Section 11.3 Rates of Change:
|
|
|
- Rhoda Parsons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Section 11.3 Rates of Change: 1. Consider the following table, which describes a driver making a 168-mile trip from Cleveland to Columbus, Ohio in 3 hours. t Time (in hours) f(t) Distance (in miles) (a) What does f(2) = 118 mean in the context of the problem? (b) What does f(3) f(2) mean in the context of the problem? (c) Calculate the average speed with the time intervals stated below: Time Interval Average Speed [2, 3] [1, 3] [0, 2.5] [0.5, 1] [a, b] 12
2 2. Quantity Meaning for the Distance Function Meaning for an Arbitrary Function f b a Time interval = change in time from Change in x from x = a to x = b x = a to x = b f(b) f(a) Distance traveled = corresponding Corresponding change in f(x) as x change in distance as time changes changes from a to b f(b) f(a) b a from a to b Average speed = average rate of Average rate of change of f(x) with change of distance with respect to respect to x as x changes from a to b time as time changes from a to b (where a < b) 3. Graphing Average Rate of Change: 4. If f(x) = x 2 + 4x + 5, find the average rate of change of f(x) with respect to x as x changes from 2 to 3. 13
3 5. Suppose D(t) is the value of the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) at time t. Approximate the average rate of change of the DJIA with respect to time over the given intervals. (a) From end of 2000 to end of 2006 (b) From end of 2000 to end of 2002 (c) From end of 2000 to end of Suppose a car is stopped at a traffic light. When the light turns green, the car begins to move along a straight road. Assume that the distance traveled by the car is given by the function s(t) = 2t 2 (0 t 30), where t is measured in seconds and the distance, s(t) is the distance in feet. Find the average speed for each time interval below: Time Interval Average Speed Time Interval Average Speed [10, 20] [10, 10.1] [10, 15] [10, 10.01] [10, 11] [10, ] [10, 10.5] [10, 10 + h] 14
4 7. Velocity: If an object moves along a straight line, with position s(t) at time t, then the velocity of the object at t = a is s(a + h) s(a) lim, h 0 h provided that this limit exists. 8. The distance, in feet, of an object from a starting point is given by s(t) = 2t 2 5t + 40, where t is time in seconds. (a) Find the average velocity of the object from 2 to 4 seconds. (b) Find the instantaneous velocity at 4 seconds. 9. The velocity of blood cells is of interest to physicians; a velocity slower than normal might indicate a constriction, for example. Suppose the position of a red blood cell in a capillary is given by s(t) = 1.2t + 5, where s(t) gives the position of a cell in millimeters from some reference point and t is time in seconds. Find the velocity of this cell at time t = a. 15
5 10. Instantaneous Rate of Change: The instantaneous rate of change for a function f when x = a is f f(a + h) f(a) (a) = lim, h 0 h provided that this limit exists. Note, R (x), C (x) and P (x) are also called, marginal revenue, marginal cost and marginal profit. 11. A company determines that the cost (in hundreds of dollars) of manufacturing x cases of computer mice is C(x) = 0.2x 2 + 8x + 40 (0 x 20). (a) Find the average rate of change of cost for manufacturing between 5 and 10 cases. Use units in your answer! (b) Find the instantaneous rate of change with respect to the number of cases produced when 5 cases are produced. Explain what this means in the context of the problem. 16
6 Section 11.4 Tangent Lines and Derivatives: 1. Graph of the Secant Lines transforming into the Tangent line. Recall, the instantaneous rate of change for f(x) at a: f f(a + h) f(a) (a) = lim, h 0 h This is also the slope of the tangent line of the graph of f(x) at the point (a, f(a)). This is also called the derivative of f(x). Note, without the limit this is the slope of the secant line connecting the points x = a + h and x = a on the graph of f(x). 2. Tangent Line: Note, the tangent line to the graph of a function f(x) at x = a is a good approximation of the function f(x) near x = a. This is useful if the function you are looking at is complicated to evaluate, you can always evaluate a line y = mx + b at a point x. (This will also be useful when we look at multi variables.) 3. Graph of places where the derivative does not exist. 17
7 4. Consider y = x (a) Find the slope of the tangent line to the graph when x = 1. (b) Find the equation of the tangent line. 5. Let a be any real number. Find the equation of the tangent line to the graph of f(x) = 7x + 3 at the point when x = a. (a) Is f (3) positive or negative? 6. (b) Which is larger, f (1) or f (5)? (c) For which values of x is f (x) positive? 18
8 7. A student brings a cold soft drink to a 50-minute math class but is too busy during class to drink it. If C(t) represents the temperature of the soft drink (in Fahrenheit) t minutes after the start of class, interpret the meaning of the following statements, including units. (a) C(0) = 38 (b) C(50) C(0) = 30 (c) C(50) C(0) 50 0 = 0.6 (d) C (0) = Let f(x) = 1 x find f (x) 9. Let f(x) = x find f (x) 19
9 10. Let f(x) = x 2 4x (a) Find f (x) (Note, if you ever see a 4-step process in homework, do not do this, follow how we solve this problem!) (b) Calculate and interpret f (1) (c) Find the equation of the tangent line to the graph of f(x) at the point where x = 1. 20
10 11. A sales representative for a textbook-publishing company frequently makes a 4-hour drive from her home in a large city to a university in another city. Let s(t) represent her position t hours into the trip (where position is measured in miles on the highway, with position 0 corresponding to her home). Then s(t) = 5t 3 +30t 2. How would you answer the following questions. (I do not care about the values, just the work for this example.) (a) How far from home will she be after 1 hour? after 1.5 hours? (b) How far apart are the two cities? (c) What is her velocity 1 hour into the trip? 1.5 hours? 12. Approximating the derivative: If $15,000 is deposited in a money market account that pays 1.2% per year compounded monthly, then the amount in the account after n months is ( A(n) = 15, ) n. 12 Approximate A (120) and interpret what this means. 21
11 Section 11.5 Techniques for Finding Derivatives: 1. Notation: f (x), y, dy dx, d dx f(x), D xy, D x [f(x)] 2. Derivative Rules: Let k be a constant 1. If f(x) = k then f (x) = If f(x) = x n then f (x) = nx n If f(x) = k g(x) then f (x) = k g (x). 4. If f(x) = u(x) ± v(x) then f (x) = u (x) ± v (x). 3. Some examples: Find f (x) where f(x) is defined below. (a) f(x) = 5. (b) f(x) = π. (c) f(x) = x. (d) f(x) = x 3. (e) f(x) = 3x 2. (f) f(x) = x. (g) f(x) = 3 x. (h) f(x) = 1 x. (i) f(x) = x x x 8. (j) f(x) = x2 + 4x + 1 x 2 (k) f(x) = x(x 2 + 5x) 22
12 4. Marginal: If C(x) is the cost function, then the marginal cost (rate of change of cost) is given by the derivative C (x) which is the approximate cost of making one more item after x items have been made. 5. Average Cost: If C(x) is the cost, average cost is C(x) = C(x) x. 6. Revenue: If a demand function p = D(q) is given, where p is price and q is quantity, the total revenue is R(q) = q p = q D(q). 7. Let a demand function be p = 500, 000 q, 25, 000 and cost be C(q) = q for selling q items of something (very exciting). Using this information answer the following questions: (a) Find and simplify the revenue function. (b) Find and simplify the marginal revenue function. (c) Find R (10, 000) and explain what this means. 23
13 (d) Find and simplify the profit function. (e) Find and simplify the marginal profit function. (f) Find and simplify the average cost function. (g) Find the marginal average cost. (h) What is the average cost of producing this very exciting item, as production grows without bound? 8. Word problems: What can the problem say which indicates we want to find the derivative?
