Scale Analysis of the Equations of Motion
|
|
|
- Terence Conley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 hen are curvature terms important? Important for GCMs and large-scale (global) weather. ere, we consider sub-global scale referred to as synoptic scale. Scale Analysis of the Equations of Motion e use typically observed values of synoptic-scale features to perform scale analysis. variable description value L z length scale ~ radius low/high pressure 000 km Vertical length scale ~ scale height 0 km z velocity scale ~ u or v component 0 ms - Vertical velocity scale ~ w component cms - δp h hz pressure diff. ~ change in p over L 0 mb δp h /ρ ρ is typically kg m m 2 s -2 δp v /ρ vertical pressure diff. ~ change in p over 0 5 m 2 s -2 T h (=L/) time for parcel travelling at to cover L 0 6 m/0ms - =0 5 s T v (=/w) time for a parcel moving at w to cover 0 4 m/0-2 ms - =0 6 s (0 days!) T v and T h are referred to as advective time scales. Estimating order of magnitudes for our terms in the equations and, x --- y x y L ---, , and - x y L The local time derivative terms
2 and, - or T h or ---- whichever is larger T h T v ---- whichever is larger T v Order of magnitude theory, i.e. normal math order o mag math + = 2 + ~ ++=3 ++ ~ = ~ =5 ++++=5 (too close to call) -=0 -=0 (maybe not! ARNING) sing our scaling parameters in the previous table, we note that the magnitude of Dt is given by the largest term (i.e. either the advective terms of local tendency term), thus looking at the component equation we have /T h 2 /L / - Dt = + u + v + w 0 4 x y (e can show that Dv/Dt~0-4 as well). Note that above we showed, 2 - L > --- or L ---- Store this into your memory as we will revisit this a little later when looking at mass conservation. A typical value for the mid latitude magnitude of the Coriolis is f 0 = 2Ωsinφ = 2Ωcosφ = sin45 0 4
3 Also -> tan45=.0 (for curvature terms) Apx earth s radius -> a~6000 km ~ 0 7 m orizontal eqns of motion: x-eq /Dt -2Ωvsinφ 2Ωwcosφ uw/a -uvtanφ/a y-eq Dv/Dt 2Ωusinφ vw/a u 2 tanφ/a scale 2 /L f 0 f 0 /a 2 /a ( ρ) p x ( ρ) p y δp ( ρl) OM Thus we see that the largest terms in the hz eqns of motion are the Coriolis and the pressure gradient! Thus, to a first order of magnitude, our x and y component eqns reduce to fv -- p, and fu -- p ρ x ρ y where f=2ωsinφ. These are the geostrophic relationship, i.e. the Coriolis and pressure gradient terms balance one another. In chapter 3 (section 3.2.2), we ll see what this means from a dynamical perspective. In vector notation (i.e. combine the two eqns above), Or, fkˆ v = -- p ρ v v g = ---- kˆ p = u ρf g î + v g ĵ LO p LO IG IG u kˆ p kˆ out of paper
4 Thus, from the eqn and figure we have -Geostrophic wind vector is parallel to isobars. - Buys Ballots's law: ith geostrophic wind at your back, low pressure is to your left (in N. hemisphere) - Geostrophic wind speed is proportional to magnitude of pressure gradient (packing of isobars). Note however that for the same pressure gradient, the geostrophic wind speed is greater equatorward (/f). Geos wind is hypothetical wind, i.e. the wind you'd have in an atmos in a pure geos balance. The true wind is nearly equal to geostrophic wind for synoptic flows above the boundary layer (i.e. for z>km) ere, u u g, v v g with 0-5% error. The actual wind differs from geostrophic wind near fronts, and near the earth's surface. Y IS TIS IS? Note that in general, if the weather is interesting it is not generally in geostrophic balance! And more on geosgtrophic balance... The geos balance is a diagnostic relation btw pressure gradient and velocity. Thus, knowledge of the horizontal pressure distribution exactly determines the velocity field. Not a bad eyeball estimate of wind speed and direction for large-scale flow (synoptic or larger). For a prognostic set of horizontal equations that are more representative of the true atmosphere, we keep the next most important term (i.e. the acceleration), - fv -- p Dv = f( v v Dt ρ x g ) and -, fu -- p = fu ( u Dt ρ y g ) where we have substituted the geostrophic relationship for the pressure gradient. The above eqn can be used for prognostic meteorology (predictions, Y?) One issue is that we know from our scaling arguments earlier that the acceleration terms (/Dt and Dv/Dt) are, for large-scale flows, an order of magnitude smaller than the pressure gradient and Coriolis terms. Thus, the acceleration terms are the resultant of a slight difference between two (much) larger terms. STDENTS: hat does this mean in terms of observations of u, v, and p? They best be accurate!
5 e can get an estimate of the relative order of magnitude of these terms by taking the ratio of the acceleration term and Coriolis term (see table for scaling values), - -- Dt Rossby # (famous Met C. G. Rossby) fv L f fl The ratio of /Dt to fu is the same! NON-DIMNENSIONAL (as are all of the scaling numbers in meteorology, e.g. Froude, Reynolds etc.) IF R >, then accelerations are important! IF R <, then Coriolis dominates For small Rossby # s the flow is apx geostrophic. hat about our atmosphere? /fl = 0/(0-4 x0 6 )= 0 -. Therefore, << fl and to a first Order, the atmosphere is geostrophic! hat about a tornado? = 00 ms-, L = 00 m, thus /fl = 0 2 /(0-4 x0 2 ) = 0 4 Thus we can neglect the Coriolis force for a tornado! Coriolis force is important to the tornado indirectly in that it affects the way the winds turn with height in the atmosphere (e.g. hodographs). Certain wind profiles are more conducive than others to tornado formation, thus the Coriolis force affects "initial conditions, i.e the environment in which the tornadic thunderstorm develops. Recall curvature terms (e.g. uw/a ~ 0-5 and 0-8 ) are smaller than acceleration, Coriolis force, and pgf terms (~0-3 ). e can safely neglect them for synoptic scale flows. This is equivalent to treating spherical x,y,z coords as if they were Cartesian x,y,z coords. Flat earth society!
