ECE Test #1: Name
|
|
|
- Ezra Frederick Washington
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ECE Test #1: Name Closed Book, Closed Notes. Calculators Permitted. February 12, 2016 Design an embedded system which is placed inside a refrigerator and, each time the door is opened The PIC increments a counter on PORTD, Beeps at a frequency of Hz (E4) for 100ms on RC0 The beep is made by an 8 Ohm speaker, driven with a square wave at 0 / 250mA Each problem corresponds to a different part of this system. 1) Hardware - Binary Inputs. To detect that the refrigerator door has been opened, a light sensor is used. Assume the light sensor has the following light vs. resistance relationship R 100,000 Lux Design a circuit which Outputs 5V when the light level is more than 35 Lux, Outputs 0V when the light level is less than 30 Lux, and Remains unchanged in-between 30 and 35 Lux. Assume a 3k resistor gain 35 Lux = 2587 Ohms = 2.439V 30 Lus = 3333 Ohms = Volts 5V0V 2.439V2.6316V V 2.439V 100k 2.59M 3k 100k 2.59M
2 2) Hardware - Binary Outputs. To produce the Hz signal, an 8 Ohm speaker is to be used. The requirements are When the PIC outputs 0V, the current to the speaker should be 0mA When the PIC outputs 5V, the current to the speaker should be 250mA. Design a circuit so that a PIC can turn on and off the 8 Ohm speaker at 0mA and 250mA. Assume A 5V DC power supply and A transistor with a current gain of 100 (3904) Assume a 5V power supply. To set the current to 250mA R total 5V0.2V 250mA R c To saturate a transistor with a gain of 100 Let Ib = 5mA I b I c 250mA I b 250mA mA R b 5V0.7V 5mA V Ic = 250mA 11.2 Ohms 8 Ohms 860 PIC NPN Ib = 5mA
3 3) Software: To play a note of Hz, you need a wait routine that burns ms (15,169 clocks). 3a) Determine how many clocks the following wait routine takes. Wait: movlw 53 movwf CNT1 L1: movlw 174 movwf CNT0 L0: decfsz CNT0,F goto L0 2 clocks executed 1 time = 2 clocks 2 clocks executed 53 times = 106 clocks 6 clocks 5 instructions plus a jump = 6 clocks executed 174 * 53 times = 6 * 174 * 53 = 55,332 clocks decfsz CNT1,F goto L1 3 clocks executed 53 times = 159 clocks return 2 clocks executed 1 time = 2 clocks Adding up the number of clocks gives 55,602 clocks 3b) Modify this code so that it takes ms (15,169 clocks) to execute. ( 6 * ) * = 15,169 Wait: L1: L0: movlw 10 movwf CNT1 movlw 251 movwf CNT0 decfsz CNT0,F goto L0 decfsz CNT1,F goto L1 return 2 clocks executed 1 time = 2 clocks 2 clocks executed 10 times = 20 clocks 6 clocks 5 instructions plus a jump = 6 clocks executed 251 * 10 times = 6 * 251 * 10 = 15,060 clocks 8 clocks executed 10 times = 80 clocks 7 clocks executed 1 time = 7 clocks
4 4) Software: Given a wait routine which takes ms to execute, write an assembler routine, BEEP, which outputs a Hz square wave on RC0 for 100ms when called. 4a) If RC0 is toggling at a frequency of Hz, how many times does it toggle in 100ms? N 100ms ms b) Write the routine, BEEP, which outputs a Hz square wave on RC0 for 100ms. Assume you have a wait routine, Wait:, which pauses ms (i.e. problem 3). Beep: Loop: movlw 66 movwf X btg PORTC,0 call decfsz goto Wait X,F Loop return
5 5) Main Routine: Write the main routine which Monitors RB0 to detect when the refrigerator door has been opened When the door is opened, it - Beeps at Hz for 100ms (problem 4), - Displays on PORTD how many times the door has been opened, and - Clears the count (PORTD) if button RB1 is pressed Write the corresponding assembler code: org 0x800 ; Initialize Ports clrf TRISC clrf TRISD movlw 0xFF movwf TRISB movlw 0x0F movwf ADCON1 clrf PORTD Start Initialize ports PORTD=0 A1: btfss goto PORTB,0 A1 RB0 = 0? yes no call Beep Beep incf PORTD,F Inc PORTD A2: btfss goto PORTB,0 A1 no RB0 = 1? yes btfsc PORTB,1 no RB1 = 1? yes clrf PORTD Clear PORTD goto A2
6 Bonus! One clock on a PIC processor is 100ns. How fast do you have to travel for time to slow down 100ns every hour? Time slows down as 1 1 v2 c 2 1hr + 100ns 1hour 1 1 v2 2 c 2 using a Taylor's series 1 a 1 a 1 100ns 1hour 1 v2 2c 2 v 2 100ns 1 hour 2c2 v 2243 m s v 8044 km/h v 4998 mph note: 100ns in one year is equal to 23.8 m/s = 53 mph
7 Memory Read & Write MOVWF PORTA memory write PORTA = W MOVFF PORTA PORTB copy PORTB = PORTA MOVF PORTA,W memory read W = PORTA MOVLW 234 Move Literal to WREG W = 123 Memory Clear, Negation CLRF PORTA clear memory PORTA = 0x00 COMF PORTA toggle bits PORTA =!PORTA NEGF PORTA negate PORTA = -PORTA Addition & Subtraction INCF PORTA,F increment PORTA = PORTA + 1 ADDWF PORTA, F add PORTA = PORTA + W ADDWFC PORTA, W add with carry W = PORTA + W + carry ADDLW Add Literal and WREG DECF PORTA,F decrement PORTA = PORTA - 1 SUBFWB PORTA,F subtract with borrow PORTA = W - PORTA - c SUBWF PORTA,F subtract no borrow PORTA = PORTA - W SUBWFB PORTA,F subtract with borrow PORTA = PORTA - W - c SUBLW 223 Subtract WREG from # W = W Shift left (*2), shift right (/2) RLCF PORTA,F rotate left through carry (9-bit rotate) RLNCF PORTA,F rotate left no carry RRCF PORTA,F rotate right through carry RRNCF PORTA,F rotate right no carry Bit Operations BCF PORTA, 3 Bit Clear f clear bit 3 of PORTA BSF PORTA, 4 Bit Set f set bit 4 of PORTA BTG PORTA, 2 Bit Toggle f toggle bit 2 of PORTA Logical Operations ANDWF PORTA, F logical and PORTA = PORTA and W ANDLW 0x23 AND Literal with WREG W = W and 0x23 IORWF PORTA,F logical or PORTA = PORTA or W IORLW 0x23 Inclusive OR Literal W = W or 0x23 XORWF PORTA,F logical exclusive or PORTA = PORTA xor W XORLW 0x23 Exclusive OR Literal W = W xor 0x23 Tests (skip the next instruction if...) CPFSEQ PORTA Compare PORTA to W, skip if PORTA = W CPFSGT PORTA Compare PORTA to W, Skip if PORTA > W CPFSLT PORTA Compare PORTA to W, Skip if PORTA < W DECFSZ PORTA,F decrement, skip if zero DCFSNZ PORTA,F decrement, skip if not zero INCFSZ PORTA,F increment, skip if zero INFSNZ PORTA,F increment, skip if not zero BTFSC PORTA, 5 Bit Test f, Skip if Clear BTFSS PORTA, 1 Bit Test f, Skip if Set Flow Control GOTO Label Go to Address 1st word CALL Label Call Subroutine 1st word RETURN Return from Subroutine RETLW 0x23 Return with 0x23 in WREG RETFIE Return from Interrupt Other Stuff... NOP No Operation MULLW Multiply Literal with WREG MULWF PORTA multiply TSTFSZ PORTA test, skip if zero
8
2013 Technological Studies. Advanced Higher. Finalised Marking Instructions
 03 Technological Studies Advanced Higher Finalised Marking Instructions Scottish Qualifications Authority 03 The information in this publication may be reproduced to support SQA qualifications only on