14 9. Suppose the total cost in hundreds of dollars to produce x thousand barrels of a beverage is given by C(x) = 5x 3 10x , find the marginal cost when x = 100. And explain what this means. 10. The number of Americans (in thousands) who are expected to be over 100 years old can be approximated by the function f(t) = t t t , where t is the year, with t = 0 corresponding to 2000 and 0 t 50. (a) Find a formula giving the rate of change of the number of Americans over 100 years old. (b) Find the rate of change in the number of Americans who are expected to be over 100 years old in the year (c) What is the number of Americans who are expected to be over 100 years old in the year 2015? 25
15 Section 11.6 Derivatives of Products and Quotients: Derivative rules are getting more complicated. For most of these problems, the only calculus we are doing is in the first step. The rest of the problem we are using algebra to simplify. If you are struggling with simplifying the answers, make sure that you either get the help, or practice you need to do well. (Algebra is a must in this section, if you have poor algebra skills you need to find time to work on them.) 1. Product Rule: If f(x) = u(x) v(x) then Quotient Rule: if f(x) = u(x) v(x) then f (x) = u (x) v(x) + v (x) u(x). f (x) = v(x)u (x) u(x)v (x) [v(x)] 2. Nice saying for quotient rule: low d high minus high d low all over the square of what s below. (Remember, you don t want Heidi.) 2. Let f(x) = (2x + 3) (3x 2 ). Find f (x) 3. Let f(x) = (5x 2 +3x)(x 3 +6x+5 x+100) be a profit function. Find the marginal profit function. 26
16 4. Let f(x) = 3x 2 be the population of some animal, at year x. Find the rate of change of this 5 + 2x animal at year x. 5. Find [ ] (5z 3)(2z + 7) D z 3z
17 6. Let g(z) = (2x2 + 3)(5x + 4), find g (z). 6x 7 28
18 7. Let the cost in dollars of manufacturing x hundred small motors be given by Answer the following questions: (a) Find the marginal cost function C(x) = 3x x + 1. (b) Find the average cost per hundred motors. (c) Find the marginal average cost. (d) Find the level of production that minimizes average cost. minimized when the marginal average cost is zero.) (Note: Average cost is generally 29
19 Section 11.7: The Chain Rule Algebra Portion: 1. Let f(x) = 2x 1 and g(x) = 3x + 5. Find the following: (a) g[f(4)] (b) f[g(4)] (c) g[f(x)] (d) f[g(x)] 2. Write h(x) = 2(4x + 1) 2 + 5(4x + 1) as the composition of two functions h(x) = f[g(x)]. 3. Write h(x) = 1 x 2 as the composition of two functions h(x) = f[g(x)]. 30
20 Calculus Portion: 4. Chain Rule: If y is a function of u, say y = f(u) and if u is a function of x, say u = g(x), then y = f(u) = f[g(x)] and dy dx = dy du du dx. If y = f[g(x)], then 5. Find dy dx if y = 3x 2 5x dy dx = f [g(x)] g (x) 6. Let f(x) = (x 2 + 5x) 8 be the function of some population, somewhere. Find the rate of change of the population. 7. Factor the following problems: (a) 4z xz 4 (b) 4(x + 3) (4x)(x + 3) 4 31
21 8. Let P (x) = 4x(3x+5) 5 be the profit function of some company. Find the marginal profit function. 9. Let C(x) = (3x + 2)7 x 1 be the cost function of some company. Find the marginal cost function. 32
22 10. Suppose a sum of $500 is deposited in an account with an interest rate of r percent per year compounded monthly. At the end of 10 years, the balance in the account is given by ( A = r ) Find the rate of change of A with respect to r if r = 5 or 7. And what does this mean? 11. Marginal-Revenue Product: This is an economic concept that approximates the change in revenue when a manufacturer hires an additional employee. Let R(n) = p x where p is price per unit, or the demand function p = f(x) and x is the number of units produced per day. Note, the number of units produced depends on the number of employees, n. So we can really write x as a function of n. dr dn = p dx dn + x dp dn. As we mentioned p can be a function of the number of employees, so we know that If we re-write the first formula we have: dp dn = dp dx dx dn. dr dn = p dx dn + x by factoring out the greatest common factor we have: ( dp dx dx ) dn 12. Find the marginal-revenue product dr dn function is p = 600 x and x = 5n. (in dollars per employee) when n = 20 if the demand 33
Section 11.7 The Chain Rule
 Section.7 The Chain Rule Composition of Functions There is another way of combining two functions to obtain a new function. For example, suppose that y = fu) = u and u = gx) = x 2 +. Since y is a function
Section.7 The Chain Rule Composition of Functions There is another way of combining two functions to obtain a new function. For example, suppose that y = fu) = u and u = gx) = x 2 +. Since y is a function
Math 116: Business Calculus Chapter 4 - Calculating Derivatives
 Math 116: Business Calculus Chapter 4 - Calculating Derivatives Instructor: Colin Clark Spring 2017 Exam 2 - Thursday March 9. 4.1 Techniques for Finding Derivatives. 4.2 Derivatives of Products and Quotients.
Math 116: Business Calculus Chapter 4 - Calculating Derivatives Instructor: Colin Clark Spring 2017 Exam 2 - Thursday March 9. 4.1 Techniques for Finding Derivatives. 4.2 Derivatives of Products and Quotients.
MA 181 Lecture Chapter 7 College Algebra and Calculus by Larson/Hodgkins Limits and Derivatives
 7.5) Rates of Change: Velocity and Marginals MA 181 Lecture Chapter 7 College Algebra and Calculus by Larson/Hodgkins Limits and Derivatives Previously we learned two primary applications of derivatives.
7.5) Rates of Change: Velocity and Marginals MA 181 Lecture Chapter 7 College Algebra and Calculus by Larson/Hodgkins Limits and Derivatives Previously we learned two primary applications of derivatives.
Study Guide - Part 2
 Math 116 Spring 2015 Study Guide - Part 2 1. Which of the following describes the derivative function f (x) of a quadratic function f(x)? (A) Cubic (B) Quadratic (C) Linear (D) Constant 2. Find the derivative
Math 116 Spring 2015 Study Guide - Part 2 1. Which of the following describes the derivative function f (x) of a quadratic function f(x)? (A) Cubic (B) Quadratic (C) Linear (D) Constant 2. Find the derivative
Final Exam Review. MATH Intuitive Calculus Fall 2013 Circle lab day: Mon / Fri. Name:. Show all your work.
