Kelley: Sectional Anatomy for Imaging Professionals, 3rd Edition
|
|
|
- Barrie Owens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Kelley: Sectional Anatomy for Imaging Professionals, 3rd Edition Chapter 1: Introduction to Sectional Anatomy Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A vertical plane that passes through the body, dividing it into anterior and posterior portions, is the plane. a. sagittal b. coronal c. axial d. oblique ANS: B REF: page 2 OBJ: Define the four anatomic planes. 2. The directional term contralateral refers to which of the following? a. On the same side b. On the opposite side c. Toward the midsagittal plane d. Away from the midsagittal plane ANS: B REF: page 4 3. The directional term rostral refers to which of the following? a. The front or palm of the hand b. The sole of the foot c. Toward the feet d. Toward the nose ANS: D REF: page 4 4. The term popliteal refers to the area of the: a. upper portion of the leg. b. back of the knee. c. lower portion of the leg. d. sole of the foot. ANS: B REF: page 4
2 Test Bank The term flank refers to the area of the: a. upper chest or breast. b. lower back between the ribs and hips. c. side of the trunk adjoining the lumbar region. d. abdomen. ANS: C REF: page 4 6. The aortic arch is located: a. 2.5 cm below the jugular notch. b. at T4-T5, sternal angle. c. 4 cm above the transpyloric plane. d. 2 cm above the transpyloric plane. ANS: A REF: page 6 OBJ: Identify the location of commonly used internal landmarks. 7. The carotid bifurcation is located: a. 4 cm above the pyloric plane. b. 4 cm above bifurcation of the abdominal aorta. c. at the upper border of the thyroid cartilage. d. at the upper margin of the sacroiliac joint. ANS: C REF: page 6 OBJ: Identify the location of commonly used internal landmarks. 8. The inferior mesenteric artery is located: a. 2 cm above the transpyloric plane. b. 4 cm above the transpyloric plane. c. 2.5 cm below the jugular notch. d. 4 cm above the bifurcation of the abdominal aorta. ANS: D REF: page 6 OBJ: Identify the location of commonly used internal landmarks. 9. Most of the small intestine is located in which of the abdominal quadrants? a. Right upper quadrant (RUQ) b. Right lower quadrant (RLQ)
3 Test Bank 1-3 c. Left upper quadrant (LUQ) d. Left lower quadrant (LLQ) ANS: D REF: page 8 OBJ: List the four abdominal quadrants. 10. Which of the body cavities is the largest? a. Dorsal b. Ventral c. Abdominal d. Pelvic ANS: B REF: page 6 OBJ: Describe the dorsal and ventral cavities of the body. 11. The plane that passes diagonally between the axes of two other planes is the plane. a. sagittal b. coronal c. axial d. oblique ANS: D REF: page 2 OBJ: Define the four anatomic planes. 12. The directional term caudal refers to which of the following? a. On the same side b. On the opposite side c. Toward the feet d. Toward the head ANS: C REF: page The directional term proximal refers to which of the following? a. On the same side b. On the opposite side c. Away from a reference point d. Toward a reference point ANS: D REF: page 4
4 Test Bank The term axillary refers to the area of the: a. armpit. b. forearm. c. front of elbow. d. upper arm. ANS: A REF: page The term cubital refers to the area of the: a. lower posterior portion of the leg. b. posterior surface of elbow area of the arm. c. lower back between the ribs and hips. d. upper portion of the leg. ANS: B REF: page The term antebrachial refers to the area of the: a. armpit. b. ribs. c. forearm. d. upper arm. ANS: C REF: page The term inguinal refers to the area of the: a. spine. b. naval. c. sternum. d. groin. ANS: D REF: page The carina is located at: a. L4 to L5. b. T4 to T5, sternal angle.
5 Test Bank 1-5 c. L1 to L2. d. T1 to T2, sternal angle. ANS: B REF: page 6 OBJ: Identify the location of commonly used internal landmarks. 19. The dorsal cavity can be further subdivided into which of the following cavities? a. Cranial and spinal b. Thoracic and abdominopelvic c. Two lateral pleural d. Abdominal and pelvic ANS: A REF: page 6 OBJ: Describe the dorsal and ventral cavities of the body. 20. The stomach and tail of the pancreas are located in which of the following abdominal quadrants? a. Right upper b. Left upper c. Right lower d. Left lower ANS: B REF: page 8 OBJ: List the four abdominal quadrants. 21. Which of the following is a parameter that allows for the adjustment of the gray scale? a. CT number b. Hounsfield unit c. Window width d. Window level ANS: C REF: page 8 OBJ: Describe the gray scale used in CT and MR imaging. 22. Images reconstructed from data obtained along any projection through the cube that result in a sagittal, coronal, transverse, or oblique image are termed: a. multiplanar reformation. b. shaded surface display. c. maximum intensity projection. d. volume rendering. ANS: A REF: page 9 OBJ: "Describe MPR, CPR, SSD, MIP, and VR."
6 Test Bank Which of the following techniques can be described as a ray from the camera s viewpoint that is directed to stop at a particular user-defined threshold value? a. Multiplanar reformation b. Shaded surface display c. Maximum intensity projection d. Volume rendering ANS: B REF: page 12 OBJ: "Describe MPR, CPR, SSD, MIP, and VR." 24. Water is used as a reference tissue and is given the CT number of: a b c. 0. d ANS: C REF: page 8 OBJ: Describe the gray scale used in CT and MR imaging. 25. The transpyloric plane is found midway between the: a. xiphosternal joint and the pubic symphysis. b. xiphosternal joint and umbilicus. c. tubercles of the iliac crests. d. tubercles of the iliac crests and L3. ANS: B REF: page 7 OBJ: Identify the location of commonly used internal landmarks. 26. The figure below illustrates which of the following imaging planes? a. Axial b. Coronal
7 Test Bank 1-7 c. Sagittal d. Oblique ANS: B REF: page 2 OBJ: Define the four anatomic planes. 27. The figure below illustrates which of the following imaging planes? a. Axial b. Coronal c. Sagittal d. Oblique ANS: A REF: page 2 OBJ: Define the four anatomic planes. 28. The figure below illustrates which of the following imaging planes?
8 Test Bank 1-8 a. Axial b. Coronal c. Sagittal d. Oblique ANS: B REF: page 2 OBJ: Define the four anatomic planes. 29. The figure below illustrates which of the following imaging planes?
