CHM 233 : Fall 2017 Quiz #11 - Answer Key Question 1
|
|
|
- Norman Adrian Hood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CM 233 : Fall 2017 Quiz #11 - Answer Key Question 1 MC26k Which best describes the stereochemistry of the C=C double bonds 1 and 2 in the following structure? 1 2 Br A) 1 = E, 2 = E B) 1 = E, 2 = Z Br C) 1 = Z, 2 = Z D) 1 = Z, 2 = E priorities at each double bond are indicated highest = 1 and lowest = Br Z 2 E Br 1
2 Question 2 MC26m For which of the following isomers is the following reaction MST exothermic? C C 8 18 A 2,3-dimethyl-(3E)-hexene B 4,5-dimethyl-(2E)-hexene C 2,3-dimethyl-2-hexene D 4,5-dimethyl-1-hexene C all reactions give the same alkane product, all "end" at the same energy, the difference must be where they "start" A 2,3-dimethyl-(3E)-hexene = TRIsubstituted alkene (1 on the C=C bond) B 4,5-dimethyl-(2E)-hexene = DIsubstituted alkene (2 on the C=C bond) C 2,3-dimethyl-2-hexene = TETRAsubstituted alkene (0 on the C=C bond) D 4,5-dimethyl-1-hexene = MNsubstituted alkene (3 on the C=C bond) among these isomeric alkenes, the least substituted alkene will be the highest energy isomer, since D has only NE substituent on the C=C bond, it is a MNsubstituted alkene, it is highest in energy, it thus starts higher in energy, its reaction is thus most exothermic
3 Question 3 MCmxnd For a reaction energy diagram corresponding to the following mechanism, how many energy minima will there be corresponding to INTERMEDIATES (do not include minima associated with the reactants or the products)? A five minima C seven minima B six minima D eight minima Energy reaction coordinate remember, resonance contributors describe the SAME species note, you would not normally be expected to be able to get all of the relative energies of the intermediates correct at this stage = NE cation does NT imply another step in the mechanism
4 Question 4 MC20q Using the homolytic bond dissociation energies provided, which statement best describes the following reaction? C + C Br C Br Br C Br + B.D.E. (kcal/mol) A The reaction is exothermic by 41 kcal/mol B The reaction is exothermic by 5 kcal/mol C The reaction is endothermic by 5 kcal/mol D The reaction is endothermic by 41 kcal/mol Even though the reaction involves heterolytic bond cleavage in Lewis acid/base reactions, we are only comparing the reactants and products The bond dissocaition energies measure the energies of the electrons in bonds, and reactions involve breaking bonds and making new ones All we need to do is to compare the energy cost of breaking the bonds that are broken to the energy gain of the bonds that are made Energy "cost" due to breaking bonds = 86 (C-) + 88 (-Br) Total = 174 kcal/mol Energy "gain" due to making bonds = 68 (C-Br) (-) Total = 179 kcal/mol Electron energy in products lower than in reactants (the bonds are stronger in the products than in the reactants, thus the reaction is EXTERMIC by = 5 kcal/mol
5 Question 5 MC20o ow many transition states are involved in the following complex mechanism. You do not have to understand the details of this mechanism, just how many transition states are involved (hint, there is one transition state for each individual step in the mechanism). 1 no here, resonance again #5 #2 #3 #4 no here, this is just a resonance arrow, not a step in the mechanism A 4 transition states B 5 transition states C 6 transition states D 7 transition states
6 Question 6 MCalkenesIb Which is the major product of the following reaction???? A C B D simple electrophilic addition to a C=C bond, Markovnkov, adds to the most substituted "end" of the C=C bond, reaction proceeds via the most stable cation intermediate 2 substituents at this "end", most substituted end 1 substituent at this "end" ( does not "count") LB/BB LA/BA LB mechanism LA adds to most substituted end (reaction proceds via most stable cation intermediate), thus Markovnikov 3 cation and resonance stabilized (resonance contributors not shown)
7 Question 7 MC20m Which of the following statements is most correct for the reaction described by the following reaction energy diagram? (remember, a reaction with a negative free energy is exergonic, a reaction with a negative enthalpy is exothermic) 3 transition states ( ) ΔG reactants intermediates 1 intermediates 2 exergonic products reaction coordinate A the mechanism involves 2 transition states and the reaction is exergonic B the mechanism has 3 steps and the reaction is endergonic C the mechanism involves 2 intermediates and the reaction is exergonic D the mechanism involves 2 transition states and the reaction is endergonic
8 Question 8 MC26q Which of the following will be the MAJR organic product of the following reaction? 2 S 4 2 A B C D LB BB BB LB BB BA LA BA note the YDRIDE SIFT carbocation rearrangement ERE BA LA
CHM 233 : Fall 2018 Quiz #12 - Answer Key Question 1 MCalkenesIn Which are the best reagents/conditions for the following reaction?
 M 233 : Fall 2018 Quiz #12 - nswer Key Question 1 MalkenesIn Which are the best reagents/conditions for the following reaction? 2 / 2 S 4 (cat.) conc. 2 S 4 /heat 1. 3.TF 2. Na/ 2 2 1. g(c) 2 / 2 2. Na
M 233 : Fall 2018 Quiz #12 - nswer Key Question 1 MalkenesIn Which are the best reagents/conditions for the following reaction? 2 / 2 S 4 (cat.) conc. 2 S 4 /heat 1. 3.TF 2. Na/ 2 2 1. g(c) 2 / 2 2. Na
More Tutorial at
 1. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question (50 pts). 1) Which of the following statements about propene, CH3CH CH2, is 1) correct? A) There
1. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question (50 pts). 1) Which of the following statements about propene, CH3CH CH2, is 1) correct? A) There
Name: Chapter 3: The Nature Of Organic Reactions: Alkenes
 Name: Chapter 3: The Nature Of Organic Reactions: Alkenes 1 Vocabulary cis-trans isomerism: E,Z designation: Addition: Elimination: Substitution: Rearrangement: Homolytic: Heterolytic Homogenic: Heterogenic:
Name: Chapter 3: The Nature Of Organic Reactions: Alkenes 1 Vocabulary cis-trans isomerism: E,Z designation: Addition: Elimination: Substitution: Rearrangement: Homolytic: Heterolytic Homogenic: Heterogenic:
An Overview of Organic Reactions. Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants:
 An Overview of Organic Reactions Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants: 1. Addition (forward) Gain of atoms across a bond Example:
An Overview of Organic Reactions Reaction types: Classification by outcome Most reactions produce changes in the functional group of the reactants: 1. Addition (forward) Gain of atoms across a bond Example:
C C. sp 2. π M.O. atomic. orbitals. carbon 1. σ M.O. molecular. orbitals. H C C rotate D. D H zero overlap of p orbitals: π bond broken!
