Plan for 2 nd half. Just when you thought it was safe. Just when you thought it was safe. Theory Hall of Fame. Chomsky Normal Form
|
|
|
- Bertha Bennett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Plan for 2 nd half Pumping Lemma for CFLs The Return of the Pumping Lemma Just when you thought it was safe Return of the Pumping Lemma Recall: With Regular Languages The Pumping Lemma showed that if a string in a regular language is long enough, it would have to visit at least one state in the corresponding FA more than once. Just when you thought it was safe CFLs have a Pumping Lemma as well But before we start that! A context free grammar is in Chomsky Normal Form (CNF) if every production is of the form: A BC A a Where A,B, and C are variables and a is a terminal. Theory Hall of Fame Noam Chomsky The Grammar Guy 1928 b. Philadelphia, PA PhD UPenn (1955) Linguistics Prof at MIT (Linguistics) ( present) Probably more famous for his leftist political views.
2 If we can put a CFG into CNF, then we can calculate the depth of the longest branch of a parse tree for the derivation of a string. B A C At most 2 branches at every node 3 Step process: 1. Remove ε - Productions 2. Remove Unit Productions 3. Remove Useless Symbols a A ε -Productions is a production of the form A ε Basic idea Very similar to removing ε transitions from a NFAε Find the set of all variables A such that A * ε (set of nullable variables) For all productions that contain a nullable variable on the right hand side, add a production that eliminates the nullable from the right hand side We must be a bit careful here If ε is in a CFL, then the production S ε must be in the production set. The algorithm to be described will generate L {ε} Step 1: Find the set of nullable variables: Example: S AB A aaa ε B bbb ε Step 2: Remove nullable variables For all productions A βwhere β contains nullable variables, add a new production with each nullable removed from β All variables are nullable A and B are nullable since A εand B ε S is nullable since S AB and A and B are nullable
3 Step 2: Remove nullable variables Example: S AB A aaa ε B bbb ε All variables are nullable Step 2: Remove nullable variables Example: Consider: S AB Add to P: S A and S B Consider: A aaa Add to P: A aa and A a Consider: B bbb Add to P: B bb and B b Step 2: Remove nullable variables Our grammar now looks like: S AB A B A aaa aa a ε B bbb bb b ε Step 3: Remove your ε -Productions Example: Remove A εand B ε Our final grammar looks like: S AB A B A aaa aa a B bbb bb b Questions? A Unit Productions is a production of the form A B where A and B are variable Basic idea Very similar to removing ε productions For each variable A, find the set of all variables B such that A * B by just following unit productions (A-derivable) For all variables B that are A derivable and for all productions B α, add the production A α Step 0: Remove ε -Productions using the previous algorithm.
4 Step 1: For all variables A find the set of A-derivable variables: Recursive definition of A-derivable 1. If A B then B is A-derivable 2. If C is A derivable and C B (and B A), then B is A derivable 3. No other variables are A-derivable. Step 1: For all variables A find the set of A- derivable variables: Example: S S + T T T T * F F F (S) a Let s find the set of S-derivable variables: T is S derivable since S T F is S derivable since T F and T is S derivable Step 1: For all variables A find the set of A- derivable variables: Example: S S + T T T T * F F F (S) a Step 2: For each variable A, if B is A- derivable, for each non-unit production B β, add the production A β S-derivable = {T, F} T-derivable = {F} F-derivable = Step 2: Example: S S + T T T T * F F F (S) a S-derivable = {T, F} T-derivable = {F} Step 2: Our new grammar now looks like: S S + T T * F (S) a T T T * F (S) a F F (S) a Add to P: S T * F, S (S) a : T (S) a
5 Step 3: Remove Unit Productions Our final grammar looks like: Our new grammar now looks like: S S + T T * F (S) a T T * F (S) a Remove S T, T F Questions Removing Useless Symbols A symbol X is useful for a grammar G = (V, T, P, S) if S * αxβ * w where w L(G) In other words, a useful symbol will be used somewhere in the derivation of a string in the language. Any symbol that is not useful is useless. Useless symbols do not add to the language generated by a grammar, so it s okay to remove them. Removing Useless Symbols Definitions: We say a symbol X is generating if: X * w for some w L(G) We say a symbol X is reachable if: S * α Xβ for some α, β Symbols that are useful must be both generating and reachable. Such symbols (and assoc. productions) can be removed Removing useless symbols Algorithm: 1. Eliminate all non generating symbols 2. Eliminate all non reachable symbols from resultant grammar. Removing useless symbols Finding generating symbols 1. All symbols in T are generating 2. If A α and all symbols in α are generating, then A is generating. 3. No other symbols are generating. Removing useless symbols Finding reachable symbols 1. S is reachable 2. If A is reachable, and A α, then all variables in α are reachable.
6 Removing Useless Symbols Example: S AB a A b B is useless since it is not generating Eliminate it Removing useless symbols Example: S a A b Now A is not reachable, eliminate it! S a Note that you must eliminate non-generating symbols before non-reachable symbols. Recall our goal A context free grammar is in Chomsky Normal Form (CNF) if every production is of the form: A BC A a Given a CFG G, there is an equivalent CFG, G in Chomsky Normal form such that L(G ) = L(G) {ε} Where A,B, and C are variables and a is a terminal. Step 1: Remove ε -Productions Step 2: Remove Unit Productions Step 3: Remove useless symbols After steps 1 3 : All productions are of the form: A a where A is a variable and a is a terminal A βwhere β 2 and β contains variables and/or terminals. Step 4: Derive terminals from new variables: For all productions of the 2 nd type: A β, for all terminals a in β, create a new variable X a Add a new production X a a Replace a in β with X a
7 Let s go back to our first example: S AB A B A aaa aa a B bbb bb b Removing unit transitions: S AB aaa aa a bbb bb b A aaa aa a B bbb bb b Note that S, A, and B are all useful. Define new productions: X a a and X b b and replace instance of a with X a, similarly for b S AB aaa aa a bbb bb b A aaa aa a B bbb bb b New: S AB X a AA X a A a X b BB X b B b A X a AA X a A a B X b BB X b B b X a a X b b After steps 1 4 : All productions are of the form: A a where A is a variable and a is a terminal A βwhere β 2 and β contains only variables. Step 5: For all productions of type 2 where β > 2, replace the production with a series of new productions each having exactly 2 variables on the right Best illustrated with an example The production: A BCDBCE Would be replaced with A BY 1 Y 1 CY 2 Y 2 DY 3 Y 3 BY 4 Y 4 CE Back to our example S AB X a AA X a A a X b BB X b B b A X a AA X a A a B X b BB X b B b X a a X b b Add productions Y 1 AA Y 2 BB Our final grammar S AB X a Y 1 X a A a X b Y 2 X b B b A X a Y 1 X a A a B X b Y 2 X b B b Y 1 AA Y 2 BB X a a X b b Questions
