Sugar Beet Petiole Tests as a Measure Of Soil Fertility
|
|
|
- Posy Griffith
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sugar Beet Petiole Tests as a Measure Of Soil Fertility ROBERT J. BROWN 1 The beet grower who owns his farm can maintain the fertility of the soil at a high point with no fear that money spent on surplus plant nutrients during one season will be lost. The tenant grower too often is in the position where the only certain returns he can see are in the current season. And therefore the tendency is merely to maintain such farms, at best, at the range of the dividing line between sufficiency and deficiency. The low level of the average beet yield indicates that a larger percentage of the farms are in this class. The growers in this class require that any fertilizer treatment produce an immediate response which repays for the treatment. Soil tests measure the available phosphate and potash with a satisfactory degree of accuracy, but give little useful information regarding nitrogen. In the present discussion we have only slight interest in potash, since field trials on our soils, lowest in available potash, have not indicated a potash deficiency. Although soil tests measure the available phosphate with a high degree of accuracy, various factors, such as the variable requirement of the sugar beet for phosphate in different environments, make the interpretation of the results of the soil test unsatisfactory on a large percentage of soils. Too many soils fall in the doubtful classification. It appears logical that the plant itself which is the integration of all factors soil nutrient status, climate, etc. may be used to determine fertilization requirements. To be useful in the sugar beet crop it must be possible to gain the desired information sufficiently early in the season to permit of correction in the current crop. Plant tissue tests are steadily becoming more popular as a measure of soil fertility. Investigators are not agreed as to which part of the plant should be tested, nor as to how 1ests should be made. One school favors tests on conducting tissue for non-assimilated plant nutrients. The other uses leaf tissue and analyzes for total content of those constituents. Various investigators have found that the sugar beet petiole is a good indicator of the supply of available nutrients, and the following presents results of petiole tests made in the Great Western Sugar Company area during recent years. Petiole tests were made on cold water extracts of petiole matter ground in a mortar or food blender. All results are reported on the basis of parts per million of nitrate nitrogen and phosphate phos- Great Western Sugar Company research laboratory.
2 PROCEEDINGS FOURTH GENERAL MEETING 97 phorus on original petiole matter. The earlier samples consisted of 10 to 12 petioles taken from as many randomly selected beets. In 1942 an accurate sampling technique was developed and since that date larger samples have been used. Tn 1940 the primary interest was in phosphate, and periodic soil and petiole tests were made on samples from six widely scattered fields. Results of individual petiole tests were very erratic. Below are given the results of the average petiole tests on three samplings during June, July, and August, compared with beet yields. Table 1. Petiole tests for phosphate and beet yields, p.p.m. of P Root yield Field No. in petioles Tons per acre Soil and petiole tests showed excellent correlation. 11 is curious that yield varies inversely with the phosphate test. There was no visual evidence that nitrogen was a controlling factor in these yields. In 1941 periodic petiole tests were made on 66 commercial beet fields in the Colorado and Nebraska area of the Great Western Sugar Company. Results were very erratic and in table 2 are given average results of tests on 46 fields sampled during July, August, and September, grouped according to beet yield. Table 2. Periodic petiole tests, Average of petiole tests during July, August, and September. 17 to to to 13.9 Less than Yield group +20 tons tons tons tons 11 tons No. of fields in group p.p.m. N p.p.m. N p.p.m. N p.p.m. N p.p.m. N July August September p.p.m. P p.p.m. P p.p.m. P p.p.m. P p.p.m. P July August September Some may be inclined to discount the significance of group averages, especially in the low-yield groups, since reciprocal relations of N and P are often observed. This is most common in the high-yield groups, when high yield associated with very low nitrate test is often accompanied by high phosphate test, and vice versa. Among the 14 fields comprising the two low-yield groups, only 2 gave results indi-
3 98 AMERICAN SOCIETY SUGAR-BEET TECHNOLOGISTS eating that low phosphate was responsible for accumulation of nitrates and only 1 indicated that high phosphate accumulated as the result of low nitrates. In 1942 petiole tests were made with the primary object of determining sampling requirements necessary to provide a petiole sample of known error limits. The results of this work were published in Soil Science, Vol. 56, p. 213 (Sept. 1943). Since that date the samples taken have consisted of a composite of single petioles from one of the group of youngest mature leaves from 72 to 75 randomly selected beets. This sample has an error limit of not over 20 percent at the 9 to 1 probability ratio. The 1942 work has little bearing on the present discussion, but it may be pointed out that the various fields sampled during this work showed almost complete loss of nitrates by the end of July. Accurate samples were taken periodically from 10 fields in a single factory district in A summary of average results is given in table 3. The figures shown are averages of results from fields grouped according to yield. Figures on individual fields are of little value, and on averages of a small number of fields they are of doubtful value. Results from one field, far out of line, are not included in the averages. Table 3. Periodic petiole tests, Yield group + 17 tons 17 to 10 tons Minus l0 tons Fields in group July August September p. p. m. N p.p.m. N p.p.m. N July August September p.p.m. P p.p.m. P p. p. m. P One field which yielded 17.5 tons of beets showed practically no nitrates at any time during the season. The average phosphate test was 116 p.p.m. The 1945 tests were made on five pairs of fields in five factory districts in Colorado and Nebraska, sampled periodically throughout the season. Each pair consisted of one fertile and one infertile field. The average results of petiole tests on fields grouped according to yield are given in table 4.
4 PROCEEDINGS FOURTH GENERAL MEETING 90 Table 4. Periodic petiole tests, Although the evidence as presented does not indicate it, 1941 and 1945 were years when nitrates held up generally high until late in the season, and 1942 and 1944 were seasons of early depletion of nitrates. In 1941 we had enough individuals in a group to give the averages definite significance. In 1945 two fields in the high-yield group were such that high yield was obtained with nitrate content of petioles at a low level. In 1944 one field in the medium-yield group gave petioles exceedingly low in phosphate and highest of all in September tests in nitrate, and thus upset the group average completely. In addition in 1944 an unknown source of interference with the nitrate test caused all low tests to be read falsely high. Tn the following table the results of the 3 years are compared on the basis of yield produced per unit of N and P. For this purpose the July and August results are used. The average yield in each group is divided by 1he average petiole test of that group. The highest factor obtained on any group in 1941 is taken as 100 and all others are calculated proportionally. Table 5 N mid P performance factors in and 1945.
5 100 AMERICAN SOCIETY SUGAR-BEET TECHNOLOGISTS This table brings out a number of valuable points. If fertility level were the controlling factor in the low-yield fields, the highest performance factors for phosphate or nitrate or both should be found in those groups, since they never have an excess of at least one of the elements. Therefore our interest at. present turns to the medium- to high-yield groups. In 1941, a year of high nitrate levels and high average yield, phosphate appeared to control the yield except in the highest yield group where a slight excess probably existed and nitrate controlled. Tn 1944, a year of early nitrate depletion, nitrate performance jumped up. as would be expected. Low phosphate performance would be expected. In two of the three groups it was demonstrated, and on one of the two high-yield fields it occurred also. In 1945, a year of low yields and high nitrates, nitrate performance was low. The explanation of the 102 factor on the high-yield group is that the nitrate tests on two of the high-yield fields dropped to low values early in the season, yet the field produced high yields. In a high nitrate season, high phosphate performance might be expected. If one could explain why during 1945 the activities of the beet went toward developing tops rather than roots, he could probably explain why phosphate performance was low in During the 1945 season a number of potash tests were run in an attempt to learn whether inter-relations of N, P, and K content of petioles might show something about fertility which tests for individual components do not indicate. The tests showed increasing potash content of petioles as the season progressed. On August 6 potash content of petioles ranged from 5,000 to 8,000 parts per million of K 2 -O. Tests on high-yield fields averaged lower than tests on lowyield fields, but no inter-relation of N, P, and K could be worked out which was definitely associated with yields. It has been necessary to condense the results we have obtained beyond a point where anyone examining those results can find just what has gone into them. The best that can be done is to point out what an examination of all results indicates. If petiole samples are taken from various plots on the same field, differences in fertility will be reflected by differences in results of tests. But if a single petiole sample is taken from a field, interpretation of the results of the tests is questionable, unless the results are high. While it appears that on the average a phosphate test of 100 p.p.m. or more is required to produce a sufficiency, it does not follow that applications of phosphate to a crop showing less than 100 p.p.m. will produce a response. Too many exceptions to the rule exist.
