Observational constraints from the Solar System and from Extrasolar Planets
|
|
|
- Ami Sullivan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture 1 Part II Observational constraints from the Solar System and from Extrasolar Planets Lecture Universität Heidelberg WS 11/12 Dr. Christoph Mordasini mordasini@mpia.de Mentor Prof. T. Henning
2 Lecture overview 1. Introduction 2. Planet formation paradigm 3. Structure of the Solar System 4. The surprise: 51 Peg b 5. Detection techniques: radial velocity, transits, direct imaging, (microlensing, timing, astrometry) 6. Properties of extrasolar planets: mass, distance, eccentricity distributions, metallicity effect, massradius diagram,...
3 6. Properties of extrasolar planets
4 Current status 692 planets Candidates detected by radial velocity or astrometry 524 planetary systems 640 planets 76 multiple planet systems Transiting planets 171 planetary systems 184 planets 14 multiple planet systems Candidates detected by microlensing 12 planetary systems 13 planets 1 multiple planet systems planet candidates from the KEPLER satellite (transit) Candidates detected by imaging 22 planetary systems 25 planets 1 multiple planet systems Candidates detected by timing 9 planetary systems 14 planets 4 multiple planet systems Extra-solar planet encyclopedia (
5 Different techniques - different constraints direct imaging
6 A quickly progressing field Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Earth Venus Mars Incredible wealth of data provided by already flying space mission (e.g. CoRoT and Kepler). More to come. Field observationally driven. Formation theory struggles to keep up... Observation and theory often don t match well. Common characteristic: provide observations of a large number of exoplanets. This data should therefore be treated as a statistical ensemble. This could help.
7 Overview on observed exoplanet properties Extrasolar planets exhibit a very large diversity (all techniques). Frequencies -Low mass close-in planets: approx. 50 % (radial velocity) -Jovian planets inside a few AU: approx % (rv) -Hot Jupiters: 0.5-1% (rv, transits) -Cold Neptunes are common (microlensing) -Overall (FGK stars): any mass, P<10 years: 75% (rv) The mass function is strongly rising towards small masses. There might be local minimum in the planetary mass function around Mearth (rv). The radius distribution is strongly increasing towards small radii (transits). The semimajor axis distribution of giant planets consists of a pile up at a period of about 3 days, a period valley, and an upturn at about 1 AU. (rv) Close-in low mass (or small radius) planets are found somewhat further out than Hot Jupiters (rv, transits). Hot Jupiters are lonely (rv, transits). Low mass close-in planets are in multiple systems (rv, transits). Massive giants planets at large distances are rare, at least around solar like stars (direct imaging). Giant planet frequency and host star [Fe/H] are positively correlated.
8 Today, formation theory cannot explain all these observed characteristics in one coherent picture. But at least for some observations, theory can give us ideas about possible mechanisms responsible for them.
9 6.1 a-m diagram
10 Diversity & structures in the a-m diagram Direct imaging Diversity - close-in giant planets - evaporating planets - eccentric planets - super Jupiters - Hot Neptunes & Super Earth - pile-ups and voids: planetary desert period valley - planets at large distances Microlensing Radial velocity & Transits J. Schneider s exoplanet.eu ~2010 (already outdated!) HARPS high precision sample 2011
11 Frequency of planet types Bias-corrected frequency (at least one planet per star) in the a-m (or equivalently period-mass) plane found by high precision RV around solar like FGK stars. Mayor et al Close in planets: P<50 d
12 6.2 Mass distribution
13 Mass distribution: old versions (giants) Udry et al Marcy et al Number of Planets Planet Mass Distribution dn/dm! M Planets Keck, Lick, AAT M sin i (M JUP )? HARPS mass distribution from RV observations. rising towards smaller masses. No obs. bias: smaller masses are more difficult to detect. beware of uncorrected (biased) distributions! frequency of Jovian planets falls as about M -1. maximum of giant planet masses at about 1 Jupiter mass. HARPS gave around 2007 the first hint of a second population of low mass planets.
14 Mass distribution II: new view (w. low masses) uncorrected for obs. bias corrected for obs. bias Mayor et al Mayor et al RV: thanks to 1 m/s precision observations, a new huge population of low mass planets has emerged in the last few years (mostly planets found by HARPS). bi (tri?) modal distribution: minimum at about 30 Earth masses. Imprint of formation? neptunian bump: strong increase between ME. overall maximum at small masses more than 50% of solar-type stars harbor at least one planet of any mass and with period up to 100 days (!)
15 Mass distribution III: upper boundary Grether & Lineweaver 2006 Sahlmann et al desert Segresan et al. less than 0.6 % of Sun-like stars have a brown-dwarf companion: so called Brown dwarf desert mass distribution function shows a lack of objects between MJ. Upper end of planet mass distribution? Nothing particular is seen at 13 MJ (Dburning limit). A distinction of BD vs. planets based on formation seems advisable, but difficult to realize in practice.
16 6.3 Semimajor axis distribution
17 Semimajor axis distribution I: giants Msini>0.75 MJ Msini<0.75 MJ Msini<21 Mearth Msini>50 Mearth uncorrected for obs. bias corrected for obs. bias N Udry & Santos log(period) (days) uncorrected for obs. bias Mayor et al The semimajor axis distribution of giant planets found by RV consists of a pile up at a period of about 3 days (0.04 AU). Stopping mechanism for migration? Tidal circularization? Magnetospheric cavity? maybe this pile up is only tiny, when properly correcting for obs. bias... a period valley (10 d < P < 100 d). Timescale effect? an upturn at about 1 AU. Reservoir at large distances. Original formation region?
18 Number of Planets per Star Transits P 0 = 1.7 days P 0 = 2.2 days Orbital Period (days) Howard et al Semimajor axis distribution II: P 0 = 7.0 days low mass/radius planets 2!4 R E 4!8 R E 8!32 R E Cut off below P0: -small radii 2-4 Re: P0 = 7 days -large radii >4 Re : P0 = 2 days. Neptunian and smaller sized further out than giant planets. No pile up at 3 days. Consistent with earlier results from high precision RV. Lovis et al estimated 10 days. Different stopping mechanism? RV Msini<50 Mearth uncorrected for obs. bias corrected for obs. bias The semimajor axis distribution of low mass planets found by RV consists of a continuous increase to about 40 d. then again a decrease. Why? affected by obs. bias? In principle corrected... such planets seem extremely abundant. Mayor et al. 2011
19 6.4 Eccentricity distribution
20 high and even very high eccentricities are common among exoplanets. This is very different than in the Solar System. mean eccentricity for giants: 0.28 > any planet of the Solar System. lower mass planets seem to have lower (but still quite high) e <0.5. planets very close to the star get tidally circularized. origin? formation - evolution? several possible explanations: Planet-planet interactions, influence of stellar or planet companion (Kozai effect), planet-disk interaction (M >10 MJ), dynamical interactions in a cluster Eccentricity distribution Mayor et al. 2011
21 6.5 Metallicity
22 Stellar metallicity Mordasini et al [Fe/H]: iron content of the star ([Fe/H]=0: solar composition, [Fe/H]=0.5: ~ 3 times more iron than the sun). Iron serves as a proxy for the overall metal content in the star (scaled solar composition). Stars in the the solar neighborhood have a distribution of metallicities which is roughly Gaussian around zero. Other parts in the galaxies can have completely different [Fe/H] distributions. These stars can also have a non-scaled solar composition (e.g. thick disk stars). There exists also a galactic metallicity gradient (higher [Fe/H] towards the center).
