Homework 4 Solutions. 2. Find context-free grammars for the language L = {a n b m c k : k n + m}. (with n 0,
|
|
|
- Duane Lee
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Formal Language, Fall 2016 Due: 21-Apr-2016 (Thursday) Instructor: Prof. Wen-Guey Tzeng Homework 4 Solutions Scribe: Yi-Ruei Chen 1. Find context-free grammars for the language L = {a n b m : n 2m} with n 0, m 0. [Solution 1] Parse L as L = L 1 L 2, where L 1 = {a n b m : n > 2m} and L 2 = {a n b m : n < 2m}. Then construct productions for L 1 and L 2, respectively. A context-free grammar for L is G = ({S, S 1, S 2, A, B}, {a, b}, S, P ) with the productions S S 1 S 2, S 1 aas 1 b A, A a aa, S 2 aas 2 b B, B b Bb ab. [Solution 2] Produce L = {a n b m : n = 2m} then add extra a s or b s. A context-free grammar for L is G = ({S, A, B}, {a, b}, S, P ) with the productions S aasb A B, A a aa, B b Bb ab. 2. Find context-free grammars for the language L = {a n b m c k : k n + m}. (with n 0, m 0, k 0) Parse L as L = L 1 L 2, where L 1 = {a n b m c k : k > n + m} and L 2 = {a n b m c k : k < n + m}. Then construct productions for L 1 and L 2, respectively. A context-free grammar for L is G = ({S, S 1, S 2, T 1, T 2, A, B, C}, {a, b, c}, S, P ) with the productions S S 1 S 2, S 1 as 1 c T 1, T 1 bt 1 c C, C cc c, S 2 as 2 c T 2 AB A B, T 2 bt 2 c B, A aa a, B bb b. 3. Show that L = {w {a, b, c} : w = 3n a (w)} is a context-free language. A context-free grammar for L is G = ({S, T }, {a, b, c}, S, P ) with the productions S SaST ST S ST SaST S ST ST SaS λ, T b c. 1
2 4. Let L = {a n b n : n 0}. Show that L and L are context-free. (1) L = {a m b k : m k} {(a + b) ba(a + b) }. A context-free grammar for L is G = ({S, S 1, S 2, A, B, T }, {a, b}, S, P ) with the productions S S 1 S 2, S 1 as 1 b A B, A a aa, B b bb, S 2 T bat, T at bt λ. (2) L = {(a n b n ) m : n, m 0}. A context-free grammar for L is G = ({S, S 1, S 2, A, B, T }, {a, b}, S, P ) with the productions S SS 1 λ, S 1 as 1 b λ. 5. Show a derivation tree for the string aabbbb with the grammar S AB λ, A ab, B Sb. 2
3 6. Define what one might mean by properly nested parenthesis structures involving two kinds of parentheses, say ( ) and [ ]. Intuitively, properly nested strings in this situation are ([ ]), ([[ ]])[( )], but not ([ )] or (( ]]. Using your definition, give a context-free grammar for generating all properly nested parentheses. A context-free grammar for generating all properly nested parentheses is G = ({S}, {(, ), [, ]}, S, P ) with production S [S] (S) λ. 7. Find an s-grammar for L = {a n b n+1 : n 2}. An s-grammar for L is G = ({S, S 1, S 2, B}, {a, b}, S, P ) with the productions S as 1 B, S 1 as 2 B, S 2 as 2 B b, B b. 8. Construct an unambiguous grammar equivalent to the following grammar. S AB aab, A a Aa, B b. This grammar generates the strings a + b. A desirable grammar is G = ({S, A}, {a, b}, S, P ) with the productions S as b, A aa a. 9. Show that the following grammar is ambiguous. S asbs bsas λ. The string w = abab has the following two derivation trees: 3
4 10. Eliminate useless productions from S a aa B C, A ab λ, B Aa, C ccd, D ddd. There are two cases for useless variables Case 1: Variables that cannot generate strings in T. V 1 = {}, (T V 1 ) = {a, b, c, d} ; Since S a, A λ, and D ddd, add S, A, and D to V 1 ; V 1 = {S, A, D}, (T V 1 ) = ({a, b, c, d, S, A, D}) ; Since S aa and B Aa, add S and B to V 1 ; V 1 = {S, A, B, D}, (T V 1 ) = ({a, b, c, d, S, A, B, D}) ; Since S B and A ab, B Aa, the algorithm stops since there is no new rules can be added to V 1 ; Thus, we have V 1 = {S, A, B, D}. After removing the related useless productions, we have: S a aa B, A ab λ, B Aa, D ddd. Case 2: Variables that cannot be reached from S. The dependency graph of the result grammar in Case 1 is as follows. 4
5 D is unreachable from S; Thus, after removing the related useless productions, we have: S a aa B, A ab λ, B Aa. 11. Eliminate all λ-productions from S AaB abb, A λ, B bba λ. A procedure of removing all λ-productions is as follows. Find the nullable variable set V N = {A, B}; The λ-production A λ can be removed after adding new productions obtained by substituting λ for A where it occurs on the right: S AaB abb ab, B bba λ bb; The λ-production B λ can be removed after adding new productions obtained by substituting λ for B where it occurs on the right: S AaB Aa abb ab a, B bba bb; 5
6 12. Eliminate all unit-productions in Question 10. From the dependency graph of the grammar, we add the new rules S Aa ccd to the non-unit productions S a aa Aa ccd, A ab λ, B Aa, C ccd, D ddd. 13. Transform the grammar with production into Chomsky normal form. The transform procedure is as follows. Removing λ-productions: S abab, A baa λ, B BAa A λ Removing A λ: S abab abb, A baa ba, B BAa A λ Ba. Removing B λ: S abab abb aba ab, A baa ba, B BAa A Ba Aa a. Removing unit-production B A: S abab abb aba ab, A baa ba, B BAa baa ba Ba Aa a. Removing useless productions: No useless productions. Convert the grammar into Chomsky normal form: Introduce new variables S x for each x T : S S a S b AB S a S b B S a S b A S a S b, A S b AS a S b S a, B BAS a S b AS a BS a AS a a, S a a, S b b. Introduce additional variables to get the first two productions into normal 6
7 form and we get the final result S S a U S a X S a Y S a S b, A S b W S b S a, B BZ S b V S b B S b A S b BS a AS a a, U S b V, V AB, X S b B, Y S b A, W AS a, Z AS a, S a a, S b b. 14. Convert the grammar with production into Greibach normal form. We introduce new variables X and Y : S ABb a, A aaa B, B bab λ S ABX Y, A Y Y A B, B XAX λ, X b, Y a Then, by using the substitution, we immediately get the equivalent grammar S ay ABX baxbx baxx b a, A ay A B, B bax λ, X b, Y a 7
8 15. Use the CYK algorithm to determine whether the strings aabb, aabba, and abbbb are in the language generated by the grammar in Example (1) For the string aabb: Firstly, we have V 1,1 = {A}, V 2,2 = {A}, V 3,3 = {B}, V 4,4 = {B}. 8
9 Then, by using the equation V ij = {A BC, with B V ik, C V k+1,j }, k {i,i+1,...,j 1} we have V 1,2 = {A BC, B V 1,1, C V 2,2 } = {}, V 2,3 = {A BC, B V 2,2, C V 3,3 } = {S, B}, V 3,4 = {A BC, B V 3,3, C V 4,4 } = {A}, V 1,3 = {A BC, B V 1,1, C V 2,3 } {A BC, B V 1,2, C V 3,3 } = {S, B}, V 2,4 = {A BC, B V 2,2, C V 3,4 } {A BC, B V 2,3, C V 4,4 } = {A}, V 1,4 = {A BC, B V 1,1, C V 2,4 } {A BC, B V 1,2, C V 3,4 } Thus, we have {A BC, B V 1,3, C V 4,4 } = {A}. 9
10 V 1,4 = {A} V 1,3 = {S, B} V 2,4 = {A} V 1,2 = {} V 2,3 = {S, B} V 3,4 = {A} V 1,1 = {A} V 2,2 = {A} V 3,3 = {B} V 4,4 = {B} Because V 1,4 = {A}, S V 1,4, we conclude that aabb is not in the language generated by the given grammar, i.e., aabb L(G), by using the CYK algorithm. (2) For the string aabba: Similarly, we have 10
