Chapter 5: Context-Free Languages
|
|
|
- Alaina Moore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 5: Context-Free Languages Peter Cappello Department of Computer Science University of California, Santa Barbara Santa Barbara, CA Please read the corresponding chapter before attending this lecture. These notes are supplemented with figures, and material that arises during the lecture in response to questions. Please report any errors in these notes to I ll fix them immediately. Based on An Introduction to Formal Languages and Automata, 3rd Ed., Peter Linz, Jones and Bartlett Publishers, Inc. 1
2 5.1 Context-Free Grammars Def. 1.1: A grammar G is a 4-tuple G = (V, T, S, P ), where V is a finite set of objects called variables, T is a finite set of objects called terminal symbols, S V is called the start variable, P is a finite set of productions. Example: Let G = ({S}, {a, b}, S, P ), where P has the following 2 productions: S asb, S λ. 2
3 We denote a derivation, for example, of the word aabb as follows: This is spoken S derives aasbb. S asb aasbb aabb. The strings S, asb, aasbb, and aabb are called sentential forms of the derivation. We may summarize the entire derivation using the notation S aabb. Def. 1.2 Let G = (V, T, S, P ) be a grammar. Then, the set is the language generated by G. L(G) = {w T : S w} 3
4 Def. 5.1: A grammar G = (V, T, S, P ) is called a context-free grammar (CFG) if all productions in P are of the form A x, where A V and x (V T ). A language L is called a context-free language (CFL) when there is a CFG G such that L = L(G). Every regular grammar is context-free. A context-free grammar is so called because when a variable A appears in a derivation, it always can be replaced with the right-hand-side (RHS) of its production (A xy z, e.g.): Its substitutability does not depend on the surrounding symbols or context. 4
5 Examples of Context-Free Languages Example 5.1 G = ({S}, {a, b}, S, P ) with productions S asa, S bsb, S λ. For example, S bsb bbsbb bbasabb bbaabb. In general, L(G) is what language (describe in English)? We know that L(G) is irregular. Thus, the family of CFLs properly contains the family of regular languages. 5
6 Example 5.4 G = ({S}, {(, )}, S, P ) with productions S (S), S SS, S λ. Is the string (()) in L(G)? Describe L(G) in English. What is the point, if any, of the 2 nd production? Do you think L(G) is regular? What is L(G) ( )? 6
7 Example G E = ({E, T, F }, {a, +,, [, ]}, E, P ) with productions E E + T T, T T F F, F [ E ] a. Is [a + a] * a in L(G E )? Do you think L(G E ) is regular? Consider the homomorphism h: h(a) = λ h(+) = λ h( ) = λ h([) = [ h(]) = ]. What is h(l(g E )) [ ]? 7
8 Leftmost and Rightmost Derivations A nonlinear grammar has a production whose RHS has more than 1 variable. In a production with n variables on the RHS, there are n! orders of replacing those variables. 8
9 For example, Let G = ({A, B, S}, {0, 1}, S, P ) with productions 1. S AB 2. A aaa 3. A λ 4. B Bb 5. B λ L(G) = {a 2n b m : n, m 0}. In particular, aab L(G), as the following 2 distinct derivations show: S AB aaab aab aabb aab S AB ABb aaabb aaab aab 9
10 To remove such differences, we can require that variables are replaced in a specific order. Def. 5.2: A derivation is leftmostwhen in each step the leftmost variable in the sentential form is replaced. If in each step the rightmost variable in the sentential form is replaced, we call the derivation rightmost. The following derivation is leftmost: S AB aaab aab aabb aab. 10
11 Derivation Trees (Illustrate a derivation tree for the word aab, using the previous grammar.) Def. 5.3: Let G = (V, T, S, P ) be a CFG. An ordered tree is a derivation tree for G when it has the following properties: 1. The root is labelled S. 2. Ever leaf has a label from T {λ}. 3. Every interior vertex has a label from V. 4. If a vertex has label A V, and its children are labelled, from left to right, a 1, a 2,..., a n, then P has a production A a 1 a 2 a n. 5. A leaf labelled λ has no siblings. A tree with properties 3, 4, and 5, and in which property 2 is replaced by 2a. Every leaf has a label from V T {λ} is called a partial derivation tree. 11
12 Example: (Using G E, illustrate a partial derivation tree and a derivation tree.) 12
13 Relation between Sentential Forms and Derivation Trees Thm. 5.1: Let G = (V, T, S, P ) be a CFG. w L(G) there is a derivation tree of G whose yield is w. If t G is a partial derivation tree for G whose root is labelled S, then the yield of t G is a sentential form of G. Proof: We prove a part of what is claimed, and leave the remainder as an exercise. We claim, using induction on the length of the derivation, that if s is a sentential form of L(G), then there is a partial derivation tree whose yield is s. Basis n = 1: If the length of the derivation is 1, the derivation must be of the form S a 1 a n. By the definition of derivation trees (rules 1 and 4), there is a partial 13
14 derivation tree whose root is S and whose children, from left to right, are a 1,..., a n. Induction hypothesis: Assume that for every sentential form derivable in n steps, there is a partial derivation tree. Induction step: Any sentential form s derivable in n + 1 steps must be such that S xay, where x, y (V T ), A V, in n steps (illustrate), and in the n + 1 st step xay xa 1 a n y = s (V T ). By the I.H., there is a partial derivation tree with yield xay By the definition of derivation trees, rule 4, the grammar must have a production of the form A a 1 a n. 14
15 We see that by putting children under the leaf labelled A, we get a partial derivation tree whose yield is xa 1 a n y = s (Illustrate.) By induction, we thus claim that it is true for all finitely derived sentential forms. As a consequence of the foregoing, since a derivation tree is a partial derivation tree whose leaves are terminals, every w L(G) is the yield of some derivation tree. 15
Context-Free Grammars and Languages
 Context-Free Grammars and Languages Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
Context-Free Grammars and Languages Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
Chapter 2: Finite Automata
 Chapter 2: Finite Automata Peter Cappello Department of Computer Science University of California, Santa Barbara Santa Barbara, CA 93106 cappello@cs.ucsb.edu Please read the corresponding chapter before
Chapter 2: Finite Automata Peter Cappello Department of Computer Science University of California, Santa Barbara Santa Barbara, CA 93106 cappello@cs.ucsb.edu Please read the corresponding chapter before
Lecture 11 Context-Free Languages
 Lecture 11 Context-Free Languages COT 4420 Theory of Computation Chapter 5 Context-Free Languages n { a b : n n { ww } 0} R Regular Languages a *b* ( a + b) * Example 1 G = ({S}, {a, b}, S, P) Derivations:
Lecture 11 Context-Free Languages COT 4420 Theory of Computation Chapter 5 Context-Free Languages n { a b : n n { ww } 0} R Regular Languages a *b* ( a + b) * Example 1 G = ({S}, {a, b}, S, P) Derivations:
Chapter 16: Non-Context-Free Languages
 Chapter 16: Non-Context-Free Languages Peter Cappello Department of Computer Science University of California, Santa Barbara Santa Barbara, CA 93106 cappello@cs.ucsb.edu Please read the corresponding chapter
Chapter 16: Non-Context-Free Languages Peter Cappello Department of Computer Science University of California, Santa Barbara Santa Barbara, CA 93106 cappello@cs.ucsb.edu Please read the corresponding chapter