03 Technological Studies Advanced Higher Finalised Marking Instructions Scottish Qualifications Authority 03 The information in this publication may be reproduced to support SQA qualifications only on
ECE Final Exam: Name Solution
 ECE 376 - Final Exam: Name Solution December 10, 2018 1) Binary Outputs: Design a circuit which allows a PIC to turn on and off a 40mW LED at 10mA: On = 10mA Off = 0mA Assume the LED characteristics are:
ECE 376 - Final Exam: Name Solution December 10, 2018 1) Binary Outputs: Design a circuit which allows a PIC to turn on and off a 40mW LED at 10mA: On = 10mA Off = 0mA Assume the LED characteristics are:
2014 Technological Studies. Advanced Higher. Finalised Marking Instructions
 204 Technological Studies Advanced Higher Finalised Marking Instructions Scottish Qualifications Authority 204 The information in this publication may be reproduced to support SQA qualifications only on
204 Technological Studies Advanced Higher Finalised Marking Instructions Scottish Qualifications Authority 204 The information in this publication may be reproduced to support SQA qualifications only on
2011 Technological Studies. Advanced Higher. Finalised Marking Instructions
 0 Technological Studies Advanced Higher Finalised Marking Instructions Scottish ualifications Authority 0 The information in this publication may be reproduced to support SA qualifications only on a noncommercial
0 Technological Studies Advanced Higher Finalised Marking Instructions Scottish ualifications Authority 0 The information in this publication may be reproduced to support SA qualifications only on a noncommercial
LABORATORY MANUAL MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER
 LABORATORY MANUAL S u b j e c t : MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER TE (E lectr onics) ( S e m V ) 1 I n d e x Serial No T i tl e P a g e N o M i c r o p r o c e s s o r 8 0 8 5 1 8 Bit Addition by Direct
LABORATORY MANUAL S u b j e c t : MICROPROCESSOR AND MICROCONTROLLER TE (E lectr onics) ( S e m V ) 1 I n d e x Serial No T i tl e P a g e N o M i c r o p r o c e s s o r 8 0 8 5 1 8 Bit Addition by Direct
Assembly Programming through Arduino
 1 Assembly Programming through Arduino G V V Sharma Contents 1 Components 1 2 Seven Segment Display 1 2.1 Hardware Setup....... 1 2.2 Software Setup........ 2 2.3 Controlling the Display... 2 3 Display
1 Assembly Programming through Arduino G V V Sharma Contents 1 Components 1 2 Seven Segment Display 1 2.1 Hardware Setup....... 1 2.2 Software Setup........ 2 2.3 Controlling the Display... 2 3 Display
Chapter 5. Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition. David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris. Chapter 5 <1>
 Chapter 5 Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Chapter 5 Chapter 5 :: Topics Introduction Arithmetic Circuits umber Systems Sequential Building
Chapter 5 Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Chapter 5 Chapter 5 :: Topics Introduction Arithmetic Circuits umber Systems Sequential Building
System Data Bus (8-bit) Data Buffer. Internal Data Bus (8-bit) 8-bit register (R) 3-bit address 16-bit register pair (P) 2-bit address
 Intel 8080 CPU block diagram 8 System Data Bus (8-bit) Data Buffer Registry Array B 8 C Internal Data Bus (8-bit) F D E H L ALU SP A PC Address Buffer 16 System Address Bus (16-bit) Internal register addressing:
Intel 8080 CPU block diagram 8 System Data Bus (8-bit) Data Buffer Registry Array B 8 C Internal Data Bus (8-bit) F D E H L ALU SP A PC Address Buffer 16 System Address Bus (16-bit) Internal register addressing:
CSE 140 Spring 2017: Final Solutions (Total 50 Points)
 CSE 140 Spring 2017: Final Solutions (Total 50 Points) 1. (Boolean Algebra) Prove the following Boolean theorem using Boolean laws only, i.e. no theorem is allowed for the proof. State the name of the
CSE 140 Spring 2017: Final Solutions (Total 50 Points) 1. (Boolean Algebra) Prove the following Boolean theorem using Boolean laws only, i.e. no theorem is allowed for the proof. State the name of the
Counters. We ll look at different kinds of counters and discuss how to build them
 Counters We ll look at different kinds of counters and discuss how to build them These are not only examples of sequential analysis and design, but also real devices used in larger circuits 1 Introducing
Counters We ll look at different kinds of counters and discuss how to build them These are not only examples of sequential analysis and design, but also real devices used in larger circuits 1 Introducing
Arithme(c logic units and memory
 Arithme(c logic units and memory CSCI 255: Introduc/on to Embedded Systems Keith Vertanen Copyright 2011 Layers of abstrac-on abstrac(on building blocks examples computer components Macbook Pro components
Arithme(c logic units and memory CSCI 255: Introduc/on to Embedded Systems Keith Vertanen Copyright 2011 Layers of abstrac-on abstrac(on building blocks examples computer components Macbook Pro components
Lecture 10: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design
 Lecture 0: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design. General Form Input Combinational Flip-flops Combinational Output Circuit Circuit Clock.. Moore type has outputs dependent only on the state, e.g. ripple
Lecture 0: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design. General Form Input Combinational Flip-flops Combinational Output Circuit Circuit Clock.. Moore type has outputs dependent only on the state, e.g. ripple
UNIT 8A Computer Circuitry: Layers of Abstraction. Boolean Logic & Truth Tables
 UNIT 8 Computer Circuitry: Layers of bstraction 1 oolean Logic & Truth Tables Computer circuitry works based on oolean logic: operations on true (1) and false (0) values. ( ND ) (Ruby: && ) 0 0 0 0 0 1
UNIT 8 Computer Circuitry: Layers of bstraction 1 oolean Logic & Truth Tables Computer circuitry works based on oolean logic: operations on true (1) and false (0) values. ( ND ) (Ruby: && ) 0 0 0 0 0 1
ENGG1015: Homework 1
 ENGG1015 Homework 1 Question 1 ENGG1015: Homework 1 Due: Nov 5, 2012, 11:55pm Instruction: Submit your answers electronically through Moodle (Link to Homework 1). You may type your answers using any text
ENGG1015 Homework 1 Question 1 ENGG1015: Homework 1 Due: Nov 5, 2012, 11:55pm Instruction: Submit your answers electronically through Moodle (Link to Homework 1). You may type your answers using any text
Digital Circuits. 1. Inputs & Outputs are quantized at two levels. 2. Binary arithmetic, only digits are 0 & 1. Position indicates power of 2.
