ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Spring 2014 Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers R.6 8) 27, 30) 25
|
|
|
- Malcolm Henry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Spring 2014, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers Review Assignment: Precalculus Even Answers to Sections R1 R7 R.1 24) 4a 2 16ab + 16b 2 R.2 24) Prime 5x 2 + 4x 4 R.3 38) x(x 1)(x + 1) R.6 8) 27, 30) Lecture 1 6x 2 6 1) 2) x = 2 or x = 2 2x ) a) 2x2 2x 4 b) x = 1 or x = 2 4) ( 6, 3] [6, ) (2x 1) 4/3 5) x + 4 x +, excluded value: x = 3 6) y = 2 or y = 6 12 x 7) (x + 3) 2 + (y 2) 2 = 17 Supplemental Problems in Written Homework x 2 4 1) a. b. x = ±2 2) a. 2x2 2x + 2 x x + 1 3) (3, 5) and (3, 1) 4) x 2 + y 2 = 36 Lecture 2 Even Answers to Sec ) x = 8 36) (a) k = 1 2, (b) k = 7 2 1) (a) y = 4: slope is 0 (b) x = 2: undefined slope 2) Find the slope of each line by solving for y. Then since parallel lines have the same slope, you can set up an equation to show the desired result. 3) k = 1 3 4) (a) N = 3 x + 89 (b) approximately 103 deaths (c) mg/m3 50 5) V (t) = ( )t + 20, 000 In 5 years, trade-in value is $ The machine will have no trade-in value after approximately 9.14 years. 1
2 Lecture 3 1) V (t) = 5 t + 200; 90 days 3 2) 75 miles: Avis charges $63.75 and Enterprise charges $ She should use Enterprise. The charge will be the same for a trip of 120 miles. 3) For a linear function, marginal cost and profit are simply the slope of the corresponding functions. In this example, marginal cost is 19: cost increases by $19 per unit. Marginal profit is 6: profit increases by $6 per unit. 4) (a) The supplier will provide no items (b) Equilibrium quantity: 25 and price: $176 5) (a) y = 7.25x , correlation coefficient: r = (b) approximately $ billion Lecture 3 Text Homework: Even Answers Sec. 1.2: 4) 12 8) ) C(x) = 45x ) C(x) = 120x + 12, ) a. C(x) = 1140x + 486, 000 b. $1,056,000 c. 450 Lecture 4 : 2 1. (a) only 2. k = 3 3. (for h 0): a. 4x+2h 3 b. (x + h + 2)(x + 2) [ ) 1 4. domain of f(x): (, ), domain of g(s): (, 2] 2, 5. domain: (, 3) (3, ) and range: [ 1, ) 6. a. neither b. odd 7. (a) 42,000 (b) 2002 (c) difference is thousand which rounds to 133 people (d) population will approach 48,000 since as t increases without bound, 12 t + 2 approaches 0 8. (a) Area: A(x) = 600x 2x 2, domain: (0, 300) (b) C(x) = 4800 (constant function) (c) C(x) = x 2
3 Lecture 4 Text Homework: Even Answers Sec. 2.1: 4) Not a function 6) function 8) not a function 18) (, ) 20) (, ) 26) (, 6) ( 6, 6) (6, ) 28) (, ) 32) (, 3) 40) domain: [ 2, 4], range: [3], a c: 3, d) nowhere 42) a. 0 b c. (a + 3)(a 4) d. 2(2 + 3m)(1 2m) m 2 54) a. 4x 2 8hx 4h 2 + 3x + 3h + 2 b. 8hx 4h 2 + 3h c. 8x 4h ) odd 70) neither 74) a. $410 b. $ c. $855 Lecture 5: Additional Exercises 1. Translate the graph of y = x to the right 4 units, then reflect across the x-axis, and finally shift up 3 units. 2. a) f(g(x)) = x 3, domain: [ 1, ), g(f(x)) = x 2 3, domain (, 3] [ 3, ) 2(x 1) b) f(g(x)) =, domain: (, 0) (0, 1) (1, ), x g(f(x)) = 2, domain: (, 0) (0, 2) (2, ) 2 x Lecture 5 1. a) 3 b) 4 c) 3 4) (f g)(4) = f( 1) which is not defined 2. (fg)(x) = 2, domain: (, 0) (0, 1) (1, ) ( ) x 1 f 2(x 1) (x) =, domain: (, 0) (0, 1) (1, ) g x 2 3. a) f(g(x)) = x 4, domain: [5, ), g(f(x)) = x 2 4, domain: (, 2] [2, ) 2(x 1) b) f(g(x)) =, domain: (, 0) (0, 1) (1, ), x g(f(x)) = 2, domain: (, 0) (0, 2) (2, ) 2 x 4. a) c(x(t)) = 0.05t b) 4 years 3
4 5. f(x) is neither even nor odd. f(x) = { x x < 0 3x x (a) (b) (c) (d) 7. a. reflect y = x across y-axis, shift left 3, up 2; domain (, ), range (, 2] a. b. f(x) = (x 4): reflect y = x across the y-axis, then shift 4 units to the right and reflect across the x-axis. domain: (, 4], range (, 0] b. c. Always reflect before you shift! 4
5 Lecture 5 Text Homework: Even Answers Sec. 4.3: 6) 1000z 2 80z ) f[g(x)] = (2 x), domain: (, 2) (2, ), g[f(x)] = x, domain: 4 (, 0) (0, ) Sec. 2.2: 4) F 6) B 8) E 26) A 28) B 30) F 32) shifts graph right 2, up 2 36) shifts y = x left 2, down 3 48) a. b b. b c. b Lecture 6 1. f(x) = (x + 2) To graph: translate the graph of y = x 2 left two units, reflect over the x-axis, and then shift up 7 units. ( ) ( ) vertex: 3, 51, x-intercepts: ( 1, 0), 3 3, 0, y-intercept (0, 5); parabola opens up 3. (a) p = 0.1x + 24 (b) R(x) = 0.1x x; maximum revenue is $1440, when the price is p(120) = 12 (c) break even when x = 50 or x = 150 (d) will earn a profit for 50 < x < 150. Maximum profit when 100 are sold. 4. R(x) = 0.05x 2 + x ; he will maximize his harvest when x = 10, or September a is negative and the smallest value of n is 5. Lecture 6 Text Homework: Even Answers Sec. 2.2: 2) reflects across the x-axis, stretches graph of y = x 2 if a < 1 and compresses graph if 1 < x < 0. 58) a. $15,000, b. $40,000 c) reflects the graph of f(x) = x 2 across the x-axis, compresses by a factor of 4, shifts right 10 units and up 40 units. 60) a mm and mm, b. 8.48mm and 39.4 weeks Sec. 2.3: 48) a. $54 billion, c. $750 billion, d. $1104 billion Lecture 7 1. x 2 5n y 5n 2n2 2) x = 0 and x = 3 5
6 3) a) b) ) x 4) B = 80 and e k = 7 ( 7 4 so f(x) = ) P (t) = 500(2) t/4 ; in ten years the population should be about ) After 2 years you would have $ in the first account, and $ in the second. So you get a better return in the account with interest compounded monthly. 7) 100%; 34%; in the long run, 24% since e 0.5x 0 as x increases without bound. Lecture 7 Text Homework: Even Answers Sec. 2.3: 40) No asymptotes; graph is the graph of the line y = 3 x with a hole at (3, 0). 58) a. [0, ) c. As x, denominator A + x x, so Kx A + x Kx x = K. d. limiting value of the growth rate as x increases over time e. replace x in the formula with A and simplify. Sec. 2.4: 4) D 6) F 8) D 10) B 30) graph of y = e x is reflected across the x-axis and stretched by a factor of 2, then the graph is shifted down 3 50) a. yes, although a linear model seems reasonable as well b. f(x) = e t c. 805,800; 855,900 Lecture 8 1) (b) and (c) are one-to-one 2) f(f(x)) = x. The graph of g is a semicircle centered at the origin with radius 3: not one-to-one so does not have an inverse 3) h 1 (x) = 2 x 1. Range of h is the domain of h 1 : (, 1) (1, ) 4) f 1 (x) = x2 + 1, x 0 2 5) not equivalent: domain of f is (, 0) (0, ) but domain of g is (0, ) 6