9 Test Bank 1-9 a. Axial b. Coronal c. Sagittal d. Oblique ANS: C REF: page 2 OBJ: Define the four anatomic planes. 30. The figure below is an example of which of the following?
10 Test Bank 1-10 a. Multiplanar reformation b. Shaded surface display c. Maximum intensity projection d. Volume rendering ANS: B REF: page 12 OBJ: "Describe MPR, CPR, SSD, MIP, and VR." 31. The figure below is an example of which of the following? a. Multiplanar reformation b. Shaded surface display c. Maximum intensity projection d. Volume rendering
11 Test Bank 1-11 ANS: C REF: page 12 OBJ: "Describe MPR, CPR, SSD, MIP, and VR."
Unit 1: Body Plan & Organization Test Review 1. Define anatomy and contrast it with physiology.
 Name: Period: Unit 1: Body Plan & Organization Test Review 1. Define anatomy and contrast it with physiology. 2. Arrange and identify, in order, the six levels of structural organization of the human body.
Name: Period: Unit 1: Body Plan & Organization Test Review 1. Define anatomy and contrast it with physiology. 2. Arrange and identify, in order, the six levels of structural organization of the human body.
Applegate: The Anatomy and Physiology Learning System, 3 rd Edition
 Applegate: The Anatomy and Physiology Learning System, 3 rd Edition Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body TRUE/FALSE 1. The cell is the simplest living unit of organization within the human body. T
Applegate: The Anatomy and Physiology Learning System, 3 rd Edition Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body TRUE/FALSE 1. The cell is the simplest living unit of organization within the human body. T
Introduction Chpt 1. Study Slides
 Introduction Chpt 1 Study Slides A group of molecules working together toward a common function is a: A. Cell B. Atom C. Organelle D. Tissue E. Organ ANSWER A group of molecules working together toward
Introduction Chpt 1 Study Slides A group of molecules working together toward a common function is a: A. Cell B. Atom C. Organelle D. Tissue E. Organ ANSWER A group of molecules working together toward
Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition
 Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following describes anatomy? a. Using devices to investigate parameters such as heart rate
Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following describes anatomy? a. Using devices to investigate parameters such as heart rate
1. The basic vocabulary used in anatomy is primarily derived from. A. Greek. B. Hebrew. C. Latin. D. German. E. Greek and Latin
 Page 1 of 28 1. The basic vocabulary used in anatomy is primarily derived from A. Greek B. Hebrew C. Latin D. German E. Greek and Latin 1 Student: 2. The early anatomist known as the "Prince of Physicians"
Page 1 of 28 1. The basic vocabulary used in anatomy is primarily derived from A. Greek B. Hebrew C. Latin D. German E. Greek and Latin 1 Student: 2. The early anatomist known as the "Prince of Physicians"
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body NOTES
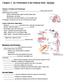 Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body NOTES Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body NOTES Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable
18. Which body system is needed for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide? A. Respiratory B. Integumentary C. Digestive D. Urinary 19.
 1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT a part of the study of anatomy? A. The structure of body parts B. Predicting the body's responses to stimuli C. Microscopic organization D. The relationship
1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT a part of the study of anatomy? A. The structure of body parts B. Predicting the body's responses to stimuli C. Microscopic organization D. The relationship
Name: Period: Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Study Outline
 Name: Period: Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Study Outline I. Introduction A. The interests of our earliest ancestors most likely concerned. B. Primitive people certainly suffered
Name: Period: Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Study Outline I. Introduction A. The interests of our earliest ancestors most likely concerned. B. Primitive people certainly suffered
II. Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy is. B. Physiology is.
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Human Anatomy and Physiology, 13 th ed. Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. The
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Human Anatomy and Physiology, 13 th ed. Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. The
Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology. I. Introduction A. The interests of our earliest ancestors most likely concerned
 Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11 th ed. Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. The
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Human Anatomy and Physiology, 11 th ed. Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1: Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology I. Introduction A. The
Chapter 01 The Sciences of Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 01 The Sciences of Anatomy and Physiology Multiple Choice Questions 1. The word "anatomy" comes from A. Latin and means "to be born." B. Hebrew and means "shape." C. Greek and means "to cut apart."
Chapter 01 The Sciences of Anatomy and Physiology Multiple Choice Questions 1. The word "anatomy" comes from A. Latin and means "to be born." B. Hebrew and means "shape." C. Greek and means "to cut apart."
Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The anatomic term means toward the midline. a. anterior b. posterior c. medial d. cranial The term medial indicates an anatomic direction
Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The anatomic term means toward the midline. a. anterior b. posterior c. medial d. cranial The term medial indicates an anatomic direction
Test Bank forprinciples of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition by Tortora
 Test Bank forprinciples of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition by Tortora Chapter Number: 01 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) Which term describes the study of the functions of body structures? a) anatomy
Test Bank forprinciples of Anatomy and Physiology 14th Edition by Tortora Chapter Number: 01 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) Which term describes the study of the functions of body structures? a) anatomy
1. Anatomy is. 2. Which subdivision of anatomy involves the study of organs that function together?
 1 of 19 1 Student: 1. Anatomy is A. the study of function. B. a branch of physiology. C. the study of structure. D. the study of living organisms. E. the study of homeostasis. 2. Which subdivision of anatomy
1 of 19 1 Student: 1. Anatomy is A. the study of function. B. a branch of physiology. C. the study of structure. D. the study of living organisms. E. the study of homeostasis. 2. Which subdivision of anatomy
BIO 115 SP 2012 Homework 1: Introduction to A&P and Chemistry Please note that this is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 115 SP 2012 Homework 1: Introduction to A&P and Chemistry Please note that this is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. When a body is in the anatomical position, it is A. Standing erect,
BIO 115 SP 2012 Homework 1: Introduction to A&P and Chemistry Please note that this is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. When a body is in the anatomical position, it is A. Standing erect,
CHAPTER 1. Quick Check and Active Learning Answer Keys QUICK CHECK
 CHAPTER 1 QUICK CHECK Page 9 1. Anatomy is the study of the structure of an organism and the relationships of its parts. Physiology is the study of the functions of living organisms and their parts. Pathology
CHAPTER 1 QUICK CHECK Page 9 1. Anatomy is the study of the structure of an organism and the relationships of its parts. Physiology is the study of the functions of living organisms and their parts. Pathology
16. Why are many anatomical terms based on Greek and Latin roots? A. because they are easy to spell B. because many terms are based on the names of
 1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT true? A. Anatomy is the study of the structure of the body. B. Gross anatomy is the study of tissues and cells. C. Comparative anatomy is the study of more than
1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT true? A. Anatomy is the study of the structure of the body. B. Gross anatomy is the study of tissues and cells. C. Comparative anatomy is the study of more than
3) Using your fingers to find your pulse on your wrist is an example of
 Package Title: Testbank Course Title: PAP13 Chapter Number: 01 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) This is the study of the functions of body structures. a) anatomy b) physiology c) endocrinology d) histology
Package Title: Testbank Course Title: PAP13 Chapter Number: 01 Question type: Multiple Choice 1) This is the study of the functions of body structures. a) anatomy b) physiology c) endocrinology d) histology
Journal #1: How might an Anatomist and Physiologist see a computer differently?