Balanced Flow Geostrophic, Inertial, Gradient, and Cyclostrophic Flow
 Balanced Flow Geostrophic, Inertial, Gradient, and Cyclostrophic Flow The types of atmospheric flows describe here have the following characteristics: 1) Steady state (meaning that the flows do not change
Balanced Flow Geostrophic, Inertial, Gradient, and Cyclostrophic Flow The types of atmospheric flows describe here have the following characteristics: 1) Steady state (meaning that the flows do not change
Synoptic Meteorology I: Other Force Balances
 Synoptic Meteorology I: Other Force Balances For Further Reading Section.1.3 of Mid-Latitude Atmospheric Dynamics by J. Martin provides a discussion of the frictional force and considerations related to
Synoptic Meteorology I: Other Force Balances For Further Reading Section.1.3 of Mid-Latitude Atmospheric Dynamics by J. Martin provides a discussion of the frictional force and considerations related to
Dust devils, water spouts, tornados
 Balanced flow Things we know Primitive equations are very comprehensive, but there may be a number of vast simplifications that may be relevant (e.g., geostrophic balance). Seems that there are things
Balanced flow Things we know Primitive equations are very comprehensive, but there may be a number of vast simplifications that may be relevant (e.g., geostrophic balance). Seems that there are things
Dynamic Meteorology 1
 Dynamic Meteorology 1 Lecture 14 Sahraei Department of Physics, Razi University http://www.razi.ac.ir/sahraei Buys-Ballot rule (Northern Hemisphere) If the wind blows into your back, the Low will be to
Dynamic Meteorology 1 Lecture 14 Sahraei Department of Physics, Razi University http://www.razi.ac.ir/sahraei Buys-Ballot rule (Northern Hemisphere) If the wind blows into your back, the Low will be to
The dynamics of high and low pressure systems
 The dynamics of high and low pressure systems Newton s second law for a parcel of air in an inertial coordinate system (a coordinate system in which the coordinate axes do not change direction and are
The dynamics of high and low pressure systems Newton s second law for a parcel of air in an inertial coordinate system (a coordinate system in which the coordinate axes do not change direction and are
Problem #1: The Gradient Wind in Natural Coordinates (Due Friday, Feb. 28; 20 pts total)
 METR 50: Atmospheric Dynamics II Dr. Dave Dempsey Spring 014 Problem #1: The Gradient Wind in Natural Coordinates (Due Friday, Feb. 8; 0 pts total) In natural (s,n,p) coordinates, the synoptic-scaled,
METR 50: Atmospheric Dynamics II Dr. Dave Dempsey Spring 014 Problem #1: The Gradient Wind in Natural Coordinates (Due Friday, Feb. 8; 0 pts total) In natural (s,n,p) coordinates, the synoptic-scaled,
1/18/2011. From the hydrostatic equation, it is clear that a single. pressure and height in each vertical column of the atmosphere.
 Lecture 3: Applications of Basic Equations Pressure as Vertical Coordinate From the hydrostatic equation, it is clear that a single valued monotonic relationship exists between pressure and height in each
Lecture 3: Applications of Basic Equations Pressure as Vertical Coordinate From the hydrostatic equation, it is clear that a single valued monotonic relationship exists between pressure and height in each
Solution to Problems #1. I. Information Given or Otherwise Known. = 28 m/s. Heading of the ultralight aircraft!! h
 METR 520: Atmospheric Dynamics II Dr. Dave Dempsey Dept. of Geosciences, SFSU Spring 2012 Solution to Problems 1 Problem 1 An ultralight aircraft is flying. I. Information Given or Otherwise Known Horizontal
METR 520: Atmospheric Dynamics II Dr. Dave Dempsey Dept. of Geosciences, SFSU Spring 2012 Solution to Problems 1 Problem 1 An ultralight aircraft is flying. I. Information Given or Otherwise Known Horizontal
The Equations of Motion in a Rotating Coordinate System. Chapter 3
 The Equations of Motion in a Rotating Coordinate System Chapter 3 Since the earth is rotating about its axis and since it is convenient to adopt a frame of reference fixed in the earth, we need to study
The Equations of Motion in a Rotating Coordinate System Chapter 3 Since the earth is rotating about its axis and since it is convenient to adopt a frame of reference fixed in the earth, we need to study
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter 1. Introduction In this class, we will examine atmospheric phenomena that occurs at the mesoscale, including some boundary layer processes, convective storms, and hurricanes. We will emphasize
Chapter 1. Introduction In this class, we will examine atmospheric phenomena that occurs at the mesoscale, including some boundary layer processes, convective storms, and hurricanes. We will emphasize
Dynamics Rotating Tank
 Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science - IACETH Atmospheric Physics Lab Work Dynamics Rotating Tank Large scale flows on different latitudes of the rotating Earth Abstract The large scale atmospheric
Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science - IACETH Atmospheric Physics Lab Work Dynamics Rotating Tank Large scale flows on different latitudes of the rotating Earth Abstract The large scale atmospheric
+ ω = 0, (1) (b) In geometric height coordinates in the rotating frame of the Earth, momentum balance for an inviscid fluid is given by
 Problem Sheet 1: Due Thurs 3rd Feb 1. Primitive equations in different coordinate systems (a) Using Lagrangian considerations and starting from an infinitesimal mass element in cartesian coordinates (x,y,z)
Problem Sheet 1: Due Thurs 3rd Feb 1. Primitive equations in different coordinate systems (a) Using Lagrangian considerations and starting from an infinitesimal mass element in cartesian coordinates (x,y,z)
Class exercises Chapter 3. Elementary Applications of the Basic Equations
 Class exercises Chapter 3. Elementary Applications of the Basic Equations Section 3.1 Basic Equations in Isobaric Coordinates 3.1 For some (in fact many) applications we assume that the change of the Coriolis
Class exercises Chapter 3. Elementary Applications of the Basic Equations Section 3.1 Basic Equations in Isobaric Coordinates 3.1 For some (in fact many) applications we assume that the change of the Coriolis
Houze sections 7.4, 8.3, 8.5, Refer back to equations in Section 2.3 when necessary.
 Thunderstorm Dynamics Houze sections 7.4, 8.3, 8.5, Refer back to equations in Section.3 when necessary. Bluestein Vol. II section 3.4.6. Review article "Dynamics of Tornadic Thunderstorms" by Klemp handout.
Thunderstorm Dynamics Houze sections 7.4, 8.3, 8.5, Refer back to equations in Section.3 when necessary. Bluestein Vol. II section 3.4.6. Review article "Dynamics of Tornadic Thunderstorms" by Klemp handout.
Chapter 9. Geostrophy, Quasi-Geostrophy and the Potential Vorticity Equation
 Chapter 9 Geostrophy, Quasi-Geostrophy and the Potential Vorticity Equation 9.1 Geostrophy and scaling. We examined in the last chapter some consequences of the dynamical balances for low frequency, nearly
Chapter 9 Geostrophy, Quasi-Geostrophy and the Potential Vorticity Equation 9.1 Geostrophy and scaling. We examined in the last chapter some consequences of the dynamical balances for low frequency, nearly
Fundamentals of Atmospheric Modelling
 M.Sc. in Computational Science Fundamentals of Atmospheric Modelling Peter Lynch, Met Éireann Mathematical Computation Laboratory (Opp. Room 30) Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield. January April, 2004.
M.Sc. in Computational Science Fundamentals of Atmospheric Modelling Peter Lynch, Met Éireann Mathematical Computation Laboratory (Opp. Room 30) Dept. of Maths. Physics, UCD, Belfield. January April, 2004.
