Chapter 6 H 2 H 3 C C H CH 3 C H H 2 C C CH 3. (b) =2 H 2 C C C H H C H CH 2 C CH 3 H 3 C C C CH 3. (c) =2
|
|
|
- Camilla Ball
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 hapter alculate the degree of the unsaturation in the following hydrocarbons: 8 14 ; 5 6 (c) (d) (e) =2 =3 (c) =3 (d) =5 (e) = alculate the degree of the unsaturation in the following formula, and the draw as many structures as you can for each: 4 5 ; 4 6 ; (c) 3 4 ; = = (c) =2
2 alculate the degree of unsaturation in the following formulas: (1) 6 5 N 5 (2) 6 5 N 2 5 (3) 8 9 l 3 3 (4) (5) N (6) ln Give the IUPA name for the following compounds: (1) 3,4,4-trimethyl-1-pentene (2) (3) 3-methyl-3-hexene 4,7-dimethyl-2,5-octadiene 6.5 Draw structures corresponding to the following IUPA names: 2-Methyl-1,5-hexadiene 3-Ethyl-2,2-dimethyl-3-heptene (c)2,3,3-trimethyl-1,4,6-octatriene (d)3,4-diisopropyl-2,5-dimethyl-3-hexene (e)4-tert-butyl-2-methylheptane
3 (c) 3 3 (d) (e) Name the following cycloalkenes: ( 3 ) 2 3 1,2-Dimethyl-cyclohexene 4,4-Dimethyl-cycloheptene (c) 3-Isopropyl-cyclopentene (c) 6.7 Which of the following compounds can exist as pairs of cis-trans isomers? Draw each cis-trans pair, and indicate the geometry of each isomer. 3 2 ( 3 ) 2 3 (c) (d) ( 3 ) 2 ( 3 ) 2 3 (e) l l (f) l (c) cis: trans: 3
4 (e) l l l cis: (f) l trans: l cis: trans: l 6.8 Name the following alkenes, including the cis or trans designation: cis-4,5-dimethyl-2-hexene trans-6-methyl-3-heptene 6.9 Which member in each of the following sets has higher priority? or l or (c) 3 or 2 3 (d) N 2 or (e) 2 or 3 (f) 2 or = (c) 2 3 (d) (e) 2 (f) = 6.10 Rank the following sets of substituents in order of ahn-ingold-prelog priorities. 3, -, -, l 3, 2 3, -= 2 (c) 2, - 2, - N, - 2 N 2 (d) 2 3, -, - N, (From igh to low) l, -, 3, - -= 2, 2 3, 3 (c) 2, - 2, - N, - 2 N 2 (d) - 2 3, - N, -, 2 3
5 6.11 Assign E or Z configuration to the following alkenes: 3 2 l l Z E N 2 N 2 2 Z E 6.12 Assign stereochemistry to the following alkene, and convert the drawing into a skeletal structure: 3 2 Z 6.13 Name the following alkenes, and tell which compounds in each of the following pairs are more stable: or 1-butene 2-methyl-1-propene 2-methyl-1-propene is more stable because it is more substituents.
6 2 2 3 or cis-2-hexene trans-2-hexene trans-2-hexene is more stable because it is trans isomer. (c) 3 or 3 1-methyl-1-cyclohexene 3-methyl-1-cyclohexene 1-methyl-1-cyclohexene is more stable because the carbon has only sp 2 -sp 2 bonds while the other has sp 2 -sp 3 bonds Predict the products of the following reactions: + l l I (c) P 4 2 KI 2 3 (d) What alkenes would you start with to prepare the following alkyl halides? omocyclopentane 1-Ethyl-1-iodocyclohexane (c)
7 yclopentene 1-Ethylcyclohexene (c) Show the structures of carboations you would expect in the following reactions: ? 3 + I? Draw a skeletal structure of the following carbocation. Identify it as primary, secondary, or tertiary, and identify the hydrogen atoms that are involved in hyperconjugation in the conformation shown It is secondary carbocation. nly the methyl-group that is parallel to the carbocation p orbital can show hyperconjugation What about the second step in the electrophilic addition of l to an alkene the reaction of chloride ion with the carbocation intermediate? Is this step exergonic or endergonic? Does the transition state for this second step resemble the reactant (carbocation) or product (alkyl chloride)? Make a rough drawing of what the transition-state structure might look like. This step is exergonic. The transition state for this second step resemble carbocation.
8 R R R R transition state Intermediate Product 6.19 n treatment with, vinylcyclohexane undergoes addition and rearrangement to yield 1-bromo-1-ethylcyclohexane. Using curved arrows, propose a mechanism to account for this result vinylcyclohexane Name the following alkenes, and convert each drawing into a skeletal structure. 2,4,5-trimethyl-2-hexene
9 1-ethyl-3,3-dimethyl-1-cyclohexene Assign stereochemistry (E or Z) to each of the following alkenes, and convert each drawing into a skeletal structure: SLUTIN: l E Z The following carbocation is an intermediate in the electrophilic addition reaction of l with two different alkenes. Identify both, and tell which bonds in the carbocation are aligned for maximum hyperconjugation with the vacant p orbital on the positively charged carbon. SLUTIN: alculate the degree of unsaturation in the following formulas, and draw five possible for each: (c) 710l2
10 (d) (e) 59N2 (f) 810lN Solution a) It has 3 unsaturation degrees. Possible structures: b) It has 5 unsaturation degrees. Possible structures: c) It has 2 unsaturation degrees. l l l l l l l l l Possible structures: l d) It has 3 unsaturation degrees. Possible structures: e) it has 2 unsaturation degrees.
11 N N N N N Possible structures: f) it has 4 unsaturation degrees. N N N Possible structures: N N 6.24 A compound of formula 1014 undergoes catalytic hydrogenation but absorbs only 2 molar equivalents of hydrogen. ow many rings does the compound have? It has 4 unsaturation degrees. Two of them are rings A compound of formula N contains two rings. ow many molar equivalents of hydrogen does it absorb if all the remaining unsaturations are double bonds? N= ( ) 2 Degree of Unsaturation: = 7 It can absorb 7-2=5 molar equivalents of hydrogen Name the following alkenes:
12 (c) (d) (e) (f) 2 3.trans-4-Methyl-2-hexene or (E)-4-Methyl-2-hexene.cis-4-Ethyl-7-methyl-2-octene or (Z)-4-Ethyl-7-methyl-2-octene (c).2-ethyl-1-butene (d).trans-3,4-dimethyl-1,5-heptadiene or (E)-3,4-Dimethyl-1,5-heptadiene (e).(2-cis,4-trans)-4,5-dimethyl-2,4-octadiene or (2Z,4E)-4,5-Dimethyl-2,4-octadiene (f).1,2-butadiene 6.27 cimene is a triene found in the essential oils of many plants. What is its IUPA name, including stereochemistry? (3E)3,7-dimethyl-octa-1,3,6-triene 6.28 α-farnesene is a constituent of the natural wax found on apples. What is its IUPA name, including stereochemistry? α-farnesene (3E,6E)3,7,11-trimethyl-dodeca-1,3,6,10-tetraene
13 6.29 Draw structures corresponding to the following systematic names: (4E)-2,4-Dimethyl-1,4-hexadiene cis-3,3-dimethyl-4-propyl-1,5-octadiene (c) 4-Methyl-1,2-pentadiene 3 3 (d) (3E,5Z)-2,6-Dimethyl-1,3,5,7-octatetraene. 3 3 (e) 3-Butyl-2-heptene (f) trans-2,2,5,5-tetramethyl-3-hexene Menthene, a hydrocarbon found in mint plants, has the systematic name
14 1-isopropyl-4-methylcyclohexhene. Draw its structure Draw and name the 6 pentene isomers, 5 10, including E, Z isomers. 1-Pentene (Z)-2-Pentene (E)-2-Pentene 2-Methyl-1-butene 2-Methyl-2-butene 3-Methyl-1-butene 6.32 Draw and name the 17 hexene isomers, 6 12, including E, Z isomers.