Context-Free Grammars and Languages. Reading: Chapter 5
 Context-Free Grammars and Languages Reading: Chapter 5 1 Context-Free Languages The class of context-free languages generalizes the class of regular languages, i.e., every regular language is a context-free
Context-Free Grammars and Languages Reading: Chapter 5 1 Context-Free Languages The class of context-free languages generalizes the class of regular languages, i.e., every regular language is a context-free
FLAC Context-Free Grammars
 FLAC Context-Free Grammars Klaus Sutner Carnegie Mellon Universality Fall 2017 1 Generating Languages Properties of CFLs Generation vs. Recognition 3 Turing machines can be used to check membership in
FLAC Context-Free Grammars Klaus Sutner Carnegie Mellon Universality Fall 2017 1 Generating Languages Properties of CFLs Generation vs. Recognition 3 Turing machines can be used to check membership in
Automata Theory CS F-08 Context-Free Grammars
 Automata Theory CS411-2015F-08 Context-Free Grammars David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 08-0: Context-Free Grammars Set of Terminals (Σ) Set of Non-Terminals Set of
Automata Theory CS411-2015F-08 Context-Free Grammars David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 08-0: Context-Free Grammars Set of Terminals (Σ) Set of Non-Terminals Set of
Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x where
 Recitation 11 Notes Context Free Grammars Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x A V, and x (V T)*. Examples Problem 1. Given the
Recitation 11 Notes Context Free Grammars Definition: A grammar G = (V, T, P,S) is a context free grammar (cfg) if all productions in P have the form A x A V, and x (V T)*. Examples Problem 1. Given the
Pushdown Automata. Reading: Chapter 6
 Pushdown Automata Reading: Chapter 6 1 Pushdown Automata (PDA) Informally: A PDA is an NFA-ε with a infinite stack. Transitions are modified to accommodate stack operations. Questions: What is a stack?
Pushdown Automata Reading: Chapter 6 1 Pushdown Automata (PDA) Informally: A PDA is an NFA-ε with a infinite stack. Transitions are modified to accommodate stack operations. Questions: What is a stack?
CS5371 Theory of Computation. Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF)
 CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF) Announcement Homework 2 will be given soon (before Tue) Due date: Oct 31 (Tue), before class Midterm: Nov 3, (Fri), first hour
CS5371 Theory of Computation Lecture 7: Automata Theory V (CFG, CFL, CNF) Announcement Homework 2 will be given soon (before Tue) Due date: Oct 31 (Tue), before class Midterm: Nov 3, (Fri), first hour
5/10/16. Grammar. Automata and Languages. Today s Topics. Grammars Definition A grammar G is defined as G = (V, T, P, S) where:
 Grammar Automata and Languages Grammar Prof. Mohamed Hamada oftware Engineering Lab. The University of Aizu Japan Regular Grammar Context-free Grammar Context-sensitive Grammar Left-linear Grammar right-linear
Grammar Automata and Languages Grammar Prof. Mohamed Hamada oftware Engineering Lab. The University of Aizu Japan Regular Grammar Context-free Grammar Context-sensitive Grammar Left-linear Grammar right-linear
Concordia University Department of Computer Science & Software Engineering
 Concordia University Department of Computer Science & Software Engineering COMP 335/4 Theoretical Computer Science Winter 2015 Assignment 3 1. In each case, what language is generated by CFG s below. Justify
Concordia University Department of Computer Science & Software Engineering COMP 335/4 Theoretical Computer Science Winter 2015 Assignment 3 1. In each case, what language is generated by CFG s below. Justify
Computational Models - Lecture 4 1
 Computational Models - Lecture 4 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University. November 21, 2016 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University.
Computational Models - Lecture 4 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University. November 21, 2016 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University.
Parsing. Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer. Winter 2017/18. Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf 1 / 26
 Parsing Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Winter 2017/18 1 / 26 Table of contents 1 Context-Free Grammars 2 Simplifying CFGs Removing useless symbols Eliminating
Parsing Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Winter 2017/18 1 / 26 Table of contents 1 Context-Free Grammars 2 Simplifying CFGs Removing useless symbols Eliminating
TAFL 1 (ECS-403) Unit- III. 3.1 Definition of CFG (Context Free Grammar) and problems. 3.2 Derivation. 3.3 Ambiguity in Grammar
 TAFL 1 (ECS-403) Unit- III 3.1 Definition of CFG (Context Free Grammar) and problems 3.2 Derivation 3.3 Ambiguity in Grammar 3.3.1 Inherent Ambiguity 3.3.2 Ambiguous to Unambiguous CFG 3.4 Simplification
TAFL 1 (ECS-403) Unit- III 3.1 Definition of CFG (Context Free Grammar) and problems 3.2 Derivation 3.3 Ambiguity in Grammar 3.3.1 Inherent Ambiguity 3.3.2 Ambiguous to Unambiguous CFG 3.4 Simplification
60-354, Theory of Computation Fall Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor
 60-354, Theory of Computation Fall 2013 Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor Pushdown Automata (PDA) PDA = ε-nfa + stack Acceptance ε-nfa enters a final state or Stack is
60-354, Theory of Computation Fall 2013 Asish Mukhopadhyay School of Computer Science University of Windsor Pushdown Automata (PDA) PDA = ε-nfa + stack Acceptance ε-nfa enters a final state or Stack is
This lecture covers Chapter 5 of HMU: Context-free Grammars
 This lecture covers Chapter 5 of HMU: Context-free rammars (Context-free) rammars (Leftmost and Rightmost) Derivations Parse Trees An quivalence between Derivations and Parse Trees Ambiguity in rammars
This lecture covers Chapter 5 of HMU: Context-free rammars (Context-free) rammars (Leftmost and Rightmost) Derivations Parse Trees An quivalence between Derivations and Parse Trees Ambiguity in rammars
Computational Models - Lecture 4 1
 Computational Models - Lecture 4 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner and Yishay Mansour. Tel Aviv University. April 3/8, 2013 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice
Computational Models - Lecture 4 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner and Yishay Mansour. Tel Aviv University. April 3/8, 2013 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs Harry Lewis October 8, 2013 Reading: Sipser, pp. 119-128. Pushdown Automata (review) Pushdown Automata = Finite automaton
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 10: CFLs: PDAs, Closure Properties, and Non-CFLs Harry Lewis October 8, 2013 Reading: Sipser, pp. 119-128. Pushdown Automata (review) Pushdown Automata = Finite automaton
Solutions to Problem Set 3
 V22.0453-001 Theory of Computation October 8, 2003 TA: Nelly Fazio Solutions to Problem Set 3 Problem 1 We have seen that a grammar where all productions are of the form: A ab, A c (where A, B non-terminals,
V22.0453-001 Theory of Computation October 8, 2003 TA: Nelly Fazio Solutions to Problem Set 3 Problem 1 We have seen that a grammar where all productions are of the form: A ab, A c (where A, B non-terminals,
Context Free Languages (CFL) Language Recognizer A device that accepts valid strings. The FA are formalized types of language recognizer.
