FAULT DETECTION AND DIAGNOSIS METHOD FOR VAV TERMINAL UNITS
|
|
|
- Elwin Dennis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
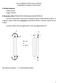
1 ESL-IC FAUL DEECION AND DIAGNOSIS MEHOD FOR VAV ERMINAL UNIS Maao Miyaa*, Harunori Yohida*, Maahiko Aada*, Fulin Wang*, and Shiro Hahiguhi** * Deparmen of Uran and Environmenal Engineering, yoo Univeriy, ** Yamaake, Co., Ld Summary: hi paper propoe wo faul deeion and diagnoi mehod for VAV uni wihou a enor of upply air volume, and he reul of applying hee mehod o a real uilding are preened. One mehod dee faul y applying a aiial mehod o four value alulaed uing he room air emperaure and he demand value of VAV damper opening of eah uni during a eady ae operaion period. From he reul of ae udie, he mehod an redue he numer of uni o e heked a fauly one down o 1% of he oal numer and all he uni ha really have a faul are inluded in hi group. he oher mehod judge he faul y applying dynami yem analyi o he operaional daa when he VAV yem ar up. From he reul of he ae udie, he mehod an redue he numer of uni down o 3%, among whih five uni aually have a faul and only one fauly uni wa no inluded in hi group. Boh mehod an redue ime and o for ommiioning of VAV uni ignifianly y he help of BEMS. eyword: Commiioning, VAV erminal uni, Faul deeion and diagnoi mehod 1. INRODUCION Variale Air Volume (VAV) Air Condiioning Syem are widely ued all over he world eaue of he high energy aving feaure. However i i repored ha he poiiliy of faul ourrene, uh a damper and auaor uk, and defe in onrol logi, i unforunaely high 1) ). Epeially ine he numer of VAV uni inalled in large uilding i omeime more han one houand, deeing he faul i eoming an imporan iue. For example in a uilding, whih he auhor inveigaed, all he VAV uni are manually and rouinely heked every year pending a grea deal of udge and manpower and quie many faul have een aually deeed. o ope wih hi iue, i i needed o develop an auomai faul deeion and diagnoi (FDD) ehnology. In he pa a few ype of FDD mehod, uh a, an Exponenially Weighed Moving Average (EWMA) mehod y J. Seem e al. and an RAR model mehod y H. Yohida e al., were propoed 3) 4) 5) 6). hee mehod require he airflow rae of eah VAV uni for FDD, however, i i no availale in old ype VAV uni eaue of no inallaion of an airflow rae enor. hi paper propoe wo kind of FDD mehod for hi ype of VAV uni. One mehod (Mehod A) i aed on a aiial deeion of oulier daa among onrol ignal of VAV opening raio during eady ae period (non-arup and lunh ime period). he oher mehod (Mehod B) i aed on applying dynami yem analyi o arup period daa. he oh mehod are verified uing operaion daa oained a a real offie uilding.. FDD MEHOD USING HE DAA OF SEADY SAE PERIOD (MEHOD A) Figure-1 repreen a general model of a VAV yem ha i ued o derie propoed FDD mehod. he yem ha an air-handling uni and M N zone, eah of whih ha one VAV uni. Eah zone i named a Zi (, j) and eah uni i named a Ui (, j ) (i =1,,..., M, j =1,,..., N ). he zone urrounding Z (1,1), for example, are defined a Z (,1) and Z (1,). he zone urrounding Z (,1) are defined a Z (1,1), Z (,) and Z (1,3). In he ae of he zone Z (,), he urrounding zone are defined a Z (1,), Z (,1), Z (3,) and Z (,3). All uni do no have an airflow enor. hi aumpion i no proper for he reen VAV produ u here are ill a grea numer of yem equipped wih old ype (1,1) (1,)... (1, N) VAV uni like he uilding udied y preen reearh. In hi paper, wo kind of faul are analyzed, whih are fully-loe damper (,1) (,)... (, N) and fully-open damper. he reaon of eleing hee wo faul i ha he M uni oher kind of faul, for example damper uk a middle-range poiion, were no found in he uilding ha he auhor inveigaed..1 Definiion of FDD Parameer he following four FDD parameer are defined for eah uni uing he zone air emperaure θ r, he e poin of room emperaure θ r and he (M, 1) (M, ) N uni (M, N) Figure-1 Aumed VAV yem Proeeding of he Fourh Inernaional Conferene for Enhaned Building Operaion, Pari, Frane, Ooer 18-19, 4
2 ESL-IC demand onrol ignal of VAV damper opening φ during eady ae period. a) Differene eween zone emperaure and emperaure e poin = θ θ (1) ai (, j) r r ) Demand onrol ignal of VAV damper opening φ φmin( i, j) i (, j) = 1 φ min( i, j) ) emperaure differene eween he analyzed zone and he average of he urrounding zone = θ ( θ )/ N (3) i (, j) r r( kl,) d) Differene eween demand ignal of VAV damper opening and he average of hoe of urrounding zone = φ ( φ )/ N (4) d ( kl,) One or all parameer of a fauly uni are expeed o e aiially anormal ompared wih hoe of normal uni. Namely, in he ae of a fully-loe damper faul ome of hem are expeed o e larger and in he ae of a fully-open damper faul ome of hem are expeed o e maller during ooling operaion.. Gru e In order o dee a faul auomaially, a aiial mehod alled a Gru e i applied o he aove-menioned four parameer. hi e i a ommon aiial mehod o dee oulier among a e of daa 7). he hypohei and he Gru e aii are defined a follow. Null hypohei Alernaive hypohei Gru e aii : : here are no oulier in he daae : here i a lea one oulier in he daae e xmax x = (5) () Where, x i he ample mean, x max i a ample wih maximum diane from x, and i he andard deviaion. Gru e aii e i he large aolue deviaion from he ample mean in uni of he ample andard deviaion. When he ignifiane level i e α, he null hypohei of no oulier i rejeed if e ( n 1) > SG = n α /n α /n ( n ) + Where, α /n i he riial value of he -diriuion wih ( n ) degree of freedom and a ignifiane level of α /n. hi mehod an hek only one oulier per rial. So if x max i judged a an oulier, i i expunged from he daa e and he e i oninued unil he null hypohei i aeped. he proedure of Gru e i hown in Figure-. Gru e i aed on he aumpion of normaliy. ha i, i mu e verified wheher he daa e an e reaonaly approximaed y a normal diriuion efore applying hi e. (6) Daa Se = { x i i = 1,,...,n} Find x max wih he maximum diane fromx Equion 5 Equion 6 v. < > x max in' unexpeed value x max i unexpeed value Remove x max from Finih Condu Again Figure- Flow of Gru e.3 FDD Proedure Uing Operaional Daa of Seady Sae Period Baed on he aove diuion, he FDD mehod uing operaional daa of eady ae period i propoed a follow. 1) Reord θ r, θ r and φ during eady ae period (non-arup and lunh ime period). ) Calulae he average of eah parameer defined y Equaion (1) o (4), i.e. ai (, j), i (, j), i (, j) and d, for eah VAV uni uing he daa oained a ep 1). 3) Apply Gru e o he ample of ai (, j), i (, j), i (, j) and d eparaely, and dee an exreme value in Proeeding of he Fourh Inernaional Conferene for Enhaned Building Operaion, Pari, Frane, Ooer 18-19, 4
3 ESL-IC eah daa e. he VAV uni whoe parameer i judged a exreme value i a fauly uni. If he exreme value i larger han he oher value, he uni i upeed o have a fully-loe damper faul. If he exreme value i maller han he oher, he uni i upeed o have a fully-open damper faul. 3. FDD MEHOD USING DYNAMIC MODEL AND DAA OF SARUP PERIOD (MEHOD B) In hi eion a FDD mehod aed on dynami yem analyi i propoed eaue he FDD Mehod A menioned in he previou eion ha a limiaion in deeing faul when φ alway ik o he minimum value. Even hough hi i a kind of a onrol or deign faul we need o dee hardware faul of VAV uni. During he arup ime of air ondiioning, airflow rae generally egin from maximum and dereae o a erain low level. hi period an e defined a a dynami ae and a new FDD mehod aed on a dynami yem analyi an e applied. 3.1 Single-Inpu Single-Oupu Dynami Syem A ingle-inpu and ingle-oupu (SISO) dynami yem i onidered a hown in Figure-3. he relaionhip eween he inpu u and he oupu y of he yem an e expreed y he following equaion if aking he yem a he fir order differenial equaion y approximaion. dy y u d + = (7) When he iniial value of y equal zero, he general oluion of Equaion (7) i hown in Equaion (8). he oluion of an impule repone y i and a ep repone y are expreed y Equaion (9) and (1) repeively. ( τ ) y () = e u( τ) dτ (8) yi = e (9) y = (1 e ) (1) Figure-4 and Figure-5 how he ehavior of he impule repone and he ep repone. In he Figure-5, how he eady ae value of y and how he ime onan of he yem. 3. FDD Mehod Uing he Repone Funion Figure-5 Sep repone he repone of zone air emperaure during VAV yem arup period i imilar o he ep repone of SISO yem. herefore he ep repone Equaion (1) i ued in hi FDD mehod. he VAV yem arup period i defined a he period during whih zone air emperaure goe down or up unil i eome eady. he required ime i defined a and he eady zone air emperaure i defined a θr ( ). We define upply air enile hea a he inpu and room air emperaure a he oupu. he inpu u, he oupu y and he eady ae value are expreed a follow. u () = ρv φ()( θ () θ ()) ( ) (11) p max r y () = θr() θr() ( ) (1) = θ () θ ( ) (13) r r For differen VAV yem, he value of θr ( ) and are generally differen. In order o deermine he value of θr ( ) and uiale for he yem, he emperaure of all meaured zone i averaged and he average emperaure θ () i approximaed uing he following equaion. θ () ae + (14) Figure-3 SISO dynami yem Figure-4 Impule repone Figure-6 Convergene ondiion a, and of he equaion are fied uing he meaured emperaure y he lea quare mehod. A hown in Figure-6, θr ( ) i defined a he value of, and i defined a he ime when he differene eween θ () and onvergen value eome 1% of. Alhough he ehavior of zone air emperaure i aumed o e he ep repone a hown in Equaion (1), i i no he.63 Inpu y() y() u() S Oupu y() Proeeding of he Fourh Inernaional Conferene for Enhaned Building Operaion, Pari, Frane, Ooer 18-19, 4
