User Guide for the MATCH stand alone Module of RODOS-PV 5.0
|
|
|
- Neal Curtis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 User Guide for the MATCH stand alone Module of RODOS-PV 5.0 Lennart Robertson USER GUIDE FOR THE MATCH STAND ALONE MODULE OF RODOS-PV Overview Resource files File input and output Fixed data files Log File Input weather data in GRIB format Output data in GRIB format 6 2 Starting the stand-alone module Before the run Starting the long range atmospheric dispersion module MATCH Archived runs 12 3 Initialization Windows for standalone MATCH Overview Description Source Source 2 (optional) Source 3 (optional) Source 4 (optional) Nuclides (Switch on/off nuclides in the source term(s)) End date of the calculations (Optional) Output Selection Graphics on/off Grid for presentation in RoGIS Path weather data Select subarea in weather data 26 4 Results and Data Output Output to the Graphics system Possible results Interface data MATCH - FDMT interface 29 5 Error Correction Procedures Trouble shouting 31 Document History
2 1 Overview MATCH (Multi-scale Atmospheric Transport and CHemistry model) is the long-range transport model in the system. The model operates on the European scale and calculates activity and depositions of a selected number of nuclides. A necessary requirement is access to numerical weather prediction (NWP) data e.g. HIRLAM or ALADIN. There are five different installations of MATCH, however, this user guide refers only to the stand alone version MATCH. MATCH, a stand-alone version where the source input is described in a simple fashion by the user, MATCH/LSMC a model chain version where the source input is taken from a local or meso-scale dispersion model. INT-MA-FDM, an interface part to the food chain model (FDMT), where the output from either MATCH or RMATCH are post processed to fit into FDMT. MATCHVIEW is provided in order to redisplay the model results in RoGIS as model results are not stored in the RODOS data base, but in a more obscure packed format (WMO GRIB standard) MATCH is an all purpose model developed with the objective to cover a range of atmospheric transport problems from the meso to the continental scale and for application like accidental releases, acidic deposition and photo-chemical oxidant generation. Accidental releases requires high degree of details in the description of the transport and dispersion. To this end a Lagrangian particle model is used for the initial phase of the release. Of special concern is that MATCH operates on an entirely different model area than most of other application in RODOS. The output from MATCH in terms of activity and deposition are not stored directly into the data base and therefor not directly available for other applications. The module PMatch98 is developed with the purpose to extract MATCH results for any desired area that conforms with standard and the result for a such domain is subsequently archived in the data base. For the same reasons MATCH results can not be redisplayed by just activating the data base. Again a special module, MATCHVIEW, is developed to meet such a requirement. The purpose of MATCH in is RODOS to describe the transport and fallout of radio-nuclides on the European scale. To keep the computation load on a - 2 -
3 reasonable level as small subset of important nuclides are selected, namely Cs137, I131, Ba140, Xe133 and Kr Resource files The resource files are used to integrate MATCH in the RODOS system. The following files are of interest to the standalone MATCH. MATCH_define MATCH_assign MATCH_load Definition of the MATCH modules and shared memory Assignment of default values Load instructions 1.2 File input and output File input is in ASCII and in GRIdded Binary (GRIB) format. The latter is the format for input weather data and output from MATCH (see for details). The input ASCII files are fixed files with setup parameters Fixed data files A set of fixed data files for model setup are located in ~/roextern/data/match/scripts. The purpose of each file is described in the table below. NameList General parameter setup Output.dat Description of output parameters Nuclides.dat Description of usable nuclides Ba-140 Parameters for Ba-140 Cs-137 Parameters for Cs-137 I-131 Parameters for I-131 Kr-85 Parameters for Kr-85 Xe-133 Parameters for Xe
4 Inert ListResults ListDates Parameters for any inert species Help script for listing stored MATCH data Help script for listing stored MATCH data Log File A log-file is generated with rather extensive output. The file is found in ~/roextern/outall/"user"/"runid/ and named Match.log Input weather data in GRIB format The weather data should be always located in the directory ~/romet/provider/eu/yyyymmddhhmm00 During runtime of MATCH weather data are delivered to the directory ~/romess/user/provider/ The system task ronetservice delivers the weather data after MATCH sends a request for a specified releasetime. to ronetservice. Input weather data are supposed to come in the so called GRIB file format and divided into files with weather information for one time-stamp in each file. The data has to be retrieved from a numerical weather prediction model, like HIRLAM, ALADIN etc. The file name is constructed by a prefix and a time-stamp, e.g. DMI , with format PREFIXyymmddhhll, where yy is the year, mm is the month, dd is the day, hh is the hour, and ll is the forecast length. All dates are in UTC time. An analysis is marked by forecast length zero (ll=00). Obviously can several time-stamps denote the same date. So are e.g the same date as and Weather data should be available at a minimum of three days backwards, but preferably one or two weeks. Only the latest full forecast is needed (normally a 48 hour forecast). The rest of the forecasted data are all covered by analyses and can be removed. However, MATCH still needs the 3 and 6 hour forecasts that contain precipitation information and for filling the gap between analyses that normally are given for every 6 hour. The content required for each data file is listed below. The numbers are the internal GRIB representation of parameters given by the WMO standard. Single level fields PAR TYPE LEV - 4 -
5 Geopotential Height of the model surface Pressure at model surface Sea surface temperature Temperature at the surface Temperature at 2m Specific Humidity at 2m U-component of Wind at 10m V-component of Wind at 10m Ice Concentration Land Sea Mask Albedo Surface Roughness (dynamic) Surface Roughness (fixed) Sensible heat flux Latent heat flux Friction velocity Large Scale Precipitation Convective Precipitation Mixing layer depth (optional) Multi layer fields PAR TYPE LEV # U-componemt of Wind # V-component of Wind # Temperature # Specific Humidity where # is the model level number. It is important that the layers are true model layers and not standard pressure levels. Not all layers that could be retrieved from any numerical weather prediction model are necessary to include, even though it is desirable. You have to be sure though that at least the lowest 5 km of the atmosphere is covered. Note that numerical weather prediction models normally have pressure as vertical co-ordinate that makes the earth surface as the model "top"
6 1.2.4 Output data in GRIB format The output from the MATCH model is stored in GRIB format in the directory ~/roextern/outall//"user"/"runid"/ The naming of the files are NUCLIDE_match_yyyymmddhhmi00, where yyyy is the year, mm is the month, dd is the day, hh is the hour, and mi is the minute. If every possible parameter is selected for output (see section 3.2.7) the output listed below can be found. The numbers refer to internal GRIB representation of parameters, and are necessary for retrieval. Single level fields PAR TYPE LEV Description Concentration Mean Concentration 1 Hour Dose Mean Acc. Total Deposition Acc. Wet Deposition Boundary layer height Sensible heat flux Total Precipitation Net solar radiation U-wind at 10m V-wind at 10m Temperature at 2m Specific humidity at 2m Atmospheric resistance Multi layer fields PAR TYPE LEV Description # Concentration # U-componemt of Wind # V-component of Wind - 6 -
7 where # is the MATCH model layer that ranges between 1 and 5 where 1 is the layer closest to the earth surface
8 2 Starting the stand-alone module 2.1 Before the run One has to assure that prognostic weather data for the period requested by the MATCH module are available. You may check for the default path to weather data, see section Some features of the standalone MATCH that may be of interest. Just a limited number of nuclides could be selected. The simulation starts with the start date of the first source. Default a 48 hour simulation will be performed. A specific stop date may be specified. Model results are not stored in the RODOS database but in a file format GRIB. The module INT-MA-FDMT may be used to transform the MATCH output for storage in the RODOS database. Results may be forwarded to RoGIS graphical system for just on-the-fly inspection of the model run. Reviewing the results are made by MATCHVIEW. 2.2 Starting the long range atmospheric dispersion module MATCH An interactive computation run of the stand-alone version of MATCH is started in the following way: In the Main Dialogue window of RODOS select the button [Interactive]. Then the following window pops up
9 Click on the button [MATCH] in the Interactive Manager window to start a new run of MATCH. A Start window for the definition of the RunId pops up, the RunId has to be entered by the user. The RunID can be any character string using letters and numbers (maximum 12 characters) and must be different from the RunIDs of previous runs which are still in the data base. By selecting [Initializing] in the window, Initialization windows can be opened which enable the selection of input parameter for MATCH. The windows are described in detail in chapter 3. When returning from the Initialization windows a window Program Initialization appears: - 9 -
10 Now, three options are available: To apply the selection made in the Initialization windows before click on [Apply] and then [Return]. To make new selections in the Initialization windows click on [unlock buttons] and then [MATCH] again. To start the program with the preset selections click on [Return]. The Initialization windows should be called in any case, as important parameters such as the source strength and duration of release have to be set. If no initialization via the Initialization windows is done, the program run is started with the preset selections (as described in section 3); however, this option is only recommended when runs have been performed in the past and no changes are requested. The program run is started by clicking on [Start] in the Start window. To enable the graphics output of MATCH, the Graphics System of RODOS has to be started before MATCH is started by selecting the button [Graphics] in the Main Dialogue window of RODOS. After the program has been started, a Control & Services window appears. This control window is divided into an upper and lower part. The upper part contains the RunID of the currently selected run as well as four buttons to control the runs. The lower part contains five buttons with which various services can be chosen. Both types of buttons are described in detail in the User Guide for the Graphical System. The only button in the lower part which is of interest for MATCH is the button:
11 [Process Status] Selecting this service opens a window with the list of all modules of the selected run and their actual state. The colour coding of the modules indicates whether the module has not yet started (blue), data is loaded from the database (yellow), the module is calculating (green), the results are archived in the database (red) or the module has finished its work (grey)
12 2.3 Archived runs Archived graphical output of MATCH can be displayed by selecting [File] and further [Display Results] in the menu bar of the Interactive Manager window of RODOS. Thereafter, a windows pops up with the program groups where a run can be selected. In the Program Groups window the requested MATCH button has to be selected. By pressing the button [MATCH], a window pops up with the list of all MATCH runs archived
13 One run out of the list has to be selected and the button [Apply] has to be pressed. Thereafter, two windows appear: The Control & Services window (see above) and the Application List window. The next step is first to select the run in the Application List window by simply clicking on it (colour does not change), and in second to select the [Graphics] button in the Control & Services window. Thereafter, a window with the list of results archived for this run is displayed
14 In this window either individual results can be selected by clicking through the context menu up to a result which is marked with a red cross. This can be selected by pressing the [Apply] button. Or it is also possible to select all results by pressing first the [All] button and thereafter the [Apply] button. The [Close] button can be selected if no further result is requested. A second option is to select the program MATCHVIEW to display the graphical results in a continuos loop in the graphics system. The Graphics System of RODOS has to be started beforehand. This module is described in a separate user guide (or chapter)
15 3 Initialization Windows for standalone MATCH 3.1 Overview By selecting [Initializing] in the Start window (see previous Chapter) the Initialization windows can be used to select the requested input and also the output which has to be produced by MATCH. The window hierarchy is shown below (WINDOWS, Options): MATCH stand alone input +- Source 1 +- Position +- Emission +- Start time (Note! This is the start date of the simulation) +- Stop time +- Emission height +- Source 2 (optional) +- Position +- Emission +- Start time +- Stop time +- Emission height +- Source 3 (optional) +- Position +- Emission +- Start time +- Stop time +- Emission height +- Source 4 (optional) +- Position +- Emission +- Start time +- Stop time +- Emission height +- Nuclides (switch on/off nuclides in the source term(s) +- Nuclides +- End date of calculation (optional) +- End date (Note! This is the end date of the simulation) +- Output parameter +- Output selection for graphical display +- Graphics on/off +- Send results to graphics +- Grid for presentation in RoGIS +- West-East extension +- South-North extension +- Path to weather data +- Path +- Generator +- Select subarea in weather data +- Indices of rows and columns omitted
16 3.2 Description By selecting [Initializing] in the Start window (see Chapter 2) and then selecting [MATCH] in the following Program Initialization window the Dataset Selection window comes up. This window switches between modification of either the data from the previous initialization, or the data from another initialization made earlier. After pressing the appropriate button, the Initialization windows are called to define parameter values to be used by the MATCH calculations. In various sub-windows the input parameters requested by MATCH can be filled in. These sub-windows can be accessed by clicking on one of the main topics in the main Initialization Window (MATCH: MATCH stand alone input) which appears
17 Selecting the button [Close] stores the selection and closes the window, the button [Help] opens a help window including some comments for this main menu. For all windows exist default settings which are activated by having selected [default] in the Option menu of the Interactive Manager window. However, modifications from previous runs will be active independent of the selection temporary and default. This is special to MATCH and does not correspond to the description of these options in the system manual Source 1 Choosing [Source 1] brings up the following window in which the mandatory input for one run has to be filled in. The standalone version of MATCH requires at least input for one of the four sources: Input window for Source 1 continued
18 Position: Specify the latitude and longitude of the source point in degrees. Emission: Set a constant source term. Only those nuclides that are switch on will be considered in the calculations. Emission rate is in Bq/s Start time: Set the start date of the source term. Note that this date is also used as start date for the simulation. The meteorological data are requested from for this starting time onwards. The time is UTC and the format is YYYYMMDDHH[.mm] (YYYY = year, MM = month, DD = day, HH = hour, [.mm] = minutes which are optional). Stop time: Set stop date of source emission. Note: The stop date of the simulation is set in [End data of calculation] in the main window. The time is UTC and the format is YYYYMMDDHH[.mm] (YYYY = year, MM = month, DD = day, HH = hour, [.mm] = minutes which are optional). Emission height: Set the emission height in meters. Note! If the date is not set the source is omitted, or if date starts with YYYY i.e. a character text string. Selecting the button [Update] stores the selection and closes this window, [Close] closes the window without storing the selections. The button [Help] opens a help window including some comments for this window
19 3.2.2 Source 2 (optional) Choosing [Source2 (optional)] in the 'Main Menu'-window brings up a similar window as for source 1. Input for sources 2 to 4 are not mandatory and can differ in their source strength from each other. Sources are treated individually in the calculations but concentrations and doses will be added up in the output. If character strings are in the input windows, the source will not be considered in the dispersion calculation Source 3 (optional) Source 4 (optional) Choosing [Source3 (optional)] in the 'Main Menu'-window brings up a similar window as for source 1. Input for sources 2 to 4 are not mandatory and can differ in their source strength from each other. Sources are treated individually in the calculations but concentrations and doses will be added up in the output. If character strings are in the input windows, the source will not be considered in the dispersion calculation. Choosing [Source4 (optional)] in the 'Main Menu'-window brings up a similar window as for source 1. Input for sources 2 to 4 are not mandatory and can differ in their source strength from each other. Sources are treated individually in the calculations but concentrations and doses will be added up in the output. If character strings are in the input windows, the source will not be considered in the dispersion calculation
20 3.2.5 Nuclides (Switch on/off nuclides in the source term(s)) Choosing [Nuclides (Switch on/off nuclides in the source term(s))] in the 'Main Menu'-window brings up a selection window where up to five radionuclides can be selected for one run. The button [Inert] refers to an ideal traces and should not be selected if further calculations with a foodchain and dose module will be carried out. Selecting the button [Update] stores the selection and closes this window, [Close] closes the window without storing the selections. The button [Help] opens a help window including some comments for this window
21 3.2.6 End date of the calculations (Optional) Choosing [End date of the calculations (Optional)] in the 'Main Menu'- window brings up a window where the end date of the calculation can be specified. In the present version, up to 48 hours of prognosis are possible. There are 3 different options: 1. If this window remains empty, calculations will be carried out for a 48 hour prognosis. 2. If a date far in the future is selected, MATCH will carry out calculations as long as weather data are available (Note: not activated!) 3. End date in the same format as the start date defines an end date prior to the maximum of 48 hours possible. The time is UTC and the format is YYYYMMDDHH (YYYY = year, MM = month, DD = day, HH = hour). Selecting the button [Update] stores the selection and closes this window, [Close] closes the window without storing the selections. The button [Help] opens a help window including some comments for this window
22 3.2.7 Output Selection Choosing [Output Selection] in the 'Main Menu'-window brings up a window where the output can be defined for which calculations are performed and which are displayed in the Graphical System of RODOS. If further calculations with the food chain model FDMT are requested, some selections should always be present to get an impression on the concentrations and potential doses: Instantaneous concentration Dose Total Deposition Wet Deposition Precipitation [Close] exits the window without storing any selections, [Update] confirms any selections, and [Help] brings up a comment window
23 Graphics on/off Choosing [Graphics on/off] in the 'Main Menu'-window brings up a window where it is possible to activate or deactivate the sending of the results to the Graphics System for displaying. The communication with the graphics is rather slow and therefore is this option available. [Close] exits the window without storing any selections, [Update] confirms any selections, and [Help] brings up a comment window
24 3.2.8 Grid for presentation in RoGIS Choosing [Grid for presentation in RoGIS] in the 'Main Menu'-window brings up a window where it is possible to define the number of grid cells and the bounding box for displaying in the Graphical System of RODOS. This does neither affect the grid area for the calculation, which is defined by the weather data, nor the area available for postprocessing. The output grid for RoGIS in latitude - longitude coordinates (degrees). Make sure that the source location lies within your grid specified. [Close] exits the window without storing any selections, [Update] confirms any selections, and [Help] brings up a comment window