23 the detection probability for giant planets is a strongly increasing function of the host star metallicity. No hot Jupiters found in globular cluster 47 Tuc ([Fe/H]=-0.76). Expected for solar neighborhood frequency (~0.5%): seven discoveries. Best known star-planet correlation for exoplanets. Important constraint for formation. Explanation: planets form more readily in metal rich systems (primordial hypothesis). Likely. falling in planets have enriched the star (pollution hypothesis) Metallicity effect for giant planets N. Santos et al. (2005) search sample (all stars) stars with giant planets
24 No metallicity effect for low mass planets?? Mayor et al Mayor et al HARPS high precision sample: [Fe/H] for giant gaseous planets (black), for planets less massive than 30 ME (red), and for the global combined sample stars (blue). No metallicity effect for low mass planets. Even absence of low mass planets at high [Fe/H]? Natural outcome in the core accretion formation model.
25 Metallicity effect as function of mass Sousa et al The division between metalophile and not metalophile planets coincides with a minimum in the planetary mass function. (ca. 30 ME) Different populations: Giant planets (w. gas runaway accretion) vs. Neptunian planets. Correlation with other elemental abundances in the stars are less clear (maybe Lithium-planet anticorrelation).
26 6.6 Stellar mass
27 Influence of the host star mass Equal bin in log(mstar) M dwarfs solar stars intermediate masses Planetary system mass / star number => mass of planetary material scales with Mstar Planets around more massive stars are more massive and more frequent. RV bias underestimate the last bin. The Neptunian vs Jovian planet ratio is higher around M dwarfs. Consistent with a correlation of stellar mass, protoplanetary disk mass, and (giant) planet formation probability.
28 6.7 Multiplicity
29 Multiplicity Fraction of giant planets in multiple systems: ~25%. Incomplete... Fraction of low mass planets in multiple systems: ~70% Hot Jupiters seem to be lonely. Formation? Disk cleaning? Kozai? HD10180: up to 7 planets (RV) HD10180 a[au] Msini (b) c d e f g h Lovis et al Eccentricities Solar like star Fe/H=0.08, M=1.06 Msun Some period ratios are fairly close to integer or half-integer values, but no mean-motion resonances. Roughly regularly spaced on a logarithmic scale Kepler-11: six transiting planets Kepler-11 a[au] Msini b c d e f g 0.46 <300 Lissauer et al all within i 1.5 deg. Very complanar. Solar like star Fe/H=0, M=0.95 Msun b, c close to 5:4 resonance, but otherwise not in resonances. Low densities Dynamically packed
30 Packed systems numbers=distance in mutual Hill spheres. Lovis et al Low mass planets seem to follow a radius exclusion law: they cannot be too close together when measured in mutual Hill spheres. Many systems seem to be dynamically packed. Could not add another planet. Numerical simulations show that systems with 3 5 planets and masses between a few ME and a few MJ, separations between adjacent planets should be of at least 7 9 mutual Hill radii to ensure stability on a 10-Gyr timescale. Additional stability islands exist at resonances. Dynamical evolution of the systems. Ejection/collision of surplus planets.
31 Kepler multiple systems Lissauer et al N/N TOT < 5 Kepler adjacent pairings RV adjacent pairings Kepler has detected a lot of systems with multiple transiting planet candidates. The distribution of observed period ratios shows that the majority of candidate pairs are neither in nor near low-order mean motion resonances. Nonetheless, there is a small but statistically significant excesses of pairs both in resonance and spaced slightly further apart, particularly near 2:1. Resonant capture due during migration? Slope of Cumulative Period Ratio Period Ratio Kepler adjacent pairings RV adjacent pairings Period Ratio
32 6.8 Radius distribution
33 Kepler results Planet Radius, R p (R E ) (2) (4) (5) (6) (11) (6) (21) (17) (9) (39) (34) (9) (45) (20) (64) (85) Planet Occurrence! d 2 f/dlogp/dlogr p Planet Occurrence! f cell (69) (25) (73) (18) (104) (269) (262) (15) (15) (74) (60) (353) (521) (159) (28) (70) (31) (153) (607) (893) (375) (25) (154) (160) (208) (591) (1101) (410) (10) (10) (50) (59) (18) (85) (41) Orbital Period, P (days) 1 (15) (168) (52) (278) (198) (799) (749) (295) Howard et al Planet Radius (R E ) Only reliable KEPLER candidates around bright, main sequence GK stars. Correct for observational bias. Complete to p=50 d, and R > 2 RE. decrease with period decrease with size (S/N) Diagonal band of increasing planet frequency. Number of Planets per Star with P < 50 days Incompleteness Strong increase towards small radius. Reminiscent of RV results. But absolute fraction less than HARPS. Radius - mass relationship? Does HARPS detect high density planets that KEPLER cannot see?
34 6.9 Mass-Radius diagram
35 M-R: Giant planets During evolution on Gyrs, giant planets contract and cool. The more massive the core, the smaller the total radius. Many transiting Hot Jupiters are bloated planets: not explainable by standard internal structure modeling. Energy source must act deep in the interior. Several mechanism proposed for explanation. Some giant exoplanets seem to contain very large amounts of metals (>100 ME)
36 M-R: Low mass planets Kepler-11 b,c,d,e,f Kepler 10b Corot-7b Diversity: very different radii for a given M. Some are clearly rocky planets. Observational constraints on the internal composition. Migration? Problem: degeneracy. different composition can give the same M-R. e.g. Ice=rock + some H2/He. Spectra of atmospheres can help to distinguish: Water vapor atmosphere has a smaller scale height than a H2/He atmosphere. Close in planets! Evaporation (atmospheric escape) could play an important role on Gyrs. Must consider formation and evolution. Origin unknown... low mass planets from the beginning or boiled down giant planets?
37 Additional observations
38 Direct imaging: planets form hot Janson et al The two competing models for giant planet formation, core accretion and direct collapse, predict different initial conditions for planet evolution. For direct collapse, planets should initially be very hot. For core accretion, they can also be cold. Observations point to a Hot start. This could help to distinguish formation models.
39 Transits: correlation planetary core mass and stellar metallicity Guillot et al. Miller & Fortney 2010 Transit observations & RV mass measurements show that the core mass of giant planets, and the stellar metallicity are positively correlated. This is reproduced by core accretion models. Recent observations maybe even indicate that that all giant planets contain at least 10 ME of metals. For direct collapse, planets can result both enriched and depleted.
40 Questions?
Data from: The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia.