 Alkenes Electrophilic Addition 1 Alkene Structures chemistry of double bond σ BDE ~ 80 kcal/mol π = BDE ~ 65 kcal/mol The p-bond is weaker than the sigma-bond The, electrons in the p-bond are higher in
Alkenes Electrophilic Addition 1 Alkene Structures chemistry of double bond σ BDE ~ 80 kcal/mol π = BDE ~ 65 kcal/mol The p-bond is weaker than the sigma-bond The, electrons in the p-bond are higher in
CONCERTED sp 2 H. HO Et
 Alkyl alides Substitution and Elimination 1 Substitutions (Quick Review) 1.1 SN2 Reactions LB nucleophile "backside attack!" NERTED reaction This is fundamentally just a Lewis acid/base reaction, the Lewis
Alkyl alides Substitution and Elimination 1 Substitutions (Quick Review) 1.1 SN2 Reactions LB nucleophile "backside attack!" NERTED reaction This is fundamentally just a Lewis acid/base reaction, the Lewis
Chapter 6 Chemical Reactivity and Mechanisms
 Chapter 6 Chemical Reactivity and Mechanisms 6.1 Enthalpy Enthalpy (ΔH or q) is the heat energy exchange between the reaction and its surroundings at constant pressure Breaking a bond requires the system
Chapter 6 Chemical Reactivity and Mechanisms 6.1 Enthalpy Enthalpy (ΔH or q) is the heat energy exchange between the reaction and its surroundings at constant pressure Breaking a bond requires the system
Chapter 6. Chemical Reactivity and Reaction Mechanisms
 hapter 6 hemical Reactivity and Reaction Mechanisms hemical Reactivity Enthalpy A simple chemical reaction can be broken down into bond creating and bond breaking components: A-B + Y-Z A-Y + B-Z A-B A
hapter 6 hemical Reactivity and Reaction Mechanisms hemical Reactivity Enthalpy A simple chemical reaction can be broken down into bond creating and bond breaking components: A-B + Y-Z A-Y + B-Z A-B A
Lecture 11 Organic Chemistry 1
 EM 232 rganic hemistry I at hicago Lecture 11 rganic hemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop February 16, 2010 1 Self Test Question What is the product(s) of the following reaction? 3 K( 3 ) 3 A 3 ( 3 ) 3
EM 232 rganic hemistry I at hicago Lecture 11 rganic hemistry 1 Professor Duncan Wardrop February 16, 2010 1 Self Test Question What is the product(s) of the following reaction? 3 K( 3 ) 3 A 3 ( 3 ) 3
1. Root of name depends on longest chain of C containing the double bond; ends in "ene"
 Alkenes (β-carotene, an antioxidant pigment) n 2n (acyclic) n 2n-2 (cyclic) R R R R Key features sp 2 -hybridized carbons, 120 o bond angles σ + π bonding between = planar geometry around = "unsaturated"
Alkenes (β-carotene, an antioxidant pigment) n 2n (acyclic) n 2n-2 (cyclic) R R R R Key features sp 2 -hybridized carbons, 120 o bond angles σ + π bonding between = planar geometry around = "unsaturated"
O Enolate. = Electrophile/ Lewis acid. = Electrophile/ Lewis acid O B. Enolate. = Electrophile/ Lewis acid. Enolate. O O Enolate
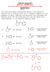 CM 234, Spring 2017 QUIZ #12 ANSWER KEY (hit the RETURN Button to return to the Main Quiz Page) QUESTIN 1 MC34r The following Aldol condensation product was formed by reaction of an enolate anion and a
CM 234, Spring 2017 QUIZ #12 ANSWER KEY (hit the RETURN Button to return to the Main Quiz Page) QUESTIN 1 MC34r The following Aldol condensation product was formed by reaction of an enolate anion and a
An Overview of Organic Reactions
 An Overview of Organic Reactions Radical Reactions Reactions involving symmetrical bond breaking and bond forming omolytic bond breaking omogenic bond formation Radical Reaction with alkanes and uv light
An Overview of Organic Reactions Radical Reactions Reactions involving symmetrical bond breaking and bond forming omolytic bond breaking omogenic bond formation Radical Reaction with alkanes and uv light
CHEM Lecture 7
 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago CEM 494 - Lecture 7 Prof. Duncan Wardrop ctober 22, 2012 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago Preparation of Alkenes Elimination
CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago CEM 494 - Lecture 7 Prof. Duncan Wardrop ctober 22, 2012 CEM 494 Special Topics in Chemistry Illinois at Chicago Preparation of Alkenes Elimination
use iso-, tert-, sec- prefixes in your substituent names, where necessary
 Chapter 07.2: 1 1) Name. Include E/Z stereochemistry in name, if necessary. a) 3 C b) c) d) e) f) use iso-, tert-, sec- prefixes in your substituent names, where necessary g) Do NT use iso-, tert-, sec-
Chapter 07.2: 1 1) Name. Include E/Z stereochemistry in name, if necessary. a) 3 C b) c) d) e) f) use iso-, tert-, sec- prefixes in your substituent names, where necessary g) Do NT use iso-, tert-, sec-
Study of Chemical Reactions
 Study of Chemical Reactions Introduction to Mechanisms There are four different types of organic reactions: Additions Eliminations Substitutions Rearrangements 149 Addition Reactions Occur when 2 reactants
Study of Chemical Reactions Introduction to Mechanisms There are four different types of organic reactions: Additions Eliminations Substitutions Rearrangements 149 Addition Reactions Occur when 2 reactants
Chapter 5. 3-Chloro-2-methylpentane. Cl 2. 2-Chloro-2-methylpentane. 1-Chloro-2-methylpentane. Cl 2-Chloro-4-methylpentane. 1-Chloro-4-methylpentane
 hapter 5 5.1 lassify each of the following reactions as an addition, elimination, substitution, or rearrangement: (a) 3Br K 3 KBr (b) 3 2 2 2 2 (c) 2 2 2 3 3 a. substitution b. elimination c. addition
hapter 5 5.1 lassify each of the following reactions as an addition, elimination, substitution, or rearrangement: (a) 3Br K 3 KBr (b) 3 2 2 2 2 (c) 2 2 2 3 3 a. substitution b. elimination c. addition
Department of Chemistry SUNY/Oneonta. Chem Organic Chemistry I. Examination #2 - October 18, 2004 ANSWERS
 Department of hemistry SUNY/Oneonta hem 221 - Organic hemistry I Examination #2 - October 18 2004 ANSWERS INSTRUTIONS This examination is in multiple choice format; the questions are in this Exam Booklet
Department of hemistry SUNY/Oneonta hem 221 - Organic hemistry I Examination #2 - October 18 2004 ANSWERS INSTRUTIONS This examination is in multiple choice format; the questions are in this Exam Booklet
Objective 3. Draw resonance structures, use curved arrows, determine extent of delocalization. Identify major/minor contributor.
