Parametric Equations
|
|
|
- Dale Short
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Parametric Equations Suppose a cricket jumps off of the round with an initial velocity v 0 at an anle θ. If we take his initial position as the oriin, his horizontal and vertical positions follow the equations: = t y = v 0 sinθ t t These are called parametric equations, with time bein the parameter upon which the positions depend. If we had numeric values for the initial velocity and anle, it would be easy to make a chart of the motion. Supposin v 0 = m/s and θ = 30º. = 1.73 t y = t 4.9 t Time (s) (m) y (m) The raph of which is a simple parabola y (m) (m)
2 We can also eliminate the parameter throuh alebraic substitution: = t so t = y = v 0 sinθ t t y = tanθ - so y = v 0 sinθ ( ) - ( ) which is eactly the parabola raphed above So the question arises, if we can etract the parameter and simply have y as a function of, what is the value of parametric equations in the first place? There are several answers: 1. It is not always possible to etract the parameter from simultaneous equations. Often, even when possible, the result is uninformatively comple.. In many physical situations, we would like to know how the positions depend upon the parameter. For the cricket, the parametric equations tell us where he is at any iven time. 3. The parametric equations provide a direction for the curve. In our eample, the cricket was clearly jumpin from left to riht, but etractin time from the equations and writin y as a function of removed this information. We can see those advantaes with another eample, a car drivin around in circle, counterclockwise. Suppose the speed is a constant v, the radius of the track is R, the oriin is at the center of the track, and the car has the position shown at time zero. The parametric equations for the car s horizontal and vertical positions are then: = R cos( v R t) y = R sin( v R t)
3 We can etract the parameter of time as follows: + y = R cos ( v t) + R sin ( v t) = R R R or just + y = R But, aain, this Cartesian version has the followin disadvantaes: 1. + y = R is not a function, so cannot be written in simple functional notation. + y = R does not tell us where the car is at any iven time 3. + y = R does not tell us that the car is movin counter-clockwise What calculus can be applied to parametric equations? Suppose we wanted the instantaneous trajectory of the cricket at any time or position, that is, we want to find the tanent to the spatial curve, or. One way is to simply differentiate the equation y = tanθ - = tanθ - v 0 cos θ and find Another is to use the parametric equations. Let s bein with the chain rule: = or = If = t If y = v 0 sinθ t t then then = = v 0 sinθ t = = v 0 sinθ t or = tanθ - t as a function of time
4 We can also replace t with from earlier to et = tanθ - v 0 cos θ as we found before Incidentally, it s a ood habit, once equations are derived, to play with various values. Do the equations make sense when t = 0? Do they make sense where = 0? Why is t in the numerator and cosθ in the denominator? Now suppose we want the arc lenth traveled by the cricket. Let s define ds to be an infinitely small piece of this arc lenth. Then ds = + By the chain rule, =, so ds = + ( ) = [1 + ( ) ] Takin the square root of both sides and interatin yields: Arc lenth = 1 + ( ) By symmetry, we could also use Arc lenth = 1 + ( ) If we use the first form for our cricket, we would have Arc lenth = 1 + (tanθ v 0 cos θ ) where the boundaries for the full fliht would be = 0 to = v 0 sin (θ) (from the rane equation) That is not a particularly pleasant interal, so let s try usin parametric equations: If we remember = then arc lenth = 1 + ( ) becomes:
5 Arc lenth = 1 + ( ) or arc lenth = ( ) + ( ) For our cricket, arc lenth = (v 0 cosθ) + (v 0 sinθ t) where the boundaries for the full fliht are t = 0 and t = v 0sinθ This is still a comple interal and it takes some work, but the solution is: Arc lenth = v 0 cos θ 1+sin (θ) [ sec(θ) tan(θ) + ln ] 1 sin (θ) Lastly, what is the area under the arc jumped by the cricket? We could simply interate y = tanθ - = v 0 sin(θ)cos (θ) between the boundaries of = 0 and This would be: Area = tanθ = tanθ v 0 cos θ And with the boundaries entered: Area = v 0 4 sin 3 θ cosθ 3 What would this look like usin parametric equations? f Area = y() = y(t) ( ) i t f t i by usin substitution for definite interals For our cricket, y(t) = v 0 sinθ t t With the boundaries of t = 0 and t = v 0sinθ and = v0sinθ Area = (v 0 sinθ t t ) (v 0 cosθ) 0 Area = v 0 4 sin 3 θ cosθ 3 as we found before
2.2 Differentiation and Integration of Vector-Valued Functions
 .. DIFFERENTIATION AND INTEGRATION OF VECTOR-VALUED FUNCTIONS133. Differentiation and Interation of Vector-Valued Functions Simply put, we differentiate and interate vector functions by differentiatin
.. DIFFERENTIATION AND INTEGRATION OF VECTOR-VALUED FUNCTIONS133. Differentiation and Interation of Vector-Valued Functions Simply put, we differentiate and interate vector functions by differentiatin
Vector Valued Functions
 SUGGESTED REFERENCE MATERIAL: Vector Valued Functions As you work throuh the problems listed below, you should reference Chapters. &. of the recommended textbook (or the equivalent chapter in your alternative
SUGGESTED REFERENCE MATERIAL: Vector Valued Functions As you work throuh the problems listed below, you should reference Chapters. &. of the recommended textbook (or the equivalent chapter in your alternative
Parameterization and Vector Fields
 Parameterization and Vector Fields 17.1 Parameterized Curves Curves in 2 and 3-space can be represented by parametric equations. Parametric equations have the form x x(t), y y(t) in the plane and x x(t),
Parameterization and Vector Fields 17.1 Parameterized Curves Curves in 2 and 3-space can be represented by parametric equations. Parametric equations have the form x x(t), y y(t) in the plane and x x(t),
REVIEW: Going from ONE to TWO Dimensions with Kinematics. Review of one dimension, constant acceleration kinematics. v x (t) = v x0 + a x t
 Lecture 5: Projectile motion, uniform circular motion 1 REVIEW: Goin from ONE to TWO Dimensions with Kinematics In Lecture 2, we studied the motion of a particle in just one dimension. The concepts of
Lecture 5: Projectile motion, uniform circular motion 1 REVIEW: Goin from ONE to TWO Dimensions with Kinematics In Lecture 2, we studied the motion of a particle in just one dimension. The concepts of