 MATH 11012 Intuitive Calculus Fall 2013 Circle lab day: Mon / Fri Dr. Kracht Name:. 1. Consider the function f depicted below. Final Exam Review Show all your work. y 1 1 x (a) Find each of the following
MATH 11012 Intuitive Calculus Fall 2013 Circle lab day: Mon / Fri Dr. Kracht Name:. 1. Consider the function f depicted below. Final Exam Review Show all your work. y 1 1 x (a) Find each of the following
Math 142 (Summer 2018) Business Calculus 5.8 Notes
 Math 142 (Summer 2018) Business Calculus 5.8 Notes Implicit Differentiation and Related Rates Why? We have learned how to take derivatives of functions, and we have seen many applications of this. However
Math 142 (Summer 2018) Business Calculus 5.8 Notes Implicit Differentiation and Related Rates Why? We have learned how to take derivatives of functions, and we have seen many applications of this. However
x C) y = - A) $20000; 14 years B) $28,000; 14 years C) $28,000; 28 years D) $30,000; 15 years
 Dr. Lee - Math 35 - Calculus for Business - Review of 3 - Show Complete Work for Each Problem MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find
Dr. Lee - Math 35 - Calculus for Business - Review of 3 - Show Complete Work for Each Problem MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find
UNIT 2 DERIVATIVES 2.1 EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FUNCTION APPLICATIONS. Pre-Class:
 1830 UNIT 2 DERIVATIVES 2.1 EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FUNCTION APPLICATIONS Pre-Class: Take notes on the videos and readings (use the space below). Work and check problem #1 in the 2.1 NOTES section.
1830 UNIT 2 DERIVATIVES 2.1 EXPONENTIAL AND LOGARITHMIC FUNCTION APPLICATIONS Pre-Class: Take notes on the videos and readings (use the space below). Work and check problem #1 in the 2.1 NOTES section.
OBJECTIVE Find limits of functions, if they exist, using numerical or graphical methods.
 1.1 Limits: A Numerical and Graphical Approach OBJECTIVE Find limits of functions, if they exist, using numerical or graphical methods. 1.1 Limits: A Numerical and Graphical Approach DEFINITION: As x approaches
1.1 Limits: A Numerical and Graphical Approach OBJECTIVE Find limits of functions, if they exist, using numerical or graphical methods. 1.1 Limits: A Numerical and Graphical Approach DEFINITION: As x approaches
12 Rates of Change Average Rates of Change. Concepts: Average Rates of Change
 12 Rates of Change Concepts: Average Rates of Change Calculating the Average Rate of Change of a Function on an Interval Secant Lines Difference Quotients Approximating Instantaneous Rates of Change (Section
12 Rates of Change Concepts: Average Rates of Change Calculating the Average Rate of Change of a Function on an Interval Secant Lines Difference Quotients Approximating Instantaneous Rates of Change (Section
3.1 Derivative Formulas for Powers and Polynomials
 3.1 Derivative Formulas for Powers and Polynomials First, recall that a derivative is a function. We worked very hard in 2.2 to interpret the derivative of a function visually. We made the link, in Ex.
3.1 Derivative Formulas for Powers and Polynomials First, recall that a derivative is a function. We worked very hard in 2.2 to interpret the derivative of a function visually. We made the link, in Ex.
MATH150-E01 Test #2 Summer 2016 Show all work. Name 1. Find an equation in slope-intercept form for the line through (4, 2) and (1, 3).
 1. Find an equation in slope-intercept form for the line through (4, 2) and (1, 3). 2. Let the supply and demand functions for sugar be given by p = S(q) = 1.4q 0.6 and p = D(q) = 2q + 3.2 where p is the
1. Find an equation in slope-intercept form for the line through (4, 2) and (1, 3). 2. Let the supply and demand functions for sugar be given by p = S(q) = 1.4q 0.6 and p = D(q) = 2q + 3.2 where p is the
CLASS NOTES: BUSINESS CALCULUS
 CLASS NOTES: BUSINESS CALCULUS These notes can be thought of as the logical skeleton of my lectures, although they will generally contain a fuller exposition of concepts but fewer examples than my lectures.
CLASS NOTES: BUSINESS CALCULUS These notes can be thought of as the logical skeleton of my lectures, although they will generally contain a fuller exposition of concepts but fewer examples than my lectures.
Evaluating Piecewise-defined Functions Sketching the Graph of a Piecewise-defined Functions
 7 Functions Concepts: The Definition of A Function Function Notation Piecewise-defined Functions Evaluating Piecewise-defined Functions Sketching the Graph of a Piecewise-defined Functions The Domain of
7 Functions Concepts: The Definition of A Function Function Notation Piecewise-defined Functions Evaluating Piecewise-defined Functions Sketching the Graph of a Piecewise-defined Functions The Domain of
Review Assignment II
 MATH 11012 Intuitive Calculus KSU Name:. Review Assignment II 1. Let C(x) be the cost, in dollars, of manufacturing x widgets. Fill in the table with a mathematical expression and appropriate units corresponding
MATH 11012 Intuitive Calculus KSU Name:. Review Assignment II 1. Let C(x) be the cost, in dollars, of manufacturing x widgets. Fill in the table with a mathematical expression and appropriate units corresponding
Chapter 4 Notes, Calculus I with Precalculus 3e Larson/Edwards
 4.1 The Derivative Recall: For the slope of a line we need two points (x 1,y 1 ) and (x 2,y 2 ). Then the slope is given by the formula: m = y x = y 2 y 1 x 2 x 1 On a curve we can find the slope of a
4.1 The Derivative Recall: For the slope of a line we need two points (x 1,y 1 ) and (x 2,y 2 ). Then the slope is given by the formula: m = y x = y 2 y 1 x 2 x 1 On a curve we can find the slope of a
MATH 2554 (Calculus I)
 MATH 2554 (Calculus I) Dr. Ashley K. University of Arkansas February 21, 2015 Table of Contents Week 6 1 Week 6: 16-20 February 3.5 Derivatives as Rates of Change 3.6 The Chain Rule 3.7 Implicit Differentiation
MATH 2554 (Calculus I) Dr. Ashley K. University of Arkansas February 21, 2015 Table of Contents Week 6 1 Week 6: 16-20 February 3.5 Derivatives as Rates of Change 3.6 The Chain Rule 3.7 Implicit Differentiation
MA Lesson 12 Notes Section 3.4 of Calculus part of textbook
 MA 15910 Lesson 1 Notes Section 3.4 of Calculus part of textbook Tangent Line to a curve: To understand the tangent line, we must first discuss a secant line. A secant line will intersect a curve at more
MA 15910 Lesson 1 Notes Section 3.4 of Calculus part of textbook Tangent Line to a curve: To understand the tangent line, we must first discuss a secant line. A secant line will intersect a curve at more
Math 142 Week-in-Review #11 (Final Exam Review: All previous sections as well as sections 6.6 and 6.7)
 Math 142 Week-in-Review #11 (Final Exam Review: All previous sections as well as sections 6.6 and 6.7) Note: This review is intended to highlight the topics covered on the Final Exam (with emphasis on
Math 142 Week-in-Review #11 (Final Exam Review: All previous sections as well as sections 6.6 and 6.7) Note: This review is intended to highlight the topics covered on the Final Exam (with emphasis on
