1. Which of the following statements correctly describes the phenomenon of apical dominance in woody plants?
|
|
|
- Amelia Gilbert
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PLSC 210-Horticulture Science Examination II October 29, 2003 Name 1. Which of the following statements correctly describes the phenomenon of apical dominance in woody plants? a. Suppression of the growth of apical shoots by auxin compounds produced in the axillary buds. b. Suppression of the breaking (growth) of lateral buds on a stem below the apical meristem which produces auxin compounds. c. Suppression of the growth of apical shoots by cytokinin compounds produced in the axillary buds. d. Suppression of the breaking (growth) of lateral buds on a stem below the apical meristem which produces cytokinin compounds. 2. If you would like to convert female flowers to male flowers on a monoecious cucumber plant, which of the following growth regulators can be used as a spray? a. IAA (indoleacetic acid) b. Gibberellin (GA 3 ) c. Ethephon (chemical that releases ethylene) d. Kinetin (a synthetic cytokinin) 3. Chrysanthemum is a short-day plant. If chrysanthemum is grown under a 16-hr-day/8-hr-night condition, it will: a. initiate flower buds and bloom. b. continue to grow vegetatively without blooming. c. be stunted and die eventually. d. be confused, with some plants staying vegetative and others blooming. 4. The phytochrome system (P r as red light absorbing and P fr as far-red light absorbing form) is responsible for plant response to photoperiods. Phytochromes are also responsible for phototropism. a. Both statements are true. b. The first statement is true, but the second statement is wrong. c. The first statement is wrong, but the second statement is true. d. Both statements are wrong. 5. Synthetic cytokinins like naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA) and benzyl adenine (BA) can be used to induce shoot proliferation from tissues cultured in vitro. a. True b. False 6. Ethylene gas as a growth regulator can be used to ripen green bananas. a. True b. False 1
2 7. Seed dormancy which is caused by impermeable seed coat can be eliminated by: a. stratification. b. vernalization. c. scarification. d. growth regulator treatment. 8. Which of the following seed dormancy is caused by the presence of germination inhibitors in the embryo? a. Physical dormancy b. Seed coat dormancy c. Physiological dormancy d. All of the above 9. Which of the following fruit trees would require a chilling period for flower bud dormancy breaking and flowering? a. Orange, mango, and pineapple b. Apple, peach, and pear c. Avocado, almond, and papaya d. None of the above 10. Which of the following flower crops requires a cold treatment for flower induction? a. Poinsettia b. Azalea c. Chrysanthemum d. Rose 11. The carbohydrate to nitrogen ratio (C/N ratio) influences the onset of phase change from vegetative growth to reproductive growth in many plants. Which of the following statements explains the influence of C/N ratio best? a. The higher the C/N ratio, the faster the onset of reproductive growth. b. The higher the C/N ratio, the higher the vegetative growth. c. The lower the C/N ratio, the greater the reproductive growth. d. The lower the C/N ratio, the earlier the plant bloom. 12. The cultivated potato is a long-day plant. If a commercial cultivar of potato is grown on a farm near the equator, would it bloom? a. Yes, the potato will bloom continuously, because the equator has a long-day condition year round. b. No, the potato will not bloom, because the equator has a short-day condition year round. c. Yes, the potato will bloom during the summer months when the equator has a long-day condition. d. No, the potato will not bloom during the winter months when the equator has a short-day condition. 2
3 13. Which of the following is a short-day plant? a. Geranium b. Tomato c. Petunia d. Poinsettia 14. The influence of pollination on ovary growth and enlargement into fruit is called metaxinia. a. True b. False 15. Parthenocarpy is a phenomenon of fruit development without pollination and fertilization. Fruits formed by parthenogenesis contain viable seeds. a. Both statements are true. b. The first statement is true, but the second statement is wrong. c. The first statement is wrong, but the second statement is true. d. Both statements are wrong. 16. Segregation of certain genetic traits can be found in the progenies obtained from: a. sexual (seed) propagation. b. asexual reproduction. c. vegetative propagation. d. clonal reproduction. 17. In which of the following cell divisions would the number of chromosomes be reduced to one half? a. Mitosis b. Somatic cell division c. Meiosis d. Both mitosis and meiosis 18. Which of the following identifies a monosomic (aneuploid) condition in spinach (X=12)? a. 2N = 3X = 36 chromosomes b. 2N = 4X = 48 chromosomes c. 2N-1 =2X-1 = 23 chromosomes d. 2N+1 = 2X+1 = 25 chromosomes 19. The genomic (X) number of chromosomes for watermelon is 11. How many chromosomes would a seedless watermelon (triploid) have in each cell? a. 2N = 1X = 11 b. 2N = 2X = 22 c. 2N = 3X = 33 d. 2N = 4X = 44 3
4 20. Life cycle is defined as the alternation of sporophytic and gametophytic generations in cycle. Which of the following is true for life cycle in plants? a. The gametophytic generation is much shorter than the sporophytic generation. b. The sporophytic generation is shorter than the gametophytic generation. c. Seed or fruit ripening occurs during the sporophytic generation. d. Both the sporophytic and gametophytic generations have the same number of chromosomes in their cells. 21. Colchicine is used to induce polyploidy plants. Select the best statement on the mode of colchicine action in doubling chromosome numbers during mitosis. a. Colchicine induces rapid DNA replication in the nucleus. b. Colchicine kills diploid cells allowing only the polyploid cells to survive. c. Colchicine interferes with the function of spindle fibers during the anaphase of mitosis, sending all chromosomes into one pole. d. None of the above. 22. Which of the following statement is not true for double fertilization? a. One sperm nucleus combines with the egg nucleus to form a zygotic embryo, and the other sperm nucleus combines with the polar nuclei to form the endosperm. b. Double fertilization ends up with the production of two seeds per ovule. c. The endosperm tissues formed from double fertilization contain 3N number of chromosomes. d. Double fertilization occurs in higher plants. 23. Given that the genomic (X) number of chromosomes for potato is 12 and the cultivated potato is a tetraploid (2N = 4X), how many chromosomes would a potato pollen grain have? a. N = 6 b. N = 12 c. N = 24 d. N = Which of the following turfgrasses is a cool-season grass? a. Kentucky bluegrass b. Buffalograss c. Zoysia grass d. Bermuda grass 25. Which of the following statements is not true for golf courses and athletic fields? a. There are more athletic turfgrass fields than golf courses in the U.S. b. The number of golf courses in North America exceeds that of golf courses in the rest of the world combined. c. Europe has the highest number of golf courses per capita. d. South America has the least number of golf courses among the five continents. 4