Problem Set: Fall #1 - Solutions
 Problem Set: Fall #1 - Solutions 1. (a) The car stops speedin up in the neative direction and beins deceleratin, probably brakin. (b) Calculate the averae velocity over each time interval. v av0 v 0 +
Problem Set: Fall #1 - Solutions 1. (a) The car stops speedin up in the neative direction and beins deceleratin, probably brakin. (b) Calculate the averae velocity over each time interval. v av0 v 0 +
(a) 1m s -2 (b) 2 m s -2 (c) zero (d) -1 m s -2
 11 th Physics - Unit 2 Kinematics Solutions for the Textbook Problems One Marks 1. Which one of the followin Cartesian coordinate system is not followed in physics? 5. If a particle has neative velocity
11 th Physics - Unit 2 Kinematics Solutions for the Textbook Problems One Marks 1. Which one of the followin Cartesian coordinate system is not followed in physics? 5. If a particle has neative velocity
Example 2.1. Draw the points with polar coordinates: (i) (3, π) (ii) (2, π/4) (iii) (6, 2π/4) We illustrate all on the following graph:
 Section 10.3: Polar Coordinates The polar coordinate system is another way to coordinatize the Cartesian plane. It is particularly useful when examining regions which are circular. 1. Cartesian Coordinates
Section 10.3: Polar Coordinates The polar coordinate system is another way to coordinatize the Cartesian plane. It is particularly useful when examining regions which are circular. 1. Cartesian Coordinates
XI PHYSICS M. AFFAN KHAN LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K. https://promotephysics.wordpress.com
 XI PHYSICS M. AFFAN KHAN LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K affan_414@live.com https://promotephysics.wordpress.com [MOTION IN TWO DIMENSIONS] CHAPTER NO. 4 In this chapter we are oin to discuss motion in projectile
XI PHYSICS M. AFFAN KHAN LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K affan_414@live.com https://promotephysics.wordpress.com [MOTION IN TWO DIMENSIONS] CHAPTER NO. 4 In this chapter we are oin to discuss motion in projectile
1 CHAPTER 7 PROJECTILES. 7.1 No Air Resistance
 CHAPTER 7 PROJECTILES 7 No Air Resistance We suppose that a particle is projected from a point O at the oriin of a coordinate system, the y-axis bein vertical and the x-axis directed alon the round The
CHAPTER 7 PROJECTILES 7 No Air Resistance We suppose that a particle is projected from a point O at the oriin of a coordinate system, the y-axis bein vertical and the x-axis directed alon the round The
v( t) g 2 v 0 sin θ ( ) ( ) g t ( ) = 0
 PROJECTILE MOTION Velocity We seek to explore the velocity of the projectile, includin its final value as it hits the round, or a taret above the round. The anle made by the velocity vector with the local
PROJECTILE MOTION Velocity We seek to explore the velocity of the projectile, includin its final value as it hits the round, or a taret above the round. The anle made by the velocity vector with the local
Ground Rules. PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I. Position and Displacement. Average Velocity. Lectures 7 and 8 Motion in Two Dimensions
 PC11 Fundamentals of Physics I Lectures 7 and 8 Motion in Two Dimensions Dr Tay Sen Chuan 1 Ground Rules Switch off your handphone and paer Switch off your laptop computer and keep it No talkin while lecture
PC11 Fundamentals of Physics I Lectures 7 and 8 Motion in Two Dimensions Dr Tay Sen Chuan 1 Ground Rules Switch off your handphone and paer Switch off your laptop computer and keep it No talkin while lecture
Linear Motion. Miroslav Mihaylov. February 13, 2014
 Linear Motion Miroslav Mihaylov February 13, 2014 1 Vector components Vector A has manitude A and direction θ with respect to the horizontal. On Fiure 1 we chose the eastbound as a positive x direction
Linear Motion Miroslav Mihaylov February 13, 2014 1 Vector components Vector A has manitude A and direction θ with respect to the horizontal. On Fiure 1 we chose the eastbound as a positive x direction
Energizing Math with Engineering Applications
 Enerizin Math with Enineerin Applications Understandin the Math behind Launchin a Straw-Rocket throuh the use of Simulations. Activity created by Ira Rosenthal (rosenthi@palmbeachstate.edu) as part of
Enerizin Math with Enineerin Applications Understandin the Math behind Launchin a Straw-Rocket throuh the use of Simulations. Activity created by Ira Rosenthal (rosenthi@palmbeachstate.edu) as part of
Firing an Ideal Projectile
 92 Chapter 13: Vector-Valued Functions and Motion in Space 13.2 Modelin Projectile Motion 921 r at time t v v cos i a j (a) v sin j Newton s second law of motion sas that the force actin on the projectile
92 Chapter 13: Vector-Valued Functions and Motion in Space 13.2 Modelin Projectile Motion 921 r at time t v v cos i a j (a) v sin j Newton s second law of motion sas that the force actin on the projectile
Problem 2: Experiment 09 Physical Pendulum. Part One: Ruler Pendulum
 Problem : Experiment 9 Physical Pendulum Part One: Ruler Pendulum The ruler has a mass m r =.159 k, a width a =.8 m, a lenth b = 1. m, and the distance from the pivot point to the center of mass is l =.479
Problem : Experiment 9 Physical Pendulum Part One: Ruler Pendulum The ruler has a mass m r =.159 k, a width a =.8 m, a lenth b = 1. m, and the distance from the pivot point to the center of mass is l =.479
MATH 100 REVIEW PACKAGE
 SCHOOL OF UNIVERSITY ARTS AND SCIENCES MATH 00 REVIEW PACKAGE Gearing up for calculus and preparing for the Assessment Test that everybody writes on at. You are strongly encouraged not to use a calculator
SCHOOL OF UNIVERSITY ARTS AND SCIENCES MATH 00 REVIEW PACKAGE Gearing up for calculus and preparing for the Assessment Test that everybody writes on at. You are strongly encouraged not to use a calculator
10.1 Curves Defined by Parametric Equation
 10.1 Curves Defined by Parametric Equation 1. Imagine that a particle moves along the curve C shown below. It is impossible to describe C by an equation of the form y = f (x) because C fails the Vertical
10.1 Curves Defined by Parametric Equation 1. Imagine that a particle moves along the curve C shown below. It is impossible to describe C by an equation of the form y = f (x) because C fails the Vertical
2.5 Velocity and Acceleration
