This Week. Basic Problem. Instantaneous Rate of Change. Compute the tangent line to the curve y = f (x) at x = a.
|
|
|
- Junior Fitzgerald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 This Week Basic Problem Compute the tangent line to the curve y = f (x) at x = a. Read Sections 2.7,2.8 and 3.1 in Stewart Homework #2 due 11:30 Thursday evening worksheet #3 in section on Tuesday slope of line through P and Q = f (b) f (a). b a f (x) f (a) f (a + h) f (a) m = slope of tangent line = lim = lim. x a x a h 0 h Instantaneous Rate of Change We say that f (x) f (a) lim x a x a is the instantaneous rate of change of y = f (x) f (x) f (a) f (a + h) f (a) m = slope of tangent line = lim = lim. x a x a h 0 h equation of tangent line : y f (a) = m(x a). For example if f (t) is the distance traveled at time t. Then f (t) f (a) lim t a t a is the instantaneous velocity at t = a.
2 Find the equation of the tangent line to y = 1/ 5 2x at x = a. f (x) f (a) m = lim x a x a 1 = lim 5 2x 1 5 2a x a x a 5 2a 5 2x = lim x a ( 5 2a 5 2x)(x a) ( 5 2a 5 2x)( 5 2a + 5 2x) = lim x a ( 5 2a 5 2x)(x a)( 5 2a + 5 2x) = lim x a (5 2a) (5 2x) ( 5 2a 5 2x)(x a)( 5 2a + 5 2x) m = lim x a 2(x a) ( 5 2a 5 2x)(x a)( 5 2a + 5 2x) 2 = lim x a ( 5 2a 5 2x)( 5 2a + 5 2x) 2 = ( 5 2a 5 2a)(2 5 2a) 1 = (5 2a) 3/2 Thus the equation of the tangent line is y 1/ 1 5 2a = (x a). (5 2a) 3/2 If the distance (in feet) traveled by a car at time t is given by 1 s(t) = 5 2t then the instantaneous velocity of the car at time t = a is 1 ft/sec. (5 2a) 3/2 A cylindrical tank holds 100,000 gallons of water which can be drained from the bottom of the tank in an hour. By Toricelli s law the volume V (t) remaining at time t (in minutes) is V (t) = 100, 000(1 t/60) 2 gallons, 0 t 60. What is the rate (as a function of time) at which water is flowing out of the tank? What is the rate at which water is flowing out half way through the hour?
3 We are looking for the instantaneous rate of change which is given by V (t) V (a) lim t a t a = lim t a 100, 000(1 t/60) 2 100, 000(1 a/60) 2 t a = 100, 000 lim t a (1 t/60) 2 (1 a/60) 2 t a = 100, 000 lim t a 1 2t/60 + (t/60) a/60 (a/60) 2 t a ( 1/30)(t a) + (1/3600)(t 2 a 2 ) = 100, 000 lim t a t a ( 1/30)(t a) + (1/3600)(t a)(t + a) = 100, 000 lim t a t a = 100, 000 lim(( 1/30) + (1/3600)(t + a)) t a = 100, 000(( 1/30) + (1/3600)(2a)) Thus the instantaneous rate of change is 100, 000(( 1/30) + (1/3600)(2a)). Halfway through the hour we are at t = 30 and 100, 000( 1/30 + (1/3600)(2(30))) 1, 667 gallons per minute. Derivatives At t = 0 a car is at the 15 mile marker on the freeway. For the next hour it travels at a constant speed of 55 miles per hour. The car slows gradually over a 2 minute period and comes to a stop. After 20 minutes it restarts gradually speeding up to 65 miles per hour over a two minute period. Then the car goes at 65 miles per hour for two hours and then it slows to a stop over a three minute period. Sketch a graph of the position of a car as a function of time. Given a function y = f (x) and a value x = a the derivative of f at x = a is f f (x) f (a) f (a + h) f (a) (a) = lim = lim. x a x a h 0 h As we saw last time this is the slope of the tangent line to y = f (x) at x = a. This is also the instantaneous rate of change of f (x) at x = a.
4 Notation We have a lot of different notation for the derivative of y = f (x). y d dx f (x) dy dx df dx f (x) ḟ(x) Df (x) Dxf (x) A ball is thrown up in the air with a speed of 40ft/sec. It s height (in feet) after t seconds is given by g(t) = 40t 16t 2. Calculate the instantaneous velocity as a function of t. When does it reach its maximum height? g (t) = lim h 0 g(t + h) g(t) h = lim h 0 40(t + h) 16(t + h) 2 (40t 16t 2 ) h = lim h 0 40t + 40h 16t 2 32th 16h 2 40t + 16t 2 h 40h 32th 16h 2 = lim h 0 h = lim 40 32t 16h h 0 = 40 32t Looking at the graph we can see that g(t) is increasing until t = 5/4 and decreasing afterwards. Notice that this is when the instantaneous velocity changes from positive to negative. Thus the ball reaches its maximum height of 25 feet at time t = 5/4.
5 Speed and Velocity Find the formula for g (t) and graph g (t) as a function of time. Find the formula for g (t) and graph g (t) as a function of time. If f (t) is the position of a car at time t. Then f (a) is the velocity of a car at time t = a. Then f (a) is the speed of a car at time t = a. Law of Decreasing Marginal Returns Petroleum beneath the earth s surface The Law of diminishing marginal returns says that each additional person (dollar invested in machinery, etc.) will increase your production by less than the previous. Restate the law of diminishing marginal returns in terms of derivatives. Petroleum has accumulated under the earth s surface for millions of years. Let P(t) be the number of barrels of petroleum that are below the earth s surface t years after We are currently pumping 63 million barrels per day. The earth s proven reserves are at least 1.2 trillion barrels. What does this tell you about P(t)? about P (t)? We are currently pumping at a rate of 63 million barrels per day is about 23 billion per year. This is the instantaneous rate of change so P (10) 23 billion barrels per year. The earth s proven reserves are at least 1.2 trillion barrels so P(10) 1.2 trillion barrels.
6 ipad sales Apple started selling the ipad on April 3. Let I(t) be the number of ipads sold t days after the launch. What do the following statements mean in terms of I(t) and its derivatives. Apple will sell 12 million ipads in 2010 and 28 million in By April Apple will be selling 1.8 million ipad per month. Derivatives and Graphs Below is the graph of a function y = f (x) and y = f (x). What does this tell you about I(t)? about I (t)? I(273) = 12 million and I(638) = 40million I(393) I(363) = 1.8 million or I (363) I(393) I(363) 1, 800, 000 = = 60, Ways a function can fail to be differentiable if f (x) > 0 for all x on [a, b] then f is increasing on [a, b] if f (x) < 0 for all x on [a, b] then f is decreasing on [a, b] if f (x) = 0 for all x on [a, b] then f is constant on [a, b] We say that f is differentiable at x = a if f (a) exists. There are a number of ways that f (x) can fail to be differentiable at x = a. 1 f is not continuous 2 f has a sharp corner or 3 f has a vertical tangent line
7 Ways a function can fail to be differentiable Is f (x) = x differentiable at x = 0? To see if f f (h) f (0) h 0 (0) = lim = lim h 0 h h 0 h exists we take both one sided limits. h 0 h lim = lim h 0 + h h 0 + h = lim 1 = 1 h 0 + h 0 h lim = lim h 0 h h 0 h = lim 1 = 1 h 0 This function is not differentiable at x = 1, x = 0 and x = 1. As h 0 h 0 1 = lim lim = 1 h 0 + h h 0 h Thus limh 0 h 0 h does not exist and f (x) = x is not differentiable at x = 0. Graphically we can see that y = x doesn t have a well defined tangent line at x = 0. Below is the graph of a function y = f (x). Where is f differentiable? Sketch the graph of the function f (x).
