One-On-One With the Sun
|
|
|
- Leona Wilkerson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 One-On-One With the Sun This text is provided courtesy of OLogy, the American Museum of Natural History s website for kids. Hey, Stella Stardust here. Welcome to another cosmic conversation. Let s give a warm welcome to the Sun! Illustration Credit: Jim Steck Ninety-three million miles from Earth, a giant ball of hot gas brightens the sky. Nuclear reactions in the Sun's core create energy, which gradually flows to the Sun's surface. This energy reaches Earth in the form of sunlight. The Sun's heat and light warm Earth's surface, drive weather and currents, and make life possible on our planet. We experience the Sun's energy every time we feel its warmth on our skin or see with the aid of sunlight. Image Credit: Courtesy of NASA; Neil Tyson: AMNH STELLA: You know, everyone here on Earth loves your work. If it weren t for you, we wouldn t be here. SUN: Thanks, Stella. I ve been cranking out energy for billions of years and not one day off. STELLA: Impressive. Your agent told me that you re the biggest star in the universe. Is that true? You have to be a really big thinker to imagine the size of the Universe. It's so big that light from the most distant galaxies takes over 10 billion years just to reach us on Earth! That's twice as long as Earth's been around. Everything we've ever observed in space is part of our Universe. We don't know what's beyond it or if there are other Universes out there. Image credits: The image of the universe American Museum of Natural History and the National Center for Supercomputing Applications, 1999; Charles Liu: courtesy of AMNH.
2 SUN: Actually, no. My agent tends to exaggerate. I m just a medium-sized star. To my fans on Earth, I look much bigger than the other stars in the sky. That s because I m much closer to you than the other stars. I m 93 million miles away from you. The bigger stars are millions of times farther away from your planet. STELLA: I can t believe it. You, the Sun, are just an average, ordinary, run-of-the-mill star! SUN: Hey, take it easy. I may be an average star, but I m still a LOT bigger than your puny planet. Guess how many Earth-sized planets could fit inside me? STELLA: I don t know. Maybe ten? SUN: Not even close! More than a million! I'm big and I've got lots of mass. That's why I've got a lot of gravity. You guys don t call this the Solar system for nothing. "Solar" means "sun." This is my show. All the planets, comets, and asteroids orbit around ME. STELLA: I know you star types tend to be touchy about age, but how old are you? SUN: Well, I began shining about 4.6 billion years ago. It was so long ago I don t remember the exact day. Gravity is the force of attraction between all objects in the Universe. Objects with more mass have greater gravitational pull than objects with less mass. Gravity keeps Earth and the planets orbiting around the Sun instead of floating off into space. What would the Universe be like without gravity? Image Credits: Jim Paillot STELLA: Was it a Sunday? Just kidding. Actually, I m curious to know how stars begin. What s your story? SUN: We stars begin as huge spinning clouds of gas and dust. Gravity pulls the gas and dust together in round clumps, which get hot. At that point, we're called protostars. Eventually we get hot enough to start fusing hydrogen atoms together, which releases energy. Then we really shine. Stars are born in batches, which are like star nurseries. Then, over millions of years, these stars drift apart and spread out around the galaxy.
3 If you ever go to Mercury, bring your sunscreen because it is the planet closest to the Sun. You'll also need a pair of thermal underwear because at night Mercury cools down fast. Temperatures can drop to as low as -292 degrees F! Now that's cold! You will also need a pair of hiking boots so you can travel and climb in and out of the craters that cover Mercury's scarred landscape. Image credits: courtesy of JPL, California Institute of Technology and NASA; Frank Summers: AMNH. Venus and Earth are sometimes called sister planets because of their similar size, but don't let this comparison fool you! Venus, the second planet from the Sun, has a thick and heavy atmosphere that traps the Sun's heat to produce sizzling temperatures. This planetary greenhouse has been visited by over twenty spacecrafts. Each mission returned with important data about this mysterious planet. Image credits: courtesy of NASA; Mordecai-Mark MacLow: AMNH. The Earth is our home. So far, it's the only place that we know of that has life. Everywhere you look on Earth there is life. This is possible because Earth has lots of water. It's also just the right distance from the Sun. Some people call Earth the "Goldilocks planet." It's not too hot (like Venus), and not too cold (like Mars), it's just right! Image credits: courtesy of NASA; Rosamond Kinzler: AMNH. STELLA: Let s turn to a delicate subject. How do stars die? SUN: After stars like me shine for billions of years, we eventually run out of fuel. When that happens, we swell up as much as 100 times bigger and are called red giants. Astronomers predict that I ll eventually become a red giant. At that time, my heat will vaporize the inner planets - Mercury, Venus, and Earth STELLA: That sounds really scary.