Fundamental Meteo Concepts
 Fundamental Meteo Concepts Atmos 5110 Synoptic Dynamic Meteorology I Instructor: Jim Steenburgh jim.steenburgh@utah.edu 801-581-8727 Suite 480/Office 488 INSCC Suggested reading: Lackmann (2011), sections
Fundamental Meteo Concepts Atmos 5110 Synoptic Dynamic Meteorology I Instructor: Jim Steenburgh jim.steenburgh@utah.edu 801-581-8727 Suite 480/Office 488 INSCC Suggested reading: Lackmann (2011), sections
Vorticity in natural coordinates
 Vorticity in natural coordinates (see Holton pg 95, section 4.2.) Let s consider the vertical vorticity component only, i.e. ζ kˆ ω, we have ω u dl kˆ ω lim --- lim ----------------- curve is in xy plane
Vorticity in natural coordinates (see Holton pg 95, section 4.2.) Let s consider the vertical vorticity component only, i.e. ζ kˆ ω, we have ω u dl kˆ ω lim --- lim ----------------- curve is in xy plane
Goal: Use understanding of physically-relevant scales to reduce the complexity of the governing equations
 Scale analysis relevant to the tropics [large-scale synoptic systems]* Goal: Use understanding of physically-relevant scales to reduce the complexity of the governing equations *Reminder: Midlatitude scale
Scale analysis relevant to the tropics [large-scale synoptic systems]* Goal: Use understanding of physically-relevant scales to reduce the complexity of the governing equations *Reminder: Midlatitude scale
Circulation and Vorticity
 Circulation and Vorticity Example: Rotation in the atmosphere water vapor satellite animation Circulation a macroscopic measure of rotation for a finite area of a fluid Vorticity a microscopic measure
Circulation and Vorticity Example: Rotation in the atmosphere water vapor satellite animation Circulation a macroscopic measure of rotation for a finite area of a fluid Vorticity a microscopic measure
Dynamic Meteorology - Introduction
 Dynamic Meteorology - Introduction Atmospheric dynamics the study of atmospheric motions that are associated with weather and climate We will consider the atmosphere to be a continuous fluid medium, or
Dynamic Meteorology - Introduction Atmospheric dynamics the study of atmospheric motions that are associated with weather and climate We will consider the atmosphere to be a continuous fluid medium, or
d v 2 v = d v d t i n where "in" and "rot" denote the inertial (absolute) and rotating frames. Equation of motion F =
 Governing equations of fluid dynamics under the influence of Earth rotation (Navier-Stokes Equations in rotating frame) Recap: From kinematic consideration, d v i n d t i n = d v rot d t r o t 2 v rot
Governing equations of fluid dynamics under the influence of Earth rotation (Navier-Stokes Equations in rotating frame) Recap: From kinematic consideration, d v i n d t i n = d v rot d t r o t 2 v rot
1/18/2011. Conservation of Momentum Conservation of Mass Conservation of Energy Scaling Analysis ESS227 Prof. Jin-Yi Yu
 Lecture 2: Basic Conservation Laws Conservation Law of Momentum Newton s 2 nd Law of Momentum = absolute velocity viewed in an inertial system = rate of change of Ua following the motion in an inertial
Lecture 2: Basic Conservation Laws Conservation Law of Momentum Newton s 2 nd Law of Momentum = absolute velocity viewed in an inertial system = rate of change of Ua following the motion in an inertial
Governing Equations and Scaling in the Tropics
 Governing Equations and Scaling in the Tropics M 1 ( ) e R ε er Tropical v Midlatitude Meteorology Why is the general circulation and synoptic weather systems in the tropics different to the those in the
Governing Equations and Scaling in the Tropics M 1 ( ) e R ε er Tropical v Midlatitude Meteorology Why is the general circulation and synoptic weather systems in the tropics different to the those in the
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES
 EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week Radiative Transfer Black body radiation, Planck function, Wien s law Absorption, emission, opacity, optical depth Intensity, flux Radiative diffusion,
EART164: PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES Francis Nimmo Last Week Radiative Transfer Black body radiation, Planck function, Wien s law Absorption, emission, opacity, optical depth Intensity, flux Radiative diffusion,
= vorticity dilution + tilting horizontal vortices + microscopic solenoid
 4.4 Vorticity Eq 4.4.1 Cartesian Coordinates Because ζ = ˆk V, gives D(ζ + f) x minus [v momentum eq. in Cartesian Coordinates] y [u momentum eq. in Cartesian Coordinates] = vorticity dilution + tilting
4.4 Vorticity Eq 4.4.1 Cartesian Coordinates Because ζ = ˆk V, gives D(ζ + f) x minus [v momentum eq. in Cartesian Coordinates] y [u momentum eq. in Cartesian Coordinates] = vorticity dilution + tilting
t tendency advection convergence twisting baroclinicity
 RELATIVE VORTICITY EQUATION Newton s law in a rotating frame in z-coordinate (frictionless): U + U U = 2Ω U Φ α p U + U U 2 + ( U) U = 2Ω U Φ α p Applying to both sides, and noting ω U and using identities
RELATIVE VORTICITY EQUATION Newton s law in a rotating frame in z-coordinate (frictionless): U + U U = 2Ω U Φ α p U + U U 2 + ( U) U = 2Ω U Φ α p Applying to both sides, and noting ω U and using identities
ESCI 342 Atmospheric Dynamics I Lesson 12 Vorticity
 ESCI 34 tmospheric Dynamics I Lesson 1 Vorticity Reference: n Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology (4 rd edition), Holton n Informal Introduction to Theoretical Fluid Mechanics, Lighthill Reading: Martin,
ESCI 34 tmospheric Dynamics I Lesson 1 Vorticity Reference: n Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology (4 rd edition), Holton n Informal Introduction to Theoretical Fluid Mechanics, Lighthill Reading: Martin,
Chapter 10 Atmospheric Forces & Winds
 Chapter 10 Atospheric Forces & Winds Chapter overview: Atospheric Pressure o Horizontal pressure variations o Station vs sea level pressure Winds and weather aps Newton s 2 nd Law Horizontal Forces o Pressure
Chapter 10 Atospheric Forces & Winds Chapter overview: Atospheric Pressure o Horizontal pressure variations o Station vs sea level pressure Winds and weather aps Newton s 2 nd Law Horizontal Forces o Pressure
g (z) = 1 (1 + z/a) = 1
 1.4.2 Gravitational Force g is the gravitational force. It always points towards the center of mass, and it is proportional to the inverse square of the distance above the center of mass: g (z) = GM (a
1.4.2 Gravitational Force g is the gravitational force. It always points towards the center of mass, and it is proportional to the inverse square of the distance above the center of mass: g (z) = GM (a
7 Balanced Motion. 7.1 Return of the...scale analysis for hydrostatic balance! CSU ATS601 Fall 2015
 7 Balanced Motion We previously discussed the concept of balance earlier, in the context of hydrostatic balance. Recall that the balanced condition means no accelerations (balance of forces). That is,
7 Balanced Motion We previously discussed the concept of balance earlier, in the context of hydrostatic balance. Recall that the balanced condition means no accelerations (balance of forces). That is,
ρ x + fv f 'w + F x ρ y fu + F y Fundamental Equation in z coordinate p = ρrt or pα = RT Du uv tanφ Dv Dt + u2 tanφ + vw a a = 1 p Dw Dt u2 + v 2
 Fundamental Equation in z coordinate p = ρrt or pα = RT Du uv tanφ + uw Dt a a = 1 p ρ x + fv f 'w + F x Dv Dt + u2 tanφ + vw a a = 1 p ρ y fu + F y Dw Dt u2 + v 2 = 1 p a ρ z g + f 'u + F z Dρ Dt + ρ
Fundamental Equation in z coordinate p = ρrt or pα = RT Du uv tanφ + uw Dt a a = 1 p ρ x + fv f 'w + F x Dv Dt + u2 tanφ + vw a a = 1 p ρ y fu + F y Dw Dt u2 + v 2 = 1 p a ρ z g + f 'u + F z Dρ Dt + ρ
g (z) = 1 (1 + z/a) = 1 1 ( km/10 4 km) 2
 1.4.2 Gravitational Force g is the gravitational force. It always points towards the center of mass, and it is proportional to the inverse square of the distance above the center of mass: g (z) = GM (a
1.4.2 Gravitational Force g is the gravitational force. It always points towards the center of mass, and it is proportional to the inverse square of the distance above the center of mass: g (z) = GM (a
Atmospheric Fronts. The material in this section is based largely on. Lectures on Dynamical Meteorology by Roger Smith.