 Context Free Languages (CFL) Language Recognizer A device that accepts valid strings. The FA are formalized types of language recognizer. Language Generator: Context free grammars are language generators,
Context Free Languages (CFL) Language Recognizer A device that accepts valid strings. The FA are formalized types of language recognizer. Language Generator: Context free grammars are language generators,
Finite Automata and Formal Languages TMV026/DIT321 LP Useful, Useless, Generating and Reachable Symbols
 Finite Automata and Formal Languages TMV026/DIT321 LP4 2012 Lecture 13 Ana Bove May 7th 2012 Overview of today s lecture: Normal Forms for Context-Free Languages Pumping Lemma for Context-Free Languages
Finite Automata and Formal Languages TMV026/DIT321 LP4 2012 Lecture 13 Ana Bove May 7th 2012 Overview of today s lecture: Normal Forms for Context-Free Languages Pumping Lemma for Context-Free Languages
cse303 ELEMENTS OF THE THEORY OF COMPUTATION Professor Anita Wasilewska
 cse303 ELEMENTS OF THE THEORY OF COMPUTATION Professor Anita Wasilewska LECTURE 11 CHAPTER 3 CONTEXT-FREE LANGUAGES 1. Context Free Grammars 2. Pushdown Automata 3. Pushdown automata and context -free
cse303 ELEMENTS OF THE THEORY OF COMPUTATION Professor Anita Wasilewska LECTURE 11 CHAPTER 3 CONTEXT-FREE LANGUAGES 1. Context Free Grammars 2. Pushdown Automata 3. Pushdown automata and context -free
Lecture 12 Simplification of Context-Free Grammars and Normal Forms
 Lecture 12 Simplification of Context-Free Grammars and Normal Forms COT 4420 Theory of Computation Chapter 6 Normal Forms for CFGs 1. Chomsky Normal Form CNF Productions of form A BC A, B, C V A a a T
Lecture 12 Simplification of Context-Free Grammars and Normal Forms COT 4420 Theory of Computation Chapter 6 Normal Forms for CFGs 1. Chomsky Normal Form CNF Productions of form A BC A, B, C V A a a T
Automata Theory Final Exam Solution 08:10-10:00 am Friday, June 13, 2008
 Automata Theory Final Exam Solution 08:10-10:00 am Friday, June 13, 2008 Name: ID #: This is a Close Book examination. Only an A4 cheating sheet belonging to you is acceptable. You can write your answers
Automata Theory Final Exam Solution 08:10-10:00 am Friday, June 13, 2008 Name: ID #: This is a Close Book examination. Only an A4 cheating sheet belonging to you is acceptable. You can write your answers
Context Free Grammars
 Automata and Formal Languages Context Free Grammars Sipser pages 101-111 Lecture 11 Tim Sheard 1 Formal Languages 1. Context free languages provide a convenient notation for recursive description of languages.
Automata and Formal Languages Context Free Grammars Sipser pages 101-111 Lecture 11 Tim Sheard 1 Formal Languages 1. Context free languages provide a convenient notation for recursive description of languages.
Context Free Languages and Grammars
 Algorithms & Models of Computation CS/ECE 374, Fall 2017 Context Free Languages and Grammars Lecture 7 Tuesday, September 19, 2017 Sariel Har-Peled (UIUC) CS374 1 Fall 2017 1 / 36 What stack got to do
Algorithms & Models of Computation CS/ECE 374, Fall 2017 Context Free Languages and Grammars Lecture 7 Tuesday, September 19, 2017 Sariel Har-Peled (UIUC) CS374 1 Fall 2017 1 / 36 What stack got to do
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1
 Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University. November 28, 2016 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University.
Computational Models - Lecture 5 1 Handout Mode Iftach Haitner. Tel Aviv University. November 28, 2016 1 Based on frames by Benny Chor, Tel Aviv University, modifying frames by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University.
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation
 CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: Captured by Regular Operations a b
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: Captured by Regular Operations a b
An automaton with a finite number of states is called a Finite Automaton (FA) or Finite State Machine (FSM).
 Automata The term "Automata" is derived from the Greek word "αὐτόματα" which means "self-acting". An automaton (Automata in plural) is an abstract self-propelled computing device which follows a predetermined
Automata The term "Automata" is derived from the Greek word "αὐτόματα" which means "self-acting". An automaton (Automata in plural) is an abstract self-propelled computing device which follows a predetermined
Problem Session 5 (CFGs) Talk about the building blocks of CFGs: S 0S 1S ε - everything. S 0S0 1S1 A - waw R. S 0S0 0S1 1S0 1S1 A - xay, where x = y.
 CSE2001, Fall 2006 1 Problem Session 5 (CFGs) Talk about the building blocks of CFGs: S 0S 1S ε - everything. S 0S0 1S1 A - waw R. S 0S0 0S1 1S0 1S1 A - xay, where x = y. S 00S1 A - xay, where x = 2 y.
CSE2001, Fall 2006 1 Problem Session 5 (CFGs) Talk about the building blocks of CFGs: S 0S 1S ε - everything. S 0S0 1S1 A - waw R. S 0S0 0S1 1S0 1S1 A - xay, where x = y. S 00S1 A - xay, where x = 2 y.