5 26. Turfgrasses are plants that form a more or less contiguous ground cover that persists under regular mowing and traffic. A turf is an interconnecting community of turfgrasses and the soil adhering to their foots and other below-ground organs. a. Both statements are true. b. The first statement is true, but the second statement is wrong. c. The first statement is wrong, but the second statement is true. d. Both statements are wrong. 27. The gas phase of growing media is needed for: a. photosynthesis. b. root respiration. c. transpiration of water. d. conduction of water through xylem tissues. 28. At container capacity, the moisture condition in the growing medium is maintained by: a. capillary water, hygroscopic water, and gravitational water. b. hygroscopic water and capillary water. c. gravitational water only. d. hygroscopic water only. 29. Which of the following is correct for the optimum ph range required by plants? a. It enhances the availability of water to plants. b. It controls the amount of oxygen available in the growing medium. c. It maximized the absorption of essential nutrients by roots. d. It limits the growth of soil microorganisms. 30. Soils having a high level of cation exchange capacity (CEC) would: a. have the individual soil particles positively charged. b. absorb and store negatively charged ions. c. absorb and store positively charged ions. d. repel positively charged ions. 31. Which of the following chemicals can be used to raise the ph of a growing medium. a. Aluminum sulfate b. Iron sulfate c. Phosphoric acid d. Dolomite 32. The tap water in Fargo is high in ph (around 8.8). Which of the following chemicals can be used to lower the ph (around 6.5) of the water for greenhouse irrigation? a. Sulfuric acid b. Potassium hydroxide c. Calcium carbonate d. Calcium nitrate 5
6 33. Which of the following crops tolerates high ph soils? a. Alfalfa b. Blueberry c. Azalea d. Hydrangea 34. Which of the following statements is true for soil nitrification? a. The ammonifying bacteria (Actinomycetes) convert ammonium (NH 4+ ) to nitrite (NO 2 ) during nitrification. b. The final product of soil nitrification is nitrate (NO 3- ). c. Nitrosomonas, as nitrifying bacteria, converts nitrite (NO 2 ) into nitrate (NO 3- ) during soil nitrification. d. The first step of soil nitrification involves the conversion of nitrite (NO 2 ) into ammonium (NH 4+ ). 35. Which of the following soil amendments would have the lowest ph? a. Perlite b. Vermiculite c. Peat d. Sand 36. Which of the following is not true for the Cornell peat-lite mix? a. The major ingredients are peat, perlite and vermiculite. b. It contains sand. c. It is used for pot plant culture. d. It contains no soil. 37. Which of the following lights has the longest wave length? a. Red light b. Blue light c. UV light d. Green light 38. Which of the following photometric units shows the highest light intensity? a. 1 foot candle b. 1 lux c. 1 mol m -2 s Which of the following statements is not true for the atmospheric window? a. It allows the visible light to reach the earth s surface. b. It allows the photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) to reach the earth s surface. c. The ozone layer, CO 2 and water vapor filter out cosmic ray, -ray, x-ray, and UV light as well as infra-red lights in the atmosphere. d. It allows more UV light on earth s surface. 6
7 40. Which of the following lights is responsible for so-called greenhouse effect in warming up the atmosphere or a greenhouse? a. UV light b. visible light c. PAR (photosynthetically active radiation) d. infra-red light 41. The spectral range of the photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) is: a. 100 nm nm. b. 400 nm nm. c. 700 nm -1,000 nm. d. 1,000 nm - 2,000 nm. 42. For photosynthesis enhancement, fluorescent lamps are less energy efficient than the incandescent lamps. a. True b. False 43. Incandescent lamps are commonly used to light plants for photoperiod control, because: a. the cost of incandescent light bulbs is cheaper than that of fluorescent lamps. b. incandescent lamps are more energy efficient in emitting the red and far-red light compared to fluorescent lamps. c. incandescent lamps last longer than the fluorescent lamps. d. it is easier to screw in an incandescent light bulb than to install fluorescent lamps. 44. At a dew point, the relative humidity (RH) reaches: a. 50%. b. 75%. c. 95% d. 100%. 45. Provided that 1 kg = 2.2 lb = 1,000 g and o F = 9/5 o C + 32, which of the following would contain the greatest amount of heat energy? a. 1 kcal b. 500 cal c. 1 BTU 46. The heat of fusion is: a. released to the surrounding when water evaporates. b. absorbed from the surrounding when steam condenses to form water. c. absorbed from the surrounding when water evaporates to form vapor. d. released the surrounding when water freezes. 7
8 47. The wet-bulb temperature of an ambient air: a. increases as the relative humidity decreases. b. decreases as the relative humidity decreases. c. stays the same over a range of relative humidity when dry-bulb temperature is the same. d. is always higher than the dry-bulb temperature. 48. Transfer of heat energy from one place to another by movement of air or water current is called as: a. conduction. b. convection. c. radiation. d. condensation. 49. A deciduous fruit orchard is usually established on a thermal belt rather than in the low-lying valley area. In addition, a north-facing thermal belt is better than a south-facing thermal belt as a site for growing deciduous fruit trees, because: a. flowering time is delayed for the plants grown on the north slope than those grown on the south slope, reducing the chances for freeze damage. b. plants grown on the north slope receive more winter chilling than those grown on the south slope, allowing more profuse blooming. c. flowering time is more hastened for the plants grown on the north slope than those grown on the south slope, leading to an earlier crop. d. plants grown on the south slope are more vulnerable to insect pests and diseases during the entire growing season. 50. Which of the following statements best describes smudging? a. Spraying water over fruit trees to protect them from freezing b. Covering fruit trees with plastic film material to keep them warm. c. Burning fuel in an orchard to heat the ambient air so that fruit trees are protected from cold d. Mulching the beds with straw or plastic film to keep the soil warm. 51. Bonus Question (4 points). Make a question of your own from subjects you have studied but was not covered in this exam and answer it correctly. Honor Pledge: Upon my honor I have neither given nor received aid in writing this examination. Signed 8
PLSC 210-Horticulture Science Examination II October 23, is a plant hormone responsible for apical dominance.