 Digital Circuits 1. Inputs & Outputs are quantized at two levels. 2. inary arithmetic, only digits are 0 & 1. Position indicates power of 2. 11001 = 2 4 + 2 3 + 0 + 0 +2 0 16 + 8 + 0 + 0 + 1 = 25 Digital
Digital Circuits 1. Inputs & Outputs are quantized at two levels. 2. inary arithmetic, only digits are 0 & 1. Position indicates power of 2. 11001 = 2 4 + 2 3 + 0 + 0 +2 0 16 + 8 + 0 + 0 + 1 = 25 Digital
Computer organization
 Computer organization Levels of abstraction Assembler Simulator Applications C C++ Java High-level language SOFTWARE add lw ori Assembly language Goal 0000 0001 0000 1001 0101 Machine instructions/data
Computer organization Levels of abstraction Assembler Simulator Applications C C++ Java High-level language SOFTWARE add lw ori Assembly language Goal 0000 0001 0000 1001 0101 Machine instructions/data
ALUs and Data Paths. Subtitle: How to design the data path of a processor. 1/8/ L3 Data Path Design Copyright Joanne DeGroat, ECE, OSU 1
 ALUs and Data Paths Subtitle: How to design the data path of a processor. Copyright 2006 - Joanne DeGroat, ECE, OSU 1 Lecture overview General Data Path of a multifunction ALU Copyright 2006 - Joanne DeGroat,
ALUs and Data Paths Subtitle: How to design the data path of a processor. Copyright 2006 - Joanne DeGroat, ECE, OSU 1 Lecture overview General Data Path of a multifunction ALU Copyright 2006 - Joanne DeGroat,
FPGA Resource Utilization Estimates for NI crio LabVIEW FPGA Version: 8.6 NI-RIO Version: 3.0 Date: 8/5/2008
 FPGA Resource Utilization Estimates for NI crio-9104 LabVIEW FPGA Version: 8.6 NI-RIO Version: 3.0 Date: 8/5/2008 Note: The numbers presented in this document are estimates. Actual resource usage for your
FPGA Resource Utilization Estimates for NI crio-9104 LabVIEW FPGA Version: 8.6 NI-RIO Version: 3.0 Date: 8/5/2008 Note: The numbers presented in this document are estimates. Actual resource usage for your
ELEN Electronique numérique
 ELEN0040 - Electronique numérique Patricia ROUSSEAUX Année académique 2014-2015 CHAPITRE 3 Combinational Logic Circuits ELEN0040 3-4 1 Combinational Functional Blocks 1.1 Rudimentary Functions 1.2 Functions
ELEN0040 - Electronique numérique Patricia ROUSSEAUX Année académique 2014-2015 CHAPITRE 3 Combinational Logic Circuits ELEN0040 3-4 1 Combinational Functional Blocks 1.1 Rudimentary Functions 1.2 Functions
Design of Sequential Circuits
 Design of Sequential Circuits Seven Steps: Construct a state diagram (showing contents of flip flop and inputs with next state) Assign letter variables to each flip flop and each input and output variable
Design of Sequential Circuits Seven Steps: Construct a state diagram (showing contents of flip flop and inputs with next state) Assign letter variables to each flip flop and each input and output variable
ENGG1015 Homework 1 Question 1. ENGG1015: Homework 1
 ENGG1015 Homework 1 Question 1 ENGG1015: Homework 1 Due: Nov 5, 2012, 11:55pm Instruction: Submit your answers electronically through Moodle (Link to Homework 1). You may type your answers using any text
ENGG1015 Homework 1 Question 1 ENGG1015: Homework 1 Due: Nov 5, 2012, 11:55pm Instruction: Submit your answers electronically through Moodle (Link to Homework 1). You may type your answers using any text
Roger L. Tokheim. Chapter 8 Counters Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
 Digital Electronics Principles & Applications Sixth Edition Roger L. Tokheim Chapter 8 Counters 2003 Glencoe/McGraw-Hill INTRODUCTION Overview of Counters Characteristics of Counters Ripple Up Counter
Digital Electronics Principles & Applications Sixth Edition Roger L. Tokheim Chapter 8 Counters 2003 Glencoe/McGraw-Hill INTRODUCTION Overview of Counters Characteristics of Counters Ripple Up Counter
Gates and Flip-Flops
 Gates and Flip-Flops Chris Kervick (11355511) With Evan Sheridan and Tom Power December 2012 On a scale of 1 to 10, how likely is it that this question is using binary?...4? What s a 4? Abstract The operation
Gates and Flip-Flops Chris Kervick (11355511) With Evan Sheridan and Tom Power December 2012 On a scale of 1 to 10, how likely is it that this question is using binary?...4? What s a 4? Abstract The operation
EEE Lecture 1 -1-
 EEE3410 - Lecture 1-1- 1. PC -> Address Move content of the Program Counter to Address Bus 2. Mem(Add) -> ID Move the Data at Location Add from main memory to Instruction Decoder (ID) 3. Acc s -> ALU Move
EEE3410 - Lecture 1-1- 1. PC -> Address Move content of the Program Counter to Address Bus 2. Mem(Add) -> ID Move the Data at Location Add from main memory to Instruction Decoder (ID) 3. Acc s -> ALU Move
FPGA Resource Utilization Estimates for NI PXI-7854R. LabVIEW FPGA Version: 8.6 NI-RIO Version: 3.0 Date: 8/5/2008
 FPGA Resource Utilization Estimates for NI PXI-7854R LabVIEW FPGA Version: 8.6 NI-RIO Version: 3.0 Date: 8/5/2008 Note: The numbers presented in this document are estimates. Actual resource usage for your
FPGA Resource Utilization Estimates for NI PXI-7854R LabVIEW FPGA Version: 8.6 NI-RIO Version: 3.0 Date: 8/5/2008 Note: The numbers presented in this document are estimates. Actual resource usage for your
CprE 281: Digital Logic
 CprE 28: Digital Logic Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev http://www.ece.iastate.edu/~alexs/classes/ Simple Processor CprE 28: Digital Logic Iowa State University, Ames, IA Copyright Alexander Stoytchev Digital
CprE 28: Digital Logic Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev http://www.ece.iastate.edu/~alexs/classes/ Simple Processor CprE 28: Digital Logic Iowa State University, Ames, IA Copyright Alexander Stoytchev Digital
ECE 341. Lecture # 3
 ECE 341 Lecture # 3 Instructor: Zeshan Chishti zeshan@ece.pdx.edu October 7, 2013 Portland State University Lecture Topics Counters Finite State Machines Decoders Multiplexers Reference: Appendix A of
ECE 341 Lecture # 3 Instructor: Zeshan Chishti zeshan@ece.pdx.edu October 7, 2013 Portland State University Lecture Topics Counters Finite State Machines Decoders Multiplexers Reference: Appendix A of
LECTURE 28. Analyzing digital computation at a very low level! The Latch Pipelined Datapath Control Signals Concept of State
