyme-catalysed steps yields highly reactive carbocation known as as the ultimate carcinogen. Carbocation may alkylate base pairs of of DNA ÍÍcarcinogenicity.
19 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Examples of electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. E E 1. Electrophilic aromatic halogenation. X X 2 X 2. Electrophilic aromatic nitration. NO 2 2 SO 4 NO 3 2 O
20 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution 3. Electrophilic aromatic sulfonation. 2 SO 4 SO 3 SO 3
Introduction to Organic Chemistry. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Introduction to Organic Chemistry Copyright The McGraw-ill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Common Elements in Organic Compounds 2 Classification of ydrocarbons ydrocarbons
Introduction to Organic Chemistry Copyright The McGraw-ill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Common Elements in Organic Compounds 2 Classification of ydrocarbons ydrocarbons
Chemistry 110. Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell. Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes.
 Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes Chapter 12 Alkenes are hydrocarbons which have one or more
Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes Chapter 12 Alkenes are hydrocarbons which have one or more
Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes
 Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes Chapter 12 Alkenes are hydrocarbons which have one or more
Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes Chapter 12 Alkenes are hydrocarbons which have one or more
Chapter 12: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
 Chapter 12: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS contain carbon-carbon multiple bonds. Alkenes C=C double bonds Alkynes triple bonds Aromatics benzene rings 1 2 NAMING ALKENES Step 1: Name
Chapter 12: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS contain carbon-carbon multiple bonds. Alkenes C=C double bonds Alkynes triple bonds Aromatics benzene rings 1 2 NAMING ALKENES Step 1: Name
Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes & Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes & Aromatic Compounds Chapter Outline 13.1 Alkenes and Alkynes 13.2 Nomenclature of Alkenes and Alkynes 13.3 Cis Trans Isomers 13.4 Alkenes in Food and Medicine 13.6 Reactions
Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes & Aromatic Compounds Chapter Outline 13.1 Alkenes and Alkynes 13.2 Nomenclature of Alkenes and Alkynes 13.3 Cis Trans Isomers 13.4 Alkenes in Food and Medicine 13.6 Reactions
Class XI Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons Chemistry
 Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 3. AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS Aromatic
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 3. AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS Aromatic
Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing.
 Chapter 21 Lecture Notes Organic Chemistry Intro Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing. The Bonding of Carbon Because carbon has four valence electrons, it can form covalent bonds.
Chapter 21 Lecture Notes Organic Chemistry Intro Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing. The Bonding of Carbon Because carbon has four valence electrons, it can form covalent bonds.
Chapter 3. Alkenes And Alkynes
 Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King I. Conjugation
 Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King Chapter 16 Conjugation, Resonance, and Dienes I. Conjugation Conjugation occurs whenever p-orbitals can overlap on three or more adjacent atoms. Conjugated systems are more
Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King Chapter 16 Conjugation, Resonance, and Dienes I. Conjugation Conjugation occurs whenever p-orbitals can overlap on three or more adjacent atoms. Conjugated systems are more
Unsaturated hydrocarbons. Chapter 13
 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Chapter 13 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons which contain at least one C-C multiple (double or triple) bond. The multiple bond is a site for chemical reactions in these molecules.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons Chapter 13 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons which contain at least one C-C multiple (double or triple) bond. The multiple bond is a site for chemical reactions in these molecules.
Chemistry 11. Unit 10 Organic Chemistry Part III Unsaturated and aromatic hydrocarbons
 Chemistry 11 Unit 10 Organic Chemistry Part III Unsaturated and aromatic hydrocarbons 2 1. Unsaturated hydrocarbons So far, we have studied the hydrocarbons in which atoms are connected exclusively by
Chemistry 11 Unit 10 Organic Chemistry Part III Unsaturated and aromatic hydrocarbons 2 1. Unsaturated hydrocarbons So far, we have studied the hydrocarbons in which atoms are connected exclusively by
CHAPTER 12: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons IMPORTANT COMMON NAMES: 12.1 NOMENCLATURE GEOMETRY of ALKENES. Page 12-1
 APTER 12: Unsaturated ydrocarbons lassify unsaturated hydrocarbons as alkenes, alkynes, or aromatics Write the IUPA names of alkenes from structural formulas Predict and describe geometric (cis-trans)
APTER 12: Unsaturated ydrocarbons lassify unsaturated hydrocarbons as alkenes, alkynes, or aromatics Write the IUPA names of alkenes from structural formulas Predict and describe geometric (cis-trans)
Chem101 General Chemistry. Lecture 11 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
 hem101 General hemistry Lecture 11 Unsaturated ydrocarbons Unsaturated ydrocarbons ontain one or more double or triple carbon-carbon bond. University of Wisconsin-Eau laire hem101 - Lecture 11 2 Unsaturated
hem101 General hemistry Lecture 11 Unsaturated ydrocarbons Unsaturated ydrocarbons ontain one or more double or triple carbon-carbon bond. University of Wisconsin-Eau laire hem101 - Lecture 11 2 Unsaturated
Straight. C C bonds are sp 3 hybridized. Butane, C 4 H 10 H 3 C
 Hydrocarbons Straight Chain Alkanes aren t Straight C C bonds are sp 3 hybridized Butane, C 4 H 10 Structural Shorthand Explicit hydrogens (those required to complete carbon s valence) are usually left
Hydrocarbons Straight Chain Alkanes aren t Straight C C bonds are sp 3 hybridized Butane, C 4 H 10 Structural Shorthand Explicit hydrogens (those required to complete carbon s valence) are usually left
TOK: The relationship between a reaction mechanism and the experimental evidence to support it could be discussed. See
 Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/22 hours) SL students study the core of these options and HL students study the whole option (the core and the extension material). TOK: The relationship between
Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/22 hours) SL students study the core of these options and HL students study the whole option (the core and the extension material). TOK: The relationship between
Benzene and Aromatic Compounds. Chapter 15 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry
 Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Chapter 15 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Background Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Four degrees of unsaturation. It
Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Chapter 15 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Background Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Four degrees of unsaturation. It
3. What number would be used to indicate the double bond position in the IUPAC name for CH 3 CH 2 CH=CH CH 3 a. 1 b. 2 c. 3 d.