 PLSC 210-Horticulture Science Examination II October 23, 2002 Name 1. is a plant hormone responsible for apical dominance. a. Cytokinin b. Auxin c. Abscisic acid d. Ethylene 2. Which of the following plant
PLSC 210-Horticulture Science Examination II October 23, 2002 Name 1. is a plant hormone responsible for apical dominance. a. Cytokinin b. Auxin c. Abscisic acid d. Ethylene 2. Which of the following plant
PRACTICE EXAM HORT 201 2nd EXAM from Fall 1999
 PRACTICE EXAM HORT 201 2nd EXAM from Fall 1999 1) Which of the following is the naturally occurring auxin in plants? a) indolebutyric acid b) naphthaleneacetic acid c) indoleacetic acid d) zeatin e) kinetin
PRACTICE EXAM HORT 201 2nd EXAM from Fall 1999 1) Which of the following is the naturally occurring auxin in plants? a) indolebutyric acid b) naphthaleneacetic acid c) indoleacetic acid d) zeatin e) kinetin
1 These are living cells that lack nuclei and ribosomes; they transport sugars and other organic nutrients
 1 These are living cells that lack nuclei and ribosomes; they transport sugars and other organic nutrients collenchyma parenchyma sclerenchyma sieve cells tracheids 2 The fiber cells of plants are a type
1 These are living cells that lack nuclei and ribosomes; they transport sugars and other organic nutrients collenchyma parenchyma sclerenchyma sieve cells tracheids 2 The fiber cells of plants are a type
Sporic life cycles involve 2 types of multicellular bodies:
 Chapter 3- Human Manipulation of Plants Sporic life cycles involve 2 types of multicellular bodies: -a diploid, spore-producing sporophyte -a haploid, gamete-producing gametophyte Sexual Reproduction in
Chapter 3- Human Manipulation of Plants Sporic life cycles involve 2 types of multicellular bodies: -a diploid, spore-producing sporophyte -a haploid, gamete-producing gametophyte Sexual Reproduction in
Autotrophs/producers- make own energy through
 Name Class EXAM Date Unit 11 Plant Kingdom Characteristics of Plants Multicellular- made of cells Eukaryotes- have & membrane bound organelles Cell - made of Autotrophs/producers- make own energy through
Name Class EXAM Date Unit 11 Plant Kingdom Characteristics of Plants Multicellular- made of cells Eukaryotes- have & membrane bound organelles Cell - made of Autotrophs/producers- make own energy through
I. ESSAY QUESTIONS (5 Points Each)
 PLSC 210-Horticulture Science Fall Semester, 2003 Exam I Name I. ESSAY QUESTIONS (5 Points Each) 1. Define the term horticulture, and discuss the role of horticulture in enhancing human well-being and
PLSC 210-Horticulture Science Fall Semester, 2003 Exam I Name I. ESSAY QUESTIONS (5 Points Each) 1. Define the term horticulture, and discuss the role of horticulture in enhancing human well-being and
Plant Growth & Development. By: Johnny M. Jessup Agriculture Teacher/FFA Advisor
 Plant Growth & Development By: Johnny M. Jessup Agriculture Teacher/FFA Advisor Introduction There are 7 plant processes that effect growth which are. Photosynthesis Respiration Absorption Transpiration
Plant Growth & Development By: Johnny M. Jessup Agriculture Teacher/FFA Advisor Introduction There are 7 plant processes that effect growth which are. Photosynthesis Respiration Absorption Transpiration
Useful Propagation Terms. Propagation The application of specific biological principles and concepts in the multiplication of plants.
 Useful Propagation Terms Propagation The application of specific biological principles and concepts in the multiplication of plants. Adventitious Typically describes new organs such as roots that develop
Useful Propagation Terms Propagation The application of specific biological principles and concepts in the multiplication of plants. Adventitious Typically describes new organs such as roots that develop
Slide 1 / 86. Angiosperms: The Flowering Plants
 Slide 1 / 86 Angiosperms: The Flowering Plants Slide 2 / 86 Brief Phylogeny of Plants Monocot Dicot This presentation will focus on angiosperms Angiosperm Gymnosperm Seeded Plants Non-Seeded plants Vascular
Slide 1 / 86 Angiosperms: The Flowering Plants Slide 2 / 86 Brief Phylogeny of Plants Monocot Dicot This presentation will focus on angiosperms Angiosperm Gymnosperm Seeded Plants Non-Seeded plants Vascular
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms
 Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Date: 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms Date: 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and
Is that artificial turf or real grass? Its thicker than Bermuda!
 Is that artificial turf or real grass? Its thicker than Bermuda! 1 Using Plant Growth Regulators Growth regulators DO NOT interfere with plant respiration, photosynthesis, or other internal plant functions
Is that artificial turf or real grass? Its thicker than Bermuda! 1 Using Plant Growth Regulators Growth regulators DO NOT interfere with plant respiration, photosynthesis, or other internal plant functions
Plant Growth & Development. Growth Processes Photosynthesis. Plant Growth & Development
 Plant Growth & Development Growth Processes Growth Requirements Types of Growth & Development Factors Growth Processes Photosynthesis Creating carbohydrates (stored energy) from CO 2 + water + sunlight
Plant Growth & Development Growth Processes Growth Requirements Types of Growth & Development Factors Growth Processes Photosynthesis Creating carbohydrates (stored energy) from CO 2 + water + sunlight
Plant Growth and Development
 1. Define plasticity. Give an example? A: Plant Growth and Development The ability of the plants to follow different pathways in response to the environment or phases of life to form different kinds of
1. Define plasticity. Give an example? A: Plant Growth and Development The ability of the plants to follow different pathways in response to the environment or phases of life to form different kinds of
Horticulture 201H Spring, 2002 Exam 2 Name:
 Horticulture 201H Spring, 2002 Exam 2 Name: Section 1. In the space to the left of the statements below, write the word(s) that best fit the definition or description. (20 pts) Vegetative reproduction
Horticulture 201H Spring, 2002 Exam 2 Name: Section 1. In the space to the left of the statements below, write the word(s) that best fit the definition or description. (20 pts) Vegetative reproduction
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms
 Structures and Functions of Living Organisms 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and functions
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms 6.L.1 Understand the structures, processes and behaviors of plants that enable them to survive and reproduce. 6.L.1.1 Summarize the basic structures and functions
a. capture sunlight and absorb CO 2
 BIO 274-01 Exam 1 Name Matching (10 pts) 1. Match each plant part with its function: root c a. capture sunlight and absorb CO 2 for photosynthesis leaves a b. provides support, conducts water and nutrients
BIO 274-01 Exam 1 Name Matching (10 pts) 1. Match each plant part with its function: root c a. capture sunlight and absorb CO 2 for photosynthesis leaves a b. provides support, conducts water and nutrients
Chap 5. Differentiation and Development. 1. General Information 2. Plant Growth Hormones 3. Vegetative Physiology 4. Reproductive Physiology
 Chap 5. Differentiation and Development 1. General Information 2. Plant Growth Hormones 3. Vegetative Physiology 4. Reproductive Physiology 1. Process of Differentiation Differential growth in cell and
Chap 5. Differentiation and Development 1. General Information 2. Plant Growth Hormones 3. Vegetative Physiology 4. Reproductive Physiology 1. Process of Differentiation Differential growth in cell and
Reproduction, Seeds and Propagation
 Reproduction, Seeds and Propagation Diploid (2n) somatic cell Two diploid (2n) somatic cells Telophase Anaphase Metaphase Prophase I One pair of homologous chromosomes (homologues) II Homologues condense
Reproduction, Seeds and Propagation Diploid (2n) somatic cell Two diploid (2n) somatic cells Telophase Anaphase Metaphase Prophase I One pair of homologous chromosomes (homologues) II Homologues condense