25 3.2.9 Path weather data Choosing [Path weather data] in the 'Main Menu'-window opens a window where the user can insert the entry keyword in the file $RODOS_DIR/roenvdir/metlistenv. This keyword consists of the provider name and the string eu. The default provider is dmi. On the basis of this keyword the following attributes of meteorological forecast weather data are specified: Sample_Time[h]: cycle time of the incoming forecast weather data Data_Interval[h]: interval of prognosis data Prognosis_Time: prognosis period of the forecast weather data Time_Zone; e.g. UTC DIR_Pattern, File_Pattern and Data_Directory specify the location of the files. The weather data has to be in WMO GRIB format.. Data are supposed to be found with each time-point in separate files with the following naming: WEATHERDATAPATH/PROVIDERYYMMDDHHLLL with (YY=year, MM=month, DD=day, HH=hour, LLL=forecast length) If the provider name is used for the naming it is a generally applied method writing the provider name in capital letters. The default path and PROVIDER will lead to the following example location / file: romet/dmi/eu/dmi [Close] exits the window without storing any selections, [Update] confirms any selections, and [Help] brings up a comment window
26 Select subarea in weather data Choosing [Select subarea in weather data] in the 'Main Menu'-window brings up a window where it is possible to define rows and columns which should be omitted from the weather domain. To cut out a sub-area out of the input weather data, it is necessary to specify how many rows and columns that should be left out. The rows and columns on the north and east boundary, respectively, are set to a negative number if you want to exclude those. A positive number in the latter case will be regarded as the absolute index to be kept. This means that -5 will cut down the area on either east or north boundary with 5 columns or rows, while 5 will cut the are at column or row 5 (apparently a very small area). [Close] exits the window without storing any selections, [Update] confirms any selections, and [Help] brings up a comment window
27 4 Results and Data Output 4.1 Output to the Graphics system Possible results Dependent on the selections made in the Initialization windows of MATCH, results will be displayed as maps in the Graphical System of RODOS. The following subgroups are available: Activity concentrations in air Wet and dry deposited activity Dose from cloud passage Dose rate from cloud passage Meteorological parameter such as boundary layer height, heat flux, humidity, precipitation and temperature
28 Default results If the preset selections in the Initialization Window in chapter are not changed by the user, the following results will be calculated by MATCH and are accessible in the Graphics system: Maps Activity concentrations in air (nuclide dependent) Instantaneous Mean Deposited activity (nuclide dependent) Total Wet Dose from cloud passage (nuclide dependent) Dose rate from cloud passage (nuclide dependent) Meteorological parameter Boundary layer height Heat flux Humidity Precipitation Temperature
29 4.2 Interface data MATCH produces data needed by other modules of RODOS: the Terrestrial Foodchain and Dose Module FDMT These data are stored in files. To generate the necessary shared memory and to store the data in the RODOS data base, the module INT-MA-FDM is required. A description of INT-MA-FDM can be found in a separate chapter of user guide MATCH - FDMT interface For estimation of the activity concentrations in feed- and foodstuffs as well as doses without countermeasures, data is being transferred to FDMT via INT-MA-FDM: Mean time-integrated air concentration in each time interval Wet deposited activity External dose from cloud passage Rain intensity In addition, several other model and program steering parameters are included in the interface. As mentioned above, the module INT-MA-FDM is needed for this procedure
30 5 Error Correction Procedures General error messages Error flag (2): Insufficient space for continuation. The weather data contains too many grid cells, and the arrays in MATCH that holds the data are too short. The solution is to cut down the weather data area, see section for details. If this is not sufficient the MATCH model has to be recompiled with other settings of NXDIM, NYDIM, NLEVDIM or NCHEMDIM. Consult the system manager. Error flag (3): Insufficient space for puffdata. The MATCH model has to be recompiled with other setting of the NPOINTDIM parameter. Consult the system manager. Error flag (4): Insufficient space for continuation. The MATCH model has to be recompiled with other setting of the NSDIM parameter. Consult the system manager. Error messages from checking input data and model parameters Error flag (10): Missing first set of weather data. Check path to weather data and the period of data that is available, see section for details. Error flag (11): Missing weather data during runtime. There is a gap in available weather data. Consult the system manager. Error flag (12): Puff data missing Error when running RMATCH. File with puff data missing. Error flag (20): Point source outside model area
31 Error when running standalone MATCH. The model discontinues if the specified source location is outside the model domain. Error flag (21): Date string in error Any of the date specifications is erroneous. Check what you have typed in the graphical user interface of MATCH. Error flag (41): Error in grid specification Error when running PMATCH The dynamic grid specification is not correct. Error flag (44): Area for interpolation outside Match model domain Error when running PMATCH. The area for interpolation is outside the model domain. No meaning to continue. 5.1 Trouble shouting MATCH/LSMC can not find weather data The system program delivers the meteorological data into romess/userid/provider e.g. romess/userid/dmieu and each file is composed by a prefix and a date stamp, e.g. DMI Please check, if the data fit to the time you requested. In case of problems, please check also the location of the original data in romet/provider/eu/ Data files have to be present there. The model starts but exits after check of memory requirements The weather data contains too many grid cells, and the arrays in MATCH that holds the data are too short. The solution is to cut down the weather data area, see section for details
32 Segmentation fault occurs The compiled MATCH executable is too large for the RAMmemory of your computer. The MATCH model has to be recompiled with other settings of NXDIM, NYDIM, NLEVDIM or NCHEMDIM. Consult the system manager. The results presented in RoGIS looks like strips over the map You have most likely rerun MATCH with some other size of the output grid to RoGIS. Close the graphics and restart the model. The dimension specified in the shared memory transferring data from MATCH to the RoGIS graphics is only set once. Changing the area for the graphics, see section 3.2.8, could therefor lead to strange results
33 Document History Document Title: User Guide for the MATCH stand alone Module of RODOS-PV 5.0 Version and status: Version 1.1 (draft) Authors/Editors: Lennart Robertson Address: Issued by: W. Raskob File Name: Match_UGui_50e.doc Date of print: April 22,
User Guide for the MATCH stand alone Module of RODOS-PV 6.0
 User Guide for the MATCH stand alone Module of RODOS-PV 6.0 Lennart Robertson USER GUIDE FOR THE MATCH STAND ALONE MODULE OF RODOS-PV 6.0 1 1 Overview 3 1.1 Resource files 4 1.2 File input and output 4
User Guide for the MATCH stand alone Module of RODOS-PV 6.0 Lennart Robertson USER GUIDE FOR THE MATCH STAND ALONE MODULE OF RODOS-PV 6.0 1 1 Overview 3 1.1 Resource files 4 1.2 File input and output 4
User Guide for the Terrestrial Food Chain and Dose Module FDMT of
 Version 1.1 User Guide for the Terrestrial Food Chain and Dose Module FDMT of RODOS PV6.0 User Guide for the Terrestrial Food Chain and Dose Module FDMT of RODOS PV6.0 Florian Gering, Heinz Müller USER
Version 1.1 User Guide for the Terrestrial Food Chain and Dose Module FDMT of RODOS PV6.0 User Guide for the Terrestrial Food Chain and Dose Module FDMT of RODOS PV6.0 Florian Gering, Heinz Müller USER
DSJRA-55 Product Users Handbook. Climate Prediction Division Global Environment and Marine Department Japan Meteorological Agency July 2017
 DSJRA-55 Product Users Handbook Climate Prediction Division Global Environment and Marine Department Japan Meteorological Agency July 2017 Change record Version Date Remarks 1.0 13 July 2017 First version
DSJRA-55 Product Users Handbook Climate Prediction Division Global Environment and Marine Department Japan Meteorological Agency July 2017 Change record Version Date Remarks 1.0 13 July 2017 First version
Chapter of the RODOS PV4.0 User Guide for the Aquatic Food Chain
 Version 1.0 Chapter of the RODOS PV4.0 User Guide for the Aquatic Food Chain and Dose Module FDMA Chapter of the RODOS PV4.0 User Guide for the Aquatic Food Chain and Dose Module FDMA Florian Gering, Stephan
Version 1.0 Chapter of the RODOS PV4.0 User Guide for the Aquatic Food Chain and Dose Module FDMA Chapter of the RODOS PV4.0 User Guide for the Aquatic Food Chain and Dose Module FDMA Florian Gering, Stephan
AN INTERNATIONAL SOLAR IRRADIANCE DATA INGEST SYSTEM FOR FORECASTING SOLAR POWER AND AGRICULTURAL CROP YIELDS
 AN INTERNATIONAL SOLAR IRRADIANCE DATA INGEST SYSTEM FOR FORECASTING SOLAR POWER AND AGRICULTURAL CROP YIELDS James Hall JHTech PO Box 877 Divide, CO 80814 Email: jameshall@jhtech.com Jeffrey Hall JHTech
AN INTERNATIONAL SOLAR IRRADIANCE DATA INGEST SYSTEM FOR FORECASTING SOLAR POWER AND AGRICULTURAL CROP YIELDS James Hall JHTech PO Box 877 Divide, CO 80814 Email: jameshall@jhtech.com Jeffrey Hall JHTech
WindNinja Tutorial 3: Point Initialization
 WindNinja Tutorial 3: Point Initialization 6/27/2018 Introduction Welcome to WindNinja Tutorial 3: Point Initialization. This tutorial will step you through the process of downloading weather station data
WindNinja Tutorial 3: Point Initialization 6/27/2018 Introduction Welcome to WindNinja Tutorial 3: Point Initialization. This tutorial will step you through the process of downloading weather station data
Output Module (last updated 8/27/2015)
 Output Module (last updated 8/27/2015) Goals: Provide a common output format and content from all modeling groups for Tier 2 files. Provide a data file that is compatible with the GFDL Vortex Tracker program
Output Module (last updated 8/27/2015) Goals: Provide a common output format and content from all modeling groups for Tier 2 files. Provide a data file that is compatible with the GFDL Vortex Tracker program