 Chapter 2 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Name a difference between a saturated and an unsaturated hydrocarbon. a. Saturated hydrocarbons are composed of only carbon and hydrogen, and unsaturated
Chapter 2 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Name a difference between a saturated and an unsaturated hydrocarbon. a. Saturated hydrocarbons are composed of only carbon and hydrogen, and unsaturated
240 Chem. Aromatic Compounds. Chapter 6
 240 Chem Aromatic Compounds Chapter 6 1 The expressing aromatic compounds came to mean benzene and derivatives of benzene. Structure of Benzene: Resonance Description C 6 H 6 1.It contains a six-membered
240 Chem Aromatic Compounds Chapter 6 1 The expressing aromatic compounds came to mean benzene and derivatives of benzene. Structure of Benzene: Resonance Description C 6 H 6 1.It contains a six-membered
DAV CENTENARY PUBLIC SCHOOL, PASCHIM ENCLAVE, NEW DELHI - 87
 HYDROCARBONS 1. Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain. 2. Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia
HYDROCARBONS 1. Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain. 2. Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia
16.1 Draw Newman projections for these staggered and three eclipsed conformations of 1, 2 - dichlorobutane as viewed downt he central C-C bond.
 CAPTER 16 Practice Exercises 16.1 Draw Newman projections for these staggered and three eclipsed conformations of 1, 2 - dichlorobutane as viewed downt he central C-C bond. 16.3 (a) The more stable conformation
CAPTER 16 Practice Exercises 16.1 Draw Newman projections for these staggered and three eclipsed conformations of 1, 2 - dichlorobutane as viewed downt he central C-C bond. 16.3 (a) The more stable conformation
Chapter 4: Aromatic Compounds. Bitter almonds are the source of the aromatic compound benzaldehyde
 Chapter 4: Aromatic Compounds Bitter almonds are the source of the aromatic compound benzaldehyde Sources of Benzene Benzene, C 6 H 6, is the parent hydrocarbon of the especially stable compounds known
Chapter 4: Aromatic Compounds Bitter almonds are the source of the aromatic compound benzaldehyde Sources of Benzene Benzene, C 6 H 6, is the parent hydrocarbon of the especially stable compounds known
5. Reactions of Alkenes (text )
 2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 5.1 5. Reactions of Alkenes (text 5.1 5.5) A. Addition Reactions In hapter 4, we saw that π bonds have electron density on two sides of the
2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 5.1 5. Reactions of Alkenes (text 5.1 5.5) A. Addition Reactions In hapter 4, we saw that π bonds have electron density on two sides of the
1. Root of name depends on longest chain of C containing the double bond; ends in "ene"
 Alkenes (β-carotene, an antioxidant pigment) n 2n (acyclic) n 2n-2 (cyclic) R R R R Key features sp 2 -hybridized carbons, 120 o bond angles σ + π bonding between = planar geometry around = "unsaturated"
Alkenes (β-carotene, an antioxidant pigment) n 2n (acyclic) n 2n-2 (cyclic) R R R R Key features sp 2 -hybridized carbons, 120 o bond angles σ + π bonding between = planar geometry around = "unsaturated"
UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS
 C20 09/16/2013 15:47:28 Page 295 CHAPTER 20 UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. The sigma bond in the double bond of ethene is formed by the overlap of two sp 2 electron orbitals
C20 09/16/2013 15:47:28 Page 295 CHAPTER 20 UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. The sigma bond in the double bond of ethene is formed by the overlap of two sp 2 electron orbitals
Topic 2 Alkenes and alkynes
 Topic 2 Alkenes and alkynes lassification of rganic Reactions Four basic types of organic reaction Acid base reactions Substitution reactions Addition elimination reactions xidation reduction reactions
Topic 2 Alkenes and alkynes lassification of rganic Reactions Four basic types of organic reaction Acid base reactions Substitution reactions Addition elimination reactions xidation reduction reactions
CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA
 CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems conjugation a series of overlapping p orbitals The Allyl Group allylic position is the next to a double bond 1 allyl
CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems conjugation a series of overlapping p orbitals The Allyl Group allylic position is the next to a double bond 1 allyl
6.1.1 Aromatic Compounds
 6.1.1 Aromatic ompounds There are two major classes of organic chemicals aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six carbon ams with delocalised
6.1.1 Aromatic ompounds There are two major classes of organic chemicals aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six carbon ams with delocalised
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)
 Unit 13 HYDROCARBONS I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Arrange the following in decreasing order of their boiling points. (A) n butane (B) 2 methylbutane (C) n-pentane (D) 2,2 dimethylpropane A