 Today LECTURE 28 Analyzing digital computation at a very low level! The Latch Pipelined Datapath Control Signals Concept of State Time permitting, RC circuits (where we intentionally put in resistance
Today LECTURE 28 Analyzing digital computation at a very low level! The Latch Pipelined Datapath Control Signals Concept of State Time permitting, RC circuits (where we intentionally put in resistance
CSE. 1. In following code. addi. r1, skip1 xor in r2. r3, skip2. counter r4, top. taken): PC1: PC2: PC3: TTTTTT TTTTTT
 CSE 560 Practice Problem Set 4 Solution 1. In this question, you will examine several different schemes for branch prediction, using the following code sequence for a simple load store ISA with no branch
CSE 560 Practice Problem Set 4 Solution 1. In this question, you will examine several different schemes for branch prediction, using the following code sequence for a simple load store ISA with no branch
Sequential Logic Worksheet
 Sequential Logic Worksheet Concept Inventory: Notes: D-latch & the Dynamic Discipline D-register Timing constraints for sequential circuits Set-up and hold times for sequential circuits 6.004 Worksheet
Sequential Logic Worksheet Concept Inventory: Notes: D-latch & the Dynamic Discipline D-register Timing constraints for sequential circuits Set-up and hold times for sequential circuits 6.004 Worksheet
Design at the Register Transfer Level
 Week-7 Design at the Register Transfer Level Algorithmic State Machines Algorithmic State Machine (ASM) q Our design methodologies do not scale well to real-world problems. q 232 - Logic Design / Algorithmic
Week-7 Design at the Register Transfer Level Algorithmic State Machines Algorithmic State Machine (ASM) q Our design methodologies do not scale well to real-world problems. q 232 - Logic Design / Algorithmic
Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals. Chapter 5 Arithmetic Functions and Circuits
 Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 5 Arithmetic Functions and Circuits Arithmetic functions Operate on binary vectors Use the same subfunction in each bit position Can design functional block
Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals Chapter 5 Arithmetic Functions and Circuits Arithmetic functions Operate on binary vectors Use the same subfunction in each bit position Can design functional block
From Sequential Circuits to Real Computers
 1 / 36 From Sequential Circuits to Real Computers Lecturer: Guillaume Beslon Original Author: Lionel Morel Computer Science and Information Technologies - INSA Lyon Fall 2017 2 / 36 Introduction What we
1 / 36 From Sequential Circuits to Real Computers Lecturer: Guillaume Beslon Original Author: Lionel Morel Computer Science and Information Technologies - INSA Lyon Fall 2017 2 / 36 Introduction What we
Basic Electronics Prof. Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati
 Basic Electronics Prof. Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module: 2 Bipolar Junction Transistors Lecture-4 Biasing
Basic Electronics Prof. Dr. Chitralekha Mahanta Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati Module: 2 Bipolar Junction Transistors Lecture-4 Biasing
Looking at a two binary digit sum shows what we need to extend addition to multiple binary digits.
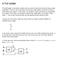 A Full Adder The half-adder is extremely useful until you want to add more that one binary digit quantities. The slow way to develop a two binary digit adders would be to make a truth table and reduce
A Full Adder The half-adder is extremely useful until you want to add more that one binary digit quantities. The slow way to develop a two binary digit adders would be to make a truth table and reduce
BOOLEAN ALGEBRA INTRODUCTION SUBSETS
 BOOLEAN ALGEBRA M. Ragheb 1/294/2018 INTRODUCTION Modern algebra is centered around the concept of an algebraic system: A, consisting of a set of elements: ai, i=1, 2,, which are combined by a set of operations
BOOLEAN ALGEBRA M. Ragheb 1/294/2018 INTRODUCTION Modern algebra is centered around the concept of an algebraic system: A, consisting of a set of elements: ai, i=1, 2,, which are combined by a set of operations
2012 Technological Studies. Higher. Finalised Marking Instructions
 0 Technological Studies Higher Finalised Marking Instructions Scottish Qualifications Authority 0 The information in this publication may be reproduced to support SQA qualifications only on a noncommercial
0 Technological Studies Higher Finalised Marking Instructions Scottish Qualifications Authority 0 The information in this publication may be reproduced to support SQA qualifications only on a noncommercial
Models of Computation, Recall Register Machines. A register machine (sometimes abbreviated to RM) is specified by:
 Models of Computation, 2010 1 Definition Recall Register Machines A register machine (sometimes abbreviated M) is specified by: Slide 1 finitely many registers R 0, R 1,..., R n, each capable of storing
Models of Computation, 2010 1 Definition Recall Register Machines A register machine (sometimes abbreviated M) is specified by: Slide 1 finitely many registers R 0, R 1,..., R n, each capable of storing
Lecture 9: Digital Electronics
 Introduction: We can classify the building blocks of a circuit or system as being either analog or digital in nature. If we focus on voltage as the circuit parameter of interest: nalog: The voltage can
Introduction: We can classify the building blocks of a circuit or system as being either analog or digital in nature. If we focus on voltage as the circuit parameter of interest: nalog: The voltage can
CSCI 2150 Intro to State Machines
 CSCI 2150 Intro to State Machines Topic: Now that we've created flip-flops, let's make stuff with them Reading: igital Fundamentals sections 6.11 and 9.4 (ignore the JK flip-flop stuff) States Up until
CSCI 2150 Intro to State Machines Topic: Now that we've created flip-flops, let's make stuff with them Reading: igital Fundamentals sections 6.11 and 9.4 (ignore the JK flip-flop stuff) States Up until
Digital Electronics II Mike Brookes Please pick up: Notes from the front desk