11 V 1,5 = {} V 1,4 = {A} V 2,5 = {} V 1,3 = {S, B} V 2,4 = {A} V 3,5 = {} V 1,2 = {} V 2,3 = {S, B} V 3,4 = {A} V 4,5 = {} V 1,1 = {A} V 2,2 = {A} V 3,3 = {B} V 4,4 = {B} V 5,5 = {A} Because V 1,5 = {}, we conclude that aabba is not in the language generated by the given grammar, i.e., aabba / L(G), by using the CYK algorithm. (3) For the string abbbb: Similarly, we have V 1,5 = {A} V 1,4 = {S, B} V 2,5 = {A} V 1,3 = {A} V 2,4 = {S, B} V 3,5 = {S, B} V 1,2 = {S, B} V 2,3 = {A} V 3,4 = {A} V 4,5 = {A} V 1,1 = {A} V 2,2 = {B} V 3,3 = {B} V 4,4 = {B} V 5,5 = {B} Because V 1,5 = {A}, S V 1,5, we conclude that abbbb is not in the language generated by the given grammar, i.e., abbbb / L(G), by using the CYK algorithm. 11
Simplification of CFG and Normal Forms. Wen-Guey Tzeng Computer Science Department National Chiao Tung University
 Simplification of CFG and Normal Forms Wen-Guey Tzeng Computer Science Department National Chiao Tung University Normal Forms We want a cfg with either Chomsky or Greibach normal form Chomsky normal form
Simplification of CFG and Normal Forms Wen-Guey Tzeng Computer Science Department National Chiao Tung University Normal Forms We want a cfg with either Chomsky or Greibach normal form Chomsky normal form
Simplification of CFG and Normal Forms. Wen-Guey Tzeng Computer Science Department National Chiao Tung University
 Simplification of CFG and Normal Forms Wen-Guey Tzeng Computer Science Department National Chiao Tung University Normal Forms We want a cfg with either Chomsky or Greibach normal form Chomsky normal form
Simplification of CFG and Normal Forms Wen-Guey Tzeng Computer Science Department National Chiao Tung University Normal Forms We want a cfg with either Chomsky or Greibach normal form Chomsky normal form
Automata Theory Final Exam Solution 08:10-10:00 am Friday, June 13, 2008
 Automata Theory Final Exam Solution 08:10-10:00 am Friday, June 13, 2008 Name: ID #: This is a Close Book examination. Only an A4 cheating sheet belonging to you is acceptable. You can write your answers
Automata Theory Final Exam Solution 08:10-10:00 am Friday, June 13, 2008 Name: ID #: This is a Close Book examination. Only an A4 cheating sheet belonging to you is acceptable. You can write your answers
Lecture 12 Simplification of Context-Free Grammars and Normal Forms
 Lecture 12 Simplification of Context-Free Grammars and Normal Forms COT 4420 Theory of Computation Chapter 6 Normal Forms for CFGs 1. Chomsky Normal Form CNF Productions of form A BC A, B, C V A a a T
Lecture 12 Simplification of Context-Free Grammars and Normal Forms COT 4420 Theory of Computation Chapter 6 Normal Forms for CFGs 1. Chomsky Normal Form CNF Productions of form A BC A, B, C V A a a T
CS A Term 2009: Foundations of Computer Science. Homework 2. By Li Feng, Shweta Srivastava, and Carolina Ruiz.
 CS3133 - A Term 2009: Foundations of Computer Science Prof. Carolina Ruiz Homework 2 WPI By Li Feng, Shweta Srivastava, and Carolina Ruiz Chapter 4 Problem 1: (10 Points) Exercise 4.3 Solution 1: S is
CS3133 - A Term 2009: Foundations of Computer Science Prof. Carolina Ruiz Homework 2 WPI By Li Feng, Shweta Srivastava, and Carolina Ruiz Chapter 4 Problem 1: (10 Points) Exercise 4.3 Solution 1: S is
TAFL 1 (ECS-403) Unit- III. 3.1 Definition of CFG (Context Free Grammar) and problems. 3.2 Derivation. 3.3 Ambiguity in Grammar
 TAFL 1 (ECS-403) Unit- III 3.1 Definition of CFG (Context Free Grammar) and problems 3.2 Derivation 3.3 Ambiguity in Grammar 3.3.1 Inherent Ambiguity 3.3.2 Ambiguous to Unambiguous CFG 3.4 Simplification
TAFL 1 (ECS-403) Unit- III 3.1 Definition of CFG (Context Free Grammar) and problems 3.2 Derivation 3.3 Ambiguity in Grammar 3.3.1 Inherent Ambiguity 3.3.2 Ambiguous to Unambiguous CFG 3.4 Simplification
Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x where
 Recitation 11 Notes Context Free Grammars Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x A V, and x (V T)*. Examples Problem 1. Given the
Recitation 11 Notes Context Free Grammars Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x A V, and x (V T)*. Examples Problem 1. Given the
Theory of Computation - Module 3
 Theory of Computation - Module 3 Syllabus Context Free Grammar Simplification of CFG- Normal forms-chomsky Normal form and Greibach Normal formpumping lemma for Context free languages- Applications of
Theory of Computation - Module 3 Syllabus Context Free Grammar Simplification of CFG- Normal forms-chomsky Normal form and Greibach Normal formpumping lemma for Context free languages- Applications of
Parsing. Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer. Winter 2017/18. Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf 1 / 26
 Parsing Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Winter 2017/18 1 / 26 Table of contents 1 Context-Free Grammars 2 Simplifying CFGs Removing useless symbols Eliminating
Parsing Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Winter 2017/18 1 / 26 Table of contents 1 Context-Free Grammars 2 Simplifying CFGs Removing useless symbols Eliminating
Automata Theory CS F-08 Context-Free Grammars
 Automata Theory CS411-2015F-08 Context-Free Grammars David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 08-0: Context-Free Grammars Set of Terminals (Σ) Set of Non-Terminals Set of
Automata Theory CS411-2015F-08 Context-Free Grammars David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 08-0: Context-Free Grammars Set of Terminals (Σ) Set of Non-Terminals Set of
Context-Free Grammar
 Context-Free Grammar CFGs are more powerful than regular expressions. They are more powerful in the sense that whatever can be expressed using regular expressions can be expressed using context-free grammars,
Context-Free Grammar CFGs are more powerful than regular expressions. They are more powerful in the sense that whatever can be expressed using regular expressions can be expressed using context-free grammars,
Concordia University Department of Computer Science & Software Engineering
 Concordia University Department of Computer Science & Software Engineering COMP 335/4 Theoretical Computer Science Winter 2015 Assignment 3 1. In each case, what language is generated by CFG s below. Justify
Concordia University Department of Computer Science & Software Engineering COMP 335/4 Theoretical Computer Science Winter 2015 Assignment 3 1. In each case, what language is generated by CFG s below. Justify
CFG Simplification. (simplify) 1. Eliminate useless symbols 2. Eliminate -productions 3. Eliminate unit productions
 CFG Simplification (simplify) 1. Eliminate useless symbols 2. Eliminate -productions 3. Eliminate unit productions 1 Eliminating useless symbols 1. A symbol X is generating if there exists: X * w, for
CFG Simplification (simplify) 1. Eliminate useless symbols 2. Eliminate -productions 3. Eliminate unit productions 1 Eliminating useless symbols 1. A symbol X is generating if there exists: X * w, for
1. (a) Explain the procedure to convert Context Free Grammar to Push Down Automata.