 Atmospheric Fronts The material in this section is based largely on Lectures on Dynamical Meteorology by Roger Smith. Atmospheric Fronts 2 Atmospheric Fronts A front is the sloping interfacial region of
Atmospheric Fronts The material in this section is based largely on Lectures on Dynamical Meteorology by Roger Smith. Atmospheric Fronts 2 Atmospheric Fronts A front is the sloping interfacial region of
Conservation of Mass Conservation of Energy Scaling Analysis. ESS227 Prof. Jin-Yi Yu
 Lecture 2: Basic Conservation Laws Conservation of Momentum Conservation of Mass Conservation of Energy Scaling Analysis Conservation Law of Momentum Newton s 2 nd Law of Momentum = absolute velocity viewed
Lecture 2: Basic Conservation Laws Conservation of Momentum Conservation of Mass Conservation of Energy Scaling Analysis Conservation Law of Momentum Newton s 2 nd Law of Momentum = absolute velocity viewed
By convention, C > 0 for counterclockwise flow, hence the contour must be counterclockwise.
 Chapter 4 4.1 The Circulation Theorem Circulation is a measure of rotation. It is calculated for a closed contour by taking the line integral of the velocity component tangent to the contour evaluated
Chapter 4 4.1 The Circulation Theorem Circulation is a measure of rotation. It is calculated for a closed contour by taking the line integral of the velocity component tangent to the contour evaluated
SIO 210 Problem Set 3 November 15, 2013 Due Nov. 22, 2013 Answerkey
 SIO 210 Problem Set 3 November 15, 2013 Due Nov. 22, 2013 Answerkey 1. Dynamics: rotation (a) Draw the direction of an inertial current in (i) the northern hemisphere and (ii) the southern hemisphere and
SIO 210 Problem Set 3 November 15, 2013 Due Nov. 22, 2013 Answerkey 1. Dynamics: rotation (a) Draw the direction of an inertial current in (i) the northern hemisphere and (ii) the southern hemisphere and
Measurement of Rotation. Circulation. Example. Lecture 4: Circulation and Vorticity 1/31/2017
 Lecture 4: Circulation and Vorticity Measurement of Rotation Circulation Bjerknes Circulation Theorem Vorticity Potential Vorticity Conservation of Potential Vorticity Circulation and vorticity are the
Lecture 4: Circulation and Vorticity Measurement of Rotation Circulation Bjerknes Circulation Theorem Vorticity Potential Vorticity Conservation of Potential Vorticity Circulation and vorticity are the
On side wall labeled A: we can express the pressure in a Taylor s series expansion: x 2. + higher order terms,
 Chapter 1 Notes A Note About Coordinates We nearly always use a coordinate system in this class where the vertical, ˆk, is normal to the Earth s surface and the x-direction, î, points to the east and the
Chapter 1 Notes A Note About Coordinates We nearly always use a coordinate system in this class where the vertical, ˆk, is normal to the Earth s surface and the x-direction, î, points to the east and the
NWP Equations (Adapted from UCAR/COMET Online Modules)
 NWP Equations (Adapted from UCAR/COMET Online Modules) Certain physical laws of motion and conservation of energy (for example, Newton's Second Law of Motion and the First Law of Thermodynamics) govern
NWP Equations (Adapted from UCAR/COMET Online Modules) Certain physical laws of motion and conservation of energy (for example, Newton's Second Law of Motion and the First Law of Thermodynamics) govern
The atmosphere in motion: forces and wind. AT350 Ahrens Chapter 9
 The atmosphere in motion: forces and wind AT350 Ahrens Chapter 9 Recall that Pressure is force per unit area Air pressure is determined by the weight of air above A change in pressure over some distance
The atmosphere in motion: forces and wind AT350 Ahrens Chapter 9 Recall that Pressure is force per unit area Air pressure is determined by the weight of air above A change in pressure over some distance
( ) (9.1.1) Chapter 9. Geostrophy, Quasi-Geostrophy and the Potential Vorticity Equation. 9.1 Geostrophy and scaling.
 Chapter 9 Geostrophy, Quasi-Geostrophy and the Potential Vorticity Equation 9.1 Geostrophy and scaling. We examined in the last chapter some consequences of the dynamical balances for low frequency, nearly
Chapter 9 Geostrophy, Quasi-Geostrophy and the Potential Vorticity Equation 9.1 Geostrophy and scaling. We examined in the last chapter some consequences of the dynamical balances for low frequency, nearly
1/25/2010. Circulation and vorticity are the two primary
 Lecture 4: Circulation and Vorticity Measurement of Rotation Circulation Bjerknes Circulation Theorem Vorticity Potential Vorticity Conservation of Potential Vorticity Circulation and vorticity are the
Lecture 4: Circulation and Vorticity Measurement of Rotation Circulation Bjerknes Circulation Theorem Vorticity Potential Vorticity Conservation of Potential Vorticity Circulation and vorticity are the
ATMOSPHERIC MOTION I (ATM S 441/503 )
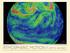 http://earth.nullschool.net/ ATMOSPHERIC MOTION I (ATM S 441/503 ) INSTRUCTOR Daehyun Kim Born in 1980 B.S. 2003 Ph.D. 2010 2010-2013 2014- Assistant Professor at Dept. of Atmospheric Sciences Office:
http://earth.nullschool.net/ ATMOSPHERIC MOTION I (ATM S 441/503 ) INSTRUCTOR Daehyun Kim Born in 1980 B.S. 2003 Ph.D. 2010 2010-2013 2014- Assistant Professor at Dept. of Atmospheric Sciences Office:
Lecture 25: Ocean circulation: inferences from geostrophic and thermal wind balance
 Lecture 25: Ocean circulation: inferences from geostrophic and thermal wind balance November 5, 2003 Today we are going to study vertical sections through the ocean and discuss what we can learn about
Lecture 25: Ocean circulation: inferences from geostrophic and thermal wind balance November 5, 2003 Today we are going to study vertical sections through the ocean and discuss what we can learn about
1/3/2011. This course discusses the physical laws that govern atmosphere/ocean motions.