7 6) domain: x2 2x x + 3 7) x = 2 only 8) x = 2 > 0, so the domain is ( 3, 0) (2, ) 9) f 1 (x) = ln(x 1) + 2 Lecture 8 Additional Exercises from the Lecture Outline and Homework 1) a) 4 b) 1 c) 4 (Note that if g 1 (4) = 2 its graph contains (4, 2). What does that tell you about g(2)?) d) f 1 (x) = x (1, ), domain: (, ) 2) (a) f 1 (x) = 2x + 1, domain (, 1) 1 x (b) g 1 (x) = 3 x 2, domain [0, ) (c) h 1 (x) = ln x 1, domain (0, ) 2 3) Lecture 8 Text Homework: Even Answers Sec.2.5: 6) log 5/4 (16/25) = 2 24) 0 34) a + 2c 48) x = 1 56) x = 1 70) (, 3) (3, ) e 1 Lecture 9 (a) W (1) = 49.9 years (b) t 2.4, year 1955 (c) W (6) 80.5 years 2) Solve for r in the equation 10, 800 = 10, 000e 2r to get an interest rate of 3.8% 3) P = 100, 000 $72, 730 (1.01) 32 4) (a) p $16.39; Revenue is (400)(p) = $
8 (b) x = 200 ln(42/62) 78 (c) as x, p (0) = 8 dollars 5700 ln(.76) 5) t = 2257 years ln ) P (t) =, P (6) eln(99/249)t Since ln(99/249) < 0, e ln(99/249)t 0 as t, so the number of cases has an upper limit of Lecture a) 4 b) 0 c) DNE d) e) + f) DNE 2. f(x) is the parabola y = x 2 reflected over the x-axis and shifted up 4 units. The graph of g(x) is the same graph, with a hole at the point (0, 4). lim f(x) = lim g(x) = 4. x 0 x x2 + 3x x + 1 = 3x, x 1. Its graph is the graph of y = 3x with a hole at the point ( 1, 3); lim x 1 3x 2 + 3x x + 1 = 3 4. (1) 2 (2) DNE (3) 2 5. a. 1 b. 2 c. 1 4 Lecture 10 Text Homework: Even Answers Sec. 3.1: Problem 6) a. 4, b. 4 8) a. 2, b. Does not exist (DNE) 10) a. i. 1, ii. 1, iii. 1, iv. 2; i. 0, ii. 0, iii. 0, iv. 0 56) a. DNE, b. 7 82) a. 3, b. DNE, c. 2, d. 16 months Lecture (a) 7 16 (b) 3 2 (c) 4 5 (d) 0 (e) 2a 2. (a) Might be true: for example, if f(x) = x + 1, lim f(x) = 2 = f(1). But if { x 1 x + 1 x 1 g(x) =, then lim g(x) = 2, but g(1) = 5. 5 x = 1 x 1 (b) must be false: if lim f(x) = 1, then lim f(x) must equal 1 as well. x 0 8 x 0
9 (c) might be true: Let f(x) = x 2 + x and g(x) = x 3 + x 2. Then lim x 0 f(x) = 1 lim g(x) = 0, but lim[f(x)/g(x)] = lim which does not exist as a finite limit. x 0 x 0 x 0 x But consider problem 1c above, and let f(x) be the numerator and g(x) be the denominator. Note that lim ( ) 4 as a finite number. 5 x 4 f(x) = lim x 4 g(x) = 0, and lim x 4 3. (a) limit is 0; HA: y = 0 (b) limit is 0; HA: y = 0 (c) limit is ; no HA (d) limit is 1 2 ; HA: y = 1 2 * *For (d), note that as x, the function f(x) = 5 x2 3 4x properties we see that the limit can be found by finding lim x f(x) = [f(x)][g(x)] does exist > 0, so from the limit VA: x = ln 4 for horizontal asymptotes lim f(x) = 0, but lim f(x) = 2 x x 4 = 1 2. HA: y = 0 and y = lim x 4 f(x) = lim x 4 1 x 4 x 2 4 x = Lecture 11 Text Homework: Even Answers Sec. 3.1: 2) a 24) 2 28) 100 Lecture (a) x = 1: removable, x = 3: removable, x = 5: infinite, x = 7: jump (b) can define f( 1) = 0 and redefine f(3) = 1 but cannot so define at the other discontinuities since the limits do not exist at those points (nonremovable discontinuities) (c) (, 1), ( 1, 3), (3, 5), (5, 7), [7, ) 2. (a) (b) (c) (d) 0 3. (a) 1) 2 and 2) (b) x = 1: removable, x = 1: infinite (c) can define f( 1) = 2 = lim f(x); cannot so define f(1) since the limit does x 1 not exist 4. (a) (1) + (2) 1 (3) 2 (4) does not exist 9
10 (b) x = 1: infinite, x = 0: removable, x = 1: jump 5. (a) x = 5 and x = 1 (b) 1 6 (c) + (d) x = 5: infinite, cannot define f( 5) to make f continuous there since it is a nonremovable discontinuity. x = 1: removable, define f(1) = 1 to make f continuous at x = 1. 6 x 2 2( x) = 1 x < 0 6. Note that f(x) = x 3 4x x 2 x 2 2x x 3 4x = 1 x > 0 x + 2 (a) (1) 1 2 (2) 1 2 (b) x = 0: jump discontinuity, x = ±2, removable discontinuities (c) Lecture 12 Text Homework: Even Answers Sec. 3.1: 4) b 20) does not exist 56) a. Does not exist, b. 7 62) a., b. x = 4 Sec. 3.2: 12) nowhere 34) x = 6: infinite, x = 4: jump, x = 0: removable, x = 3: infinite, x = 4: removable Lecture 13 Additional Exercises 1) CORRECTION: f(x) = x2 2x x 3 + x 2 6x discontinuities are x = 3: infinite, x = 0 and x = 2: removable define f(0) = 1 3 and f(2) = 1 ; cannot so define f( 3) 5 10
11 2) f(x) has one jump (nonremovable) discontinuity at x = 2 since lim f(x) = 2 and lim f(x) = 2 x 2 x 2 + 3) x = 1: jump discontinuity, x = 2: removable discontinuity can define f(2) = 1 to make f continuous at x = 2, cannot so define f( 1) 4) removable discontinuity at x = 1; note that lim x 1 f(x) = 5 4 5) Note that f is continuous on [0, 1] and compare f(0) and f(1) to use the IVT Lecture (a) vertical asymptote: x = 6, x = 0, horizontal asymptote: y = 0 (b) (1) (2) (3) 1 8 or f(0) (c) can define f(6) = 1 8 to make f continuous at x = 6; cannot so define f( 6) 2. f has a jump discontinuity at x = 3 and an infinite discontinuity at x = 4; both are nonremovable. f is continuous at x = (a) f has a jump discontinuity at x = 3 11
12 (b) f has a jump discontinuity at x = 0 and an infinite discontinuity at x = 2 4. (a) c = 4 and d = 6 (b) K = Note that f is continuous on [0, 1] and compare f(0) and f(1) to use the IVT 6. The function is discontinuous at x = 160, x = 220, and x = 280 (x in thousands) Lecture 13 Text Homework: Even Answers Sec. 3.2: 28) k = 4 Lecture (a) concentration is increasing by 6/5 mg/ml per minute (b) concentration is increasing by 3.6 mg/ml per minute (c) 2mg/ml per minute increase 2. (a) cost increases by $2.84 (b) cost increases by $2.80 per unit 3. (a) object ends up where it started, so average velocity is 0 in/sec (b) traveling at 1 in/sec (c) v(a) = 2a 3 in/sec; object first comes to a stop after 3/2 seconds 4. (a) $3000 increase in profit per $1000 increase in advertising dollars (b) 2 a + 8 thousand dollar change in profit per $1000 increase in adv dollars 3 (c) $2000 decrease in profit per $1000 increase in advertising dollars (d) Profit is maximized when $12,000 is spent on advertising. 5. (a) 270 (b) population is increasing by 5 per year (c) population is increasing by 3 per year 12