 Code No: R09220504 R09 Set No. 2 II B.Tech II Semester Examinations,December-January, 2011-2012 FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Computer Science And Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 75 Answer
Code No: R09220504 R09 Set No. 2 II B.Tech II Semester Examinations,December-January, 2011-2012 FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Computer Science And Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 75 Answer
CS 373: Theory of Computation. Fall 2010
 CS 373: Theory of Computation Gul Agha Mahesh Viswanathan Fall 2010 1 1 Normal Forms for CFG Normal Forms for Grammars It is typically easier to work with a context free language if given a CFG in a normal
CS 373: Theory of Computation Gul Agha Mahesh Viswanathan Fall 2010 1 1 Normal Forms for CFG Normal Forms for Grammars It is typically easier to work with a context free language if given a CFG in a normal
Homework 5 - Solution
 DCP3122 Introduction to Formal Languages, Spring 2015 Instructor: Prof. Wen-Guey Tzeng Homework 5 - Solution 5-May-2015 Due: 18-May-2015 1. Given Σ = {a, b, c}, find an NPDA that accepts L = {a n b n+m
DCP3122 Introduction to Formal Languages, Spring 2015 Instructor: Prof. Wen-Guey Tzeng Homework 5 - Solution 5-May-2015 Due: 18-May-2015 1. Given Σ = {a, b, c}, find an NPDA that accepts L = {a n b n+m
Solutions to Problem Set 3
 V22.0453-001 Theory of Computation October 8, 2003 TA: Nelly Fazio Solutions to Problem Set 3 Problem 1 We have seen that a grammar where all productions are of the form: A ab, A c (where A, B non-terminals,
V22.0453-001 Theory of Computation October 8, 2003 TA: Nelly Fazio Solutions to Problem Set 3 Problem 1 We have seen that a grammar where all productions are of the form: A ab, A c (where A, B non-terminals,
CPSC 313 Introduction to Computability
 CPSC 313 Introduction to Computability Grammars in Chomsky Normal Form (Cont d) (Sipser, pages 109-111 (3 rd ed) and 107-109 (2 nd ed)) Renate Scheidler Fall 2018 Chomsky Normal Form A context-free grammar
CPSC 313 Introduction to Computability Grammars in Chomsky Normal Form (Cont d) (Sipser, pages 109-111 (3 rd ed) and 107-109 (2 nd ed)) Renate Scheidler Fall 2018 Chomsky Normal Form A context-free grammar
Sheet 1-8 Dr. Mostafa Aref Format By : Mostafa Sayed
 Sheet -8 Dr. Mostafa Aref Format By : Mostafa Sayed 09 Introduction Assignment. For = {a, } a) Write 0 strings of the following languages i) All strings with no more than one a,,, a, a, a, a, a, a, a ii)
Sheet -8 Dr. Mostafa Aref Format By : Mostafa Sayed 09 Introduction Assignment. For = {a, } a) Write 0 strings of the following languages i) All strings with no more than one a,,, a, a, a, a, a, a, a ii)
EXAMPLE CFG. L = {a 2n : n 1 } L = {a 2n : n 0 } S asa aa. L = {a n b : n 0 } L = {a n b : n 1 } S asb ab S 1S00 S 1S00 100
 EXAMPLE CFG L = {a 2n : n 1 } L = {a 2n : n 0 } S asa aa S asa L = {a n b : n 0 } L = {a n b : n 1 } S as b S as ab L { a b : n 0} L { a b : n 1} S asb S asb ab n 2n n 2n L {1 0 : n 0} L {1 0 : n 1} S
EXAMPLE CFG L = {a 2n : n 1 } L = {a 2n : n 0 } S asa aa S asa L = {a n b : n 0 } L = {a n b : n 1 } S as b S as ab L { a b : n 0} L { a b : n 1} S asb S asb ab n 2n n 2n L {1 0 : n 0} L {1 0 : n 1} S
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV026/TMV027/DIT321 Responsible: Ana Bove
 Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV026/TMV027/DIT321 Responsible: Ana Bove Tuesday 28 of May 2013 Total: 60 points TMV027/DIT321 registration VT13 TMV026/DIT321 registration before VT13 Exam
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV026/TMV027/DIT321 Responsible: Ana Bove Tuesday 28 of May 2013 Total: 60 points TMV027/DIT321 registration VT13 TMV026/DIT321 registration before VT13 Exam
Homework 4. Chapter 7. CS A Term 2009: Foundations of Computer Science. By Li Feng, Shweta Srivastava, and Carolina Ruiz
 CS3133 - A Term 2009: Foundations of Computer Science Prof. Carolina Ruiz Homework 4 WPI By Li Feng, Shweta Srivastava, and Carolina Ruiz Chapter 7 Problem: Chap 7.1 part a This PDA accepts the language
CS3133 - A Term 2009: Foundations of Computer Science Prof. Carolina Ruiz Homework 4 WPI By Li Feng, Shweta Srivastava, and Carolina Ruiz Chapter 7 Problem: Chap 7.1 part a This PDA accepts the language
COSE212: Programming Languages. Lecture 1 Inductive Definitions (1)
 COSE212: Programming Languages Lecture 1 Inductive Definitions (1) Hakjoo Oh 2017 Fall Hakjoo Oh COSE212 2017 Fall, Lecture 1 September 4, 2017 1 / 9 Inductive Definitions Inductive definition (induction)
COSE212: Programming Languages Lecture 1 Inductive Definitions (1) Hakjoo Oh 2017 Fall Hakjoo Oh COSE212 2017 Fall, Lecture 1 September 4, 2017 1 / 9 Inductive Definitions Inductive definition (induction)
60-354, Theory of Computation Fall Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor
 60-354, Theory of Computation Fall 2013 Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor Pushdown Automata (PDA) PDA = ε-nfa + stack Acceptance ε-nfa enters a final state or Stack is
60-354, Theory of Computation Fall 2013 Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor Pushdown Automata (PDA) PDA = ε-nfa + stack Acceptance ε-nfa enters a final state or Stack is
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018
 Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 14 Ana Bove May 14th 2018 Recap: Context-free Grammars Simplification of grammars: Elimination of ǫ-productions; Elimination of
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 14 Ana Bove May 14th 2018 Recap: Context-free Grammars Simplification of grammars: Elimination of ǫ-productions; Elimination of
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF) Announcement Homework 2 will be given soon (before Tue) Due date: Oct 31 (Tue), before class Midterm: Nov 3, (Fri), first hour