 Lecture 1: Introduction and Review Dynamics and Kinematics Kinematics: The term kinematics means motion. Kinematics is the study of motion without regard for the cause. Dynamics: On the other hand, dynamics
Lecture 1: Introduction and Review Dynamics and Kinematics Kinematics: The term kinematics means motion. Kinematics is the study of motion without regard for the cause. Dynamics: On the other hand, dynamics
EESC V2100 The Climate System spring 2004 Lecture 4: Laws of Atmospheric Motion and Weather
 EESC V2100 The Climate System spring 2004 Lecture 4: Laws of Atmospheric Motion and Weather Yochanan Kushnir Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University Palisades, NY 10964, USA kushnir@ldeo.columbia.edu
EESC V2100 The Climate System spring 2004 Lecture 4: Laws of Atmospheric Motion and Weather Yochanan Kushnir Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory of Columbia University Palisades, NY 10964, USA kushnir@ldeo.columbia.edu
Lecture D15 - Gravitational Attraction. The Earth as a Non-Inertial Reference Frame
 J. Peraire 16.07 Dynamics Fall 2004 Version 1.3 Lecture D15 - Gravitational Attraction. The Earth as a Non-Inertial Reference Frame Gravitational attraction The Law of Universal Attraction was already
J. Peraire 16.07 Dynamics Fall 2004 Version 1.3 Lecture D15 - Gravitational Attraction. The Earth as a Non-Inertial Reference Frame Gravitational attraction The Law of Universal Attraction was already
Synoptic Meteorology I: The Geostrophic Approximation. 30 September, 7 October 2014
 The Equations of Motion Synotic Meteorology I: The Geostrohic Aroimation 30 Setember, 7 October 2014 In their most general form, and resented without formal derivation, the equations of motion alicable
The Equations of Motion Synotic Meteorology I: The Geostrohic Aroimation 30 Setember, 7 October 2014 In their most general form, and resented without formal derivation, the equations of motion alicable
Dynamics of Upper-Level Waves
 Dynamics of Upper-Level Waves Atmos 5110 Synoptic Dynamic Meteorology I Instructor: Jim Steenburgh jim.steenburgh@utah.edu 801-581-8727 Suite 480/Office 488 INSCC Suggested reading: Lackman (2011) section
Dynamics of Upper-Level Waves Atmos 5110 Synoptic Dynamic Meteorology I Instructor: Jim Steenburgh jim.steenburgh@utah.edu 801-581-8727 Suite 480/Office 488 INSCC Suggested reading: Lackman (2011) section
Chapter 5. Shallow Water Equations. 5.1 Derivation of shallow water equations
 Chapter 5 Shallow Water Equations So far we have concentrated on the dynamics of small-scale disturbances in the atmosphere and ocean with relatively simple background flows. In these analyses we have
Chapter 5 Shallow Water Equations So far we have concentrated on the dynamics of small-scale disturbances in the atmosphere and ocean with relatively simple background flows. In these analyses we have
Chapter VII. Rotating Coordinate Systems
 Chapter VII. Rotating Coordinate Systems 7.1. Frames of References In order to really look at particle dynamics in the context of the atmosphere, we must now deal with the fact that we live and observe
Chapter VII. Rotating Coordinate Systems 7.1. Frames of References In order to really look at particle dynamics in the context of the atmosphere, we must now deal with the fact that we live and observe
2. Temperature, Pressure, Wind, and Minor Constituents.
 2. Temperature, Pressure, Wind, and Minor Constituents. 2. Distributions of temperature, pressure and wind. Close examination of Figs..7-.0 of MS reveals te following features tat cry out for explanation:
2. Temperature, Pressure, Wind, and Minor Constituents. 2. Distributions of temperature, pressure and wind. Close examination of Figs..7-.0 of MS reveals te following features tat cry out for explanation:
( u,v). For simplicity, the density is considered to be a constant, denoted by ρ 0
 ! Revised Friday, April 19, 2013! 1 Inertial Stability and Instability David Randall Introduction Inertial stability and instability are relevant to the atmosphere and ocean, and also in other contexts
! Revised Friday, April 19, 2013! 1 Inertial Stability and Instability David Randall Introduction Inertial stability and instability are relevant to the atmosphere and ocean, and also in other contexts
Models of ocean circulation are all based on the equations of motion.
 Equations of motion Models of ocean circulation are all based on the equations of motion. Only in simple cases the equations of motion can be solved analytically, usually they must be solved numerically.
Equations of motion Models of ocean circulation are all based on the equations of motion. Only in simple cases the equations of motion can be solved analytically, usually they must be solved numerically.
Module 9 Weather Systems
 Module 9 Weather Systems In this module the theory of atmospheric dynamics is applied to different weather phenomena. The first section deals with extratropical cyclones, low and high pressure areas of
Module 9 Weather Systems In this module the theory of atmospheric dynamics is applied to different weather phenomena. The first section deals with extratropical cyclones, low and high pressure areas of
dv dt = f (M M g ) (1)
 Inertial, Symmetric and Conditional Symmetric Instability (CSI) The following is not meant to be a self-contained tutorial. It is meant to accompany active discussion and demonstration in the classroom.
Inertial, Symmetric and Conditional Symmetric Instability (CSI) The following is not meant to be a self-contained tutorial. It is meant to accompany active discussion and demonstration in the classroom.