3. Find the slope of the tangent line to the curve given by 3x y e x+y = 1 + ln x at (1, 1).
 1. Find the derivative of each of the following: (a) f(x) = 3 2x 1 (b) f(x) = log 4 (x 2 x) 2. Find the slope of the tangent line to f(x) = ln 2 ln x at x = e. 3. Find the slope of the tangent line to
1. Find the derivative of each of the following: (a) f(x) = 3 2x 1 (b) f(x) = log 4 (x 2 x) 2. Find the slope of the tangent line to f(x) = ln 2 ln x at x = e. 3. Find the slope of the tangent line to
Sample Mathematics 106 Questions
 Sample Mathematics 106 Questions x 2 + 8x 65 (1) Calculate lim x 5. x 5 (2) Consider an object moving in a straight line for which the distance s (measured in feet) it s travelled from its starting point
Sample Mathematics 106 Questions x 2 + 8x 65 (1) Calculate lim x 5. x 5 (2) Consider an object moving in a straight line for which the distance s (measured in feet) it s travelled from its starting point
Midterm Study Guide and Practice Problems
 Midterm Study Guide and Practice Problems Coverage of the midterm: Sections 10.1-10.7, 11.2-11.6 Sections or topics NOT on the midterm: Section 11.1 (The constant e and continuous compound interest, Section
Midterm Study Guide and Practice Problems Coverage of the midterm: Sections 10.1-10.7, 11.2-11.6 Sections or topics NOT on the midterm: Section 11.1 (The constant e and continuous compound interest, Section
Chapter 4. Section Derivatives of Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
 Chapter 4 Section 4.2 - Derivatives of Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Objectives: The student will be able to calculate the derivative of e x and of lnx. The student will be able to compute the
Chapter 4 Section 4.2 - Derivatives of Exponential and Logarithmic Functions Objectives: The student will be able to calculate the derivative of e x and of lnx. The student will be able to compute the
Re: January 27, 2015 Math 080: Final Exam Review Page 1 of 6
 Re: January 7, 015 Math 080: Final Exam Review Page 1 of 6 Note: If you have difficulty with any of these problems, get help, then go back to the appropriate sections and work more problems! 1. Solve for
Re: January 7, 015 Math 080: Final Exam Review Page 1 of 6 Note: If you have difficulty with any of these problems, get help, then go back to the appropriate sections and work more problems! 1. Solve for
Chapter 6: Sections 6.1, 6.2.1, Chapter 8: Section 8.1, 8.2 and 8.5. In Business world the study of change important
 Study Unit 5 : Calculus Chapter 6: Sections 6., 6.., 6.3. Chapter 8: Section 8., 8. and 8.5 In Business world the study of change important Example: change in the sales of a company; change in the value
Study Unit 5 : Calculus Chapter 6: Sections 6., 6.., 6.3. Chapter 8: Section 8., 8. and 8.5 In Business world the study of change important Example: change in the sales of a company; change in the value
MAC 2233 Chapter 3 Practice for the Test
 Class: Date: MAC 33 Chapter 3 Practice for the Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. At which labeled point is the slope of the tangent
Class: Date: MAC 33 Chapter 3 Practice for the Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. At which labeled point is the slope of the tangent
Chapter 3 The Integral Business Calculus 197
 Chapter The Integral Business Calculus 97 Chapter Exercises. Let A(x) represent the area bounded by the graph and the horizontal axis and vertical lines at t=0 and t=x for the graph in Fig.. Evaluate A(x)
Chapter The Integral Business Calculus 97 Chapter Exercises. Let A(x) represent the area bounded by the graph and the horizontal axis and vertical lines at t=0 and t=x for the graph in Fig.. Evaluate A(x)
Lecture 2. Derivative. 1 / 26
 Lecture 2. Derivative. 1 / 26 Basic Concepts Suppose we wish to nd the rate at which a given function f (x) is changing with respect to x when x = c. The simplest idea is to nd the average rate of change
Lecture 2. Derivative. 1 / 26 Basic Concepts Suppose we wish to nd the rate at which a given function f (x) is changing with respect to x when x = c. The simplest idea is to nd the average rate of change
ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Spring 2014 Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers R.6 8) 27, 30) 25
 ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Spring 2014, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers Review Assignment: Precalculus Even Answers to Sections R1 R7 R.1 24) 4a 2 16ab + 16b 2 R.2 24) Prime 5x
ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Spring 2014, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers Review Assignment: Precalculus Even Answers to Sections R1 R7 R.1 24) 4a 2 16ab + 16b 2 R.2 24) Prime 5x
Math 112 Group Activity: The Vertical Speed of a Shell
 Name: Section: Math 112 Group Activity: The Vertical Speed of a Shell A shell is fired straight up by a mortar. The graph below shows its altitude as a function of time. 400 300 altitude (in feet) 200
Name: Section: Math 112 Group Activity: The Vertical Speed of a Shell A shell is fired straight up by a mortar. The graph below shows its altitude as a function of time. 400 300 altitude (in feet) 200
Math 1071 Final Review Sheet The following are some review questions to help you study. They do not
 Math 1071 Final Review Sheet The following are some review questions to help you study. They do not They do The exam represent the entirety of what you could be expected to know on the exam; reflect distribution
Math 1071 Final Review Sheet The following are some review questions to help you study. They do not They do The exam represent the entirety of what you could be expected to know on the exam; reflect distribution
MATH 236 ELAC FALL 2017 CA 9 NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 MATH 236 ELAC FALL 207 CA 9 NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. ) 27 p 3 27 p 3 ) 2) If 9 t 3 4t 9-2t = 3, find t. 2) Solve the equation.
MATH 236 ELAC FALL 207 CA 9 NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. ) 27 p 3 27 p 3 ) 2) If 9 t 3 4t 9-2t = 3, find t. 2) Solve the equation.
