6.8 Laplace Transform: General Formulas
|
|
|
- Holly McLaughlin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 48 HAP. 6 Laplace Tranform 6.8 Laplace Tranform: General Formula Formula Name, ommen Sec. F() l{ f ()} e f () d f () l {F()} Definiion of Tranform Invere Tranform 6. l{af () bg()} al{f ()} bl{g()} Lineariy 6. l{e a f ()} F( a) l {F( a)} e a f () -Shifing (Fir Shifing Theorem) 6. l( f r) l( f ) f () l( f ) l( f ) f () f r() l( f (n) ) n l( f ) (n ) f () Á Á f (n ) () l e f () df l( f ) Differeniaion of Funcion Inegraion of Funcion 6. ( f * g)() f ()g( ) d f ( )g() d l( f * g) l( f )l(g) onvoluion 6.5 l{ f ( a) u( a)} e a F() l {e a F ()} f ( a) u( a) -Shifing (Second Shifing Theorem) 6. l{f ()} Fr() l e f () f F( ) d Differeniaion of Tranform Inegraion of Tranform 6.6 l( f ) p p e f () d e f Periodic wih Period p 6.4 Projec 6
2 SE. 6.9 Table of Laplace Tranform Table of Laplace Tranform For more exenive able, ee Ref. [A9] in Appendix. F () l{ f ()} > > > n > > > > a (n,, Á ) (a ) n >(n )! > p >p a > (a) f () Sec a ( a) ( a) n (n,, Á ) ( a) k (k ) e a e a (n )! n e a (k) k e a 6. ( a)( b) ( a)( b) (a b) (a b) a b (ea e b ) a b (aea be b ) v v a a ( a) v a ( a) v in v v co v inh a a coh a v ea inh v e a co v 6. 9 ( v ) ( v ) ( co v) v (v in v) v x 6. (coninued )
3 5 HAP. 6 Laplace Tranform Table of Laplace Tranform (coninued ) F () l{ f ()} f () Sec. 4 ( v ) ( v ) ( v ) ( a )( b ) (a b ) (in v v co v) v in v v (in v v co v) v (co a co b) b a k 4 4 4k 4 4 k 4 4 k 4 (in k co k co k inh k) 4k in k inh k k (inh k in k) k (coh k co k) k 9 e (a b)> I a a b b I 5.5 a b J (a) J 5.4 a p ea ( a) ( a) > p (k) a k > (k ) a b I k > (a) ( a ) k I e a > u( a) 6. 5 e a d( a) J (k) J a b e k> e k> ek> > e k (k ) p (eb e a ) co k p inh k pk k p e k >4 (coninued )
4 haper 6 Review Queion and Problem 5 Table of Laplace Tranform (coninued ) F () l{ f ()} f () Sec. 4 ln ln g (g.577) g ln a b (eb e a ) 4 ln v ( co v) ln a arcan v arcco ( coh a) in v Si() App. A. HAPTER 6 REVIEW QUESTIONS AND PROBLEMS. Sae he Laplace ranform of a few imple funcion from memory.. Wha are he ep of olving an ODE by he Laplace ranform?. In wha cae of olving ODE i he preen mehod preferable o ha in hap.? 4. Wha propery of he Laplace ranform i crucial in olving ODE? 5. I l{f () g()} l{f ()} l{g()}? l{f ()g()} l{f ()}l{g()}? Explain. 6. When and how do you ue he uni ep funcion and Dirac dela? 7. If you know f () l {F()}, how would you find l {F()> }? 8. Explain he ue of he wo hifing heorem from memory. 9. an a diconinuou funcion have a Laplace ranform? Give reaon.. If wo differen coninuou funcion have ranform, he laer are differen. Why i hi pracically imporan? 9 LAPLAE TRANSFORMS Find he ranform, indicaing he mehod ued and howing he deail.. 5 coh inh. e (co 4 in 4). in ( p) 4. 6 u( 4) 5. e > u( ) 6. u( p) in 7. co in 8. (in v) * (co v) 9. * e 8 INVERSE LAPLAE TRANSFORM Find he invere ranform, indicaing he mehod ued and howing he deail: e v co u in u v ( ) ( 6.5) 4 6. e ODE AND SYSTEMS Solve by he Laplace ranform, howing he deail and graphing he oluion: 9. y 4yr 5y 5, y() 5, yr() 5. y 6y 4d( p), y(), yr()
5 5 HAP. 6 Laplace Tranform. y yr y u( p) in, y(), yr(). y 4y d( p) d( p), y(), yr() y yr y u( ), y(), yr(). 4. y r y, y r 4y d( p), y (), y () 5. y r y 4y, y () y r y y, y (), 6. y r y 4y, y r y y, y () 4, y () 4 7. y r y u( p), y r y u( p), y (), y () 8 45 MASS SPRING SYSTEMS, IRUITS, NETWORKS Model and olve by he Laplace ranform: 8. Show ha he model of he mechanical yem in Fig. 49 (no fricion, no damping) i m y m y k y k ( y y ) k ( y y ) k y ). y k k k y 4. Find and graph he charge q() and he curren i() in he L-circui in Fig. 5, auming L H, F, v() e if p, v() if p, and zero iniial curren and charge. 4. Find he curren i() in he RL-circui in Fig. 5, where R 6, L H,. F, v() 7 in V, and curren and charge a are zero. v() v() Fig. 5. L-circui Fig. 5. RL-circui 44. Show ha, by Kirchhoff Volage Law (Sec..9), he curren in he nework in Fig. 5 are obained from he yem Li r R(i i ) v() R(i r i r) i. Solve hi yem, auming ha R, L H,.5 F, v V, i (), i () A. L L R L Fig. 49. Syem in Problem 8 and 9 v() i i R 9. In Prob. 8, le m kg>ec m kg, k k, k 4 kg>ec. Find he oluion aifying he iniial condiion y () y (), y r() meer>ec, y r() meer>ec. 4. Find he model (he yem of ODE) in Prob. 8 exended by adding anoher ma m and anoher pring of modulu k 4 in erie. 4. Find he curren i() in he R-circui in Fig. 5, where R,. F, v() V if 4, v() 4 V if 4, and he iniial charge on he capacior i. Fig. 5. Nework in Problem Se up he model of he nework in Fig. 54 and find he oluion, auming ha all charge and curren are when he wich i cloed a. Find he limi of i () and i () a :, (i) from he oluion, (ii) direcly from he given nework. L = 5 H i i V =.5 F R Swich Fig. 54. Nework in Problem 45 v() Fig. 5. R-circui
6 Summary of haper 6 5 SUMMARY OF HAPTER 6 Laplace Tranform The main purpoe of Laplace ranform i he oluion of differenial equaion and yem of uch equaion, a well a correponding iniial value problem. The Laplace ranform F() l( f ) of a funcion f () i defined by () F() l( f ) e f () d (Sec. 6.). Thi definiion i moivaed by he propery ha he differeniaion of f wih repec o correpond o he muliplicaion of he ranform F by ; more preciely, l( f r) l( f ) f () () (Sec. 6.) l( f ) l( f ) f () f r() ec. Hence by aking he ranform of a given differenial equaion () y ayr by r() (a, b conan) and wriing l(y) Y(), we obain he ubidiary equaion (4) ( a b)y l(r) f () f r() af (). Here, in obaining he ranform l(r) we can ge help from he mall able in Sec. 6. or he larger able in Sec Thi i he fir ep. In he econd ep we olve he ubidiary equaion algebraically for Y(). In he hird ep we deermine he invere ranform y() l (Y), ha i, he oluion of he problem. Thi i generally he harde ep, and in i we may again ue one of hoe wo able. Y() will ofen be a raional funcion, o ha we can obain he invere l (Y) by parial fracion reducion (Sec. 6.4) if we ee no impler way. The Laplace mehod avoid he deerminaion of a general oluion of he homogeneou ODE, and we alo need no deermine value of arbirary conan in a general oluion from iniial condiion; inead, we can iner he laer direcly ino (4). Two furher fac accoun for he pracical imporance of he Laplace ranform. Fir, i ha ome baic properie and reuling echnique ha implify he deerminaion of ranform and invere. The mo imporan of hee properie are lied in Sec. 6.8, ogeher wih reference o he correponding ecion. More on he ue of uni ep funcion and Dirac dela can be found in Sec. 6. and 6.4, and more on convoluion in Sec Second, due o hee properie, he preen mehod i paricularly uiable for handling righ ide r() given by differen expreion over differen inerval of ime, for inance, when r() i a quare wave or an impule or of a form uch a r() co if 4p and elewhere. The applicaion of he Laplace ranform o yem of ODE i hown in Sec (The applicaion o PDE follow in Sec...)