 Data from: The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia http://exoplanet.eu/ 2009->10 Status of Exoplanet Searches Direct Detection: 5->9 planets detected Sensitive to large planets in large orbits around faint
Data from: The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia http://exoplanet.eu/ 2009->10 Status of Exoplanet Searches Direct Detection: 5->9 planets detected Sensitive to large planets in large orbits around faint
III The properties of extrasolar planets
 III The properties of extrasolar planets (as of early 2016) http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 3.0 Introduction This lecture will discuss what we have found so far. It is important to remember
III The properties of extrasolar planets (as of early 2016) http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 3.0 Introduction This lecture will discuss what we have found so far. It is important to remember
Extrasolar Planets. Properties Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
 Extrasolar Planets Properties 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Finding extrasolar planets is hard quick recap Planet Detection Direct: pictures or spectra of the planets
Extrasolar Planets Properties 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley Finding extrasolar planets is hard quick recap Planet Detection Direct: pictures or spectra of the planets
Sta%s%cal Proper%es of Exoplanets
 Sta%s%cal Proper%es of Exoplanets Mordasini et al. 2009, A&A, 501, 1139 Next: Popula%on Synthesis 1 Goals of Population Synthesis: incorporate essential planet formation processes, with simplifying approximation
Sta%s%cal Proper%es of Exoplanets Mordasini et al. 2009, A&A, 501, 1139 Next: Popula%on Synthesis 1 Goals of Population Synthesis: incorporate essential planet formation processes, with simplifying approximation
Time: a new dimension of constraints for planet formation and evolution theory
 S. Jin, P. Mollière Max Planck Institut for Astronomy, Heidelberg, Germany Y. Alibert & W. Benz University of Bern, Switzerland Christoph Mordasini PLATO meeting Taormina 3.12.2014 Time: a new dimension
S. Jin, P. Mollière Max Planck Institut for Astronomy, Heidelberg, Germany Y. Alibert & W. Benz University of Bern, Switzerland Christoph Mordasini PLATO meeting Taormina 3.12.2014 Time: a new dimension
Practical Numerical Training UKNum
 Practical Numerical Training UKNum Conclusions PD. Dr. C. Mordasini Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Heidelberg Programm: 1) Weiterführende Vorlesungen 2) Fragebogen 3) Eigene Forschung 4) Bachelor/Masterarbeiten
Practical Numerical Training UKNum Conclusions PD. Dr. C. Mordasini Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Heidelberg Programm: 1) Weiterführende Vorlesungen 2) Fragebogen 3) Eigene Forschung 4) Bachelor/Masterarbeiten
Architecture and demographics of planetary systems
 Architecture and demographics of planetary systems Struve (1952) The demography of the planets that we detect is strongly affected by detection methods psychology of the observer Understanding planet demography
Architecture and demographics of planetary systems Struve (1952) The demography of the planets that we detect is strongly affected by detection methods psychology of the observer Understanding planet demography
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES
 EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week - Dynamics Reynolds number, turbulent vs. laminar flow Velocity fluctuations, Kolmogorov cascade Brunt-Vaisala frequency, gravity waves Rossby waves,
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week - Dynamics Reynolds number, turbulent vs. laminar flow Velocity fluctuations, Kolmogorov cascade Brunt-Vaisala frequency, gravity waves Rossby waves,
Actuality of Exoplanets Search. François Bouchy OHP - IAP
 Actuality of Exoplanets Search François Bouchy OHP - IAP How detect extrasolar planets? Two main difficulties : 1 A tiny angular separation 0.75 arcsec Sun Jupiter at 4 light years 4 Sun Jupiter at 100
Actuality of Exoplanets Search François Bouchy OHP - IAP How detect extrasolar planets? Two main difficulties : 1 A tiny angular separation 0.75 arcsec Sun Jupiter at 4 light years 4 Sun Jupiter at 100
Internal structure and atmospheres of planets
 Internal structure and atmospheres of planets SERGEI POPOV 1312.3323 Sizes and masses Radius vs. mass Results of modeling. Old (relaxed) planets. Colors correspond to different fractions of light elements.
Internal structure and atmospheres of planets SERGEI POPOV 1312.3323 Sizes and masses Radius vs. mass Results of modeling. Old (relaxed) planets. Colors correspond to different fractions of light elements.
II Planet Finding.
 II Planet Finding http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 1.0 Introduction There are a lot of slides in this lecture. Much of this should be familiar from PHY104 (Introduction to Astrophysics) and
II Planet Finding http://sgoodwin.staff.shef.ac.uk/phy229.html 1.0 Introduction There are a lot of slides in this lecture. Much of this should be familiar from PHY104 (Introduction to Astrophysics) and
The Transit Method: Results from the Ground
 The Transit Method: Results from the Ground Results from individual transit search programs The Mass-Radius relationships (internal structure) Global Properties The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect There are
The Transit Method: Results from the Ground Results from individual transit search programs The Mass-Radius relationships (internal structure) Global Properties The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect There are
Extrasolar Planets. Today. Dwarf Planets. Extrasolar Planets. Next week. Review Tuesday. Exam Thursday. also, Homework 6 Due
 Extrasolar Planets Today Dwarf Planets Extrasolar Planets Next week Review Tuesday Exam Thursday also, Homework 6 Due will count best 5 of 6 homeworks 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson
Extrasolar Planets Today Dwarf Planets Extrasolar Planets Next week Review Tuesday Exam Thursday also, Homework 6 Due will count best 5 of 6 homeworks 2007 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson
On the relation between stars and their planets
 On the relation between stars and their planets Nuno C. Santos Centro de Astrofísica, Universidade do Porto Instituto de Astrofísica e Ciências do Espaço Why we stellar parameters are important in exoplanets
On the relation between stars and their planets Nuno C. Santos Centro de Astrofísica, Universidade do Porto Instituto de Astrofísica e Ciências do Espaço Why we stellar parameters are important in exoplanets
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 15. Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 15 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 15 The Formation of Planetary Systems Units of Chapter 15 15.1 Modeling Planet Formation 15.2 Terrestrial and Jovian Planets
Lecture Outlines Chapter 15 Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 15 The Formation of Planetary Systems Units of Chapter 15 15.1 Modeling Planet Formation 15.2 Terrestrial and Jovian Planets
Kozai-Lidov oscillations
 Kozai-Lidov oscillations Kozai (1962 - asteroids); Lidov (1962 - artificial satellites) arise most simply in restricted three-body problem (two massive bodies on a Kepler orbit + a test particle) e.g.,
Kozai-Lidov oscillations Kozai (1962 - asteroids); Lidov (1962 - artificial satellites) arise most simply in restricted three-body problem (two massive bodies on a Kepler orbit + a test particle) e.g.,
Planet formation in protoplanetary disks. Dmitry Semenov Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg, Germany
 Planet formation in protoplanetary disks Dmitry Semenov Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg, Germany Suggested literature "Protoplanetary Dust" (2010), eds. D. Apai & D. Lauretta, CUP "Protostars
Planet formation in protoplanetary disks Dmitry Semenov Max Planck Institute for Astronomy Heidelberg, Germany Suggested literature "Protoplanetary Dust" (2010), eds. D. Apai & D. Lauretta, CUP "Protostars
What Have We Found? 1978 planets in 1488 systems as of 11/15/15 (http://exoplanet.eu/ ) 1642 planets candidates (http://exoplanets.