 NOTATION.PPT(10/8/2010) 1.1 Digital Electronics II Mike Brookes Please pick up: Notes from the front desk 1. What does Digital mean? 2. Where is it used? 3. Why is it used? 4. What are the important features
NOTATION.PPT(10/8/2010) 1.1 Digital Electronics II Mike Brookes Please pick up: Notes from the front desk 1. What does Digital mean? 2. Where is it used? 3. Why is it used? 4. What are the important features
Program Notes Use 2:1 voltage divider on Differential Input channel 1 to get full output range from C7
 {CR10X} PROGRAM C7_datalogger_with_autogain Cyclops 7 (C7) Datalogger with Auto Gain Program example Program Notes Use 2:1 voltage divider on Differential Input channel 1 to get full output range from
{CR10X} PROGRAM C7_datalogger_with_autogain Cyclops 7 (C7) Datalogger with Auto Gain Program example Program Notes Use 2:1 voltage divider on Differential Input channel 1 to get full output range from
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 11 - Shifters & Counters. Register Summary
 EECS50 - Digital Design Lecture - Shifters & Counters February 24, 2003 John Wawrzynek Spring 2005 EECS50 - Lec-counters Page Register Summary All registers (this semester) based on Flip-flops: q 3 q 2
EECS50 - Digital Design Lecture - Shifters & Counters February 24, 2003 John Wawrzynek Spring 2005 EECS50 - Lec-counters Page Register Summary All registers (this semester) based on Flip-flops: q 3 q 2
Binary addition by hand. Adding two bits
 Chapter 3 Arithmetic is the most basic thing you can do with a computer We focus on addition, subtraction, multiplication and arithmetic-logic units, or ALUs, which are the heart of CPUs. ALU design Bit
Chapter 3 Arithmetic is the most basic thing you can do with a computer We focus on addition, subtraction, multiplication and arithmetic-logic units, or ALUs, which are the heart of CPUs. ALU design Bit
Verilog HDL:Digital Design and Modeling. Chapter 11. Additional Design Examples. Additional Figures
 Chapter Additional Design Examples Verilog HDL:Digital Design and Modeling Chapter Additional Design Examples Additional Figures Chapter Additional Design Examples 2 Page 62 a b y y 2 y 3 c d e f Figure
Chapter Additional Design Examples Verilog HDL:Digital Design and Modeling Chapter Additional Design Examples Additional Figures Chapter Additional Design Examples 2 Page 62 a b y y 2 y 3 c d e f Figure
Mark Redekopp, All rights reserved. Lecture 1 Slides. Intro Number Systems Logic Functions
 Lecture Slides Intro Number Systems Logic Functions EE 0 in Context EE 0 EE 20L Logic Design Fundamentals Logic Design, CAD Tools, Lab tools, Project EE 357 EE 457 Computer Architecture Using the logic
Lecture Slides Intro Number Systems Logic Functions EE 0 in Context EE 0 EE 20L Logic Design Fundamentals Logic Design, CAD Tools, Lab tools, Project EE 357 EE 457 Computer Architecture Using the logic
(Refer Time Slide: 1:35)
 Analog Electronic Circuits Prof. S. C. Dutta Roy Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology Delhi Lecture No 04 Problem Session 1 On DC Analysis of BJT Circuits This is the fourth
Analog Electronic Circuits Prof. S. C. Dutta Roy Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology Delhi Lecture No 04 Problem Session 1 On DC Analysis of BJT Circuits This is the fourth
Lab 10: DC RC circuits
 Name: Lab 10: DC RC circuits Group Members: Date: TA s Name: Objectives: 1. To understand current and voltage characteristics of a DC RC circuit 2. To understand the effect of the RC time constant Apparatus:
Name: Lab 10: DC RC circuits Group Members: Date: TA s Name: Objectives: 1. To understand current and voltage characteristics of a DC RC circuit 2. To understand the effect of the RC time constant Apparatus:
SERIALLY PROGRAMMABLE CLOCK SOURCE. Features
 DATASHEET ICS307-03 Description The ICS307-03 is a dynamic, serially programmable clock source which is flexible and takes up minimal board space. Output frequencies are programmed via a 3-wire SPI port.
DATASHEET ICS307-03 Description The ICS307-03 is a dynamic, serially programmable clock source which is flexible and takes up minimal board space. Output frequencies are programmed via a 3-wire SPI port.
Combinational Logic Design Arithmetic Functions and Circuits
 Combinational Logic Design Arithmetic Functions and Circuits Overview Binary Addition Half Adder Full Adder Ripple Carry Adder Carry Look-ahead Adder Binary Subtraction Binary Subtractor Binary Adder-Subtractor
Combinational Logic Design Arithmetic Functions and Circuits Overview Binary Addition Half Adder Full Adder Ripple Carry Adder Carry Look-ahead Adder Binary Subtraction Binary Subtractor Binary Adder-Subtractor
Measurement and Instrumentation. Sampling, Digital Devices, and Data Acquisition
 2141-375 Measurement and Instrumentation Sampling, Digital Devices, and Data Acquisition Basic Data Acquisition System Analog Form Analog Form Digital Form Display Physical varialble Sensor Signal conditioning
2141-375 Measurement and Instrumentation Sampling, Digital Devices, and Data Acquisition Basic Data Acquisition System Analog Form Analog Form Digital Form Display Physical varialble Sensor Signal conditioning
An Ultra Low Resistance Continuity Checker
 An Ultra Low Resistance Continuity Checker By R. G. Sparber Copyleft protects this document. 1 Some understanding of electronics is assumed. Although the title claims this is a continuity checker, its
An Ultra Low Resistance Continuity Checker By R. G. Sparber Copyleft protects this document. 1 Some understanding of electronics is assumed. Although the title claims this is a continuity checker, its
Digital Electronics Final Examination. Part A
 Digital Electronics Final Examination Part A Spring 2009 Student Name: Date: Class Period: Total Points: /50 Converted Score: /40 Page 1 of 13 Directions: This is a CLOSED BOOK/CLOSED NOTES exam. Select
Digital Electronics Final Examination Part A Spring 2009 Student Name: Date: Class Period: Total Points: /50 Converted Score: /40 Page 1 of 13 Directions: This is a CLOSED BOOK/CLOSED NOTES exam. Select
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 25 Shifters and Counters. Recap
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 25 Shifters and Counters Nov. 21, 2013 Prof. Ronald Fearing Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley (slides courtesy of Prof. John