6 PROCEEDINGS FOURTH GENERAL. MEETING 101 The average value for incipient nitrate deficiency appears to be about 400 p.p.m. during the third week of July. It appears that earlier than this date fields which will develop nitrate deficiency do not show it. And if tests are made later, results are known too late to permit of correction of the deficiency without delaying maturity unduly. Again, many exceptions to the rule are to be found. As a measure of general fertility, where a large number of fields may be sampled and the results averaged, the sugar beet petiole test is very useful. Many reports of successful application of petiole tests are to be found in the literature. However, the majority of references appear to be perennial crops, such as orchards. Thomas, in Social Science, Vol. 59, p. 353, reviews the subject of tissue analysis and finds analysis of leaf tissue for total components superior to analysis of conducting tissue for unassimilated components if the results are to be correlated with yields. The results we have obtained on analysis for total components have not been encouraging. In complete analysis was made of total tops from 20 beet fields, 10 fields of high-yield history and 10 fields of low-yield history. Samples were taken twice during the season, first at about July 1 and the second at harvest time. The results show no clear-cut distinctions between tops from fertile and non-fertile fields. The maximum and minimum values are given in table 6. Table 6. Maximum and minimum nutrients in beet tops, percent total N, P', and K on dry matter. High-yield fields Low-yield fields Maximum Minimum Maximum Minimum Inspection of results on individual samples rarely reveals evidence of inter-relations of N, P, and K levels which may bear a relation to fertility or yields, and even the group averages show rather small differences. Possibly we ask too much of plant tissue tests, but he demands upon us are severe. Will the field respond to application of fertilizer? We cannot today answer that question on the basis of results from a single sample, regardless of how accurately the sample represents the field, because unknown environmental factors, other than level of available soil nutrients, often control the level of nutrients in the tissue.
3 Numbers in parentheses refer to literature cited.
 Petiole Sampling of Sugar Beet Fields in Relation to Their Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium and Sodium Status 1 ALBERT ULRICH AND F. J. HILLS 2 A technique for collecting petiole samples from sugar beet
Petiole Sampling of Sugar Beet Fields in Relation to Their Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium and Sodium Status 1 ALBERT ULRICH AND F. J. HILLS 2 A technique for collecting petiole samples from sugar beet
Nutrient Recommendations for Russet Burbank Potatoes in Southern Alberta
 Revised May 2011 Agdex 258/541-1 Nutrient Recommendations for Russet Burbank Potatoes in Southern Alberta Precise fertilizer application rates are critical for optimal potato production. Sufficient nutrients
Revised May 2011 Agdex 258/541-1 Nutrient Recommendations for Russet Burbank Potatoes in Southern Alberta Precise fertilizer application rates are critical for optimal potato production. Sufficient nutrients
Volume XVII, Number July Chasing Petioles
 Research & Extension for the Potato Industry of Idaho, Oregon, & Washington Andrew Jensen, Editor. ajensen@potatoes.com; 509-760-4859 www.nwpotatoresearch.com Volume XVII, Number 12 25 July 2017 Chasing
Research & Extension for the Potato Industry of Idaho, Oregon, & Washington Andrew Jensen, Editor. ajensen@potatoes.com; 509-760-4859 www.nwpotatoresearch.com Volume XVII, Number 12 25 July 2017 Chasing
Nutrient status of potatoes grown on compost amended soils as determined by sap nitrate levels.
 Nutrient status of potatoes grown on compost amended soils as determined by sap nitrate levels. Katherine Buckley, Ramona Mohr, Randy Westwood Brandon Research Centre, AAFC Van Coulter, Kristen Phillips,
Nutrient status of potatoes grown on compost amended soils as determined by sap nitrate levels. Katherine Buckley, Ramona Mohr, Randy Westwood Brandon Research Centre, AAFC Van Coulter, Kristen Phillips,
2 Numbers in parentheses refer to literature cited.
 A Genetic Study of Monogerm and Multigerm Characters in Beets V. F. SAVITSKY 1 Introduction Monogerm beets were found in the variety Michigan Hybrid 18 in Oregon in 1948. Two of these monogerm plants,
A Genetic Study of Monogerm and Multigerm Characters in Beets V. F. SAVITSKY 1 Introduction Monogerm beets were found in the variety Michigan Hybrid 18 in Oregon in 1948. Two of these monogerm plants,
VitiNotes. Grapevine nutrition 3: Petiole analysis
 VitiNotes www.crcv.com.au 2006 Grapevine nutrition 3: Petiole analysis Current titles in this Grapevine nutrition VitiNote series include: 1. Nitrogen fertilisation 2. Phosphorus fertilisation 3. Petiole
VitiNotes www.crcv.com.au 2006 Grapevine nutrition 3: Petiole analysis Current titles in this Grapevine nutrition VitiNote series include: 1. Nitrogen fertilisation 2. Phosphorus fertilisation 3. Petiole
AGRONOMIC POTENTIAL AND LIMITATIONS OF USING PRECIPITATED CALCIUM CARBONATE IN THE HIGH PLAINS
 GRONOMIC POTENTIL ND LIMITTIONS OF USING PRECIPITTED CLCIUM CRONTE IN THE HIGH PLINS Gary W Hergert*, Murali K Darapuneni, Robert H. Wilson, Robert M. Harveson, Jeffrey D. radshaw and Rex. Nielsen University
GRONOMIC POTENTIL ND LIMITTIONS OF USING PRECIPITTED CLCIUM CRONTE IN THE HIGH PLINS Gary W Hergert*, Murali K Darapuneni, Robert H. Wilson, Robert M. Harveson, Jeffrey D. radshaw and Rex. Nielsen University
Major Nutrients Trends and some Statistics
 Environmental Factors Nutrients K. Raja Reddy Krreddy@pss.msstate.edu Environmental and Cultural Factors Limiting Potential Yields Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Temperature (Extremes) Solar Radiation Water
Environmental Factors Nutrients K. Raja Reddy Krreddy@pss.msstate.edu Environmental and Cultural Factors Limiting Potential Yields Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Temperature (Extremes) Solar Radiation Water
Christopher ISU
 Christopher Anderson @ ISU Excessive spring rain will be more frequent (except this year). Will it be more manageable? Christopher J. Anderson, PhD 89th Annual Soil Management and Land Valuation Conference
Christopher Anderson @ ISU Excessive spring rain will be more frequent (except this year). Will it be more manageable? Christopher J. Anderson, PhD 89th Annual Soil Management and Land Valuation Conference
2010 Crop Year Fertilizer Report