 Exoplanets. II What Have We Found? 1978 planets in 1488 systems as of 11/15/15 (http://exoplanet.eu/ ) 1642 planets + 3787 candidates (http://exoplanets.org) Detected by radial velocity/astrometry: 621
Exoplanets. II What Have We Found? 1978 planets in 1488 systems as of 11/15/15 (http://exoplanet.eu/ ) 1642 planets + 3787 candidates (http://exoplanets.org) Detected by radial velocity/astrometry: 621
RV- method: disturbing oscilla8ons Example: F- star Procyon
 Star spots RV- method: disturbing oscilla8ons Example: F- star Procyon In- class ac8vity (1) 1) You are working with the HARPS instrument and you want to unambiguously detect Jupiter-twins around nearby
Star spots RV- method: disturbing oscilla8ons Example: F- star Procyon In- class ac8vity (1) 1) You are working with the HARPS instrument and you want to unambiguously detect Jupiter-twins around nearby
[25] Exoplanet Characterization (11/30/17)
![[25] Exoplanet Characterization (11/30/17) [25] Exoplanet Characterization (11/30/17)](/thumbs/86/94788164.jpg) 1 [25] Exoplanet Characterization (11/30/17) Upcoming Items APOD 12/2/16 1. Read chapters 24.1-24.3 for Tuesday 2. We will have a final exam review in the last discussion section (Friday, Dec 8) and also
1 [25] Exoplanet Characterization (11/30/17) Upcoming Items APOD 12/2/16 1. Read chapters 24.1-24.3 for Tuesday 2. We will have a final exam review in the last discussion section (Friday, Dec 8) and also
Lecture 12: Extrasolar planets. Astronomy 111 Monday October 9, 2017
 Lecture 12: Extrasolar planets Astronomy 111 Monday October 9, 2017 Reminders Star party Thursday night! Homework #6 due Monday The search for extrasolar planets The nature of life on earth and the quest
Lecture 12: Extrasolar planets Astronomy 111 Monday October 9, 2017 Reminders Star party Thursday night! Homework #6 due Monday The search for extrasolar planets The nature of life on earth and the quest
Observations of Extrasolar Planets
 Observations of Extrasolar Planets Hamilton 2005 Shay Zucker Observations of Extrasolar Planets Spectroscopic detection of exoplanets Emerging properties of the sample Transiting planets Future prospects
Observations of Extrasolar Planets Hamilton 2005 Shay Zucker Observations of Extrasolar Planets Spectroscopic detection of exoplanets Emerging properties of the sample Transiting planets Future prospects
Planets and Brown Dwarfs
 Extra Solar Planets Extra Solar Planets We have estimated there may be 10 20 billion stars in Milky Way with Earth like planets, hospitable for life. But what evidence do we have that such planets even
Extra Solar Planets Extra Solar Planets We have estimated there may be 10 20 billion stars in Milky Way with Earth like planets, hospitable for life. But what evidence do we have that such planets even
Exoplanet Host Stars
 Exoplanet Host Stars The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR)Diagram The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR)Diagram Standard Doppler Surveys The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR)Diagram Direct Imaging detections Standard Doppler Surveys
Exoplanet Host Stars The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR)Diagram The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR)Diagram Standard Doppler Surveys The Hertzsprung-Russel (HR)Diagram Direct Imaging detections Standard Doppler Surveys
Why Search for Extrasolar Planets?
 Why Search for Extrasolar Planets? What is the diversity of habitats for life in the universe? Are Earth-like planets common or rare in our region of the galaxy? We have an elaborate and self-consistent
Why Search for Extrasolar Planets? What is the diversity of habitats for life in the universe? Are Earth-like planets common or rare in our region of the galaxy? We have an elaborate and self-consistent
Adam Burrows, Princeton April 7, KITP Public Lecture
 Adam Burrows, Princeton April 7, 2010 KITP Public Lecture The Ancient History of Comparative Planetology There are infinite worlds both like and unlike this world of ours...we must believe that in all
Adam Burrows, Princeton April 7, 2010 KITP Public Lecture The Ancient History of Comparative Planetology There are infinite worlds both like and unlike this world of ours...we must believe that in all
Who was here? How can you tell? This is called indirect evidence!
 1 Who was here? How can you tell? This is called indirect evidence! 2 How does a planetary system form? The one we can study in the most detail is our solar system. If we want to know whether the solar
1 Who was here? How can you tell? This is called indirect evidence! 2 How does a planetary system form? The one we can study in the most detail is our solar system. If we want to know whether the solar
Design Reference Mission. DRM approach
 Design Reference Mission The Design Reference Mission (DRM) is a set of observing programs which together provide a tool to assist with tradeoff decisions in the design of the E-ELT (examples of observing
Design Reference Mission The Design Reference Mission (DRM) is a set of observing programs which together provide a tool to assist with tradeoff decisions in the design of the E-ELT (examples of observing
Importance of the study of extrasolar planets. Exoplanets Introduction. Importance of the study of extrasolar planets
 Importance of the study of extrasolar planets Exoplanets Introduction Planets and Astrobiology (2017-2018) G. Vladilo Technological and scientific spin-offs Exoplanet observations are driving huge technological
Importance of the study of extrasolar planets Exoplanets Introduction Planets and Astrobiology (2017-2018) G. Vladilo Technological and scientific spin-offs Exoplanet observations are driving huge technological
Heavy meteal rules. Vardan Adibekyan Institute of Astrophysics and Space Sciences. The star-planet connection. 1 June 2015 NAOJ, Tokyo
 The star-planet connection Institute of Astrophysics and Space Sciences 1 June 2015 NAOJ, Tokyo 1 Introduction to exoplanets Diversity of exoplanets Planet formation theories 2 Planet formation and metallicity
The star-planet connection Institute of Astrophysics and Space Sciences 1 June 2015 NAOJ, Tokyo 1 Introduction to exoplanets Diversity of exoplanets Planet formation theories 2 Planet formation and metallicity
Lecture Outlines. Chapter 15. Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Outlines Chapter 15 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 15 Exoplanets Units of Chapter 15 15.1 Modeling Planet Formation 15.2 Solar System Regularities and Irregularities 15.3
Lecture Outlines Chapter 15 Astronomy Today 8th Edition Chaisson/McMillan Chapter 15 Exoplanets Units of Chapter 15 15.1 Modeling Planet Formation 15.2 Solar System Regularities and Irregularities 15.3
The Main Point(s) Lecture #36: Planets Around Other Stars. Extrasolar Planets! Reading: Chapter 13. Theory Observations
 Lecture #36: Planets Around Other Stars Extrasolar Planets! Theory Observations Detection methods Results to date... Implications for "Habitable Zones" Reading: Chapter 13 Astro 102/104 1 The Main Point(s)
Lecture #36: Planets Around Other Stars Extrasolar Planets! Theory Observations Detection methods Results to date... Implications for "Habitable Zones" Reading: Chapter 13 Astro 102/104 1 The Main Point(s)
Planets & Life. Planets & Life PHYS 214. Please start all class related s with 214: 214: Dept of Physics (308A)
 Planets & Life Planets & Life PHYS 214 Dr Rob Thacker Dept of Physics (308A) thacker@astro.queensu.ca Please start all class related emails with 214: 214: Today s s lecture Assignment 1 marked will hand
Planets & Life Planets & Life PHYS 214 Dr Rob Thacker Dept of Physics (308A) thacker@astro.queensu.ca Please start all class related emails with 214: 214: Today s s lecture Assignment 1 marked will hand
Imprints of Formation on Exoplanets
 Imprints of Formation on Exoplanets The role of Stellar Mass and Metallicity ILARIA PASCUCCI Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, Department of Planetary Sciences The University of Arizona https://almascience.nrao.edu/alma-science/planet-forming-disks
Imprints of Formation on Exoplanets The role of Stellar Mass and Metallicity ILARIA PASCUCCI Lunar and Planetary Laboratory, Department of Planetary Sciences The University of Arizona https://almascience.nrao.edu/alma-science/planet-forming-disks
Extrasolar Planets. Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects
 Extrasolar Planets Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects Methods of detection Methods of detection Methods of detection Pulsar timing Planetary motion around pulsar
Extrasolar Planets Methods of detection Characterization Theoretical ideas Future prospects Methods of detection Methods of detection Methods of detection Pulsar timing Planetary motion around pulsar
Characterization of the exoplanet host stars. Exoplanets Properties of the host stars. Characterization of the exoplanet host stars
 Characterization of the exoplanet host stars Exoplanets Properties of the host stars Properties of the host stars of exoplanets are derived from a combination of astrometric, photometric, and spectroscopic
Characterization of the exoplanet host stars Exoplanets Properties of the host stars Properties of the host stars of exoplanets are derived from a combination of astrometric, photometric, and spectroscopic