 82 CHAPTER 2. VECTOR FUNCTIONS 2.5 Velocity and Acceleration In this section, we study the motion of an object alon a space curve. In other words, as the object moves with time, its trajectory follows
82 CHAPTER 2. VECTOR FUNCTIONS 2.5 Velocity and Acceleration In this section, we study the motion of an object alon a space curve. In other words, as the object moves with time, its trajectory follows
AP Calculus (BC) Chapter 10 Test No Calculator Section. Name: Date: Period:
 AP Calculus (BC) Chapter 10 Test No Calculator Section Name: Date: Period: Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions (5 points each; please circle the correct answer.) 1. The graph in the xy-plane represented
AP Calculus (BC) Chapter 10 Test No Calculator Section Name: Date: Period: Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions (5 points each; please circle the correct answer.) 1. The graph in the xy-plane represented
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics. Physics 8.01x Fall Term 2001 EXAM 1 SOLUTIONS
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01x Fall Term 2001 EXAM 1 SOLUTIONS Problem 1: We define a vertical coordinate system with positive upwards. The only forces actin
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics Physics 8.01x Fall Term 2001 EXAM 1 SOLUTIONS Problem 1: We define a vertical coordinate system with positive upwards. The only forces actin
Math156 Review for Exam 4
 Math56 Review for Eam 4. What will be covered in this eam: Representing functions as power series, Taylor and Maclaurin series, calculus with parametric curves, calculus with polar coordinates.. Eam Rules:
Math56 Review for Eam 4. What will be covered in this eam: Representing functions as power series, Taylor and Maclaurin series, calculus with parametric curves, calculus with polar coordinates.. Eam Rules:
Dynamics 4600:203 Homework 03 Due: February 08, 2008 Name:
 Dynamics 4600:03 Homework 03 Due: ebruary 08, 008 Name: Please denote your answers clearly, i.e., bo in, star, etc., and write neatly. There are no points for small, messy, unreadable work... please use
Dynamics 4600:03 Homework 03 Due: ebruary 08, 008 Name: Please denote your answers clearly, i.e., bo in, star, etc., and write neatly. There are no points for small, messy, unreadable work... please use
Do not turn over until you are told to do so by the Invigilator.
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2016 17 ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS AND MECHANICS ENG-4004Y Time allowed: 2 Hours Attempt QUESTIONS 1 and 2, and ONE other question.
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Mathematics Main Series UG Examination 2016 17 ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS AND MECHANICS ENG-4004Y Time allowed: 2 Hours Attempt QUESTIONS 1 and 2, and ONE other question.
PHY 133 Lab 1 - The Pendulum
 3/20/2017 PHY 133 Lab 1 The Pendulum [Stony Brook Physics Laboratory Manuals] Stony Brook Physics Laboratory Manuals PHY 133 Lab 1 - The Pendulum The purpose of this lab is to measure the period of a simple
3/20/2017 PHY 133 Lab 1 The Pendulum [Stony Brook Physics Laboratory Manuals] Stony Brook Physics Laboratory Manuals PHY 133 Lab 1 - The Pendulum The purpose of this lab is to measure the period of a simple
KINEMATICS PREVIOUS EAMCET BITS ENGINEERING PAPER
 KINEMATICS PREVIOUS EAMCET BITS ENGINEERING PAPER. A body is projected vertically upwards at time t = 0 and is seen at a heiht at time t and t seconds durin its fliht. The maximum heiht attained is [ =
KINEMATICS PREVIOUS EAMCET BITS ENGINEERING PAPER. A body is projected vertically upwards at time t = 0 and is seen at a heiht at time t and t seconds durin its fliht. The maximum heiht attained is [ =
Motion in Two Dimensions Sections Covered in the Text: Chapters 6 & 7, except 7.5 & 7.6
 Motion in Two Dimensions Sections Covered in the Tet: Chapters 6 & 7, ecept 7.5 & 7.6 It is time to etend the definitions we developed in Note 03 to describe motion in 2D space. In doin so we shall find
Motion in Two Dimensions Sections Covered in the Tet: Chapters 6 & 7, ecept 7.5 & 7.6 It is time to etend the definitions we developed in Note 03 to describe motion in 2D space. In doin so we shall find
the equations for the motion of the particle are written as
 Dynamics 4600:203 Homework 02 Due: ebruary 01, 2008 Name: Please denote your answers clearly, ie, box in, star, etc, and write neatly There are no points for small, messy, unreadable work please use lots
Dynamics 4600:203 Homework 02 Due: ebruary 01, 2008 Name: Please denote your answers clearly, ie, box in, star, etc, and write neatly There are no points for small, messy, unreadable work please use lots
Mathematics Extension 1 Time allowed: 2 hours (plus 5 minutes reading time)
 Name: Teacher: Class: FORT STREET HIGH SCHOOL 0 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE COURSE ASSESSMENT TASK : TRIAL HSC Mathematics Extension Time allowed: hours (plus 5 minutes readin time) Syllabus Assessment Area
Name: Teacher: Class: FORT STREET HIGH SCHOOL 0 HIGHER SCHOOL CERTIFICATE COURSE ASSESSMENT TASK : TRIAL HSC Mathematics Extension Time allowed: hours (plus 5 minutes readin time) Syllabus Assessment Area
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 3 2, 5 2 C) - 5 2
 Test Review (chap 0) Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. ) Find the point on the curve x = sin t, y = cos t, -
Test Review (chap 0) Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Solve the problem. ) Find the point on the curve x = sin t, y = cos t, -
Parametric Curves. Calculus 2 Lia Vas
 Calculus Lia Vas Parametric Curves In the past, we mostly worked with curves in the form y = f(x). However, this format does not encompass all the curves one encounters in applications. For example, consider
Calculus Lia Vas Parametric Curves In the past, we mostly worked with curves in the form y = f(x). However, this format does not encompass all the curves one encounters in applications. For example, consider
Math Section 4.3 Unit Circle Trigonometry
 Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
Math 10 - Section 4. Unit Circle Trigonometry An angle is in standard position if its vertex is at the origin and its initial side is along the positive x axis. Positive angles are measured counterclockwise
An angle in the Cartesian plane is in standard position if its vertex lies at the origin and its initial arm lies on the positive x-axis.