Theory of Computation - Module 3
 Theory of Computation - Module 3 Syllabus Context Free Grammar Simplification of CFG- Normal forms-chomsky Normal form and Greibach Normal formpumping lemma for Context free languages- Applications of
Theory of Computation - Module 3 Syllabus Context Free Grammar Simplification of CFG- Normal forms-chomsky Normal form and Greibach Normal formpumping lemma for Context free languages- Applications of
Einführung in die Computerlinguistik
 Einführung in die Computerlinguistik Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Summer 2016 1 / 22 CFG (1) Example: Grammar G telescope : Productions: S NP VP NP
Einführung in die Computerlinguistik Context-Free Grammars (CFG) Laura Kallmeyer Heinrich-Heine-Universität Düsseldorf Summer 2016 1 / 22 CFG (1) Example: Grammar G telescope : Productions: S NP VP NP
Context Free Languages. Automata Theory and Formal Grammars: Lecture 6. Languages That Are Not Regular. Non-Regular Languages
 Context Free Languages Automata Theory and Formal Grammars: Lecture 6 Context Free Languages Last Time Decision procedures for FAs Minimum-state DFAs Today The Myhill-Nerode Theorem The Pumping Lemma Context-free
Context Free Languages Automata Theory and Formal Grammars: Lecture 6 Context Free Languages Last Time Decision procedures for FAs Minimum-state DFAs Today The Myhill-Nerode Theorem The Pumping Lemma Context-free
Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata Lecture 5
 Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata Lecture 5 Helle Hvid Hansen helle@cs.ru.nl http://www.cs.ru.nl/~helle/ Foundations Group Intelligent Systems Section Institute for Computing and Information Sciences
Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata Lecture 5 Helle Hvid Hansen helle@cs.ru.nl http://www.cs.ru.nl/~helle/ Foundations Group Intelligent Systems Section Institute for Computing and Information Sciences
CS375: Logic and Theory of Computing
 CS375: Logic and Theory of Computing Fuhua (Frank) Cheng Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky 1 Table of Contents: Week 1: Preliminaries (set algebra, relations, functions) (read Chapters
CS375: Logic and Theory of Computing Fuhua (Frank) Cheng Department of Computer Science University of Kentucky 1 Table of Contents: Week 1: Preliminaries (set algebra, relations, functions) (read Chapters
Context-free Grammars and Languages
 Context-free Grammars and Languages COMP 455 002, Spring 2019 Jim Anderson (modified by Nathan Otterness) 1 Context-free Grammars Context-free grammars provide another way to specify languages. Example:
Context-free Grammars and Languages COMP 455 002, Spring 2019 Jim Anderson (modified by Nathan Otterness) 1 Context-free Grammars Context-free grammars provide another way to specify languages. Example:
Miscellaneous. Closure Properties Decision Properties
 Miscellaneous Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms and inverse homomorphisms.
Miscellaneous Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms and inverse homomorphisms.
Context-Free Grammars. 2IT70 Finite Automata and Process Theory
 Context-Free Grammars 2IT70 Finite Automata and Process Theory Technische Universiteit Eindhoven May 18, 2016 Generating strings language L 1 = {a n b n n > 0} ab L 1 if w L 1 then awb L 1 production rules
Context-Free Grammars 2IT70 Finite Automata and Process Theory Technische Universiteit Eindhoven May 18, 2016 Generating strings language L 1 = {a n b n n > 0} ab L 1 if w L 1 then awb L 1 production rules
Homework 4. Chapter 7. CS A Term 2009: Foundations of Computer Science. By Li Feng, Shweta Srivastava, and Carolina Ruiz
 CS3133 - A Term 2009: Foundations of Computer Science Prof. Carolina Ruiz Homework 4 WPI By Li Feng, Shweta Srivastava, and Carolina Ruiz Chapter 7 Problem: Chap 7.1 part a This PDA accepts the language
CS3133 - A Term 2009: Foundations of Computer Science Prof. Carolina Ruiz Homework 4 WPI By Li Feng, Shweta Srivastava, and Carolina Ruiz Chapter 7 Problem: Chap 7.1 part a This PDA accepts the language
Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules).
 Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules). 1a) G = ({R, S, T}, {0,1}, P, S) where P is: S R0R R R0R1R R1R0R T T 0T ε (S generates the first 0. R generates
Note: In any grammar here, the meaning and usage of P (productions) is equivalent to R (rules). 1a) G = ({R, S, T}, {0,1}, P, S) where P is: S R0R R R0R1R R1R0R T T 0T ε (S generates the first 0. R generates
Theory of Computer Science
 Theory of Computer Science C1. Formal Languages and Grammars Malte Helmert University of Basel March 14, 2016 Introduction Example: Propositional Formulas from the logic part: Definition (Syntax of Propositional
Theory of Computer Science C1. Formal Languages and Grammars Malte Helmert University of Basel March 14, 2016 Introduction Example: Propositional Formulas from the logic part: Definition (Syntax of Propositional
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation
 MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation Bottom-up parsing Pumping Theorem for CFLs Recap: Going One Way Lemma: Each context-free language is accepted by some PDA. Proof (by construction): The idea: Let the stack
MA/CSSE 474 Theory of Computation Bottom-up parsing Pumping Theorem for CFLs Recap: Going One Way Lemma: Each context-free language is accepted by some PDA. Proof (by construction): The idea: Let the stack
Theory Of Computation UNIT-II
 Regular Expressions and Context Free Grammars: Regular expression formalism- equivalence with finite automata-regular sets and closure properties- pumping lemma for regular languages- decision algorithms
Regular Expressions and Context Free Grammars: Regular expression formalism- equivalence with finite automata-regular sets and closure properties- pumping lemma for regular languages- decision algorithms
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 9: Regular Languages Wrap-Up, Context-Free Grammars
 Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 9: Regular Languages Wrap-Up, Context-Free Grammars Salil Vadhan October 2, 2012 Reading: Sipser, 2.1 (except Chomsky Normal Form). Algorithmic questions about regular
Harvard CS 121 and CSCI E-207 Lecture 9: Regular Languages Wrap-Up, Context-Free Grammars Salil Vadhan October 2, 2012 Reading: Sipser, 2.1 (except Chomsky Normal Form). Algorithmic questions about regular
Properties of Context-Free Languages
 Properties of Context-Free Languages Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
Properties of Context-Free Languages Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
Computational Models - Lecture 3
 Slides modified by Benny Chor, based on original slides by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University. p. 1 Computational Models - Lecture 3 Equivalence of regular expressions and regular languages (lukewarm leftover
Slides modified by Benny Chor, based on original slides by Maurice Herlihy, Brown University. p. 1 Computational Models - Lecture 3 Equivalence of regular expressions and regular languages (lukewarm leftover
CISC4090: Theory of Computation
 CISC4090: Theory of Computation Chapter 2 Context-Free Languages Courtesy of Prof. Arthur G. Werschulz Fordham University Department of Computer and Information Sciences Spring, 2014 Overview In Chapter
CISC4090: Theory of Computation Chapter 2 Context-Free Languages Courtesy of Prof. Arthur G. Werschulz Fordham University Department of Computer and Information Sciences Spring, 2014 Overview In Chapter
COSE212: Programming Languages. Lecture 1 Inductive Definitions (1)
 COSE212: Programming Languages Lecture 1 Inductive Definitions (1) Hakjoo Oh 2017 Fall Hakjoo Oh COSE212 2017 Fall, Lecture 1 September 4, 2017 1 / 9 Inductive Definitions Inductive definition (induction)
COSE212: Programming Languages Lecture 1 Inductive Definitions (1) Hakjoo Oh 2017 Fall Hakjoo Oh COSE212 2017 Fall, Lecture 1 September 4, 2017 1 / 9 Inductive Definitions Inductive definition (induction)
Theory of Computation (IV) Yijia Chen Fudan University
 Theory of Computation (IV) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review language regular context-free machine DFA/ NFA PDA syntax regular expression context-free grammar Pushdown automata Definition A pushdown automaton
Theory of Computation (IV) Yijia Chen Fudan University Review language regular context-free machine DFA/ NFA PDA syntax regular expression context-free grammar Pushdown automata Definition A pushdown automaton
download instant at Assume that (w R ) R = w for all strings w Σ of length n or less.
