International Workshop on Instrumentation for Planetary Missions (2012)
|
|
|
- Amice Patrick
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 COMPACT IMAGERS BASED ON MESSENGER S MERCURY DUAL IMAGING SYSTEM. Nancy L. Chabot 1, Scott L. Murchie 1, S. Edward Hawkins III 1, John R. Hayes 1, John D. Boldt 1, Olivier S. Barnouin 1, Kevin Heffernan 1, and Matthew W. Noble 1 ; 1 Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, Johns Hopkins Road, Laurel, MD, 20723, USA. Introduction Two planetary characteristics addressed by imaging are the morphology and spectral properties of planetary surfaces and atmospheres. These characteristics can inform questions about the geologic materials present on a planetary surface, their histories, the nature and timing of tectonic deformation, the history of such processes as cratering, volcanism, and erosion, and the characteristics and dynamics of atmospheres. Fitting the images required to address such science questions into available resources, including onboard recorder space and downlink bandwidth, is a universal challenge. A data collection strategy commonly used is to collect higher-resolution, single-band images to characterize morphology, and multispectral images that employ some strategy to reduce data volume and compensate for the number of wavelengths. For example on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment [1] collects color images at reduced spatial resolution, and the Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars [2] collects most of its spectral measurements at reduced spatial resolution to extend coverage. Alternatively, the Pancam imagers on the Mars Exploration Rovers (MERs) use a mix of strategies to control volume of multispectral images, including greater compression for panoramas and less compression for nested "spots" [3]. Supporting objectives include imaging of stars to characterize alignment or for optical navigation, and imaging of a radiometric target to improve calibration accuracy. MESSENGER s Mercury Dual Imaging System (MDIS) [4] addresses these challenges with two miniature cameras, a monochrome narrow-angle camera (NAC) optimized for imaging morphology, and a multispectral wide-angle camera (WAC). With updates that incorporate newer technologies, these two designs have capabilities well matched to science questions at a variety of inner solar system and small-body targets. Design Approach to MDIS Both MDIS cameras use a common focal plane design with a Thomson-Atmel 7887A charge-coupled device (CCD). The NAC is an off-axis reflective system with a 550-mm focal length, a 1.5 square field of view (FOV), and an instantaneous field of view (IFOV) of 25 µrad/pixel, providing 10 m/pixel from 400 km range. The WAC is a four-element refractive telescope with a 78-mm focal length, 10.5 FOV, 178 µrad IFOV, and 12-position filter wheel. Eleven of the filters are narrow-band and were selected to measure absorptions due to Fe 2+ in glass and silicates. A single clear filter is used for star imaging and optical navigation. Both cameras are supported by Instrument Control Electronics that host instrument software, including automatic exposure control with an internal model of the camera filters and pixel-binning states that allow rapid switching between cameras or filters. Exposure times can be clamped by command, providing a simple way to prevent image saturation and smear without prior knowledge of the radiometry of any given scene, requiring knowledge only of spacecraft altitude and velocity. Four design challenges specific to a Mercury-orbiting spacecraft drove the integration of the WAC and NAC into a dual-camera system (Fig. 1) [5]. First, a relatively small mass for the payload forced miniaturization and light-weighting of the imagers. Second, the phased-array antenna's downlink capabilities require aggressive data compression to fit images with the best attainable resolution into available bandwidth. A menu of options includes pixel binning, conversion of image data from 12 to 8 bits using look-up tables optimized to different types of scenes, and two methods of image compression: a lossless Fast algorithm performed in hardware, and a more aggressive wavelet algorithm. Wavelet compression is performed on "raw" images stored temporarily on the spacecraft solid-state recorder using the spacecraft main processor. A major limitation on imaging campaigns is thus recorder space. Figure 1. The Mercury Dual Imaging System (MDIS), showing the WAC, NAC, radiators, and pivot.
2 Third, the spacecraft's pointing capability is limited by its need to keep a sunshade pointed toward the Sun. To point as required for imaging campaigns, both the WAC and NAC are mounted on and use the same pivot platform. Fourth, a thermal control system including a Be radiator and heat pipes manages the thermal load from Mercury while keeping both camera CCDs at operating temperatures usually below -10 C. In addition, the spectral filters are narrow-band by design to prevent image saturation at Mercury's distance from the Sun and to attenuate input of Mercury thermal radiation. The pivot provides additional capabilities for calibration and serves to prevent contamination. MDIS is mounted inside of MESSENGER's launch adaptor ring. In its "stowed" position both cameras look into the shaded spacecraft deck and are protected from contamination by volatiles outgassed from hot, solarilluminated parts of the spacecraft. With 180 of rotation, the boresights align with those of other instruments. At an intermediate angle, both cameras view a solar-illuminated Spectralon plaque on the inside of the adaptor ring, which can be illuminated (at large heliocentric distances) by slewing the spacecraft. The plaque allowed WAC and NAC flat-field calibrations to be rederived in flight, enabling correction of shifts in the shadows cast by small particulates ("dust donuts") during launch that otherwise would have persisted as instrument calibration artifacts. MDIS Observations and Performance MESSENGER was launched in August 2004 and experienced a cruise of ~6.5 years prior to insertion into orbit about Mercury on 18 March MESSENGER s trajectory included six planetary flybys: one of Earth (Aug. 2005), two of Venus (Oct. 2006, June 2007), and three of Mercury (Jan. 2008, Sep. 2008, Sep. 2009). During the Mercury flybys, images were acquired with both NAC and WAC, providing the first spacecraft images of Mercury since the Mariner 10 mission. Additionally, during the cruise phase, MDIS obtained images of stars, Earth, and Venus for calibration and end-to-end testing, to conduct repeated observations near perihelion to search for vulcanoids, and to capture a portrait of the Solar System from near Mercury orbit. A total of 13,080 MDIS images were acquired during cruise. Cruise observations by MDIS refined instrument alignment and calibration knowledge, proved operational scenarios, and readied the instrument for Mercury orbit. During MESSENGER s one-year primary mission, MDIS successfully acquired global imaging of Mercury for morphology, stereo, and color studies as well as targeted high-resolution imaging of areas of high science priority, adding 88,746 images in all. Figure 2 shows orthographic projections of the global monochrome and color maps of Mercury acquired during the primary mission. The monochrome map, acquired with MDIS pointed near nadir at times of low-sun illumination, is well suited for discerning surface morphology and covers >99% of the surface at an average resolution of 200 m/pixel. MESSENGER s orbit about Mercury is highly eccentric, passing low over the northern periapsis (~ km altitude) and high over the south (~15,000 km apoapsis altitude during the primary mission). To balance global resolution and manage data volume, the WAC is used for the northern part of the monochrome map and the NAC to image the southern regions. Figure 2. Monochrome and enhanced color global maps of Mercury assembled from MDIS orbital images acquired during MESSENGER s primary mission.