4 ESL-IC ep repone exaly. In order o imulae he ehavior of y more auraely, he following equaion ha omine he impule repone and he upply air enile hea i ued inead of Equaion (1). j y () = yi ( τ) u ( τ) dτ e u ( j ) (15) j= Uing he meaured daa y ˆ( ) and u ˆ( ), i alulaed y he lea quare mehod. In general, i ake a few minue ha zone air emperaure ge down afer he VAV yem ar up. L i defined a he ime delay and i eimaed uing he operaional daa afer VAV yem ar up exep he daa during he ime delay period L (5 15 min). L τ L min y ˆ() e uˆ( τ + L) = L τ = (16) Beaue migh e differen on differen day and for differen yem, i andardized uing he average µ and he andard deviaion σ of a yem on a ame meaured day a hown in Equaion (17). µ = (17) σ Faul of VAV uni are deeed and diagnoed uing he differene of eween he analyzed uni and he urrounding uni. he definiion of he urrounding uni i he ame a he previou eion. = ( )/ N (18) ( kl,) If a uni ha a fully-loe damper faul, of he uni i larger han he oher uni eaue he peed of repone i mall. If he uni ha a fully-open damper faul, hould e maller han he oher uni. 3.3 FDD Proedure Uing he Dynami Sae Daa Baed on he aove diuion, he FDD mehod uing he dynami ae daa i propoed a follow. 1) Reord θ r (), θ (), φ () in dynami ae. Reommended daa ampling ime i 6 eond. ) Calulae θ () and deermine and θr ( ) uing Equaion (14). 3) Calulae of eah uni uing he operaional daa in minue afer VAV yem ar up. 4) Calulae, he average of in all meaured day. If i larger han he oher uni, he uni migh have fully-loe damper faul. If i maller, he uni migh have fully-open damper faul. 4. VERIFICAION FOR HE WO FDD MEHODS he wo FDD mehod are validaed uing he daa olleed from VAV yem in a real uilding in okyo Japan. he informaion on he VAV yem i deried in he following eion Informaion of he VAV Syem for Verifiaion In order o verify he propoed mehod, operaional daa of he VAV yem in a large offie uilding were olleed. he onfiguraion of he uilding ogeher wih du work, VAV uni and he air-handling uni are hown in Figure-7. Every floor i divided ino four zone and eah zone ha a VAV air handling uni () yem (WN, WS, EN and ES). Eah yem ha 15 VAV uni (W1, W,..., E5). he oal numer of VAV uni in he uilding i aou 1, and no uni i equipped wih an airflow rae enor. Meauremen wa ondued from Augu o Ooer 3. he deail of meauremen are hown in ale-1. In hi Enlarged WN EN WS ES W1 W W3 W4 W5 Figure-7 Building plan and VAV yem plan C1 C C3 C4 C5 E1 E E3 E4 E5 Floor ale-1 Ouline of meaured daa Syem Amoun of meaured daa 11h ES 7 day 1h ES 4 day 13h EN 3 day 15h WS 9 day 16h WS 1 day 5h WN 9 day 6h WN 5 day 1h ES 7 day 1h EN 5 day W3( loe ) C3( open ) W1( loe ) W( open ) C3( loe ) none none none none 13h ES 5 day none Real fauly uni E5( loe ) Proeeding of he Fourh Inernaional Conferene for Enhaned Building Operaion, Pari, Frane, Ooer 18-19, 4
5 ESL-IC E5 (Cloed) C C3 (Cloed) E5 (Cloed) C5 W Se Poin E3 W3 C3 (Cloed) 6: 8: 1: 1: 14: 16: 18: : :. 6: 8: 1: 1: 14: 16: 18: : : Figure-8 Operaional daa in WS yem on 16h floor (3/8/9) E3 C3 (Opened) 5 Se Poin 4 C3 (Opened) E4 3 E3 6: 8: 1: 1: 14: 16: 18: : :. 6: 8: 1: 1: 14: 16: 18: : : Figure-9 Operaional daa in ES yem on 1h floor (3/9/9) uilding, aou 5 o 1 % of he oal uni have een found o e fauly every year y rouine manual hek aou he airflow rae of he VAV uni. In he preen reearh, aed on he reul of he hek ondued in April 3, we hoe 1 yem and arried ou he meauremen. 5 yem of whih inluded fauly uni and he oher 5 yem didn' inlude any fauly uni. he kind of reorded daa are room air emperaure, e poin of room emperaure, demand ignal of VAV damper opening, and upply air emperaure of eah uni and he ampling ime i 1 minue. Figure-8 and Figure-9 how he example of he meauremen reul. Figure-8 how he operaional daa of WS yem on 16h floor and hi yem ha wo fauly uni wih fully-loe malfunion. One i Uni-E5, whih uanially affe he room emperaure. he oher i Uni-C3, whih doen' muh affe he room emperaure eaue he zone i urrounded y eigh uni wih no faul. Figure-9 how he daa of ES yem on 1h floor and he yem ha one fauly uni wih fully-open malfunion. he zone emperaure of fauly Uni-C3 i lower han he emperaure e poin eaue of he faul. Bu he emperaure of Zone-E3 ha i ounded y Zone-C3 i lower han ha of Zone-C3. he fauly uni omeime affe no only he i zone emperaure u alo hoe of he urround zone. he meaured daa how ha he demand ignal of VAV damper opening of mo uni are auraed a a minimum value e for eah uni. hi mean ha he airflow rae of eah uni i no well onrolled a inended. 4. Verifiaion of he FDD Mehod A In order o verify he effeivene of Mehod A, he mehod i applied o he real operaional daa menioned aove. FDD e i ondued on 15 VAV uni in 1 yem. he exiene of four VAV uni wih a fully-loe damper faul and wo uni wih a fully-open damper faul ou of 15 VAV uni had een repored y he preliminary manual hek o all uni. Alhough he loaion of he fauly uni are known, however, he FDD e i ondued o he yem auming hey are unknown. he period of eady ae are defined a he period from wo hour afer yem arup unil hudown exep lunhime (1: 14:). In hi reearh, he ignifiane level α for he Gru e i.1. he general value of α i.1 or.5, u he faul ouldn e deeed when we ued hee value. If α wa e larger han.1, he numer of fale alarm go larger and he reliane of alarm wa down. From he e, we reommend ha he uiale value of α i.1. Figure-1 o Figure-13 how he hiogram of a,, and d. he hrehold eween normal uni and fauly uni defined y he Gru e are hown on he figure. From Figure-11, i an e aid ha he diriuion of i no normal diriuion and Gru e hould no e applied o he parameer. Bu here are 11 uni whoe value i zero. I mean he demand ignal of VAV damper opening i alway zero over he meauring period. A we an eaily ay ha i i anormal, uh uni an e judged o have fully-open damper faul. Similarly, when he Proeeding of he Fourh Inernaional Conferene for Enhaned Building Operaion, Pari, Frane, Ooer 18-19, 4
6 ESL-IC Faul (Opened) Normal Faul (Cloed) ES-C WS-W 1ES-C3 11ES-W WS-W 11ES-W Defferene eween emperaure and emperaure e poin [ o C] Figure-1 Hiogram of Faul (Opened) Normal Mehod 15WS-W 1ES-C3 emperaure differene eween analyzed zone and urrounding zone [ o C] 11ES-W3 Figure-1 Hiogram of Faul (Cloed) Faul (Opened) Demand value of VAV damper opening [-] Figure-11 Hiogram of a 1ES-C3 Normal 15WS-W Differene eween demand of damper opening and ha of urrounding zone [-] Figure-13 Hiogram of d ale- FDD reul of Mehod A Fully-loed damper faul Fully-opened damper faul 11ES 13EN 16WS 16WS 1ES 15WS W3 W1 C3 E5 C3 W Numer of alarm Numer of fale alarm Faul (Cloed) 11ES-W3 Numer of real fauly uni ha an' e deeed Parameer a) 15 1% 1 67% 1 17% Parameer ) 11 7% 9 8% 4 67% Parameer ) 7 5% 4 57% 3 5% Parameer d) 1% % 4 67% a) U ) 17 11% 1 71% 1 17% ) U d) 8 5% 4 5% 33% a) U ) U ) U d) 18 1% 1 67% % 1. value of i one, hoe uni an e judged o have fully-loe damper faul. ale- how wheher he rue fauly uni an e idenified and diagnoed orrely or no y he preen e mehod. he amoun of alarm, fale alarm, and he rue fauly uni ha were deeed are lied in ale-. In he ale, he mark of " " how he VAV uni whoe faul an e idenified and diagnoed orrely y he e and he mark of " " how he fauly uni ha an e idenified u anno e diagnoed orrely. By aking he union of he four e, i.e. (a d ), he numer of upeed fauly uni an e redued from 15 (1%) o 18 (1%) and all he uni ha ruly have faul are inluded in he 18 uni. hi reul mean ha Mehod A an redue he required ime, and manpower or o for 8.5 ommiioning y aou 9% ompared wih hoe needed y he Simulaed preen manual hek, whih i generally done y eing all he uni. 8 Moreover, if he union of he wo e, namely onidering he omparion wih he urrounding uni ( d ), i applied, we an idenify and diagnoe he faul ha ignifianly affe he room air emperaure y heking only 8 uni (5%). If idenifying ju he uni ha ignifianly affe room emperaure i enough, hi mehod i appropriae. In all e mehod, he faul of Uni-C3 in WS yem on 16h floor, whih i urrounded y many normally operaed uni, Average emperaure of all zone Figure-14 Fiing reul of θ Proeeding of he Fourh Inernaional Conferene for Enhaned Building Operaion, Pari, Frane, Ooer 18-19, 4