 Objective 3 Draw resonance structures, use curved arrows, determine extent of delocalization. Identify major/minor contributor. Structure Should Fit Experimental Data The chemical formula of benzene is
Objective 3 Draw resonance structures, use curved arrows, determine extent of delocalization. Identify major/minor contributor. Structure Should Fit Experimental Data The chemical formula of benzene is
CH 3 OCH 3. Question 4. Provide the missing reactants for the following Diels-Alder reaction. heat
 CHEMISTRY 234, MIDTERM #2 PRACTICE TEST #1-3 - NAME Question 3 For each reaction 1) Provide the missing reagents/conditions or major organic products as appropriate 2) State whether the OVERALL reaction
CHEMISTRY 234, MIDTERM #2 PRACTICE TEST #1-3 - NAME Question 3 For each reaction 1) Provide the missing reagents/conditions or major organic products as appropriate 2) State whether the OVERALL reaction
10/26/2010. An Example of a Polar Reaction: Addition of H 2 O to Ethylene. to Ethylene
 6.5 An Example of a Polar Reaction: Addition of H 2 O to Ethylene Addition of water to ethylene Typical polar process Acid catalyzed addition reaction (Electophilic addition reaction) Polar Reaction All
6.5 An Example of a Polar Reaction: Addition of H 2 O to Ethylene Addition of water to ethylene Typical polar process Acid catalyzed addition reaction (Electophilic addition reaction) Polar Reaction All
Organic Chemistry I Lesson Objectives, Lesson Problems, Course Outline Spring 2008
 Organic Chemistry I Lesson Objectives, Lesson Problems, Course Outline Spring 2008 Lesson Date Assignment Lesson Objective Description Lesson Problems 4 14-Jan Chapter 1 Quiz Describe how bond polarity
Organic Chemistry I Lesson Objectives, Lesson Problems, Course Outline Spring 2008 Lesson Date Assignment Lesson Objective Description Lesson Problems 4 14-Jan Chapter 1 Quiz Describe how bond polarity
The carbon-carbon double bond is the distinguishing feature of alkenes.
 Alkenes: Structure & Properties Alkane (acyclic): n 2n+2 > saturated. Alkene (acyclic): n 2n > unsaturated. eg ethylene (IUPA: ethene), 2 4 : 2 = 2 The carbon-carbon double bond is the distinguishing feature
Alkenes: Structure & Properties Alkane (acyclic): n 2n+2 > saturated. Alkene (acyclic): n 2n > unsaturated. eg ethylene (IUPA: ethene), 2 4 : 2 = 2 The carbon-carbon double bond is the distinguishing feature
Chemistry 231 Organic I Exam 2 Dr. Gallo (Brown & Foote) October 29, 2004
 hemistry 231 rganic I Exam 2 Dr. Gallo (Brown & Foote) ctober 29, 2004 1 Name: I(24). ircle the correct answer for each of the following multiple choice questions. 1.) Which alkene would yield 3-methylpentane
hemistry 231 rganic I Exam 2 Dr. Gallo (Brown & Foote) ctober 29, 2004 1 Name: I(24). ircle the correct answer for each of the following multiple choice questions. 1.) Which alkene would yield 3-methylpentane
Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory
 Molecular rbital (M) Theory Molecular orbital mixing takes place at all times along reaction coordinate. (S N 2) + + C- σ As - approaches, and as - departs, orbitals mix. sp 3 C- σ Molecular rbital (M)
Molecular rbital (M) Theory Molecular orbital mixing takes place at all times along reaction coordinate. (S N 2) + + C- σ As - approaches, and as - departs, orbitals mix. sp 3 C- σ Molecular rbital (M)
Alkenescontain a C=C double bond (also occasionally called olefins). Alkenes are very common in natural and synthetic organic compounds.
 Chapter 6: Alkenes: structure and reactivity Alkenescontain a C=C double bond (also occasionally called olefins). Alkenes are very common in natural and synthetic organic compounds. 6.2 Degree of unsaturation
Chapter 6: Alkenes: structure and reactivity Alkenescontain a C=C double bond (also occasionally called olefins). Alkenes are very common in natural and synthetic organic compounds. 6.2 Degree of unsaturation
What is the major product of the following reaction?
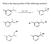 What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
Química Orgânica I. Organic Reactions
 Química Orgânica I 2008/09 w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 A6 1 Organic Reactions Addition two molecules combine Elimination one molecule splits Substitution parts from two molecules exchange Rearrangement
Química Orgânica I 2008/09 w3.ualg.pt\~abrigas QOI 0809 A6 1 Organic Reactions Addition two molecules combine Elimination one molecule splits Substitution parts from two molecules exchange Rearrangement
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH.8 - HALOALKANES, HALOGENATION AND RADICALS
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALKYL HALIDES Alkyl halides are named by naming them as a substituent before the root chain and indicating their location. Prefixes: -F, -Cl -Br -I Alkyl halides have NO
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALKYL HALIDES Alkyl halides are named by naming them as a substituent before the root chain and indicating their location. Prefixes: -F, -Cl -Br -I Alkyl halides have NO
The Study of Chemical Reactions. Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order.