8 CNF Any grammar can be placed into CNF Questions? Do we have time for the Pumping Lemma?
CFG Simplification. (simplify) 1. Eliminate useless symbols 2. Eliminate -productions 3. Eliminate unit productions
 CFG Simplification (simplify) 1. Eliminate useless symbols 2. Eliminate -productions 3. Eliminate unit productions 1 Eliminating useless symbols 1. A symbol X is generating if there exists: X * w, for
CFG Simplification (simplify) 1. Eliminate useless symbols 2. Eliminate -productions 3. Eliminate unit productions 1 Eliminating useless symbols 1. A symbol X is generating if there exists: X * w, for
CS 373: Theory of Computation. Fall 2010
 CS 373: Theory of Computation Gul Agha Mahesh Viswanathan Fall 2010 1 1 Normal Forms for CFG Normal Forms for Grammars It is typically easier to work with a context free language if given a CFG in a normal
CS 373: Theory of Computation Gul Agha Mahesh Viswanathan Fall 2010 1 1 Normal Forms for CFG Normal Forms for Grammars It is typically easier to work with a context free language if given a CFG in a normal
Finite Automata and Formal Languages TMV026/DIT321 LP Useful, Useless, Generating and Reachable Symbols
 Finite Automata and Formal Languages TMV026/DIT321 LP4 2012 Lecture 13 Ana Bove May 7th 2012 Overview of today s lecture: Normal Forms for Context-Free Languages Pumping Lemma for Context-Free Languages
Finite Automata and Formal Languages TMV026/DIT321 LP4 2012 Lecture 13 Ana Bove May 7th 2012 Overview of today s lecture: Normal Forms for Context-Free Languages Pumping Lemma for Context-Free Languages
Simplification of CFG and Normal Forms. Wen-Guey Tzeng Computer Science Department National Chiao Tung University
 Simplification of CFG and Normal Forms Wen-Guey Tzeng Computer Science Department National Chiao Tung University Normal Forms We want a cfg with either Chomsky or Greibach normal form Chomsky normal form
Simplification of CFG and Normal Forms Wen-Guey Tzeng Computer Science Department National Chiao Tung University Normal Forms We want a cfg with either Chomsky or Greibach normal form Chomsky normal form
Simplification of CFG and Normal Forms. Wen-Guey Tzeng Computer Science Department National Chiao Tung University
 Simplification of CFG and Normal Forms Wen-Guey Tzeng Computer Science Department National Chiao Tung University Normal Forms We want a cfg with either Chomsky or Greibach normal form Chomsky normal form
Simplification of CFG and Normal Forms Wen-Guey Tzeng Computer Science Department National Chiao Tung University Normal Forms We want a cfg with either Chomsky or Greibach normal form Chomsky normal form
Properties of Context-free Languages. Reading: Chapter 7
 Properties of Context-free Languages Reading: Chapter 7 1 Topics 1) Simplifying CFGs, Normal forms 2) Pumping lemma for CFLs 3) Closure and decision properties of CFLs 2 How to simplify CFGs? 3 Three ways
Properties of Context-free Languages Reading: Chapter 7 1 Topics 1) Simplifying CFGs, Normal forms 2) Pumping lemma for CFLs 3) Closure and decision properties of CFLs 2 How to simplify CFGs? 3 Three ways
Parsing. Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer. Winter 2017/18. Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf 1 / 26
 Parsing Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Winter 2017/18 1 / 26 Table of contents 1 Context-Free Grammars 2 Simplifying CFGs Removing useless symbols Eliminating
Parsing Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Winter 2017/18 1 / 26 Table of contents 1 Context-Free Grammars 2 Simplifying CFGs Removing useless symbols Eliminating
Properties of context-free Languages
 Properties of context-free Languages We simplify CFL s. Greibach Normal Form Chomsky Normal Form We prove pumping lemma for CFL s. We study closure properties and decision properties. Some of them remain,
Properties of context-free Languages We simplify CFL s. Greibach Normal Form Chomsky Normal Form We prove pumping lemma for CFL s. We study closure properties and decision properties. Some of them remain,
Lecture 12 Simplification of Context-Free Grammars and Normal Forms
 Lecture 12 Simplification of Context-Free Grammars and Normal Forms COT 4420 Theory of Computation Chapter 6 Normal Forms for CFGs 1. Chomsky Normal Form CNF Productions of form A BC A, B, C V A a a T
Lecture 12 Simplification of Context-Free Grammars and Normal Forms COT 4420 Theory of Computation Chapter 6 Normal Forms for CFGs 1. Chomsky Normal Form CNF Productions of form A BC A, B, C V A a a T
Context-Free Grammar
 Context-Free Grammar CFGs are more powerful than regular expressions. They are more powerful in the sense that whatever can be expressed using regular expressions can be expressed using context-free grammars,
Context-Free Grammar CFGs are more powerful than regular expressions. They are more powerful in the sense that whatever can be expressed using regular expressions can be expressed using context-free grammars,
Context-Free Grammars: Normal Forms
 Context-Free Grammars: Normal Forms Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
Context-Free Grammars: Normal Forms Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
This lecture covers Chapter 7 of HMU: Properties of CFLs
 This lecture covers Chapter 7 of HMU: Properties of CFLs Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for CFs Closure Properties of CFLs Decision Properties of CFLs Additional Reading: Chapter 7 of HMU. Chomsky Normal
This lecture covers Chapter 7 of HMU: Properties of CFLs Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for CFs Closure Properties of CFLs Decision Properties of CFLs Additional Reading: Chapter 7 of HMU. Chomsky Normal
Einführung in die Computerlinguistik
 Einführung in die Computerlinguistik Context-Free Grammars formal properties Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Summer 2018 1 / 20 Normal forms (1) Hopcroft and Ullman (1979) A normal
Einführung in die Computerlinguistik Context-Free Grammars formal properties Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Summer 2018 1 / 20 Normal forms (1) Hopcroft and Ullman (1979) A normal
Before We Start. The Pumping Lemma. Languages. Context Free Languages. Plan for today. Now our picture looks like. Any questions?