 2010 Crop Year Fertilizer Report This report is based on the tonnage of fertilizer reported from licensed dealers that has been either distributed OR sold in Minnesota 1. Each registrant under section
2010 Crop Year Fertilizer Report This report is based on the tonnage of fertilizer reported from licensed dealers that has been either distributed OR sold in Minnesota 1. Each registrant under section
Avocado Thrips Subproject 2: Pesticide Evaluations and Phenology in the Field
 1999 California Avocado Research Symposium pages 27-35 California Avocado Society and University of California, Riverside Avocado Thrips Subproject 2: Pesticide Evaluations and Phenology in the Field Phil
1999 California Avocado Research Symposium pages 27-35 California Avocado Society and University of California, Riverside Avocado Thrips Subproject 2: Pesticide Evaluations and Phenology in the Field Phil
THE IRON-CHLOROPHYLL RELATEONSHIP IN YOUNG HASS AVOCADO LEAVES
 Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 83:372-375. 1970. THE IRON-CHLOROPHYLL RELATEONSHIP IN YOUNG HASS AVOCADO LEAVES E. F. Wallihan and R. G. Sharpless University of California, Riverside ABSTRACT Young summer
Proc. Fla. State Hort. Soc. 83:372-375. 1970. THE IRON-CHLOROPHYLL RELATEONSHIP IN YOUNG HASS AVOCADO LEAVES E. F. Wallihan and R. G. Sharpless University of California, Riverside ABSTRACT Young summer
Response of Russet Potato to Source and Rate of Phosphorus Fertilizer Application
 Response of Russet Potato to Source and Rate of Phosphorus Fertilizer Application Samuel Y.C. Essah, Colorado State University Department of Horticulture and Landscape Architecture San Luis Valley Research
Response of Russet Potato to Source and Rate of Phosphorus Fertilizer Application Samuel Y.C. Essah, Colorado State University Department of Horticulture and Landscape Architecture San Luis Valley Research
The Colorado Drought of 2002 in Perspective
 The Colorado Drought of 2002 in Perspective Colorado Climate Center Nolan Doesken and Roger Pielke, Sr. Prepared by Tara Green and Odie Bliss http://climate.atmos.colostate.edu Known Characteristics of
The Colorado Drought of 2002 in Perspective Colorado Climate Center Nolan Doesken and Roger Pielke, Sr. Prepared by Tara Green and Odie Bliss http://climate.atmos.colostate.edu Known Characteristics of
2012 Crop Year Fertilizer Report
 2012 Crop Year Fertilizer Report This report is based on the tonnage of fertilizer reported from licensed dealers that has been either distributed OR sold in Minnesota. Fertilizer can be reported as distributed
2012 Crop Year Fertilizer Report This report is based on the tonnage of fertilizer reported from licensed dealers that has been either distributed OR sold in Minnesota. Fertilizer can be reported as distributed
STOLLER ENTERPRISES, INC. World leader in crop nutrition
 A new paradigm for crop production - Page 1 of 6 A NEW PARADIGM FOR CROP PRODUCTION Most agronomists are taught about the chemical process of manufacturing photosynthates (PS). The plants breathe in carbon
A new paradigm for crop production - Page 1 of 6 A NEW PARADIGM FOR CROP PRODUCTION Most agronomists are taught about the chemical process of manufacturing photosynthates (PS). The plants breathe in carbon
A Level. A Level Biology. AQA, OCR, Edexcel. Photosynthesis, Respiration Succession and Nutrient Cycle Questions. Name: Total Marks: Page 1
 AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Photosynthesis, Respiration Succession and Nutrient Cycle Questions Name: Total Marks: Page 1 Q1. The diagram shows the energy flow through a freshwater ecosystem.
AQA, OCR, Edexcel A Level A Level Biology Photosynthesis, Respiration Succession and Nutrient Cycle Questions Name: Total Marks: Page 1 Q1. The diagram shows the energy flow through a freshwater ecosystem.
Impact on Agriculture
 Weather Variability and the Impact on Agriculture InfoAg 2017 Copyright 2017, awhere. All Rights Reserved The Problem: The Earth s Atmosphere is a Heat Engine In transition 1 C warming of atmosphere Triples
Weather Variability and the Impact on Agriculture InfoAg 2017 Copyright 2017, awhere. All Rights Reserved The Problem: The Earth s Atmosphere is a Heat Engine In transition 1 C warming of atmosphere Triples
Input Costs Trends for Arkansas Field Crops, AG -1291
 Input Costs Trends for Arkansas Field Crops, 2007-2013 AG -1291 Input Costs Trends for Arkansas Field Crops, 2007-2013 October 2013 AG-1291 Archie Flanders Department of Agricultural Economics and Agribusiness
Input Costs Trends for Arkansas Field Crops, 2007-2013 AG -1291 Input Costs Trends for Arkansas Field Crops, 2007-2013 October 2013 AG-1291 Archie Flanders Department of Agricultural Economics and Agribusiness
Teacher s Discussion Notes Part 1
 Teacher s Discussion Notes Part 1 PHOTOSYNTHESIS Vocabulary: Chlorophyll--A green substance which gives leaves their color. Chlorophyll absorbs energy from sunlight, which a plant uses to make food. Chloroplast--A
Teacher s Discussion Notes Part 1 PHOTOSYNTHESIS Vocabulary: Chlorophyll--A green substance which gives leaves their color. Chlorophyll absorbs energy from sunlight, which a plant uses to make food. Chloroplast--A
Part I Absorbtion and Reflection
 A Colorful Picnic with Photosynthetic Pathways and RuBisCO on the Menu by David J. Grisé Oso Bay Educational Consulting, Corpus Christi, TX Part I Absorbtion and Reflection Hey Ben, this looks like a nice
A Colorful Picnic with Photosynthetic Pathways and RuBisCO on the Menu by David J. Grisé Oso Bay Educational Consulting, Corpus Christi, TX Part I Absorbtion and Reflection Hey Ben, this looks like a nice
The table lists some functions of parts of a plant. Match the part of the plant (A, B, C or D) to its function by writing the letters in the table.
 Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows a flowering plant. A Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D. (c) (d) B C D A... B C... D [4] The table lists some functions of parts of a plant. Match
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The diagram shows a flowering plant. A Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D. (c) (d) B C D A... B C... D [4] The table lists some functions of parts of a plant. Match
2018 mid-winter ag weather update
 E-book Bryce Anderson s 2018 mid-winter ag weather update Table of contents Contributing weather patterns... 3 About the author An updated mid-winter forecast... 4 Early expectations for the growing season...
E-book Bryce Anderson s 2018 mid-winter ag weather update Table of contents Contributing weather patterns... 3 About the author An updated mid-winter forecast... 4 Early expectations for the growing season...