 The Study of Chemical Reactions Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order. Thermodynamics: The study of the energy changes that accompany
The Study of Chemical Reactions Mechanism: The complete, step by step description of exactly which bonds are broken, formed, and in which order. Thermodynamics: The study of the energy changes that accompany
Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry
 Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Structure and Bonding 2 Structure and Bonding Rotation around the C=C bond is restricted 90 rotation The p orbitals are orthogonal
Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Structure and Bonding 2 Structure and Bonding Rotation around the C=C bond is restricted 90 rotation The p orbitals are orthogonal
Rearrangement: a single reactant rearranges its
 Chapter 5: An overview of organic reactions 5.1 Kinds of organic reactions Even though there are hundreds of reactions to study, organic chemistry is governed by only a few key ideas that determine chemical
Chapter 5: An overview of organic reactions 5.1 Kinds of organic reactions Even though there are hundreds of reactions to study, organic chemistry is governed by only a few key ideas that determine chemical
Nucleophile. Reaction Intermediate. Introduction to Reaction mechanisms. Definitions 2/25/2012
 Introduction to Reaction mechanisms Definition A reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical change occurs. It is also a detailed description of the
Introduction to Reaction mechanisms Definition A reaction mechanism is the step by step sequence of elementary reactions by which overall chemical change occurs. It is also a detailed description of the
Chapter 3. Alkenes And Alkynes
 Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
Chapter 6: Alkenes: Structure and Reactivity
 hapter 6: Alkenes: Structure and eactivity overage: 1. Degrees of Unsaturation 2. Nomenclature cis/trans E/Z 3. Alkene Stability 4. Electrophilic Addition eactions/markovinikov s ule 5. The ammond Postulate
hapter 6: Alkenes: Structure and eactivity overage: 1. Degrees of Unsaturation 2. Nomenclature cis/trans E/Z 3. Alkene Stability 4. Electrophilic Addition eactions/markovinikov s ule 5. The ammond Postulate
Learning Guide for Chapter 7 - Organic Reactions I
 Learning Guide for Chapter 7 - rganic Reactions I I. Introduction to Reactions II. Principles of Kinetics III. Principles of Thermodynamics IV. Nucleophiles and Electrophiles V. Acids and Bases What a
Learning Guide for Chapter 7 - rganic Reactions I I. Introduction to Reactions II. Principles of Kinetics III. Principles of Thermodynamics IV. Nucleophiles and Electrophiles V. Acids and Bases What a
Ch.6 Alkenes: Structure and Reactivity
 alkene = olefin 2 2 Ethylene α-pinene 3 β-arotene (orange pigment and vitamin A precursor) 6.1 Industrial Preparation and Use of Alkenes ompounds derived industrially from ethylene 2 2 Ethylene (26 million
alkene = olefin 2 2 Ethylene α-pinene 3 β-arotene (orange pigment and vitamin A precursor) 6.1 Industrial Preparation and Use of Alkenes ompounds derived industrially from ethylene 2 2 Ethylene (26 million
H H H H S H H H NO 2 O H H 3 C. OMe CH 3
 Fall Workshop #9 Question #1 Using the tables on pages 18-19 of SAM, the table inside the back cover of Jones, and the figure we created in class: (a) Report an estimated pka value for each hydrogen atom
Fall Workshop #9 Question #1 Using the tables on pages 18-19 of SAM, the table inside the back cover of Jones, and the figure we created in class: (a) Report an estimated pka value for each hydrogen atom
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2
 C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
Chemistry 2321 OLD TEST QUESTIONS CH 3
 Test No. 2 hemistry 2321 LD TEST QUESTNS Professor M. Pomerantz 1. n the following reaction the electrophile is: 3 3 + the group none of these 2. Given the reaction shown and the bond dissociation energies
Test No. 2 hemistry 2321 LD TEST QUESTNS Professor M. Pomerantz 1. n the following reaction the electrophile is: 3 3 + the group none of these 2. Given the reaction shown and the bond dissociation energies
A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) Complete the following reaction and provide a detailed, step-by-step mechanism for the process.
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) Complete the following reaction and provide a detailed, step-by-step mechanism for the process.
2/26/18. Practice Questions. Practice Questions B F. How many steps are there in this reaction?
 Practice Questions Practice Questions D B F C E A G How many steps are there in this reaction? 1 Practice Questions D B F C E A G What is the highest-energy transitions state? Practice Questions D B F
Practice Questions Practice Questions D B F C E A G How many steps are there in this reaction? 1 Practice Questions D B F C E A G What is the highest-energy transitions state? Practice Questions D B F
Chapter 19: Alkenes and Alkynes
 Chapter 19: Alkenes and Alkynes The vast majority of chemical compounds that we know anything about and that we synthesize in the lab or the industrial plant are organic compounds. The simplest organic
Chapter 19: Alkenes and Alkynes The vast majority of chemical compounds that we know anything about and that we synthesize in the lab or the industrial plant are organic compounds. The simplest organic
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions
 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
Classification of Reactions by:
 lassification of Reactions by: 1) Functional group 2) Kind a) Addition: A + B > b) Elimination: A > B + c) Substitution: A-B + -D > A- + B-D d) Rearrangement: A > B, where B is a constitutional isomer
lassification of Reactions by: 1) Functional group 2) Kind a) Addition: A + B > b) Elimination: A > B + c) Substitution: A-B + -D > A- + B-D d) Rearrangement: A > B, where B is a constitutional isomer
6.10 Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes. Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes
 Acid-atalyzed ydration of Alkenes 6.10 Acid-atalyzed ydration of Alkenes O O reaction is acid catalyzed; typical hydration medium is 50% 2 SO 4-50% 2 O Follows Markovnikov's Rule Follows Markovnikov's
Acid-atalyzed ydration of Alkenes 6.10 Acid-atalyzed ydration of Alkenes O O reaction is acid catalyzed; typical hydration medium is 50% 2 SO 4-50% 2 O Follows Markovnikov's Rule Follows Markovnikov's
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS CHM200 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I. 5 Credit Hours. Prepared by: Richard A. Pierce
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS CHM200 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Richard A. Pierce Revised Date: January 2008 by Ryan H. Groeneman Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor, Dean
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS CHM200 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Richard A. Pierce Revised Date: January 2008 by Ryan H. Groeneman Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor, Dean
CHM 233 : Fall 2018 Quiz #10 - Answer Key
 M 233 : Fall 2018 Quiz #10 - nswer Key Question 1 M20a Which of the following is The strongest Bronsted cid? R- 2 is a carboxylic acid and R-S 3 is a solfonic acid, you will want to draw these two as Lewis
M 233 : Fall 2018 Quiz #10 - nswer Key Question 1 M20a Which of the following is The strongest Bronsted cid? R- 2 is a carboxylic acid and R-S 3 is a solfonic acid, you will want to draw these two as Lewis
Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid
![Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid Acid-Base -Bronsted-Lowry model: -Lewis model: -The more equilibrium lies to the right = More [H 3 O + ] = Higher K a = Lower pk a = Stronger acid](/thumbs/95/123929992.jpg) Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Revision Hybridisation -The valence electrons of a Carbon atom sit in 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2 orbitals that are different in energy. It has 2 x 2s electrons + 2 x 2p electrons are available to form 4 covalent bonds.