8 Below is the graph of a function y = f (x). Below is the graph of a function y = f (x). Sketch the graph of the function f (x). Sketch the graph of the function f (x) if f (0) = 0. Estimating Derivatives from graphs Draw the graph of a function with the following properties. 1 f (x) > 0 on (, 3) and (2, ) 2 f (x) < 0 on ( 3, 2) 3 f (x) < 0 on ( 5, 1) 4 f (x) > 0 on (, 5) and (1, ) 5 f (x) < 0 on (, 3.5) and (.5, 1.5) 6 f (x) > 0 on ( 3.5,.5) and (1.5, ) Below is the graph of the function y = f (x). Estimate the values of f (1) and f (2) and f (3).
9 Estimating Derivatives from graphs To estimate the value of f (1) we draw the tangent line at x = 1. Estimating Derivatives from graphs To estimate the value of f (2) we draw the tangent line at x = 2. The tangent line at (1, f (1)) appears to go through (0,1.3) and (2,2) so its slope is about.35 and f (1).35. The tangent line at (2, f (2)) appears to go through (2,1.5) and (4,.1) so its slope is about.7 and f (2).7. Estimating Derivatives from graphs Four functions To estimate the value of f (3) we draw the tangent line at x = 3. Below is the graph of a function f (x) and its derivatives f (x), f (x) and f (x). Determine which of the functions is which. The tangent line at (3, f (3)) appears to go through (2,2) and (4,-1) so its slope is about 1.5 and f (3) 1.5.
10 Below is the graph of the function y = f (x). Put the terms below in increasing order. Normal line to a parabola The graph of the equation y = x 2 8x + 9 forms a parabola. For a point (a, a 2 8a + 9) on the graph find the 1 equation of the tangent line. 2 equation of the normal line. 3 other point on the graph where the normal line intersects the graph. f (3) (3) < 0 < f f (3) (5) < f f (5). (3) Applications Draw the graph of a function satisfying the following conditions 1 f (x) > 0 on [0. ] 2 f (x) < 0 on [0. ] 3 f (x) > 0 on [0. ]
11 Continuity and differentiability Derivative Rules f is continuous at x = a does not imply that f is differentiable at x = a but f is differentiable at x = a does imply that f is continuous at x = a. Limit laws give us the following. Suppose f and g are differentiable the 1 (f + g) (x) = f (x) + g (x) 2 (f g) (x) = f (x) g (x) 3 (cf ) (x) = cf (x) Power Rule Find the derivative of the function f (x) = 1/x. Suppose f (x) = x n for some positive integer n. Find f (x) f (x + h) n x n (x) = lim h 0 h = lim h 0 x n + nx n 1 h + + nxh n 1 + h n x n h nx n 1 h + + nxh n 1 + h n = lim h 0 h = lim nx n nxh n 2 + h n 1 h 0 = nx n 1. 1 f (x) = lim h 0 x+h x h = lim h 0 1 x+h 1 x x(x + h) h x(x + h) x (x + h) = lim h 0 x(x + h)h = lim h 0 = lim h 0 = 1 x 2 h x(x + h)h 1 x(x + h)
12 Find the derivative of the function f (x) = x. x + h h f (x) = lim h 0 h x + h x x + h + x = lim h 0 h x + h + x x + h x = lim h 0 h( x + h + x) h = lim h 0 h( x + h + x) 1 = lim h 0 ( x + h + x) 1 = 2 x We just showed that d dx (x 1 ) = ( 1)x 2 and d dx (x 1/2 ) = (1/2)x 1/2 This suggests that the power rule may be true for more than just positive integers. Power Rule Derivatives of Polynomials In fact the following is true Theorem If n is any real number d dx (x n ) = nx n 1 Using the rules 1 (f + g) (x) = f (x) + g (x) 2 (cf ) (x) = cf (x)) 3 (x n ) = nx n 1 we can calculate the derivative of any polynomial.
13 Examples Find the derivative of f (x) = f (x) = 7x 4 + 3x 3 + 2x 2 + 5x + 9 ( ) 7x 4 + 3x 3 + 2x 2 + 5x + 9 = (7x 4 ) + (3x 3 ) + (2x 2 ) + (5x) + (9) = 7(x 4 ) + 3(x 3 ) + 2(x 2 ) + 5(x) + 0 = 7(4x 3 ) + 3(3x 2 ) + 2(2x) + 5(1) = 28x 3 + 9x 2 + 4x + 5. Examples Find the derivative of f (x) = = f (x) = 3 x + 2 x + 2x x.1 ( 3 x + 2 ) + 2x x.1 x ( 3x 1/2 + 2x 1/2 + 2x x.1) = ( 3x 1/2 ) + (2x 1/2 ) + (2x 4.3 ) + (5x.1 ) = 3(x 1/2 ) + 2(x 1/2 ) + 2(x 4.3 ) + 5(x.1 ) = 3((1/2)x 1/2 ) + 2(( 1/2)x 3/2 ) + 2(( 4.3)x 5.3 ) + 5((.1)x.9 ) = 1.5x 1/2 x 3/2 8.6x x.9. Derivatives of Exponentials Find the derivative of g(x) = e cx. g e c(x+h) e cx (x) = lim h 0 h e cx e ch e cx = lim h 0 h e cx (e ch 1) = lim h 0 h = ce cx e ch 1 lim h 0 ch e ch 1 = cg(x) lim ch 0 ch e y 1 = cg(x) lim. y 0 y So if we can figure out the value of the last limit then we know the derivative at every point. Here is a graph of m(y) = ey 1 y. We can see that as y 0 m(y) 1 so d dx (ex ) = e x. This is the reason that we choose to use base e.
14 Derivatives of Exponentials Theorem If f (x) = e cx then f (x) = ce cx. As a = e ln(a) and a x = e ln(a)x another way to write this is Find the derivative of g(t) = 5 4 t + π t. ( g (t) = 5(4 t ) + π( ) t) = 5(4 t ) + π( t) = 5(ln(4))4 t + π(t 1/2 ) = 5(ln(4))4 t + π 2 t 1/2. Theorem If f (x) = a x then f (x) = ln(a)a x. Find the derivative of g(t) = 5 e 2t + a/t 2. g (t) = (5 e 2t + a/t 2) = 5(e 2t ) + a(t 2 ) = 5( 2)e 2t 2at 3. At what point on the curve y = f (x) = 2 x is the tangent line parallel to the line y = 3x? We want to find x such that f (x) = 3. f (x) = (ln(2))2 x. Setting f (x) = 3 we get 3 = ln(2)2 x or 2 x = 3/ ln(2). ( ) 3 ln(2)x = ln ln(2) or x = 1 ( ) 3 ln(2) ln. ln(2)
15 ( ( ) ) Thus the point is 1 ln 2 ln 3 ln(2), 3/ ln(2) and the line is ( y 3/ ln(2) = 3 x 1 ( )) 3 ln 2 ln. ln(2)
MAC 2233, Survey of Calculus, Exam 3 Review This exam covers lectures 21 29,
 MAC 2233, Survey of Calculus, Exam 3 Review This exam covers lectures 21 29, This review includes typical exam problems. It is not designed to be comprehensive, but to be representative of topics covered
MAC 2233, Survey of Calculus, Exam 3 Review This exam covers lectures 21 29, This review includes typical exam problems. It is not designed to be comprehensive, but to be representative of topics covered
Tangent Lines Sec. 2.1, 2.7, & 2.8 (continued)
 Tangent Lines Sec. 2.1, 2.7, & 2.8 (continued) Prove this Result How Can a Derivative Not Exist? Remember that the derivative at a point (or slope of a tangent line) is a LIMIT, so it doesn t exist whenever
Tangent Lines Sec. 2.1, 2.7, & 2.8 (continued) Prove this Result How Can a Derivative Not Exist? Remember that the derivative at a point (or slope of a tangent line) is a LIMIT, so it doesn t exist whenever
OBJECTIVE Find limits of functions, if they exist, using numerical or graphical methods.