 Chapter 2 Languages 3. We prove, by induction on the length of the string, that w = (w R ) R for every string w Σ. Basis: The basis consists of the null string. In this case, (λ R ) R = (λ) R = λ as desired.
Chapter 2 Languages 3. We prove, by induction on the length of the string, that w = (w R ) R for every string w Σ. Basis: The basis consists of the null string. In this case, (λ R ) R = (λ) R = λ as desired.
Part 4 out of 5 DFA NFA REX. Automata & languages. A primer on the Theory of Computation. Last week, we showed the equivalence of DFA, NFA and REX
 Automata & languages A primer on the Theory of Computation Laurent Vanbever www.vanbever.eu Part 4 out of 5 ETH Zürich (D-ITET) October, 12 2017 Last week, we showed the equivalence of DFA, NFA and REX
Automata & languages A primer on the Theory of Computation Laurent Vanbever www.vanbever.eu Part 4 out of 5 ETH Zürich (D-ITET) October, 12 2017 Last week, we showed the equivalence of DFA, NFA and REX
Context-Free Grammar
 Context-Free Grammar CFGs are more powerful than regular expressions. They are more powerful in the sense that whatever can be expressed using regular expressions can be expressed using context-free grammars,
Context-Free Grammar CFGs are more powerful than regular expressions. They are more powerful in the sense that whatever can be expressed using regular expressions can be expressed using context-free grammars,
Context-Free Grammars and Languages. We have seen that many languages cannot be regular. Thus we need to consider larger classes of langs.
 Context-Free Grammars and Languages We have seen that many languages cannot be regular. Thus we need to consider larger classes of langs. Contex-Free Languages (CFL s) played a central role natural languages
Context-Free Grammars and Languages We have seen that many languages cannot be regular. Thus we need to consider larger classes of langs. Contex-Free Languages (CFL s) played a central role natural languages
Introduction to Theory of Computing
 CSCI 2670, Fall 2012 Introduction to Theory of Computing Department of Computer Science University of Georgia Athens, GA 30602 Instructor: Liming Cai www.cs.uga.edu/ cai 0 Lecture Note 3 Context-Free Languages
CSCI 2670, Fall 2012 Introduction to Theory of Computing Department of Computer Science University of Georgia Athens, GA 30602 Instructor: Liming Cai www.cs.uga.edu/ cai 0 Lecture Note 3 Context-Free Languages
Grammars and Context Free Languages
 Grammars and Context Free Languages H. Geuvers and J. Rot Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Version: fall 2016 H. Geuvers & J. Rot Version: fall 2016 Talen en Automaten 1 / 24 Outline Grammars
Grammars and Context Free Languages H. Geuvers and J. Rot Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Version: fall 2016 H. Geuvers & J. Rot Version: fall 2016 Talen en Automaten 1 / 24 Outline Grammars
Context-Free Grammars. 2IT70 Finite Automata and Process Theory
 Context-Free Grammars 2IT70 Finite Automata and Process Theory Technische Universiteit Eindhoven Quartile2, 2014-2015 Generating strings language L 1 èa n b n Ë n 0 í ab L 1 if w L 1 then awb L 1 2 IT70
Context-Free Grammars 2IT70 Finite Automata and Process Theory Technische Universiteit Eindhoven Quartile2, 2014-2015 Generating strings language L 1 èa n b n Ë n 0 í ab L 1 if w L 1 then awb L 1 2 IT70
COSE212: Programming Languages. Lecture 1 Inductive Definitions (1)
 COSE212: Programming Languages Lecture 1 Inductive Definitions (1) Hakjoo Oh 2018 Fall Hakjoo Oh COSE212 2018 Fall, Lecture 1 September 5, 2018 1 / 10 Inductive Definitions Inductive definition (induction)
COSE212: Programming Languages Lecture 1 Inductive Definitions (1) Hakjoo Oh 2018 Fall Hakjoo Oh COSE212 2018 Fall, Lecture 1 September 5, 2018 1 / 10 Inductive Definitions Inductive definition (induction)
C1.1 Introduction. Theory of Computer Science. Theory of Computer Science. C1.1 Introduction. C1.2 Alphabets and Formal Languages. C1.