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 25 Shifters and Counters Nov. 21, 2013 Prof. Ronald Fearing Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley (slides courtesy of Prof. John
Technological Studies Data Booklet Higher
 Technological Studies Data Booklet Higher For use in National Qualification Courses leading to the 009 examinations and beyond. Published date: July 008 Publication code: BB4470 ISBN: 978 1 8969 608 8
Technological Studies Data Booklet Higher For use in National Qualification Courses leading to the 009 examinations and beyond. Published date: July 008 Publication code: BB4470 ISBN: 978 1 8969 608 8
Exam for Physics 4051, October 31, 2008
 Exam for Physics 45, October, 8 5 points - closed book - calculators allowed - show your work Problem : (6 Points) The 4 bit shift register circuit shown in Figure has been initialized to contain the following
Exam for Physics 45, October, 8 5 points - closed book - calculators allowed - show your work Problem : (6 Points) The 4 bit shift register circuit shown in Figure has been initialized to contain the following
EECS Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. FSMs 9/11/2007
 EECS 150 - Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems FSMs 9/11/2007 Sarah Bird Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Slides borrowed from David Culler
EECS 150 - Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems FSMs 9/11/2007 Sarah Bird Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Slides borrowed from David Culler
Digital Electronics. Delay Max. FF Rate Power/Gate High Low (ns) (MHz) (mw) (V) (V) Standard TTL (7400)
 P57/67 Lec9, P Digital Electronics Introduction: In electronics we can classify the building blocks of a circuit or system as being either analog or digital in nature. If we focus on voltage as the circuit
P57/67 Lec9, P Digital Electronics Introduction: In electronics we can classify the building blocks of a circuit or system as being either analog or digital in nature. If we focus on voltage as the circuit
School of Computer Science and Electrical Engineering 28/05/01. Digital Circuits. Lecture 14. ENG1030 Electrical Physics and Electronics
 Digital Circuits 1 Why are we studying digital So that one day you can design something which is better than the... circuits? 2 Why are we studying digital or something better than the... circuits? 3 Why
Digital Circuits 1 Why are we studying digital So that one day you can design something which is better than the... circuits? 2 Why are we studying digital or something better than the... circuits? 3 Why
MOSIS REPORT. Spring MOSIS Report 1. MOSIS Report 2. MOSIS Report 3
 MOSIS REPORT Spring 2010 MOSIS Report 1 MOSIS Report 2 MOSIS Report 3 MOSIS Report 1 Design of 4-bit counter using J-K flip flop I. Objective The purpose of this project is to design one 4-bit counter
MOSIS REPORT Spring 2010 MOSIS Report 1 MOSIS Report 2 MOSIS Report 3 MOSIS Report 1 Design of 4-bit counter using J-K flip flop I. Objective The purpose of this project is to design one 4-bit counter
Binary addition (1-bit) P Q Y = P + Q Comments Carry = Carry = Carry = Carry = 1 P Q
 Digital Arithmetic In Chapter 2, we have discussed number systems such as binary, hexadecimal, decimal, and octal. We have also discussed sign representation techniques, for example, sign-bit representation
Digital Arithmetic In Chapter 2, we have discussed number systems such as binary, hexadecimal, decimal, and octal. We have also discussed sign representation techniques, for example, sign-bit representation
EECS 579: Logic and Fault Simulation. Simulation
 EECS 579: Logic and Fault Simulation Simulation: Use of computer software models to verify correctness Fault Simulation: Use of simulation for fault analysis and ATPG Circuit description Input data for
EECS 579: Logic and Fault Simulation Simulation: Use of computer software models to verify correctness Fault Simulation: Use of simulation for fault analysis and ATPG Circuit description Input data for
4 Switching Algebra 4.1 Axioms; Signals and Switching Algebra
 4 Switching Algebra 4.1 Axioms; Signals and Switching Algebra To design a digital circuit that will perform a required function, it is necessary to manipulate and combine the various input signals in certain
4 Switching Algebra 4.1 Axioms; Signals and Switching Algebra To design a digital circuit that will perform a required function, it is necessary to manipulate and combine the various input signals in certain
EECS 270 Midterm Exam 2 Fall 2009
 EECS 270 Midterm Exam 2 Fall 2009 Name: unique name: UMID: Sign the honor code: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam nor observed anyone else doing so. Scores: NOTES: Problem # Points 1&2
EECS 270 Midterm Exam 2 Fall 2009 Name: unique name: UMID: Sign the honor code: I have neither given nor received aid on this exam nor observed anyone else doing so. Scores: NOTES: Problem # Points 1&2
Additional Gates COE 202. Digital Logic Design. Dr. Muhamed Mudawar King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals
 Additional Gates COE 202 Digital Logic Design Dr. Muhamed Mudawar King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline Additional Gates and Symbols Universality of NAND and NOR gates NAND-NAND
Additional Gates COE 202 Digital Logic Design Dr. Muhamed Mudawar King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline Additional Gates and Symbols Universality of NAND and NOR gates NAND-NAND
PROBLEMS FOR EXPERIMENT ES: ESTIMATING A SECOND Solutions
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics Department 801X Fall 2002 PROBLEMS FOR EXPERIMENT ES: ESTIMATING A SECOND Solutions Problem 1: Use your calculator or your favorite software program to compute
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Physics Department 801X Fall 2002 PROBLEMS FOR EXPERIMENT ES: ESTIMATING A SECOND Solutions Problem 1: Use your calculator or your favorite software program to compute
Boolean algebra. Examples of these individual laws of Boolean, rules and theorems for Boolean algebra are given in the following table.