Soil - the battery of your business
 Soil - the battery of your business By DAVID HANLON The basis of our farm business is the soil and increasingly all growers are focusing their attention on this vital resource. Just what state it is in
Soil - the battery of your business By DAVID HANLON The basis of our farm business is the soil and increasingly all growers are focusing their attention on this vital resource. Just what state it is in
Variability of Reference Evapotranspiration Across Nebraska
 Know how. Know now. EC733 Variability of Reference Evapotranspiration Across Nebraska Suat Irmak, Extension Soil and Water Resources and Irrigation Specialist Kari E. Skaggs, Research Associate, Biological
Know how. Know now. EC733 Variability of Reference Evapotranspiration Across Nebraska Suat Irmak, Extension Soil and Water Resources and Irrigation Specialist Kari E. Skaggs, Research Associate, Biological
VEGETABLE CULTIVAR AND CULTURAL TRIALS 2009
 VEGETABLE CULTIVAR AND CULTURAL TRIALS 2009 PREPARED BY: D. WATERER D. ROY P. SZAROZ FUNDED BY: AGRICULTURE DEVELOPMENT FUND Department of Plant Sciences University of Saskatchewan, 51 Campus Drive Saskatoon,
VEGETABLE CULTIVAR AND CULTURAL TRIALS 2009 PREPARED BY: D. WATERER D. ROY P. SZAROZ FUNDED BY: AGRICULTURE DEVELOPMENT FUND Department of Plant Sciences University of Saskatchewan, 51 Campus Drive Saskatoon,
Plant Water Stress Frequency and Periodicity in Western North Dakota
 Plant Water Stress Frequency and Periodicity in Western North Dakota Llewellyn L. Manske PhD, Sheri Schneider, John A. Urban, and Jeffery J. Kubik Report DREC 10-1077 Range Research Program Staff North
Plant Water Stress Frequency and Periodicity in Western North Dakota Llewellyn L. Manske PhD, Sheri Schneider, John A. Urban, and Jeffery J. Kubik Report DREC 10-1077 Range Research Program Staff North
CRITICAL PETIOLE POTASSIUM LEVELS AS RELATED TO PHYSIOLOGICAL RESPONSES OF CHAMBER- GROWN COTTON TO POTASSIUM DEFICIENCY
 Summaries of Arkansas Cotton Research 23 CRITICAL PETIOLE POTASSIUM LEVELS AS RELATED TO PHYSIOLOGICAL RESPONSES OF CHAMBER- GROWN COTTON TO POTASSIUM DEFICIENCY D.L. Coker, D.M. Oosterhuis, M. Arevalo,
Summaries of Arkansas Cotton Research 23 CRITICAL PETIOLE POTASSIUM LEVELS AS RELATED TO PHYSIOLOGICAL RESPONSES OF CHAMBER- GROWN COTTON TO POTASSIUM DEFICIENCY D.L. Coker, D.M. Oosterhuis, M. Arevalo,
BioWash as an Adjuvant, Translocation Promoter, and Cationic Exchange Stimulator Overview of Processes within the Plant
 BioWash as an Adjuvant, Translocation Promoter, and Cationic Exchange Stimulator Overview of Processes within the Plant Photosynthesis is the primary driver of the plant. Through a series of complex steps,
BioWash as an Adjuvant, Translocation Promoter, and Cationic Exchange Stimulator Overview of Processes within the Plant Photosynthesis is the primary driver of the plant. Through a series of complex steps,
2012 Growing Season. Niagara Report. Wayne Heinen
 2012 Growing Season Niagara Report Wayne Heinen Overview The 2012 growing season was a phenomenal one for grapes. Vines entered bud break in good shape following a mild winter. The spring of 2012 was similar
2012 Growing Season Niagara Report Wayne Heinen Overview The 2012 growing season was a phenomenal one for grapes. Vines entered bud break in good shape following a mild winter. The spring of 2012 was similar
September 2018 Weather Summary West Central Research and Outreach Center Morris, MN
 September 2018 Weather Summary The mean temperature for September was 60.6 F, which is 1.5 F above the average of 59.1 F (1886-2017). The high temperature for the month was 94 F on September 16 th. The
September 2018 Weather Summary The mean temperature for September was 60.6 F, which is 1.5 F above the average of 59.1 F (1886-2017). The high temperature for the month was 94 F on September 16 th. The
Garden Mum Crop Scheduling October 3, 2018 Mark Smith
 Garden Mum Crop Scheduling October 3, 2018 Mark Smith mark.a.smith@syngenta.com 2018 Syngenta. Some or all of the varieties may be protected under one or more of the following: Plant Variety Protection,
Garden Mum Crop Scheduling October 3, 2018 Mark Smith mark.a.smith@syngenta.com 2018 Syngenta. Some or all of the varieties may be protected under one or more of the following: Plant Variety Protection,
Topic 9: Factorial treatment structures. Introduction. Terminology. Example of a 2x2 factorial
 Topic 9: Factorial treatment structures Introduction A common objective in research is to investigate the effect of each of a number of variables, or factors, on some response variable. In earlier times,
Topic 9: Factorial treatment structures Introduction A common objective in research is to investigate the effect of each of a number of variables, or factors, on some response variable. In earlier times,
1 29 g, 18% Potato chips 32 g, 23% 2 30 g, 18% Sugar cookies 35 g, 30% 3 28 g, 19% Mouse food 27 g, 18%
 1. When testing the benefits of a new fertilizer on the growth of tomato plants, the control group should include which of the following? A Tomato plants grown in soil with no fertilizer B Tomato plants
1. When testing the benefits of a new fertilizer on the growth of tomato plants, the control group should include which of the following? A Tomato plants grown in soil with no fertilizer B Tomato plants
Evaluation of rapid field methods for determining the nitrogen status of potato crops
 Evaluation of rapid field methods for determining the nitrogen status of potato crops R. J. Martin New Zealand Institute for Crop & Food Research Limited, Private Bag 474, Christchurch Abstract Petiole
Evaluation of rapid field methods for determining the nitrogen status of potato crops R. J. Martin New Zealand Institute for Crop & Food Research Limited, Private Bag 474, Christchurch Abstract Petiole
Nebraska experienced a wide
 Issue 1 August 2016 CLIMATE UPDATE A MONTHLY SUMMARY FROM THE neclimate.unl.edu August saw reprieve from dryness, cooler temps Overview Nebraska experienced a wide range of conditions across the state
Issue 1 August 2016 CLIMATE UPDATE A MONTHLY SUMMARY FROM THE neclimate.unl.edu August saw reprieve from dryness, cooler temps Overview Nebraska experienced a wide range of conditions across the state
Crop Enterprise Budget Sugar Beets, Thick-Planted, Wheatland Area
 Crop Enterprise Budget Sugar Beets, Thick-Planted, Wheatland Area John P. Hewlett, Farm/Ranch Management Extension Specialist Chris Bastian, Research Associate MP-72.3 University of Wyoming - August, 1994
Crop Enterprise Budget Sugar Beets, Thick-Planted, Wheatland Area John P. Hewlett, Farm/Ranch Management Extension Specialist Chris Bastian, Research Associate MP-72.3 University of Wyoming - August, 1994
NUTRIENT CYCLES. Water Carbon Nitrogen
 NUTRIENT CYCLES Water Carbon Nitrogen NUTRIENT CYCLES Energy transfer through an ecosystem is ONE WAY Most energy is lost as heat Nutrients such as nitrogen, water and carbon are able to cycle through
NUTRIENT CYCLES Water Carbon Nitrogen NUTRIENT CYCLES Energy transfer through an ecosystem is ONE WAY Most energy is lost as heat Nutrients such as nitrogen, water and carbon are able to cycle through
November 2018 Weather Summary West Central Research and Outreach Center Morris, MN
 November 2018 Weather Summary Lower than normal temperatures occurred for the second month. The mean temperature for November was 22.7 F, which is 7.2 F below the average of 29.9 F (1886-2017). This November
November 2018 Weather Summary Lower than normal temperatures occurred for the second month. The mean temperature for November was 22.7 F, which is 7.2 F below the average of 29.9 F (1886-2017). This November
INTRO TO SCIENCE. Chapter 1. 8 th grade
 INTRO TO SCIENCE Chapter 1 8 th grade 1.1- INTRODUCTION TO SCIENCE Science- the study of the matter and movement of God s physical creation. Matter- the substances of the physical world- anything that
INTRO TO SCIENCE Chapter 1 8 th grade 1.1- INTRODUCTION TO SCIENCE Science- the study of the matter and movement of God s physical creation. Matter- the substances of the physical world- anything that
Monthly Overview. Rainfall
 Monthly Overview Rainfall during August occurred mainly over the Western and Eastern Cape provinces, and KwaZulu- Natal. Rain in these provinces were regularly accompanied by cold fronts as they made landfall
