Electron microscopy of glial cells of the central nervous system in the crab Ucides cordatus
|
|
|
- Karin Hunter
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brazilian Glial cells Journal in crustaceans of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: ISSN X Short Communication 327 Electron microscopy of glial cells of the central nervous system in the crab Ucides cordatus S. Allodi and M. Taffarel Departamento de Histologia e Embriologia, Instituto de Ciências Biomédicas, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brasil Correspondence S. Allodi Departamento de Histologia e Embriologia, ICB, CCS, UFRJ Rio de Janeiro, RJ Brasil Fax: sallodi@chagas.biof.ufrj.br Presented at the XIII Annual Meeting of the Federação de Sociedades de Biologia Experimental, Caxambu, MG, Brasil, August 26-29, Research supported by CNPq, CAPES, FINEP, CEPEG/UFRJ, FUJB. Received March 24, 1998 Accepted November 10, 1998 Abstract Key words Glial cells Crustaceans Electron microscopy Cytochemistry Ucides cordatus
2 328 S. Allodi and M. Taffarel Figure 1 - A, Electron micrograph of the protocerebral tract (PT) treated according to Angermüller and Fahimi (12). Observe that there is no relationship between the axon diameter and thickness of the ensheathment. Note vesicular structures (arrows) and mitochondria inside the axons (arrowheads). Also note the dark (stars) and light (asterisks) glial processes. Bar: 1.0 µm. B, Electron micrograph of the PT showing a light glial cell enveloping an axon (asterisk). Glial cell nucleus (N). Note that the outermost ensheathment of this axon is composed of a dark cell process (star). Bar: 0.6 µm. A B
3 Glial cells in crustaceans 329 A B Figure 2 - A, Electron micrograph of the PT treated according to Thiéry showing glycogen aggregates in the cytoplasm of dark (large arrows) and light (large arrowheads) glial cell processes. Note that both the dark and the light processes clearly present a plasma membrane (thin arrows). Microtubules are observed in the light process (double small arrowheads) and also gap junctions (small arrowheads). Bar: 0.3 µm. B, Electron micrograph of the zona fasciculata treated according to Thiéry (11). The dark process displays mitochondrial profiles in different degrees of disruption (arrowheads). Observe a plasma membrane between the dark and light processes (curved arrows). Bar: 0.4 µm.
4 330 S. Allodi and M. Taffarel
5 Glial cells in crustaceans 331 Acknowledgments References 1. Hámori J & Horridge GA (1966). The lobster optic lamina. IV. Glial cells. Journal of Cell Science, 1: Radojcic T & Pentreath VW (1979). Invertebrate glia. Progress in Neurobiology, 12: Heuser JE & Doggenweiler CF (1966). The fine structural organization of nerve fibers, sheaths, and glial cells in the prawn Palaemonetes vulgaris. Journal of Cell Biology, 30: Bullock TH, Orkand R & Grinnel A (1977). Introduction to Nervous Systems. W.H. Freeman and Co., San Francisco, London. 5. Abbott NJ, Bundgaard M & Cserr HF (1986). Comparative physiology. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 481: Abbott NJ (1995). Morphology of nonmammalian glial cells: functional implications. In: Kettermann H & Ransom B (Editors), Neuroglia. Oxford University Press, Oxford and New York. 7. Peters A, Palay SL & Webster H de F (1991). In: The Fine Structure of the Nervous System: Neurons and their Supporting Cells. Oxford University Press, Oxford, New York. 8. Abbott NJ (1972). Access of ferritin to the interstitial space of Carcinus brain from intracerebral blood vessels. Tissue Cell, 4: Pentreath VW (1987). Functions of invertebrate glia. In: Ali MA (Editor), Nervous System in Invertebrates. Plenum Press, New York and London, Sanes JR (1989). Extracellular matrix molecules that influence neural development. Annual Review of Neuroscience, 12: Thiéry JP & Rambourg A (1974). Cytochimie des polysaccharides. Journal de Microscopie, 21: Angermüller S & Fahimi HD (1982). Imidazole-buffered osmium tetroxide: an excellent stain for visualization of lipids in transmission electron microscopy. Histochemical Journal, 14: Cuadras J, Martin G, Czternasty G & Bruner J (1985). Gap-like junctions between neuron cell bodies and glial cells of crayfish. Brain Research, 326: Tsacopoulos M, Coles JA & Van Der Werve G (1987). The supply of metabolic substrate from glia to photoreceptors in the retina of the honeybee drone. Journal de Phisiologie, 82: Wigglesworth VB (1960). The nutrition of the central nervous system in the cockroach Periplaneta americana L: the role of the perineurium and glial cells in the mobilization of reserves. Journal of Experimental Biology, 37: Shivers RR & Brightman MW (1976). Trans-glial channels in ventral nerve roots of crayfish. Journal of Comparative Neurology, 167: Parnas I, Shahrabany-Baranes O, Feinstein N, Grant P, Adelsberger H & Dudel J (1998). Changes in the ultrastructure of surviving distal segments of severed axons of the rock lobster. Journal of Experimental Biology, 201: Grossfeld RM (1991). Axon-glia exchange of macromolecules. In: Abbot NJ (Editor), Glial-Neuronal Interaction. New York Academy of Sciences, New York, Gartner LP & Hiatt JL (1997). Color Textbook of Histology. W.B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia. 20. Pentreath VW (1989). Invertebrate glial cells. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology, 93A:
Cells. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cells Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Microscopy Methods of histology: Treat the tissue with a preservative (e.g. formaldehyde). Dissect the region of interest. Embed
Cells Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Microscopy Methods of histology: Treat the tissue with a preservative (e.g. formaldehyde). Dissect the region of interest. Embed
Fine structure of the retina of black bass, Micropterus salmoides (Centrarchidae, Teleostei)
 Histol Histopathol (1 999) 14: 1053-1 065 http://www.ehu.es/histoi-hlstopathol Histology and Histopathology Fine structure of the retina of black bass, Micropterus salmoides (Centrarchidae, Teleostei)
Histol Histopathol (1 999) 14: 1053-1 065 http://www.ehu.es/histoi-hlstopathol Histology and Histopathology Fine structure of the retina of black bass, Micropterus salmoides (Centrarchidae, Teleostei)
Introduction Principles of Signaling and Organization p. 3 Signaling in Simple Neuronal Circuits p. 4 Organization of the Retina p.