15 1-exene (E)-2-exene (Z)-2-exene (E)-3-exene (Z)-3-exene 2-Methyl-1-pantene 2-Methyl-2-pantene (E)-4-Methyl-2-pantene (Z)-4-Methyl-2-pantene 4-Methyl-1-pantene 3-Methyl-1-pantene 2-Ethyl-1-butene (E)-3-Methyl-2-pantene (Z)-3-Methyl-2-pantene 3,3-Dimethyl-1-butene 2,3-Dimethyl-1-butene 2,3-Dimethyl-2-butene 6.33 trans-2-butene is more stable than cis-2-butene by only 4 KJ/mol, but trans-2, 2, 5, 5-tetramethyl-3-hexene is more stable than cis-2, 2, 5, 5-tetrameethyl-3-hexene by 39 KJ/mol. Explain. Alkene (KJ/mol) ΔΗ o hydrog (kcal/mol) cis-2-butene trans-2-butene cis-2, 2, 5, 5-tetrameethyl-3-hexene trans-2,2,5,5-tetrameethyl-3-hexene Between cis-2-butene and trans-2-butene, the cis-2-butene has steric strain, so the trans-2-butene is more stable. But the steric strain is not large, the difference between them is not very large. And the cis-2, 2, 5, 5-tetrameethyl-3-hexene has large steric strain, so the
16 difference between cis-2, 2, 5, 5-tetrameethyl-3-hexene and trans-2, 2, 5, 5-tetrameethyl-3-hexene is larger yclodecene can exist in both cis and trans forms, but cyclohexene cannot. Explain.(Making molecular models is helpful.) the cyclodecene can be But the cyclohexene can only be: 6.35 Normally, a trans alkene is more stable than its cis isomer. trans-yclooctene, however, is less stable than cis-cyclooctene by 38.5 kj/mol. Explain. Build models of the two cyclooctenes and notice that the large amount of torsional strain in trns-cyclooctene relative to cis-cyclooctene. This strain causes the trans isomer ot be of higher energy Trans-yclooctene is less stable than cis-cyclooctene by 38.5 kj/mol, but trans-cyclononene is less stable than cis-cyclononene by only 12.2 kj/mol. Explain. trans-yclononene has more carbon than trans-yclooctene, and the ring is bigger, so the steric strain is smaller Allene(1.2-propadiene), 2 2,has two adjacent double bonds. What kind of hybridization must the central carbon have? Sketch the bonding π orbitals in allene. What shape do you predict for allene. The central carbon is sp hybridized. The bonding πorbitals in allene is showed as follow: The structure of allene is showed as follow: 6.38 The heat of hydrogenation for allene(problem 6.37) to yield propaneis -298 kj/mol, and the heat
17 of hydrogenation for a typical monosubsituted alkene such as propene is -126kJ/mol. Is allene more or less stable then you might except for diene? Explain. Less stable. Because allene give out more heat than diene in hydrogenation which means that it contains more energy Predict the major product in each of the following reactions: l l + 1-Ethylcyclopentene (c) I ,2,4-Trimethyl-3-hexene (d) l 3 I l 1,6-eptadiene + 2l (e) Predict the major product from addition of to each of following alkenes:
18 (c) Rank the following sets of substituents in order of priority according to the ahn-ingold-prelog sequence rules: 3,,, I 1. I, 2., 3. 3, 4.., 3,, 1. 3, 2., 3., 4.. (c) 2, 2 3, 2, , , (d) 3, 2 3, 2 2, , , , (e) 2, N, 2 N 2, , 2. N, 3. 2 N 2, (f) 2, 2 3, 2 3, , 2. 2, , Assign E or Z configuration to each of the following alkenes:
19 2 3 Z Z 3 l 3 N E Z 2 (c) (d) Name the following cycloalkenes: 3 (c) (d) (e) (f) 3-Methyl-1-cyclohexene 2,3-Dimethyl-1-cyclopentene (c) 1-Ethyl-1,3-cyclobutadiene (d) 1,2-Dimethyl-1,4-cyclohexadiene (e) 5-Methyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene (g) 1,5- cyclooctadiene 6.44 Which of the following E,Z designations are correct, and which are incorrect? ( 3 ) 2 Z E 2 N 2 N 3 2 N 3 ( (c) Z 3 ) 2 N (d) E 2 2 (e) Z (f) E correct orrect (c) incorrect, it should be E (d) correct (e) Doesn t show E / Z isomerism. (f) correct 6.45 tert-butyl esters [R 2 ( 3 ) 3 ] are converted into carboxylic acids (R 2 ) by reaction with
20 trifluoroacetic acid, a reaction useful in protein synthesis (see Section 26.10). Assign E,Z designation to the double bonds of both reactant and product in the following scheme, and explain why there is an apparent change of double-bond stereochemistry: 3 F ( 3 ) 3 3 The reactant is Z designation, while the product is E designation. Because ( 3 ) 3 receives higher priority than 3, while 3 receives higher priority than, and in the reaction substitute for ( 3 ) Use the bond dissociation energies in Table 5.4 to calculate Δ 0 for the reaction of ethylene with l,, and I. Which reaction is most favorable? l 235 KJ / mol 432 KJ / mol 2 2 l 420 KJ / mol 338 KJ / mol o = -91 KJ / mol KJ / mol 366 KJ / mol KJ / mol 285 KJ / mol o = -104 KJ / mol I 235 KJ / mol 298 KJ / mol KJ / mol 222 KJ / mol I o = -109 KJ / mol 6.47: Each of the following carboncations can rearrange to a more stable ion. Propose structure for the likely rearranges for the likely rearrangement product. (c) (c)
21 6.48 Addition of l to 1-isopropyl-cyclohexane yields a rearranged product. Propose a mechanism, showing the structures of the intermediates and using curved arrows to indicate electron flow in each step. l + l l (E) + + l l + l 6.49 Addition of l to 1-isopropenyl-1-methylcyclopentane yields 1-chloro-1, 2, 2-trimethylcyclohexane. Propose a mechanism, showing the structures of the intermediates and using curved arrows to indicate electron flow in each step. l 3 + l l 3 3 l 3 3 l Vinylcyclopropane reacts with to yield a rearranged alkyl bromide. Follow the flow of electrons as represented by the curved arrows, show the structure of the carbocation intermediate in brackets, and show the structure of the final product.
22 ?? 6.51: alculate the degree of unsaturation in each of the following formulas D= l 5 D=8 (c) D=4 (d) 8 10 N 4 2 D=6 (e) D=8 (f) N 3 D=7 6.52: Is the rearrangement exergonic or endergonic? Draw the transition state. It is a exergonic. State Draw a reaction energy diagram for the addition of to 1-pentene. Let one curve on your diagram show the formation of 1-bromopentane product and another curve on the same diagram show the formation of 2-bromopentane product. Label the postions for all reactants, intermediates, and products. Which curve has higher-energy carbocation intermediate? Which curve has the higher-energy first transition state?
23 The vertical axial presents energy, and the horizontal one shows the progress of the reaction. The red one stands for 2-bromopentane, and the blue one stands for 1-bromopentane. The blue one has higher-energy cabocation intermediate and the higher-energy first transition state Make sketches of the transition state structures involved in the reaction of with 1-pentene (Problem 6.53). Tell whether each structure resembles reactant or product. The first one is for forming 1-bromopentane, and the second one is for forming 2-bromopentane.