Chapter 6. Laplace Transforms
 6- Chaper 6. Laplace Tranform 6.4 Shor Impule. Dirac Dela Funcion. Parial Fracion 6.5 Convoluion. Inegral Equaion 6.6 Differeniaion and Inegraion of Tranform 6.7 Syem of ODE 6.4 Shor Impule. Dirac Dela
6- Chaper 6. Laplace Tranform 6.4 Shor Impule. Dirac Dela Funcion. Parial Fracion 6.5 Convoluion. Inegral Equaion 6.6 Differeniaion and Inegraion of Tranform 6.7 Syem of ODE 6.4 Shor Impule. Dirac Dela
Chapter 6. Laplace Transforms
 Chaper 6. Laplace Tranform Kreyzig by YHLee;45; 6- An ODE i reduced o an algebraic problem by operaional calculu. The equaion i olved by algebraic manipulaion. The reul i ranformed back for he oluion of
Chaper 6. Laplace Tranform Kreyzig by YHLee;45; 6- An ODE i reduced o an algebraic problem by operaional calculu. The equaion i olved by algebraic manipulaion. The reul i ranformed back for he oluion of
To become more mathematically correct, Circuit equations are Algebraic Differential equations. from KVL, KCL from the constitutive relationship
 Laplace Tranform (Lin & DeCarlo: Ch 3) ENSC30 Elecric Circui II The Laplace ranform i an inegral ranformaion. I ranform: f ( ) F( ) ime variable complex variable From Euler > Lagrange > Laplace. Hence,
Laplace Tranform (Lin & DeCarlo: Ch 3) ENSC30 Elecric Circui II The Laplace ranform i an inegral ranformaion. I ranform: f ( ) F( ) ime variable complex variable From Euler > Lagrange > Laplace. Hence,
Laplace Transform. Inverse Laplace Transform. e st f(t)dt. (2)
 Laplace Tranform Maoud Malek The Laplace ranform i an inegral ranform named in honor of mahemaician and aronomer Pierre-Simon Laplace, who ued he ranform in hi work on probabiliy heory. I i a powerful
Laplace Tranform Maoud Malek The Laplace ranform i an inegral ranform named in honor of mahemaician and aronomer Pierre-Simon Laplace, who ued he ranform in hi work on probabiliy heory. I i a powerful
CHAPTER. Forced Equations and Systems { } ( ) ( ) 8.1 The Laplace Transform and Its Inverse. Transforms from the Definition.
 CHAPTER 8 Forced Equaion and Syem 8 The aplace Tranform and I Invere Tranform from he Definiion 5 5 = b b {} 5 = 5e d = lim5 e = ( ) b {} = e d = lim e + e d b = (inegraion by par) = = = = b b ( ) ( )
CHAPTER 8 Forced Equaion and Syem 8 The aplace Tranform and I Invere Tranform from he Definiion 5 5 = b b {} 5 = 5e d = lim5 e = ( ) b {} = e d = lim e + e d b = (inegraion by par) = = = = b b ( ) ( )
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 31 Signal & Syem Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #27 C-T Syem: Laplace Tranform Power Tool for yem analyi Reading Aignmen: Secion 6.1 6.3 of Kamen and Heck 1/18 Coure Flow Diagram The arrow here how concepual
EECE 31 Signal & Syem Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #27 C-T Syem: Laplace Tranform Power Tool for yem analyi Reading Aignmen: Secion 6.1 6.3 of Kamen and Heck 1/18 Coure Flow Diagram The arrow here how concepual
EE202 Circuit Theory II
 EE202 Circui Theory II 2017-2018, Spring Dr. Yılmaz KALKAN I. Inroducion & eview of Fir Order Circui (Chaper 7 of Nilon - 3 Hr. Inroducion, C and L Circui, Naural and Sep epone of Serie and Parallel L/C
EE202 Circui Theory II 2017-2018, Spring Dr. Yılmaz KALKAN I. Inroducion & eview of Fir Order Circui (Chaper 7 of Nilon - 3 Hr. Inroducion, C and L Circui, Naural and Sep epone of Serie and Parallel L/C
6.2 Transforms of Derivatives and Integrals.
 SEC. 6.2 Transforms of Derivaives and Inegrals. ODEs 2 3 33 39 23. Change of scale. If l( f ()) F(s) and c is any 33 45 APPLICATION OF s-shifting posiive consan, show ha l( f (c)) F(s>c)>c (Hin: In Probs.
SEC. 6.2 Transforms of Derivaives and Inegrals. ODEs 2 3 33 39 23. Change of scale. If l( f ()) F(s) and c is any 33 45 APPLICATION OF s-shifting posiive consan, show ha l( f (c)) F(s>c)>c (Hin: In Probs.
18.03SC Unit 3 Practice Exam and Solutions
 Sudy Guide on Sep, Dela, Convoluion, Laplace You can hink of he ep funcion u() a any nice mooh funcion which i for < a and for > a, where a i a poiive number which i much maller han any ime cale we care
Sudy Guide on Sep, Dela, Convoluion, Laplace You can hink of he ep funcion u() a any nice mooh funcion which i for < a and for > a, where a i a poiive number which i much maller han any ime cale we care
CONTROL SYSTEMS. Chapter 3 Mathematical Modelling of Physical Systems-Laplace Transforms. Prof.Dr. Fatih Mehmet Botsalı
 CONTROL SYSTEMS Chaper Mahemaical Modelling of Phyical Syem-Laplace Tranform Prof.Dr. Faih Mehme Boalı Definiion Tranform -- a mahemaical converion from one way of hinking o anoher o make a problem eaier
CONTROL SYSTEMS Chaper Mahemaical Modelling of Phyical Syem-Laplace Tranform Prof.Dr. Faih Mehme Boalı Definiion Tranform -- a mahemaical converion from one way of hinking o anoher o make a problem eaier
Chapter 7: Inverse-Response Systems
 Chaper 7: Invere-Repone Syem Normal Syem Invere-Repone Syem Baic Sar ou in he wrong direcion End up in he original eady-ae gain value Two or more yem wih differen magniude and cale in parallel Main yem
Chaper 7: Invere-Repone Syem Normal Syem Invere-Repone Syem Baic Sar ou in he wrong direcion End up in he original eady-ae gain value Two or more yem wih differen magniude and cale in parallel Main yem