 1.1 Limits: A Numerical and Graphical Approach OBJECTIVE Find limits of functions, if they exist, using numerical or graphical methods. 1.1 Limits: A Numerical and Graphical Approach DEFINITION: As x approaches
1.1 Limits: A Numerical and Graphical Approach OBJECTIVE Find limits of functions, if they exist, using numerical or graphical methods. 1.1 Limits: A Numerical and Graphical Approach DEFINITION: As x approaches
Math 142 Week-in-Review #4 (Sections , 4.1, and 4.2)
 Math 142 WIR, copyright Angie Allen, Fall 2018 1 Math 142 Week-in-Review #4 (Sections 3.1-3.3, 4.1, and 4.2) Note: This collection of questions is intended to be a brief overview of the exam material (with
Math 142 WIR, copyright Angie Allen, Fall 2018 1 Math 142 Week-in-Review #4 (Sections 3.1-3.3, 4.1, and 4.2) Note: This collection of questions is intended to be a brief overview of the exam material (with
ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Spring 2014 Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers R.6 8) 27, 30) 25
 ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Spring 2014, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers Review Assignment: Precalculus Even Answers to Sections R1 R7 R.1 24) 4a 2 16ab + 16b 2 R.2 24) Prime 5x
ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Spring 2014, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers Review Assignment: Precalculus Even Answers to Sections R1 R7 R.1 24) 4a 2 16ab + 16b 2 R.2 24) Prime 5x
Average rates of change May be used to estimate the derivative at a point
 Derivatives Big Ideas Rule of Four: Numerically, Graphically, Analytically, and Verbally Average rate of Change: Difference Quotient: y x f( a+ h) f( a) f( a) f( a h) f( a+ h) f( a h) h h h Average rates
Derivatives Big Ideas Rule of Four: Numerically, Graphically, Analytically, and Verbally Average rate of Change: Difference Quotient: y x f( a+ h) f( a) f( a) f( a h) f( a+ h) f( a h) h h h Average rates
1 y = Recitation Worksheet 1A. 1. Simplify the following: b. ( ) a. ( x ) Solve for y : 3. Plot these points in the xy plane:
 Math 13 Recitation Worksheet 1A 1 Simplify the following: a ( ) 7 b ( ) 3 4 9 3 5 3 c 15 3 d 3 15 Solve for y : 8 y y 5= 6 3 3 Plot these points in the y plane: A ( 0,0 ) B ( 5,0 ) C ( 0, 4) D ( 3,5) 4
Math 13 Recitation Worksheet 1A 1 Simplify the following: a ( ) 7 b ( ) 3 4 9 3 5 3 c 15 3 d 3 15 Solve for y : 8 y y 5= 6 3 3 Plot these points in the y plane: A ( 0,0 ) B ( 5,0 ) C ( 0, 4) D ( 3,5) 4
Multiple Choice Review Problems
 Multiple Choice Review Problems 1. (NC) Which graph best represents the position of a particle, st ( ), as a function of time, if the particle's velocity is negative and the particle's acceleration is
Multiple Choice Review Problems 1. (NC) Which graph best represents the position of a particle, st ( ), as a function of time, if the particle's velocity is negative and the particle's acceleration is
1 The Derivative and Differrentiability
 1 The Derivative and Differrentiability 1.1 Derivatives and rate of change Exercise 1 Find the equation of the tangent line to f (x) = x 2 at the point (1, 1). Exercise 2 Suppose that a ball is dropped
1 The Derivative and Differrentiability 1.1 Derivatives and rate of change Exercise 1 Find the equation of the tangent line to f (x) = x 2 at the point (1, 1). Exercise 2 Suppose that a ball is dropped
MATH The Derivative as a Function - Section 3.2. The derivative of f is the function. f x h f x. f x lim
 MATH 90 - The Derivative as a Function - Section 3.2 The derivative of f is the function f x lim h 0 f x h f x h for all x for which the limit exists. The notation f x is read "f prime of x". Note that
MATH 90 - The Derivative as a Function - Section 3.2 The derivative of f is the function f x lim h 0 f x h f x h for all x for which the limit exists. The notation f x is read "f prime of x". Note that
MATH 116, LECTURE 13, 14 & 15: Derivatives
 MATH 116, LECTURE 13, 14 & 15: Derivatives 1 Formal Definition of the Derivative We have seen plenty of limits so far, but very few applications. In particular, we have seen very few functions for which
MATH 116, LECTURE 13, 14 & 15: Derivatives 1 Formal Definition of the Derivative We have seen plenty of limits so far, but very few applications. In particular, we have seen very few functions for which
DIFFERENTIATION RULES
 3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES We have: Seen how to interpret derivatives as slopes and rates of change Seen how to estimate derivatives of functions given by tables of values Learned how
3 DIFFERENTIATION RULES DIFFERENTIATION RULES We have: Seen how to interpret derivatives as slopes and rates of change Seen how to estimate derivatives of functions given by tables of values Learned how
2.1 The Tangent and Velocity Problems
 2.1 The Tangent and Velocity Problems Tangents What is a tangent? Tangent lines and Secant lines Estimating slopes from discrete data: Example: 1. A tank holds 1000 gallons of water, which drains from
2.1 The Tangent and Velocity Problems Tangents What is a tangent? Tangent lines and Secant lines Estimating slopes from discrete data: Example: 1. A tank holds 1000 gallons of water, which drains from
3. Find the slope of the tangent line to the curve given by 3x y e x+y = 1 + ln x at (1, 1).
 1. Find the derivative of each of the following: (a) f(x) = 3 2x 1 (b) f(x) = log 4 (x 2 x) 2. Find the slope of the tangent line to f(x) = ln 2 ln x at x = e. 3. Find the slope of the tangent line to
1. Find the derivative of each of the following: (a) f(x) = 3 2x 1 (b) f(x) = log 4 (x 2 x) 2. Find the slope of the tangent line to f(x) = ln 2 ln x at x = e. 3. Find the slope of the tangent line to
Math 1314 Test 2 Review Lessons 2 8
 Math 1314 Test Review Lessons 8 CASA reservation required. GGB will be provided on the CASA computers. 50 minute exam. 15 multiple choice questions. Do Practice Test for extra practice and extra credit.
Math 1314 Test Review Lessons 8 CASA reservation required. GGB will be provided on the CASA computers. 50 minute exam. 15 multiple choice questions. Do Practice Test for extra practice and extra credit.