3 A complementary map, acquired under similar illumination conditions but with an off-nadir viewing geometry to provide stereo convergence, covers >92% of the surface. The color map was acquired through eight of the 11 narrow-band color filters on the WAC, emphasizing spectral coverage at the expense of resolution (1 km/pixel) to fit within available spacecraft recorder resources. The 8-color map covers >99% of Mercury s surface. In general, images were acquired as 8-bit images with wavelet compression, to fit imaging into available spacecraft resources. Due to MESSENGER s highly eccentric orbit, NAC can image much of Mercury s northern hemisphere at resolutions substantially higher than are regularly utilized during global mapping. Targeted, high-resolution NAC images acquired by the MESSENGER mission to date have an average resolution of 26 m/pixel, and only ~4% of Mercury s surface has been imaged at resolutions of 50 m/pixel or better. Despite the small fraction of Mercury s surface covered to date, targeting of the high-resolution NAC images has enabled them to be of high scientific value, leading to observations of small-scale geologic features on Mercury, such as the previously unknown hollows [6] (Fig. 3). In addition to acquiring global maps and highresolution targeted images, MDIS observations during MESSENGER s primary mission included repeated imaging of Mercury s south polar region to map regions of permanent shadow; weekly imaging of Mercury s limb to help constrain global shape; other targeted images to obtain color at high resolution or under specific photometric conditions; simultaneous imaging with observations by other MDIS instruments to provide "context;" and regular imaging of stars to track possible drift of the camera alignment due to extreme thermal cycling in Mercury orbit. The MDIS thermal design and other instrument features have performed as expected from instrument design and prior testing. MESSENGER is currently conducting an extended mission. New global maps are being acquired that are better optimized for terrain modeling, recognition of low-slope landforms, and smaller-scale color variations than was possible during the primary mission when the focus was on obtaining the first global maps. One pair of maps is designed for stereo with reduced gaps due to shadows: a near-nadir global map at ~200 m/pixel with higher-sun illumination than during the primary mission monochrome mapping, and a second, off-nadir map at the same illumination that is its stereo complement. A third new monochrome map, also at ~200 m/pixel, is taken with very low-sun illumination to accentuate subtle topography. In addition, the northern hemisphere is being mapped in color at much better resolution of ~ m/pixel, this time using only three of 11 filters to fit within resources. Other imaging campaigns include repeated imaging of the north polar region to improve mapping of that pole's permanently shadowed regions, and continued targeted, limb, and calibration imaging. To date, MDIS has acquired >130,000 images since launch. Figure 3. Strip of targeted NAC images of hollows on Mercury, with enhanced WAC color overlaid. Image width is 20 km. Adapting the WAC and NAC to New Missions The basic designs of the NAC and WAC are capable of addressing morphologic and multispectral investigations at a variety of planetary bodies. In terms of spatial sampling and usage, NAC is comparable to the MRO
4 Context Imager [8] but with a framing camera instead of a line scanner design. WAC is comparable to MER Pancam [3] but with better spatial resolution. Without the temperature environment specific to MESSENGER that drives the needs for sophisticated thermal control and pivoting, the WAC and NAC each become a free-standing imager (Fig. 4), with a mass of 2.6 or 2.3 kg, respectively. Lessons learned from in-flight performance of MDIS [7] and newer technology developed internally at the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory enable four design updates that suit the WAC and NAC well for missions to small bodies at distances to ~5 AU, where downlink bandwidth and recorder size are limitations. First, replacement of the Thomson-Atmel 7887A with a back-thinned E2V CCD, currently used by the Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) camera on the New Horizons mission, provides a fourfold increase in quantum efficiency and eliminates scattered light from the 7887A CCD s structure, which functions as a diffraction grating [7]. Second, widening of filter bandpasses provides additional throughput and enables short exposure times for low-albedo bodies, and for optical navigation or alignment calibrations imaging of at least three stars per frame with v mag (visual magnitude) <6.5 in the WAC and v mag <11 in the NAC. Third, optionally, a re-closeable cover can be added for protection during activities that risk contamination; the optional re-closable cover and cover motor are shown in the CAD models in Fig. 4. The inside of the cover, painted white, provides an easily accessible calibration target when illuminated by the Sun. The cover can be controlled by a copy of the CRISM shutter stepper motor [2], which has seen >400,000 cycles in-flight without incident. Fourth, data compression routines that on MESSENGER [4] (and MER [3] and MRO [1]) are performed by the spacecraft processor can be implemented in real time by instrument control electronics, relieving limitations driven by recorder size [9]. Testing on prototype instrument electronics demonstrates application to full-size images acquired at a 1 Hz rate, with compression artifacts no larger than those from the current MESSENGER flight software implementation. Example Use in New Missions Versions of the NAC and WAC have recently been included in several missions proposed for flight in the Discovery Program. One example is the Mars Moon Reconnaissance, Orbital, and Landed Investigation (MERLIN) [10]. In that mission concept, a spacecraft would rendezvous with one of the moons of Mars, conduct orbital measurements, make low flyovers to certify a site for landing, and then land and conduct in situ measurements. In the MERLIN mission profile, WAC images address geologic processes and effects of space weathering with near-global color mapping. WAC color images at millimeters-resolution that remain in focus during descent to the surface also address regolith heterogeneity. Near-global, morphologic and stereo imaging with the NAC addresses surface geologic processes and internal structure. NAC images also help certify a candidate landing site during low flyovers, and NAC is the primary optical navigation imager. a b Figure 4. CAD renderings of a next-generation (a) WAC and (b) NAC as free-standing instruments. A modified version of the NAC has also been proposed for the Comet Hopper (CHopper) mission currently under consideration by NASA for the next Discovery Mission selection. In that mission, an Advanced Stirling Radioisotope Generator (ASRG) powered spacecraft will rendezvous with a comet near its aphelion at 4.5 AU and follow the comet to perihelion near 0.7 AU. The CHopper Imager (CHI) has been adapted for the low light conditions expected at 4.5 AU. CHI is responsible for first acquiring the comet and then imaging the comet to develop a shape model. CHI takes advantage of the wellunderstood MDIS NAC optical design, with only its aperture increased to allow more light, and the sensitive E2V detector used by the LORRI camera currently flying aboard the New Horizons spacecraft.
5 References: [1] McEwen, A.S. et al. (2007), J. Geophys. Res., 112, E05S02, doi: / 2005JE [2] Murchie, S.L. et al. (2007), J. Geophys. Res., 112, doi: / 2006JE [3] Bell, J.F. et al. (2003) J. Geophys. Res., 108, 8063, doi: /2003je [4] Hawkins, S.E., III et al. (2007) Space Sci. Rev., 131, [5] Leary, J.C. et al. (2007) Space Sci. Rev., 131, [6] Blewett, D.T. et al. (2011), Science, 333, [7] Hawkins, S.E., III et al. (2009) Proceedings SPIE, 7441, 74410Z. [8] Malin, M.C. et al. (2007), J. Geophys. Res., 112, E05S04, doi: / 2006JE [9] Hayes, J.R. et al. (2009) Proceedings SPIE, 7455, 74550D. [10] Murchie, S.L. et al. (2012) Lunar Planet. Sci. 43, abstract Figure 5. CAD rendering of the proposed CHI camera derived from the MDIS NAC for the Comet Hopper mission.
SciBox, a Proven Automated Planning and Commanding System
 SciBox, a Proven Automated Planning and Commanding System Teck Choo, Edward Russell, Michael Kim February 25, 2014 2014 by The Johns Hopkins University/Applied Physics Laboratory. Published by The Aerospace
