CIVE322 BASIC HYDROLOGY
|
|
|
- Griffin Armstrong
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CIVE322 BASIC HYDROLOGY Homework No.3 Solution 1. The coordinates of four precipitation gauging stations are A = (3,4), B = (9,4), C = (3,12), and D = (9,12). The observed precipitation amounts at these gauges are P A = 25 mm, P B = 33 mm, P C = 20 mm, P D = 29 mm, respectively. These stations are located in a rectangular basin whose boundaries are defined by the following coordinates (0,0), (14,0), (14,16), (0,16). Compute the mean areal precipitation over this basin using a) the Thiessen polygons method and b) the arithmetic average method. If the units of the coordinate points given above are km, compute the total volume of water produced by the recorded rainfall. n P = λp i (1) i=1 λ i = A i A basin (2) Using Thiessen polygons, the areas of influence are A A = 48; A B = 64; A C = 48; A D = 64. The basin area is A basin = 224. Thus, the mean areal precipitation is obtained as: Thiessen Polygons: MAP = (48/224)25 + (64/224)33 + (48/224)20 + (64/224)29 = mm Arithmetic Average method: MAP = ( )/4 = mm Total volume of water: Volume = MAP x A basin = m x m 2 = 6,128, m 3 2. Assume that a rainfall event of intensity 2.25 cm/h falls over a uniformly forested watershed of area 20 km 2. If there is no infiltration and no surface depression storage, compute the volume of water that leaves the basin as storm runoff for a 30-min and a 105-min rainfall, using the two models presented in class and whose equations are repeated below. Model A: L i = h S + KEt h < S Otherwise (4) Assume that K is 1.5, S is 0.2 cm and that the evaporation rate E is 0.05 cm/h. Compute total precipitation volume: P = (2.25 cm/h) (0.5 h) = cm P = (2.25 cm/h) (1.75 h) = cm Use equation 4 to obtain the interception losses. Observe that because the precipitation depth is larger than S, we will use the lower branch of equation 4. L i = (0.2 cm) + (1.5) (0.05 cm/h) (0.5 h) = cm
2 L i = (0.2 cm) + (1.5) (0.05 cm/h) (1.75 h) = cm to: Assuming that there is no change in basin storage, then the output of the basin is equal Volume of Output = (P - L i )*A basin = ((1.125 cm cm)/100 cm/m ) ( m 2 ) = 177,500.0 m 3 Volume of Output = (P - L i )*A basin = (( cm cm)/100 cm/m ) ( m 2 ) = 721,250.0 m 3 Model B: L i = S(1 e P/S ) + KEt (5) Assume that K is 1.5, S is 0.2 cm and that the evaporation rate E is 0.05 cm/h. Use equation 5 to obtain: L i = (0.2 cm) (1 - exp(-1.125/0.2)) + (1.5) (0.05 cm/h) (0.5 h) = cm L i = (0.2 cm) (1 - exp( /0.2)) + (1.5) (0.05 cm/h) (1.75 h) = cm to: Assuming that there is no change in basin storage, then the output of the basin is equal Volume of Output = (P - L i )*A basin = ((1.125 cm cm)/100 cm/m ) ( m 2 ) = 177,640.0 m 3 Volume of Output = (P - L i )*A basin = (( cm cm)/100 cm/m ) ( m 2 ) = 721,250.0 m 3 3. Repeat Problem 2 but assuming that in addition to interception there are also losses due to depression storage. The depression storage equation is: V = S d (1 e P e/s d ) (6) Assume that S d is 0.2 cm. What is the runoff ratio for these conditions? How much runoff would have been produced halfway into the storm? 0.5-hour: P e = P - L i = ( ) cm = cm. P e = P - L i = ( ) cm = cm hour: P e = P - L i = ( ) cm = cm. Runoff Ratio: σ i f = 1 e P e/s d (7)
3 Instantaneous runoff ratio at 0.5-hour: Model A: σ/(i-f) = 1-exp( /0.2) = Model B: σ/(i-f) = 1-exp( /0.2) = Instantaneous runoff ratio at 1.75-hour: σ/(i-f) = 1-exp( /0.2) = 1.0 Volume of surface depression (use equation 6): 0.5-hour: V = (0.2 cm) (1 - exp( /0.2)) = cm V = (0.2 cm) (1 - exp( /0.2)) = cm 1.75-hour: V = (0.2 cm) (1 - exp( /0.2)) = 0.2 cm Again, assuming that there is no change in basin storage, then the output of the basin is equal to: 0.5-hour: Model A: Volume of Output = (P e - V)*A basin = (( cm cm)/100 cm/m ) ( m 2 ) = 137,980. m 3 Model B: Volume of Output = (P e - V)*A basin = (( cm cm)/100 cm/m ) ( m 2 ) = 138,120. m hour: Volume of Output = (P e - V)*A basin = (( cm cm)/100 cm/m ) ( m 2 ) = 681,250. m 3 4. Assume that the time evolution of the infiltration capacity for a given soil is governed by Horton's equation (Note that this equation assumes an infinite water supply at the surface, that is, it assumes saturation conditions at the soil surface). f p (t) = f c + ( f o )e kt (1) For this soil, the asymptotic or final equilibrium infiltration capacity is f c = 0.75 cm/h; and the initial infiltration capacity is f o = 5 cm/h. The rate of decay of infiltration capacity parameter is k = 4 h -1. For the precipitation hyetograph tabulated below, carry out a complete infiltration analysis, including evaluation of cumulative infiltration and rate of production of precipitation excess, σ + v
4 1) Compute accumulated precipitation volume as a function of time. The incremental volume over each time period of 10 minutes is: ΔP = i Δt Intensity, i. ), P Intensity, i. (cm/h, P ) Compute infiltration capacity using Horton's equation for conditions of unlimited water supply at the surface using equation 1 (Table 1 - Column 2). 3) Compute the accumulated infiltration that would occur under conditions of unlimited water supply at the surface using the following equation 2 (Table 1 - Column 3), F(t) = f c t + f o k (1 e kt ) (2) 4) Compare infiltration capacity with precipitation intensity (Figure 1). Observe that during the first 10 minutes of the rainstorm, the infiltration capacity exceeds the precipitation intensity. Thus, during this period, all of the precipitation infiltrates. The actual infiltration rate is (Table 2 - Column 5), f (t) = min[i(t), f p (t)] = i(t), f p (t), i(t) f p (t) otherwise (3)
5 5) Because the actual infiltration rate is less than the infiltration capacity during the first 10 minutes, the actual infiltration capacity does not decay as predicted by Horton's equation. This is because, as indicated above, Horton's equation assumes that the supply rate exceeds the infiltration capacity from the start of infiltration. Therefore, we must determine the true infiltration capacity at t = 10 min. To do so, first determine the time t p by solving the following equation: F(t) = t 0 i(t)dt and then evaluate f p (t p ) as follows. = f c t p + f o k At t = 10 min the actual volume of accumulated infiltration is: (1 e kt p ) (4) F(t = 10 min) = [(1.5) cm/h] (10 min/60 min/h) = 0.25 cm. Substituting this value for F(t) in equation 3 and solving for t p obtain: t p = h = min. Finally, the true infiltration capacity at 10 minutes is obtained using equation 1 as f p (t p ) = cm/h = f op. Alternatively, using equations 1 and 2 to eliminate time and expressing cumulative infiltration as a function of infiltration capacity obtain the following equation, F(t) = k ln( f p ) + f o f p f o k (5) 6) The rainfall rate at 10 minutes i = 6 cm/h exceeds the corresponding infiltration capacity f op = cm/h. Therefore, the actual infiltration rate equals the infiltration capacity, and the decay of infiltration capacity follows Horton's equation with an initial infiltration capacity equal to f op and starting at time t * = 10 min (Table 1 - Column 5 and Table 2 Column 3). That is (see Figure 2 and Figure 3), f p (t) = f c + ( f op )e k(t t * ) (6)
6 7) Because the precipitation rate exceeds the infiltration capacity there is excess precipitation available for runoff and depression storage, σ + v (Table 2 - Column 6). σ + v = i(t) f (t) (7) Table Eq Eq Eq. 6 Capacity, f p, F, P Actual Capacity
7 Table Eq Eq Eq Eq. 7 Capacity, f p Actual Capacity Intensity, i Actual Rate, f(t) Runoff rate σ + v
+ ( f o. (t) = f c. f c. )e kt (1)
 CIVE Basic Hydrology Jorge A. Ramírez Computations Example Assume that the time evolution of the infiltration capacity for a given soil is governed by Horton's equation (Note that this equation assumes
CIVE Basic Hydrology Jorge A. Ramírez Computations Example Assume that the time evolution of the infiltration capacity for a given soil is governed by Horton's equation (Note that this equation assumes
Module 1. Lecture 2: Weather and hydrologic cycle (contd.)
