EECS 579: Logic and Fault Simulation. Simulation
|
|
|
- Rosamund Conley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EECS 579: Logic and Fault Simulation Simulation: Use of computer software models to verify correctness Fault Simulation: Use of simulation for fault analysis and ATPG Circuit description Input data for C Simulation run commands Model C of target circuit Simulation control Host computer Output data for C Performance data for C Emulation: Hardware-assisted simulation using FPGA-based emulators John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page Simulation Uses Reduce/eliminate need to build physical prototypes Alternative design comparison Functional design verification Timing/performance design verification Fault analysis and test generation Simulation Levels Analog (continuous) ELECTRIC CIRCUIT DEVICE/ LAYOUT Level of detail Digital (discrete) SYSTEM (BEHAVIORAL) REGISTER- TRANSFER LOGIC (GATE) SWITCH Simulation cost John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page 2
2 Logic Simulation Component types Gates, flip-flops, switches, macro elements Signal accuracy,, X (unknown) plus a few others Timing accuracy (delay models) Transport: unit, nominal Rise/fall delay Simulator structures Compiled-code (compiler-driven) Non-compiled event-driven John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page 3 Example Logic Simulation B CLK A t t +25 t 5 ns ns t +5 t + J C K Setup time Hold time t +5 Z6 Z7 Z8 Event John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page 4
3 Compiled-Code Simulation Circuit model is executable code. Circuit elements are program routines linked toreflect circuit structure Simulation steps Levelize and code circuit Compile and execute Characteristics All signals are evaluated in all time periods Fast simulation of simpler circuits Inefficient with complex signal/timing Frequent recompilation often necessary John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page 5 Compiled-Code Simulation (Code to compute x) Level i- x y Level i NAND gate G z (Code to compute y) LDA x Load x from memory into CPU accumulator A AND y Compute A.y; put in A NOT Compute complement of A STA z Store A in z (To next element) John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page 6
4 Compiled-Code Simulator procedure compiled_sim Read circuit description; Break feedback and levelize circuit; Generate code for gates; Initialize signal values; for each input signal vector do for each logic level do for each gate do execute gate code (simulate); end end Output desired results; end end procedure John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page 7 Event-Driven Simulation Circuit model is a data structure consisting of set of linked tables specifying components, their attributes, and connections Separate simulation control program processes the circuit Characteristics Signal timing calculations are event-directed Handles complex signal/timing models Circuit models are easy to change Supports forward/backward tracing Slower for large, simple models John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page 8
5 Event-Driven Simulation A B G G2 CLK J C K FF Z6 Z7 Z8 Name Type Inputs Outputs Delay Other attributes G NAND A,B FF-J, Z6,5... G2 NOT A FF-K,... FF JKFF G, CLK, G2 Z7, Z8... A PI G,G2 Z6 PO G etc. John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page 9 Event-Driven Simulation Name Type Fan-in Fan-out Fan-in Fan-out Delay Other attributes list list G NAND P P2 2 2,5... G2 NOT P3 P4,... FF JKFF P5 P A PI P7 2 Z6 PO P8 etc. P P2 P3 P4 P5 A B FF- J Z6 A FF- K G CLK G2 etc. Fan-in/ fan-out table John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page
6 Example Event-Driven Simulation B CLK A t t +25 t 5 ns ns t +5 t + J C K Setup time Hold time t +5 Z6 Z7 Z8 Event John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page Event-Driven Simulator procedure table_sim Read circuit description; Construct circuit data structures (tables); Initialize signal values and event time t repeat {with set of current events} Select event and examine its fanout list; while (unevaluated fanout signals remain) do Evaluate and schedule fanout events; Output desired results; end until (no more current events) Increment t to next event time; end procedure John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page 2
7 Time Simulation Time driven: simulate entire circuit at every time step Event driven: emulate active parts of circuit only when a signal change or event occurs. Event-Driven Simulation. Simulate the current event 2. Scan the circuit for implied events and schedule them 3. Advance simulation time to the next event Event scheduling methods Indexed array A[i]: Given A[current], go to A[current + T] Fast, large storage needs (static allocation) Linear list (linked list) Slow, efficient storage (dynamic allocation) Timing wheel: indexed-list that trades off speed and storage John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page 3 Linked List Event Scheduling t Time Line Value Link X P P4 P Y4 X P7 - X2 Other events at t = P7 5 Y5 - - John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page 4
8 Timing Wheel Time Link 2 3 Event Scheduling Event data Event data Avoids long searches but is subject to overflow John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page 5 Fault Simulation Definition Simulation designed for fault analysis and ATPG Applications Evaluate effects, e.g., criticality of given faults Evaluate coverage of a given test pattern set To aid in test pattern set generation To construct fault dictionaries To estimate manufacturing yield DL = Y d DL = probability of shipping a defective IC Y = probability that a manufactured IC is OK d = defect coverage of testing approximated by fault coverage John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page 6
9 Fault Simulation Fault Models Single stuck-line fault model is standard: any logic line may be stuck at or ; the logic elements are fault free Others: delay faults, short/open faults, etc. Fault Simulation Methods Serial: one fault is simulated at a time Parallel: n faults are simulated at a time Parallel method Deductive simulation Concurrent simulation etc. Statistical: fault sampling John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page 7 Fault Simulation Parallel Method Each n-bit word in host computer stores m k-bit values, n > mk Exploits logical instruction set of host Relatively inflexible and usually requires multiple passes x x y To Evaluate z z z/ z/ y/ x/ Fault positions Mask I z : fault positions for z Mask S z : fault values Basic evaluation : z = x.y Fault insertion : z* = z.i z + I z.s z John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page 8
10 Deductive Method Fault Simulation The signal on each simulated line is a list L of all faults causing errors on that line. All faults can be simulated in one pass L a L b L k a b k... F z L a = list of faults causing errors on line a L a = list of faults not causing errors on line a L a L b L c a b c d L d = {d/} L a L b L c John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page 9 Example Deductive Fault Simulation a b d i h c e f L a = {a }; L b = {b }; L d = {d } L c = L a L b {c } = {dc } L e = L c L d {e } = {c,d,e } L f = {f }; L g = L e {g } = {c,d,e,g } L h = {h }; L i = {i }; L d = {d } L j = L e {j } = {c,d,e,j } g j l k n m p John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page 2
11 Deductive Fault Simulation Example (cont d) a b d i h c e f g j L k = L i L h {k }= {i,h,k } L l = L j {l }= {c,d,e,j,l } L m = L k L l {m } = {i,h,k,m } L n = L g L f {n } = {c,d,e,g,n } L p = L m L n {p } = {c,d,e,g,n,i,h,k,m,p } l k n m p John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page 2 Approach Emulation Map target design into a network of field-programmable gate array (FPGA) ICs The programmed FPGA forms a hardware prototype of the design and can run at effective clock speed of, say, 5 MHz The emulated circuit can be instrumented as a logic analyzer to capture normal or faulty behavior Drawback Limited ability to do performance measurement John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page 22
12 FPGA: Xilinx 3 series Emulation Interconnection switch box Interconnections Configurable logic block (cell) (a) Logic block Programmable connections (b) John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page 23 Emulation System Emulation Host computer Host interface FPGA FPGA FPGA... FPGA FPGA Config. system Programmable interconnect John P. Hayes University of Michigan EECS 579 Fall 2 Lecture 23: Page 24
Testability. Shaahin Hessabi. Sharif University of Technology. Adapted from the presentation prepared by book authors.