24 δ R δ δ R δ δ δ Each structure resembles carbocation Aromatic compounds such as benzene react with alkyl chlorides in the presence of All 3 catalyst to yield alkylbenzenes. The reaction occurs through a carbocation intermediate, formed by reaction of the alkyl chloride with All 3 (R-l+ All 3 R + +All - 4 ). ow can you explain the observation that reaction of benzene with 1-chloropropane yields isopropylbenzene as the major product? l All3
25 3 2 2 l All3 3 All4 3 3 All4 l All Alkenes can be converted into alcohols by acid-catalyzed addition of water. Assuming that Markonikov s rule is valid, predict the major product from each of the following alkenes (c) (c) ( 3 ) Reaction of 2,3-dimethyl-1-butene with leads to an alkyl bromide n treatment of this alkyl bromide with K in methanol, elimination of occurs and a hydrocarbon that is isomeric with the starting alkene is formed. What is the structure of this hydrocarbon, and how do
26 you think is formed from the alkyl bormide?
Ch.6 Alkenes: Structure and Reactivity
 alkene = olefin 2 2 Ethylene α-pinene 3 β-arotene (orange pigment and vitamin A precursor) 6.1 Industrial Preparation and Use of Alkenes ompounds derived industrially from ethylene 2 2 Ethylene (26 million
alkene = olefin 2 2 Ethylene α-pinene 3 β-arotene (orange pigment and vitamin A precursor) 6.1 Industrial Preparation and Use of Alkenes ompounds derived industrially from ethylene 2 2 Ethylene (26 million
Unsaturated hydrocarbons. Chapter 13
 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Chapter 13 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons which contain at least one C-C multiple (double or triple) bond. The multiple bond is a site for chemical reactions in these molecules.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons Chapter 13 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons which contain at least one C-C multiple (double or triple) bond. The multiple bond is a site for chemical reactions in these molecules.
Chapter 12 Alkenes and Alkynes
 BR M 102 lass Notes hapter 12 Page 1 of 8 hapter 12 Alkenes and Alkynes * alkenes = double bonds * alkynes triple bonds * aromatics or arenes alternating double and single bonds such as in benzene * saturated
BR M 102 lass Notes hapter 12 Page 1 of 8 hapter 12 Alkenes and Alkynes * alkenes = double bonds * alkynes triple bonds * aromatics or arenes alternating double and single bonds such as in benzene * saturated
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2
 C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
C h a p t e r S e v e n : Haloalkanes: Nucleophilc Substitution and Elimination Reactions S N 2 CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts Concepts for Chapter 7: Substitution Reactions I. Nomenclature of
Chapter 6: Alkenes: Structure and Reactivity
 hapter 6: Alkenes: Structure and eactivity overage: 1. Degrees of Unsaturation 2. Nomenclature cis/trans E/Z 3. Alkene Stability 4. Electrophilic Addition eactions/markovinikov s ule 5. The ammond Postulate
hapter 6: Alkenes: Structure and eactivity overage: 1. Degrees of Unsaturation 2. Nomenclature cis/trans E/Z 3. Alkene Stability 4. Electrophilic Addition eactions/markovinikov s ule 5. The ammond Postulate
1. Root of name depends on longest chain of C containing the double bond; ends in "ene"
 Alkenes (β-carotene, an antioxidant pigment) n 2n (acyclic) n 2n-2 (cyclic) R R R R Key features sp 2 -hybridized carbons, 120 o bond angles σ + π bonding between = planar geometry around = "unsaturated"
Alkenes (β-carotene, an antioxidant pigment) n 2n (acyclic) n 2n-2 (cyclic) R R R R Key features sp 2 -hybridized carbons, 120 o bond angles σ + π bonding between = planar geometry around = "unsaturated"
Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes
 Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes In an alkane, all covalent bonds between carbon were σ (σ bonds are defined as bonds where the electron density is symmetric about the internuclear axis) In an alkene,
Introduction to Alkenes and Alkynes In an alkane, all covalent bonds between carbon were σ (σ bonds are defined as bonds where the electron density is symmetric about the internuclear axis) In an alkene,
Question. Chapter 5 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes (C n H 2n ): Elimination Reactions
 hapter 5 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes ( n 2n ): Elimination Reactions The molecular formula of β-arotene is 40 On catalytic hydrogenation, β-carotene is converted to a saturated hydrocarbon of
hapter 5 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes ( n 2n ): Elimination Reactions The molecular formula of β-arotene is 40 On catalytic hydrogenation, β-carotene is converted to a saturated hydrocarbon of
Solutions. Department of Chemistry SUNY/Oneonta. Chem Organic Chemistry I. Examination #2 - October 23, 2000
 Solutions Department of hemistry SUNY/Oneonta hem 221 - Organic hemistry I Examination #2 - October 23, 2000 INSTRUTIONS --- This examination has two parts. The first part is in multiple choice format;
Solutions Department of hemistry SUNY/Oneonta hem 221 - Organic hemistry I Examination #2 - October 23, 2000 INSTRUTIONS --- This examination has two parts. The first part is in multiple choice format;
C h a p t e r E i g h t: Alkenes: Structure and Preparation via Elimination Reactions. 5-Androstene, the parent alkene for most anabolic steroids
 C h a p t e r E i g h t: Alkenes: Structure and Preparation via Elimination Reactions 5-Androstene, the parent alkene for most anabolic steroids CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts YConcepts for Chapter
C h a p t e r E i g h t: Alkenes: Structure and Preparation via Elimination Reactions 5-Androstene, the parent alkene for most anabolic steroids CHM 321: Summary of Important Concepts YConcepts for Chapter
Chemistry 2321 OLD TEST QUESTIONS CH 3
 Test No. 2 hemistry 2321 LD TEST QUESTNS Professor M. Pomerantz 1. n the following reaction the electrophile is: 3 3 + the group none of these 2. Given the reaction shown and the bond dissociation energies
Test No. 2 hemistry 2321 LD TEST QUESTNS Professor M. Pomerantz 1. n the following reaction the electrophile is: 3 3 + the group none of these 2. Given the reaction shown and the bond dissociation energies
Chapter 4: Alkenes and Alkynes
 Chapter 4: Alkenes and Alkynes 99 Chapter 4: Alkenes and Alkynes Problems 4.1 Write the IUPAC name of each unsaturated hydrocarbon: (a) (b) (c) 3,3-dimethyl-1-pentene 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene 3,3-dimethyl-1-butyne
Chapter 4: Alkenes and Alkynes 99 Chapter 4: Alkenes and Alkynes Problems 4.1 Write the IUPAC name of each unsaturated hydrocarbon: (a) (b) (c) 3,3-dimethyl-1-pentene 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene 3,3-dimethyl-1-butyne
C C. sp 2. π M.O. atomic. orbitals. carbon 1. σ M.O. molecular. orbitals. H C C rotate D. D H zero overlap of p orbitals: π bond broken!