 Learning Goals 1. To understand what standard position represents. 2. To understand what a principal and related acute angle are. 3. To understand that positive angles are measured by a counter-clockwise
Learning Goals 1. To understand what standard position represents. 2. To understand what a principal and related acute angle are. 3. To understand that positive angles are measured by a counter-clockwise
Homework # 2. SOLUTION - We start writing Newton s second law for x and y components: F x = 0, (1) F y = mg (2) x (t) = 0 v x (t) = v 0x (3)
 Physics 411 Homework # Due:..18 Mechanics I 1. A projectile is fired from the oriin of a coordinate system, in the x-y plane (x is the horizontal displacement; y, the vertical with initial velocity v =
Physics 411 Homework # Due:..18 Mechanics I 1. A projectile is fired from the oriin of a coordinate system, in the x-y plane (x is the horizontal displacement; y, the vertical with initial velocity v =
PROJECTILE MOTION. ( ) g y 0. Equations ( ) General time of flight (TOF) General range. Angle for maximum range ("optimum angle")
 PROJECTILE MOTION Equations General time of fliht (TOF) T sin θ y 0 sin( θ) General rane R cos( θ) T R cos θ sin( θ) sin( θ) y 0 Anle for maximum rane ("optimum anle") θ opt atan y 0 atan v f atan v f
PROJECTILE MOTION Equations General time of fliht (TOF) T sin θ y 0 sin( θ) General rane R cos( θ) T R cos θ sin( θ) sin( θ) y 0 Anle for maximum rane ("optimum anle") θ opt atan y 0 atan v f atan v f
( )( ) Algebra 136 Semester 2 Review. ( ) 6. g( h( x) ( ) Name. In 1-6, use the functions below to find the solutions.
 Algebra 136 Semester Review In 1-6, use the functions below to find the solutions. Name f ( x) = 3x x + g( x) = x 3 h( x) = x + 3 1. ( f + h) ( x). ( h g) ( x) 3. h x g ( ) 4. ( gh) ( x). f g( x) ( ) 6.
Algebra 136 Semester Review In 1-6, use the functions below to find the solutions. Name f ( x) = 3x x + g( x) = x 3 h( x) = x + 3 1. ( f + h) ( x). ( h g) ( x) 3. h x g ( ) 4. ( gh) ( x). f g( x) ( ) 6.
Exam 1 Review SOLUTIONS
 1. True or False (and give a short reason): Exam 1 Review SOLUTIONS (a) If the parametric curve x = f(t), y = g(t) satisfies g (1) = 0, then it has a horizontal tangent line when t = 1. FALSE: To make
1. True or False (and give a short reason): Exam 1 Review SOLUTIONS (a) If the parametric curve x = f(t), y = g(t) satisfies g (1) = 0, then it has a horizontal tangent line when t = 1. FALSE: To make
= ( 2) = p 5.
 MATH 0 Exam (Version ) Solutions Setember, 00 S. F. Ellermeyer Name Instructions. Your work on this exam will be raded accordin to two criteria: mathematical correctness clarity of resentation. In other
MATH 0 Exam (Version ) Solutions Setember, 00 S. F. Ellermeyer Name Instructions. Your work on this exam will be raded accordin to two criteria: mathematical correctness clarity of resentation. In other
AP Calculus Summer Packet
 AP Calculus Summer Packet Writing The Equation Of A Line Example: Find the equation of a line that passes through ( 1, 2) and (5, 7). ü Things to remember: Slope formula, point-slope form, slopeintercept
AP Calculus Summer Packet Writing The Equation Of A Line Example: Find the equation of a line that passes through ( 1, 2) and (5, 7). ü Things to remember: Slope formula, point-slope form, slopeintercept
Math 120: Precalculus Autumn 2017 A List of Topics for the Final
 Math 120: Precalculus Autumn 2017 A List of Topics for the Final Here s a fairly comprehensive list of things you should be comfortable doing for the final. Really Old Stuff 1. Unit conversion and rates
Math 120: Precalculus Autumn 2017 A List of Topics for the Final Here s a fairly comprehensive list of things you should be comfortable doing for the final. Really Old Stuff 1. Unit conversion and rates
A different parametric curve ( t, t 2 ) traces the same curve, but this time the par-
 Parametric Curves: Suppose a particle is moving around in a circle or any curve that fails the vertical line test, then we cannot describe the path of this particle using an equation of the form y fx)
Parametric Curves: Suppose a particle is moving around in a circle or any curve that fails the vertical line test, then we cannot describe the path of this particle using an equation of the form y fx)
MATH 1080 Test 2 -Version A-SOLUTIONS Fall a. (8 pts) Find the exact length of the curve on the given interval.
 MATH 8 Test -Version A-SOLUTIONS Fall 4. Consider the curve defined by y = ln( sec x), x. a. (8 pts) Find the exact length of the curve on the given interval. sec x tan x = = tan x sec x L = + tan x =
MATH 8 Test -Version A-SOLUTIONS Fall 4. Consider the curve defined by y = ln( sec x), x. a. (8 pts) Find the exact length of the curve on the given interval. sec x tan x = = tan x sec x L = + tan x =
There are some trigonometric identities given on the last page.