OpenWeatherMap Module
 OpenWeatherMap Module Installation and Usage Guide Revision: Date: Author(s): 1.0 Friday, October 13, 2017 Richard Mullins Contents Overview 2 Installation 3 Import the TCM in to accelerator 3 Add the
OpenWeatherMap Module Installation and Usage Guide Revision: Date: Author(s): 1.0 Friday, October 13, 2017 Richard Mullins Contents Overview 2 Installation 3 Import the TCM in to accelerator 3 Add the
Weather observations from Tórshavn, The Faroe Islands
 Weather observations from Tórshavn, The Faroe Islands 1953-2014 - Observation data with description John Cappelen Copenhagen 2015 http://www.dmi.dk/fileadmin/rapporter/tr/tr15-09 page 1 of 14 Colophon
Weather observations from Tórshavn, The Faroe Islands 1953-2014 - Observation data with description John Cappelen Copenhagen 2015 http://www.dmi.dk/fileadmin/rapporter/tr/tr15-09 page 1 of 14 Colophon
Manual Seatrack Web Brofjorden
 December 2011 Manual Seatrack Web Brofjorden A user-friendly system for forecasts and backtracking of drift and spreading of oil, chemicals and substances in water 1. Introduction and Background... 3 1.1
December 2011 Manual Seatrack Web Brofjorden A user-friendly system for forecasts and backtracking of drift and spreading of oil, chemicals and substances in water 1. Introduction and Background... 3 1.1
Using the EartH2Observe data portal to analyse drought indicators. Lesson 4: Using Python Notebook to access and process data
 Using the EartH2Observe data portal to analyse drought indicators Lesson 4: Using Python Notebook to access and process data Preface In this fourth lesson you will again work with the Water Cycle Integrator
Using the EartH2Observe data portal to analyse drought indicators Lesson 4: Using Python Notebook to access and process data Preface In this fourth lesson you will again work with the Water Cycle Integrator
CSU RAMS. Standard Input Formats for Pressure Coordinate and Observational Data (Data Prep Stage)
 CSU RAMS Standard Input Formats for Pressure Coordinate and Observational Data (Data Prep Stage) This document contains detailed notes on how gridded pressure level datasets (such as NCEP-reanalysis, GFS
CSU RAMS Standard Input Formats for Pressure Coordinate and Observational Data (Data Prep Stage) This document contains detailed notes on how gridded pressure level datasets (such as NCEP-reanalysis, GFS
DMI Report Weather observations from Tórshavn, The Faroe Islands Observation data with description
 DMI Report 17-09 Weather observations from Tórshavn, The Faroe Islands 1953-2016 - Observation data with description John Cappelen Copenhagen 2017 http://www.dmi.dk/laer-om/generelt/dmi-publikationer/
DMI Report 17-09 Weather observations from Tórshavn, The Faroe Islands 1953-2016 - Observation data with description John Cappelen Copenhagen 2017 http://www.dmi.dk/laer-om/generelt/dmi-publikationer/
TECDIS and TELchart ECS Weather Overlay Guide
 1 of 24 TECDIS and TELchart ECS provides a very advanced weather overlay feature, using top quality commercial maritime weather forecast data available as a subscription service from Jeppesen Marine. The
1 of 24 TECDIS and TELchart ECS provides a very advanced weather overlay feature, using top quality commercial maritime weather forecast data available as a subscription service from Jeppesen Marine. The
WeatherHawk Weather Station Protocol
 WeatherHawk Weather Station Protocol Purpose To log atmosphere data using a WeatherHawk TM weather station Overview A weather station is setup to measure and record atmospheric measurements at 15 minute
WeatherHawk Weather Station Protocol Purpose To log atmosphere data using a WeatherHawk TM weather station Overview A weather station is setup to measure and record atmospheric measurements at 15 minute
MxVision WeatherSentry Web Services Content Guide
 MxVision WeatherSentry Web Services Content Guide July 2014 DTN 11400 Rupp Drive Minneapolis, MN 55337 00.1.952.890.0609 This document and the software it describes are copyrighted with all rights reserved.
MxVision WeatherSentry Web Services Content Guide July 2014 DTN 11400 Rupp Drive Minneapolis, MN 55337 00.1.952.890.0609 This document and the software it describes are copyrighted with all rights reserved.
Quick Start Guide New Mountain Visit our Website to Register Your Copy (weatherview32.com)
 Quick Start Guide New Mountain Visit our Website to Register Your Copy (weatherview32.com) Page 1 For the best results follow all of the instructions on the following pages to quickly access real-time
Quick Start Guide New Mountain Visit our Website to Register Your Copy (weatherview32.com) Page 1 For the best results follow all of the instructions on the following pages to quickly access real-time
Model Output Statistics (MOS)
 Model Output Statistics (MOS) Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) models calculate the future state of the atmosphere at certain points of time (forecasts). The calculation of these forecasts is based on
Model Output Statistics (MOS) Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) models calculate the future state of the atmosphere at certain points of time (forecasts). The calculation of these forecasts is based on
New SPOT Program. Customer Tutorial. Tim Barry Fire Weather Program Leader National Weather Service Tallahassee
 New SPOT Program Customer Tutorial Tim Barry Fire Weather Program Leader National Weather Service Tallahassee tim.barry@noaa.gov Live Demonstration http://www.weather.gov/spot/ Live Demonstration http://www.weather.gov/spot/
New SPOT Program Customer Tutorial Tim Barry Fire Weather Program Leader National Weather Service Tallahassee tim.barry@noaa.gov Live Demonstration http://www.weather.gov/spot/ Live Demonstration http://www.weather.gov/spot/
Hui-Ya Chuang. Presented by Matthew Pyle
 Hui-Ya Chuang (Hui-Ya.Chuang@noaa.gov) Presented by Matthew Pyle (Matthew.Pyle@noaa.gov) Overview Components and Functions Sample fields generated Installation Running unipost Controlling output generation
Hui-Ya Chuang (Hui-Ya.Chuang@noaa.gov) Presented by Matthew Pyle (Matthew.Pyle@noaa.gov) Overview Components and Functions Sample fields generated Installation Running unipost Controlling output generation
Using Smoke Modeling Tools for Prescribed Fire Planning and Implementation A Quick Set of Instructions (Revised October 2015)
 Using Smoke Modeling Tools for Prescribed Fire Planning and Implementation A Quick Set of Instructions (Revised October 2015) Fire Management Officers (FMOs) in Region 8 are using smoke modeling more often
Using Smoke Modeling Tools for Prescribed Fire Planning and Implementation A Quick Set of Instructions (Revised October 2015) Fire Management Officers (FMOs) in Region 8 are using smoke modeling more often
CALIOPE EU: Air Quality
 CALIOPE EU: Air Quality CALIOPE EU air quality forecast application User Guide caliope@bsc.es Version 30/09/2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Description... 1 2. Installation... 1 3. User Guide... 2 3.1 Air quality
CALIOPE EU: Air Quality CALIOPE EU air quality forecast application User Guide caliope@bsc.es Version 30/09/2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Description... 1 2. Installation... 1 3. User Guide... 2 3.1 Air quality
Software BioScout-Calibrator June 2013
 SARAD GmbH BioScout -Calibrator 1 Manual Software BioScout-Calibrator June 2013 SARAD GmbH Tel.: ++49 (0)351 / 6580712 Wiesbadener Straße 10 FAX: ++49 (0)351 / 6580718 D-01159 Dresden email: support@sarad.de
SARAD GmbH BioScout -Calibrator 1 Manual Software BioScout-Calibrator June 2013 SARAD GmbH Tel.: ++49 (0)351 / 6580712 Wiesbadener Straße 10 FAX: ++49 (0)351 / 6580718 D-01159 Dresden email: support@sarad.de
Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute
 Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute Norrköping, Sweden 1. Summary of highlights HIRLAM at SMHI is run on a CRAY T3E with 272 PEs at the National Supercomputer Centre (NSC) organised together
Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute Norrköping, Sweden 1. Summary of highlights HIRLAM at SMHI is run on a CRAY T3E with 272 PEs at the National Supercomputer Centre (NSC) organised together
ON SITE SYSTEMS Chemical Safety Assistant
 ON SITE SYSTEMS Chemical Safety Assistant CS ASSISTANT WEB USERS MANUAL On Site Systems 23 N. Gore Ave. Suite 200 St. Louis, MO 63119 Phone 314-963-9934 Fax 314-963-9281 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION
ON SITE SYSTEMS Chemical Safety Assistant CS ASSISTANT WEB USERS MANUAL On Site Systems 23 N. Gore Ave. Suite 200 St. Louis, MO 63119 Phone 314-963-9934 Fax 314-963-9281 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.4.1. Tutorial on how to predict Skin sensitization potential taking into account alert performance
 OECD QSAR Toolbox v.4.1 Tutorial on how to predict Skin sensitization potential taking into account alert performance Outlook Background Objectives Specific Aims Read across and analogue approach The exercise
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.4.1 Tutorial on how to predict Skin sensitization potential taking into account alert performance Outlook Background Objectives Specific Aims Read across and analogue approach The exercise
C:\Dokumente und Einstellungen \All Users\Anwendungsdaten \Mathematica. C:\Dokumente und Einstellungen \albert.retey\anwendungsdaten \Mathematica
 Installation SmartCAE`HeatTransmission` is delivered as either a Microsoft Windows Installer Package (SmartCAEHeatTransmission-1.0.msi) or a ZIP-File. If you have trouble installing the package, please
Installation SmartCAE`HeatTransmission` is delivered as either a Microsoft Windows Installer Package (SmartCAEHeatTransmission-1.0.msi) or a ZIP-File. If you have trouble installing the package, please
Investigating Factors that Influence Climate
 Investigating Factors that Influence Climate Description In this lesson* students investigate the climate of a particular latitude and longitude in North America by collecting real data from My NASA Data
Investigating Factors that Influence Climate Description In this lesson* students investigate the climate of a particular latitude and longitude in North America by collecting real data from My NASA Data
Overlaying GRIB data over NOAA APT weather satellite images using OpenCPN
 Overlaying GRIB data over NOAA APT weather satellite images using OpenCPN I receive NOAA weather satellite images which are quite useful when used alone but with GRIB wind and rain data overlaid they can
Overlaying GRIB data over NOAA APT weather satellite images using OpenCPN I receive NOAA weather satellite images which are quite useful when used alone but with GRIB wind and rain data overlaid they can
1D-HAM. Coupled Heat, Air and Moisture Transport in Multi-layered Wall Structures. Manual with brief theory and an example. Version 2.