 Lecture 2: Weather and hydrologic cycle (contd.) Hydrology Hydor + logos (Both are Greek words) Hydor means water and logos means study. Hydrology is a science which deals with the occurrence, circulation
Lecture 2: Weather and hydrologic cycle (contd.) Hydrology Hydor + logos (Both are Greek words) Hydor means water and logos means study. Hydrology is a science which deals with the occurrence, circulation
Lecture 6: Precipitation Averages and Interception
 Lecture 6: Precipitation Averages and Interception Key Questions 1. How much and when does Whatcom County receive rain? 2. Where online can you find rainfall data for the state? 3. How is rainfall averaged
Lecture 6: Precipitation Averages and Interception Key Questions 1. How much and when does Whatcom County receive rain? 2. Where online can you find rainfall data for the state? 3. How is rainfall averaged
Precipitation Rabi H. Mohtar
 Precipitation Rabi H. Mohtar The objectives of this module are to present and analyze: 1) Precipitation forms, characteristics, and measurements 2) Intensity, Duration, Frequency (IDF) curves and rainfall
Precipitation Rabi H. Mohtar The objectives of this module are to present and analyze: 1) Precipitation forms, characteristics, and measurements 2) Intensity, Duration, Frequency (IDF) curves and rainfall
CIVIL ENGINEERING. Engineering Hydrology RIB-R T11 RIB. Detailed Explanations. Rank Improvement Batch ANSWERS. RIB(R)-18 CE Engineering Hydrology
 RIB-R T11 RIB Rank Improvement Batch Session 18-1 S.No. : 118_SK CIVIL ENGINEERING Engineering Hydrology ANSWERS 1. (b) 7. (c) 1. (c) 1. (b). (d). (c) 8. (a) 1. (a). (b). (c). (a). (d) 1. (c) 1. (a) 7.
RIB-R T11 RIB Rank Improvement Batch Session 18-1 S.No. : 118_SK CIVIL ENGINEERING Engineering Hydrology ANSWERS 1. (b) 7. (c) 1. (c) 1. (b). (d). (c) 8. (a) 1. (a). (b). (c). (a). (d) 1. (c) 1. (a) 7.
Rainfall Analysis. Prof. M.M.M. Najim
 Rainfall Analysis Prof. M.M.M. Najim Learning Outcome At the end of this section students will be able to Estimate long term mean rainfall for a new station Describe the usage of a hyetograph Define recurrence
Rainfall Analysis Prof. M.M.M. Najim Learning Outcome At the end of this section students will be able to Estimate long term mean rainfall for a new station Describe the usage of a hyetograph Define recurrence
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE STOCHASTIC HYDROLOGY. Lecture -29 Course Instructor : Prof. P. P. MUJUMDAR Department of Civil Engg., IISc.
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE STOCHASTIC HYDROLOGY Lecture -29 Course Instructor : Prof. P. P. MUJUMDAR Department of Civil Engg., IISc. Summary of the previous lecture Goodness of fit Chi-square test χ
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE STOCHASTIC HYDROLOGY Lecture -29 Course Instructor : Prof. P. P. MUJUMDAR Department of Civil Engg., IISc. Summary of the previous lecture Goodness of fit Chi-square test χ
12 SWAT USER S MANUAL, VERSION 98.1
 12 SWAT USER S MANUAL, VERSION 98.1 CANOPY STORAGE. Canopy storage is the water intercepted by vegetative surfaces (the canopy) where it is held and made available for evaporation. When using the curve
12 SWAT USER S MANUAL, VERSION 98.1 CANOPY STORAGE. Canopy storage is the water intercepted by vegetative surfaces (the canopy) where it is held and made available for evaporation. When using the curve
Geography 415 Hydrology
 1 Geography 415 Hydrology LAB 1 (January 23, 2003) TA: Drew Lejbak Office: ES 310, 220-5590, atlejbak@ucalgary.ca Hours: Friday 10:00am 12:00pm, or by appointment Drop Box: Outside ES 313 1. Estimation
1 Geography 415 Hydrology LAB 1 (January 23, 2003) TA: Drew Lejbak Office: ES 310, 220-5590, atlejbak@ucalgary.ca Hours: Friday 10:00am 12:00pm, or by appointment Drop Box: Outside ES 313 1. Estimation
Hydrologic Overview & Quantities
 Hydrologic Overview & Quantities It is important to understand the big picture when attempting to forecast. This includes the interactive components and hydrologic quantities. Hydrologic Cycle The complexity
Hydrologic Overview & Quantities It is important to understand the big picture when attempting to forecast. This includes the interactive components and hydrologic quantities. Hydrologic Cycle The complexity
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE STOCHASTIC HYDROLOGY. Lecture -30 Course Instructor : Prof. P. P. MUJUMDAR Department of Civil Engg., IISc.