 Journal #1: How might an Anatomist and Physiologist see a computer differently? Objective #1: Define Anatomy and Physiology and describe various specialties of each discipline. Identify the major levels
Journal #1: How might an Anatomist and Physiologist see a computer differently? Objective #1: Define Anatomy and Physiology and describe various specialties of each discipline. Identify the major levels
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Prepared by Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar
The Human Body: An Orientation Prepared by Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar
Organization of the Body
 Name: Hmwk # 1 - Chapter 1 Organization of the Body The study of human anatomy and physiology the structure and function of an organism and the relationship of its parts. It begins with a basic organization
Name: Hmwk # 1 - Chapter 1 Organization of the Body The study of human anatomy and physiology the structure and function of an organism and the relationship of its parts. It begins with a basic organization
Human Anatomy, 7e (Martini/Timmons/Tallitsch) Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy. 1.1 Multiple-Choice Questions
 Human Anatomy, 7e (Martini/Timmons/Tallitsch) Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy 1.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which is the most accurate statement? A) Historically, the relationship
Human Anatomy, 7e (Martini/Timmons/Tallitsch) Chapter 1 Foundations: An Introduction to Anatomy 1.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which is the most accurate statement? A) Historically, the relationship
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION. Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1
 CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 Anatomy and Physiology Four basic properties of life: Reception The ability of the organism to control its actions
CHAPTER 9 BODY ORGANIZATION Copyright 2007 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 Anatomy and Physiology Four basic properties of life: Reception The ability of the organism to control its actions
HTHS 1110 / Biomedical Core Module 1
 HTHS 1110 / Biomedical Core Module 1 Body Plan & Organization Homeostasis Disease: A Disruption in Homeostasis Measurement Systems and Calculations Used for the Human Body Body Plan & Organization Anatomy
HTHS 1110 / Biomedical Core Module 1 Body Plan & Organization Homeostasis Disease: A Disruption in Homeostasis Measurement Systems and Calculations Used for the Human Body Body Plan & Organization Anatomy
Chapter 1. The Human Organism 1-1
 Chapter 1 The Human Organism 1-1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: Scientific discipline that investigates the body s structure Physiology: Scientific investigation of the processes or functions
Chapter 1 The Human Organism 1-1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: Scientific discipline that investigates the body s structure Physiology: Scientific investigation of the processes or functions
An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 C h a p t e r 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris 1-1 The common functions of all living things include responsiveness,
C h a p t e r 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris 1-1 The common functions of all living things include responsiveness,
The STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN BODY
 The STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN BODY The topography of organs and organ systems 1. The organs are: a. clusters of identical tissues; b. different tissue groups; c. morphological units that fulfill the function
The STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN BODY The topography of organs and organ systems 1. The organs are: a. clusters of identical tissues; b. different tissue groups; c. morphological units that fulfill the function
2. Anatomy is the study of structure and form. Physiology is the study of how the structures function.
 McKinley/O Loughlin/Bidle Anatomy and Physiology: An Integrative Approach, 2/e Instructor Answer Key to In-chapter and End-of-chapter Questions Completed download Solutions Manual, Instructor Manual, Case
McKinley/O Loughlin/Bidle Anatomy and Physiology: An Integrative Approach, 2/e Instructor Answer Key to In-chapter and End-of-chapter Questions Completed download Solutions Manual, Instructor Manual, Case
Bio 103 Introduction 13
 13 BIO 103 Lecture Outline Introduction/Organic Molecules/Cells/Cell Division Hole s Human Anatomy & Physiology [Chapters 1, 2 (p. 6169), 3, 4, 22 (p. 835837, 849852)] Introduction [Chapter 1] A. Anatomy
13 BIO 103 Lecture Outline Introduction/Organic Molecules/Cells/Cell Division Hole s Human Anatomy & Physiology [Chapters 1, 2 (p. 6169), 3, 4, 22 (p. 835837, 849852)] Introduction [Chapter 1] A. Anatomy
McKinley/O Loughlin/Bidle Anatomy and Physiology: An Integrative Approach, 1/e Answer Key
 Chapter 1 Answers to What Did You Learn? 1. Comparative anatomy McKinley/O Loughlin/Bidle Anatomy and Physiology: An Integrative Approach, 1/e Answer Key 2. Anatomy is the study of structure and form.
Chapter 1 Answers to What Did You Learn? 1. Comparative anatomy McKinley/O Loughlin/Bidle Anatomy and Physiology: An Integrative Approach, 1/e Answer Key 2. Anatomy is the study of structure and form.