 1D-HAM Coupled Heat, Air and Moisture Transport in Multi-layered Wall Structures. Manual with brief theory and an example. Version 2.0 30 t=70 days (1680 h) 100 Temperatures ( C) v (g/m³) 25 20 15 10 5
1D-HAM Coupled Heat, Air and Moisture Transport in Multi-layered Wall Structures. Manual with brief theory and an example. Version 2.0 30 t=70 days (1680 h) 100 Temperatures ( C) v (g/m³) 25 20 15 10 5
Tutorial 11. Use of User-Defined Scalars and User-Defined Memories for Modeling Ohmic Heating
 Tutorial 11. Use of User-Defined Scalars and User-Defined Memories for Modeling Ohmic Heating Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the use of user-defined scalars (UDS) and user defined
Tutorial 11. Use of User-Defined Scalars and User-Defined Memories for Modeling Ohmic Heating Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the use of user-defined scalars (UDS) and user defined
Advanced Forecast. For MAX TM. Users Manual
 Advanced Forecast For MAX TM Users Manual www.maxtoolkit.com Revised: June 24, 2014 Contents Purpose:... 3 Installation... 3 Requirements:... 3 Installer:... 3 Setup: spreadsheet... 4 Setup: External Forecast
Advanced Forecast For MAX TM Users Manual www.maxtoolkit.com Revised: June 24, 2014 Contents Purpose:... 3 Installation... 3 Requirements:... 3 Installer:... 3 Setup: spreadsheet... 4 Setup: External Forecast
ST-Links. SpatialKit. Version 3.0.x. For ArcMap. ArcMap Extension for Directly Connecting to Spatial Databases. ST-Links Corporation.
 ST-Links SpatialKit For ArcMap Version 3.0.x ArcMap Extension for Directly Connecting to Spatial Databases ST-Links Corporation www.st-links.com 2012 Contents Introduction... 3 Installation... 3 Database
ST-Links SpatialKit For ArcMap Version 3.0.x ArcMap Extension for Directly Connecting to Spatial Databases ST-Links Corporation www.st-links.com 2012 Contents Introduction... 3 Installation... 3 Database
Lab Exploration #4: Solar Radiation & Temperature Part II: A More Complex Computer Model
 METR 104: Our Dynamic Weather (w/lab) Lab Exploration #4: Solar Radiation & Temperature Part II: A More Complex Computer Model Dr. Dave Dempsey, Department of Earth & Climate Sciences, SFSU, Spring 2014
METR 104: Our Dynamic Weather (w/lab) Lab Exploration #4: Solar Radiation & Temperature Part II: A More Complex Computer Model Dr. Dave Dempsey, Department of Earth & Climate Sciences, SFSU, Spring 2014
Estimation of accidental environmental release based on containment measurements
 Estimation of accidental environmental release based on containment measurements Péter Szántó, Sándor Deme, Edit Láng, Istvan Németh, Tamás Pázmándi Hungarian Academy of Sciences Centre for Energy Research,
Estimation of accidental environmental release based on containment measurements Péter Szántó, Sándor Deme, Edit Láng, Istvan Németh, Tamás Pázmándi Hungarian Academy of Sciences Centre for Energy Research,
User's Guide. DISTO online. Leica Geosystems
 User's Guide DISTO online Leica Geosystems Copyright 2001 by PMS Photo Mess Systeme AG. All rights reserved. This manual describes the versions 2.x of the program DISTO online. PMS PHOTO-MESS-SYSTEME AG
User's Guide DISTO online Leica Geosystems Copyright 2001 by PMS Photo Mess Systeme AG. All rights reserved. This manual describes the versions 2.x of the program DISTO online. PMS PHOTO-MESS-SYSTEME AG
Bloomsburg University Weather Viewer Quick Start Guide. Software Version 1.2 Date 4/7/2014
 Bloomsburg University Weather Viewer Quick Start Guide Software Version 1.2 Date 4/7/2014 Program Background / Objectives: The Bloomsburg Weather Viewer is a weather visualization program that is designed
Bloomsburg University Weather Viewer Quick Start Guide Software Version 1.2 Date 4/7/2014 Program Background / Objectives: The Bloomsburg Weather Viewer is a weather visualization program that is designed
Splatalogue Quickstart Guide
 Splatalogue Quickstart Guide Anthony J. Remijan NRAO STATUS: v2.1 PURPOSE: The purpose of this document is to provide a brief overview of the functionality of the Splatalogue homepage available at www.splatalogue.net.
Splatalogue Quickstart Guide Anthony J. Remijan NRAO STATUS: v2.1 PURPOSE: The purpose of this document is to provide a brief overview of the functionality of the Splatalogue homepage available at www.splatalogue.net.
THE METEOROLOGICAL DATA QUALITY MANAGEMENT OF THE ROMANIAN NATIONAL SURFACE OBSERVATION NETWORK
 THE METEOROLOGICAL DATA QUALITY MANAGEMENT OF THE ROMANIAN NATIONAL SURFACE OBSERVATION NETWORK Ioan Ralita, Ancuta Manea, Doina Banciu National Meteorological Administration, Romania Ionel Dragomirescu
THE METEOROLOGICAL DATA QUALITY MANAGEMENT OF THE ROMANIAN NATIONAL SURFACE OBSERVATION NETWORK Ioan Ralita, Ancuta Manea, Doina Banciu National Meteorological Administration, Romania Ionel Dragomirescu
Mass Asset Additions. Overview. Effective mm/dd/yy Page 1 of 47 Rev 1. Copyright Oracle, All rights reserved.