 Alkenes Electrophilic Addition 1 Alkene Structures chemistry of double bond σ BDE ~ 80 kcal/mol π = BDE ~ 65 kcal/mol The p-bond is weaker than the sigma-bond The, electrons in the p-bond are higher in
Alkenes Electrophilic Addition 1 Alkene Structures chemistry of double bond σ BDE ~ 80 kcal/mol π = BDE ~ 65 kcal/mol The p-bond is weaker than the sigma-bond The, electrons in the p-bond are higher in
Chapter Name the following compounds: (a) 2,5-dimethyl-3-hexyne (b) 3,3-dimethyl-1-butyne (c) 2,4-octadiene-6-yne (d) 3,3-dimethyl-4-octyne (e)
 hapter 8 8.1 Name the following compounds: 3 3 3 3 2,5-dimethyl-3-hexyne 3 3 3 3,3-dimethyl-1-butyne (c) 3 3 2,4-octadiene-6-yne (d) 3 3 2 2 2 3 3 3,3-dimethyl-4-octyne (e) 3 3 3 2 3 3 2,5,5-trimethyl-3-heptyne
hapter 8 8.1 Name the following compounds: 3 3 3 3 2,5-dimethyl-3-hexyne 3 3 3 3,3-dimethyl-1-butyne (c) 3 3 2,4-octadiene-6-yne (d) 3 3 2 2 2 3 3 3,3-dimethyl-4-octyne (e) 3 3 3 2 3 3 2,5,5-trimethyl-3-heptyne
Organic Chemistry The Functional Group Approach. Organic Chemistry The Functional Group Approach
 Organic Chemistry The Functional Group Approach OH Br alkane (no F.G.) alcohol halide alkene non-polar (grease, fats) O NH alkyne aromatic aldehyde/ketone imine linear flat Organic Chemistry The Functional
Organic Chemistry The Functional Group Approach OH Br alkane (no F.G.) alcohol halide alkene non-polar (grease, fats) O NH alkyne aromatic aldehyde/ketone imine linear flat Organic Chemistry The Functional
Exam. Name. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements is incorrect about benzene? 1) A) All of the carbon
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements is incorrect about benzene? 1) A) All of the carbon
CHAPTER 3 ALKENES, ALKYNES & CONJUGATE DIENES
 CHEM 244 PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERING STUDENTS, COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING PRE-REQUISITES COURSE; CHEM 101 CREDIT HOURS; 2 (2+0) Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College
CHEM 244 PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERING STUDENTS, COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING PRE-REQUISITES COURSE; CHEM 101 CREDIT HOURS; 2 (2+0) Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College
Test Bank for Organic Chemistry 8th Edition by Wade
 Test Bank for Organic Chemistry 8th Edition by Wade Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bankfororganic-chemistry-8th-edition-by-wade/ Organic Chemistry 8th Edition Test Bank Wade
Test Bank for Organic Chemistry 8th Edition by Wade Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bankfororganic-chemistry-8th-edition-by-wade/ Organic Chemistry 8th Edition Test Bank Wade
Chapter 5. 3-Chloro-2-methylpentane. Cl 2. 2-Chloro-2-methylpentane. 1-Chloro-2-methylpentane. Cl 2-Chloro-4-methylpentane. 1-Chloro-4-methylpentane
 hapter 5 5.1 lassify each of the following reactions as an addition, elimination, substitution, or rearrangement: (a) 3Br K 3 KBr (b) 3 2 2 2 2 (c) 2 2 2 3 3 a. substitution b. elimination c. addition
hapter 5 5.1 lassify each of the following reactions as an addition, elimination, substitution, or rearrangement: (a) 3Br K 3 KBr (b) 3 2 2 2 2 (c) 2 2 2 3 3 a. substitution b. elimination c. addition
Chapter 7 Alkenes; Elimination Reactions
 hapter 7 Alkenes; Elimination Reactions Alkenes Alkenes contain a carbon-carbon double bond. They are named as derivatives of alkanes with the suffix -ane changed to -ene. The parent alkane is the longest
hapter 7 Alkenes; Elimination Reactions Alkenes Alkenes contain a carbon-carbon double bond. They are named as derivatives of alkanes with the suffix -ane changed to -ene. The parent alkane is the longest
Vision. Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. How rods work H 3 C CH 3. Protein opsin. 11-cis-retinal. Opsin. Rhodopsin.
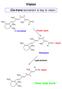 Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
As time allows, additional practice questions for Exam 2 follow. This is an incomplete collection. Content & emphasis will vary.
 Chem 226 Exam 2 Fall 2005: will cover Bruice, Chaps 3 through 6; Note: review e-mail & inclass quizzes and Worksheets, suggest on-line practice questions and quizzes plus ACS rganic Chemistry Guide As
Chem 226 Exam 2 Fall 2005: will cover Bruice, Chaps 3 through 6; Note: review e-mail & inclass quizzes and Worksheets, suggest on-line practice questions and quizzes plus ACS rganic Chemistry Guide As
1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound?
 EM 331: hapter 1/2: Structures (Atoms, Molecules, Bonding) 1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound? N 2 N 2 N 1 2 3 4 2. What hybrid orbitals are used to
EM 331: hapter 1/2: Structures (Atoms, Molecules, Bonding) 1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound? N 2 N 2 N 1 2 3 4 2. What hybrid orbitals are used to
Chapter 10. BrCH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CCH 2 Br CH 3. CH 3 CCH 2 CH 2 Cl CH 3 CHCH 2 CH 2 CHCH Give IUPAC names for the following alkyl halides:
 hapter 10 10.1 Give IUPA names for the following alkyl halides: (a), 3 2 2 2 I 1-iodobutane 3 (b), 3 2 2 l 1-chloro-3-methylbutane (c), 3 2 2 2 2 3 1,5-Dibromo-2,2-dimethylpentane 3 3 2 2 l (d), l 1,3-Dichloro-3-methylbutane
hapter 10 10.1 Give IUPA names for the following alkyl halides: (a), 3 2 2 2 I 1-iodobutane 3 (b), 3 2 2 l 1-chloro-3-methylbutane (c), 3 2 2 2 2 3 1,5-Dibromo-2,2-dimethylpentane 3 3 2 2 l (d), l 1,3-Dichloro-3-methylbutane
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 203/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry
 E1502/203/1/2016 Tutorial letter 203/1/2016 General hemistry 1B E1502 Semester 1 Department of hemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 3. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY T
E1502/203/1/2016 Tutorial letter 203/1/2016 General hemistry 1B E1502 Semester 1 Department of hemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 3. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY T
Counterclockwise (Leftward turning) S. 3 2 Clockwise (Rightward turning) R
 Stereochemistry I and S in Alkanes A chiral carbon has four different groups attached to it, the differences may be several bonds away, but so long as they are different in any way the groups are considered
Stereochemistry I and S in Alkanes A chiral carbon has four different groups attached to it, the differences may be several bonds away, but so long as they are different in any way the groups are considered
5.5 Physical Properties of Alkenes
 5.5 Physical Properties of Alkenes Dipole moments What is direction of dipole moment? Does a methyl group donate electrons to the double bond, or does it withdraw them? µ = 0 D 3 µ = 0.3 D µ = 1.4 D Dipole
5.5 Physical Properties of Alkenes Dipole moments What is direction of dipole moment? Does a methyl group donate electrons to the double bond, or does it withdraw them? µ = 0 D 3 µ = 0.3 D µ = 1.4 D Dipole
Department of Chemistry SUNY/Oneonta. Chem Organic Chemistry I. Examination #2 - October 18, 2004 ANSWERS
 Department of hemistry SUNY/Oneonta hem 221 - Organic hemistry I Examination #2 - October 18 2004 ANSWERS INSTRUTIONS This examination is in multiple choice format; the questions are in this Exam Booklet
Department of hemistry SUNY/Oneonta hem 221 - Organic hemistry I Examination #2 - October 18 2004 ANSWERS INSTRUTIONS This examination is in multiple choice format; the questions are in this Exam Booklet
Name: Chapter 3: The Nature Of Organic Reactions: Alkenes
 Name: Chapter 3: The Nature Of Organic Reactions: Alkenes 1 Vocabulary cis-trans isomerism: E,Z designation: Addition: Elimination: Substitution: Rearrangement: Homolytic: Heterolytic Homogenic: Heterogenic:
Name: Chapter 3: The Nature Of Organic Reactions: Alkenes 1 Vocabulary cis-trans isomerism: E,Z designation: Addition: Elimination: Substitution: Rearrangement: Homolytic: Heterolytic Homogenic: Heterogenic:
Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes
 Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes I. Isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes II. Reactions involving allylic cations or radicals III. Diels-Alder Reactions IV. Aromaticity I. Isolated, Conjugated,
Learning Guide for Chapter 17 - Dienes I. Isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes II. Reactions involving allylic cations or radicals III. Diels-Alder Reactions IV. Aromaticity I. Isolated, Conjugated,
Chapter 13 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
 hapter 1 1 hapter 1 Unsaturated ydrocarbons Solutions to In-hapter Problems 1.1 To draw a complete structure for each condensed structure, first draw in the multiple bonds. Then draw in all the other s
hapter 1 1 hapter 1 Unsaturated ydrocarbons Solutions to In-hapter Problems 1.1 To draw a complete structure for each condensed structure, first draw in the multiple bonds. Then draw in all the other s
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions
 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
much more stable then the
 8.1 Give the structure and name of the product that would be obtained from the ionic addition of I to propene. I I I 8.3 Provide mechanistic explanations for the following observations:(a)the addition
8.1 Give the structure and name of the product that would be obtained from the ionic addition of I to propene. I I I 8.3 Provide mechanistic explanations for the following observations:(a)the addition
5.1 Alkene Nomenclature
 5.1 Alkene Nomenclature Alkenes Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain a carbon-carbon double bond also called "olefins" characterized by molecular formula n 2n said to be "unsaturated" Alkene Nomenclature
5.1 Alkene Nomenclature Alkenes Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain a carbon-carbon double bond also called "olefins" characterized by molecular formula n 2n said to be "unsaturated" Alkene Nomenclature
Chem 341 Organic Chemistry I Lecture Summary 16 October 01, 2007
 hem 341 Organic hemistry I Lecture Summary 16 October 01, 2007 hapter 6 - Alkenes: Structure and eactivity Nomenclature Double bond geometry is important in biology. For example, the trans to cis isomerization
hem 341 Organic hemistry I Lecture Summary 16 October 01, 2007 hapter 6 - Alkenes: Structure and eactivity Nomenclature Double bond geometry is important in biology. For example, the trans to cis isomerization
Department of Chemistry SUNY/Oneonta. Chem Organic Chemistry I. Examination #2 - October 14, 2002
 Department of hemistry SUNY/Oneonta hem 221 - Organic hemistry Examination #2 - October 14, 2002 ANSWERS NSTRUTONS This examination is in multiple choice format; the questions are in this Exam Booklet
Department of hemistry SUNY/Oneonta hem 221 - Organic hemistry Examination #2 - October 14, 2002 ANSWERS NSTRUTONS This examination is in multiple choice format; the questions are in this Exam Booklet
Chemistry 231 Organic I Exam 2 Dr. Gallo (Brown & Foote) October 29, 2004
 hemistry 231 rganic I Exam 2 Dr. Gallo (Brown & Foote) ctober 29, 2004 1 Name: I(24). ircle the correct answer for each of the following multiple choice questions. 1.) Which alkene would yield 3-methylpentane
hemistry 231 rganic I Exam 2 Dr. Gallo (Brown & Foote) ctober 29, 2004 1 Name: I(24). ircle the correct answer for each of the following multiple choice questions. 1.) Which alkene would yield 3-methylpentane
Chapter 15 Dienes, Resonance, and Aromaticity
 Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 15 Dienes, Resonance, and Aromaticity Solutions to In-Text Problems 15.2 The delocalization energy is the energy
Instructor Supplemental Solutions to Problems 2010 Roberts and Company Publishers Chapter 15 Dienes, Resonance, and Aromaticity Solutions to In-Text Problems 15.2 The delocalization energy is the energy
CHAPTER 15. Practice exercises 15.1
 CAPTER 15 Practice exercises 15.1 15.3 (a) C 9 18 : isobutylcyclopentane C 11 22 : sec-butylcycloheptane C 6 2 : 1-ethyl-1-methylcyclopropane 15.5 (a) 3,3-dimethyl-1-pentene 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene 3,3-dimethyl-1-butyne
CAPTER 15 Practice exercises 15.1 15.3 (a) C 9 18 : isobutylcyclopentane C 11 22 : sec-butylcycloheptane C 6 2 : 1-ethyl-1-methylcyclopropane 15.5 (a) 3,3-dimethyl-1-pentene 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene 3,3-dimethyl-1-butyne
B. A transition state represents a maximum on the reaction path diagram and can be isolated.
 Practice Hour Exam 2, Chemistry 2210, Organic Chemistry I 1. The most stable carbocation is: 2. Which of the following statements is true of transition states? A. A transition state represents a minimum
Practice Hour Exam 2, Chemistry 2210, Organic Chemistry I 1. The most stable carbocation is: 2. Which of the following statements is true of transition states? A. A transition state represents a minimum
Alkenes. Alkenes are unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons.
 Alkenes Alkenes Each member contains one double covalent bond between two C atoms. Draw condensed structural formulas of first three members of alkenes family. Alkenes are unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons.
Alkenes Alkenes Each member contains one double covalent bond between two C atoms. Draw condensed structural formulas of first three members of alkenes family. Alkenes are unsaturated aliphatic hydrocarbons.
Dr. Dina akhotmah-232 1
 Dr. Dina akhotmah-232 1 Chemistry of polyfunction 1. Types of carbon atom Dr. Dina akhotmah-232 2 Classification of multiple bonds of polyunsaturated compounds Dr. Dina akhotmah-232 3 Organic chemistry,
Dr. Dina akhotmah-232 1 Chemistry of polyfunction 1. Types of carbon atom Dr. Dina akhotmah-232 2 Classification of multiple bonds of polyunsaturated compounds Dr. Dina akhotmah-232 3 Organic chemistry,
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320
 Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
Nuggets of Knowledge for Chapter 17 Dienes and Aromaticity Chem 2320 I. Isolated, cumulated, and conjugated dienes A diene is any compound with two or C=C's is a diene. Compounds containing more than two
More Tutorial at
 1. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question (50 pts). 1) Which of the following statements about propene, CH3CH CH2, is 1) correct? A) There
1. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question (50 pts). 1) Which of the following statements about propene, CH3CH CH2, is 1) correct? A) There
Chapter 7. dehydration
 hapter 7 7.1 ne problem with elimination reactions is that mixtures of products are often formed. For example, treatment of 2-bromo-2-methylbutane with K in ethanol yields a mixture of two alkene products.
hapter 7 7.1 ne problem with elimination reactions is that mixtures of products are often formed. For example, treatment of 2-bromo-2-methylbutane with K in ethanol yields a mixture of two alkene products.
ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE (AUTONOMOUS) ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE ROAD, CUDDALORE CH101T ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I (SEMESTER-I)
 UNIT I 1. The hybridization involved in the formation of acetylene is a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) sp 3 d 2. The IUPAC name of is 1. 3-hexene b) 4-hexene c) 3-hexyne d) 4-hexyne 3. -------- is the type of
UNIT I 1. The hybridization involved in the formation of acetylene is a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) sp 3 d 2. The IUPAC name of is 1. 3-hexene b) 4-hexene c) 3-hexyne d) 4-hexyne 3. -------- is the type of
Full file at
 Chapter 2 - Alkanes: The Nature of Organic Compounds 1. Which of the following functional group classifications do not contain oxygen? A. ether B. thiol C. aldehyde D. ester E. amide 2. To which functional
Chapter 2 - Alkanes: The Nature of Organic Compounds 1. Which of the following functional group classifications do not contain oxygen? A. ether B. thiol C. aldehyde D. ester E. amide 2. To which functional
1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound?