Coconuts, grapes, and peppers: Home-made models in the learning process of post-processing softwares used in computed-tomography (CT) imaging
 Coconuts, grapes, and peppers: Home-made models in the learning process of post-processing softwares used in computed-tomography (CT) imaging Poster No.: C-3019 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit
Coconuts, grapes, and peppers: Home-made models in the learning process of post-processing softwares used in computed-tomography (CT) imaging Poster No.: C-3019 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit
Lesson 10. References: Chapter 8: Reading for Next Lesson: Chapter 8:
 Lesson 10 Lesson Outline: General Features of the Skeletal System Axial Skeleton (Vertebral Column) Ontogenetic Origins (Morphogenesis) of the Skeletal System Functions of the Axial Skeleton Phylogenetic
Lesson 10 Lesson Outline: General Features of the Skeletal System Axial Skeleton (Vertebral Column) Ontogenetic Origins (Morphogenesis) of the Skeletal System Functions of the Axial Skeleton Phylogenetic
Biomechanical Modelling of Musculoskeletal Systems
 Biomechanical Modelling of Musculoskeletal Systems Lecture 6 Presented by Phillip Tran AMME4981/9981 Semester 1, 2016 The University of Sydney Slide 1 The Musculoskeletal System The University of Sydney
Biomechanical Modelling of Musculoskeletal Systems Lecture 6 Presented by Phillip Tran AMME4981/9981 Semester 1, 2016 The University of Sydney Slide 1 The Musculoskeletal System The University of Sydney
Introduction to the Human Body. Cells. Body Functions. Tissues. Organs. Systems. Body Functions & Life Process
 complex functions for the body. Ten major systems compose the human body: Introduction to the Human Body Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic
complex functions for the body. Ten major systems compose the human body: Introduction to the Human Body Human beings are arguably the most complex organisms on this planet. Imagine billions of microscopic
Anatomy and Physiology of Domestic Animals. Second Edition COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL
 Anatomy and Physiology of Domestic Animals Second Edition COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 Introduction to a natomy and p hysiology Contents Anatomy and Physiology 3 Levels of Organization 4 Homeostasis 5 Homeostatic
Anatomy and Physiology of Domestic Animals Second Edition COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL 1 Introduction to a natomy and p hysiology Contents Anatomy and Physiology 3 Levels of Organization 4 Homeostasis 5 Homeostatic
What is a Skeleton? SKELETONS: Museum of Osteology Lesson Curriculum K 5 th Grade 55 Minute Program
 Kindergarten: SC.K.N.1.2 Make observations of the natural world and know that they are descriptors collected using the five senses. SC.K.N.1.4 Observe and create a visual representation of an object which
Kindergarten: SC.K.N.1.2 Make observations of the natural world and know that they are descriptors collected using the five senses. SC.K.N.1.4 Observe and create a visual representation of an object which
Mesoderm Divided into three main types - Paraxial (somite) - Intermediate - Lateral (somatic and splanchnic)
 Mesoderm Divided into three main types - Paraxial (somite) - Intermediate - Lateral (somatic and splanchnic) Fates of Mesoderm Paraxial - Dermis of skin - Axial Skeleton - Axial and limb muscles/tendons
Mesoderm Divided into three main types - Paraxial (somite) - Intermediate - Lateral (somatic and splanchnic) Fates of Mesoderm Paraxial - Dermis of skin - Axial Skeleton - Axial and limb muscles/tendons
Introduction to Embryology. He who sees things grow from the beginning will have the finest view of them.
 He who sees things grow from the beginning will have the finest view of them. Aristotle 384 322 B.C. Introduction to Embryology This lecture will introduce you to the science of developmental biology or
He who sees things grow from the beginning will have the finest view of them. Aristotle 384 322 B.C. Introduction to Embryology This lecture will introduce you to the science of developmental biology or
1. Why Dissect. Why are frogs a good model to use when studying the digestive system (as well as other systems)?
 Name: Date: Period: Frog Dissection Virtual Lab Use the frog Dissection link that follows to answer the questions. http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/virtual_labs/bl_16/bl_16.html Introduction 1. Why Dissect.
Name: Date: Period: Frog Dissection Virtual Lab Use the frog Dissection link that follows to answer the questions. http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/genbio/virtual_labs/bl_16/bl_16.html Introduction 1. Why Dissect.
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY (FOR PARAMEDICAL STUDENTS) Poonam Bachheti Managing Director DPMI Aruna Singh Principal DPMI (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Company) Vayu Education of India 2/25, Ansari Road, Darya Ganj,
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY (FOR PARAMEDICAL STUDENTS) Poonam Bachheti Managing Director DPMI Aruna Singh Principal DPMI (An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Company) Vayu Education of India 2/25, Ansari Road, Darya Ganj,
Introductions. Biology 241: Human Anatomy and Physiology 1. Contact info. Syllabus highlights. Course website. Course website. Instructor: Joel Dahms
 Biology 241: Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Instructor: Joel Dahms Introductions Note cards Name Year you graduated HS and where Career goal List of classes you have taken that may help prepare you for
Biology 241: Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Instructor: Joel Dahms Introductions Note cards Name Year you graduated HS and where Career goal List of classes you have taken that may help prepare you for
of Rigid Segments Global or Laboratory Coordinate System 36 } Research Methods in Biomechanics
 36 } Research Methods in Biomechanics Camera 5 Camera 6 Camera 4 Direction of motion Calibrated 3-D space Camera 1 Camera 3 Computer Camera 2 Figure 2.1 Typical multicamera setup for a 3-D kinematic analysis.
36 } Research Methods in Biomechanics Camera 5 Camera 6 Camera 4 Direction of motion Calibrated 3-D space Camera 1 Camera 3 Computer Camera 2 Figure 2.1 Typical multicamera setup for a 3-D kinematic analysis.
Pericardial Abdominal Pelvic
 1. A mid-sagittal section of the human body would contain which of the following? Write the name of the smallest body cavity that each of the organs in your first answer here would be located within. a)
1. A mid-sagittal section of the human body would contain which of the following? Write the name of the smallest body cavity that each of the organs in your first answer here would be located within. a)
PHYSICS & BIOLOGY IN MEDICINE 218 RADIOLOGIC FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY. Fall 2017
 PHYSICS & BIOLOGY IN MEDICINE 218 RADIOLOGIC FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY Fall 2017 INSTRUCTORS Allan MacKenzie-Graham, PhD Jeff Alger, PhD Neuroscience Research Building 225Z 635 Charles Young Drive Email: amg@ucla.edu
PHYSICS & BIOLOGY IN MEDICINE 218 RADIOLOGIC FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY Fall 2017 INSTRUCTORS Allan MacKenzie-Graham, PhD Jeff Alger, PhD Neuroscience Research Building 225Z 635 Charles Young Drive Email: amg@ucla.edu
The Human Body: An Orientation
 16 The Human Body: An Orientation 17 The Human Body: An Orientation Unit Front Page (See reference page 21 for directions) 18 The Human Body: An Orientation This checklist will serve as your study guide
16 The Human Body: An Orientation 17 The Human Body: An Orientation Unit Front Page (See reference page 21 for directions) 18 The Human Body: An Orientation This checklist will serve as your study guide
Overview terminology used in Laban/Bartenieff Movement Analysis
 Overview terminology used in Laban/Bartenieff Movement Analysis Categories Laban/Bartenieff Movement Analysis: Body Effort Relationship Space Shape Body 9 Bartenieff Principles Movement Principles that
Overview terminology used in Laban/Bartenieff Movement Analysis Categories Laban/Bartenieff Movement Analysis: Body Effort Relationship Space Shape Body 9 Bartenieff Principles Movement Principles that
Gut Tube Development. For it s rare that a man thinks of anything so seriously as his dinner!