Monthly Overview Rainfall during August occurred mainly over the Western and Eastern Cape provinces, and KwaZulu- Natal. Rain in these provinces were regularly accompanied by cold fronts as they made landfall
Remote Sensing as a Tool to Manage Nitrogen for Irrigated Potato Production
 Remote Sensing as a Tool to Manage Nitrogen for Irrigated Potato Production Brian Bohman, Carl Rosen, and David Mulla Department of Soil, Water, and Climate University of Minnesota Potato Remote Sensing
Remote Sensing as a Tool to Manage Nitrogen for Irrigated Potato Production Brian Bohman, Carl Rosen, and David Mulla Department of Soil, Water, and Climate University of Minnesota Potato Remote Sensing
CHANGES WITH AGE IN THE PHOTOSYNTHETIC AND RESPIRATORY COMPONENTS OF THE NET ASSIMILATION RATES OF SUGAR BEET AND WHEAT
 CHANGES WITH AGE IN THE PHOTOSYNTHETIC AND RESPIRATORY COMPONENTS OF THE NET ASSIMILATION RATES OF SUGAR BEET AND WHEAT BY D. J. WATSON, J. H. WILSON*, MARGARET A. FORD AND S. A. W. FRENCH Rothamsted Experimental
CHANGES WITH AGE IN THE PHOTOSYNTHETIC AND RESPIRATORY COMPONENTS OF THE NET ASSIMILATION RATES OF SUGAR BEET AND WHEAT BY D. J. WATSON, J. H. WILSON*, MARGARET A. FORD AND S. A. W. FRENCH Rothamsted Experimental
THE PERFORMANCE OF SUGARCANE VARIETIES N23 AND N25 ON LOW YIELD POTENTIAL SOILS IN SWAZILAND
 THE PERFORMANCE OF SUGARCANE VARIETIES N23 AND N25 ON LOW YIELD POTENTIAL SOILS IN SWAZILAND DWF BUTLER Swaziland Sugar Association, PO Box 367, Simunye, Swaziland Abstract South African sugarcane varieties
THE PERFORMANCE OF SUGARCANE VARIETIES N23 AND N25 ON LOW YIELD POTENTIAL SOILS IN SWAZILAND DWF BUTLER Swaziland Sugar Association, PO Box 367, Simunye, Swaziland Abstract South African sugarcane varieties
those in Arizona. This period would extend through the fall equinox (September 23, 1993). Thus, pending variation due to cloudiness, total light flux
 PERFORMANCE OF KENTUCKY BLUEGRASS SEED TREATED WITH METHANOL Fred J. Crowe, D. Dale Coats, and Marvin D. Butler, Central Oregon Agricultural Research Center Abstract Foliar-applied methanol was purported
PERFORMANCE OF KENTUCKY BLUEGRASS SEED TREATED WITH METHANOL Fred J. Crowe, D. Dale Coats, and Marvin D. Butler, Central Oregon Agricultural Research Center Abstract Foliar-applied methanol was purported
Seed Development and Yield Components. Thomas G Chastain CROP 460/560 Seed Production
 Seed Development and Yield Components Thomas G Chastain CROP 460/560 Seed Production The Seed The zygote develops into the embryo which contains a shoot (covered by the coleoptile) and a root (radicle).
Seed Development and Yield Components Thomas G Chastain CROP 460/560 Seed Production The Seed The zygote develops into the embryo which contains a shoot (covered by the coleoptile) and a root (radicle).
Math: Question 1 A. 4 B. 5 C. 6 D. 7
 Math: Question 1 Abigail can read 200 words in one minute. If she were to read at this rate for 30 minutes each day, how many days would Abigail take to read 30,000 words of a book? A. 4 B. 5 C. 6 D. 7
Math: Question 1 Abigail can read 200 words in one minute. If she were to read at this rate for 30 minutes each day, how many days would Abigail take to read 30,000 words of a book? A. 4 B. 5 C. 6 D. 7
Cultural practices improve color, size of Crimson Seedless. Nick Dokoozlian o Don Luvisi o Mike Moriyama o Peggy Schrader
 Cultural practices improve color, size of Crimson Seedless Nick Dokoozlian o Don Luvisi o Mike Moriyama o Peggy Schrader Poor color and small berry size associated with Crimson Seedless, a late-season,
Cultural practices improve color, size of Crimson Seedless Nick Dokoozlian o Don Luvisi o Mike Moriyama o Peggy Schrader Poor color and small berry size associated with Crimson Seedless, a late-season,
Formulation Problems: Possible Answers
 Formulation Problems: Possible Answers 1. Let x 1 = number of cans of cheap mix; x 2 = number of cans of party mix; and x 3 = number of cans of deluxe mix. These are what you want to find. Finding the
Formulation Problems: Possible Answers 1. Let x 1 = number of cans of cheap mix; x 2 = number of cans of party mix; and x 3 = number of cans of deluxe mix. These are what you want to find. Finding the
Click to edit Master title style Effect of seed and foliar treatments on vigor of soybean plants Jerseyville, IL
 Click to edit Master title style Effect of seed and treatments on vigor of soybean plants Jerseyville, IL Click to edit Master text styles Plant vigor 8.0 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 Second level UTC
Click to edit Master title style Effect of seed and treatments on vigor of soybean plants Jerseyville, IL Click to edit Master text styles Plant vigor 8.0 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 Second level UTC
Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 15 Laser - I In the last lecture, we discussed various
Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 15 Laser - I In the last lecture, we discussed various
YELLOW NUTSEDGE CONTROL IN LIBERTY AND ROUNDUP RESISTANT SUGAR BEETS
 YELLOW NUTSEDGE CONTROL IN LIBERTY AND ROUNDUP RESISTANT SUGAR BEETS Corey V. Ransom, Joey K. Ishida, and Corey J. Guza Malheur Experiment Station Oregon State University Ontario, OR, 1999 Introduction
YELLOW NUTSEDGE CONTROL IN LIBERTY AND ROUNDUP RESISTANT SUGAR BEETS Corey V. Ransom, Joey K. Ishida, and Corey J. Guza Malheur Experiment Station Oregon State University Ontario, OR, 1999 Introduction
UNITED STATES AND SOUTH AMERICA OUTLOOK (FULL REPORT) Wednesday, April 18, 2018
 T-storm Weather Summary Coolness continues over the next week in much of the central U.S., most likely producing the coldest April since 1907 in the Corn Belt, but followed by seasonable to mild weather
T-storm Weather Summary Coolness continues over the next week in much of the central U.S., most likely producing the coldest April since 1907 in the Corn Belt, but followed by seasonable to mild weather
JRC MARS Bulletin global outlook 2017 Crop monitoring European neighbourhood Turkey June 2017
 MARS Bulletin global outlook 2015-06 r JRC MARS Bulletin global outlook 2017 Crop monitoring European neighbourhood Turkey June 2017 Favourable spring conditions, but slight delay Yield forecasts for winter
MARS Bulletin global outlook 2015-06 r JRC MARS Bulletin global outlook 2017 Crop monitoring European neighbourhood Turkey June 2017 Favourable spring conditions, but slight delay Yield forecasts for winter
Soil Moisture Probe Newsletter: October 2015
 Soil Moisture Probe Newsletter: October 2015 Southern Farming Systems aims to improve nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) of growers in the high rainfall zones of Victoria and Tasmania. SFS has installed 62
Soil Moisture Probe Newsletter: October 2015 Southern Farming Systems aims to improve nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) of growers in the high rainfall zones of Victoria and Tasmania. SFS has installed 62
List of Equipment, Tools, Supplies, and Facilities:
 Unit D: ph of Soil Lesson 2: Identifying ph Connection With Plant Growth Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in the students achieving the following objectives: 1. Explain
Unit D: ph of Soil Lesson 2: Identifying ph Connection With Plant Growth Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in the students achieving the following objectives: 1. Explain
Scientific Method. Section 1. Observation includes making measurements and collecting data. Main Idea
 Scientific Method Section 1 2B, 2C, 2D Key Terms scientific method system hypothesis model theory s Observation includes making measurements and collecting data. Sometimes progress in science comes about
Scientific Method Section 1 2B, 2C, 2D Key Terms scientific method system hypothesis model theory s Observation includes making measurements and collecting data. Sometimes progress in science comes about
Moisture Situation Update December 19, 2016
 Synopsis November marked a notable shift in Alberta s precipitation patterns, with most of the province experiencing a drying trend over the past 7 weeks (see map 1). This is particularly true for those
Synopsis November marked a notable shift in Alberta s precipitation patterns, with most of the province experiencing a drying trend over the past 7 weeks (see map 1). This is particularly true for those
Inspired by nature. Callisto is currently under review by the Pest Management Regulatory Agency and not yet registered for use in Canada.