Chapter 15 The Formation of Planetary Systems
 Chapter 15 The Formation of Planetary Systems Units of Chapter 15 15.1 Modeling Planet Formation 15.2 Formation of the Solar System 15.3 Terrestrial and Jovian Planets 15.4 Interplanetary Debris 15.5 Solar
Chapter 15 The Formation of Planetary Systems Units of Chapter 15 15.1 Modeling Planet Formation 15.2 Formation of the Solar System 15.3 Terrestrial and Jovian Planets 15.4 Interplanetary Debris 15.5 Solar
Finding Other Earths. Jason H. Steffen. Asset Earth Waubonsee Community College October 1, 2009
 Finding Other Earths Jason H. Steffen Asset Earth Waubonsee Community College October 1, 2009 True Earth Analog Necessities: 1) Main Sequence Star 2) Within the Stellar Habitable Zone 3) Roughly Earth
Finding Other Earths Jason H. Steffen Asset Earth Waubonsee Community College October 1, 2009 True Earth Analog Necessities: 1) Main Sequence Star 2) Within the Stellar Habitable Zone 3) Roughly Earth
Lecture 20: Planet formation II. Clues from Exoplanets
 Lecture 20: Planet formation II. Clues from Exoplanets 1 Outline Definition of a planet Properties of exoplanets Formation models for exoplanets gravitational instability model core accretion scenario
Lecture 20: Planet formation II. Clues from Exoplanets 1 Outline Definition of a planet Properties of exoplanets Formation models for exoplanets gravitational instability model core accretion scenario
Practical Numerical Training UKNum
 Practical Numerical Training UKNum Conclusions Dr. H. Klahr & Dr. C. Mordasini Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Heidelberg Programm: 1) Weiterführende Vorlesungen 2) Fragebogen 3) Eigene Forschung 4)
Practical Numerical Training UKNum Conclusions Dr. H. Klahr & Dr. C. Mordasini Max Planck Institute for Astronomy, Heidelberg Programm: 1) Weiterführende Vorlesungen 2) Fragebogen 3) Eigene Forschung 4)
Planets in different environments
 Planets in different environments Is the formation and evolution of planets effected by the stellar environment? Eike W. Guenther Thüringer Landessternwarte Tautenburg Which factors are important for the
Planets in different environments Is the formation and evolution of planets effected by the stellar environment? Eike W. Guenther Thüringer Landessternwarte Tautenburg Which factors are important for the
Observational Cosmology Journal Club
 Observational Cosmology Journal Club 07/09/2018 Shijie Wang 1. Heller, R. (2018). Formation of hot Jupiters through disk migration and evolving stellar tides. Retrieved from arxiv.1806.06601 2. Rey, J.,
Observational Cosmology Journal Club 07/09/2018 Shijie Wang 1. Heller, R. (2018). Formation of hot Jupiters through disk migration and evolving stellar tides. Retrieved from arxiv.1806.06601 2. Rey, J.,
Finding Extra-Solar Earths with Kepler. William Cochran McDonald Observatory
 Finding Extra-Solar Earths with Kepler William Cochran McDonald Observatory Who is Bill Cochran? Senior Research Scien;st McDonald Observatory Originally interested in outer planet atmospheres Started
Finding Extra-Solar Earths with Kepler William Cochran McDonald Observatory Who is Bill Cochran? Senior Research Scien;st McDonald Observatory Originally interested in outer planet atmospheres Started
Probing the Galactic Planetary Census
 Probing the Galactic Planetary Census Greg Laughlin -- UCSC Astronomy Exoplanet News from the AAS meeting (New York Times) The finding was called exciting by Dr. Kenneth Franklin of the American Museum-Hayden
Probing the Galactic Planetary Census Greg Laughlin -- UCSC Astronomy Exoplanet News from the AAS meeting (New York Times) The finding was called exciting by Dr. Kenneth Franklin of the American Museum-Hayden
II. Results from Transiting Planets. 1. Global Properties 2. The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect
 II. Results from Transiting Planets 1. Global Properties 2. The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect Planet Radius Most transiting planets tend to be inflated. Approximately 68% of all transiting planets have radii
II. Results from Transiting Planets 1. Global Properties 2. The Rossiter-McClaughlin Effect Planet Radius Most transiting planets tend to be inflated. Approximately 68% of all transiting planets have radii
Ruth Murray-Clay University of California, Santa Barbara
 A Diversity of Worlds: Toward a Theoretical Framework for the Structures of Planetary Systems Ruth Murray-Clay University of California, Santa Barbara Strange New Worlds. Slide credit: Scott Gaudi ~1500
A Diversity of Worlds: Toward a Theoretical Framework for the Structures of Planetary Systems Ruth Murray-Clay University of California, Santa Barbara Strange New Worlds. Slide credit: Scott Gaudi ~1500
What is it like? When did it form? How did it form. The Solar System. Fall, 2005 Astronomy 110 1
 What is it like? When did it form? How did it form The Solar System Fall, 2005 Astronomy 110 1 Fall, 2005 Astronomy 110 2 The planets all orbit the sun in the same direction. The Sun spins in the same
What is it like? When did it form? How did it form The Solar System Fall, 2005 Astronomy 110 1 Fall, 2005 Astronomy 110 2 The planets all orbit the sun in the same direction. The Sun spins in the same
Planetary interiors: What they can(not) tell us about formation
 Planetary interiors: What they can(not) tell us about formation Methods and constraints Jérémy Leconte Timeline Formation ( 1-10 Myr) Mass Radius Orbital Parameters Stellar Parameters... Evolution ( 1-10
Planetary interiors: What they can(not) tell us about formation Methods and constraints Jérémy Leconte Timeline Formation ( 1-10 Myr) Mass Radius Orbital Parameters Stellar Parameters... Evolution ( 1-10
Exoplanet Search Techniques: Overview. PHY 688, Lecture 28 April 3, 2009
 Exoplanet Search Techniques: Overview PHY 688, Lecture 28 April 3, 2009 Course administration final presentations Outline see me for paper recommendations 2 3 weeks before talk see me with draft of presentation
Exoplanet Search Techniques: Overview PHY 688, Lecture 28 April 3, 2009 Course administration final presentations Outline see me for paper recommendations 2 3 weeks before talk see me with draft of presentation
Exploring the giant planet - brown dwarf connection with astrometry. Johannes Sahlmann ESA Research Fellow at ESAC
 Exploring the giant planet - brown dwarf connection with astrometry ESA Research Fellow at ESAC Who s Who, Paris - 2 July 215 IS MASS A GOOD DEMOGRAPHIC INDICATOR? 2MASSWJ127334 393254 first image of a
Exploring the giant planet - brown dwarf connection with astrometry ESA Research Fellow at ESAC Who s Who, Paris - 2 July 215 IS MASS A GOOD DEMOGRAPHIC INDICATOR? 2MASSWJ127334 393254 first image of a
Star-planet connection:
 : The role of stellar metallicity Centro de Astrofísica da Universidade do Porto Instituto de Astrofísica e Ciências do Espaço 18 September 2014 Porto, Portugal 1 Planet formation and metallicity Giant
: The role of stellar metallicity Centro de Astrofísica da Universidade do Porto Instituto de Astrofísica e Ciências do Espaço 18 September 2014 Porto, Portugal 1 Planet formation and metallicity Giant
ASTB01 Exoplanets Lab
 ASTB01 Exoplanets Lab Author: Anders Johansen Revision date: $Date: 2015/08/28 14:55:59 $ Planets orbiting stars other than the Sun are called exoplanets. Stellar light reflected off
ASTB01 Exoplanets Lab Author: Anders Johansen Revision date: $Date: 2015/08/28 14:55:59 $ Planets orbiting stars other than the Sun are called exoplanets. Stellar light reflected off
EXOPLANETS. Aurélien CRIDA
 EXOPLANETS Aurélien CRIDA EXOPLANETS Giordano Bruno said that the many stars are like our Sun, with planets like our Earth, inhabited as well (in de l'infinito universo e mondi (1574) ). He was burnt alive
EXOPLANETS Aurélien CRIDA EXOPLANETS Giordano Bruno said that the many stars are like our Sun, with planets like our Earth, inhabited as well (in de l'infinito universo e mondi (1574) ). He was burnt alive
ASTR 200 : Lecture 6 Introduction to the Solar System Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley
 ASTR 200 : Lecture 6 Introduction to the Solar System 1 2004 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley Comparative Planetology Studying the similarities among and differences between the planets
ASTR 200 : Lecture 6 Introduction to the Solar System 1 2004 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley Comparative Planetology Studying the similarities among and differences between the planets
Chapter 13 Lecture. The Cosmic Perspective. Seventh Edition. Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant Worlds Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 13 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant Worlds 13.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Our goals for learning: Why is it so challenging
Chapter 13 Lecture The Cosmic Perspective Seventh Edition Other Planetary Systems: The New Science of Distant Worlds 13.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Our goals for learning: Why is it so challenging
Doppler Technique Measuring a star's Doppler shift can tell us its motion toward and away from us.