4 SUN: Don t worry. That won t happen for about 5 billion years! After I become a red giant, I ll lose my outer gas layers and reveal my inner core, known as a white dwarf. When I m a white dwarf, I ll be only as big as Earth, but still very hot, and very dense. Finally, I ll cool down and disappear from view. STELLA: I hear that some stars die differently. What s a supernova? SUN: When a star more massive than I gets old and runs out of nuclear fuel, it blows up in a great flash of light called a supernova. This explosion splatters the star s guts in all directions. Illustration Credit: Jim Steck STELLA: Huh? STELLA: I d like to show the people at home a picture of a star that exploded as a supernova. Its remains are called the Crab Nebula. SUN: What a mess that star made. Want to know something amazing? Humans saw this star explode in the year But the explosion actually happened about 6,000 years before that. About 1,000 years ago, a massive star exploded at the end of its life cycle. What remains is the Crab Nebula, a glowing cloud of gas and dust. At the center of the Crab Nebula is a pulsar, the small, spinning core of the massive dead star. The pulsar emits all kinds of light, making the Crab Nebula easy to detect with a telescope. Image credits: In the Heart of the Crab, courtesy of William P. Blair (JHU) et al. Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA), and NASA. SUN: I ll explain. Stars give off light, right? Light travels incredibly fast - at a speed of 186,000 miles per second. Light can travel from Earth to the Moon in about one second. My sunlight reaches you Earthlings in about eight minutes. Most stars are much farther away. That s why astronomers don t use miles when they talk about the distances between stars. That s like describing the distance between New York and Los Angeles in inches! Astronomers talk about light-years. A light-year is the distance light travels in one year. Since the star in that picture was about 6,000 light-years away from Earth when it exploded, it took about 6,000 years for us to get the newsflash. STELLA: In Hollywood, I meet a lot of people filled with hot air. What gases are inside you? SUN: Ah, you want to know what gives me that special glow! Well, like most other stars, I m made up of mostly two gases, hydrogen and helium. These light gases stay close to me because of my massive gravity. Inside, I m so hot that I use a fancy process called
5 thermonuclear fusion. By turning hydrogen into helium, I create lots of energy. It makes me shine. Would you measure the distance between New York and New Delhi in inches? For the same reason, astronomers don't use miles to measure vast distances in space. Instead, they use light-years: the distance that light travels in a year. That makes Proxima Centauri, the closest known star to the Sun, 4.28 light-years away; that's a lot easier than saying 24,000,000,000,000,000 miles. Image credits: Eric Hamilton; Mordecai-Mark MacLow: AMNH. STELLA: This may be a little rude, but what are those dark splotches on you? Are those, like, star zits? SUN: (sigh) No, those dark splotches are called sunspots. All normal stars have them. They look dark because they re cooler than the gases around them. By the way, when I say cooler, keep in mind that my outside is about 10,000o F. That s many times hotter than the hottest kitchen oven. My inner core is even hotter, something like 30,000,000o F. STELLA: Is there anything else you d like to say? SUN: You think your sunglasses are star-shaped, right? STELLA: Sure. Illustration Credit: Jim Steck
6 SUN: Well, if they were really star-shaped, they d be round. You Earthlings have the strange idea that stars have points. We don t. Gravity keeps us shaped like spheres. STELLA: Thanks to the Sun for a great interview. Good night. The Sun is speckled with markings called sunspots that look darker than the rest of its surface. These spots show up where strong magnetic fields inside the Sun keep currents of hot gas from reaching the surface. Sunspots follow an 11-year cycle. The first spots appear near the poles; as years pass, more spots develop and move towards the equator. Image credits: courtesy of AURA/NOAO/NSF; Mordecai-Mark MacLow: AMNH.
7
Life Cycle of a Star - Activities
 Name: Class Period: Life Cycle of a Star - Activities A STAR IS BORN STAGES COMMON TO ALL STARS All stars start as a nebula. A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas
Name: Class Period: Life Cycle of a Star - Activities A STAR IS BORN STAGES COMMON TO ALL STARS All stars start as a nebula. A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas
Introduction to Astronomy
 Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
Introduction to Astronomy Have you ever wondered what is out there in space besides Earth? As you see the stars and moon, many questions come up with the universe, possibility of living on another planet
21/11/ /11/2017 Space Physics AQA Physics topic 8
 Space Physics AQA Physics topic 8 8.1 Solar System, Orbits and Satellites The eight planets of our Solar System Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune As well as the eight planets, the
Space Physics AQA Physics topic 8 8.1 Solar System, Orbits and Satellites The eight planets of our Solar System Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune As well as the eight planets, the
Life Cycle of a Star Worksheet
 Life Cycle of a Star Worksheet A STAR IS BORN STAGES COMMON TO ALL STARS All stars start as a nebula. A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas and dust in a nebula together.
Life Cycle of a Star Worksheet A STAR IS BORN STAGES COMMON TO ALL STARS All stars start as a nebula. A nebula is a large cloud of gas and dust. Gravity can pull some of the gas and dust in a nebula together.
the nature of the universe, galaxies, and stars can be determined by observations over time by using telescopes
 the nature of the universe, galaxies, and stars can be determined by observations over time by using telescopes The spectral lines of stars tell us their approximate composition Remember last year in Physics?
the nature of the universe, galaxies, and stars can be determined by observations over time by using telescopes The spectral lines of stars tell us their approximate composition Remember last year in Physics?
Stars and Galaxies. Evolution of Stars
 Stars and Galaxies Evolution of Stars What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
Stars and Galaxies Evolution of Stars What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with the statement
1 A Solar System Is Born
 CHAPTER 16 1 A Solar System Is Born SECTION Our Solar System California Science Standards 8.2.g, 8.4.b, 8.4.c, 8.4.d BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
CHAPTER 16 1 A Solar System Is Born SECTION Our Solar System California Science Standards 8.2.g, 8.4.b, 8.4.c, 8.4.d BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
A star is a massive sphere of gases with a core like a thermonuclear reactor. They are the most common celestial bodies in the universe are stars.
 A star is a massive sphere of gases with a core like a thermonuclear reactor. They are the most common celestial bodies in the universe are stars. They radiate energy (electromagnetic radiation) from a
A star is a massive sphere of gases with a core like a thermonuclear reactor. They are the most common celestial bodies in the universe are stars. They radiate energy (electromagnetic radiation) from a
1 The Life Cycle of a Star
 CHAPTER 1 The Life Cycle of a Star Describe the life cycle of various size stars. Rings of glowing gas encircling Supernova 1987A, about 179,000 light-years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud, one of the
CHAPTER 1 The Life Cycle of a Star Describe the life cycle of various size stars. Rings of glowing gas encircling Supernova 1987A, about 179,000 light-years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud, one of the
Beyond the Book. FOCUS Book
 FOCUS Book You have learned that a nebula can turn into a star, and that the star can turn into a new nebula. Now design a comic, timeline, flowchart, or cycle diagram to explain this process. Include
FOCUS Book You have learned that a nebula can turn into a star, and that the star can turn into a new nebula. Now design a comic, timeline, flowchart, or cycle diagram to explain this process. Include
CHAPTER 9: STARS AND GALAXIES
 CHAPTER 9: STARS AND GALAXIES Characteristics of the Sun 1. The Sun is located about 150 million kilometres from the Earth. 2. The Sun is made up of hot gases, mostly hydrogen and helium. 3. The size of
CHAPTER 9: STARS AND GALAXIES Characteristics of the Sun 1. The Sun is located about 150 million kilometres from the Earth. 2. The Sun is made up of hot gases, mostly hydrogen and helium. 3. The size of
Answers. The Universe. Year 10 Science Chapter 6
 Answers The Universe Year 10 Science Chapter 6 p133 1 The universe is considered to be the whole of all matter, energy, planets, solar systems, galaxies, and space. Many definitions of the universe also
Answers The Universe Year 10 Science Chapter 6 p133 1 The universe is considered to be the whole of all matter, energy, planets, solar systems, galaxies, and space. Many definitions of the universe also
Stars and Galaxies 1
 Stars and Galaxies 1 Characteristics of Stars 2 Star - body of gases that gives off great amounts of radiant energy as light and heat 3 Most stars look white but are actually different colors Antares -
Stars and Galaxies 1 Characteristics of Stars 2 Star - body of gases that gives off great amounts of radiant energy as light and heat 3 Most stars look white but are actually different colors Antares -
Study Guide Chapter 2
 Section: Stars Pages 32-38 Study Guide Chapter 2 Circle the letter of the best answer for each question. 1. What do scientists study to learn about stars? a. gravity c. space b. starlight d. colors COLOR
Section: Stars Pages 32-38 Study Guide Chapter 2 Circle the letter of the best answer for each question. 1. What do scientists study to learn about stars? a. gravity c. space b. starlight d. colors COLOR
TABLE OF CONTENTS. click one to go to that page, or just go on. What is the Solar System? Neptune (Pluto) The Sun. Asteroids. Mercury.