 Testability Lecture 6: Logic Simulation Shaahin Hessabi Department of Computer Engineering Sharif University of Technology Adapted from the presentation prepared by book authors Slide 1 of 27 Outline What
Testability Lecture 6: Logic Simulation Shaahin Hessabi Department of Computer Engineering Sharif University of Technology Adapted from the presentation prepared by book authors Slide 1 of 27 Outline What
VLSI Design Verification and Test Simulation CMPE 646. Specification. Design(netlist) True-value Simulator
 Design Verification Simulation used for ) design verification: verify the correctness of the design and 2) test verification. Design verification: Response analysis Specification Design(netlist) Critical
Design Verification Simulation used for ) design verification: verify the correctness of the design and 2) test verification. Design verification: Response analysis Specification Design(netlist) Critical
Outline Fault Simulation
 K.T. Tim Cheng, 4_fault_sim, v. Outline Fault Simulation Applications of fault simulation Fault coverage vs product quality Fault simulation scenarios Fault simulation algorithms Fault sampling K.T. Tim
K.T. Tim Cheng, 4_fault_sim, v. Outline Fault Simulation Applications of fault simulation Fault coverage vs product quality Fault simulation scenarios Fault simulation algorithms Fault sampling K.T. Tim
ECE 1767 University of Toronto
 Applications Why Two Fault Simulators Never Agree General Techniques Parallel Pattern Simulation Inactive Fault Removal Critical Path Tracing Fault Sampling Statistical Fault Analysis ECE 767 Fault grading
Applications Why Two Fault Simulators Never Agree General Techniques Parallel Pattern Simulation Inactive Fault Removal Critical Path Tracing Fault Sampling Statistical Fault Analysis ECE 767 Fault grading
VLSI Physical Design Prof. Indranil Sengupta Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 VLSI Physical Design Prof. Indranil Sengupta Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 54 Design for Testability So, in the last lecture we talked
VLSI Physical Design Prof. Indranil Sengupta Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 54 Design for Testability So, in the last lecture we talked
LOGIC CIRCUITS. Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics. Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D.
 Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Digital IC packages TTL (transistor-transistor
Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Digital IC packages TTL (transistor-transistor
ECE 407 Computer Aided Design for Electronic Systems. Simulation. Instructor: Maria K. Michael. Overview
 407 Computer Aided Design for Electronic Systems Simulation Instructor: Maria K. Michael Overview What is simulation? Design verification Modeling Levels Modeling circuits for simulation True-value simulation
407 Computer Aided Design for Electronic Systems Simulation Instructor: Maria K. Michael Overview What is simulation? Design verification Modeling Levels Modeling circuits for simulation True-value simulation
LOGIC CIRCUITS. Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics
 Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Outline Combinational logic circuits Output
Basic Experiment and Design of Electronics LOGIC CIRCUITS Ho Kyung Kim, Ph.D. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr School of Mechanical Engineering Pusan National University Outline Combinational logic circuits Output
Hardware testing and design for testability. EE 3610 Digital Systems
 EE 3610: Digital Systems 1 Hardware testing and design for testability Introduction A Digital System requires testing before and after it is manufactured 2 Level 1: behavioral modeling and test benches
EE 3610: Digital Systems 1 Hardware testing and design for testability Introduction A Digital System requires testing before and after it is manufactured 2 Level 1: behavioral modeling and test benches
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 11 - Shifters & Counters. Register Summary
 EECS50 - Digital Design Lecture - Shifters & Counters February 24, 2003 John Wawrzynek Spring 2005 EECS50 - Lec-counters Page Register Summary All registers (this semester) based on Flip-flops: q 3 q 2
EECS50 - Digital Design Lecture - Shifters & Counters February 24, 2003 John Wawrzynek Spring 2005 EECS50 - Lec-counters Page Register Summary All registers (this semester) based on Flip-flops: q 3 q 2
Introduction to VLSI Testing
 Introduction to 李昆忠 Kuen-Jong Lee Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan Class Problems to Think How are you going to test A 32 bit adder A 32 bit counter A 32Mb
Introduction to 李昆忠 Kuen-Jong Lee Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan Class Problems to Think How are you going to test A 32 bit adder A 32 bit counter A 32Mb
Advanced Testing. EE5375 ADD II Prof. MacDonald
 Advanced Testing EE5375 ADD II Prof. MacDonald Functional Testing l Original testing method l Run chip from reset l Tester emulates the outside world l Chip runs functionally with internally generated
Advanced Testing EE5375 ADD II Prof. MacDonald Functional Testing l Original testing method l Run chip from reset l Tester emulates the outside world l Chip runs functionally with internally generated
Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Digital Logic Design and Analysis Prelim Question Paper Solution
![Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Digital Logic Design and Analysis Prelim Question Paper Solution Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Digital Logic Design and Analysis Prelim Question Paper Solution](/thumbs/90/103673562.jpg) . (a) (i) ( B C 5) H (A 2 B D) H S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Digital Logic Design and Analysis Prelim Question Paper Solution ( B C 5) H (A 2 B D) H = (FFFF 698) H (ii) (2.3) 4 + (22.3) 4 2 2. 3 2. 3 2 3. 2 (2.3)
. (a) (i) ( B C 5) H (A 2 B D) H S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Digital Logic Design and Analysis Prelim Question Paper Solution ( B C 5) H (A 2 B D) H = (FFFF 698) H (ii) (2.3) 4 + (22.3) 4 2 2. 3 2. 3 2 3. 2 (2.3)
Chapter 5. Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition. David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris. Chapter 5 <1>
 Chapter 5 Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Chapter 5 Chapter 5 :: Topics Introduction Arithmetic Circuits umber Systems Sequential Building
Chapter 5 Digital Design and Computer Architecture, 2 nd Edition David Money Harris and Sarah L. Harris Chapter 5 Chapter 5 :: Topics Introduction Arithmetic Circuits umber Systems Sequential Building
Logic BIST. Sungho Kang Yonsei University
 Logic BIST Sungho Kang Yonsei University Outline Introduction Basics Issues Weighted Random Pattern Generation BIST Architectures Deterministic BIST Conclusion 2 Built In Self Test Test/ Normal Input Pattern
Logic BIST Sungho Kang Yonsei University Outline Introduction Basics Issues Weighted Random Pattern Generation BIST Architectures Deterministic BIST Conclusion 2 Built In Self Test Test/ Normal Input Pattern
Lecture 7: Logic design. Combinational logic circuits
 /24/28 Lecture 7: Logic design Binary digital circuits: Two voltage levels: and (ground and supply voltage) Built from transistors used as on/off switches Analog circuits not very suitable for generic
/24/28 Lecture 7: Logic design Binary digital circuits: Two voltage levels: and (ground and supply voltage) Built from transistors used as on/off switches Analog circuits not very suitable for generic
UMBC. At the system level, DFT includes boundary scan and analog test bus. The DFT techniques discussed focus on improving testability of SAFs.