Review for the Final Exam
 Calculus Lia Vas. Integrals. Evaluate the following integrals. (a) ( x 4 x 2 ) dx (b) (2 3 x + x2 4 ) dx (c) (3x + 5) 6 dx (d) x 2 dx x 3 + (e) x 9x 2 dx (f) x dx x 2 (g) xe x2 + dx (h) 2 3x+ dx (i) x
Calculus Lia Vas. Integrals. Evaluate the following integrals. (a) ( x 4 x 2 ) dx (b) (2 3 x + x2 4 ) dx (c) (3x + 5) 6 dx (d) x 2 dx x 3 + (e) x 9x 2 dx (f) x dx x 2 (g) xe x2 + dx (h) 2 3x+ dx (i) x
Sample Mathematics 106 Questions
 Sample Mathematics 106 Questions x 2 + 8x 65 (1) Calculate lim x 5. x 5 (2) Consider an object moving in a straight line for which the distance s (measured in feet) it s travelled from its starting point
Sample Mathematics 106 Questions x 2 + 8x 65 (1) Calculate lim x 5. x 5 (2) Consider an object moving in a straight line for which the distance s (measured in feet) it s travelled from its starting point
Purdue University Study Guide for MA Credit Exam
 Purdue University Study Guide for MA 16010 Credit Exam Students who pass the credit exam will gain credit in MA16010. The credit exam is a two-hour long exam with multiple choice questions. No books or
Purdue University Study Guide for MA 16010 Credit Exam Students who pass the credit exam will gain credit in MA16010. The credit exam is a two-hour long exam with multiple choice questions. No books or
m(x) = f(x) + g(x) m (x) = f (x) + g (x) (The Sum Rule) n(x) = f(x) g(x) n (x) = f (x) g (x) (The Difference Rule)
 Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules 3.1 Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Aka The Short Cuts! Yay! f(x) = c f (x) = 0 g(x) = x g (x) = 1 h(x) = x n h (x) = n x n-1 (The Power Rule) k(x)
Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules 3.1 Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Aka The Short Cuts! Yay! f(x) = c f (x) = 0 g(x) = x g (x) = 1 h(x) = x n h (x) = n x n-1 (The Power Rule) k(x)
Math 142 Week-in-Review #11 (Final Exam Review: All previous sections as well as sections 6.6 and 6.7)
 Math 142 Week-in-Review #11 (Final Exam Review: All previous sections as well as sections 6.6 and 6.7) Note: This review is intended to highlight the topics covered on the Final Exam (with emphasis on
Math 142 Week-in-Review #11 (Final Exam Review: All previous sections as well as sections 6.6 and 6.7) Note: This review is intended to highlight the topics covered on the Final Exam (with emphasis on
Math Practice Final - solutions
 Math 151 - Practice Final - solutions 2 1-2 -1 0 1 2 3 Problem 1 Indicate the following from looking at the graph of f(x) above. All answers are small integers, ±, or DNE for does not exist. a) lim x 1
Math 151 - Practice Final - solutions 2 1-2 -1 0 1 2 3 Problem 1 Indicate the following from looking at the graph of f(x) above. All answers are small integers, ±, or DNE for does not exist. a) lim x 1
Math 1071 Final Review Sheet The following are some review questions to help you study. They do not
 Math 1071 Final Review Sheet The following are some review questions to help you study. They do not They do The exam represent the entirety of what you could be expected to know on the exam; reflect distribution
Math 1071 Final Review Sheet The following are some review questions to help you study. They do not They do The exam represent the entirety of what you could be expected to know on the exam; reflect distribution
All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit.
 AP Calculus.4 Worksheet All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit.. What is a difference quotient?. How do you find the slope of a curve (aka slope
AP Calculus.4 Worksheet All work must be shown in this course for full credit. Unsupported answers may receive NO credit.. What is a difference quotient?. How do you find the slope of a curve (aka slope
Intermediate Algebra Final Exam Review
 Intermediate Algebra Final Exam Review Note to students: The final exam for MAT10, MAT 11 and MAT1 will consist of 30 multiple-choice questions and a few open-ended questions. The exam itself will cover
Intermediate Algebra Final Exam Review Note to students: The final exam for MAT10, MAT 11 and MAT1 will consist of 30 multiple-choice questions and a few open-ended questions. The exam itself will cover
1.5 The Derivative (2.7, 2.8 & 2.9)
 1.5. THE DERIVATIVE (2.7, 2.8 & 2.9) 47 1.5 The Derivative (2.7, 2.8 & 2.9) The concept we are about to de ne is not new. We simply give it a new name. Often in mathematics, when the same idea seems to
1.5. THE DERIVATIVE (2.7, 2.8 & 2.9) 47 1.5 The Derivative (2.7, 2.8 & 2.9) The concept we are about to de ne is not new. We simply give it a new name. Often in mathematics, when the same idea seems to
UNIT 3: DERIVATIVES STUDY GUIDE
 Calculus I UNIT 3: Derivatives REVIEW Name: Date: UNIT 3: DERIVATIVES STUDY GUIDE Section 1: Section 2: Limit Definition (Derivative as the Slope of the Tangent Line) Calculating Rates of Change (Average
Calculus I UNIT 3: Derivatives REVIEW Name: Date: UNIT 3: DERIVATIVES STUDY GUIDE Section 1: Section 2: Limit Definition (Derivative as the Slope of the Tangent Line) Calculating Rates of Change (Average
Section 12.2 The Second Derivative
 Section 12.2 The Second Derivative Higher derivatives If f is a differentiable function, then f is also a function. So, f may have a derivative of its own, denoted by (f ) = f. This new function f is called
Section 12.2 The Second Derivative Higher derivatives If f is a differentiable function, then f is also a function. So, f may have a derivative of its own, denoted by (f ) = f. This new function f is called
April 9, 2009 Name The problems count as marked. The total number of points available is 160. Throughout this test, show your work.
 April 9, 009 Name The problems count as marked The total number of points available is 160 Throughout this test, show your work 1 (15 points) Consider the cubic curve f(x) = x 3 + 3x 36x + 17 (a) Build
April 9, 009 Name The problems count as marked The total number of points available is 160 Throughout this test, show your work 1 (15 points) Consider the cubic curve f(x) = x 3 + 3x 36x + 17 (a) Build
Math 131. The Derivative and the Tangent Line Problem Larson Section 2.1
 Math 131. The Derivative and the Tangent Line Problem Larson Section.1 From precalculus, the secant line through the two points (c, f(c)) and (c +, f(c + )) is given by m sec = rise f(c + ) f(c) f(c +
Math 131. The Derivative and the Tangent Line Problem Larson Section.1 From precalculus, the secant line through the two points (c, f(c)) and (c +, f(c + )) is given by m sec = rise f(c + ) f(c) f(c +
1 Functions and Graphs
 1 Functions and Graphs 1.1 Functions Cartesian Coordinate System A Cartesian or rectangular coordinate system is formed by the intersection of a horizontal real number line, usually called the x axis,
1 Functions and Graphs 1.1 Functions Cartesian Coordinate System A Cartesian or rectangular coordinate system is formed by the intersection of a horizontal real number line, usually called the x axis,
Math 180, Lowman, Summer 2008, Old Exam Problems 1 Limit Problems
 Math 180, Lowman, Summer 2008, Old Exam Problems 1 Limit Problems 1. Find the limit of f(x) = (sin x) x x 3 as x 0. 2. Use L Hopital s Rule to calculate lim x 2 x 3 2x 2 x+2 x 2 4. 3. Given the function
Math 180, Lowman, Summer 2008, Old Exam Problems 1 Limit Problems 1. Find the limit of f(x) = (sin x) x x 3 as x 0. 2. Use L Hopital s Rule to calculate lim x 2 x 3 2x 2 x+2 x 2 4. 3. Given the function
Lecture 5 - Logarithms, Slope of a Function, Derivatives
 Lecture 5 - Logarithms, Slope of a Function, Derivatives 5. Logarithms Note the graph of e x This graph passes the horizontal line test, so f(x) = e x is one-to-one and therefore has an inverse function.
Lecture 5 - Logarithms, Slope of a Function, Derivatives 5. Logarithms Note the graph of e x This graph passes the horizontal line test, so f(x) = e x is one-to-one and therefore has an inverse function.