 For it s rare that a man thinks of anything so seriously as his dinner! Ben Johnson Gut Tube Development This chapter will follow the development of the embryonic gut caudal to the developing pharynx,
For it s rare that a man thinks of anything so seriously as his dinner! Ben Johnson Gut Tube Development This chapter will follow the development of the embryonic gut caudal to the developing pharynx,
Center of Mass of Human s Body Segments
 Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 21, No. 3 2017 485 497 c Lodz University of Technology Center of Mass of Human s Body Segments Melvin Adolphe Joseph Clerval Zbyszko Kirchof Robin Lacombe Delpech
Mechanics and Mechanical Engineering Vol. 21, No. 3 2017 485 497 c Lodz University of Technology Center of Mass of Human s Body Segments Melvin Adolphe Joseph Clerval Zbyszko Kirchof Robin Lacombe Delpech
2. Skeletal muscle cells need large numbers of to make the many proteins they contain.
 BIOL 2010 Human Anatomy & Physiology I -- Exam 1 -Form A- Name: 1. Vesicles are formed from A. lysosomal membrane. B. nuclear membrane. C. cell membrane. D. endoplasmic reticulum. E. none of the above.
BIOL 2010 Human Anatomy & Physiology I -- Exam 1 -Form A- Name: 1. Vesicles are formed from A. lysosomal membrane. B. nuclear membrane. C. cell membrane. D. endoplasmic reticulum. E. none of the above.
An Introduction to Anatomy
 C h a p t e r 1 An Introduction to Anatomy PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
C h a p t e r 1 An Introduction to Anatomy PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
Illustrative exercises for the lectures
 Biomechanics, LTH, 2013 Biomechanics Illustrative exercises for the lectures Ingrid Svensson 2013 1 1. To practise the use of free-body diagram, consider the problem of analyzing the stress in man s back
Biomechanics, LTH, 2013 Biomechanics Illustrative exercises for the lectures Ingrid Svensson 2013 1 1. To practise the use of free-body diagram, consider the problem of analyzing the stress in man s back
A) Collection of changing/dynamic information dealing with measurable phenomena. 2) study of matter and the energy changes that matter undergoes
 Human Biology 175 Lecture Notes: Introduction Part I Science and the Scientific Method A) Collection of changing/dynamic information dealing with measurable phenomena B) Disciplines of Science 1) study
Human Biology 175 Lecture Notes: Introduction Part I Science and the Scientific Method A) Collection of changing/dynamic information dealing with measurable phenomena B) Disciplines of Science 1) study
BIO130 Lab Practice Exam 1 Questions
 BIO130 Lab Practice Exam 1 Questions 1. Refer to Figure 1.1 or Figure 1.2 and answer the following: A. Name the heavy bottom part labeled A. B. Name the circular part indicated by the arrow B. C. Name
BIO130 Lab Practice Exam 1 Questions 1. Refer to Figure 1.1 or Figure 1.2 and answer the following: A. Name the heavy bottom part labeled A. B. Name the circular part indicated by the arrow B. C. Name
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Pleiotropic Scaling of Gene Effects and the Cost of Complexity by Günter P. Wagner et al. Figure S1: Figure S1: schematic summary of findings. (a) Most QTL affect a relatively small number of traits (
Pleiotropic Scaling of Gene Effects and the Cost of Complexity by Günter P. Wagner et al. Figure S1: Figure S1: schematic summary of findings. (a) Most QTL affect a relatively small number of traits (
Skeletal 2 - joints. Puzzle 1 bones
 Puzzle 1 bones Listed below are the names of some of the bones that make up your skeletal system. But the names have been encrypted using a secret code. Can you decipher this code to find out what they
Puzzle 1 bones Listed below are the names of some of the bones that make up your skeletal system. But the names have been encrypted using a secret code. Can you decipher this code to find out what they
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. After you know the basic terms of anatomy but before studying the. Chapter 1 ANATOMY AND CHEMISTRY BASICS
 hapter 1 AATMY AD EMISTRY BASIS hapter heck-in Understanding the basics of anatomy oting the basic chemical constituents that help form matter Listing the types of bonds that form between two atoms Understanding
hapter 1 AATMY AD EMISTRY BASIS hapter heck-in Understanding the basics of anatomy oting the basic chemical constituents that help form matter Listing the types of bonds that form between two atoms Understanding
U.S. Army Injury Surveillance Summary 2014
 U.S. Army Injury Surveillance Summary 2014 Epidemiology and Disease Surveillance Portfolio Injury Prevention Program Website: http://phc.amedd.army.mil/organization/hq/deds/pages/injurypreventionprogram.aspx
U.S. Army Injury Surveillance Summary 2014 Epidemiology and Disease Surveillance Portfolio Injury Prevention Program Website: http://phc.amedd.army.mil/organization/hq/deds/pages/injurypreventionprogram.aspx
Natl Res SUM. Natl Res MODE. Natl Res AVE. Natl Res MED. Natl Res STD
 Reporting Period: Total Experience of idents Completing Programs in 2007-2008 idency Review Committee for Vascular Surgery [PART 1 ] Number of Programs in the Nation: 78 Number of idents in the Nation:
Reporting Period: Total Experience of idents Completing Programs in 2007-2008 idency Review Committee for Vascular Surgery [PART 1 ] Number of Programs in the Nation: 78 Number of idents in the Nation:
Head and Face Development
 Head and Face Development Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ Larsen s Human Embryology The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical Sciences,
Head and Face Development Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ Larsen s Human Embryology The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical Sciences,
ME 176 Final Exam, Fall 1997
 Tuesday, December 16, 5:00 8:00 PM, 1997. Answer all questions for a maximum of 100 points. Please write all answers in the space provided. If you need additional space, write on the back sides. Indicate
Tuesday, December 16, 5:00 8:00 PM, 1997. Answer all questions for a maximum of 100 points. Please write all answers in the space provided. If you need additional space, write on the back sides. Indicate
Folding of the embryo.. the embryo is becoming a tube like structure
 The embryo is a Folding of the embryo.. the embryo is becoming a tube like structure WEEK 4 EMBRYO General features Primordia of the brain Somites Primordia of the heart Branchial arches Primordia
The embryo is a Folding of the embryo.. the embryo is becoming a tube like structure WEEK 4 EMBRYO General features Primordia of the brain Somites Primordia of the heart Branchial arches Primordia
Chapter 9. Benefits of Being Large. Levels of Organization in Organismal Complexity. Hierarchical Organization of Animal Complexity. Fig. 9.