 Overview Design for testability(dft) makes it possible to: Assure the detection of all faults in a circuit. Reduce the cost and time associated with test development. Reduce the execution time of performing
Overview Design for testability(dft) makes it possible to: Assure the detection of all faults in a circuit. Reduce the cost and time associated with test development. Reduce the execution time of performing
Single Stuck-At Fault Model Other Fault Models Redundancy and Untestable Faults Fault Equivalence and Fault Dominance Method of Boolean Difference
 Single Stuck-At Fault Model Other Fault Models Redundancy and Untestable Faults Fault Equivalence and Fault Dominance Method of Boolean Difference Copyright 1998 Elizabeth M. Rudnick 1 Modeling the effects
Single Stuck-At Fault Model Other Fault Models Redundancy and Untestable Faults Fault Equivalence and Fault Dominance Method of Boolean Difference Copyright 1998 Elizabeth M. Rudnick 1 Modeling the effects
Fault Modeling. 李昆忠 Kuen-Jong Lee. Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan. VLSI Testing Class
 Fault Modeling 李昆忠 Kuen-Jong Lee Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan Class Fault Modeling Some Definitions Why Modeling Faults Various Fault Models Fault Detection
Fault Modeling 李昆忠 Kuen-Jong Lee Dept. of Electrical Engineering National Cheng-Kung University Tainan, Taiwan Class Fault Modeling Some Definitions Why Modeling Faults Various Fault Models Fault Detection
Lecture 14: State Tables, Diagrams, Latches, and Flip Flop
 EE210: Switching Systems Lecture 14: State Tables, Diagrams, Latches, and Flip Flop Prof. YingLi Tian Nov. 6, 2017 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University
EE210: Switching Systems Lecture 14: State Tables, Diagrams, Latches, and Flip Flop Prof. YingLi Tian Nov. 6, 2017 Department of Electrical Engineering The City College of New York The City University
ECE 3060 VLSI and Advanced Digital Design. Testing
 ECE 3060 VLSI and Advanced Digital Design Testing Outline Definitions Faults and Errors Fault models and definitions Fault Detection Undetectable Faults can be used in synthesis Fault Simulation Observability
ECE 3060 VLSI and Advanced Digital Design Testing Outline Definitions Faults and Errors Fault models and definitions Fault Detection Undetectable Faults can be used in synthesis Fault Simulation Observability
S No. Questions Bloom s Taxonomy Level UNIT-I
 GROUP-A (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) S No. Questions Bloom s UNIT-I 1 Define oxidation & Classify different types of oxidation Remember 1 2 Explain about Ion implantation Understand 1 3 Describe lithography
GROUP-A (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) S No. Questions Bloom s UNIT-I 1 Define oxidation & Classify different types of oxidation Remember 1 2 Explain about Ion implantation Understand 1 3 Describe lithography
Shift Register Counters
 Shift Register Counters Shift register counter: a shift register with the serial output connected back to the serial input. They are classified as counters because they give a specified sequence of states.
Shift Register Counters Shift register counter: a shift register with the serial output connected back to the serial input. They are classified as counters because they give a specified sequence of states.
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 17 - Sequential Circuits 3 (Counters)
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 17 - Sequential Circuits 3 (Counters) March 19&21, 2002 John Wawrzynek Spring 2002 EECS150 - Lec13-seq3 version 2 Page 1 Counters Special sequential circuits (FSMs) that
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 17 - Sequential Circuits 3 (Counters) March 19&21, 2002 John Wawrzynek Spring 2002 EECS150 - Lec13-seq3 version 2 Page 1 Counters Special sequential circuits (FSMs) that
Clock signal in digital circuit is responsible for synchronizing the transfer to the data between processing elements.
 1 2 Introduction Clock signal in digital circuit is responsible for synchronizing the transfer to the data between processing elements. Defines the precise instants when the circuit is allowed to change
1 2 Introduction Clock signal in digital circuit is responsible for synchronizing the transfer to the data between processing elements. Defines the precise instants when the circuit is allowed to change
Problem Set 9 Solutions
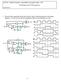 CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
CSE 26 Digital Computers: Organization and Logical Design - 27 Jon Turner Problem Set 9 Solutions. For each of the sequential circuits shown below, draw in the missing parts of the timing diagrams. You
Design for Testability
 Design for Testability Outline Ad Hoc Design for Testability Techniques Method of test points Multiplexing and demultiplexing of test points Time sharing of I/O for normal working and testing modes Partitioning
Design for Testability Outline Ad Hoc Design for Testability Techniques Method of test points Multiplexing and demultiplexing of test points Time sharing of I/O for normal working and testing modes Partitioning
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN. Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering TIMING ANALYSIS Overview Circuits do not respond instantaneously to input changes
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 9 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering TIMING ANALYSIS Overview Circuits do not respond instantaneously to input changes
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 18 - Counters
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 18 - Counters October 24, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS150 - Lec18-counters Page 1 Counters Special sequential circuits (FSMs) that sequence though a set outputs.
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 18 - Counters October 24, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS150 - Lec18-counters Page 1 Counters Special sequential circuits (FSMs) that sequence though a set outputs.
