Absorbing Light Waves in Photosynthesis. Evan Bradley, Tara Popik, Ava Tillman
|
|
|
- Dustin Reeves
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Absorbing Light Waves in Photosynthesis Evan Bradley, Tara Popik, Ava Tillman
2 Question How do different wavelengths of light affect the rate of photosynthesis in leaves? spinach
3 Hypothesis/Prediction Prediction: If the spinach leaves are placed under blue or red light, the rate of photosynthesis will be faster than green light because chlorophyll a and b as well as several types of carotenoids are present in the spinach. This causes an absorption of energy from red and blue wavelengths which is used in photosynthesis. If the spinach leaves are placed under green light, they will cease to perform photosynthesis because green wavelengths are reflected by plants and not absorbed. Hypothesis: When spinach is in the presence of red or blue light, it will have a faster rate of photosynthesis compared to other wavelengths in the light spectrum due to the plants abundance of chlorophyll a and b as well as several carotenoids which help absorb red and blue wavelengths and turn them into chemical energy during photosynthesis.
4 Procedure First, 12 leaf disks were created with a hole punch. Then, a bicarbonate solution was made using a pinch of baking soda, a drop of dish soap, and approximately 25 ml water. The leaves were placed in the syringe and 1/3 of the syringe was filled with the bicarbonate and soap solution. A vacuum was formed using the syringe. Someone's finger was placed on the tip and the back of the syringe was pulled backward. This process was repeated approximately three times until the leaves sank to the bottom of the solution. After they were infiltrated, the leaves were dumped back into the cup containing the bicarbonate and soap solution. The cup was placed approximately 8 cm away from a light that was covered in clear cellophane. Every minute for 16 minutes, the number of leaves that floated to the top of the solution was counted and recorded. This entire process was repeated while covering the light with green, blue, and red cellophane.
5 Experimental Control The control for this experiment involved placing the leaf disks underneath the light covered with clear cellophane. This is an effective control because instead of radiating one specific wavelength, the clear cellophane would allow the light to radiate all of the different wavelengths of visible light. For the entire experiment, the control could be compared to as the ideal situation for a given plant to perform photosynthesis.
6 Data As time increases, more leaves rise. Out of the three colors/wavelengths tested, red light was the most effective with blue light trailing slightly.
7 Data Leaves Risen Minute Control Red Green Blue Total Count Total %
8 Discussion In this lab, the rate of photosynthesis under different colors and wavelengths of light was measured. In order to measure the rate at which photosynthesis occurs, the number of leaf disks that floated per minute was recorded. This method was used to measure the rate of photosynthesis. It is known to be effective, because the factor that allowed the leaf disks to float was the fact that they were producing oxygen, and since oxygen is a known product of photosynthesis, it can then be safely assumed that the leaf disks were performing photosynthesis Therefore, if more leaf disks rose during the allotted time, the rate of photosynthesis was quicker. Not all of the leaf disks rose at once, though, for some of the leaf disks had more direct access to the light source than others. From the data collected, it can be concluded that spinach leaves absorb red and blue light the best, showing that photosynthesis occurs at a faster rate when red or blue light is present compared to when green light was present. When the spinach leaves were exposed to the green light the rate of photosynthesis fell immensely and almost stopped completely. These results can be explained by understanding the way leaves absorb light.the spinach leaves contain chlorophyll a and b as well as several carotenoids which help absorb red and blue light wavelengths that they receive from the sun and turn into chemical energy during photosythesis. As for why green was not as effective as red or blue, this was due to the fact that spinach leaves reflect green light. Reflecting green light is what gives spinach its green color. Even though the desired results were produced, there is one unusual data point that did occur. Under the red light, during minutes ten to sixteen, a plateau was experienced, and no leaf disks rose. This is most likely simply due to the leaf disks access to the light. If all leaf disks had equal access to the light, the plateau would probably have been avoided.
9 Errors Possible sources of error in this lab include the spinach leaves exposure to small amounts of fluorescent light and the mass of the leaf disks. If the leaves were being exposed to small amounts of fluorescent light during the experiment, the data collected would be disqualified, for it would be impossible to draw valid conclusions without knowing what wavelengths were included due to the fact that the fluorescent light contains several different light wavelengths. This can be exemplified by simply using a prism with the fluorescent light and showing it true composition of several different wavelengths of light. At blame for this possible error would be the light bulbs in the classroom shining on the cup when it was being exposed to the green, red and blue wavelengths. This could have been prevented by shutting off these light bulbs or using some type of contraption to help block out those waves of light. The mass of the leaf disks not being uniform throughout would skew the results, for leaf disks with larger masses would require more oxygen to be produced in order to rise than ones with lower masses. Therefore, not all of the leaf disks would have had an equal opportunity to rise, since time was limited.
10 Conclusion The original hypothesis was supported by this experiment. It was originally stated that when the spinach leaves are placed under blue or red light, the rate of photosynthesis will be faster than green light because chlorophyll a and b as well as several types of carotenoids are present in the spinach. This causes an absorption of energy from red and blue wavelengths which is used in photosynthesis. This was supported by our experiment because red and blue light were the most effective when measuring the rate of photosynthesis compared to green light which was simply reflected by the leaves. For example, our data shows that red had 7 leaves float and blue light had 6 leaves float whereas green only had 5 leaves float. In conclusion, different wavelengths of light do affect the rate of photosynthesis because some wavelengths such as red and blue are absorbed and used by the plant whereas others like the green light are reflected.