Dynamics II: rotation L. Talley SIO 210 Fall, 2011
 Dynamics II: rotation L. Talley SIO 210 Fall, 2011 DATES: Oct. 24: second problem due Oct. 24: short info about your project topic Oct. 31: mid-term Nov. 14: project due Rotation definitions Centrifugal
Dynamics II: rotation L. Talley SIO 210 Fall, 2011 DATES: Oct. 24: second problem due Oct. 24: short info about your project topic Oct. 31: mid-term Nov. 14: project due Rotation definitions Centrifugal
Using simplified vorticity equation,* by assumption 1 above: *Metr 430 handout on Circulation and Vorticity. Equations (4) and (5) on that handout
 Rossby Wave Equation A. Assumptions 1. Non-divergence 2. Initially, zonal flow, or nearly zonal flow in which u>>v>>w. 3. Initial westerly wind is geostrophic and does not vary along the x-axis and equations
Rossby Wave Equation A. Assumptions 1. Non-divergence 2. Initially, zonal flow, or nearly zonal flow in which u>>v>>w. 3. Initial westerly wind is geostrophic and does not vary along the x-axis and equations
The Boundary Layer and Related Phenomena
 The Boundary Layer and Related Phenomena Jeremy A. Gibbs University of Oklahoma gibbz@ou.edu February 19, 2015 1 / 49 Overview Nocturnal Low-Level Jets Introduction Climatology of LLJs Meteorological Importance
The Boundary Layer and Related Phenomena Jeremy A. Gibbs University of Oklahoma gibbz@ou.edu February 19, 2015 1 / 49 Overview Nocturnal Low-Level Jets Introduction Climatology of LLJs Meteorological Importance
Control Volume. Dynamics and Kinematics. Basic Conservation Laws. Lecture 1: Introduction and Review 1/24/2017
 Lecture 1: Introduction and Review Dynamics and Kinematics Kinematics: The term kinematics means motion. Kinematics is the study of motion without regard for the cause. Dynamics: On the other hand, dynamics
Lecture 1: Introduction and Review Dynamics and Kinematics Kinematics: The term kinematics means motion. Kinematics is the study of motion without regard for the cause. Dynamics: On the other hand, dynamics
Lecture 1: Introduction and Review
 Lecture 1: Introduction and Review Review of fundamental mathematical tools Fundamental and apparent forces Dynamics and Kinematics Kinematics: The term kinematics means motion. Kinematics is the study
Lecture 1: Introduction and Review Review of fundamental mathematical tools Fundamental and apparent forces Dynamics and Kinematics Kinematics: The term kinematics means motion. Kinematics is the study
Geostrophic and Quasi-Geostrophic Balances
 Geostrophic and Quasi-Geostrophic Balances Qiyu Xiao June 19, 2018 1 Introduction Understanding how the atmosphere and ocean behave is important to our everyday lives. Techniques such as weather forecasting
Geostrophic and Quasi-Geostrophic Balances Qiyu Xiao June 19, 2018 1 Introduction Understanding how the atmosphere and ocean behave is important to our everyday lives. Techniques such as weather forecasting
ATM The thermal wind Fall, 2016 Fovell
 ATM 316 - The thermal wind Fall, 2016 Fovell Reca and isobaric coordinates We have seen that for the synotic time and sace scales, the three leading terms in the horizontal equations of motion are du dt
ATM 316 - The thermal wind Fall, 2016 Fovell Reca and isobaric coordinates We have seen that for the synotic time and sace scales, the three leading terms in the horizontal equations of motion are du dt
Examples of Pressure Gradient. Pressure Gradient Force. Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances. Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion 2/7/2019
 Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion Fundamental force - Apparent force - Pressure gradient force Gravitational force Frictional force Centrifugal force Forces that
Chapter 7: Forces and Force Balances Forces that Affect Atmospheric Motion Fundamental force - Apparent force - Pressure gradient force Gravitational force Frictional force Centrifugal force Forces that
Hydrostatic Equation and Thermal Wind. Meteorology 411 Iowa State University Week 5 Bill Gallus
 Hydrostatic Equation and Thermal Wind Meteorology 411 Iowa State University Week 5 Bill Gallus Hydrostatic Equation In the atmosphere, vertical accelerations (dw/dt) are normally fairly small, and we can
Hydrostatic Equation and Thermal Wind Meteorology 411 Iowa State University Week 5 Bill Gallus Hydrostatic Equation In the atmosphere, vertical accelerations (dw/dt) are normally fairly small, and we can
Ocean dynamics: the wind-driven circulation
 Ocean dynamics: the wind-driven circulation Weston Anderson March 13, 2017 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 The wind driven circulation (Ekman Transport) 3 3 Sverdrup flow 5 4 Western boundary currents (western
Ocean dynamics: the wind-driven circulation Weston Anderson March 13, 2017 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 The wind driven circulation (Ekman Transport) 3 3 Sverdrup flow 5 4 Western boundary currents (western
The Shallow Water Equations
 If you have not already done so, you are strongly encouraged to read the companion file on the non-divergent barotropic vorticity equation, before proceeding to this shallow water case. We do not repeat
If you have not already done so, you are strongly encouraged to read the companion file on the non-divergent barotropic vorticity equation, before proceeding to this shallow water case. We do not repeat
Lecture 10 March 15, 2010, Monday. Atmospheric Pressure & Wind: Part 1
 Lecture 10 March 15, 2010, Monday Atmospheric Pressure & Wind: Part 1 Speed, Velocity, Acceleration, Force, Pressure Atmospheric Pressure & Its Measurement Ideal Gas Law (Equation of State) Pressure Gradient
Lecture 10 March 15, 2010, Monday Atmospheric Pressure & Wind: Part 1 Speed, Velocity, Acceleration, Force, Pressure Atmospheric Pressure & Its Measurement Ideal Gas Law (Equation of State) Pressure Gradient
4/29/2011. Frictional force in the boundary layer ultimately destroys extratropical cyclones.
 Chapter 8: Development of igh- and low-pressure Systems Main Points to earn Because extratropical cyclones are the parent storms for many hazardous weather, it is essential to understand how they are created
Chapter 8: Development of igh- and low-pressure Systems Main Points to earn Because extratropical cyclones are the parent storms for many hazardous weather, it is essential to understand how they are created
Eliassen-Palm Theory
 Eliassen-Palm Theory David Painemal MPO611 April 2007 I. Introduction The separation of the flow into its zonal average and the deviations therefrom has been a dominant paradigm for analyses of the general
Eliassen-Palm Theory David Painemal MPO611 April 2007 I. Introduction The separation of the flow into its zonal average and the deviations therefrom has been a dominant paradigm for analyses of the general
Lecture 2. Lecture 1. Forces on a rotating planet. We will describe the atmosphere and ocean in terms of their:
 Lecture 2 Lecture 1 Forces on a rotating planet We will describe the atmosphere and ocean in terms of their: velocity u = (u,v,w) pressure P density ρ temperature T salinity S up For convenience, we will
Lecture 2 Lecture 1 Forces on a rotating planet We will describe the atmosphere and ocean in terms of their: velocity u = (u,v,w) pressure P density ρ temperature T salinity S up For convenience, we will
Vertical Structure of Atmosphere
 ATMOS 3110 Introduction to Atmospheric Sciences Distribution of atmospheric mass and gaseous constituents Because of the earth s gravitational field, the atmosphere exerts a downward forces on the earth
ATMOS 3110 Introduction to Atmospheric Sciences Distribution of atmospheric mass and gaseous constituents Because of the earth s gravitational field, the atmosphere exerts a downward forces on the earth
Solutions to Comprehensive Final Examination Given on Thursday, 13 December 2001
 Name & Signature Dr. Droegemeier Student ID Meteorology 1004 Introduction to Meteorology Fall, 2001 Solutions to Comprehensive Final Examination Given on Thursday, 13 December 2001 BEFORE YOU BEGIN!! Please
Name & Signature Dr. Droegemeier Student ID Meteorology 1004 Introduction to Meteorology Fall, 2001 Solutions to Comprehensive Final Examination Given on Thursday, 13 December 2001 BEFORE YOU BEGIN!! Please
Physical Oceanography, MSCI 3001 Oceanographic Processes, MSCI Dr. Katrin Meissner Ocean Dynamics.