 Introduction Principles of Signaling and Organization p. 3 Signaling in Simple Neuronal Circuits p. 4 Organization of the Retina p. 5 Signaling in Nerve Cells p. 9 Cellular and Molecular Biology of Neurons
Introduction Principles of Signaling and Organization p. 3 Signaling in Simple Neuronal Circuits p. 4 Organization of the Retina p. 5 Signaling in Nerve Cells p. 9 Cellular and Molecular Biology of Neurons
Atypical Neural Sheaths Formed by Muller Cells in Chicken Retina
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 57(2-3) : 79-88, August 1980 Atypical Neural Sheaths Formed by Muller Cells in Chicken Retina By YOSHIRO INOUE, YOSHIHIRO SUGIHARA,Yozo NISHIMURA and KAZUYO SHIMAI Department
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 57(2-3) : 79-88, August 1980 Atypical Neural Sheaths Formed by Muller Cells in Chicken Retina By YOSHIRO INOUE, YOSHIHIRO SUGIHARA,Yozo NISHIMURA and KAZUYO SHIMAI Department
Dendrites - receives information from other neuron cells - input receivers.
 The Nerve Tissue Neuron - the nerve cell Dendrites - receives information from other neuron cells - input receivers. Cell body - includes usual parts of the organelles of a cell (nucleus, mitochondria)
The Nerve Tissue Neuron - the nerve cell Dendrites - receives information from other neuron cells - input receivers. Cell body - includes usual parts of the organelles of a cell (nucleus, mitochondria)
Fig. S1. Expression pattern of moody-gal4 in third instar. Maximum projection illustrating a dissected moody-gal4>ngfp L3 larva stained for Repo
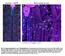 Fig. S1. Expression pattern of moody-gal4 in third instar. Maximum projection illustrating a dissected moody-gal4>ngfp L3 larva stained for Repo (magenta), Fas2 (blue) and GFP (green) in overview (A) and
Fig. S1. Expression pattern of moody-gal4 in third instar. Maximum projection illustrating a dissected moody-gal4>ngfp L3 larva stained for Repo (magenta), Fas2 (blue) and GFP (green) in overview (A) and
Intro and Homeostasis
 Intro and Homeostasis Physiology - how the body works. Homeostasis - staying the same. Functional Types of Neurons Sensory (afferent - coming in) neurons: Detects the changes in the body. Informations
Intro and Homeostasis Physiology - how the body works. Homeostasis - staying the same. Functional Types of Neurons Sensory (afferent - coming in) neurons: Detects the changes in the body. Informations
Neurochemistry 1. Nervous system is made of neurons & glia, as well as other cells. Santiago Ramon y Cajal Nobel Prize 1906
 Neurochemistry 1 Nervous system is made of neurons & glia, as well as other cells. Santiago Ramon y Cajal Nobel Prize 1906 How Many Neurons Do We Have? The human brain contains ~86 billion neurons and
Neurochemistry 1 Nervous system is made of neurons & glia, as well as other cells. Santiago Ramon y Cajal Nobel Prize 1906 How Many Neurons Do We Have? The human brain contains ~86 billion neurons and
NEURONS, SENSE ORGANS, AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS CHAPTER 34
 NEURONS, SENSE ORGANS, AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS CHAPTER 34 KEY CONCEPTS 34.1 Nervous Systems Are Composed of Neurons and Glial Cells 34.2 Neurons Generate Electric Signals by Controlling Ion Distributions 34.3
NEURONS, SENSE ORGANS, AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS CHAPTER 34 KEY CONCEPTS 34.1 Nervous Systems Are Composed of Neurons and Glial Cells 34.2 Neurons Generate Electric Signals by Controlling Ion Distributions 34.3
[ 5 ] THE NUTRITION OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM IN THE COCKROACH PERIPLANETA AMERICANA L.
![[ 5 ] THE NUTRITION OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM IN THE COCKROACH PERIPLANETA AMERICANA L. [ 5 ] THE NUTRITION OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM IN THE COCKROACH PERIPLANETA AMERICANA L.](/thumbs/79/80233200.jpg) [ 5 ] THE NUTRITION OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM IN THE COCKROACH PERIPLANETA AMERICANA L. THE ROLE OF PERINEURIUM AND GLIAL CELLS IN THE MOBILIZATION OF RESERVES BY V. B. WIGGLESWORTH Agricultural Research
[ 5 ] THE NUTRITION OF THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM IN THE COCKROACH PERIPLANETA AMERICANA L. THE ROLE OF PERINEURIUM AND GLIAL CELLS IN THE MOBILIZATION OF RESERVES BY V. B. WIGGLESWORTH Agricultural Research
Chapter 37 Active Reading Guide Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Section 1 1. What is a neuron? Chapter 37 Active Reading Guide Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling 2. Neurons can be placed into three groups, based on their location and function.
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Section 1 1. What is a neuron? Chapter 37 Active Reading Guide Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling 2. Neurons can be placed into three groups, based on their location and function.
Membrane Potentials and Bioelectricity
 Membrane Potentials and Bioelectricity Hugh Purdy Honors University Physics II November 29, 2010 Most, if not all, cells in the human body have a net electric charge to some degree on either side of their
Membrane Potentials and Bioelectricity Hugh Purdy Honors University Physics II November 29, 2010 Most, if not all, cells in the human body have a net electric charge to some degree on either side of their
Biosciences in the 21st century
 Biosciences in the 21st century Lecture 1: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Dr. Michael Burger Outline: 1. Why neuroscience? 2. The neuron 3. Action potentials 4. Synapses 5. Organization of the nervous
Biosciences in the 21st century Lecture 1: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Dr. Michael Burger Outline: 1. Why neuroscience? 2. The neuron 3. Action potentials 4. Synapses 5. Organization of the nervous
MEMBRANE POTENTIALS AND ACTION POTENTIALS:
 University of Jordan Faculty of Medicine Department of Physiology & Biochemistry Medical students, 2017/2018 +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ Review: Membrane physiology
University of Jordan Faculty of Medicine Department of Physiology & Biochemistry Medical students, 2017/2018 +++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++ Review: Membrane physiology
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Electron-dense inter-mitochondrial junctions (IMJs) and associated cristae organization are evolutionary conserved features of mitochondria-mitochondria contacts. Shown are electron
Supplementary Figure 1 Electron-dense inter-mitochondrial junctions (IMJs) and associated cristae organization are evolutionary conserved features of mitochondria-mitochondria contacts. Shown are electron
REVIEW FENESTRATION NODES AND THE WIDE SUBMYELINIC SPACE FORM THE BASIS FOR THE UNUSUALLY FAST IMPULSE CONDUCTION OF SHRIMP MYELINATED AXONS
 The Journal of Experimental Biology 202, 1979 1989 (1999) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1999 JEB2168 1979 REVIEW FENESTRATION NODES AND THE WIDE SUBMYELINIC SPACE FORM THE
The Journal of Experimental Biology 202, 1979 1989 (1999) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1999 JEB2168 1979 REVIEW FENESTRATION NODES AND THE WIDE SUBMYELINIC SPACE FORM THE
Cellular Neuroanatomy II The Prototypical Neuron: Neurites. Reading: BCP Chapter 2
 Cellular Neuroanatomy II The Prototypical Neuron: Neurites Reading: BCP Chapter 2 Major Internal Features of a Neuron The neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. A typical neuron has a soma
Cellular Neuroanatomy II The Prototypical Neuron: Neurites Reading: BCP Chapter 2 Major Internal Features of a Neuron The neuron is the functional unit of the nervous system. A typical neuron has a soma
Overview of Physiology & Homeostasis. Biological explanations Levels of organization Homeostasis
 Overview of Physiology & Homeostasis 1 Biological explanations Levels of organization Homeostasis 2 Biological Explanations Proximate Proximate causation: an explanation of an animal's behavior based on
Overview of Physiology & Homeostasis 1 Biological explanations Levels of organization Homeostasis 2 Biological Explanations Proximate Proximate causation: an explanation of an animal's behavior based on
CELL BIOLOGY. Which of the following cell structures does not have membranes? A. Ribosomes B. Mitochondria C. Chloroplasts D.