13 Lecture 14 Text Homework: Even Answers Sec. 3.3: 24) increasing 30) a. $3000 b. 0 c. $ ) a. 5 ft/sec b. 2 ft/sec c. 3 ft/sec. d. 5 ft/sec. e. i. and ii. 2.5 ft/sec., f. i. and ii. 4 ft/sec. Lecture x = 5: approximately 2.5, x = 0: approximately 1.5, x = 4: 0 (answers may vary) 2. 2 : yes, f(x) is linear so the derivative is the slope of the line at each point 3 3. f 3 (x) = 2 ; graph is the square root function stretched up and reflected 10 3x across the y-axis, and then shifted 10/3 units to the right. At x = 5 the slope is 3 10 and at x = 1 3 the slope is 1 2. The slopes ; vertical tangent line at x = y = 3 4 x slope of the tangent line at any point is given by f 2 (x) = (1 x). ( ) ( ) Points are 2, 4 and 2, 4 6. (a) v(t) = 2t 2: at t = 4, the velocity is 6 in/sec, and at t = 10, the velocity is 18 in/sec (b) at one second 7. (a) MR = 8 x + 10; when x = 12, revenue is decreasing by $9.20 per unit 5 (b) P (x) = 4 5 x2 + 8x 15 ; MP = 8 5 x + 8 profit is maximized when MP = 0, at x = 5. This is the vertex of the graph of the profit function. 13
14 Lecture 15 Text Homework: Even Answers Sec. 3.4: 4) tangent line is horizontal 10) undefined 24) a) y = 1 4 x 7 4, b) y = 3 4 x ) a) 13, 13.4, 13 b) 13, 13.04, 13 58) answers may vary, for example at h = 5000, T (h) = dt dh 2.5 or degrees/foot 2000 Lecture The graph will look somewhat like a parabola opening down, with two x-intercepts, one negative and one positive 2. (a) car A is farthest from the starting point after 8 minutes, B is farthest after 12 minutes (comparing function values at those points) (b) first, after 7 minutes (on interval [0, 7]); next after 10 minutes (on interval [0, 10], also [7, 10]) (c) after two minutes, car B; after five minutes, car A (compare slopes of tangent lines at those points) (d) twice when tangent lines are parallel, for example approximately at t = 3 3. (a) x = 3 and x = 2 (b) x = 0 and x = 5 (c) x = 5 The graph of the derivative of f(x) has a hole at x = 3, at x = 2 a jump or asymptote (depending on whether you visualize f having a vertical asymptote at x = 2), a nonremovable discontinuity at x = 0 and a vertical asymptote at x = 5 4. (a) does not exist (sharp corner at x = 0) (b) f (0) = lim x 0 f(x) f(0) x 0 = 0; graph has horizontal tangent line at x = 0 (c) f(x) is not continuous at x = 0 so cannot be differentiable at x = 0 (d) f(x) is continuous at x = 0, but f f(x) f(0) (0) = lim does not exist x 0 x 0 (one-sided limits are not the same) so f(x) is not differentiable at x = 0 14
15 Lecture 16 Text Homework: Even Answers Sec. 3.4: 2) does not exist 16) f (x) = 3 x 2, f ( 2) = 3 4, f (0) does not exist, f (3) = ) 6 38) 5, 3, 0, 2, 4 40) a) distance, b) velocity Sec. 3.5: 10) 22) graph is an increasing function on (0, ) with vertical asymptote v = 0 and crosses the v-axis between 7 and 8. The derivative values approach as v approaches 0. Lecture (a) f(3) = 2 (b) f (3) = (a) P (2) = 6.08 so spending is 6.08% of GDP (b) average rate is 1.94; spending increased by 1.94% per decade (c) in 2010: P (2) = 1.94 so spending increased by 1.94% per decade, but in 2020, P (2) = 2.48 so spending is increasing by 2.48% per decade 3. N(10) = 6.926: number of cases after 10 years of exposure N (10) = ; number of cases is increasing by per year 4. (a) y = 43x + 44 (b) x = 2 and x = 6 5. f (x) = 2 x 4 x 2. Horizontal tangent line at x = 4 with equation y = 0 6. a = 3 4 and b =
16 7. (a) v(t) = 80 32t (b) v(t) = 0 at t = 5 2 ( ) 5 (c) maximum height: h = 900 feet 2 8. This limit represents f f(a + h) f(a) (a) = lim h 0 h Its value: f (1) = 8 for a = 1 and f(x) = x 8. Lecture 18! 1. (a) 6 25 (b) (x 2 + 2x + 3) 1 (2x + 2) = (4x + 4)(x 2 + 2x + 3) (illustrates the Chain rule) 3. y = 1 2 x f (x) = 1 x2/3 x 2 5. f (x) = 1 3x Horizontal tangent line at x =. x(x 2 + 1) (a) f (x) = x2 4 x 2 (b) x = ± price is decreasing by $14.15 per thousand units and revenue is increasing by $41.66 per thousand items 16
ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Fall 2014: Lectures Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers. 24x + 72 (x 2 6x + 4) 4
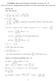 ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Fall 014: Lectures 19 35 Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers Lecture 19 1. d [ 4 ] dx x 6x + 4) 3 = 4x + 7 x 6x + 4) 4. a) P 0) = 800 b)
ANSWERS, Homework Problems, Fall 014: Lectures 19 35 Now You Try It, Supplemental problems in written homework, Even Answers Lecture 19 1. d [ 4 ] dx x 6x + 4) 3 = 4x + 7 x 6x + 4) 4. a) P 0) = 800 b)
MA Lesson 12 Notes Section 3.4 of Calculus part of textbook
 MA 15910 Lesson 1 Notes Section 3.4 of Calculus part of textbook Tangent Line to a curve: To understand the tangent line, we must first discuss a secant line. A secant line will intersect a curve at more
MA 15910 Lesson 1 Notes Section 3.4 of Calculus part of textbook Tangent Line to a curve: To understand the tangent line, we must first discuss a secant line. A secant line will intersect a curve at more
MATH150-E01 Test #2 Summer 2016 Show all work. Name 1. Find an equation in slope-intercept form for the line through (4, 2) and (1, 3).
 1. Find an equation in slope-intercept form for the line through (4, 2) and (1, 3). 2. Let the supply and demand functions for sugar be given by p = S(q) = 1.4q 0.6 and p = D(q) = 2q + 3.2 where p is the
1. Find an equation in slope-intercept form for the line through (4, 2) and (1, 3). 2. Let the supply and demand functions for sugar be given by p = S(q) = 1.4q 0.6 and p = D(q) = 2q + 3.2 where p is the
Lecture 6: Sections 2.2 and 2.3 Polynomial Functions, Quadratic Models
 L6-1 Lecture 6: Sections 2.2 and 2.3 Polynomial Functions, Quadratic Models Polynomial Functions Def. A polynomial function of degree n is a function of the form f(x) = a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 +... + a 1
L6-1 Lecture 6: Sections 2.2 and 2.3 Polynomial Functions, Quadratic Models Polynomial Functions Def. A polynomial function of degree n is a function of the form f(x) = a n x n + a n 1 x n 1 +... + a 1