Chapter 2 Describing Change: Rates
 Chapter Describing Change: Rates Section.1 Change, Percentage Change, and Average Rates of Change 1. 3. $.30 $0.46 per day 5 days = The stock price rose an average of 46 cents per day during the 5-day
Chapter Describing Change: Rates Section.1 Change, Percentage Change, and Average Rates of Change 1. 3. $.30 $0.46 per day 5 days = The stock price rose an average of 46 cents per day during the 5-day
Given the table of values, determine the equation
 3.1 Properties of Quadratic Functions Recall: Standard Form f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c Factored Form f(x) = a(x r)(x s) Vertex Form f(x) = a(x h) 2 + k Given the table of values, determine the equation x y 1
3.1 Properties of Quadratic Functions Recall: Standard Form f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c Factored Form f(x) = a(x r)(x s) Vertex Form f(x) = a(x h) 2 + k Given the table of values, determine the equation x y 1
MATH150-E01 Test #2 Summer 2016 Show all work. Name 1. Find an equation in slope-intercept form for the line through (4, 2) and (1, 3).
 1. Find an equation in slope-intercept form for the line through (4, 2) and (1, 3). 2. Let the supply and demand functions for sugar be given by p = S(q) = 1.4q 0.6 and p = D(q) = 2q + 3.2 where p is the
1. Find an equation in slope-intercept form for the line through (4, 2) and (1, 3). 2. Let the supply and demand functions for sugar be given by p = S(q) = 1.4q 0.6 and p = D(q) = 2q + 3.2 where p is the
Section 11.3 Rates of Change:
 Section 11.3 Rates of Change: 1. Consider the following table, which describes a driver making a 168-mile trip from Cleveland to Columbus, Ohio in 3 hours. t Time (in hours) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 f(t) Distance
Section 11.3 Rates of Change: 1. Consider the following table, which describes a driver making a 168-mile trip from Cleveland to Columbus, Ohio in 3 hours. t Time (in hours) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 f(t) Distance
Math 611b Assignment #6 Name. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Math 611b Assignment #6 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find a formula for the function graphed. 1) 1) A) f(x) = 5 + x, x < -
Math 611b Assignment #6 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find a formula for the function graphed. 1) 1) A) f(x) = 5 + x, x < -
Sample Math 115 Midterm Exam Spring, 2014
 Sample Math 5 Midterm Exam Spring, 04 The midterm examination is on Wednesday, March at 5:45PM 7:45PM The midterm examination will be in Budig 0 Look for your instructor who will direct you where to sit
Sample Math 5 Midterm Exam Spring, 04 The midterm examination is on Wednesday, March at 5:45PM 7:45PM The midterm examination will be in Budig 0 Look for your instructor who will direct you where to sit
Review questions for Math 111 final. Please SHOW your WORK to receive full credit Final Test is based on 150 points
 Please SHOW your WORK to receive full credit Final Test is based on 150 points 1. True or False questions (17 pts) a. Common Logarithmic functions cross the y axis at (0,1) b. A square matrix has as many
Please SHOW your WORK to receive full credit Final Test is based on 150 points 1. True or False questions (17 pts) a. Common Logarithmic functions cross the y axis at (0,1) b. A square matrix has as many
Math 120 Final Exam Practice Problems, Form: A
 Math 120 Final Exam Practice Problems, Form: A Name: While every attempt was made to be complete in the types of problems given below, we make no guarantees about the completeness of the problems. Specifically,
Math 120 Final Exam Practice Problems, Form: A Name: While every attempt was made to be complete in the types of problems given below, we make no guarantees about the completeness of the problems. Specifically,
a b c d e GOOD LUCK! 3. a b c d e 12. a b c d e 4. a b c d e 13. a b c d e 5. a b c d e 14. a b c d e 6. a b c d e 15. a b c d e
 MA23 Elem. Calculus Spring 206 Final Exam 206-05-05 Name: Sec.: Do not remove this answer page you will turn in the entire exam. No books or notes may be used. You may use an ACT-approved calculator during
MA23 Elem. Calculus Spring 206 Final Exam 206-05-05 Name: Sec.: Do not remove this answer page you will turn in the entire exam. No books or notes may be used. You may use an ACT-approved calculator during
Free Response Questions Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom
 Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
Lecture 26: Section 5.3 Higher Derivatives and Concavity
 L26-1 Lecture 26: Section 5.3 Higher Derivatives and Concavity ex. Let f(x) = ln(e 2x + 1) 1) Find f (x). 2) Find d dx [f (x)]. L26-2 We define f (x) = Higher Order Derivatives For y = f(x), we can write
L26-1 Lecture 26: Section 5.3 Higher Derivatives and Concavity ex. Let f(x) = ln(e 2x + 1) 1) Find f (x). 2) Find d dx [f (x)]. L26-2 We define f (x) = Higher Order Derivatives For y = f(x), we can write
MAT 210 TEST 2 REVIEW (Ch 12 and 13)
 Class: Date: MAT 0 TEST REVIEW (Ch and ) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. The population P is currently 0,000 and growing at a rate of 7,000
Class: Date: MAT 0 TEST REVIEW (Ch and ) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.. The population P is currently 0,000 and growing at a rate of 7,000
Calculus I Sample Exam #01
 Calculus I Sample Exam #01 1. Sketch the graph of the function and define the domain and range. 1 a) f( x) 3 b) g( x) x 1 x c) hx ( ) x x 1 5x6 d) jx ( ) x x x 3 6 . Evaluate the following. a) 5 sin 6
Calculus I Sample Exam #01 1. Sketch the graph of the function and define the domain and range. 1 a) f( x) 3 b) g( x) x 1 x c) hx ( ) x x 1 5x6 d) jx ( ) x x x 3 6 . Evaluate the following. a) 5 sin 6
b) The trend is for the average slope at x = 1 to decrease. The slope at x = 1 is 1.