 MA 114 Calculus II Fall 2015 Exam 4 December 15, 2015 Name: Section: Last 4 digits of student ID #: No books or notes may be used. Turn off all your electronic devices and do not wear ear-plugs during
MA 114 Calculus II Fall 2015 Exam 4 December 15, 2015 Name: Section: Last 4 digits of student ID #: No books or notes may be used. Turn off all your electronic devices and do not wear ear-plugs during
Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates
 Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates Parametrizations of Plane Curves In previous chapters, we have studied curves as the graphs of functions or equations involving the two variables x and y. Another
Parametric Equations and Polar Coordinates Parametrizations of Plane Curves In previous chapters, we have studied curves as the graphs of functions or equations involving the two variables x and y. Another
Transformations of Quadratic Functions
 .1 Transormations o Quadratic Functions Essential Question How do the constants a, h, and k aect the raph o the quadratic unction () = a( h) + k? The parent unction o the quadratic amil is. A transormation
.1 Transormations o Quadratic Functions Essential Question How do the constants a, h, and k aect the raph o the quadratic unction () = a( h) + k? The parent unction o the quadratic amil is. A transormation
Phys207: Lecture 04. Today s Agenda 3-D Kinematics Independence of x and y components Baseball projectile Shoot the monkey Uniform circular motion
 Phys7: Lecture 4 Reminders All Discussion and Lab sections start meetin this week Homework is posted on course website Solutions to preious hwks will be posted Thursday mornins Today s Aenda 3-D Kinematics
Phys7: Lecture 4 Reminders All Discussion and Lab sections start meetin this week Homework is posted on course website Solutions to preious hwks will be posted Thursday mornins Today s Aenda 3-D Kinematics
This Week. Next Week
 This Week Tutorial and Test 1, in the lab (chapters 1 and 2) Next Week Experiment 1: Measurement of Lenth and Mass WileyPLUS Assinment 1 now available Due Monday, October 5 at 11:00 pm Chapters 2 & 3 28
This Week Tutorial and Test 1, in the lab (chapters 1 and 2) Next Week Experiment 1: Measurement of Lenth and Mass WileyPLUS Assinment 1 now available Due Monday, October 5 at 11:00 pm Chapters 2 & 3 28
PHYS 314 HOMEWORK #3
 PHYS 34 HOMEWORK #3 Due : 8 Feb. 07. A unifrm chain f mass M, lenth L and density λ (measured in k/m) hans s that its bttm link is just tuchin a scale. The chain is drpped frm rest nt the scale. What des
PHYS 34 HOMEWORK #3 Due : 8 Feb. 07. A unifrm chain f mass M, lenth L and density λ (measured in k/m) hans s that its bttm link is just tuchin a scale. The chain is drpped frm rest nt the scale. What des
NON-AP CALCULUS SUMMER PACKET
 NON-AP CALCULUS SUMMER PACKET These problems are to be completed to the best of your ability by the first day of school. You will be given the opportunity to ask questions about problems you found difficult
NON-AP CALCULUS SUMMER PACKET These problems are to be completed to the best of your ability by the first day of school. You will be given the opportunity to ask questions about problems you found difficult
PHYS 1114, Lecture 9, February 6 Contents:
 PHYS 4, Lecture 9, February 6 Contents: Continued with projectile motion: The kicko problem in football was treated analytically, obtainin formulas for maimum heiht and rane in terms of initial speed and
PHYS 4, Lecture 9, February 6 Contents: Continued with projectile motion: The kicko problem in football was treated analytically, obtainin formulas for maimum heiht and rane in terms of initial speed and
Physics 11 Fall 2012 Practice Problems 2 - Solutions
 Physics 11 Fall 01 Practice Problems - s 1. True or false (inore any effects due to air resistance): (a) When a projectile is fired horizontally, it takes the same amount of time to reach the round as
Physics 11 Fall 01 Practice Problems - s 1. True or false (inore any effects due to air resistance): (a) When a projectile is fired horizontally, it takes the same amount of time to reach the round as
Chapter 9 Overview: Parametric and Polar Coordinates
 Chapter 9 Overview: Parametric and Polar Coordinates As we saw briefly last year, there are axis systems other than the Cartesian System for graphing (vector coordinates, polar coordinates, rectangular
Chapter 9 Overview: Parametric and Polar Coordinates As we saw briefly last year, there are axis systems other than the Cartesian System for graphing (vector coordinates, polar coordinates, rectangular
ONLINE: MATHEMATICS EXTENSION 2 Topic 6 MECHANICS 6.3 HARMONIC MOTION
 ONINE: MATHEMATICS EXTENSION Topic 6 MECHANICS 6.3 HARMONIC MOTION Vibrations or oscillations are motions that repeated more or less reularly in time. The topic is very broad and diverse and covers phenomena
ONINE: MATHEMATICS EXTENSION Topic 6 MECHANICS 6.3 HARMONIC MOTION Vibrations or oscillations are motions that repeated more or less reularly in time. The topic is very broad and diverse and covers phenomena
Physics 111. Lecture 7 (Walker: 4.2-5) 2D Motion Examples Projectile Motion
 Physics 111 Lecture 7 (Walker: 4.-5) D Motion Eamples Projectile Motion Sept. 16, 9 -D Motion -- Constant Acceleration r r r r = v t at t v t a t y y yt y v t at r r r v = v at v = v a t v = v a t y y
Physics 111 Lecture 7 (Walker: 4.-5) D Motion Eamples Projectile Motion Sept. 16, 9 -D Motion -- Constant Acceleration r r r r = v t at t v t a t y y yt y v t at r r r v = v at v = v a t v = v a t y y
8.1 Solutions to Exercises
 Last edited 9/6/17 8.1 Solutions to Exercises 1. Since the sum of all angles in a triangle is 180, 180 = 70 + 50 + α. Thus α = 60. 10 α B The easiest way to find A and B is to use Law of Sines. sin( )
Last edited 9/6/17 8.1 Solutions to Exercises 1. Since the sum of all angles in a triangle is 180, 180 = 70 + 50 + α. Thus α = 60. 10 α B The easiest way to find A and B is to use Law of Sines. sin( )
Section 14.1 Vector Functions and Space Curves
 Section 14.1 Vector Functions and Space Curves Functions whose range does not consists of numbers A bulk of elementary mathematics involves the study of functions - rules that assign to a given input a
Section 14.1 Vector Functions and Space Curves Functions whose range does not consists of numbers A bulk of elementary mathematics involves the study of functions - rules that assign to a given input a
Assignment 6. Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Assinment 6 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Round your answer, if appropriate. 1) A man 6 ft tall walks at a rate of 3 ft/sec
Assinment 6 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Round your answer, if appropriate. 1) A man 6 ft tall walks at a rate of 3 ft/sec
Prince Sultan University Physics Department First Semester 2012 /2013. PHY 105 First Major Exam Allowed Time: 60 min
 Prince Sultan University Physics Department First Semester 01 /01 PHY 105 First Major Exam Allowed Time: 60 min Student Name: 1. Write your name in the specified space NOW.. Any paper without name will
Prince Sultan University Physics Department First Semester 01 /01 PHY 105 First Major Exam Allowed Time: 60 min Student Name: 1. Write your name in the specified space NOW.. Any paper without name will
Physics 18 Spring 2011 Homework 2 - Solutions Wednesday January 26, 2011
 Physics 18 Sprin 011 Homework - s Wednesday January 6, 011 Make sure your name is on your homework, and please box your final answer. Because we will be ivin partial credit, be sure to attempt all the
