Exploring Transpiration Regularity of Single Loquat Tree under Indoor. Environmental Conditions
|
|
|
- Clinton Hunter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Forum on Energy, Environment and Sustainable Development (IFEESD 2016) Exploring Transpiration Regularity of Single Loquat Tree under Indoor Environmental Conditions LIU Zhuo1, 2, LI Ruiping1, DONG Xiaohua1, 2, * 1 College of Hydraulics & Environment Engineering, China Three Gorges University, Yi Chang, China, Hubei Provincial Collaborative Innovation Center for Water Resources Security,Wuhan ,China Keywords:Transpiration rate; Response Surface Methodology (RSM); meteorological factor; phytotron; stem heat balance method Abstract: Transpiration has an important impact not only on the growth of plants, but also on the hydrological cycle.determining quantificationally the plant transpiration rate helps understanding the hydrological cycle more accurately. The transpiration rate of a single loquat tree at different relative humidity, temperature and illumination intensity was measured in a phytotron chamber with a sap flow system (Dynamax, USA).The effects of the three factors on the transpiration rate of single loquat tree was analyzed by Response Surface Methodology (RSM). The results indicated that the effect of relative humidity, temperature and illumination intensity at given conditions followed the importance order of temperature > illumination intensity > relative humidity. The transpiration rate of single loquat tree is increasing with the accretion of relative humidity and reduction of temperature, but decreasing at the initial stage and subsequently kept constant with the illumination intensity increasing. Through response surface analysis, a model of three factors vs. transpiration rate was acquired and can provide a reference for the calculation of evapotranspiration. Introduction As an important part in hydrology research, hydrologic cycle is closely related to the plant evapotranspiration. The total global precipitation is about 113,500 km3 y-1 (cubic kilometers per year), among which the infiltration amount is about 80,000 km3 y-1, and the rest 33,500 km3 y-1 becomes surface runoff. In the infiltration of soil water, every year about 7,500 km3 groundwater of the infiltration is supplied to rivers and the rest about 72,500 km3 becomes "green" water back to the atmosphere, among which the productive and non-productive transpiration stream has been roughly estimated as 30,000-35,000 and 35,000-40,000 km3, respectively. From the above, it can be seen that the productive transpiration almost occupies a half of the total land surface evaporation. Therefore, it is of great significance to strengthen the research on productive transpiration, namely the role of plants in the water cycle research, for an accurate and comprehensive understanding the whole process of hydrologic cycle. However, it s difficult to measure the plant transpiration for its complicated physiological process influenced not only by the adjustment and control of its morphology and physiological conditions, but also by various environmental conditions. The existing methods for the testing plant water consumption, such as empirical formula method, water balance method, eddy correlation method, and remote sensing method, can only determine the total amount of evapotranspiration. In The authors - Published by Atlantis Press 794
2 the most cases, the evapotranspiration is required to be divided into transpiration and evaporation. Scholars have tried injury flow method, leaf chamber method and covering method for direct determination of transpiration, but the shortages of these methods are also very obvious, such as interfering the plant growing, consuming time and having low practical value. So far, in the study of water consumption at different dimension, the research field on the water consumption of single plant has been developed with most technical means, such as heat pulse and heat balance [1]. In the 1932, Huber, the famous physiologist, on the basis of the predecessors' work, adopted a new method to measure the water consumption of per plant of plants- heat pulse velocity record method (HPVR). This method had aroused attention of many experts in the botanical field since its first use. In the 1980s, the method of stem heat balance (SHB) has been developed based on HPVR. Compared with HPVR, the SHB does not need to insert the temperature probe into the stem without calibration,, thus the measurement is more convenient and accurate with the lowest trees damage, and the time for fixed-point measurement can be long; moreover, the invention of the parcel probe can make a more accurate determination for the plants stem flow [2]. In the process of research on the stem sap flux rate of plant, many researchers have done many works on the following aspects: the theoretical basis of calculating the plant sap flux with SHB, rule of stem sap flux change and the error analysis [3]. The results showed that the plant stem sap flux could be monitored effectively by SHB, and could be transformed into transpiration rate. However, most of the previous research work was carried out in the outdoor environment without controlling meteorological factors, and that in the greenhouse is relatively less, let alone the relative research with the phytotron under strict control of meteorological conditions. In this paper, plant transpiration rate was researched with a single loquat tree as the pointer plant under different temperature, relative humidity, and illumination, with single factor analysis and the response surface analysis method to analyze the test data. The effects of different environmental conditions on the transpiration rate of single loquat tree were expected to be clarified, providing a reference for the research of plant evapotranspiration in the hydrologic cycle. Materials and Methods The loquat transpiration rate at established conditions was obtained by a Dynamix stem flow measurement system in a PQS type phytotron (5 x 3 x 2.5 m) with a TDR300 for measuring soil moisture and a Vernier caliper for surveying the diameter of objects plant. The test object is a loquat tree seedlings of 3 years with a trunk diameter of 11 mm and a height of 1.2 m. To avoiding the damage to the seedling roots, a wide range of dig transplanting was employed. The seedling was moved into a deep flower pot with a diameter of 1.5 m and depth of 0.5 m and kept for nine days to restore the original state before test. According to GAO Jun [4] and QIU Guangyang [5], the plant transpiration water consumption in short term, is mainly relative to the intensity of solar radiation (Lx), relative humidity of atmosphere (%) and atmospheric temperature ( C). In the phytotron, the plant transpiration rate under different conditions was observed when the above three variables were mainly controlled with other environmental factors fixed. The single factor test method and orthogonal experiment method were adopted in this work. All of the experiments were divided into nine groups with three sets of test for each factor, of which the test time lasted 3.5 hours in each group. Illumination (16000, and Lx), temperature (5, 20 and 35 C) and relative humidity of atmosphere (60, 75 and 90 %) were set as the main factor in the orthogonal experiment. At the night before test, the potted loquat tree was watered to ensure the adequate water supply in the soil (the average relative humidity is 43%) and moved into the 795
3 phytotron, then the packaged stem sap flow gauge in the dark and data collection system were opened to calculate the K sh (0.7164). The experiment is to explore the effect of temperature, light intensity and the relative humidity on the loquat transpiration rate when the water supply in the soil is sufficient, so the CO 2 concentration was set as 400 ppm, similar to that in the atmosphere. Naturally, the air is slowly flowing, hence, the fan in the phytotron was turned on to maintain a wind speed of 0.2 m/s. In the process of test, the soil moisture content would gradually decrease with the continuous plant transpiration, therefore, the soil should be watered to ensure adequate water supplying. In the test, the straight part without side branches and scars on the stem of potted plant was chosen and pretreated for the installation of SGA10 probe. Set up the parameters with collecting data interval of 30 min. Results Selection of factor and levels of response surface analysis According to the principles of the center combination design proposed by Box-Behnken, the results of single factor test were summarized to elect the three factors of the light, temperature, and relative humidity for the further orthogonal experiments. The three factors and three levels would be employed for the response surface analysis based on single factor experiment. Factors and levels are shown in Table 1. Table 1 Factors and levels of response surface methodology Factor Level X 1 : Illumination / Lx X 2 : relative humidity of atmosphere X 3 : temperature / C The design and results of the response surface experiment The central composite model was employed to carry out the response surface analysis experiments of 17 test points (5 center points) with three factors and three levels. All of the 17 test points can be divided into two types. One group was the points for analysis, the value of independent variables at the various factors that constitute the three-dimensional vertices, which is a sum of 12 factorial points. The other was zero points, as the center point of the region, which was repeated test 5 times to estimate the test error. The transpiration rate of loquat tree is as the response value (index value). Response surface analysis and test results are shown in Table 2. Table 2 Design and results of Response surface Box Behnken experimental Number actual value of factor coded value of factor Y: plant transpiration rate (g/h) X 1 X 2 X 3 x 1 x 2 x 3 actual value predicted value