Name: Hour: Photosynthesis in Leaf Disks
 Name: Hour: Photosynthesis in Leaf Disks Safety Information: While the solutions may be handled without gloves and may be disposed of in the sink drains, goggles must be worn during the experiment. Background
Name: Hour: Photosynthesis in Leaf Disks Safety Information: While the solutions may be handled without gloves and may be disposed of in the sink drains, goggles must be worn during the experiment. Background
Photosynthesis in Leaf Disks Teacher Preparation and Background Information
 AP Biology Name: Date: Photosynthesis in Leaf Disks Teacher Preparation and Background Information General Information: Solutions may be handled without gloves and may be disposed of in sink drains. In
AP Biology Name: Date: Photosynthesis in Leaf Disks Teacher Preparation and Background Information General Information: Solutions may be handled without gloves and may be disposed of in sink drains. In
CO2 Concentration & Photosynthesis. By Ellie Nir, Eliese Ottinger, and Zach Zatuchni
 CO2 Concentration & Photosynthesis By Ellie Nir, Eliese Ottinger, and Zach Zatuchni Question The purpose of this experiment was to examine how the concentration of carbon dioxide affects the rate of photosynthesis
CO2 Concentration & Photosynthesis By Ellie Nir, Eliese Ottinger, and Zach Zatuchni Question The purpose of this experiment was to examine how the concentration of carbon dioxide affects the rate of photosynthesis
The Effect of ph on Photosynthesis. By: Matthew Holmes, Rohit Kusupudi, Dylan Joyce
 The Effect of ph on Photosynthesis By: Matthew Holmes, Rohit Kusupudi, Dylan Joyce How does a change in ph affect the overall rate of photosynthesis in Spinach leaves? Prediction: Like in enzymes, ph will
The Effect of ph on Photosynthesis By: Matthew Holmes, Rohit Kusupudi, Dylan Joyce How does a change in ph affect the overall rate of photosynthesis in Spinach leaves? Prediction: Like in enzymes, ph will
MEASURING THE RATE OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS
 MEASURING THE RATE OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS QUESTION: What factors affect the rate of photosynthesis in plants? BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE Leaf disks float, normally. When the air spaces in the leaf are filled with
MEASURING THE RATE OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS QUESTION: What factors affect the rate of photosynthesis in plants? BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE Leaf disks float, normally. When the air spaces in the leaf are filled with
Materials Per Class Per Bench. 50 ml beakers 6 1. Hole punch 6 1. Forceps 6 1. Timers or a clock with second hand 6 1
 Photosynthesis Materials Per Class Per Bench 1% solution of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO 3 ) (by adding approximately 1g sodium bicarbonate to 100 ml DI water). Light sources, 60 watt bulb or higher 3 or
Photosynthesis Materials Per Class Per Bench 1% solution of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO 3 ) (by adding approximately 1g sodium bicarbonate to 100 ml DI water). Light sources, 60 watt bulb or higher 3 or
LAB: Photosynthesis in Leaf Disks
 Name Date Period LAB: Photosynthesis in Leaf Disks H O N O R S B I O L O G Y : U N I T 3 Introduction: Photosynthesis is a process in which plants convert light energy (sunlight) into usable chemical energy
Name Date Period LAB: Photosynthesis in Leaf Disks H O N O R S B I O L O G Y : U N I T 3 Introduction: Photosynthesis is a process in which plants convert light energy (sunlight) into usable chemical energy
Floating Disks: An Investigation of Photosynthesis Student Materials. Introduction Lab Protocol Data Collection Worksheet...
 Student Materials Introduction... 2 Lab Protocol... 3 Data Collection Worksheet... 5 Pre-Lab Questions... 6 Post-Lab Questions and Analysis... 7 Students You should read the Introduction and Lab Protocol
Student Materials Introduction... 2 Lab Protocol... 3 Data Collection Worksheet... 5 Pre-Lab Questions... 6 Post-Lab Questions and Analysis... 7 Students You should read the Introduction and Lab Protocol
Purpose. Procedure. Photosynthesis OVERVIEW:
 Photosynthesis OVERVIEW: During lab this week you will perform experiments to help you understand two of the basic processes that convert energy from one form to another in biological systems. Your investigations
Photosynthesis OVERVIEW: During lab this week you will perform experiments to help you understand two of the basic processes that convert energy from one form to another in biological systems. Your investigations
Floating Leaf Disc Lab
 Floating Leaf Disc Lab Background and Pre-Lab: Photosynthesis fuels ecosystems and replenishes the Earth's atmosphere with oxygen. Like all enzyme-driven reactions, the rate of photosynthesis can be measured
Floating Leaf Disc Lab Background and Pre-Lab: Photosynthesis fuels ecosystems and replenishes the Earth's atmosphere with oxygen. Like all enzyme-driven reactions, the rate of photosynthesis can be measured
Photosynthesis: How do plants get engery? Teacher Version
 Photosynthesis: How do plants get engery? Teacher Version In this lab, students explore the process of photosynthesis in spinach leaves. As oxygen is produced, the density of the leaves change and they
Photosynthesis: How do plants get engery? Teacher Version In this lab, students explore the process of photosynthesis in spinach leaves. As oxygen is produced, the density of the leaves change and they
Photosynthesis Lab. (adapted from: Photosynthesis.pdf )
 Photosynthesis Lab (adapted from: http://media.collegeboard.com/digitalservices/pdf/ap/bio-manual/bio_lab5- Photosynthesis.pdf ) Background and PreLab: Photosynthesis fuels ecosystems and replenishes the
Photosynthesis Lab (adapted from: http://media.collegeboard.com/digitalservices/pdf/ap/bio-manual/bio_lab5- Photosynthesis.pdf ) Background and PreLab: Photosynthesis fuels ecosystems and replenishes the
Photosynthesis. Introduction: Objectives:
 Photosynthesis Introduction: Photosynthesis is a process in which plants convert light energy (sunlight) into usable chemical energy (carbohydrates). Photosynthesis involves two simultaneous processes:
Photosynthesis Introduction: Photosynthesis is a process in which plants convert light energy (sunlight) into usable chemical energy (carbohydrates). Photosynthesis involves two simultaneous processes:
The Floating Leaf Disk Assay for Investigating Photosynthesis
 Background: The Floating Leaf Disk Assay for Investigating Photosynthesis Photosynthesis fuels ecosystems and replenishes the Earth s atmosphere with oxygen. Like all enzyme-driven reactions, the rate
Background: The Floating Leaf Disk Assay for Investigating Photosynthesis Photosynthesis fuels ecosystems and replenishes the Earth s atmosphere with oxygen. Like all enzyme-driven reactions, the rate
Turning Over a New Leaf (2)
 Turning Over a New Leaf (2) W 336-H Credits: Elizabeth Gall & Laura Moribe, University of Tennessee Extension Skill Level 7th Grade High School Biology Learner Outcomes Youth will be able to list two products
Turning Over a New Leaf (2) W 336-H Credits: Elizabeth Gall & Laura Moribe, University of Tennessee Extension Skill Level 7th Grade High School Biology Learner Outcomes Youth will be able to list two products
PHOTOSYNTHESIS What factors affect the rate of photosynthesis in living leaves?