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE STOCHASTIC HYDROLOGY Lecture -30 Course Instructor : Prof. P. P. MUJUMDAR Department of Civil Engg., IISc. Summary of the previous lecture IDF relationship Procedure for creating
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE STOCHASTIC HYDROLOGY Lecture -30 Course Instructor : Prof. P. P. MUJUMDAR Department of Civil Engg., IISc. Summary of the previous lecture IDF relationship Procedure for creating
WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Applications Precipitation Methods in GSSHA Learn how to use different precipitation sources in GSSHA models
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Applications Precipitation Methods in GSSHA Learn how to use different precipitation sources in GSSHA models Objectives Learn how to use several precipitation sources and
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Applications Precipitation Methods in GSSHA Learn how to use different precipitation sources in GSSHA models Objectives Learn how to use several precipitation sources and
Lecture 2: Precipitation
 2-1 GEOG415 Lecture 2: Precipitation Why do we study precipitation? Precipitation measurement -- depends on the study purpose. Non-recording (cumulative) Recording (tipping bucket) Important parameters
2-1 GEOG415 Lecture 2: Precipitation Why do we study precipitation? Precipitation measurement -- depends on the study purpose. Non-recording (cumulative) Recording (tipping bucket) Important parameters
CHAPTER VII FULLY DISTRIBUTED RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODEL USING GIS
 80 CHAPTER VII FULLY DISTRIBUTED RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODEL USING GIS 7.1GENERAL This chapter is discussed in six parts. Introduction to Runoff estimation using fully Distributed model is discussed in first
80 CHAPTER VII FULLY DISTRIBUTED RAINFALL-RUNOFF MODEL USING GIS 7.1GENERAL This chapter is discussed in six parts. Introduction to Runoff estimation using fully Distributed model is discussed in first
ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY
 ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY Prof. Rajesh Bhagat Asst. Professor Civil Engineering Department Yeshwantrao Chavan College Of Engineering Nagpur B. E. (Civil Engg.) M. Tech. (Enviro. Engg.) GCOE, Amravati VNIT,
ENGINEERING HYDROLOGY Prof. Rajesh Bhagat Asst. Professor Civil Engineering Department Yeshwantrao Chavan College Of Engineering Nagpur B. E. (Civil Engg.) M. Tech. (Enviro. Engg.) GCOE, Amravati VNIT,
THE DEVELOPMENT OF RAIN-BASED URBAN FLOOD FORECASTING METHOD FOR RIVER MANAGEMENT PRACTICE USING X-MP RADAR OBSERVATION
 Research Paper Advances in River Engineering, JSCE, Vol.19, 2013,June THE DEVELOPMENT OF RAIN-BASED URBAN FLOOD FORECASTING METHOD FOR RIVER MANAGEMENT PRACTICE USING X-MP RADAR OBSERVATION Seongsim YOON
Research Paper Advances in River Engineering, JSCE, Vol.19, 2013,June THE DEVELOPMENT OF RAIN-BASED URBAN FLOOD FORECASTING METHOD FOR RIVER MANAGEMENT PRACTICE USING X-MP RADAR OBSERVATION Seongsim YOON
Forest Hydrology: Lect. 9. Contents. Runoff, soil water and infiltration
 Forest Hydrology: Lect. 9 Contents Runoff, soil water and infiltration Learning objectives:. - Hillslope runoff generation processes; - Dynamics of runoff generation processes; - Hortonian and Dunnian
Forest Hydrology: Lect. 9 Contents Runoff, soil water and infiltration Learning objectives:. - Hillslope runoff generation processes; - Dynamics of runoff generation processes; - Hortonian and Dunnian
Impact of climate change on freshwater resources in the Changjiang river basin
 Impact of climate change on freshwater resources in the Changjiang river basin Wenfa Yang, Yan Huang Bureau of Hydrology, Changjiang Water Resources Commission, MWR, China April,2009 Objective To identify
Impact of climate change on freshwater resources in the Changjiang river basin Wenfa Yang, Yan Huang Bureau of Hydrology, Changjiang Water Resources Commission, MWR, China April,2009 Objective To identify
Quantitative Flood Forecasts using Short-term Radar Nowcasting
 Quantitative Flood Forecasts using Short-term Radar Nowcasting Enrique R. Vivoni *, Dara Entekhabi *, Rafael L. Bras *, Matthew P. Van Horne *, Valeri Y. Ivanov *, Chris Grassotti + and Ross Hoffman +
Quantitative Flood Forecasts using Short-term Radar Nowcasting Enrique R. Vivoni *, Dara Entekhabi *, Rafael L. Bras *, Matthew P. Van Horne *, Valeri Y. Ivanov *, Chris Grassotti + and Ross Hoffman +
GEOG415 Mid-term Exam 110 minute February 27, 2003
 GEOG415 Mid-term Exam 110 minute February 27, 2003 1 Name: ID: 1. The graph shows the relationship between air temperature and saturation vapor pressure. (a) Estimate the relative humidity of an air parcel
GEOG415 Mid-term Exam 110 minute February 27, 2003 1 Name: ID: 1. The graph shows the relationship between air temperature and saturation vapor pressure. (a) Estimate the relative humidity of an air parcel
Rucker Pond. Background
 Rucker Pond Background The Rucker Basin consists of two subbasins (East and West) that drain to a single area known as Rucker Pond. Both subbasins have the same hydraulic parameters, but have different
Rucker Pond Background The Rucker Basin consists of two subbasins (East and West) that drain to a single area known as Rucker Pond. Both subbasins have the same hydraulic parameters, but have different
TXHYETO.XLS: A Tool To Facilitate Use of Texas- Specific Hyetographs for Design Storm Modeling. Caroline M. Neale Texas Tech University
 TXHYETO.XLS: A Tool To Facilitate Use of Texas- Specific Hyetographs for Design Storm Modeling Caroline M. Neale Texas Tech University Acknowledgements Funding and direction provided by the Texas Department
TXHYETO.XLS: A Tool To Facilitate Use of Texas- Specific Hyetographs for Design Storm Modeling Caroline M. Neale Texas Tech University Acknowledgements Funding and direction provided by the Texas Department
Error Propagation from Radar Rainfall Nowcasting Fields to a Fully-Distributed Flood Forecasting Model
 Error Propagation from Radar Rainfall Nowcasting Fields to a Fully-Distributed Flood Forecasting Model Enrique R. Vivoni 1, Dara Entekhabi 2 and Ross N. Hoffman 3 1. Department of Earth and Environmental
Error Propagation from Radar Rainfall Nowcasting Fields to a Fully-Distributed Flood Forecasting Model Enrique R. Vivoni 1, Dara Entekhabi 2 and Ross N. Hoffman 3 1. Department of Earth and Environmental
GEOL 474/674 Practice Exam #1 Fall This exam counts 20% of your grade for this course; your instructions are as follows:
 Write your name here: This exam counts 20% of your grade for this course; your instructions are as follows: 1) You have 75 minutes to finish this exam. 2) No books, notes, or discussion is allowed. If
Write your name here: This exam counts 20% of your grade for this course; your instructions are as follows: 1) You have 75 minutes to finish this exam. 2) No books, notes, or discussion is allowed. If
Table (6): Annual precipitation amounts as recorded by stations X and Y. No. X Y
 Example: X and Y are two neighboring rainfall stations. Station X has complete records and station Y has some missing values. Find the linear correlation equation between the two series as mentioned in
Example: X and Y are two neighboring rainfall stations. Station X has complete records and station Y has some missing values. Find the linear correlation equation between the two series as mentioned in
Response of Flash Flood Early Warning Critical Rainfall to Storm Pattern in South Branch of Censhui Watershed
 Journal of Environmental Science and Engineering B 4 (2015) 637-648 doi:10.17265/2162-5263/2015.12.003 D DAVID PUBLISHING Response of Flash Flood Early Warning Critical Rainfall to Storm Changzhi Li, Baozhao
Journal of Environmental Science and Engineering B 4 (2015) 637-648 doi:10.17265/2162-5263/2015.12.003 D DAVID PUBLISHING Response of Flash Flood Early Warning Critical Rainfall to Storm Changzhi Li, Baozhao
Storm rainfall. Lecture content. 1 Analysis of storm rainfall 2 Predictive model of storm rainfall for a given
 Storm rainfall Lecture content 1 Analysis of storm rainfall 2 Predictive model of storm rainfall for a given max rainfall depth 1 rainfall duration and return period à Depth-Duration-Frequency curves 2
Storm rainfall Lecture content 1 Analysis of storm rainfall 2 Predictive model of storm rainfall for a given max rainfall depth 1 rainfall duration and return period à Depth-Duration-Frequency curves 2
CARFFG System Development and Theoretical Background
 CARFFG Steering Committee Meeting 15 SEPTEMBER 2015 Astana, KAZAKHSTAN CARFFG System Development and Theoretical Background Theresa M. Modrick, PhD Hydrologic Research Center Key Technical Components -
CARFFG Steering Committee Meeting 15 SEPTEMBER 2015 Astana, KAZAKHSTAN CARFFG System Development and Theoretical Background Theresa M. Modrick, PhD Hydrologic Research Center Key Technical Components -
Solution: The ratio of normal rainfall at station A to normal rainfall at station i or NR A /NR i has been calculated and is given in table below.