7 ESL-IC Meaured Simulaed Meaured Simulaed Meaured Simulaed Figure-15 Uni-C3 in WN yem on 6h floor (3/9/1) Figure-16 Uni-C3 in WN yem on 16h floor (3/8/7) Figure-17 Uni-C3 in WN yem on 1h floor (3/9/1) anno e idenified or diagnoed orrely. When a fauly uni i urrounded y many normally operaed uni, he preen mehod omeime fail. 4.3 Verifiaion of he FDD Mehod B Mehod B i verified y applying i o he real operaional daa of he uilding formerly menioned. A FDD ep ), and θr ( ) of he yem i deided. Figure-14 how he reul of he alulaion. of he yem i 115 minue and θr ( ) i 6.79 o C. i alulaed per meaured day per uni. A he example of he alulaion, he reul of Uni-C3 in WN yem on 6h floor, Uni-C3 in WS yem on 16h floor and Uni-C3 in ES yem on 1h floor are hown in Figure-15 o Figure-17. he figure how ha he auray of he imulaion i no good eaue of he aumpion ha hi yem i he fir order yem. Figure-18 how he hiogram of and ale-3 how he numer of alarm, fale alarm and undeeale real fauly uni when he hrehold hange from µ ± σ, µ ± σ, µ ± 3σ. I i lear ha all real fauly uni exep for Uni-C3 in WS yem on 16h floor an e deeed if he hrehold i µ ± σ, u Uni-W in WS yem on 15h floor anno e diagnoed orrely. he numer of alarm 46 (31% of all uni) i larger han ha of Mehod A and he reduion of o and ime for ommiioning i alo maller han Mehod A. If he hrehold i µ ± 3σ, he mehod give he alarm for four uni and hree of he alarm are righ, and he oher 3 fauly uni anno e deeed. From he ae udie uing he real offie uilding, 16 3σ σ - σ σ σ 3σ Mehod B i no o effiien from he view poin of he 14 numer of alarm and undeeale uni ompared wih 1 Mehod A. We ondued ae udie in variale ondiion, 1 1ES-C3 for example hanging he amoun of daa or load ondiion, 8 15WS-W 11ES-W3 u no aendany of Mehod B over Mehod A wa found. 6 he mehod may no dee and diagnoe faul orrely 4 if he ooling load haraerii of a zone are largely differen from he urrounding zone. In hi ae, he operaional daa of he uni in uh zone mu e removed from he daa e for analyzing. And he mehod are aed Figure-18 Hiogram of on he aumpion ha room emperaure enor are free of ale-3 FDD reul uing Mehod B faul. I mu e heked wheher he emperaure enor indiae proper value efore applying he FDD mehod. 5. CONCLUSIONS wo FDD mehod for VAV uni are propoed in he preen work. Boh mehod only require imple daa, room emperaure, demand onrol ignal of VAV damper opening hrehold Numer of alarm Numer of fale alarm Numer of real fauly uni ha an' e deeed µ ± 46 31% 41 89% 1 17% µ ± 11 7% 8 73% 3 5% µ ± 3 4 3% 1 5% 3 5% Proeeding of he Fourh Inernaional Conferene for Enhaned Building Operaion, Pari, Frane, Ooer 18-19, 4
8 ESL-IC and upply air emperaure, whih are eaily oained from BEMS. he following are he onluion aed on he ae udie uing real uilding operaional daa. 1) A mehod i propoed o dee faul y applying he Gru e o four parameer alulaed from he room air emperaure and he demand onrol ignal of VAV damper opening of eah uni under eady ae operaion. When omining all he FDD reul of he four parameer, he numer of upeed fauly uni an e redued down o 1% of he oal numer and every uni ha ruly ha a faul i inluded in he uni. hu, he 9% o or manpower for he ommiioning an e redue ompared wih he preen e proedure hrough whih all uni are manually heked. ) When omining he FDD reul of he wo parameer aed on omparing he room emperaure and he demand ignal wih hoe of he urrounding VAV uni, he numer of he upeed fauly uni an e redued down o 5% of he oal numer. In hi ae however, a fauly uni ha doe no ignifianly affe he room air emperaure urrounded y normal uni i very diffiul o e deeed. 3) A FDD mehod uing dynami yem analyi i propoed. In hi mehod he operaion during arup period i regarded dynami. he numer of upeed uni y hi mehod i aou 3% of he whole VAV uni and five uni wih a rue faul an e deeed ou of ix uni. However deeing a fauly uni urrounded y a few normal uni i alo diffiul. NOMENCLAURE a,, : Fiing parameer of Equaion (14) [ -] p : Speifi hea of air [kj/kg * ] : Gain of a fir order yem L : ime delay of SISO yem [min] n : Numer of ample in daa e [-] N : Numer of zone urrounding Zi (, j ) [-] α : Criial Value of diriuion wih ( n ) /n degree of freedom and a ignifiane level α /n : ime onan of a fir order yem u : Inpu of SISO yem : Sandard deviaion of daa e V max : Maximum value of upply air volume [m 3 /h] x : Sample mean of daa e x max : Sample wih he maximum diane from x in daa e y : Oupu of SISO yem y : Iniial value of y : Sandardizaion value of µ : Average of σ : Sandard deviaion of θ r : Zone air emperaure of Zi (, j ) [ o C] θ r : Se poin of room air emperaure [ o C] θ : emperaure of he zone urrounding Zi (, j ) r( kl,) [ o C] θ () : Average air emperaure in all meaured day [ o C] θ : Supply air emperaure [ o C] φ : Demand onrol ignal of VAV damper opening of Ui (, j ) [-] φ : Demand onrol ignal of VAV damper opening of ( kl,) he zone urrounding Ui (, j ) [-] φ min( i, j) : Minimum value of VAV damper opening [-] ρ : Air deniy [kg/m 3 ] REFERENCES 1) IEA Annex 5, Building Opimizaion and Faul Diagnoi Soure Book, Ed. J. Hyvarinen and S. arki, ehnial Reearh Cener of Finland, 1996 ) Harunori Yohida: ypial Faul of Air Condiioning Syem and Faul Deeion y AR Model and Exended alman Filer, ASHRAE ranaion, Vol.1, Par 1, pp , Fe ) Seem, J.E., Houe, J.M. and Monroe, R.H.: On-Line Monioring and Faul Deeion, ASHRAE Journal, Vol.41, No.7, pp1-6, ) Galler, M.A., Park, C., Coa, N.S., Buhy, S..: Uing he Virual Cyernei Building eed and FDD e Shell for FDD ool Developmen, NISIR ) Daniel Choiniere, Samuel Beaudoin: Faul Deeion and Diagnoi ool for VAV Boxe, IEA Annex 34 Deeion and Diagnoi Mehod in Real Building, Ed. A. Dexer and J. Pakanen, Seion C., pp , 1 6) Harunori Yohida, Sanjay umar, Yaunori Moria: Online Faul Deeion and Diagnoi in VAV Air Handling Uni y RAR Modeling, Energy and Building, Vol.33, pp , 1 7) NIS/SEMAECH e-handook of Saiial Mehod: hp:// Gru e for Oulier Proeeding of he Fourh Inernaional Conferene for Enhaned Building Operaion, Pari, Frane, Ooer 18-19, 4
8.1. a) For step response, M input is u ( t) Taking inverse Laplace transform. as α 0. Ideal response, K c. = Kc Mτ D + For ramp response, 8-1
 8. a For ep repone, inpu i u, U Y a U α α Y a α α Taking invere Laplae ranform a α e e / α / α A α 0 a δ 0 e / α a δ deal repone, α d Y i Gi U i δ Hene a α 0 a i For ramp repone, inpu i u, U Soluion anual
8. a For ep repone, inpu i u, U Y a U α α Y a α α Taking invere Laplae ranform a α e e / α / α A α 0 a δ 0 e / α a δ deal repone, α d Y i Gi U i δ Hene a α 0 a i For ramp repone, inpu i u, U Soluion anual
Chapter 7: Inverse-Response Systems
 Chaper 7: Invere-Repone Syem Normal Syem Invere-Repone Syem Baic Sar ou in he wrong direcion End up in he original eady-ae gain value Two or more yem wih differen magniude and cale in parallel Main yem
Chaper 7: Invere-Repone Syem Normal Syem Invere-Repone Syem Baic Sar ou in he wrong direcion End up in he original eady-ae gain value Two or more yem wih differen magniude and cale in parallel Main yem
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 31 Signal & Syem Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #27 C-T Syem: Laplace Tranform Power Tool for yem analyi Reading Aignmen: Secion 6.1 6.3 of Kamen and Heck 1/18 Coure Flow Diagram The arrow here how concepual
EECE 31 Signal & Syem Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #27 C-T Syem: Laplace Tranform Power Tool for yem analyi Reading Aignmen: Secion 6.1 6.3 of Kamen and Heck 1/18 Coure Flow Diagram The arrow here how concepual
Control Systems -- Final Exam (Spring 2006)
 6.5 Conrol Syem -- Final Eam (Spring 6 There are 5 prolem (inluding onu prolem oal poin. (p Given wo marie: (6 Compue A A e e. (6 For he differenial equaion [ ] ; y u A wih ( u( wha i y( for >? (8 For
6.5 Conrol Syem -- Final Eam (Spring 6 There are 5 prolem (inluding onu prolem oal poin. (p Given wo marie: (6 Compue A A e e. (6 For he differenial equaion [ ] ; y u A wih ( u( wha i y( for >? (8 For
u(t) Figure 1. Open loop control system
 Open loop conrol v cloed loop feedbac conrol The nex wo figure preen he rucure of open loop and feedbac conrol yem Figure how an open loop conrol yem whoe funcion i o caue he oupu y o follow he reference
Open loop conrol v cloed loop feedbac conrol The nex wo figure preen he rucure of open loop and feedbac conrol yem Figure how an open loop conrol yem whoe funcion i o caue he oupu y o follow he reference
To become more mathematically correct, Circuit equations are Algebraic Differential equations. from KVL, KCL from the constitutive relationship
 Laplace Tranform (Lin & DeCarlo: Ch 3) ENSC30 Elecric Circui II The Laplace ranform i an inegral ranformaion. I ranform: f ( ) F( ) ime variable complex variable From Euler > Lagrange > Laplace. Hence,
Laplace Tranform (Lin & DeCarlo: Ch 3) ENSC30 Elecric Circui II The Laplace ranform i an inegral ranformaion. I ranform: f ( ) F( ) ime variable complex variable From Euler > Lagrange > Laplace. Hence,
Let. x y. denote a bivariate time series with zero mean.
 Linear Filer Le x y : T denoe a bivariae ime erie wih zero mean. Suppoe ha he ime erie {y : T} i conruced a follow: y a x The ime erie {y : T} i aid o be conruced from {x : T} by mean of a Linear Filer.