 Big Cellular Processes: Energy and Communication INVESTIGATION 5 PHOTOSYNTHESIS What factors affect the rate of photosynthesis in living leaves? BACKGROUND Photosynthesis fuels ecosystems and replenishes
Big Cellular Processes: Energy and Communication INVESTIGATION 5 PHOTOSYNTHESIS What factors affect the rate of photosynthesis in living leaves? BACKGROUND Photosynthesis fuels ecosystems and replenishes
Cellular Processes: Energy and Communication
 Cellular Processes: Energy and Communication Big Idea 2 investigation 5 PHOTOSYNTHESIS What factors affect the rate of photosynthesis in living leaves? BACKGROUND Photosynthesis fuels ecosystems and replenishes
Cellular Processes: Energy and Communication Big Idea 2 investigation 5 PHOTOSYNTHESIS What factors affect the rate of photosynthesis in living leaves? BACKGROUND Photosynthesis fuels ecosystems and replenishes
Biology behind the Floating Disk Method
 Name: Bio AP Lab: Photosynthesis (Modified from AP Biology Investigative Labs) BACKGROUND: Photosynthesis fuels ecosystems and replenishes the Earth s atmosphere with oxygen. Like all enzyme-driven reactions,
Name: Bio AP Lab: Photosynthesis (Modified from AP Biology Investigative Labs) BACKGROUND: Photosynthesis fuels ecosystems and replenishes the Earth s atmosphere with oxygen. Like all enzyme-driven reactions,
INVESTIGATION 5 PHOTOSYNTHESIS What factors affect the rate of photosynthesis in living leaves?
 Cellular Processes: Energy and Communication Big Idea 2 INVESTIGATION 5 PHOTOSYNTHESIS What factors affect the rate of photosynthesis in living leaves? BACKGROUND Photosynthesis fuels ecosystems and replenishes
Cellular Processes: Energy and Communication Big Idea 2 INVESTIGATION 5 PHOTOSYNTHESIS What factors affect the rate of photosynthesis in living leaves? BACKGROUND Photosynthesis fuels ecosystems and replenishes
Lab 3: Photosynthesis & Respiration I
 BIOL 153L General Biology II Lab Black Hills State University Lab 3: Photosynthesis & Respiration I Photosynthesis is the process by which plants utilize light energy to fix carbon into chemical energy
BIOL 153L General Biology II Lab Black Hills State University Lab 3: Photosynthesis & Respiration I Photosynthesis is the process by which plants utilize light energy to fix carbon into chemical energy
Photosynthesis Investigation 1
 Photosynthesis Investigation 1 Part 1. Measuring the Rate of Photosynthesis You will use the "floating leaf disk" method to measure the rate of photosynthesis. To begin, cut several disks from a spinach
Photosynthesis Investigation 1 Part 1. Measuring the Rate of Photosynthesis You will use the "floating leaf disk" method to measure the rate of photosynthesis. To begin, cut several disks from a spinach
Plant Pigments and Photosynthesis
 Plant Pigments and Photosynthesis Introduction In photosynthesis, plant cells convert light energy into chemical energy that is stored in sugars and other organic compounds. Critical to the process is
Plant Pigments and Photosynthesis Introduction In photosynthesis, plant cells convert light energy into chemical energy that is stored in sugars and other organic compounds. Critical to the process is
Photo Finish. Investigative Lab 8. Racer 1 Young, actively growing, light green ivy leaf. Racer 2 Older, fully grown, dark green ivy leaf
 Name Class Date Photo Finish Comparing Rates of Photosynthesis Investigative Lab 8 Question Which will photosynthesize at a faster rate, a young ivy leaf or an older ivy leaf? Lab Overview In this investigation,
Name Class Date Photo Finish Comparing Rates of Photosynthesis Investigative Lab 8 Question Which will photosynthesize at a faster rate, a young ivy leaf or an older ivy leaf? Lab Overview In this investigation,
Bio 6 Photosynthesis Lab
 Bio 6 Photosynthesis Lab Introduction In order to survive, organisms require a source of energy and molecular building blocks to construct all of their biological molecules. The ultimate source of energy
Bio 6 Photosynthesis Lab Introduction In order to survive, organisms require a source of energy and molecular building blocks to construct all of their biological molecules. The ultimate source of energy
EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVE:
 BIG IDEA 2 EDVO-Kit: See Page 3 for storage instructions. OBJECTIVE: In this experiment, students will learn how to measure the rate of photosynthesis indirectly by using the floating leaf disk method.
BIG IDEA 2 EDVO-Kit: See Page 3 for storage instructions. OBJECTIVE: In this experiment, students will learn how to measure the rate of photosynthesis indirectly by using the floating leaf disk method.
GR QUIZ WITH ANS KEY Cellular Processes. Part I: Multiple Choice. 1. In leaf cell, the synthesis of ATP occurs in which of the following?