Shoot System. Root System. below-ground organs (roots) Dermal Tissue. Ground Tissue. Vascular Tissue. above-ground organs (leaves, stems, flowers)
 Shoot System above-ground organs (leaves, stems, flowers) Root System below-ground organs (roots) Dermal Tissue type of plant tissue that is the outer covering of the plant and serves as a protective barrier
Shoot System above-ground organs (leaves, stems, flowers) Root System below-ground organs (roots) Dermal Tissue type of plant tissue that is the outer covering of the plant and serves as a protective barrier
Plant Growth Regulators(NCERT)
 Plant Growth Regulators(NCERT) Promoters: 1. Auxins: -first isolated from urine, contains Zinc. -Natural: Indole Acetic Acid (IAA) Indole Butyric Acid (IBA) -Synthetic: Naphthalene Acetic Acid (NAA) 2-4
Plant Growth Regulators(NCERT) Promoters: 1. Auxins: -first isolated from urine, contains Zinc. -Natural: Indole Acetic Acid (IAA) Indole Butyric Acid (IBA) -Synthetic: Naphthalene Acetic Acid (NAA) 2-4
Basic Botany Master Gardener and Horticulture Training. Mark Heitstuman. WSU Asotin and Garfield County Director January 12, 2016
 Basic Botany 2016 Master Gardener and Horticulture Training Mark Heitstuman WSU Asotin and Garfield County Director January 12, 2016 Topics we ll discuss in Chapter 1- Basic Botany Plant life cycles Internal
Basic Botany 2016 Master Gardener and Horticulture Training Mark Heitstuman WSU Asotin and Garfield County Director January 12, 2016 Topics we ll discuss in Chapter 1- Basic Botany Plant life cycles Internal
PLANT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
 84 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 15 PLANT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Ethylene is used for a. Retarding ripening of tomatoes b. Hastening of ripening of fruits c. Slowing down
84 BIOLOGY, EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS CHAPTER 15 PLANT GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Ethylene is used for a. Retarding ripening of tomatoes b. Hastening of ripening of fruits c. Slowing down
Flowers Seeds Pollination Germination
 * Flowers Seeds Pollination Germination *In order for plants to be successful in many different environments they must be able to reproduce themselves. *The reproductive patterns of plants reflect the
* Flowers Seeds Pollination Germination *In order for plants to be successful in many different environments they must be able to reproduce themselves. *The reproductive patterns of plants reflect the
Types of Plants. Unit 6 Review 5/2/2011. Plants. A. pine B. moss C. corn plant D. bean plant E. liverwort
 Unit 6 Review Plants Initial questions are worth 1 point each. Each question will be followed by an explanation All questions will be asked a second time at the very end, each of those questions will be
Unit 6 Review Plants Initial questions are worth 1 point each. Each question will be followed by an explanation All questions will be asked a second time at the very end, each of those questions will be
Plant Development. Chapter 31 Part 1
 Plant Development Chapter 31 Part 1 Impacts, Issues Foolish Seedlings, Gorgeous Grapes Gibberellin and other plant hormones control the growth and development of plants environmental cues influence hormone
Plant Development Chapter 31 Part 1 Impacts, Issues Foolish Seedlings, Gorgeous Grapes Gibberellin and other plant hormones control the growth and development of plants environmental cues influence hormone
Plant Growth and Development Part I I
 Plant Growth and Development Part I I 1 Simply defined as: making with light Chlorophyll is needed (in the cells) to trap light energy to make sugars and starches Optimum temperature: 65 o F to 85 o F
Plant Growth and Development Part I I 1 Simply defined as: making with light Chlorophyll is needed (in the cells) to trap light energy to make sugars and starches Optimum temperature: 65 o F to 85 o F
Class XI Chapter 15 Plant Growth and Development Biology
 Question 1: Define growth, differentiation, development, dedifferentiation, redifferentiation, determinate growth, meristem and growth rate. (a) Growth It is an irreversible and permanent process, accomplished
Question 1: Define growth, differentiation, development, dedifferentiation, redifferentiation, determinate growth, meristem and growth rate. (a) Growth It is an irreversible and permanent process, accomplished
Class XI Chapter 15 Plant Growth and Development Biology
 Question 1: Define growth, differentiation, development, dedifferentiation, redifferentiation, determinate growth, meristem and growth rate. (a) Growth It is an irreversible and permanent process, accomplished
Question 1: Define growth, differentiation, development, dedifferentiation, redifferentiation, determinate growth, meristem and growth rate. (a) Growth It is an irreversible and permanent process, accomplished
Angiosperms: The Flowering Plants
 Slide 1 / 86 ngiosperms: The Flowering Plants rief Phylogeny of Plants Slide 2 / 86 Monocot icot This presentation will focus on angiosperms ngiosperm Gymnosperm Seeded Plants Non-Seeded plants Vascular
Slide 1 / 86 ngiosperms: The Flowering Plants rief Phylogeny of Plants Slide 2 / 86 Monocot icot This presentation will focus on angiosperms ngiosperm Gymnosperm Seeded Plants Non-Seeded plants Vascular
Chapter 25 Plant Processes. Biology II
 Chapter 25 Plant Processes Biology II 25.1 Nutrients and Transport Plants grow by adding new cells through cell division Must have steady supply of raw materials to build new cells Nutrients (most) Plants
Chapter 25 Plant Processes Biology II 25.1 Nutrients and Transport Plants grow by adding new cells through cell division Must have steady supply of raw materials to build new cells Nutrients (most) Plants
Unit 11: Plants Guided Reading Questions (75 pts total)
 Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Unit 11: Plants Guided Reading Questions (75 pts total) Chapter 29 Plant
Name: AP Biology Biology, Campbell and Reece, 7th Edition Adapted from chapter reading guides originally created by Lynn Miriello Unit 11: Plants Guided Reading Questions (75 pts total) Chapter 29 Plant
Plants can be either herbaceous or woody.
 Plant Structure Plants can be either herbaceous or woody. Herbaceous plants are plants with growth which dies back to the ground each year, in contrast with woody plants Most herbaceous plants have stems
Plant Structure Plants can be either herbaceous or woody. Herbaceous plants are plants with growth which dies back to the ground each year, in contrast with woody plants Most herbaceous plants have stems
Name Class Date. In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase.
 Assessment Chapter Test B Plant Responses In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. 1. thigmonasty 2. auxin 3. ethylene 4. phytochrome 5. abscisic
Assessment Chapter Test B Plant Responses In the space provided, write the letter of the description that best matches the term or phrase. 1. thigmonasty 2. auxin 3. ethylene 4. phytochrome 5. abscisic
REVIEW 7: PLANT ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY UNIT. A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned:
 Period Date REVIEW 7: PLANT ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY UNIT A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Gas exchange a. structure: stomates b. function: diffusion, supports
Period Date REVIEW 7: PLANT ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY UNIT A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Gas exchange a. structure: stomates b. function: diffusion, supports
-Producers & Cellular Energy Notes-
 -Producers & Cellular Energy Notes- Part 1 Plants LT 5.1 - I can describe basic information about plants, including the ways they move materials, are classified, reproduce, and evolved. What are plants?
-Producers & Cellular Energy Notes- Part 1 Plants LT 5.1 - I can describe basic information about plants, including the ways they move materials, are classified, reproduce, and evolved. What are plants?