 1 CELL BIOLOGY PROKARYOTIC and EUKARYOTIC SP/1. SP/2. SP/4. Plant and animal cells both have A. ribosomes, cell walls and mitochondria. B. Golgi apparatus, chromosomes and mitochondria. C. Golgi apparatus,
1 CELL BIOLOGY PROKARYOTIC and EUKARYOTIC SP/1. SP/2. SP/4. Plant and animal cells both have A. ribosomes, cell walls and mitochondria. B. Golgi apparatus, chromosomes and mitochondria. C. Golgi apparatus,
Form and Function. Physical Laws and Form. Chapter 40: Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function. AP Biology Fig Figs & 40.
 Chapter 40: Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function AP Biology 2013 1 Form and Function Comparative studies show that form and function are closely related Natural selection can fit the form (anatomy)
Chapter 40: Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function AP Biology 2013 1 Form and Function Comparative studies show that form and function are closely related Natural selection can fit the form (anatomy)
Potassium Uptake Mechanisms of Cultured Oligodendrocytes Studied with lon-sensitive Electrodes
 Potassium Uptake Mechanisms of Cultured Oligodendrocytes Studied with lon-sensitive Electrodes H. Kettenmann, R. K. Orkand, and M. Schachner Introduction Physiological studies over the past two decades
Potassium Uptake Mechanisms of Cultured Oligodendrocytes Studied with lon-sensitive Electrodes H. Kettenmann, R. K. Orkand, and M. Schachner Introduction Physiological studies over the past two decades
Introduction to CNS neurobiology: focus on retina
 Introduction to CNS neurobiology: focus on retina September 27, 2017 The retina is part of the CNS Calloway et al., 2009) 1 Retinal circuits: neurons and synapses Rods and Cones Bipolar cells Horizontal
Introduction to CNS neurobiology: focus on retina September 27, 2017 The retina is part of the CNS Calloway et al., 2009) 1 Retinal circuits: neurons and synapses Rods and Cones Bipolar cells Horizontal
AN AUTORADIOGRAPHICAL STUDY OF THE LOCALIZATION OF THE UPTAKE OF GLUTAMATE BY THE PERIPHERAL NERVES OF THE CRAB, CARCINUS MAENAS (L.
 J. Cell Sci. 14, 351-367 (i974) 351 Printed in Great Britain AN AUTORADIOGRAPHICAL STUDY OF THE LOCALIZATION OF THE UPTAKE OF GLUTAMATE BY THE PERIPHERAL NERVES OF THE CRAB, CARCINUS MAENAS (L.) P. D.
J. Cell Sci. 14, 351-367 (i974) 351 Printed in Great Britain AN AUTORADIOGRAPHICAL STUDY OF THE LOCALIZATION OF THE UPTAKE OF GLUTAMATE BY THE PERIPHERAL NERVES OF THE CRAB, CARCINUS MAENAS (L.) P. D.
Sheaths of the motor axons of the crab Carcinus
 175 Sheaths of the motor axons of the crab Carcinus By G. A. HORRIDGE and R. A. CHAPMAN (From the Gatty Marine Laboratory and Department of Natural History, the University, St. Andrews, Fife) With 3 plates
175 Sheaths of the motor axons of the crab Carcinus By G. A. HORRIDGE and R. A. CHAPMAN (From the Gatty Marine Laboratory and Department of Natural History, the University, St. Andrews, Fife) With 3 plates
Neurons and Nervous Systems
 34 Neurons and Nervous Systems Concept 34.1 Nervous Systems Consist of Neurons and Glia Nervous systems have two categories of cells: Neurons, or nerve cells, are excitable they generate and transmit electrical
34 Neurons and Nervous Systems Concept 34.1 Nervous Systems Consist of Neurons and Glia Nervous systems have two categories of cells: Neurons, or nerve cells, are excitable they generate and transmit electrical
Studies on ATP-diphosphohydrolase nucleotide-binding sites by intrinsic fluorescence
 Brazilian ATP-diphosphohydrolase Journal of Medical fluorescence and Biological studies Research (2000) 33: 725-729 ISSN 0100-879X 725 Studies on ATP-diphosphohydrolase nucleotide-binding sites by intrinsic
Brazilian ATP-diphosphohydrolase Journal of Medical fluorescence and Biological studies Research (2000) 33: 725-729 ISSN 0100-879X 725 Studies on ATP-diphosphohydrolase nucleotide-binding sites by intrinsic
CYTOLOGY & HISTOLOGY THE STUDY OF CELLS AND TISSUES
 NAME: DATE: PARTNER: CYTOLOGY & HISTOLOGY THE STUDY OF CELLS AND TISSUES For ease of study, multicellular animals are often examined at various levels of structural organization. Starting from the most
NAME: DATE: PARTNER: CYTOLOGY & HISTOLOGY THE STUDY OF CELLS AND TISSUES For ease of study, multicellular animals are often examined at various levels of structural organization. Starting from the most
Xenopus laevis (Daudin)
 The Structure of Myelin Sheaths in the Central Nervous System of Xenopus laevis (Daudin) By A. PETERS, Ph.D. (From the Department of Anatomy, University of Edinburgh, Scotland) PLATES 43 To 47 (Received
The Structure of Myelin Sheaths in the Central Nervous System of Xenopus laevis (Daudin) By A. PETERS, Ph.D. (From the Department of Anatomy, University of Edinburgh, Scotland) PLATES 43 To 47 (Received