 CEM 331: Chapter 1/2: Structures (Atoms, Molecules, Bonding) 1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound? N C 2 C N C 2 C N 1 2 3 4 1: three sigma bonds and
CEM 331: Chapter 1/2: Structures (Atoms, Molecules, Bonding) 1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound? N C 2 C N C 2 C N 1 2 3 4 1: three sigma bonds and
Detailed Course Content
 Detailed Course Content Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds The Structural Theory of Organic Chemistry 4 Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule 6 Lewis Structures 8 Formal Charge 11 Resonance 14 Quantum
Detailed Course Content Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds The Structural Theory of Organic Chemistry 4 Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule 6 Lewis Structures 8 Formal Charge 11 Resonance 14 Quantum
CHEM120 - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY WORK SHEET Answer the following questions with respect to compounds (A) and (B):
 EM120 - RGANI EMISTRY WRK SEET 1 1. Answer the following questions with respect to compounds (A) and (B): (B) (A) 5 2 ( 3 ) 2 6 3 2 2 2 ( 3 ) 3 1 2 4 3 () 2 2 3 3 1 3 2 3 (a) Draw the bond-line notation
EM120 - RGANI EMISTRY WRK SEET 1 1. Answer the following questions with respect to compounds (A) and (B): (B) (A) 5 2 ( 3 ) 2 6 3 2 2 2 ( 3 ) 3 1 2 4 3 () 2 2 3 3 1 3 2 3 (a) Draw the bond-line notation
CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA
 CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems conjugation a series of overlapping p orbitals The Allyl Group allylic position is the next to a double bond 1 allyl
CHAPTER 9 THEORY OF RESONANCE BY, G.DEEPA Conjugation in Alkadienes and Allylic Systems conjugation a series of overlapping p orbitals The Allyl Group allylic position is the next to a double bond 1 allyl
General Chemistry Unit 7A ( )
 Organic Chemistry Allotropes Isomers Hydrocarbons o Alkanes o Alkenes o Alkynes o Aromatics Alkyl Halides General Chemistry Unit 7A (2017-2018) 1 2 3 4 Parent Chain: Methane Ethane CH4 C2H6 Propane C3H8
Organic Chemistry Allotropes Isomers Hydrocarbons o Alkanes o Alkenes o Alkynes o Aromatics Alkyl Halides General Chemistry Unit 7A (2017-2018) 1 2 3 4 Parent Chain: Methane Ethane CH4 C2H6 Propane C3H8
Organic Halogen Compounds
 8 Organic alogen ompounds APTER SUMMARY 8.1 Introduction Although organic halogen compounds are rarely found in nature, they do have a variety of commercial applications including use as insecticides,
8 Organic alogen ompounds APTER SUMMARY 8.1 Introduction Although organic halogen compounds are rarely found in nature, they do have a variety of commercial applications including use as insecticides,
nsaturated Hydrocarbons: Alkenes, Cycloalkenes and Dienes
 240 Chem nsaturated Hydrocarbons: Alkenes, Cycloalkenes and Dienes 1 Chapter 3 Alkenes or Olefines Crabon-Carbon double bond C n H 2n Hybridization in Alkenes: 1.34 A 2 Nomenclature of Alkenes and Cycloalkenes
240 Chem nsaturated Hydrocarbons: Alkenes, Cycloalkenes and Dienes 1 Chapter 3 Alkenes or Olefines Crabon-Carbon double bond C n H 2n Hybridization in Alkenes: 1.34 A 2 Nomenclature of Alkenes and Cycloalkenes
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 201/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry CHE1502/201/1/2016
 CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
Alkenescontain a C=C double bond (also occasionally called olefins). Alkenes are very common in natural and synthetic organic compounds.
 Chapter 6: Alkenes: structure and reactivity Alkenescontain a C=C double bond (also occasionally called olefins). Alkenes are very common in natural and synthetic organic compounds. 6.2 Degree of unsaturation
Chapter 6: Alkenes: structure and reactivity Alkenescontain a C=C double bond (also occasionally called olefins). Alkenes are very common in natural and synthetic organic compounds. 6.2 Degree of unsaturation
CHEM 203 Exam 1. Name Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 CHEM 203 Exam 1 Name Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following elements is a large percentage of both the earth's
CHEM 203 Exam 1 Name Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following elements is a large percentage of both the earth's
CH Organic Chemistry I (Katz) Practice Exam #3- Fall 2013
 C2710 - rganic Chemistry I (Katz) Practice Exam #3- all 2013 Name: Score: Part I - Choose the best answer and write the letter of your choice in the space provided. (32 pts) 1. f the following, which reaction
C2710 - rganic Chemistry I (Katz) Practice Exam #3- all 2013 Name: Score: Part I - Choose the best answer and write the letter of your choice in the space provided. (32 pts) 1. f the following, which reaction
Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy
 Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double (e.g.
Chapter 15: Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and UV Spectroscopy Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double (e.g.
CHEM120 - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY WORKSHEET 1
 EM120 - RGANI EMISTRY WRKSEET 1 Some of the objectives To understand and know the hybridization concept Be able to distinguish different geometries, including basic bond lengths and angles within organic
EM120 - RGANI EMISTRY WRKSEET 1 Some of the objectives To understand and know the hybridization concept Be able to distinguish different geometries, including basic bond lengths and angles within organic
use iso-, tert-, sec- prefixes in your substituent names, where necessary
 Chapter 07.2: 1 1) Name. Include E/Z stereochemistry in name, if necessary. a) 3 C b) c) d) e) f) use iso-, tert-, sec- prefixes in your substituent names, where necessary g) Do NT use iso-, tert-, sec-
Chapter 07.2: 1 1) Name. Include E/Z stereochemistry in name, if necessary. a) 3 C b) c) d) e) f) use iso-, tert-, sec- prefixes in your substituent names, where necessary g) Do NT use iso-, tert-, sec-
Chemistry 110. Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell. Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes.
 Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes Chapter 12 Alkenes are hydrocarbons which have one or more
Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes Chapter 12 Alkenes are hydrocarbons which have one or more
Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes
 Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes Chapter 12 Alkenes are hydrocarbons which have one or more
Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes Chapter 12 Alkenes are hydrocarbons which have one or more
CHEM 2312 practice final. Version - II
 EM 2312 practice final Version - II The following standardized final examination covers the entire introductory year of organic chemistry (EM 2311 and 2312 at Georgia Tech). The exam consists of 70 multiple
EM 2312 practice final Version - II The following standardized final examination covers the entire introductory year of organic chemistry (EM 2311 and 2312 at Georgia Tech). The exam consists of 70 multiple
Chemistry M11 Spring 2010 Examination #3 ANSWER KEY pp. 1
 Chemistry M11 Spring 2010 Examination #3 ASWER KEY pp. 1 or Questions 1 2, consider the hydrogenation of trans-3-methyl-2-pentene in the presence of a transition metal catalyst. 1. C Determine the major
Chemistry M11 Spring 2010 Examination #3 ASWER KEY pp. 1 or Questions 1 2, consider the hydrogenation of trans-3-methyl-2-pentene in the presence of a transition metal catalyst. 1. C Determine the major
17.3 REACTIONS INVOLVING ALLYLIC AND BENZYLIC ANIONS
 798 HAPTER 17 ALLYLI AND BENZYLI REATIVITY Because the unpaired electron is shared by two different carbons, this radical can react in the final propagation step to give two different products. Reaction
798 HAPTER 17 ALLYLI AND BENZYLI REATIVITY Because the unpaired electron is shared by two different carbons, this radical can react in the final propagation step to give two different products. Reaction
Reading: Chapter 4 Practice Problems: in text problems and 19 22, 24, 26, 27, 29, 30, 33 35, 39, 40.