SciBox, a Proven Automated Planning and Commanding System Teck Choo, Edward Russell, Michael Kim February 25, 2014 2014 by The Johns Hopkins University/Applied Physics Laboratory. Published by The Aerospace
Feasible Mission Designs for Solar Probe Plus to Launch in 2015, 2016, 2017, or November 19, 2008
 Feasible Mission Designs for Solar Probe Plus to Launch in 2015, 2016, 2017, or 2018 2007 Solar Probe Study & Mission Requirements Trajectory study and mission design trades were conducted in the fall
Feasible Mission Designs for Solar Probe Plus to Launch in 2015, 2016, 2017, or 2018 2007 Solar Probe Study & Mission Requirements Trajectory study and mission design trades were conducted in the fall
Seminar BELA STAR SIMULATOR
 Seminar BELA STAR SIMULATOR Sumita Chakraborty, Michael Affolter, Jakob Neubert (external contractor), Stefan Graf, Daniele Piazza and many more Universität Bern Content > Mercury > BepiColombo > MPO and
Seminar BELA STAR SIMULATOR Sumita Chakraborty, Michael Affolter, Jakob Neubert (external contractor), Stefan Graf, Daniele Piazza and many more Universität Bern Content > Mercury > BepiColombo > MPO and
Presentation to SBAG January 2016
 Presentation to SBAG January 2016 Julie Castillo-Rogez (JPL/Caltech/NASA) Les Johnson (Marshall Space Flight Center/NASA) And the NEAScout Team Edit as appropriate AES EM-1 Secondary Payload Overview HEOMD
Presentation to SBAG January 2016 Julie Castillo-Rogez (JPL/Caltech/NASA) Les Johnson (Marshall Space Flight Center/NASA) And the NEAScout Team Edit as appropriate AES EM-1 Secondary Payload Overview HEOMD
Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera Image Retrieval For the Big Moon Dig
 Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera Image Retrieval For the Big Moon Dig Tom Riley TomRiley@WoodwareDesigns.com November 22, 2014 File: LROCameraRetrivalmmdddyy.docx Work in Progress LRO in orbit (artist
Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera Image Retrieval For the Big Moon Dig Tom Riley TomRiley@WoodwareDesigns.com November 22, 2014 File: LROCameraRetrivalmmdddyy.docx Work in Progress LRO in orbit (artist
HERA MISSION & CM16 lessons learned
 HERA MISSION HERA MISSION & CM16 lessons learned (CM16) Schedule criticality for 2020 launch Prepare Asteroid mission with launch opportunities in 2023 (with back-up in 2024 and 2025) (CM16) Payload selection
HERA MISSION HERA MISSION & CM16 lessons learned (CM16) Schedule criticality for 2020 launch Prepare Asteroid mission with launch opportunities in 2023 (with back-up in 2024 and 2025) (CM16) Payload selection
REVISED COORDINATES FOR APOLLO HARDWARE
 REVISED COORDINATES FOR APOLLO HARDWARE R. V. Wagner *, E. J. Speyerer, K. N. Burns, J. Danton, M.S. Robinson Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera, School of Earth and Space Exploration, Arizona State University,
REVISED COORDINATES FOR APOLLO HARDWARE R. V. Wagner *, E. J. Speyerer, K. N. Burns, J. Danton, M.S. Robinson Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera, School of Earth and Space Exploration, Arizona State University,
The Compact Infrared Imager and Radiometer
 The Compact Infrared Imager and Radiometer Earth System Science from a 6U nanosat? Neil Bowles (Univ. Oxford) On behalf of the CIIR Consortium. 22 April 2015 CEOI-ST Technology 1 The Why study a tightly
The Compact Infrared Imager and Radiometer Earth System Science from a 6U nanosat? Neil Bowles (Univ. Oxford) On behalf of the CIIR Consortium. 22 April 2015 CEOI-ST Technology 1 The Why study a tightly
Toward Venus orbit insertion of Akatsuki
 Toward Venus orbit insertion of Akatsuki Takeshi Imamura (JAXA, Japan) Lightning and Airglow Camera Mid-IR Camera UV Imager Ultra-Stable Oscillator 1µm Camera 2µm Camera Development and launch Objective:
Toward Venus orbit insertion of Akatsuki Takeshi Imamura (JAXA, Japan) Lightning and Airglow Camera Mid-IR Camera UV Imager Ultra-Stable Oscillator 1µm Camera 2µm Camera Development and launch Objective:
AVIATR: Aerial Vehicle for In situ and Airborne Titan Reconnaissance
 AVIATR: Aerial Vehicle for In situ and Airborne Titan Reconnaissance Jason W. Barnes Assistant Professor of Physics University of Idaho OPAG Meeting 2011 October 20 Pasadena, CA TSSM: Titan Saturn System
AVIATR: Aerial Vehicle for In situ and Airborne Titan Reconnaissance Jason W. Barnes Assistant Professor of Physics University of Idaho OPAG Meeting 2011 October 20 Pasadena, CA TSSM: Titan Saturn System
Europa Lander Mission Study: Science Dave Senske (JPL) Deputy Europa Study Scientist OPAG March 29, 2012
 Europa Lander Mission Study: Science Dave Senske (JPL) Deputy Europa Study Scientist OPAG March 29, 2012 3/29/12 23 Science from Europa s Surface For key habitability science, Europa surface materials
Europa Lander Mission Study: Science Dave Senske (JPL) Deputy Europa Study Scientist OPAG March 29, 2012 3/29/12 23 Science from Europa s Surface For key habitability science, Europa surface materials
Exercise 1: Earth s Moon
 PHYS1014 Physical Science Summer 2013 Professor Kenny L. Tapp Exercise 1: Earth s Moon Complete and submit this packet, securely stapled, at the beginning of Exam 1. PART I --- Online Video Lecture from
PHYS1014 Physical Science Summer 2013 Professor Kenny L. Tapp Exercise 1: Earth s Moon Complete and submit this packet, securely stapled, at the beginning of Exam 1. PART I --- Online Video Lecture from
*C. Pan 1, F. Weng 2, T. Beck 2 and S. Ding 3
 S NPP Ozone Mapping Profiler Suite Nadir Instrument Radiometric Calibration *C. Pan 1, F. Weng 2, T. Beck 2 and S. Ding 3 Curtsey of Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. * 1 ESSIC, University of Maryland,
S NPP Ozone Mapping Profiler Suite Nadir Instrument Radiometric Calibration *C. Pan 1, F. Weng 2, T. Beck 2 and S. Ding 3 Curtsey of Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. * 1 ESSIC, University of Maryland,
NASA Planetary Science Programs
 NASA Planetary Science Programs James L. Green NASA, Planetary Science Division February 19, 2015 Presentation at OPAG 1 Outline Mission events Passed FY15 Budget elements President s FY16 Budget Discovery
NASA Planetary Science Programs James L. Green NASA, Planetary Science Division February 19, 2015 Presentation at OPAG 1 Outline Mission events Passed FY15 Budget elements President s FY16 Budget Discovery
BOWSER Balloon Observatory for Wavelength and Spectral Emission Readings
 COSGC Space Research Symposium 2009 BOWSER Balloon Observatory for Wavelength and Spectral Emission Readings BOWSER 1 Mission Premise 4.3 km above sea level 402.3km above sea level BOWSER 2 Information
COSGC Space Research Symposium 2009 BOWSER Balloon Observatory for Wavelength and Spectral Emission Readings BOWSER 1 Mission Premise 4.3 km above sea level 402.3km above sea level BOWSER 2 Information
Part 1: the terrestrial planets
 Mercury close up Part 1: the terrestrial planets The weird day on Mercury Weirdness is due to the fact that the rota:on period is comparable to period of revolu:on, and that they are related by the ra:o
Mercury close up Part 1: the terrestrial planets The weird day on Mercury Weirdness is due to the fact that the rota:on period is comparable to period of revolu:on, and that they are related by the ra:o
1 A photometric probe for Pan-STARRS
 The Pan-STARRS Imaging Sky Probe B.R. Granett, K.C. Chambers, E.A. Magnier, K. Fletcher and the Pan-STARRS Project Team University of Hawai i Institute for Astronomy Abstract Photometric performance is
The Pan-STARRS Imaging Sky Probe B.R. Granett, K.C. Chambers, E.A. Magnier, K. Fletcher and the Pan-STARRS Project Team University of Hawai i Institute for Astronomy Abstract Photometric performance is
Juno UV, Optical, & IR Remote Sensing
 Juno UV, Optical, & IR Remote Sensing Randy Gladstone UVS Lead Workshop on Jupiter s Aurora Anticipating Juno s Arrival 4 th July 2016 CU-LASP Boulder, CO 1 UVS Concept Drawing Telescope/Spectrograph Detector
Juno UV, Optical, & IR Remote Sensing Randy Gladstone UVS Lead Workshop on Jupiter s Aurora Anticipating Juno s Arrival 4 th July 2016 CU-LASP Boulder, CO 1 UVS Concept Drawing Telescope/Spectrograph Detector
Europe to the Moon. BHF 10 Feb 2005 SPC
 Europe to the Moon V162 lift-off on 27 September 2003 at 23:14:39 UTC The launch was perfect SMART-1 separated at 23:56:03 into a GTO (656 x 35,881 km): perfect injection 100 s later telemetry was received
Europe to the Moon V162 lift-off on 27 September 2003 at 23:14:39 UTC The launch was perfect SMART-1 separated at 23:56:03 into a GTO (656 x 35,881 km): perfect injection 100 s later telemetry was received
SBUV(/2) and SSBUV Solar Irradiance Measurements Matthew DeLand, Richard Cebula, Liang-Kang Huang Science Systems and Applications, Inc.