 The Solar System TABLE OF CONTENTS click one to go to that page, or just go on. What is the Solar System? The Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune (Pluto) Asteroids Meteors and Meteorites
The Solar System TABLE OF CONTENTS click one to go to that page, or just go on. What is the Solar System? The Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune (Pluto) Asteroids Meteors and Meteorites
*Generally speaking, there are two main life cycles for stars. *The factor which determines the life cycle of the star is its mass.
 Generally speaking, there are two main life cycles for stars. The factor which determines the life cycle of the star is its mass. 1 solar mass = size of our Sun Any star less than about three solar masses
Generally speaking, there are two main life cycles for stars. The factor which determines the life cycle of the star is its mass. 1 solar mass = size of our Sun Any star less than about three solar masses
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 The View from Earth Lesson 2 The Sun and Other Stars Lesson 3 Evolution of Stars Lesson 4 Galaxies and the Universe
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 The View from Earth Lesson 2 The Sun and Other Stars Lesson 3 Evolution of Stars Lesson 4 Galaxies and the Universe Chapter Wrap-Up What makes up the universe and how does
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 The View from Earth Lesson 2 The Sun and Other Stars Lesson 3 Evolution of Stars Lesson 4 Galaxies and the Universe Chapter Wrap-Up What makes up the universe and how does
The Universe and Galaxies
 The Universe and Galaxies 16.1 http://dingo.care-mail.com/cards/flash/5409/galaxy.swf Universe The sum of all matter and energy that exists, that has ever existed, and that will ever exist. We will focus
The Universe and Galaxies 16.1 http://dingo.care-mail.com/cards/flash/5409/galaxy.swf Universe The sum of all matter and energy that exists, that has ever existed, and that will ever exist. We will focus
Chapter 28 Stars and Their Characteristics
 Chapter 28 Stars and Their Characteristics Origin of the Universe Big Bang Theory about 10-20 bya all matter in the universe existed in a hot dense state about the size of an atom (tiny). That matter sort
Chapter 28 Stars and Their Characteristics Origin of the Universe Big Bang Theory about 10-20 bya all matter in the universe existed in a hot dense state about the size of an atom (tiny). That matter sort
Universe Celestial Object Galaxy Solar System
 ASTRONOMY Universe- Includes all known matter (everything). Celestial Object Any object outside or above Earth s atmosphere. Galaxy- A large group (billions) of stars (held together by gravity). Our galaxy
ASTRONOMY Universe- Includes all known matter (everything). Celestial Object Any object outside or above Earth s atmosphere. Galaxy- A large group (billions) of stars (held together by gravity). Our galaxy
Earth Space Systems. Semester 1 Exam. Astronomy Vocabulary
 Earth Space Systems Semester 1 Exam Astronomy Vocabulary Astronomical Unit- Aurora- Big Bang- Black Hole- 1AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun (93 million miles). This unit of measurement
Earth Space Systems Semester 1 Exam Astronomy Vocabulary Astronomical Unit- Aurora- Big Bang- Black Hole- 1AU is the average distance between the Earth and the Sun (93 million miles). This unit of measurement
Directed Reading A. Section: The Life Cycle of Stars TYPES OF STARS THE LIFE CYCLE OF SUNLIKE STARS A TOOL FOR STUDYING STARS.
 Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: The Life Cycle of Stars TYPES OF STARS (pp. 444 449) 1. Besides by mass, size, brightness, color, temperature, and composition, how are stars classified? a.
Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: The Life Cycle of Stars TYPES OF STARS (pp. 444 449) 1. Besides by mass, size, brightness, color, temperature, and composition, how are stars classified? a.
Gravity simplest. fusion
 Gravity simplest fusion The life of a star has a complex relationship with gravity: 1. Gravity is what brings the original dust together to make a star 2. Gravity wants to crush the star Gravity pulls
Gravity simplest fusion The life of a star has a complex relationship with gravity: 1. Gravity is what brings the original dust together to make a star 2. Gravity wants to crush the star Gravity pulls
UNIT 1: THE UNIVERSE VOCABULARY
 UNIT 1: THE UNIVERSE VOCABULARY Asteroids Asteroid belt Astronomical unit (AU) Black hole Celestial body Cluster of galaxies Comets Constellation Dwarf planets Galaxy Light-year (LY) meteorites Milky Way
UNIT 1: THE UNIVERSE VOCABULARY Asteroids Asteroid belt Astronomical unit (AU) Black hole Celestial body Cluster of galaxies Comets Constellation Dwarf planets Galaxy Light-year (LY) meteorites Milky Way
4 HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED 750L
 4 HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED 750L HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED A CLOSE LOOK AT THE PLANETS ORBITING OUR SUN By Cynthia Stokes Brown, adapted by Newsela Planets come from the clouds of gas and dust that
4 HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED 750L HOW OUR SOLAR SYSTEM FORMED A CLOSE LOOK AT THE PLANETS ORBITING OUR SUN By Cynthia Stokes Brown, adapted by Newsela Planets come from the clouds of gas and dust that
CST Prep- 8 th Grade Astronomy
 CST Prep- 8 th Grade Astronomy Chapter 15 (Part 1) 1. The theory of how the universe was created is called the 2. Which equation states that matter and energy are interchangeable? 3. All matter in the
CST Prep- 8 th Grade Astronomy Chapter 15 (Part 1) 1. The theory of how the universe was created is called the 2. Which equation states that matter and energy are interchangeable? 3. All matter in the
The Moon s relationship with Earth The formation of the Moon The surface of the Moon Phases of the Moon Travelling to the Moon
 The Moon The Moon s relationship with Earth The Moon orbits the Earth every 27.3 days. The tides on Earth are caused mostly by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun. The Moon's gravitational pull
The Moon The Moon s relationship with Earth The Moon orbits the Earth every 27.3 days. The tides on Earth are caused mostly by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun. The Moon's gravitational pull
1. Galaxy (a) the length of a planet s day. 2. Rotational Period (b) dust and gases floating in space
 Vocabulary: Match the vocabulary terms on the left with the definitions on the right 1. Galaxy (a) the length of a planet s day 2. Rotational Period (b) dust and gases floating in space 3. Orbital Period
Vocabulary: Match the vocabulary terms on the left with the definitions on the right 1. Galaxy (a) the length of a planet s day 2. Rotational Period (b) dust and gases floating in space 3. Orbital Period
Formation of the Universe The organization of Space
 February 21, 2014 Formation of the Universe The organization of Space Theory: A theory is An example is cell Cell Theory Cell Theory states 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells 2.