Unit 13 HYDROCARBONS I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Arrange the following in decreasing order of their boiling points. (A) n butane (B) 2 methylbutane (C) n-pentane (D) 2,2 dimethylpropane A
Time Allowed: 60 minutes MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC AND BIOCHEMISTRY QUIZ 5 Time Allowed: 60 minutes MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What is the IUPAC name
INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC AND BIOCHEMISTRY QUIZ 5 Time Allowed: 60 minutes MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What is the IUPAC name
Alkenes. Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents
 Alkenes Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents Alkenes Family of hydrocarbons, the alkenes, which contain less hydrogen, carbon for carbon, than the alkanes Structure of ethylene, The carbon-carbon
Alkenes Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents Alkenes Family of hydrocarbons, the alkenes, which contain less hydrogen, carbon for carbon, than the alkanes Structure of ethylene, The carbon-carbon
Organic Chemistry. February 18, 2014
 Organic Chemistry February 18, 2014 What does organic mean? Organic Describes products Grown through natural biological process Without synthetic materials In the 18 th century Produced by a living system
Organic Chemistry February 18, 2014 What does organic mean? Organic Describes products Grown through natural biological process Without synthetic materials In the 18 th century Produced by a living system
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY- 1
 ORGANIC CEMISTRY- 1 ALKENES Alkenes are also called Olefins (C n 2n ) unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes occur abundantly in nature. Ethylene ( 2 C=C 2 ) is a plant hormone that induces ripening in fruit.
ORGANIC CEMISTRY- 1 ALKENES Alkenes are also called Olefins (C n 2n ) unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes occur abundantly in nature. Ethylene ( 2 C=C 2 ) is a plant hormone that induces ripening in fruit.
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Chem 263 ct. 8, 2013 lectrophilic Aromatic Substitution Benzene appears to be a remarkably stable and unreactive compared to alkenes, such as cyclohexene or ethylene, or even alkanes, such as cyclohexane
Chem 263 ct. 8, 2013 lectrophilic Aromatic Substitution Benzene appears to be a remarkably stable and unreactive compared to alkenes, such as cyclohexene or ethylene, or even alkanes, such as cyclohexane
Aliphatic Hydrocarbons Anthracite alkanes arene alkenes aromatic compounds alkyl group asymmetric carbon Alkynes benzene 1a
 Aliphatic Hydrocarbons Anthracite alkanes arene alkenes aromatic compounds alkyl group asymmetric carbon Alkynes benzene 1a Hard coal, which is high in carbon content any straight-chain or branched-chain
Aliphatic Hydrocarbons Anthracite alkanes arene alkenes aromatic compounds alkyl group asymmetric carbon Alkynes benzene 1a Hard coal, which is high in carbon content any straight-chain or branched-chain
Chapter 5. Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 5. Aromatic Compounds 5.1 Structure of Benzene: The Kekule Proposal Mid-1800s, benzene was known to have the molecular formula C 6 6. Benzene reacts with 2 in the presence of iron to give substitution
Chapter 5. Aromatic Compounds 5.1 Structure of Benzene: The Kekule Proposal Mid-1800s, benzene was known to have the molecular formula C 6 6. Benzene reacts with 2 in the presence of iron to give substitution
BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
 BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS The discovery of benzene: 1825 - Michael Faraday, empirical formula of C 1834 - Eilhard Mitscherlich synthesized benzin from gum benzoin, empirical formula C Aromatic The
BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS The discovery of benzene: 1825 - Michael Faraday, empirical formula of C 1834 - Eilhard Mitscherlich synthesized benzin from gum benzoin, empirical formula C Aromatic The
Chem 121 Winter 2016: Section 03, Sample Problems. Alkenes and Alkynes
 Chem 121 Winter 2016: Section 03, Sample Problems Alkenes and Alkynes Problems adapted from Chemistry - The Central Science, 3 rd edition. 24.2 Consider the hydrocarbon drawn below. (a) What is the hybridisation
Chem 121 Winter 2016: Section 03, Sample Problems Alkenes and Alkynes Problems adapted from Chemistry - The Central Science, 3 rd edition. 24.2 Consider the hydrocarbon drawn below. (a) What is the hybridisation
Also called an olefin but alkene is better General formula C n H 2n (if one alkene present) Can act as weak nucleophiles
 Alkenes - Structure, Stability, Nomenclature Also called an olefin but alkene is better General formula C n H 2n (if one alkene present) unsaturated - contain fewer than maximum H's possible per C Can
Alkenes - Structure, Stability, Nomenclature Also called an olefin but alkene is better General formula C n H 2n (if one alkene present) unsaturated - contain fewer than maximum H's possible per C Can
Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes Based on Material Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette
 Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes Based on Material Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes Based on Material Prepared by Andrea D. Leonard University of Louisiana at Lafayette 1 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
Alkenes. Alkenes-hydrocarbons with a carbon-carbon double bond. Alkenes have the formula C n H 2n. Nomenclature
 Alkenes Alkenes-hydrocarbons with a carbon-carbon double bond. Alkenes have the formula n 2n. Nomenclature Alkenes are named in the same manner as alkanes with the following adjustments. 1. Find the longest
Alkenes Alkenes-hydrocarbons with a carbon-carbon double bond. Alkenes have the formula n 2n. Nomenclature Alkenes are named in the same manner as alkanes with the following adjustments. 1. Find the longest
CHAPTER 3 ALKENES, ALKYNES & CONJUGATE DIENES
 CHEM 244 PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERING STUDENTS, COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING PRE-REQUISITES COURSE; CHEM 101 CREDIT HOURS; 2 (2+0) Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College
CHEM 244 PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERING STUDENTS, COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING PRE-REQUISITES COURSE; CHEM 101 CREDIT HOURS; 2 (2+0) Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College
Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/22 hours)
 Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/) TOK: The relationship between a reaction mechanism and the experimental evidence to support it could be discussed. See 16... Core material: G1 G8 are core material
Option G: Further organic chemistry (15/) TOK: The relationship between a reaction mechanism and the experimental evidence to support it could be discussed. See 16... Core material: G1 G8 are core material
Aromatic Hydrocarbons / Arenes
 Aromatic ydrocarbons / Arenes There are two major classes of organic chemicals aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six carbon atoms
Aromatic ydrocarbons / Arenes There are two major classes of organic chemicals aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six carbon atoms
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophile substitutes for a hydrogen on the benzene ring. Chapter 17: Aromatics 2-Reactions Slide 17-2 1 Mechanism Step
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophile substitutes for a hydrogen on the benzene ring. Chapter 17: Aromatics 2-Reactions Slide 17-2 1 Mechanism Step
Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry
 Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Structure and Bonding 2 Structure and Bonding Rotation around the C=C bond is restricted 90 rotation The p orbitals are orthogonal
Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Structure and Bonding 2 Structure and Bonding Rotation around the C=C bond is restricted 90 rotation The p orbitals are orthogonal
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
 Interchapter G Unsaturated ydrocarbons The flame from an acetylene torch. Acetylene, which is used extensively in welding, is an example of an unsaturated hydrocarbon. University Science Books, 2011. All
Interchapter G Unsaturated ydrocarbons The flame from an acetylene torch. Acetylene, which is used extensively in welding, is an example of an unsaturated hydrocarbon. University Science Books, 2011. All
Organic Chemistry Worksheets
 Highlight the single longest, continuous carbon-carbon chain. Note the alkyl branches that are connected to the root chain. Count the carbons in the root chain, starting from the end closest to the alkyl
Highlight the single longest, continuous carbon-carbon chain. Note the alkyl branches that are connected to the root chain. Count the carbons in the root chain, starting from the end closest to the alkyl
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY. Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction
 DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 5 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction The vertical axis in this graph represents the potential energy. The transition
DAMIETTA UNIVERSITY CHEM-103: BASIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LECTURE 5 Dr Ali El-Agamey 1 Energy Diagram of One-Step Exothermic Reaction The vertical axis in this graph represents the potential energy. The transition
Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Excluded sections 3.15&3.16
 Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes Excluded sections 3.15&3.16 3.1 Definition and Classification Alkene: a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carboncarbon double bonds. ethylene is the simplest alkene. Alkyne:
Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes Excluded sections 3.15&3.16 3.1 Definition and Classification Alkene: a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carboncarbon double bonds. ethylene is the simplest alkene. Alkyne:
CHEMISTRY CHAPTER- HYDROCARBONS (I PUC) One mark questions