13.1 Circuit Elements in the s Domain Circuit Analysis in the s Domain The Transfer Function and Natural Response 13.
 Chaper 3 The Laplace Tranform in Circui Analyi 3. Circui Elemen in he Domain 3.-3 Circui Analyi in he Domain 3.4-5 The Tranfer Funcion and Naural Repone 3.6 The Tranfer Funcion and he Convoluion Inegral
Chaper 3 The Laplace Tranform in Circui Analyi 3. Circui Elemen in he Domain 3.-3 Circui Analyi in he Domain 3.4-5 The Tranfer Funcion and Naural Repone 3.6 The Tranfer Funcion and he Convoluion Inegral
EE Control Systems LECTURE 2
 Copyrigh F.L. Lewi 999 All righ reerved EE 434 - Conrol Syem LECTURE REVIEW OF LAPLACE TRANSFORM LAPLACE TRANSFORM The Laplace ranform i very ueful in analyi and deign for yem ha are linear and ime-invarian
Copyrigh F.L. Lewi 999 All righ reerved EE 434 - Conrol Syem LECTURE REVIEW OF LAPLACE TRANSFORM LAPLACE TRANSFORM The Laplace ranform i very ueful in analyi and deign for yem ha are linear and ime-invarian
Exponential Sawtooth
 ECPE 36 HOMEWORK 3: PROPERTIES OF THE FOURIER TRANSFORM SOLUTION. Exponenial Sawooh: The eaie way o do hi problem i o look a he Fourier ranform of a ingle exponenial funcion, () = exp( )u(). From he able
ECPE 36 HOMEWORK 3: PROPERTIES OF THE FOURIER TRANSFORM SOLUTION. Exponenial Sawooh: The eaie way o do hi problem i o look a he Fourier ranform of a ingle exponenial funcion, () = exp( )u(). From he able
LAPLACE TRANSFORMS. 1. Basic transforms
 LAPLACE TRANSFORMS. Bic rnform In hi coure, Lplce Trnform will be inroduced nd heir properie exmined; ble of common rnform will be buil up; nd rnform will be ued o olve ome dierenil equion by rnforming
LAPLACE TRANSFORMS. Bic rnform In hi coure, Lplce Trnform will be inroduced nd heir properie exmined; ble of common rnform will be buil up; nd rnform will be ued o olve ome dierenil equion by rnforming
More on ODEs by Laplace Transforms October 30, 2017
 More on OE b Laplace Tranfor Ocober, 7 More on Ordinar ifferenial Equaion wih Laplace Tranfor Larr areo Mechanical Engineering 5 Seinar in Engineering nali Ocober, 7 Ouline Review la cla efiniion of Laplace
More on OE b Laplace Tranfor Ocober, 7 More on Ordinar ifferenial Equaion wih Laplace Tranfor Larr areo Mechanical Engineering 5 Seinar in Engineering nali Ocober, 7 Ouline Review la cla efiniion of Laplace
CHAPTER 7: SECOND-ORDER CIRCUITS
 EEE5: CI RCUI T THEORY CHAPTER 7: SECOND-ORDER CIRCUITS 7. Inroducion Thi chaper conider circui wih wo orage elemen. Known a econd-order circui becaue heir repone are decribed by differenial equaion ha
EEE5: CI RCUI T THEORY CHAPTER 7: SECOND-ORDER CIRCUITS 7. Inroducion Thi chaper conider circui wih wo orage elemen. Known a econd-order circui becaue heir repone are decribed by differenial equaion ha
Laplace Transforms. Examples. Is this equation differential? y 2 2y + 1 = 0, y 2 2y + 1 = 0, (y ) 2 2y + 1 = cos x,
 Laplace Transforms Definiion. An ordinary differenial equaion is an equaion ha conains one or several derivaives of an unknown funcion which we call y and which we wan o deermine from he equaion. The equaion
Laplace Transforms Definiion. An ordinary differenial equaion is an equaion ha conains one or several derivaives of an unknown funcion which we call y and which we wan o deermine from he equaion. The equaion
Chapter 9 - The Laplace Transform
 Chaper 9 - The Laplace Tranform Selece Soluion. Skech he pole-zero plo an region of convergence (if i exi) for hee ignal. ω [] () 8 (a) x e u = 8 ROC σ ( ) 3 (b) x e co π u ω [] ( ) () (c) x e u e u ROC
Chaper 9 - The Laplace Tranform Selece Soluion. Skech he pole-zero plo an region of convergence (if i exi) for hee ignal. ω [] () 8 (a) x e u = 8 ROC σ ( ) 3 (b) x e co π u ω [] ( ) () (c) x e u e u ROC
ECE 2100 Circuit Analysis
 ECE 1 Circui Analysis Lesson 35 Chaper 8: Second Order Circuis Daniel M. Liynski, Ph.D. ECE 1 Circui Analysis Lesson 3-34 Chaper 7: Firs Order Circuis (Naural response RC & RL circuis, Singulariy funcions,
ECE 1 Circui Analysis Lesson 35 Chaper 8: Second Order Circuis Daniel M. Liynski, Ph.D. ECE 1 Circui Analysis Lesson 3-34 Chaper 7: Firs Order Circuis (Naural response RC & RL circuis, Singulariy funcions,
SEC. 6.3 Unit Step Function (Heaviside Function). Second Shifting Theorem (t-shifting) 217. Second Shifting Theorem (t-shifting)
 SEC. 6.3 Uni Sep Funcion (Heaviside Funcion). Second Shifing Theorem (-Shifing) 7. PROJECT. Furher Resuls by Differeniaion. Proceeding as in Example, obain (a) and from his and Example : (b) formula, (c),
SEC. 6.3 Uni Sep Funcion (Heaviside Funcion). Second Shifing Theorem (-Shifing) 7. PROJECT. Furher Resuls by Differeniaion. Proceeding as in Example, obain (a) and from his and Example : (b) formula, (c),
Chapter 7 Response of First-order RL and RC Circuits
 Chaper 7 Response of Firs-order RL and RC Circuis 7.- The Naural Response of RL and RC Circuis 7.3 The Sep Response of RL and RC Circuis 7.4 A General Soluion for Sep and Naural Responses 7.5 Sequenial
Chaper 7 Response of Firs-order RL and RC Circuis 7.- The Naural Response of RL and RC Circuis 7.3 The Sep Response of RL and RC Circuis 7.4 A General Soluion for Sep and Naural Responses 7.5 Sequenial
Piecewise-Defined Functions and Periodic Functions
 28 Piecewie-Defined Funcion and Periodic Funcion A he ar of our udy of he Laplace ranform, i wa claimed ha he Laplace ranform i paricularly ueful when dealing wih nonhomogeneou equaion in which he forcing
28 Piecewie-Defined Funcion and Periodic Funcion A he ar of our udy of he Laplace ranform, i wa claimed ha he Laplace ranform i paricularly ueful when dealing wih nonhomogeneou equaion in which he forcing
Sample Final Exam (finals03) Covering Chapters 1-9 of Fundamentals of Signals & Systems
 Sample Final Exam Covering Chaper 9 (final04) Sample Final Exam (final03) Covering Chaper 9 of Fundamenal of Signal & Syem Problem (0 mar) Conider he caual opamp circui iniially a re depiced below. I LI
Sample Final Exam Covering Chaper 9 (final04) Sample Final Exam (final03) Covering Chaper 9 of Fundamenal of Signal & Syem Problem (0 mar) Conider he caual opamp circui iniially a re depiced below. I LI
1 CHAPTER 14 LAPLACE TRANSFORMS
 CHAPTER 4 LAPLACE TRANSFORMS 4 nroducion f x) i a funcion of x, where x lie in he range o, hen he funcion p), defined by p) px e x) dx, 4 i called he Laplace ranform of x) However, in hi chaper, where
CHAPTER 4 LAPLACE TRANSFORMS 4 nroducion f x) i a funcion of x, where x lie in he range o, hen he funcion p), defined by p) px e x) dx, 4 i called he Laplace ranform of x) However, in hi chaper, where
Mon Apr 2: Laplace transform and initial value problems like we studied in Chapter 5
 Mah 225-4 Week 2 April 2-6 coninue.-.3; alo cover par of.4-.5, EP 7.6 Mon Apr 2:.-.3 Laplace ranform and iniial value problem like we udied in Chaper 5 Announcemen: Warm-up Exercie: Recall, The Laplace
Mah 225-4 Week 2 April 2-6 coninue.-.3; alo cover par of.4-.5, EP 7.6 Mon Apr 2:.-.3 Laplace ranform and iniial value problem like we udied in Chaper 5 Announcemen: Warm-up Exercie: Recall, The Laplace
CONTROL SYSTEMS. Chapter 10 : State Space Response
 CONTROL SYSTEMS Chaper : Sae Space Repone GATE Objecive & Numerical Type Soluion Queion 5 [GATE EE 99 IIT-Bombay : Mark] Conider a econd order yem whoe ae pace repreenaion i of he form A Bu. If () (),
CONTROL SYSTEMS Chaper : Sae Space Repone GATE Objecive & Numerical Type Soluion Queion 5 [GATE EE 99 IIT-Bombay : Mark] Conider a econd order yem whoe ae pace repreenaion i of he form A Bu. If () (),
Instrumentation & Process Control
 Chemical Engineering (GTE & PSU) Poal Correpondence GTE & Public Secor Inrumenaion & Proce Conrol To Buy Poal Correpondence Package call a -999657855 Poal Coure ( GTE & PSU) 5 ENGINEERS INSTITUTE OF INDI.