 3.6 ESTIMATION OF MISSING DATA Data for the period of missing rainfall data could be filled using estimation technique. The length of period up to which the data could be filled is dependent on individual
3.6 ESTIMATION OF MISSING DATA Data for the period of missing rainfall data could be filled using estimation technique. The length of period up to which the data could be filled is dependent on individual
STUDY ON THE PRECISION OF 1-MINUTE X-BAND MP RADAR RAINFALL DATA IN A SMALL URBAN WATERSHED
 Y. Yonese, et al., Int. J. Sus. Dev. Plann. Vol. 13, No. 4 (2018) 614 625 STUDY ON THE PRECISION OF 1-MINUTE X-BAND MP RADAR RAINFALL DATA IN A SMALL URBAN WATERSHED YOSHITOMO YONESE 1, AKIRA KAWAMURA
Y. Yonese, et al., Int. J. Sus. Dev. Plann. Vol. 13, No. 4 (2018) 614 625 STUDY ON THE PRECISION OF 1-MINUTE X-BAND MP RADAR RAINFALL DATA IN A SMALL URBAN WATERSHED YOSHITOMO YONESE 1, AKIRA KAWAMURA
At a certain moment the following temperatures are measured with a psychrometer: 25 C and 17,5 C
 ANSWERS Practical Day 1 Exercise Humidity Saturated vapour pressure e s (kpa) γ Temperature t ( C) In the figure above you see (an example of) the relation between vapour pressure and temperature. The
ANSWERS Practical Day 1 Exercise Humidity Saturated vapour pressure e s (kpa) γ Temperature t ( C) In the figure above you see (an example of) the relation between vapour pressure and temperature. The
Hillslope Hydrology Q 1 Q Understand hillslope runoff processes. 2. Understand the contribution of groundwater to storm runoff.
 Objectives Hillslope Hydrology Streams are the conduits of the surface and subsurface runoff generated in watersheds. SW-GW interaction needs to be understood from the watershed perspective. During a storm
Objectives Hillslope Hydrology Streams are the conduits of the surface and subsurface runoff generated in watersheds. SW-GW interaction needs to be understood from the watershed perspective. During a storm
CARPE DIEM CENTRE FOR WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH DELIVERABLE 9.5(NUID-CWRR) PRECIPITATION DATA ANALYSIS AND ERRORS DRAFT
 CARPE DIEM CENTRE FOR WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH DELIVERABLE 9.5(NUID-CWRR) PRECIPITATION DATA ANALYSIS AND ERRORS DRAFT by Micheal Bruen & Benoit Parmentier December 2004 Department of Civil Engineering
CARPE DIEM CENTRE FOR WATER RESOURCES RESEARCH DELIVERABLE 9.5(NUID-CWRR) PRECIPITATION DATA ANALYSIS AND ERRORS DRAFT by Micheal Bruen & Benoit Parmentier December 2004 Department of Civil Engineering
A new probability density function for spatial distribution of soil water storage capacity. leads to SCS curve number method
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 A new probability density function for spatial distribution of soil water storage capacity leads to SCS curve number method Dingbao ang Department of Civil, Environmental,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 A new probability density function for spatial distribution of soil water storage capacity leads to SCS curve number method Dingbao ang Department of Civil, Environmental,
Non-linearity effects in the process of floods generation
 Non-linearity effects in the process of floods generation M. FIORENTINO a & V. IACOBELLIS b a Dipartimento di Ingegneria e Fisica dell Ambiente, Università della Basilicata, Contrada Macchia Romana, I-851,
Non-linearity effects in the process of floods generation M. FIORENTINO a & V. IACOBELLIS b a Dipartimento di Ingegneria e Fisica dell Ambiente, Università della Basilicata, Contrada Macchia Romana, I-851,
KINEROS2/AGWA. Fig. 1. Schematic view (Woolhiser et al., 1990).
 KINEROS2/AGWA Introduction Kineros2 (KINematic runoff and EROSion) (K2) model was originated at the USDA-ARS in late 1960s and released until 1990 (Smith et al., 1995; Woolhiser et al., 1990). The spatial
KINEROS2/AGWA Introduction Kineros2 (KINematic runoff and EROSion) (K2) model was originated at the USDA-ARS in late 1960s and released until 1990 (Smith et al., 1995; Woolhiser et al., 1990). The spatial
1 BASIC CONCEPTS AND MODELS
 1 BASIC CONCEPTS AND ODELS 1.1 INTRODUCTION This Volume III in the series of textbooks is focused on applications of environmental isotopes in surface water hydrology. The term environmental means that
1 BASIC CONCEPTS AND ODELS 1.1 INTRODUCTION This Volume III in the series of textbooks is focused on applications of environmental isotopes in surface water hydrology. The term environmental means that
Workshop: Build a Basic HEC-HMS Model from Scratch
 Workshop: Build a Basic HEC-HMS Model from Scratch This workshop is designed to help new users of HEC-HMS learn how to apply the software. Not all the capabilities in HEC-HMS are demonstrated in the workshop
Workshop: Build a Basic HEC-HMS Model from Scratch This workshop is designed to help new users of HEC-HMS learn how to apply the software. Not all the capabilities in HEC-HMS are demonstrated in the workshop
Chapter 5 CALIBRATION AND VERIFICATION
 Chapter 5 CALIBRATION AND VERIFICATION This chapter contains the calibration procedure and data used for the LSC existing conditions model. The goal of the calibration effort was to develop a hydraulic
Chapter 5 CALIBRATION AND VERIFICATION This chapter contains the calibration procedure and data used for the LSC existing conditions model. The goal of the calibration effort was to develop a hydraulic
ABSTRACT. Dr. Richard H. McCuen, Civil and Environmental Engineering
 ABSTRACT Title of Document: SPATIAL MODELING AND UNIT HYDROGRAPH DEVELOPMENT WITH RADAR RAINFALL Stephanie Nicole Rew, Master of Science, 2009 Directed By: Dr. Richard H. McCuen, Civil and Environmental
ABSTRACT Title of Document: SPATIAL MODELING AND UNIT HYDROGRAPH DEVELOPMENT WITH RADAR RAINFALL Stephanie Nicole Rew, Master of Science, 2009 Directed By: Dr. Richard H. McCuen, Civil and Environmental
Rainfall and Design Storms
 Methods in Stormwater Management Using HydroCAD Rainfall and Design Storms H03 Rainfall and Design Storms.pdf 1 Topics Covered 1. Rainfall characteristics 2. Rainfall sources 3. Design Storms 4. Example:
Methods in Stormwater Management Using HydroCAD Rainfall and Design Storms H03 Rainfall and Design Storms.pdf 1 Topics Covered 1. Rainfall characteristics 2. Rainfall sources 3. Design Storms 4. Example:
INFLOW DESIGN FLOOD CONTROL SYSTEM PLAN 40 C.F.R. PART PLANT YATES ASH POND 2 (AP-2) GEORGIA POWER COMPANY
 INFLOW DESIGN FLOOD CONTROL SYSTEM PLAN 40 C.F.R. PART 257.82 PLANT YATES ASH POND 2 (AP-2) GEORGIA POWER COMPANY EPA s Disposal of Coal Combustion Residuals from Electric Utilities Final Rule (40 C.F.R.
INFLOW DESIGN FLOOD CONTROL SYSTEM PLAN 40 C.F.R. PART 257.82 PLANT YATES ASH POND 2 (AP-2) GEORGIA POWER COMPANY EPA s Disposal of Coal Combustion Residuals from Electric Utilities Final Rule (40 C.F.R.