 SBUV(/2) and SSBUV Solar Irradiance Measurements Matthew DeLand, Richard Cebula, Liang-Kang Huang Science Systems and Applications, Inc. (SSAI) Solar Spectral Irradiance Variations Workshop NIST, Gaithersburg,
SBUV(/2) and SSBUV Solar Irradiance Measurements Matthew DeLand, Richard Cebula, Liang-Kang Huang Science Systems and Applications, Inc. (SSAI) Solar Spectral Irradiance Variations Workshop NIST, Gaithersburg,
Abstract HISAKI (SPRINT A) satellite is an earth orbiting EUV spectroscopic mission and launched on 14 Sep Extreme ultraviolet spectroscope (EX
 Pointing control of extreme ultraviolet spectroscope onboard the SPRINT A satellite F. Tsuchiya(1*), A. Yamazaki(2), G. Murakami(2), K. Yoshioka(2), T. Kimura(2), S. Sakai(2), K. Uemizu(3), T. Sakanoi(1),
Pointing control of extreme ultraviolet spectroscope onboard the SPRINT A satellite F. Tsuchiya(1*), A. Yamazaki(2), G. Murakami(2), K. Yoshioka(2), T. Kimura(2), S. Sakai(2), K. Uemizu(3), T. Sakanoi(1),
Feasibility of Using Commercial Star Trackers for On-Orbit Resident Space Object Detection
 Feasibility of Using Commercial Star Trackers for On-Orbit Resident Space Object Detection Samuel Clemens York University Regina Lee York University Paul Harrison Magellan Aerospace Warren Soh Magellan
Feasibility of Using Commercial Star Trackers for On-Orbit Resident Space Object Detection Samuel Clemens York University Regina Lee York University Paul Harrison Magellan Aerospace Warren Soh Magellan
SCIENCE WITH DIRECTED AERIAL DR. ALEXEY PANKINE GLOBAL AEROSPACE CORPORATION SAILING THE PLANETS
 : SCIENCE WITH DIRECTED AERIAL ROBOT EXPLORERS (DARE) DR. ALEXEY PANKINE GLOBAL AEROSPACE CORPORATION 1 NEW ARCHITECTURE FOR PLANETARY EXPLORATION KEY ELEMENTS: Long-Duration Planetary Balloon Platforms
: SCIENCE WITH DIRECTED AERIAL ROBOT EXPLORERS (DARE) DR. ALEXEY PANKINE GLOBAL AEROSPACE CORPORATION 1 NEW ARCHITECTURE FOR PLANETARY EXPLORATION KEY ELEMENTS: Long-Duration Planetary Balloon Platforms
PROBA 1. F. Teston ESA/ESTEC D/TEC-EL
 PROBA 1 F. Teston ESA/ESTEC D/TEC-EL Frederic.Teston@esa.int PROBA 1 launch PROBA 1 has been launched on 21 October 2001 Orbital parameters: Altitude: 681-561 km Near polar (inclination of 97.9 ) Sun-synchronous
PROBA 1 F. Teston ESA/ESTEC D/TEC-EL Frederic.Teston@esa.int PROBA 1 launch PROBA 1 has been launched on 21 October 2001 Orbital parameters: Altitude: 681-561 km Near polar (inclination of 97.9 ) Sun-synchronous
Science planning and operations for Mars Express
 Science planning and operations for Mars Express René Pischel and Tanja Zegers ESA/ESTEC, Research and Scientific Support Department, Postbus 299, 2200 AG Noordwijk, The Netherlands I. Introduction The
Science planning and operations for Mars Express René Pischel and Tanja Zegers ESA/ESTEC, Research and Scientific Support Department, Postbus 299, 2200 AG Noordwijk, The Netherlands I. Introduction The
JUICE/Laplace Mission Summary & Status
 JUICE/Laplace Mission Summary & Status C. Erd JUICE Instrument WS, Darmstadt 9/11/2011 Activities during the Reformulation Phase 1. Feasible JGO s/c as a starting point a. no re-design of s/c necessary
JUICE/Laplace Mission Summary & Status C. Erd JUICE Instrument WS, Darmstadt 9/11/2011 Activities during the Reformulation Phase 1. Feasible JGO s/c as a starting point a. no re-design of s/c necessary
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 ASTRO 102/104 Prelim 2 Name Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) This is version E of the exam. Please fill in (E). A) This
ASTRO 102/104 Prelim 2 Name Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) This is version E of the exam. Please fill in (E). A) This
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 ASTRO 102/104 Prelim 2 Name Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) This is version B of the exam. Please fill in (B). A) This
ASTRO 102/104 Prelim 2 Name Section MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) This is version B of the exam. Please fill in (B). A) This
NEW HORIZONS PLUTO APPROACH NAVIGATION
 AAS 04-136 NEW HORIZONS PLUTO APPROACH NAVIGATION James K. Miller, Dale R. Stanbridge, and Bobby G. Williams The navigation of the New Horizons spacecraft during approach to Pluto and its satellite Charon
AAS 04-136 NEW HORIZONS PLUTO APPROACH NAVIGATION James K. Miller, Dale R. Stanbridge, and Bobby G. Williams The navigation of the New Horizons spacecraft during approach to Pluto and its satellite Charon
The European Student Moon Orbiter (ESMO) A Small Mission for Education, Outreach, and Science
 (ESMO) A Small Mission for Education, Outreach, and Science Roger Walker, Matthew Cross Education Projects Unit, ESA Education Office ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands LEAG-ILEWG-SRR Meeting Cape Canaveral,
(ESMO) A Small Mission for Education, Outreach, and Science Roger Walker, Matthew Cross Education Projects Unit, ESA Education Office ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands LEAG-ILEWG-SRR Meeting Cape Canaveral,
FANTASTIC!! MARINER VENUS / MERCURY 1973 STATUS BULLETIN BULLETIN NO. 27
 MARINER VENUS / MERCURY 1973 STATUS BULLETIN FANTASTIC!! This picture of the densely cratered surface of Mercury was taken by Mariner 10 when the spacecraft was 18,200 kilometers (8085 miles) from the
MARINER VENUS / MERCURY 1973 STATUS BULLETIN FANTASTIC!! This picture of the densely cratered surface of Mercury was taken by Mariner 10 when the spacecraft was 18,200 kilometers (8085 miles) from the
MAVEN Community Meeting IUVS: The Imaging UltraViolet Spectrograph
 Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) MAVEN Community Meeting IUVS: The Imaging UltraViolet Spectrograph December 2, 2012 Nick Schneider IUVS Science Lead nick.schneider@lasp.colorado.edu Outline
Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) MAVEN Community Meeting IUVS: The Imaging UltraViolet Spectrograph December 2, 2012 Nick Schneider IUVS Science Lead nick.schneider@lasp.colorado.edu Outline
Cassini ISS. The Imaging Science Subsystem. (The Cameras)
 Cassini ISS The Imaging Science Subsystem (The Cameras) "We are the eyes of Cassini, our cameras capture all the dramatic sights and vistas there are to see around Saturn. And through their imagery, they
Cassini ISS The Imaging Science Subsystem (The Cameras) "We are the eyes of Cassini, our cameras capture all the dramatic sights and vistas there are to see around Saturn. And through their imagery, they
SCIAMACHY REFLECTANCE AND POLARISATION VALIDATION: SCIAMACHY VERSUS POLDER
 SCIAMACHY REFLECTANCE AND POLARISATION VALIDATION: SCIAMACHY VERSUS POLDER L. G. Tilstra (1), P. Stammes (1) (1) Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI), P.O. Box 201, 3730 AE de Bilt, The Netherlands
SCIAMACHY REFLECTANCE AND POLARISATION VALIDATION: SCIAMACHY VERSUS POLDER L. G. Tilstra (1), P. Stammes (1) (1) Royal Netherlands Meteorological Institute (KNMI), P.O. Box 201, 3730 AE de Bilt, The Netherlands
The Ozone Mapping and Profiler Suite (OMPS): From SNPP to JPSS-1
 The Ozone Mapping and Profiler Suite (OMPS): From SNPP to JPSS-1 *C. Pan 1 and F. Weng 2 Curtsey of BATC Aerosol Index * 1 ESSIC, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20740; 2 NOAA NESDIS/STAR, College
The Ozone Mapping and Profiler Suite (OMPS): From SNPP to JPSS-1 *C. Pan 1 and F. Weng 2 Curtsey of BATC Aerosol Index * 1 ESSIC, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20740; 2 NOAA NESDIS/STAR, College
Science Update SBAG July, Andrew Cheng (JHU/APL) Karl Hibbitts (JHU/APL) Eliot Young (SwRI)
 Science Update SBAG July, 2014 Andrew Cheng (JHU/APL) Karl Hibbitts (JHU/APL) Eliot Young (SwRI) Overview BOPPS science objectives BIRC calibration results UVVis update Science operations 4/23/14 2 BOPPS