 H E R B I C I D E Inspired by nature Callisto is currently under review by the Pest Management Regulatory Agency and not yet registered for use in Canada. H E R B I C I D E Inspired by nature Callisto
H E R B I C I D E Inspired by nature Callisto is currently under review by the Pest Management Regulatory Agency and not yet registered for use in Canada. H E R B I C I D E Inspired by nature Callisto
Southern Africa Growing Season : Recovery Hampered by Floods and Drought?
 Southern Africa Growing Season 2016-2017: Recovery Hampered by Floods and Drought? HIGHLIGHTS Good performance of the current growing season (October 2016 - April 2017) is badly needed for Southern Africa
Southern Africa Growing Season 2016-2017: Recovery Hampered by Floods and Drought? HIGHLIGHTS Good performance of the current growing season (October 2016 - April 2017) is badly needed for Southern Africa
Example problem in Birge & Louveaux, Introduction to Stochastic Programming. SLPwR: Farmer Problem page 1 D.L.Bricker
 Example problem in Birge & Louveaux, Introduction to Stochastic Programming SLPwR: Farmer Problem page 1 D.L.Bricker A farmer raises wheat, corn, and sugar beets on 500 acres of land. Before the planting
Example problem in Birge & Louveaux, Introduction to Stochastic Programming SLPwR: Farmer Problem page 1 D.L.Bricker A farmer raises wheat, corn, and sugar beets on 500 acres of land. Before the planting
Developing and Validating a Model for a Plant Growth Regulator
 Environmental Factors Special Topics Mepiquat Chloride (PIX) K. Raja Reddy Krreddy@pss.msstate.edu Environmental and Cultural Factors Limiting Potential Yields Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Temperature (Extremes)
Environmental Factors Special Topics Mepiquat Chloride (PIX) K. Raja Reddy Krreddy@pss.msstate.edu Environmental and Cultural Factors Limiting Potential Yields Atmospheric Carbon Dioxide Temperature (Extremes)
Leaf Wetting and Uptake of Fluid Foliar P Fertilizers for Wheat
 Leaf Wetting and Uptake of Fluid Foliar P Fertilizers for Wheat Courtney Peirce, Craig Priest, Evelina Facelli, Therese McBeath, Victoria Fernández and Mike McLaughlin Tactical Foliar P Fertilization Fertilizer
Leaf Wetting and Uptake of Fluid Foliar P Fertilizers for Wheat Courtney Peirce, Craig Priest, Evelina Facelli, Therese McBeath, Victoria Fernández and Mike McLaughlin Tactical Foliar P Fertilization Fertilizer
Carbon Assimilation and Its Variation among Plant Communities
 Carbon Assimilation and Its Variation among Plant Communities Introduction By, Susan Boersma, Andrew Wiersma Institution: Calvin College Faculty Advisor: David Dornbos Currently, global warming remains
Carbon Assimilation and Its Variation among Plant Communities Introduction By, Susan Boersma, Andrew Wiersma Institution: Calvin College Faculty Advisor: David Dornbos Currently, global warming remains
Hand Pollination Effects in the Cheyrimoya (Annona cherimola)
 California Avocado Society 1941 Yearbook 26: 94-98 Hand Pollination Effects in the Cheyrimoya (Annona cherimola) C. A. Schroeder University of California, Los Angeles Although the cherimoya was introduced
California Avocado Society 1941 Yearbook 26: 94-98 Hand Pollination Effects in the Cheyrimoya (Annona cherimola) C. A. Schroeder University of California, Los Angeles Although the cherimoya was introduced
SEPTEMBER 2013 REVIEW
 Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: October 21, 2013 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO sroot@weatherbank.com SEPTEMBER 2013 REVIEW Climate Highlights The Month in Review The average temperature
Monthly Long Range Weather Commentary Issued: October 21, 2013 Steven A. Root, CCM, President/CEO sroot@weatherbank.com SEPTEMBER 2013 REVIEW Climate Highlights The Month in Review The average temperature
Appendix 2b. NRCS Soil Survey
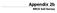 Appendix 2b NRCS Soil Survey 118 19' 25'' W Nonirrigated Capability Class Antelope Valley Area, California (Del Sur Solar Site) 118 17' 28'' W 378900 379200 379500 379800 380100 380400 380700 381000 381300
Appendix 2b NRCS Soil Survey 118 19' 25'' W Nonirrigated Capability Class Antelope Valley Area, California (Del Sur Solar Site) 118 17' 28'' W 378900 379200 379500 379800 380100 380400 380700 381000 381300
Precipitation. Standardized Precipitation Index. NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System September 5, 2017
 9/6/2017 NIDIS Drought and Water Assessment NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System September 5, 2017 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS,
9/6/2017 NIDIS Drought and Water Assessment NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System September 5, 2017 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS,
U.S. Hard Red Winter Wheat Crop Update
 U.S. Hard Red Winter Wheat Crop Update 2015 Summer Meeting and Technical Conference JULY 31 Mark Hodges Plains Grains, Inc. Overview 2015 HRW wheat crop early information Growing conditions and production
U.S. Hard Red Winter Wheat Crop Update 2015 Summer Meeting and Technical Conference JULY 31 Mark Hodges Plains Grains, Inc. Overview 2015 HRW wheat crop early information Growing conditions and production
over the next three weeks could lower this estimate significantly. Near perfect conditions are needed to realize this projected yield.