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 18 - Counters
 EECS50 - Digital Design Lecture 8 - Counters October 24, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS50 - Lec8-counters Page Counters Special sequential circuits (FSMs) that sequence though a set outputs. Examples:
EECS50 - Digital Design Lecture 8 - Counters October 24, 2002 John Wawrzynek Fall 2002 EECS50 - Lec8-counters Page Counters Special sequential circuits (FSMs) that sequence though a set outputs. Examples:
Fundamentals of Digital Design
 Fundamentals of Digital Design Digital Radiation Measurement and Spectroscopy NE/RHP 537 1 Binary Number System The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, is a numeral system that represents numeric
Fundamentals of Digital Design Digital Radiation Measurement and Spectroscopy NE/RHP 537 1 Binary Number System The binary numeral system, or base-2 number system, is a numeral system that represents numeric
ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN
 ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Dr. Eng. Haitham Omran, haitham.omran@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Wassim Alexan, wassim.joseph@guc.edu.eg Lecture 6 Following the slides of Dr. Ahmed H. Madian محرم 1439 ه Winter
ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Dr. Eng. Haitham Omran, haitham.omran@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Wassim Alexan, wassim.joseph@guc.edu.eg Lecture 6 Following the slides of Dr. Ahmed H. Madian محرم 1439 ه Winter
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison. Fall Final Examination
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison ECE 553: Testing and Testable Design of Digital Systems Fall 2013-2014 Final Examination CLOSED BOOK Kewal K. Saluja Date:
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison ECE 553: Testing and Testable Design of Digital Systems Fall 2013-2014 Final Examination CLOSED BOOK Kewal K. Saluja Date:
Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements
 CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Adders 2 Circuit Delay Transistors have instrinsic resistance and capacitance
CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Adders 2 Circuit Delay Transistors have instrinsic resistance and capacitance
NCU EE -- DSP VLSI Design. Tsung-Han Tsai 1
 NCU EE -- DSP VLSI Design. Tsung-Han Tsai 1 Multi-processor vs. Multi-computer architecture µp vs. DSP RISC vs. DSP RISC Reduced-instruction-set Register-to-register operation Higher throughput by using
NCU EE -- DSP VLSI Design. Tsung-Han Tsai 1 Multi-processor vs. Multi-computer architecture µp vs. DSP RISC vs. DSP RISC Reduced-instruction-set Register-to-register operation Higher throughput by using
For smaller NRE cost For faster time to market For smaller high-volume manufacturing cost For higher performance
 University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS5 J. Wawrzynek Spring 22 2/22/2. [2 pts] Short Answers. Midterm Exam I a) [2 pts]
University of California at Berkeley College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS5 J. Wawrzynek Spring 22 2/22/2. [2 pts] Short Answers. Midterm Exam I a) [2 pts]
Sequential Logic. Rab Nawaz Khan Jadoon DCS. Lecturer COMSATS Lahore Pakistan. Department of Computer Science
 Sequential Logic Rab Nawaz Khan Jadoon DCS COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Lecturer COMSATS Lahore Pakistan Digital Logic and Computer Design Sequential Logic Combinational circuits with memory
Sequential Logic Rab Nawaz Khan Jadoon DCS COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Lecturer COMSATS Lahore Pakistan Digital Logic and Computer Design Sequential Logic Combinational circuits with memory
Section 3: Combinational Logic Design. Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Waterloo. Combinational Logic
 Section 3: Combinational Logic Design Major Topics Design Procedure Multilevel circuits Design with XOR gates Adders and Subtractors Binary parallel adder Decoders Encoders Multiplexers Programmed Logic
Section 3: Combinational Logic Design Major Topics Design Procedure Multilevel circuits Design with XOR gates Adders and Subtractors Binary parallel adder Decoders Encoders Multiplexers Programmed Logic
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits. Lecture 19: Timing Analysis
 EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 19: Timing Analysis Outline Timing parameters Clock nonidealities (skew and jitter) Impact of Clk skew on timing Impact of Clk jitter on timing Flip-flop-
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 19: Timing Analysis Outline Timing parameters Clock nonidealities (skew and jitter) Impact of Clk skew on timing Impact of Clk jitter on timing Flip-flop-
CS470: Computer Architecture. AMD Quad Core
 CS470: Computer Architecture Yashwant K. Malaiya, Professor malaiya@cs.colostate.edu AMD Quad Core 1 Architecture Layers Building blocks Gates, flip-flops Functional bocks: Combinational, Sequential Instruction
CS470: Computer Architecture Yashwant K. Malaiya, Professor malaiya@cs.colostate.edu AMD Quad Core 1 Architecture Layers Building blocks Gates, flip-flops Functional bocks: Combinational, Sequential Instruction
Example: vending machine
 Example: vending machine Release item after 15 cents are deposited Single coin slot for dimes, nickels o change Reset Coin Sensor Vending Machine FSM Open Release Mechanism Clock Spring 2005 CSE370 - guest
Example: vending machine Release item after 15 cents are deposited Single coin slot for dimes, nickels o change Reset Coin Sensor Vending Machine FSM Open Release Mechanism Clock Spring 2005 CSE370 - guest
Fault Modeling. Fault Modeling Outline
 Fault Modeling Outline Single Stuck-t Fault Model Other Fault Models Redundancy and Untestable Faults Fault Equivalence and Fault Dominance Method of oolean Difference Copyright 1998 Elizabeth M. Rudnick
Fault Modeling Outline Single Stuck-t Fault Model Other Fault Models Redundancy and Untestable Faults Fault Equivalence and Fault Dominance Method of oolean Difference Copyright 1998 Elizabeth M. Rudnick
Basic Computer Organization and Design Part 3/3
 Basic Computer Organization and Design Part 3/3 Adapted by Dr. Adel Ammar Computer Organization Interrupt Initiated Input/Output Open communication only when some data has to be passed --> interrupt. The
Basic Computer Organization and Design Part 3/3 Adapted by Dr. Adel Ammar Computer Organization Interrupt Initiated Input/Output Open communication only when some data has to be passed --> interrupt. The
ELEN Electronique numérique
 ELEN0040 - Electronique numérique Patricia ROUSSEAUX Année académique 2014-2015 CHAPITRE 3 Combinational Logic Circuits ELEN0040 3-4 1 Combinational Functional Blocks 1.1 Rudimentary Functions 1.2 Functions
ELEN0040 - Electronique numérique Patricia ROUSSEAUX Année académique 2014-2015 CHAPITRE 3 Combinational Logic Circuits ELEN0040 3-4 1 Combinational Functional Blocks 1.1 Rudimentary Functions 1.2 Functions