What were some challenges that plants had to overcome as they moved to land? Drying out in the sun Conserving water Reproduction without water
 Classification of Plants (Ch. 22) The 3 major characteristics that make an organism a plant are: Multicellular eukaryote Cell walls with cellulose Carry out photosynthesis Plants most likely evolved from:
Classification of Plants (Ch. 22) The 3 major characteristics that make an organism a plant are: Multicellular eukaryote Cell walls with cellulose Carry out photosynthesis Plants most likely evolved from:
Asexual & Plant Reproduction
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ sexual & Plant Reproduction Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ sexual & Plant Reproduction Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
The Science of Plants in Agriculture Pl.Sci 102. Getting to Know Plants
 The Science of Plants in Agriculture Pl.Sci 102 Getting to Know Plants Growth and Development of Plants Growth and Development of Plants Why it s important to have knowledge about plant development. What
The Science of Plants in Agriculture Pl.Sci 102 Getting to Know Plants Growth and Development of Plants Growth and Development of Plants Why it s important to have knowledge about plant development. What
Unit 5: Plant Science. Mr. Nagel Meade High School
 Unit 5: Plant Science Mr. Nagel Meade High School Warm Up What significant roles do plants perform on Earth? How do you know? Name two modern issues that could be interrelated with plants. IB Syllabus
Unit 5: Plant Science Mr. Nagel Meade High School Warm Up What significant roles do plants perform on Earth? How do you know? Name two modern issues that could be interrelated with plants. IB Syllabus
Plant Anatomy and Physiology. What are the parts of the plant, and how do they work?
 Plant Anatomy and Physiology What are the parts of the plant, and how do they work? What is Classification GROUPING things according to their CHARACTERISTICS Plant Classification (5 Kingdoms) ANIMAL PLANT
Plant Anatomy and Physiology What are the parts of the plant, and how do they work? What is Classification GROUPING things according to their CHARACTERISTICS Plant Classification (5 Kingdoms) ANIMAL PLANT
TREES. Functions, structure, physiology
 TREES Functions, structure, physiology Trees in Agroecosystems - 1 Microclimate effects lower soil temperature alter soil moisture reduce temperature fluctuations Maintain or increase soil fertility biological
TREES Functions, structure, physiology Trees in Agroecosystems - 1 Microclimate effects lower soil temperature alter soil moisture reduce temperature fluctuations Maintain or increase soil fertility biological
Name Date Class. As you read Chapter 12, which begins on page 278 of your textbook, answer the following questions.
 CHAPTER 12 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Plant Processes As you read Chapter 12, which begins on page 278 of your textbook, answer the following questions. Strange but True! (p. 278) 1. How do wasps act as
CHAPTER 12 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Plant Processes As you read Chapter 12, which begins on page 278 of your textbook, answer the following questions. Strange but True! (p. 278) 1. How do wasps act as
Classification of Plants
 Classification of Plants Plants Aquatic Plants Ex. green algae Similarities between green algae and land plants: A) have chlorophylls a and b B) cellulose cell walls C) store food energy in the form of
Classification of Plants Plants Aquatic Plants Ex. green algae Similarities between green algae and land plants: A) have chlorophylls a and b B) cellulose cell walls C) store food energy in the form of
CONTROL SYSTEMS IN PLANTS
 AP BIOLOGY PLANTS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROL SYSTEMS IN PLANTS HORMONES MECHANISM FOR HORMONE ACTION Plant Form and Function Activity #5 page 1 CONTROL OF CELL ELONGATION Plant
AP BIOLOGY PLANTS FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROL SYSTEMS IN PLANTS HORMONES MECHANISM FOR HORMONE ACTION Plant Form and Function Activity #5 page 1 CONTROL OF CELL ELONGATION Plant
Biology 213 Exam 3 Practice Key
 Biology 213 Practice Key 1. (4) Explain the difference between a macronutrient and a micronutrient and cite two examples of each category? Macronutrients are the minerals needed by the plant in greater
Biology 213 Practice Key 1. (4) Explain the difference between a macronutrient and a micronutrient and cite two examples of each category? Macronutrients are the minerals needed by the plant in greater
This is sometimes referred to as an Organizational Hierarchy
 Chapter 11 Plant Structure and Function Introduction: Cell Specialization 1. Life in general In order to carry out the basic processes of life: Food production (photosynthesis) Intake of water and nutrients
Chapter 11 Plant Structure and Function Introduction: Cell Specialization 1. Life in general In order to carry out the basic processes of life: Food production (photosynthesis) Intake of water and nutrients
Reproduction & Development. 1 parent cell divides to form 2 daughter cells All offspring have exact same DNA as parent
 Living Environment Dr. Golub Reproduction & Development Asexual reproduction 1 parent cell divides to form 2 daughter cells All offspring have exact same DNA as parent Sexual Reproduction Requires 2 parents
Living Environment Dr. Golub Reproduction & Development Asexual reproduction 1 parent cell divides to form 2 daughter cells All offspring have exact same DNA as parent Sexual Reproduction Requires 2 parents
Water Potential. The physical property predicting the direction in which water will flow. Pressure
 Transport In Plants Water Potential The physical property predicting the direction in which water will flow Pressure water moves from high water potential to low water potential Water Potential (a) Left
Transport In Plants Water Potential The physical property predicting the direction in which water will flow Pressure water moves from high water potential to low water potential Water Potential (a) Left
Describe plant meristems. Where are they located? perpetually embryonic cells found at tips of roots and shoots (apical vs.
 Which conditions have the higher rate of transpiration? Light or dark: Humid or dry: Breezy or still air: Hot or warm: light (need CO 2 for photosyn.) dry (lower H 2 O potential out) breezy (greater evaporation)
Which conditions have the higher rate of transpiration? Light or dark: Humid or dry: Breezy or still air: Hot or warm: light (need CO 2 for photosyn.) dry (lower H 2 O potential out) breezy (greater evaporation)
Chapter 23: Plant Diversity and Life Cycles
 Chapter 23: Plant Diversity and Life Cycles Section 1: Introduction to Plants Cuticle: a waxy or fatty and watertight layer on the external wall of epidermal cells Spore: a reproductive cell or multicellular
Chapter 23: Plant Diversity and Life Cycles Section 1: Introduction to Plants Cuticle: a waxy or fatty and watertight layer on the external wall of epidermal cells Spore: a reproductive cell or multicellular
Plant. Responses and Adaptations. Plant Hormones. Plant Hormones. Auxins. Auxins. Hormones tell plants:
 Plant Responses and Adaptations Plant Hormones Hormone - a substance that is produced in 1 part of an organism & affects another part of the same individual (a chemical messenger) Plant hormones are chemical
Plant Responses and Adaptations Plant Hormones Hormone - a substance that is produced in 1 part of an organism & affects another part of the same individual (a chemical messenger) Plant hormones are chemical
Rapid Learning Center Presents. Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours. Plant Function. AP Biology Rapid Learning Series
 Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not endorse,
Rapid Learning Center Chemistry :: Biology :: Physics :: Math Rapid Learning Center Presents Teach Yourself AP Biology in 24 Hours *AP is a registered trademark of the College Board, which does not endorse,
Plants. Chapter Test A. Multiple Choice. 1 Pearson Education, Inc., or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
 Plants Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. The leaf s cuticle a. stores water. b. reduces evaporation. c. transports water in the leaf. d.