 Overview Effective mm/dd/yy Page 1 of 47 Rev 1 System References None Distribution Oracle Assets Job Title * Ownership The Job Title [list@yourcompany.com?subject=eduxxxxx] is responsible for ensuring
Overview Effective mm/dd/yy Page 1 of 47 Rev 1 System References None Distribution Oracle Assets Job Title * Ownership The Job Title [list@yourcompany.com?subject=eduxxxxx] is responsible for ensuring
Faults Loading and Display in HRS-9. David Worsick, Calgary September 12, 2012
 Faults Loading and Display in HRS-9 David Worsick, Calgary September 12, 2012 Faults Loading and Display Contents Faults in Hampson-Russell Normal Faults Strike-slip Faults Reverse Faults Thrust Faults
Faults Loading and Display in HRS-9 David Worsick, Calgary September 12, 2012 Faults Loading and Display Contents Faults in Hampson-Russell Normal Faults Strike-slip Faults Reverse Faults Thrust Faults
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.3. Step-by-step example of how to build and evaluate a category based on mechanism of action with protein and DNA binding
 OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.3 Step-by-step example of how to build and evaluate a category based on mechanism of action with protein and DNA binding Outlook Background Objectives Specific Aims The exercise Workflow
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.3 Step-by-step example of how to build and evaluate a category based on mechanism of action with protein and DNA binding Outlook Background Objectives Specific Aims The exercise Workflow
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.3
 OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.3 Step-by-step example on how to predict the skin sensitisation potential of a chemical by read-across based on an analogue approach Outlook Background Objectives Specific Aims Read
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.3 Step-by-step example on how to predict the skin sensitisation potential of a chemical by read-across based on an analogue approach Outlook Background Objectives Specific Aims Read
Creation and modification of a geological model Program: Stratigraphy
 Engineering manual No. 39 Updated: 11/2018 Creation and modification of a geological model Program: Stratigraphy File: Demo_manual_39.gsg Introduction The aim of this engineering manual is to explain the
Engineering manual No. 39 Updated: 11/2018 Creation and modification of a geological model Program: Stratigraphy File: Demo_manual_39.gsg Introduction The aim of this engineering manual is to explain the
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.3. Step-by-step example of how to categorize an inventory by mechanistic behaviour of the chemicals which it consists
 OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.3 Step-by-step example of how to categorize an inventory by mechanistic behaviour of the chemicals which it consists Background Objectives Specific Aims Trend analysis The exercise
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.3 Step-by-step example of how to categorize an inventory by mechanistic behaviour of the chemicals which it consists Background Objectives Specific Aims Trend analysis The exercise
Planning Softproviding Meat User Documentation
 Great ideas are always simple Softproviding simply makes them happen. Planning Softproviding Meat User Documentation Version: 1.00 Date: 24 August 2017 Release: v5.50 Softproviding AG Riehenring 175 CH-4058
Great ideas are always simple Softproviding simply makes them happen. Planning Softproviding Meat User Documentation Version: 1.00 Date: 24 August 2017 Release: v5.50 Softproviding AG Riehenring 175 CH-4058
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.4.0. Tutorial on how to predict Skin sensitization potential taking into account alert performance
 OECD QSAR Toolbox v.4.0 Tutorial on how to predict Skin sensitization potential taking into account alert performance Outlook Background Objectives Specific Aims Read across and analogue approach The exercise
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.4.0 Tutorial on how to predict Skin sensitization potential taking into account alert performance Outlook Background Objectives Specific Aims Read across and analogue approach The exercise
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.4
 OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.4 Step-by-step example on how to predict the skin sensitisation potential approach of a chemical by read-across based on an analogue approach Outlook Background Objectives Specific
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.4 Step-by-step example on how to predict the skin sensitisation potential approach of a chemical by read-across based on an analogue approach Outlook Background Objectives Specific
APlocate: Location and Weather User Guide
 APlocate: Location and Weather User Guide IES Virtual Environment Copyright Integrated Environmental Solutions Limited. All rights reserved. No part of the manual is to be copied or reproduced in any form
APlocate: Location and Weather User Guide IES Virtual Environment Copyright Integrated Environmental Solutions Limited. All rights reserved. No part of the manual is to be copied or reproduced in any form
Cloud Top Height Product: Product Guide
 Cloud Top Height Product: Product Guide Doc.No. : Issue : v1c e-signed Date : 26 April 2017 WBS : EUM/TSS/MAN/14/786420 EUMETSAT Eumetsat-Allee 1, D-64295 Darmstadt, Germany Tel: +49 6151 807-7 Fax: +49
Cloud Top Height Product: Product Guide Doc.No. : Issue : v1c e-signed Date : 26 April 2017 WBS : EUM/TSS/MAN/14/786420 EUMETSAT Eumetsat-Allee 1, D-64295 Darmstadt, Germany Tel: +49 6151 807-7 Fax: +49
OPERATING MANUAL. EIB-Kombisensor AS 315 N
 EIB-Kombisensor AS 315 N OPERATING MANUAL EIB-Kombisensor AS 315 N 1 Contents Page 3 1. Description 4 1.1 Automated Operations 1.1.1 Sun System 1.1.2 Half-Light System 5 1.1.3 Wind System 1.1.4 Rain System
EIB-Kombisensor AS 315 N OPERATING MANUAL EIB-Kombisensor AS 315 N 1 Contents Page 3 1. Description 4 1.1 Automated Operations 1.1.1 Sun System 1.1.2 Half-Light System 5 1.1.3 Wind System 1.1.4 Rain System
User's Guide for the NMM Core of the Weather Research and Forecast (WRF) Modeling System Version 3. Chapter 4: WRF-NMM Initialization
 User's Guide for the NMM Core of the Weather Research and Forecast (WRF) Modeling System Version 3 Table of Contents Chapter 4: WRF-NMM Initialization Introduction Initialization for Real Data Cases Running
User's Guide for the NMM Core of the Weather Research and Forecast (WRF) Modeling System Version 3 Table of Contents Chapter 4: WRF-NMM Initialization Introduction Initialization for Real Data Cases Running
Extracting Canadian Climate Data from Environment Canada dataset
 University of British Columbia Department of Statistics Technical Report #244 May 2009 Extracting Canadian Climate Data from Environment Canada dataset by Reza Hosseini 1 1 University of British Columbia
University of British Columbia Department of Statistics Technical Report #244 May 2009 Extracting Canadian Climate Data from Environment Canada dataset by Reza Hosseini 1 1 University of British Columbia
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.4. Step-by-step example of how to build and evaluate a category based on mechanism of action with protein and DNA binding
 OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.4 Step-by-step example of how to build and evaluate a category based on mechanism of action with protein and DNA binding Outlook Background Objectives Specific Aims The exercise Workflow
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.4 Step-by-step example of how to build and evaluate a category based on mechanism of action with protein and DNA binding Outlook Background Objectives Specific Aims The exercise Workflow
JRA-55 Product Users Handbook
 Climate Prediction Division Global Environment and Marine Department Japan Meteorological Agency September 2013 Change record Version Date Remarks 1.0 30 September 2013 First version 2.0 3 March 2014 Corrected
Climate Prediction Division Global Environment and Marine Department Japan Meteorological Agency September 2013 Change record Version Date Remarks 1.0 30 September 2013 First version 2.0 3 March 2014 Corrected
Finnish Open Data Portal for Meteorological Data
 18.11.2013 1 Finnish Open Data Portal for Meteorological Data 14th Workshop on meteorological operational systems Roope Tervo Finnish Meteorological Institute Example of Data Sets -- Observations Data
18.11.2013 1 Finnish Open Data Portal for Meteorological Data 14th Workshop on meteorological operational systems Roope Tervo Finnish Meteorological Institute Example of Data Sets -- Observations Data
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.0
 OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.0 Step-by-step example of how to categorize an inventory by mechanistic behaviour of the chemicals which it consists Background Objectives Specific Aims Trend analysis The exercise
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.0 Step-by-step example of how to categorize an inventory by mechanistic behaviour of the chemicals which it consists Background Objectives Specific Aims Trend analysis The exercise
isma-b-aac20 isma Weather kit User Manual Version 1.0 Page 1 / 11
 isma-b-aac20 User Manual isma Weather kit Version 1.0 Page 1 / 11 Table of contents Sedona Weather module... 3 Installing isma Weather kit... 3 2.1 Install isma_weather kit on the AAC20 controller... 4
isma-b-aac20 User Manual isma Weather kit Version 1.0 Page 1 / 11 Table of contents Sedona Weather module... 3 Installing isma Weather kit... 3 2.1 Install isma_weather kit on the AAC20 controller... 4
Graphical User Interfaces for Emittance and Correlation Plot. Henrik Loos
 Graphical User Interfaces for Emittance and Correlation Plot Common GUI Features Overview Files Configs Measure Data Point Export Common GUI Features Save Saves the present data. Auto-generated file name
Graphical User Interfaces for Emittance and Correlation Plot Common GUI Features Overview Files Configs Measure Data Point Export Common GUI Features Save Saves the present data. Auto-generated file name
JRA-55 Product Users' Handbook
 Climate Prediction Division Global Environment and Marine Department Japan Meteorological Agency September 2013 Change record Version Date Remarks 1.0 30 September 2013 First version 2.0 3 March 2014 Corrected
Climate Prediction Division Global Environment and Marine Department Japan Meteorological Agency September 2013 Change record Version Date Remarks 1.0 30 September 2013 First version 2.0 3 March 2014 Corrected
Section 26.1: Reporting Conventions. Section 26.2: Fluxes Through Boundaries. Section 26.3: Forces on Boundaries
 Chapter 26. Alphanumeric Reporting FLUENT provides tools for computing and reporting integral quantities at surfaces and boundaries. These tools enable you to find the mass flow rate and heat transfer
Chapter 26. Alphanumeric Reporting FLUENT provides tools for computing and reporting integral quantities at surfaces and boundaries. These tools enable you to find the mass flow rate and heat transfer
Forecast.io Driver. Installation and Usage Guide. Revision: 1.0 Date: Tuesday, May 20, 2014 Authors: Alan Chow
 Forecast.io Driver Installation and Usage Guide Revision: 1.0 Date: Tuesday, May 20, 2014 Authors: Alan Chow Contents Overview... 2 Features... 3 Usage Scenarios... 4 Change Log... 4 Disclaimer... 4 Driver
Forecast.io Driver Installation and Usage Guide Revision: 1.0 Date: Tuesday, May 20, 2014 Authors: Alan Chow Contents Overview... 2 Features... 3 Usage Scenarios... 4 Change Log... 4 Disclaimer... 4 Driver
Lab 1 Uniform Motion - Graphing and Analyzing Motion
 Lab 1 Uniform Motion - Graphing and Analyzing Motion Objectives: < To observe the distance-time relation for motion at constant velocity. < To make a straight line fit to the distance-time data. < To interpret
Lab 1 Uniform Motion - Graphing and Analyzing Motion Objectives: < To observe the distance-time relation for motion at constant velocity. < To make a straight line fit to the distance-time data. < To interpret
INTEGRAL. Science Operations Centre. Announcement of Opportunity for Observing Proposals (AO-11) INT/OAG/ /Dc Issue 1.