Linear Filer Le x y : T denoe a bivariae ime erie wih zero mean. Suppoe ha he ime erie {y : T} i conruced a follow: y a x The ime erie {y : T} i aid o be conruced from {x : T} by mean of a Linear Filer.
A Theoretical Model of a Voltage Controlled Oscillator
 A Theoreical Model of a Volage Conrolled Ocillaor Yenming Chen Advior: Dr. Rober Scholz Communicaion Science Iniue Univeriy of Souhern California UWB Workhop, April 11-1, 6 Inroducion Moivaion The volage
A Theoreical Model of a Volage Conrolled Ocillaor Yenming Chen Advior: Dr. Rober Scholz Communicaion Science Iniue Univeriy of Souhern California UWB Workhop, April 11-1, 6 Inroducion Moivaion The volage
Study of simple inductive-capacitive series circuits using MATLAB software package
 ecen Advance in ircui, Syem and Auomaic onrol Sudy of imple inducive-capaciive erie circui uing MAAB ofware package NIUESU IU, PĂSUESU DAGOŞ Faculy of Mechanical and Elecrical Engineering Univeriy of Peroani
ecen Advance in ircui, Syem and Auomaic onrol Sudy of imple inducive-capaciive erie circui uing MAAB ofware package NIUESU IU, PĂSUESU DAGOŞ Faculy of Mechanical and Elecrical Engineering Univeriy of Peroani
Analysis of Members with Axial Loads and Moments. (Length effects Disregarded, Short Column )
 Analyi o emer wih Axial Loa an omen (Lengh ee Diregare, Shor Column ) A. Reaing Aignmen Chaper 9 o ex Chaper 10 o ACI B. reenaion o he INTERACTION DIAGRA or FAILURE ENVELO We have een ha a given eion an
Analyi o emer wih Axial Loa an omen (Lengh ee Diregare, Shor Column ) A. Reaing Aignmen Chaper 9 o ex Chaper 10 o ACI B. reenaion o he INTERACTION DIAGRA or FAILURE ENVELO We have een ha a given eion an
Fast Recursive Least Squares Algorithm for Acoustic Echo Cancellation Application
 SEI 7 4 h Inernaional Conferene: Siene of Eleroni, ehnologie of Informaion and eleommuniaion Marh 5-9, 7 UNISIA Fa Reurive Lea Square Algorihm for Aoui Eho Canellaion Appliaion Farid Ykhlef, A. Gueoum
SEI 7 4 h Inernaional Conferene: Siene of Eleroni, ehnologie of Informaion and eleommuniaion Marh 5-9, 7 UNISIA Fa Reurive Lea Square Algorihm for Aoui Eho Canellaion Appliaion Farid Ykhlef, A. Gueoum
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 30 Signal & Syem Prof. ark Fowler oe Se #34 C-T Tranfer Funcion and Frequency Repone /4 Finding he Tranfer Funcion from Differenial Eq. Recall: we found a DT yem Tranfer Funcion Hz y aking he ZT of
EECE 30 Signal & Syem Prof. ark Fowler oe Se #34 C-T Tranfer Funcion and Frequency Repone /4 Finding he Tranfer Funcion from Differenial Eq. Recall: we found a DT yem Tranfer Funcion Hz y aking he ZT of
ANALYSIS OF SOME SAFETY ASSESSMENT STANDARD ON GROUNDING SYSTEMS
 ANAYSIS OF SOME SAFETY ASSESSMENT STANDARD ON GROUNDING SYSTEMS Shang iqun, Zhang Yan, Cheng Gang School of Elecrical and Conrol Engineering, Xi an Univeriy of Science & Technology, 710054, Xi an, China,
ANAYSIS OF SOME SAFETY ASSESSMENT STANDARD ON GROUNDING SYSTEMS Shang iqun, Zhang Yan, Cheng Gang School of Elecrical and Conrol Engineering, Xi an Univeriy of Science & Technology, 710054, Xi an, China,
6.8 Laplace Transform: General Formulas
 48 HAP. 6 Laplace Tranform 6.8 Laplace Tranform: General Formula Formula Name, ommen Sec. F() l{ f ()} e f () d f () l {F()} Definiion of Tranform Invere Tranform 6. l{af () bg()} al{f ()} bl{g()} Lineariy
48 HAP. 6 Laplace Tranform 6.8 Laplace Tranform: General Formula Formula Name, ommen Sec. F() l{ f ()} e f () d f () l {F()} Definiion of Tranform Invere Tranform 6. l{af () bg()} al{f ()} bl{g()} Lineariy
EE Control Systems LECTURE 2
 Copyrigh F.L. Lewi 999 All righ reerved EE 434 - Conrol Syem LECTURE REVIEW OF LAPLACE TRANSFORM LAPLACE TRANSFORM The Laplace ranform i very ueful in analyi and deign for yem ha are linear and ime-invarian
Copyrigh F.L. Lewi 999 All righ reerved EE 434 - Conrol Syem LECTURE REVIEW OF LAPLACE TRANSFORM LAPLACE TRANSFORM The Laplace ranform i very ueful in analyi and deign for yem ha are linear and ime-invarian
A First Course on Kinetics and Reaction Engineering. Class 19 on Unit 18
 A Firs ourse on Kineics and Reacion Engineering lass 19 on Uni 18 Par I - hemical Reacions Par II - hemical Reacion Kineics Where We re Going Par III - hemical Reacion Engineering A. Ideal Reacors B. Perfecly
A Firs ourse on Kineics and Reacion Engineering lass 19 on Uni 18 Par I - hemical Reacions Par II - hemical Reacion Kineics Where We re Going Par III - hemical Reacion Engineering A. Ideal Reacors B. Perfecly
Problem Set If all directed edges in a network have distinct capacities, then there is a unique maximum flow.
 CSE 202: Deign and Analyi of Algorihm Winer 2013 Problem Se 3 Inrucor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Due on: Tue. Feb 26, 2013 Inrucion For your proof, you may ue any lower bound, algorihm or daa rucure from he ex
CSE 202: Deign and Analyi of Algorihm Winer 2013 Problem Se 3 Inrucor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Due on: Tue. Feb 26, 2013 Inrucion For your proof, you may ue any lower bound, algorihm or daa rucure from he ex
6.302 Feedback Systems Recitation : Phase-locked Loops Prof. Joel L. Dawson
 6.32 Feedback Syem Phae-locked loop are a foundaional building block for analog circui deign, paricularly for communicaion circui. They provide a good example yem for hi cla becaue hey are an excellen
6.32 Feedback Syem Phae-locked loop are a foundaional building block for analog circui deign, paricularly for communicaion circui. They provide a good example yem for hi cla becaue hey are an excellen
Randomized Perfect Bipartite Matching
 Inenive Algorihm Lecure 24 Randomized Perfec Biparie Maching Lecurer: Daniel A. Spielman April 9, 208 24. Inroducion We explain a randomized algorihm by Ahih Goel, Michael Kapralov and Sanjeev Khanna for
Inenive Algorihm Lecure 24 Randomized Perfec Biparie Maching Lecurer: Daniel A. Spielman April 9, 208 24. Inroducion We explain a randomized algorihm by Ahih Goel, Michael Kapralov and Sanjeev Khanna for
The Purpose of this talk The generation of the high-frequency resonant FEL wave by means of it s low-frequency wave as a pomp wave
 The Purpoe of hi alk The generaion of he high-frequency reonan FEL wave y mean of i low-frequency wave a a pomp wave A free elecron laer ha wo reonan frequencie wih : λ 1, = ( 1 ± β β ) λ w In a waveguide:
The Purpoe of hi alk The generaion of he high-frequency reonan FEL wave y mean of i low-frequency wave a a pomp wave A free elecron laer ha wo reonan frequencie wih : λ 1, = ( 1 ± β β ) λ w In a waveguide:
Simulation-Solving Dynamic Models ABE 5646 Week 2, Spring 2010
 Simulaion-Solving Dynamic Models ABE 5646 Week 2, Spring 2010 Week Descripion Reading Maerial 2 Compuer Simulaion of Dynamic Models Finie Difference, coninuous saes, discree ime Simple Mehods Euler Trapezoid
Simulaion-Solving Dynamic Models ABE 5646 Week 2, Spring 2010 Week Descripion Reading Maerial 2 Compuer Simulaion of Dynamic Models Finie Difference, coninuous saes, discree ime Simple Mehods Euler Trapezoid
Sample Final Exam (finals03) Covering Chapters 1-9 of Fundamentals of Signals & Systems
 Sample Final Exam Covering Chaper 9 (final04) Sample Final Exam (final03) Covering Chaper 9 of Fundamenal of Signal & Syem Problem (0 mar) Conider he caual opamp circui iniially a re depiced below. I LI
Sample Final Exam Covering Chaper 9 (final04) Sample Final Exam (final03) Covering Chaper 9 of Fundamenal of Signal & Syem Problem (0 mar) Conider he caual opamp circui iniially a re depiced below. I LI
18.03SC Unit 3 Practice Exam and Solutions
 Sudy Guide on Sep, Dela, Convoluion, Laplace You can hink of he ep funcion u() a any nice mooh funcion which i for < a and for > a, where a i a poiive number which i much maller han any ime cale we care
Sudy Guide on Sep, Dela, Convoluion, Laplace You can hink of he ep funcion u() a any nice mooh funcion which i for < a and for > a, where a i a poiive number which i much maller han any ime cale we care
Consider a Binary antipodal system which produces data of δ (t)
 Modulaion Polem PSK: (inay Phae-hi keying) Conide a inay anipodal yem whih podue daa o δ ( o + δ ( o inay and epeively. Thi daa i paed o pule haping ile and he oupu o he pule haping ile i muliplied y o(
Modulaion Polem PSK: (inay Phae-hi keying) Conide a inay anipodal yem whih podue daa o δ ( o + δ ( o inay and epeively. Thi daa i paed o pule haping ile and he oupu o he pule haping ile i muliplied y o(
Math 10B: Mock Mid II. April 13, 2016
 Name: Soluions Mah 10B: Mock Mid II April 13, 016 1. ( poins) Sae, wih jusificaion, wheher he following saemens are rue or false. (a) If a 3 3 marix A saisfies A 3 A = 0, hen i canno be inverible. True.
Name: Soluions Mah 10B: Mock Mid II April 13, 016 1. ( poins) Sae, wih jusificaion, wheher he following saemens are rue or false. (a) If a 3 3 marix A saisfies A 3 A = 0, hen i canno be inverible. True.