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 9 Architectural Pattern of an Animal Levels of Organization in Organismal Complexity Zoologists recognize
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 9 Architectural Pattern of an Animal Levels of Organization in Organismal Complexity Zoologists recognize
Active movement Cancer. Cell. Cell inclusion Cytoplasm Diffusion Organelle Osmosis Passive movement Plasma membrane. Cell
 CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Learning Objective At the end of this chapter, the students should be able to: - Define Anatomy and Physiology - Explain Homeostasis - Describe levels
CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Learning Objective At the end of this chapter, the students should be able to: - Define Anatomy and Physiology - Explain Homeostasis - Describe levels
METHODOLOGY FOR ESTIMATING THORACIC IMPACT RESPONSE IN FRONTAL CRASH TESTS
 METHODOLOGY FOR ESTIMATING THORACIC IMPACT RESPONSE IN FRONTAL CRASH TESTS Craig P. Thor, Hampton C. Gabler Virginia Tech-Wake Forest, Center for Injury Biomechanics ABSTRACT This study has investigated
METHODOLOGY FOR ESTIMATING THORACIC IMPACT RESPONSE IN FRONTAL CRASH TESTS Craig P. Thor, Hampton C. Gabler Virginia Tech-Wake Forest, Center for Injury Biomechanics ABSTRACT This study has investigated
2/23/09. Regional differentiation of mesoderm. Morphological changes at early postgastrulation. Segments organize the body plan during embryogenesis
 Regional differentiation of mesoderm Axial Paraxial Intermediate Somatic Splanchnic Chick embryo Morphological changes at early postgastrulation stages Segments organize the body plan during embryogenesis
Regional differentiation of mesoderm Axial Paraxial Intermediate Somatic Splanchnic Chick embryo Morphological changes at early postgastrulation stages Segments organize the body plan during embryogenesis
Sneak Preview. The Human Body. Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology Black and white edition
 Sneak Preview The Human Body Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology Black and white edition By Bruce Wingerd Included in this preview: Copyrights Preface A Note to Students Table of Contents Chapter 1 For
Sneak Preview The Human Body Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology Black and white edition By Bruce Wingerd Included in this preview: Copyrights Preface A Note to Students Table of Contents Chapter 1 For
Voigts MF. Affiliated: Atlasprofilax Academy of Switzerland. General Osteopathic Council, United Kingdom. British Acupuncture Council
 A MEASUREMENT STUDY, USING AN ILIAC CREST INCLINOMETER, OF HOW THE AT- LASPROFILAX METHOD TO CORRECT MALROTATION OF THE ATLAS BONE CHANGES ILIAC FRONTAL PLANE LEVELS IN THE STANDING POSITION. Voigts MF
A MEASUREMENT STUDY, USING AN ILIAC CREST INCLINOMETER, OF HOW THE AT- LASPROFILAX METHOD TO CORRECT MALROTATION OF THE ATLAS BONE CHANGES ILIAC FRONTAL PLANE LEVELS IN THE STANDING POSITION. Voigts MF
Chapter 6 General Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 6 General Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The study of the human body structures that can be seen with the naked eye is. a. anatomy c. biology b. physiology d. pathology Anatomy is the
Chapter 6 General Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The study of the human body structures that can be seen with the naked eye is. a. anatomy c. biology b. physiology d. pathology Anatomy is the
Road vehicles Dummies for restraint system testing Part 1: Adult dummies
 ISO 2013 All rights reserved ISO TC 22/SC 12/WG 5 N1019 Date: 2013-02-20 ISO/PDTR 12349-1/WD 12349-1 ISO TC 22/SC 12/WG 5 Secretariat: AFNOR Road vehicles Dummies for restraint system testing Part 1: Adult
ISO 2013 All rights reserved ISO TC 22/SC 12/WG 5 N1019 Date: 2013-02-20 ISO/PDTR 12349-1/WD 12349-1 ISO TC 22/SC 12/WG 5 Secretariat: AFNOR Road vehicles Dummies for restraint system testing Part 1: Adult
Mesoderm Development
 Quiz rules: Spread out across available tables No phones, text books, or (lecture) notes on your desks No consultation with your colleagues No websites open other than the Quiz page No screen snap shots
Quiz rules: Spread out across available tables No phones, text books, or (lecture) notes on your desks No consultation with your colleagues No websites open other than the Quiz page No screen snap shots
Angular Motion Maximum Hand, Foot, or Equipment Linear Speed
 Motion Maximum Hand, Foot, or Equipment Linear Speed Biomechanical Model: Mo3on Maximum Hand, Foot, or Equipment Linear Speed Hand, Foot, or Equipment Linear Speed Sum of Joint Linear Speeds Principle
Motion Maximum Hand, Foot, or Equipment Linear Speed Biomechanical Model: Mo3on Maximum Hand, Foot, or Equipment Linear Speed Hand, Foot, or Equipment Linear Speed Sum of Joint Linear Speeds Principle
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 7, 2006 Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of BMPs more lateral mesoderm
Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 7, 2006 Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of BMPs more lateral mesoderm
The Effect of Inflated Backrest Stiffness on Shearing Loads Estimated with Articulated Total Body
 The Effect of Inflated Backrest Stiffness on Shearing Loads Estimated with Articulated Total Body Bob J. Scurlock, Ph.D., ACTAR *, James R. Ipser, Ph.D. *, Paul A. Borsa, Ph.D., ATC, FACSM # * Department
The Effect of Inflated Backrest Stiffness on Shearing Loads Estimated with Articulated Total Body Bob J. Scurlock, Ph.D., ACTAR *, James R. Ipser, Ph.D. *, Paul A. Borsa, Ph.D., ATC, FACSM # * Department
JEFFERSON COLLEGE VERTEBRATE ANATOMY
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO207 VERTEBRATE ANATOMY 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Mr. Jim McCain Revised Date: November 2005 by Dr. Ken Balak Division of Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor,
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO207 VERTEBRATE ANATOMY 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Mr. Jim McCain Revised Date: November 2005 by Dr. Ken Balak Division of Arts & Science Education Dr. Mindy Selsor,
2. Examine the external anatomy of the squid and identify the following structures: tentacles, arms, fins, siphon, mantle, eyes and collar.