Homework 10. Logan Dry Canyon Detention Basin Design Case Study Date: 4/14/14 Due: 4/25/14
 Homework 10. Logan Dry Canyon Detention Basin Design Case Study Date: 4/14/14 Due: 4/25/14 Section 1: Case Study Introduction This case study serves as an integrative problem based learning exercise. In
Homework 10. Logan Dry Canyon Detention Basin Design Case Study Date: 4/14/14 Due: 4/25/14 Section 1: Case Study Introduction This case study serves as an integrative problem based learning exercise. In
LESSON HEC-HMS
 LESSON 2.2 - HEC-HMS Introduction: TEAM 8 SCS method: The input data: Thiessen Polygons: Concentration Lag Time: SCS Method: Calculation of CN: Result figures: CONSTRUCTING HYDROGRAPH WITH HEC-HMS: Rainfall
LESSON 2.2 - HEC-HMS Introduction: TEAM 8 SCS method: The input data: Thiessen Polygons: Concentration Lag Time: SCS Method: Calculation of CN: Result figures: CONSTRUCTING HYDROGRAPH WITH HEC-HMS: Rainfall
Basin characteristics
 Basin characteristics From hydrological processes at the point scale to hydrological processes throughout the space continuum: point scale à river basin The watershed characteristics (shape, length, topography,
Basin characteristics From hydrological processes at the point scale to hydrological processes throughout the space continuum: point scale à river basin The watershed characteristics (shape, length, topography,
Assessment of rainfall observed by weather radar and its effect on hydrological simulation performance
 386 Hydrology in a Changing World: Environmental and Human Dimensions Proceedings of FRIED-Water 2014, Montpellier, France, October 2014 (IAHS Publ. 363, 2014). Assessment of rainfall observed by weather
386 Hydrology in a Changing World: Environmental and Human Dimensions Proceedings of FRIED-Water 2014, Montpellier, France, October 2014 (IAHS Publ. 363, 2014). Assessment of rainfall observed by weather
Advanced Hydrology Prof. Dr. Ashu Jain Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur. Lecture 14
 Advanced Hydrology Prof. Dr. Ashu Jain Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 14 Good morning and welcome to this video course on advanced hydrology. In the last
Advanced Hydrology Prof. Dr. Ashu Jain Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur Lecture 14 Good morning and welcome to this video course on advanced hydrology. In the last
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE STOCHASTIC HYDROLOGY. Lecture -27 Course Instructor : Prof. P. P. MUJUMDAR Department of Civil Engg., IISc.
 INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE STOCHASTIC HYDROLOGY Lecture -27 Course Instructor : Prof. P. P. MUJUMDAR Department of Civil Engg., IISc. Summary of the previous lecture Frequency factors Normal distribution
INDIAN INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE STOCHASTIC HYDROLOGY Lecture -27 Course Instructor : Prof. P. P. MUJUMDAR Department of Civil Engg., IISc. Summary of the previous lecture Frequency factors Normal distribution
2016 Fall Conditions Report
 2016 Fall Conditions Report Prepared by: Hydrologic Forecast Centre Date: December 13, 2016 Table of Contents TABLE OF FIGURES... ii EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 1 BACKGROUND... 5 SUMMER AND FALL PRECIPITATION...
2016 Fall Conditions Report Prepared by: Hydrologic Forecast Centre Date: December 13, 2016 Table of Contents TABLE OF FIGURES... ii EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 1 BACKGROUND... 5 SUMMER AND FALL PRECIPITATION...
Snow Melt with the Land Climate Boundary Condition
 Snow Melt with the Land Climate Boundary Condition GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1200, 700-6th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada T2P 0T8 Main: +1 403 269 2002 Fax: +1 888 463 2239 Introduction
Snow Melt with the Land Climate Boundary Condition GEO-SLOPE International Ltd. www.geo-slope.com 1200, 700-6th Ave SW, Calgary, AB, Canada T2P 0T8 Main: +1 403 269 2002 Fax: +1 888 463 2239 Introduction
H Y D R O L O G Y I R R I G A T I O N C E
 H Y D R O L O G Y & I R R I G A T I O N C E Chapter 1: HYDROLOGICAL CYCLE AND PRECIPITATION 7 HYDROLOGIC CYCLE... 7 PRECIPITATION... 8 MEASUREMENT OF PRECIPITATION... 9 ESTIMATION OF MISSING DATA... 15
H Y D R O L O G Y & I R R I G A T I O N C E Chapter 1: HYDROLOGICAL CYCLE AND PRECIPITATION 7 HYDROLOGIC CYCLE... 7 PRECIPITATION... 8 MEASUREMENT OF PRECIPITATION... 9 ESTIMATION OF MISSING DATA... 15
Detailed Storm Rainfall Analysis for Hurricane Ivan Flooding in Georgia Using the Storm Precipitation Analysis System (SPAS) and NEXRAD Weather Radar
 Detailed Storm Rainfall Analysis for Hurricane Ivan Flooding in Georgia Using the Storm Precipitation Analysis System (SPAS) and NEXRAD Weather Radar Ed Tomlinson, PhD and Bill Kappel Applied Weather Associates
Detailed Storm Rainfall Analysis for Hurricane Ivan Flooding in Georgia Using the Storm Precipitation Analysis System (SPAS) and NEXRAD Weather Radar Ed Tomlinson, PhD and Bill Kappel Applied Weather Associates
EFFECTS OF TEMPORAL RESOLUTION ON RIVER FLOW FORECASTING WITH SIMPLE INTERCEPTION MODEL WITHIN A DISTRIBUTED HYDROLOGICAL MODEL
 www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol8issue1/ijrras_8_1_02.pdf EFFECTS OF TEMPORAL RESOLUTION ON RIVER FLOW FORECASTING WITH SIMPLE INTERCEPTION MODEL WITHIN A DISTRIBUTED HYDROLOGICAL MODEL Azinoor Azida ABU
www.arpapress.com/volumes/vol8issue1/ijrras_8_1_02.pdf EFFECTS OF TEMPORAL RESOLUTION ON RIVER FLOW FORECASTING WITH SIMPLE INTERCEPTION MODEL WITHIN A DISTRIBUTED HYDROLOGICAL MODEL Azinoor Azida ABU
Type of Precipitation
 Precipitation Type of Precipitation Measurement of rainfall Location of rain gauges Categorisation Climate Estimation of basin rainfall Finding Average rainfall, Standard deviation, and Coefficient of
Precipitation Type of Precipitation Measurement of rainfall Location of rain gauges Categorisation Climate Estimation of basin rainfall Finding Average rainfall, Standard deviation, and Coefficient of
APPENDIX B Hydrologic Model Spring Event
 Jock River Flood Risk Mapping (within the City of Ottawa) Hydrology Report July 2004 PageB1 APPENDIX B Hydrologic Model Spring Event Snowmelt+Rainfall Calibration and Validation Results Design Events Explanation
Jock River Flood Risk Mapping (within the City of Ottawa) Hydrology Report July 2004 PageB1 APPENDIX B Hydrologic Model Spring Event Snowmelt+Rainfall Calibration and Validation Results Design Events Explanation
5/4/2017 Fountain Creek. Gage Analysis. Homework 6. Clifton, Cundiff, Pour, Queen, and Zey CIVE 717
 5/4/2017 Fountain Creek Gage Analysis Homework 6 Clifton, Cundiff, Pour, Queen, and Zey CIVE 717 Introduction: The CIVE 717 class members, Nate Clifton, Susan Cundiff, Ali Reza Nowrooz Pour, Robbie Queen
5/4/2017 Fountain Creek Gage Analysis Homework 6 Clifton, Cundiff, Pour, Queen, and Zey CIVE 717 Introduction: The CIVE 717 class members, Nate Clifton, Susan Cundiff, Ali Reza Nowrooz Pour, Robbie Queen
Darcy s Law, Richards Equation, and Green-Ampt Equation
 Darcy s Law, Richards Equation, and Green-Ampt Equation 1. Darcy s Law Fluid potential: in classic hydraulics, the fluid potential M is stated in terms of Bernoulli Equation (1.1) P, pressure, [F L!2 ]