 GR QUIZ WITH ANS KEY Cellular Processes Part I: Multiple Choice 1. In leaf cell, the synthesis of ATP occurs in which of the following? I. Ribosomes II. Mitochondria III. Chloroplasts A. I only B. II only
GR QUIZ WITH ANS KEY Cellular Processes Part I: Multiple Choice 1. In leaf cell, the synthesis of ATP occurs in which of the following? I. Ribosomes II. Mitochondria III. Chloroplasts A. I only B. II only
carbon dioxide water oxygen
 HASPI Medical Biology Lab 06 Background/Introduction The Purpose of Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is a process that takes light energy and converts it into chemical energy. Why this is important: Because
HASPI Medical Biology Lab 06 Background/Introduction The Purpose of Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is a process that takes light energy and converts it into chemical energy. Why this is important: Because
SPINACH LEAF CHROMATOGRAPHY. Photosynthesis and Respiration Unit
 SPINACH LEAF CHROMATOGRAPHY Photosynthesis and Respiration Unit OBJECTIVE Identify the pigment chlorophyll and other colored pigments, and explain how the color that is seen is the color of light reflected
SPINACH LEAF CHROMATOGRAPHY Photosynthesis and Respiration Unit OBJECTIVE Identify the pigment chlorophyll and other colored pigments, and explain how the color that is seen is the color of light reflected
LAB 7 Photosynthesis
 LAB 7 Photosynthesis Introduction In order to survive, organisms require a source of energy and molecular building blocks to construct all of their biological molecules. The ultimate source of energy for
LAB 7 Photosynthesis Introduction In order to survive, organisms require a source of energy and molecular building blocks to construct all of their biological molecules. The ultimate source of energy for
EB Education Revision Guide. How to work with Photosynthesis: Part 2
 EB Education Revision Guide How to work with Photosynthesis: Part 2 Investigating Photosynthesis As photosynthesis is a chemical reaction, it can happen at different rates. You need to be able to investigate
EB Education Revision Guide How to work with Photosynthesis: Part 2 Investigating Photosynthesis As photosynthesis is a chemical reaction, it can happen at different rates. You need to be able to investigate
BIOLOGY 1101 LAB 3: PHOTOSYNTHESIS
 BIOLOGY 1101 LAB 3: PHOTOSYNTHESIS READING: Please read chapter 7 in your textbook prior to lab. INTRODUCTION: Photosynthesis is the process by which certain organisms use energy from sunlight and carbon
BIOLOGY 1101 LAB 3: PHOTOSYNTHESIS READING: Please read chapter 7 in your textbook prior to lab. INTRODUCTION: Photosynthesis is the process by which certain organisms use energy from sunlight and carbon
Biology 3A Laboratory Photosynthesis
 Biology 3A Laboratory Photosynthesis Objectives To observe the spectral absorbance of a mixed chlorophyll sample To separate and identify several common plant pigments using paper chromatography To investigate
Biology 3A Laboratory Photosynthesis Objectives To observe the spectral absorbance of a mixed chlorophyll sample To separate and identify several common plant pigments using paper chromatography To investigate
PLANT PIGMENTS AND PHOTOSYNTHESIS LAB
 AP BIOLOGY CELLULAR ENERGETICS ACTIVITY #6 NAME DATE HOUR PLANT PIGMENTS AND PHOTOSYNTHESIS LAB OBJECTIVES: After completing this lab you should be able to: 1. separate pigments and calculate their R f
AP BIOLOGY CELLULAR ENERGETICS ACTIVITY #6 NAME DATE HOUR PLANT PIGMENTS AND PHOTOSYNTHESIS LAB OBJECTIVES: After completing this lab you should be able to: 1. separate pigments and calculate their R f
For Examiner s Use Total EMPA mark Surname. Candidate. Number. Other Names
 Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Total EMPA mark Surname Other Names Notice to Candidate. The work you submit for assessment must be your own. If you copy from someone else or allow another
Centre Number Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Total EMPA mark Surname Other Names Notice to Candidate. The work you submit for assessment must be your own. If you copy from someone else or allow another
REACTIONS of PHOTOSYNTHESIS
 http://vilenski.org/science/safari/cellstructure/chloroplasts.html REACTIONS of PHOTOSYNTHESIS http://www.science.siu.edu/plant-biology/plb117/jpegs%20cd/0076.jpg Law of Thermodynamics *energy cannot be
http://vilenski.org/science/safari/cellstructure/chloroplasts.html REACTIONS of PHOTOSYNTHESIS http://www.science.siu.edu/plant-biology/plb117/jpegs%20cd/0076.jpg Law of Thermodynamics *energy cannot be
BIOL 221 Concepts of Botany
 BIOL 221 Concepts of Botany Topic 13: Photosynthesis A. Introduction Through photosynthesis, the abundant energy from the sun is collected and converted into chemical forms by photosynthetic organisms
BIOL 221 Concepts of Botany Topic 13: Photosynthesis A. Introduction Through photosynthesis, the abundant energy from the sun is collected and converted into chemical forms by photosynthetic organisms
#22 Visible Spectrum of Chlorophyll from Spinach
 #22 Visible Spectrum of Chlorophyll from Spinach Purpose: Chlorophyll is extracted from spinach. From a spectrum of the solution produced, the ratio of chlorophyll a and b present is estimated. Introduction:
#22 Visible Spectrum of Chlorophyll from Spinach Purpose: Chlorophyll is extracted from spinach. From a spectrum of the solution produced, the ratio of chlorophyll a and b present is estimated. Introduction:
1. Determination of the light absorption/emission properties of a set of colored filters.
 Sequencing leaf disc assay with related lessons. For Grade 9 Biology students: In its simplest form (see leaf disc assay protocol), the assay was used for grade 9 Biology students. This was done as a partnership
Sequencing leaf disc assay with related lessons. For Grade 9 Biology students: In its simplest form (see leaf disc assay protocol), the assay was used for grade 9 Biology students. This was done as a partnership
PHOTOSYNTHESIS UNIT PACKET
 This packet contains all of the papers you will need for the next week of class. You will be turning it in at the end of every class period, and picking it up in the beginning of class. Name: Class Period:
This packet contains all of the papers you will need for the next week of class. You will be turning it in at the end of every class period, and picking it up in the beginning of class. Name: Class Period:
Version A. AP* Biology: Photosynthesis. Name: Period
 Name: Period Version A AP* Biology: Photosynthesis Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by four suggested answers or completions. Select the one that is best in
Name: Period Version A AP* Biology: Photosynthesis Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by four suggested answers or completions. Select the one that is best in
Rakia Segev, Renuka Nannapaneni, Princy Sindurakar, Helena Kim, Hannah Read, and Suzanne Lijek. Journal of
 The Effect of the Stomatal Index on the Net Rate of Photosynthesis in the Leaves of Spinacia oleracea, Vinca minor, Rhododendron spp, Epipremnum aureum, and Hedera spp Rakia Segev, Renuka Nannapaneni,
The Effect of the Stomatal Index on the Net Rate of Photosynthesis in the Leaves of Spinacia oleracea, Vinca minor, Rhododendron spp, Epipremnum aureum, and Hedera spp Rakia Segev, Renuka Nannapaneni,
Terrestrial Sequestration Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Science
 Terrestrial Sequestration Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Science Goal: Students define key terms and link plant cellular functions based on experimental data and observations. Objectives: Students
Terrestrial Sequestration Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Science Goal: Students define key terms and link plant cellular functions based on experimental data and observations. Objectives: Students