 CEMISTRY CAPTER- YDROCARBONS (I PUC) One mark questions 1. What type of structural isomerism is shown by alkanes? 2. Which metal is used in Wurtz reaction? 3. What happens when isopropyl bromide is subjected
CEMISTRY CAPTER- YDROCARBONS (I PUC) One mark questions 1. What type of structural isomerism is shown by alkanes? 2. Which metal is used in Wurtz reaction? 3. What happens when isopropyl bromide is subjected
Name Date Class HYDROCARBONS
 22.1 HYDROCARBONS Section Review Objectives Describe the relationship between number of valence electrons and bonding in carbon Define and describe alkanes Relate the polarity of hydrocarbons to their
22.1 HYDROCARBONS Section Review Objectives Describe the relationship between number of valence electrons and bonding in carbon Define and describe alkanes Relate the polarity of hydrocarbons to their
Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes
 Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes I. Isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes II. Reactions involving allylic cations or radicals III. Diels-Alder Reactions IV. Aromaticity I. Isolated, Conjugated,
Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes I. Isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes II. Reactions involving allylic cations or radicals III. Diels-Alder Reactions IV. Aromaticity I. Isolated, Conjugated,
11/26/ Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds. Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds
 9.5 Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds The general concept of aromaticity can be extended to include polycyclic aromatic compounds Benzo[a]pyrene is one of the cancer-causing substances found in tobacco smoke
9.5 Polycyclic Aromatic Compounds The general concept of aromaticity can be extended to include polycyclic aromatic compounds Benzo[a]pyrene is one of the cancer-causing substances found in tobacco smoke
11/30/ Substituent Effects in Electrophilic Substitutions. Substituent Effects in Electrophilic Substitutions
 Chapter 9 Problems: 9.1-29, 32-34, 36-37, 39-45, 48-56, 58-59, 61-69, 71-72. 9.8 Substituent effects in the electrophilic substitution of an aromatic ring Substituents affect the reactivity of the aromatic
Chapter 9 Problems: 9.1-29, 32-34, 36-37, 39-45, 48-56, 58-59, 61-69, 71-72. 9.8 Substituent effects in the electrophilic substitution of an aromatic ring Substituents affect the reactivity of the aromatic
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Chem 263 Sept 29, 2016 lectrophilic Aromatic Substitution Benzene appears to be a remarkably stable (36 kcal/mole more) and unreactive compared to alkenes, such as cyclohexene or ethylene, or even alkanes,
Chem 263 Sept 29, 2016 lectrophilic Aromatic Substitution Benzene appears to be a remarkably stable (36 kcal/mole more) and unreactive compared to alkenes, such as cyclohexene or ethylene, or even alkanes,
4.15 Halogenation of Alkanes RH + X 2 RX + HX
 4.15 alogenation of Alkanes R + X 2 RX + X Energetics R + X 2 RX + X explosive for F 2 exothermic for Cl 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 4.16 Chlorination of Methane Chlorination of Methane carried out
4.15 alogenation of Alkanes R + X 2 RX + X Energetics R + X 2 RX + X explosive for F 2 exothermic for Cl 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 4.16 Chlorination of Methane Chlorination of Methane carried out
Learning Guide for Chapter 11 - Alkenes I
 Learning Guide for Chapter 11 - Alkenes I I. Introduction to alkenes - p 1 bond structure, classifying alkenes, reactivity, physical properties, occurrences and uses, spectroscopy, stabilty II. Unsaturation
Learning Guide for Chapter 11 - Alkenes I I. Introduction to alkenes - p 1 bond structure, classifying alkenes, reactivity, physical properties, occurrences and uses, spectroscopy, stabilty II. Unsaturation
Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes
 Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes In an alkane, all covalent bonds between carbon were σ (σ bonds are defined as bonds where the electron density is symmetric about the internuclear axis) In an alkene,
Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes In an alkane, all covalent bonds between carbon were σ (σ bonds are defined as bonds where the electron density is symmetric about the internuclear axis) In an alkene,
Aromatic Hydrocarbons / Arenes
 Aromatic ydrocarbons / Arenes There are two major classes of organic chemicals aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six carbon atoms
Aromatic ydrocarbons / Arenes There are two major classes of organic chemicals aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six carbon atoms
Chapter 12 Alkenes and Alkynes
 BR M 102 lass Notes hapter 12 Page 1 of 8 hapter 12 Alkenes and Alkynes * alkenes = double bonds * alkynes triple bonds * aromatics or arenes alternating double and single bonds such as in benzene * saturated
BR M 102 lass Notes hapter 12 Page 1 of 8 hapter 12 Alkenes and Alkynes * alkenes = double bonds * alkynes triple bonds * aromatics or arenes alternating double and single bonds such as in benzene * saturated
What is the major product of the following reaction?