Plants Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. The leaf s cuticle a. stores water. b. reduces evaporation. c. transports water in the leaf. d.
Plants Notes. Plant Behavior Phototropism - growing towards light
 Plants Notes Plant Behavior Phototropism - growing towards light Geotropism - roots knowing which direction is down Thigmotropism - a plant's response to touch Ex. a vine wrapping around and climbing a
Plants Notes Plant Behavior Phototropism - growing towards light Geotropism - roots knowing which direction is down Thigmotropism - a plant's response to touch Ex. a vine wrapping around and climbing a
The Plant Kingdom If you were to walk around a forest, what would you see? Most things that you would probably name are plants.
 INTRODUCTION TO PLANTS The Plant Kingdom If you were to walk around a forest, what would you see? Most things that you would probably name are plants. Plants are abundant in almost every environment that
INTRODUCTION TO PLANTS The Plant Kingdom If you were to walk around a forest, what would you see? Most things that you would probably name are plants. Plants are abundant in almost every environment that
Biology 102 Environmental Biology Plants/Agriculture Unit Page 1 of 5
 Biology 102 Environmental Biology Plants/Agriculture Unit Page 1 of 5 Based on Mader, Sylvia S. 1996. Biology - 5th Ed. WCB and Cox, G.W. 1997. Conservation Biology - 2nd ed. WCB and Levine, J.S. and K.R.
Biology 102 Environmental Biology Plants/Agriculture Unit Page 1 of 5 Based on Mader, Sylvia S. 1996. Biology - 5th Ed. WCB and Cox, G.W. 1997. Conservation Biology - 2nd ed. WCB and Levine, J.S. and K.R.
Chapter 11 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
 Chapter 11 Meiosis and Sexual S Section 1: S Gamete: Haploid reproductive cell that unites with another haploid reproductive cell to form a zygote. S Zygote: The cell that results from the fusion of gametes
Chapter 11 Meiosis and Sexual S Section 1: S Gamete: Haploid reproductive cell that unites with another haploid reproductive cell to form a zygote. S Zygote: The cell that results from the fusion of gametes
Biology. Chapter 27. Plant Reproduction and Development. Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr. Cengage Learning 2015
 Biology Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr Chapter 27 Plant Reproduction and Development 27.1 What Are the Structure and Function of Flowers? Flowers: reproductive structures of angiosperms
Biology Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr Chapter 27 Plant Reproduction and Development 27.1 What Are the Structure and Function of Flowers? Flowers: reproductive structures of angiosperms
GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT
 CHAPTER IX Stages of Growth and Development VEGETATIVE GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT 4/6/2008 DMA: Chapter 9 Hartmann's Plant 1 Shoot and Root Systems The root system and the shoot system tend to maintain a balance:
CHAPTER IX Stages of Growth and Development VEGETATIVE GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT 4/6/2008 DMA: Chapter 9 Hartmann's Plant 1 Shoot and Root Systems The root system and the shoot system tend to maintain a balance:
Introduction to Plants
 Introduction to Plants Plants Alive What are the characteristics of plants? All plants are multicellular, which means their bodies are made up of more than one cell. Plants are eukaryotes, which means
Introduction to Plants Plants Alive What are the characteristics of plants? All plants are multicellular, which means their bodies are made up of more than one cell. Plants are eukaryotes, which means
Plant Growth and Development Part I. Levels of Organization
 Plant Growth and Development Part I Levels of Organization Whole Plant Organs Tissues Cells Organelles Macromolecules Levels of Organization Whole Plant Organs Tissues Cells Organelles Macromolecules 1
Plant Growth and Development Part I Levels of Organization Whole Plant Organs Tissues Cells Organelles Macromolecules Levels of Organization Whole Plant Organs Tissues Cells Organelles Macromolecules 1
1. Losing excessive amounts of water through evaporation may affect a plant s ability to carry out photosynthesis. Figure 22 1
 Plants Practice Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. Losing excessive amounts of water
Plants Practice Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. Losing excessive amounts of water
Lesson Overview Meiosis
 11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
Major Plant Hormones 1.Auxins 2.Cytokinins 3.Gibberelins 4.Ethylene 5.Abscisic acid
 Plant Hormones Lecture 9: Control Systems in Plants What is a Plant Hormone? Compound produced by one part of an organism that is translocated to other parts where it triggers a response in target cells
Plant Hormones Lecture 9: Control Systems in Plants What is a Plant Hormone? Compound produced by one part of an organism that is translocated to other parts where it triggers a response in target cells
Ch 25 - Plant Hormones and Plant Growth
 Ch 25 - Plant Hormones and Plant Growth I. Patterns of plant growth A. Plant continue to grow, even in old age. i.e. new leaves, needles, new wood, new cones, new flowers, etc. B. Meristem continues to
Ch 25 - Plant Hormones and Plant Growth I. Patterns of plant growth A. Plant continue to grow, even in old age. i.e. new leaves, needles, new wood, new cones, new flowers, etc. B. Meristem continues to
Plant Vocabulary. Define
 Define Plant Vocabulary 1. Photosynthesis 2. Eukaryotic 3. Monocot 4. Dicot 5. Cotyledon 6. Roots 7. Stems 8. Leaves 9. Xylem 10. Phloem 11. Capillary action 12. Meristem 13. Apical meristem 14. Vascular
Define Plant Vocabulary 1. Photosynthesis 2. Eukaryotic 3. Monocot 4. Dicot 5. Cotyledon 6. Roots 7. Stems 8. Leaves 9. Xylem 10. Phloem 11. Capillary action 12. Meristem 13. Apical meristem 14. Vascular
7/31/2014 WHAT IS LIGHT? SUPPLEMENTAL LIGHTING JOHANNA OOSTERWYK DC SMITH GREENHOUSE MANAGER UW-MADISON DEPARTMENT OF HORTICULTURE
 WHAT IS LIGHT? SUPPLEMENTAL LIGHTING JOHANNA OOSTERWYK DC SMITH GREENHOUSE MANAGER UW-MADISON DEPARTMENT OF HORTICULTURE Electromagnetic radiation Energy emitted by a light source Measured in watts Visible
WHAT IS LIGHT? SUPPLEMENTAL LIGHTING JOHANNA OOSTERWYK DC SMITH GREENHOUSE MANAGER UW-MADISON DEPARTMENT OF HORTICULTURE Electromagnetic radiation Energy emitted by a light source Measured in watts Visible
Kingdom: Plantae. Domain Archaea. Domain Eukarya. Domain Bacteria. Common ancestor
 Kingdom: Plantae Domain Eukarya Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya Common ancestor The First Plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the
Kingdom: Plantae Domain Eukarya Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya Common ancestor The First Plants For more than 3 billion years, Earth s terrestrial surface was lifeless life evolved in the
1.1 The Body of Seed Plants Seed Plants those
 1.1 The Body of Seed Plants Seed Plants those plants that make seeds. come in all shapes and sizes. have the same structures, which do the same job in all plants. Structures: Flowers each flower usually