AP Biology Lab 4 PLANT PIGMENTS AND PHOTOSYNTHESIS
 AP Biology Laboratory Date: Name and Period: AP Biology Lab 4 PLANT PIGMENTS AND PHOTOSYNTHESIS OVERVIEW In this lab you will: 1. separate plant pigments using chromatography, and 2. measure the rate of
AP Biology Laboratory Date: Name and Period: AP Biology Lab 4 PLANT PIGMENTS AND PHOTOSYNTHESIS OVERVIEW In this lab you will: 1. separate plant pigments using chromatography, and 2. measure the rate of
AP Biology. Investigation 5: Photosynthesis. Investigation 5: Photosynthesis. Investigation 5: Photosynthesis
 AP Biology Learning Objectives To design and conduct an experiment to explore the Investigation 5: Photosynthesis effect of certain factors, including different environmental variables, on the rate of
AP Biology Learning Objectives To design and conduct an experiment to explore the Investigation 5: Photosynthesis effect of certain factors, including different environmental variables, on the rate of
Lab #5 Multicellular Marine Primary Producers. Part 1: Photosynthesis and Photosynthetic Pigments
 Lab #5 Multicellular Marine Primary Producers Part 1: Photosynthesis and Photosynthetic Pigments Introduction Photosynthesis is a fundamental life process upon which all living things depend. Organisms
Lab #5 Multicellular Marine Primary Producers Part 1: Photosynthesis and Photosynthetic Pigments Introduction Photosynthesis is a fundamental life process upon which all living things depend. Organisms
The Power of Sunlight: Investigations in Photosynthesis & Respiration
 The Power of Sunlight: Investigations in Photosynthesis & Respiration Student s Guide In this module, you will join a research team to ask questions about photosynthesis and cellular respiration, then
The Power of Sunlight: Investigations in Photosynthesis & Respiration Student s Guide In this module, you will join a research team to ask questions about photosynthesis and cellular respiration, then
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6232824306* BIOLOGY 0610/62 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2017 1 hour Candidates answer
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6232824306* BIOLOGY 0610/62 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2017 1 hour Candidates answer
Photosynthesis: Limiting Factors
 Name: Date: Period: Photosynthesis: Limiting Factors Purpose: 1. To determine the effect of temperature, light intensity, and light color on the rate of photosynthesis. 2. To calculate the rate of photosynthesis
Name: Date: Period: Photosynthesis: Limiting Factors Purpose: 1. To determine the effect of temperature, light intensity, and light color on the rate of photosynthesis. 2. To calculate the rate of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis Questions C. 2. Chloro means- and plast-. Thylakoid. 3. Where does photosynthesis occur? In the c which contains chlorophyll.
 Photosynthesis Name- Date- Per. Station 1 Photosynthesis Questions C 1. Photo means - and synthesis -. 2. Chloro means- and plast-. Thylakoid. 3. Where does photosynthesis occur? In the c which contains
Photosynthesis Name- Date- Per. Station 1 Photosynthesis Questions C 1. Photo means - and synthesis -. 2. Chloro means- and plast-. Thylakoid. 3. Where does photosynthesis occur? In the c which contains
Photosynthesis Questions C. 2. Chloro means- and plast-. Thylakoid. 3. Where does photosynthesis occur? In the c which contains chlorophyll.
 Photosynthesis Name- Date- Per. Station 1 Photosynthesis Questions C 1. Photo means - and synthesis -. 2. Chloro means- and plast-. Thylakoid. 3. Where does photosynthesis occur? In the c which contains
Photosynthesis Name- Date- Per. Station 1 Photosynthesis Questions C 1. Photo means - and synthesis -. 2. Chloro means- and plast-. Thylakoid. 3. Where does photosynthesis occur? In the c which contains
Science Skills Station
 Science Skills Station Objective Analyze the effects of sunlight intensity on the rate of photosynthesis. Determine the importance of carbon dioxide on the rate of photosynthesis. Skills Utilized Infer
Science Skills Station Objective Analyze the effects of sunlight intensity on the rate of photosynthesis. Determine the importance of carbon dioxide on the rate of photosynthesis. Skills Utilized Infer
c = λν 10/23/13 What gives gas-filled lights their colors? Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms
 CHEMISTRY & YOU What gives gas-filled lights their colors? Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model 5. Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.3 Atomic and the Quantum Mechanical Model An electric
CHEMISTRY & YOU What gives gas-filled lights their colors? Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Revising the Atomic Model 5. Electron Arrangement in Atoms 5.3 Atomic and the Quantum Mechanical Model An electric
Photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the conversion of light energy to chemical energy and its subsequent use in the synthesis of organic molecules.
 Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is the conversion of light energy to chemical energy and its subsequent use in the synthesis of organic molecules. In its simplest form the process can be expressed as: Carbon
Photosynthesis Photosynthesis is the conversion of light energy to chemical energy and its subsequent use in the synthesis of organic molecules. In its simplest form the process can be expressed as: Carbon
Photosynthesis. Introduction
 Photosynthesis Learning Objectives: Explain the importance of photosynthetic pigments for transformation of light energy into chemical bond and the advantage of having more than one pigment in the same
Photosynthesis Learning Objectives: Explain the importance of photosynthetic pigments for transformation of light energy into chemical bond and the advantage of having more than one pigment in the same
1. What is the primary source of energy for most living things on earth?
 Photosynthesis Objectives: At the end of this lab you should be able to: 1. describe the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration 2. describe the function of a pigment and explain their
Photosynthesis Objectives: At the end of this lab you should be able to: 1. describe the relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration 2. describe the function of a pigment and explain their
Photosynthesis: Using Light to Make Food
 Chapter 7 Photosynthesis: Using Light to Make Food Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition
Chapter 7 Photosynthesis: Using Light to Make Food Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition
Cellular Processes: Energy and Communication
 Cellular Processes: Energy and Communication Big Idea 2 investigation 5 PHOTOSYNTHESIS What factors affect the rate of photosynthesis in living leaves? BACKGROUND Living systems require free energy and
Cellular Processes: Energy and Communication Big Idea 2 investigation 5 PHOTOSYNTHESIS What factors affect the rate of photosynthesis in living leaves? BACKGROUND Living systems require free energy and
Photosynthesis. Lab Exercise 9. Contents. Introduction. Objectives
 Lab Exercise Photosynthesis Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Action Spectrum 2 Activity.2 Effects of Temperature 4 Activity.3 Photosynthesis Experiment 4 Resutls Section 5 Objectives - Quantify
Lab Exercise Photosynthesis Contents Objectives 1 Introduction 1 Activity.1 Action Spectrum 2 Activity.2 Effects of Temperature 4 Activity.3 Photosynthesis Experiment 4 Resutls Section 5 Objectives - Quantify
The main form of energy from the sun is in the form of electromagnetic radiation. Visible radiation (white light) used for photosynthesis ROY G.