CS4445/9544 Analysis of Algorithms II Solution for Assignment 1
 Conider he following flow nework CS444/944 Analyi of Algorihm II Soluion for Aignmen (0 mark) In he following nework a minimum cu ha capaciy 0 Eiher prove ha hi aemen i rue, or how ha i i fale Uing he
Conider he following flow nework CS444/944 Analyi of Algorihm II Soluion for Aignmen (0 mark) In he following nework a minimum cu ha capaciy 0 Eiher prove ha hi aemen i rue, or how ha i i fale Uing he
, the. L and the L. x x. max. i n. It is easy to show that these two norms satisfy the following relation: x x n x = (17.3) max
 ecure 8 7. Sabiliy Analyi For an n dimenional vecor R n, he and he vecor norm are defined a: = T = i n i (7.) I i eay o how ha hee wo norm aify he following relaion: n (7.) If a vecor i ime-dependen, hen
ecure 8 7. Sabiliy Analyi For an n dimenional vecor R n, he and he vecor norm are defined a: = T = i n i (7.) I i eay o how ha hee wo norm aify he following relaion: n (7.) If a vecor i ime-dependen, hen
Notes on cointegration of real interest rates and real exchange rates. ρ (2)
 Noe on coinegraion of real inere rae and real exchange rae Charle ngel, Univeriy of Wiconin Le me ar wih he obervaion ha while he lieraure (mo prominenly Meee and Rogoff (988) and dion and Paul (993))
Noe on coinegraion of real inere rae and real exchange rae Charle ngel, Univeriy of Wiconin Le me ar wih he obervaion ha while he lieraure (mo prominenly Meee and Rogoff (988) and dion and Paul (993))
Cork Institute of Technology. Autumn 2006 Building Services Mechanical Paper 1 (Time: 3 Hours)
 Cork Iniue of Tehnology Bahelor of Engineering in Building Servie Engineering ward NFQ - Level 7 uumn 2006 Building Servie Mehanial Paper Time: 3 Hour Inruion Examiner: Dr. N. J. Hewi nwer FOU queion.
Cork Iniue of Tehnology Bahelor of Engineering in Building Servie Engineering ward NFQ - Level 7 uumn 2006 Building Servie Mehanial Paper Time: 3 Hour Inruion Examiner: Dr. N. J. Hewi nwer FOU queion.
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum II
 DS-SS II 7. Dire Sequene Spread Speru II ER One igh hink ha DS-SS would have he following drawak. Sine he RF andwidh i ie ha needed for a narrowand PSK ignal a he ae daa rae R, here will e ie a uh noie
DS-SS II 7. Dire Sequene Spread Speru II ER One igh hink ha DS-SS would have he following drawak. Sine he RF andwidh i ie ha needed for a narrowand PSK ignal a he ae daa rae R, here will e ie a uh noie
04. Kinetics of a second order reaction
 4. Kineics of a second order reacion Imporan conceps Reacion rae, reacion exen, reacion rae equaion, order of a reacion, firs-order reacions, second-order reacions, differenial and inegraed rae laws, Arrhenius
4. Kineics of a second order reacion Imporan conceps Reacion rae, reacion exen, reacion rae equaion, order of a reacion, firs-order reacions, second-order reacions, differenial and inegraed rae laws, Arrhenius
Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR) - State Feedback Design
 Linear Quadrai Regulaor (LQR) - Sae Feedbak Design A sysem is expressed in sae variable form as x = Ax + Bu n m wih x( ) R, u( ) R and he iniial ondiion x() = x A he sabilizaion problem using sae variable
Linear Quadrai Regulaor (LQR) - Sae Feedbak Design A sysem is expressed in sae variable form as x = Ax + Bu n m wih x( ) R, u( ) R and he iniial ondiion x() = x A he sabilizaion problem using sae variable
Algorithmic Discrete Mathematics 6. Exercise Sheet
 Algorihmic Dicree Mahemaic. Exercie Shee Deparmen of Mahemaic SS 0 PD Dr. Ulf Lorenz 7. and 8. Juni 0 Dipl.-Mah. David Meffer Verion of June, 0 Groupwork Exercie G (Heap-Sor) Ue Heap-Sor wih a min-heap
Algorihmic Dicree Mahemaic. Exercie Shee Deparmen of Mahemaic SS 0 PD Dr. Ulf Lorenz 7. and 8. Juni 0 Dipl.-Mah. David Meffer Verion of June, 0 Groupwork Exercie G (Heap-Sor) Ue Heap-Sor wih a min-heap
Mass Transfer Coefficients (MTC) and Correlations I
 Mass Transfer Mass Transfer Coeffiiens (MTC) and Correlaions I 7- Mass Transfer Coeffiiens and Correlaions I Diffusion an be desribed in wo ways:. Deailed physial desripion based on Fik s laws and he diffusion
Mass Transfer Mass Transfer Coeffiiens (MTC) and Correlaions I 7- Mass Transfer Coeffiiens and Correlaions I Diffusion an be desribed in wo ways:. Deailed physial desripion based on Fik s laws and he diffusion
Modeling the Evolution of Demand Forecasts with Application to Safety Stock Analysis in Production/Distribution Systems
 Modeling he Evoluion of Demand oreca wih Applicaion o Safey Sock Analyi in Producion/Diribuion Syem David Heah and Peer Jackon Preened by Kai Jiang Thi ummary preenaion baed on: Heah, D.C., and P.L. Jackon.
Modeling he Evoluion of Demand oreca wih Applicaion o Safey Sock Analyi in Producion/Diribuion Syem David Heah and Peer Jackon Preened by Kai Jiang Thi ummary preenaion baed on: Heah, D.C., and P.L. Jackon.
CONTROL SYSTEMS. Chapter 10 : State Space Response
 CONTROL SYSTEMS Chaper : Sae Space Repone GATE Objecive & Numerical Type Soluion Queion 5 [GATE EE 99 IIT-Bombay : Mark] Conider a econd order yem whoe ae pace repreenaion i of he form A Bu. If () (),
CONTROL SYSTEMS Chaper : Sae Space Repone GATE Objecive & Numerical Type Soluion Queion 5 [GATE EE 99 IIT-Bombay : Mark] Conider a econd order yem whoe ae pace repreenaion i of he form A Bu. If () (),
CHAPTER 7: SECOND-ORDER CIRCUITS
 EEE5: CI RCUI T THEORY CHAPTER 7: SECOND-ORDER CIRCUITS 7. Inroducion Thi chaper conider circui wih wo orage elemen. Known a econd-order circui becaue heir repone are decribed by differenial equaion ha
EEE5: CI RCUI T THEORY CHAPTER 7: SECOND-ORDER CIRCUITS 7. Inroducion Thi chaper conider circui wih wo orage elemen. Known a econd-order circui becaue heir repone are decribed by differenial equaion ha
1 Motivation and Basic Definitions
 CSCE : Deign and Analyi of Algorihm Noe on Max Flow Fall 20 (Baed on he preenaion in Chaper 26 of Inroducion o Algorihm, 3rd Ed. by Cormen, Leieron, Rive and Sein.) Moivaion and Baic Definiion Conider
CSCE : Deign and Analyi of Algorihm Noe on Max Flow Fall 20 (Baed on he preenaion in Chaper 26 of Inroducion o Algorihm, 3rd Ed. by Cormen, Leieron, Rive and Sein.) Moivaion and Baic Definiion Conider
EE202 Circuit Theory II
 EE202 Circui Theory II 2017-2018, Spring Dr. Yılmaz KALKAN I. Inroducion & eview of Fir Order Circui (Chaper 7 of Nilon - 3 Hr. Inroducion, C and L Circui, Naural and Sep epone of Serie and Parallel L/C
EE202 Circui Theory II 2017-2018, Spring Dr. Yılmaz KALKAN I. Inroducion & eview of Fir Order Circui (Chaper 7 of Nilon - 3 Hr. Inroducion, C and L Circui, Naural and Sep epone of Serie and Parallel L/C