Chemical Engineering (GTE & PSU) Poal Correpondence GTE & Public Secor Inrumenaion & Proce Conrol To Buy Poal Correpondence Package call a -999657855 Poal Coure ( GTE & PSU) 5 ENGINEERS INSTITUTE OF INDI.
Study of simple inductive-capacitive series circuits using MATLAB software package
 ecen Advance in ircui, Syem and Auomaic onrol Sudy of imple inducive-capaciive erie circui uing MAAB ofware package NIUESU IU, PĂSUESU DAGOŞ Faculy of Mechanical and Elecrical Engineering Univeriy of Peroani
ecen Advance in ircui, Syem and Auomaic onrol Sudy of imple inducive-capaciive erie circui uing MAAB ofware package NIUESU IU, PĂSUESU DAGOŞ Faculy of Mechanical and Elecrical Engineering Univeriy of Peroani
REPETITION before the exam PART 2, Transform Methods. Laplace transforms: τ dτ. L1. Derive the formulas : L2. Find the Laplace transform F(s) if.
 Tranform Mhod and Calculu of Svral Variabl H7, p Lcurr: Armin Halilovic KTH, Campu Haning E-mail: armin@dkh, wwwdkh/armin REPETITION bfor h am PART, Tranform Mhod Laplac ranform: L Driv h formula : a L[
Tranform Mhod and Calculu of Svral Variabl H7, p Lcurr: Armin Halilovic KTH, Campu Haning E-mail: armin@dkh, wwwdkh/armin REPETITION bfor h am PART, Tranform Mhod Laplac ranform: L Driv h formula : a L[
Main Reference: Sections in CLRS.
 Maximum Flow Reied 09/09/200 Main Reference: Secion 26.-26. in CLRS. Inroducion Definiion Muli-Source Muli-Sink The Ford-Fulkeron Mehod Reidual Nework Augmening Pah The Max-Flow Min-Cu Theorem The Edmond-Karp
Maximum Flow Reied 09/09/200 Main Reference: Secion 26.-26. in CLRS. Inroducion Definiion Muli-Source Muli-Sink The Ford-Fulkeron Mehod Reidual Nework Augmening Pah The Max-Flow Min-Cu Theorem The Edmond-Karp
Discussion Session 2 Constant Acceleration/Relative Motion Week 03
 PHYS 100 Dicuion Seion Conan Acceleraion/Relaive Moion Week 03 The Plan Today you will work wih your group explore he idea of reference frame (i.e. relaive moion) and moion wih conan acceleraion. You ll
PHYS 100 Dicuion Seion Conan Acceleraion/Relaive Moion Week 03 The Plan Today you will work wih your group explore he idea of reference frame (i.e. relaive moion) and moion wih conan acceleraion. You ll
, the. L and the L. x x. max. i n. It is easy to show that these two norms satisfy the following relation: x x n x = (17.3) max
 ecure 8 7. Sabiliy Analyi For an n dimenional vecor R n, he and he vecor norm are defined a: = T = i n i (7.) I i eay o how ha hee wo norm aify he following relaion: n (7.) If a vecor i ime-dependen, hen
ecure 8 7. Sabiliy Analyi For an n dimenional vecor R n, he and he vecor norm are defined a: = T = i n i (7.) I i eay o how ha hee wo norm aify he following relaion: n (7.) If a vecor i ime-dependen, hen
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 3 Signals & Sysems Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se # Wha are Coninuous-Time Signals??? /6 Coninuous-Time Signal Coninuous Time (C-T) Signal: A C-T signal is defined on he coninuum of ime values. Tha is:
EECE 3 Signals & Sysems Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se # Wha are Coninuous-Time Signals??? /6 Coninuous-Time Signal Coninuous Time (C-T) Signal: A C-T signal is defined on he coninuum of ime values. Tha is:
t )? How would you have tried to solve this problem in Chapter 3?
 Exercie 9) Ue Laplace ranform o wrie down he oluion o 2 x x = F in x = x x = v. wha phenomena do oluion o hi DE illurae (even hough we're forcing wih in co )? How would you have ried o olve hi problem
Exercie 9) Ue Laplace ranform o wrie down he oluion o 2 x x = F in x = x x = v. wha phenomena do oluion o hi DE illurae (even hough we're forcing wih in co )? How would you have ried o olve hi problem
Randomized Perfect Bipartite Matching
 Inenive Algorihm Lecure 24 Randomized Perfec Biparie Maching Lecurer: Daniel A. Spielman April 9, 208 24. Inroducion We explain a randomized algorihm by Ahih Goel, Michael Kapralov and Sanjeev Khanna for
Inenive Algorihm Lecure 24 Randomized Perfec Biparie Maching Lecurer: Daniel A. Spielman April 9, 208 24. Inroducion We explain a randomized algorihm by Ahih Goel, Michael Kapralov and Sanjeev Khanna for
ECE 2100 Circuit Analysis
 ECE 1 Circui Analysis Lesson 37 Chaper 8: Second Order Circuis Discuss Exam Daniel M. Liynski, Ph.D. Exam CH 1-4: On Exam 1; Basis for work CH 5: Operaional Amplifiers CH 6: Capaciors and Inducor CH 7-8:
ECE 1 Circui Analysis Lesson 37 Chaper 8: Second Order Circuis Discuss Exam Daniel M. Liynski, Ph.D. Exam CH 1-4: On Exam 1; Basis for work CH 5: Operaional Amplifiers CH 6: Capaciors and Inducor CH 7-8:
s-domain Circuit Analysis
 Domain ircui Analyi Operae direcly in he domain wih capacior, inducor and reior Key feaure lineariy i preerved c decribed by ODE and heir I Order equal number of plu number of Elemenbyelemen and ource
Domain ircui Analyi Operae direcly in he domain wih capacior, inducor and reior Key feaure lineariy i preerved c decribed by ODE and heir I Order equal number of plu number of Elemenbyelemen and ource
Chapter 1 Fundamental Concepts
 Chaper 1 Fundamenal Conceps 1 Signals A signal is a paern of variaion of a physical quaniy, ofen as a funcion of ime (bu also space, disance, posiion, ec). These quaniies are usually he independen variables
Chaper 1 Fundamenal Conceps 1 Signals A signal is a paern of variaion of a physical quaniy, ofen as a funcion of ime (bu also space, disance, posiion, ec). These quaniies are usually he independen variables
Problem Set If all directed edges in a network have distinct capacities, then there is a unique maximum flow.
 CSE 202: Deign and Analyi of Algorihm Winer 2013 Problem Se 3 Inrucor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Due on: Tue. Feb 26, 2013 Inrucion For your proof, you may ue any lower bound, algorihm or daa rucure from he ex
CSE 202: Deign and Analyi of Algorihm Winer 2013 Problem Se 3 Inrucor: Kamalika Chaudhuri Due on: Tue. Feb 26, 2013 Inrucion For your proof, you may ue any lower bound, algorihm or daa rucure from he ex
EE202 Circuit Theory II , Spring. Dr. Yılmaz KALKAN & Dr. Atilla DÖNÜK
 EE202 Circui Theory II 2018 2019, Spring Dr. Yılmaz KALKAN & Dr. Ailla DÖNÜK 1. Basic Conceps (Chaper 1 of Nilsson - 3 Hrs.) Inroducion, Curren and Volage, Power and Energy 2. Basic Laws (Chaper 2&3 of
EE202 Circui Theory II 2018 2019, Spring Dr. Yılmaz KALKAN & Dr. Ailla DÖNÜK 1. Basic Conceps (Chaper 1 of Nilsson - 3 Hrs.) Inroducion, Curren and Volage, Power and Energy 2. Basic Laws (Chaper 2&3 of
First Order RC and RL Transient Circuits
 Firs Order R and RL Transien ircuis Objecives To inroduce he ransiens phenomena. To analyze sep and naural responses of firs order R circuis. To analyze sep and naural responses of firs order RL circuis.