 PHOTOSYNTHESIS The main form of energy from the sun is in the form of electromagnetic radiation Visible radiation (white light) used for photosynthesis ROY G. BIV The electromagnetic spectrum A Red Object
PHOTOSYNTHESIS The main form of energy from the sun is in the form of electromagnetic radiation Visible radiation (white light) used for photosynthesis ROY G. BIV The electromagnetic spectrum A Red Object
PHOTOSYNTHESIS Student Packet SUMMARY
 PHOTOSYNTHESIS Student Packet SUMMARY LIVING SYSTEMS REQUIRE ENERGY AND MATTER TO MAINTAIN ORDER, GROW AND REPRODUCE Energy input must exceed energy lost and used by an organism. Organisms use various
PHOTOSYNTHESIS Student Packet SUMMARY LIVING SYSTEMS REQUIRE ENERGY AND MATTER TO MAINTAIN ORDER, GROW AND REPRODUCE Energy input must exceed energy lost and used by an organism. Organisms use various
Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis
 Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis Imagine an abandoned house that is falling apart. Restoring order to the house will require an input of energy (for example: hammering nails, applying paint). Living
Cellular Respiration and Photosynthesis Imagine an abandoned house that is falling apart. Restoring order to the house will require an input of energy (for example: hammering nails, applying paint). Living
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Name Period Date Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Biology A - STUDY GUIDE 1. Know the parts of the process. (MTS_LT1 ) a. The site (organelle) in a plant cell where photosynthesis takes place: b.
Name Period Date Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Biology A - STUDY GUIDE 1. Know the parts of the process. (MTS_LT1 ) a. The site (organelle) in a plant cell where photosynthesis takes place: b.
Recommended Resources: The following resources may be useful in teaching this
 Unit C: Plant Physiology Lesson 1: Understanding Plant Physiology Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1. Describe the process
Unit C: Plant Physiology Lesson 1: Understanding Plant Physiology Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1. Describe the process
Topic 8. Exercises on Photosynthesis. I. Where Photosynthesis Occurs in Plant Cells
 Topic 8. Exercises on Photosynthesis The pathways of photosynthesis and respiration are quite different. However, at the global level, one is perfectly complementary to the other as the end products of
Topic 8. Exercises on Photosynthesis The pathways of photosynthesis and respiration are quite different. However, at the global level, one is perfectly complementary to the other as the end products of
Understanding Light, Temperature, Air, and Water Effects on Plant Growth
 Lesson A2 7 Understanding Light, Temperature, Air, and Water Effects on Plant Growth Unit A. Horticultural Science Problem Area 2. Plant Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 7. Understanding Light, Temperature,
Lesson A2 7 Understanding Light, Temperature, Air, and Water Effects on Plant Growth Unit A. Horticultural Science Problem Area 2. Plant Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 7. Understanding Light, Temperature,
How colors of visible light affect the activity of photosynthesis,
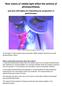 How colors of visible light affect the activity of photosynthesis, and why LED lights are interesting for production in greenhouses. Figure 1: Blue and red LED-light on spinach leaves On the basis of Inquiry-based
How colors of visible light affect the activity of photosynthesis, and why LED lights are interesting for production in greenhouses. Figure 1: Blue and red LED-light on spinach leaves On the basis of Inquiry-based
Complete the notes on photosynthesis in the spaces below.
 Section: 3.2 Name: Opening Activity: What type of energy is absorbed by pigment molecules in plant cells to start photosynthesis? Latin Root Word: Review of Old Information: ATP then provides the energy
Section: 3.2 Name: Opening Activity: What type of energy is absorbed by pigment molecules in plant cells to start photosynthesis? Latin Root Word: Review of Old Information: ATP then provides the energy
Effect of Light Intensity on the Re-opening time of Leaves of Sensitive Plant (Mimosa Pudica)
 Effect of Light Intensity on the Re-opening time of Leaves of Sensitive Plant (Mimosa Pudica) S5 Choy Hiu Ching Fung Hang Tsz Leung Tsz Wan Tang Chi Yi Yau Tsz Ping Yam Long Hin Aims To find out the relationship
Effect of Light Intensity on the Re-opening time of Leaves of Sensitive Plant (Mimosa Pudica) S5 Choy Hiu Ching Fung Hang Tsz Leung Tsz Wan Tang Chi Yi Yau Tsz Ping Yam Long Hin Aims To find out the relationship
Unit C: Plant Physiology. Lesson 2: Understanding Light, Temperature, Air, and Water Effects on Plant Growth
 Unit C: Plant Physiology Lesson 2: Understanding Light, Temperature, Air, and Water Effects on Plant Growth 1 Terms Day neutral plant (DNP) Foot-candles Hardiness Long day plant (LDP) Photoperiod Short
Unit C: Plant Physiology Lesson 2: Understanding Light, Temperature, Air, and Water Effects on Plant Growth 1 Terms Day neutral plant (DNP) Foot-candles Hardiness Long day plant (LDP) Photoperiod Short
Photosynthesis. 1) Heterotrophs: 2) Autotrophs: 3) Phytoplankton:
 CAPE BIO UNIT 2 Lesson 1-10 th Sept 2012 1 Define the following: Photosynthesis 1) Heterotrophs: 2) Autotrophs: 3) Phytoplankton: Photosynthesis is simply the process by which organisms convert solar energy
CAPE BIO UNIT 2 Lesson 1-10 th Sept 2012 1 Define the following: Photosynthesis 1) Heterotrophs: 2) Autotrophs: 3) Phytoplankton: Photosynthesis is simply the process by which organisms convert solar energy
Virtual Lab 5 Photosynthesis
 Name Period Assignment # Virtual Lab 5 Photosynthesis http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/lab4/intro.html 1) Define photosynthesis 2) Define chlorophyll Click 4-I Chromatography on the
Name Period Assignment # Virtual Lab 5 Photosynthesis http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/lab4/intro.html 1) Define photosynthesis 2) Define chlorophyll Click 4-I Chromatography on the
Sweet Sunshine Lexile 1060L
 Sweet Sunshine Lexile 1060L 1 Photosynthesis is the foundation of most life on earth. The basic chemistry of photo-synthesis was explained by several scientists in the 16 th, 17 th, and 18 th centuries.