 Reading: Chapter Practice Problems: in text problems and 19 22, 24, 26, 27, 29, 30, 33 35, 39, 40. Alkenes: Structure, Nomenclature, Stability, and an Introduction to Reactivity Alkenes are unsaturated
Reading: Chapter Practice Problems: in text problems and 19 22, 24, 26, 27, 29, 30, 33 35, 39, 40. Alkenes: Structure, Nomenclature, Stability, and an Introduction to Reactivity Alkenes are unsaturated
Conjugated Systems & Pericyclic Reactions
 onjugated Systems & Pericyclic Reactions 1 onjugated Dienes from heats of hydrogenation-relative stabilities of conjugated vs unconjugated dienes can be studied: Name 1-Butene 1-Pentene Structural Formula
onjugated Systems & Pericyclic Reactions 1 onjugated Dienes from heats of hydrogenation-relative stabilities of conjugated vs unconjugated dienes can be studied: Name 1-Butene 1-Pentene Structural Formula
Departmental Final Examination. Organic Chemistry I Caffein
 Departmental Final Examination rganic Chemistry I 2423 Caffein Name CEMISTRY 2423 FINAL EXAM FALL, 2005 DIRECTINS: A periodic table is attached at the end of this exam. Please answer all questions as completely
Departmental Final Examination rganic Chemistry I 2423 Caffein Name CEMISTRY 2423 FINAL EXAM FALL, 2005 DIRECTINS: A periodic table is attached at the end of this exam. Please answer all questions as completely
Also called an olefin but alkene is better General formula C n H 2n (if one alkene present) Can act as weak nucleophiles
 Alkenes - Structure, Stability, Nomenclature Also called an olefin but alkene is better General formula C n H 2n (if one alkene present) unsaturated - contain fewer than maximum H's possible per C Can
Alkenes - Structure, Stability, Nomenclature Also called an olefin but alkene is better General formula C n H 2n (if one alkene present) unsaturated - contain fewer than maximum H's possible per C Can
A) I B) II C) III D) IV E) V
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) Complete the following reaction and provide a detailed, step-by-step mechanism for the process.
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. 1) Complete the following reaction and provide a detailed, step-by-step mechanism for the process.
OChem1 Old Exams. Chemistry 3719 Practice Exams
 OChem1 Old Exams Chemistry 3719 Practice Exams Fall 2017 Chemistry 3719 Practice Exam A1 This exam is worth 100 points out of a total of 600 points for Chemistry 3719/3719L. You have 50 minutes to complete
OChem1 Old Exams Chemistry 3719 Practice Exams Fall 2017 Chemistry 3719 Practice Exam A1 This exam is worth 100 points out of a total of 600 points for Chemistry 3719/3719L. You have 50 minutes to complete
Lab Workshop 1: Nomenclature of alkane and cycloalkanes
 Lab Workshop 1: Nomenclature of alkane and cycloalkanes Each student work group choose a Leader (reads activity out loud, poses questions to group), Facilitator (makes sure everyone is participating equally,
Lab Workshop 1: Nomenclature of alkane and cycloalkanes Each student work group choose a Leader (reads activity out loud, poses questions to group), Facilitator (makes sure everyone is participating equally,
CHEM 2311 HW1. COMPLETELY FILL THE BOXES IN DARK PENCIL, i.e.:, NOT or or STRUCTURE
 EM 2311 W1 Provide answers to the following multiple choice questions on the Scantron form provided in lecture. Make sure that you put your name and bubble in your GTID # on the answer form. MPLETELY FILL
EM 2311 W1 Provide answers to the following multiple choice questions on the Scantron form provided in lecture. Make sure that you put your name and bubble in your GTID # on the answer form. MPLETELY FILL
Chapter 5. Nucleophilic aliphatic substitution mechanism. by G.DEEPA
 Chapter 5 Nucleophilic aliphatic substitution mechanism by G.DEEPA 1 Introduction The polarity of a carbon halogen bond leads to the carbon having a partial positive charge In alkyl halides this polarity
Chapter 5 Nucleophilic aliphatic substitution mechanism by G.DEEPA 1 Introduction The polarity of a carbon halogen bond leads to the carbon having a partial positive charge In alkyl halides this polarity
Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes & Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes & Aromatic Compounds Chapter Outline 13.1 Alkenes and Alkynes 13.2 Nomenclature of Alkenes and Alkynes 13.3 Cis Trans Isomers 13.4 Alkenes in Food and Medicine 13.6 Reactions
Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes & Aromatic Compounds Chapter Outline 13.1 Alkenes and Alkynes 13.2 Nomenclature of Alkenes and Alkynes 13.3 Cis Trans Isomers 13.4 Alkenes in Food and Medicine 13.6 Reactions
Final Exam Professor R. Hoenigman
 I pledge to uphold the CU onor Code: CEM 3311-200 Fall 2006 Final Exam Professor. oenigman Average Score = 145 igh Score = 235 Low Score = 27 Signature Name (printed) Last four digits of your student ID
I pledge to uphold the CU onor Code: CEM 3311-200 Fall 2006 Final Exam Professor. oenigman Average Score = 145 igh Score = 235 Low Score = 27 Signature Name (printed) Last four digits of your student ID
CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Text Sections (N0 1.9, 9-11) Homework: Chapter 1:
 CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Atomic Structure - Valence Electrons Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule - Ionic bond - Covalent bond How to write Lewis
CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Atomic Structure - Valence Electrons Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule - Ionic bond - Covalent bond How to write Lewis
Chemistry 261 Exam 2 Practice Fall 2017
 Chemistry 261 Exam 2 Practice Fall 2017 The following practice examination contains 30 questions valued at 3 point/question unless otherwise noted. Wednesday s exam will also contain 30 questions, with
Chemistry 261 Exam 2 Practice Fall 2017 The following practice examination contains 30 questions valued at 3 point/question unless otherwise noted. Wednesday s exam will also contain 30 questions, with
Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry
 Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Structure and Bonding 2 Structure and Bonding Rotation around the C=C bond is restricted 90 rotation The p orbitals are orthogonal
Alkenes (Olefins) Chapters 7 & 8 Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition John McMurry 1 Structure and Bonding 2 Structure and Bonding Rotation around the C=C bond is restricted 90 rotation The p orbitals are orthogonal
Replace one H with a Br for every mole of Br 2
 Substitution A substitution reaction occurs when a hydrogen atom is removed from a hydrocarbon and replaced by a halide substituent. When a bromine molecule absorbs energy, the covalent bond is broken
Substitution A substitution reaction occurs when a hydrogen atom is removed from a hydrocarbon and replaced by a halide substituent. When a bromine molecule absorbs energy, the covalent bond is broken
Part C- section 1 p-bonds as nucleophiles
 Part C- section 1 p-bonds as nucleophiles Chemistry of Alkenes (Ch 8, 9, 10) - the double bond prevents free rotation - isomerism cis and trans - nomenclature E and Z (3 or 4 different substituents around
Part C- section 1 p-bonds as nucleophiles Chemistry of Alkenes (Ch 8, 9, 10) - the double bond prevents free rotation - isomerism cis and trans - nomenclature E and Z (3 or 4 different substituents around
and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
 Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy 2010, Prentice all Conjugated Systems Conjugated double bonds are separated
Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 15 Conjugated Systems, Orbital Symmetry, and Ultraviolet Spectroscopy 2010, Prentice all Conjugated Systems Conjugated double bonds are separated
eg ethylene (IUPAC: ethene), C 2
 Alkenes: Structure & Properties Alkane (acyclic): n 2n+2 > saturated. Alkene (acyclic): n 2n > unsaturated. eg ethylene (IUPA: ethene), 2 4 : 2 = 2 The carbon-carbon double bond is the distinguishing feature
Alkenes: Structure & Properties Alkane (acyclic): n 2n+2 > saturated. Alkene (acyclic): n 2n > unsaturated. eg ethylene (IUPA: ethene), 2 4 : 2 = 2 The carbon-carbon double bond is the distinguishing feature