February 21, 2014 Formation of the Universe The organization of Space Theory: A theory is An example is cell Cell Theory Cell Theory states 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells 2.
What is the solar system?
 Notes Astronomy What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the Solar System Our solar system includes planets and dwarf planets, their moons, a star called the Sun, asteroids and comets. Planets, dwarf
Notes Astronomy What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the Solar System Our solar system includes planets and dwarf planets, their moons, a star called the Sun, asteroids and comets. Planets, dwarf
WHAT WE KNOW. Scientists observe that every object in the universe is moving away from each other. Objects furthest away are moving the fastest. So..
 ASTRONOMY THE BIG BANG THEORY WHAT WE KNOW Scientists observe that every object in the universe is moving away from each other. Objects furthest away are moving the fastest. So.. WHAT DOES THIS MEAN? If
ASTRONOMY THE BIG BANG THEORY WHAT WE KNOW Scientists observe that every object in the universe is moving away from each other. Objects furthest away are moving the fastest. So.. WHAT DOES THIS MEAN? If
4 HOW DID THE EARTH FORM?
 4 HOW DID THE EARTH FORM? New stars and space debris spinning like pizza dough are a couple of the things that explain the formation of solar systems like ours. In this three-part lecture, David Christian
4 HOW DID THE EARTH FORM? New stars and space debris spinning like pizza dough are a couple of the things that explain the formation of solar systems like ours. In this three-part lecture, David Christian
Unit 1: Space. Section 2- Stars
 Unit 1: Space Section 2- Stars Stars Recall: stars are celestial bodies of hot gas that give off heat and light Stars The milky way contains hundreds of billions of stars and is only one of hundreds of
Unit 1: Space Section 2- Stars Stars Recall: stars are celestial bodies of hot gas that give off heat and light Stars The milky way contains hundreds of billions of stars and is only one of hundreds of
8.8A describe components of the universe, including stars, nebulae, galaxies and use models such as HR diagrams for classification
 8.8A describe components of the universe, including stars, nebulae, galaxies and use models such as HR diagrams for classification 8.8B recognize that the Sun is a medium-sized star near the edge of a
8.8A describe components of the universe, including stars, nebulae, galaxies and use models such as HR diagrams for classification 8.8B recognize that the Sun is a medium-sized star near the edge of a
A Star is born: The Sun. SNC1D7-Space
 A Star is born: The Sun SNC1D7-Space Exploring the Sun Our Sun, a star, is the most important celestial object for life on Earth. The solar nebula theory is the current theory used to explain the formation
A Star is born: The Sun SNC1D7-Space Exploring the Sun Our Sun, a star, is the most important celestial object for life on Earth. The solar nebula theory is the current theory used to explain the formation
8/30/2010. Classifying Stars. Classifying Stars. Classifying Stars
 Classifying Stars In the early 1900s, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Russell made some important observations. They noticed that, in general, stars with higher temperatures also have brighter absolute magnitudes.
Classifying Stars In the early 1900s, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Russell made some important observations. They noticed that, in general, stars with higher temperatures also have brighter absolute magnitudes.
M42 (The Orion Nebula) and M43
 3.4b demonstrate an understanding that emission nebulae, absorption nebulae and open clusters are associated with the birth of stars 3.4c demonstrate an understanding that planetary nebulae and supernovae
3.4b demonstrate an understanding that emission nebulae, absorption nebulae and open clusters are associated with the birth of stars 3.4c demonstrate an understanding that planetary nebulae and supernovae
We ask questions. Like this one. What does this word make you think of? What is the first "thing" you think of? Hold on to that thought a minute.
 I'm glad you are here. I've made these notes for you to read while I'm presenting, and I've tried to say only what is most important. If you want to learn more, please use your interpreter, if you have
I'm glad you are here. I've made these notes for you to read while I'm presenting, and I've tried to say only what is most important. If you want to learn more, please use your interpreter, if you have
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS
 NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 2 BASIC ASTRONOMY, AND STARS AND THEIR EVOLUTION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics CSUSB COURSE WEBPAGE: http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen MOTIONS IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM
NSCI 314 LIFE IN THE COSMOS 2 BASIC ASTRONOMY, AND STARS AND THEIR EVOLUTION Dr. Karen Kolehmainen Department of Physics CSUSB COURSE WEBPAGE: http://physics.csusb.edu/~karen MOTIONS IN THE SOLAR SYSTEM
CONTENT EXPECTATIONS
 THE SUN & THE STARS CONTENT EXPECTATIONS STARS What are stars? Are they all the same? What makes them different? What is our nearest star? THE SUN Why is it important? provides heat and light that we need
THE SUN & THE STARS CONTENT EXPECTATIONS STARS What are stars? Are they all the same? What makes them different? What is our nearest star? THE SUN Why is it important? provides heat and light that we need
LESSON 1. Solar System
 Astronomy Notes LESSON 1 Solar System 11.1 Structure of the Solar System axis of rotation period of rotation period of revolution ellipse astronomical unit What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the
Astronomy Notes LESSON 1 Solar System 11.1 Structure of the Solar System axis of rotation period of rotation period of revolution ellipse astronomical unit What is the solar system? 11.1 Structure of the
Daily Science 03/30/2017
 Daily Science 03/30/2017 The atmospheres of different planets contain different gases. Which planet is most likely Earth? a. planet 1 b. planet 2 c. planet 3 d. planet 4 KeslerScience.com Can you name
Daily Science 03/30/2017 The atmospheres of different planets contain different gases. Which planet is most likely Earth? a. planet 1 b. planet 2 c. planet 3 d. planet 4 KeslerScience.com Can you name