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320
 Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions
 Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Introduction Homolytic bond cleavage leads to the formation of radicals (also called free radicals) Radicals are highly reactive, short-lived species Single-barbed arrows are
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Introduction Homolytic bond cleavage leads to the formation of radicals (also called free radicals) Radicals are highly reactive, short-lived species Single-barbed arrows are
4.15 Halogenation of Alkanes RH + X 2 RX + HX
 4.15 alogenation of Alkanes R + X 2 RX + X Energetics R + X 2 RX + X explosive for F 2 exothermic for Cl 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 4.16 Chlorination of Methane Chlorination of Methane carried out
4.15 alogenation of Alkanes R + X 2 RX + X Energetics R + X 2 RX + X explosive for F 2 exothermic for Cl 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 4.16 Chlorination of Methane Chlorination of Methane carried out
As time allows, additional practice questions for Exam 2 follow. This is an incomplete collection. Content & emphasis will vary.
 Chem 226 Exam 2 Fall 2005: will cover Bruice, Chaps 3 through 6; Note: review e-mail & inclass quizzes and Worksheets, suggest on-line practice questions and quizzes plus ACS rganic Chemistry Guide As
Chem 226 Exam 2 Fall 2005: will cover Bruice, Chaps 3 through 6; Note: review e-mail & inclass quizzes and Worksheets, suggest on-line practice questions and quizzes plus ACS rganic Chemistry Guide As
2. Hydrohalogenation: Propylene reacts with HBr to form 2-bromopropane.
 Objective 12. Apply reactivity principles to Electrophilic Addition reactions 1: alkenes identify structural features (pi bond) and electrophiles, use curved arrows to predict product. Structural features:
Objective 12. Apply reactivity principles to Electrophilic Addition reactions 1: alkenes identify structural features (pi bond) and electrophiles, use curved arrows to predict product. Structural features:
LECTURE #13 Tues., Oct.18, Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, , 7.10, 2, Sections
 CEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #13 Tues., Oct.18, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSGNED READNGS: TODAY S CLASS: Sections 4.1 4.6 NEXT CLASS: rest of Ch.4 http://artsandscience.concordia.ca/facstaff/p-r/rogers
CEM 221 section 01 LECTURE #13 Tues., Oct.18, 2005 Midterm exam: Tues.Oct.25 during class Ch.1, 7.2-7.5, 7.10, 2, 3.1-3.5 ASSGNED READNGS: TODAY S CLASS: Sections 4.1 4.6 NEXT CLASS: rest of Ch.4 http://artsandscience.concordia.ca/facstaff/p-r/rogers
Department of Chemistry SUNY/Oneonta. Chem Organic Chemistry I. Examination #2 - October 14, 2002
 Department of hemistry SUNY/Oneonta hem 221 - Organic hemistry Examination #2 - October 14, 2002 ANSWERS NSTRUTONS This examination is in multiple choice format; the questions are in this Exam Booklet
Department of hemistry SUNY/Oneonta hem 221 - Organic hemistry Examination #2 - October 14, 2002 ANSWERS NSTRUTONS This examination is in multiple choice format; the questions are in this Exam Booklet
Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions. Alkenes are electron rich. Additions to Alkenes
 Additions to Alkenes Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Generally the reaction is exothermic because one p and one s bond are converted to two s bonds Alkenes are electron rich The carbocation
Additions to Alkenes Chapter 8 Alkenes and Alkynes II: Addition Reactions Generally the reaction is exothermic because one p and one s bond are converted to two s bonds Alkenes are electron rich The carbocation
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 203/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry
 E1502/203/1/2016 Tutorial letter 203/1/2016 General hemistry 1B E1502 Semester 1 Department of hemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 3. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY T
E1502/203/1/2016 Tutorial letter 203/1/2016 General hemistry 1B E1502 Semester 1 Department of hemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 3. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY T
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH.4 - ACIDS AND BASES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: FREE ENERGY DIAGRAMS Atoms save energy by forming bonds. Free energy diagrams show overall changes in potential energy during reactions. Free energy diagrams give us information
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: FREE ENERGY DIAGRAMS Atoms save energy by forming bonds. Free energy diagrams show overall changes in potential energy during reactions. Free energy diagrams give us information
Also called an olefin but alkene is better General formula C n H 2n (if one alkene present) Can act as weak nucleophiles
 Alkenes - Structure, Stability, Nomenclature Also called an olefin but alkene is better General formula C n H 2n (if one alkene present) unsaturated - contain fewer than maximum H's possible per C Can
Alkenes - Structure, Stability, Nomenclature Also called an olefin but alkene is better General formula C n H 2n (if one alkene present) unsaturated - contain fewer than maximum H's possible per C Can
Chapter 8: Alkene Structure and Preparation via Elimination Reactions
 Nature of the pi bond Chapter 8: Alkene Structure and Preparation via Elimination eactions [Sections: 8.1-8.13] C C 3 C C 3 bond length bond strength 2 C C 2 a C=C double bond is stronger than a C C single
Nature of the pi bond Chapter 8: Alkene Structure and Preparation via Elimination eactions [Sections: 8.1-8.13] C C 3 C C 3 bond length bond strength 2 C C 2 a C=C double bond is stronger than a C C single
C h a p t e r N i n e: Addition Reactions of Alkenes
 C h a p t e r N i n e: Addition Reactions of Alkenes. H C 2 H Biosynthesis of a prostaglandin from arachidonic acid: intermediate intramolecular radical addition CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts
C h a p t e r N i n e: Addition Reactions of Alkenes. H C 2 H Biosynthesis of a prostaglandin from arachidonic acid: intermediate intramolecular radical addition CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts
Chemical Reactions Energy Exchanges
 Chemical Reactions Energy Exchanges An explosion of dynamite is an example of a rapid chemical reaction. Most chemical reactions proceed more slowly, but all chemical reactions release or absorb energy.
Chemical Reactions Energy Exchanges An explosion of dynamite is an example of a rapid chemical reaction. Most chemical reactions proceed more slowly, but all chemical reactions release or absorb energy.