Science Update SBAG July, 2014 Andrew Cheng (JHU/APL) Karl Hibbitts (JHU/APL) Eliot Young (SwRI) Overview BOPPS science objectives BIRC calibration results UVVis update Science operations 4/23/14 2 BOPPS
James L. Green Director, Planetary Science NASA
 James L. Green Director, Planetary Science NASA 1 Year of the Solar System Planetary Science Mission Events 2010 * September 16 Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter in PSD * November 4 EPOXI encounters Comet Hartley
James L. Green Director, Planetary Science NASA 1 Year of the Solar System Planetary Science Mission Events 2010 * September 16 Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter in PSD * November 4 EPOXI encounters Comet Hartley
Photometric modeling of the Moon using Lommel-Seeliger function and Chang E-1 IIM data
 Article Astronomy December 013 Vol.58 No.36: 4588459 doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-6097-3 Photometric modeling of the Moon using Lommel-Seeliger function and Chang E-1 IIM data ZHANG Jiang 1,*, LING ZongCheng,
Article Astronomy December 013 Vol.58 No.36: 4588459 doi: 10.1007/s11434-013-6097-3 Photometric modeling of the Moon using Lommel-Seeliger function and Chang E-1 IIM data ZHANG Jiang 1,*, LING ZongCheng,
ASTRONOMY 340 FALL September 2007 Class #6-#7
 ASTRONOMY 340 FALL 2007 25 September 2007 Class #6-#7 Review Physical basis of spectroscopy Einstein A,B coefficients probabilities of transistions Absorption/emission coefficients are functions of ρ,
ASTRONOMY 340 FALL 2007 25 September 2007 Class #6-#7 Review Physical basis of spectroscopy Einstein A,B coefficients probabilities of transistions Absorption/emission coefficients are functions of ρ,
Mini-RF: An Imaging Radar for the Moon. Ben Bussey The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory
 Mini-RF: An Imaging Radar for the Moon Ben Bussey The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory Paul D. Spudis President s Commission on Implementation of United States Space Exploration Policy
Mini-RF: An Imaging Radar for the Moon Ben Bussey The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory Paul D. Spudis President s Commission on Implementation of United States Space Exploration Policy
Lunar Satellite Attitude Determination System
 Lunar Satellite Attitude Determination System SENIOR DESIGN PROPOSAL PRESENTATION TEAM EPOCH KUPOLUYI, TOLULOPE (LEAD DEVELOPER) SONOIKI, OLUWAYEMISI (LEAD RESEARCHER) WARREN, DANAH (PROJECT MANAGER) NOVEMBER
Lunar Satellite Attitude Determination System SENIOR DESIGN PROPOSAL PRESENTATION TEAM EPOCH KUPOLUYI, TOLULOPE (LEAD DEVELOPER) SONOIKI, OLUWAYEMISI (LEAD RESEARCHER) WARREN, DANAH (PROJECT MANAGER) NOVEMBER
StellarXplorers IV Qualifying Round 2 (QR2) Quiz Answer Key
 1. Which of these Electromagnetic radiation bands has the longest wavelength (λ)? [Section 12.1] a. X-Ray b. Visible Light c. Infrared d. Radio 2. How is energy in Electromagnetic (EM) radiation related
1. Which of these Electromagnetic radiation bands has the longest wavelength (λ)? [Section 12.1] a. X-Ray b. Visible Light c. Infrared d. Radio 2. How is energy in Electromagnetic (EM) radiation related
Contents. Summer School Alpbach 2008 Team Red
 Contents 1. Scientific Motivation and Goals 2. Mission Scenario 3. Close to Comet Operations 4. Sampling System 5. Planetary Protection 6. Budgets 7. Conclusion Scientific Motivation Scientific Objectives
Contents 1. Scientific Motivation and Goals 2. Mission Scenario 3. Close to Comet Operations 4. Sampling System 5. Planetary Protection 6. Budgets 7. Conclusion Scientific Motivation Scientific Objectives
ROSETTA. One Comet Rendezvous and two Asteroid Fly-bys. Rita Schulz Rosetta Project Scientist
 ROSETTA One Comet Rendezvous and two Asteroid Fly-bys Rita Schulz Rosetta Project Scientist Giotto Mission 1986 1P/Halley DS-1 Mission 2001 19P/Borrelly Stardust Mission 2004 81P/ Wild 2 Deep Impact Mission
ROSETTA One Comet Rendezvous and two Asteroid Fly-bys Rita Schulz Rosetta Project Scientist Giotto Mission 1986 1P/Halley DS-1 Mission 2001 19P/Borrelly Stardust Mission 2004 81P/ Wild 2 Deep Impact Mission
images may not align well. For this reason ripple migrations have only been calculated over two
 GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2013126 S. Silvestro et al. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION: PERVASIVE AEOLIAN ACTIVITY ALONG ROVER CURIOSITY S TRAVERSE IN GALE CRATER, MARS S.Silvestro, D.A. Vaz, R.C. Ewing, A.P. Rossi,
GSA DATA REPOSITORY 2013126 S. Silvestro et al. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION: PERVASIVE AEOLIAN ACTIVITY ALONG ROVER CURIOSITY S TRAVERSE IN GALE CRATER, MARS S.Silvestro, D.A. Vaz, R.C. Ewing, A.P. Rossi,
NASA's Discovery Program gives scientists the opportunity to dig deep into their imaginations and find innovative ways to unlock the mysteries of the
 The Discovery Program's prime objective is to enhance our understanding of the Solar System by exploring the planets, their moons and small bodies such as comets and asteroids. Another important objective
The Discovery Program's prime objective is to enhance our understanding of the Solar System by exploring the planets, their moons and small bodies such as comets and asteroids. Another important objective
New Worlds Observer Final Report Appendix J. Appendix J: Trajectory Design and Orbit Determination Lead Author: Karen Richon
 Appendix J: Trajectory Design and Orbit Determination Lead Author: Karen Richon The two NWO spacecraft will orbit about the libration point created by the Sun and Earth/Moon barycenter at the far side
Appendix J: Trajectory Design and Orbit Determination Lead Author: Karen Richon The two NWO spacecraft will orbit about the libration point created by the Sun and Earth/Moon barycenter at the far side
Spitzer Space Telescope
 Spitzer Space Telescope (A.K.A. The Space Infrared Telescope Facility) The Infrared Imaging Chain 1/38 The infrared imaging chain Generally similar to the optical imaging chain... 1) Source (different
Spitzer Space Telescope (A.K.A. The Space Infrared Telescope Facility) The Infrared Imaging Chain 1/38 The infrared imaging chain Generally similar to the optical imaging chain... 1) Source (different
Lunar Geology ASTR 2120 Sarazin
 Lunar Geology ASTR 2120 Sarazin Interior of the Moon Density low (3.3 gm/cc), very little iron No iron core Very small heat flow out of interior Little radioactive heating No magnetic field No molten iron
Lunar Geology ASTR 2120 Sarazin Interior of the Moon Density low (3.3 gm/cc), very little iron No iron core Very small heat flow out of interior Little radioactive heating No magnetic field No molten iron
Chandrayaan Mission Objectives and future lunar programs
 Chandrayaan Mission Objectives and future lunar programs CHANDRAYAAN -I Paul Spudis, channeling J. N. Goswami Principal Scientist, Chandrayaan-1 Mission The Clementine & Lunar Prospector Missions to Moon
Chandrayaan Mission Objectives and future lunar programs CHANDRAYAAN -I Paul Spudis, channeling J. N. Goswami Principal Scientist, Chandrayaan-1 Mission The Clementine & Lunar Prospector Missions to Moon
Weather in the Solar System
 Weather in the Solar System Sanjay S. Limaye Space Science and Engineering Center University of Wisconsin-Madison 8 February 2002 What is Weather? Webster s New Collegiate Dictionary: state of the atmosphere
Weather in the Solar System Sanjay S. Limaye Space Science and Engineering Center University of Wisconsin-Madison 8 February 2002 What is Weather? Webster s New Collegiate Dictionary: state of the atmosphere
New Horizons Pluto Kuiper Belt mission: design and simulation of the Pluto Charon encounter