 Before We Start The Pumping Lemma Any questions? The Lemma & Decision/ Languages Future Exam Question What is a language? What is a class of languages? Context Free Languages Context Free Languages(CFL)
Before We Start The Pumping Lemma Any questions? The Lemma & Decision/ Languages Future Exam Question What is a language? What is a class of languages? Context Free Languages Context Free Languages(CFL)
MTH401A Theory of Computation. Lecture 17
 MTH401A Theory of Computation Lecture 17 Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s For every context free language, L, the language L {ε} has a grammar in which every production looks
MTH401A Theory of Computation Lecture 17 Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s For every context free language, L, the language L {ε} has a grammar in which every production looks
Context-Free Grammars. 2IT70 Finite Automata and Process Theory
 Context-Free Grammars 2IT70 Finite Automata and Process Theory Technische Universiteit Eindhoven May 18, 2016 Generating strings language L 1 = {a n b n n > 0} ab L 1 if w L 1 then awb L 1 production rules
Context-Free Grammars 2IT70 Finite Automata and Process Theory Technische Universiteit Eindhoven May 18, 2016 Generating strings language L 1 = {a n b n n > 0} ab L 1 if w L 1 then awb L 1 production rules
The Pumping Lemma for Context Free Grammars
 The Pumping Lemma for Context Free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Chomsky Normal Form (CNF) is a simple and useful form of a CFG Every rule of a CNF grammar is in the form A BC A a Where a is any terminal
The Pumping Lemma for Context Free Grammars Chomsky Normal Form Chomsky Normal Form (CNF) is a simple and useful form of a CFG Every rule of a CNF grammar is in the form A BC A a Where a is any terminal
Notes for Comp 497 (Comp 454) Week 10 4/5/05
 Notes for Comp 497 (Comp 454) Week 10 4/5/05 Today look at the last two chapters in Part II. Cohen presents some results concerning context-free languages (CFL) and regular languages (RL) also some decidability
Notes for Comp 497 (Comp 454) Week 10 4/5/05 Today look at the last two chapters in Part II. Cohen presents some results concerning context-free languages (CFL) and regular languages (RL) also some decidability
Chap. 7 Properties of Context-free Languages
 Chap. 7 Properties of Context-free Languages 7.1 Normal Forms for Context-free Grammars Context-free grammars A where A N, (N T). 0. Chomsky Normal Form A BC or A a except S where A, B, C N, a T. 1. Eliminating
Chap. 7 Properties of Context-free Languages 7.1 Normal Forms for Context-free Grammars Context-free grammars A where A N, (N T). 0. Chomsky Normal Form A BC or A a except S where A, B, C N, a T. 1. Eliminating
Context Free Grammars: Introduction. Context Free Grammars: Simplifying CFGs
 Context Free Grammars: Introduction CFGs are more powerful than RGs because of the following 2 properties: 1. Recursion Rule is recursive if it is of the form X w 1 Y w 2, where Y w 3 Xw 4 and w 1, w 2,
Context Free Grammars: Introduction CFGs are more powerful than RGs because of the following 2 properties: 1. Recursion Rule is recursive if it is of the form X w 1 Y w 2, where Y w 3 Xw 4 and w 1, w 2,
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad
 St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad-500 014 Subject: FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Class : CSE II PART A (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) UNIT- I 1 Explain transition diagram, transition
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad-500 014 Subject: FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Class : CSE II PART A (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) UNIT- I 1 Explain transition diagram, transition
Einführung in die Computerlinguistik Kontextfreie Grammatiken - Formale Eigenschaften
 Normal forms (1) Einführung in die Computerlinguistik Kontextfreie Grammatiken - Formale Eigenschaften Laura Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Sommersemester 2013 normal form of a grammar formalism
Normal forms (1) Einführung in die Computerlinguistik Kontextfreie Grammatiken - Formale Eigenschaften Laura Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Sommersemester 2013 normal form of a grammar formalism
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018
 Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 14 Ana Bove May 14th 2018 Recap: Context-free Grammars Simplification of grammars: Elimination of ǫ-productions; Elimination of
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 14 Ana Bove May 14th 2018 Recap: Context-free Grammars Simplification of grammars: Elimination of ǫ-productions; Elimination of
CPS 220 Theory of Computation
 CPS 22 Theory of Computation Review - Regular Languages RL - a simple class of languages that can be represented in two ways: 1 Machine description: Finite Automata are machines with a finite number of
CPS 22 Theory of Computation Review - Regular Languages RL - a simple class of languages that can be represented in two ways: 1 Machine description: Finite Automata are machines with a finite number of
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1
 Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University. November 28, 2016 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University.
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University. November 28, 2016 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University.
Simplification and Normalization of Context-Free Grammars
 implification and Normalization, of Context-Free Grammars 20100927 Slide 1 of 23 Simplification and Normalization of Context-Free Grammars 5DV037 Fundamentals of Computer Science Umeå University Department
implification and Normalization, of Context-Free Grammars 20100927 Slide 1 of 23 Simplification and Normalization of Context-Free Grammars 5DV037 Fundamentals of Computer Science Umeå University Department
COMP-330 Theory of Computation. Fall Prof. Claude Crépeau. Lec. 10 : Context-Free Grammars
 COMP-330 Theory of Computation Fall 2017 -- Prof. Claude Crépeau Lec. 10 : Context-Free Grammars COMP 330 Fall 2017: Lectures Schedule 1-2. Introduction 1.5. Some basic mathematics 2-3. Deterministic finite
COMP-330 Theory of Computation Fall 2017 -- Prof. Claude Crépeau Lec. 10 : Context-Free Grammars COMP 330 Fall 2017: Lectures Schedule 1-2. Introduction 1.5. Some basic mathematics 2-3. Deterministic finite
Notes for Comp 497 (454) Week 10
 Notes for Comp 497 (454) Week 10 Today we look at the last two chapters in Part II. Cohen presents some results concerning the two categories of language we have seen so far: Regular languages (RL). Context-free
Notes for Comp 497 (454) Week 10 Today we look at the last two chapters in Part II. Cohen presents some results concerning the two categories of language we have seen so far: Regular languages (RL). Context-free
CS375: Logic and Theory of Computing
 CS375: Logic and Theory of Computing Fuhua (Frank) Cheng Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky 1 Table of Contents: Week 1: Preliminaries (set algebra, relations, functions) (read Chapters
CS375: Logic and Theory of Computing Fuhua (Frank) Cheng Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky 1 Table of Contents: Week 1: Preliminaries (set algebra, relations, functions) (read Chapters
Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules).
 Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules). 1a) G = ({R, S, T}, {0,1}, P, S) where P is: S R0R R R0R1R R1R0R T T 0T ε (S generates the first 0. R generates
Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules). 1a) G = ({R, S, T}, {0,1}, P, S) where P is: S R0R R R0R1R R1R0R T T 0T ε (S generates the first 0. R generates
NPDA, CFG equivalence
 NPDA, CFG equivalence Theorem A language L is recognized by a NPDA iff L is described by a CFG. Must prove two directions: ( ) L is recognized by a NPDA implies L is described by a CFG. ( ) L is described
NPDA, CFG equivalence Theorem A language L is recognized by a NPDA iff L is described by a CFG. Must prove two directions: ( ) L is recognized by a NPDA implies L is described by a CFG. ( ) L is described
Context-Free Grammars and Languages. Reading: Chapter 5
 Context-Free Grammars and Languages Reading: Chapter 5 1 Context-Free Languages The class of context-free languages generalizes the class of regular languages, i.e., every regular language is a context-free
Context-Free Grammars and Languages Reading: Chapter 5 1 Context-Free Languages The class of context-free languages generalizes the class of regular languages, i.e., every regular language is a context-free
Theory of Computation - Module 3
 Theory of Computation - Module 3 Syllabus Context Free Grammar Simplification of CFG- Normal forms-chomsky Normal form and Greibach Normal formpumping lemma for Context free languages- Applications of
Theory of Computation - Module 3 Syllabus Context Free Grammar Simplification of CFG- Normal forms-chomsky Normal form and Greibach Normal formpumping lemma for Context free languages- Applications of
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 12: General Context-Free Recognition
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 12: General Context-Free Recognition Salil Vadhan October 11, 2012 Reading: Sipser, Section 2.3 and Section 2.1 (material on Chomsky Normal Form). Pumping Lemma for
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 12: General Context-Free Recognition Salil Vadhan October 11, 2012 Reading: Sipser, Section 2.3 and Section 2.1 (material on Chomsky Normal Form). Pumping Lemma for
Non-context-Free Languages. CS215, Lecture 5 c
 Non-context-Free Languages CS215, Lecture 5 c 2007 1 The Pumping Lemma Theorem. (Pumping Lemma) Let be context-free. There exists a positive integer divided into five pieces, Proof for for each, and..
Non-context-Free Languages CS215, Lecture 5 c 2007 1 The Pumping Lemma Theorem. (Pumping Lemma) Let be context-free. There exists a positive integer divided into five pieces, Proof for for each, and..
Properties of Context-Free Languages
 Properties of Context-Free Languages Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
Properties of Context-Free Languages Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
CFLs and Regular Languages. CFLs and Regular Languages. CFLs and Regular Languages. Will show that all Regular Languages are CFLs. Union.
 We can show that every RL is also a CFL Since a regular grammar is certainly context free. We can also show by only using Regular Expressions and Context Free Grammars That is what we will do in this half.
We can show that every RL is also a CFL Since a regular grammar is certainly context free. We can also show by only using Regular Expressions and Context Free Grammars That is what we will do in this half.
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 9: Automata Theory VII (Pumping Lemma, Non-CFL)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 9: Automata Theory VII (Pumping Lemma, Non-CFL) Objectives Introduce Pumping Lemma for CFL Apply Pumping Lemma to show that some languages are non-cfl Pumping Lemma
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 9: Automata Theory VII (Pumping Lemma, Non-CFL) Objectives Introduce Pumping Lemma for CFL Apply Pumping Lemma to show that some languages are non-cfl Pumping Lemma
Properties of Context-Free Languages. Closure Properties Decision Properties
 Properties of Context-Free Languages Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms
Properties of Context-Free Languages Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms
VTU QUESTION BANK. Unit 1. Introduction to Finite Automata. 1. Obtain DFAs to accept strings of a s and b s having exactly one a.
 VTU QUESTION BANK Unit 1 Introduction to Finite Automata 1. Obtain DFAs to accept strings of a s and b s having exactly one a.(5m )( Dec-2014) 2. Obtain a DFA to accept strings of a s and b s having even
VTU QUESTION BANK Unit 1 Introduction to Finite Automata 1. Obtain DFAs to accept strings of a s and b s having exactly one a.(5m )( Dec-2014) 2. Obtain a DFA to accept strings of a s and b s having even
Context Free Grammars: Introduction
 Context Free Grammars: Introduction Context free grammar (CFG) G = (V, Σ, R, S), where V is a set of grammar symbols Σ V is a set of terminal symbols R is a set of rules, where R (V Σ) V S is a distinguished
Context Free Grammars: Introduction Context free grammar (CFG) G = (V, Σ, R, S), where V is a set of grammar symbols Σ V is a set of terminal symbols R is a set of rules, where R (V Σ) V S is a distinguished
Part 4 out of 5 DFA NFA REX. Automata & languages. A primer on the Theory of Computation. Last week, we showed the equivalence of DFA, NFA and REX
 Automata & languages A primer on the Theory of Computation Laurent Vanbever www.vanbever.eu Part 4 out of 5 ETH Zürich (D-ITET) October, 12 2017 Last week, we showed the equivalence of DFA, NFA and REX
Automata & languages A primer on the Theory of Computation Laurent Vanbever www.vanbever.eu Part 4 out of 5 ETH Zürich (D-ITET) October, 12 2017 Last week, we showed the equivalence of DFA, NFA and REX
Homework 4. Chapter 7. CS A Term 2009: Foundations of Computer Science. By Li Feng, Shweta Srivastava, and Carolina Ruiz
 CS3133 - A Term 2009: Foundations of Computer Science Prof. Carolina Ruiz Homework 4 WPI By Li Feng, Shweta Srivastava, and Carolina Ruiz Chapter 7 Problem: Chap 7.1 part a This PDA accepts the language
CS3133 - A Term 2009: Foundations of Computer Science Prof. Carolina Ruiz Homework 4 WPI By Li Feng, Shweta Srivastava, and Carolina Ruiz Chapter 7 Problem: Chap 7.1 part a This PDA accepts the language
CSE 355 Test 2, Fall 2016
 CSE 355 Test 2, Fall 2016 28 October 2016, 8:35-9:25 a.m., LSA 191 Last Name SAMPLE ASU ID 1357924680 First Name(s) Ima Regrading of Midterms If you believe that your grade has not been added up correctly,
CSE 355 Test 2, Fall 2016 28 October 2016, 8:35-9:25 a.m., LSA 191 Last Name SAMPLE ASU ID 1357924680 First Name(s) Ima Regrading of Midterms If you believe that your grade has not been added up correctly,
TAFL 1 (ECS-403) Unit- III. 3.1 Definition of CFG (Context Free Grammar) and problems. 3.2 Derivation. 3.3 Ambiguity in Grammar