4 After being coded, the testing data were fitted with the Expert Design 7.0 software, as shown in Table 3. The resulting correlation equation of monomial, quadratic term and their interaction items of factors were achieved. Basing on this, the response surface analysis was made. The quadratic equation model relationship between the transpiration rate of loquat tree and variable factors was acquired by multiple regression fitting analysis Y = X X X XX XX X X X 1.111X X The reliability of model and correlation of transpiration and all factors in the model were determined through variance analysis of monomial, quadratic term and their interaction items of model. The analysis results are shown in Table 3. Table 3 Results of variance analysis sources of mean of sum of squares number of degree of freedom variation square F value P value Model < X < X X < X 1 X X 1 X X 2 X X < X X total residual lack of fit pure error If the above regression equation was used to describe the relationship between the factors and the response value, the influence of independent variables on the dependent variable would be significant, for the significance level of model was less than 0.05, meanwhile, the quadratic regression variance model was very significant. From the results of variance analysis of regression equation, it can also be inferred that the equation could fit testing data well with a slight error, therefore, the regression equation could be employed to analyze and predict the testing results in 797
5 place of real testing points. The effect turn of the factors for the transpiration rate of loquat trees is X3 > X1 >X2 (seen as Table 3). Response surface analysis The graphics of the Response Surface Methodology (RSM) method is a three-dimensional space in the two-dimensional plane contour map, which is constituted by a specific response surface (Y) and the corresponding factors X1, X2, X3, each response surface analyzes the two factors, and other two factors fixed at zero level. The effect of every factor on the response values can be directly reflected from the experimental results, and the interaction of these factors can be found in the process of loquat trees transpiration. The regression response surface is shown in Figure 1. The graph in the RSM is a contour map constituted by a three-dimensional space on a two-dimensional plane. The three-dimensional space that was formed with a specific response surface (Y) and the corresponding factors X1, X2, X3. Two factors were analyzed in each response surface with the other two factors fixed at zero level. The effect of every factor on the response values could be clearly reflected from the RSM graph, and the interaction of these factors could also be found in the process of loquat trees transpiration. The graphs of regression response surface are shown in Figure 1. A1 A2 B1 B2 798
6 C1 C2 Figure.1 Contour map and RSM graph of interactions among illumination intensity, temperature, and relative humidity on transpiration rate at (A) temperature fixed at 20 C, (B) relative humidity stable at 75 % and (C) illumination intensity immobilized at Lx, respectively. The Figure 1 directly reflects the influence of the various factors on the response value. The factor X3, temperature has the most significant effect on plant transpiration, which shows a relatively steep curve. While the factor X2, relative humidity shows a relatively smooth one, and when it changes, the response value is relatively small. Discussion The relationship between plant transpiration rate and relative humidity has not yet been decided whether by model simulation or by experimental study. In our work, the transpiration rate of loquat trees was increased with the addition of relative humidity. The response of plant stomata to relative humidity is the reaction to transpiration rate in nature. Therefore, the increase of relative humidity would not directly induce to the decrease of leaf stomatal conductance, while the stomata conductance directly determines the intensity of transpiration rate. Plants could experience the relative humidity with two possible means, through directly answering the relative humidity (equivalent to a hygrometer) and the transpiration rate. The experiments made by Mott and Parkhurst showed that the plant answered the transpiration rate rather than the relative humidity itself [6]. For loquat trees, the high humidity would not directly lead to the stomatal conductance decreased and stomata closed. It also concluded by CHEN Qin [7] that the stomatal conductance would decrease with the reduction of relative humidity through model simulation. It was found that the transpiration rate of loquat trees decreased with the increase of temperature, which could be attributed to a self-protection reaction of loquat tree to the temperature changes. Usually, under the stress of low temperature, the water content of plants would decrease to make the solid matter concentrated to increase the concentration of cell sap, which could reduce the possibility of freezing, enhance the ability of cold resistance and anti-freezing, and thus improve the cold resistance [8]. Under the conditions of high temperature stress, the physiological activities of plants would be affected, including the cell membrane damage, inhibition of photosynthesis, and cell aging and death. QU Mingnan [9] has observed that high temperature stress reduced the leaf transpiration and stomatal conductance. When the high temperature put stress on the plant, the stomatal aperture began to decrease, accompany with the transpiration dropping, reducing the plant s transport of mineral ions and the demand for water [10]. 799
7 According to our testing results and existing theoretical researches and test reports, it can be concluded that transpiration rate of loquat trees would increase with the decrease of temperature at given conditions, which should be attributed to loquat trees increase their transpiration rate because of the pressure of low temperature. One side, increasing transpiration rate could decrease the water content and increase the concentration of solid matters and cell sap; on the other side, it could promote photosynthesis for more sugar to improve the content of soluble sugar in cell, which was in favor of good ability of cold resistance and anti-freezing. If the temperature was high, the stomatal aperture of loquat trees would decrease, resulting in evapotranspiration decreasing and transpiration rate falling. In our work, the relationship between plant transpiration rate and illumination was studied under manual control of illumination intensity in a phytotron, which was quite different from that under natural state. It was found that the transpiration rate of loquat tree decreased with the illumination intensity at first and then remained stable, which could be attributed to self-adaption of loquat tree to illumination. When illumination saturation state is achieved, the continuous increase of illumination intensity would induce the photoinhibition phenomenon, which means that when the illumination intensity received by the photosynthetic organization exceed the available amounts for photosynthesis, the function of photosynthesis would be weakened, and the continuous increase of illumination intensity would induce the damage of photosynthetic organization. In most cases, when the light intensity decreases, the plant photosynthetic function could be restored gradually. The stomata conductance of plant would be reduced by the strong illumination. In the study of photosynthetic and transpiration rate for different parts of an apple tree, ZHANG Xianchuan found that stomatal conductance in sunny days presented a concave type curve, and there was a clear "midday rest" phenomenon, which of the ambient leaves was prominent. Daily variation of stomata for different parts was similar. Within one day, the stomatal conductance for the center leaves was big and that for the ambient leaves was small. It might because of the strong illumination of the ambient leaves, which would induce photoinhibition [11]. The stomatal conductance of leaves with photoinhibition induced by supersaturated illumination intensity would grow smaller, dropping down the transpiration rate. The research results showed that the transpiration rate of loquat trees decreased with the addition of illumination intensity. Under the test condition, the light saturation point of loquat trees was Lx. When the illumination intensity grew over Lx, the photoinhibition arose, and when the illumination intensity arrived at some point, the transpiration rate almost kept stable, which might because that the change of stomatal conductance induced by illumination intensity was not obvious. The illumination intensity of Lx in this experiment was corresponding to a moderate value. The illumination intensity of summer midday could reach Lx. Under the illumination intensity of Lx, the loquat trees could reach to the light saturation point, indicating high light efficiency, that s to say, the photosynthesis under lower illumination intensity was quite efficient. Moreover, a layer of tomentum was observed on the loquat leaf surface in the experiment and leaf margin slightly curled downwards, which might be the result of the long-term evolution of the environment adaptation, reducing light energy absorption to weaken the damage caused by excessive light. The transpiration rate of plants was influenced by meteorological factors and biological factors. Under natural conditions, the plant transpiration rate is a comprehensive problem influenced by many ecological environment factors, thus, a lot of experiment research were needed to carry out to understand the relationship between influence factors and transpiration rate. An open environment 800