 Acta Astronautica 56 (2005) 421 429 www.elsevier.com/locate/actaastro New Horizons Pluto Kuiper Belt mission: design and simulation of the Pluto Charon encounter Yanping Guo, Robert W. Farquhar Applied
Acta Astronautica 56 (2005) 421 429 www.elsevier.com/locate/actaastro New Horizons Pluto Kuiper Belt mission: design and simulation of the Pluto Charon encounter Yanping Guo, Robert W. Farquhar Applied
BepiColombo MPO Science Operations Planning Drivers IWPSS-2013
 BepiColombo MPO Science Operations Planning Drivers IWPSS-2013 Sara de la Fuente sfuente@sciops.esa.int BepiColombo MPO Science Ground Segment ESA, ESAC, Villanueva de la Cañada, Madrid, 28691, Spain Summary
BepiColombo MPO Science Operations Planning Drivers IWPSS-2013 Sara de la Fuente sfuente@sciops.esa.int BepiColombo MPO Science Ground Segment ESA, ESAC, Villanueva de la Cañada, Madrid, 28691, Spain Summary
Vision-based navigation around small bodies
 Astronet-II, International Final Conference Vision-based navigation around small bodies Pawel Kicman VISION-BASED NAVIGATION IN SPACE Camera LOS (Line-of-sight) sensor Star-horizon measurements Apparent
Astronet-II, International Final Conference Vision-based navigation around small bodies Pawel Kicman VISION-BASED NAVIGATION IN SPACE Camera LOS (Line-of-sight) sensor Star-horizon measurements Apparent
InSight Spacecraft Launch for Mission to Interior of Mars
 InSight Spacecraft Launch for Mission to Interior of Mars InSight is a robotic scientific explorer to investigate the deep interior of Mars set to launch May 5, 2018. It is scheduled to land on Mars November
InSight Spacecraft Launch for Mission to Interior of Mars InSight is a robotic scientific explorer to investigate the deep interior of Mars set to launch May 5, 2018. It is scheduled to land on Mars November
SP-1291 June Mars Express. The Scientific Investigations
 SP-1291 June 2009 Mars Express The Scientific Investigations Operations and Archiving Mars Express Science Planning and Operations R. Pischel & T. Zegers ESA/ESTEC, Research and Scientific Support Department,
SP-1291 June 2009 Mars Express The Scientific Investigations Operations and Archiving Mars Express Science Planning and Operations R. Pischel & T. Zegers ESA/ESTEC, Research and Scientific Support Department,
Operational Aspects of Space Weather-Related Missions
 Operational Aspects of Space Weather-Related Missions Richard G. Marsden, ESA/SCI-SH Outline SOHO: Example of Near-Earth Observatory-class Mission Ulysses: Example of Deep Space Monitor-class Mission Solar
Operational Aspects of Space Weather-Related Missions Richard G. Marsden, ESA/SCI-SH Outline SOHO: Example of Near-Earth Observatory-class Mission Ulysses: Example of Deep Space Monitor-class Mission Solar
Flight S4-002 Status of Hayabusa2: Asteroid Sample Return Mission to C-type Asteroid Ryugu. Yuichi Tsuda, Makoto Yoshikawa (ISAS/JAXA)
 Flight S4-002 Status of Hayabusa2: Asteroid Sample Return Mission to C-type Asteroid Ryugu Yuichi Tsuda, Makoto Yoshikawa (ISAS/JAXA) Highlights of Hayabusa2 Hayabusa2 is the 2nd Japanese sample return
Flight S4-002 Status of Hayabusa2: Asteroid Sample Return Mission to C-type Asteroid Ryugu Yuichi Tsuda, Makoto Yoshikawa (ISAS/JAXA) Highlights of Hayabusa2 Hayabusa2 is the 2nd Japanese sample return
Rosetta Optical Navigation
 Rosetta Optical Navigation Mathias Lauer ESA / ESOC / Flight Dynamics Page 1 Overview Rosetta: Mission and Spacecraft Asteroid Flybys (Steins): - Scenario - Navigation Strategy - Image Processing - Autonomous
Rosetta Optical Navigation Mathias Lauer ESA / ESOC / Flight Dynamics Page 1 Overview Rosetta: Mission and Spacecraft Asteroid Flybys (Steins): - Scenario - Navigation Strategy - Image Processing - Autonomous
The Orbiting Carbon Observatory (OCO)
 GEMS 2006 Assembly The Orbiting Carbon Observatory (OCO) http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov David Crisp, OCO PI (JPL/Caltech) February 2006 1 of 13, OCO Dec 2005 Page 1 The Orbiting Carbon Observatory (OCO) OCO will
GEMS 2006 Assembly The Orbiting Carbon Observatory (OCO) http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov David Crisp, OCO PI (JPL/Caltech) February 2006 1 of 13, OCO Dec 2005 Page 1 The Orbiting Carbon Observatory (OCO) OCO will
Calibration of Ocean Colour Sensors
 Dr. A. Neumann German Aerospace Centre DLR Remote Sensing Technology Institute Marine Remote Sensing What is Calibration, why do we need it? Sensor Components Definition of Terms Calibration Standards
Dr. A. Neumann German Aerospace Centre DLR Remote Sensing Technology Institute Marine Remote Sensing What is Calibration, why do we need it? Sensor Components Definition of Terms Calibration Standards
The Genealogy of OSIRIS-REx Asteroid Sample Return Mission
 The Genealogy of OSIRIS-REx Asteroid Sample Return Mission New Frontiers-3 Proposal Due July 31, 2009 Principal Investigator Michael Drake (UA) Deputy PI Dante Lauretta (UA) May 18, 2009 University of
The Genealogy of OSIRIS-REx Asteroid Sample Return Mission New Frontiers-3 Proposal Due July 31, 2009 Principal Investigator Michael Drake (UA) Deputy PI Dante Lauretta (UA) May 18, 2009 University of
Direct Aerial Robot Explorers (DARE) For Planetary Exploration
 Direct Aerial Robot Explorers (DARE) For Planetary Exploration Presentation to NIAC Fellows Meeting By Dr. Alexey Pankine Global www.gaerospace.com Global October 23, 2002 CONTRIBUTORS Global Prof. Andrew
Direct Aerial Robot Explorers (DARE) For Planetary Exploration Presentation to NIAC Fellows Meeting By Dr. Alexey Pankine Global www.gaerospace.com Global October 23, 2002 CONTRIBUTORS Global Prof. Andrew
Chapter 4 Nadir looking UV measurement. Part-I: Theory and algorithm
 Chapter 4 Nadir looking UV measurement. Part-I: Theory and algorithm -Aerosol and tropospheric ozone retrieval method using continuous UV spectra- Atmospheric composition measurements from satellites are
Chapter 4 Nadir looking UV measurement. Part-I: Theory and algorithm -Aerosol and tropospheric ozone retrieval method using continuous UV spectra- Atmospheric composition measurements from satellites are
Astronomy 103: First Exam
 Name: Astronomy 103: First Exam Stephen Lepp October 27, 2010 Each question is worth 2 points. Write your name on this exam and on the scantron. 1 Short Answer A. What is the largest of the terrestrial
Name: Astronomy 103: First Exam Stephen Lepp October 27, 2010 Each question is worth 2 points. Write your name on this exam and on the scantron. 1 Short Answer A. What is the largest of the terrestrial
Science Scenario Modeling
 Science Scenario Modeling Rob Lock, Erick Sturm, Tracy Van Houten Presented to OPAG Satellite Break-out Group February 2010 Introduction Scenario Strategy For Europa Explorer and Jupiter Europa Orbiter
Science Scenario Modeling Rob Lock, Erick Sturm, Tracy Van Houten Presented to OPAG Satellite Break-out Group February 2010 Introduction Scenario Strategy For Europa Explorer and Jupiter Europa Orbiter
Toward Venus orbit insertion of Akatsuki
 Toward Venus orbit insertion of Akatsuki Takeshi Imamura (JAXA, Japan) Lightning and Airglow Camera Mid-IR Camera UV Imager Ultra-Stable Oscillator 1µm Camera 2µm Camera Development and launch Objective:
Toward Venus orbit insertion of Akatsuki Takeshi Imamura (JAXA, Japan) Lightning and Airglow Camera Mid-IR Camera UV Imager Ultra-Stable Oscillator 1µm Camera 2µm Camera Development and launch Objective:
OSIRIS-REX OVERVIEW PRESENTATION TO THE PLANETARY SCIENCE SUBCOMMITTEE
 OSIRIS-REX OVERVIEW PRESENTATION TO THE PLANETARY SCIENCE SUBCOMMITTEE OCTOBER 3, 2012 GORDON JOHNSTON PROGRAM EXECUTIVE OSIRIS-REx Science Objectives 1. Return and analyze a sample of pristine carbonaceous
OSIRIS-REX OVERVIEW PRESENTATION TO THE PLANETARY SCIENCE SUBCOMMITTEE OCTOBER 3, 2012 GORDON JOHNSTON PROGRAM EXECUTIVE OSIRIS-REx Science Objectives 1. Return and analyze a sample of pristine carbonaceous