Physics 18 Sprin 011 Homework - s Wednesday January 6, 011 Make sure your name is on your homework, and please box your final answer. Because we will be ivin partial credit, be sure to attempt all the
Motion in Space Parametric Equations of a Curve
 Motion in Space Parametric Equations of a Curve A curve, C, inr 3 can be described by parametric equations of the form x x t y y t z z t. Any curve can be parameterized in many different ways. For example,
Motion in Space Parametric Equations of a Curve A curve, C, inr 3 can be described by parametric equations of the form x x t y y t z z t. Any curve can be parameterized in many different ways. For example,
Mechanics Cycle 3 Chapter 12++ Chapter 12++ Revisit Circular Motion
 Chapter 12++ Revisit Circular Motion Revisit: Anular variables Second laws for radial and tanential acceleration Circular motion CM 2 nd aw with F net To-Do: Vertical circular motion in ravity Complete
Chapter 12++ Revisit Circular Motion Revisit: Anular variables Second laws for radial and tanential acceleration Circular motion CM 2 nd aw with F net To-Do: Vertical circular motion in ravity Complete
Math 113 Final Exam Practice
 Math Final Exam Practice The Final Exam is comprehensive. You should refer to prior reviews when studying material in chapters 6, 7, 8, and.-9. This review will cover.0- and chapter 0. This sheet has three
Math Final Exam Practice The Final Exam is comprehensive. You should refer to prior reviews when studying material in chapters 6, 7, 8, and.-9. This review will cover.0- and chapter 0. This sheet has three
Worksheet 1.7: Introduction to Vector Functions - Position
 Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 1.7: Introduction to Vector Functions - Position From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes): Cartesian Coordinates: Coordinates of points in general,
Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 1.7: Introduction to Vector Functions - Position From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes): Cartesian Coordinates: Coordinates of points in general,
(C) 7 s. (C) 13 s. (C) 10 m
 NAME: Ms. Dwarka, Principal Period: #: WC Bryant HS Ms. Simonds, AP Science Base your answers to questions 1 throuh 3 on the position versus time raph below which shows the motion of a particle on a straiht
NAME: Ms. Dwarka, Principal Period: #: WC Bryant HS Ms. Simonds, AP Science Base your answers to questions 1 throuh 3 on the position versus time raph below which shows the motion of a particle on a straiht
Math Worksheet 1 SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK! f(x) = (x a) 2 + b. = x 2 + 6x + ( 6 2 )2 ( 6 2 )2 + 7 = (x 2 + 6x + 9) = (x + 3) 2 2
 Names Date. Consider the function Math 0550 Worksheet SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK! f() = + 6 + 7 (a) Complete the square and write the function in the form f() = ( a) + b. f() = + 6 + 7 = + 6 + ( 6 ) ( 6 ) +
Names Date. Consider the function Math 0550 Worksheet SHOW ALL OF YOUR WORK! f() = + 6 + 7 (a) Complete the square and write the function in the form f() = ( a) + b. f() = + 6 + 7 = + 6 + ( 6 ) ( 6 ) +
Name These exercises cover topics from Algebra I and Algebra II. Complete each question the best you can.
 Name These eercises cover topics from Algebra I and Algebra II. Complete each question the best you can. Multiple Choice: Place through the letter of the correct answer. You may only use your calculator
Name These eercises cover topics from Algebra I and Algebra II. Complete each question the best you can. Multiple Choice: Place through the letter of the correct answer. You may only use your calculator
MATH 130 FINAL REVIEW
 MATH 130 FINAL REVIEW Problems 1 5 refer to triangle ABC, with C=90º. Solve for the missing information. 1. A = 40, c = 36m. B = 53 30', b = 75mm 3. a = 91 ft, b = 85 ft 4. B = 1, c = 4. ft 5. A = 66 54',
MATH 130 FINAL REVIEW Problems 1 5 refer to triangle ABC, with C=90º. Solve for the missing information. 1. A = 40, c = 36m. B = 53 30', b = 75mm 3. a = 91 ft, b = 85 ft 4. B = 1, c = 4. ft 5. A = 66 54',
PreCalculus First Semester Exam Review
 PreCalculus First Semester Eam Review Name You may turn in this eam review for % bonus on your eam if all work is shown (correctly) and answers are correct. Please show work NEATLY and bo in or circle
PreCalculus First Semester Eam Review Name You may turn in this eam review for % bonus on your eam if all work is shown (correctly) and answers are correct. Please show work NEATLY and bo in or circle
7.2 Maximization of the Range of a Rocket
 138 CHAPTER 7. SOME APPLICATIONS The counterintuitive answer that a supersonic aircraft must dive first in order to climb to a iven altitude in minimum time was first discovered by Walter Denham and Art
138 CHAPTER 7. SOME APPLICATIONS The counterintuitive answer that a supersonic aircraft must dive first in order to climb to a iven altitude in minimum time was first discovered by Walter Denham and Art
CHAPTER 4 Stress Transformation
 CHAPTER 4 Stress Transformation ANALYSIS OF STRESS For this topic, the stresses to be considered are not on the perpendicular and parallel planes only but also on other inclined planes. A P a a b b P z
CHAPTER 4 Stress Transformation ANALYSIS OF STRESS For this topic, the stresses to be considered are not on the perpendicular and parallel planes only but also on other inclined planes. A P a a b b P z
10.1 Review of Parametric Equations
 10.1 Review of Parametric Equations Recall that often, instead of representing a curve using just x and y (called a Cartesian equation), it is more convenient to define x and y using parametric equations
10.1 Review of Parametric Equations Recall that often, instead of representing a curve using just x and y (called a Cartesian equation), it is more convenient to define x and y using parametric equations
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com
 . A particle of mass m is projected vertically upwards, at time t =, with speed. The particle is mv subject to air resistance of manitude, where v is the speed of the particle at time t and is a positive
. A particle of mass m is projected vertically upwards, at time t =, with speed. The particle is mv subject to air resistance of manitude, where v is the speed of the particle at time t and is a positive
Problem Set 2 Solutions
 UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 125 / LeClair Sprin 2009 Problem Set 2 Solutions The followin three problems are due 20 January 2009 at the beinnin of class. 1. (H,R,&W 4.39)
UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA Department of Physics and Astronomy PH 125 / LeClair Sprin 2009 Problem Set 2 Solutions The followin three problems are due 20 January 2009 at the beinnin of class. 1. (H,R,&W 4.39)
Physics 20 Homework 1 SIMS 2016
 Physics 20 Homework 1 SIMS 2016 Due: Wednesday, Auust 17 th Problem 1 The idea of this problem is to et some practice in approachin a situation where you miht not initially know how to proceed, and need
Physics 20 Homework 1 SIMS 2016 Due: Wednesday, Auust 17 th Problem 1 The idea of this problem is to et some practice in approachin a situation where you miht not initially know how to proceed, and need
Ground Rules. PC1221 Fundamentals of Physics I. Position and Displacement. Average Velocity. Lectures 7 and 8 Motion in Two Dimensions
 PC11 Fndamentals of Physics I Lectres 7 and 8 Motion in Two Dimensions A/Prof Tay Sen Chan 1 Grond Rles Switch off yor handphone and paer Switch off yor laptop compter and keep it No talkin while lectre
PC11 Fndamentals of Physics I Lectres 7 and 8 Motion in Two Dimensions A/Prof Tay Sen Chan 1 Grond Rles Switch off yor handphone and paer Switch off yor laptop compter and keep it No talkin while lectre