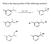 What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
2. Which one of the following structures represents a different compound from the other three?
 1. Provide a Newman projection of the most stable conformation of 2-methylpentane, (CH 3 ) 2 CHCH 2 CH 2 CH 3, looking along the C2-C3 bond 2. Which one of the following structures represents a different
1. Provide a Newman projection of the most stable conformation of 2-methylpentane, (CH 3 ) 2 CHCH 2 CH 2 CH 3, looking along the C2-C3 bond 2. Which one of the following structures represents a different
Chemistry 2000 Lecture 18: Reactions of organic compounds
 hemistry 2000 Lecture 18: Reactions of organic compounds Marc R. Roussel March 6, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Reactions of organic compounds March 6, 2018 1 / 27 Reactions of organic compounds Organic chemists
hemistry 2000 Lecture 18: Reactions of organic compounds Marc R. Roussel March 6, 2018 Marc R. Roussel Reactions of organic compounds March 6, 2018 1 / 27 Reactions of organic compounds Organic chemists
Chemical Reactions of Unsaturated Compounds
 hemical Reactions of Unsaturated ompounds hemical Reactions of Alkenes hemical Reactions of Alkenes Structure of the Double Bond in Alkenes The two components of the double bond are pictured the same,
hemical Reactions of Unsaturated ompounds hemical Reactions of Alkenes hemical Reactions of Alkenes Structure of the Double Bond in Alkenes The two components of the double bond are pictured the same,
Unsaturated hydrocarbons Alkenes
 Dr. Seham ALTERARY Chem 145 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Alkenes Chapter 3 1434-1435 2013-2014 2 nd semester By the end of this chapter you should be familiar with: Definition of Alkenes. Nomenclature of Alkenes.
Dr. Seham ALTERARY Chem 145 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Alkenes Chapter 3 1434-1435 2013-2014 2 nd semester By the end of this chapter you should be familiar with: Definition of Alkenes. Nomenclature of Alkenes.
CH 3 Cl + Cl 2 CH 2 Cl 2 + HCl
 Energetics 414 alogenation of Alkanes X 2 X X X 2 X X explosive for F 2 exothermic for l 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 hlorination of Methane carried out at high temperature (400 ) 415 hlorination of
Energetics 414 alogenation of Alkanes X 2 X X X 2 X X explosive for F 2 exothermic for l 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 hlorination of Methane carried out at high temperature (400 ) 415 hlorination of
Chemistry B11 Chapters Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes and Benzene
 Chapters 10-11 Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes and Benzene Organic compounds: organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon and only a few other elements-chiefly, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, halogens,
Chapters 10-11 Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes and Benzene Organic compounds: organic chemistry is the chemistry of carbon and only a few other elements-chiefly, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, halogens,
ALKENES. select the longest chain of C atoms containing the double bond; end in ENE
 Alkenes 1 ALKENES Structure form a homologous series of general formula n 2n - non cyclic alkenes only contain a carbon-carbon double bond somewhere in their structure unsaturated hydrocarbons - can still
Alkenes 1 ALKENES Structure form a homologous series of general formula n 2n - non cyclic alkenes only contain a carbon-carbon double bond somewhere in their structure unsaturated hydrocarbons - can still
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Organic Chemistry, Fifth Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 10 Lecture Outline Modified by Dr. Juliet Hahn Copyright 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction
Organic Chemistry, Fifth Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 10 Lecture Outline Modified by Dr. Juliet Hahn Copyright 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. All rights reserved. No reproduction
Benzene and Aromaticity
 Benzene and Aromaticity Why this Chapter? Reactivity of substituted aromatic compounds is tied to their structure Aromatic compounds provide a sensitive probe for studying relationship between structure
Benzene and Aromaticity Why this Chapter? Reactivity of substituted aromatic compounds is tied to their structure Aromatic compounds provide a sensitive probe for studying relationship between structure
2. Hydrohalogenation: Propylene reacts with HBr to form 2-bromopropane.
 Objective 12. Apply reactivity principles to Electrophilic Addition reactions 1: alkenes identify structural features (pi bond) and electrophiles, use curved arrows to predict product. Structural features:
Objective 12. Apply reactivity principles to Electrophilic Addition reactions 1: alkenes identify structural features (pi bond) and electrophiles, use curved arrows to predict product. Structural features:
Theoretically because there are 3 double bonds one might expect the amount of energy to be 3 times as much.
 18. Arenes There are two major classes of organic chemicals aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six carbon ams with delocalised bonding.
18. Arenes There are two major classes of organic chemicals aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six carbon ams with delocalised bonding.