Nucleus and Mitosis. VIBS 443 and VIBS 602. Undergraduate Graduate Histology Lecture Series
 Nucleus and Mitosis VIBS 443 and VIBS 602 Undergraduate Graduate Histology Lecture Series Larry Johnson, Professor Veterinary Integrative Biosciences Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843 Objectives
Nucleus and Mitosis VIBS 443 and VIBS 602 Undergraduate Graduate Histology Lecture Series Larry Johnson, Professor Veterinary Integrative Biosciences Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843 Objectives
tre of Mark Louie D. Lop
 NERVE PHYSIOLOGY Mark Louie D. Lopez College of Science Polytechnic University of the Philippines FUNCTIONS OF NERVOUS SYSTEM Sensory input or detection Integration processing transmission of information
NERVE PHYSIOLOGY Mark Louie D. Lopez College of Science Polytechnic University of the Philippines FUNCTIONS OF NERVOUS SYSTEM Sensory input or detection Integration processing transmission of information
FINE STRUCTUREOF THE CENTRALNERVOUS SYSTEMOF
 Reprinted from the JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY Vol. 60, No.4, August 1974 p. 687-698 Made in United States of America Copyright @ 1974 by the American Society of Parasitologists 0{; FINE STRUCTUREOF THE CENTRALNERVOUS
Reprinted from the JOURNAL OF PARASITOLOGY Vol. 60, No.4, August 1974 p. 687-698 Made in United States of America Copyright @ 1974 by the American Society of Parasitologists 0{; FINE STRUCTUREOF THE CENTRALNERVOUS
Prelab Exercise 1. Cell structure
 Prelab Exercise 1 CELLS, EPITHELIA, GLANDS AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Prelab guide: this will function as a review of material that will be important to your performance of the lab. The first lab will examine
Prelab Exercise 1 CELLS, EPITHELIA, GLANDS AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE Prelab guide: this will function as a review of material that will be important to your performance of the lab. The first lab will examine
Novel Organization and Development of Copepod Myelin. II. Nonglial Origin
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Novel Organization and Development of Copepod Myelin. II. Nonglial Origin Caroline H. Wilson, 1,2 and Daniel K. Hartline 1 * 1 Békésy Laboratory of Neurobiology, Pacific Biosciences Research
RESEARCH ARTICLE Novel Organization and Development of Copepod Myelin. II. Nonglial Origin Caroline H. Wilson, 1,2 and Daniel K. Hartline 1 * 1 Békésy Laboratory of Neurobiology, Pacific Biosciences Research
Intercellular Communication. Department of Physiology School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara
 Intercellular Communication Department of Physiology School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara Intercellular Communication and Signal Transduction The ability of cells to communicate with each other
Intercellular Communication Department of Physiology School of Medicine University of Sumatera Utara Intercellular Communication and Signal Transduction The ability of cells to communicate with each other
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues
 Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
Biology 13A Lab #3: Cells and Tissues Lab #3 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes.... 28 Introduction...... 28 Activity 1: Eukaryotic Cell Structure... 29 Activity 2: Perspectives on Tissue Preparations.
POTENTIALS ASSOCIATED WITH THE BLOOD- BRAIN BARRIER OF AN INSECT: RECORDINGS FROM IDENTIFIED NEUROGLIA
 J. exp. Biol. 109, 307-318 (1984) 307 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1984 POTENTIALS ASSOCIATED WITH THE BLOOD- BRAIN BARRIER OF AN INSECT: RECORDINGS FROM IDENTIFIED NEUROGLIA
J. exp. Biol. 109, 307-318 (1984) 307 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1984 POTENTIALS ASSOCIATED WITH THE BLOOD- BRAIN BARRIER OF AN INSECT: RECORDINGS FROM IDENTIFIED NEUROGLIA
Nervous System Organization
 The Nervous System Nervous System Organization Receptors respond to stimuli Sensory receptors detect the stimulus Motor effectors respond to stimulus Nervous system divisions Central nervous system Command
The Nervous System Nervous System Organization Receptors respond to stimuli Sensory receptors detect the stimulus Motor effectors respond to stimulus Nervous system divisions Central nervous system Command
Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function. Chapter 40
 Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function Chapter 40 Form and Function Anatomy- biological form of an organism. Physiology- biological function. Size and Shape Development of body plan and shape is
Basic Principles of Animal Form and Function Chapter 40 Form and Function Anatomy- biological form of an organism. Physiology- biological function. Size and Shape Development of body plan and shape is
According to the diagram, which of the following is NOT true?