 Theory of Computer Science March 20, 2017 C1. Formal Languages and Grammars Theory of Computer Science C1. Formal Languages and Grammars Malte Helmert University of Basel March 20, 2017 C1.1 Introduction
Theory of Computer Science March 20, 2017 C1. Formal Languages and Grammars Theory of Computer Science C1. Formal Languages and Grammars Malte Helmert University of Basel March 20, 2017 C1.1 Introduction
Grammars and Context Free Languages
 Grammars and Context Free Languages H. Geuvers and A. Kissinger Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Version: fall 2015 H. Geuvers & A. Kissinger Version: fall 2015 Talen en Automaten 1 / 23
Grammars and Context Free Languages H. Geuvers and A. Kissinger Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Version: fall 2015 H. Geuvers & A. Kissinger Version: fall 2015 Talen en Automaten 1 / 23
CS 373: Theory of Computation. Fall 2010
 CS 373: Theory of Computation Gul Agha Mahesh Viswanathan Fall 2010 1 1 Normal Forms for CFG Normal Forms for Grammars It is typically easier to work with a context free language if given a CFG in a normal
CS 373: Theory of Computation Gul Agha Mahesh Viswanathan Fall 2010 1 1 Normal Forms for CFG Normal Forms for Grammars It is typically easier to work with a context free language if given a CFG in a normal
Context-Free Grammars (and Languages) Lecture 7
 Context-Free Grammars (and Languages) Lecture 7 1 Today Beyond regular expressions: Context-Free Grammars (CFGs) What is a CFG? What is the language associated with a CFG? Creating CFGs. Reasoning about
Context-Free Grammars (and Languages) Lecture 7 1 Today Beyond regular expressions: Context-Free Grammars (CFGs) What is a CFG? What is the language associated with a CFG? Creating CFGs. Reasoning about
AC68 FINITE AUTOMATA & FORMULA LANGUAGES JUNE 2014
 Q.2 a. Show by using Mathematical Induction that n i= 1 i 2 n = ( n + 1) ( 2 n + 1) 6 b. Define language. Let = {0; 1} denote an alphabet. Enumerate five elements of the following languages: (i) Even binary
Q.2 a. Show by using Mathematical Induction that n i= 1 i 2 n = ( n + 1) ( 2 n + 1) 6 b. Define language. Let = {0; 1} denote an alphabet. Enumerate five elements of the following languages: (i) Even binary
Context-Free Grammars: Normal Forms
 Context-Free Grammars: Normal Forms Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
Context-Free Grammars: Normal Forms Seungjin Choi Department of Computer Science and Engineering Pohang University of Science and Technology 77 Cheongam-ro, Nam-gu, Pohang 37673, Korea seungjin@postech.ac.kr
Properties of Context-Free Languages. Closure Properties Decision Properties
 Properties of Context-Free Languages Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms
Properties of Context-Free Languages Closure Properties Decision Properties 1 Closure Properties of CFL s CFL s are closed under union, concatenation, and Kleene closure. Also, under reversal, homomorphisms
Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30
 CS 454 Theory of Computation Fall 2011 Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30 1. Which of the following are true? (a) a PDA can always be converted to an equivalent PDA that at each step pops or pushes
CS 454 Theory of Computation Fall 2011 Section 1 (closed-book) Total points 30 1. Which of the following are true? (a) a PDA can always be converted to an equivalent PDA that at each step pops or pushes
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad
 St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad-500 014 Subject: FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Class : CSE II PART A (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) UNIT- I 1 Explain transition diagram, transition
St.MARTIN S ENGINEERING COLLEGE Dhulapally, Secunderabad-500 014 Subject: FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Class : CSE II PART A (SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS) UNIT- I 1 Explain transition diagram, transition
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018
 Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 14 Ana Bove May 14th 2018 Recap: Context-free Grammars Simplification of grammars: Elimination of ǫ-productions; Elimination of
Finite Automata Theory and Formal Languages TMV027/DIT321 LP4 2018 Lecture 14 Ana Bove May 14th 2018 Recap: Context-free Grammars Simplification of grammars: Elimination of ǫ-productions; Elimination of
6.1 The Pumping Lemma for CFLs 6.2 Intersections and Complements of CFLs
 CSC4510/6510 AUTOMATA 6.1 The Pumping Lemma for CFLs 6.2 Intersections and Complements of CFLs The Pumping Lemma for Context Free Languages One way to prove AnBn is not regular is to use the pumping lemma
CSC4510/6510 AUTOMATA 6.1 The Pumping Lemma for CFLs 6.2 Intersections and Complements of CFLs The Pumping Lemma for Context Free Languages One way to prove AnBn is not regular is to use the pumping lemma
1. (a) Explain the procedure to convert Context Free Grammar to Push Down Automata.
 Code No: R09220504 R09 Set No. 2 II B.Tech II Semester Examinations,December-January, 2011-2012 FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Computer Science And Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 75 Answer
Code No: R09220504 R09 Set No. 2 II B.Tech II Semester Examinations,December-January, 2011-2012 FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Computer Science And Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 75 Answer
CSE 355 Test 2, Fall 2016
 CSE 355 Test 2, Fall 2016 28 October 2016, 8:35-9:25 a.m., LSA 191 Last Name SAMPLE ASU ID 1357924680 First Name(s) Ima Regrading of Midterms If you believe that your grade has not been added up correctly,
CSE 355 Test 2, Fall 2016 28 October 2016, 8:35-9:25 a.m., LSA 191 Last Name SAMPLE ASU ID 1357924680 First Name(s) Ima Regrading of Midterms If you believe that your grade has not been added up correctly,
5 Context-Free Languages
 CA320: COMPUTABILITY AND COMPLEXITY 1 5 Context-Free Languages 5.1 Context-Free Grammars Context-Free Grammars Context-free languages are specified with a context-free grammar (CFG). Formally, a CFG G
CA320: COMPUTABILITY AND COMPLEXITY 1 5 Context-Free Languages 5.1 Context-Free Grammars Context-Free Grammars Context-free languages are specified with a context-free grammar (CFG). Formally, a CFG G
The View Over The Horizon
 The View Over The Horizon enumerable decidable context free regular Context-Free Grammars An example of a context free grammar, G 1 : A 0A1 A B B # Terminology: Each line is a substitution rule or production.
The View Over The Horizon enumerable decidable context free regular Context-Free Grammars An example of a context free grammar, G 1 : A 0A1 A B B # Terminology: Each line is a substitution rule or production.