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY. Classification of organic compounds
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Organic chemistry is very important branch of chemistry and it study the compounds which contain carbon (C) and hydrogen (H), in general, and may contains other atoms such as oxygen (O),
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Organic chemistry is very important branch of chemistry and it study the compounds which contain carbon (C) and hydrogen (H), in general, and may contains other atoms such as oxygen (O),
Chemistry 20 Chapters 2 Alkanes
 Chemistry 20 Chapters 2 Alkanes ydrocarbons: a large family of organic compounds and they contain only carbon and hydrogen. ydrocarbons are divided into two groups: 1. Saturated hydrocarbon: a hydrocarbon
Chemistry 20 Chapters 2 Alkanes ydrocarbons: a large family of organic compounds and they contain only carbon and hydrogen. ydrocarbons are divided into two groups: 1. Saturated hydrocarbon: a hydrocarbon
Common Elements in Organic Compounds
 Organic hemistry ommon Elements in Organic ompounds lassification of ydrocarbons Alkanes Alkanes have the general formula n 2n+2 where n = 1,2,3, only single covalent bonds saturated hydrocarbons because
Organic hemistry ommon Elements in Organic ompounds lassification of ydrocarbons Alkanes Alkanes have the general formula n 2n+2 where n = 1,2,3, only single covalent bonds saturated hydrocarbons because
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 rganic Chemistry, 6 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District 2006, Prentice all Electrophilic
rganic Chemistry, 6 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District 2006, Prentice all Electrophilic
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 201/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry CHE1502/201/1/2016
 CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
Chemistry 1110 Exam 4 Study Guide
 Chapter 10 Chemistry 1110 Exam 4 Study Guide 10.1 Know that unstable nuclei can undergo radioactive decay. Identify alpha particles, beta particles, and/or gamma rays based on physical properties such
Chapter 10 Chemistry 1110 Exam 4 Study Guide 10.1 Know that unstable nuclei can undergo radioactive decay. Identify alpha particles, beta particles, and/or gamma rays based on physical properties such
A. They all have a benzene ring structure in the molecule. B. They all have the same molecular formula. C. They all have carbon and hydrogen only
 Ch 21 G12 CoreI- Choose the best answer, then transfer your answers to page (1) [32 marks; 2 each] 1. What characteristic do all aromatic hydrocarbons share? A. They all have a benzene ring structure in
Ch 21 G12 CoreI- Choose the best answer, then transfer your answers to page (1) [32 marks; 2 each] 1. What characteristic do all aromatic hydrocarbons share? A. They all have a benzene ring structure in
08. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition, Chapter 16
 08. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition, Chapter 16 Benzene is a nucleophile p electrons make benzene nucleophile, like alkenes.
08. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition, Chapter 16 Benzene is a nucleophile p electrons make benzene nucleophile, like alkenes.
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320
 Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
3.10 Benzene : Aromatic Hydrocarbons / Arenes
 3.10 Benzene : Aromatic ydrocarbons / Arenes There are two major classes of organic chemicals aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six
3.10 Benzene : Aromatic ydrocarbons / Arenes There are two major classes of organic chemicals aliphatic : straight or branched chain organic substances aromatic or arene: includes one or more ring of six
AP Chemistry Chapter 22 - Organic and Biological Molecules
 AP Chemistry Chapter - Organic and Biological Molecules.1 Alkanes: Saturated Hydrocarbons A. Straight-chain Hydrocarbons 1. Straight-chain alkanes have the formula C n H n+. Carbons are sp hybridized The
AP Chemistry Chapter - Organic and Biological Molecules.1 Alkanes: Saturated Hydrocarbons A. Straight-chain Hydrocarbons 1. Straight-chain alkanes have the formula C n H n+. Carbons are sp hybridized The
Q.1 Draw out suitable structures which fit the molecular formula C 6 H 6
 Aromatic compounds 2814 1 BENZENE Structure Primary analysis revealed benzene had an... empirical formula of and a molecular formula of 6 6 Q.1 Draw out suitable structures which fit the molecular formula
Aromatic compounds 2814 1 BENZENE Structure Primary analysis revealed benzene had an... empirical formula of and a molecular formula of 6 6 Q.1 Draw out suitable structures which fit the molecular formula
Lecture 11 Organic Chemistry 1
 EM 232 rganic hemistry I at hicago Lecture 11 rganic hemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop February 16, 2010 1 Self Test Question What is the product(s) of the following reaction? 3 K( 3 ) 3 A 3 ( 3 ) 3
EM 232 rganic hemistry I at hicago Lecture 11 rganic hemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop February 16, 2010 1 Self Test Question What is the product(s) of the following reaction? 3 K( 3 ) 3 A 3 ( 3 ) 3
Ch 14 Conjugated Dienes and UV Spectroscopy
 Ch 14 Conjugated Dienes and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated Systems - Conjugated systems have alternating single and double bonds. For example: C=C C=C C=C and C=C C=O - This is not conjugated because the double
Ch 14 Conjugated Dienes and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated Systems - Conjugated systems have alternating single and double bonds. For example: C=C C=C C=C and C=C C=O - This is not conjugated because the double
Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds. Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons
 Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons Reactions of Alkanes Single bonds (C-C) are strong and very hard to break, therefore these compounds are relatively unreactive
Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons Reactions of Alkanes Single bonds (C-C) are strong and very hard to break, therefore these compounds are relatively unreactive
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions
 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
less stable intermediate
 166 CAPTER 4 INTRODUCTION TO ALKENES. STRUCTURE AND REACTIVITY STANDARD FREE ENERGY higher-energy transition state less stable intermediate (C 3 ) 2 CC 2 Br _ (C 3 ) 2 C A C 2 + Br (C 3 ) 2 CC 2 L Br slower
166 CAPTER 4 INTRODUCTION TO ALKENES. STRUCTURE AND REACTIVITY STANDARD FREE ENERGY higher-energy transition state less stable intermediate (C 3 ) 2 CC 2 Br _ (C 3 ) 2 C A C 2 + Br (C 3 ) 2 CC 2 L Br slower
Chapter 8: Chemistry of Alkynes (C n H 2n-2 )
 hapter 8: hemistry of Alkynes ( n 2n-2 ) Bonding & hybridization Both are sp-hybridized Bond angles = 180 o 1 σ + 2 π bonds Linear around lassification R R R' σ bond energy: 88 kcal/mol π bond energy:
hapter 8: hemistry of Alkynes ( n 2n-2 ) Bonding & hybridization Both are sp-hybridized Bond angles = 180 o 1 σ + 2 π bonds Linear around lassification R R R' σ bond energy: 88 kcal/mol π bond energy:
Alkenes, Alkynes and Aromatic
 BIO-ORGANI EMISTRY (Organic hemistry for Biology Students) (SQBS 1603) Alkenes, Alkynes and Aromatic Dr Nik Ahmad Nizam Bin Nik Malek, BSc (Ind. hem.)(utm), MSc (hem)(utm), PhD (hem)(utm), A.M.I. Senior
BIO-ORGANI EMISTRY (Organic hemistry for Biology Students) (SQBS 1603) Alkenes, Alkynes and Aromatic Dr Nik Ahmad Nizam Bin Nik Malek, BSc (Ind. hem.)(utm), MSc (hem)(utm), PhD (hem)(utm), A.M.I. Senior
Organic and Biochemical Molecules. 1. Compounds composed of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons.
 Organic and Biochemical Molecules 1. Compounds composed of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons. 2. A compound is said to be saturated if it contains only singly bonded carbons. Such hydrocarbons
Organic and Biochemical Molecules 1. Compounds composed of carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons. 2. A compound is said to be saturated if it contains only singly bonded carbons. Such hydrocarbons
3 free radical is most stable. Q.5. A + Cl 2 hv monochloro product To maximize the yield of monochloro product in the above reaction? Cl 2 must be add
 Q.1. I II III IV IV III II I I III II IV IV II III I I II III IV The decreasing order of the anti knocking value of octane number of the following is: (I) CH 4 (II) C 2 H 6 (III) C 3 H 8 (IV) C 4 H 10
Q.1. I II III IV IV III II I I III II IV IV II III I I II III IV The decreasing order of the anti knocking value of octane number of the following is: (I) CH 4 (II) C 2 H 6 (III) C 3 H 8 (IV) C 4 H 10
Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
 5 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes APTER SUMMARY Addition is the characteristic reaction of alkenes and alkynes. Since the carbons of a double or triple bond do not have the maximum number
5 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes APTER SUMMARY Addition is the characteristic reaction of alkenes and alkynes. Since the carbons of a double or triple bond do not have the maximum number
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions "
 Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The π
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Additions to Alkenes Generally the reaction is exothermic because one π and one σ bond are converted to two σ bonds Alkenes are electron rich The π
2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Isolated and Conjugated Dienes
 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Isolated and Conjugated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Reactions of Isolated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. The Mechanism Double Bonds can have Different Reactivities
2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Isolated and Conjugated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Reactions of Isolated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. The Mechanism Double Bonds can have Different Reactivities
Alkenes. Alkenes are unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons.
 Alkenes Alkenes Each member contains one double covalent bond between two C atoms. Draw condensed structural formulas of first three members of alkenes family. Alkenes are unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons.
Alkenes Alkenes Each member contains one double covalent bond between two C atoms. Draw condensed structural formulas of first three members of alkenes family. Alkenes are unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons.
CHEM 203. Topics Discussed on Oct. 16
 EM 203 Topics Discussed on Oct. 16 ydrogenation (= saturation) of olefins in the presence of finely divided transition metal catalysts (Ni, Pd, Pt, Rh, Ru...): generic alkene R 1 finely divided Pd (or
EM 203 Topics Discussed on Oct. 16 ydrogenation (= saturation) of olefins in the presence of finely divided transition metal catalysts (Ni, Pd, Pt, Rh, Ru...): generic alkene R 1 finely divided Pd (or
Chapter 17: Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 1 Chapter 17: Reactions of Aromatic Compounds I. Introduction to Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS) A. General Mechanism II. Reactions of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution A. Halogenation (E =
1 Chapter 17: Reactions of Aromatic Compounds I. Introduction to Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS) A. General Mechanism II. Reactions of Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution A. Halogenation (E =