3. Find the slope of the tangent line to the curve given by 3x y e x+y = 1 + ln x at (1, 1).
 1. Find the derivative of each of the following: (a) f(x) = 3 2x 1 (b) f(x) = log 4 (x 2 x) 2. Find the slope of the tangent line to f(x) = ln 2 ln x at x = e. 3. Find the slope of the tangent line to
1. Find the derivative of each of the following: (a) f(x) = 3 2x 1 (b) f(x) = log 4 (x 2 x) 2. Find the slope of the tangent line to f(x) = ln 2 ln x at x = e. 3. Find the slope of the tangent line to
Math 110 Final Exam General Review. Edward Yu
 Math 110 Final Exam General Review Edward Yu Da Game Plan Solving Limits Regular limits Indeterminate Form Approach Infinities One sided limits/discontinuity Derivatives Power Rule Product/Quotient Rule
Math 110 Final Exam General Review Edward Yu Da Game Plan Solving Limits Regular limits Indeterminate Form Approach Infinities One sided limits/discontinuity Derivatives Power Rule Product/Quotient Rule
Final Jeopardy! Appendix Ch. 1 Ch. 2 Ch. 3 Ch. 4 Ch. 5
 Final Jeopardy! Appendix Ch. 1 Ch. Ch. 3 Ch. 4 Ch. 5 00 00 00 00 00 00 400 400 400 400 400 400 600 600 600 600 600 600 800 800 800 800 800 800 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 APPENDIX 00 Is the triangle
Final Jeopardy! Appendix Ch. 1 Ch. Ch. 3 Ch. 4 Ch. 5 00 00 00 00 00 00 400 400 400 400 400 400 600 600 600 600 600 600 800 800 800 800 800 800 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 1000 APPENDIX 00 Is the triangle
Math 106 Answers to Exam 1a Fall 2015
 Math 06 Answers to Exam a Fall 05.. Find the derivative of the following functions. Do not simplify your answers. (a) f(x) = ex cos x x + (b) g(z) = [ sin(z ) + e z] 5 Using the quotient rule on f(x) and
Math 06 Answers to Exam a Fall 05.. Find the derivative of the following functions. Do not simplify your answers. (a) f(x) = ex cos x x + (b) g(z) = [ sin(z ) + e z] 5 Using the quotient rule on f(x) and
MAC 2233, Survey of Calculus, Exam 3 Review This exam covers lectures 21 29,
 MAC 2233, Survey of Calculus, Exam 3 Review This exam covers lectures 21 29, This review includes typical exam problems. It is not designed to be comprehensive, but to be representative of topics covered
MAC 2233, Survey of Calculus, Exam 3 Review This exam covers lectures 21 29, This review includes typical exam problems. It is not designed to be comprehensive, but to be representative of topics covered
Math 1120 Calculus Test 3
 March 27, 2002 Your name The first 7 problems count 5 points each Problems 8 through 11 are multiple choice and count 7 points each and the final ones counts as marked In the multiple choice section, circle
March 27, 2002 Your name The first 7 problems count 5 points each Problems 8 through 11 are multiple choice and count 7 points each and the final ones counts as marked In the multiple choice section, circle
Final Exam Study Aid
 Math 112 Final Exam Study Aid 1 of 33 Final Exam Study Aid Note: This study aid is intended to help you review for the final exam. It covers the primary concepts in the course, with a large emphasis on
Math 112 Final Exam Study Aid 1 of 33 Final Exam Study Aid Note: This study aid is intended to help you review for the final exam. It covers the primary concepts in the course, with a large emphasis on
Math 2003 Test D This part of the Exam is to be done without a calculator
 Math 00 Test D This part of the Eam is to be done without a calculator. Which of the following is the correct graph of =? b) c) d) e). Find all the intercepts of = -intercept: 0 -intercepts: 0, -, b) -intercepts:
Math 00 Test D This part of the Eam is to be done without a calculator. Which of the following is the correct graph of =? b) c) d) e). Find all the intercepts of = -intercept: 0 -intercepts: 0, -, b) -intercepts:
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB
 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969-present AB 1969 1. Consider the following functions defined for all x: f 1 (x) = x, f (x) = xcos x, f 3 (x) = 3e x, f 4 (x) = x - x. Answer the following questions
PMI Unit 2 Working With Functions
 Vertical Shifts Class Work 1. a) 2. a) 3. i) y = x 2 ii) Move down 2 6. i) y = x ii) Move down 1 4. i) y = 1 x ii) Move up 3 7. i) y = e x ii) Move down 4 5. i) y = x ii) Move up 1 Vertical Shifts Homework
Vertical Shifts Class Work 1. a) 2. a) 3. i) y = x 2 ii) Move down 2 6. i) y = x ii) Move down 1 4. i) y = 1 x ii) Move up 3 7. i) y = e x ii) Move down 4 5. i) y = x ii) Move up 1 Vertical Shifts Homework
4x 2-5x+3. 7x-1 HOMEWORK 1-1
 HOMEWORK 1-1 As it is always the case that correct answers without sufficient mathematical justification may not receive full credit, make sure that you show all your work. Please circle, draw a box around,
HOMEWORK 1-1 As it is always the case that correct answers without sufficient mathematical justification may not receive full credit, make sure that you show all your work. Please circle, draw a box around,
Math 120 Final Exam Practice Problems, Form: A
 Math 120 Final Exam Practice Problems, Form: A Name: While every attempt was made to be complete in the types of problems given below, we make no guarantees about the completeness of the problems. Specifically,
Math 120 Final Exam Practice Problems, Form: A Name: While every attempt was made to be complete in the types of problems given below, we make no guarantees about the completeness of the problems. Specifically,
Free Response Questions Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom
 Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
Free Response Questions 1969-010 Compiled by Kaye Autrey for face-to-face student instruction in the AP Calculus classroom 1 AP Calculus Free-Response Questions 1969 AB 1 Consider the following functions
Review for Final Review
 Topics Review for Final Review 1. Functions and equations and graphing: linear, absolute value, quadratic, polynomials, rational (first 1/3 of semester) 2. Simple Interest, compounded interest, and continuously
Topics Review for Final Review 1. Functions and equations and graphing: linear, absolute value, quadratic, polynomials, rational (first 1/3 of semester) 2. Simple Interest, compounded interest, and continuously
Calculus I Sample Exam #01
 Calculus I Sample Exam #01 1. Sketch the graph of the function and define the domain and range. 1 a) f( x) 3 b) g( x) x 1 x c) hx ( ) x x 1 5x6 d) jx ( ) x x x 3 6 . Evaluate the following. a) 5 sin 6
Calculus I Sample Exam #01 1. Sketch the graph of the function and define the domain and range. 1 a) f( x) 3 b) g( x) x 1 x c) hx ( ) x x 1 5x6 d) jx ( ) x x x 3 6 . Evaluate the following. a) 5 sin 6
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. x )
 Midterm Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Decide whether or not the arrow diagram defines a function. 1) Domain Range 1) Determine
Midterm Review Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Decide whether or not the arrow diagram defines a function. 1) Domain Range 1) Determine
Final Exam Review Packet
 1 Exam 1 Material Sections A.1, A.2 and A.6 were review material. There will not be specific questions focused on this material but you should know how to: Simplify functions with exponents. Factor quadratics
1 Exam 1 Material Sections A.1, A.2 and A.6 were review material. There will not be specific questions focused on this material but you should know how to: Simplify functions with exponents. Factor quadratics
Final Exam Review Packet
 1 Exam 1 Material Sections A.1, A.2 and A.6 were review material. There will not be specific questions focused on this material but you should know how to: Simplify functions with exponents. Factor quadratics
1 Exam 1 Material Sections A.1, A.2 and A.6 were review material. There will not be specific questions focused on this material but you should know how to: Simplify functions with exponents. Factor quadratics
Midterm Study Guide and Practice Problems
 Midterm Study Guide and Practice Problems Coverage of the midterm: Sections 10.1-10.7, 11.2-11.6 Sections or topics NOT on the midterm: Section 11.1 (The constant e and continuous compound interest, Section
Midterm Study Guide and Practice Problems Coverage of the midterm: Sections 10.1-10.7, 11.2-11.6 Sections or topics NOT on the midterm: Section 11.1 (The constant e and continuous compound interest, Section
1 Functions and Graphs
 1 Functions and Graphs 1.1 Functions Cartesian Coordinate System A Cartesian or rectangular coordinate system is formed by the intersection of a horizontal real number line, usually called the x axis,
1 Functions and Graphs 1.1 Functions Cartesian Coordinate System A Cartesian or rectangular coordinate system is formed by the intersection of a horizontal real number line, usually called the x axis,
MATH 121: EXTRA PRACTICE FOR TEST 2. Disclaimer: Any material covered in class and/or assigned for homework is a fair game for the exam.
 MATH 121: EXTRA PRACTICE FOR TEST 2 Disclaimer: Any material covered in class and/or assigned for homework is a fair game for the exam. 1 Linear Functions 1. Consider the functions f(x) = 3x + 5 and g(x)
MATH 121: EXTRA PRACTICE FOR TEST 2 Disclaimer: Any material covered in class and/or assigned for homework is a fair game for the exam. 1 Linear Functions 1. Consider the functions f(x) = 3x + 5 and g(x)
CHAPTER 2 Differentiation
 CHAPTER Differentiation Section. The Derivative and the Slope of a Graph............. 9 Section. Some Rules for Differentiation.................. 56 Section. Rates of Change: Velocit and Marginals.............
CHAPTER Differentiation Section. The Derivative and the Slope of a Graph............. 9 Section. Some Rules for Differentiation.................. 56 Section. Rates of Change: Velocit and Marginals.............
Section 11.3 Rates of Change:
 Section 11.3 Rates of Change: 1. Consider the following table, which describes a driver making a 168-mile trip from Cleveland to Columbus, Ohio in 3 hours. t Time (in hours) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 f(t) Distance
Section 11.3 Rates of Change: 1. Consider the following table, which describes a driver making a 168-mile trip from Cleveland to Columbus, Ohio in 3 hours. t Time (in hours) 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 f(t) Distance
CHAPTER FIVE. g(t) = t, h(n) = n, v(z) = z, w(c) = c, u(k) = ( 0.003)k,
 CHAPTER FIVE 5.1 SOLUTIONS 121 Solutions for Section 5.1 EXERCISES 1. Since the distance is decreasing, the rate of change is negative. The initial value of D is 1000 and it decreases by 50 each day, so
CHAPTER FIVE 5.1 SOLUTIONS 121 Solutions for Section 5.1 EXERCISES 1. Since the distance is decreasing, the rate of change is negative. The initial value of D is 1000 and it decreases by 50 each day, so
Math 2413 General Review for Calculus Last Updated 02/23/2016
 Math 243 General Review for Calculus Last Updated 02/23/206 Find the average velocity of the function over the given interval.. y = 6x 3-5x 2-8, [-8, ] Find the slope of the curve for the given value of
Math 243 General Review for Calculus Last Updated 02/23/206 Find the average velocity of the function over the given interval.. y = 6x 3-5x 2-8, [-8, ] Find the slope of the curve for the given value of
Study Guide - Part 2
 Math 116 Spring 2015 Study Guide - Part 2 1. Which of the following describes the derivative function f (x) of a quadratic function f(x)? (A) Cubic (B) Quadratic (C) Linear (D) Constant 2. Find the derivative
Math 116 Spring 2015 Study Guide - Part 2 1. Which of the following describes the derivative function f (x) of a quadratic function f(x)? (A) Cubic (B) Quadratic (C) Linear (D) Constant 2. Find the derivative
(MATH 1203, 1204, 1204R)
 College Algebra (MATH 1203, 1204, 1204R) Departmental Review Problems For all questions that ask for an approximate answer, round to two decimal places (unless otherwise specified). The most closely related
College Algebra (MATH 1203, 1204, 1204R) Departmental Review Problems For all questions that ask for an approximate answer, round to two decimal places (unless otherwise specified). The most closely related
MATH 151 Engineering Mathematics I
 MATH 151 Engineering Mathematics I Spring 2018, WEEK 3 JoungDong Kim Week 3 Section 2.5, 2.6, 2.7, Continuity, Limits at Infinity; Horizontal Asymptotes, Derivatives and Rates of Change. Section 2.5 Continuity
MATH 151 Engineering Mathematics I Spring 2018, WEEK 3 JoungDong Kim Week 3 Section 2.5, 2.6, 2.7, Continuity, Limits at Infinity; Horizontal Asymptotes, Derivatives and Rates of Change. Section 2.5 Continuity
Determine whether the formula determines y as a function of x. If not, explain. Is there a way to look at a graph and determine if it's a function?