Darcy s Law, Richards Equation, and Green-Ampt Equation 1. Darcy s Law Fluid potential: in classic hydraulics, the fluid potential M is stated in terms of Bernoulli Equation (1.1) P, pressure, [F L!2 ]
Parameterization using ArcView GIS in medium and large watershed modelling
 50 GIS and Remote Sensing in Hydrology, Water Resources and Environment (Proceedings of ICGRHWE held at the Three Gorges Dam, China, September 2003). IAHS Publ. 289, 2004 Parameterization using ArcView
50 GIS and Remote Sensing in Hydrology, Water Resources and Environment (Proceedings of ICGRHWE held at the Three Gorges Dam, China, September 2003). IAHS Publ. 289, 2004 Parameterization using ArcView
DETECTION AND FORECASTING - THE CZECH EXPERIENCE
 1 STORM RAINFALL DETECTION AND FORECASTING - THE CZECH EXPERIENCE J. Danhelka * Czech Hydrometeorological Institute, Prague, Czech Republic Abstract Contribution presents the state of the art of operational
1 STORM RAINFALL DETECTION AND FORECASTING - THE CZECH EXPERIENCE J. Danhelka * Czech Hydrometeorological Institute, Prague, Czech Republic Abstract Contribution presents the state of the art of operational
Each basin is surrounded & defined by a drainage divide (high point from which water flows away) Channel initiation
 DRAINAGE BASINS A drainage basin or watershed is defined from a downstream point, working upstream, to include all of the hillslope & channel areas which drain to that point Each basin is surrounded &
DRAINAGE BASINS A drainage basin or watershed is defined from a downstream point, working upstream, to include all of the hillslope & channel areas which drain to that point Each basin is surrounded &
HYDRAULIC MODELING OF SOIL ERORION
 18-21 August 28, Daejeon, Korea HYDRAULIC MODELING OF SOIL ERORION Liu Qing-quan Institute of Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 18, China. Email: qqliu@imech.ac.cn ABSTRACT: The prediction
18-21 August 28, Daejeon, Korea HYDRAULIC MODELING OF SOIL ERORION Liu Qing-quan Institute of Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 18, China. Email: qqliu@imech.ac.cn ABSTRACT: The prediction
Sediment Capture in Pervious Concrete Pavement tsystems: Effects on Hydrological Performance and Suspended Solids
 Concrete Sustainability Conference April 14 th 2010, Tempe, AZ Sediment Capture in Pervious Concrete Pavement tsystems: Effects on Hydrological l Performance and Suspended Solids Discharge Luis A. Mata,
Concrete Sustainability Conference April 14 th 2010, Tempe, AZ Sediment Capture in Pervious Concrete Pavement tsystems: Effects on Hydrological l Performance and Suspended Solids Discharge Luis A. Mata,
Lecture 5: Precipitation
 Lecture 5: Precipitation Key Questions 1. What physical concepts control the formation of precipitation (air pressure, expanding gases and cooling, and vapor pressure)? 2. What are some air mass lifting
Lecture 5: Precipitation Key Questions 1. What physical concepts control the formation of precipitation (air pressure, expanding gases and cooling, and vapor pressure)? 2. What are some air mass lifting
Appendix B Equations and Examples
 Equations and Examples Purpose The purpose of this appendix is to provide background equations and example problems for clarity of calculations used throughout the manual. This appendix is divided into
Equations and Examples Purpose The purpose of this appendix is to provide background equations and example problems for clarity of calculations used throughout the manual. This appendix is divided into
CE 394K.2 Hydrology. Homework Problem Set #3. Due Thurs March Theoretical study of infiltration at ponding time using Philip's equation
 CE 394K2 Hydrology Homework Problem Set #3 Due Thurs March 29 Problems in "Applied Hydrology" 423 nfiltration by Horton's method 432 nfiltration by Green-Ampt method 443 Ponding time and cumulative infiltration
CE 394K2 Hydrology Homework Problem Set #3 Due Thurs March 29 Problems in "Applied Hydrology" 423 nfiltration by Horton's method 432 nfiltration by Green-Ampt method 443 Ponding time and cumulative infiltration
Governing Rules of Water Movement
 Governing Rules of Water Movement Like all physical processes, the flow of water always occurs across some form of energy gradient from high to low e.g., a topographic (slope) gradient from high to low
Governing Rules of Water Movement Like all physical processes, the flow of water always occurs across some form of energy gradient from high to low e.g., a topographic (slope) gradient from high to low
Jones Creek Case Study
 Jones Creek Case Study Introduction In this case study we will examine the fictitious watershed of Jones Creek. This watershed has one confluence and can therefore be divided into three subbasins. The
Jones Creek Case Study Introduction In this case study we will examine the fictitious watershed of Jones Creek. This watershed has one confluence and can therefore be divided into three subbasins. The
Design Storms for Hydrologic Analysis
 Design Storms for Hydrologic Analysis Course Description This course is designed to fulfill two hours of continuing education credit for Professional Engineers. Its objective is to provide students with
Design Storms for Hydrologic Analysis Course Description This course is designed to fulfill two hours of continuing education credit for Professional Engineers. Its objective is to provide students with
Determination of Urban Runoff Using ILLUDAS and GIS
 Texas A&M University Department of Civil Engineering Instructor: Dr. Francisco Olivera CVEN689 Applications of GIS to Civil Engineering Determination of Urban Runoff Using ILLUDAS and GIS Tae Jin Kim 03.
Texas A&M University Department of Civil Engineering Instructor: Dr. Francisco Olivera CVEN689 Applications of GIS to Civil Engineering Determination of Urban Runoff Using ILLUDAS and GIS Tae Jin Kim 03.
Project Description. Project Options. End Analysis On... Apr 26, :00:00. Rainfall Details
 Project Description File Name... 323 - Att Pond 3 East PIPES ONLY.SPF Project Options Flow Units... Elevation Type... Hydrology Method... EPA SWMM Infiltration Method... Link Routing Method... Enable Overflow
Project Description File Name... 323 - Att Pond 3 East PIPES ONLY.SPF Project Options Flow Units... Elevation Type... Hydrology Method... EPA SWMM Infiltration Method... Link Routing Method... Enable Overflow
2012 Rainfall, Runoff, Water Level & Temperature Beebe Lake Wright County, MN (# )
 www.fixmylake.com 18029 83 rd Avenue North Maple Grove, MN 55311 mail@freshwatersci.com (651) 336-8696 2012 Rainfall, Runoff, Water Level & Temperature Beebe Lake Wright County, MN (#86-0023) Prepared
www.fixmylake.com 18029 83 rd Avenue North Maple Grove, MN 55311 mail@freshwatersci.com (651) 336-8696 2012 Rainfall, Runoff, Water Level & Temperature Beebe Lake Wright County, MN (#86-0023) Prepared
ψ ae is equal to the height of the capillary rise in the soil. Ranges from about 10mm for gravel to 1.5m for silt to several meters for clay.
 Contents 1 Infiltration 1 1a Hydrologic soil horizons...................... 1 1b Infiltration Process......................... 2 1c Measurement............................ 2 1d Richard s Equation.........................
Contents 1 Infiltration 1 1a Hydrologic soil horizons...................... 1 1b Infiltration Process......................... 2 1c Measurement............................ 2 1d Richard s Equation.........................