 Chapters 1 to 8 Course Review Chapters 1 to 8 Course Review Question 1 Page 509 a) i) ii) [2(16) 12 + 4][2 3+ 4] 4 1 [2(2.25) 4.5+ 4][2 3+ 4] 1.51 = 21 3 = 7 = 1 0.5 = 2 [2(1.21) 3.3+ 4][2 3+ 4] iii) =
Chapters 1 to 8 Course Review Chapters 1 to 8 Course Review Question 1 Page 509 a) i) ii) [2(16) 12 + 4][2 3+ 4] 4 1 [2(2.25) 4.5+ 4][2 3+ 4] 1.51 = 21 3 = 7 = 1 0.5 = 2 [2(1.21) 3.3+ 4][2 3+ 4] iii) =
This Week. Professor Christopher Hoffman Math 124
 This Week Sections 2.1-2.3,2.5,2.6 First homework due Tuesday night at 11:30 p.m. Average and instantaneous velocity worksheet Tuesday available at http://www.math.washington.edu/ m124/ (under week 2)
This Week Sections 2.1-2.3,2.5,2.6 First homework due Tuesday night at 11:30 p.m. Average and instantaneous velocity worksheet Tuesday available at http://www.math.washington.edu/ m124/ (under week 2)
Review Assignment II
 MATH 11012 Intuitive Calculus KSU Name:. Review Assignment II 1. Let C(x) be the cost, in dollars, of manufacturing x widgets. Fill in the table with a mathematical expression and appropriate units corresponding
MATH 11012 Intuitive Calculus KSU Name:. Review Assignment II 1. Let C(x) be the cost, in dollars, of manufacturing x widgets. Fill in the table with a mathematical expression and appropriate units corresponding
Business and Life Calculus
 Business and Life Calculus George Voutsadakis Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 2 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Calculus For Business and Life Sciences Fall 203 / 55
Business and Life Calculus George Voutsadakis Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 2 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Calculus For Business and Life Sciences Fall 203 / 55
Math 1310 Lab 10. (Sections )
 Math 131 Lab 1. (Sections 5.1-5.3) Name/Unid: Lab section: 1. (Properties of the integral) Use the properties of the integral in section 5.2 for answering the following question. (a) Knowing that 2 2f(x)
Math 131 Lab 1. (Sections 5.1-5.3) Name/Unid: Lab section: 1. (Properties of the integral) Use the properties of the integral in section 5.2 for answering the following question. (a) Knowing that 2 2f(x)
Course Outline. Linear Equations Linear Inequalities (1.6)
 Course Outline Functions/Graphing Solving Equations Applications Definitions of function, graph, domain, range, x- and y- intercepts, vertical line test(.-.) Linear functions (.-.5) -Parallel and perpendicular
Course Outline Functions/Graphing Solving Equations Applications Definitions of function, graph, domain, range, x- and y- intercepts, vertical line test(.-.) Linear functions (.-.5) -Parallel and perpendicular
Sections 2.7, 2.8 Rates of Change Part III Rates of Change in the Natural and Social Sciences
 Math 180 wwwtimetodarecom Sections 7, 8 Rates of Change Part III Rates of Change in the Natural and Social Sciences Physics s If s= f ( t) is the position function of a particle that is moving in a straight
Math 180 wwwtimetodarecom Sections 7, 8 Rates of Change Part III Rates of Change in the Natural and Social Sciences Physics s If s= f ( t) is the position function of a particle that is moving in a straight
Calculus I 5. Applications of differentiation
 2301107 Calculus I 5. Applications of differentiation Chapter 5:Applications of differentiation C05-2 Outline 5.1. Extreme values 5.2. Curvature and Inflection point 5.3. Curve sketching 5.4. Related rate
2301107 Calculus I 5. Applications of differentiation Chapter 5:Applications of differentiation C05-2 Outline 5.1. Extreme values 5.2. Curvature and Inflection point 5.3. Curve sketching 5.4. Related rate
ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Fall 2014: Lectures Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers. 24x + 72 (x 2 6x + 4) 4
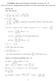 ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Fall 014: Lectures 19 35 Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers Lecture 19 1. d [ 4 ] dx x 6x + 4) 3 = 4x + 7 x 6x + 4) 4. a) P 0) = 800 b)
ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Fall 014: Lectures 19 35 Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers Lecture 19 1. d [ 4 ] dx x 6x + 4) 3 = 4x + 7 x 6x + 4) 4. a) P 0) = 800 b)
MAC 2233 Chapter 3 Practice for the Test
 Class: Date: MAC 33 Chapter 3 Practice for the Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. At which labeled point is the slope of the tangent
Class: Date: MAC 33 Chapter 3 Practice for the Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. At which labeled point is the slope of the tangent
3.1 Day 1: The Derivative of a Function
 A P Calculus 3.1 Day 1: The Derivative of a Function I CAN DEFINE A DERIVATIVE AND UNDERSTAND ITS NOTATION. Last chapter we learned to find the slope of a tangent line to a point on a graph by using a
A P Calculus 3.1 Day 1: The Derivative of a Function I CAN DEFINE A DERIVATIVE AND UNDERSTAND ITS NOTATION. Last chapter we learned to find the slope of a tangent line to a point on a graph by using a
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB
 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS
 RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS Definitions A RELATION is any set of ordered pairs. A FUNCTION is a relation in which every input value is paired with exactly one output value. Example 1: Table of Values One way
RELATIONS AND FUNCTIONS Definitions A RELATION is any set of ordered pairs. A FUNCTION is a relation in which every input value is paired with exactly one output value. Example 1: Table of Values One way
Midterm Study Guide and Practice Problems
 Midterm Study Guide and Practice Problems Coverage of the midterm: Sections 10.1-10.7, 11.2-11.6 Sections or topics NOT on the midterm: Section 11.1 (The constant e and continuous compound interest, Section
Midterm Study Guide and Practice Problems Coverage of the midterm: Sections 10.1-10.7, 11.2-11.6 Sections or topics NOT on the midterm: Section 11.1 (The constant e and continuous compound interest, Section
DRAFT - Math 101 Lecture Note - Dr. Said Algarni
 2 Limits 2.1 The Tangent Problems The word tangent is derived from the Latin word tangens, which means touching. A tangent line to a curve is a line that touches the curve and a secant line is a line that
2 Limits 2.1 The Tangent Problems The word tangent is derived from the Latin word tangens, which means touching. A tangent line to a curve is a line that touches the curve and a secant line is a line that
Name: Practice A, Math Final Exam December 11, 2018
 Practice A, Math 10250 Final Exam December 11, 2018 Name: Instructor: Be sure that you have all 15 pages of the test. Calculators are allowed for this examination. The exam lasts for two hours. The Honor
Practice A, Math 10250 Final Exam December 11, 2018 Name: Instructor: Be sure that you have all 15 pages of the test. Calculators are allowed for this examination. The exam lasts for two hours. The Honor
f ', the first derivative of a differentiable function, f. Use the
 f, f ', and The graph given to the right is the graph of graph to answer the questions below. f '' Relationships and The Extreme Value Theorem 1. On the interval [0, 8], are there any values where f(x)
f, f ', and The graph given to the right is the graph of graph to answer the questions below. f '' Relationships and The Extreme Value Theorem 1. On the interval [0, 8], are there any values where f(x)
Unit IV Derivatives 20 Hours Finish by Christmas
 Unit IV Derivatives 20 Hours Finish by Christmas Calculus There two main streams of Calculus: Differentiation Integration Differentiation is used to find the rate of change of variables relative to one
Unit IV Derivatives 20 Hours Finish by Christmas Calculus There two main streams of Calculus: Differentiation Integration Differentiation is used to find the rate of change of variables relative to one
Unit IV Derivatives 20 Hours Finish by Christmas
 Unit IV Derivatives 20 Hours Finish by Christmas Calculus There two main streams of Calculus: Differentiation Integration Differentiation is used to find the rate of change of variables relative to one
Unit IV Derivatives 20 Hours Finish by Christmas Calculus There two main streams of Calculus: Differentiation Integration Differentiation is used to find the rate of change of variables relative to one
Mini-Lesson 9. Section 9.1: Relations and Functions. Definitions
 9 Section 9.1: Relations and Functions A RELATION is any set of ordered pairs. Definitions A FUNCTION is a relation in which every input value is paired with exactly one output value. Table of Values One
9 Section 9.1: Relations and Functions A RELATION is any set of ordered pairs. Definitions A FUNCTION is a relation in which every input value is paired with exactly one output value. Table of Values One
Math Exam 02 Review
 Math 10350 Exam 02 Review 1. A differentiable function g(t) is such that g(2) = 2, g (2) = 1, g (2) = 1/2. (a) If p(t) = g(t)e t2 find p (2) and p (2). (Ans: p (2) = 7e 4 ; p (2) = 28.5e 4 ) (b) If f(t)
Math 10350 Exam 02 Review 1. A differentiable function g(t) is such that g(2) = 2, g (2) = 1, g (2) = 1/2. (a) If p(t) = g(t)e t2 find p (2) and p (2). (Ans: p (2) = 7e 4 ; p (2) = 28.5e 4 ) (b) If f(t)
Chapter 3: Derivatives
 Name: Date: Period: AP Calc AB Mr. Mellina Chapter 3: Derivatives Sections: v 2.4 Rates of Change & Tangent Lines v 3.1 Derivative of a Function v 3.2 Differentiability v 3.3 Rules for Differentiation
Name: Date: Period: AP Calc AB Mr. Mellina Chapter 3: Derivatives Sections: v 2.4 Rates of Change & Tangent Lines v 3.1 Derivative of a Function v 3.2 Differentiability v 3.3 Rules for Differentiation
Study Guide - Part 2
 Math 116 Spring 2015 Study Guide - Part 2 1. Which of the following describes the derivative function f (x) of a quadratic function f(x)? (A) Cubic (B) Quadratic (C) Linear (D) Constant 2. Find the derivative
Math 116 Spring 2015 Study Guide - Part 2 1. Which of the following describes the derivative function f (x) of a quadratic function f(x)? (A) Cubic (B) Quadratic (C) Linear (D) Constant 2. Find the derivative
Dr. Sophie Marques. MAM1020S Tutorial 8 August Divide. 1. 6x 2 + x 15 by 3x + 5. Solution: Do a long division show your work.