1.1 The Body of Seed Plants Seed Plants those plants that make seeds. come in all shapes and sizes. have the same structures, which do the same job in all plants. Structures: Flowers each flower usually
Meiosis. Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and meiosis II
 Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
plant physiology and energy conversion to plant systems. identify the components and the functions of plant describe the processes of
 Plant Systems-AG1 Essential Questions: 1. How do plant classification, plant anatomy, and plant physiology affect the production and management of plants? 2. What are the necessary steps to Prepare and
Plant Systems-AG1 Essential Questions: 1. How do plant classification, plant anatomy, and plant physiology affect the production and management of plants? 2. What are the necessary steps to Prepare and
Propagating Plants Sexually
 Lesson C5 1 Propagating Plants Sexually Unit C. Plant and Soil Science Problem Area 5. Plant Propagation Lesson 1. Propagating Plants Sexually New Mexico Content Standard: Pathway Strand: Plant Systems
Lesson C5 1 Propagating Plants Sexually Unit C. Plant and Soil Science Problem Area 5. Plant Propagation Lesson 1. Propagating Plants Sexually New Mexico Content Standard: Pathway Strand: Plant Systems
Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline)
 Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline) Review the Life cycle of Fungi Characteristics of organisms in the Kingdom Plantae. Evolution of plants: Challenges and adaptations to living on land Highlights of
Plant Diversity & Evolution (Outline) Review the Life cycle of Fungi Characteristics of organisms in the Kingdom Plantae. Evolution of plants: Challenges and adaptations to living on land Highlights of
SPRING SEMESTER 2017 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE NAME: HR:
 SPRING SEMESTER 2017 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE NAME: HR: Parent signature for 10% bonus points on final: Chapter 5.1: Cell Cycle Notes 1. A cycle of growth, development, and division that most cells in an
SPRING SEMESTER 2017 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE NAME: HR: Parent signature for 10% bonus points on final: Chapter 5.1: Cell Cycle Notes 1. A cycle of growth, development, and division that most cells in an
Levels of Organization
 Plant Growth and Development Part I Levels of Organization Whole Plant Organs Tissues Cells Organelles Macromolecules Levels of Organization Whole Plant Organs Tissues Cells Organelles Macromolecules Plant
Plant Growth and Development Part I Levels of Organization Whole Plant Organs Tissues Cells Organelles Macromolecules Levels of Organization Whole Plant Organs Tissues Cells Organelles Macromolecules Plant
AP Biology. Evolution of Land Plants. Kingdom: Plants. Plant Diversity. Animal vs. Plant life cycle. Bryophytes: mosses & liverworts
 Kingdom: Plants Domain Eukarya Domain Domain Domain Eubacteria Archaea Eukarya 2007-2008 Common ancestor Evolution of Land Plants 500 mya land plants evolved special adaptations for life on dry land protection
Kingdom: Plants Domain Eukarya Domain Domain Domain Eubacteria Archaea Eukarya 2007-2008 Common ancestor Evolution of Land Plants 500 mya land plants evolved special adaptations for life on dry land protection
Meiosis. Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and meiosis II
 Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
PLANT GROWTH. IB Topic 9.3 & 9.4 Urry text ref: Ch 28 & 31
 PLANT GROWTH IB Topic 9.3 & 9.4 Urry text ref: Ch 28 & 31 INDETERMINATE GROWTH = throughout life meristems like stem cells in humans Shoot tip (shoot apical meristem and young leaves) lateral Axillary
PLANT GROWTH IB Topic 9.3 & 9.4 Urry text ref: Ch 28 & 31 INDETERMINATE GROWTH = throughout life meristems like stem cells in humans Shoot tip (shoot apical meristem and young leaves) lateral Axillary
Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28
 Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28 Characteristics of Plants p. 316 1. Multicellular eukaryotic organisms 2. Composed of tissues, organs and organ systems. 3. Cell walls made of cellulose. 4. Store energy as starch.
Topic 2: Plants Ch. 16,28 Characteristics of Plants p. 316 1. Multicellular eukaryotic organisms 2. Composed of tissues, organs and organ systems. 3. Cell walls made of cellulose. 4. Store energy as starch.
Ch. 22: Plant Growth, Reproduction & Response
 Ch. 22: Plant Growth, Reproduction & Response generally reproduce sexually, though many can also reproduce asexually. Some have lost ability to reproduce sexually. All plant lifecycles involve alternation
Ch. 22: Plant Growth, Reproduction & Response generally reproduce sexually, though many can also reproduce asexually. Some have lost ability to reproduce sexually. All plant lifecycles involve alternation
BIO10 Plant Lecture Notes ch. 17. Plant Kingdom
 Plant Kingdom Characteristics of the Plant Kingdom; eukaryotic, multicellular, sexually reproducing organisms autotroph feed themselves by photosynthesis Facts about members of this kingdom the dominant
Plant Kingdom Characteristics of the Plant Kingdom; eukaryotic, multicellular, sexually reproducing organisms autotroph feed themselves by photosynthesis Facts about members of this kingdom the dominant
Dr. Ramesh U4L3 Meiosis
 Dr. Ramesh U4L3 Meiosis The Cell Cycle and Cell Division: MEIOSIS The Cell Cycle and Cell Division KEY CONCEPT: Meiosis Halves the Nuclear Chromosome Content and Generates Diversity Organisms have two
Dr. Ramesh U4L3 Meiosis The Cell Cycle and Cell Division: MEIOSIS The Cell Cycle and Cell Division KEY CONCEPT: Meiosis Halves the Nuclear Chromosome Content and Generates Diversity Organisms have two
Unit 10 Plants/ Study Guide
 Name Class Date Section 20.1: Origins of Plant Life Unit 10 Plants/ Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Plant life began in the water and became adapted to land. VOCABULARY plant vascular system seed cuticle stomata
Name Class Date Section 20.1: Origins of Plant Life Unit 10 Plants/ Study Guide KEY CONCEPT Plant life began in the water and became adapted to land. VOCABULARY plant vascular system seed cuticle stomata
PLANT STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Read pages Re-read and then complete the questions below.
 PLANT STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Read pages 600-602. Re-read and then complete the questions below. 1. PLANT TISSUES - plant tissues are made up of 3 basic cell types: Parenchyma, Collenchyma or Sclerenchyma
PLANT STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Read pages 600-602. Re-read and then complete the questions below. 1. PLANT TISSUES - plant tissues are made up of 3 basic cell types: Parenchyma, Collenchyma or Sclerenchyma
Big Advantage!:Vegetative reproduction is a faster way to reproduce compared to sexual reproduction if the environment is favorable.