College Algebra. George Voutsadakis 1. LSSU Math 111. Lake Superior State University. 1 Mathematics and Computer Science
 College Algebra George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 111 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) College Algebra December 2014 1 / 74 Outline 1 Additional
College Algebra George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 111 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) College Algebra December 2014 1 / 74 Outline 1 Additional
Practice Problems for Exam 1
 Practice Problems for Exam 1 Basic Linear Functions: 1. Find the equation of the line that has slope 2 and y-intercept equal to 100. 2. Find the equation of the line that has slope 1.5 and passes through
Practice Problems for Exam 1 Basic Linear Functions: 1. Find the equation of the line that has slope 2 and y-intercept equal to 100. 2. Find the equation of the line that has slope 1.5 and passes through
Math Review ECON 300: Spring 2014 Benjamin A. Jones MATH/CALCULUS REVIEW
 MATH/CALCULUS REVIEW SLOPE, INTERCEPT, and GRAPHS REVIEW (adapted from Paul s Online Math Notes) Let s start with some basic review material to make sure everybody is on the same page. The slope of a line
MATH/CALCULUS REVIEW SLOPE, INTERCEPT, and GRAPHS REVIEW (adapted from Paul s Online Math Notes) Let s start with some basic review material to make sure everybody is on the same page. The slope of a line
Math 1325 Final Exam Review. (Set it up, but do not simplify) lim
 . Given f( ), find Math 5 Final Eam Review f h f. h0 h a. If f ( ) 5 (Set it up, but do not simplify) If c. If f ( ) 5 f (Simplify) ( ) 7 f (Set it up, but do not simplify) ( ) 7 (Simplify) d. If f. Given
. Given f( ), find Math 5 Final Eam Review f h f. h0 h a. If f ( ) 5 (Set it up, but do not simplify) If c. If f ( ) 5 f (Simplify) ( ) 7 f (Set it up, but do not simplify) ( ) 7 (Simplify) d. If f. Given
Business and Life Calculus
 Business and Life Calculus George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 112 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Calculus For Business and Life Sciences Fall 2013
Business and Life Calculus George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 112 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Calculus For Business and Life Sciences Fall 2013
MATH 122 FALL Final Exam Review Problems
 MATH 122 FALL 2013 Final Exam Review Problems Chapter 1 1. As a person hikes down from the top of a mountain, the variable t represents the time, in minutes, since the person left the top of the mountain,
MATH 122 FALL 2013 Final Exam Review Problems Chapter 1 1. As a person hikes down from the top of a mountain, the variable t represents the time, in minutes, since the person left the top of the mountain,
Math 1314 Test 2 Review Lessons 2 8
 Math 1314 Test Review Lessons 8 CASA reservation required. GGB will be provided on the CASA computers. 50 minute exam. 15 multiple choice questions. Do Practice Test for extra practice and extra credit.
Math 1314 Test Review Lessons 8 CASA reservation required. GGB will be provided on the CASA computers. 50 minute exam. 15 multiple choice questions. Do Practice Test for extra practice and extra credit.
Math 106 Calculus 1 Topics for first exam
 Chapter 2: Limits and Continuity Rates of change and its: Math 06 Calculus Topics for first exam Limit of a function f at a point a = the value the function should take at the point = the value that the
Chapter 2: Limits and Continuity Rates of change and its: Math 06 Calculus Topics for first exam Limit of a function f at a point a = the value the function should take at the point = the value that the
1 Functions And Change
 1 Functions And Change 1.1 What Is a Function? * Function A function is a rule that takes certain numbers as inputs and assigns to each a definite output number. The set of all input numbers is called
1 Functions And Change 1.1 What Is a Function? * Function A function is a rule that takes certain numbers as inputs and assigns to each a definite output number. The set of all input numbers is called
The Mean Value Theorem Rolle s Theorem
 The Mean Value Theorem In this section, we will look at two more theorems that tell us about the way that derivatives affect the shapes of graphs: Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. Rolle s Theorem
The Mean Value Theorem In this section, we will look at two more theorems that tell us about the way that derivatives affect the shapes of graphs: Rolle s Theorem and the Mean Value Theorem. Rolle s Theorem
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Objectives Evaluate a definite integral using the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. Understand and use the Mean Value Theorem for Integrals. Find the average value of
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus Objectives Evaluate a definite integral using the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. Understand and use the Mean Value Theorem for Integrals. Find the average value of
Chapter 2 Derivatives And Their Uses
 Chapter Derivatives And Their Uses 1. Complete the table and use it to predict the limit, if it eists. 6 f( ) 0. 1 lim f( )? 0.1 0.01 0.001 0.? 0.999 0.99 f ( ) 0.9 160.0 80.0 80.0 0. does not eist. Use
Chapter Derivatives And Their Uses 1. Complete the table and use it to predict the limit, if it eists. 6 f( ) 0. 1 lim f( )? 0.1 0.01 0.001 0.? 0.999 0.99 f ( ) 0.9 160.0 80.0 80.0 0. does not eist. Use
MATH 236 ELAC FALL 2017 TEST 3 NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 MATH 6 ELAC FALL 7 TEST NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Evaluate the integral using integration by parts. ) 9x ln x dx ) ) x 5 -
MATH 6 ELAC FALL 7 TEST NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Evaluate the integral using integration by parts. ) 9x ln x dx ) ) x 5 -
Math 142 Week-in-Review #4 (Sections , 4.1, and 4.2)
 Math 142 WIR, copyright Angie Allen, Fall 2018 1 Math 142 Week-in-Review #4 (Sections 3.1-3.3, 4.1, and 4.2) Note: This collection of questions is intended to be a brief overview of the exam material (with
Math 142 WIR, copyright Angie Allen, Fall 2018 1 Math 142 Week-in-Review #4 (Sections 3.1-3.3, 4.1, and 4.2) Note: This collection of questions is intended to be a brief overview of the exam material (with
Midterm 1 Review Problems Business Calculus
 Midterm 1 Review Problems Business Calculus 1. (a) Show that the functions f and g are inverses of each other by showing that f g(x) = g f(x) given that (b) Sketch the functions and the line y = x f(x)
Midterm 1 Review Problems Business Calculus 1. (a) Show that the functions f and g are inverses of each other by showing that f g(x) = g f(x) given that (b) Sketch the functions and the line y = x f(x)
ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Fall 2014: Lectures Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers. 24x + 72 (x 2 6x + 4) 4
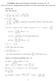 ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Fall 014: Lectures 19 35 Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers Lecture 19 1. d [ 4 ] dx x 6x + 4) 3 = 4x + 7 x 6x + 4) 4. a) P 0) = 800 b)
ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Fall 014: Lectures 19 35 Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers Lecture 19 1. d [ 4 ] dx x 6x + 4) 3 = 4x + 7 x 6x + 4) 4. a) P 0) = 800 b)
MAC 2233, Survey of Calculus, Exam 3 Review This exam covers lectures 21 29,
 MAC 2233, Survey of Calculus, Exam 3 Review This exam covers lectures 21 29, This review includes typical exam problems. It is not designed to be comprehensive, but to be representative of topics covered
MAC 2233, Survey of Calculus, Exam 3 Review This exam covers lectures 21 29, This review includes typical exam problems. It is not designed to be comprehensive, but to be representative of topics covered
Review for Final Review
 Topics Review for Final Review 1. Functions and equations and graphing: linear, absolute value, quadratic, polynomials, rational (first 1/3 of semester) 2. Simple Interest, compounded interest, and continuously
Topics Review for Final Review 1. Functions and equations and graphing: linear, absolute value, quadratic, polynomials, rational (first 1/3 of semester) 2. Simple Interest, compounded interest, and continuously
Table of contents. Functions The Function Concept The Vertical Line Test. Function Notation Piecewise-defined functions
 Table of contents Functions The Function Concept The Vertical Line Test Function Notation Piecewise-defined functions The Domain of a Function The Graph of a Function Average Rates of Change Difference
Table of contents Functions The Function Concept The Vertical Line Test Function Notation Piecewise-defined functions The Domain of a Function The Graph of a Function Average Rates of Change Difference
Final Exam Review Packet
 1 Exam 1 Material Sections A.1, A.2 and A.6 were review material. There will not be specific questions focused on this material but you should know how to: Simplify functions with exponents. Factor quadratics
1 Exam 1 Material Sections A.1, A.2 and A.6 were review material. There will not be specific questions focused on this material but you should know how to: Simplify functions with exponents. Factor quadratics
Final Exam Review Packet
 1 Exam 1 Material Sections A.1, A.2 and A.6 were review material. There will not be specific questions focused on this material but you should know how to: Simplify functions with exponents. Factor quadratics
1 Exam 1 Material Sections A.1, A.2 and A.6 were review material. There will not be specific questions focused on this material but you should know how to: Simplify functions with exponents. Factor quadratics
Question 1. (8 points) The following diagram shows the graphs of eight equations.