Chemistry 210 Organic Chemistry I Winter Semester 2001 Dr. Rainer Glaser
 hemistry 210 rganic hemistry I Winter Semester 2001 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Structure, Synthesis and Reactions. Friday, April 20, 2001, 9:00-9:50 Name: Answer Key Question
hemistry 210 rganic hemistry I Winter Semester 2001 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Structure, Synthesis and Reactions. Friday, April 20, 2001, 9:00-9:50 Name: Answer Key Question
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY- 1
 ORGANIC CEMISTRY- 1 ALKENES Alkenes are also called Olefins (C n 2n ) unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes occur abundantly in nature. Ethylene ( 2 C=C 2 ) is a plant hormone that induces ripening in fruit.
ORGANIC CEMISTRY- 1 ALKENES Alkenes are also called Olefins (C n 2n ) unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes occur abundantly in nature. Ethylene ( 2 C=C 2 ) is a plant hormone that induces ripening in fruit.
CHEM 231 (Davis) Organic Chemistry FINAL EXAM May 15, YOUR NAME (Last, First, M.I.) DISCUSSION SECTION #53 (5 Points)
 CHEM 231 (Davis) rganic Chemistry FINAL EXAM May 15, 2006 YUR NAME (Last, First, M.I.) DISCUSSIN SECTIN #53 (5 Points) Initial of last name Instructions Please fill in your name in the space above and
CHEM 231 (Davis) rganic Chemistry FINAL EXAM May 15, 2006 YUR NAME (Last, First, M.I.) DISCUSSIN SECTIN #53 (5 Points) Initial of last name Instructions Please fill in your name in the space above and
Loudon Ch. 4 Review: Alkene Structure/Reactivity Jacquie Richardson, CU Boulder Last updated 5/30/2017
 We already saw in Ch. 1 that π bonds are based on side-on overlap of leftover p orbitals. C atom C=C bond C atom orbital comes from destructive (differentcolor) interference: (note extra node) + 2p 2p
We already saw in Ch. 1 that π bonds are based on side-on overlap of leftover p orbitals. C atom C=C bond C atom orbital comes from destructive (differentcolor) interference: (note extra node) + 2p 2p
α,γ-bisdiphenylene-β-phenylallyl, an unusual example of a persistent carbon radical
 C h a p t e r E l e v e n: Radical Reactions α,γ-bisdiphenylene-β-phenylallyl, an unusual example of a persistent carbon radical CM 321: Summary of Important Concepts YConcepts for Chapter 11: Radical
C h a p t e r E l e v e n: Radical Reactions α,γ-bisdiphenylene-β-phenylallyl, an unusual example of a persistent carbon radical CM 321: Summary of Important Concepts YConcepts for Chapter 11: Radical
Homework for Chapter 17 Chem 2320
 Homework for Chapter 17 Chem 2320 I. Cumulated, isolated, and conjugated dienes Name 1. Draw structures which fit the following descriptions. Use correct geometry! a conjugated diene with the formula C
Homework for Chapter 17 Chem 2320 I. Cumulated, isolated, and conjugated dienes Name 1. Draw structures which fit the following descriptions. Use correct geometry! a conjugated diene with the formula C
CHAPTER 8 HW SOLUTIONS: ELIMINATIONS REACTIONS
 APTER 8 W SLUTNS: ELMNATNS REATNS S-TRANS SMERSM 1. Use a discussion and drawing of orbitals to help explain why it is generally easy to rotate around single bonds at room temperature, while it is difficult
APTER 8 W SLUTNS: ELMNATNS REATNS S-TRANS SMERSM 1. Use a discussion and drawing of orbitals to help explain why it is generally easy to rotate around single bonds at room temperature, while it is difficult
Chapter 1: Orbitals And Bonding
 hapter 1: rbitals And Bonding hapter 1 Topics: Bonding oncepts Look back at your General hemistry Textbook!!! Ionization Potential Ionic Bonds und s Rule Aufbau Principle Lewis Structures Electronegativity
hapter 1: rbitals And Bonding hapter 1 Topics: Bonding oncepts Look back at your General hemistry Textbook!!! Ionization Potential Ionic Bonds und s Rule Aufbau Principle Lewis Structures Electronegativity
Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King I. Conjugation
 Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King Chapter 16 Conjugation, Resonance, and Dienes I. Conjugation Conjugation occurs whenever p-orbitals can overlap on three or more adjacent atoms. Conjugated systems are more
Lecture Notes Chem 51B S. King Chapter 16 Conjugation, Resonance, and Dienes I. Conjugation Conjugation occurs whenever p-orbitals can overlap on three or more adjacent atoms. Conjugated systems are more
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS CHM200 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I. 5 Credit Hours. Prepared by: Richard A. Pierce. Revised by: Sean Birke October, 2013
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS CHM200 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Richard A. Pierce Revised by: Sean Birke October, 2013 Ms. Linda Abernathy, Math, Science & Business Division Chair
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS CHM200 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I 5 Credit Hours Prepared by: Richard A. Pierce Revised by: Sean Birke October, 2013 Ms. Linda Abernathy, Math, Science & Business Division Chair
What are radicals? H. Cl. Chapter 10 Radical Reactions. Production of radicals. Reactions of radicals. Electronic structure of methyl radical
 What are radicals? Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron Chapter 10 Radical Reactions H. Cl. Hydrogen radical Chlorine radical Methyl radical Often called free radicals Formed by homolytic
What are radicals? Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron Chapter 10 Radical Reactions H. Cl. Hydrogen radical Chlorine radical Methyl radical Often called free radicals Formed by homolytic
Synthesis and Retrosynthesis
 Synthesis and Retrosynthesis opyright, Arizona State University Putting Reactions Together A large part of organic chemistry involves building more complex molecules from smaller ones using a designed
Synthesis and Retrosynthesis opyright, Arizona State University Putting Reactions Together A large part of organic chemistry involves building more complex molecules from smaller ones using a designed
REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW
 REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO PREDICT PRODUCTS, IDENTIFY REACTANTS, GIVE REACTION CONDITIONS, PROPOSE SYNTHESES, AND PROPOSE MECHANISMS (AS LISTED BELOW). REVIEW THE MECHANISM