Sheet 1-8 Dr. Mostafa Aref Format By : Mostafa Sayed
 Sheet -8 Dr. Mostafa Aref Format By : Mostafa Sayed 09 Introduction Assignment. For = {a, } a) Write 0 strings of the following languages i) All strings with no more than one a,,, a, a, a, a, a, a, a ii)
Sheet -8 Dr. Mostafa Aref Format By : Mostafa Sayed 09 Introduction Assignment. For = {a, } a) Write 0 strings of the following languages i) All strings with no more than one a,,, a, a, a, a, a, a, a ii)
Introduction and Motivation. Introduction and Motivation. Introduction to Computability. Introduction and Motivation. Theory. Lecture5: Context Free
 ntroduction to Computability Theory Lecture5: Context Free Languages Prof. Amos sraeli 1 ntroduction and Motivation n our study of RL-s we Covered: 1. Motivation and definition of regular languages. 2.
ntroduction to Computability Theory Lecture5: Context Free Languages Prof. Amos sraeli 1 ntroduction and Motivation n our study of RL-s we Covered: 1. Motivation and definition of regular languages. 2.
CPS 220 Theory of Computation Pushdown Automata (PDA)
 CPS 220 Theory of Computation Pushdown Automata (PDA) Nondeterministic Finite Automaton with some extra memory Memory is called the stack, accessed in a very restricted way: in a First-In First-Out fashion
CPS 220 Theory of Computation Pushdown Automata (PDA) Nondeterministic Finite Automaton with some extra memory Memory is called the stack, accessed in a very restricted way: in a First-In First-Out fashion
THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET
 THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET Regular Languages and FA A language is a set of strings over a finite alphabet Σ. All languages are finite or countably infinite. The set of all languages
THEORY OF COMPUTATION (AUBER) EXAM CRIB SHEET Regular Languages and FA A language is a set of strings over a finite alphabet Σ. All languages are finite or countably infinite. The set of all languages
ÖVNINGSUPPGIFTER I SAMMANHANGSFRIA SPRÅK. 17 april Classrum Edition
 ÖVNINGSUPPGIFTER I SAMMANHANGSFRIA SPRÅK 7 april 23 Classrum Edition CONTEXT FREE LANGUAGES & PUSH-DOWN AUTOMATA CONTEXT-FREE GRAMMARS, CFG Problems Sudkamp Problem. (3.2.) Which language generates the
ÖVNINGSUPPGIFTER I SAMMANHANGSFRIA SPRÅK 7 april 23 Classrum Edition CONTEXT FREE LANGUAGES & PUSH-DOWN AUTOMATA CONTEXT-FREE GRAMMARS, CFG Problems Sudkamp Problem. (3.2.) Which language generates the
CFG Simplification. (simplify) 1. Eliminate useless symbols 2. Eliminate -productions 3. Eliminate unit productions
 CFG Simplification (simplify) 1. Eliminate useless symbols 2. Eliminate -productions 3. Eliminate unit productions 1 Eliminating useless symbols 1. A symbol X is generating if there exists: X * w, for
CFG Simplification (simplify) 1. Eliminate useless symbols 2. Eliminate -productions 3. Eliminate unit productions 1 Eliminating useless symbols 1. A symbol X is generating if there exists: X * w, for
Pushdown automata. Twan van Laarhoven. Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Radboud University Nijmegen
 Pushdown automata Twan van Laarhoven Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Version: fall 2014 T. van Laarhoven Version: fall 2014 Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata
Pushdown automata Twan van Laarhoven Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Intelligent Systems Version: fall 2014 T. van Laarhoven Version: fall 2014 Formal Languages, Grammars and Automata
Introduction to Formal Languages, Automata and Computability p.1/42
 Introduction to Formal Languages, Automata and Computability Pushdown Automata K. Krithivasan and R. Rama Introduction to Formal Languages, Automata and Computability p.1/42 Introduction We have considered
Introduction to Formal Languages, Automata and Computability Pushdown Automata K. Krithivasan and R. Rama Introduction to Formal Languages, Automata and Computability p.1/42 Introduction We have considered
Computational Learning Theory Extending Patterns with Deductive Inference
 Computational Learning Theory Extending Patterns with Deductive Inference Akihiro Yamamoto 山本章博 http://www.iip.ist.i.kyoto-u.ac.jp/member/akihiro/ akihiro@i.kyoto-u.ac.jp 1 Contents What about a pair of
Computational Learning Theory Extending Patterns with Deductive Inference Akihiro Yamamoto 山本章博 http://www.iip.ist.i.kyoto-u.ac.jp/member/akihiro/ akihiro@i.kyoto-u.ac.jp 1 Contents What about a pair of
Context-Free Languages
 CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Context-Free Languages Non-Context-Free Languages Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 2 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Section 2.3. Proving context-freeness
CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Context-Free Languages Non-Context-Free Languages Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 2 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Section 2.3. Proving context-freeness
Syntactical analysis. Syntactical analysis. Syntactical analysis. Syntactical analysis
 Context-free grammars Derivations Parse Trees Left-recursive grammars Top-down parsing non-recursive predictive parsers construction of parse tables Bottom-up parsing shift/reduce parsers LR parsers GLR
Context-free grammars Derivations Parse Trees Left-recursive grammars Top-down parsing non-recursive predictive parsers construction of parse tables Bottom-up parsing shift/reduce parsers LR parsers GLR
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter Introduction.0 BASICS.0. Sets A set is a collection of objects. For example, the collection of four letters a, b, c and d is a set, which is written as L ={a, b, c, d } The objects comprising a
Chapter Introduction.0 BASICS.0. Sets A set is a collection of objects. For example, the collection of four letters a, b, c and d is a set, which is written as L ={a, b, c, d } The objects comprising a
Outline. We will cover (over the next few weeks) Induction Strong Induction Constructive Induction Structural Induction
 Outline We will cover (over the next few weeks) Induction Strong Induction Constructive Induction Structural Induction Induction P(1) ( n 2)[P(n 1) P(n)] ( n 1)[P(n)] Why Does This Work? I P(1) ( n 2)[P(n
Outline We will cover (over the next few weeks) Induction Strong Induction Constructive Induction Structural Induction Induction P(1) ( n 2)[P(n 1) P(n)] ( n 1)[P(n)] Why Does This Work? I P(1) ( n 2)[P(n
Recitation 4: Converting Grammars to Chomsky Normal Form, Simulation of Context Free Languages with Push-Down Automata, Semirings
 Recitation 4: Converting Grammars to Chomsky Normal Form, Simulation of Context Free Languages with Push-Down Automata, Semirings 11-711: Algorithms for NLP October 10, 2014 Conversion to CNF Example grammar