 1.2 Functions and Their Properties Name: Objectives: Students will be able to represent functions numerically, algebraically, and graphically, determine the domain and range for functions, and analyze
1.2 Functions and Their Properties Name: Objectives: Students will be able to represent functions numerically, algebraically, and graphically, determine the domain and range for functions, and analyze
Section 1.2 DOMAIN, RANGE, INTERCEPTS, SYMMETRY, EVEN/ODD
 Section 1.2 DOMAIN, RANGE, INTERCEPTS, SYMMETRY, EVEN/ODD zeros roots line symmetry point symmetry even function odd function Estimate Function Values A. ADVERTISING The function f (x) = 5x 2 + 50x approximates
Section 1.2 DOMAIN, RANGE, INTERCEPTS, SYMMETRY, EVEN/ODD zeros roots line symmetry point symmetry even function odd function Estimate Function Values A. ADVERTISING The function f (x) = 5x 2 + 50x approximates
Math 611b Assignment #6 Name. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Math 611b Assignment #6 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find a formula for the function graphed. 1) 1) A) f(x) = 5 + x, x < -
Math 611b Assignment #6 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find a formula for the function graphed. 1) 1) A) f(x) = 5 + x, x < -
Calculus I 5. Applications of differentiation
 2301107 Calculus I 5. Applications of differentiation Chapter 5:Applications of differentiation C05-2 Outline 5.1. Extreme values 5.2. Curvature and Inflection point 5.3. Curve sketching 5.4. Related rate
2301107 Calculus I 5. Applications of differentiation Chapter 5:Applications of differentiation C05-2 Outline 5.1. Extreme values 5.2. Curvature and Inflection point 5.3. Curve sketching 5.4. Related rate
This Week. Basic Problem. Instantaneous Rate of Change. Compute the tangent line to the curve y = f (x) at x = a.
 This Week Basic Problem Compute the tangent line to the curve y = f (x) at x = a. Read Sections 2.7,2.8 and 3.1 in Stewart Homework #2 due 11:30 Thursday evening worksheet #3 in section on Tuesday slope
This Week Basic Problem Compute the tangent line to the curve y = f (x) at x = a. Read Sections 2.7,2.8 and 3.1 in Stewart Homework #2 due 11:30 Thursday evening worksheet #3 in section on Tuesday slope
Given the table of values, determine the equation
 3.1 Properties of Quadratic Functions Recall: Standard Form f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c Factored Form f(x) = a(x r)(x s) Vertex Form f(x) = a(x h) 2 + k Given the table of values, determine the equation x y 1
3.1 Properties of Quadratic Functions Recall: Standard Form f(x) = ax 2 + bx + c Factored Form f(x) = a(x r)(x s) Vertex Form f(x) = a(x h) 2 + k Given the table of values, determine the equation x y 1
F. KEEP YOUR BUBBLE SHEET COVERED AT ALL TIMES.
 UF UNIVERSITY of Department of Mathematics FLORIDA MAC 2233 Exam 2A Spring 2017 A. Sign your bubble sheet on the back at the bottom in ink. B. In pencil, write and encode in the spaces indicated: 1) Name
UF UNIVERSITY of Department of Mathematics FLORIDA MAC 2233 Exam 2A Spring 2017 A. Sign your bubble sheet on the back at the bottom in ink. B. In pencil, write and encode in the spaces indicated: 1) Name
Math 1101 Test 2 Practice Problems
 Math 1101 Test 2 Practice Problems These problems are not intended to cover all possible test topics. These problems should serve as on activity in preparing for your test, but other study is required
Math 1101 Test 2 Practice Problems These problems are not intended to cover all possible test topics. These problems should serve as on activity in preparing for your test, but other study is required
Solve the problem. Determine the center and radius of the circle. Use the given information about a circle to find its equation.
 Math1314-TestReview2-Spring2016 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) Is the point (-5, -3) on the circle defined
Math1314-TestReview2-Spring2016 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. 1) Is the point (-5, -3) on the circle defined
Solutions to Selected Exercises
 59 Solutions to Selected Exercises Chapter Section.. a. f 0 b. Tons of garbage per week is produced by a city with a population of 5,000.. a. In 995 there are 0 ducks in the lake b. In 000 there are 0
59 Solutions to Selected Exercises Chapter Section.. a. f 0 b. Tons of garbage per week is produced by a city with a population of 5,000.. a. In 995 there are 0 ducks in the lake b. In 000 there are 0
Exam 1 KEY MATH 142 Summer 18 Version A. Name (printed):
 Exam 1 KEY MATH 1 Summer 18 Version A Name (printed): On my honor, as an Aggie, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this academic work. Name (signature): Section: Instructions: You must
Exam 1 KEY MATH 1 Summer 18 Version A Name (printed): On my honor, as an Aggie, I have neither given nor received unauthorized aid on this academic work. Name (signature): Section: Instructions: You must
Quadratic function and equations Quadratic function/equations, supply, demand, market equilibrium
 Exercises 8 Quadratic function and equations Quadratic function/equations, supply, demand, market equilibrium Objectives - know and understand the relation between a quadratic function and a quadratic
Exercises 8 Quadratic function and equations Quadratic function/equations, supply, demand, market equilibrium Objectives - know and understand the relation between a quadratic function and a quadratic
Math 101 Final Exam Review Solutions. Eric Schmutz
 Math 101 Final Exam Review Solutions Eric Schmutz Problem 1. Write an equation of the line passing through (,7) and (-1,1). Let (x 1, y 1 ) = (, 7) and (x, y ) = ( 1, 1). The slope is m = y y 1 x x 1 =
Math 101 Final Exam Review Solutions Eric Schmutz Problem 1. Write an equation of the line passing through (,7) and (-1,1). Let (x 1, y 1 ) = (, 7) and (x, y ) = ( 1, 1). The slope is m = y y 1 x x 1 =
MAT 12 - SEC 021 PRECALCULUS SUMMER SESSION II 2014 LECTURE 3
 MAT 12 - SEC 021 PRECALCULUS SUMMER SESSION II 2014 LECTURE 3 JAMIE HADDOCK 1. Agenda Functions Composition Graphs Average Rate of Change..............................................................................................................
MAT 12 - SEC 021 PRECALCULUS SUMMER SESSION II 2014 LECTURE 3 JAMIE HADDOCK 1. Agenda Functions Composition Graphs Average Rate of Change..............................................................................................................
Solutions Manual for Precalculus An Investigation of Functions
 Solutions Manual for Precalculus An Investigation of Functions David Lippman, Melonie Rasmussen nd Edition Solutions created at The Evergreen State College and Shoreline Community College Last edited 9/6/17
Solutions Manual for Precalculus An Investigation of Functions David Lippman, Melonie Rasmussen nd Edition Solutions created at The Evergreen State College and Shoreline Community College Last edited 9/6/17
1.2 Functions and Their Properties Name:
 1.2 Functions and Their Properties Name: Objectives: Students will be able to represent functions numerically, algebraically, and graphically, determine the domain and range for functions, and analyze
1.2 Functions and Their Properties Name: Objectives: Students will be able to represent functions numerically, algebraically, and graphically, determine the domain and range for functions, and analyze
Homework 1. 3x 12, 61.P (x) = 3t 21 Section 1.2
 Section 1.1 Homework 1 (34, 36) Determine whether the equation defines y as a function of x. 34. x + h 2 = 1, 36. y = 3x 1 x + 2. (40, 44) Find the following for each function: (a) f(0) (b) f(1) (c) f(
Section 1.1 Homework 1 (34, 36) Determine whether the equation defines y as a function of x. 34. x + h 2 = 1, 36. y = 3x 1 x + 2. (40, 44) Find the following for each function: (a) f(0) (b) f(1) (c) f(
e) Find the average revenue when 100 units are made and sold.