1 Read the title and the first two paragraphs of this extract of a text. Then check ( ) the correct answers.
 Reading 1 Read the title and the first two paragraphs of this extract of a text. Then check ( ) the correct answers. / 0.4 point What is the main objective of the text? a. To present information about
Reading 1 Read the title and the first two paragraphs of this extract of a text. Then check ( ) the correct answers. / 0.4 point What is the main objective of the text? a. To present information about
The sun, yellow dwarf star at the heart of the solar system NASA.gov, adapted by Newsela staff
 Name: Period: Date: Article of the Week Directions: Read the following article carefully and annotate. You need to include at least 1 annotation per paragraph. Be sure to include all of the following in
Name: Period: Date: Article of the Week Directions: Read the following article carefully and annotate. You need to include at least 1 annotation per paragraph. Be sure to include all of the following in
The Earth in the Universe
 The Earth in the Universe (OCR) Evidence for the age of the Earth Scientists once thought that the Earth was only 6000 years old. Rocks have provided lots of evidence for the world being older. 1) Erosion
The Earth in the Universe (OCR) Evidence for the age of the Earth Scientists once thought that the Earth was only 6000 years old. Rocks have provided lots of evidence for the world being older. 1) Erosion
The Universe. is space and everything in it.
 The Universe is space and everything in it. Galaxies A galaxy is a supercluster of stars, gas, and dust that are held together by gravity. There are three main types of galaxies: Irregular Elliptical Spiral
The Universe is space and everything in it. Galaxies A galaxy is a supercluster of stars, gas, and dust that are held together by gravity. There are three main types of galaxies: Irregular Elliptical Spiral
GALAXIES AND STARS. 2. Which star has a higher luminosity and a lower temperature than the Sun? A Rigel B Barnard s Star C Alpha Centauri D Aldebaran
 GALAXIES AND STARS 1. Compared with our Sun, the star Betelgeuse is A smaller, hotter, and less luminous B smaller, cooler, and more luminous C larger, hotter, and less luminous D larger, cooler, and more
GALAXIES AND STARS 1. Compared with our Sun, the star Betelgeuse is A smaller, hotter, and less luminous B smaller, cooler, and more luminous C larger, hotter, and less luminous D larger, cooler, and more
The Sun s center is much hotter than the surface. The Sun looks large and bright in the sky. Other stars look much smaller.
 The Sun A star is a huge ball of hot, glowing gases. The Sun is a star. The width of the Sun is equal to the width of 100 Earths placed side by side. The Sun is extremely hot. The surface of the Sun has
The Sun A star is a huge ball of hot, glowing gases. The Sun is a star. The width of the Sun is equal to the width of 100 Earths placed side by side. The Sun is extremely hot. The surface of the Sun has
To infinity, and beyond!
 stars The night sky is filled with stars that shine at different levels of brightness. The brightness of the stars we observe can be related to the size of the star or its distance from Earth. In order
stars The night sky is filled with stars that shine at different levels of brightness. The brightness of the stars we observe can be related to the size of the star or its distance from Earth. In order
GraspIT Questions AQA GCSE Physics Space physics
 A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
A. Solar system: stability of orbital motions; satellites (physics only) 1. Put these astronomical objects in order of size from largest to smallest. (3) Fill in the boxes in the correct order. the Moon
Plan. Questions? Syllabus; administrative details. Some Definitions. An Idea of Scale
 Plan Questions? Syllabus; administrative details Some Definitions An Idea of Scale All material available from http://astroweb.case.edu/ssm/astr101/ which is the primary document for the course (not Canvas).
Plan Questions? Syllabus; administrative details Some Definitions An Idea of Scale All material available from http://astroweb.case.edu/ssm/astr101/ which is the primary document for the course (not Canvas).
Stars and Galaxies. Evolution of Stars
 chapter 13 3 Stars and Galaxies section 3 Evolution of Stars Before You Read What makes one star different from another? Do you think the Sun is the same as other stars? Write your ideas on the lines below.
chapter 13 3 Stars and Galaxies section 3 Evolution of Stars Before You Read What makes one star different from another? Do you think the Sun is the same as other stars? Write your ideas on the lines below.
Chapter 33 The History of a Star. Introduction. Radio telescopes allow us to look into the center of the galaxy. The milky way
 Chapter 33 The History of a Star Introduction Did you read chapter 33 before coming to class? A. Yes B. No You can see about 10,000 stars with the naked eye. The milky way Radio telescopes allow us to
Chapter 33 The History of a Star Introduction Did you read chapter 33 before coming to class? A. Yes B. No You can see about 10,000 stars with the naked eye. The milky way Radio telescopes allow us to
18. Which graph best represents the relationship between the number of sunspots and the amount of magnetic activity in the Sun?
 1. Which star has a surface temperature most similar to the surface temperature of Alpha Centauri? A) Polaris B) Betelgeuse C) Procyon B D) Sirius 2. Giant stars have greater luminosity than our sun mainly
1. Which star has a surface temperature most similar to the surface temperature of Alpha Centauri? A) Polaris B) Betelgeuse C) Procyon B D) Sirius 2. Giant stars have greater luminosity than our sun mainly
Stellar Evolution Notes
 Name: Block: Stellar Evolution Notes Stars mature, grow old and die. The more massive a star is, the shorter its life will be. Our Sun will live about 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old,
Name: Block: Stellar Evolution Notes Stars mature, grow old and die. The more massive a star is, the shorter its life will be. Our Sun will live about 10 billion years. It is already 5 billion years old,
The Earth and the Universe
 The Earth and the Universe The exploration of space is called astronomy. Most of our observations in space have come from using telescopes of different kinds. Observing the universe from the ground has
The Earth and the Universe The exploration of space is called astronomy. Most of our observations in space have come from using telescopes of different kinds. Observing the universe from the ground has
The Sun. - this is the visible surface of the Sun. The gases here are very still hot, but much cooler than inside about 6,000 C.