 TAFL 1 (ECS-403) Unit- III 3.1 Definition of CFG (Context Free Grammar) and problems 3.2 Derivation 3.3 Ambiguity in Grammar 3.3.1 Inherent Ambiguity 3.3.2 Ambiguous to Unambiguous CFG 3.4 Simplification
TAFL 1 (ECS-403) Unit- III 3.1 Definition of CFG (Context Free Grammar) and problems 3.2 Derivation 3.3 Ambiguity in Grammar 3.3.1 Inherent Ambiguity 3.3.2 Ambiguous to Unambiguous CFG 3.4 Simplification
Even More on Dynamic Programming
 Algorithms & Models of Computation CS/ECE 374, Fall 2017 Even More on Dynamic Programming Lecture 15 Thursday, October 19, 2017 Sariel Har-Peled (UIUC) CS374 1 Fall 2017 1 / 26 Part I Longest Common Subsequence
Algorithms & Models of Computation CS/ECE 374, Fall 2017 Even More on Dynamic Programming Lecture 15 Thursday, October 19, 2017 Sariel Har-Peled (UIUC) CS374 1 Fall 2017 1 / 26 Part I Longest Common Subsequence
60-354, Theory of Computation Fall Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor
 60-354, Theory of Computation Fall 2013 Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor Pushdown Automata (PDA) PDA = ε-nfa + stack Acceptance ε-nfa enters a final state or Stack is
60-354, Theory of Computation Fall 2013 Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor Pushdown Automata (PDA) PDA = ε-nfa + stack Acceptance ε-nfa enters a final state or Stack is
6.1 The Pumping Lemma for CFLs 6.2 Intersections and Complements of CFLs
 CSC4510/6510 AUTOMATA 6.1 The Pumping Lemma for CFLs 6.2 Intersections and Complements of CFLs The Pumping Lemma for Context Free Languages One way to prove AnBn is not regular is to use the pumping lemma
CSC4510/6510 AUTOMATA 6.1 The Pumping Lemma for CFLs 6.2 Intersections and Complements of CFLs The Pumping Lemma for Context Free Languages One way to prove AnBn is not regular is to use the pumping lemma
Context-free Grammars and Languages
 Context-free Grammars and Languages COMP 455 002, Spring 2019 Jim Anderson (modified by Nathan Otterness) 1 Context-free Grammars Context-free grammars provide another way to specify languages. Example:
Context-free Grammars and Languages COMP 455 002, Spring 2019 Jim Anderson (modified by Nathan Otterness) 1 Context-free Grammars Context-free grammars provide another way to specify languages. Example:
AC68 FINITE AUTOMATA & FORMULA LANGUAGES DEC 2013
 Q.2 a. Prove by mathematical induction n 4 4n 2 is divisible by 3 for n 0. Basic step: For n = 0, n 3 n = 0 which is divisible by 3. Induction hypothesis: Let p(n) = n 3 n is divisible by 3. Induction
Q.2 a. Prove by mathematical induction n 4 4n 2 is divisible by 3 for n 0. Basic step: For n = 0, n 3 n = 0 which is divisible by 3. Induction hypothesis: Let p(n) = n 3 n is divisible by 3. Induction
(b) If G=({S}, {a}, {S SS}, S) find the language generated by G. [8+8] 2. Convert the following grammar to Greibach Normal Form G = ({A1, A2, A3},
![(b) If G=({S}, {a}, {S SS}, S) find the language generated by G. [8+8] 2. Convert the following grammar to Greibach Normal Form G = ({A1, A2, A3}, (b) If G=({S}, {a}, {S SS}, S) find the language generated by G. [8+8] 2. Convert the following grammar to Greibach Normal Form G = ({A1, A2, A3},](/thumbs/81/83182922.jpg) Code No: 07A50501 R07 Set No. 2 III B.Tech I Semester Examinations,MAY 2011 FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Computer Science And Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All
Code No: 07A50501 R07 Set No. 2 III B.Tech I Semester Examinations,MAY 2011 FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Computer Science And Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All
Homework 4 Solutions. 2. Find context-free grammars for the language L = {a n b m c k : k n + m}. (with n 0,
 Introduction to Formal Language, Fall 2016 Due: 21-Apr-2016 (Thursday) Instructor: Prof. Wen-Guey Tzeng Homework 4 Solutions Scribe: Yi-Ruei Chen 1. Find context-free grammars for the language L = {a n
Introduction to Formal Language, Fall 2016 Due: 21-Apr-2016 (Thursday) Instructor: Prof. Wen-Guey Tzeng Homework 4 Solutions Scribe: Yi-Ruei Chen 1. Find context-free grammars for the language L = {a n
Context-Free and Noncontext-Free Languages
 Examples: Context-Free and Noncontext-Free Languages a*b* is regular. A n B n = {a n b n : n 0} is context-free but not regular. A n B n C n = {a n b n c n : n 0} is not context-free The Regular and the
Examples: Context-Free and Noncontext-Free Languages a*b* is regular. A n B n = {a n b n : n 0} is context-free but not regular. A n B n C n = {a n b n c n : n 0} is not context-free The Regular and the
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF) Announcement Homework 2 will be given soon (before Tue) Due date: Oct 31 (Tue), before class Midterm: Nov 3, (Fri), first hour
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF) Announcement Homework 2 will be given soon (before Tue) Due date: Oct 31 (Tue), before class Midterm: Nov 3, (Fri), first hour
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 9: Automata Theory VII (Pumping Lemma, Non-CFL, DPDA PDA)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 9: Automata Theory VII (Pumping Lemma, Non-CFL, DPDA PDA) Objectives Introduce the Pumping Lemma for CFL Show that some languages are non- CFL Discuss the DPDA, which
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 9: Automata Theory VII (Pumping Lemma, Non-CFL, DPDA PDA) Objectives Introduce the Pumping Lemma for CFL Show that some languages are non- CFL Discuss the DPDA, which
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV026/TMV027/DIT321 Responsible: Ana Bove
 Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV026/TMV027/DIT321 Responsible: Ana Bove Tuesday 28 of May 2013 Total: 60 points TMV027/DIT321 registration VT13 TMV026/DIT321 registration before VT13 Exam
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV026/TMV027/DIT321 Responsible: Ana Bove Tuesday 28 of May 2013 Total: 60 points TMV027/DIT321 registration VT13 TMV026/DIT321 registration before VT13 Exam
CS20a: summary (Oct 24, 2002)
 CS20a: summary (Oct 24, 2002) Context-free languages Grammars G = (V, T, P, S) Pushdown automata N-PDA = CFG D-PDA < CFG Today What languages are context-free? Pumping lemma (similar to pumping lemma for
CS20a: summary (Oct 24, 2002) Context-free languages Grammars G = (V, T, P, S) Pushdown automata N-PDA = CFG D-PDA < CFG Today What languages are context-free? Pumping lemma (similar to pumping lemma for
FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY
 15-453 FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY REVIEW for MIDTERM 1 THURSDAY Feb 6 Midterm 1 will cover everything we have seen so far The PROBLEMS will be from Sipser, Chapters 1, 2, 3 It will be
15-453 FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTABILITY REVIEW for MIDTERM 1 THURSDAY Feb 6 Midterm 1 will cover everything we have seen so far The PROBLEMS will be from Sipser, Chapters 1, 2, 3 It will be
Problem Session 5 (CFGs) Talk about the building blocks of CFGs: S 0S 1S ε - everything. S 0S0 1S1 A - waw R. S 0S0 0S1 1S0 1S1 A - xay, where x = y.