 Peanuts across the V-C region experienced excessive rainfall in many areas as a result of Hurricane Florence. Rainfall was particularly heavy in southeastern North Carolina and northeastern South Carolina.
Peanuts across the V-C region experienced excessive rainfall in many areas as a result of Hurricane Florence. Rainfall was particularly heavy in southeastern North Carolina and northeastern South Carolina.
Kentucky Seed Certification Standards. I. Explanation of General Standards as Applied to Corn Hybrids
 Kentucky Seed Certification Standards H Y B R I D C O R N I. Explanation of General Standards as Applied to Corn Hybrids A. The General Seed Certification Standards as adopted are basic and, together with
Kentucky Seed Certification Standards H Y B R I D C O R N I. Explanation of General Standards as Applied to Corn Hybrids A. The General Seed Certification Standards as adopted are basic and, together with
but 2012 was dry Most farmers pulled in a crop
 After a winter that wasn t, conditions late in the year pointed to a return to normal snow and cold conditions Most farmers pulled in a crop but 2012 was dry b y M i k e Wr o b l e w s k i, w e a t h e
After a winter that wasn t, conditions late in the year pointed to a return to normal snow and cold conditions Most farmers pulled in a crop but 2012 was dry b y M i k e Wr o b l e w s k i, w e a t h e
2008 Growing Season. Niagara Region
 28 Growing Season Niagara Region Weather INnovations Staff November 14, 28 Overview The start of the 28 growing season looked promising. After an extremely dry 27 growing season, soil moisture levels had
28 Growing Season Niagara Region Weather INnovations Staff November 14, 28 Overview The start of the 28 growing season looked promising. After an extremely dry 27 growing season, soil moisture levels had
Identifying Wheat Growth Stages
 AGR-224 Identifying Wheat Growth Stages Carrie A. Knott, Plant and Soil Sciences University of Kentucky College of Agriculture, Food and Environment Cooperative Extension Service Identifying growth stages
AGR-224 Identifying Wheat Growth Stages Carrie A. Knott, Plant and Soil Sciences University of Kentucky College of Agriculture, Food and Environment Cooperative Extension Service Identifying growth stages
Midwest/Great Plains Climate-Drought Outlook September 20, 2018
 Midwest/Great Plains Climate-Drought Outlook September 20, 2018 Brian Fuchs National Drought Mitigation Center University of Nebraska-Lincoln School of Natural Resources September 20, 2018 General Information
Midwest/Great Plains Climate-Drought Outlook September 20, 2018 Brian Fuchs National Drought Mitigation Center University of Nebraska-Lincoln School of Natural Resources September 20, 2018 General Information
Great Plains & Midwest Climate Outlook June 18, 2015
 Great Plains & Midwest Climate Outlook June 18, 2015 Pat Guinan Extension/State Climatologist University of Missouri guinanp@missouri.edu 573-882-5908 Saturated Soybeans, Monroe County, MO Yellow Corn,
Great Plains & Midwest Climate Outlook June 18, 2015 Pat Guinan Extension/State Climatologist University of Missouri guinanp@missouri.edu 573-882-5908 Saturated Soybeans, Monroe County, MO Yellow Corn,
USDA FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH NOTE NE-198
 USDA FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH NOTE NE-198 FOREST SERVICE, U.S. DEPT. OF AGRICULTURE, 6816 MARKET STREET, UPPER DARBY, PA. 19082 -- 2 x 3 NUTRIENT COMPOSITION OF BLADES, $ PETIOLES, AND WHOLE LEAVES FROM
USDA FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH NOTE NE-198 FOREST SERVICE, U.S. DEPT. OF AGRICULTURE, 6816 MARKET STREET, UPPER DARBY, PA. 19082 -- 2 x 3 NUTRIENT COMPOSITION OF BLADES, $ PETIOLES, AND WHOLE LEAVES FROM
temperature. March ended unseasonably warm but was followed by an extended cold
 2007 Turfgrass Weed Control Summary Crabgrass Ronald Calhoun and Aaron Hathaway Dept of Crop and Soil Sciences Michigan State University Crabgrass populations were moderate to low in 2007 due to inconsistent
2007 Turfgrass Weed Control Summary Crabgrass Ronald Calhoun and Aaron Hathaway Dept of Crop and Soil Sciences Michigan State University Crabgrass populations were moderate to low in 2007 due to inconsistent
Photosynthetic productivity of sugar beet depending on periods of sowing and fertilizer system
 UDC 633.63:631.8:631.53 2016 Photosynthetic productivity of sugar beet depending on periods of sowing and fertilizer system V. Lyhochvor Corresponding Member of the National Academy of Agrarian Sciences,
UDC 633.63:631.8:631.53 2016 Photosynthetic productivity of sugar beet depending on periods of sowing and fertilizer system V. Lyhochvor Corresponding Member of the National Academy of Agrarian Sciences,
Crop / Weather Update
 Crop / Weather Update We would like to welcome you to another season of Doane s Weekly Crop Weather Update Progress Chartbook. The goal is to provide a quick visual overview of a number of the key gauges
Crop / Weather Update We would like to welcome you to another season of Doane s Weekly Crop Weather Update Progress Chartbook. The goal is to provide a quick visual overview of a number of the key gauges
Growth Stages of Wheat: Identification and Understanding Improve Crop Management
 Growth Stages of Wheat: Identification and Understanding Improve Crop Management B y Travis D. Miller Understanding growth stages of wheat is important in matching management decisions and inputs with
Growth Stages of Wheat: Identification and Understanding Improve Crop Management B y Travis D. Miller Understanding growth stages of wheat is important in matching management decisions and inputs with
Agricultural Fertilizer Applicator Soil Test Results What the heck do they mean?
 Agricultural Fertilizer Applicator Soil Test Results What the heck do they mean? Northeast Ohio Pesticide Safety Education Program Lee Beers, OSU Extension Trumbull County beers.66@osu.edu 330-638-6783
Agricultural Fertilizer Applicator Soil Test Results What the heck do they mean? Northeast Ohio Pesticide Safety Education Program Lee Beers, OSU Extension Trumbull County beers.66@osu.edu 330-638-6783
Crop / Weather Update
 Crop / Weather Update Corn Crop Condition Percent of Acreage Rated Good or Excellent 85 80 75 70 65 60 55 50 45 The U.S. corn crop was rated 69% good-to-excellent on September 23, up 1% from week-ago,
Crop / Weather Update Corn Crop Condition Percent of Acreage Rated Good or Excellent 85 80 75 70 65 60 55 50 45 The U.S. corn crop was rated 69% good-to-excellent on September 23, up 1% from week-ago,
NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System October 17, 2017
 NIDIS Drought and Water Assessment NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System October 17, 2017 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS, and
NIDIS Drought and Water Assessment NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System October 17, 2017 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS, and
How Does an Almond Tree Grow? December 8, 2015
 How Does an Almond Tree Grow? December 8, 2015 Gabriele Ludwig, Almond Board Speakers Gabriele Ludwig, Almond Board (Moderator) Ted DeJong, University of California, Davis Maciej Zwieniecki, University
How Does an Almond Tree Grow? December 8, 2015 Gabriele Ludwig, Almond Board Speakers Gabriele Ludwig, Almond Board (Moderator) Ted DeJong, University of California, Davis Maciej Zwieniecki, University
Herbicide Label Changes for Asparagus - Doug
 VegNet Vol. 13, No. 6. May 11, 2006 Ohio State University Extension Vegetable Crops On the WEB at: http://vegnet.osu.edu If experiencing problems receiving this fax, Call 614-292-3857 In This Issue 1.