 MAC 2233/-6 Business Calculus, Spring 2 Final Eam Name: Date: 5/3/2 Time: :am-2:nn Section: Show ALL steps. One hundred points equal % Question. (8 points) The following diagram shows the graphs of eight
MAC 2233/-6 Business Calculus, Spring 2 Final Eam Name: Date: 5/3/2 Time: :am-2:nn Section: Show ALL steps. One hundred points equal % Question. (8 points) The following diagram shows the graphs of eight
1 Functions and Graphs
 1 Functions and Graphs 1.1 Functions Cartesian Coordinate System A Cartesian or rectangular coordinate system is formed by the intersection of a horizontal real number line, usually called the x axis,
1 Functions and Graphs 1.1 Functions Cartesian Coordinate System A Cartesian or rectangular coordinate system is formed by the intersection of a horizontal real number line, usually called the x axis,
AP CALCULUS BC SUMMER PREVIEW
 AP CALCULUS BC SUMMER PREVIEW Name: Your summer homework assignment is to write complete solutions for all of the problems listed in this packet. It is important that you have mastered the concepts covered
AP CALCULUS BC SUMMER PREVIEW Name: Your summer homework assignment is to write complete solutions for all of the problems listed in this packet. It is important that you have mastered the concepts covered
The questions listed below are drawn from midterm and final exams from the last few years at OSU. As the text book and structure of the class have
 The questions listed below are drawn from midterm and final eams from the last few years at OSU. As the tet book and structure of the class have recently changed, it made more sense to list the questions
The questions listed below are drawn from midterm and final eams from the last few years at OSU. As the tet book and structure of the class have recently changed, it made more sense to list the questions
Name: Practice A, Math Final Exam December 11, 2018
 Practice A, Math 10250 Final Exam December 11, 2018 Name: Instructor: Be sure that you have all 15 pages of the test. Calculators are allowed for this examination. The exam lasts for two hours. The Honor
Practice A, Math 10250 Final Exam December 11, 2018 Name: Instructor: Be sure that you have all 15 pages of the test. Calculators are allowed for this examination. The exam lasts for two hours. The Honor
1 Cost, Revenue and Profit
 MATH 104 - SECTION 101 FIN AL REVIEW 1 Cost, Revenue and Profit C(x), R(x), and P(x); marginal cost MC(x), marginal revenue MR(x), and marginal profit M P(x). 1. Profit is the difference between cost and
MATH 104 - SECTION 101 FIN AL REVIEW 1 Cost, Revenue and Profit C(x), R(x), and P(x); marginal cost MC(x), marginal revenue MR(x), and marginal profit M P(x). 1. Profit is the difference between cost and
x f(x)
 1. Name three different reasons that a function can fail to be differential at a point. Give an example for each reason, and explain why your examples are valid. 2. Given the following table of values,
1. Name three different reasons that a function can fail to be differential at a point. Give an example for each reason, and explain why your examples are valid. 2. Given the following table of values,
x f(x)
 1. Name three different reasons that a function can fail to be differentiable at a point. Give an example for each reason, and explain why your examples are valid. 2. Given the following table of values,
1. Name three different reasons that a function can fail to be differentiable at a point. Give an example for each reason, and explain why your examples are valid. 2. Given the following table of values,
Identifying Graphs of Functions (Vertical Line Test) Evaluating Piecewise-defined Functions Sketching the Graph of a Piecewise-defined Functions
 9 Functions Concepts: The Definition of A Function Identifying Graphs of Functions (Vertical Line Test) Function Notation Piecewise-defined Functions Evaluating Piecewise-defined Functions Sketching the
9 Functions Concepts: The Definition of A Function Identifying Graphs of Functions (Vertical Line Test) Function Notation Piecewise-defined Functions Evaluating Piecewise-defined Functions Sketching the
The Mean Value Theorem
 Math 31A Discussion Session Week 6 Notes February 9 and 11, 2016 This week we ll discuss some (unsurprising) properties of the derivative, and then try to use some of these properties to solve a real-world
Math 31A Discussion Session Week 6 Notes February 9 and 11, 2016 This week we ll discuss some (unsurprising) properties of the derivative, and then try to use some of these properties to solve a real-world
CORE. Chapter 3: Interacting Linear Functions, Linear Systems. Algebra Assessments
 CORE Algebra Assessments Chapter 3: Interacting Linear Functions, Linear Systems 97 98 Bears Band Booster Club The Bears Band Booster Club has decided to sell calendars to the band members and their parents.
CORE Algebra Assessments Chapter 3: Interacting Linear Functions, Linear Systems 97 98 Bears Band Booster Club The Bears Band Booster Club has decided to sell calendars to the band members and their parents.
Sample Math 115 Midterm Exam Spring, 2014
 Sample Math 5 Midterm Exam Spring, 04 The midterm examination is on Wednesday, March at 5:45PM 7:45PM The midterm examination will be in Budig 0 Look for your instructor who will direct you where to sit
Sample Math 5 Midterm Exam Spring, 04 The midterm examination is on Wednesday, March at 5:45PM 7:45PM The midterm examination will be in Budig 0 Look for your instructor who will direct you where to sit
Math Practice Final - solutions
 Math 151 - Practice Final - solutions 2 1-2 -1 0 1 2 3 Problem 1 Indicate the following from looking at the graph of f(x) above. All answers are small integers, ±, or DNE for does not exist. a) lim x 1
Math 151 - Practice Final - solutions 2 1-2 -1 0 1 2 3 Problem 1 Indicate the following from looking at the graph of f(x) above. All answers are small integers, ±, or DNE for does not exist. a) lim x 1
Functions. A function is a rule that gives exactly one output number to each input number.
 Functions A function is a rule that gives exactly one output number to each input number. Why it is important to us? The set of all input numbers to which the rule applies is called the domain of the function.
Functions A function is a rule that gives exactly one output number to each input number. Why it is important to us? The set of all input numbers to which the rule applies is called the domain of the function.