 Physical Oceanography, MSCI 3001 Oceanographic Processes, MSCI 5004 Dr. Katrin Meissner k.meissner@unsw.e.au Ocean Dynamics The Equations of Motion d u dt = 1 ρ Σ F dt = 1 ρ ΣF x dt = 1 ρ ΣF y dw dt =
Physical Oceanography, MSCI 3001 Oceanographic Processes, MSCI 5004 Dr. Katrin Meissner k.meissner@unsw.e.au Ocean Dynamics The Equations of Motion d u dt = 1 ρ Σ F dt = 1 ρ ΣF x dt = 1 ρ ΣF y dw dt =
2.5 Shallow water equations, quasigeostrophic filtering, and filtering of inertia-gravity waves
 Chapter. The continuous equations φ=gh Φ=gH φ s =gh s Fig..5: Schematic of the shallow water model, a hydrostatic, incompressible fluid with a rigid bottom h s (x,y), a free surface h(x,y,t), and horizontal
Chapter. The continuous equations φ=gh Φ=gH φ s =gh s Fig..5: Schematic of the shallow water model, a hydrostatic, incompressible fluid with a rigid bottom h s (x,y), a free surface h(x,y,t), and horizontal
Ocean currents: some misconceptions and some dynamics
 Ocean currents: some misconceptions and some dynamics Joe LaCasce Dept. Geosciences October 30, 2012 Where is the Gulf Stream? BBC Weather Center Where is the Gulf Stream? Univ. Bergen news website (2011)
Ocean currents: some misconceptions and some dynamics Joe LaCasce Dept. Geosciences October 30, 2012 Where is the Gulf Stream? BBC Weather Center Where is the Gulf Stream? Univ. Bergen news website (2011)
Reynolds Averaging. We separate the dynamical fields into slowly varying mean fields and rapidly varying turbulent components.
 Reynolds Averaging Reynolds Averaging We separate the dynamical fields into sloly varying mean fields and rapidly varying turbulent components. Reynolds Averaging We separate the dynamical fields into
Reynolds Averaging Reynolds Averaging We separate the dynamical fields into sloly varying mean fields and rapidly varying turbulent components. Reynolds Averaging We separate the dynamical fields into
Part 4. Atmospheric Dynamics
 Part 4. Atmospheric Dynamics We apply Newton s Second Law: ma =Σ F i to the atmosphere. In Cartesian coordinates dx u = dt dy v = dt dz w = dt 1 ai = F m i i du dv dw a = ; ay = ; az = x dt dt dt 78 Coordinate
Part 4. Atmospheric Dynamics We apply Newton s Second Law: ma =Σ F i to the atmosphere. In Cartesian coordinates dx u = dt dy v = dt dz w = dt 1 ai = F m i i du dv dw a = ; ay = ; az = x dt dt dt 78 Coordinate
p = ρrt p = ρr d = T( q v ) dp dz = ρg
 Chapter 1: Properties of the Atmosphere What are the major chemical components of the atmosphere? Atmospheric Layers and their major characteristics: Troposphere, Stratosphere Mesosphere, Thermosphere
Chapter 1: Properties of the Atmosphere What are the major chemical components of the atmosphere? Atmospheric Layers and their major characteristics: Troposphere, Stratosphere Mesosphere, Thermosphere
GEF 1100 Klimasystemet. Chapter 7: Balanced flow
 GEF1100 Autumn 2016 27.09.2016 GEF 1100 Klimasystemet Chapter 7: Balanced flow Prof. Dr. Kirstin Krüger (MetOs, UiO) 1 Lecture Outline Ch. 7 Ch. 7 Balanced flow 1. Motivation 2. Geostrophic motion 2.1
GEF1100 Autumn 2016 27.09.2016 GEF 1100 Klimasystemet Chapter 7: Balanced flow Prof. Dr. Kirstin Krüger (MetOs, UiO) 1 Lecture Outline Ch. 7 Ch. 7 Balanced flow 1. Motivation 2. Geostrophic motion 2.1
Lecture 1. Equations of motion - Newton s second law in three dimensions. Pressure gradient + force force
 Lecture 3 Lecture 1 Basic dynamics Equations of motion - Newton s second law in three dimensions Acceleration = Pressure Coriolis + gravity + friction gradient + force force This set of equations is the
Lecture 3 Lecture 1 Basic dynamics Equations of motion - Newton s second law in three dimensions Acceleration = Pressure Coriolis + gravity + friction gradient + force force This set of equations is the
The Hydrostatic Approximation. - Euler Equations in Spherical Coordinates. - The Approximation and the Equations
 OUTLINE: The Hydrostatic Approximation - Euler Equations in Spherical Coordinates - The Approximation and the Equations - Critique of Hydrostatic Approximation Inertial Instability - The Phenomenon - The
OUTLINE: The Hydrostatic Approximation - Euler Equations in Spherical Coordinates - The Approximation and the Equations - Critique of Hydrostatic Approximation Inertial Instability - The Phenomenon - The
ERTH 465 Fall Lab 5. Absolute Geostrophic Vorticity. 200 points.
 Name Date ERTH 465 Fall 2015 Lab 5 Absolute Geostrophic Vorticity 200 points. 1. All labs are to be kept in a three hole binder. Turn in the binder when you have finished the Lab. 2. Show all work in mathematical
Name Date ERTH 465 Fall 2015 Lab 5 Absolute Geostrophic Vorticity 200 points. 1. All labs are to be kept in a three hole binder. Turn in the binder when you have finished the Lab. 2. Show all work in mathematical
Chapter 5. Fundamentals of Atmospheric Modeling
 Overhead Slides for Chapter 5 of Fundamentals of Atmospheric Modeling by Mark Z. Jacobson Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305-4020 January 30, 2002 Altitude
Overhead Slides for Chapter 5 of Fundamentals of Atmospheric Modeling by Mark Z. Jacobson Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305-4020 January 30, 2002 Altitude
SIO 210: Dynamics VI (Potential vorticity) L. Talley Fall, 2014 (Section 2: including some derivations) (this lecture was not given in 2015)
 SIO 210: Dynamics VI (Potential vorticity) L. Talley Fall, 2014 (Section 2: including some derivations) (this lecture was not given in 2015) Variation of Coriolis with latitude: β Vorticity Potential vorticity
SIO 210: Dynamics VI (Potential vorticity) L. Talley Fall, 2014 (Section 2: including some derivations) (this lecture was not given in 2015) Variation of Coriolis with latitude: β Vorticity Potential vorticity
EAS372 Open Book Final Exam 11 April, 2013
 EAS372 Open Book Final Exam 11 April, 2013 Professor: J.D. Wilson Time available: 2 hours Value: 30% Please check the Terminology, Equations and Data section before beginning your responses. Answer all
EAS372 Open Book Final Exam 11 April, 2013 Professor: J.D. Wilson Time available: 2 hours Value: 30% Please check the Terminology, Equations and Data section before beginning your responses. Answer all
Inertial Instability. 1. Perspective from the Horizontal Equations of Motion (Momentum Equations) x component. y component
 Inertial Instability The following is not meant to be a self-contained tutorial. It is meant to accompany active discussion and demonstration in the classroom. 1. Perspective from the Horizontal Equations
Inertial Instability The following is not meant to be a self-contained tutorial. It is meant to accompany active discussion and demonstration in the classroom. 1. Perspective from the Horizontal Equations