 Name: The Sun The Sun is an average sized. Earth, Mars, Jupiter and Uranus are. A star is the only object in space that makes its own. This includes and. The sun is about million miles from Earth. This
Name: The Sun The Sun is an average sized. Earth, Mars, Jupiter and Uranus are. A star is the only object in space that makes its own. This includes and. The sun is about million miles from Earth. This
Science Space Lessons 1-5 Notes
 Science Space Lessons 1-5 Notes The Planets in order from the Sun are: Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune To help us remember, we use the sentence: My Very Excited Mother Just Served
Science Space Lessons 1-5 Notes The Planets in order from the Sun are: Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune To help us remember, we use the sentence: My Very Excited Mother Just Served
Our Place in the Universe (Chapter 1) The Structure and Size of the Universe
 Our Place in the Universe (Chapter 1) The Structure and Size of the Universe Based on Chapter 1 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 2, 3, and 13 on Years, Seasons, and Months, The Orbits
Our Place in the Universe (Chapter 1) The Structure and Size of the Universe Based on Chapter 1 This material will be useful for understanding Chapters 2, 3, and 13 on Years, Seasons, and Months, The Orbits
Galaxies and Stars. 3. Base your answer to the following question on The reaction below represents an energy-producing process.
 Galaxies and Stars 1. To an observer on Earth, the Sun appears brighter than the star Rigel because the Sun is A) hotter than Rigel B) more luminous than Rigel C) closer than Rigel D) larger than Rigel
Galaxies and Stars 1. To an observer on Earth, the Sun appears brighter than the star Rigel because the Sun is A) hotter than Rigel B) more luminous than Rigel C) closer than Rigel D) larger than Rigel
CA Physical Science Benchmark Test 4. 1 A rocket accelerates from the launch pad. The forces on the rocket are
 Physical Science enchmark Test 4 Name: ate: 1 rocket accelerates from the launch pad. The forces on the rocket are action forces. balanced. reaction forces. unbalanced. 2 What force(s) act(s) on a rocket
Physical Science enchmark Test 4 Name: ate: 1 rocket accelerates from the launch pad. The forces on the rocket are action forces. balanced. reaction forces. unbalanced. 2 What force(s) act(s) on a rocket
STARS. THE LIGHT BILLIONS of MILES AWAY
 STARS THE LIGHT BILLIONS of MILES AWAY Sit back and enjoy the stars! They're BRIGHT!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! THE BIGGEST STAR IN OUR GALAXY Some people think that the stars in our galaxy are right outside
STARS THE LIGHT BILLIONS of MILES AWAY Sit back and enjoy the stars! They're BRIGHT!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! THE BIGGEST STAR IN OUR GALAXY Some people think that the stars in our galaxy are right outside
STARS AND GALAXIES STARS
 STARS AND GALAXIES STARS enormous spheres of plasma formed from strong gravitational forces PLASMA the most energetic state of matter; responsible for the characteristic glow emitted by these heavenly
STARS AND GALAXIES STARS enormous spheres of plasma formed from strong gravitational forces PLASMA the most energetic state of matter; responsible for the characteristic glow emitted by these heavenly
Parenting Tip of the Month. April. Lower Elementary Teachers
 Parenting Tip of the Month April Lower Elementary Teachers Why Use Higher Order Thinking Skills Everyday? Research tells us that Higher Order Thinking Skills help to build life long interaction and communication
Parenting Tip of the Month April Lower Elementary Teachers Why Use Higher Order Thinking Skills Everyday? Research tells us that Higher Order Thinking Skills help to build life long interaction and communication
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES
 SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
SOLAR SYSTEM, STABILITY OF ORBITAL MOTIONS, SATELLITES Q1. The figure below shows what scientists over 1000 years ago thought the solar system was like. Give one way that the historical model of the solar
LESSON topic: formation of the solar system Solar system formation Star formation Models of the solar system Planets in our solar system
 Unit 2 Lesson 1 LESSON topic: formation of the solar system - Solar system formation - Star formation - Models of the solar system - Planets in our solar system Big bang theory Origin of the universe According
Unit 2 Lesson 1 LESSON topic: formation of the solar system - Solar system formation - Star formation - Models of the solar system - Planets in our solar system Big bang theory Origin of the universe According
What is Earth Science?
 What is Earth Science? A.EARTH SCIENCE: the study of Earth and its history B. Earth science is divided into 4 main branches: 1. Geology: study of the lithosphere 2. Oceanography: study of oceans 3. Meteorology:
What is Earth Science? A.EARTH SCIENCE: the study of Earth and its history B. Earth science is divided into 4 main branches: 1. Geology: study of the lithosphere 2. Oceanography: study of oceans 3. Meteorology:
Science Practice Astronomy (AstronomyJSuber)
 Name: Date: 1. The pull of gravity on Earth is a direct result of the A. mass of Earth. B. magnetic field of Earth. C. rotation of Earth on its axis. D. weight of Earth's atmosphere. This online assessment
Name: Date: 1. The pull of gravity on Earth is a direct result of the A. mass of Earth. B. magnetic field of Earth. C. rotation of Earth on its axis. D. weight of Earth's atmosphere. This online assessment
Low-mass Stellar Evolution
 Low-mass Stellar Evolution The lives of low-mass stars And the lives of massive stars The Structure of the Sun Let s review: The Sun is held together by? The inward force is balanced by? Thinking about
Low-mass Stellar Evolution The lives of low-mass stars And the lives of massive stars The Structure of the Sun Let s review: The Sun is held together by? The inward force is balanced by? Thinking about
Our Sun. The centre of our solar system
 Our Sun The centre of our solar system Nicolaus Copernicus Our Sun The sun represents 99.86% of the mass in our solar system. It is ¾ hydrogen and ¼ helium. More than 1 million Earths can fit inside the
Our Sun The centre of our solar system Nicolaus Copernicus Our Sun The sun represents 99.86% of the mass in our solar system. It is ¾ hydrogen and ¼ helium. More than 1 million Earths can fit inside the
A supernova is the explosion of a star. It is the largest explosion that takes place in space.