41. The ancient Babylonians (circa 1700 B.C.) approximated N by applying the formula. x n x n N x n. with respect to output
 48 Chapter 2 Differentiation: Basic Concepts 4. The ancient Babylonians (circa 700 B.C.) approximated N by applying the formula x n 2 x n N x n for n, 2, 3,... (a) Show that this formula can be derived
48 Chapter 2 Differentiation: Basic Concepts 4. The ancient Babylonians (circa 700 B.C.) approximated N by applying the formula x n 2 x n N x n for n, 2, 3,... (a) Show that this formula can be derived
Math 120 Final Exam Practice Problems, Form: A
 Math 120 Final Exam Practice Problems, Form: A Name: While every attempt was made to be complete in the types of problems given below, we make no guarantees about the completeness of the problems. Specifically,
Math 120 Final Exam Practice Problems, Form: A Name: While every attempt was made to be complete in the types of problems given below, we make no guarantees about the completeness of the problems. Specifically,
Calculus I 5. Applications of differentiation
 2301107 Calculus I 5. Applications of differentiation Chapter 5:Applications of differentiation C05-2 Outline 5.1. Extreme values 5.2. Curvature and Inflection point 5.3. Curve sketching 5.4. Related rate
2301107 Calculus I 5. Applications of differentiation Chapter 5:Applications of differentiation C05-2 Outline 5.1. Extreme values 5.2. Curvature and Inflection point 5.3. Curve sketching 5.4. Related rate
(MATH 1203, 1204, 1204R)
 College Algebra (MATH 1203, 1204, 1204R) Departmental Review Problems For all questions that ask for an approximate answer, round to two decimal places (unless otherwise specified). The most closely related
College Algebra (MATH 1203, 1204, 1204R) Departmental Review Problems For all questions that ask for an approximate answer, round to two decimal places (unless otherwise specified). The most closely related
Math Final Exam Review. 1. The following equation gives the rate at which the angle between two objects is changing during a game:
 Math 131 Spring 2008 c Sherry Scarborough and Heather Ramsey Page 1 Math 131 - Final Exam Review 1. The following equation gives the rate at which the angle between two objects is changing during a game:
Math 131 Spring 2008 c Sherry Scarborough and Heather Ramsey Page 1 Math 131 - Final Exam Review 1. The following equation gives the rate at which the angle between two objects is changing during a game:
MATH 115 SECOND MIDTERM
 MATH 115 SECOND MIDTERM March 31, 2009 NAME: SOLUTIONS INSTRUCTOR: SECTION NUMBER: 1. Do not open this exam until you are told to begin. 2. This exam has 9 pages including this cover. There are 9 questions.
MATH 115 SECOND MIDTERM March 31, 2009 NAME: SOLUTIONS INSTRUCTOR: SECTION NUMBER: 1. Do not open this exam until you are told to begin. 2. This exam has 9 pages including this cover. There are 9 questions.
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. x )
 Midterm Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Decide whether or not the arrow diagram defines a function. 1) Domain Range 1) Determine
Midterm Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Decide whether or not the arrow diagram defines a function. 1) Domain Range 1) Determine
Doug Clark The Learning Center 100 Student Success Center learningcenter.missouri.edu Overview
 Math 1400 Final Exam Review Saturday, December 9 in Ellis Auditorium 1:00 PM 3:00 PM, Saturday, December 9 Part 1: Derivatives and Applications of Derivatives 3:30 PM 5:30 PM, Saturday, December 9 Part
Math 1400 Final Exam Review Saturday, December 9 in Ellis Auditorium 1:00 PM 3:00 PM, Saturday, December 9 Part 1: Derivatives and Applications of Derivatives 3:30 PM 5:30 PM, Saturday, December 9 Part
Mathematics for Economics ECON MA/MSSc in Economics-2017/2018. Dr. W. M. Semasinghe Senior Lecturer Department of Economics
 Mathematics for Economics ECON 53035 MA/MSSc in Economics-2017/2018 Dr. W. M. Semasinghe Senior Lecturer Department of Economics MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS LERNING OUTCOMES: By the end of this course unit
Mathematics for Economics ECON 53035 MA/MSSc in Economics-2017/2018 Dr. W. M. Semasinghe Senior Lecturer Department of Economics MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS LERNING OUTCOMES: By the end of this course unit
MATH 1113 Exam 1 Review
 MATH 1113 Exam 1 Review Topics Covered Section 1.1: Rectangular Coordinate System Section 1.3: Functions and Relations Section 1.4: Linear Equations in Two Variables and Linear Functions Section 1.5: Applications
MATH 1113 Exam 1 Review Topics Covered Section 1.1: Rectangular Coordinate System Section 1.3: Functions and Relations Section 1.4: Linear Equations in Two Variables and Linear Functions Section 1.5: Applications
Chapter. Integration. 1. Antidifferentiation: The Indefinite Integral. 2. Integration by Substitution. 3. Introduction to Differential Equations
 Integration Chapter. Antidifferentiation: The Indefinite Integral 2. Integration by Substitution 3. Introduction to Differential Equations 4. Integration by Parts Chapter Summary and Review Problems Antidifferentiation:
Integration Chapter. Antidifferentiation: The Indefinite Integral 2. Integration by Substitution 3. Introduction to Differential Equations 4. Integration by Parts Chapter Summary and Review Problems Antidifferentiation:
Math 180, Lowman, Summer 2008, Old Exam Problems 1 Limit Problems
 Math 180, Lowman, Summer 2008, Old Exam Problems 1 Limit Problems 1. Find the limit of f(x) = (sin x) x x 3 as x 0. 2. Use L Hopital s Rule to calculate lim x 2 x 3 2x 2 x+2 x 2 4. 3. Given the function
Math 180, Lowman, Summer 2008, Old Exam Problems 1 Limit Problems 1. Find the limit of f(x) = (sin x) x x 3 as x 0. 2. Use L Hopital s Rule to calculate lim x 2 x 3 2x 2 x+2 x 2 4. 3. Given the function
Final Exam Study Guide
 Final Exam Study Guide Final Exam Coverage: Sections 10.1-10.2, 10.4-10.5, 10.7, 11.2-11.4, 12.1-12.6, 13.1-13.2, 13.4-13.5, and 14.1 Sections/topics NOT on the exam: Sections 10.3 (Continuity, it definition
Final Exam Study Guide Final Exam Coverage: Sections 10.1-10.2, 10.4-10.5, 10.7, 11.2-11.4, 12.1-12.6, 13.1-13.2, 13.4-13.5, and 14.1 Sections/topics NOT on the exam: Sections 10.3 (Continuity, it definition
Purdue University Study Guide for MA for students who plan to obtain credit in MA by examination.
 Purdue University Study Guide for MA 224 for students who plan to obtain credit in MA 224 by examination. Textbook: Applied Calculus For Business, Economics, and the Social and Life Sciences, Expanded
Purdue University Study Guide for MA 224 for students who plan to obtain credit in MA 224 by examination. Textbook: Applied Calculus For Business, Economics, and the Social and Life Sciences, Expanded
Fall 2009 Math 113 Final Exam Solutions. f(x) = 1 + ex 1 e x?