 Math 142 Week in Review Set of Problems Week 7 1) Find the derivative, y ', if a) y=x 5 x 3/2 e 4 b) y= 1 5 x 4 c) y=7x 2 0.5 5 x 2 d) y=x 2 1.5 x 10 x e) y= x7 5x 5 2 x 4 2) The price-demand function
Math 142 Week in Review Set of Problems Week 7 1) Find the derivative, y ', if a) y=x 5 x 3/2 e 4 b) y= 1 5 x 4 c) y=7x 2 0.5 5 x 2 d) y=x 2 1.5 x 10 x e) y= x7 5x 5 2 x 4 2) The price-demand function
Business and Life Calculus
 Business and Life Calculus George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 112 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Calculus For Business and Life Sciences Fall 2013
Business and Life Calculus George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 112 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) Calculus For Business and Life Sciences Fall 2013
MATH 1113 Exam 1 Review
 MATH 1113 Exam 1 Review Topics Covered Section 1.1: Rectangular Coordinate System Section 1.3: Functions and Relations Section 1.4: Linear Equations in Two Variables and Linear Functions Section 1.5: Applications
MATH 1113 Exam 1 Review Topics Covered Section 1.1: Rectangular Coordinate System Section 1.3: Functions and Relations Section 1.4: Linear Equations in Two Variables and Linear Functions Section 1.5: Applications
Chapter 2: Functions, Limits and Continuity
 Chapter 2: Functions, Limits and Continuity Functions Limits Continuity Chapter 2: Functions, Limits and Continuity 1 Functions Functions are the major tools for describing the real world in mathematical
Chapter 2: Functions, Limits and Continuity Functions Limits Continuity Chapter 2: Functions, Limits and Continuity 1 Functions Functions are the major tools for describing the real world in mathematical
1. Find all relations which are functions. 2. Find all one to one functions.
 1 PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR FINAL (1) Function or not (vertical line test or y = x expression) 1. Find all relations which are functions. (A) x + y = (C) y = x (B) y = x 1 x+ (D) y = x 5 x () One to one function
1 PRACTICE PROBLEMS FOR FINAL (1) Function or not (vertical line test or y = x expression) 1. Find all relations which are functions. (A) x + y = (C) y = x (B) y = x 1 x+ (D) y = x 5 x () One to one function
Final Exam Study Guide
 Final Exam Study Guide Final Exam Coverage: Sections 10.1-10.2, 10.4-10.5, 10.7, 11.2-11.4, 12.1-12.6, 13.1-13.2, 13.4-13.5, and 14.1 Sections/topics NOT on the exam: Sections 10.3 (Continuity, it definition
Final Exam Study Guide Final Exam Coverage: Sections 10.1-10.2, 10.4-10.5, 10.7, 11.2-11.4, 12.1-12.6, 13.1-13.2, 13.4-13.5, and 14.1 Sections/topics NOT on the exam: Sections 10.3 (Continuity, it definition
MATH 236 ELAC FALL 2017 TEST 3 NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 MATH 6 ELAC FALL 7 TEST NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Evaluate the integral using integration by parts. ) 9x ln x dx ) ) x 5 -
MATH 6 ELAC FALL 7 TEST NAME: SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Evaluate the integral using integration by parts. ) 9x ln x dx ) ) x 5 -
Directions: This is a final exam review which covers all of the topics of the course. Please use this as a guide to assist you in your studies.
 MATH 1113 Precalculus FINAL EXAM REVIEW irections: This is a final exam review which covers all of the topics of the course. Please use this as a guide to assist you in your studies. Question: 1 QI: 758
MATH 1113 Precalculus FINAL EXAM REVIEW irections: This is a final exam review which covers all of the topics of the course. Please use this as a guide to assist you in your studies. Question: 1 QI: 758
MAC College Algebra
 MAC 05 - College Algebra Name Review for Test 2 - Chapter 2 Date MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the exact distance between the
MAC 05 - College Algebra Name Review for Test 2 - Chapter 2 Date MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the exact distance between the
Chapter 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions
 SECTION.1 Linear and Quadratic Functions Chapter Polynomial and Rational Functions Section.1: Linear and Quadratic Functions Linear Functions Quadratic Functions Linear Functions Definition of a Linear
SECTION.1 Linear and Quadratic Functions Chapter Polynomial and Rational Functions Section.1: Linear and Quadratic Functions Linear Functions Quadratic Functions Linear Functions Definition of a Linear
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. C) x 8. C) y = x + 3 2
 Precalculus Fall Final Exam Review Name Date Period MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplify the expression. Assume that the variables
Precalculus Fall Final Exam Review Name Date Period MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Simplify the expression. Assume that the variables
Math 111: Final Review
 Math 111: Final Review Suggested Directions: Start by reviewing the new material with the first portion of the review sheet. Then take every quiz again as if it were a test. No book. No notes. Limit yourself
Math 111: Final Review Suggested Directions: Start by reviewing the new material with the first portion of the review sheet. Then take every quiz again as if it were a test. No book. No notes. Limit yourself
1. Use the properties of exponents to simplify the following expression, writing your answer with only positive exponents.
 Math120 - Precalculus. Final Review. Fall, 2011 Prepared by Dr. P. Babaali 1 Algebra 1. Use the properties of exponents to simplify the following expression, writing your answer with only positive exponents.
Math120 - Precalculus. Final Review. Fall, 2011 Prepared by Dr. P. Babaali 1 Algebra 1. Use the properties of exponents to simplify the following expression, writing your answer with only positive exponents.
(a) The best linear approximation of f at x = 2 is given by the formula. L(x) = f(2) + f (2)(x 2). f(2) = ln(2/2) = ln(1) = 0, f (2) = 1 2.
 Math 180 Written Homework Assignment #8 Due Tuesday, November 11th at the beginning of your discussion class. Directions. You are welcome to work on the following problems with other MATH 180 students,
Math 180 Written Homework Assignment #8 Due Tuesday, November 11th at the beginning of your discussion class. Directions. You are welcome to work on the following problems with other MATH 180 students,
Final Exam Review. MATH Intuitive Calculus Fall 2013 Circle lab day: Mon / Fri. Name:. Show all your work.
 MATH 11012 Intuitive Calculus Fall 2013 Circle lab day: Mon / Fri Dr. Kracht Name:. 1. Consider the function f depicted below. Final Exam Review Show all your work. y 1 1 x (a) Find each of the following
MATH 11012 Intuitive Calculus Fall 2013 Circle lab day: Mon / Fri Dr. Kracht Name:. 1. Consider the function f depicted below. Final Exam Review Show all your work. y 1 1 x (a) Find each of the following
MATH 2053 Calculus I Review for the Final Exam
 MATH 05 Calculus I Review for the Final Exam (x+ x) 9 x 9 1. Find the limit: lim x 0. x. Find the limit: lim x + x x (x ).. Find lim x (x 5) = L, find such that f(x) L < 0.01 whenever 0 < x
MATH 05 Calculus I Review for the Final Exam (x+ x) 9 x 9 1. Find the limit: lim x 0. x. Find the limit: lim x + x x (x ).. Find lim x (x 5) = L, find such that f(x) L < 0.01 whenever 0 < x
3. Go over old quizzes (there are blank copies on my website try timing yourself!)
 final exam review General Information The time and location of the final exam are as follows: Date: Tuesday, June 12th Time: 10:15am-12:15pm Location: Straub 254 The exam will be cumulative; that is, it
final exam review General Information The time and location of the final exam are as follows: Date: Tuesday, June 12th Time: 10:15am-12:15pm Location: Straub 254 The exam will be cumulative; that is, it
MATH 121: EXTRA PRACTICE FOR TEST 2. Disclaimer: Any material covered in class and/or assigned for homework is a fair game for the exam.