13.1 Circuit Elements in the s Domain Circuit Analysis in the s Domain The Transfer Function and Natural Response 13.
 Chaper 3 The Laplace Tranform in Circui Analyi 3. Circui Elemen in he Domain 3.-3 Circui Analyi in he Domain 3.4-5 The Tranfer Funcion and Naural Repone 3.6 The Tranfer Funcion and he Convoluion Inegral
Chaper 3 The Laplace Tranform in Circui Analyi 3. Circui Elemen in he Domain 3.-3 Circui Analyi in he Domain 3.4-5 The Tranfer Funcion and Naural Repone 3.6 The Tranfer Funcion and he Convoluion Inegral
Introduction to Congestion Games
 Algorihmic Game Theory, Summer 2017 Inroducion o Congeion Game Lecure 1 (5 page) Inrucor: Thoma Keelheim In hi lecure, we ge o know congeion game, which will be our running example for many concep in game
Algorihmic Game Theory, Summer 2017 Inroducion o Congeion Game Lecure 1 (5 page) Inrucor: Thoma Keelheim In hi lecure, we ge o know congeion game, which will be our running example for many concep in game
2. VECTORS. R Vectors are denoted by bold-face characters such as R, V, etc. The magnitude of a vector, such as R, is denoted as R, R, V
 ME 352 VETS 2. VETS Vecor algebra form he mahemaical foundaion for kinemaic and dnamic. Geomer of moion i a he hear of boh he kinemaic and dnamic of mechanical em. Vecor anali i he imehonored ool for decribing
ME 352 VETS 2. VETS Vecor algebra form he mahemaical foundaion for kinemaic and dnamic. Geomer of moion i a he hear of boh he kinemaic and dnamic of mechanical em. Vecor anali i he imehonored ool for decribing
Two Coupled Oscillators / Normal Modes
 Lecure 3 Phys 3750 Two Coupled Oscillaors / Normal Modes Overview and Moivaion: Today we ake a small, bu significan, sep owards wave moion. We will no ye observe waves, bu his sep is imporan in is own
Lecure 3 Phys 3750 Two Coupled Oscillaors / Normal Modes Overview and Moivaion: Today we ake a small, bu significan, sep owards wave moion. We will no ye observe waves, bu his sep is imporan in is own
Network Flows: Introduction & Maximum Flow
 CSC 373 - lgorihm Deign, nalyi, and Complexiy Summer 2016 Lalla Mouaadid Nework Flow: Inroducion & Maximum Flow We now urn our aenion o anoher powerful algorihmic echnique: Local Search. In a local earch
CSC 373 - lgorihm Deign, nalyi, and Complexiy Summer 2016 Lalla Mouaadid Nework Flow: Inroducion & Maximum Flow We now urn our aenion o anoher powerful algorihmic echnique: Local Search. In a local earch
5.2 GRAPHICAL VELOCITY ANALYSIS Polygon Method
 ME 352 GRHICL VELCITY NLYSIS 52 GRHICL VELCITY NLYSIS olygon Mehod Velociy analyi form he hear of kinemaic and dynamic of mechanical yem Velociy analyi i uually performed following a poiion analyi; ie,
ME 352 GRHICL VELCITY NLYSIS 52 GRHICL VELCITY NLYSIS olygon Mehod Velociy analyi form he hear of kinemaic and dynamic of mechanical yem Velociy analyi i uually performed following a poiion analyi; ie,
Types of Exponential Smoothing Methods. Simple Exponential Smoothing. Simple Exponential Smoothing
 M Business Forecasing Mehods Exponenial moohing Mehods ecurer : Dr Iris Yeung Room No : P79 Tel No : 788 8 Types of Exponenial moohing Mehods imple Exponenial moohing Double Exponenial moohing Brown s
M Business Forecasing Mehods Exponenial moohing Mehods ecurer : Dr Iris Yeung Room No : P79 Tel No : 788 8 Types of Exponenial moohing Mehods imple Exponenial moohing Double Exponenial moohing Brown s
Biol. 356 Lab 8. Mortality, Recruitment, and Migration Rates
 Biol. 356 Lab 8. Moraliy, Recruimen, and Migraion Raes (modified from Cox, 00, General Ecology Lab Manual, McGraw Hill) Las week we esimaed populaion size hrough several mehods. One assumpion of all hese
Biol. 356 Lab 8. Moraliy, Recruimen, and Migraion Raes (modified from Cox, 00, General Ecology Lab Manual, McGraw Hill) Las week we esimaed populaion size hrough several mehods. One assumpion of all hese
Discussion Session 2 Constant Acceleration/Relative Motion Week 03
 PHYS 100 Dicuion Seion Conan Acceleraion/Relaive Moion Week 03 The Plan Today you will work wih your group explore he idea of reference frame (i.e. relaive moion) and moion wih conan acceleraion. You ll
PHYS 100 Dicuion Seion Conan Acceleraion/Relaive Moion Week 03 The Plan Today you will work wih your group explore he idea of reference frame (i.e. relaive moion) and moion wih conan acceleraion. You ll
20. Applications of the Genetic-Drift Model
 0. Applicaions of he Geneic-Drif Model 1) Deermining he probabiliy of forming any paricular combinaion of genoypes in he nex generaion: Example: If he parenal allele frequencies are p 0 = 0.35 and q 0
0. Applicaions of he Geneic-Drif Model 1) Deermining he probabiliy of forming any paricular combinaion of genoypes in he nex generaion: Example: If he parenal allele frequencies are p 0 = 0.35 and q 0
T L. t=1. Proof of Lemma 1. Using the marginal cost accounting in Equation(4) and standard arguments. t )+Π RB. t )+K 1(Q RB
 Elecronic Companion EC.1. Proofs of Technical Lemmas and Theorems LEMMA 1. Le C(RB) be he oal cos incurred by he RB policy. Then we have, T L E[C(RB)] 3 E[Z RB ]. (EC.1) Proof of Lemma 1. Using he marginal
Elecronic Companion EC.1. Proofs of Technical Lemmas and Theorems LEMMA 1. Le C(RB) be he oal cos incurred by he RB policy. Then we have, T L E[C(RB)] 3 E[Z RB ]. (EC.1) Proof of Lemma 1. Using he marginal
6 December 2013 H. T. Hoang - www4.hcmut.edu.vn/~hthoang/ 1
 Lecure Noe Fundamenal of Conrol Syem Inrucor: Aoc. Prof. Dr. Huynh Thai Hoang Deparmen of Auomaic Conrol Faculy of Elecrical & Elecronic Engineering Ho Chi Minh Ciy Univeriy of Technology Email: hhoang@hcmu.edu.vn
Lecure Noe Fundamenal of Conrol Syem Inrucor: Aoc. Prof. Dr. Huynh Thai Hoang Deparmen of Auomaic Conrol Faculy of Elecrical & Elecronic Engineering Ho Chi Minh Ciy Univeriy of Technology Email: hhoang@hcmu.edu.vn
Explaining Total Factor Productivity. Ulrich Kohli University of Geneva December 2015
 Explaining Toal Facor Produciviy Ulrich Kohli Universiy of Geneva December 2015 Needed: A Theory of Toal Facor Produciviy Edward C. Presco (1998) 2 1. Inroducion Toal Facor Produciviy (TFP) has become
Explaining Toal Facor Produciviy Ulrich Kohli Universiy of Geneva December 2015 Needed: A Theory of Toal Facor Produciviy Edward C. Presco (1998) 2 1. Inroducion Toal Facor Produciviy (TFP) has become
Chapter 6. Laplace Transforms
 Chaper 6. Laplace Tranform Kreyzig by YHLee;45; 6- An ODE i reduced o an algebraic problem by operaional calculu. The equaion i olved by algebraic manipulaion. The reul i ranformed back for he oluion of
Chaper 6. Laplace Tranform Kreyzig by YHLee;45; 6- An ODE i reduced o an algebraic problem by operaional calculu. The equaion i olved by algebraic manipulaion. The reul i ranformed back for he oluion of
( ) = Q 0. ( ) R = R dq. ( t) = I t
 ircuis onceps The addiion of a simple capacior o a circui of resisors allows wo relaed phenomena o occur The observaion ha he ime-dependence of a complex waveform is alered by he circui is referred o as
ircuis onceps The addiion of a simple capacior o a circui of resisors allows wo relaed phenomena o occur The observaion ha he ime-dependence of a complex waveform is alered by he circui is referred o as
Topic Astable Circuits. Recall that an astable circuit has two unstable states;
 Topic 2.2. Asable Circuis. Learning Objecives: A he end o his opic you will be able o; Recall ha an asable circui has wo unsable saes; Explain he operaion o a circui based on a Schmi inverer, and esimae
Topic 2.2. Asable Circuis. Learning Objecives: A he end o his opic you will be able o; Recall ha an asable circui has wo unsable saes; Explain he operaion o a circui based on a Schmi inverer, and esimae
Angular Motion, Speed and Velocity
 Add Imporan Angular Moion, Speed and Velociy Page: 163 Noe/Cue Here Angular Moion, Speed and Velociy NGSS Sandard: N/A MA Curriculum Framework (006): 1.1, 1. AP Phyic 1 Learning Objecive: 3.A.1.1, 3.A.1.3
Add Imporan Angular Moion, Speed and Velociy Page: 163 Noe/Cue Here Angular Moion, Speed and Velociy NGSS Sandard: N/A MA Curriculum Framework (006): 1.1, 1. AP Phyic 1 Learning Objecive: 3.A.1.1, 3.A.1.3
Lecture 3: Exponential Smoothing
 NATCOR: Forecasing & Predicive Analyics Lecure 3: Exponenial Smoohing John Boylan Lancaser Cenre for Forecasing Deparmen of Managemen Science Mehods and Models Forecasing Mehod A (numerical) procedure
NATCOR: Forecasing & Predicive Analyics Lecure 3: Exponenial Smoohing John Boylan Lancaser Cenre for Forecasing Deparmen of Managemen Science Mehods and Models Forecasing Mehod A (numerical) procedure
Problem Set 5. Graduate Macro II, Spring 2017 The University of Notre Dame Professor Sims
 Problem Se 5 Graduae Macro II, Spring 2017 The Universiy of Nore Dame Professor Sims Insrucions: You may consul wih oher members of he class, bu please make sure o urn in your own work. Where applicable,
Problem Se 5 Graduae Macro II, Spring 2017 The Universiy of Nore Dame Professor Sims Insrucions: You may consul wih oher members of he class, bu please make sure o urn in your own work. Where applicable,
INTRODUCTION TO INERTIAL CONFINEMENT FUSION
 INTODUCTION TO INETIAL CONFINEMENT FUSION. Bei Lecure 7 Soluion of he imple dynamic igniion model ecap from previou lecure: imple dynamic model ecap: 1D model dynamic model ρ P() T enhalpy flux ino ho
INTODUCTION TO INETIAL CONFINEMENT FUSION. Bei Lecure 7 Soluion of he imple dynamic igniion model ecap from previou lecure: imple dynamic model ecap: 1D model dynamic model ρ P() T enhalpy flux ino ho
Chapter 7: Solving Trig Equations
 Haberman MTH Secion I: The Trigonomeric Funcions Chaper 7: Solving Trig Equaions Le s sar by solving a couple of equaions ha involve he sine funcion EXAMPLE a: Solve he equaion sin( ) The inverse funcions
Haberman MTH Secion I: The Trigonomeric Funcions Chaper 7: Solving Trig Equaions Le s sar by solving a couple of equaions ha involve he sine funcion EXAMPLE a: Solve he equaion sin( ) The inverse funcions
Notes 04 largely plagiarized by %khc
 Noes 04 largely plagiarized by %khc Convoluion Recap Some ricks: x() () =x() x() (, 0 )=x(, 0 ) R ț x() u() = x( )d x() () =ẋ() This hen ells us ha an inegraor has impulse response h() =u(), and ha a differeniaor
Noes 04 largely plagiarized by %khc Convoluion Recap Some ricks: x() () =x() x() (, 0 )=x(, 0 ) R ț x() u() = x( )d x() () =ẋ() This hen ells us ha an inegraor has impulse response h() =u(), and ha a differeniaor
RC, RL and RLC circuits
 Name Dae Time o Complee h m Parner Course/ Secion / Grade RC, RL and RLC circuis Inroducion In his experimen we will invesigae he behavior of circuis conaining combinaions of resisors, capaciors, and inducors.
Name Dae Time o Complee h m Parner Course/ Secion / Grade RC, RL and RLC circuis Inroducion In his experimen we will invesigae he behavior of circuis conaining combinaions of resisors, capaciors, and inducors.