 . What are the domain and range of the function Fall 9 Math 3 Final Exam Solutions f(x) = + ex e x? Answer: The function is well-defined everywhere except when the denominator is zero, which happens when
. What are the domain and range of the function Fall 9 Math 3 Final Exam Solutions f(x) = + ex e x? Answer: The function is well-defined everywhere except when the denominator is zero, which happens when
Chapter 2 Describing Change: Rates
 Chapter Describing Change: Rates Section.1 Change, Percentage Change, and Average Rates of Change 1. 3. $.30 $0.46 per day 5 days = The stock price rose an average of 46 cents per day during the 5-day
Chapter Describing Change: Rates Section.1 Change, Percentage Change, and Average Rates of Change 1. 3. $.30 $0.46 per day 5 days = The stock price rose an average of 46 cents per day during the 5-day
Essential Functions Practice for Students of TASC-math
 Essential Functions Practice for Students of TASC-math This packet was created by NYSED Teacher Leader, Todd Orelli in collaboration with the CUNY Adult Literacy & HSE professional development team as
Essential Functions Practice for Students of TASC-math This packet was created by NYSED Teacher Leader, Todd Orelli in collaboration with the CUNY Adult Literacy & HSE professional development team as
2.7: Derivatives and Rates of Change
 2.7: Derivatives and Rates of Change Recall from section 2.1, that the tangent line to a curve at a point x = a has a slope that can be found by finding the slopes of secant lines through the curve at
2.7: Derivatives and Rates of Change Recall from section 2.1, that the tangent line to a curve at a point x = a has a slope that can be found by finding the slopes of secant lines through the curve at
3 Geometrical Use of The Rate of Change
 Arkansas Tech University MATH 224: Business Calculus Dr. Marcel B. Finan Geometrical Use of The Rate of Change Functions given by tables of values have their limitations in that nearly always leave gaps.
Arkansas Tech University MATH 224: Business Calculus Dr. Marcel B. Finan Geometrical Use of The Rate of Change Functions given by tables of values have their limitations in that nearly always leave gaps.
3. Go over old quizzes (there are blank copies on my website try timing yourself!)
 final exam review General Information The time and location of the final exam are as follows: Date: Tuesday, June 12th Time: 10:15am-12:15pm Location: Straub 254 The exam will be cumulative; that is, it
final exam review General Information The time and location of the final exam are as follows: Date: Tuesday, June 12th Time: 10:15am-12:15pm Location: Straub 254 The exam will be cumulative; that is, it
2 Integration by Substitution
 86 Chapter 5 Integration 2 Integration by Substitution (a) Find a function P(x) that satisfies these conditions. Use the graphing utility of your calculator to graph this function. (b) Use trace and zoom
86 Chapter 5 Integration 2 Integration by Substitution (a) Find a function P(x) that satisfies these conditions. Use the graphing utility of your calculator to graph this function. (b) Use trace and zoom
Part A: Short Answer Questions
 Math 111 Practice Exam Your Grade: Fall 2015 Total Marks: 160 Instructor: Telyn Kusalik Time: 180 minutes Name: Part A: Short Answer Questions Answer each question in the blank provided. 1. If a city grows
Math 111 Practice Exam Your Grade: Fall 2015 Total Marks: 160 Instructor: Telyn Kusalik Time: 180 minutes Name: Part A: Short Answer Questions Answer each question in the blank provided. 1. If a city grows
THE USE OF A CALCULATOR, CELL PHONE, OR ANY OTHER ELECTRONIC DEVICE IS NOT PERMITTED IN THIS EXAMINATION.
 MATH 110 FINAL EXAM SPRING 2008 FORM A NAME STUDENT NUMBER INSTRUCTOR SECTION NUMBER This examination will be machine processed by the University Testing Service. Use only a number 2 pencil on your scantron.
MATH 110 FINAL EXAM SPRING 2008 FORM A NAME STUDENT NUMBER INSTRUCTOR SECTION NUMBER This examination will be machine processed by the University Testing Service. Use only a number 2 pencil on your scantron.
Polynomial Operations Polly s Pasta
 Polynomial Operations ACTIVITY 4.2 SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Close Reading, Discussion Group, Create Representations, Think/Pair/Share, Self/Peer Revision and Pizza Supply sells wholesale goods to
Polynomial Operations ACTIVITY 4.2 SUGGESTED LEARNING STRATEGIES: Close Reading, Discussion Group, Create Representations, Think/Pair/Share, Self/Peer Revision and Pizza Supply sells wholesale goods to
Free Response Questions Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom
 Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
CALCULUS. Berkant Ustaoğlu CRYPTOLOUNGE.NET
 CALCULUS Berkant Ustaoğlu CRYPTOLOUNGE.NET Secant 1 Definition Let f be defined over an interval I containing u. If x u and x I then f (x) f (u) Q = x u is the difference quotient. Also if h 0, such that
CALCULUS Berkant Ustaoğlu CRYPTOLOUNGE.NET Secant 1 Definition Let f be defined over an interval I containing u. If x u and x I then f (x) f (u) Q = x u is the difference quotient. Also if h 0, such that
Section K MATH 211 Homework Due Friday, 8/30/96 Professor J. Beachy Average: 15.1 / 20. ), and f(a + 1).
 Section K MATH 211 Homework Due Friday, 8/30/96 Professor J. Beachy Average: 15.1 / 20 # 18, page 18: If f(x) = x2 x 2 1, find f( 1 2 ), f( 1 2 ), and f(a + 1). # 22, page 18: When a solution of acetylcholine
Section K MATH 211 Homework Due Friday, 8/30/96 Professor J. Beachy Average: 15.1 / 20 # 18, page 18: If f(x) = x2 x 2 1, find f( 1 2 ), f( 1 2 ), and f(a + 1). # 22, page 18: When a solution of acetylcholine
MATH 2070 Test 3 (Sections , , & )
 Multiple Choice: Use a #2 pencil and completely fill in each bubble on your scantron to indicate the answer to each question. Each question has one correct answer. If you indicate more than one answer,
Multiple Choice: Use a #2 pencil and completely fill in each bubble on your scantron to indicate the answer to each question. Each question has one correct answer. If you indicate more than one answer,
Calculus : 2-credit version
 1 / 50 Calculus : 2-credit version Tan s textbook : 7th edition Chapter 3 Hua-Huai, Félix, Chern Department of Computer Science National Taiwan Ocean University September 15, 2009 Calculus of several variables
1 / 50 Calculus : 2-credit version Tan s textbook : 7th edition Chapter 3 Hua-Huai, Félix, Chern Department of Computer Science National Taiwan Ocean University September 15, 2009 Calculus of several variables
Math 1120 Calculus Test 3
 March 27, 2002 Your name The first 7 problems count 5 points each Problems 8 through 11 are multiple choice and count 7 points each and the final ones counts as marked In the multiple choice section, circle
March 27, 2002 Your name The first 7 problems count 5 points each Problems 8 through 11 are multiple choice and count 7 points each and the final ones counts as marked In the multiple choice section, circle
1) Solve the formula for the indicated variable. P = 2L + 2W for W. 2) Solve the formula for the variable y. 5 = 7x - 8y
 Math120 Cumulative Review This is to help prepare you for the 40 question final exam. It is not all inclusive of the material covered in your course. Therefore items not on this review may appear on the
Math120 Cumulative Review This is to help prepare you for the 40 question final exam. It is not all inclusive of the material covered in your course. Therefore items not on this review may appear on the
Section Derivatives and Rates of Change
 Section. - Derivatives and Rates of Change Recall : The average rate of change can be viewed as the slope of the secant line between two points on a curve. In Section.1, we numerically estimated the slope
Section. - Derivatives and Rates of Change Recall : The average rate of change can be viewed as the slope of the secant line between two points on a curve. In Section.1, we numerically estimated the slope
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB
 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