CSE370: Introduction to Digital Design
 CSE370: Introduction to Digital Design Course staff Gaetano Borriello, Brian DeRenzi, Firat Kiyak Course web www.cs.washington.edu/370/ Make sure to subscribe to class mailing list (cse370@cs) Course text
CSE370: Introduction to Digital Design Course staff Gaetano Borriello, Brian DeRenzi, Firat Kiyak Course web www.cs.washington.edu/370/ Make sure to subscribe to class mailing list (cse370@cs) Course text
ALU A functional unit
 ALU A functional unit that performs arithmetic operations such as ADD, SUB, MPY logical operations such as AND, OR, XOR, NOT on given data types: 8-,16-,32-, or 64-bit values A n-1 A n-2... A 1 A 0 B n-1
ALU A functional unit that performs arithmetic operations such as ADD, SUB, MPY logical operations such as AND, OR, XOR, NOT on given data types: 8-,16-,32-, or 64-bit values A n-1 A n-2... A 1 A 0 B n-1
Lab 3 Revisited. Zener diodes IAP 2008 Lecture 4 1
 Lab 3 Revisited Zener diodes R C 6.091 IAP 2008 Lecture 4 1 Lab 3 Revisited +15 Voltage regulators 555 timers 270 1N758 0.1uf 5K pot V+ V- 2N2222 0.1uf V o. V CC V Vin s = 5 V Vc V c Vs 1 e t = RC Threshold
Lab 3 Revisited Zener diodes R C 6.091 IAP 2008 Lecture 4 1 Lab 3 Revisited +15 Voltage regulators 555 timers 270 1N758 0.1uf 5K pot V+ V- 2N2222 0.1uf V o. V CC V Vin s = 5 V Vc V c Vs 1 e t = RC Threshold
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison. Fall Midterm Examination CLOSED BOOK
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison ECE 553: Testing and Testable Design of Digital Systems Fall 2014-2015 Midterm Examination CLOSED BOOK Kewal K. Saluja
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison ECE 553: Testing and Testable Design of Digital Systems Fall 2014-2015 Midterm Examination CLOSED BOOK Kewal K. Saluja
T st Cost Reduction LG Electronics Lee Y, ong LG Electronics 2009
 Test Cost Reduction LG Electronics Lee, Yong LG Electronics 2009 Contents Introduction Key factors for test cost reduction in DFT Test vector volume Low cost ATE Test time Reuse a large block Test cost
Test Cost Reduction LG Electronics Lee, Yong LG Electronics 2009 Contents Introduction Key factors for test cost reduction in DFT Test vector volume Low cost ATE Test time Reuse a large block Test cost
Programmable Logic Devices
 Programmable Logic Devices Mohammed Anvar P.K AP/ECE Al-Ameen Engineering College PLDs Programmable Logic Devices (PLD) General purpose chip for implementing circuits Can be customized using programmable
Programmable Logic Devices Mohammed Anvar P.K AP/ECE Al-Ameen Engineering College PLDs Programmable Logic Devices (PLD) General purpose chip for implementing circuits Can be customized using programmable
NTE74177 Integrated Circuit TTL 35Mhz Presettable Binary Counter/Latch
 NTE74177 Integrated Circuit TTL 35Mhz Presettable Binary Counter/Latch Description: The NTE74177 is a high speed monolithic counter in a 14 Lead plastic DIP type package consisting of four DC coupled master
NTE74177 Integrated Circuit TTL 35Mhz Presettable Binary Counter/Latch Description: The NTE74177 is a high speed monolithic counter in a 14 Lead plastic DIP type package consisting of four DC coupled master
 vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com ANNA UNIVERSITY- COMBATORE B.E./ B.TECH. DEGREE EXAMINATION - JUNE 2009. ELECTRICAL & ELECTONICS ENGG. - FOURTH SEMESTER DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS PART-A
vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com vidyarthiplus.com ANNA UNIVERSITY- COMBATORE B.E./ B.TECH. DEGREE EXAMINATION - JUNE 2009. ELECTRICAL & ELECTONICS ENGG. - FOURTH SEMESTER DIGITAL LOGIC CIRCUITS PART-A
Counters. We ll look at different kinds of counters and discuss how to build them
 Counters We ll look at different kinds of counters and discuss how to build them These are not only examples of sequential analysis and design, but also real devices used in larger circuits 1 Introducing
Counters We ll look at different kinds of counters and discuss how to build them These are not only examples of sequential analysis and design, but also real devices used in larger circuits 1 Introducing
S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [DE/ED/EI/EJ/EN/ET/EV/EX/IC/IE/IS/IU/MU] Principles of Digital Techniques
![S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [DE/ED/EI/EJ/EN/ET/EV/EX/IC/IE/IS/IU/MU] Principles of Digital Techniques S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [DE/ED/EI/EJ/EN/ET/EV/EX/IC/IE/IS/IU/MU] Principles of Digital Techniques](/thumbs/82/86792063.jpg) S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [DE/ED/EI/EJ/EN/ET/EV/EX/IC/IE/IS/IU/MU] Principles of Digital Techniques Time: 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1(a) Attempt any SIX of the following : [12]
S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [DE/ED/EI/EJ/EN/ET/EV/EX/IC/IE/IS/IU/MU] Principles of Digital Techniques Time: 3 Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 100 Q.1(a) Attempt any SIX of the following : [12]
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: J. Rose and
University of Toronto Faculty of Applied Science and Engineering Edward S. Rogers Sr. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Examination ECE 241F - Digital Systems Examiners: J. Rose and
Latches. October 13, 2003 Latches 1
 Latches The second part of CS231 focuses on sequential circuits, where we add memory to the hardware that we ve already seen. Our schedule will be very similar to before: We first show how primitive memory
Latches The second part of CS231 focuses on sequential circuits, where we add memory to the hardware that we ve already seen. Our schedule will be very similar to before: We first show how primitive memory
NTE74176 Integrated Circuit TTL 35Mhz Presettable Decade Counter/Latch
 NTE74176 Integrated Circuit TTL 35Mhz Presettable Decade Counter/Latch Description: The NTE74176 is a high speed monolithic counter in a 14 Lead plastic DIP type package consisting of four DC coupled master
NTE74176 Integrated Circuit TTL 35Mhz Presettable Decade Counter/Latch Description: The NTE74176 is a high speed monolithic counter in a 14 Lead plastic DIP type package consisting of four DC coupled master
Parity Checker Example. EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 9 - Finite State Machines 1. Formal Design Process. Formal Design Process
 Parity Checker Example A string of bits has even parity if the number of 1 s in the string is even. Design a circuit that accepts a bit-serial stream of bits and outputs a 0 if the parity thus far is even
Parity Checker Example A string of bits has even parity if the number of 1 s in the string is even. Design a circuit that accepts a bit-serial stream of bits and outputs a 0 if the parity thus far is even
Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements
 CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Instructor: Mohsen Imani UC San Diego Slides from: Prof.Tajana Simunic Rosing