8 is inadequate for strict control of the each factors, resulting in the experiment results easily affected by other factors, so it is difficult to clarify the impact of individual factor on plant transpiration rate. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out experiments in a phytotron. Due to the limit of time and experimental conditions, three main factors were chosen from many factors influencing the transpiration rate on the individual loquat, so it was difficult to estimate test error. In the next step, the author will increase the number of test plants, consider more environmental variables, and add the soil water stress and other factors to enhance the accuracy, reliability, and general applicability of the test. Conclusions Under the strict control of meteorological conditions in a phytotron, a response surface model was established to find that the most important factor affecting the transpiration rate of a loquat tree was temperature, followed by illumination intensity and relative humidity of atmosphere in turn. The transpiration rate was increased with addition of relative humidity, decreased with the accretion of temperature, decreased at first and then kept stable with the increase of illumination intensity. The P value of the established model is far less than 0.01, indicating that the model is actual available. The model can provide a reference for the region that lacks of parameter to predict the evapotranspiration of per plant only with illumination intensity, temperature, and relative humidity, and for the study of evapotranspiration in the hydrological cycle. References [1] Aiwang Duan: Farmland Irrigation Research Institute Vol. 14 (1995), p (In Chinese) [2] Hongxi Jin, Zuojun Liu, Jihe Wang, Xianying Xu, Jinnian Tang, Dunming Zhang: Protection Forest Science and Technology Issu 06 (2004), p (In Chinese) [3] V.L. Grime, F.L. Sinclair: Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, Vol. 94 (1999), p [4] Jun Gao, Bin Wu, Ping Meng: Jorunal of Beijing Forestry University Vlo.32 (2010), p (In Chinese) [5] Guangyang Yue, Tonghui Zhang, Halin Zhao, Li Niu, XinpingLiu, Gang Huang : Acta Ecologica Sinica, Vol. 26 (2006), p (In Chinese) [6] K.A. Mott, D.F. Parkhurst :Plant, Cell & Environment, Vol. 14 (1991), p [7] Qin Chen: Stomatal responses to soil and air humidity and models of stomatal conductance (PhD dissertation, Research Center of Soil & Water Conservation and Ecology and Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Ministry of Education 2013). (In Chinese) [8] Ruizhi Pan: Plant Physiology 4th ed. (China Higher Education Press, Beijing 2001). (In Chinese) [9] Mingnan Qu: Effects of elevated CO 2 and short-term heat stress on physiological and biochemical variables in maize seedlings. (PhD dissertation, Shenyang Agricultural University 2013). (In Chinese) [10] Xiaoju Tu, Qiming Wang, Liqun Rao: Hunan Agricultural Sciences Vol. 13 (2013), p (In Chinese) [11] Xianchuan Zhang, Zhaoquan Gao, Xianyu Shu, Qinping Wei: Acta Horticulturae Sinica, Vol. 32 (2005), p (In Chinese) 801
Temperature and light as ecological factors for plants
 PLB/EVE 117 Plant Ecology Fall 2005 1 Temperature and light as ecological factors for plants I. Temperature as an environmental factor A. The influence of temperature as an environmental factor is pervasive
PLB/EVE 117 Plant Ecology Fall 2005 1 Temperature and light as ecological factors for plants I. Temperature as an environmental factor A. The influence of temperature as an environmental factor is pervasive
The Study of Dynamic Monitor of Rice Drought in Jiangxi Province with Remote Sensing
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Environmental Sciences 10 (2011 ) 1847 1853 2011 3rd International Conference on Environmental Science and Information Conference Application Title Technology
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Procedia Environmental Sciences 10 (2011 ) 1847 1853 2011 3rd International Conference on Environmental Science and Information Conference Application Title Technology
Studies on the Growth-development Law and Suitable Period for Harvesting of Pinellia ternata (Thunb)Breit
 Modern Applied Science December, 2009 Studies on the Growth-development Law and Suitable Period for Harvesting of Pinellia ternata (Thunb)Breit Shuhong Wei (Corresponding author) Life Science College,
Modern Applied Science December, 2009 Studies on the Growth-development Law and Suitable Period for Harvesting of Pinellia ternata (Thunb)Breit Shuhong Wei (Corresponding author) Life Science College,
Sunlight and Temperature
 Sunlight and Temperature Name Purpose: Study microclimate differences due to sunlight exposure, location, and surface; practice environmental measurements; study natural energy flows; compare measurements;
Sunlight and Temperature Name Purpose: Study microclimate differences due to sunlight exposure, location, and surface; practice environmental measurements; study natural energy flows; compare measurements;
Effects of Exogenous Melatonin on Photosynthetic Characteristics. of Eggplant Seedlings under Low Temperature and Weak Light Stress
 International Conference on Manufacturing Science and Engineering (ICMSE 2015) Effects of Exogenous Melatonin on Photosynthetic Characteristics of Eggplant Seedlings under Low Temperature and Weak Light
International Conference on Manufacturing Science and Engineering (ICMSE 2015) Effects of Exogenous Melatonin on Photosynthetic Characteristics of Eggplant Seedlings under Low Temperature and Weak Light
Plant Ecophysiology in a Restoration Context
 Objectives: How can the foundations of and theory in plant ecophysiological restoration ecology ecological restoration? Light and energy relations Photosynthesis Microclimate Belowground resource availability
Objectives: How can the foundations of and theory in plant ecophysiological restoration ecology ecological restoration? Light and energy relations Photosynthesis Microclimate Belowground resource availability
Plant Growth and Development Part I I
 Plant Growth and Development Part I I 1 Simply defined as: making with light Chlorophyll is needed (in the cells) to trap light energy to make sugars and starches Optimum temperature: 65 o F to 85 o F
Plant Growth and Development Part I I 1 Simply defined as: making with light Chlorophyll is needed (in the cells) to trap light energy to make sugars and starches Optimum temperature: 65 o F to 85 o F
Plant Water Stress Frequency and Periodicity in Western North Dakota
 Plant Water Stress Frequency and Periodicity in Western North Dakota Llewellyn L. Manske PhD, Sheri Schneider, John A. Urban, and Jeffery J. Kubik Report DREC 10-1077 Range Research Program Staff North
Plant Water Stress Frequency and Periodicity in Western North Dakota Llewellyn L. Manske PhD, Sheri Schneider, John A. Urban, and Jeffery J. Kubik Report DREC 10-1077 Range Research Program Staff North
Oxygen and Hydrogen in Plants
 Oxygen and Hydrogen in Plants Outline: Environmental factors Fractionation associated with uptake of water Metabolic Fractionation C3, CAM and C4 plants Environmental factors Regional Precipitation d 18
Oxygen and Hydrogen in Plants Outline: Environmental factors Fractionation associated with uptake of water Metabolic Fractionation C3, CAM and C4 plants Environmental factors Regional Precipitation d 18
Effects of Potassium Fertilizer on the Growth and Physiology of Phoebe bournei Seedlings
 International Journal of Current Research in Biosciences and Plant Biology Volume 4 Number 11 (November-2017) ISSN: 2349-8080 (Online) Journal homepage: www.ijcrbp.com Original Research Article doi: https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcrbp.2017.411.004
International Journal of Current Research in Biosciences and Plant Biology Volume 4 Number 11 (November-2017) ISSN: 2349-8080 (Online) Journal homepage: www.ijcrbp.com Original Research Article doi: https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcrbp.2017.411.004
Relationship between Leaf Water Potential and Photosynthesis in Rice Plants
 Relationship between Leaf Water Potential and Photosynthesis in Rice Plants By KUNI ISHIHARA and HIDEO SAITO Faculty of Agriculture, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology (Saiwaicho,Fuchu, Tokyo,
Relationship between Leaf Water Potential and Photosynthesis in Rice Plants By KUNI ISHIHARA and HIDEO SAITO Faculty of Agriculture, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology (Saiwaicho,Fuchu, Tokyo,
Key words: insulator, the equivalent diameter, natural icing, icing thickness, icing degree, characterization method
 Study on characterization method of icing degree of Porcelain and Glass insulators based on icing thickness of equivalent diameter Zhang Zhijin 1, Zheng Qiang 1, Jiang Xingliang 1, Zhu Chengzhi 2 1. State
Study on characterization method of icing degree of Porcelain and Glass insulators based on icing thickness of equivalent diameter Zhang Zhijin 1, Zheng Qiang 1, Jiang Xingliang 1, Zhu Chengzhi 2 1. State
Name AP Biology - Lab 06
 LAB 06 Transpiration Objectives: To understand how water moves from roots to leaves in terms of the physical/chemical properties of water and the forces provided by differences in water potential. To test
LAB 06 Transpiration Objectives: To understand how water moves from roots to leaves in terms of the physical/chemical properties of water and the forces provided by differences in water potential. To test
Global Water Cycle. Surface (ocean and land): source of water vapor to the atmosphere. Net Water Vapour Flux Transport 40.
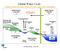 Global Water Cycle Surface (ocean and land): source of water vapor to the atmosphere Water Vapour over Land 3 Net Water Vapour Flux Transport 40 Water Vapour over Sea 10 Glaciers and Snow 24,064 Permafrost
Global Water Cycle Surface (ocean and land): source of water vapor to the atmosphere Water Vapour over Land 3 Net Water Vapour Flux Transport 40 Water Vapour over Sea 10 Glaciers and Snow 24,064 Permafrost
Introduction to Plant Transport
 Introduction to Plant Transport The algal ancestors of plants were completely immersed in water and dissolved minerals. The adaptation to land involved the differentiation of the plant body into roots,
Introduction to Plant Transport The algal ancestors of plants were completely immersed in water and dissolved minerals. The adaptation to land involved the differentiation of the plant body into roots,
Which process is represented by letter F? A) capillarity B) infiltration C) condensation D) vaporization
 1. Water's covalent bond is due to A) water's ability to stick to stick to other materials B) a slight negative charge of O and positive charge of H C) an uneven sharing of electrons D) both B and C 2.
1. Water's covalent bond is due to A) water's ability to stick to stick to other materials B) a slight negative charge of O and positive charge of H C) an uneven sharing of electrons D) both B and C 2.