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF) Announcement Homework 2 will be given soon (before Tue) Due date: Oct 31 (Tue), before class Midterm: Nov 3, (Fri), first hour
SFWR ENG 2FA3. Solution to the Assignment #4
 SFWR ENG 2FA3. Solution to the Assignment #4 Total = 131, 100%= 115 The solutions below are often very detailed on purpose. Such level of details is not required from students solutions. Some questions
SFWR ENG 2FA3. Solution to the Assignment #4 Total = 131, 100%= 115 The solutions below are often very detailed on purpose. Such level of details is not required from students solutions. Some questions
COSE212: Programming Languages. Lecture 1 Inductive Definitions (1)
 COSE212: Programming Languages Lecture 1 Inductive Definitions (1) Hakjoo Oh 2018 Fall Hakjoo Oh COSE212 2018 Fall, Lecture 1 September 5, 2018 1 / 10 Inductive Definitions Inductive definition (induction)
COSE212: Programming Languages Lecture 1 Inductive Definitions (1) Hakjoo Oh 2018 Fall Hakjoo Oh COSE212 2018 Fall, Lecture 1 September 5, 2018 1 / 10 Inductive Definitions Inductive definition (induction)
Theory of Computer Science
 Theory of Computer Science C1. Formal Languages and Grammars Malte Helmert University of Basel March 14, 2016 Introduction Example: Propositional Formulas from the logic part: Definition (Syntax of Propositional
Theory of Computer Science C1. Formal Languages and Grammars Malte Helmert University of Basel March 14, 2016 Introduction Example: Propositional Formulas from the logic part: Definition (Syntax of Propositional
Context-Free Grammars: Normal Forms
 Context-Free Grammars: Normal Forms Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
Context-Free Grammars: Normal Forms Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
CS375: Logic and Theory of Computing
 CS375: Logic and Theory of Computing Fuhua (Frank) Cheng Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky 1 Table of Contents: Week 1: Preliminaries (set algebra, relations, functions) (read Chapters
CS375: Logic and Theory of Computing Fuhua (Frank) Cheng Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky 1 Table of Contents: Week 1: Preliminaries (set algebra, relations, functions) (read Chapters
HW 3 Solutions. Tommy November 27, 2012
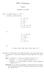 HW 3 Solutions Tommy November 27, 2012 5.1.1 (a) Online solution: S 0S1 ɛ. (b) Similar to online solution: S AY XC A aa ɛ b ɛ C cc ɛ X axb aa b Y by c b cc (c) S X A A A V AV a V V b V a b X V V X V (d)
HW 3 Solutions Tommy November 27, 2012 5.1.1 (a) Online solution: S 0S1 ɛ. (b) Similar to online solution: S AY XC A aa ɛ b ɛ C cc ɛ X axb aa b Y by c b cc (c) S X A A A V AV a V V b V a b X V V X V (d)
AC68 FINITE AUTOMATA & FORMULA LANGUAGES JUNE 2014
 Q.2 a. Show by using Mathematical Induction that n i= 1 i 2 n = ( n + 1) ( 2 n + 1) 6 b. Define language. Let = {0; 1} denote an alphabet. Enumerate five elements of the following languages: (i) Even binary
Q.2 a. Show by using Mathematical Induction that n i= 1 i 2 n = ( n + 1) ( 2 n + 1) 6 b. Define language. Let = {0; 1} denote an alphabet. Enumerate five elements of the following languages: (i) Even binary
Plan for 2 nd half. Just when you thought it was safe. Just when you thought it was safe. Theory Hall of Fame. Chomsky Normal Form
 Plan for 2 nd half Pumping Lemma for CFLs The Return of the Pumping Lemma Just when you thought it was safe Return of the Pumping Lemma Recall: With Regular Languages The Pumping Lemma showed that if a
Plan for 2 nd half Pumping Lemma for CFLs The Return of the Pumping Lemma Just when you thought it was safe Return of the Pumping Lemma Recall: With Regular Languages The Pumping Lemma showed that if a
download instant at Assume that (w R ) R = w for all strings w Σ of length n or less.
 Chapter 2 Languages 3. We prove, by induction on the length of the string, that w = (w R ) R for every string w Σ. Basis: The basis consists of the null string. In this case, (λ R ) R = (λ) R = λ as desired.
Chapter 2 Languages 3. We prove, by induction on the length of the string, that w = (w R ) R for every string w Σ. Basis: The basis consists of the null string. In this case, (λ R ) R = (λ) R = λ as desired.
Lecture 11 Context-Free Languages
 Lecture 11 Context-Free Languages COT 4420 Theory of Computation Chapter 5 Context-Free Languages n { a b : n n { ww } 0} R Regular Languages a *b* ( a + b) * Example 1 G = ({S}, {a, b}, S, P) Derivations:
Lecture 11 Context-Free Languages COT 4420 Theory of Computation Chapter 5 Context-Free Languages n { a b : n n { ww } 0} R Regular Languages a *b* ( a + b) * Example 1 G = ({S}, {a, b}, S, P) Derivations:
Computability and Complexity
 Computability and Complexity Rewriting Systems and Chomsky Grammars CAS 705 Ryszard Janicki Department of Computing and Software McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario, Canada janicki@mcmaster.ca Ryszard
Computability and Complexity Rewriting Systems and Chomsky Grammars CAS 705 Ryszard Janicki Department of Computing and Software McMaster University Hamilton, Ontario, Canada janicki@mcmaster.ca Ryszard
Notes for Comp 497 (Comp 454) Week 10 4/5/05
 Notes for Comp 497 (Comp 454) Week 10 4/5/05 Today look at the last two chapters in Part II. Cohen presents some results concerning context-free languages (CFL) and regular languages (RL) also some decidability
Notes for Comp 497 (Comp 454) Week 10 4/5/05 Today look at the last two chapters in Part II. Cohen presents some results concerning context-free languages (CFL) and regular languages (RL) also some decidability
C1.1 Introduction. Theory of Computer Science. Theory of Computer Science. C1.1 Introduction. C1.2 Alphabets and Formal Languages. C1.