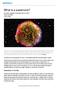 What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
What is a supernova? By NASA, adapted by Newsela staff on 03.28.17 Word Count 974 Level 1110L TOP: A vivid view of a supernova remnant captured by NASA's Spitzer and Chandra space observatories and the
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION
 TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION (The Universe) A. THE UNIVERSE: The universe encompasses all matter in existence. According to the Big Bang Theory, the universe was formed 10-20 billion years ago from a
TEACHER BACKGROUND INFORMATION (The Universe) A. THE UNIVERSE: The universe encompasses all matter in existence. According to the Big Bang Theory, the universe was formed 10-20 billion years ago from a
The Outer Planets. Video Script: The Outer Planets. Visual Learning Company
 11 Video Script: 1. For thousands of years people have looked up at the night sky pondering the limits of our solar system. 2. Perhaps you too, have looked up at the evening stars and planets, and wondered
11 Video Script: 1. For thousands of years people have looked up at the night sky pondering the limits of our solar system. 2. Perhaps you too, have looked up at the evening stars and planets, and wondered
Properties of Stars. Characteristics of Stars
 Properties of Stars Characteristics of Stars A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for mythical characters. The sky contains 88 constellations. Star Color and Temperature Color
Properties of Stars Characteristics of Stars A constellation is an apparent group of stars originally named for mythical characters. The sky contains 88 constellations. Star Color and Temperature Color
Introduction to the Solar System
 Introduction to the Solar System Sep. 11, 2002 1) Introduction 2) Angular Momentum 3) Formation of the Solar System 4) Cowboy Astronomer Review Kepler s Laws empirical description of planetary motion Newton
Introduction to the Solar System Sep. 11, 2002 1) Introduction 2) Angular Momentum 3) Formation of the Solar System 4) Cowboy Astronomer Review Kepler s Laws empirical description of planetary motion Newton
Learning About Our Solar System
 Learning About Our Solar System By debbie Routh COPYRIGHT 2004 Mark Twain Media, Inc. ISBN 978-1-58037-876-5 Printing No. 404007-EB Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers Distributed by Carson-Dellosa Publishing
Learning About Our Solar System By debbie Routh COPYRIGHT 2004 Mark Twain Media, Inc. ISBN 978-1-58037-876-5 Printing No. 404007-EB Mark Twain Media, Inc., Publishers Distributed by Carson-Dellosa Publishing
JOURNEY TO THE STARS
 JOURNEY TO THE STARS Narrator: Whoopi Goldberg Curators: Mordecai Mac Low and Ben Oppenheimer We live on a planet powered by a star. It brightens our days, providing us with more light and energy than
JOURNEY TO THE STARS Narrator: Whoopi Goldberg Curators: Mordecai Mac Low and Ben Oppenheimer We live on a planet powered by a star. It brightens our days, providing us with more light and energy than
TAKE A LOOK 2. Identify This star is in the last stage of its life cycle. What is that stage?
 CHAPTER 15 2 SECTION Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe The Life Cycle of Stars BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do stars change over time?
CHAPTER 15 2 SECTION Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe The Life Cycle of Stars BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: How do stars change over time?
The Sun and the Stars
 Objective Concepts (gravity, climate, solar system, hydrogen, helium, elements, ultraviolet rays, cluster, galaxy, Milky Way Galaxy); Sight words (surface, core, dangerous, causes, amount, glowing, tiny,
Objective Concepts (gravity, climate, solar system, hydrogen, helium, elements, ultraviolet rays, cluster, galaxy, Milky Way Galaxy); Sight words (surface, core, dangerous, causes, amount, glowing, tiny,
FCAT Review Space Science
 FCAT Review Space Science The Law of Universal Gravitation The law of universal gravitation states that ALL matter in the universe attracts each other. Gravity is greatly impacted by both mass and distance
FCAT Review Space Science The Law of Universal Gravitation The law of universal gravitation states that ALL matter in the universe attracts each other. Gravity is greatly impacted by both mass and distance
What s in Our Solar System?
 The Planets What s in Our Solar System? Our Solar System consists of a central star (the Sun), the main eight planets orbiting the sun, the dwarf planets, moons, asteroids, comets, meteors, interplanetary
The Planets What s in Our Solar System? Our Solar System consists of a central star (the Sun), the main eight planets orbiting the sun, the dwarf planets, moons, asteroids, comets, meteors, interplanetary
Name: Space Questions. Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comment s:
 Space 2 33 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comment s: Q. Read the passage. In the SolarSystem, the inner planets, such as the Earth, contain elements which are eavierthan the elements hydrogen
Space 2 33 Questions Name: Class: Date: Time: Marks: Comment s: Q. Read the passage. In the SolarSystem, the inner planets, such as the Earth, contain elements which are eavierthan the elements hydrogen
Mass: 1.99 x 1030 kg. Diameter: about km = 100 x the Earth diameter. Density: about kg/m3
 Mass: 1.99 x 1030 kg Diameter: about 1 400 00 km = 100 x the Earth diameter Produces a strong gravitational forces: about 28 times greater than the gravitational force produces by the Earth Temperature:
Mass: 1.99 x 1030 kg Diameter: about 1 400 00 km = 100 x the Earth diameter Produces a strong gravitational forces: about 28 times greater than the gravitational force produces by the Earth Temperature:
The Birth and Death of Stars
 The Birth and Death of Stars 2013 Simulation Curriculum Teachers may make copies for their classes Part 1: Stellar Cradles With a small telescope the central region of M42 reveals a group of at least four
The Birth and Death of Stars 2013 Simulation Curriculum Teachers may make copies for their classes Part 1: Stellar Cradles With a small telescope the central region of M42 reveals a group of at least four
The Life Cycle of Stars. : Is the current theory of how our Solar System formed.