Understanding how vines deal with heat and water deficit
 Understanding how vines deal with heat and water deficit Everard Edwards CSIRO AGRICULTURE & FOOD How hot is too hot? Cell death will occur in any vine tissue beyond a threshold (lethal) temperature cell
Understanding how vines deal with heat and water deficit Everard Edwards CSIRO AGRICULTURE & FOOD How hot is too hot? Cell death will occur in any vine tissue beyond a threshold (lethal) temperature cell
Atmospheric Sciences 321. Science of Climate. Lecture 14: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4
 Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 14: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4 Community Business Check the assignments HW #4 due Today, HW#5 is posted Quiz Today on Chapter 3, too. Mid Term
Atmospheric Sciences 321 Science of Climate Lecture 14: Surface Energy Balance Chapter 4 Community Business Check the assignments HW #4 due Today, HW#5 is posted Quiz Today on Chapter 3, too. Mid Term
2016 International Conference on Modern Economic Development and Environment Protection (ICMED 2016) ISBN:
 2016 International Conference on Modern Economic Development and Environment Protection (ICMED 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-355-7 Difference in FVC Changes between Desert Grasslands with Different Stocking
2016 International Conference on Modern Economic Development and Environment Protection (ICMED 2016) ISBN: 978-1-60595-355-7 Difference in FVC Changes between Desert Grasslands with Different Stocking
Contents. 1. Evaporation
 Contents 1 Evaporation 1 1a Evaporation from Wet Surfaces................... 1 1b Evaporation from Wet Surfaces in the absence of Advection... 4 1c Bowen Ratio Method........................ 4 1d Potential
Contents 1 Evaporation 1 1a Evaporation from Wet Surfaces................... 1 1b Evaporation from Wet Surfaces in the absence of Advection... 4 1c Bowen Ratio Method........................ 4 1d Potential
Measurement and Analysis of the Vertical Distribution Characteristic of the Atmospheric Particle Concentration in Beijing District
 International Journal of Environmental Science and Development, Vol. 5, No. 2, April 214 Measurement and Analysis of the Vertical Distribution Characteristic of the Atmospheric Particle Concentration in
International Journal of Environmental Science and Development, Vol. 5, No. 2, April 214 Measurement and Analysis of the Vertical Distribution Characteristic of the Atmospheric Particle Concentration in
ONE DIMENSIONAL CLIMATE MODEL
 JORGE A. RAMÍREZ Associate Professor Water Resources, Hydrologic and Environmental Sciences Civil Wngineering Department Fort Collins, CO 80523-1372 Phone: (970 491-7621 FAX: (970 491-7727 e-mail: Jorge.Ramirez@ColoState.edu
JORGE A. RAMÍREZ Associate Professor Water Resources, Hydrologic and Environmental Sciences Civil Wngineering Department Fort Collins, CO 80523-1372 Phone: (970 491-7621 FAX: (970 491-7727 e-mail: Jorge.Ramirez@ColoState.edu
1 BASIC CONCEPTS AND MODELS
 1 BASIC CONCEPTS AND ODELS 1.1 INTRODUCTION This Volume III in the series of textbooks is focused on applications of environmental isotopes in surface water hydrology. The term environmental means that
1 BASIC CONCEPTS AND ODELS 1.1 INTRODUCTION This Volume III in the series of textbooks is focused on applications of environmental isotopes in surface water hydrology. The term environmental means that
EVAPORATION GEOG 405. Tom Giambelluca
 EVAPORATION GEOG 405 Tom Giambelluca 1 Evaporation The change of phase of water from liquid to gas; the net vertical transport of water vapor from the surface to the atmosphere. 2 Definitions Evaporation:
EVAPORATION GEOG 405 Tom Giambelluca 1 Evaporation The change of phase of water from liquid to gas; the net vertical transport of water vapor from the surface to the atmosphere. 2 Definitions Evaporation:
How Plants Grow HOME GARDENING OSHER LIFELONG LEARNING SPRING 2015
 How Plants Grow HOME GARDENING OSHER LIFELONG LEARNING SPRING 2015 What is a plant? 1.bp.blogspot.com What is a plant? Living organism that, unlike an animal, cannot move voluntarily, manufactures food
How Plants Grow HOME GARDENING OSHER LIFELONG LEARNING SPRING 2015 What is a plant? 1.bp.blogspot.com What is a plant? Living organism that, unlike an animal, cannot move voluntarily, manufactures food
Generation of Three-Dimensional Meteorological Field based on Sounding Data
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 186 The Open Cybernetics & Systemics Journal, 2015, 9, 186-198 Open Access Generation of Three-Dimensional Meteorological Field based on Sounding
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 186 The Open Cybernetics & Systemics Journal, 2015, 9, 186-198 Open Access Generation of Three-Dimensional Meteorological Field based on Sounding
1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States. Which sequence of events forms the clouds associated with
1. Base your answer to the following question on the weather map below, which shows a weather system that is affecting part of the United States. Which sequence of events forms the clouds associated with
CORRELATION BETWEEN URBAN HEAT ISLAND EFFECT AND THE THERMAL INERTIA USING ASTER DATA IN BEIJING, CHINA
 CORRELATION BETWEEN URBAN HEAT ISLAND EFFECT AND THE THERMAL INERTIA USING ASTER DATA IN BEIJING, CHINA Yurong CHEN a, *, Mingyi DU a, Rentao DONG b a School of Geomatics and Urban Information, Beijing
CORRELATION BETWEEN URBAN HEAT ISLAND EFFECT AND THE THERMAL INERTIA USING ASTER DATA IN BEIJING, CHINA Yurong CHEN a, *, Mingyi DU a, Rentao DONG b a School of Geomatics and Urban Information, Beijing
Stomatal conductance has a strong dependence upon humidity deficits
 Stomatal conductance has a strong dependence upon humidity deficits 1 There is no universal function between stomatal conductance and humidity deficits. Some plants are more sensitive than others Hall
Stomatal conductance has a strong dependence upon humidity deficits 1 There is no universal function between stomatal conductance and humidity deficits. Some plants are more sensitive than others Hall
% FOREST LEAF AREA. Figure I. Structure of the forest in proximity of the Proctor Maple Research Center -~--~ ~
 NTRODUCTON There is a critical need to develop methods to address issues of forest canopy productivity and the role of environmental conditions in regulating forest productivity. Recent observations of
NTRODUCTON There is a critical need to develop methods to address issues of forest canopy productivity and the role of environmental conditions in regulating forest productivity. Recent observations of
Water cycle changes during the past 50 years over the Tibetan Plateau: review and synthesis
 130 Cold Region Hydrology in a Changing Climate (Proceedings of symposium H02 held during IUGG2011 in Melbourne, Australia, July 2011) (IAHS Publ. 346, 2011). Water cycle changes during the past 50 years
130 Cold Region Hydrology in a Changing Climate (Proceedings of symposium H02 held during IUGG2011 in Melbourne, Australia, July 2011) (IAHS Publ. 346, 2011). Water cycle changes during the past 50 years
A PARAMETER ESTIMATE FOR THE LAND SURFACE MODEL VIC WITH HORTON AND DUNNE RUNOFF MECHANISM FOR RIVER BASINS IN CHINA
 A PARAMETER ESTIMATE FOR THE LAND SURFACE MODEL VIC WITH HORTON AND DUNNE RUNOFF MECHANISM FOR RIVER BASINS IN CHINA ZHENGHUI XIE Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences Beijing,
A PARAMETER ESTIMATE FOR THE LAND SURFACE MODEL VIC WITH HORTON AND DUNNE RUNOFF MECHANISM FOR RIVER BASINS IN CHINA ZHENGHUI XIE Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences Beijing,
Soil moisture retrieval with remote sensing images for debris flow forecast in humid regions
 Monitoring, Simulation, Prevention and Remediation of Dense and Debris Flows III 89 Soil moisture retrieval with remote sensing images for debris flow forecast in humid regions Y. Zhao 1,2,3, H. Yang 1,2
Monitoring, Simulation, Prevention and Remediation of Dense and Debris Flows III 89 Soil moisture retrieval with remote sensing images for debris flow forecast in humid regions Y. Zhao 1,2,3, H. Yang 1,2
Automatic Drawing of the Complicated Geological Faults
 Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 6(18): 3349-3353, 2013 ISSN: 2040-7459; e-issn: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2013 Submitted: December 12, 2012 Accepted: January
Research Journal of Applied Sciences, Engineering and Technology 6(18): 3349-3353, 2013 ISSN: 2040-7459; e-issn: 2040-7467 Maxwell Scientific Organization, 2013 Submitted: December 12, 2012 Accepted: January
Consolidation properties of dredger fill under surcharge preloading in coast region of Tianjin
 30 2 2011 6 GLOBAL GEOLOGY Vol. 30 No. 2 Jun. 2011 1004-5589 2011 02-0289 - 07 1 1 2 3 4 4 1. 130026 2. 130026 3. 110015 4. 430074 45 cm 100% ` TU447 A doi 10. 3969 /j. issn. 1004-5589. 2011. 02. 020 Consolidation
30 2 2011 6 GLOBAL GEOLOGY Vol. 30 No. 2 Jun. 2011 1004-5589 2011 02-0289 - 07 1 1 2 3 4 4 1. 130026 2. 130026 3. 110015 4. 430074 45 cm 100% ` TU447 A doi 10. 3969 /j. issn. 1004-5589. 2011. 02. 020 Consolidation