 Instructions: Review Chapter 44 on muscular-skeletal systems and locomotion, and then complete the following Blackboard activity. This activity will introduce topics that will be covered in the next few
Instructions: Review Chapter 44 on muscular-skeletal systems and locomotion, and then complete the following Blackboard activity. This activity will introduce topics that will be covered in the next few
Biology the study of life. Lecture 15
 Biology the study of life Lecture 15 Life (a life form: an organism ) can be defined as an organized genetic unit capable of metabolism, reproduction, & evolution (Purves et al., 2003) There is order to
Biology the study of life Lecture 15 Life (a life form: an organism ) can be defined as an organized genetic unit capable of metabolism, reproduction, & evolution (Purves et al., 2003) There is order to
Guided Reading Activities
 Name Period Chapter 4: A Tour of the Cell Guided Reading Activities Big Idea: Introduction to the Cell Answer the following questions as you read Modules 4.1 4.4: 1. A(n) uses a beam of light to illuminate
Name Period Chapter 4: A Tour of the Cell Guided Reading Activities Big Idea: Introduction to the Cell Answer the following questions as you read Modules 4.1 4.4: 1. A(n) uses a beam of light to illuminate
Part One: The Chemistry of Life
 Part One: The Chemistry of Life Chemistry is the study of matter and its changes. Organisms obtain and use many chemicals The metabolism of organisms involves many chemical reactions To understand all
Part One: The Chemistry of Life Chemistry is the study of matter and its changes. Organisms obtain and use many chemicals The metabolism of organisms involves many chemical reactions To understand all
THE ULTRASTRUCTURE OF THE PERI- NEURIUM IN TWO INSECT SPECIES, CARAUSIUS MOROSUS AND PERIPLANETA AMERICANA
 J. Ceil Set. 2, 119-138 (1967) 119 Printed in Great Britain THE ULTRASTRUCTURE OF THE PERI- NEURIUM IN TWO INSECT SPECIES, CARAUSIUS MOROSUS AND PERIPLANETA AMERICANA S. H. P. MADDRELL* AND J. E. TREHERNEf
J. Ceil Set. 2, 119-138 (1967) 119 Printed in Great Britain THE ULTRASTRUCTURE OF THE PERI- NEURIUM IN TWO INSECT SPECIES, CARAUSIUS MOROSUS AND PERIPLANETA AMERICANA S. H. P. MADDRELL* AND J. E. TREHERNEf
Physiology 2 nd year. Neuroscience Optional Lecture
 Academic year 2018/2019 Physiology 2 nd year Semester 1 Curricula Nervous system physiology Blood physiology Acid-base equilibrium Bibliography: Boron & Boulpaep Medical Physiology, 3 rd edition Physiology
Academic year 2018/2019 Physiology 2 nd year Semester 1 Curricula Nervous system physiology Blood physiology Acid-base equilibrium Bibliography: Boron & Boulpaep Medical Physiology, 3 rd edition Physiology
Lecture Notes 8C120 Inleiding Meten en Modelleren. Cellular electrophysiology: modeling and simulation. Nico Kuijpers
 Lecture Notes 8C2 Inleiding Meten en Modelleren Cellular electrophysiology: modeling and simulation Nico Kuijpers nico.kuijpers@bf.unimaas.nl February 9, 2 2 8C2 Inleiding Meten en Modelleren Extracellular
Lecture Notes 8C2 Inleiding Meten en Modelleren Cellular electrophysiology: modeling and simulation Nico Kuijpers nico.kuijpers@bf.unimaas.nl February 9, 2 2 8C2 Inleiding Meten en Modelleren Extracellular
DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST Topic 3- Cells and Transport
 Topic 3- Cells and Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma membranes D) All cells can
Topic 3- Cells and Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma membranes D) All cells can
Aberrant Mitochondria with Longitudinal Cristae Observed in the Normal Rat Hepatic Parenchymal Cell. Takuma Saito and Kazuo Ozawa
 Okajimas Fol. anat. jap., 44 : 357-363, 1968 Aberrant Mitochondria with Longitudinal Cristae Observed in the Normal Rat Hepatic Parenchymal Cell By Takuma Saito and Kazuo Ozawa Department of Anatomy, Kansai
Okajimas Fol. anat. jap., 44 : 357-363, 1968 Aberrant Mitochondria with Longitudinal Cristae Observed in the Normal Rat Hepatic Parenchymal Cell By Takuma Saito and Kazuo Ozawa Department of Anatomy, Kansai
Nervous Tissue. Neurons Neural communication Nervous Systems
 Nervous Tissue Neurons Neural communication Nervous Systems What is the function of nervous tissue? Maintain homeostasis & respond to stimuli Sense & transmit information rapidly, to specific cells and
Nervous Tissue Neurons Neural communication Nervous Systems What is the function of nervous tissue? Maintain homeostasis & respond to stimuli Sense & transmit information rapidly, to specific cells and
Computational Neuroscience
 Computational Neuroscience Zoltán Somogyvári senior research fellow Wigner Research Institute for Physics, Theoretical Department Supporting materials: http://www.kfki.hu/~soma/bscs/ BSCS 2012 Lengyel
Computational Neuroscience Zoltán Somogyvári senior research fellow Wigner Research Institute for Physics, Theoretical Department Supporting materials: http://www.kfki.hu/~soma/bscs/ BSCS 2012 Lengyel
Math in systems neuroscience. Quan Wen
 Math in systems neuroscience Quan Wen Human brain is perhaps the most complex subject in the universe 1 kg brain 10 11 neurons 180,000 km nerve fiber 10 15 synapses 10 18 synaptic proteins Multiscale
Math in systems neuroscience Quan Wen Human brain is perhaps the most complex subject in the universe 1 kg brain 10 11 neurons 180,000 km nerve fiber 10 15 synapses 10 18 synaptic proteins Multiscale
The Nervous System. Nervous System Organization. Nerve Tissue. Two parts to the nervous system 11/27/2016
 The Nervous System Nervous System Organization Animals must be able to respond to environmental stimuli. Three functions of the nervous system: Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors.
The Nervous System Nervous System Organization Animals must be able to respond to environmental stimuli. Three functions of the nervous system: Sensory input conduction of signals from sensory receptors.
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
* ra. VOL. 53, 1965 ANATOMY: D. BODIAN 419. FIG. 1.-Synaptic contact in spinal motoneuron of a chimpanzee. Large dendrite (D) shows
 A SUGGESTIVE RELATIONSHIP OF NERVE CELL RNA WITh1 SPECIFIC SYNAPTIC SITES* BY DAVID BODIAN DEPARTMENT OF ANATOMY, JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE Communicated December 29, 1964 In a previous
A SUGGESTIVE RELATIONSHIP OF NERVE CELL RNA WITh1 SPECIFIC SYNAPTIC SITES* BY DAVID BODIAN DEPARTMENT OF ANATOMY, JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE Communicated December 29, 1964 In a previous