 MATH 121: EXTRA PRACTICE FOR TEST 2 Disclaimer: Any material covered in class and/or assigned for homework is a fair game for the exam. 1 Linear Functions 1. Consider the functions f(x) = 3x + 5 and g(x)
MATH 121: EXTRA PRACTICE FOR TEST 2 Disclaimer: Any material covered in class and/or assigned for homework is a fair game for the exam. 1 Linear Functions 1. Consider the functions f(x) = 3x + 5 and g(x)
Solutions to Selected Exercises
 59 Solutions to Selected Exercises Chapter Section.. a. f ( 0) = b. Tons of garbage per week is produced by a city with a population of 5,000.. a. In 995 there are 0 ducks in the lake b. In 000 there are
59 Solutions to Selected Exercises Chapter Section.. a. f ( 0) = b. Tons of garbage per week is produced by a city with a population of 5,000.. a. In 995 there are 0 ducks in the lake b. In 000 there are
Math 142 Week-in-Review #11 (Final Exam Review: All previous sections as well as sections 6.6 and 6.7)
 Math 142 Week-in-Review #11 (Final Exam Review: All previous sections as well as sections 6.6 and 6.7) Note: This review is intended to highlight the topics covered on the Final Exam (with emphasis on
Math 142 Week-in-Review #11 (Final Exam Review: All previous sections as well as sections 6.6 and 6.7) Note: This review is intended to highlight the topics covered on the Final Exam (with emphasis on
Foothill High School. AP Calculus BC. Note Templates Semester 1, Student Name.
 Foothill High School AP Calculus BC Note Templates Semester 1, 2011-2012 Student Name Teacher: Burt Dixon bdixon@pleasanton.k12.ca.us 2.1 Limits Chap1-2 Page 1 Chap1-2 Page 2 Chap1-2 Page 3 Chap1-2 Page
Foothill High School AP Calculus BC Note Templates Semester 1, 2011-2012 Student Name Teacher: Burt Dixon bdixon@pleasanton.k12.ca.us 2.1 Limits Chap1-2 Page 1 Chap1-2 Page 2 Chap1-2 Page 3 Chap1-2 Page
Marginal Propensity to Consume/Save
 Marginal Propensity to Consume/Save The marginal propensity to consume is the increase (or decrease) in consumption that an economy experiences when income increases (or decreases). The marginal propensity
Marginal Propensity to Consume/Save The marginal propensity to consume is the increase (or decrease) in consumption that an economy experiences when income increases (or decreases). The marginal propensity
College Algebra. George Voutsadakis 1. LSSU Math 111. Lake Superior State University. 1 Mathematics and Computer Science
 College Algebra George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 111 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) College Algebra December 2014 1 / 74 Outline 1 Additional
College Algebra George Voutsadakis 1 1 Mathematics and Computer Science Lake Superior State University LSSU Math 111 George Voutsadakis (LSSU) College Algebra December 2014 1 / 74 Outline 1 Additional
( ) = 2 x + 3 B. f ( x) = x 2 25
 PRACTICE - Algebra Final Exam (Semester 1) - PRACTICE 1. Which function contains only a vertical translation? A. f x ( ) = x + 3 B. f ( x) = x 5 C. f ( x) = 1( x 9) D. f ( x) = x + 4. Which function is
PRACTICE - Algebra Final Exam (Semester 1) - PRACTICE 1. Which function contains only a vertical translation? A. f x ( ) = x + 3 B. f ( x) = x 5 C. f ( x) = 1( x 9) D. f ( x) = x + 4. Which function is
2.1 Quadratic Functions
 Date:.1 Quadratic Functions Precalculus Notes: Unit Polynomial Functions Objective: The student will sketch the graph of a quadratic equation. The student will write the equation of a quadratic function.
Date:.1 Quadratic Functions Precalculus Notes: Unit Polynomial Functions Objective: The student will sketch the graph of a quadratic equation. The student will write the equation of a quadratic function.
Chapter 3 The Integral Business Calculus 197
 Chapter The Integral Business Calculus 97 Chapter Exercises. Let A(x) represent the area bounded by the graph and the horizontal axis and vertical lines at t=0 and t=x for the graph in Fig.. Evaluate A(x)
Chapter The Integral Business Calculus 97 Chapter Exercises. Let A(x) represent the area bounded by the graph and the horizontal axis and vertical lines at t=0 and t=x for the graph in Fig.. Evaluate A(x)
Calculus - Chapter 2 Solutions
 Calculus - Chapter Solutions. a. See graph at right. b. The velocity is decreasing over the entire interval. It is changing fastest at the beginning and slowest at the end. c. A = (95 + 85)(5) = 450 feet
Calculus - Chapter Solutions. a. See graph at right. b. The velocity is decreasing over the entire interval. It is changing fastest at the beginning and slowest at the end. c. A = (95 + 85)(5) = 450 feet
. State whether the triangle is an isosceles triangle, a right triangle, neither of these, or both.
 PRECALCULUS MIDTERM PRACTICE TEST (2008-2009) Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the distance d(, ) between the points and.
PRECALCULUS MIDTERM PRACTICE TEST (2008-2009) Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the distance d(, ) between the points and.
Math 180, Lowman, Summer 2008, Old Exam Problems 1 Limit Problems
 Math 180, Lowman, Summer 2008, Old Exam Problems 1 Limit Problems 1. Find the limit of f(x) = (sin x) x x 3 as x 0. 2. Use L Hopital s Rule to calculate lim x 2 x 3 2x 2 x+2 x 2 4. 3. Given the function
Math 180, Lowman, Summer 2008, Old Exam Problems 1 Limit Problems 1. Find the limit of f(x) = (sin x) x x 3 as x 0. 2. Use L Hopital s Rule to calculate lim x 2 x 3 2x 2 x+2 x 2 4. 3. Given the function
Fall 2009 Math 113 Final Exam Solutions. f(x) = 1 + ex 1 e x?
 . What are the domain and range of the function Fall 9 Math 3 Final Exam Solutions f(x) = + ex e x? Answer: The function is well-defined everywhere except when the denominator is zero, which happens when
. What are the domain and range of the function Fall 9 Math 3 Final Exam Solutions f(x) = + ex e x? Answer: The function is well-defined everywhere except when the denominator is zero, which happens when
f(x) = 2x + 5 3x 1. f 1 (x) = x + 5 3x 2. f(x) = 102x x
 1. Let f(x) = x 3 + 7x 2 x 2. Use the fact that f( 1) = 0 to factor f completely. (2x-1)(3x+2)(x+1). 2. Find x if log 2 x = 5. x = 1/32 3. Find the vertex of the parabola given by f(x) = 2x 2 + 3x 4. (Give
1. Let f(x) = x 3 + 7x 2 x 2. Use the fact that f( 1) = 0 to factor f completely. (2x-1)(3x+2)(x+1). 2. Find x if log 2 x = 5. x = 1/32 3. Find the vertex of the parabola given by f(x) = 2x 2 + 3x 4. (Give
Math Exam Jam Concise. Contents. 1 Algebra Review 2. 2 Functions and Graphs 2. 3 Exponents and Radicals 3. 4 Quadratic Functions and Equations 4
 Contents 1 Algebra Review 2 2 Functions and Graphs 2 3 Exponents and Radicals 3 4 Quadratic Functions and Equations 4 5 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 5 6 Systems of Linear Equations 6 7 Inequalities
Contents 1 Algebra Review 2 2 Functions and Graphs 2 3 Exponents and Radicals 3 4 Quadratic Functions and Equations 4 5 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions 5 6 Systems of Linear Equations 6 7 Inequalities
x 3x 1 if x 3 On problems 8 9, use the definition of continuity to find the values of k and/or m that will make the function continuous everywhere.
 CALCULUS AB WORKSHEET ON CONTINUITY AND INTERMEDIATE VALUE THEOREM Work the following on notebook paper. On problems 1 4, sketch the graph of a function f that satisfies the stated conditions. 1. f has
CALCULUS AB WORKSHEET ON CONTINUITY AND INTERMEDIATE VALUE THEOREM Work the following on notebook paper. On problems 1 4, sketch the graph of a function f that satisfies the stated conditions. 1. f has
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. C) ±
 Final Review for Pre Calculus 009 Semester Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the equation algebraically. ) v + 5 = 7 - v
Final Review for Pre Calculus 009 Semester Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the equation algebraically. ) v + 5 = 7 - v
Solutions to Intermediate and College Algebra by Rhodes
 Solutions to Intermediate and College Algebra by Rhodes Section 1.1 1. 20 2. -21 3. 105 4. -5 5. 18 6. -3 7. 65/2 = 32.5 8. -36 9. 539 208 2.591 10. 13/3 11. 81 12. 60 = 2 15 7.746 13. -2 14. -1/3 15.
Solutions to Intermediate and College Algebra by Rhodes Section 1.1 1. 20 2. -21 3. 105 4. -5 5. 18 6. -3 7. 65/2 = 32.5 8. -36 9. 539 208 2.591 10. 13/3 11. 81 12. 60 = 2 15 7.746 13. -2 14. -1/3 15.