Common Effects of Abiotic Stress Factors on Plants
 Common Effects of Abiotic Stress Factors on Plants Plants are living organisms which lack ability of locomotion. Animals can move easily from one location to other. Immovable property of plants makes it
Common Effects of Abiotic Stress Factors on Plants Plants are living organisms which lack ability of locomotion. Animals can move easily from one location to other. Immovable property of plants makes it
The Mine Geostress Testing Methods and Design
 Open Journal of Geology, 2014, 4, 622-626 Published Online December 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojg http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojg.2014.412046 The Mine Geostress Testing Methods and Design
Open Journal of Geology, 2014, 4, 622-626 Published Online December 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojg http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojg.2014.412046 The Mine Geostress Testing Methods and Design
Water Relations in Viticulture BRIANNA HOGE AND JIM KAMAS
 Water Relations in Viticulture BRIANNA HOGE AND JIM KAMAS Overview Introduction Important Concepts for Understanding water Movement through Vines Osmosis Water Potential Cell Expansion and the Acid Growth
Water Relations in Viticulture BRIANNA HOGE AND JIM KAMAS Overview Introduction Important Concepts for Understanding water Movement through Vines Osmosis Water Potential Cell Expansion and the Acid Growth
STUDY ON ESTABLISHMENT SOYBEAN CONTROLLABLE STRUCUTURAL MODEL
 STUDY ON ESTABLISHMENT SOYBEAN CONTROLLABLE STRUCUTURAL MODEL 1,2,* Zhongbin Su, Ping Zheng 2, Hongmin Sun 2, Jicheng Zhang 2, Xiaoming Li 2 1 Computer Science and Technology Academy Department, Beijing
STUDY ON ESTABLISHMENT SOYBEAN CONTROLLABLE STRUCUTURAL MODEL 1,2,* Zhongbin Su, Ping Zheng 2, Hongmin Sun 2, Jicheng Zhang 2, Xiaoming Li 2 1 Computer Science and Technology Academy Department, Beijing
Analysis on Temperature Variation over the Past 55 Years in Guyuan City, China
 Analysis on Temperature Variation over the Past 55 Years in Guyuan City, China Liu Rui 1, 2,*, Zhang ZhiHua 1, 2 1 School of Environmental Science and Engineering, Chang an University, No.126 Yanta Road,
Analysis on Temperature Variation over the Past 55 Years in Guyuan City, China Liu Rui 1, 2,*, Zhang ZhiHua 1, 2 1 School of Environmental Science and Engineering, Chang an University, No.126 Yanta Road,
(i) The respiratory openings found on stems of woody plants. (ii) An apparatus to compare the rate of transpiration in cut shoots.
 SN Kansagra School Assignment-Transpiration Grade10 TRANSPIRATION :ASSIGNMENT Question.1. Name the following : (i) The respiratory openings found on stems of woody plants. (ii) An apparatus to compare
SN Kansagra School Assignment-Transpiration Grade10 TRANSPIRATION :ASSIGNMENT Question.1. Name the following : (i) The respiratory openings found on stems of woody plants. (ii) An apparatus to compare
Mapping the Baseline of Terrestrial Gamma Radiation in China
 Radiation Environment and Medicine 2017 Vol.6, No.1 29 33 Note Mapping the Baseline of Terrestrial Gamma Radiation in China Zhen Yang, Weihai Zhuo* and Bo Chen Institute of Radiation Medicine, Fudan University,
Radiation Environment and Medicine 2017 Vol.6, No.1 29 33 Note Mapping the Baseline of Terrestrial Gamma Radiation in China Zhen Yang, Weihai Zhuo* and Bo Chen Institute of Radiation Medicine, Fudan University,
12 SWAT USER S MANUAL, VERSION 98.1
 12 SWAT USER S MANUAL, VERSION 98.1 CANOPY STORAGE. Canopy storage is the water intercepted by vegetative surfaces (the canopy) where it is held and made available for evaporation. When using the curve
12 SWAT USER S MANUAL, VERSION 98.1 CANOPY STORAGE. Canopy storage is the water intercepted by vegetative surfaces (the canopy) where it is held and made available for evaporation. When using the curve
ADVANCES IN EARTH SCIENCE
 29 2 2014 2 ADVANCES IN EARTH SCIENCE Vol. 29 No. 2 Feb. 2014. J. 2014 29 2 207-215 doi 10. 11867 /j. issn. 1001-8166. 2014. 02. 0207. Ma Yaoming Hu Zeyong Tian Lide et al. Study progresses of the Tibet
29 2 2014 2 ADVANCES IN EARTH SCIENCE Vol. 29 No. 2 Feb. 2014. J. 2014 29 2 207-215 doi 10. 11867 /j. issn. 1001-8166. 2014. 02. 0207. Ma Yaoming Hu Zeyong Tian Lide et al. Study progresses of the Tibet
Reassessing the conservation status of the giant panda using remote sensing
 SUPPLEMENTARY Brief Communication INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/s41559-017-0317-1 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Reassessing the conservation status of the giant panda using remote sensing
SUPPLEMENTARY Brief Communication INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/s41559-017-0317-1 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Reassessing the conservation status of the giant panda using remote sensing
RESEARCH ON THE SPATIAL VARIABILITY OF SOIL MOISTURE
 RESEARCH ON THE SPATIAL VARIABILITY OF SOIL MOISTURE Changli Zhang 1, Shuqiang Liu 2,*, Xianyue Zhang 2, Kezhu Tan 3 1 Engineering College, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China,
RESEARCH ON THE SPATIAL VARIABILITY OF SOIL MOISTURE Changli Zhang 1, Shuqiang Liu 2,*, Xianyue Zhang 2, Kezhu Tan 3 1 Engineering College, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, Heilongjiang, China,
Geostatistical Analysis of Rainfall Temperature and Evaporation Data of Owerri for Ten Years
 Atmospheric and Climate Sciences, 2012, 2, 196-205 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/acs.2012.22020 Published Online April 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/acs) Geostatistical Analysis of Rainfall Temperature
Atmospheric and Climate Sciences, 2012, 2, 196-205 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/acs.2012.22020 Published Online April 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/acs) Geostatistical Analysis of Rainfall Temperature
Evapotranspiration. Andy Black. CCRN Processes Workshop, Hamilton, ON, Sept Importance of evapotranspiration (E)
 Evapotranspiration Andy Black CCRN Processes Workshop, Hamilton, ON, 12-13 Sept 213 Importance of evapotranspiration (E) This process is important in CCRN goals because 1. Major component of both terrestrial
Evapotranspiration Andy Black CCRN Processes Workshop, Hamilton, ON, 12-13 Sept 213 Importance of evapotranspiration (E) This process is important in CCRN goals because 1. Major component of both terrestrial
Measuring integral soil moisture variations using a geoelectrical resistivity meter
 Measuring integral soil moisture variations using a geoelectrical resistivity meter Thomas Klügel 1, Günter Harnisch 2 & Martina Harnisch 2 1 Bundesamt für Kartographie und Geodäsie, Fundamentalstation
Measuring integral soil moisture variations using a geoelectrical resistivity meter Thomas Klügel 1, Günter Harnisch 2 & Martina Harnisch 2 1 Bundesamt für Kartographie und Geodäsie, Fundamentalstation
The Relationship between Vegetation Changes and Cut-offs in the Lower Yellow River Based on Satellite and Ground Data
 Journal of Natural Disaster Science, Volume 27, Number 1, 2005, pp1-7 The Relationship between Vegetation Changes and Cut-offs in the Lower Yellow River Based on Satellite and Ground Data Xiufeng WANG
Journal of Natural Disaster Science, Volume 27, Number 1, 2005, pp1-7 The Relationship between Vegetation Changes and Cut-offs in the Lower Yellow River Based on Satellite and Ground Data Xiufeng WANG
Estimation of Wavelet Based Spatially Enhanced Evapotranspiration Using Energy Balance Approach
 Estimation of Wavelet Based Spatially Enhanced Evapotranspiration Using Energy Balance Approach Dr.Gowri 1 Dr.Thirumalaivasan 2 1 Associate Professor, Jerusalem College of Engineering, Department of Civil
Estimation of Wavelet Based Spatially Enhanced Evapotranspiration Using Energy Balance Approach Dr.Gowri 1 Dr.Thirumalaivasan 2 1 Associate Professor, Jerusalem College of Engineering, Department of Civil
Short Term Scientific Mission: Dendrometers and LVDT-sensors
 STSM: Dendrometers and LVDT-sensors Short Term Scientific Mission: Dendrometers and LVDT-sensors Selecting the one that truly captures the heartbeat of the tree COST STSM Reference Number: COST-STSM-ECOST-STSM-FP116-14714-4722
STSM: Dendrometers and LVDT-sensors Short Term Scientific Mission: Dendrometers and LVDT-sensors Selecting the one that truly captures the heartbeat of the tree COST STSM Reference Number: COST-STSM-ECOST-STSM-FP116-14714-4722
DEM-based Ecological Rainfall-Runoff Modelling in. Mountainous Area of Hong Kong
 DEM-based Ecological Rainfall-Runoff Modelling in Mountainous Area of Hong Kong Qiming Zhou 1,2, Junyi Huang 1* 1 Department of Geography and Centre for Geo-computation Studies, Hong Kong Baptist University,
DEM-based Ecological Rainfall-Runoff Modelling in Mountainous Area of Hong Kong Qiming Zhou 1,2, Junyi Huang 1* 1 Department of Geography and Centre for Geo-computation Studies, Hong Kong Baptist University,
To Understand How Trees Decline and Die, We Must: What is Stress? Tree Physiology. Understand stress and how it affects trees. Why Do Trees Die?