An Alternative Temporal Rainfall Distribution for Hydrologic Analysis and Design
 An Alternative Temporal Rainfall Distribution for Hydrologic Analysis and Design Joseph P. Wilson, PE, PH Wilson Hydro, LLC PhD Candidate Missouri University of Science Technology Rolla, Missouri Sorry
An Alternative Temporal Rainfall Distribution for Hydrologic Analysis and Design Joseph P. Wilson, PE, PH Wilson Hydro, LLC PhD Candidate Missouri University of Science Technology Rolla, Missouri Sorry
Memorandum. Background
 Memorandum To: Kevin Stewart, P.E., Information Systems & Flood Warning Program Manager From: Mark Mitisek, H.I.T. Reviewed by: Kelly Close, P.E. Date: 02/11/2013 Project: Boulder Creek Hydromodel Subject:
Memorandum To: Kevin Stewart, P.E., Information Systems & Flood Warning Program Manager From: Mark Mitisek, H.I.T. Reviewed by: Kelly Close, P.E. Date: 02/11/2013 Project: Boulder Creek Hydromodel Subject:
HEC-HMS Lab 2 Using Thiessen Polygon and Inverse Distance Weighting
 HEC-HMS Lab 2 Using Thiessen Polygon and Inverse Distance Weighting Created by Venkatesh Merwade (vmerwade@purdue.edu) Learning outcomes The objective of this lab is to learn how to input data from multiple
HEC-HMS Lab 2 Using Thiessen Polygon and Inverse Distance Weighting Created by Venkatesh Merwade (vmerwade@purdue.edu) Learning outcomes The objective of this lab is to learn how to input data from multiple
Flood Frequency Mapping using Multirun results from Infoworks RS applied to the river basin of the Yser, Belgium
 Flood Frequency Mapping using Multirun results from Infoworks RS applied to the river basin of the Yser, Belgium Ir. Sven Verbeke Aminal, division Water, Flemish Government, Belgium Introduction Aminal
Flood Frequency Mapping using Multirun results from Infoworks RS applied to the river basin of the Yser, Belgium Ir. Sven Verbeke Aminal, division Water, Flemish Government, Belgium Introduction Aminal
INTRODUCTION TO HYDROLOGIC MODELING USING HEC-HMS
 INTRODUCTION TO HYDROLOGIC MODELING USING HEC-HMS By Thomas T. Burke, Jr., PhD, PE Luke J. Sherry, PE, CFM Christopher B. Burke Engineering, Ltd. October 8, 2014 1 SEMINAR OUTLINE Overview of hydrologic
INTRODUCTION TO HYDROLOGIC MODELING USING HEC-HMS By Thomas T. Burke, Jr., PhD, PE Luke J. Sherry, PE, CFM Christopher B. Burke Engineering, Ltd. October 8, 2014 1 SEMINAR OUTLINE Overview of hydrologic
TABLE OF CONTENTS. 3.1 Synoptic Patterns Precipitation and Topography Precipitation Regionalization... 11
 TABLE OF CONTENTS ABSTRACT... iii 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 DATA SOURCES AND METHODS... 2 2.1 Data Sources... 2 2.2 Frequency Analysis... 2 2.2.1 Precipitation... 2 2.2.2 Streamflow... 2 2.3 Calculation of
TABLE OF CONTENTS ABSTRACT... iii 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 DATA SOURCES AND METHODS... 2 2.1 Data Sources... 2 2.2 Frequency Analysis... 2 2.2.1 Precipitation... 2 2.2.2 Streamflow... 2 2.3 Calculation of
Review of existing statistical methods for flood frequency estimation in Greece
 EU COST Action ES0901: European Procedures for Flood Frequency Estimation (FloodFreq) 3 rd Management Committee Meeting, Prague, 28 29 October 2010 WG2: Assessment of statistical methods for flood frequency
EU COST Action ES0901: European Procedures for Flood Frequency Estimation (FloodFreq) 3 rd Management Committee Meeting, Prague, 28 29 October 2010 WG2: Assessment of statistical methods for flood frequency
Haiti and Dominican Republic Flash Flood Initial Planning Meeting
 Dr Rochelle Graham Climate Scientist Haiti and Dominican Republic Flash Flood Initial Planning Meeting September 7 th to 9 th, 2016 Hydrologic Research Center http://www.hrcwater.org Haiti and Dominican
Dr Rochelle Graham Climate Scientist Haiti and Dominican Republic Flash Flood Initial Planning Meeting September 7 th to 9 th, 2016 Hydrologic Research Center http://www.hrcwater.org Haiti and Dominican
Use of SWAT to Scale Sediment Delivery from Field to Watershed in an Agricultural Landscape with Depressions
 Use of SWAT to Scale Sediment Delivery from Field to Watershed in an Agricultural Landscape with Depressions James E. Almendinger St. Croix Watershed Research Station, Science Museum of Minnesota Marylee
Use of SWAT to Scale Sediment Delivery from Field to Watershed in an Agricultural Landscape with Depressions James E. Almendinger St. Croix Watershed Research Station, Science Museum of Minnesota Marylee
Haiti-Dominican Republic Flash Flood Guidance (HDRFFG) System: Development of System Products
 Haiti-Dominican Republic Flash Flood Guidance (HDRFFG) System: Development of System Products Theresa M. Modrick, PhD Hydrologic Research Center HDRFFG Initial Planning Meeting 07-09 Sep 2015 Santo Domingo,
Haiti-Dominican Republic Flash Flood Guidance (HDRFFG) System: Development of System Products Theresa M. Modrick, PhD Hydrologic Research Center HDRFFG Initial Planning Meeting 07-09 Sep 2015 Santo Domingo,
Precipitation. Prof. M.M.M. Najim
 Precipitation Prof. M.M.M. Najim Learning Outcome At the end of this section students will be able to Explain different forms of precipitation Identify different types of rain gauges Measure rainfall using
Precipitation Prof. M.M.M. Najim Learning Outcome At the end of this section students will be able to Explain different forms of precipitation Identify different types of rain gauges Measure rainfall using
Inflow forecasting for lakes using Artificial Neural Networks
 Flood Recovery Innovation and Response III 143 Inflow forecasting for lakes using Artificial Neural Networks R. K. Suryawanshi 1, S. S. Gedam 1 & R. N. Sankhua 2 1 CSRE, IIT Bombay, Mumbai, India 2 National
Flood Recovery Innovation and Response III 143 Inflow forecasting for lakes using Artificial Neural Networks R. K. Suryawanshi 1, S. S. Gedam 1 & R. N. Sankhua 2 1 CSRE, IIT Bombay, Mumbai, India 2 National
Engineering Hydrology
 Engineering Hydrology Prof. Rajesh Bhagat Asst. Professor Civil Engineering Department Yeshwantrao Chavan College Of Engineering Nagpur B. E. (Civil Engg.) M. Tech. (Enviro. Engg.) GCOE, Amravati VNIT,
Engineering Hydrology Prof. Rajesh Bhagat Asst. Professor Civil Engineering Department Yeshwantrao Chavan College Of Engineering Nagpur B. E. (Civil Engg.) M. Tech. (Enviro. Engg.) GCOE, Amravati VNIT,
Engineering Hydrology
 Engineering Hydrology Prof. Rajesh Bhagat Asst. Professor Civil Engineering Department Yeshwantrao Chavan College Of Engineering Nagpur B. E. (Civil Engg.) M. Tech. (Enviro. Engg.) GCOE, Amravati VNIT,
Engineering Hydrology Prof. Rajesh Bhagat Asst. Professor Civil Engineering Department Yeshwantrao Chavan College Of Engineering Nagpur B. E. (Civil Engg.) M. Tech. (Enviro. Engg.) GCOE, Amravati VNIT,