A. Correct! These are the corresponding rectangular coordinates.
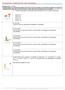 Precalculus - Problem Drill 20: Polar Coordinates No. 1 of 10 1. Find the rectangular coordinates given the point (0, π) in polar (A) (0, 0) (B) (2, 0) (C) (0, 2) (D) (2, 2) (E) (0, -2) A. Correct! These
Precalculus - Problem Drill 20: Polar Coordinates No. 1 of 10 1. Find the rectangular coordinates given the point (0, π) in polar (A) (0, 0) (B) (2, 0) (C) (0, 2) (D) (2, 2) (E) (0, -2) A. Correct! These
VECTORS REVIEW. ii. How large is the angle between lines A and B? b. What is angle C? 45 o. 30 o. c. What is angle θ? d. How large is θ?
 VECTOS EVIEW Solve the following geometric problems. a. Line touches the circle at a single point. Line etends through the center of the circle. i. What is line in reference to the circle? ii. How large
VECTOS EVIEW Solve the following geometric problems. a. Line touches the circle at a single point. Line etends through the center of the circle. i. What is line in reference to the circle? ii. How large
EXAM. Practice for Second Exam. Math , Fall Nov 4, 2003 ANSWERS
 EXAM Practice for Second Eam Math 135-006, Fall 003 Nov 4, 003 ANSWERS i Problem 1. In each part, find the integral. A. d (4 ) 3/ Make the substitution sin(θ). d cos(θ) dθ. We also have Then, we have d/dθ
EXAM Practice for Second Eam Math 135-006, Fall 003 Nov 4, 003 ANSWERS i Problem 1. In each part, find the integral. A. d (4 ) 3/ Make the substitution sin(θ). d cos(θ) dθ. We also have Then, we have d/dθ
Review of Topics in Algebra and Pre-Calculus I. Introduction to Functions function Characteristics of a function from set A to set B
 Review of Topics in Algebra and Pre-Calculus I. Introduction to Functions A function f from a set A to a set B is a relation that assigns to each element x in the set A exactly one element y in set B.
Review of Topics in Algebra and Pre-Calculus I. Introduction to Functions A function f from a set A to a set B is a relation that assigns to each element x in the set A exactly one element y in set B.
Math 1272 Solutions for Fall 2005 Final Exam
 Math 7 Solutions for Fall 5 Final Exam ) This fraction appears in Problem 5 of the undated-? exam; a solution can be found in that solution set. (E) ) This integral appears in Problem 6 of the Fall 4 exam;
Math 7 Solutions for Fall 5 Final Exam ) This fraction appears in Problem 5 of the undated-? exam; a solution can be found in that solution set. (E) ) This integral appears in Problem 6 of the Fall 4 exam;
Get Solution of These Packages & Learn by Video Tutorials on PROJECTILE MOTION
 FREE Download Study Packae from website: www.tekoclasses.com & www.mathsbysuha.com Get Solution of These Packaes & Learn by Video Tutorials on www.mathsbysuha.com. BASIC CONCEPT :. PROJECTILE PROJECTILE
FREE Download Study Packae from website: www.tekoclasses.com & www.mathsbysuha.com Get Solution of These Packaes & Learn by Video Tutorials on www.mathsbysuha.com. BASIC CONCEPT :. PROJECTILE PROJECTILE
Pre-Calc Unit 15: Polar Assignment Sheet May 4 th to May 31 st, 2012
 Pre-Calc Unit 15: Polar Assignment Sheet May 4 th to May 31 st, 2012 Date Objective/ Topic Assignment Did it Friday Polar Discover y Activity Day 1 pp. 2-3 May 4 th Monday Polar Discover y Activity Day
Pre-Calc Unit 15: Polar Assignment Sheet May 4 th to May 31 st, 2012 Date Objective/ Topic Assignment Did it Friday Polar Discover y Activity Day 1 pp. 2-3 May 4 th Monday Polar Discover y Activity Day
Vectors. In kinematics, the simplest concept is position, so let s begin with a position vector shown below:
 Vectors Extending the concepts of kinematics into two and three dimensions, the idea of a vector becomes very useful. By definition, a vector is a quantity with both a magnitude and a spatial direction.
Vectors Extending the concepts of kinematics into two and three dimensions, the idea of a vector becomes very useful. By definition, a vector is a quantity with both a magnitude and a spatial direction.
Section 6.2 Trigonometric Functions: Unit Circle Approach
 Section. Trigonometric Functions: Unit Circle Approach The unit circle is a circle of radius centered at the origin. If we have an angle in standard position superimposed on the unit circle, the terminal
Section. Trigonometric Functions: Unit Circle Approach The unit circle is a circle of radius centered at the origin. If we have an angle in standard position superimposed on the unit circle, the terminal
Created by T. Madas LINE INTEGRALS. Created by T. Madas
 LINE INTEGRALS LINE INTEGRALS IN 2 DIMENSIONAL CARTESIAN COORDINATES Question 1 Evaluate the integral ( x + 2y) dx, C where C is the path along the curve with equation y 2 = x + 1, from ( ) 0,1 to ( )
LINE INTEGRALS LINE INTEGRALS IN 2 DIMENSIONAL CARTESIAN COORDINATES Question 1 Evaluate the integral ( x + 2y) dx, C where C is the path along the curve with equation y 2 = x + 1, from ( ) 0,1 to ( )
APPM 1360 Final Exam Spring 2016
 APPM 36 Final Eam Spring 6. 8 points) State whether each of the following quantities converge or diverge. Eplain your reasoning. a) The sequence a, a, a 3,... where a n ln8n) lnn + ) n!) b) ln d c) arctan
APPM 36 Final Eam Spring 6. 8 points) State whether each of the following quantities converge or diverge. Eplain your reasoning. a) The sequence a, a, a 3,... where a n ln8n) lnn + ) n!) b) ln d c) arctan
IYGB Mathematical Methods 1
 IYGB Mathematical Methods Practice Paper B Time: 3 hours Candidates may use any non programmable, non graphical calculator which does not have the capability of storing data or manipulating algebraic expressions
IYGB Mathematical Methods Practice Paper B Time: 3 hours Candidates may use any non programmable, non graphical calculator which does not have the capability of storing data or manipulating algebraic expressions
Physics 2212 GJ Quiz #1 Solutions Fall 2015
 Physics 2212 GJ Quiz #1 Solutions Fall 2015 I. (14 points) A 2.0 µg dust particle, that has a charge of q = +3.0 nc, leaves the ground with an upward initial speed of v 0 = 1.0 m/s. It encounters a E =
Physics 2212 GJ Quiz #1 Solutions Fall 2015 I. (14 points) A 2.0 µg dust particle, that has a charge of q = +3.0 nc, leaves the ground with an upward initial speed of v 0 = 1.0 m/s. It encounters a E =
Analytic Trigonometry. Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved.