Vehicle Arrival Models : Headway
 Chaper 12 Vehicle Arrival Models : Headway 12.1 Inroducion Modelling arrival of vehicle a secion of road is an imporan sep in raffic flow modelling. I has imporan applicaion in raffic flow simulaion where
Chaper 12 Vehicle Arrival Models : Headway 12.1 Inroducion Modelling arrival of vehicle a secion of road is an imporan sep in raffic flow modelling. I has imporan applicaion in raffic flow simulaion where
EF 151 Exam #2 - Spring, 2014 Page 1 of 6
 EF 5 Exam # - Spring, 04 Page of 6 Name: Secion: Inrucion: Pu your name and ecion on he exam. Do no open he e unil you are old o do o. Wrie your final anwer in he box proided If you finih wih le han 5
EF 5 Exam # - Spring, 04 Page of 6 Name: Secion: Inrucion: Pu your name and ecion on he exam. Do no open he e unil you are old o do o. Wrie your final anwer in he box proided If you finih wih le han 5
Chapter 8 The Complete Response of RL and RC Circuits
 Chaper 8 he Complee Response of R and RC Ciruis Exerises Ex 8.3-1 Before he swih loses: Afer he swih loses: 2 = = 8 Ω so = 8 0.05 = 0.4 s. 0.25 herefore R ( ) Finally, 2.5 ( ) = o + ( (0) o ) = 2 + V for
Chaper 8 he Complee Response of R and RC Ciruis Exerises Ex 8.3-1 Before he swih loses: Afer he swih loses: 2 = = 8 Ω so = 8 0.05 = 0.4 s. 0.25 herefore R ( ) Finally, 2.5 ( ) = o + ( (0) o ) = 2 + V for
Lecture 12. Aperture and Noise. Jaeha Kim Mixed-Signal IC and System Group (MICS) Seoul National University
 Lecure. Aperure and Noie Analyi of locked omparaor Jaeha Kim Mixed-Signal I and Syem Group MIS Seoul Naional Univeriy jaeha@ieee.org locked omparaor a.k.a. regeneraive amplifier, ene-amplifier, flip-flop,
Lecure. Aperure and Noie Analyi of locked omparaor Jaeha Kim Mixed-Signal I and Syem Group MIS Seoul Naional Univeriy jaeha@ieee.org locked omparaor a.k.a. regeneraive amplifier, ene-amplifier, flip-flop,
3.1.3 INTRODUCTION TO DYNAMIC OPTIMIZATION: DISCRETE TIME PROBLEMS. A. The Hamiltonian and First-Order Conditions in a Finite Time Horizon
 3..3 INRODUCION O DYNAMIC OPIMIZAION: DISCREE IME PROBLEMS A. he Hamilonian and Firs-Order Condiions in a Finie ime Horizon Define a new funcion, he Hamilonian funcion, H. H he change in he oal value of
3..3 INRODUCION O DYNAMIC OPIMIZAION: DISCREE IME PROBLEMS A. he Hamilonian and Firs-Order Condiions in a Finie ime Horizon Define a new funcion, he Hamilonian funcion, H. H he change in he oal value of
Boyce/DiPrima 9 th ed, Ch 6.1: Definition of. Laplace Transform. In this chapter we use the Laplace transform to convert a
 Boye/DiPrima 9 h ed, Ch 6.: Definiion of Laplae Transform Elemenary Differenial Equaions and Boundary Value Problems, 9 h ediion, by William E. Boye and Rihard C. DiPrima, 2009 by John Wiley & Sons, In.
Boye/DiPrima 9 h ed, Ch 6.: Definiion of Laplae Transform Elemenary Differenial Equaions and Boundary Value Problems, 9 h ediion, by William E. Boye and Rihard C. DiPrima, 2009 by John Wiley & Sons, In.
Math 116 Second Midterm March 21, 2016
 Mah 6 Second Miderm March, 06 UMID: EXAM SOLUTIONS Iniials: Insrucor: Secion:. Do no open his exam unil you are old o do so.. Do no wrie your name anywhere on his exam. 3. This exam has pages including
Mah 6 Second Miderm March, 06 UMID: EXAM SOLUTIONS Iniials: Insrucor: Secion:. Do no open his exam unil you are old o do so.. Do no wrie your name anywhere on his exam. 3. This exam has pages including
Optimal Waveform Design with Constant Modulus Constraint for Rank-One Target Detection
 Senor & Tranduer Vol. 63 Iue January 4 pp. 39-43 Senor & Tranduer 4 by IFSA Publihing S. L. p://www.enorporal.om Opimal Waveform Deign wih Conan odulu Conrain for Rank-One Targe Deeion Fengming XIN Bin
Senor & Tranduer Vol. 63 Iue January 4 pp. 39-43 Senor & Tranduer 4 by IFSA Publihing S. L. p://www.enorporal.om Opimal Waveform Deign wih Conan odulu Conrain for Rank-One Targe Deeion Fengming XIN Bin
LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION
 CHBE320 LECTURE V LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dep. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 5-1 Road Map of he Lecure V Laplace Transform and Transfer funcions
CHBE320 LECTURE V LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dep. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 5-1 Road Map of he Lecure V Laplace Transform and Transfer funcions
KEY. Math 334 Midterm I Fall 2008 sections 001 and 003 Instructor: Scott Glasgow
 1 KEY Mah 4 Miderm I Fall 8 secions 1 and Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his eam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on our own paper, preferabl engineering
1 KEY Mah 4 Miderm I Fall 8 secions 1 and Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his eam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on our own paper, preferabl engineering
Module 2 F c i k c s la l w a s o s f dif di fusi s o i n
 Module Fick s laws of diffusion Fick s laws of diffusion and hin film soluion Adolf Fick (1855) proposed: d J α d d d J (mole/m s) flu (m /s) diffusion coefficien and (mole/m 3 ) concenraion of ions, aoms
Module Fick s laws of diffusion Fick s laws of diffusion and hin film soluion Adolf Fick (1855) proposed: d J α d d d J (mole/m s) flu (m /s) diffusion coefficien and (mole/m 3 ) concenraion of ions, aoms
Lab 10: RC, RL, and RLC Circuits
 Lab 10: RC, RL, and RLC Circuis In his experimen, we will invesigae he behavior of circuis conaining combinaions of resisors, capaciors, and inducors. We will sudy he way volages and currens change in
Lab 10: RC, RL, and RLC Circuis In his experimen, we will invesigae he behavior of circuis conaining combinaions of resisors, capaciors, and inducors. We will sudy he way volages and currens change in
Design of Controller for Robot Position Control
 eign of Conroller for Robo oiion Conrol Two imporan goal of conrol: 1. Reference inpu racking: The oupu mu follow he reference inpu rajecory a quickly a poible. Se-poin racking: Tracking when he reference
eign of Conroller for Robo oiion Conrol Two imporan goal of conrol: 1. Reference inpu racking: The oupu mu follow he reference inpu rajecory a quickly a poible. Se-poin racking: Tracking when he reference
Stat13 Homework 7. Suggested Solutions
 Sa3 Homework 7 hp://www.a.ucla.edu/~dinov/coure_uden.hml Suggeed Soluion Queion 7.50 Le denoe infeced and denoe noninfeced. H 0 : Malaria doe no affec red cell coun (µ µ ) H A : Malaria reduce red cell
Sa3 Homework 7 hp://www.a.ucla.edu/~dinov/coure_uden.hml Suggeed Soluion Queion 7.50 Le denoe infeced and denoe noninfeced. H 0 : Malaria doe no affec red cell coun (µ µ ) H A : Malaria reduce red cell
Chapter 7 Response of First-order RL and RC Circuits
 Chaper 7 Response of Firs-order RL and RC Circuis 7.- The Naural Response of RL and RC Circuis 7.3 The Sep Response of RL and RC Circuis 7.4 A General Soluion for Sep and Naural Responses 7.5 Sequenial
Chaper 7 Response of Firs-order RL and RC Circuis 7.- The Naural Response of RL and RC Circuis 7.3 The Sep Response of RL and RC Circuis 7.4 A General Soluion for Sep and Naural Responses 7.5 Sequenial
Some Basic Information about M-S-D Systems
 Some Basic Informaion abou M-S-D Sysems 1 Inroducion We wan o give some summary of he facs concerning unforced (homogeneous) and forced (non-homogeneous) models for linear oscillaors governed by second-order,
Some Basic Informaion abou M-S-D Sysems 1 Inroducion We wan o give some summary of he facs concerning unforced (homogeneous) and forced (non-homogeneous) models for linear oscillaors governed by second-order,
Performance Comparison of LCMV-based Space-time 2D Array and Ambiguity Problem
 Inernaional journal of cience Commerce and umaniie Volume No 2 No 3 April 204 Performance Comparion of LCMV-baed pace-ime 2D Arra and Ambigui Problem 2 o uan Chang and Jin hinghia Deparmen of Communicaion
Inernaional journal of cience Commerce and umaniie Volume No 2 No 3 April 204 Performance Comparion of LCMV-baed pace-ime 2D Arra and Ambigui Problem 2 o uan Chang and Jin hinghia Deparmen of Communicaion
Laplace Transform. Inverse Laplace Transform. e st f(t)dt. (2)
 Laplace Tranform Maoud Malek The Laplace ranform i an inegral ranform named in honor of mahemaician and aronomer Pierre-Simon Laplace, who ued he ranform in hi work on probabiliy heory. I i a powerful
Laplace Tranform Maoud Malek The Laplace ranform i an inegral ranform named in honor of mahemaician and aronomer Pierre-Simon Laplace, who ued he ranform in hi work on probabiliy heory. I i a powerful
An Improved Anti-windup Control Using a PI Controller
 05 Third nernaional Conference on Arificial nelligence, Modelling and Simulaion An mroved Ani-windu Conrol Uing a P Conroller Kyohei Saai Graduae School of Science and Technology Meiji univeriy Kanagawa,
05 Third nernaional Conference on Arificial nelligence, Modelling and Simulaion An mroved Ani-windu Conrol Uing a P Conroller Kyohei Saai Graduae School of Science and Technology Meiji univeriy Kanagawa,
Diebold, Chapter 7. Francis X. Diebold, Elements of Forecasting, 4th Edition (Mason, Ohio: Cengage Learning, 2006). Chapter 7. Characterizing Cycles