 Theory of Computer Science March 20, 2017 C1. Formal Languages and Grammars Theory of Computer Science C1. Formal Languages and Grammars Malte Helmert University of Basel March 20, 2017 C1.1 Introduction
Theory of Computer Science March 20, 2017 C1. Formal Languages and Grammars Theory of Computer Science C1. Formal Languages and Grammars Malte Helmert University of Basel March 20, 2017 C1.1 Introduction
CS500 Homework #2 Solutions
 CS500 Homework #2 Solutions 1. Consider the two languages Show that L 1 is context-free but L 2 is not. L 1 = {a i b j c k d l i = j k = l} L 2 = {a i b j c k d l i = k j = l} Answer. L 1 is the concatenation
CS500 Homework #2 Solutions 1. Consider the two languages Show that L 1 is context-free but L 2 is not. L 1 = {a i b j c k d l i = j k = l} L 2 = {a i b j c k d l i = k j = l} Answer. L 1 is the concatenation
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad
 St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad-500 014 Subject: FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Class : CSE II PART A (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) UNIT- I 1 Explain transition diagram, transition
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad-500 014 Subject: FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Class : CSE II PART A (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) UNIT- I 1 Explain transition diagram, transition
5.A Examples of Context-Free Grammars 3.1 and 3.2 of Du & Ko s book(pp )
 5.A Examples of Context-Free Grammars 3.1 and 3.2 of Du & Ko s book(pp. 91-108) Example 3.1 Consider S ε asb. What is L(S)? Solution S asb aasbb a n Sb n a n b n. L(S) = {a n b n n 0} Example 3.2 Consider
5.A Examples of Context-Free Grammars 3.1 and 3.2 of Du & Ko s book(pp. 91-108) Example 3.1 Consider S ε asb. What is L(S)? Solution S asb aasbb a n Sb n a n b n. L(S) = {a n b n n 0} Example 3.2 Consider
Finite Automata and Formal Languages TMV026/DIT321 LP Useful, Useless, Generating and Reachable Symbols
 Finite Automata and Formal Languages TMV026/DIT321 LP4 2012 Lecture 13 Ana Bove May 7th 2012 Overview of today s lecture: Normal Forms for Context-Free Languages Pumping Lemma for Context-Free Languages
Finite Automata and Formal Languages TMV026/DIT321 LP4 2012 Lecture 13 Ana Bove May 7th 2012 Overview of today s lecture: Normal Forms for Context-Free Languages Pumping Lemma for Context-Free Languages
CSCI 340: Computational Models. Regular Expressions. Department of Computer Science
 CSCI 340: Computational Models Regular Expressions Chapter 4 Department of Computer Science Yet Another New Method for Defining Languages Given the Language: L 1 = {x n for n = 1 2 3...} We could easily
CSCI 340: Computational Models Regular Expressions Chapter 4 Department of Computer Science Yet Another New Method for Defining Languages Given the Language: L 1 = {x n for n = 1 2 3...} We could easily
Solution. S ABc Ab c Bc Ac b A ABa Ba Aa a B Bbc bc.
 Section 12.4 Context-Free Language Topics Algorithm. Remove Λ-productions from grammars for langauges without Λ. 1. Find nonterminals that derive Λ. 2. For each production A w construct all productions
Section 12.4 Context-Free Language Topics Algorithm. Remove Λ-productions from grammars for langauges without Λ. 1. Find nonterminals that derive Λ. 2. For each production A w construct all productions
HW6 Solutions. Micha l Dereziński. March 20, 2015
 HW6 Solutions Micha l Dereziński March 20, 2015 1 Exercise 5.5 (a) The PDA accepts odd-length strings whose middle symbol is a and whose other letters are as and bs. Its diagram is below. b, Z 0 /XZ 0
HW6 Solutions Micha l Dereziński March 20, 2015 1 Exercise 5.5 (a) The PDA accepts odd-length strings whose middle symbol is a and whose other letters are as and bs. Its diagram is below. b, Z 0 /XZ 0
1.[3] Give an unambiguous grammar that generates the set of all regular expressions on Ó = {a,b}. Justify your construction.
![1.[3] Give an unambiguous grammar that generates the set of all regular expressions on Ó = {a,b}. Justify your construction. 1.[3] Give an unambiguous grammar that generates the set of all regular expressions on Ó = {a,b}. Justify your construction.](/thumbs/78/78529386.jpg) CAS 705. Sample solutions to the assignment 2 (many questions have more than one solutions). Total of this assignment is 135 pts. Each assignment is worth 25%. 1.[3] Give an unambiguous grammar that generates
CAS 705. Sample solutions to the assignment 2 (many questions have more than one solutions). Total of this assignment is 135 pts. Each assignment is worth 25%. 1.[3] Give an unambiguous grammar that generates
Context Free Languages and Grammars
 Algorithms & Models of Computation CS/ECE 374, Fall 2017 Context Free Languages and Grammars Lecture 7 Tuesday, September 19, 2017 Sariel Har-Peled (UIUC) CS374 1 Fall 2017 1 / 36 What stack got to do
Algorithms & Models of Computation CS/ECE 374, Fall 2017 Context Free Languages and Grammars Lecture 7 Tuesday, September 19, 2017 Sariel Har-Peled (UIUC) CS374 1 Fall 2017 1 / 36 What stack got to do
VTU QUESTION BANK. Unit 1. Introduction to Finite Automata. 1. Obtain DFAs to accept strings of a s and b s having exactly one a.
 VTU QUESTION BANK Unit 1 Introduction to Finite Automata 1. Obtain DFAs to accept strings of a s and b s having exactly one a.(5m )( Dec-2014) 2. Obtain a DFA to accept strings of a s and b s having even
VTU QUESTION BANK Unit 1 Introduction to Finite Automata 1. Obtain DFAs to accept strings of a s and b s having exactly one a.(5m )( Dec-2014) 2. Obtain a DFA to accept strings of a s and b s having even
Recitation 4: Converting Grammars to Chomsky Normal Form, Simulation of Context Free Languages with Push-Down Automata, Semirings
 Recitation 4: Converting Grammars to Chomsky Normal Form, Simulation of Context Free Languages with Push-Down Automata, Semirings 11-711: Algorithms for NLP October 10, 2014 Conversion to CNF Example grammar
Recitation 4: Converting Grammars to Chomsky Normal Form, Simulation of Context Free Languages with Push-Down Automata, Semirings 11-711: Algorithms for NLP October 10, 2014 Conversion to CNF Example grammar
Context Free Languages (CFL) Language Recognizer A device that accepts valid strings. The FA are formalized types of language recognizer.