VegNet Vol. 13, No. 6. May 11, 2006 Ohio State University Extension Vegetable Crops On the WEB at: http://vegnet.osu.edu If experiencing problems receiving this fax, Call 614-292-3857 In This Issue 1.
Trial Report: Slicing Cucumber Variety Evaluation Spring 2014
 Trial Report: Slicing Cucumber Variety Evaluation Spring 2014 Conducted by: Timothy Coolong, PhD Department of Horticulture University of Georgia 2360 Rainwater Road Tifton, GA 31793 Methods Location:
Trial Report: Slicing Cucumber Variety Evaluation Spring 2014 Conducted by: Timothy Coolong, PhD Department of Horticulture University of Georgia 2360 Rainwater Road Tifton, GA 31793 Methods Location:
carbon dioxide +... (+ light energy) glucose +...
 Photosynthesis 1. (i) Complete the word equation for photosynthesis. (ii) carbon dioxide +... (+ light energy) glucose +... Most of the carbon dioxide that a plant uses during photosynthesis is absorbed
Photosynthesis 1. (i) Complete the word equation for photosynthesis. (ii) carbon dioxide +... (+ light energy) glucose +... Most of the carbon dioxide that a plant uses during photosynthesis is absorbed
Grapevine Nutrition: Results of Tissue and Soil Analyses
 Grapevine Nutrition: Results of Tissue and Soil Analyses Carl Rosen University of Minnesota Northern Grape Symposium February 6, 2013 Rochester, NY Collaborators Paul Domoto, Iowa State University James
Grapevine Nutrition: Results of Tissue and Soil Analyses Carl Rosen University of Minnesota Northern Grape Symposium February 6, 2013 Rochester, NY Collaborators Paul Domoto, Iowa State University James
Climate Change in the Inland Pacific Northwest
 80 Climate Change in the Inland Pacific Northwest Week 2 Day 4 Lesson Overview The purpose of this lesson is for students to apply and extend their previous knowledge of global climate change to a regional
80 Climate Change in the Inland Pacific Northwest Week 2 Day 4 Lesson Overview The purpose of this lesson is for students to apply and extend their previous knowledge of global climate change to a regional
MONITORING PHOSPHORUS COMPOUNDS IN AVOCADO TISSUES
 South African Avocado Growers Association Yearbook 1985. 8:100-102 MONITORING PHOSPHORUS COMPOUNDS IN AVOCADO TISSUES JJ BEZUIDENHOUT, LISE KORSTEN & JM KOTZÉ DEPARTMENT MICROBIOLOGY AND PLANT PATHOLOGY
South African Avocado Growers Association Yearbook 1985. 8:100-102 MONITORING PHOSPHORUS COMPOUNDS IN AVOCADO TISSUES JJ BEZUIDENHOUT, LISE KORSTEN & JM KOTZÉ DEPARTMENT MICROBIOLOGY AND PLANT PATHOLOGY
Weather Report 31 January 2018
 Weather Report 31 January 2018 South Africa - Weather The erratic rain pattern will continue on a frequent basis for the eastern half of South Africa during the coming week. Moisture totals through next
Weather Report 31 January 2018 South Africa - Weather The erratic rain pattern will continue on a frequent basis for the eastern half of South Africa during the coming week. Moisture totals through next
Biology Article Assignment #2 Rising Carbon Dioxide Levels and Plants
 Name Biology Article Assignment #2 Rising Carbon Dioxide Levels and Plants 1. What is the atmospheric concentration of CO2 expected to be by the year 2100? 2. What percentage of the dry mass of plants
Name Biology Article Assignment #2 Rising Carbon Dioxide Levels and Plants 1. What is the atmospheric concentration of CO2 expected to be by the year 2100? 2. What percentage of the dry mass of plants
NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System February 6, 2018
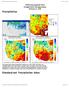 NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System February 6, 2018 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS, and CoAgMet stations. From top to bottom,
NIDIS Intermountain West Drought Early Warning System February 6, 2018 Precipitation The images above use daily precipitation statistics from NWS COOP, CoCoRaHS, and CoAgMet stations. From top to bottom,
Work with a partner. Read Section page 60 in Section 2.4, and discuss answers to questions C F. Discuss your responses with the class. Any Questions?
 Work with a partner Read Section page 60 in Section 2.4, and discuss answers to questions C F. Discuss your responses with the class. LokenTimer2.swf Any Questions? Title: Jun 7 8:32 AM (1 of 25) Title:
Work with a partner Read Section page 60 in Section 2.4, and discuss answers to questions C F. Discuss your responses with the class. LokenTimer2.swf Any Questions? Title: Jun 7 8:32 AM (1 of 25) Title:
NOS 18 Scientific Explanations
 Scientific Explanations Case Study Key Concepts How do independent and dependent variables differ? How is scientific inquiry used in a real-life scientific investigation? Identify the Main Ideas As you
Scientific Explanations Case Study Key Concepts How do independent and dependent variables differ? How is scientific inquiry used in a real-life scientific investigation? Identify the Main Ideas As you
How Do the Great Lakes Modify the Growing Season?
 How Do the Great Lakes Modify the Growing Season? Using agricultural product and frost maps and an infrared satellite image, students develop a hypothesis about the effect of the lakes on growing seasons.
How Do the Great Lakes Modify the Growing Season? Using agricultural product and frost maps and an infrared satellite image, students develop a hypothesis about the effect of the lakes on growing seasons.
N Management in Potato Production. David Mulla, Carl Rosen, Tyler Nigonand Brian Bohman Dept. Soil, Water & Climate University of Minnesota
 N Management in Potato Production David Mulla, Carl Rosen, Tyler Nigonand Brian Bohman Dept. Soil, Water & Climate University of Minnesota Topics Background and conventional nitrogen management Evaluate
N Management in Potato Production David Mulla, Carl Rosen, Tyler Nigonand Brian Bohman Dept. Soil, Water & Climate University of Minnesota Topics Background and conventional nitrogen management Evaluate
RELATIONSHIP OF WEATHER TO_SUGAR BEE~PRODUCTION
 -121- RELATONSHP OF WEATHER TO_SUGAR BEE~PRODUCTON L. T. Pierce 1, H. L. Bush 2, R. R. Wood 3 This paper represents a preliminary report of a study conducted mainly in Billings with the object of establishing
-121- RELATONSHP OF WEATHER TO_SUGAR BEE~PRODUCTON L. T. Pierce 1, H. L. Bush 2, R. R. Wood 3 This paper represents a preliminary report of a study conducted mainly in Billings with the object of establishing
REDUCTION OF INITIAL FRUIT SET THROUGH THE USE OF A CHEMICAL FRUIT SET THINNER ETHEPHON
 : 27-34 REDUCTION OF INITIAL FRUIT SET THROUGH THE USE OF A CHEMICAL FRUIT SET THINNER ETHEPHON J. Dixon, A.J. Mandemaker, T.A. Elmsly and E.M. Dixon Avocado Industry Council Ltd, P.O. Box 13267, Tauranga
: 27-34 REDUCTION OF INITIAL FRUIT SET THROUGH THE USE OF A CHEMICAL FRUIT SET THINNER ETHEPHON J. Dixon, A.J. Mandemaker, T.A. Elmsly and E.M. Dixon Avocado Industry Council Ltd, P.O. Box 13267, Tauranga