Recitation 4: Converting Grammars to Chomsky Normal Form, Simulation of Context Free Languages with Push-Down Automata, Semirings 11-711: Algorithms for NLP October 10, 2014 Conversion to CNF Example grammar
Suppose h maps number and variables to ɛ, and opening parenthesis to 0 and closing parenthesis
 1 Introduction Parenthesis Matching Problem Describe the set of arithmetic expressions with correctly matched parenthesis. Arithmetic expressions with correctly matched parenthesis cannot be described
1 Introduction Parenthesis Matching Problem Describe the set of arithmetic expressions with correctly matched parenthesis. Arithmetic expressions with correctly matched parenthesis cannot be described
Homework 4 Solutions. 2. Find context-free grammars for the language L = {a n b m c k : k n + m}. (with n 0,
 Introduction to Formal Language, Fall 2016 Due: 21-Apr-2016 (Thursday) Instructor: Prof. Wen-Guey Tzeng Homework 4 Solutions Scribe: Yi-Ruei Chen 1. Find context-free grammars for the language L = {a n
Introduction to Formal Language, Fall 2016 Due: 21-Apr-2016 (Thursday) Instructor: Prof. Wen-Guey Tzeng Homework 4 Solutions Scribe: Yi-Ruei Chen 1. Find context-free grammars for the language L = {a n
CA320 - Computability & Complexity
 CA320 - Computability & Complexity Dav Sinclair Context-Free Grammars A context-free grammar (CFG) is a 4-tuple G = (N,Σ,S,P) where N is a set of nonterminal symbols, or variables, Σ is a set of terminal
CA320 - Computability & Complexity Dav Sinclair Context-Free Grammars A context-free grammar (CFG) is a 4-tuple G = (N,Σ,S,P) where N is a set of nonterminal symbols, or variables, Σ is a set of terminal
Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture)
 Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 41 Outline Pushdown Automata Pushdown
Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Dr. Neil T. Dantam CSCI-561, Colorado School of Mines Fall 2017 Dantam (Mines CSCI-561) Pushdown Automata (Pre Lecture) Fall 2017 1 / 41 Outline Pushdown Automata Pushdown
Grammars and Context-free Languages; Chomsky Hierarchy
 Regular and Context-free Languages; Chomsky Hierarchy H. Geuvers Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Version: fall 2015 H. Geuvers Version: fall 2015 Huygens College 1 / 23 Outline Regular
Regular and Context-free Languages; Chomsky Hierarchy H. Geuvers Institute for Computing and Information Sciences Version: fall 2015 H. Geuvers Version: fall 2015 Huygens College 1 / 23 Outline Regular
Properties of Context-free Languages. Reading: Chapter 7
 Properties of Context-free Languages Reading: Chapter 7 1 Topics 1) Simplifying CFGs, Normal forms 2) Pumping lemma for CFLs 3) Closure and decision properties of CFLs 2 How to simplify CFGs? 3 Three ways
Properties of Context-free Languages Reading: Chapter 7 1 Topics 1) Simplifying CFGs, Normal forms 2) Pumping lemma for CFLs 3) Closure and decision properties of CFLs 2 How to simplify CFGs? 3 Three ways
Context-free Languages and Pushdown Automata
 Context-free Languages and Pushdown Automata Finite Automata vs CFLs E.g., {a n b n } CFLs Regular From earlier results: Languages every regular language is a CFL but there are CFLs that are not regular
Context-free Languages and Pushdown Automata Finite Automata vs CFLs E.g., {a n b n } CFLs Regular From earlier results: Languages every regular language is a CFL but there are CFLs that are not regular
PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA)
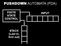 PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA) FINITE STATE CONTROL INPUT STACK (Last in, first out) input pop push ε,ε $ 0,ε 0 1,0 ε ε,$ ε 1,0 ε PDA that recognizes L = { 0 n 1 n n 0 } Definition: A (non-deterministic) PDA
PUSHDOWN AUTOMATA (PDA) FINITE STATE CONTROL INPUT STACK (Last in, first out) input pop push ε,ε $ 0,ε 0 1,0 ε ε,$ ε 1,0 ε PDA that recognizes L = { 0 n 1 n n 0 } Definition: A (non-deterministic) PDA
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation
 CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: a b c b d e a Not-regular: c n bd
CISC 4090 Theory of Computation Context-Free Languages and Push Down Automata Professor Daniel Leeds dleeds@fordham.edu JMH 332 Languages: Regular and Beyond Regular: a b c b d e a Not-regular: c n bd
FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTATION
 FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTATION DECIDABILITY ( LECTURE 15) SLIDES FOR 15-453 SPRING 2011 1 / 34 TURING MACHINES-SYNOPSIS The most general model of computation Computations of a TM are described
FORMAL LANGUAGES, AUTOMATA AND COMPUTATION DECIDABILITY ( LECTURE 15) SLIDES FOR 15-453 SPRING 2011 1 / 34 TURING MACHINES-SYNOPSIS The most general model of computation Computations of a TM are described
Computability Theory
 CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Computability Theory Decidable Problems of CFLs and beyond Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 4 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Section 4.1. Decidable
CS:4330 Theory of Computation Spring 2018 Computability Theory Decidable Problems of CFLs and beyond Haniel Barbosa Readings for this lecture Chapter 4 of [Sipser 1996], 3rd edition. Section 4.1. Decidable
(b) If G=({S}, {a}, {S SS}, S) find the language generated by G. [8+8] 2. Convert the following grammar to Greibach Normal Form G = ({A1, A2, A3},
![(b) If G=({S}, {a}, {S SS}, S) find the language generated by G. [8+8] 2. Convert the following grammar to Greibach Normal Form G = ({A1, A2, A3}, (b) If G=({S}, {a}, {S SS}, S) find the language generated by G. [8+8] 2. Convert the following grammar to Greibach Normal Form G = ({A1, A2, A3},](/thumbs/81/83182922.jpg) Code No: 07A50501 R07 Set No. 2 III B.Tech I Semester Examinations,MAY 2011 FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Computer Science And Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All
Code No: 07A50501 R07 Set No. 2 III B.Tech I Semester Examinations,MAY 2011 FORMAL LANGUAGES AND AUTOMATA THEORY Computer Science And Engineering Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All
CSC 4181Compiler Construction. Context-Free Grammars Using grammars in parsers. Parsing Process. Context-Free Grammar
 CSC 4181Compiler Construction Context-ree Grammars Using grammars in parsers CG 1 Parsing Process Call the scanner to get tokens Build a parse tree from the stream of tokens A parse tree shows the syntactic
CSC 4181Compiler Construction Context-ree Grammars Using grammars in parsers CG 1 Parsing Process Call the scanner to get tokens Build a parse tree from the stream of tokens A parse tree shows the syntactic