REACTION AND SYNTHESIS REVIEW A STUDENT SHOULD BE ABLE TO PREDICT PRODUCTS, IDENTIFY REACTANTS, GIVE REACTION CONDITIONS, PROPOSE SYNTHESES, AND PROPOSE MECHANISMS (AS LISTED BELOW). REVIEW THE MECHANISM
ORGANIC - BROWN 8E CH ALKENES AND REACTIONS OF ALKENES
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALKENES and ALKYNES Alkenes/Alkynes are named by adding the suffix modifier (- /- ) to the end of the root. Alkenes/alkynes receive in numbering alkanes Location is assigned
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: ALKENES and ALKYNES Alkenes/Alkynes are named by adding the suffix modifier (- /- ) to the end of the root. Alkenes/alkynes receive in numbering alkanes Location is assigned
Lecture 14: October 4, 2018
 CM 223 Organic Chemistry I Prof. Chad Landrie C 3 Ea + O 3 C O 2 reactant intermediate Lecture 14: October 4, 2018 Ch. 6: Section 6.8: Bond Dissociation Energies and Reaction Enthalpy Ch. 17: Sections:
CM 223 Organic Chemistry I Prof. Chad Landrie C 3 Ea + O 3 C O 2 reactant intermediate Lecture 14: October 4, 2018 Ch. 6: Section 6.8: Bond Dissociation Energies and Reaction Enthalpy Ch. 17: Sections:
HONORS ORGANIC CHEM. HAHS MRS. RICHARDS
 NRS RGANIC CEM. AS MRS. RICARDS RGANIC CEMISTRY: FINAL EXAM REVIEW List of Topics: While the exam will specifically focus on material from Quarter 2, an understanding of several important concepts from
NRS RGANIC CEM. AS MRS. RICARDS RGANIC CEMISTRY: FINAL EXAM REVIEW List of Topics: While the exam will specifically focus on material from Quarter 2, an understanding of several important concepts from
Chapter 8: Alkene Structure and Preparation via Elimination Reactions
 1. Nature of the pi bond Chapter 8: Alkene Structure and Preparation via Elimination eactions [Sections: 8.1-8.13] C C bond length bond strength 3 C C 3 3 C C 3 3 C C 3 3 C 2 C C 2 3 C a C=C double bond
1. Nature of the pi bond Chapter 8: Alkene Structure and Preparation via Elimination eactions [Sections: 8.1-8.13] C C bond length bond strength 3 C C 3 3 C C 3 3 C C 3 3 C 2 C C 2 3 C a C=C double bond
Chapter 6 H 2 H 3 C C H CH 3 C H H 2 C C CH 3. (b) =2 H 2 C C C H H C H CH 2 C CH 3 H 3 C C C CH 3. (c) =2
 hapter 6 6.1 alculate the degree of the unsaturation in the following hydrocarbons: 8 14 ; 5 6 (c) 12 20 (d) 20 32 (e) 40 56 =2 =3 (c) =3 (d) =5 (e) =13 6.2 alculate the degree of the unsaturation in the
hapter 6 6.1 alculate the degree of the unsaturation in the following hydrocarbons: 8 14 ; 5 6 (c) 12 20 (d) 20 32 (e) 40 56 =2 =3 (c) =3 (d) =5 (e) =13 6.2 alculate the degree of the unsaturation in the
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 307
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 307 CHAPTER 3 LECTURE NOTES R. Boikess II. Principles of Organic Reactions 1. Chemical reactions are the result of bond breaking and bond making. a. Most (but not all) bond making and
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 307 CHAPTER 3 LECTURE NOTES R. Boikess II. Principles of Organic Reactions 1. Chemical reactions are the result of bond breaking and bond making. a. Most (but not all) bond making and
(1) Recall the classification system for substituted alkenes. (2) Look at the alkene indicated. Count the number of bonds to non-hydrogen groups.
 Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 10: Alkenes, Alkynes, and Dienes No. 1 of 10 1. What is the substitution pattern for alkene indicated below? (A) mono (B) di (C) tri (D) tetra (E) unsubstituted Mono is
Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 10: Alkenes, Alkynes, and Dienes No. 1 of 10 1. What is the substitution pattern for alkene indicated below? (A) mono (B) di (C) tri (D) tetra (E) unsubstituted Mono is
Chapter 1 Introduction and Review
 Chapter 1 Introduction and Review Concept to review: It is your responsibility to review the following concepts before the first class to ensure success in understanding new concepts: Atomic structure
Chapter 1 Introduction and Review Concept to review: It is your responsibility to review the following concepts before the first class to ensure success in understanding new concepts: Atomic structure
Physical Properties: Structure:
 Nomenclature: Functional group suffix = -ol Functional group prefix = hydroxy- Primary, secondary or tertiary? Alcohols are described as primary (1 o ), secondary (2 o ) or tertiary (3 o ) depending on
Nomenclature: Functional group suffix = -ol Functional group prefix = hydroxy- Primary, secondary or tertiary? Alcohols are described as primary (1 o ), secondary (2 o ) or tertiary (3 o ) depending on
Chemistry 2030 Survey of Organic Chemistry Fall Semester 2014 Dr. Rainer Glaser
 Chemistry 2030 Survey of Organic Chemistry Fall Semester 2014 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #1 Bonding, Alkanes, Alkenes & Alkynes Thursday, September 18, 2014, 8:00 8:50 am Question 1. Atomic Structure
Chemistry 2030 Survey of Organic Chemistry Fall Semester 2014 Dr. Rainer Glaser Examination #1 Bonding, Alkanes, Alkenes & Alkynes Thursday, September 18, 2014, 8:00 8:50 am Question 1. Atomic Structure
Organic Chemistry The Functional Group Approach. Organic Chemistry The Functional Group Approach
 Organic Chemistry The Functional Group Approach OH Br alkane (no F.G.) alcohol halide alkene non-polar (grease, fats) O NH alkyne aromatic aldehyde/ketone imine linear flat Organic Chemistry The Functional
Organic Chemistry The Functional Group Approach OH Br alkane (no F.G.) alcohol halide alkene non-polar (grease, fats) O NH alkyne aromatic aldehyde/ketone imine linear flat Organic Chemistry The Functional
CHEM 347 Organic Chemistry II Spring Instructor: Paul Bracher. Quiz # 2
 CHEM 347 Organic Chemistry II Spring 2015 Quiz # 2 Solutions Key Page 1 of 12 CHEM 347 Organic Chemistry II Spring 2015 Instructor: Paul Bracher Quiz # 2 Due: Monday, February 9 th, 2015 2:00 p.m. (in
CHEM 347 Organic Chemistry II Spring 2015 Quiz # 2 Solutions Key Page 1 of 12 CHEM 347 Organic Chemistry II Spring 2015 Instructor: Paul Bracher Quiz # 2 Due: Monday, February 9 th, 2015 2:00 p.m. (in
Gibb s Free Energy. This value represents the maximum amount of useful work (non PV-work) that can be obtained by a system.