 To Understand How Trees Decline and Die, We Must: Why Do Trees Die? Rex Bastian, Ph.D. The Davey Tree Expert Co./The Care of Trees Wheeling, IL Understand stress and how it affects trees» To do this, we
To Understand How Trees Decline and Die, We Must: Why Do Trees Die? Rex Bastian, Ph.D. The Davey Tree Expert Co./The Care of Trees Wheeling, IL Understand stress and how it affects trees» To do this, we
Effect of 1-MCP on Water Relations Parameters of Well-Watered and Water-Stressed Cotton Plants
 Effect of 1-MCP on Water Relations Parameters of Well-Watered and Water-Stressed Cotton Plants Eduardo M. Kawakami, Derrick M. Oosterhuis, and John L. Snider 1 RESEARCH PROBLEM The cotton crop in the U.S.
Effect of 1-MCP on Water Relations Parameters of Well-Watered and Water-Stressed Cotton Plants Eduardo M. Kawakami, Derrick M. Oosterhuis, and John L. Snider 1 RESEARCH PROBLEM The cotton crop in the U.S.
Characteristic Temperatures of Waxy Crude Oils
 2007 Petroleum Science Vol.4 No.3 Characteristic Temperatures of Waxy Crude Oils Zhu Yingru, Zhang Jinjun, Li Hongying and Chen Jun (Beijing Key Laboratory of Urban Oil and Gas Distribution Technology,
2007 Petroleum Science Vol.4 No.3 Characteristic Temperatures of Waxy Crude Oils Zhu Yingru, Zhang Jinjun, Li Hongying and Chen Jun (Beijing Key Laboratory of Urban Oil and Gas Distribution Technology,
INFLUENCE OF SOUND WAVE STIMULATION ON THE GROWTH OF STRAWBERRY IN SUNLIGHT GREENHOUSE
 INFLUENCE OF SOUND WAVE STIMULATION ON THE GROWTH OF STRAWBERRY IN SUNLIGHT GREENHOUSE Lirong Qi 1,, Guanghui Teng 1, Tianzhen Hou 1, Baoying Zhu 2, Xiaona Liu 1 1 College of Water Conservancy and Civil
INFLUENCE OF SOUND WAVE STIMULATION ON THE GROWTH OF STRAWBERRY IN SUNLIGHT GREENHOUSE Lirong Qi 1,, Guanghui Teng 1, Tianzhen Hou 1, Baoying Zhu 2, Xiaona Liu 1 1 College of Water Conservancy and Civil
The layered water injection research of thin oil zones of Xing Shu Gang oil field Yikun Liu, Qingyu Meng, Qiannan Yu, Xinyuan Zhao
 International Conference on Education, Management and Computing Technology (ICEMCT 2015) The layered water injection research of thin oil zones of Xing Shu Gang oil field Yikun Liu, Qingyu Meng, Qiannan
International Conference on Education, Management and Computing Technology (ICEMCT 2015) The layered water injection research of thin oil zones of Xing Shu Gang oil field Yikun Liu, Qingyu Meng, Qiannan
ACTA ECOLOGICA SINICA ( > 90 %)
 26 12 2006 12 ACTA ECOLOGICA SINICA Vol. 26,No. 12 Dec.,2006 ( Haloxylon), (, 830052) : : ( > 90 %) ( < 50 %), ; (4 ) 5915 %, 1 80 %, + (, ),,, : ; ; :100020933(2006) 1224014205 :Q945. 34 :A Role of winged
26 12 2006 12 ACTA ECOLOGICA SINICA Vol. 26,No. 12 Dec.,2006 ( Haloxylon), (, 830052) : : ( > 90 %) ( < 50 %), ; (4 ) 5915 %, 1 80 %, + (, ),,, : ; ; :100020933(2006) 1224014205 :Q945. 34 :A Role of winged
Introduction to Plant Transport
 Introduction to Plant Transport The algal ancestors of plants were completely immersed in water and dissolved minerals. The adaptation to land involved the differentiation of the plant body into roots,
Introduction to Plant Transport The algal ancestors of plants were completely immersed in water and dissolved minerals. The adaptation to land involved the differentiation of the plant body into roots,
Stomata and water fluxes through plants
 Stomata and water fluxes through plants Bill Davies The Lancaster Environment Centre, UK Summary Stomata and responses to the environment Conductance, a function of frequency and aperture Measuring/estimating
Stomata and water fluxes through plants Bill Davies The Lancaster Environment Centre, UK Summary Stomata and responses to the environment Conductance, a function of frequency and aperture Measuring/estimating
Effects of rising temperatures and [CO 2 ] on physiology of tropical forests
![Effects of rising temperatures and [CO 2 ] on physiology of tropical forests Effects of rising temperatures and [CO 2 ] on physiology of tropical forests](/thumbs/96/127803481.jpg) Effects of rising temperatures and [CO 2 ] on physiology of tropical forests We are happy to advise that reports of our impending demise may have been very much exaggerated Jon Lloyd and Graham Farquhar
Effects of rising temperatures and [CO 2 ] on physiology of tropical forests We are happy to advise that reports of our impending demise may have been very much exaggerated Jon Lloyd and Graham Farquhar
Analysis on Climate Change of Guangzhou in Nearly 65 Years
 , pp.111-117 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016.138.24 Analysis on Climate Change of Guangzhou in Nearly 65 Years Wenzheng Yu, Haitao Liu, Chunyong Yin, Jin Wang College of Environmental Science and
, pp.111-117 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016.138.24 Analysis on Climate Change of Guangzhou in Nearly 65 Years Wenzheng Yu, Haitao Liu, Chunyong Yin, Jin Wang College of Environmental Science and
Basic stoichiometric equation on photosynthesis and the production of sugar and oxygen via the consumption of CO2, water, and light
 1 2 Basic stoichiometric equation on photosynthesis and the production of sugar and oxygen via the consumption of CO2, water, and light 3 Several pathways exist for fixing CO2 into sugar 4 Photosynthesis
1 2 Basic stoichiometric equation on photosynthesis and the production of sugar and oxygen via the consumption of CO2, water, and light 3 Several pathways exist for fixing CO2 into sugar 4 Photosynthesis
Soil Water Atmosphere Plant (SWAP) Model: I. INTRODUCTION AND THEORETICAL BACKGROUND
 Soil Water Atmosphere Plant (SWAP) Model: I. INTRODUCTION AND THEORETICAL BACKGROUND Reinder A.Feddes Jos van Dam Joop Kroes Angel Utset, Main processes Rain fall / irrigation Transpiration Soil evaporation
Soil Water Atmosphere Plant (SWAP) Model: I. INTRODUCTION AND THEORETICAL BACKGROUND Reinder A.Feddes Jos van Dam Joop Kroes Angel Utset, Main processes Rain fall / irrigation Transpiration Soil evaporation
Abiotic Stress in Crop Plants
 1 Abiotic Stress in Crop Plants Mirza Hasanuzzaman, PhD Professor Department of Agronomy Sher-e-Bangla Agricultural University E-mail: mhzsauag@yahoo.com Stress Stress is usually defined as an external
1 Abiotic Stress in Crop Plants Mirza Hasanuzzaman, PhD Professor Department of Agronomy Sher-e-Bangla Agricultural University E-mail: mhzsauag@yahoo.com Stress Stress is usually defined as an external
Evaluating shrub architectural performance in sun and shade environments with the 3-D model Y-plant: are there optimal strategies?