6 Two-layer shallow water theory.
 6 Two-layer shallow water theory. Wewillnowgoontolookatashallowwatersystemthathastwolayersofdifferent density. This is the next level of complexity and a simple starting point for understanding the behaviour
6 Two-layer shallow water theory. Wewillnowgoontolookatashallowwatersystemthathastwolayersofdifferent density. This is the next level of complexity and a simple starting point for understanding the behaviour
Meteorology 6150 Cloud System Modeling
 Meteorology 6150 Cloud System Modeling Steve Krueger Spring 2009 1 Fundamental Equations 1.1 The Basic Equations 1.1.1 Equation of motion The movement of air in the atmosphere is governed by Newton s Second
Meteorology 6150 Cloud System Modeling Steve Krueger Spring 2009 1 Fundamental Equations 1.1 The Basic Equations 1.1.1 Equation of motion The movement of air in the atmosphere is governed by Newton s Second
Precipitation and Wind AOSC 200 Tim Canty. Current Weather
 Precipitation and Wind AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Precipitation cont. RADAR Pressure Coriolis force Lecture 12 Oct 5 2017 1 Current Weather
Precipitation and Wind AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Precipitation cont. RADAR Pressure Coriolis force Lecture 12 Oct 5 2017 1 Current Weather
On Derivation and Interpretation of Kuo Eliassen Equation
 1 On Derivation and Interpretation of Kuo Eliassen Equation Jun-Ichi Yano 1 1 GAME/CNRM, Météo-France and CNRS, 31057 Toulouse Cedex, France Manuscript submitted 22 September 2010 The Kuo Eliassen equation
1 On Derivation and Interpretation of Kuo Eliassen Equation Jun-Ichi Yano 1 1 GAME/CNRM, Météo-France and CNRS, 31057 Toulouse Cedex, France Manuscript submitted 22 September 2010 The Kuo Eliassen equation
A Gradient Wind Correction for Surface Pressure Fields Retrieved from Scatterometer Winds
 133 A Gradient Wind Correction for Surface Pressure Fields Retrieved from Scatterometer Winds JÉRÔME PATOUX AND ROBERT A. BROWN Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington
133 A Gradient Wind Correction for Surface Pressure Fields Retrieved from Scatterometer Winds JÉRÔME PATOUX AND ROBERT A. BROWN Department of Atmospheric Sciences, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington
1/27/2010. With this method, all filed variables are separated into. from the basic state: Assumptions 1: : the basic state variables must
 Lecture 5: Waves in Atmosphere Perturbation Method With this method, all filed variables are separated into two parts: (a) a basic state part and (b) a deviation from the basic state: Perturbation Method
Lecture 5: Waves in Atmosphere Perturbation Method With this method, all filed variables are separated into two parts: (a) a basic state part and (b) a deviation from the basic state: Perturbation Method
Houze sections 7.4, 8.3, 8.5, Refer back to equations in Section 2.3 when necessary.
 Theory of Thunderstorm Dynamics Houze sections 7.4, 8.3, 8.5, Refer back to equations in Section 2.3 when necessary. Bluestein Vol. II section 3.4.6. Review article "Dynamics of Tornadic Thunderstorms"
Theory of Thunderstorm Dynamics Houze sections 7.4, 8.3, 8.5, Refer back to equations in Section 2.3 when necessary. Bluestein Vol. II section 3.4.6. Review article "Dynamics of Tornadic Thunderstorms"
Daniel J. Jacob, Models of Atmospheric Transport and Chemistry, 2007.
 1 0. CHEMICAL TRACER MODELS: AN INTRODUCTION Concentrations of chemicals in the atmosphere are affected by four general types of processes: transport, chemistry, emissions, and deposition. 3-D numerical
1 0. CHEMICAL TRACER MODELS: AN INTRODUCTION Concentrations of chemicals in the atmosphere are affected by four general types of processes: transport, chemistry, emissions, and deposition. 3-D numerical
Chapter 7: Circulation and Vorticity
 Chapter 7: Circulation and Vorticity Circulation C = u ds Integration is performed in a counterclockwise direction C is positive for counterclockwise flow!!! Kelvin s Circulation Theorem The rate of change
Chapter 7: Circulation and Vorticity Circulation C = u ds Integration is performed in a counterclockwise direction C is positive for counterclockwise flow!!! Kelvin s Circulation Theorem The rate of change
where p oo is a reference level constant pressure (often 10 5 Pa). Since θ is conserved for adiabatic motions, a prognostic temperature equation is:
 1 Appendix C Useful Equations Purposes: Provide foundation equations and sketch some derivations. These equations are used as starting places for discussions in various parts of the book. C.1. Thermodynamic
1 Appendix C Useful Equations Purposes: Provide foundation equations and sketch some derivations. These equations are used as starting places for discussions in various parts of the book. C.1. Thermodynamic
Chapter 4: Fundamental Forces
 Chapter 4: Fundamental Forces Newton s Second Law: F=ma In atmospheric science it is typical to consider the force per unit mass acting on the atmosphere: Force mass = a In order to understand atmospheric
Chapter 4: Fundamental Forces Newton s Second Law: F=ma In atmospheric science it is typical to consider the force per unit mass acting on the atmosphere: Force mass = a In order to understand atmospheric
ESCI 485 Air/Sea Interaction Lesson 1 Stresses and Fluxes Dr. DeCaria
 ESCI 485 Air/Sea Interaction Lesson 1 Stresses and Fluxes Dr DeCaria References: An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology, Holton MOMENTUM EQUATIONS The momentum equations governing the ocean or atmosphere
ESCI 485 Air/Sea Interaction Lesson 1 Stresses and Fluxes Dr DeCaria References: An Introduction to Dynamic Meteorology, Holton MOMENTUM EQUATIONS The momentum equations governing the ocean or atmosphere