 Gibb s Free Energy 1. What is Gibb s free energy? What is its symbol? This value represents the maximum amount of useful work (non PV-work) that can be obtained by a system. It is symbolized by G. We only
Gibb s Free Energy 1. What is Gibb s free energy? What is its symbol? This value represents the maximum amount of useful work (non PV-work) that can be obtained by a system. It is symbolized by G. We only
Key ideas: In EAS, pi bond is Nu and undergoes addition.
 Objective 7. Apply addition and elimination concepts to predict electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions (EAS) of benzene and monosubstituted benzenes. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features
Objective 7. Apply addition and elimination concepts to predict electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions (EAS) of benzene and monosubstituted benzenes. Skills: Draw structure ID structural features
Homework - Review of Chem 2310
 omework - Review of Chem 2310 Chapter 1 - Atoms and Molecules Name 1. What is organic chemistry? 2. Why is there an entire one year course devoted to the study of organic compounds? 3. Give 4 examples
omework - Review of Chem 2310 Chapter 1 - Atoms and Molecules Name 1. What is organic chemistry? 2. Why is there an entire one year course devoted to the study of organic compounds? 3. Give 4 examples
CH 3 Cl + Cl 2 CH 2 Cl 2 + HCl
 Energetics 414 alogenation of Alkanes X 2 X X X 2 X X explosive for F 2 exothermic for l 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 hlorination of Methane carried out at high temperature (400 ) 415 hlorination of
Energetics 414 alogenation of Alkanes X 2 X X X 2 X X explosive for F 2 exothermic for l 2 and Br 2 endothermic for I 2 hlorination of Methane carried out at high temperature (400 ) 415 hlorination of
CHAPTER 2. Structure and Reactivity: Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar Molecules
 CHAPTER 2 Structure and Reactivity: Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar Molecules 2-1 Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Simple Chemical Processes Chemical thermodynamics: Is concerned with the extent that
CHAPTER 2 Structure and Reactivity: Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar Molecules 2-1 Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Simple Chemical Processes Chemical thermodynamics: Is concerned with the extent that
Alkenes. Structure, Nomenclature, and an introduc1on to Reac1vity Thermodynamics and Kine1cs
 Alkenes Structure, Nomenclature, and an introduc1on to Reac1vity Thermodynamics and Kine1cs 1 Alkene - Hydrocarbon With Carbon- Carbon Double Bond Also called an olefin but alkene is be>er Hydrocarbon
Alkenes Structure, Nomenclature, and an introduc1on to Reac1vity Thermodynamics and Kine1cs 1 Alkene - Hydrocarbon With Carbon- Carbon Double Bond Also called an olefin but alkene is be>er Hydrocarbon
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions"
 Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron H. Cl. Hydrogen radical t Often called free radicals What are radicals? Chlorine radical t Formed by homolytic bond cleavage
Chapter 10 Radical Reactions Radicals are intermediates with an unpaired electron H. Cl. Hydrogen radical t Often called free radicals What are radicals? Chlorine radical t Formed by homolytic bond cleavage
Chem 261 Nov 20, Conjugated = separated by a single bond from a double bond
 7 hem 6 Nov 0, 07 REVIEW: onjugated = separated by a single bond from a double bond Examples of onjugated Systems. Double bonds ( or more). Allylic ations. Allylic Anions. Allylic Radicals REVIEW: Molecules
7 hem 6 Nov 0, 07 REVIEW: onjugated = separated by a single bond from a double bond Examples of onjugated Systems. Double bonds ( or more). Allylic ations. Allylic Anions. Allylic Radicals REVIEW: Molecules
Chem 341 Jasperse Ch Handouts 1
 Chem 341 Jasperse Ch. 5 + 10 Handouts 1 Ch. 5 The Study of Chemical Reactions 5.1 Four general types of chemical reactions 1. Addition reactions 2. Elimination Reactions 3. Substitution Reactions 4. Rearrangement
Chem 341 Jasperse Ch. 5 + 10 Handouts 1 Ch. 5 The Study of Chemical Reactions 5.1 Four general types of chemical reactions 1. Addition reactions 2. Elimination Reactions 3. Substitution Reactions 4. Rearrangement
5. Reactions of Alkenes (text )
 2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 5.1 5. Reactions of Alkenes (text 5.1 5.5) A. Addition Reactions In hapter 4, we saw that π bonds have electron density on two sides of the
2009, Department of hemistry, The University of Western Ontario 5.1 5. Reactions of Alkenes (text 5.1 5.5) A. Addition Reactions In hapter 4, we saw that π bonds have electron density on two sides of the
LECTURE #06 Thurs., Feb.07, 2008
 CEM 221 section 52 LECTURE #06 Thurs., Feb.07, 2008 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: 3.6-3.8 Introduction to organic rxn mechanisms 4.1-4.5 Alkene reactions electrophilic addition mechanism carbocation
CEM 221 section 52 LECTURE #06 Thurs., Feb.07, 2008 ASSIGNED READINGS: TODAY S CLASS: 3.6-3.8 Introduction to organic rxn mechanisms 4.1-4.5 Alkene reactions electrophilic addition mechanism carbocation
Alkenes. Alkenes-hydrocarbons with a carbon-carbon double bond. Alkenes have the formula C n H 2n. Nomenclature
 Alkenes Alkenes-hydrocarbons with a carbon-carbon double bond. Alkenes have the formula n 2n. Nomenclature Alkenes are named in the same manner as alkanes with the following adjustments. 1. Find the longest
Alkenes Alkenes-hydrocarbons with a carbon-carbon double bond. Alkenes have the formula n 2n. Nomenclature Alkenes are named in the same manner as alkanes with the following adjustments. 1. Find the longest
Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes
 Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes In an alkane, all covalent bonds between carbon were σ (σ bonds are defined as bonds where the electron density is symmetric about the internuclear axis) In an alkene,
Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes In an alkane, all covalent bonds between carbon were σ (σ bonds are defined as bonds where the electron density is symmetric about the internuclear axis) In an alkene,