CSE4: Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems Adders, subtractors comparators, multipliers and other ALU elements Instructor: Mohsen Imani UC San Diego Slides from: Prof.Tajana Simunic Rosing
Fundamentals of Boolean Algebra
 UNIT-II 1 Fundamentals of Boolean Algebra Basic Postulates Postulate 1 (Definition): A Boolean algebra is a closed algebraic system containing a set K of two or more elements and the two operators and
UNIT-II 1 Fundamentals of Boolean Algebra Basic Postulates Postulate 1 (Definition): A Boolean algebra is a closed algebraic system containing a set K of two or more elements and the two operators and
EECS Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. FSMs 9/11/2007
 EECS 150 - Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems FSMs 9/11/2007 Sarah Bird Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Slides borrowed from David Culler
EECS 150 - Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems FSMs 9/11/2007 Sarah Bird Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley Slides borrowed from David Culler
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FFs revisited, FIFOs, ECCs, LSFRs. Cross-coupled NOR gates
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FFs revisited, FIFOs, ECCs, LSFRs April 16, 2009 John Wawrzynek Spring 2009 EECS150 - Lec24-blocks Page 1 Cross-coupled NOR gates remember, If both R=0 & S=0, then
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FFs revisited, FIFOs, ECCs, LSFRs April 16, 2009 John Wawrzynek Spring 2009 EECS150 - Lec24-blocks Page 1 Cross-coupled NOR gates remember, If both R=0 & S=0, then
Chapter 2 Fault Modeling
 Chapter 2 Fault Modeling Jin-Fu Li Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Outline Why Model Faults? Fault Models (Faults)
Chapter 2 Fault Modeling Jin-Fu Li Advanced Reliable Systems (ARES) Lab. Department of Electrical Engineering National Central University Jungli, Taiwan Outline Why Model Faults? Fault Models (Faults)
Digital Control of Electric Drives
 Digital Control of Electric Drives Logic Circuits - equential Description Form, Finite tate Machine (FM) Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering Ver.. J. Zdenek 27 Logic
Digital Control of Electric Drives Logic Circuits - equential Description Form, Finite tate Machine (FM) Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering Ver.. J. Zdenek 27 Logic
MOSIS REPORT. Spring MOSIS Report 1. MOSIS Report 2. MOSIS Report 3
 MOSIS REPORT Spring 2010 MOSIS Report 1 MOSIS Report 2 MOSIS Report 3 MOSIS Report 1 Design of 4-bit counter using J-K flip flop I. Objective The purpose of this project is to design one 4-bit counter
MOSIS REPORT Spring 2010 MOSIS Report 1 MOSIS Report 2 MOSIS Report 3 MOSIS Report 1 Design of 4-bit counter using J-K flip flop I. Objective The purpose of this project is to design one 4-bit counter
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits. Lecture 6: Power Consumption
 EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 6: Power Consumption Four Key Design Metrics for Digital ICs Cost of ICs Reliability Speed Power EE115C Winter 2017 2 Power and Energy Challenges
EE115C Winter 2017 Digital Electronic Circuits Lecture 6: Power Consumption Four Key Design Metrics for Digital ICs Cost of ICs Reliability Speed Power EE115C Winter 2017 2 Power and Energy Challenges
VLSI Design I. Defect Mechanisms and Fault Models
 VLSI Design I Defect Mechanisms and Fault Models He s dead Jim... Overview Defects Fault models Goal: You know the difference between design and fabrication defects. You know sources of defects and you
VLSI Design I Defect Mechanisms and Fault Models He s dead Jim... Overview Defects Fault models Goal: You know the difference between design and fabrication defects. You know sources of defects and you
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 26 - Faults and Error Correction. Types of Faults in Digital Designs
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 26 - Faults and Error Correction April 25, 2013 John Wawrzynek 1 Types of Faults in Digital Designs Design Bugs (function, timing, power draw) detected and corrected at
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 26 - Faults and Error Correction April 25, 2013 John Wawrzynek 1 Types of Faults in Digital Designs Design Bugs (function, timing, power draw) detected and corrected at
Introduction EE 224: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL CIRCUITS & COMPUTER DESIGN. Lecture 6: Sequential Logic 3 Registers & Counters 5/9/2010
 EE 224: INTROUCTION TO IGITAL CIRCUITS & COMPUTER ESIGN Lecture 6: Sequential Logic 3 Registers & Counters 05/10/2010 Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohio.edu Introduction 2 A Flip-Flop stores one bit of information
EE 224: INTROUCTION TO IGITAL CIRCUITS & COMPUTER ESIGN Lecture 6: Sequential Logic 3 Registers & Counters 05/10/2010 Avinash Kodi, kodi@ohio.edu Introduction 2 A Flip-Flop stores one bit of information
Memory, Latches, & Registers
 Memory, Latches, & Registers 1) Structured Logic Arrays 2) Memory Arrays 3) Transparent Latches 4) How to save a few bucks at toll booths 5) Edge-triggered Registers L13 Memory 1 General Table Lookup Synthesis
Memory, Latches, & Registers 1) Structured Logic Arrays 2) Memory Arrays 3) Transparent Latches 4) How to save a few bucks at toll booths 5) Edge-triggered Registers L13 Memory 1 General Table Lookup Synthesis
Ch 7. Finite State Machines. VII - Finite State Machines Contemporary Logic Design 1
 Ch 7. Finite State Machines VII - Finite State Machines Contemporary Logic esign 1 Finite State Machines Sequential circuits primitive sequential elements combinational logic Models for representing sequential
Ch 7. Finite State Machines VII - Finite State Machines Contemporary Logic esign 1 Finite State Machines Sequential circuits primitive sequential elements combinational logic Models for representing sequential
Sequential Logic Circuits
 Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of a sequential circuit,
Chapter 4 Sequential Logic Circuits 4 1 The defining characteristic of a combinational circuit is that its output depends only on the current inputs applied to the circuit. The output of a sequential circuit,
Design for Testability
 Design for Testability Outline Ad Hoc Design for Testability Techniques Method of test points Multiplexing and demultiplexing of test points Time sharing of I/O for normal working and testing modes Partitioning
Design for Testability Outline Ad Hoc Design for Testability Techniques Method of test points Multiplexing and demultiplexing of test points Time sharing of I/O for normal working and testing modes Partitioning
CPE/EE 422/522. Chapter 1 - Review of Logic Design Fundamentals. Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH. 1.1 Combinational Logic