 The Laws of Boolean Boolean algebra As well as the logic symbols 0 and 1 being used to represent a digital input or output, we can also use them as constants for a permanently Open or Closed circuit or
The Laws of Boolean Boolean algebra As well as the logic symbols 0 and 1 being used to represent a digital input or output, we can also use them as constants for a permanently Open or Closed circuit or
EC 413 Computer Organization
 EC 413 Computer Organization rithmetic Logic Unit (LU) and Register File Prof. Michel. Kinsy Computing: Computer Organization The DN of Modern Computing Computer CPU Memory System LU Register File Disks
EC 413 Computer Organization rithmetic Logic Unit (LU) and Register File Prof. Michel. Kinsy Computing: Computer Organization The DN of Modern Computing Computer CPU Memory System LU Register File Disks
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department
 King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department Page of COE 22: Digital Logic Design (3--3) Term (Fall 22) Final Exam Sunday January
King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals College of Computer Science and Engineering Computer Engineering Department Page of COE 22: Digital Logic Design (3--3) Term (Fall 22) Final Exam Sunday January
Amdahl's Law. Execution time new = ((1 f) + f/s) Execution time. S. Then:
 Amdahl's Law Useful for evaluating the impact of a change. (A general observation.) Insight: Improving a feature cannot improve performance beyond the use of the feature Suppose we introduce a particular
Amdahl's Law Useful for evaluating the impact of a change. (A general observation.) Insight: Improving a feature cannot improve performance beyond the use of the feature Suppose we introduce a particular
Binary addition example worked out
 Binary addition example worked out Some terms are given here Exercise: what are these numbers equivalent to in decimal? The initial carry in is implicitly 0 1 1 1 0 (Carries) 1 0 1 1 (Augend) + 1 1 1 0
Binary addition example worked out Some terms are given here Exercise: what are these numbers equivalent to in decimal? The initial carry in is implicitly 0 1 1 1 0 (Carries) 1 0 1 1 (Augend) + 1 1 1 0
ELECTROMAGNETIC FAULT INJECTION: TOWARDS A FAULT MODEL ON A 32-BIT MICROCONTROLLER
 ELECTROMAGNETIC FAULT INJECTION: TOWARDS A FAULT MODEL ON A 32-BIT MICROCONTROLLER Nicolas Moro 1,3, Amine Dehbaoui 2, Karine Heydemann 3, Bruno Robisson 1, Emmanuelle Encrenaz 3 1 CEA Commissariat à l
ELECTROMAGNETIC FAULT INJECTION: TOWARDS A FAULT MODEL ON A 32-BIT MICROCONTROLLER Nicolas Moro 1,3, Amine Dehbaoui 2, Karine Heydemann 3, Bruno Robisson 1, Emmanuelle Encrenaz 3 1 CEA Commissariat à l
Lecture 13: Sequential Circuits, FSM
 Lecture 13: Sequential Circuits, FSM Today s topics: Sequential circuits Finite state machines 1 Clocks A microprocessor is composed of many different circuits that are operating simultaneously if each
Lecture 13: Sequential Circuits, FSM Today s topics: Sequential circuits Finite state machines 1 Clocks A microprocessor is composed of many different circuits that are operating simultaneously if each
INTERVALOMETER POWER CONSUMPTION
 INTERVALOMETER POWER CONSUMPTION One of the key things I wanted from the design was to keep the power consumption low. By putting the PIC to sleep one can get ridiculously low power consumption but it
INTERVALOMETER POWER CONSUMPTION One of the key things I wanted from the design was to keep the power consumption low. By putting the PIC to sleep one can get ridiculously low power consumption but it
Logic Design II (17.342) Spring Lecture Outline
 Logic Design II (17.342) Spring 2012 Lecture Outline Class # 10 April 12, 2012 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture First half of the class Circuits for Arithmetic Operations Chapter 18 Should finish at least
Logic Design II (17.342) Spring 2012 Lecture Outline Class # 10 April 12, 2012 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture First half of the class Circuits for Arithmetic Operations Chapter 18 Should finish at least
Hardware Design I Chap. 4 Representative combinational logic
 Hardware Design I Chap. 4 Representative combinational logic E-mail: shimada@is.naist.jp Already optimized circuits There are many optimized circuits which are well used You can reduce your design workload
Hardware Design I Chap. 4 Representative combinational logic E-mail: shimada@is.naist.jp Already optimized circuits There are many optimized circuits which are well used You can reduce your design workload
[2] Predicting the direction of a branch is not enough. What else is necessary?
![[2] Predicting the direction of a branch is not enough. What else is necessary? [2] Predicting the direction of a branch is not enough. What else is necessary?](/thumbs/74/69859984.jpg) [2] When we talk about the number of operands in an instruction (a 1-operand or a 2-operand instruction, for example), what do we mean? [2] What are the two main ways to define performance? [2] Predicting
[2] When we talk about the number of operands in an instruction (a 1-operand or a 2-operand instruction, for example), what do we mean? [2] What are the two main ways to define performance? [2] Predicting
MACHINE COMPUTING. the limitations
 MACHINE COMPUTING the limitations human computing stealing brain cycles of the masses word recognition: to digitize all printed writing language education: to translate web content games with a purpose
MACHINE COMPUTING the limitations human computing stealing brain cycles of the masses word recognition: to digitize all printed writing language education: to translate web content games with a purpose
Building a Computer. Quiz #2 on 10/31, open book and notes. (This is the last lecture covered) I wonder where this goes? L16- Building a Computer 1
 Building a Computer I wonder where this goes? B LU MIPS Kit Quiz # on /3, open book and notes (This is the last lecture covered) Comp 4 Fall 7 /4/7 L6- Building a Computer THIS IS IT! Motivating Force
Building a Computer I wonder where this goes? B LU MIPS Kit Quiz # on /3, open book and notes (This is the last lecture covered) Comp 4 Fall 7 /4/7 L6- Building a Computer THIS IS IT! Motivating Force
Review for B33DV2-Digital Design. Digital Design
 Review for B33DV2 The Elements of Modern Behaviours Design Representations Blocks Waveforms Gates Truth Tables Boolean Algebra Switches Rapid Prototyping Technologies Circuit Technologies TTL MOS Simulation
Review for B33DV2 The Elements of Modern Behaviours Design Representations Blocks Waveforms Gates Truth Tables Boolean Algebra Switches Rapid Prototyping Technologies Circuit Technologies TTL MOS Simulation
14.1. Unit 14. State Machine Design
 4. Unit 4 State Machine Design 4.2 Outcomes I can create a state diagram to solve a sequential problem I can implement a working state machine given a state diagram STATE MACHINES OVERVIEW 4.3 4.4 Review
4. Unit 4 State Machine Design 4.2 Outcomes I can create a state diagram to solve a sequential problem I can implement a working state machine given a state diagram STATE MACHINES OVERVIEW 4.3 4.4 Review
Counting in Different Number Systems
 Counting in Different Number Systems Base 1 (Decimal) is important because that is the base that we first learn in our culture. Base 2 (Binary) is important because that is the base used for computer codes
Counting in Different Number Systems Base 1 (Decimal) is important because that is the base that we first learn in our culture. Base 2 (Binary) is important because that is the base used for computer codes
Computer Science 324 Computer Architecture Mount Holyoke College Fall Topic Notes: Digital Logic
 Computer Science 324 Computer Architecture Mount Holyoke College Fall 2007 Topic Notes: Digital Logic Our goal for the next few weeks is to paint a a reasonably complete picture of how we can go from transistor
Computer Science 324 Computer Architecture Mount Holyoke College Fall 2007 Topic Notes: Digital Logic Our goal for the next few weeks is to paint a a reasonably complete picture of how we can go from transistor
US ARMY INTELLIGENCE CENTER CIRCUITS
 SUBCOURSE IT 0334 EDITION C US ARMY INTELLIGENCE CENTER CIRCUITS CIRCUITS Subcourse Number IT0334 EDITION C US ARMY INTELLIGENCE CENTER FORT HUACHUCA, AZ 85613-6000 4 Credit Hours Edition Date: December
SUBCOURSE IT 0334 EDITION C US ARMY INTELLIGENCE CENTER CIRCUITS CIRCUITS Subcourse Number IT0334 EDITION C US ARMY INTELLIGENCE CENTER FORT HUACHUCA, AZ 85613-6000 4 Credit Hours Edition Date: December
Differences between PCL-240MK and PCL-240MS
 1. General PCL-240MS, which replaces PCL-240MK, can offer S curve acceleration/deceleration control. There are no board or software changes required for S curve acceleration/deceleration. Here are lists
1. General PCL-240MS, which replaces PCL-240MK, can offer S curve acceleration/deceleration control. There are no board or software changes required for S curve acceleration/deceleration. Here are lists
ENGR4300 Fall 2005 Test 3S. Name solution. Section. Question 1 (25 points) Question 2 (25 points) Question 3 (25 points) Question 4 (25 points)
 ENGR400 Test S Fall 005 ENGR400 Fall 005 Test S Name solution Section uestion (5 points) uestion (5 points) uestion (5 points) uestion 4 (5 points) Total (00 points): Please do not write on the crib sheets.