 CSE2001, Fall 2006 1 Problem Session 5 (CFGs) Talk about the building blocks of CFGs: S 0S 1S ε - everything. S 0S0 1S1 A - waw R. S 0S0 0S1 1S0 1S1 A - xay, where x = y. S 00S1 A - xay, where x = 2 y.
CSE2001, Fall 2006 1 Problem Session 5 (CFGs) Talk about the building blocks of CFGs: S 0S 1S ε - everything. S 0S0 1S1 A - waw R. S 0S0 0S1 1S0 1S1 A - xay, where x = y. S 00S1 A - xay, where x = 2 y.
Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture)
 Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 34 Outline Pumping Lemma
Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Context-Free Languages (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 34 Outline Pumping Lemma
Ogden s Lemma for CFLs
 Ogden s Lemma for CFLs Theorem If L is a context-free language, then there exists an integer l such that for any u L with at least l positions marked, u can be written as u = vwxyz such that 1 x and at
Ogden s Lemma for CFLs Theorem If L is a context-free language, then there exists an integer l such that for any u L with at least l positions marked, u can be written as u = vwxyz such that 1 x and at
Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30
 CS 454 Theory of Computation Fall 2011 Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30 1. Which of the following are true? (a) a PDA can always be converted to an equivalent PDA that at each step pops or pushes
CS 454 Theory of Computation Fall 2011 Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30 1. Which of the following are true? (a) a PDA can always be converted to an equivalent PDA that at each step pops or pushes
Homework #7. True False. d. Given a CFG, G, and a string w, it is decidable whether w ε L(G) True False
 Hmewrk #7 #1. True/ False a. The Pumping Lemma fr CFL s can be used t shw a language is cntext-free b. The string z = a k b k+1 c k can be used t shw {a n b n c n } is nt cntext free c. The string z =
Hmewrk #7 #1. True/ False a. The Pumping Lemma fr CFL s can be used t shw a language is cntext-free b. The string z = a k b k+1 c k can be used t shw {a n b n c n } is nt cntext free c. The string z =
Context Free Languages: Decidability of a CFL
 Theorem 14.1 Context Free Languages: Decidability of a CFL Statement: Given a CFL L and string w, there is a decision procedure that determines whether w L. Proof: By construction. 1. Proof using a grammar
Theorem 14.1 Context Free Languages: Decidability of a CFL Statement: Given a CFL L and string w, there is a decision procedure that determines whether w L. Proof: By construction. 1. Proof using a grammar
Chapter 16: Non-Context-Free Languages
 Chapter 16: Non-Context-Free Languages Peter Cappello Department of Computer Science University of California, Santa Barbara Santa Barbara, CA 93106 cappello@cs.ucsb.edu Please read the corresponding chapter
Chapter 16: Non-Context-Free Languages Peter Cappello Department of Computer Science University of California, Santa Barbara Santa Barbara, CA 93106 cappello@cs.ucsb.edu Please read the corresponding chapter
1. Draw a parse tree for the following derivation: S C A C C A b b b b A b b b b B b b b b a A a a b b b b a b a a b b 2. Show on your parse tree u,
 1. Draw a parse tree for the following derivation: S C A C C A b b b b A b b b b B b b b b a A a a b b b b a b a a b b 2. Show on your parse tree u, v, x, y, z as per the pumping theorem. 3. Prove that
1. Draw a parse tree for the following derivation: S C A C C A b b b b A b b b b B b b b b a A a a b b b b a b a a b b 2. Show on your parse tree u, v, x, y, z as per the pumping theorem. 3. Prove that
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation
 MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation Bottom-up parsing Pumping Theorem for CFLs Recap: Going One Way Lemma: Each context-free language is accepted by some PDA. Proof (by construction): The idea: Let the stack
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation Bottom-up parsing Pumping Theorem for CFLs Recap: Going One Way Lemma: Each context-free language is accepted by some PDA. Proof (by construction): The idea: Let the stack
Closure Properties of Context-Free Languages. Foundations of Computer Science Theory
 Closure Properties of Context-Free Languages Foundations of Computer Science Theory Closure Properties of CFLs CFLs are closed under: Union Concatenation Kleene closure Reversal CFLs are not closed under
Closure Properties of Context-Free Languages Foundations of Computer Science Theory Closure Properties of CFLs CFLs are closed under: Union Concatenation Kleene closure Reversal CFLs are not closed under
Decidability (What, stuff is unsolvable?)
 University of Georgia Fall 2014 Outline Decidability Decidable Problems for Regular Languages Decidable Problems for Context Free Languages The Halting Problem Countable and Uncountable Sets Diagonalization
University of Georgia Fall 2014 Outline Decidability Decidable Problems for Regular Languages Decidable Problems for Context Free Languages The Halting Problem Countable and Uncountable Sets Diagonalization
PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA)
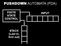 PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA) FINITE STATE CONTROL INPUT STACK (Last in, first out) input pop push ε,ε $ 0,ε 0 1,0 ε ε,$ ε 1,0 ε PDA that recognizes L = { 0 n 1 n n 0 } Definition: A (non-deterministic) PDA
PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA) FINITE STATE CONTROL INPUT STACK (Last in, first out) input pop push ε,ε $ 0,ε 0 1,0 ε ε,$ ε 1,0 ε PDA that recognizes L = { 0 n 1 n n 0 } Definition: A (non-deterministic) PDA
Introduction to Theory of Computing
 CSCI 2670, Fall 2012 Introduction to Theory of Computing Department of Computer Science University of Georgia Athens, GA 30602 Instructor: Liming Cai www.cs.uga.edu/ cai 0 Lecture Note 3 Context-Free Languages
CSCI 2670, Fall 2012 Introduction to Theory of Computing Department of Computer Science University of Georgia Athens, GA 30602 Instructor: Liming Cai www.cs.uga.edu/ cai 0 Lecture Note 3 Context-Free Languages
CPSC 313 Introduction to Computability
 CPSC 313 Introduction to Computability Grammars in Chomsky Normal Form (Cont d) (Sipser, pages 109-111 (3 rd ed) and 107-109 (2 nd ed)) Renate Scheidler Fall 2018 Chomsky Normal Form A context-free grammar
CPSC 313 Introduction to Computability Grammars in Chomsky Normal Form (Cont d) (Sipser, pages 109-111 (3 rd ed) and 107-109 (2 nd ed)) Renate Scheidler Fall 2018 Chomsky Normal Form A context-free grammar
Context Free Grammars
 Automata and Formal Languages Context Free Grammars Sipser pages 101-111 Lecture 11 Tim Sheard 1 Formal Languages 1. Context free languages provide a convenient notation for recursive description of languages.