1. Dendrites contain the nuclei, ribosomes, mitochondria, and other structures found in most cells.
 : Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses TRUE/FALSE 1. Dendrites contain the nuclei, ribosomes, mitochondria, and other structures found in most cells. ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: factual REF: Anatomy of Neurons 2. A small
: Nerve Cells and Nerve Impulses TRUE/FALSE 1. Dendrites contain the nuclei, ribosomes, mitochondria, and other structures found in most cells. ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: factual REF: Anatomy of Neurons 2. A small
University of Jordan School of Medicine MD Program Curriculum
 University of Jordan School of Medicine MD Program Curriculum Course Title: General Histology Course number: 0502111 Credit Hours: 2 credits Academic Year Level: 1st year, 2nd semester 2016/2017 Course
University of Jordan School of Medicine MD Program Curriculum Course Title: General Histology Course number: 0502111 Credit Hours: 2 credits Academic Year Level: 1st year, 2nd semester 2016/2017 Course
Control and Integration. Nervous System Organization: Bilateral Symmetric Animals. Nervous System Organization: Radial Symmetric Animals
 Control and Integration Neurophysiology Chapters 10-12 Nervous system composed of nervous tissue cells designed to conduct electrical impulses rapid communication to specific cells or groups of cells Endocrine
Control and Integration Neurophysiology Chapters 10-12 Nervous system composed of nervous tissue cells designed to conduct electrical impulses rapid communication to specific cells or groups of cells Endocrine
THE FINE STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF NERVE FIBERS, SHEATHS, AND GLIAL CELLS IN
 THE FINE STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF NERVE FIBERS, SHEATHS, AND GLIAL CELLS IN THE PRAWN, PALAEMONETES VULGARIS JOHN E. HEUSER and CARLOS F. DOGGENWEILER From the Harvard Medical School, Departments of
THE FINE STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF NERVE FIBERS, SHEATHS, AND GLIAL CELLS IN THE PRAWN, PALAEMONETES VULGARIS JOHN E. HEUSER and CARLOS F. DOGGENWEILER From the Harvard Medical School, Departments of
LOCALIZATION OF THE BLOOD-BRAIN BARRIER OF AN INSECT: ELECTRICAL MODEL AND ANALYSIS
 J. exp. Biol. 109, 319-331 (1984) 319 printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1984 LOCALIZATION OF THE BLOOD-BRAIN BARRIER OF AN INSECT: ELECTRICAL MODEL AND ANALYSIS BY P. K. SCHOFIELD
J. exp. Biol. 109, 319-331 (1984) 319 printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1984 LOCALIZATION OF THE BLOOD-BRAIN BARRIER OF AN INSECT: ELECTRICAL MODEL AND ANALYSIS BY P. K. SCHOFIELD
MECHANISMS OF IONIC HOMEOSTASIS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM OF AN INSECT
 J. exp. Biol. (1981), 95, 61-73 6l Hyith 6 figuret Printed in Great Britain MECHANISMS OF IONIC HOMEOSTASIS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM OF AN INSECT BY J. E. TREHERNE AND P. K. SCHOFIELD A.R.C. Unit
J. exp. Biol. (1981), 95, 61-73 6l Hyith 6 figuret Printed in Great Britain MECHANISMS OF IONIC HOMEOSTASIS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM OF AN INSECT BY J. E. TREHERNE AND P. K. SCHOFIELD A.R.C. Unit
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were not seen and described until 1665, when Robert Hooke first looked at dead cells from an oak tree.
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were not seen and described until 1665, when Robert Hooke first looked at dead cells from an oak tree.
Name # Class Date Regents Review: Cells & Cell Transport
 Name # Class Date Regents Review: Cells & Cell Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma
Name # Class Date Regents Review: Cells & Cell Transport 1. All of the following are true regarding cells except? A) All cells have genetic material B) All cells have cell walls C) All cells have plasma
REVIEW 2: CELLS & CELL COMMUNICATION. A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned:
 Name AP Biology REVIEW 2: CELLS & CELL COMMUNICATION A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes No internal membranes vs. membrane-bound organelles
Name AP Biology REVIEW 2: CELLS & CELL COMMUNICATION A. Top 10 If you learned anything from this unit, you should have learned: 1. Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes No internal membranes vs. membrane-bound organelles
MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning
 MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning Learning Goals for Lecture 29 4.1 Describe the contributions of early developmental events in the embryo to the formation
MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning Learning Goals for Lecture 29 4.1 Describe the contributions of early developmental events in the embryo to the formation
REQUIREMENTS FOR THE BIOCHEMISTRY MAJOR
 REQUIREMENTS FOR THE BIOCHEMISTRY MAJOR Grade Requirement: All courses required for the Biochemistry major (CH, MATH, PHYS, BI courses) must be graded and passed with a grade of C- or better. Core Chemistry
REQUIREMENTS FOR THE BIOCHEMISTRY MAJOR Grade Requirement: All courses required for the Biochemistry major (CH, MATH, PHYS, BI courses) must be graded and passed with a grade of C- or better. Core Chemistry
Localization of connexins in neurons and glia cells of the Helix aspersa suboesophageal brain ganglia by immunocytochemistry
 Histol Histopathol (2007) 22: 497-504 http://www.hh.um.es Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Localization of connexins in neurons and glia cells of the Helix aspersa suboesophageal
Histol Histopathol (2007) 22: 497-504 http://www.hh.um.es Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Localization of connexins in neurons and glia cells of the Helix aspersa suboesophageal
BIOLOGY 374 MAMMALIAN CELL MICROANATOMY. Wayne L. Rickoll Phone:
 BIOLOGY 374 MAMMALIAN CELL MICROANATOMY Wayne L. Rickoll Phone: 879-3120 Thompson 257B email: rickoll@ups.edu OFFICE/LAB CHATS GENEROUSLY AVAILABLE. Just email me or send a voice mail as to when you would
BIOLOGY 374 MAMMALIAN CELL MICROANATOMY Wayne L. Rickoll Phone: 879-3120 Thompson 257B email: rickoll@ups.edu OFFICE/LAB CHATS GENEROUSLY AVAILABLE. Just email me or send a voice mail as to when you would
Basic Chemistry. Chemistry Review. Bio 250: Anatomy & Physiology
 Basic Chemistry Bio 250: Anatomy & Physiology Chemistry Review It is going to be your responsibility to review the basic principles of chemistry you learned in BIO 101 This basic set of notes will help
Basic Chemistry Bio 250: Anatomy & Physiology Chemistry Review It is going to be your responsibility to review the basic principles of chemistry you learned in BIO 101 This basic set of notes will help
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell
 AP Biology Reading Guide Fred and Theresa Holtzclaw Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Name Period Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry
AP Biology Reading Guide Fred and Theresa Holtzclaw Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Name Period Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry
VOCABULARY. Cell Membrane Nucleus Cell Wall Chloroplast Vacuole Tissue Organ Organ System
 CELLS VOCABULARY Cell Membrane Nucleus Cell Wall Chloroplast Vacuole Tissue Organ Organ System THE IMPORTANCE OF CELLS Cells are the smallest unit of life in all living things They are organized structures
CELLS VOCABULARY Cell Membrane Nucleus Cell Wall Chloroplast Vacuole Tissue Organ Organ System THE IMPORTANCE OF CELLS Cells are the smallest unit of life in all living things They are organized structures
SPRINGFIELD TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC AFFAIRS
 SPRINGFIELD TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC AFFAIRS Course Number: BIOL 132 Department: Biological Sciences Course Title: Anatomy & Physiology 1 Semester: Spring Year: 1997 Objectives/ 1. Recognize
SPRINGFIELD TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC AFFAIRS Course Number: BIOL 132 Department: Biological Sciences Course Title: Anatomy & Physiology 1 Semester: Spring Year: 1997 Objectives/ 1. Recognize
BIOLOGY. 1. Overview of Neurons 11/3/2014. Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling. Communication in Neurons