 Evaluating shrub architectural performance in sun and shade environments with the 3-D model Y-plant: are there optimal strategies? Robert W. Pearcy 1, Hiroyuki Muraoka 2 and Fernando Valladares 3 1 Section
Evaluating shrub architectural performance in sun and shade environments with the 3-D model Y-plant: are there optimal strategies? Robert W. Pearcy 1, Hiroyuki Muraoka 2 and Fernando Valladares 3 1 Section
Climate Change or Climate Variability?
 Climate Change or Climate Variability? Key Concepts: Greenhouse Gas Climate Climate change Climate variability Climate zones Precipitation Temperature Water cycle Weather WHAT YOU WILL LEARN 1. You will
Climate Change or Climate Variability? Key Concepts: Greenhouse Gas Climate Climate change Climate variability Climate zones Precipitation Temperature Water cycle Weather WHAT YOU WILL LEARN 1. You will
The Community Noah LSM with Multi-physics Options
 The Community Noah LSM with Multi-physics Options Guo-Yue Niu Collaborators: ZL Yang, KE Mitchell, F Chen, MB Ek, M. Barlage, L. Longuevergne, A Kumar, K Manning, D Niyogi, E Rosero, M Tewari, and Y. Xia
The Community Noah LSM with Multi-physics Options Guo-Yue Niu Collaborators: ZL Yang, KE Mitchell, F Chen, MB Ek, M. Barlage, L. Longuevergne, A Kumar, K Manning, D Niyogi, E Rosero, M Tewari, and Y. Xia
SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences. Climatic change features of fog and haze in winter over North China and Huang-Huai Area
 SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences RESEARCH PAPER August 2015 Vol.58 No.8: 1370 1376 doi: 10.1007/s11430-015-5089-3 Climatic change features of fog and haze in winter over North China and Huang-Huai Area YIN
SCIENCE CHINA Earth Sciences RESEARCH PAPER August 2015 Vol.58 No.8: 1370 1376 doi: 10.1007/s11430-015-5089-3 Climatic change features of fog and haze in winter over North China and Huang-Huai Area YIN
Describe plant meristems. Where are they located? perpetually embryonic cells found at tips of roots and shoots (apical vs.
 Which conditions have the higher rate of transpiration? Light or dark: Humid or dry: Breezy or still air: Hot or warm: light (need CO 2 for photosyn.) dry (lower H 2 O potential out) breezy (greater evaporation)
Which conditions have the higher rate of transpiration? Light or dark: Humid or dry: Breezy or still air: Hot or warm: light (need CO 2 for photosyn.) dry (lower H 2 O potential out) breezy (greater evaporation)
RANGE AND ANIMAL SCIENCES AND RESOURCES MANAGEMENT - Vol. II - Catchment Management A Framework for Managing Rangelands - Hugh Milner
 CATCHMENT MANAGEMENT A FRAMEWORK FOR MANAGING RANGELANDS Hugh Milner International Water Management Consultant, Australia Keywords: Rangeland management; catchments and watersheds; catchment management
CATCHMENT MANAGEMENT A FRAMEWORK FOR MANAGING RANGELANDS Hugh Milner International Water Management Consultant, Australia Keywords: Rangeland management; catchments and watersheds; catchment management
Lecture notes: Interception and evapotranspiration
 Lecture notes: Interception and evapotranspiration I. Vegetation canopy interception (I c ): Portion of incident precipitation (P) physically intercepted, stored and ultimately evaporated from vegetation
Lecture notes: Interception and evapotranspiration I. Vegetation canopy interception (I c ): Portion of incident precipitation (P) physically intercepted, stored and ultimately evaporated from vegetation
Freshwater. 1. The diagram below is a cross-sectional view of rain falling on a farm field and then moving to the water table.
 Name: ate: 1. The diagram below is a cross-sectional view of rain falling on a farm field and then moving to the water table. 3. Which conditions produce the most surface water runoff? A. steep slope,
Name: ate: 1. The diagram below is a cross-sectional view of rain falling on a farm field and then moving to the water table. 3. Which conditions produce the most surface water runoff? A. steep slope,
Environmental Plant Physiology Photosynthesis - Aging. Department of Plant and Soil Sciences
 Environmental Plant Physiology Photosynthesis - Aging krreddy@ra.msstate.edu Department of Plant and Soil Sciences Photosynthesis and Environment Leaf and Canopy Aging Goals and Learning Objectives: To
Environmental Plant Physiology Photosynthesis - Aging krreddy@ra.msstate.edu Department of Plant and Soil Sciences Photosynthesis and Environment Leaf and Canopy Aging Goals and Learning Objectives: To
Avocado Tree Physiology Understanding the Basis of Productivity
 Avocado Tree Physiology Understanding the Basis of Productivity R. L. Heath, M. L. Arpaia UC, Riverside M. V. Mickelbart Purdue University Raw Materials Labor Product Light Carbon Dioxide Temperature Water
Avocado Tree Physiology Understanding the Basis of Productivity R. L. Heath, M. L. Arpaia UC, Riverside M. V. Mickelbart Purdue University Raw Materials Labor Product Light Carbon Dioxide Temperature Water
Photosynthesis - Aging Leaf Level. Environmental Plant Physiology Photosynthesis - Aging. Department of Plant and Soil Sciences
 Environmental Plant Physiology Photosynthesis and Environment Leaf and Canopy Aging krreddy@ra.msstate.edu Department of Plant and Soil Sciences Goals and Learning Objectives: To understand the effects
Environmental Plant Physiology Photosynthesis and Environment Leaf and Canopy Aging krreddy@ra.msstate.edu Department of Plant and Soil Sciences Goals and Learning Objectives: To understand the effects
Soft stems. Wind pollinated
 Plant Adaptations The temperature in grassland or the prairies are windy, have hot summers and cold winters. Rainfall is uncertain and in the range of about 25-27 cm per year, and drought is common. The
Plant Adaptations The temperature in grassland or the prairies are windy, have hot summers and cold winters. Rainfall is uncertain and in the range of about 25-27 cm per year, and drought is common. The
Research Proposal: Tara Gupta (CSE Style)
 Research Proposal: Tara Gupta (CSE Style) Specific and informative title, name, and other relevant information centered on title page Field Measurements of Photosynthesis and Transpiration Rates in Dwarf
Research Proposal: Tara Gupta (CSE Style) Specific and informative title, name, and other relevant information centered on title page Field Measurements of Photosynthesis and Transpiration Rates in Dwarf
THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARYLAYER DURING FOGGY DAYS IN WINTER AND SPRING SEASONS AT SOUTHERT OF BEIJING
 THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARYLAYER DURING FOGGY DAYS IN WINTER AND SPRING SEASONS AT SOUTHERT OF BEIJING HONGSHENG ZHANG, KAI WANG, FUYU LI, XINJIAN LIU, JIAYI CHEN Department of Atmospheric
THE STRUCTURE OF THE ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARYLAYER DURING FOGGY DAYS IN WINTER AND SPRING SEASONS AT SOUTHERT OF BEIJING HONGSHENG ZHANG, KAI WANG, FUYU LI, XINJIAN LIU, JIAYI CHEN Department of Atmospheric
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2013, 5(11): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2013, 5(11):403-408 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Effect of thickness of heat insulating material
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2013, 5(11):403-408 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Effect of thickness of heat insulating material
Welcome to the Iowa Certified Nursery Professional Training program Module 2: How Plants Work: Plant Growth and Development.