Firs Order R and RL Transien ircuis Objecives To inroduce he ransiens phenomena. To analyze sep and naural responses of firs order R circuis. To analyze sep and naural responses of firs order RL circuis.
ENGI 9420 Engineering Analysis Assignment 2 Solutions
 ENGI 940 Engineering Analysis Assignmen Soluions 0 Fall [Second order ODEs, Laplace ransforms; Secions.0-.09]. Use Laplace ransforms o solve he iniial value problem [0] dy y, y( 0) 4 d + [This was Quesion
ENGI 940 Engineering Analysis Assignmen Soluions 0 Fall [Second order ODEs, Laplace ransforms; Secions.0-.09]. Use Laplace ransforms o solve he iniial value problem [0] dy y, y( 0) 4 d + [This was Quesion
u(t) Figure 1. Open loop control system
 Open loop conrol v cloed loop feedbac conrol The nex wo figure preen he rucure of open loop and feedbac conrol yem Figure how an open loop conrol yem whoe funcion i o caue he oupu y o follow he reference
Open loop conrol v cloed loop feedbac conrol The nex wo figure preen he rucure of open loop and feedbac conrol yem Figure how an open loop conrol yem whoe funcion i o caue he oupu y o follow he reference
CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS 257 12.1 RESISTORS IN SERIES AND IN PARALLEL When wo resisors are conneced ogeher as shown in Figure 12.1 we said ha hey are conneced in series. As
CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS 257 12.1 RESISTORS IN SERIES AND IN PARALLEL When wo resisors are conneced ogeher as shown in Figure 12.1 we said ha hey are conneced in series. As
1 Motivation and Basic Definitions
 CSCE : Deign and Analyi of Algorihm Noe on Max Flow Fall 20 (Baed on he preenaion in Chaper 26 of Inroducion o Algorihm, 3rd Ed. by Cormen, Leieron, Rive and Sein.) Moivaion and Baic Definiion Conider
CSCE : Deign and Analyi of Algorihm Noe on Max Flow Fall 20 (Baed on he preenaion in Chaper 26 of Inroducion o Algorihm, 3rd Ed. by Cormen, Leieron, Rive and Sein.) Moivaion and Baic Definiion Conider
Lecture 13 RC/RL Circuits, Time Dependent Op Amp Circuits
 Lecure 13 RC/RL Circuis, Time Dependen Op Amp Circuis RL Circuis The seps involved in solving simple circuis conaining dc sources, resisances, and one energy-sorage elemen (inducance or capaciance) are:
Lecure 13 RC/RL Circuis, Time Dependen Op Amp Circuis RL Circuis The seps involved in solving simple circuis conaining dc sources, resisances, and one energy-sorage elemen (inducance or capaciance) are:
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 3 Signals & Sysems Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #2 Wha are Coninuous-Time Signals??? Reading Assignmen: Secion. of Kamen and Heck /22 Course Flow Diagram The arrows here show concepual flow beween ideas.
EECE 3 Signals & Sysems Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #2 Wha are Coninuous-Time Signals??? Reading Assignmen: Secion. of Kamen and Heck /22 Course Flow Diagram The arrows here show concepual flow beween ideas.
FIXED POINTS AND STABILITY IN NEUTRAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS WITH VARIABLE DELAYS
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 136, Number 3, March 28, Page 99 918 S 2-9939(7)989-2 Aricle elecronically publihed on November 3, 27 FIXED POINTS AND STABILITY IN NEUTRAL DIFFERENTIAL
PROCEEDINGS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 136, Number 3, March 28, Page 99 918 S 2-9939(7)989-2 Aricle elecronically publihed on November 3, 27 FIXED POINTS AND STABILITY IN NEUTRAL DIFFERENTIAL
8. Basic RL and RC Circuits
 8. Basic L and C Circuis This chaper deals wih he soluions of he responses of L and C circuis The analysis of C and L circuis leads o a linear differenial equaion This chaper covers he following opics
8. Basic L and C Circuis This chaper deals wih he soluions of he responses of L and C circuis The analysis of C and L circuis leads o a linear differenial equaion This chaper covers he following opics
LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION
 CHBE320 LECTURE V LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dep. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 5-1 Road Map of he Lecure V Laplace Transform and Transfer funcions
CHBE320 LECTURE V LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dep. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 5-1 Road Map of he Lecure V Laplace Transform and Transfer funcions
CHAPTER 3 SIGNALS & SYSTEMS. z -transform in the z -plane will be (A) 1 (B) 1 (D) (C) . The unilateral Laplace transform of tf() (A) s (B) + + (D) (C)
 CHAPER SIGNALS & SYSEMS YEAR ONE MARK n n MCQ. If xn [ ] (/) (/) un [ ], hen he region of convergence (ROC) of i z ranform in he z plane will be (A) < z < (B) < z < (C) < z < (D) < z MCQ. he unilaeral
CHAPER SIGNALS & SYSEMS YEAR ONE MARK n n MCQ. If xn [ ] (/) (/) un [ ], hen he region of convergence (ROC) of i z ranform in he z plane will be (A) < z < (B) < z < (C) < z < (D) < z MCQ. he unilaeral
Section 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equations; Method of Undetermined Coefficients
 Secion 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equaions; Mehod of Undeermined Coefficiens Key Terms/Ideas: Linear Differenial operaor Nonlinear operaor Second order homogeneous DE Second order nonhomogeneous DE Soluion o homogeneous
Secion 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equaions; Mehod of Undeermined Coefficiens Key Terms/Ideas: Linear Differenial operaor Nonlinear operaor Second order homogeneous DE Second order nonhomogeneous DE Soluion o homogeneous
INDEX. Transient analysis 1 Initial Conditions 1
 INDEX Secion Page Transien analysis 1 Iniial Condiions 1 Please inform me of your opinion of he relaive emphasis of he review maerial by simply making commens on his page and sending i o me a: Frank Mera
INDEX Secion Page Transien analysis 1 Iniial Condiions 1 Please inform me of your opinion of he relaive emphasis of he review maerial by simply making commens on his page and sending i o me a: Frank Mera
The complex Fourier series has an important limiting form when the period approaches infinity, i.e., T 0. 0 since it is proportional to 1/L, but
 Fourier Transforms The complex Fourier series has an imporan limiing form when he period approaches infiniy, i.e., T or L. Suppose ha in his limi () k = nπ L remains large (ranging from o ) and (2) c n