 Science Operations Centre Announcement of Opportunity for Observing Proposals (AO-11) INT/OAG/13-0383/Dc Issue 1.0 25 February 2013 Prepared by Miguel Arregui, Emilio Salazar Date: 25 February 2013 Page:
Science Operations Centre Announcement of Opportunity for Observing Proposals (AO-11) INT/OAG/13-0383/Dc Issue 1.0 25 February 2013 Prepared by Miguel Arregui, Emilio Salazar Date: 25 February 2013 Page:
RSMC WASHINGTON USER'S INTERPRETATION GUIDELINES ATMOSPHERIC TRANSPORT MODEL OUTPUTS
 RSMC WASHINGTON USER'S INTERPRETATION GUIDELINES ATMOSPHERIC TRANSPORT MODEL OUTPUTS -Version 2.0- (January 2007) 1. Introduction In the context of current agreements between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric
RSMC WASHINGTON USER'S INTERPRETATION GUIDELINES ATMOSPHERIC TRANSPORT MODEL OUTPUTS -Version 2.0- (January 2007) 1. Introduction In the context of current agreements between the National Oceanic and Atmospheric
APPMODULE WEATHER App Documentation
 REAL SMART HOME GmbH APPMODULE WEATHER App Version: 1.2.0 Type: Application Article No.: BAB-022 version I Actual state 03/2017 Date: 30. Mai 2017 EN WEATHER App REAL SMART HOME GmbH STILWERK Dortmund
REAL SMART HOME GmbH APPMODULE WEATHER App Version: 1.2.0 Type: Application Article No.: BAB-022 version I Actual state 03/2017 Date: 30. Mai 2017 EN WEATHER App REAL SMART HOME GmbH STILWERK Dortmund
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.2. Step-by-step example of how to build and evaluate a category based on mechanism of action with protein and DNA binding
 OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.2 Step-by-step example of how to build and evaluate a category based on mechanism of action with protein and DNA binding Outlook Background Objectives Specific Aims The exercise Workflow
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.2 Step-by-step example of how to build and evaluate a category based on mechanism of action with protein and DNA binding Outlook Background Objectives Specific Aims The exercise Workflow
Newton's 2 nd Law. . Your end results should only be interms of m
 Newton's nd Law Introduction: In today's lab you will demonstrate the validity of Newton's Laws in predicting the motion of a simple mechanical system. The system that you will investigate consists of
Newton's nd Law Introduction: In today's lab you will demonstrate the validity of Newton's Laws in predicting the motion of a simple mechanical system. The system that you will investigate consists of
Automatic Watershed Delineation using ArcSWAT/Arc GIS
 Automatic Watershed Delineation using ArcSWAT/Arc GIS By: - Endager G. and Yalelet.F 1. Watershed Delineation This tool allows the user to delineate sub watersheds based on an automatic procedure using
Automatic Watershed Delineation using ArcSWAT/Arc GIS By: - Endager G. and Yalelet.F 1. Watershed Delineation This tool allows the user to delineate sub watersheds based on an automatic procedure using
Collaborative WRF-based research and education enabled by software containers
 Collaborative WRF-based research and education enabled by software containers J. Hacker, J. Exby, K. Fossell National Center for Atmospheric Research Contributions from Tim See (U. North Dakota) 1 Why
Collaborative WRF-based research and education enabled by software containers J. Hacker, J. Exby, K. Fossell National Center for Atmospheric Research Contributions from Tim See (U. North Dakota) 1 Why
Demand Forecasting. for. Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Operations. User Guide. Release 7.1. April 2018
 Demand Forecasting for Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Operations User Guide Release 7.1 April 2018 2018 Farsight Solutions Limited All Rights Reserved. Portions copyright Business Forecast Systems, Inc. This
Demand Forecasting for Microsoft Dynamics 365 for Operations User Guide Release 7.1 April 2018 2018 Farsight Solutions Limited All Rights Reserved. Portions copyright Business Forecast Systems, Inc. This
Rain Watch TM Set up Manual. IC System with Rain Bird IC CONNECT
 Rain Watch TM Set up Manual IC System with Rain Bird IC CONNECT December 2018 Table of Contents Required materials to configure Rain Watch TM... 3 Installation... 4 Location... 4 Field Installation...
Rain Watch TM Set up Manual IC System with Rain Bird IC CONNECT December 2018 Table of Contents Required materials to configure Rain Watch TM... 3 Installation... 4 Location... 4 Field Installation...
Appendix 4 Weather. Weather Providers
 Appendix 4 Weather Using weather data in your automation solution can have many benefits. Without weather data, your home automation happens regardless of environmental conditions. Some things you can
Appendix 4 Weather Using weather data in your automation solution can have many benefits. Without weather data, your home automation happens regardless of environmental conditions. Some things you can
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.4.1. Tutorial of how to use Automated workflow for ecotoxicological prediction
 OECD QSAR Toolbox v.4.1 Tutorial of how to use Automated workflow for ecotoxicological prediction Outlook Aim Automated workflow The exercise Report The OECD QSAR Toolbox for Grouping Chemicals into Categories
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.4.1 Tutorial of how to use Automated workflow for ecotoxicological prediction Outlook Aim Automated workflow The exercise Report The OECD QSAR Toolbox for Grouping Chemicals into Categories
WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION THE WMO TABLE DRIVEN CODES: THE 21 ST CENTURY UNIVERSAL OBSERVATION CODES
 WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION THE WMO TABLE DRIVEN CODES: THE 21 ST CENTURY UNIVERSAL OBSERVATION CODES 1 THE WMO TABLE DRIVEN CODES: THE 21 ST CODES CENTURY UNIVERSAL OBSERVATION ABSTRACT The table
WORLD METEOROLOGICAL ORGANIZATION THE WMO TABLE DRIVEN CODES: THE 21 ST CENTURY UNIVERSAL OBSERVATION CODES 1 THE WMO TABLE DRIVEN CODES: THE 21 ST CODES CENTURY UNIVERSAL OBSERVATION ABSTRACT The table
M E R C E R W I N WA L K T H R O U G H
 H E A L T H W E A L T H C A R E E R WA L K T H R O U G H C L I E N T S O L U T I O N S T E A M T A B L E O F C O N T E N T 1. Login to the Tool 2 2. Published reports... 7 3. Select Results Criteria...
H E A L T H W E A L T H C A R E E R WA L K T H R O U G H C L I E N T S O L U T I O N S T E A M T A B L E O F C O N T E N T 1. Login to the Tool 2 2. Published reports... 7 3. Select Results Criteria...
OpenIFS practical exercises with Metview (Stockholm)
 OpenIFS practical exercises with Metview (Stockholm) Author: Date: URL: Sandor Kertesz 09-Jun-2014 15:37 https://software.ecmwf.int/wiki/pages/viewpage.action?pageid=33719209 1 of 12 Table of Contents
OpenIFS practical exercises with Metview (Stockholm) Author: Date: URL: Sandor Kertesz 09-Jun-2014 15:37 https://software.ecmwf.int/wiki/pages/viewpage.action?pageid=33719209 1 of 12 Table of Contents
Flight Utilities Metar Reader version 3.1 by Umberto Degli Esposti
 Flight Utilities http://www.flightutilities.com Metar Reader version 3.1 by Umberto Degli Esposti 1 Description The program allows inserting a Metar, to load it from a disk or from internet and to show
Flight Utilities http://www.flightutilities.com Metar Reader version 3.1 by Umberto Degli Esposti 1 Description The program allows inserting a Metar, to load it from a disk or from internet and to show
GSI Radar Data Interface for DTC community GSI release version 3.2
 GSI Radar Data Interface for DTC community GSI release version 3.2 1. Introduction This note is to help users to generate their own radar radial velocity and reflectivity BUFR files that can be used by
GSI Radar Data Interface for DTC community GSI release version 3.2 1. Introduction This note is to help users to generate their own radar radial velocity and reflectivity BUFR files that can be used by
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2018
 Application and verification of ECMWF products 2018 National Meteorological Administration, Romania 1. Summary of major highlights In the field of numerical model verification, the daily GRID_STAT method
Application and verification of ECMWF products 2018 National Meteorological Administration, Romania 1. Summary of major highlights In the field of numerical model verification, the daily GRID_STAT method
Title: ASML PAS 5500 Job Creation Semiconductor & Microsystems Fabrication Laboratory Revision: D Rev Date: 09/20/2012
 Approved by: Process Engineer / / / / Equipment Engineer 1 SCOPE The purpose of this document is to detail the creation of stepper jobs for the ASML PAS 5500. All users are expected to have read and understood
Approved by: Process Engineer / / / / Equipment Engineer 1 SCOPE The purpose of this document is to detail the creation of stepper jobs for the ASML PAS 5500. All users are expected to have read and understood
AERMOD Sensitivity to AERSURFACE Moisture Conditions and Temporal Resolution. Paper No Prepared By:
 AERMOD Sensitivity to AERSURFACE Moisture Conditions and Temporal Resolution Paper No. 33252 Prepared By: Anthony J Schroeder, CCM Managing Consultant TRINITY CONSULTANTS 7330 Woodland Drive Suite 225