 CPE/EE 422/522 Chapter - Review of Logic Design Fundamentals Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH UAH Chapter CPE/EE 422/522. Combinational Logic Combinational Logic has no control inputs. When the inputs to a combinational
CPE/EE 422/522 Chapter - Review of Logic Design Fundamentals Dr. Rhonda Kay Gaede UAH UAH Chapter CPE/EE 422/522. Combinational Logic Combinational Logic has no control inputs. When the inputs to a combinational
Roger L. Tokheim. Chapter 8 Counters Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
 Digital Electronics Principles & Applications Sixth Edition Roger L. Tokheim Chapter 8 Counters 2003 Glencoe/McGraw-Hill INTRODUCTION Overview of Counters Characteristics of Counters Ripple Up Counter
Digital Electronics Principles & Applications Sixth Edition Roger L. Tokheim Chapter 8 Counters 2003 Glencoe/McGraw-Hill INTRODUCTION Overview of Counters Characteristics of Counters Ripple Up Counter
3 Logic Function Realization with MSI Circuits
 3 Logic Function Realization with MSI Circuits Half adder A half-adder is a combinational circuit with two binary inputs (augund and addend bits) and two binary outputs (sum and carry bits). It adds the
3 Logic Function Realization with MSI Circuits Half adder A half-adder is a combinational circuit with two binary inputs (augund and addend bits) and two binary outputs (sum and carry bits). It adds the
ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN
 ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Dr. Eng. Haitham Omran, haitham.omran@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Wassim Alexan, wassim.joseph@guc.edu.eg Following the slides of Dr. Ahmed H. Madian Lecture 10 محرم 1439 ه Winter
ELCT201: DIGITAL LOGIC DESIGN Dr. Eng. Haitham Omran, haitham.omran@guc.edu.eg Dr. Eng. Wassim Alexan, wassim.joseph@guc.edu.eg Following the slides of Dr. Ahmed H. Madian Lecture 10 محرم 1439 ه Winter
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FSMs & Counters
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FSMs & Counters April 8, 2010 John Wawrzynek Spring 2010 EECS150 - Lec22-counters Page 1 One-hot encoding of states. One FF per state. State Encoding Why one-hot encoding?
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 23 - FSMs & Counters April 8, 2010 John Wawrzynek Spring 2010 EECS150 - Lec22-counters Page 1 One-hot encoding of states. One FF per state. State Encoding Why one-hot encoding?
ELEC Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10)
 ELEC 2200-002 Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10) Vishwani D. Agrawal James J. Danaher Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
ELEC 2200-002 Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2014 Sequential Circuits (Chapter 6) Finite State Machines (Ch. 7-10) Vishwani D. Agrawal James J. Danaher Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
NTE4035B Integrated Circuit CMOS, 4 Bit Parallel In/Parallel Out Shift Register
 NTE4035B Integrated Circuit CMOS, 4 Bit Parallel In/Parallel Out Shift Register Description: The NTE4035B is a 4 bit shift register in a 16 Lead DIP type package constructed with MOS P Channel an N Channel
NTE4035B Integrated Circuit CMOS, 4 Bit Parallel In/Parallel Out Shift Register Description: The NTE4035B is a 4 bit shift register in a 16 Lead DIP type package constructed with MOS P Channel an N Channel
EEE2135 Digital Logic Design
 EEE2135 Digital Logic Design Chapter 7. Sequential Circuits Design 서강대학교 전자공학과 1. Model of Sequential Circuits 1) Sequential vs. Combinational Circuits a. Sequential circuits: Outputs depend on both the
EEE2135 Digital Logic Design Chapter 7. Sequential Circuits Design 서강대학교 전자공학과 1. Model of Sequential Circuits 1) Sequential vs. Combinational Circuits a. Sequential circuits: Outputs depend on both the
2009 Spring CS211 Digital Systems & Lab CHAPTER 2: INTRODUCTION TO LOGIC CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 2: INTRODUCTION TO LOGIC CIRCUITS What will we learn? 2 Logic functions and circuits Boolean Algebra Logic gates and Synthesis CAD tools and VHDL Read Section 2.9 and 2.0 Terminology 3 Digital
CHAPTER 2: INTRODUCTION TO LOGIC CIRCUITS What will we learn? 2 Logic functions and circuits Boolean Algebra Logic gates and Synthesis CAD tools and VHDL Read Section 2.9 and 2.0 Terminology 3 Digital
Design for Manufacturability and Power Estimation. Physical issues verification (DSM)
 Design for Manufacturability and Power Estimation Lecture 25 Alessandra Nardi Thanks to Prof. Jan Rabaey and Prof. K. Keutzer Physical issues verification (DSM) Interconnects Signal Integrity P/G integrity
Design for Manufacturability and Power Estimation Lecture 25 Alessandra Nardi Thanks to Prof. Jan Rabaey and Prof. K. Keutzer Physical issues verification (DSM) Interconnects Signal Integrity P/G integrity
Lecture 5 Fault Modeling
 Lecture 5 Fault Modeling Why model faults? Some real defects in VLSI and PCB Common fault models Stuck-at faults Single stuck-at faults Fault equivalence Fault dominance and checkpoint theorem Classes
Lecture 5 Fault Modeling Why model faults? Some real defects in VLSI and PCB Common fault models Stuck-at faults Single stuck-at faults Fault equivalence Fault dominance and checkpoint theorem Classes
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison. Fall Midterm Examination CLOSED BOOK
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison ECE 553: Testing and Testable Design of Digital Systems Fall 203-204 Midterm Examination CLOSED OOK Kewal K. Saluja Date:
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Wisconsin Madison ECE 553: Testing and Testable Design of Digital Systems Fall 203-204 Midterm Examination CLOSED OOK Kewal K. Saluja Date:
Lecture 10: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design
 Lecture 0: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design. General Form Input Combinational Flip-flops Combinational Output Circuit Circuit Clock.. Moore type has outputs dependent only on the state, e.g. ripple
Lecture 0: Synchronous Sequential Circuits Design. General Form Input Combinational Flip-flops Combinational Output Circuit Circuit Clock.. Moore type has outputs dependent only on the state, e.g. ripple
( c) Give logic symbol, Truth table and circuit diagram for a clocked SR flip-flop. A combinational circuit is defined by the function
 Question Paper Digital Electronics (EE-204-F) MDU Examination May 2015 1. (a) represent (32)10 in (i) BCD 8421 code (ii) Excess-3 code (iii) ASCII code (b) Design half adder using only NAND gates. ( c)
Question Paper Digital Electronics (EE-204-F) MDU Examination May 2015 1. (a) represent (32)10 in (i) BCD 8421 code (ii) Excess-3 code (iii) ASCII code (b) Design half adder using only NAND gates. ( c)
ECE321 Electronics I
 ECE321 Electronics I Lecture 1: Introduction to Digital Electronics Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Tuesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: payman@ece.unm.edu Slide: 1 Textbook