Fourier Transforms The complex Fourier series has an imporan limiing form when he period approaches infiniy, i.e., T or L. Suppose ha in his limi () k = nπ L remains large (ranging from o ) and (2) c n
AN ANALYTICAL METHOD OF SOLUTION FOR SYSTEMS OF BOOLEAN EQUATIONS
 CHAPTER 5 AN ANALYTICAL METHOD OF SOLUTION FOR SYSTEMS OF BOOLEAN EQUATIONS 51 APPLICATIONS OF DE MORGAN S LAWS A we have een in Secion 44 of Chaer 4, any Boolean Equaion of ye (1), (2) or (3) could be
CHAPTER 5 AN ANALYTICAL METHOD OF SOLUTION FOR SYSTEMS OF BOOLEAN EQUATIONS 51 APPLICATIONS OF DE MORGAN S LAWS A we have een in Secion 44 of Chaer 4, any Boolean Equaion of ye (1), (2) or (3) could be
Chapter 2. First Order Scalar Equations
 Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
Physics 240: Worksheet 16 Name
 Phyic 4: Workhee 16 Nae Non-unifor circular oion Each of hee proble involve non-unifor circular oion wih a conan α. (1) Obain each of he equaion of oion for non-unifor circular oion under a conan acceleraion,
Phyic 4: Workhee 16 Nae Non-unifor circular oion Each of hee proble involve non-unifor circular oion wih a conan α. (1) Obain each of he equaion of oion for non-unifor circular oion under a conan acceleraion,
CHAPTER 7. Definition and Properties. of Laplace Transforms
 SERIES OF CLSS NOTES FOR 5-6 TO INTRODUCE LINER ND NONLINER PROBLEMS TO ENGINEERS, SCIENTISTS, ND PPLIED MTHEMTICINS DE CLSS NOTES COLLECTION OF HNDOUTS ON SCLR LINER ORDINRY DIFFERENTIL EQUTIONS (ODE")
SERIES OF CLSS NOTES FOR 5-6 TO INTRODUCE LINER ND NONLINER PROBLEMS TO ENGINEERS, SCIENTISTS, ND PPLIED MTHEMTICINS DE CLSS NOTES COLLECTION OF HNDOUTS ON SCLR LINER ORDINRY DIFFERENTIL EQUTIONS (ODE")
Network Flows: Introduction & Maximum Flow
 CSC 373 - lgorihm Deign, nalyi, and Complexiy Summer 2016 Lalla Mouaadid Nework Flow: Inroducion & Maximum Flow We now urn our aenion o anoher powerful algorihmic echnique: Local Search. In a local earch
CSC 373 - lgorihm Deign, nalyi, and Complexiy Summer 2016 Lalla Mouaadid Nework Flow: Inroducion & Maximum Flow We now urn our aenion o anoher powerful algorihmic echnique: Local Search. In a local earch
23.5. Half-Range Series. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Half-Range Series 2.5 Inroducion In his Secion we address he following problem: Can we find a Fourier series expansion of a funcion defined over a finie inerval? Of course we recognise ha such a funcion
Half-Range Series 2.5 Inroducion In his Secion we address he following problem: Can we find a Fourier series expansion of a funcion defined over a finie inerval? Of course we recognise ha such a funcion
Introduction to SLE Lecture Notes
 Inroducion o SLE Lecure Noe May 13, 16 - The goal of hi ecion i o find a ufficien condiion of λ for he hull K o be generaed by a imple cure. I urn ou if λ 1 < 4 hen K i generaed by a imple curve. We will
Inroducion o SLE Lecure Noe May 13, 16 - The goal of hi ecion i o find a ufficien condiion of λ for he hull K o be generaed by a imple cure. I urn ou if λ 1 < 4 hen K i generaed by a imple curve. We will
R.#W.#Erickson# Department#of#Electrical,#Computer,#and#Energy#Engineering# University#of#Colorado,#Boulder#
 .#W.#Erickson# Deparmen#of#Elecrical,#Compuer,#and#Energy#Engineering# Universiy#of#Colorado,#Boulder# Chaper 2 Principles of Seady-Sae Converer Analysis 2.1. Inroducion 2.2. Inducor vol-second balance,
.#W.#Erickson# Deparmen#of#Elecrical,#Compuer,#and#Energy#Engineering# Universiy#of#Colorado,#Boulder# Chaper 2 Principles of Seady-Sae Converer Analysis 2.1. Inroducion 2.2. Inducor vol-second balance,
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 30 Signal & Syem Prof. ark Fowler oe Se #34 C-T Tranfer Funcion and Frequency Repone /4 Finding he Tranfer Funcion from Differenial Eq. Recall: we found a DT yem Tranfer Funcion Hz y aking he ZT of
EECE 30 Signal & Syem Prof. ark Fowler oe Se #34 C-T Tranfer Funcion and Frequency Repone /4 Finding he Tranfer Funcion from Differenial Eq. Recall: we found a DT yem Tranfer Funcion Hz y aking he ZT of
Chapter 8 The Complete Response of RL and RC Circuits
 Chaper 8 The Complee Response of RL and RC Circuis Seoul Naional Universiy Deparmen of Elecrical and Compuer Engineering Wha is Firs Order Circuis? Circuis ha conain only one inducor or only one capacior
Chaper 8 The Complee Response of RL and RC Circuis Seoul Naional Universiy Deparmen of Elecrical and Compuer Engineering Wha is Firs Order Circuis? Circuis ha conain only one inducor or only one capacior
Chapter 8 Objectives
 haper 8 Engr8 ircui Analyi Dr uri Nelon haper 8 Objecive Be able o eermine he naural an he ep repone of parallel circui; Be able o eermine he naural an he ep repone of erie circui. Engr8 haper 8, Nilon
haper 8 Engr8 ircui Analyi Dr uri Nelon haper 8 Objecive Be able o eermine he naural an he ep repone of parallel circui; Be able o eermine he naural an he ep repone of erie circui. Engr8 haper 8, Nilon
6.302 Feedback Systems Recitation : Phase-locked Loops Prof. Joel L. Dawson
 6.32 Feedback Syem Phae-locked loop are a foundaional building block for analog circui deign, paricularly for communicaion circui. They provide a good example yem for hi cla becaue hey are an excellen
6.32 Feedback Syem Phae-locked loop are a foundaional building block for analog circui deign, paricularly for communicaion circui. They provide a good example yem for hi cla becaue hey are an excellen
Voltage/current relationship Stored Energy. RL / RC circuits Steady State / Transient response Natural / Step response
 Review Capaciors/Inducors Volage/curren relaionship Sored Energy s Order Circuis RL / RC circuis Seady Sae / Transien response Naural / Sep response EE4 Summer 5: Lecure 5 Insrucor: Ocavian Florescu Lecure
Review Capaciors/Inducors Volage/curren relaionship Sored Energy s Order Circuis RL / RC circuis Seady Sae / Transien response Naural / Sep response EE4 Summer 5: Lecure 5 Insrucor: Ocavian Florescu Lecure
Let. x y. denote a bivariate time series with zero mean.
 Linear Filer Le x y : T denoe a bivariae ime erie wih zero mean. Suppoe ha he ime erie {y : T} i conruced a follow: y a x The ime erie {y : T} i aid o be conruced from {x : T} by mean of a Linear Filer.
Linear Filer Le x y : T denoe a bivariae ime erie wih zero mean. Suppoe ha he ime erie {y : T} i conruced a follow: y a x The ime erie {y : T} i aid o be conruced from {x : T} by mean of a Linear Filer.