AP Calculus BC Summer Assignment
 AP Calculus BC Summer Assignment Edmodo.com: AP Calculus BC 207-208 Group Code: kdw69v Attached is an assignment for students entering AP Calculus BC in the fall. Next year we will focus more on concepts
AP Calculus BC Summer Assignment Edmodo.com: AP Calculus BC 207-208 Group Code: kdw69v Attached is an assignment for students entering AP Calculus BC in the fall. Next year we will focus more on concepts
MATH 122 FALL Final Exam Review Problems
 MATH 122 FALL 2013 Final Exam Review Problems Chapter 1 1. As a person hikes down from the top of a mountain, the variable t represents the time, in minutes, since the person left the top of the mountain,
MATH 122 FALL 2013 Final Exam Review Problems Chapter 1 1. As a person hikes down from the top of a mountain, the variable t represents the time, in minutes, since the person left the top of the mountain,
is all real numbers.
 Math 140 Spring 2017 Suggested Final Review Problems 1. Is each of the following statements true or false? Explain. (a) If f(x) = x 2, then f(x + h) = x 2 + h 2. (b) If g(x) = 3 x, then g(x) can never
Math 140 Spring 2017 Suggested Final Review Problems 1. Is each of the following statements true or false? Explain. (a) If f(x) = x 2, then f(x + h) = x 2 + h 2. (b) If g(x) = 3 x, then g(x) can never
Section 11.7 The Chain Rule
 Section.7 The Chain Rule Composition of Functions There is another way of combining two functions to obtain a new function. For example, suppose that y = fu) = u and u = gx) = x 2 +. Since y is a function
Section.7 The Chain Rule Composition of Functions There is another way of combining two functions to obtain a new function. For example, suppose that y = fu) = u and u = gx) = x 2 +. Since y is a function
Chapter 2 NAME
 QUIZ 1 Chapter NAME 1. Determine 15 - x + x by substitution. 1. xs3 (A) (B) 8 (C) 10 (D) 1 (E) 0 5-6x + x Find, if it exists. xs5 5 - x (A) -4 (B) 0 (C) 4 (D) 6 (E) Does not exist 3. For the function y
QUIZ 1 Chapter NAME 1. Determine 15 - x + x by substitution. 1. xs3 (A) (B) 8 (C) 10 (D) 1 (E) 0 5-6x + x Find, if it exists. xs5 5 - x (A) -4 (B) 0 (C) 4 (D) 6 (E) Does not exist 3. For the function y
Chapter 2 Derivatives And Their Uses
 Chapter Derivatives And Their Uses 1. Complete the table and use it to predict the limit, if it eists. 6 f( ) 0. 1 lim f( )? 0.1 0.01 0.001 0.? 0.999 0.99 f ( ) 0.9 160.0 80.0 80.0 0. does not eist. Use
Chapter Derivatives And Their Uses 1. Complete the table and use it to predict the limit, if it eists. 6 f( ) 0. 1 lim f( )? 0.1 0.01 0.001 0.? 0.999 0.99 f ( ) 0.9 160.0 80.0 80.0 0. does not eist. Use
Section K MATH 211 Homework Due Friday, 8/30/96 Professor J. Beachy Average: 15.1 / 20. ), and f(a + 1).
 Section K MATH 211 Homework Due Friday, 8/30/96 Professor J. Beachy Average: 15.1 / 20 # 18, page 18: If f(x) = x2 x 2 1, find f( 1 2 ), f( 1 2 ), and f(a + 1). # 22, page 18: When a solution of acetylcholine
Section K MATH 211 Homework Due Friday, 8/30/96 Professor J. Beachy Average: 15.1 / 20 # 18, page 18: If f(x) = x2 x 2 1, find f( 1 2 ), f( 1 2 ), and f(a + 1). # 22, page 18: When a solution of acetylcholine
Review for the Final Exam
 Calculus Lia Vas. Integrals. Evaluate the following integrals. (a) ( x 4 x 2 ) dx (b) (2 3 x + x2 4 ) dx (c) (3x + 5) 6 dx (d) x 2 dx x 3 + (e) x 9x 2 dx (f) x dx x 2 (g) xe x2 + dx (h) 2 3x+ dx (i) x
Calculus Lia Vas. Integrals. Evaluate the following integrals. (a) ( x 4 x 2 ) dx (b) (2 3 x + x2 4 ) dx (c) (3x + 5) 6 dx (d) x 2 dx x 3 + (e) x 9x 2 dx (f) x dx x 2 (g) xe x2 + dx (h) 2 3x+ dx (i) x
AP Calculus Chapter 3 Testbank (Mr. Surowski)
 AP Calculus Chapter 3 Testbank (Mr. Surowski) Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions (5 points each; please circle the correct answer.). If f(x) = 0x 4 3 + x, then f (8) = (A) (B) 4 3 (C) 83 3 (D) 2 3 (E) 2
AP Calculus Chapter 3 Testbank (Mr. Surowski) Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions (5 points each; please circle the correct answer.). If f(x) = 0x 4 3 + x, then f (8) = (A) (B) 4 3 (C) 83 3 (D) 2 3 (E) 2
Find all points where the function is discontinuous. 1) Find all vertical asymptotes of the given function. x(x - 1) 2) f(x) =
 Math 90 Final Review Find all points where the function is discontinuous. ) Find all vertical asymptotes of the given function. x(x - ) 2) f(x) = x3 + 4x Provide an appropriate response. 3) If x 3 f(x)
Math 90 Final Review Find all points where the function is discontinuous. ) Find all vertical asymptotes of the given function. x(x - ) 2) f(x) = x3 + 4x Provide an appropriate response. 3) If x 3 f(x)
Name: Practice A, Math Final Exam December 11, 2018
 Practice A, Math 10250 Final Exam December 11, 2018 Name: Instructor: Be sure that you have all 15 pages of the test. Calculators are allowed for this examination. The exam lasts for two hours. The Honor
Practice A, Math 10250 Final Exam December 11, 2018 Name: Instructor: Be sure that you have all 15 pages of the test. Calculators are allowed for this examination. The exam lasts for two hours. The Honor
Second Midterm Exam Name: Practice Problems Septmber 28, 2015
 Math 110 4. Treibergs Second Midterm Exam Name: Practice Problems Septmber 8, 015 1. Use the limit definition of derivative to compute the derivative of f(x = 1 at x = a. 1 + x Inserting the function into
Math 110 4. Treibergs Second Midterm Exam Name: Practice Problems Septmber 8, 015 1. Use the limit definition of derivative to compute the derivative of f(x = 1 at x = a. 1 + x Inserting the function into
1 Lecture 25: Extreme values
 1 Lecture 25: Extreme values 1.1 Outline Absolute maximum and minimum. Existence on closed, bounded intervals. Local extrema, critical points, Fermat s theorem Extreme values on a closed interval Rolle
1 Lecture 25: Extreme values 1.1 Outline Absolute maximum and minimum. Existence on closed, bounded intervals. Local extrema, critical points, Fermat s theorem Extreme values on a closed interval Rolle
Chapter 3: The Derivative in Graphing and Applications
 Chapter 3: The Derivative in Graphing and Applications Summary: The main purpose of this chapter is to use the derivative as a tool to assist in the graphing of functions and for solving optimization problems.
Chapter 3: The Derivative in Graphing and Applications Summary: The main purpose of this chapter is to use the derivative as a tool to assist in the graphing of functions and for solving optimization problems.
Homework for Section 1.4, Continuity and One sided Limits. Study 1.4, # 1 21, 27, 31, 37 41, 45 53, 61, 69, 87, 91, 93. Class Notes: Prof. G.
 GOAL: 1. Understand definition of continuity at a point. 2. Evaluate functions for continuity at a point, and on open and closed intervals 3. Understand the Intermediate Value Theorum (IVT) Homework for
GOAL: 1. Understand definition of continuity at a point. 2. Evaluate functions for continuity at a point, and on open and closed intervals 3. Understand the Intermediate Value Theorum (IVT) Homework for
AP Calculus AB Chapter 1 Limits
 AP Calculus AB Chapter Limits SY: 206 207 Mr. Kunihiro . Limits Numerical & Graphical Show all of your work on ANOTHER SHEET of FOLDER PAPER. In Exercises and 2, a stone is tossed vertically into the air
AP Calculus AB Chapter Limits SY: 206 207 Mr. Kunihiro . Limits Numerical & Graphical Show all of your work on ANOTHER SHEET of FOLDER PAPER. In Exercises and 2, a stone is tossed vertically into the air