 Doppler Technique Measuring a star's Doppler shift can tell us its motion toward and away from us. Current techniques can measure motions as small as 1 m/s (walking speed!). Sun motion due to: Jupiter:
Doppler Technique Measuring a star's Doppler shift can tell us its motion toward and away from us. Current techniques can measure motions as small as 1 m/s (walking speed!). Sun motion due to: Jupiter:
HD Transits HST/STIS First Transiting Exo-Planet. Exoplanet Discovery Methods. Paper Due Tue, Feb 23. (4) Transits. Transits.
 Paper Due Tue, Feb 23 Exoplanet Discovery Methods (1) Direct imaging (2) Astrometry position (3) Radial velocity velocity Seager & Mallen-Ornelas 2003 ApJ 585, 1038. "A Unique Solution of Planet and Star
Paper Due Tue, Feb 23 Exoplanet Discovery Methods (1) Direct imaging (2) Astrometry position (3) Radial velocity velocity Seager & Mallen-Ornelas 2003 ApJ 585, 1038. "A Unique Solution of Planet and Star
Project RISARD. - the story so far. Marcin P. Gawroński (Toruń Centre for Astronomy)
 Project RISARD - the story so far credit : wiki Marcin P. Gawroński (Toruń Centre for Astronomy) in collaboration with K. Goźdzewski, K. Katarzyński, G. Rycyk (TCfA) Overview RISARD motivation and current
Project RISARD - the story so far credit : wiki Marcin P. Gawroński (Toruń Centre for Astronomy) in collaboration with K. Goźdzewski, K. Katarzyński, G. Rycyk (TCfA) Overview RISARD motivation and current
Young Solar-like Systems
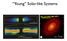 Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Young Solar-like Systems FIG.2. Panels(a),(b),and(c)show 2.9,1.3,and 0.87 mm ALMA continuum images of other panels, as well as an inset with an enlarged view of the inner 300 mas centered on the (f) show
Definitions. Stars: M>0.07M s Burn H. Brown dwarfs: M<0.07M s No Burning. Planets No Burning. Dwarf planets. cosmic composition (H+He)
 Definitions Stars: M>0.07M s Burn H cosmic composition (H+He) Brown dwarfs: M
Definitions Stars: M>0.07M s Burn H cosmic composition (H+He) Brown dwarfs: M
10/16/ Detecting Planets Around Other Stars. Chapter 10: Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds
 10/16/17 Lecture Outline 10.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Chapter 10: Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds Our goals for learning: How do we detect planets around other stars?
10/16/17 Lecture Outline 10.1 Detecting Planets Around Other Stars Chapter 10: Other Planetary Systems The New Science of Distant Worlds Our goals for learning: How do we detect planets around other stars?
Extrasolar Planets and Chemical Abundance
 Extrasolar Planets and Chemical Abundance Intermediate Graduate Physics Seminar Waqas Bhatti May 1, 2007 Abstract Over 200 extrasolar planets have been discovered since the first confirmed observation
Extrasolar Planets and Chemical Abundance Intermediate Graduate Physics Seminar Waqas Bhatti May 1, 2007 Abstract Over 200 extrasolar planets have been discovered since the first confirmed observation
Planet Detection. AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System
 Review AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System MIDTERM III this THURSDAY 04/8 covering LECT. 17 through We ve talked about the Terrestrial Planets and the Jovian Planets - What about planets around other
Review AST 105 Intro Astronomy The Solar System MIDTERM III this THURSDAY 04/8 covering LECT. 17 through We ve talked about the Terrestrial Planets and the Jovian Planets - What about planets around other
Extra Solar Planetary Systems and Habitable Zones
 Lecture Overview Extra Solar Planetary Systems and Habitable Zones Our Galaxy has 200 Billion Stars, Our Sun has 8 planets. It seems like an awful waste if we are alone Exoplanets Karen J. Meech, Svetlana
Lecture Overview Extra Solar Planetary Systems and Habitable Zones Our Galaxy has 200 Billion Stars, Our Sun has 8 planets. It seems like an awful waste if we are alone Exoplanets Karen J. Meech, Svetlana
The Physics of Exoplanets
 The Physics of Exoplanets Heike Rauer Institut für Planetenforschung, DLR, Berlin-Adlershof, Zentrum für Astronomie und Astrophysik, TU Berlin Formation in protoplanetary disk, migration Loss of primary,
The Physics of Exoplanets Heike Rauer Institut für Planetenforschung, DLR, Berlin-Adlershof, Zentrum für Astronomie und Astrophysik, TU Berlin Formation in protoplanetary disk, migration Loss of primary,
Overview of the Solar System. Solar system contents one star, several planets, lots of debris.
 Overview of the Solar System Solar system contents one star, several planets, lots of debris. Most of it is the Sun! 99.8% of the mass of the Solar System resides in the Sun. A hot ball of mostly hydrogen
Overview of the Solar System Solar system contents one star, several planets, lots of debris. Most of it is the Sun! 99.8% of the mass of the Solar System resides in the Sun. A hot ball of mostly hydrogen
Lab 5: Searching for Extra-Solar Planets
 Lab 5: Searching for Extra-Solar Planets Until 1996, astronomers only knew about planets orbiting our sun. Though other planetary systems were suspected to exist, none had been found. Now, thirteen years
Lab 5: Searching for Extra-Solar Planets Until 1996, astronomers only knew about planets orbiting our sun. Though other planetary systems were suspected to exist, none had been found. Now, thirteen years
Other Planetary Systems (Chapter 13) Extrasolar Planets. Is our solar system the only collection of planets in the universe?
 Other Planetary Systems (Chapter 13) Extrasolar Planets Is our solar system the only collection of planets in the universe? Based on Chapter 13 No subsequent chapters depend on the material in this lecture
Other Planetary Systems (Chapter 13) Extrasolar Planets Is our solar system the only collection of planets in the universe? Based on Chapter 13 No subsequent chapters depend on the material in this lecture
How Common Are Planets Around Other Stars? Transiting Exoplanets. Kailash C. Sahu Space Tel. Sci. Institute
 How Common Are Planets Around Other Stars? Transiting Exoplanets Kailash C. Sahu Space Tel. Sci. Institute Earth as viewed by Voyager Zodiacal cloud "Pale blue dot" Look again at that dot. That's here.
How Common Are Planets Around Other Stars? Transiting Exoplanets Kailash C. Sahu Space Tel. Sci. Institute Earth as viewed by Voyager Zodiacal cloud "Pale blue dot" Look again at that dot. That's here.