Serial : 4LS1_A_EC_Signal & Systems_230918
 Serial : LS_A_EC_Signal & Syem_8 CLASS TEST (GATE) Delhi oida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune Bhubanewar Kolkaa Pana Web: E-mail: info@madeeay.in Ph: -56 CLASS TEST 8- ELECTROICS EGIEERIG Subjec
Serial : LS_A_EC_Signal & Syem_8 CLASS TEST (GATE) Delhi oida Bhopal Hyderabad Jaipur Lucknow Indore Pune Bhubanewar Kolkaa Pana Web: E-mail: info@madeeay.in Ph: -56 CLASS TEST 8- ELECTROICS EGIEERIG Subjec
( ) = Q 0. ( ) R = R dq. ( t) = I t
 ircuis onceps The addiion of a simple capacior o a circui of resisors allows wo relaed phenomena o occur The observaion ha he ime-dependence of a complex waveform is alered by he circui is referred o as
ircuis onceps The addiion of a simple capacior o a circui of resisors allows wo relaed phenomena o occur The observaion ha he ime-dependence of a complex waveform is alered by he circui is referred o as
MA 366 Review - Test # 1
 MA 366 Review - Tes # 1 Fall 5 () Resuls from Calculus: differeniaion formulas, implici differeniaion, Chain Rule; inegraion formulas, inegraion b pars, parial fracions, oher inegraion echniques. (1) Order
MA 366 Review - Tes # 1 Fall 5 () Resuls from Calculus: differeniaion formulas, implici differeniaion, Chain Rule; inegraion formulas, inegraion b pars, parial fracions, oher inegraion echniques. (1) Order
Review - Quiz # 1. 1 g(y) dy = f(x) dx. y x. = u, so that y = xu and dy. dx (Sometimes you may want to use the substitution x y
 Review - Quiz # 1 (1) Solving Special Tpes of Firs Order Equaions I. Separable Equaions (SE). d = f() g() Mehod of Soluion : 1 g() d = f() (The soluions ma be given implicil b he above formula. Remember,
Review - Quiz # 1 (1) Solving Special Tpes of Firs Order Equaions I. Separable Equaions (SE). d = f() g() Mehod of Soluion : 1 g() d = f() (The soluions ma be given implicil b he above formula. Remember,
Laplace transfom: t-translation rule , Haynes Miller and Jeremy Orloff
 Laplace ransfom: -ranslaion rule 8.03, Haynes Miller and Jeremy Orloff Inroducory example Consider he sysem ẋ + 3x = f(, where f is he inpu and x he response. We know is uni impulse response is 0 for
Laplace ransfom: -ranslaion rule 8.03, Haynes Miller and Jeremy Orloff Inroducory example Consider he sysem ẋ + 3x = f(, where f is he inpu and x he response. We know is uni impulse response is 0 for
4/12/12. Applications of the Maxflow Problem 7.5 Bipartite Matching. Bipartite Matching. Bipartite Matching. Bipartite matching: the flow network
 // Applicaion of he Maxflow Problem. Biparie Maching Biparie Maching Biparie maching. Inpu: undireced, biparie graph = (, E). M E i a maching if each node appear in a mo one edge in M. Max maching: find
// Applicaion of he Maxflow Problem. Biparie Maching Biparie Maching Biparie maching. Inpu: undireced, biparie graph = (, E). M E i a maching if each node appear in a mo one edge in M. Max maching: find
Additional Methods for Solving DSGE Models
 Addiional Mehod for Solving DSGE Model Karel Meren, Cornell Univeriy Reference King, R. G., Ploer, C. I. & Rebelo, S. T. (1988), Producion, growh and buine cycle: I. he baic neoclaical model, Journal of
Addiional Mehod for Solving DSGE Model Karel Meren, Cornell Univeriy Reference King, R. G., Ploer, C. I. & Rebelo, S. T. (1988), Producion, growh and buine cycle: I. he baic neoclaical model, Journal of
Algorithmic Discrete Mathematics 6. Exercise Sheet
 Algorihmic Dicree Mahemaic. Exercie Shee Deparmen of Mahemaic SS 0 PD Dr. Ulf Lorenz 7. and 8. Juni 0 Dipl.-Mah. David Meffer Verion of June, 0 Groupwork Exercie G (Heap-Sor) Ue Heap-Sor wih a min-heap
Algorihmic Dicree Mahemaic. Exercie Shee Deparmen of Mahemaic SS 0 PD Dr. Ulf Lorenz 7. and 8. Juni 0 Dipl.-Mah. David Meffer Verion of June, 0 Groupwork Exercie G (Heap-Sor) Ue Heap-Sor wih a min-heap
2. VECTORS. R Vectors are denoted by bold-face characters such as R, V, etc. The magnitude of a vector, such as R, is denoted as R, R, V
 ME 352 VETS 2. VETS Vecor algebra form he mahemaical foundaion for kinemaic and dnamic. Geomer of moion i a he hear of boh he kinemaic and dnamic of mechanical em. Vecor anali i he imehonored ool for decribing
ME 352 VETS 2. VETS Vecor algebra form he mahemaical foundaion for kinemaic and dnamic. Geomer of moion i a he hear of boh he kinemaic and dnamic of mechanical em. Vecor anali i he imehonored ool for decribing
About the HELM Project HELM (Helping Engineers Learn Mathematics) materials were the outcome of a three-year curriculum development project
 Abou he HELM Projec HELM (Helping Engineers Learn Mahemaics) maerials were he oucome of a hree-year curriculum developmen projec underaken by a consorium of five English universiies led by Loughborough
Abou he HELM Projec HELM (Helping Engineers Learn Mahemaics) maerials were he oucome of a hree-year curriculum developmen projec underaken by a consorium of five English universiies led by Loughborough
Introduction to Congestion Games
 Algorihmic Game Theory, Summer 2017 Inroducion o Congeion Game Lecure 1 (5 page) Inrucor: Thoma Keelheim In hi lecure, we ge o know congeion game, which will be our running example for many concep in game
Algorihmic Game Theory, Summer 2017 Inroducion o Congeion Game Lecure 1 (5 page) Inrucor: Thoma Keelheim In hi lecure, we ge o know congeion game, which will be our running example for many concep in game
CHAPTER HIGHER-ORDER SYSTEMS: SECOND-ORDER AND TRANSPORTATION LAG. 7.1 SECOND-ORDER SYSTEM Transfer Function
 CHAPTER 7 HIGHER-ORDER SYSTEMS: SECOND-ORDER AND TRANSPORTATION LAG 7. SECOND-ORDER SYSTEM Tranfer Funcion Thi ecion inroduce a baic yem called a econd-order yem or a quadraic lag. Second-order yem are
CHAPTER 7 HIGHER-ORDER SYSTEMS: SECOND-ORDER AND TRANSPORTATION LAG 7. SECOND-ORDER SYSTEM Tranfer Funcion Thi ecion inroduce a baic yem called a econd-order yem or a quadraic lag. Second-order yem are
ESTIMATES FOR THE DERIVATIVE OF DIFFUSION SEMIGROUPS
 Elec. Comm. in Probab. 3 (998) 65 74 ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATIONS in PROBABILITY ESTIMATES FOR THE DERIVATIVE OF DIFFUSION SEMIGROUPS L.A. RINCON Deparmen of Mahemaic Univeriy of Wale Swanea Singleon Par
Elec. Comm. in Probab. 3 (998) 65 74 ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATIONS in PROBABILITY ESTIMATES FOR THE DERIVATIVE OF DIFFUSION SEMIGROUPS L.A. RINCON Deparmen of Mahemaic Univeriy of Wale Swanea Singleon Par
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 31 Signals & Sysems Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #1 C-T Sysems: Convoluion Represenaion Reading Assignmen: Secion 2.6 of Kamen and Heck 1/11 Course Flow Diagram The arrows here show concepual flow beween
EECE 31 Signals & Sysems Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #1 C-T Sysems: Convoluion Represenaion Reading Assignmen: Secion 2.6 of Kamen and Heck 1/11 Course Flow Diagram The arrows here show concepual flow beween
ECE Spring Prof. David R. Jackson ECE Dept. Notes 39
 ECE 6341 Spring 2016 Prof. David R. Jackon ECE Dep. Noe 39 1 Finie Source J ( y, ) For a phaed curren hee: p p j( k kyy) J y = J e + (, ) 0 The angenial elecric field ha i produced i: ( p ˆ ˆ) j( k + k
ECE 6341 Spring 2016 Prof. David R. Jackon ECE Dep. Noe 39 1 Finie Source J ( y, ) For a phaed curren hee: p p j( k kyy) J y = J e + (, ) 0 The angenial elecric field ha i produced i: ( p ˆ ˆ) j( k + k
dt = C exp (3 ln t 4 ). t 4 W = C exp ( ln(4 t) 3) = C(4 t) 3.