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION 48 Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick 1. Overview of Neurons Communication
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION 48 Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick 1. Overview of Neurons Communication
REQUIREMENTS FOR THE BIOCHEMISTRY MAJOR
 REQUIREMENTS FOR THE BIOCHEMISTRY MAJOR Grade Requirement: All courses required for the Biochemistry major (CH, MATH, PHYS, BI courses) must be graded and passed with a grade of C- or better. Core Chemistry
REQUIREMENTS FOR THE BIOCHEMISTRY MAJOR Grade Requirement: All courses required for the Biochemistry major (CH, MATH, PHYS, BI courses) must be graded and passed with a grade of C- or better. Core Chemistry
Cell Structure and Function. The Development of Cell Theory
 Cell Structure and Function The Development of Cell Theory Hooke's original microscope, that he used at Oxford University, in 1665. Robert Hooke first examined a thin piece of cork (see below), and coined
Cell Structure and Function The Development of Cell Theory Hooke's original microscope, that he used at Oxford University, in 1665. Robert Hooke first examined a thin piece of cork (see below), and coined
4. Which of the following organelles digests waste using hydrolytic enzymes:
 Multichoice questions section. You must answer ALL questions. 1. A cell contains many organelles, each of which has a specific function. What is function of mitochondria? a) production of plasma membrane
Multichoice questions section. You must answer ALL questions. 1. A cell contains many organelles, each of which has a specific function. What is function of mitochondria? a) production of plasma membrane
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 6 Tour of the Cell
 Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 6 Tour of the Cell BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the whole chapter from p. 93-121, mostly skimming Concept 6.1 on microscopy. Figure 6.8 on pp. 100-101 is really helpful in showing
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 6 Tour of the Cell BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the whole chapter from p. 93-121, mostly skimming Concept 6.1 on microscopy. Figure 6.8 on pp. 100-101 is really helpful in showing
Organization of Vertebrate Body. Organization of Vertebrate Body
 The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation Chapter 43 There are four levels of organization: 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems Bodies of vertebrates are composed of different cell types
The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation Chapter 43 There are four levels of organization: 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems Bodies of vertebrates are composed of different cell types
Squid. Announcements. L03. ROOTS of NEUROETHOLOGY IN CELLULAR NEUROBIOLOGY. Outline. The Discovery of the Giant Squid Axon KROGH S PRINCIPLE
 L03. ROOTS of NEUROETHOLOGY IN CELLULAR NEUROBIOLOGY Announcements 1) Course website: http://courses.cit.cornell.edu/bionb4240/index.htm Google Chrome? 2) Writing Assignments W1 3) Discussion section Wednesday
L03. ROOTS of NEUROETHOLOGY IN CELLULAR NEUROBIOLOGY Announcements 1) Course website: http://courses.cit.cornell.edu/bionb4240/index.htm Google Chrome? 2) Writing Assignments W1 3) Discussion section Wednesday
Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology
 Cytology Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology Email: da.hassan@psau.edu.sa Cells All living things are made up of cells Basic building blocks of life It is the smallest functional and
Cytology Dr. Dina A. A. Hassan Associate Professor, Pharmacology Email: da.hassan@psau.edu.sa Cells All living things are made up of cells Basic building blocks of life It is the smallest functional and
Physiology Unit 2. MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES
 Physiology Unit 2 MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES In Physiology Today Ohm s Law I = V/R Ohm s law: the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the
Physiology Unit 2 MEMBRANE POTENTIALS and SYNAPSES In Physiology Today Ohm s Law I = V/R Ohm s law: the current through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the
Anatomy and Physiology GRADE 12 Course Curriculum Prepared by Lou Pompilii ABINGTON SCHOOL DISTRICT Abington, Pennsylvania 2010
 Anatomy and Physiology GRADE 12 Course Curriculum Prepared by Lou Pompilii ABINGTON SCHOOL DISTRICT Abington, Pennsylvania 2010 Anatomy & Physiology A Course of Study Table of Contents Contents: Page:
Anatomy and Physiology GRADE 12 Course Curriculum Prepared by Lou Pompilii ABINGTON SCHOOL DISTRICT Abington, Pennsylvania 2010 Anatomy & Physiology A Course of Study Table of Contents Contents: Page:
Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry
 Name Period Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were
Name Period Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell Concept 6.1 To study cells, biologists use microscopes and the tools of biochemistry 1. The study of cells has been limited by their small size, and so they were
Vertebrate Physiology 437 EXAM I NAME, Section (circle): am pm 23 September Exam is worth 100 points. You have 75 minutes.
 1 Vertebrate Physiology 437 EXAM I NAME, Section (circle): am pm 23 September 2004. Exam is worth 100 points. You have 75 minutes. True or False (write true or false ; 10 points total; 1 point each) 1.
1 Vertebrate Physiology 437 EXAM I NAME, Section (circle): am pm 23 September 2004. Exam is worth 100 points. You have 75 minutes. True or False (write true or false ; 10 points total; 1 point each) 1.
BIOLOGY 11/10/2016. Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling. Concept 48.1: Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer
 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Concept 48.1: Neuron organization
48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Concept 48.1: Neuron organization
Functions of the systems of the human body and their relation to homeostasis; includes disease prevention and cure, health, wellness, and nutrition.
 UNITED STATES INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF ARTS AND SCIENCES COURSE SYLLABUS NSC 2205: HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY CREDIT 3 UNITS A. COURSE DESCRIPTION Functions of the systems of the human body and their relation
UNITED STATES INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF ARTS AND SCIENCES COURSE SYLLABUS NSC 2205: HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY CREDIT 3 UNITS A. COURSE DESCRIPTION Functions of the systems of the human body and their relation
PROPERTY OF ELSEVIER SAMPLE CONTENT - NOT FINAL. The Nervous System and Muscle
 The Nervous System and Muscle SECTION 2 2-1 Nernst Potential 2-2 Resting Membrane Potential 2-3 Axonal Action Potential 2-4 Neurons 2-5 Axonal Conduction 2-6 Morphology of Synapses 2-7 Chemical Synaptic
The Nervous System and Muscle SECTION 2 2-1 Nernst Potential 2-2 Resting Membrane Potential 2-3 Axonal Action Potential 2-4 Neurons 2-5 Axonal Conduction 2-6 Morphology of Synapses 2-7 Chemical Synaptic
The Discovery of the Cell
 7-1 Life Is Cellular Review The cell is the basic unit of life! Life began with the first cell! All living things are composed of cells! Cells make up tissues, organs, organ systems and organisms! Understanding
7-1 Life Is Cellular Review The cell is the basic unit of life! Life began with the first cell! All living things are composed of cells! Cells make up tissues, organs, organ systems and organisms! Understanding
Microsystems for Neuroscience and Medicine. Lecture 9
 1 Microsystems for Neuroscience and Medicine Lecture 9 2 Neural Microsystems Neurons - Structure and behaviour Measuring neural activity Interfacing with neurons Medical applications - DBS, Retinal Implants
1 Microsystems for Neuroscience and Medicine Lecture 9 2 Neural Microsystems Neurons - Structure and behaviour Measuring neural activity Interfacing with neurons Medical applications - DBS, Retinal Implants
Zimmerman AP Biology CBHS South Name Chapter 7&8 Guided Reading Assignment 1) What is resolving power and why is it important in biology?