Other planetary systems
 Exoplanets are faint! Other planetary systems Planets are seen only by reflected light at optical wavelengths At the distance of another star the faint light of a planet is lost in the glare of the star
Exoplanets are faint! Other planetary systems Planets are seen only by reflected light at optical wavelengths At the distance of another star the faint light of a planet is lost in the glare of the star
3.4 Transiting planets
 64 CHAPTER 3. TRANSITS OF PLANETS: MEAN DENSITIES 3.4 Transiting planets A transits of a planet in front of its parent star occurs if the line of sight is very close to the orbital plane. The transit probability
64 CHAPTER 3. TRANSITS OF PLANETS: MEAN DENSITIES 3.4 Transiting planets A transits of a planet in front of its parent star occurs if the line of sight is very close to the orbital plane. The transit probability
Formation of the Solar System Chapter 8
 Formation of the Solar System Chapter 8 To understand the formation of the solar system one has to apply concepts such as: Conservation of angular momentum Conservation of energy The theory of the formation
Formation of the Solar System Chapter 8 To understand the formation of the solar system one has to apply concepts such as: Conservation of angular momentum Conservation of energy The theory of the formation
Searching for extrasolar planets using microlensing
 Searching for extrasolar planets using microlensing Dijana Dominis Prester 7.8.2007, Belgrade Extrasolar planets Planets outside of the Solar System (exoplanets) Various methods: mostly massive hot gaseous
Searching for extrasolar planets using microlensing Dijana Dominis Prester 7.8.2007, Belgrade Extrasolar planets Planets outside of the Solar System (exoplanets) Various methods: mostly massive hot gaseous
Astronomy 330 HW 2. Outline. Presentations. ! Kira Bonk ascension.html
 Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 11): What is f p? Eric Gobst Suharsh Sivakumar Next Class: Life in the Solar System HW 2 Kira Bonk http://www.ufodigest.com/news/0308/ ascension.html Matthew Tenpas http://morphman.hubpages.com/hub/alien-
Astronomy 330 This class (Lecture 11): What is f p? Eric Gobst Suharsh Sivakumar Next Class: Life in the Solar System HW 2 Kira Bonk http://www.ufodigest.com/news/0308/ ascension.html Matthew Tenpas http://morphman.hubpages.com/hub/alien-
Observations of extrasolar planets
 Observations of extrasolar planets 1 Mercury 2 Venus radar image from Magellan (vertical scale exaggerated 10 X) 3 Mars 4 Jupiter 5 Saturn 6 Saturn 7 Uranus and Neptune 8 we need to look out about 10 parsecs
Observations of extrasolar planets 1 Mercury 2 Venus radar image from Magellan (vertical scale exaggerated 10 X) 3 Mars 4 Jupiter 5 Saturn 6 Saturn 7 Uranus and Neptune 8 we need to look out about 10 parsecs
Exoplanets: the quest for Earth twins
 369, 572 581 doi:1.198/rsta.21.245 Exoplanets: the quest for Earth twins BY MICHEL MAYOR*, STEPHANE UDRY, FRANCESCO PEPE AND CHRISTOPHE LOVIS Observatoire de Genève, Université de Genève, Geneva, Switzerland
369, 572 581 doi:1.198/rsta.21.245 Exoplanets: the quest for Earth twins BY MICHEL MAYOR*, STEPHANE UDRY, FRANCESCO PEPE AND CHRISTOPHE LOVIS Observatoire de Genève, Université de Genève, Geneva, Switzerland
Atmospheric Chemistry on Substellar Objects
 Atmospheric Chemistry on Substellar Objects Channon Visscher Lunar and Planetary Institute, USRA UHCL Spring Seminar Series 2010 Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/R. Hurt Outline introduction to substellar
Atmospheric Chemistry on Substellar Objects Channon Visscher Lunar and Planetary Institute, USRA UHCL Spring Seminar Series 2010 Image Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/R. Hurt Outline introduction to substellar
Extrasolar Planets. Dieter Schmitt Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research Katlenburg-Lindau
 Extrasolar Planets Dieter Schmitt Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research Katlenburg-Lindau Lecture Introduction to Solar System Physics Uni Göttingen, 8 June 2009 Outline Historical Overview Detection
Extrasolar Planets Dieter Schmitt Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research Katlenburg-Lindau Lecture Introduction to Solar System Physics Uni Göttingen, 8 June 2009 Outline Historical Overview Detection
Exoplanetary Atmospheres: Atmospheric Dynamics of Irradiated Planets. PHY 688, Lecture 24 Mar 23, 2009
 Exoplanetary Atmospheres: Atmospheric Dynamics of Irradiated Planets PHY 688, Lecture 24 Mar 23, 2009 Outline Review of previous lecture: atmospheric temperature structure of irradiated planets isothermal
Exoplanetary Atmospheres: Atmospheric Dynamics of Irradiated Planets PHY 688, Lecture 24 Mar 23, 2009 Outline Review of previous lecture: atmospheric temperature structure of irradiated planets isothermal
Habitability Outside the Solar System. A discussion of Bennett & Shostak Chapter 11 HNRS 228 Dr. H. Geller
 Habitability Outside the Solar System A discussion of Bennett & Shostak Chapter 11 HNRS 228 Dr. H. Geller 1 Chapter Overview Distant Suns (11.1) Life cycle of stars and their habitability zones Extrasolar
Habitability Outside the Solar System A discussion of Bennett & Shostak Chapter 11 HNRS 228 Dr. H. Geller 1 Chapter Overview Distant Suns (11.1) Life cycle of stars and their habitability zones Extrasolar
Moon Obs #1 Due! Moon visible: early morning through afternoon. 6 more due June 13 th. 15 total due June 25 th. Final Report Due June 28th
 Moon Obs #1 Due! Moon visible: early morning through afternoon 6 more due June 13 th 15 total due June 25 th Final Report Due June 28th Our Solar System Objectives Overview of what is in our solar system
Moon Obs #1 Due! Moon visible: early morning through afternoon 6 more due June 13 th 15 total due June 25 th Final Report Due June 28th Our Solar System Objectives Overview of what is in our solar system
Super-Earths as Failed Cores in Orbital Migration Traps
 Super-Earths as Failed Cores in Orbital Migration Traps Yasuhiro Hasegawa (Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology) Hasegawa 2016, ApJ, 832, 83 Copyright 2017. All rights reserved.
Super-Earths as Failed Cores in Orbital Migration Traps Yasuhiro Hasegawa (Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology) Hasegawa 2016, ApJ, 832, 83 Copyright 2017. All rights reserved.
Astronomy 405 Solar System and ISM
 Astronomy 405 Solar System and ISM Lecture 18 Planetary System Formation and Evolution February 25, 2013 grav collapse opposed by turbulence, B field, thermal Cartoon of Star Formation isolated, quasi-static,
Astronomy 405 Solar System and ISM Lecture 18 Planetary System Formation and Evolution February 25, 2013 grav collapse opposed by turbulence, B field, thermal Cartoon of Star Formation isolated, quasi-static,
Synergies between E-ELT and space instrumentation for extrasolar planet science
 Synergies between E-ELT and space instrumentation for extrasolar planet science Raffaele Gratton and Mariangela Bonavita INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Padova - ITALY Main topics in exo-planetary science
Synergies between E-ELT and space instrumentation for extrasolar planet science Raffaele Gratton and Mariangela Bonavita INAF Osservatorio Astronomico di Padova - ITALY Main topics in exo-planetary science
Planetary system dynamics Part III Mathematics / Part III Astrophysics
 Planetary system dynamics Part III Mathematics / Part III Astrophysics Lecturer: Prof. Mark Wyatt (Dr. Amy Bonsor on 9,11 Oct) Schedule: Michaelmas 2017 Mon, Wed, Fri at 10am MR11, 24 lectures, start Fri
Planetary system dynamics Part III Mathematics / Part III Astrophysics Lecturer: Prof. Mark Wyatt (Dr. Amy Bonsor on 9,11 Oct) Schedule: Michaelmas 2017 Mon, Wed, Fri at 10am MR11, 24 lectures, start Fri
Planets: Name Distance from Sun Satellites Year Day Mercury 0.4AU yr 60 days Venus yr 243 days* Earth 1 1 yr 1 day Mars 1.