 Welcome to the Iowa Certified Nursery Professional Training program Module 2: How Plants Work: Plant Growth and Development. 1 Upon completion of this module, you will be able to fulfill each of the objectives
Welcome to the Iowa Certified Nursery Professional Training program Module 2: How Plants Work: Plant Growth and Development. 1 Upon completion of this module, you will be able to fulfill each of the objectives
SUPPORTING INFORMATION. Ecological restoration and its effects on the
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Ecological restoration and its effects on the regional climate: the case in the source region of the Yellow River, China Zhouyuan Li, Xuehua Liu,* Tianlin Niu, De Kejia, Qingping
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Ecological restoration and its effects on the regional climate: the case in the source region of the Yellow River, China Zhouyuan Li, Xuehua Liu,* Tianlin Niu, De Kejia, Qingping
Irrigation water salinity limits faba bean (Vicia faba L.) photosynthesis
 5 th CASEE Conference Healthy Food Production and Environmental Preservation The Role of Agriculture, Forestry and Applied Biology Irrigation water salinity limits faba bean (Vicia faba L.) photosynthesis
5 th CASEE Conference Healthy Food Production and Environmental Preservation The Role of Agriculture, Forestry and Applied Biology Irrigation water salinity limits faba bean (Vicia faba L.) photosynthesis
SURF Progresses Contents
 SURF Progresses Contents 1 5th Workshop: June 21-23, 2017 2 SURF-2016 Summer Experiment 3 Preliminary results 4 Future plan (1) 5 th Workshop: June 21-23, 2017 SURF WS-5: Structure I. New Science Reports
SURF Progresses Contents 1 5th Workshop: June 21-23, 2017 2 SURF-2016 Summer Experiment 3 Preliminary results 4 Future plan (1) 5 th Workshop: June 21-23, 2017 SURF WS-5: Structure I. New Science Reports
River Water Circulation Model on the Natural Environment
 River Water Circulation Model on the Natural Environment Yoshirou Takanashi, Haruna Sakagami, Yuta Taki, Minetada Osano, Computer Science, University of Aizu Tsuruga, Ikki-machi, Aizu-Wakamatsu City, Fukushima,
River Water Circulation Model on the Natural Environment Yoshirou Takanashi, Haruna Sakagami, Yuta Taki, Minetada Osano, Computer Science, University of Aizu Tsuruga, Ikki-machi, Aizu-Wakamatsu City, Fukushima,
In this lab, you and your partners will try to devise a strategy that will allow your plant to thrive and reproduce (make flowers).
 The Plant Game credit: Elena DiMuzio at the Cornell Institute for Plant Biology Teachers I rewrote some of the explanatory material but the game idea is hers. Rules: First of all, to win at any game, players
The Plant Game credit: Elena DiMuzio at the Cornell Institute for Plant Biology Teachers I rewrote some of the explanatory material but the game idea is hers. Rules: First of all, to win at any game, players
Why Calcium is So Important
 Why Calcium is So Important Calcium - A Transportation Problem By Dr. Lynette Morgan As hydroponic growers we like to think that by supplying our plants with all the nutrients they need in the right ratios,
Why Calcium is So Important Calcium - A Transportation Problem By Dr. Lynette Morgan As hydroponic growers we like to think that by supplying our plants with all the nutrients they need in the right ratios,
The Study of Soil Fertility Spatial Variation Feature Based on GIS and Data Mining *
 The Study of Soil Fertility Spatial Variation Feature Based on GIS and Data Mining * Chunan Li, Guifen Chen **, Guangwei Zeng, and Jiao Ye College of Information and Technology, Jilin Agricultural University,
The Study of Soil Fertility Spatial Variation Feature Based on GIS and Data Mining * Chunan Li, Guifen Chen **, Guangwei Zeng, and Jiao Ye College of Information and Technology, Jilin Agricultural University,
Sap flow technique as a tool for irrigation schedule in grapevines: control of the plant physiological status
 Sap flow technique as a tool for irrigation schedule in grapevines: control of the plant physiological status Pons P.J., Truyols M., Flexas J., Cifre J., Medrano H., Ribas-Carbó M. in López-Francos A.
Sap flow technique as a tool for irrigation schedule in grapevines: control of the plant physiological status Pons P.J., Truyols M., Flexas J., Cifre J., Medrano H., Ribas-Carbó M. in López-Francos A.
Detection of Chlorophyll Content of Rice Leaves by Chlorophyll Fluorescence Spectrum Based on PCA-ANN Zhou Lina1,a Cheng Shuchao1,b Yu Haiye2,c 1
 7th International Conference on Mechatronics, Control and Materials (ICMCM 2016) Detection of Chlorophyll Content of Rice Leaves by Chlorophyll Fluorescence Spectrum Based on PCA-ANN Zhou Lina1,a Cheng
7th International Conference on Mechatronics, Control and Materials (ICMCM 2016) Detection of Chlorophyll Content of Rice Leaves by Chlorophyll Fluorescence Spectrum Based on PCA-ANN Zhou Lina1,a Cheng
Recap. Waxy layer which protects the plant & conserves water. Contains chloroplasts: Specialized for light absorption.
 Recap Contains chloroplasts: Specialized for light absorption Waxy layer which protects the plant & conserves water mesophyll Layer contains air spaces: Specialized for gas exchange Vascular Tissue Exchange
Recap Contains chloroplasts: Specialized for light absorption Waxy layer which protects the plant & conserves water mesophyll Layer contains air spaces: Specialized for gas exchange Vascular Tissue Exchange
Modeling Study of A Typical Summer Ozone Pollution Event over Yangtze River Delta
 36 11 2015 11 ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE Vol 36 No 11 Nov 2015 * - - 210044 WRF /Chem 2013 8 10 ~ 18 11 ~ 13 h 15 00 WRF /Chem X51 A 0250-3301 2015 11-3981-08 DOI 10 13227 /j hjkx 2015 11 006 Modeling Study
36 11 2015 11 ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE Vol 36 No 11 Nov 2015 * - - 210044 WRF /Chem 2013 8 10 ~ 18 11 ~ 13 h 15 00 WRF /Chem X51 A 0250-3301 2015 11-3981-08 DOI 10 13227 /j hjkx 2015 11 006 Modeling Study
DATE: NAME: CLASS: Chapter 2 Review (Alternative Format) CHAPTER 2 BLM 2-9
 Goal To review the concepts from Chapter 2. Reviewing Key Terms Fill in the blanks using a word from the list below. organs shoot differentiation gall epidermis root system meristem 1. The protects the
Goal To review the concepts from Chapter 2. Reviewing Key Terms Fill in the blanks using a word from the list below. organs shoot differentiation gall epidermis root system meristem 1. The protects the
A new approach for fast calculation of sloped terrace earthwork based on GIS in the hilly regions
 A new approach for fast calculation of sloped terrace earthwork based on GIS in the hilly regions Qingchun Zhang 1 1 Land Consolidation and Rehabilitation Center, the Ministry of Land and Resources; 1
A new approach for fast calculation of sloped terrace earthwork based on GIS in the hilly regions Qingchun Zhang 1 1 Land Consolidation and Rehabilitation Center, the Ministry of Land and Resources; 1
Comparison of Different Cultivars of Blueberry Overwintering Ability in Qingdao of China
 American Journal of Plant Sciences, 2012, 3, 391-396 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2012.33047 Published Online March 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajps) 391 Comparison of Different Cultivars of Blueberry
American Journal of Plant Sciences, 2012, 3, 391-396 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2012.33047 Published Online March 2012 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/ajps) 391 Comparison of Different Cultivars of Blueberry
Unit 9. Atmosphere. Natural Science 1º ESO Antonio Jesús Moreno Quintero. Colegio Guadalete. Attendis.
 9. Atmosphere Unit 9. Atmosphere. 1 1. The Earth s atmosphere. Atmosphere: envelope of gases and particles which surrounds the Earth. Evolution of the atmosphere 1 st state: hydrogen and helium. It was
9. Atmosphere Unit 9. Atmosphere. 1 1. The Earth s atmosphere. Atmosphere: envelope of gases and particles which surrounds the Earth. Evolution of the atmosphere 1 st state: hydrogen and helium. It was
Importance. The Reaction of Life : The conversion of the sun s energy into a form man and other living creatures can use.
 PLANT PROCESSES Photosynthesis Importance The Reaction of Life : The conversion of the sun s energy into a form man and other living creatures can use. Photo light Synthesis to put together 3 Important
PLANT PROCESSES Photosynthesis Importance The Reaction of Life : The conversion of the sun s energy into a form man and other living creatures can use. Photo light Synthesis to put together 3 Important
Effect of nitrogen application on nitrogen absorption, distribution and yield of Stra wberry
 26,12(3) :4-45 Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science,,,, (, 27118) : 15 N 15 N, 15 N,, 5215 %, 3412 % 85 %, 15 % ; 7212 %, 2718 % ; 3113 % 15 N 15 N, SPAD, N 225 kg/ hm 2 : ; ; 15 N ; ; ; : S66814 ; S66
26,12(3) :4-45 Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science,,,, (, 27118) : 15 N 15 N, 15 N,, 5215 %, 3412 % 85 %, 15 % ; 7212 %, 2718 % ; 3113 % 15 N 15 N, SPAD, N 225 kg/ hm 2 : ; ; 15 N ; ; ; : S66814 ; S66
Preliminary Experimental Study on Heat Transfer Characteristics of Wall with Automatic Adjustment of Heat Transfer Coefficient
 5th International Conference on Civil Engineering and Transportation (ICCET 2015) Preliminary Experimental Study on Heat Transfer Characteristics of Wall with Automatic Adjustment of Heat Transfer Coefficient
5th International Conference on Civil Engineering and Transportation (ICCET 2015) Preliminary Experimental Study on Heat Transfer Characteristics of Wall with Automatic Adjustment of Heat Transfer Coefficient