 DAY 5 OF CHAPTER 25 NOTES http://www.toto.com/misha/mavica/folliage2.jpg Asexual reproduction in plants is also known as vegetative reproduction. Methods of vegetative reproduction include plant structures
DAY 5 OF CHAPTER 25 NOTES http://www.toto.com/misha/mavica/folliage2.jpg Asexual reproduction in plants is also known as vegetative reproduction. Methods of vegetative reproduction include plant structures
Plant hormones: a. produced in many parts of the plant b. have many functions
 Plant hormones: a. produced in many parts of the plant b. have many functions Illustrated with 4 plant hormones: Gibberellins Auxin Cytokinins Ethylene Gibberellins Gibberellins illustrate how plant hormones
Plant hormones: a. produced in many parts of the plant b. have many functions Illustrated with 4 plant hormones: Gibberellins Auxin Cytokinins Ethylene Gibberellins Gibberellins illustrate how plant hormones
EXAM I HORT 326 FEBRUARY 15, Indicate the most correct answer in the left hand column (2 pts./question = 34 pts.).
 EXAM I HORT 326 FEBRUARY 15, 2005 Indicate the most correct answer in the left hand column (2 pts./question = 34 pts.). 1. 2. 3. 4. In apomixis the development of the embryo from the megaspore mother cell
EXAM I HORT 326 FEBRUARY 15, 2005 Indicate the most correct answer in the left hand column (2 pts./question = 34 pts.). 1. 2. 3. 4. In apomixis the development of the embryo from the megaspore mother cell
Level 2 Part II. MSU Extension Horticulture Associate Specialist. Pages Montana Master Gardener Handbook
 Plant Growth and Development Level 2 Part II Toby Day MSU Extension Horticulture Associate Specialist Pages 24-48 Montana Master Gardener Handbook Vegetative parts of a plant Definitions Apical bud or
Plant Growth and Development Level 2 Part II Toby Day MSU Extension Horticulture Associate Specialist Pages 24-48 Montana Master Gardener Handbook Vegetative parts of a plant Definitions Apical bud or
Level 2 Plant Growth and Development Part I Toby Day MSU Extension Horticulture Associate Specialist
 Level 2 Plant Growth and Development Part I Toby Day MSU Extension Horticulture Associate Specialist Pages 24-38 Montana Master Gardener Handbook Plant Growth and Development Whole Plant Organs Tissues
Level 2 Plant Growth and Development Part I Toby Day MSU Extension Horticulture Associate Specialist Pages 24-38 Montana Master Gardener Handbook Plant Growth and Development Whole Plant Organs Tissues
Plant Responses. NOTE: plant responses involve growth and changes in growth. Their movement is much slower than that of animals.
 Plant Responses A stimulus is anything that causes a reaction in an organism. Examples: light, gravity and temperature A response is the activity of an organism as a result of a stimulus. Examples: Growth,
Plant Responses A stimulus is anything that causes a reaction in an organism. Examples: light, gravity and temperature A response is the activity of an organism as a result of a stimulus. Examples: Growth,
What is a Plant? Plant Life Cycle. What did they evolve from? Original Habitat 1/15/2018. Plant Life Cycle Alternation of Generations
 What is a Plant? Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic (photosynthesis) Has cell walls containing cellulose Lack mobility (sessile) Display Alternation of Generations in their life cycle Introduction to
What is a Plant? Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic (photosynthesis) Has cell walls containing cellulose Lack mobility (sessile) Display Alternation of Generations in their life cycle Introduction to
Plant Responses and Adaptations Video
 Plant Responses and Adaptations Video Hormone -a substance that is produced in one part of an organism & affects another part of the same individual Plant hormones are chemical substances Control a plant
Plant Responses and Adaptations Video Hormone -a substance that is produced in one part of an organism & affects another part of the same individual Plant hormones are chemical substances Control a plant
Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic Sessile means cannot move Have cellulose in their cell walls
 1 Plant Characteristics: Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic Sessile means cannot move Have cellulose in their cell walls chloroplast vacuole Golgi body Cell wall nucleus mitochondria Cell membrane 2
1 Plant Characteristics: Multicellular Eukaryotic Autotrophic Sessile means cannot move Have cellulose in their cell walls chloroplast vacuole Golgi body Cell wall nucleus mitochondria Cell membrane 2
X-Sheet 3 Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis
 X-Sheet 3 Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis 13 Key Concepts In this session we will focus on summarising what you need to know about: Revise Mitosis (Grade 11), the process of meiosis, First Meiotic division,
X-Sheet 3 Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis 13 Key Concepts In this session we will focus on summarising what you need to know about: Revise Mitosis (Grade 11), the process of meiosis, First Meiotic division,
TOPIC 9.4 REPRODUCTION OF PLANTS
 TOPIC 9.4 REPRODUCTION OF PLANTS INTRO https://media1.britannica.com/eb-media/41/62941-004-e3f5377b.jpg IB BIO 9.4 2 Flowers are reproductive structures found in flowering plants. Their function is to
TOPIC 9.4 REPRODUCTION OF PLANTS INTRO https://media1.britannica.com/eb-media/41/62941-004-e3f5377b.jpg IB BIO 9.4 2 Flowers are reproductive structures found in flowering plants. Their function is to
Chapter 11 - Concept Mapping
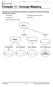 Chapter 11 - Concept Mapping Using the terms and phrases provided below, complete the concept map showing the process of meiosis. chromatids crossing-over haploid sperm and ovum homologous chromosomes
Chapter 11 - Concept Mapping Using the terms and phrases provided below, complete the concept map showing the process of meiosis. chromatids crossing-over haploid sperm and ovum homologous chromosomes
Plant Structure Size General Observations
 Kingdom Plantae Plant Structure Size General Observations Diversity Within the Plant Kingdom Pine Trees What is a plant? Multicellular Eukaryotes Perform Photosynthesis (base of all terrestrial food chains)
Kingdom Plantae Plant Structure Size General Observations Diversity Within the Plant Kingdom Pine Trees What is a plant? Multicellular Eukaryotes Perform Photosynthesis (base of all terrestrial food chains)
Sexual Reproduction. The two parent cells needed for sexual reproduction are called gametes. They are formed during a process known as meiosis.
 Sexual Reproduction Recall that asexual reproduction involves only one parent cell. This parent cell divides to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent. Sexual reproduction,
Sexual Reproduction Recall that asexual reproduction involves only one parent cell. This parent cell divides to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent. Sexual reproduction,
A. Stimulus Response:
 Plant Hormones A. Stimulus Response: A house plant on a windowsill grows light. If you rotate the plant, it reorients its growth until its leaves face the window again. The growth of a shoot towards light
Plant Hormones A. Stimulus Response: A house plant on a windowsill grows light. If you rotate the plant, it reorients its growth until its leaves face the window again. The growth of a shoot towards light
3 Plant Development and Responses
 CHAPTER 13 3 Plant Development and Responses SECTION Plant Processes 7.1.f, 7.5.a California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
CHAPTER 13 3 Plant Development and Responses SECTION Plant Processes 7.1.f, 7.5.a California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