 Life Cycle of a Star Video (5 min) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pm9cqdlqi0a The Life Cycle of Stars Solar Nebula Theory : Is the current theory of how our Solar System formed. This theory states that
Life Cycle of a Star Video (5 min) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pm9cqdlqi0a The Life Cycle of Stars Solar Nebula Theory : Is the current theory of how our Solar System formed. This theory states that
Astronomy Universe: all of space and everything in it
 Astronomy Universe: all of space and everything in it Most (90%) of the universe is made up of: dark matter: stuff we think is there due to amount of mass we think is there but is not detected by the instruments
Astronomy Universe: all of space and everything in it Most (90%) of the universe is made up of: dark matter: stuff we think is there due to amount of mass we think is there but is not detected by the instruments
Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE
 Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the universe; its nature, origin and evolution. General Relativity is the mathematical basis of cosmology from which
Cosmology, Galaxies, and Stars OUR VISIBLE UNIVERSE Cosmology Cosmology is the study of the universe; its nature, origin and evolution. General Relativity is the mathematical basis of cosmology from which
CHAPTER 11. We continue to Learn a lot about the Solar System by using Space Exploration
 CHAPTER 11 We continue to Learn a lot about the Solar System by using Space Exploration Section 11.1 The Sun page 390 -Average sized star -Millions of km away -300,000 more massive then Earth, 99% of all
CHAPTER 11 We continue to Learn a lot about the Solar System by using Space Exploration Section 11.1 The Sun page 390 -Average sized star -Millions of km away -300,000 more massive then Earth, 99% of all
days to rotate in its own axis km in diameter ( 109 diameter of the Earth ) and kg in mass ( mass of the Earth)
 The Sun - It is located at the centre of our solar system with all planets and objects (comets and asteroids) revolving around it Page 1 of 6 - It s gravitational pull keeps the planets and other objects
The Sun - It is located at the centre of our solar system with all planets and objects (comets and asteroids) revolving around it Page 1 of 6 - It s gravitational pull keeps the planets and other objects
The Sun and Water Cycle
 Have you ever jumped in a puddle or played in the rain? If so, you know you can get very wet. What you may not know is that a dinosaur could have walked through that same water millions of years ago. The
Have you ever jumped in a puddle or played in the rain? If so, you know you can get very wet. What you may not know is that a dinosaur could have walked through that same water millions of years ago. The
The History of the Solar System. From cloud to Sun, planets, and smaller bodies
 The History of the Solar System From cloud to Sun, planets, and smaller bodies The Birth of a Star Twenty years ago, we knew of only one star with planets the Sun and our understanding of the birth of
The History of the Solar System From cloud to Sun, planets, and smaller bodies The Birth of a Star Twenty years ago, we knew of only one star with planets the Sun and our understanding of the birth of
Radiation - a process in which energy travels through vacuum (without a medium) Conduction a process in which energy travels through a medium
 SOLAR SYSTEM NOTES ENERGY TRANSFERS Radiation - a process in which energy travels through vacuum (without a medium) Conduction a process in which energy travels through a medium Convection - The transfer
SOLAR SYSTEM NOTES ENERGY TRANSFERS Radiation - a process in which energy travels through vacuum (without a medium) Conduction a process in which energy travels through a medium Convection - The transfer
Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe
 Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe 1. The Universe 1.1. First ideas about the Universe 1.2. Components and origin 1.3. Sizes and distances 2. The Solar System 3. The planet Earth 3.1. Movements of the Earth
Unit 1: The Earth in the Universe 1. The Universe 1.1. First ideas about the Universe 1.2. Components and origin 1.3. Sizes and distances 2. The Solar System 3. The planet Earth 3.1. Movements of the Earth
Sun Mercury Venus. Earth Mars Jupiter
 Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Venus is the hottest planet in our solar system. The thick clouds on Venus hold the heat in. The sun s lights reflect off Venus s clouds making it look like the brightest
Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Venus is the hottest planet in our solar system. The thick clouds on Venus hold the heat in. The sun s lights reflect off Venus s clouds making it look like the brightest
Chapter 5 Newton s Universe
 Chapter 5 Newton s Universe Lecture notes about gravitation Dr. Armen Kocharian Units of Chapter 5 The Idea of Gravity: The Apple and the Moon The Law of Gravity: Moving the Farthest Star Gravitational
Chapter 5 Newton s Universe Lecture notes about gravitation Dr. Armen Kocharian Units of Chapter 5 The Idea of Gravity: The Apple and the Moon The Law of Gravity: Moving the Farthest Star Gravitational
Explain how the sun converts matter into energy in its core. Describe the three layers of the sun s atmosphere.
 Chapter 29 and 30 Explain how the sun converts matter into energy in its core. Describe the three layers of the sun s atmosphere. Explain how sunspots are related to powerful magnetic fields on the sun.
Chapter 29 and 30 Explain how the sun converts matter into energy in its core. Describe the three layers of the sun s atmosphere. Explain how sunspots are related to powerful magnetic fields on the sun.
What is a star? A body of gases that gives off tremendous amounts of energy in the form of light & heat. What star is closest to the earth?
 Stars What is a star? A body of gases that gives off tremendous amounts of energy in the form of light & heat. What star is closest to the earth? Answer: The SUN It s about 150,000,000 km from earth =
Stars What is a star? A body of gases that gives off tremendous amounts of energy in the form of light & heat. What star is closest to the earth? Answer: The SUN It s about 150,000,000 km from earth =
Star. Planet. Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe. 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe?
 Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
Chapter 1 Our Place in the Universe 1.1 A Modern View of the Universe Our goals for learning: What is our place in the universe? How did we come to be? How can we know what the universe was like in the
1. What is the primary difference between the evolution of a low-mass star and that of a high-mass star?
 FYI: The Lives of Stars E3:R6b 1. Read FYI: The Lives of Stars As you read use the spaces below to write down any information you find especially interesting. Also define the bold terms used in the text.
FYI: The Lives of Stars E3:R6b 1. Read FYI: The Lives of Stars As you read use the spaces below to write down any information you find especially interesting. Also define the bold terms used in the text.
Coriolis Effect - the apparent curved paths of projectiles, winds, and ocean currents
 Regents Earth Science Unit 5: Astronomy Models of the Universe Earliest models of the universe were based on the idea that the Sun, Moon, and planets all orbit the Earth models needed to explain how the
Regents Earth Science Unit 5: Astronomy Models of the Universe Earliest models of the universe were based on the idea that the Sun, Moon, and planets all orbit the Earth models needed to explain how the