 Diebold, Chaper 7 Francis X. Diebold, Elemens of Forecasing, 4h Ediion (Mason, Ohio: Cengage Learning, 006). Chaper 7. Characerizing Cycles Afer compleing his reading you should be able o: Define covariance
Diebold, Chaper 7 Francis X. Diebold, Elemens of Forecasing, 4h Ediion (Mason, Ohio: Cengage Learning, 006). Chaper 7. Characerizing Cycles Afer compleing his reading you should be able o: Define covariance
13.1 Accelerating Objects
 13.1 Acceleraing Objec A you learned in Chaper 12, when you are ravelling a a conan peed in a raigh line, you have uniform moion. However, mo objec do no ravel a conan peed in a raigh line o hey do no
13.1 Acceleraing Objec A you learned in Chaper 12, when you are ravelling a a conan peed in a raigh line, you have uniform moion. However, mo objec do no ravel a conan peed in a raigh line o hey do no
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION
 KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION PREVIEW Kinemaics is he sudy of how hings move how far (disance and displacemen), how fas (speed and velociy), and how fas ha how fas changes (acceleraion). We say ha an objec
KINEMATICS IN ONE DIMENSION PREVIEW Kinemaics is he sudy of how hings move how far (disance and displacemen), how fas (speed and velociy), and how fas ha how fas changes (acceleraion). We say ha an objec
Homework 6 AERE331 Spring 2019 Due 4/24(W) Name Sec. 1 / 2
 Homework 6 AERE33 Spring 9 Due 4/4(W) Name Sec / PROBLEM (5p In PROBLEM 4 of HW4 we used he frequency domain o design a yaw/rudder feedback conrol sysem for a plan wih ransfer funcion 46 Gp () s The conroller
Homework 6 AERE33 Spring 9 Due 4/4(W) Name Sec / PROBLEM (5p In PROBLEM 4 of HW4 we used he frequency domain o design a yaw/rudder feedback conrol sysem for a plan wih ransfer funcion 46 Gp () s The conroller
Mathcad Lecture #8 In-class Worksheet Curve Fitting and Interpolation
 Mahcad Lecure #8 In-class Workshee Curve Fiing and Inerpolaion A he end of his lecure, you will be able o: explain he difference beween curve fiing and inerpolaion decide wheher curve fiing or inerpolaion
Mahcad Lecure #8 In-class Workshee Curve Fiing and Inerpolaion A he end of his lecure, you will be able o: explain he difference beween curve fiing and inerpolaion decide wheher curve fiing or inerpolaion
Additional Methods for Solving DSGE Models
 Addiional Mehod for Solving DSGE Model Karel Meren, Cornell Univeriy Reference King, R. G., Ploer, C. I. & Rebelo, S. T. (1988), Producion, growh and buine cycle: I. he baic neoclaical model, Journal of
Addiional Mehod for Solving DSGE Model Karel Meren, Cornell Univeriy Reference King, R. G., Ploer, C. I. & Rebelo, S. T. (1988), Producion, growh and buine cycle: I. he baic neoclaical model, Journal of
Physics 127b: Statistical Mechanics. Fokker-Planck Equation. Time Evolution
 Physics 7b: Saisical Mechanics Fokker-Planck Equaion The Langevin equaion approach o he evoluion of he velociy disribuion for he Brownian paricle migh leave you uncomforable. A more formal reamen of his
Physics 7b: Saisical Mechanics Fokker-Planck Equaion The Langevin equaion approach o he evoluion of he velociy disribuion for he Brownian paricle migh leave you uncomforable. A more formal reamen of his
Single Phase Line Frequency Uncontrolled Rectifiers
 Single Phae Line Frequency Unconrolle Recifier Kevin Gaughan 24-Nov-03 Single Phae Unconrolle Recifier 1 Topic Baic operaion an Waveform (nucive Loa) Power Facor Calculaion Supply curren Harmonic an Th
Single Phae Line Frequency Unconrolle Recifier Kevin Gaughan 24-Nov-03 Single Phae Unconrolle Recifier 1 Topic Baic operaion an Waveform (nucive Loa) Power Facor Calculaion Supply curren Harmonic an Th
Micrologic Control units 2.0 and 5.0 Low Voltage Products
 Micrologic Conol unis.0 and 5.0 Low Volage Producs User manual We do more wih eleciciy. Micrologic Conol unis.0 and 5.0 Discovering your conol uni Idenifying your conol uni Overview of funcions 4 Seing
Micrologic Conol unis.0 and 5.0 Low Volage Producs User manual We do more wih eleciciy. Micrologic Conol unis.0 and 5.0 Discovering your conol uni Idenifying your conol uni Overview of funcions 4 Seing
Distribution of Estimates
 Disribuion of Esimaes From Economerics (40) Linear Regression Model Assume (y,x ) is iid and E(x e )0 Esimaion Consisency y α + βx + he esimaes approach he rue values as he sample size increases Esimaion
Disribuion of Esimaes From Economerics (40) Linear Regression Model Assume (y,x ) is iid and E(x e )0 Esimaion Consisency y α + βx + he esimaes approach he rue values as he sample size increases Esimaion
Shiva Akhtarian MSc Student, Department of Computer Engineering and Information Technology, Payame Noor University, Iran
 Curren Trends in Technology and Science ISSN : 79-055 8hSASTech 04 Symposium on Advances in Science & Technology-Commission-IV Mashhad, Iran A New for Sofware Reliabiliy Evaluaion Based on NHPP wih Imperfec
Curren Trends in Technology and Science ISSN : 79-055 8hSASTech 04 Symposium on Advances in Science & Technology-Commission-IV Mashhad, Iran A New for Sofware Reliabiliy Evaluaion Based on NHPP wih Imperfec
mywbut.com Lesson 11 Study of DC transients in R-L-C Circuits
 mywbu.om esson Sudy of DC ransiens in R--C Ciruis mywbu.om Objeives Be able o wrie differenial equaion for a d iruis onaining wo sorage elemens in presene of a resisane. To develop a horough undersanding
mywbu.om esson Sudy of DC ransiens in R--C Ciruis mywbu.om Objeives Be able o wrie differenial equaion for a d iruis onaining wo sorage elemens in presene of a resisane. To develop a horough undersanding
Exponential Weighted Moving Average (EWMA) Chart Under The Assumption of Moderateness And Its 3 Control Limits
 DOI: 0.545/mjis.07.5009 Exponenial Weighed Moving Average (EWMA) Char Under The Assumpion of Moderaeness And Is 3 Conrol Limis KALPESH S TAILOR Assisan Professor, Deparmen of Saisics, M. K. Bhavnagar Universiy,
DOI: 0.545/mjis.07.5009 Exponenial Weighed Moving Average (EWMA) Char Under The Assumpion of Moderaeness And Is 3 Conrol Limis KALPESH S TAILOR Assisan Professor, Deparmen of Saisics, M. K. Bhavnagar Universiy,
PHYSICS 151 Notes for Online Lecture #4
 PHYSICS 5 Noe for Online Lecure #4 Acceleraion The ga pedal in a car i alo called an acceleraor becaue preing i allow you o change your elociy. Acceleraion i how fa he elociy change. So if you ar fro re
PHYSICS 5 Noe for Online Lecure #4 Acceleraion The ga pedal in a car i alo called an acceleraor becaue preing i allow you o change your elociy. Acceleraion i how fa he elociy change. So if you ar fro re
Lecture 5. Time series: ECM. Bernardina Algieri Department Economics, Statistics and Finance
 Lecure 5 Time series: ECM Bernardina Algieri Deparmen Economics, Saisics and Finance Conens Time Series Modelling Coinegraion Error Correcion Model Two Seps, Engle-Granger procedure Error Correcion Model
Lecure 5 Time series: ECM Bernardina Algieri Deparmen Economics, Saisics and Finance Conens Time Series Modelling Coinegraion Error Correcion Model Two Seps, Engle-Granger procedure Error Correcion Model
Algorithms and Data Structures 2011/12 Week 9 Solutions (Tues 15th - Fri 18th Nov)
 Algorihm and Daa Srucure 2011/ Week Soluion (Tue 15h - Fri 18h No) 1. Queion: e are gien 11/16 / 15/20 8/13 0/ 1/ / 11/1 / / To queion: (a) Find a pair of ube X, Y V uch ha f(x, Y) = f(v X, Y). (b) Find
Algorihm and Daa Srucure 2011/ Week Soluion (Tue 15h - Fri 18h No) 1. Queion: e are gien 11/16 / 15/20 8/13 0/ 1/ / 11/1 / / To queion: (a) Find a pair of ube X, Y V uch ha f(x, Y) = f(v X, Y). (b) Find
More Digital Logic. t p output. Low-to-high and high-to-low transitions could have different t p. V in (t)
 EECS 4 Spring 23 Lecure 2 EECS 4 Spring 23 Lecure 2 More igial Logic Gae delay and signal propagaion Clocked circui elemens (flip-flop) Wriing a word o memory Simplifying digial circuis: Karnaugh maps
EECS 4 Spring 23 Lecure 2 EECS 4 Spring 23 Lecure 2 More igial Logic Gae delay and signal propagaion Clocked circui elemens (flip-flop) Wriing a word o memory Simplifying digial circuis: Karnaugh maps
TP B.2 Rolling resistance, spin resistance, and "ball turn"
 echnical proof TP B. olling reiance, pin reiance, and "ball urn" upporing: The Illuraed Principle of Pool and Billiard hp://billiard.coloae.edu by Daid G. Alciaore, PhD, PE ("Dr. Dae") echnical proof originally
echnical proof TP B. olling reiance, pin reiance, and "ball urn" upporing: The Illuraed Principle of Pool and Billiard hp://billiard.coloae.edu by Daid G. Alciaore, PhD, PE ("Dr. Dae") echnical proof originally
Errata (1 st Edition)
 P Sandborn, os Analysis of Elecronic Sysems, s Ediion, orld Scienific, Singapore, 03 Erraa ( s Ediion) S K 05D Page 8 Equaion (7) should be, E 05D E Nu e S K he L appearing in he equaion in he book does
P Sandborn, os Analysis of Elecronic Sysems, s Ediion, orld Scienific, Singapore, 03 Erraa ( s Ediion) S K 05D Page 8 Equaion (7) should be, E 05D E Nu e S K he L appearing in he equaion in he book does