 Dr. Sophie Marques MAM100S Tutorial 8 August 017 1. Divide 1. 6x + x 15 by 3x + 5. 6x + x 15 = (x 3)(3x + 5) + 0. 1a 4 17a 3 + 9a + 7a 6 by 3a 1a 4 17a 3 + 9a + 7a 6 = (4a 3 3a + a + 3)(3a ) + 0 3. 1a
Dr. Sophie Marques MAM100S Tutorial 8 August 017 1. Divide 1. 6x + x 15 by 3x + 5. 6x + x 15 = (x 3)(3x + 5) + 0. 1a 4 17a 3 + 9a + 7a 6 by 3a 1a 4 17a 3 + 9a + 7a 6 = (4a 3 3a + a + 3)(3a ) + 0 3. 1a
What will you learn?
 Section 2.2 Basic Differentiation Rules & Rates of Change Calc What will you learn? Find the derivative using the Constant Rule Find the derivative using the Power Rule Find the derivative using the Constant
Section 2.2 Basic Differentiation Rules & Rates of Change Calc What will you learn? Find the derivative using the Constant Rule Find the derivative using the Power Rule Find the derivative using the Constant
Final Exam Study Aid
 Math 112 Final Exam Study Aid 1 of 33 Final Exam Study Aid Note: This study aid is intended to help you review for the final exam. It covers the primary concepts in the course, with a large emphasis on
Math 112 Final Exam Study Aid 1 of 33 Final Exam Study Aid Note: This study aid is intended to help you review for the final exam. It covers the primary concepts in the course, with a large emphasis on
MATH 122 FALL Final Exam Review Problems
 MATH 122 FALL 2013 Final Exam Review Problems Chapter 1 1. As a person hikes down from the top of a mountain, the variable t represents the time, in minutes, since the person left the top of the mountain,
MATH 122 FALL 2013 Final Exam Review Problems Chapter 1 1. As a person hikes down from the top of a mountain, the variable t represents the time, in minutes, since the person left the top of the mountain,
Math 106 Answers to Exam 1a Fall 2015
 Math 06 Answers to Exam a Fall 05.. Find the derivative of the following functions. Do not simplify your answers. (a) f(x) = ex cos x x + (b) g(z) = [ sin(z ) + e z] 5 Using the quotient rule on f(x) and
Math 06 Answers to Exam a Fall 05.. Find the derivative of the following functions. Do not simplify your answers. (a) f(x) = ex cos x x + (b) g(z) = [ sin(z ) + e z] 5 Using the quotient rule on f(x) and
AP Calculus BC Class Starter January 22, 2018
 January 22, 2018 1. Given the function, find the following. (a) Evaluate f(4). (b) The definition of the derivative can be written two ways, as indicated below. Find both forms and evaluate the derivative
January 22, 2018 1. Given the function, find the following. (a) Evaluate f(4). (b) The definition of the derivative can be written two ways, as indicated below. Find both forms and evaluate the derivative
Math Exam 3 Review
 Math 142 Spring 2009 c Heather Ramsey Page 1 Math 142 - Exam 3 Review NOTE: Exam 3 covers sections 5.4-5.6, 6.1, 6.2, 6.4, 6.5, 7.1, and 7.2. This review is intended to highlight the material covered on
Math 142 Spring 2009 c Heather Ramsey Page 1 Math 142 - Exam 3 Review NOTE: Exam 3 covers sections 5.4-5.6, 6.1, 6.2, 6.4, 6.5, 7.1, and 7.2. This review is intended to highlight the material covered on
CHAPTER 2 Differentiation
 CHAPTER Differentiation Section. The Derivative and the Slope of a Graph............. 9 Section. Some Rules for Differentiation.................. 56 Section. Rates of Change: Velocit and Marginals.............
CHAPTER Differentiation Section. The Derivative and the Slope of a Graph............. 9 Section. Some Rules for Differentiation.................. 56 Section. Rates of Change: Velocit and Marginals.............
4x 2-5x+3. 7x-1 HOMEWORK 1-1
 HOMEWORK 1-1 As it is always the case that correct answers without sufficient mathematical justification may not receive full credit, make sure that you show all your work. Please circle, draw a box around,
HOMEWORK 1-1 As it is always the case that correct answers without sufficient mathematical justification may not receive full credit, make sure that you show all your work. Please circle, draw a box around,
Differentiation Review, Part 1 (Part 2 follows; there are answers at the end of each part.)
 Differentiation Review 1 Name Differentiation Review, Part 1 (Part 2 follows; there are answers at the end of each part.) Derivatives Review: Summary of Rules Each derivative rule is summarized for you
Differentiation Review 1 Name Differentiation Review, Part 1 (Part 2 follows; there are answers at the end of each part.) Derivatives Review: Summary of Rules Each derivative rule is summarized for you
Week In Review #8 Covers sections: 5.1, 5.2, 5.3 and 5.4. Things you must know
 Week In Review #8 Covers sections: 5.1, 5.2, 5.3 and 5. Things you must know Know how to get an accumulated change by finding an upper or a lower estimate value Know how to approximate a definite integral
Week In Review #8 Covers sections: 5.1, 5.2, 5.3 and 5. Things you must know Know how to get an accumulated change by finding an upper or a lower estimate value Know how to approximate a definite integral
Name. 3) f(x) = -x2-2. Sketch the graph of the function and find the domain and range. 1) f(x) = x2-4. 4) f(x) = x ) f(x) = -3(x + 3)2-2
 Exam 3 Final Preparation Ch 7, 9, etal v0 There will be 5 questions on Exam 3 (Final). Twenty questions from chapters 7 & 9. Five questions from chapter 5. No Book/No Notes/No Ipod/ No Phone/Yes Calculator/55
Exam 3 Final Preparation Ch 7, 9, etal v0 There will be 5 questions on Exam 3 (Final). Twenty questions from chapters 7 & 9. Five questions from chapter 5. No Book/No Notes/No Ipod/ No Phone/Yes Calculator/55
Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integrals
 Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integrals MATH 151 Calculus for Management J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives After completing this lesson we will be able to use the definition
Antiderivatives and Indefinite Integrals MATH 151 Calculus for Management J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 2018 Objectives After completing this lesson we will be able to use the definition
Using Derivatives To Measure Rates of Change
 Using Derivatives To Measure Rates of Change A rate of change is associated with a variable f(x) that changes by the same amount when the independent variable x increases by one unit. Here are two examples:
Using Derivatives To Measure Rates of Change A rate of change is associated with a variable f(x) that changes by the same amount when the independent variable x increases by one unit. Here are two examples:
Unit 3 Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey
 HW#1 Name Algebra II Unit Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey 1) In each of the following, the variable pair given are proportional to one another. Find the missing value. (a) b = 8 when a = 16 b =? when a = 18
HW#1 Name Algebra II Unit Functions HW #1 Mrs. Dailey 1) In each of the following, the variable pair given are proportional to one another. Find the missing value. (a) b = 8 when a = 16 b =? when a = 18
Section 2.1 Limits: Approached Numerically and Graphically
 Section 2.1 Limits: Approached Numerically and Graphically Foundation Concepts: Limit Left-hand limit Right-hand limit 1 = 1 = tiny big Practice: 1. What can we say about lim,. f(x)? a) If lim, 3 4 f(x)=7
Section 2.1 Limits: Approached Numerically and Graphically Foundation Concepts: Limit Left-hand limit Right-hand limit 1 = 1 = tiny big Practice: 1. What can we say about lim,. f(x)? a) If lim, 3 4 f(x)=7
Section K MATH 211 Homework Due Friday, 8/30/96 Professor J. Beachy Average: 15.1 / 20. ), and f(a + 1).