Sweet Sunshine Lexile 1060L 1 Photosynthesis is the foundation of most life on earth. The basic chemistry of photo-synthesis was explained by several scientists in the 16 th, 17 th, and 18 th centuries.
Can Photosynthesis Occur at Saturn?
 Can Photosynthesis Occur at Saturn? Middle grades Lesson Summary Students will learn the basic principle of photosynthesis and how light intensity diminishes as a function of distance from the light source.
Can Photosynthesis Occur at Saturn? Middle grades Lesson Summary Students will learn the basic principle of photosynthesis and how light intensity diminishes as a function of distance from the light source.
Photosynthesis. Objectives. Standards (NGSS and Common Core) For state specific standards visit edu.zspace.com/activities.
 Photosynthesis Lesson Overview Photosynthesis occurs when plants use sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars and oxygen. This is essential for plants because they need to produce their
Photosynthesis Lesson Overview Photosynthesis occurs when plants use sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars and oxygen. This is essential for plants because they need to produce their
Light and Photosynthesis. Supplemental notes Lab 4 Horticultural Therapy
 Light and Photosynthesis Supplemental notes Lab 4 Horticultural Therapy Light The Electromagnetic Spectrum is a continuum of all electromagnetic waves arranged according to frequency and wavelength, the
Light and Photosynthesis Supplemental notes Lab 4 Horticultural Therapy Light The Electromagnetic Spectrum is a continuum of all electromagnetic waves arranged according to frequency and wavelength, the
Final. Mark Scheme. Biology BIO6X. (Specification 2410) Unit 6X: Externally Marked Practical Assignment
 Version 1.0 General Certificate of Education (A-level) June 2013 Biology BIO6X (Specification 2410) Unit 6X: Externally Marked Practical Assignment Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal
Version 1.0 General Certificate of Education (A-level) June 2013 Biology BIO6X (Specification 2410) Unit 6X: Externally Marked Practical Assignment Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal
PHOTOSYNTHESIS. Trapping the Sun s Energy
 1 PHOTOSYNTHESIS Trapping the Sun s Energy 2 Energy is trapped in chemical bonds But where does energy come from? GLUCOSE 3 Carbohydrate sugar molecule Simple sugar, known as a monosaccharide(ex: fructose,
1 PHOTOSYNTHESIS Trapping the Sun s Energy 2 Energy is trapped in chemical bonds But where does energy come from? GLUCOSE 3 Carbohydrate sugar molecule Simple sugar, known as a monosaccharide(ex: fructose,
PHOTOSYNTHESIS LAB. PS What is it? Why is PS Important? BISC 104 Principles of Biology
 BISC 104 Principles of Biology PHOTOSYNTHESIS LAB PS What is it? Photo (use of light) Synthesis (to synthesize sugar, related biomolecules) Sunlight (Energy) is required because: 6 H2O + 6 CO2 C6H12O6
BISC 104 Principles of Biology PHOTOSYNTHESIS LAB PS What is it? Photo (use of light) Synthesis (to synthesize sugar, related biomolecules) Sunlight (Energy) is required because: 6 H2O + 6 CO2 C6H12O6
Compound. Math Focus. What are compounds? What is a chemical reaction? How are compounds used in everyday life?
 CHAPTER 3 2 Compounds SECTION Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are compounds? What is a chemical reaction?
CHAPTER 3 2 Compounds SECTION Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are compounds? What is a chemical reaction?
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Introduction... 2 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration are energy conversion processes... 2 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration are enzyme pathways... 3 Photosynthesis...
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Introduction... 2 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration are energy conversion processes... 2 Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration are enzyme pathways... 3 Photosynthesis...
Chapter 7. Photosynthesis: Using Light to Make Food. Lectures by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 7 Photosynthesis: Using Light to Make Food PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean
Chapter 7 Photosynthesis: Using Light to Make Food PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean
Photosynthesis: Using Light to Make Food
 Chapter 7 Photosynthesis: Using Light to Make Food PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition Eric Simon, Jane Reece, and Jean Dickey Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology,
Chapter 7 Photosynthesis: Using Light to Make Food PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition Eric Simon, Jane Reece, and Jean Dickey Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology,
Name. Pre-Test. Directions: Circle the T if a statement is true or F if it is false (F). 1. Matter always stays the same.
 1 Pre-est Directions: Circle the if a statement is true or if it is false (). 1. Matter always stays the same. 2. A physical change is a change in size, shape or phase of matter, without the matter changing
1 Pre-est Directions: Circle the if a statement is true or if it is false (). 1. Matter always stays the same. 2. A physical change is a change in size, shape or phase of matter, without the matter changing
Photosynthesis Life Is Solar Powered!
 Photosynthesis Life Is Solar Powered! What Would Plants Look Like On Alien Planets? 1 Why Would They Look Different? Different Stars Give off Different types of light or Electromagnetic Waves The color
Photosynthesis Life Is Solar Powered! What Would Plants Look Like On Alien Planets? 1 Why Would They Look Different? Different Stars Give off Different types of light or Electromagnetic Waves The color
Photo Rate Lab Leaf Disk Assay. Period
 Photo Rate Lab Leaf Disk Assay Period 2 2016 Claim: Plants that utilize the C3 method of photosynthesis will have the highest rate of photosynthesis when tested under direct light and during the day. Evidence:
Photo Rate Lab Leaf Disk Assay Period 2 2016 Claim: Plants that utilize the C3 method of photosynthesis will have the highest rate of photosynthesis when tested under direct light and during the day. Evidence:
FACTORS AFFECTING THE RATE OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS
 AP BIOLOGY CELLULAR ENERGETICS ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR FACTORS AFFECTING THE RATE OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS OBJECTIVES: The purpose of this activity is to: Demonstrate how photosynthetic rates in different
AP BIOLOGY CELLULAR ENERGETICS ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR FACTORS AFFECTING THE RATE OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS OBJECTIVES: The purpose of this activity is to: Demonstrate how photosynthetic rates in different
I. Energy for Life. Energy in Ecosystems Did you know you were solar powered? IN: 11/4/2018. Fill in the blanks to complete the reaction: C H O + 6 2
 11/4/2018 Energy in Ecosystems Did you know you were solar powered? IN: Fill in the blanks to complete the reaction: Light 6 2 + 6 2 Chlorophyll C H O + 6 2 Write the equation for photosynthesis in words.