AERMOD Sensitivity to AERSURFACE Moisture Conditions and Temporal Resolution Paper No. 33252 Prepared By: Anthony J Schroeder, CCM Managing Consultant TRINITY CONSULTANTS 7330 Woodland Drive Suite 225
Lecture 10 Multistep Analysis
 Lecture 10 Multistep Analysis 16.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS Mechanical 1 2015 ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015 Chapter Overview In this chapter, aspects of reviewing results will be covered: A. Multistep
Lecture 10 Multistep Analysis 16.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS Mechanical 1 2015 ANSYS, Inc. February 27, 2015 Chapter Overview In this chapter, aspects of reviewing results will be covered: A. Multistep
SuperCELL Data Programmer and ACTiSys IR Programmer User s Guide
 SuperCELL Data Programmer and ACTiSys IR Programmer User s Guide This page is intentionally left blank. SuperCELL Data Programmer and ACTiSys IR Programmer User s Guide The ACTiSys IR Programmer and SuperCELL
SuperCELL Data Programmer and ACTiSys IR Programmer User s Guide This page is intentionally left blank. SuperCELL Data Programmer and ACTiSys IR Programmer User s Guide The ACTiSys IR Programmer and SuperCELL
 http://www.wrcc.dri.edu/csc/scenic/ USER GUIDE 2017 Introduction... 2 Overview Data... 3 Overview Analysis Tools... 4 Overview Monitoring Tools... 4 SCENIC structure and layout... 5... 5 Detailed Descriptions
http://www.wrcc.dri.edu/csc/scenic/ USER GUIDE 2017 Introduction... 2 Overview Data... 3 Overview Analysis Tools... 4 Overview Monitoring Tools... 4 SCENIC structure and layout... 5... 5 Detailed Descriptions
London Heathrow Field Site Metadata
 London Heathrow Field Site Metadata Field Site Information Name: Heathrow src_id (Station ID number): 708 Geographic Area: Greater London Latitude (decimal ): 51.479 Longitude (decimal ): -0.449 OS Grid
London Heathrow Field Site Metadata Field Site Information Name: Heathrow src_id (Station ID number): 708 Geographic Area: Greater London Latitude (decimal ): 51.479 Longitude (decimal ): -0.449 OS Grid
Urban Canopy Tool User Guide `bo`
 Urban Canopy Tool User Guide `bo` ADMS Urban Canopy Tool User Guide Version 2.0 June 2014 Cambridge Environmental Research Consultants Ltd. 3, King s Parade Cambridge CB2 1SJ UK Telephone: +44 (0)1223
Urban Canopy Tool User Guide `bo` ADMS Urban Canopy Tool User Guide Version 2.0 June 2014 Cambridge Environmental Research Consultants Ltd. 3, King s Parade Cambridge CB2 1SJ UK Telephone: +44 (0)1223
Cloud Top Height Product: Product Guide
 Cloud Top Height Product: Product Guide Doc.No. Issue : : EUM/TSS/MAN/14/786420 v1a EUMETSAT Eumetsat-Allee 1, D-64295 Darmstadt, Germany Tel: +49 6151 807-7 Fax: +49 6151 807 555 Date : 21 August 2015
Cloud Top Height Product: Product Guide Doc.No. Issue : : EUM/TSS/MAN/14/786420 v1a EUMETSAT Eumetsat-Allee 1, D-64295 Darmstadt, Germany Tel: +49 6151 807-7 Fax: +49 6151 807 555 Date : 21 August 2015
THE LAND-SAF SURFACE ALBEDO AND DOWNWELLING SHORTWAVE RADIATION FLUX PRODUCTS
 THE LAND-SAF SURFACE ALBEDO AND DOWNWELLING SHORTWAVE RADIATION FLUX PRODUCTS Bernhard Geiger, Dulce Lajas, Laurent Franchistéguy, Dominique Carrer, Jean-Louis Roujean, Siham Lanjeri, and Catherine Meurey
THE LAND-SAF SURFACE ALBEDO AND DOWNWELLING SHORTWAVE RADIATION FLUX PRODUCTS Bernhard Geiger, Dulce Lajas, Laurent Franchistéguy, Dominique Carrer, Jean-Louis Roujean, Siham Lanjeri, and Catherine Meurey
The data for this lab comes from McDonald Forest. We will be working with spatial data representing the forest boundary, streams, roads, and stands.
 GIS LAB 6 Using the Projection Utility. Converting Data to Oregon s Approved Lambert Projection. Determining Stand Size, Stand Types, Road Length, and Stream Length. This lab will ask you to work with
GIS LAB 6 Using the Projection Utility. Converting Data to Oregon s Approved Lambert Projection. Determining Stand Size, Stand Types, Road Length, and Stream Length. This lab will ask you to work with
Virtual Beach Making Nowcast Predictions
 Virtual Beach 3.0.6 Making Nowcast Predictions In this module you will learn how to: A. Create a real-time connection to Web data services through EnDDaT B. Download real-time data to make a Nowcast prediction
Virtual Beach 3.0.6 Making Nowcast Predictions In this module you will learn how to: A. Create a real-time connection to Web data services through EnDDaT B. Download real-time data to make a Nowcast prediction
Import Digital Spatial Data (Shapefiles) into OneStop
 Import Digital Spatial Data (Shapefiles) into OneStop» Intended User: Pipeline Licence Applicants Overview To apply for a pipeline or pipeline installation licence, applicants must upload the proposed
Import Digital Spatial Data (Shapefiles) into OneStop» Intended User: Pipeline Licence Applicants Overview To apply for a pipeline or pipeline installation licence, applicants must upload the proposed
RSMC MONTRÉAL USERS' INTERPRETATION GUIDELINES ATMOSPHERIC TRANSPORT MODEL OUTPUTS. Version 9
 RSMC MONTRÉAL USERS' INTERPRETATION GUIDELINES ATMOSPHERIC TRANSPORT MODEL OUTPUTS Version 9 Environmental Emergency Response Section RSMC Montréal Canadian Meteorological Centre Meteorological Service
RSMC MONTRÉAL USERS' INTERPRETATION GUIDELINES ATMOSPHERIC TRANSPORT MODEL OUTPUTS Version 9 Environmental Emergency Response Section RSMC Montréal Canadian Meteorological Centre Meteorological Service
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.3. Predicting skin sensitisation potential of a chemical using skin sensitization data extracted from ECHA CHEM database
 OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.3 Predicting skin sensitisation potential of a chemical using skin sensitization data extracted from ECHA CHEM database Outlook Background The exercise Workflow Save prediction 23.02.2015
OECD QSAR Toolbox v.3.3 Predicting skin sensitisation potential of a chemical using skin sensitization data extracted from ECHA CHEM database Outlook Background The exercise Workflow Save prediction 23.02.2015
Astronomy 101 Lab: Stellarium Tutorial
 Name: Astronomy 101 Lab: Stellarium Tutorial Please install the Stellarium software on your computer using the instructions in the procedure. If you own a laptop, please bring it to class. You will submit
Name: Astronomy 101 Lab: Stellarium Tutorial Please install the Stellarium software on your computer using the instructions in the procedure. If you own a laptop, please bring it to class. You will submit
TIGGE-LAM archive development in the frame of GEOWOW. Richard Mladek (ECMWF)
 TIGGE-LAM archive development in the frame of GEOWOW Richard Mladek (ECMWF) The group on Earth Observations (GEO) initiated the Global Earth Observation System of Systems (GEOSS) GEOWOW, short for GEOSS
TIGGE-LAM archive development in the frame of GEOWOW Richard Mladek (ECMWF) The group on Earth Observations (GEO) initiated the Global Earth Observation System of Systems (GEOSS) GEOWOW, short for GEOSS
Description of. Jimy Dudhia Dave Gill. Bill Skamarock. WPS d1 output. WPS d2 output Real and WRF. real.exe General Functions.
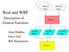 WPS d1 output WPS d2 output Real and WRF Description of real.exe General Functions Jimy Dudhia Dave Gill wrf d01 input wrf d01 bdy wrf d02 input Bill Skamarock wrf.exe Real program in a nutshell Function
WPS d1 output WPS d2 output Real and WRF Description of real.exe General Functions Jimy Dudhia Dave Gill wrf d01 input wrf d01 bdy wrf d02 input Bill Skamarock wrf.exe Real program in a nutshell Function
University of Colorado Denver Anschutz Medical Campus Online Chemical Inventory System User s Manual
 University of Colorado Denver Anschutz Medical Campus Online Chemical Inventory System User s Manual Hazardous Materials Division 303-724-0345 chemical.inventory@ucdenver.edu May, 2017 Table of Contents
University of Colorado Denver Anschutz Medical Campus Online Chemical Inventory System User s Manual Hazardous Materials Division 303-724-0345 chemical.inventory@ucdenver.edu May, 2017 Table of Contents
McIDAS-V Tutorial Displaying Point Observations from ADDE Datasets updated July 2016 (software version 1.6)
 McIDAS-V Tutorial Displaying Point Observations from ADDE Datasets updated July 2016 (software version 1.6) McIDAS-V is a free, open source, visualization and data analysis software package that is the
McIDAS-V Tutorial Displaying Point Observations from ADDE Datasets updated July 2016 (software version 1.6) McIDAS-V is a free, open source, visualization and data analysis software package that is the
NCEP s UNIFIED POST PROCESSOR (UPP) 2018 HWRF Tutorial
 NCEP s UNIFIED POST PROCESSOR (UPP) Hui-Ya Chuang NOAA/NCEP/EMC 2018 HWRF Tutorial 1 Outline Overview Components and Functions Sample fields generated Running unipost Controlling output generation Running
NCEP s UNIFIED POST PROCESSOR (UPP) Hui-Ya Chuang NOAA/NCEP/EMC 2018 HWRF Tutorial 1 Outline Overview Components and Functions Sample fields generated Running unipost Controlling output generation Running