Automata and Formal Languages Context Free Grammars Sipser pages 101-111 Lecture 11 Tim Sheard 1 Formal Languages 1. Context free languages provide a convenient notation for recursive description of languages.
SFWR ENG 2FA3. Solution to the Assignment #4
 SFWR ENG 2FA3. Solution to the Assignment #4 Total = 131, 100%= 115 The solutions below are often very detailed on purpose. Such level of details is not required from students solutions. Some questions
SFWR ENG 2FA3. Solution to the Assignment #4 Total = 131, 100%= 115 The solutions below are often very detailed on purpose. Such level of details is not required from students solutions. Some questions
CS375 Midterm Exam Solution Set (Fall 2017)
 CS375 Midterm Exam Solution Set (Fall 2017) Closed book & closed notes October 17, 2017 Name sample 1. (10 points) (a) Put in the following blank the number of strings of length 5 over A={a, b, c} that
CS375 Midterm Exam Solution Set (Fall 2017) Closed book & closed notes October 17, 2017 Name sample 1. (10 points) (a) Put in the following blank the number of strings of length 5 over A={a, b, c} that
Solution. S ABc Ab c Bc Ac b A ABa Ba Aa a B Bbc bc.
 Section 12.4 Context-Free Language Topics Algorithm. Remove Λ-productions from grammars for langauges without Λ. 1. Find nonterminals that derive Λ. 2. For each production A w construct all productions
Section 12.4 Context-Free Language Topics Algorithm. Remove Λ-productions from grammars for langauges without Λ. 1. Find nonterminals that derive Λ. 2. For each production A w construct all productions
CYK Algorithm for Parsing General Context-Free Grammars
 CYK Algorithm for Parsing General Context-Free Grammars Why Parse General Grammars Can be difficult or impossible to make grammar unambiguous thus LL(k) and LR(k) methods cannot work, for such ambiguous
CYK Algorithm for Parsing General Context-Free Grammars Why Parse General Grammars Can be difficult or impossible to make grammar unambiguous thus LL(k) and LR(k) methods cannot work, for such ambiguous
Lecture 17: Language Recognition
 Lecture 17: Language Recognition Finite State Automata Deterministic and Non-Deterministic Finite Automata Regular Expressions Push-Down Automata Turing Machines Modeling Computation When attempting to
Lecture 17: Language Recognition Finite State Automata Deterministic and Non-Deterministic Finite Automata Regular Expressions Push-Down Automata Turing Machines Modeling Computation When attempting to
Automata Theory Final Exam Solution 08:10-10:00 am Friday, June 13, 2008
 Automata Theory Final Exam Solution 08:10-10:00 am Friday, June 13, 2008 Name: ID #: This is a Close Book examination. Only an A4 cheating sheet belonging to you is acceptable. You can write your answers
Automata Theory Final Exam Solution 08:10-10:00 am Friday, June 13, 2008 Name: ID #: This is a Close Book examination. Only an A4 cheating sheet belonging to you is acceptable. You can write your answers
Languages. Languages. An Example Grammar. Grammars. Suppose we have an alphabet V. Then we can write:
 Languages A language is a set (usually infinite) of strings, also known as sentences Each string consists of a sequence of symbols taken from some alphabet An alphabet, V, is a finite set of symbols, e.g.
Languages A language is a set (usually infinite) of strings, also known as sentences Each string consists of a sequence of symbols taken from some alphabet An alphabet, V, is a finite set of symbols, e.g.
Question Bank UNIT I
 Siddhivinayak Technical Campus School of Engineering & Research Technology Department of computer science and Engineering Session 2016-2017 Subject Name- Theory of Computation Subject Code-4KS05 Sr No.
Siddhivinayak Technical Campus School of Engineering & Research Technology Department of computer science and Engineering Session 2016-2017 Subject Name- Theory of Computation Subject Code-4KS05 Sr No.
The Chomsky Hierarchy(review)
 The Chomsky Hierarchy(review) Languages Machines Other Moels Recursively Enumerable Sets Turing Machines Post System Markov Algorithms, µ-recursive Functions Context-sensitive Languages Context-free Languages
The Chomsky Hierarchy(review) Languages Machines Other Moels Recursively Enumerable Sets Turing Machines Post System Markov Algorithms, µ-recursive Functions Context-sensitive Languages Context-free Languages
Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course
 Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course Week 3: Formal Languages and Semantics Thomas Noll Lehrstuhl für Informatik 2 RWTH Aachen University noll@cs.rwth-aachen.de http://www.b-it-center.de/wob/en/view/class211_id948.html
Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course Week 3: Formal Languages and Semantics Thomas Noll Lehrstuhl für Informatik 2 RWTH Aachen University noll@cs.rwth-aachen.de http://www.b-it-center.de/wob/en/view/class211_id948.html
Context Free Languages (CFL) Language Recognizer A device that accepts valid strings. The FA are formalized types of language recognizer.
 Context Free Languages (CFL) Language Recognizer A device that accepts valid strings. The FA are formalized types of language recognizer. Language Generator: Context free grammars are language generators,
Context Free Languages (CFL) Language Recognizer A device that accepts valid strings. The FA are formalized types of language recognizer. Language Generator: Context free grammars are language generators,
Chomsky Normal Form for Context-Free Gramars
 Chomsky Normal Form for Context-Free Gramars Deepak D Souza Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. 17 September 2014 Outline 1 CNF 2 Converting to CNF 3 Correctness
Chomsky Normal Form for Context-Free Gramars Deepak D Souza Department of Computer Science and Automation Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. 17 September 2014 Outline 1 CNF 2 Converting to CNF 3 Correctness
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING DUNDIGAL 500 043, HYDERABAD COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Course Code : A40509 Class :
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING DUNDIGAL 500 043, HYDERABAD COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Course Code : A40509 Class :
The View Over The Horizon
 The View Over The Horizon enumerable decidable context free regular Context-Free Grammars An example of a context free grammar, G 1 : A 0A1 A B B # Terminology: Each line is a substitution rule or production.