11/4/2018 Energy in Ecosystems Did you know you were solar powered? IN: Fill in the blanks to complete the reaction: Light 6 2 + 6 2 Chlorophyll C H O + 6 2 Write the equation for photosynthesis in words.
Quantum Dots and Colors Worksheet Answers
 Quantum Dots and Colors Worksheet Answers Background Quantum dots are semiconducting nanoparticles that are able to confine electrons in small, discrete spaces. Also known as zero-dimensional electronic
Quantum Dots and Colors Worksheet Answers Background Quantum dots are semiconducting nanoparticles that are able to confine electrons in small, discrete spaces. Also known as zero-dimensional electronic
4.1. Photosynthesis Light-Dependent Reactions
 4.1 Photosynthesis Light-Dependent Reactions Photosynthesis Each year, Canada s boreal forest convert 12.5 million tonnes of carbon into energy-rich compounds for billions of organisms Photosynthesis
4.1 Photosynthesis Light-Dependent Reactions Photosynthesis Each year, Canada s boreal forest convert 12.5 million tonnes of carbon into energy-rich compounds for billions of organisms Photosynthesis
Separation and Identification of Plant Pigments Dr. Gergens - SD Mesa College
 Separation and Identification of Plant Pigments Dr. Gergens - SD Mesa College PURPOSE In this experiment, the photosynthetic pigments common to all flowering plants will be extracted by liquidliquid extraction.
Separation and Identification of Plant Pigments Dr. Gergens - SD Mesa College PURPOSE In this experiment, the photosynthetic pigments common to all flowering plants will be extracted by liquidliquid extraction.
2/22/2019 NEW UNIT! Chemical Interactions. Atomic Basics #19
 NEW UNIT! Chemical Interactions Atomic Basics #19 1 Vocabulary: Matter: Anything that has mass and takes up space. Atom: the smallest particle of matter. Element: A pure substance made up of only one type
NEW UNIT! Chemical Interactions Atomic Basics #19 1 Vocabulary: Matter: Anything that has mass and takes up space. Atom: the smallest particle of matter. Element: A pure substance made up of only one type
Quantum theory and models of the atom
 Guess now. It has been found experimentally that: (a) light behaves as a wave; (b) light behaves as a particle; (c) electrons behave as particles; (d) electrons behave as waves; (e) all of the above are
Guess now. It has been found experimentally that: (a) light behaves as a wave; (b) light behaves as a particle; (c) electrons behave as particles; (d) electrons behave as waves; (e) all of the above are
Plant Pigments and Photosynthesis. By: Laura Cameron, Sarah Soppe, and Zahra Naseer
 Plant Pigments and Photosynthesis By: Laura Cameron, Sarah Soppe, and Zahra Naseer The purpose of the lab was to separate the various pigments in spinach leaves through the process of chromatography. Purpose
Plant Pigments and Photosynthesis By: Laura Cameron, Sarah Soppe, and Zahra Naseer The purpose of the lab was to separate the various pigments in spinach leaves through the process of chromatography. Purpose
Let light motivate your flowers
 Let light motivate your flowers LightDec Horticulture Light recipes from LEDIG are the best in this market. Their recommendations increased my profits in year one by 23% LED Solutions from LEDIG LED Industrial
Let light motivate your flowers LightDec Horticulture Light recipes from LEDIG are the best in this market. Their recommendations increased my profits in year one by 23% LED Solutions from LEDIG LED Industrial
Using the spectrometer
 MATERIALS LIST Investigation 13.1 Stars and Spectroscopy 4 Spectrometer (also known as a spectroscope) 4 Colored pencils 4 Incandescent light source ChAPTER 13 The Universe How can we use a spectrometer
MATERIALS LIST Investigation 13.1 Stars and Spectroscopy 4 Spectrometer (also known as a spectroscope) 4 Colored pencils 4 Incandescent light source ChAPTER 13 The Universe How can we use a spectrometer
Waves. Electromagnetic. No medium required. Can travel in a vacuum (empty space).
 Electromagnetic Waves Made up of vibrating electric and magnetic fields. Carry energy. Move in the form of both a wave and a particle. No medium required. Can travel in a vacuum (empty space). Demonstrate
Electromagnetic Waves Made up of vibrating electric and magnetic fields. Carry energy. Move in the form of both a wave and a particle. No medium required. Can travel in a vacuum (empty space). Demonstrate
... + water (3)
 1 (a) Complete the equation for photosynthesis.... + water... +... (3) (b) The rate of photosynthesis in a plant depends on several factors in the environment. These factors include light intensity and
1 (a) Complete the equation for photosynthesis.... + water... +... (3) (b) The rate of photosynthesis in a plant depends on several factors in the environment. These factors include light intensity and
Biology Slide 1 of 28
 Biology 1 of 28 8-2 Photosynthesis: An Overview 2 of 28 8-2 Photosynthesis: An Overview 8-2 Photosynthesis: An Overview The key cellular process identified with energy production is photosynthesis. Photosynthesis
Biology 1 of 28 8-2 Photosynthesis: An Overview 2 of 28 8-2 Photosynthesis: An Overview 8-2 Photosynthesis: An Overview The key cellular process identified with energy production is photosynthesis. Photosynthesis
Energy Transformations Activities Students engage in different activities to observe energy changing form!
 Energy Transformations Activities Students engage in different activities to observe energy changing form! Name: Energy Labs and Activities Activity 1: Static Electricity Glue this side down Procedure:
Energy Transformations Activities Students engage in different activities to observe energy changing form! Name: Energy Labs and Activities Activity 1: Static Electricity Glue this side down Procedure:
Name Class Date. Chapter 18 The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Light Investigation 18A
 Chapter 18 The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Light Investigation 18A Predicting Spectra Background Information Some materials are transparent to nearly all frequencies of visible light. This means that
Chapter 18 The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Light Investigation 18A Predicting Spectra Background Information Some materials are transparent to nearly all frequencies of visible light. This means that