Chapter 7: Alkenes and Alkynes
 Chapter 7: Alkenes and Alkynes ydrocarbons Containing Double and Triple Bonds Unsaturated Compounds (Less than Maximum Atoms) Alkenes also Referred to as Olefins Properties Similar to those of Corresponding
Chapter 7: Alkenes and Alkynes ydrocarbons Containing Double and Triple Bonds Unsaturated Compounds (Less than Maximum Atoms) Alkenes also Referred to as Olefins Properties Similar to those of Corresponding
3) The delocalized π system in benzene is formed by a cyclic overlap of 6 orbitals. A) s B) p C) sp D) sp2 E) sp3
 Chapter 8 Questions 1) Which of the following statements is incorrect about benzene? A) All of the carbon atoms are sp hybridized. B) It has delocalized electrons. C) The carbon-carbon bond lengths are
Chapter 8 Questions 1) Which of the following statements is incorrect about benzene? A) All of the carbon atoms are sp hybridized. B) It has delocalized electrons. C) The carbon-carbon bond lengths are
IUPAC Nomenclature Chem12A, Organic Chemistry I
 IUPAC Nomenclature ChemA, rganic Chemistry I IUPAC PEFIXES Prefix Substituent Group Number of Carbons meth- methyl eth- ethyl prop- propyl but- butyl pent- pentyl hex- hexyl hept- heptyl 7 oct- octyl 8
IUPAC Nomenclature ChemA, rganic Chemistry I IUPAC PEFIXES Prefix Substituent Group Number of Carbons meth- methyl eth- ethyl prop- propyl but- butyl pent- pentyl hex- hexyl hept- heptyl 7 oct- octyl 8
c. Cl H Page 1 of 7 major P (E > Z and more substituted over less substituted alkene) LG must be axial are the same Cl -
 CEM 109A 1. Predict the products of the following reactions (a-c E2, d-f E1 KEY focuses only on elimination products, in most cases there will also be substitution products.) a. - LG must be axial - are
CEM 109A 1. Predict the products of the following reactions (a-c E2, d-f E1 KEY focuses only on elimination products, in most cases there will also be substitution products.) a. - LG must be axial - are
Homework problems Chapters 6 and Give the curved-arrow formalism for the following reaction: CH 3 OH + H 2 C CH +
 omework problems hapters 6 and 7 1. Give the curved-arrow formalism for the following reaction: : 3 - : 2 : 3 2-3 3 2. In each of the following sets, arrange the compounds in order of decreasing pka and
omework problems hapters 6 and 7 1. Give the curved-arrow formalism for the following reaction: : 3 - : 2 : 3 2-3 3 2. In each of the following sets, arrange the compounds in order of decreasing pka and
a) Use Chem3D to compare the bond lengths of the C1-C2 double bond with the C3-C4 single bond. How do you account for this difference?
 Copyright 2002 Prentice-all, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 7 - Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes 1. In Chem3D, draw the structure of 1-pentene. a) Use Chem3D to compare the bond lengths of the C1-C2
Copyright 2002 Prentice-all, Inc. All rights reserved. Chapter 7 - Structure and Synthesis of Alkenes 1. In Chem3D, draw the structure of 1-pentene. a) Use Chem3D to compare the bond lengths of the C1-C2
Part Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital of an atom overlaps with p orbital of another atoms]
![Part Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital of an atom overlaps with p orbital of another atoms] Part Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital of an atom overlaps with p orbital of another atoms]](/thumbs/89/100347388.jpg) Program Name B.Sc. (Chemistry) B.Sc. - Part I Paper Code CH- 02 (Organic chemistry) Section A (Very Short Answer Questions 2 Each Question Carries 2 Marks Part -1 1. Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital
Program Name B.Sc. (Chemistry) B.Sc. - Part I Paper Code CH- 02 (Organic chemistry) Section A (Very Short Answer Questions 2 Each Question Carries 2 Marks Part -1 1. Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems
 Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
Chapter 13 Conjugated Unsaturated Systems Introduction Conjugated unsaturated systems have a p orbital on a carbon adjacent to a double bond The p orbital can come from another double or triple bond The
Chapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes I: Properties and Synthesis Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides"
 Chapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes I: Properties and Synthesis Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides The (E)-(Z) System for Designating Alkene Diastereomers The Cahn-Ingold-Prelog convention is used to assign
Chapter 7 Alkenes and Alkynes I: Properties and Synthesis Elimination Reactions of Alkyl Halides The (E)-(Z) System for Designating Alkene Diastereomers The Cahn-Ingold-Prelog convention is used to assign
Organic Chemistry, Second Edition. Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i. Chapter 10 Alkenes
 Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 10 Alkenes Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
Organic Chemistry, Second Edition Janice Gorzynski Smith University of Hawai i Chapter 10 Alkenes Prepared by Rabi Ann Musah State University of New York at Albany Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,
10:30 AM 1:00 PM December 13, 2016 in MATH 100
 CEM 3311 ARRIGT Exam 4 10:30 AM 1:00 PM December 13, 2016 in MAT 100 Instructions. o notes, books, laptops, phones, calculators, models, or stencils are allowed. Periodic Table, Electronegativity Chart,
CEM 3311 ARRIGT Exam 4 10:30 AM 1:00 PM December 13, 2016 in MAT 100 Instructions. o notes, books, laptops, phones, calculators, models, or stencils are allowed. Periodic Table, Electronegativity Chart,
CHEM 347 Organic Chemistry II Spring Instructor: Paul Bracher. Quiz # 2
 CHEM 347 Organic Chemistry II Spring 2015 Quiz # 2 Solutions Key Page 1 of 12 CHEM 347 Organic Chemistry II Spring 2015 Instructor: Paul Bracher Quiz # 2 Due: Monday, February 9 th, 2015 2:00 p.m. (in
CHEM 347 Organic Chemistry II Spring 2015 Quiz # 2 Solutions Key Page 1 of 12 CHEM 347 Organic Chemistry II Spring 2015 Instructor: Paul Bracher Quiz # 2 Due: Monday, February 9 th, 2015 2:00 p.m. (in
1. Use appropriate curved arrows to indicate the complete mechanism of each of these reactions. KH (1 equiv.) + KCl THF. + HBr.
 1. Use appropriate curved arrows to indicate the complete mechanism of each of these reactions. K (1 equiv.) TF K 3 2 2 3 enantiomer While writing the mechanism, justify both the regiochemistry the relative
1. Use appropriate curved arrows to indicate the complete mechanism of each of these reactions. K (1 equiv.) TF K 3 2 2 3 enantiomer While writing the mechanism, justify both the regiochemistry the relative
CPS (Chapterwise Practice Sheet)
 CPS (Chapterwise Practice Sheet) C-CPS-1 General Organic Chemistry IUPAC Nomenclature (NCERT-CBSE) for NEET/AIIMS/JIPMER/JEE MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQs) both in English and Tamil 1. According to IUPAC,
CPS (Chapterwise Practice Sheet) C-CPS-1 General Organic Chemistry IUPAC Nomenclature (NCERT-CBSE) for NEET/AIIMS/JIPMER/JEE MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (MCQs) both in English and Tamil 1. According to IUPAC,
Organic Chemistry. REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling
 Organic Chemistry REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS This is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms Substitution
Organic Chemistry REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS This is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms Substitution
Alkenes CnH2n Ethene Propene But-2-ene But-1-ene exposed high electron density one sigma (σ) bond and one pi (π) bond.
 Alkenes Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons General formula is n2n Alkenes contain a carboncarbon double bond somewhere in their structure Ethene Propene Numbers need to be added to the name when positional
Alkenes Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons General formula is n2n Alkenes contain a carboncarbon double bond somewhere in their structure Ethene Propene Numbers need to be added to the name when positional