The View Over The Horizon enumerable decidable context free regular Context-Free Grammars An example of a context free grammar, G 1 : A 0A1 A B B # Terminology: Each line is a substitution rule or production.
1. (a) Explain the procedure to convert Context Free Grammar to Push Down Automata.
 Code No: R09220504 R09 Set No. 2 II B.Tech II Semester Examinations,December-January, 2011-2012 FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Computer Science And Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 75 Answer
Code No: R09220504 R09 Set No. 2 II B.Tech II Semester Examinations,December-January, 2011-2012 FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Computer Science And Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 75 Answer
The Turing Machine. Computability. The Church-Turing Thesis (1936) Theory Hall of Fame. Theory Hall of Fame. Undecidability
 The Turing Machine Computability Motivating idea Build a theoretical a human computer Likened to a human with a paper and pencil that can solve problems in an algorithmic way The theoretical provides a
The Turing Machine Computability Motivating idea Build a theoretical a human computer Likened to a human with a paper and pencil that can solve problems in an algorithmic way The theoretical provides a
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation
 MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation CFL Hierarchy CFL Decision Problems Your Questions? Previous class days' material Reading Assignments HW 12 or 13 problems Anything else I have included some slides online
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation CFL Hierarchy CFL Decision Problems Your Questions? Previous class days' material Reading Assignments HW 12 or 13 problems Anything else I have included some slides online
AC68 FINITE AUTOMATA & FORMULA LANGUAGES JUNE 2014
 Q.2 a. Show by using Mathematical Induction that n i= 1 i 2 n = ( n + 1) ( 2 n + 1) 6 b. Define language. Let = {0; 1} denote an alphabet. Enumerate five elements of the following languages: (i) Even binary
Q.2 a. Show by using Mathematical Induction that n i= 1 i 2 n = ( n + 1) ( 2 n + 1) 6 b. Define language. Let = {0; 1} denote an alphabet. Enumerate five elements of the following languages: (i) Even binary
Computational Models: Class 5
 Computational Models: Class 5 Benny Chor School of Computer Science Tel Aviv University March 27, 2019 Based on slides by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University, and modifications by Iftach Haitner and Yishay
Computational Models: Class 5 Benny Chor School of Computer Science Tel Aviv University March 27, 2019 Based on slides by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University, and modifications by Iftach Haitner and Yishay
FLAC Context-Free Grammars
 FLAC Context-Free Grammars Klaus Sutner Carnegie Mellon Universality Fall 2017 1 Generating Languages Properties of CFLs Generation vs. Recognition 3 Turing machines can be used to check membership in
FLAC Context-Free Grammars Klaus Sutner Carnegie Mellon Universality Fall 2017 1 Generating Languages Properties of CFLs Generation vs. Recognition 3 Turing machines can be used to check membership in
Concordia University Department of Computer Science & Software Engineering
 Concordia University Department of Computer Science & Software Engineering COMP 335/4 Theoretical Computer Science Winter 2015 Assignment 3 1. In each case, what language is generated by CFG s below. Justify
Concordia University Department of Computer Science & Software Engineering COMP 335/4 Theoretical Computer Science Winter 2015 Assignment 3 1. In each case, what language is generated by CFG s below. Justify
SYLLABUS. Introduction to Finite Automata, Central Concepts of Automata Theory. CHAPTER - 3 : REGULAR EXPRESSIONS AND LANGUAGES
 Contents i SYLLABUS UNIT - I CHAPTER - 1 : AUT UTOMA OMATA Introduction to Finite Automata, Central Concepts of Automata Theory. CHAPTER - 2 : FINITE AUT UTOMA OMATA An Informal Picture of Finite Automata,
Contents i SYLLABUS UNIT - I CHAPTER - 1 : AUT UTOMA OMATA Introduction to Finite Automata, Central Concepts of Automata Theory. CHAPTER - 2 : FINITE AUT UTOMA OMATA An Informal Picture of Finite Automata,
Chapter 4: Context-Free Grammars
 Chapter 4: Context-Free Grammars 4.1 Basics of Context-Free Grammars Definition A context-free grammars, or CFG, G is specified by a quadruple (N, Σ, P, S), where N is the nonterminal or variable alphabet;
Chapter 4: Context-Free Grammars 4.1 Basics of Context-Free Grammars Definition A context-free grammars, or CFG, G is specified by a quadruple (N, Σ, P, S), where N is the nonterminal or variable alphabet;
Chapter 6. Properties of Regular Languages
 Chapter 6 Properties of Regular Languages Regular Sets and Languages Claim(1). The family of languages accepted by FSAs consists of precisely the regular sets over a given alphabet. Every regular set is
Chapter 6 Properties of Regular Languages Regular Sets and Languages Claim(1). The family of languages accepted by FSAs consists of precisely the regular sets over a given alphabet. Every regular set is
Context Free Languages. Automata Theory and Formal Grammars: Lecture 6. Languages That Are Not Regular. Non-Regular Languages
 Context Free Languages Automata Theory and Formal Grammars: Lecture 6 Context Free Languages Last Time Decision procedures for FAs Minimum-state DFAs Today The Myhill-Nerode Theorem The Pumping Lemma Context-free
Context Free Languages Automata Theory and Formal Grammars: Lecture 6 Context Free Languages Last Time Decision procedures for FAs Minimum-state DFAs Today The Myhill-Nerode Theorem The Pumping Lemma Context-free
Recitation 4: Converting Grammars to Chomsky Normal Form, Simulation of Context Free Languages with Push-Down Automata, Semirings
 Recitation 4: Converting Grammars to Chomsky Normal Form, Simulation of Context Free Languages with Push-Down Automata, Semirings 11-711: Algorithms for NLP October 10, 2014 Conversion to CNF Example grammar
Recitation 4: Converting Grammars to Chomsky Normal Form, Simulation of Context Free Languages with Push-Down Automata, Semirings 11-711: Algorithms for NLP October 10, 2014 Conversion to CNF Example grammar
CS A Term 2009: Foundations of Computer Science. Homework 2. By Li Feng, Shweta Srivastava, and Carolina Ruiz.
 CS3133 - A Term 2009: Foundations of Computer Science Prof. Carolina Ruiz Homework 2 WPI By Li Feng, Shweta Srivastava, and Carolina Ruiz Chapter 4 Problem 1: (10 Points) Exercise 4.3 Solution 1: S is
CS3133 - A Term 2009: Foundations of Computer Science Prof. Carolina Ruiz Homework 2 WPI By Li Feng, Shweta Srivastava, and Carolina Ruiz Chapter 4 Problem 1: (10 Points) Exercise 4.3 Solution 1: S is