 The Solar System (Ch. 6 in text) We will skip from Ch. 6 to Ch. 15, only a survey of the solar system, the discovery of extrasolar planets (in more detail than the textbook), and the formation of planetary
The Solar System (Ch. 6 in text) We will skip from Ch. 6 to Ch. 15, only a survey of the solar system, the discovery of extrasolar planets (in more detail than the textbook), and the formation of planetary
Outline. RV Planet Searches Improving Doppler Precision Population Synthesis Planet Formation Models Eta-Earth Survey Future Directions
 The NASA-UC Eta-Earth Survey: A Systematic Search for Low-mass Planets From Keck Observatory - Andrew Howard - Townes Post-doctoral Fellow, UC Berkeley HD 7924b Collaborators Geoff Marcy Debra Fischer
The NASA-UC Eta-Earth Survey: A Systematic Search for Low-mass Planets From Keck Observatory - Andrew Howard - Townes Post-doctoral Fellow, UC Berkeley HD 7924b Collaborators Geoff Marcy Debra Fischer
Foundations of Astrophysics
 Foundations of Astrophysics Barbara Ryden The Ohio State University Bradley M. Peterson The Ohio State University Preface xi 1 Early Astronomy 1 1.1 The Celestial Sphere 1 1.2 Coordinate Systems on a Sphere
Foundations of Astrophysics Barbara Ryden The Ohio State University Bradley M. Peterson The Ohio State University Preface xi 1 Early Astronomy 1 1.1 The Celestial Sphere 1 1.2 Coordinate Systems on a Sphere
see disks around new stars in Orion nebula where planets are probably being formed 3
 Planet Formation contracting cloud forms stars swirling disk of material around forming star (H, He, C, O, heavier elements, molecules, dust ) form planets New born star heats up material, blows away solar
Planet Formation contracting cloud forms stars swirling disk of material around forming star (H, He, C, O, heavier elements, molecules, dust ) form planets New born star heats up material, blows away solar
2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Thought Question Suppose you found a star with the same mass as the Sun moving back and forth with a period of 16 months. What could you conclude? A. It has a planet orbiting at less than 1 AU. B. It has
Thought Question Suppose you found a star with the same mass as the Sun moving back and forth with a period of 16 months. What could you conclude? A. It has a planet orbiting at less than 1 AU. B. It has
ASTR 200 : Lecture 6 Introduction to the Solar System Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley
 ASTR 200 : Lecture 6 Introduction to the Solar System 1 2004 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley ANNOUNCEMENTS Keep up with reading! Always posted on course web site. Reading material
ASTR 200 : Lecture 6 Introduction to the Solar System 1 2004 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Addison-Wesley ANNOUNCEMENTS Keep up with reading! Always posted on course web site. Reading material
Transiting Hot Jupiters near the Galactic Center
 National Aeronautics and Space Administration Transiting Hot Jupiters near the Galactic Center Kailash C. Sahu Taken from: Hubble 2006 Science Year in Review The full contents of this book include more
National Aeronautics and Space Administration Transiting Hot Jupiters near the Galactic Center Kailash C. Sahu Taken from: Hubble 2006 Science Year in Review The full contents of this book include more
Searching for Other Worlds
 Searching for Other Worlds Lecture 32 1 In-Class Question What is the Greenhouse effect? a) Optical light from the Sun is reflected into space while infrared light passes through the atmosphere and heats
Searching for Other Worlds Lecture 32 1 In-Class Question What is the Greenhouse effect? a) Optical light from the Sun is reflected into space while infrared light passes through the atmosphere and heats
Observational constraints from the Solar System and from Extrasolar Planets
 Lecture 1 Part I Observational constraints from the Solar System and from Extrasolar Planets Lecture Universität Heidelberg WS 11/12 Dr. Christoph Mordasini Partially based on script by Prof. W. Benz Mentor
Lecture 1 Part I Observational constraints from the Solar System and from Extrasolar Planets Lecture Universität Heidelberg WS 11/12 Dr. Christoph Mordasini Partially based on script by Prof. W. Benz Mentor
Kepler Planets back to the origin
 Kepler Planets back to the origin Acknowledgements to the Kepler Team Yanqin Wu (Toronto) + Yoram Lithwick, James Owen, Ji-Wei Xie, Nikhil Mahajan, Bonan Pu, Ari Silburt Kepler planets: an Unexpected population
Kepler Planets back to the origin Acknowledgements to the Kepler Team Yanqin Wu (Toronto) + Yoram Lithwick, James Owen, Ji-Wei Xie, Nikhil Mahajan, Bonan Pu, Ari Silburt Kepler planets: an Unexpected population
Global models of planetary system formation. Richard Nelson Queen Mary, University of London
 Global models of planetary system formation Richard Nelson Queen Mary, University of London Hot Jupiters Cold Jupiters Super-Earths/ Neptunes 2 Sumi et al (2016) Occurence rates 30-50% of FGK stars host
Global models of planetary system formation Richard Nelson Queen Mary, University of London Hot Jupiters Cold Jupiters Super-Earths/ Neptunes 2 Sumi et al (2016) Occurence rates 30-50% of FGK stars host
Class 15 Formation of the Solar System
 Class 16 Extra-solar planets The radial-velocity technique for finding extrasolar planets Other techniques for finding extrasolar planets Class 15 Formation of the Solar System What does a successful model
Class 16 Extra-solar planets The radial-velocity technique for finding extrasolar planets Other techniques for finding extrasolar planets Class 15 Formation of the Solar System What does a successful model
8. Solar System Origins
 8. Solar System Origins Chemical composition of the galaxy The solar nebula Planetary accretion Extrasolar planets Our Galaxy s Chemical Composition es Big Bang produced hydrogen & helium Stellar processes
8. Solar System Origins Chemical composition of the galaxy The solar nebula Planetary accretion Extrasolar planets Our Galaxy s Chemical Composition es Big Bang produced hydrogen & helium Stellar processes
Astronomy 405 Solar System and ISM
 Astronomy 405 Solar System and ISM Lecture 17 Planetary System Formation and Evolution February 22, 2013 grav collapse opposed by turbulence, B field, thermal Cartoon of Star Formation isolated, quasi-static,
Astronomy 405 Solar System and ISM Lecture 17 Planetary System Formation and Evolution February 22, 2013 grav collapse opposed by turbulence, B field, thermal Cartoon of Star Formation isolated, quasi-static,
Dynamically Unstable Planetary Systems Emerging Out of Gas Disks
 EXTREME SOLAR SYSTEMS ASP Conference Series, Vol. 398, 2008 D. Fischer, F. A. Rasio, S. E. Thorsett, and A. Wolszczan Dynamically Unstable Planetary Systems Emerging Out of Gas Disks Soko Matsumura, Edward
EXTREME SOLAR SYSTEMS ASP Conference Series, Vol. 398, 2008 D. Fischer, F. A. Rasio, S. E. Thorsett, and A. Wolszczan Dynamically Unstable Planetary Systems Emerging Out of Gas Disks Soko Matsumura, Edward