ENGR400 Test S Fall 005 ENGR400 Fall 005 Test S Name solution Section uestion (5 points) uestion (5 points) uestion (5 points) uestion 4 (5 points) Total (00 points): Please do not write on the crib sheets.
ICS 233 Computer Architecture & Assembly Language
 ICS 233 Computer Architecture & Assembly Language Assignment 6 Solution 1. Identify all of the RAW data dependencies in the following code. Which dependencies are data hazards that will be resolved by
ICS 233 Computer Architecture & Assembly Language Assignment 6 Solution 1. Identify all of the RAW data dependencies in the following code. Which dependencies are data hazards that will be resolved by
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FFs revisited, FIFOs, ECCs, LSFRs. Cross-coupled NOR gates
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FFs revisited, FIFOs, ECCs, LSFRs April 16, 2009 John Wawrzynek Spring 2009 EECS150 - Lec24-blocks Page 1 Cross-coupled NOR gates remember, If both R=0 & S=0, then
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FFs revisited, FIFOs, ECCs, LSFRs April 16, 2009 John Wawrzynek Spring 2009 EECS150 - Lec24-blocks Page 1 Cross-coupled NOR gates remember, If both R=0 & S=0, then
In 1980, the yield = 48% and the Die Area = 0.16 from figure In 1992, the yield = 48% and the Die Area = 0.97 from figure 1.31.
 CS152 Homework 1 Solutions Spring 2004 1.51 Yield = 1 / ((1 + (Defects per area * Die Area / 2))^2) Thus, if die area increases, defects per area must decrease. 1.52 Solving the yield equation for Defects
CS152 Homework 1 Solutions Spring 2004 1.51 Yield = 1 / ((1 + (Defects per area * Die Area / 2))^2) Thus, if die area increases, defects per area must decrease. 1.52 Solving the yield equation for Defects
6.111 Lecture # 12. Binary arithmetic: most operations are familiar Each place in a binary number has value 2 n
 6.111 Lecture # 12 Binary arithmetic: most operations are familiar Each place in a binary number has value 2 n Representation of negative numbers: there are a number of ways we might do this: 5 = 00000101
6.111 Lecture # 12 Binary arithmetic: most operations are familiar Each place in a binary number has value 2 n Representation of negative numbers: there are a number of ways we might do this: 5 = 00000101
Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements
 CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Instructor: Mohsen Imani UC San Diego Slides from: Prof.Tajana Simunic Rosing
CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Instructor: Mohsen Imani UC San Diego Slides from: Prof.Tajana Simunic Rosing
Electric Current Unlike static electricity, electric current is a continuous flow of charged particles (electricity). For current to flow, there must
 CURRENT ELECTRICITY Electric Current Unlike static electricity, electric current is a continuous flow of charged particles (electricity). For current to flow, there must be a power source and there must
CURRENT ELECTRICITY Electric Current Unlike static electricity, electric current is a continuous flow of charged particles (electricity). For current to flow, there must be a power source and there must
ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN
 ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Dr. Eng. Haitham Omran, haitham.omran@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Wassim Alexan, wassim.joseph@guc.edu.eg Following the slides of Dr. Ahmed H. Madian Lecture 10 محرم 1439 ه Winter
ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Dr. Eng. Haitham Omran, haitham.omran@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Wassim Alexan, wassim.joseph@guc.edu.eg Following the slides of Dr. Ahmed H. Madian Lecture 10 محرم 1439 ه Winter
ELEVATOR CONTROL CIRCUIT. Project No: PRJ045 Presented by; Masila Jane Mwelu. Supervisor: Prof. Mwangi Examiner: Dr. Mang oli
 ELEVATOR CONTROL CIRCUIT Project No: PRJ045 Presented by; Masila Jane Mwelu Supervisor: Prof. Mwangi Examiner: Dr. Mang oli Presentation Outline Project objectives Design approach Implementation Results
ELEVATOR CONTROL CIRCUIT Project No: PRJ045 Presented by; Masila Jane Mwelu Supervisor: Prof. Mwangi Examiner: Dr. Mang oli Presentation Outline Project objectives Design approach Implementation Results
Lecture 8: Sequential Multipliers
 Lecture 8: Sequential Multipliers ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic 3/25/08 ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic Lecture Roadmap Sequential Multipliers Unsigned Signed Radix-2 Booth Recoding High-Radix Multiplication
Lecture 8: Sequential Multipliers ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic 3/25/08 ECE 645 Computer Arithmetic Lecture Roadmap Sequential Multipliers Unsigned Signed Radix-2 Booth Recoding High-Radix Multiplication
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring Lecture 19: Adder Design
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2011 Lecture 19: Adder Design [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] Sp11 CMPEN 411 L19
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Spring 2011 Lecture 19: Adder Design [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] Sp11 CMPEN 411 L19
Dr. Nicola Nicolici COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Nov 22, 2006
 COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Fall 2006 Page 1 Dr. Nicola Nicolici COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Nov 22, 2006 Instructions: This examination paper includes 12 pages and 20 multiple-choice questions starting
COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Fall 2006 Page 1 Dr. Nicola Nicolici COE/EE2DI4 Midterm Test #2 Nov 22, 2006 Instructions: This examination paper includes 12 pages and 20 multiple-choice questions starting
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 16 Counters. Announcements
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 16 Counters October 20, 2011 Elad Alon Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley http://www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs150 Fall 2011
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 16 Counters October 20, 2011 Elad Alon Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley http://www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs150 Fall 2011
Section 5.4 BJT Circuits at DC
 12/3/2004 section 5_4 JT Circuits at DC 1/1 Section 5.4 JT Circuits at DC Reading Assignment: pp. 421-436 To analyze a JT circuit, we follow the same boring procedure as always: ASSUME, ENFORCE, ANALYZE
12/3/2004 section 5_4 JT Circuits at DC 1/1 Section 5.4 JT Circuits at DC Reading Assignment: pp. 421-436 To analyze a JT circuit, we follow the same boring procedure as always: ASSUME, ENFORCE, ANALYZE
Lab Manual Solutions Industrial Control Electronics: Devices, Systems, and Applications
 Lab Manual Solutions Industrial Control Electronics: Devices, Systems, and Applications 3rd edition Terry L.M. Bartelt Australia Canada Mexico Singapore Spain United Kingdom United States . analog 2. linear
Lab Manual Solutions Industrial Control Electronics: Devices, Systems, and Applications 3rd edition Terry L.M. Bartelt Australia Canada Mexico Singapore Spain United Kingdom United States . analog 2. linear