 Context Free Languages (CFL) Language Recognizer A device that accepts valid strings. The FA are formalized types of language recognizer. Language Generator: Context free grammars are language generators,
Context Free Languages (CFL) Language Recognizer A device that accepts valid strings. The FA are formalized types of language recognizer. Language Generator: Context free grammars are language generators,
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING DUNDIGAL 500 043, HYDERABAD COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Course Code : A40509 Class :
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING DUNDIGAL 500 043, HYDERABAD COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Course Code : A40509 Class :
Grammars and Context Free Languages
 Grammars and Context Free Languages H. Geuvers and J. Rot Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Version: fall 2016 H. Geuvers & J. Rot Version: fall 2016 Talen en Automaten 1 / 24 Outline Grammars
Grammars and Context Free Languages H. Geuvers and J. Rot Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Version: fall 2016 H. Geuvers & J. Rot Version: fall 2016 Talen en Automaten 1 / 24 Outline Grammars
FLAC Context-Free Grammars
 FLAC Context-Free Grammars Klaus Sutner Carnegie Mellon Universality Fall 2017 1 Generating Languages Properties of CFLs Generation vs. Recognition 3 Turing machines can be used to check membership in
FLAC Context-Free Grammars Klaus Sutner Carnegie Mellon Universality Fall 2017 1 Generating Languages Properties of CFLs Generation vs. Recognition 3 Turing machines can be used to check membership in
Grammars and Context Free Languages
 Grammars and Context Free Languages H. Geuvers and A. Kissinger Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Version: fall 2015 H. Geuvers & A. Kissinger Version: fall 2015 Talen en Automaten 1 / 23
Grammars and Context Free Languages H. Geuvers and A. Kissinger Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Version: fall 2015 H. Geuvers & A. Kissinger Version: fall 2015 Talen en Automaten 1 / 23
cse303 ELEMENTS OF THE THEORY OF COMPUTATION Professor Anita Wasilewska
 cse303 ELEMENTS OF THE THEORY OF COMPUTATION Professor Anita Wasilewska LECTURE 11 CHAPTER 3 CONTEXT-FREE LANGUAGES 1. Context Free Grammars 2. Pushdown Automata 3. Pushdown automata and context -free
cse303 ELEMENTS OF THE THEORY OF COMPUTATION Professor Anita Wasilewska LECTURE 11 CHAPTER 3 CONTEXT-FREE LANGUAGES 1. Context Free Grammars 2. Pushdown Automata 3. Pushdown automata and context -free
FABER Formal Languages, Automata. Lecture 2. Mälardalen University
 CD5560 FABER Formal Languages, Automata and Models of Computation Lecture 2 Mälardalen University 2010 1 Content Languages, g Alphabets and Strings Strings & String Operations Languages & Language Operations
CD5560 FABER Formal Languages, Automata and Models of Computation Lecture 2 Mälardalen University 2010 1 Content Languages, g Alphabets and Strings Strings & String Operations Languages & Language Operations
Non-context-Free Languages. CS215, Lecture 5 c
 Non-context-Free Languages CS215, Lecture 5 c 2007 1 The Pumping Lemma Theorem. (Pumping Lemma) Let be context-free. There exists a positive integer divided into five pieces, Proof for for each, and..
Non-context-Free Languages CS215, Lecture 5 c 2007 1 The Pumping Lemma Theorem. (Pumping Lemma) Let be context-free. There exists a positive integer divided into five pieces, Proof for for each, and..
Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata Lecture 5
 Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata Lecture 5 Helle Hvid Hansen helle@cs.ru.nl http://www.cs.ru.nl/~helle/ Foundations Group Intelligent Systems Section Institute for Computing and Information Sciences
Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata Lecture 5 Helle Hvid Hansen helle@cs.ru.nl http://www.cs.ru.nl/~helle/ Foundations Group Intelligent Systems Section Institute for Computing and Information Sciences
CS 133 : Automata Theory and Computability
 CS 133 : Automata Theory and Computability Lecture Slides 1 Regular Languages and Finite Automata Nestine Hope S. Hernandez Algorithms and Complexity Laboratory Department of Computer Science University
CS 133 : Automata Theory and Computability Lecture Slides 1 Regular Languages and Finite Automata Nestine Hope S. Hernandez Algorithms and Complexity Laboratory Department of Computer Science University
(b) If G=({S}, {a}, {S SS}, S) find the language generated by G. [8+8] 2. Convert the following grammar to Greibach Normal Form G = ({A1, A2, A3},
![(b) If G=({S}, {a}, {S SS}, S) find the language generated by G. [8+8] 2. Convert the following grammar to Greibach Normal Form G = ({A1, A2, A3}, (b) If G=({S}, {a}, {S SS}, S) find the language generated by G. [8+8] 2. Convert the following grammar to Greibach Normal Form G = ({A1, A2, A3},](/thumbs/81/83182922.jpg) Code No: 07A50501 R07 Set No. 2 III B.Tech I Semester Examinations,MAY 2011 FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Computer Science And Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All
Code No: 07A50501 R07 Set No. 2 III B.Tech I Semester Examinations,MAY 2011 FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Computer Science And Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All
CYK Algorithm for Parsing General Context-Free Grammars
 CYK Algorithm for Parsing General Context-Free Grammars Why Parse General Grammars Can be difficult or impossible to make grammar unambiguous thus LL(k) and LR(k) methods cannot work, for such ambiguous
CYK Algorithm for Parsing General Context-Free Grammars Why Parse General Grammars Can be difficult or impossible to make grammar unambiguous thus LL(k) and LR(k) methods cannot work, for such ambiguous
Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules).
 Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules). 1a) G = ({R, S, T}, {0,1}, P, S) where P is: S R0R R R0R1R R1R0R T T 0T ε (S generates the first 0. R generates
Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules). 1a) G = ({R, S, T}, {0,1}, P, S) where P is: S R0R R R0R1R R1R0R T T 0T ε (S generates the first 0. R generates
Context-Free Grammars. 2IT70 Finite Automata and Process Theory
 Context-Free Grammars 2IT70 Finite Automata and Process Theory Technische Universiteit Eindhoven May 18, 2016 Generating strings language L 1 = {a n b n n > 0} ab L 1 if w L 1 then awb L 1 production rules
Context-Free Grammars 2IT70 Finite Automata and Process Theory Technische Universiteit Eindhoven May 18, 2016 Generating strings language L 1 = {a n b n n > 0} ab L 1 if w L 1 then awb L 1 production rules
Theory Of Computation UNIT-II
 Regular Expressions and Context Free Grammars: Regular expression formalism- equivalence with finite automata-regular sets and closure properties- pumping lemma for regular languages- decision algorithms
Regular Expressions and Context Free Grammars: Regular expression formalism- equivalence with finite automata-regular sets and closure properties- pumping lemma for regular languages- decision algorithms
Notes for Comp 497 (454) Week 10
 Notes for Comp 497 (454) Week 10 Today we look at the last two chapters in Part II. Cohen presents some results concerning the two categories of language we have seen so far: Regular languages (RL). Context-free
Notes for Comp 497 (454) Week 10 Today we look at the last two chapters in Part II. Cohen presents some results concerning the two categories of language we have seen so far: Regular languages (RL). Context-free
AC68 FINITE AUTOMATA & FORMULA LANGUAGES DEC 2013
 Q.2 a. Prove by mathematical induction n 4 4n 2 is divisible by 3 for n 0. Basic step: For n = 0, n 3 n = 0 which is divisible by 3. Induction hypothesis: Let p(n) = n 3 n is divisible by 3. Induction
Q.2 a. Prove by mathematical induction n 4 4n 2 is divisible by 3 for n 0. Basic step: For n = 0, n 3 n = 0 which is divisible by 3. Induction hypothesis: Let p(n) = n 3 n is divisible by 3. Induction
Properties of Context-free Languages. Reading: Chapter 7
 Properties of Context-free Languages Reading: Chapter 7 1 Topics 1) Simplifying CFGs, Normal forms 2) Pumping lemma for CFLs 3) Closure and decision properties of CFLs 2 How to simplify CFGs? 3 Three ways
Properties of Context-free Languages Reading: Chapter 7 1 Topics 1) Simplifying CFGs, Normal forms 2) Pumping lemma for CFLs 3) Closure and decision properties of CFLs 2 How to simplify CFGs? 3 Three ways
Context-Free Grammars and Languages
 Context-Free Grammars and Languages Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
Context-Free Grammars and Languages Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
Chapter 4. Regular Expressions. 4.1 Some Definitions
 Chapter 4 Regular Expressions 4.1 Some Definitions Definition: If S and T are sets of strings of letters (whether they are finite or infinite sets), we define the product set of strings of letters to be
Chapter 4 Regular Expressions 4.1 Some Definitions Definition: If S and T are sets of strings of letters (whether they are finite or infinite sets), we define the product set of strings of letters to be
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation
 CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: Captured by Regular Operations a b
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: Captured by Regular Operations a b
CSE 468, Fall 2006 Homework solutions 1
 CSE 468, Fall 2006 Homework solutions 1 Homework 1 Problem 1. (a) To accept digit strings that contain 481: Q ={λ,4,48, 481}, Σ ={0,1,...,9}, q 0 = λ, A ={481}. To define δ, weuse a for all letters (well,
CSE 468, Fall 2006 Homework solutions 1 Homework 1 Problem 1. (a) To accept digit strings that contain 481: Q ={λ,4,48, 481}, Σ ={0,1,...,9}, q 0 = λ, A ={481}. To define δ, weuse a for all letters (well,
Semigroup presentations via boundaries in Cayley graphs 1
 Semigroup presentations via boundaries in Cayley graphs 1 Robert Gray University of Leeds BMC, Newcastle 2006 1 (Research conducted while I was a research student at the University of St Andrews, under
Semigroup presentations via boundaries in Cayley graphs 1 Robert Gray University of Leeds BMC, Newcastle 2006 1 (Research conducted while I was a research student at the University of St Andrews, under
CSEP 590 Data Compression Autumn Arithmetic Coding
 CSEP 590 Data Compression Autumn 2007 Arithmetic Coding Reals in Binary Any real number x in the interval [0,1) can be represented in binary as.b 1 b 2... where b i is a bit. x 0 0 1 0 1... binary representation
CSEP 590 Data Compression Autumn 2007 Arithmetic Coding Reals in Binary Any real number x in the interval [0,1) can be represented in binary as.b 1 b 2... where b i is a bit. x 0 0 1 0 1... binary representation
Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course
 Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course Week 3: Formal Languages and Semantics Thomas Noll Lehrstuhl für Informatik 2 RWTH Aachen University noll@cs.rwth-aachen.de http://www.b-it-center.de/wob/en/view/class211_id948.html
Foundations of Informatics: a Bridging Course Week 3: Formal Languages and Semantics Thomas Noll Lehrstuhl für Informatik 2 RWTH Aachen University noll@cs.rwth-aachen.de http://www.b-it-center.de/wob/en/view/class211_id948.html
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 12: General Context-Free Recognition
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 12: General Context-Free Recognition Salil Vadhan October 11, 2012 Reading: Sipser, Section 2.3 and Section 2.1 (material on Chomsky Normal Form). Pumping Lemma for
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 12: General Context-Free Recognition Salil Vadhan October 11, 2012 Reading: Sipser, Section 2.3 and Section 2.1 (material on Chomsky Normal Form). Pumping Lemma for
Chapter 1. Formal Definition and View. Lecture Formal Pushdown Automata on the 28th April 2009
 Chapter 1 Formal and View Lecture on the 28th April 2009 Formal of PA Faculty of Information Technology Brno University of Technology 1.1 Aim of the Lecture 1 Define pushdown automaton in a formal way
Chapter 1 Formal and View Lecture on the 28th April 2009 Formal of PA Faculty of Information Technology Brno University of Technology 1.1 Aim of the Lecture 1 Define pushdown automaton in a formal way
Chapter 5: Context-Free Languages
 Chapter 5: Context-Free Languages Peter Cappello Department of Computer Science University of California, Santa Barbara Santa Barbara, CA 93106 cappello@cs.ucsb.edu Please read the corresponding chapter
Chapter 5: Context-Free Languages Peter Cappello Department of Computer Science University of California, Santa Barbara Santa Barbara, CA 93106 cappello@cs.ucsb.edu Please read the corresponding chapter
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation
 MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation CFL Hierarchy CFL Decision Problems Your Questions? Previous class days' material Reading Assignments HW 12 or 13 problems Anything else I have included some slides online
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation CFL Hierarchy CFL Decision Problems Your Questions? Previous class days' material Reading Assignments HW 12 or 13 problems Anything else I have included some slides online
5/10/16. Grammar. Automata and Languages. Today s Topics. Grammars Definition A grammar G is defined as G = (V, T, P, S) where:
 Grammar Automata and Languages Grammar Prof. Mohamed Hamada oftware Engineering Lab. The University of Aizu Japan Regular Grammar Context-free Grammar Context-sensitive Grammar Left-linear Grammar right-linear
Grammar Automata and Languages Grammar Prof. Mohamed Hamada oftware Engineering Lab. The University of Aizu Japan Regular Grammar Context-free Grammar Context-sensitive Grammar Left-linear Grammar right-linear
In English, there are at least three different types of entities: letters, words, sentences.