 Zimmerman AP Biology CBHS South Name Chapter 7&8 Guided Reading Assignment 1) What is resolving power and why is it important in biology? 2) How does an electron microscope work and what is the difference
Zimmerman AP Biology CBHS South Name Chapter 7&8 Guided Reading Assignment 1) What is resolving power and why is it important in biology? 2) How does an electron microscope work and what is the difference
Nervous Tissue. Neurons Electrochemical Gradient Propagation & Transduction Neurotransmitters Temporal & Spatial Summation
 Nervous Tissue Neurons Electrochemical Gradient Propagation & Transduction Neurotransmitters Temporal & Spatial Summation What is the function of nervous tissue? Maintain homeostasis & respond to stimuli
Nervous Tissue Neurons Electrochemical Gradient Propagation & Transduction Neurotransmitters Temporal & Spatial Summation What is the function of nervous tissue? Maintain homeostasis & respond to stimuli
Study (s) Degree Center Acad. Period
 COURSE DATA Data Subject Code 33044 Name Cellular structure Cycle Grade ECTS Credits 6.0 Academic year 2017-2018 Study (s) Degree Center Acad. Period year 1100 - Graduado/a en Biología FACULTY OF BIOLOGICAL
COURSE DATA Data Subject Code 33044 Name Cellular structure Cycle Grade ECTS Credits 6.0 Academic year 2017-2018 Study (s) Degree Center Acad. Period year 1100 - Graduado/a en Biología FACULTY OF BIOLOGICAL
Chapter 1. DNA is made from the building blocks adenine, guanine, cytosine, and. Answer: d
 Chapter 1 1. Matching Questions DNA is made from the building blocks adenine, guanine, cytosine, and. Answer: d 2. Matching Questions : Unbranched polymer that, when folded into its three-dimensional shape,
Chapter 1 1. Matching Questions DNA is made from the building blocks adenine, guanine, cytosine, and. Answer: d 2. Matching Questions : Unbranched polymer that, when folded into its three-dimensional shape,
Review. Watch the following video How Stuff Works - Cells video
 Types of Cells Review Watch the following video How Stuff Works - Cells video Multi-cellular Organisms Living things can be as simple as single-celled organisms such as a Paramecium or an Amoeba that lives
Types of Cells Review Watch the following video How Stuff Works - Cells video Multi-cellular Organisms Living things can be as simple as single-celled organisms such as a Paramecium or an Amoeba that lives
Potassium Homeostasis in Glia
 Potassium Homeostasis in Glia 867 Potassium Homeostasis in Glia P Kofuji and E A Newman, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, USA ã 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. Potassium in the Extracellular
Potassium Homeostasis in Glia 867 Potassium Homeostasis in Glia P Kofuji and E A Newman, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, USA ã 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. Potassium in the Extracellular
Department Curriculum and Assessment Outline
 Department: Science Year Group: 10 Teaching, learning and assessment during the course: Combined Science 1 2 B1 Key concepts in Biology B2 Cells and control What are the structure and function of cells.
Department: Science Year Group: 10 Teaching, learning and assessment during the course: Combined Science 1 2 B1 Key concepts in Biology B2 Cells and control What are the structure and function of cells.
Cells to Tissues. Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology
 Cells to Tissues Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology From one cell to ensembles of cells. Multicellular organisms require individual cells to work together in functional groups. This means cells
Cells to Tissues Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology From one cell to ensembles of cells. Multicellular organisms require individual cells to work together in functional groups. This means cells
Topic 3: Cells Ch. 6. Microscopes pp Microscopes. Microscopes. Microscopes. Microscopes
 Topic 3: Cells Ch. 6 -All life is composed of cells and all cells have a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA. pp.105-107 - The development of the microscope was the key to understanding that all living
Topic 3: Cells Ch. 6 -All life is composed of cells and all cells have a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA. pp.105-107 - The development of the microscope was the key to understanding that all living
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 211 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. 4 Credit Hours. Prepared by: Deborah Allen. Revised date: July, 2014
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 211 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Deborah Allen Revised date: July, 2014 Linda Abernathy, Division Chair for Math, Science, and Business Shirley
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 211 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Deborah Allen Revised date: July, 2014 Linda Abernathy, Division Chair for Math, Science, and Business Shirley
Principles of Cellular Biology
 Principles of Cellular Biology آشنایی با مبانی اولیه سلول Biologists are interested in objects ranging in size from small molecules to the tallest trees: Cell Basic building blocks of life Understanding
Principles of Cellular Biology آشنایی با مبانی اولیه سلول Biologists are interested in objects ranging in size from small molecules to the tallest trees: Cell Basic building blocks of life Understanding
Ultrastructure of the Lyonet s glands in larvae of Diatraea saccharalis Fabricius (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae)
 BIOCELL 2004, 28(2): 165-169 ISSN 0327-9545 PRINTED IN ARGENTINA Brief Note Ultrastructure of the Lyonet s glands in larvae of Diatraea saccharalis Fabricius (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) ELIANE VICTORIANO
BIOCELL 2004, 28(2): 165-169 ISSN 0327-9545 PRINTED IN ARGENTINA Brief Note Ultrastructure of the Lyonet s glands in larvae of Diatraea saccharalis Fabricius (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) ELIANE VICTORIANO
AVICENNA INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE
 AVICENNA INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES ACADEMIC CALENDAR LECTURE SYLLABUS CELL & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Characteristics of Living Organisms, Levels of Organization in Biology (Introduction
AVICENNA INTERNATIONAL COLLEGE BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES ACADEMIC CALENDAR LECTURE SYLLABUS CELL & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Characteristics of Living Organisms, Levels of Organization in Biology (Introduction