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON
 UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON University Of London Observatory PHAS1510 Certicate in Astronomy 1213.01 PHAS1510-03: Impact Craters on the Moon, Mars and Mercury Name: An experienced student should aim to complete
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON University Of London Observatory PHAS1510 Certicate in Astronomy 1213.01 PHAS1510-03: Impact Craters on the Moon, Mars and Mercury Name: An experienced student should aim to complete
EARTH TO VENUS-1 NAVIGATION RESULTS FOR NASA'S MESSENGER MISSION TO MERCURY
 AAS 07-171 INTRODUCTION EARTH TO VENUS-1 NAVIGATION RESULTS FOR NASA'S MESSENGER MISSION TO MERCURY A. Taylor, E. Carranza, J. Miller, D. Stanbridge, B. Page, J. Smith, P. Wolff, B. Williams, L. Efron
AAS 07-171 INTRODUCTION EARTH TO VENUS-1 NAVIGATION RESULTS FOR NASA'S MESSENGER MISSION TO MERCURY A. Taylor, E. Carranza, J. Miller, D. Stanbridge, B. Page, J. Smith, P. Wolff, B. Williams, L. Efron
ESSE Payload Design. 1.2 Introduction to Space Missions
 ESSE4360 - Payload Design 1.2 Introduction to Space Missions Earth, Moon, Mars, and Beyond Department of Earth and Space Science and Engineering Room 255, Petrie Science and Engineering Building Tel: 416-736
ESSE4360 - Payload Design 1.2 Introduction to Space Missions Earth, Moon, Mars, and Beyond Department of Earth and Space Science and Engineering Room 255, Petrie Science and Engineering Building Tel: 416-736
Scott Bolton OPAG February 1, 2016
 Scott Bolton OPAG February 1, 2016 Juno Status Launched August 2011 Earth flyby October 2013 Jupiter arrival July 4, 2016 Spacecraft is healthy and all instruments are working. Juno Science Juno Science
Scott Bolton OPAG February 1, 2016 Juno Status Launched August 2011 Earth flyby October 2013 Jupiter arrival July 4, 2016 Spacecraft is healthy and all instruments are working. Juno Science Juno Science
The Solar System Science Operations Laboratory
 The Solar System Science Operations Laboratory SCIOPS 2013 11 th September 2013, ESAC/ESA Marc Costa (ISDEFE/ESA) Miguel Almeida (VEGA/ESA) Nicolas Altobelli (ESA) Alejandro Cardesín (ISDEFE/ESA) SCIOPS
The Solar System Science Operations Laboratory SCIOPS 2013 11 th September 2013, ESAC/ESA Marc Costa (ISDEFE/ESA) Miguel Almeida (VEGA/ESA) Nicolas Altobelli (ESA) Alejandro Cardesín (ISDEFE/ESA) SCIOPS
APPENDIX B SUMMARY OF ORBITAL MECHANICS RELEVANT TO REMOTE SENSING
 APPENDIX B SUMMARY OF ORBITAL MECHANICS RELEVANT TO REMOTE SENSING Orbit selection and sensor characteristics are closely related to the strategy required to achieve the desired results. Different types
APPENDIX B SUMMARY OF ORBITAL MECHANICS RELEVANT TO REMOTE SENSING Orbit selection and sensor characteristics are closely related to the strategy required to achieve the desired results. Different types
Lunar Exploration Requirements and Data Acquisition Architectures
 Lunar Exploration Requirements and Data Acquisition Architectures J. Plescia P. Spudis B. Bussey Johns Hopkins University / Applied Physics Laboratory 2005 International Lunar Conference The Vision and
Lunar Exploration Requirements and Data Acquisition Architectures J. Plescia P. Spudis B. Bussey Johns Hopkins University / Applied Physics Laboratory 2005 International Lunar Conference The Vision and
Robotic Lunar Exploration Scenario JAXA Plan
 Workshop May, 2006 Robotic Lunar Exploration Scenario JAXA Plan Tatsuaki HASHIMOTO JAXA 1 Question: What is Space Exploration? Answers: There are as many answers as the number of the people who answer
Workshop May, 2006 Robotic Lunar Exploration Scenario JAXA Plan Tatsuaki HASHIMOTO JAXA 1 Question: What is Space Exploration? Answers: There are as many answers as the number of the people who answer
Presentation by Indian Delegation. to 49 th STSC UNCOPUOS. February 2012 Vienna
 Presentation by Indian Delegation to 49 th STSC UNCOPUOS February 2012 Vienna ASTROSAT Astrosat is India s first dedicated multiwavelength astronomy satellite with a capability to observe target sources
Presentation by Indian Delegation to 49 th STSC UNCOPUOS February 2012 Vienna ASTROSAT Astrosat is India s first dedicated multiwavelength astronomy satellite with a capability to observe target sources
Ground and On-Orbit Characterization and Calibration of the Geosynchronous Imaging Fourier Transform Spectrometer (GIFTS)
 Ground and On-Orbit Characterization and Calibration of the Geosynchronous Imaging Fourier Transform Spectrometer (GIFTS) John D. Elwell 1, Deron K. Scott 1 Henry E. Revercomb 2, Fred A. Best 2, Robert
Ground and On-Orbit Characterization and Calibration of the Geosynchronous Imaging Fourier Transform Spectrometer (GIFTS) John D. Elwell 1, Deron K. Scott 1 Henry E. Revercomb 2, Fred A. Best 2, Robert
ISIS Impactor for Surface and Interior Science
 ISIS Impactor for Surface and Interior Science ISIS Mission Concept!! Send an independent, autonomous impactor spacecraft to the target of the OSIRIS-REx mission!! Launch as secondary payload with InSight!!
ISIS Impactor for Surface and Interior Science ISIS Mission Concept!! Send an independent, autonomous impactor spacecraft to the target of the OSIRIS-REx mission!! Launch as secondary payload with InSight!!
PLANET-C: Venus Climate Orbiter mission -Updates- Takehiko Satoh (Kumamoto Univ / JAXA) George Hashimoto (Kobe Univ) PLANET-C team
 PLANET-C: Venus Climate Orbiter mission -Updates- Takehiko Satoh (Kumamoto Univ / JAXA) George Hashimoto (Kobe Univ) PLANET-C team Venus Climate Orbiter JAXA s 24th science spacecraft dedicated to the
PLANET-C: Venus Climate Orbiter mission -Updates- Takehiko Satoh (Kumamoto Univ / JAXA) George Hashimoto (Kobe Univ) PLANET-C team Venus Climate Orbiter JAXA s 24th science spacecraft dedicated to the
New Horizons Pluto/KBO Mission. Hal Weaver The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory
 New Horizons Pluto/KBO Mission Hal Weaver The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory KBOs 2016-2020 To Pluto and Beyond The Initial Reconnaissance of The Solar System s Third Zone Pluto-Charon
New Horizons Pluto/KBO Mission Hal Weaver The Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory KBOs 2016-2020 To Pluto and Beyond The Initial Reconnaissance of The Solar System s Third Zone Pluto-Charon
An Agile Multi-Use Nano Star Camera for Constellation Applications
 An Agile Multi-Use Nano Star Camera for Constellation Applications Scott Palo 1,2, George Stafford 2 and Alan Hoskins 1 1 University of Colorado 2 Blue Canyon Technologies Partnership The BCT technical
An Agile Multi-Use Nano Star Camera for Constellation Applications Scott Palo 1,2, George Stafford 2 and Alan Hoskins 1 1 University of Colorado 2 Blue Canyon Technologies Partnership The BCT technical
PLANETARY TEMPERATURES
 APS 1010 Astronomy Lab 97 Planetary Temperatures PLANETARY TEMPERATURES Mars is essentially in the same orbit. Mars is somewhat the same distance from the Sun, which is very important. We have seen pictures
APS 1010 Astronomy Lab 97 Planetary Temperatures PLANETARY TEMPERATURES Mars is essentially in the same orbit. Mars is somewhat the same distance from the Sun, which is very important. We have seen pictures
Spacecraft Bus / Platform
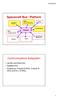 Spacecraft Bus / Platform Propulsion Thrusters ADCS: Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem Shield CDH: Command and Data Handling Subsystem Payload Communication Thermal Power Structure and Mechanisms
Spacecraft Bus / Platform Propulsion Thrusters ADCS: Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem Shield CDH: Command and Data Handling Subsystem Payload Communication Thermal Power Structure and Mechanisms