 Cephalopod Anatomy As their name implies, members of the class Cephalopoda have modified head-foot which bears an array of prehensile tentacles and arms at the cranial end of the body. The visceral mass
Cephalopod Anatomy As their name implies, members of the class Cephalopoda have modified head-foot which bears an array of prehensile tentacles and arms at the cranial end of the body. The visceral mass
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 6, 2007 Mesoderm Formation Chick Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of
Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 6, 2007 Mesoderm Formation Chick Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of
Name KEY. Biology Developmental Biology Winter Quarter Midterm 3 KEY
 Name KEY 100 Total Points Open Book Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2009 Midterm 3 KEY All of the 25 multi-choice questions are single-answer. Choose the best answer. (4 pts each) Place
Name KEY 100 Total Points Open Book Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2009 Midterm 3 KEY All of the 25 multi-choice questions are single-answer. Choose the best answer. (4 pts each) Place
and its origins G. E. Schneider 2009 Part 1: Introduction MIT 9.14 Class 1 Brain talk, and
 A sketch of the central nervous system and its origins G. E. Schneider 2009 Part 1: Introduction MIT 9.14 Class 1 Brain talk, and the ancient activities of brain cells 1. Introduction a) b) The plan for
A sketch of the central nervous system and its origins G. E. Schneider 2009 Part 1: Introduction MIT 9.14 Class 1 Brain talk, and the ancient activities of brain cells 1. Introduction a) b) The plan for
Full file at Test Bank. Agnes Yard Michael Yard INDIANA UNIVERSITY PURDUE UNIVERSITY AT INDIANAPOLIS (IUPUI)
 Test Bank Agnes Yard Michael Yard INDIANA UNIVERSITY PURDUE UNIVERSITY AT INDIANAPOLIS (IUPUI) Jason LaPres LONE STAR COLLEGE NORTH HARRIS Judi L. Nath LOURDES UNIVERSITY Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology
Test Bank Agnes Yard Michael Yard INDIANA UNIVERSITY PURDUE UNIVERSITY AT INDIANAPOLIS (IUPUI) Jason LaPres LONE STAR COLLEGE NORTH HARRIS Judi L. Nath LOURDES UNIVERSITY Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology
Is there a ventral neural ridge in chick embryos? Implications for the origin of adenohypophyseal and other APUD cells
 /. Embryol. exp. Morph. Vol. 57, pp. 71-78, 1980 7 \ Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Limited 1980 Is there a ventral neural ridge in chick embryos? Implications for the origin of adenohypophyseal
/. Embryol. exp. Morph. Vol. 57, pp. 71-78, 1980 7 \ Printed in Great Britain Company of Biologists Limited 1980 Is there a ventral neural ridge in chick embryos? Implications for the origin of adenohypophyseal
The Radiata-Bilateria split. Second branching in the evolutionary tree
 The Radiata-Bilateria split Second branching in the evolutionary tree Two very important characteristics are used to distinguish between the second bifurcation of metazoans Body symmetry Germinal layers
The Radiata-Bilateria split Second branching in the evolutionary tree Two very important characteristics are used to distinguish between the second bifurcation of metazoans Body symmetry Germinal layers
Representation of the Body Surface in Somatosensory Area I of Tree Shrews, Tupaia glis
 THE JOURNAL OF COMPARATIVE NEUROLOGY 19431-95 (1980) Representation of the Body Surface in Somatosensory Area I of Tree Shrews, Tupaia glis MRIGANKA SUR, ROSALYN E. WELLER, AND JON H. KAAS Departments
THE JOURNAL OF COMPARATIVE NEUROLOGY 19431-95 (1980) Representation of the Body Surface in Somatosensory Area I of Tree Shrews, Tupaia glis MRIGANKA SUR, ROSALYN E. WELLER, AND JON H. KAAS Departments
Simulation of Occupant Posture Change during Autonomous Emergency Braking and Occupant Kinematics in Frontal Collision.
 Simulation of Occupant Posture Change during Autonomous Emergency Braking and Occupant Kinematics in Frontal Collision. Katsunori Yamada, Mitsuaki Gotoh, Yuichi Kitagawa, Tsuyoshi Yasuki Abstract Occupant
Simulation of Occupant Posture Change during Autonomous Emergency Braking and Occupant Kinematics in Frontal Collision. Katsunori Yamada, Mitsuaki Gotoh, Yuichi Kitagawa, Tsuyoshi Yasuki Abstract Occupant
By Sudha Vashisht P.G.G.C.G. -11 CHD
 By Sudha Vashisht P.G.G.C.G. -11 CHD Pila is the common Apple snail which is found in ponds ditches, rivers and in watery fileds. The soft body is covered by a coiled shell. The first chamber of the shell
By Sudha Vashisht P.G.G.C.G. -11 CHD Pila is the common Apple snail which is found in ponds ditches, rivers and in watery fileds. The soft body is covered by a coiled shell. The first chamber of the shell
Instructor Resource Guide. Human Anatomy. Sixth Edition. Leslie Hendon. University of Alabama at Birmingham
 Instructor Resource Guide Human Anatomy Sixth Edition Leslie Hendon University of Alabama at Birmingham Editor-in-Chief: Serina Beauparlant Project Editor: Sabrina Larson Assistant Editor: Nicole Graziano
Instructor Resource Guide Human Anatomy Sixth Edition Leslie Hendon University of Alabama at Birmingham Editor-in-Chief: Serina Beauparlant Project Editor: Sabrina Larson Assistant Editor: Nicole Graziano
Rad Tech 4912 MRI Registry Review. Outline of the Registry Exam: Certification Fees
 Rad Tech 4912 MRI Registry Review Outline of the Registry Exam: Category: # of questions: A. Patient Care 30 B. Imaging Procedures 62 C. Data Acquisition and Processing 65 D. Physical Principles of Image
Rad Tech 4912 MRI Registry Review Outline of the Registry Exam: Category: # of questions: A. Patient Care 30 B. Imaging Procedures 62 C. Data Acquisition and Processing 65 D. Physical Principles of Image
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 6, 2007 Mesoderm Formation Chick Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of
Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 6, 2007 Mesoderm Formation Chick Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of