 Chapter 2 Languages 2.1 Introduction In English, there are at least three different types of entities: letters, words, sentences. letters are from a finite alphabet { a, b, c,..., z } words are made up
Chapter 2 Languages 2.1 Introduction In English, there are at least three different types of entities: letters, words, sentences. letters are from a finite alphabet { a, b, c,..., z } words are made up
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation
 CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: a b c b d e a Not-regular: c n bd
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: a b c b d e a Not-regular: c n bd
Computational Models - Lecture 4 1
 Computational Models - Lecture 4 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner and Yishay Mansour. Tel Aviv University. April 3/8, 2013 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice
Computational Models - Lecture 4 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner and Yishay Mansour. Tel Aviv University. April 3/8, 2013 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice
CPS 220 Theory of Computation
 CPS 22 Theory of Computation Review - Regular Languages RL - a simple class of languages that can be represented in two ways: 1 Machine description: Finite Automata are machines with a finite number of
CPS 22 Theory of Computation Review - Regular Languages RL - a simple class of languages that can be represented in two ways: 1 Machine description: Finite Automata are machines with a finite number of
Properties of Context-Free Languages
 Properties of Context-Free Languages Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
Properties of Context-Free Languages Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter Introduction.0 BASICS.0. Sets A set is a collection of objects. For example, the collection of four letters a, b, c and d is a set, which is written as L ={a, b, c, d } The objects comprising a
Chapter Introduction.0 BASICS.0. Sets A set is a collection of objects. For example, the collection of four letters a, b, c and d is a set, which is written as L ={a, b, c, d } The objects comprising a
Computational Models - Lecture 4 1
 Computational Models - Lecture 4 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University. November 21, 2016 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University.
Computational Models - Lecture 4 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University. November 21, 2016 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University.
Talen en Compilers. Johan Jeuring , period 2. October 29, Department of Information and Computing Sciences Utrecht University
 Talen en Compilers 2015-2016, period 2 Johan Jeuring Department of Information and Computing Sciences Utrecht University October 29, 2015 12. LL parsing 12-1 This lecture LL parsing Motivation Stack-based
Talen en Compilers 2015-2016, period 2 Johan Jeuring Department of Information and Computing Sciences Utrecht University October 29, 2015 12. LL parsing 12-1 This lecture LL parsing Motivation Stack-based
This lecture covers Chapter 7 of HMU: Properties of CFLs
 This lecture covers Chapter 7 of HMU: Properties of CFLs Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for CFs Closure Properties of CFLs Decision Properties of CFLs Additional Reading: Chapter 7 of HMU. Chomsky Normal
This lecture covers Chapter 7 of HMU: Properties of CFLs Chomsky Normal Form Pumping Lemma for CFs Closure Properties of CFLs Decision Properties of CFLs Additional Reading: Chapter 7 of HMU. Chomsky Normal
Properties of context-free Languages
 Properties of context-free Languages We simplify CFL s. Greibach Normal Form Chomsky Normal Form We prove pumping lemma for CFL s. We study closure properties and decision properties. Some of them remain,
Properties of context-free Languages We simplify CFL s. Greibach Normal Form Chomsky Normal Form We prove pumping lemma for CFL s. We study closure properties and decision properties. Some of them remain,
The View Over The Horizon
 The View Over The Horizon enumerable decidable context free regular Context-Free Grammars An example of a context free grammar, G 1 : A 0A1 A B B # Terminology: Each line is a substitution rule or production.
The View Over The Horizon enumerable decidable context free regular Context-Free Grammars An example of a context free grammar, G 1 : A 0A1 A B B # Terminology: Each line is a substitution rule or production.
Ogden s Lemma for CFLs
 Ogden s Lemma for CFLs Theorem If L is a context-free language, then there exists an integer l such that for any u L with at least l positions marked, u can be written as u = vwxyz such that 1 x and at
Ogden s Lemma for CFLs Theorem If L is a context-free language, then there exists an integer l such that for any u L with at least l positions marked, u can be written as u = vwxyz such that 1 x and at
CS20a: summary (Oct 24, 2002)
 CS20a: summary (Oct 24, 2002) Context-free languages Grammars G = (V, T, P, S) Pushdown automata N-PDA = CFG D-PDA < CFG Today What languages are context-free? Pumping lemma (similar to pumping lemma for
CS20a: summary (Oct 24, 2002) Context-free languages Grammars G = (V, T, P, S) Pushdown automata N-PDA = CFG D-PDA < CFG Today What languages are context-free? Pumping lemma (similar to pumping lemma for
MTH401A Theory of Computation. Lecture 17
 MTH401A Theory of Computation Lecture 17 Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s For every context free language, L, the language L {ε} has a grammar in which every production looks
MTH401A Theory of Computation Lecture 17 Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s Chomsky Normal Form for CFG s For every context free language, L, the language L {ε} has a grammar in which every production looks
NPDA, CFG equivalence
 NPDA, CFG equivalence Theorem A language L is recognized by a NPDA iff L is described by a CFG. Must prove two directions: ( ) L is recognized by a NPDA implies L is described by a CFG. ( ) L is described
NPDA, CFG equivalence Theorem A language L is recognized by a NPDA iff L is described by a CFG. Must prove two directions: ( ) L is recognized by a NPDA implies L is described by a CFG. ( ) L is described
6.8 The Post Correspondence Problem
 6.8. THE POST CORRESPONDENCE PROBLEM 423 6.8 The Post Correspondence Problem The Post correspondence problem (due to Emil Post) is another undecidable problem that turns out to be a very helpful tool for
6.8. THE POST CORRESPONDENCE PROBLEM 423 6.8 The Post Correspondence Problem The Post correspondence problem (due to Emil Post) is another undecidable problem that turns out to be a very helpful tool for
Theory of Computation (Classroom Practice Booklet Solutions)
 Theory of Computation (Classroom Practice Booklet Solutions) 1. Finite Automata & Regular Sets 01. Ans: (a) & (c) Sol: (a) The reversal of a regular set is regular as the reversal of a regular expression
Theory of Computation (Classroom Practice Booklet Solutions) 1. Finite Automata & Regular Sets 01. Ans: (a) & (c) Sol: (a) The reversal of a regular set is regular as the reversal of a regular expression
PART 3. CONTEXT FREE GRAMMARS AND PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA. FEATURES AND INDICES.
 PART 3. CONTEXT FREE GRAMMARS AND PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA. FEATURES AND INDICES. As we have seen, in a context free grammar, all rules are of the form Aα, with A V N and α V + (and allowing Se if the grammar
PART 3. CONTEXT FREE GRAMMARS AND PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA. FEATURES AND INDICES. As we have seen, in a context free grammar, all rules are of the form Aα, with A V N and α V + (and allowing Se if the grammar
Fundamentele Informatica II
 Fundamentele Informatica II Answer to selected exercises 5 John C Martin: Introduction to Languages and the Theory of Computation M.M. Bonsangue (and J. Kleijn) Fall 2011 5.1.a (q 0, ab, Z 0 ) (q 1, b,
Fundamentele Informatica II Answer to selected exercises 5 John C Martin: Introduction to Languages and the Theory of Computation M.M. Bonsangue (and J. Kleijn) Fall 2011 5.1.a (q 0, ab, Z 0 ) (q 1, b,
Linear conjunctive languages are closed under complement
 Linear conjunctive languages are closed under complement Alexander Okhotin okhotin@cs.queensu.ca Technical report 2002-455 Department of Computing and Information Science, Queen s University, Kingston,
Linear conjunctive languages are closed under complement Alexander Okhotin okhotin@cs.queensu.ca Technical report 2002-455 Department of Computing and Information Science, Queen s University, Kingston,