Imaging the Earth from the Moon FUV Imaging of the Earth s Space Weather. Dr. Larry J. Paxton (office)
 Imaging the Earth from the Moon FUV Imaging of the Earth s Space Weather Dr. Larry J. Paxton 240 228 6871 (office) Larry.paxton@jhuapl.edu Making Observations of the Earth from the Moon Makes Sense Once
Imaging the Earth from the Moon FUV Imaging of the Earth s Space Weather Dr. Larry J. Paxton 240 228 6871 (office) Larry.paxton@jhuapl.edu Making Observations of the Earth from the Moon Makes Sense Once
China s Chang E Program
 China s Chang E Program --- Missions Objectives, Plans, Status, and Opportunity for Astronomy Maohai Huang Science and Application Research Center for Lunar and Deepspace Explorations National Astronomical
China s Chang E Program --- Missions Objectives, Plans, Status, and Opportunity for Astronomy Maohai Huang Science and Application Research Center for Lunar and Deepspace Explorations National Astronomical
IN-FLIGHT CALIBRATION OF THE OSIRIS-REX OPTICAL NAVIGATION IMAGERS
 IN-FLIGHT CALIBRATION OF THE OSIRIS-REX OPTICAL NAVIGATION IMAGERS John Y. Pelgrift, Eric M. Sahr, Derek S. Nelson, Coralie D. Jackman, Lylia Benhacine, Brent J. Bos, Bashar Rizk, Christian d Aubigny,
IN-FLIGHT CALIBRATION OF THE OSIRIS-REX OPTICAL NAVIGATION IMAGERS John Y. Pelgrift, Eric M. Sahr, Derek S. Nelson, Coralie D. Jackman, Lylia Benhacine, Brent J. Bos, Bashar Rizk, Christian d Aubigny,
NASA Plan for Development of Optical Communication for Space Applications
 NASA Plan for Development of Optical Communication for Space Applications Titan Saturn Neptune Uranus Pluto Charon Jupiter SCaN Integra ISS ted NISNMC Service C Portal Cx MCC Mars Sun For National Research
NASA Plan for Development of Optical Communication for Space Applications Titan Saturn Neptune Uranus Pluto Charon Jupiter SCaN Integra ISS ted NISNMC Service C Portal Cx MCC Mars Sun For National Research
Measurements & Instrumentation Systems National Space Institute Technical University of Denmark
 Measurements & Instrumentation Systems National Space Institute Technical University of Denmark Assessment Study of Autonomous Optical Navigation for an Asteroid Impact Mission -Executive Summary- Prepared
Measurements & Instrumentation Systems National Space Institute Technical University of Denmark Assessment Study of Autonomous Optical Navigation for an Asteroid Impact Mission -Executive Summary- Prepared
THE EXOMARS CLIMATE SOUNDER (EMCS) INVESTIGATION.
 THE EXOMARS CLIMATE SOUNDER (EMCS) INVESTIGATION. J. T. Schofield, D. M. Kass, A. Kleinböhl, D. J. McCleese, M. A. Allen, M. C. Foote, M. Jeganathan, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of
THE EXOMARS CLIMATE SOUNDER (EMCS) INVESTIGATION. J. T. Schofield, D. M. Kass, A. Kleinböhl, D. J. McCleese, M. A. Allen, M. C. Foote, M. Jeganathan, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of
ASTR 2310: Chapter 6
 ASTR 231: Chapter 6 Astronomical Detection of Light The Telescope as a Camera Refraction and Reflection Telescopes Quality of Images Astronomical Instruments and Detectors Observations and Photon Counting
ASTR 231: Chapter 6 Astronomical Detection of Light The Telescope as a Camera Refraction and Reflection Telescopes Quality of Images Astronomical Instruments and Detectors Observations and Photon Counting
four modes. Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) mode operates at altitudes less than
 1109919 SOM 050421.doc SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIAL Instrument Detail The Cassini Titan Radar Mapper (S1) is a K u -band (13.78 GHz, = 2.17 cm) linear polarized radar instrument operating over a wide range
1109919 SOM 050421.doc SUPPORTING ONLINE MATERIAL Instrument Detail The Cassini Titan Radar Mapper (S1) is a K u -band (13.78 GHz, = 2.17 cm) linear polarized radar instrument operating over a wide range
NEW HORIZONS 2. New Horizons: A Journey to New Frontiers
 NEW HORIZONS 2 New Horizons: A Journey to New Frontiers WHY NEW HORIZONS 2? PROVIDE BACKUP FOR THE HIGHEST PRIORITY NF OBJECTIVE OF THE DECADAL SURVEY. ENABLE THE FIRST EXPLORATION OF A LARGE (500 KM CLASS)
NEW HORIZONS 2 New Horizons: A Journey to New Frontiers WHY NEW HORIZONS 2? PROVIDE BACKUP FOR THE HIGHEST PRIORITY NF OBJECTIVE OF THE DECADAL SURVEY. ENABLE THE FIRST EXPLORATION OF A LARGE (500 KM CLASS)
MESSENGER's Discoveries at Mercury
 MESSENGER's Discoveries at Mercury David T. Blewett Planetary Exploration Group Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory CAS Visiting International Scholar NAOC, Beijing July 8, 2015 Mercury:
MESSENGER's Discoveries at Mercury David T. Blewett Planetary Exploration Group Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory CAS Visiting International Scholar NAOC, Beijing July 8, 2015 Mercury:
Solution for Homework# 3. Chapter 5 : Review & Discussion
 Solution for Homework# 3 Chapter 5 : Review & Discussion. The largest telescopes are reflecting telescopes, primarily because of 3 distinct disadvantages of the refracting telescope. When light passes
Solution for Homework# 3 Chapter 5 : Review & Discussion. The largest telescopes are reflecting telescopes, primarily because of 3 distinct disadvantages of the refracting telescope. When light passes
Germany s Option for a Moon Satellite
 Germany s Option for a Moon Satellite 38th COSPAR B01-0016-10 Quantius, D. (1), Päsler, H. (2), Gülzow, P. (2), Braukhane, A. (1), Vollhardt, A. (2), Bauer, W. (1), Romberg, O. (1), Scheibe, K. (1), Hoffmann,
Germany s Option for a Moon Satellite 38th COSPAR B01-0016-10 Quantius, D. (1), Päsler, H. (2), Gülzow, P. (2), Braukhane, A. (1), Vollhardt, A. (2), Bauer, W. (1), Romberg, O. (1), Scheibe, K. (1), Hoffmann,
PLANET-C: Venus Climate Orbiter mission from Japan. Takeshi Imamura Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency PLANET-C team
 PLANET-C: Venus Climate Orbiter mission from Japan Takeshi Imamura Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency PLANET-C team Venus Climate Orbiter JAXA s 24th science spacecraft dedicated to the exploration of
PLANET-C: Venus Climate Orbiter mission from Japan Takeshi Imamura Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency PLANET-C team Venus Climate Orbiter JAXA s 24th science spacecraft dedicated to the exploration of
Final Presentation of Assessment Star Tracker for Asteroid Search. By Peter Davidsen
 Final Presentation of Assessment Star Tracker for Asteroid Search By Peter Davidsen Study Overview Study name: Assessment of Star Tracker use for Asteroid Search ESA contract: ESA contract 4000105591/12/NL/AF
Final Presentation of Assessment Star Tracker for Asteroid Search By Peter Davidsen Study Overview Study name: Assessment of Star Tracker use for Asteroid Search ESA contract: ESA contract 4000105591/12/NL/AF
Mercury = Hermes Mythology. Planet Mercury, Element, Mercredi God of Commerce, Messenger God, guide to Hades Winged sandals and staff
 Mercury = Hermes Mythology Planet Mercury, Element, Mercredi God of Commerce, Messenger God, guide to Hades Winged sandals and staff Mercury s Orbit Mercury never seen more than 28 from the sun Revolves/orbits
Mercury = Hermes Mythology Planet Mercury, Element, Mercredi God of Commerce, Messenger God, guide to Hades Winged sandals and staff Mercury s Orbit Mercury never seen more than 28 from the sun Revolves/orbits
Little Learners Activity Guide
 LUNAR RECONNAISSANCE ORBITER CAMERA Little Learners Activity Guide Learn about the Moon with puzzles, coloring, and fun facts! Mare Imbrium Mare Serenitatis Mare Tranquillitatis Oceanus Procellarum Mare
LUNAR RECONNAISSANCE ORBITER CAMERA Little Learners Activity Guide Learn about the Moon with puzzles, coloring, and fun facts! Mare Imbrium Mare Serenitatis Mare Tranquillitatis Oceanus Procellarum Mare