 Section K MATH 211 Homework Due Friday, 8/30/96 Professor J. Beachy Average: 15.1 / 20 # 18, page 18: If f(x) = x2 x 2 1, find f( 1 2 ), f( 1 2 ), and f(a + 1). # 22, page 18: When a solution of acetylcholine
Section K MATH 211 Homework Due Friday, 8/30/96 Professor J. Beachy Average: 15.1 / 20 # 18, page 18: If f(x) = x2 x 2 1, find f( 1 2 ), f( 1 2 ), and f(a + 1). # 22, page 18: When a solution of acetylcholine
Chapter 2 Overview: Introduction to Limits and Derivatives
 Chapter 2 Overview: Introduction to Limits and Derivatives In a later chapter, maximum and minimum points of a curve will be found both by calculator and algebraically. While the algebra of this process
Chapter 2 Overview: Introduction to Limits and Derivatives In a later chapter, maximum and minimum points of a curve will be found both by calculator and algebraically. While the algebra of this process
Pre-Calculus Section 12.4: Tangent Lines and Derivatives 1. Determine the interval on which the function in the graph below is decreasing.
 Pre-Calculus Section 12.4: Tangent Lines and Derivatives 1. Determine the interval on which the function in the graph below is decreasing. Determine the average rate of change for the function between
Pre-Calculus Section 12.4: Tangent Lines and Derivatives 1. Determine the interval on which the function in the graph below is decreasing. Determine the average rate of change for the function between
Section Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions
 Section 3.1 - Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Constant Function Rule: If f(x)=c where c is a constant then Power Rule: If f(x)=x n, where n is a real number, then Constant Multiple
Section 3.1 - Derivatives of Polynomials and Exponential Functions Constant Function Rule: If f(x)=c where c is a constant then Power Rule: If f(x)=x n, where n is a real number, then Constant Multiple
e x3 dx dy. 0 y x 2, 0 x 1.
 Problem 1. Evaluate by changing the order of integration y e x3 dx dy. Solution:We change the order of integration over the region y x 1. We find and x e x3 dy dx = y x, x 1. x e x3 dx = 1 x=1 3 ex3 x=
Problem 1. Evaluate by changing the order of integration y e x3 dx dy. Solution:We change the order of integration over the region y x 1. We find and x e x3 dy dx = y x, x 1. x e x3 dx = 1 x=1 3 ex3 x=
(A) 47 ft/sec (B) 52 ft/sec (C) 120 ft/sec (D) 125 ft/sec (E) 141 ft/sec
 Name Date Period Worksheet 6.1 Integral as Net Change Show all work. Calculator Permitted, but show all integral set ups. Multiple Choice 1. The graph at right shows the rate at which water is pumped from
Name Date Period Worksheet 6.1 Integral as Net Change Show all work. Calculator Permitted, but show all integral set ups. Multiple Choice 1. The graph at right shows the rate at which water is pumped from
Math 113 (Calculus II) Final Exam KEY
 Math (Calculus II) Final Exam KEY Short Answer. Fill in the blank with the appropriate answer.. (0 points) a. Let y = f (x) for x [a, b]. Give the formula for the length of the curve formed by the b graph
Math (Calculus II) Final Exam KEY Short Answer. Fill in the blank with the appropriate answer.. (0 points) a. Let y = f (x) for x [a, b]. Give the formula for the length of the curve formed by the b graph
Chapter 2 Derivatives And Their Uses
 Chapter Derivatives And Their Uses 1. Complete the table and use it to predict the limit, if it eists. 6 f( ) 0. 1 lim f( )? 0.1 0.01 0.001 0.? 0.999 0.99 f ( ) 0.9 160.0 80.0 80.0 0. does not eist. Use
Chapter Derivatives And Their Uses 1. Complete the table and use it to predict the limit, if it eists. 6 f( ) 0. 1 lim f( )? 0.1 0.01 0.001 0.? 0.999 0.99 f ( ) 0.9 160.0 80.0 80.0 0. does not eist. Use
x C) y = - A) $20000; 14 years B) $28,000; 14 years C) $28,000; 28 years D) $30,000; 15 years
 Dr. Lee - Math 35 - Calculus for Business - Review of 3 - Show Complete Work for Each Problem MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find
Dr. Lee - Math 35 - Calculus for Business - Review of 3 - Show Complete Work for Each Problem MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find
Math 1120 Calculus Final Exam
 May 4, 2001 Name The first five problems count 7 points each (total 35 points) and rest count as marked. There are 195 points available. Good luck. 1. Consider the function f defined by: { 2x 2 3 if x
May 4, 2001 Name The first five problems count 7 points each (total 35 points) and rest count as marked. There are 195 points available. Good luck. 1. Consider the function f defined by: { 2x 2 3 if x
MA Lesson 12 Notes Section 3.4 of Calculus part of textbook
 MA 15910 Lesson 1 Notes Section 3.4 of Calculus part of textbook Tangent Line to a curve: To understand the tangent line, we must first discuss a secant line. A secant line will intersect a curve at more
MA 15910 Lesson 1 Notes Section 3.4 of Calculus part of textbook Tangent Line to a curve: To understand the tangent line, we must first discuss a secant line. A secant line will intersect a curve at more
3. Solve the following inequalities and express your answer in interval notation.
 Youngstown State University College Algebra Final Exam Review (Math 50). Find all Real solutions for the following: a) x 2 + 5x = 6 b) 9 x2 x 8 = 0 c) (x 2) 2 = 6 d) 4x = 8 x 2 e) x 2 + 4x = 5 f) 36x 3
Youngstown State University College Algebra Final Exam Review (Math 50). Find all Real solutions for the following: a) x 2 + 5x = 6 b) 9 x2 x 8 = 0 c) (x 2) 2 = 6 d) 4x = 8 x 2 e) x 2 + 4x = 5 f) 36x 3
Purdue University Study Guide for MA for students who plan to obtain credit in MA by examination.
 Purdue University Study Guide for MA 224 for students who plan to obtain credit in MA 224 by examination. Textbook: Applied Calculus For Business, Economics, and the Social and Life Sciences, Expanded
Purdue University Study Guide for MA 224 for students who plan to obtain credit in MA 224 by examination. Textbook: Applied Calculus For Business, Economics, and the Social and Life Sciences, Expanded
(MATH 1203, 1204, 1204R)
 College Algebra (MATH 1203, 1204, 1204R) Departmental Review Problems For all questions that ask for an approximate answer, round to two decimal places (unless otherwise specified). The most closely related
College Algebra (MATH 1203, 1204, 1204R) Departmental Review Problems For all questions that ask for an approximate answer, round to two decimal places (unless otherwise specified). The most closely related
Algebra I EOC Review (Part 2)
 1. Let x = total miles the car can travel Answer: x 22 = 18 or x 18 = 22 2. A = 1 2 ah 1 2 bh A = 1 h(a b) 2 2A = h(a b) 2A = h a b Note that when solving for a variable that appears more than once, consider
1. Let x = total miles the car can travel Answer: x 22 = 18 or x 18 = 22 2. A = 1 2 ah 1 2 bh A = 1 h(a b) 2 2A = h(a b) 2A = h a b Note that when solving for a variable that appears more than once, consider
Business and Life Calculus
 Business and Life Calculus George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 112 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Calculus For Business and Life Sciences Fall 2013
Business and Life Calculus George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 112 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Calculus For Business and Life Sciences Fall 2013