Physics and Knobology
 Physics and Knobology Cameron Jones, MD 02/01/2012 SOUND: Series of pressure waves traveling through a medium What is ULTRASOUND Physics Words WAVELENGTH: Distance traveled in one cycle FREQUENCY: number
Physics and Knobology Cameron Jones, MD 02/01/2012 SOUND: Series of pressure waves traveling through a medium What is ULTRASOUND Physics Words WAVELENGTH: Distance traveled in one cycle FREQUENCY: number
Human Anatomy Fifth Edition
 Instructor Resource Guide Human Anatomy Fifth Edition Leslie C. Hendon University of Alabama at Birmingham San Francisco Boston New York Cape Town Hong Kong London Madrid Mexico City Montreal Munich Paris
Instructor Resource Guide Human Anatomy Fifth Edition Leslie C. Hendon University of Alabama at Birmingham San Francisco Boston New York Cape Town Hong Kong London Madrid Mexico City Montreal Munich Paris
Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos
 Ectoderm Germ Layer Frog Fate Map Frog Fate Map Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos Organizer forms three distinct regions Notochord formation in chick Beta-catenin localization How does beta-catenin
Ectoderm Germ Layer Frog Fate Map Frog Fate Map Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos Organizer forms three distinct regions Notochord formation in chick Beta-catenin localization How does beta-catenin
Amphigomphus somnuki n. sp. from North Thailand (Odonata: Gomphidae) MATTI HAMALAINEN
 Entomol. Z., 106(5), 1996 177 Amphigomphus somnuki n. sp. from North Thailand (Odonata: Gomphidae) MATTI HAMALAINEN With 8 figures Abstract: A new dragonfly species, Amphigomphus somnuki n. sp. (holotype
Entomol. Z., 106(5), 1996 177 Amphigomphus somnuki n. sp. from North Thailand (Odonata: Gomphidae) MATTI HAMALAINEN With 8 figures Abstract: A new dragonfly species, Amphigomphus somnuki n. sp. (holotype
Pamela E. Knapp, Ph.D. Dept. of Anatomy & Neurobiology DEVELOPMENT OF THE PHARYNGEAL (BRANCHIAL) ARCHES
 Embryology Pamela E. Knapp, Ph.D. Dept. of Anatomy & Neurobiology DEVELOPMENT OF THE PHARYNGEAL (BRANCHIAL) ARCHES READING: Larsen, 4 th Edition, Chapter 16; or, Langman, 8 th Edition, pp. 345-365 OBJECTIVES:
Embryology Pamela E. Knapp, Ph.D. Dept. of Anatomy & Neurobiology DEVELOPMENT OF THE PHARYNGEAL (BRANCHIAL) ARCHES READING: Larsen, 4 th Edition, Chapter 16; or, Langman, 8 th Edition, pp. 345-365 OBJECTIVES:
6 characteristics blastula
 Animals Characteristics The animal kingdom is divided into approximately 35 phyla with diverse species. However, all organisms in the animal kingdom share these 6 characteristics Eukaryotic Lack cell walls
Animals Characteristics The animal kingdom is divided into approximately 35 phyla with diverse species. However, all organisms in the animal kingdom share these 6 characteristics Eukaryotic Lack cell walls
Developmental Zoology. Ectodermal derivatives (ZOO ) Developmental Stages. Developmental Stages
 Developmental Zoology (ZOO 228.1.0) Ectodermal derivatives 1 Developmental Stages Ø Early Development Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Neurulation Ø Later Development Organogenesis Larval molts Metamorphosis
Developmental Zoology (ZOO 228.1.0) Ectodermal derivatives 1 Developmental Stages Ø Early Development Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Neurulation Ø Later Development Organogenesis Larval molts Metamorphosis
Axis Specification in Drosophila
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 2, 2006 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 2, 2006 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
1. Know the hierarchy of organization: chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organismal
 Anatomy and Physiology Anatomical Organization 1. Know the hierarchy of organization: chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organismal 2. Be able to identify and describe the necessary life
Anatomy and Physiology Anatomical Organization 1. Know the hierarchy of organization: chemical, cellular, tissue, organ, organ system, organismal 2. Be able to identify and describe the necessary life
1988 ANTHROPOMETRIC SURVEY N OF US ARMY PERSONNEL: SCORRELATION COEFFICIENTS AND REGRESSION EQUATIONS
 TECHNICAL REPORT - AD NATICK/TR-90/036 1988 ANTHROPOMETRIC SURVEY N OF US ARMY PERSONNEL: SCORRELATION COEFFICIENTS AND REGRESSION EQUATIONS PART 5 STEPWISE AND STANDARD MULTIPLE REGRESSION TABLES DTIC
TECHNICAL REPORT - AD NATICK/TR-90/036 1988 ANTHROPOMETRIC SURVEY N OF US ARMY PERSONNEL: SCORRELATION COEFFICIENTS AND REGRESSION EQUATIONS PART 5 STEPWISE AND STANDARD MULTIPLE REGRESSION TABLES DTIC
Axis Specification in Drosophila
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 6, 2007 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Axis Specification in Drosophila November 6, 2007 Axis Specification in Drosophila Fertilization Superficial cleavage Gastrulation Drosophila body plan Oocyte formation
SKILL 4 MEASUREMENTS OF VITAL SIGNS - TEMPERATURE, PULSE AND RESPIRATION (TPR)
 SKILL 4 MEASUREMENTS OF VITAL SIGNS - TEMPERATURE, PULSE AND RESPIRATION (TPR) Structure 4.0 Objectives 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Meaning and Definition of Vital Signs 4.3 Checking Temperature 4.3.1 Definition
SKILL 4 MEASUREMENTS OF VITAL SIGNS - TEMPERATURE, PULSE AND RESPIRATION (TPR) Structure 4.0 Objectives 4.1 Introduction 4.2 Meaning and Definition of Vital Signs 4.3 Checking Temperature 4.3.1 Definition
Human Evolution Comparing Primates
 Human Evolution Comparing Primates Background According to the theory of evolution, all species are are related and linked to a common ancestor. Species that are more closely related have common ancestor
Human Evolution Comparing Primates Background According to the theory of evolution, all species are are related and linked to a common ancestor. Species that are more closely related have common ancestor