Spatial Variability of Satellite Derived Rainfall Erosivity Factors (R-Factors) for a Watershed near Allahabad
 Vol. 11, pp. 71-78 (2011) Journal of Agricultural Physics ISSN 0973-032X http://www.agrophysics.in Research Article Spatial Variability of Satellite Derived Rainfall Erosivity Factors (R-Factors) for a
Vol. 11, pp. 71-78 (2011) Journal of Agricultural Physics ISSN 0973-032X http://www.agrophysics.in Research Article Spatial Variability of Satellite Derived Rainfall Erosivity Factors (R-Factors) for a
Drainage Analysis. Appendix F
 Drainage Analysis Appendix F Golden View Drive Elizabeth Street LMORE CREEK Ricky Road Rabbit Creek Road LITTLE RABBIT CREEK East 156th Avenue MOA Project #10-026 Golden View Drive Intersection
Drainage Analysis Appendix F Golden View Drive Elizabeth Street LMORE CREEK Ricky Road Rabbit Creek Road LITTLE RABBIT CREEK East 156th Avenue MOA Project #10-026 Golden View Drive Intersection
Basins-Level Heavy Rainfall and Flood Analyses
 Basins-Level Heavy Rainfall and Flood Analyses Peng Gao, Greg Carbone, and Junyu Lu Department of Geography, University of South Carolina (gaop@mailbox.sc.edu, carbone@mailbox.sc.edu, jlu@email.sc.edu)
Basins-Level Heavy Rainfall and Flood Analyses Peng Gao, Greg Carbone, and Junyu Lu Department of Geography, University of South Carolina (gaop@mailbox.sc.edu, carbone@mailbox.sc.edu, jlu@email.sc.edu)
DISCUSSIONS AND CLOSURES
 DISCUSSIONS AND CLOSURES Discussion of Rational Hydrograph Method for Small Urban Watersheds by James C. Y. Guo July/August 2001, Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 352 356. Sushil K. Singh 1 1 Scientist El, National
DISCUSSIONS AND CLOSURES Discussion of Rational Hydrograph Method for Small Urban Watersheds by James C. Y. Guo July/August 2001, Vol. 6, No. 4, pp. 352 356. Sushil K. Singh 1 1 Scientist El, National
Rainfall-runoff model with non-linear reservoir
 Rainfall-runoff model with non-linear reservoir R.J.Oosterbaan On website https://www.waterlog.info Theory of the RainOff model to be found on https://www.waterlog.info/rainoff.htm Introduction The runoff
Rainfall-runoff model with non-linear reservoir R.J.Oosterbaan On website https://www.waterlog.info Theory of the RainOff model to be found on https://www.waterlog.info/rainoff.htm Introduction The runoff
MET 3102-U01 PHYSICAL CLIMATOLOGY (ID 17901) Lecture 14
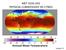 MET 3102-U01 PHYSICAL CLIMATOLOGY (ID 17901) Lecture 14 The hydrologic cycle evaporation vapor transport precipitation precipitation evaporation runoff Evaporation, precipitation, etc. in cm Vapor transported
MET 3102-U01 PHYSICAL CLIMATOLOGY (ID 17901) Lecture 14 The hydrologic cycle evaporation vapor transport precipitation precipitation evaporation runoff Evaporation, precipitation, etc. in cm Vapor transported
A PARAMETER ESTIMATE FOR THE LAND SURFACE MODEL VIC WITH HORTON AND DUNNE RUNOFF MECHANISM FOR RIVER BASINS IN CHINA
 A PARAMETER ESTIMATE FOR THE LAND SURFACE MODEL VIC WITH HORTON AND DUNNE RUNOFF MECHANISM FOR RIVER BASINS IN CHINA ZHENGHUI XIE Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences Beijing,
A PARAMETER ESTIMATE FOR THE LAND SURFACE MODEL VIC WITH HORTON AND DUNNE RUNOFF MECHANISM FOR RIVER BASINS IN CHINA ZHENGHUI XIE Institute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences Beijing,
Generation of synthetic design storms for the Upper Thames River basin
 Generation of synthetic design storms for the Upper Thames River basin CFCAS project: Assessment of Water Resources Risk and Vulnerability to Changing Climatic Conditions Project Report V. November 2004
Generation of synthetic design storms for the Upper Thames River basin CFCAS project: Assessment of Water Resources Risk and Vulnerability to Changing Climatic Conditions Project Report V. November 2004
2 Development of a Physically Based Hydrologic Model of the Upper Cosumnes Basin
 2 Development of a Physically Based Hydrologic Model of the Upper Cosumnes Basin 2.1 Introduction The physically based watershed hydrologic model, WEHY (watershed environmental hydrology) model (Kavvas
2 Development of a Physically Based Hydrologic Model of the Upper Cosumnes Basin 2.1 Introduction The physically based watershed hydrologic model, WEHY (watershed environmental hydrology) model (Kavvas
SNOW AND GLACIER HYDROLOGY
 SNOW AND GLACIER HYDROLOGY by PRATAP SINGH National Institute of Hydrology, Roorkee, India and VIJAY P. SINGH Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge,
SNOW AND GLACIER HYDROLOGY by PRATAP SINGH National Institute of Hydrology, Roorkee, India and VIJAY P. SINGH Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge,
2017 Fall Conditions Report
 2017 Fall Conditions Report Prepared by: Hydrologic Forecast Centre Date: November 15, 2017 Table of Contents TABLE OF FIGURES... ii EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 1 BACKGROUND... 4 SUMMER AND FALL PRECIPITATION...
2017 Fall Conditions Report Prepared by: Hydrologic Forecast Centre Date: November 15, 2017 Table of Contents TABLE OF FIGURES... ii EXECUTIVE SUMMARY... 1 BACKGROUND... 4 SUMMER AND FALL PRECIPITATION...
EFFICIENCY OF THE INTEGRATED RESERVOIR OPERATION FOR FLOOD CONTROL IN THE UPPER TONE RIVER OF JAPAN CONSIDERING SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF RAINFALL
 EFFICIENCY OF THE INTEGRATED RESERVOIR OPERATION FOR FLOOD CONTROL IN THE UPPER TONE RIVER OF JAPAN CONSIDERING SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF RAINFALL Dawen YANG, Eik Chay LOW and Toshio KOIKE Department of
EFFICIENCY OF THE INTEGRATED RESERVOIR OPERATION FOR FLOOD CONTROL IN THE UPPER TONE RIVER OF JAPAN CONSIDERING SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF RAINFALL Dawen YANG, Eik Chay LOW and Toshio KOIKE Department of
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards
 UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Flood and Flood Hazards Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG, Legon College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education
UGRC 144 Science and Technology in Our Lives/Geohazards Flood and Flood Hazards Dr. Patrick Asamoah Sakyi Department of Earth Science, UG, Legon College of Education School of Continuing and Distance Education
APPLICATION OF THE GRADEX METHOD TO ARID AREA OUED SEGGUEUR WATERSHED, ALGERIA
 APPLICATION OF THE GRADEX METHOD TO ARID AREA OUED SEGGUEUR WATERSHED, ALGERIA A. Talia 1, M. Meddi 2 1 Amel TALIA LSTE, Mascara University, E-mail: talia_a2003@yahoo;fr 2 Mohamed MEDD LGEE, E-mail: mmeddi@yahoo.fr
APPLICATION OF THE GRADEX METHOD TO ARID AREA OUED SEGGUEUR WATERSHED, ALGERIA A. Talia 1, M. Meddi 2 1 Amel TALIA LSTE, Mascara University, E-mail: talia_a2003@yahoo;fr 2 Mohamed MEDD LGEE, E-mail: mmeddi@yahoo.fr