ECE321 Electronics I Lecture 1: Introduction to Digital Electronics Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Tuesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: payman@ece.unm.edu Slide: 1 Textbook
IHS 3: Test of Digital Systems R.Ubar, A. Jutman, H-D. Wuttke
 IHS 3: Test of Digital Systems R.Ubar, A. Jutman, H-D. Wuttke Integrierte Hard- und Softwaresysteme RT-Level Design data path and control path on RT-level RT level simulation Functional units (F1,..,F4)
IHS 3: Test of Digital Systems R.Ubar, A. Jutman, H-D. Wuttke Integrierte Hard- und Softwaresysteme RT-Level Design data path and control path on RT-level RT level simulation Functional units (F1,..,F4)
EECS 579: Test Generation 4. Test Generation System
 EECS 579: Test Generation 4 Other Combinational ATPG Algorithms SOCRATES Structure-Oriented Cost-Reducing Automatic TESt pattern generation [Schultz et al. 988] An ATPG system not just a test generation
EECS 579: Test Generation 4 Other Combinational ATPG Algorithms SOCRATES Structure-Oriented Cost-Reducing Automatic TESt pattern generation [Schultz et al. 988] An ATPG system not just a test generation
Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital Electronics Prelim Question Paper Solution ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD = B
![Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital Electronics Prelim Question Paper Solution ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD = B Vidyalankar S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital Electronics Prelim Question Paper Solution ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD ABCD = B](/thumbs/84/91058397.jpg) . (a). (b). (c) S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] igital Electronics Prelim Question Paper Solution ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC = B LHS = ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC But ( ) = = ABC( ) ABC( ) ABC( ) ABC( )
. (a). (b). (c) S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] igital Electronics Prelim Question Paper Solution ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC = B LHS = ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC ABC But ( ) = = ABC( ) ABC( ) ABC( ) ABC( )
FAULT MODELING. Chapter Defects, Errors, and Faults
 Chapter 4 FAULT MODELING... The extreme difficulty of obtaining solutions by conventional mathematical analysis has led in the past to the use of highly unrealistic models simply because they led to equations
Chapter 4 FAULT MODELING... The extreme difficulty of obtaining solutions by conventional mathematical analysis has led in the past to the use of highly unrealistic models simply because they led to equations
CHAPTER 9: SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 9: ASYNCHRONOUS SEUENTIAL CIRCUITS Chapter Objectives 2 Sequential circuits that are not snchronized b a clock Asnchronous circuits Analsis of Asnchronous circuits Snthesis of Asnchronous circuits
CHAPTER 9: ASYNCHRONOUS SEUENTIAL CIRCUITS Chapter Objectives 2 Sequential circuits that are not snchronized b a clock Asnchronous circuits Analsis of Asnchronous circuits Snthesis of Asnchronous circuits
Topics. Dynamic CMOS Sequential Design Memory and Control. John A. Chandy Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Connecticut
 Topics Dynamic CMOS Sequential Design Memory and Control Dynamic CMOS In static circuits at every point in time (except when switching) the output is connected to either GND or V DD via a low resistance
Topics Dynamic CMOS Sequential Design Memory and Control Dynamic CMOS In static circuits at every point in time (except when switching) the output is connected to either GND or V DD via a low resistance
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals
 ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 18: March 27, 2018 Dynamic Logic, Charge Injection Lecture Outline! Sequential MOS Logic " D-Latch " Timing Constraints! Dynamic Logic " Domino
ESE 570: Digital Integrated Circuits and VLSI Fundamentals Lec 18: March 27, 2018 Dynamic Logic, Charge Injection Lecture Outline! Sequential MOS Logic " D-Latch " Timing Constraints! Dynamic Logic " Domino
Sequential vs. Combinational
 Sequential Circuits Sequential vs. Combinational Combinational Logic: Output depends only on current input TV channel selector (-9) inputs system outputs Sequential Logic: Output depends not only on current
Sequential Circuits Sequential vs. Combinational Combinational Logic: Output depends only on current input TV channel selector (-9) inputs system outputs Sequential Logic: Output depends not only on current
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN. Week 7 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 7 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS: LATCHES Overview Circuits require memory to store intermediate
ECEN 248: INTRODUCTION TO DIGITAL SYSTEMS DESIGN Week 7 Dr. Srinivas Shakkottai Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering SEQUENTIAL CIRCUITS: LATCHES Overview Circuits require memory to store intermediate
Digital Logic: Boolean Algebra and Gates. Textbook Chapter 3
 Digital Logic: Boolean Algebra and Gates Textbook Chapter 3 Basic Logic Gates XOR CMPE12 Summer 2009 02-2 Truth Table The most basic representation of a logic function Lists the output for all possible
Digital Logic: Boolean Algebra and Gates Textbook Chapter 3 Basic Logic Gates XOR CMPE12 Summer 2009 02-2 Truth Table The most basic representation of a logic function Lists the output for all possible
Vidyalankar. S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital System Design. Q.1 Solve following : [20] Q.1(a) Explain the following decimals in gray code form
![Vidyalankar. S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital System Design. Q.1 Solve following : [20] Q.1(a) Explain the following decimals in gray code form Vidyalankar. S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital System Design. Q.1 Solve following : [20] Q.1(a) Explain the following decimals in gray code form](/thumbs/96/126594189.jpg) S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital System Design Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Paper Solution [Marks : 80 Q.1 Solve following : [20] Q.1(a) Explain the following decimals in gray code form [5] (i) (42) 10 (ii) (17)
S.E. Sem. III [EXTC] Digital System Design Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Paper Solution [Marks : 80 Q.1 Solve following : [20] Q.1(a) Explain the following decimals in gray code form [5] (i) (42) 10 (ii) (17)
EE141Microelettronica. CMOS Logic
 Microelettronica CMOS Logic CMOS logic Power consumption in CMOS logic gates Where Does Power Go in CMOS? Dynamic Power Consumption Charging and Discharging Capacitors Short Circuit Currents Short Circuit
Microelettronica CMOS Logic CMOS logic Power consumption in CMOS logic gates Where Does Power Go in CMOS? Dynamic Power Consumption Charging and Discharging Capacitors Short Circuit Currents Short Circuit