 Mah Rahman Exam Review Soluions () Consider he IVP: ( 4)y 3y + 4y = ; y(3) = 0, y (3) =. (a) Please deermine he longes inerval for which he IVP is guaraneed o have a unique soluion. Soluion: The disconinuiies
Mah Rahman Exam Review Soluions () Consider he IVP: ( 4)y 3y + 4y = ; y(3) = 0, y (3) =. (a) Please deermine he longes inerval for which he IVP is guaraneed o have a unique soluion. Soluion: The disconinuiies
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE. Markov decision processes
 INFOB2KI 2017-2018 Urech Univeriy The Neherland ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE Markov deciion procee Lecurer: Silja Renooij Thee lide are par of he INFOB2KI Coure Noe available from www.c.uu.nl/doc/vakken/b2ki/chema.hml
INFOB2KI 2017-2018 Urech Univeriy The Neherland ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE Markov deciion procee Lecurer: Silja Renooij Thee lide are par of he INFOB2KI Coure Noe available from www.c.uu.nl/doc/vakken/b2ki/chema.hml
h[n] is the impulse response of the discrete-time system:
![h[n] is the impulse response of the discrete-time system: h[n] is the impulse response of the discrete-time system:](/thumbs/89/99208034.jpg) Definiion Examples Properies Memory Inveribiliy Causaliy Sabiliy Time Invariance Lineariy Sysems Fundamenals Overview Definiion of a Sysem x() h() y() x[n] h[n] Sysem: a process in which inpu signals are
Definiion Examples Properies Memory Inveribiliy Causaliy Sabiliy Time Invariance Lineariy Sysems Fundamenals Overview Definiion of a Sysem x() h() y() x[n] h[n] Sysem: a process in which inpu signals are
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING EXAMINATIONS 2008
 [E5] IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING EXAMINATIONS 008 EEE/ISE PART II MEng BEng and ACGI SIGNALS AND LINEAR SYSTEMS Time allowed: :00 hours There are FOUR quesions
[E5] IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC ENGINEERING EXAMINATIONS 008 EEE/ISE PART II MEng BEng and ACGI SIGNALS AND LINEAR SYSTEMS Time allowed: :00 hours There are FOUR quesions
ES 250 Practice Final Exam
 ES 50 Pracice Final Exam. Given ha v 8 V, a Deermine he values of v o : 0 Ω, v o. V 0 Firs, v o 8. V 0 + 0 Nex, 8 40 40 0 40 0 400 400 ib i 0 40 + 40 + 40 40 40 + + ( ) 480 + 5 + 40 + 8 400 400( 0) 000
ES 50 Pracice Final Exam. Given ha v 8 V, a Deermine he values of v o : 0 Ω, v o. V 0 Firs, v o 8. V 0 + 0 Nex, 8 40 40 0 40 0 400 400 ib i 0 40 + 40 + 40 40 40 + + ( ) 480 + 5 + 40 + 8 400 400( 0) 000
Basic Circuit Elements Professor J R Lucas November 2001
 Basic Circui Elemens - J ucas An elecrical circui is an inerconnecion of circui elemens. These circui elemens can be caegorised ino wo ypes, namely acive and passive elemens. Some Definiions/explanaions
Basic Circui Elemens - J ucas An elecrical circui is an inerconnecion of circui elemens. These circui elemens can be caegorised ino wo ypes, namely acive and passive elemens. Some Definiions/explanaions
Solutions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Math 246, Spring 2011, Professor David Levermore
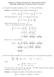 Soluions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Mah 6, Spring, Professor David Levermore Compue he Laplace ransform of f e from is definiion Soluion The definiion of he Laplace ransform gives L[f]s
Soluions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Mah 6, Spring, Professor David Levermore Compue he Laplace ransform of f e from is definiion Soluion The definiion of he Laplace ransform gives L[f]s
Math 334 Fall 2011 Homework 11 Solutions
 Dec. 2, 2 Mah 334 Fall 2 Homework Soluions Basic Problem. Transform he following iniial value problem ino an iniial value problem for a sysem: u + p()u + q() u g(), u() u, u () v. () Soluion. Le v u. Then
Dec. 2, 2 Mah 334 Fall 2 Homework Soluions Basic Problem. Transform he following iniial value problem ino an iniial value problem for a sysem: u + p()u + q() u g(), u() u, u () v. () Soluion. Le v u. Then
2.9 Modeling: Electric Circuits
 SE. 2.9 Modeling: Elecric ircuis 93 2.9 Modeling: Elecric ircuis Designing good models is a ask he compuer canno do. Hence seing up models has become an imporan ask in modern applied mahemaics. The bes
SE. 2.9 Modeling: Elecric ircuis 93 2.9 Modeling: Elecric ircuis Designing good models is a ask he compuer canno do. Hence seing up models has become an imporan ask in modern applied mahemaics. The bes
R =, C = 1, and f ( t ) = 1 for 1 second from t = 0 to t = 1. The initial charge on the capacitor is q (0) = 0. We have already solved this problem.
 Theoreical Physics Prof. Ruiz, UNC Asheville, docorphys on YouTube Chaper U Noes. Green's Funcions R, C 1, and f ( ) 1 for 1 second from o 1. The iniial charge on he capacior is q (). We have already solved
Theoreical Physics Prof. Ruiz, UNC Asheville, docorphys on YouTube Chaper U Noes. Green's Funcions R, C 1, and f ( ) 1 for 1 second from o 1. The iniial charge on he capacior is q (). We have already solved
KEY. Math 334 Midterm I Fall 2008 sections 001 and 003 Instructor: Scott Glasgow
 1 KEY Mah 4 Miderm I Fall 8 secions 1 and Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his eam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on our own paper, preferabl engineering
1 KEY Mah 4 Miderm I Fall 8 secions 1 and Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his eam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on our own paper, preferabl engineering
EEEB113 CIRCUIT ANALYSIS I
 9/14/29 1 EEEB113 CICUIT ANALYSIS I Chaper 7 Firs-Order Circuis Maerials from Fundamenals of Elecric Circuis 4e, Alexander Sadiku, McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 2 Firs-Order Circuis -Chaper 7 7.2 The Source-Free
9/14/29 1 EEEB113 CICUIT ANALYSIS I Chaper 7 Firs-Order Circuis Maerials from Fundamenals of Elecric Circuis 4e, Alexander Sadiku, McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 2 Firs-Order Circuis -Chaper 7 7.2 The Source-Free
On the Exponential Operator Functions on Time Scales
 dvance in Dynamical Syem pplicaion ISSN 973-5321, Volume 7, Number 1, pp. 57 8 (212) hp://campu.m.edu/ada On he Exponenial Operaor Funcion on Time Scale laa E. Hamza Cairo Univeriy Deparmen of Mahemaic
dvance in Dynamical Syem pplicaion ISSN 973-5321, Volume 7, Number 1, pp. 57 8 (212) hp://campu.m.edu/ada On he Exponenial Operaor Funcion on Time Scale laa E. Hamza Cairo Univeriy Deparmen of Mahemaic
Lab 10: RC, RL, and RLC Circuits
 Lab 10: RC, RL, and RLC Circuis In his experimen, we will invesigae he behavior of circuis conaining combinaions of resisors, capaciors, and inducors. We will sudy he way volages and currens change in
Lab 10: RC, RL, and RLC Circuis In his experimen, we will invesigae he behavior of circuis conaining combinaions of resisors, capaciors, and inducors. We will sudy he way volages and currens change in
ME 391 Mechanical Engineering Analysis
 Fall 04 ME 39 Mechanical Engineering Analsis Eam # Soluions Direcions: Open noes (including course web posings). No books, compuers, or phones. An calculaor is fair game. Problem Deermine he posiion of
Fall 04 ME 39 Mechanical Engineering Analsis Eam # Soluions Direcions: Open noes (including course web posings). No books, compuers, or phones. An calculaor is fair game. Problem Deermine he posiion of
non-linear oscillators
 non-linear oscillaors The invering comparaor operaion can be summarized as When he inpu is low, he oupu is high. When he inpu is high, he oupu is low. R b V REF R a and are given by he expressions derived
non-linear oscillaors The invering comparaor operaion can be summarized as When he inpu is low, he oupu is high. When he inpu is high, he oupu is low. R b V REF R a and are given by he expressions derived