 Analytic Trigonometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 7.1 Trigonometric Identities Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Simplifying Trigonometric Expressions Proving
Analytic Trigonometry Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. 7.1 Trigonometric Identities Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Objectives Simplifying Trigonometric Expressions Proving
Geodesics as gravity
 Geodesics as ravity February 8, 05 It is not obvious that curvature can account for ravity. The orbitin path of a planet, for example, does not immediately seem to be the shortest path between points.
Geodesics as ravity February 8, 05 It is not obvious that curvature can account for ravity. The orbitin path of a planet, for example, does not immediately seem to be the shortest path between points.
Christoffel Symbols. 1 In General Topologies. Joshua Albert. September 28, W. First we say W : λ n = x µ (λ) so that the world
 Christoffel Symbols Joshua Albert September 28, 22 In General Topoloies We have a metric tensor nm defined by, Note by some handy theorem that for almost any continuous function F (L), equation 2 still
Christoffel Symbols Joshua Albert September 28, 22 In General Topoloies We have a metric tensor nm defined by, Note by some handy theorem that for almost any continuous function F (L), equation 2 still
Math 323 Exam 1 Practice Problem Solutions
 Math Exam Practice Problem Solutions. For each of the following curves, first find an equation in x and y whose graph contains the points on the curve. Then sketch the graph of C, indicating its orientation.
Math Exam Practice Problem Solutions. For each of the following curves, first find an equation in x and y whose graph contains the points on the curve. Then sketch the graph of C, indicating its orientation.
Honors Solutions. Honors Lesson1Lesson 1 1. Honors Lesson2Lesson 2. Honors Lesson3Lesson 3. Trigonometry Arithmetic Algebra 3. 4.
 πhonors SOLUTIONS Honors Solutions Honors LessonLesson.... 5. Trigonometry Arithmetic Algebra Calculus Geometry Honors LessonLesson. Make negative: ) Make negative: ) In both cases, changing the variable
πhonors SOLUTIONS Honors Solutions Honors LessonLesson.... 5. Trigonometry Arithmetic Algebra Calculus Geometry Honors LessonLesson. Make negative: ) Make negative: ) In both cases, changing the variable
Lesson 8 Kinematics V - Circular Motion
 I. Circular Motion and Polar Coordinates Lesson 8 Kinematics V - Circular Motion A. Consider the motion of ball on a circle from point A to point B as shown below. We could describe the path of the ball
I. Circular Motion and Polar Coordinates Lesson 8 Kinematics V - Circular Motion A. Consider the motion of ball on a circle from point A to point B as shown below. We could describe the path of the ball
1 Exponential Functions Limit Derivative Integral... 5
 Contents Eponential Functions 3. Limit................................................. 3. Derivative.............................................. 4.3 Integral................................................
Contents Eponential Functions 3. Limit................................................. 3. Derivative.............................................. 4.3 Integral................................................
Arc Length and Surface Area in Parametric Equations
 Arc Length and Surface Area in Parametric Equations MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2011 Background We have developed definite integral formulas for arc length
Arc Length and Surface Area in Parametric Equations MATH 211, Calculus II J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Spring 2011 Background We have developed definite integral formulas for arc length
Rotational kinematics
 Rotational kinematics Suppose you cut a circle out of a piece of paper and then several pieces of string which are just as long as the radius of the paper circle. If you then begin to lay these pieces
Rotational kinematics Suppose you cut a circle out of a piece of paper and then several pieces of string which are just as long as the radius of the paper circle. If you then begin to lay these pieces
Chapter 8B - Trigonometric Functions (the first part)
 Fry Texas A&M University! Spring 2016! Math 150 Notes! Section 8B-I! Page 79 Chapter 8B - Trigonometric Functions (the first part) Recall from geometry that if 2 corresponding triangles have 2 angles of
Fry Texas A&M University! Spring 2016! Math 150 Notes! Section 8B-I! Page 79 Chapter 8B - Trigonometric Functions (the first part) Recall from geometry that if 2 corresponding triangles have 2 angles of
MATH 162. Midterm 2 ANSWERS November 18, 2005
 MATH 62 Midterm 2 ANSWERS November 8, 2005. (0 points) Does the following integral converge or diverge? To get full credit, you must justify your answer. 3x 2 x 3 + 4x 2 + 2x + 4 dx You may not be able
MATH 62 Midterm 2 ANSWERS November 8, 2005. (0 points) Does the following integral converge or diverge? To get full credit, you must justify your answer. 3x 2 x 3 + 4x 2 + 2x + 4 dx You may not be able
Vector-Valued Functions
 Vector-Valued Functions 1 Parametric curves 8 ' 1 6 1 4 8 1 6 4 1 ' 4 6 8 Figure 1: Which curve is a graph of a function? 1 4 6 8 1 8 1 6 4 1 ' 4 6 8 Figure : A graph of a function: = f() 8 ' 1 6 4 1 1
Vector-Valued Functions 1 Parametric curves 8 ' 1 6 1 4 8 1 6 4 1 ' 4 6 8 Figure 1: Which curve is a graph of a function? 1 4 6 8 1 8 1 6 4 1 ' 4 6 8 Figure : A graph of a function: = f() 8 ' 1 6 4 1 1
Ballistics Car P3-3527
 WWW.ARBORSCI.COM Ballistics Car P3-3527 BACKGROUND: The Ballistic Car demonstrates that the horizontal motion of an object is unaffected by forces which act solely in the vertical direction. It consists
WWW.ARBORSCI.COM Ballistics Car P3-3527 BACKGROUND: The Ballistic Car demonstrates that the horizontal motion of an object is unaffected by forces which act solely in the vertical direction. It consists
