SHRI RAMSWAROOP MEMORIAL COLLEGE OF ENGG. & MANAGEMENT
|
|
|
- Amber Kennedy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1) 2 kg of an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically from pressure 100kPa and temperature 220K to a final pressure of 400kPa. Make calculation for (i)initial volume, (ii) final volume and temperature, (iii) work performed,(iv) heat interaction to or from the system, and (iv) change in internal energy. It may be presumed that for the given ideal gas C p =1kJ/kg K and C v =0.707kJ/kg K (Question-6) [5] Q2) A platinum wire is used as a resistance thermometer. The wire resistance was found to be 10 ohm and 16 ohm at ice point and steam point respectively and 30 ohm at sulphur boiling point of C,Find the resistance of wire at C if the resistance varies with temperature by the relation R=R 0 (1+αt+βt 2 ) (Question-9) [5] Q1) The heat at constant pressure of a certain system is a function of temperature only and may be expressed as C p = / (t+100) J/ 0 C Where t is the temperature of the system in 0 C.The system is heated while it is maintained at pressure of 1 atmosphere until its volume increases from 2000 cm 3 to 2400 cm 3 and its temperature increases from 0 0 C to C. (a) Find the magnitude of the heat interaction. (b) How much does the internal energy of the system. Q2) A blower handles 1 kg of air at 20 0 C and consume a power of 15kW. The inlet and outlet velocities of air are 100 m/s and 150 m/s respectively. Find the exit air temperature, assuming adiabatic condition. Take C p =1.005 kj/kg-k. Q3) In a gas turbine the gas enter at the rate of 5 kg/s with the velocities of 50 m/s and enthalpy of 900 kj/kg and leaves the turbine with a velocities of 150 m/s and enthalpy of 400 kj/kg. The loss of heat from the gases to the surrounding is 25 kj/kg. Assuming for gas R=0.287 kj/kg K and C p =1.005 kj/kg K and inlet conditions to be at 100 kpa and 27 0 C. Determine the power the output of the turbine and the diameter of the inlet pipe. EME-303/ Mr. Arun Sharma,Mr.Ajay Kr.Verma Date:
2 B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1). A system comprising of a gas of 5 kg mass undergoes expansion process from 1MPa and 0.5m 3 to 0.5 MPa. Expansion process is governed by p.v 1.3 = constant. The initial energy of a gas is given by, u=1.8 pv+ 85 kj/kg. Here u is specific internal energy, p is pressure in kpa, and v is specific volume in m 3 /kg Determine heat and work interaction and change in internal energy. (Question-10) [5] Q2) A completely evacuated tank fully insulated is filled with 10 kg of air passing through a charging line maintain at a pressure of 1000kPa and enthalpy of 400 kj/kg final equilibrium state in the tank is 1000 kpa. enthalpy of 600 kj/kg and specific volume of 0.17 m 3 /kg the air in the vessel is heated by heating coil. Then find the heat transfer (Question-14) [5] Q1) The heat at constant pressure of a certain system is a function of temperature only and may be expressed as C p = / (t+100) J/ 0 C Where t is the temperature of the system in 0 C.The system is heated while it is maintained at pressure of 1 atmosphere until its volume increases from 2000 cm 3 to 2400 cm 3 and its temperature increases from 0 0 C to C. (a) Find the magnitude of the heat interaction. (b) How much does the internal energy of the system. Q2) A blower handles 1 kg of air at 20 0 C and consume a power of 15kW. The inlet and outlet velocities of air are 100 m/s and 150 m/s respectively. Find the exit air temperature, assuming adiabatic condition. Take C p =1.005 kj/kg-k. Q3) In a gas turbine the gas enter at the rate of 5 kg/s with the velocities of 50 m/s and enthalpy of 900 kj/kg and leaves the turbine with a velocities of 150 m/s and enthalpy of 400 kj/kg. The loss of heat from the gases to the surrounding is 25 kj/kg. Assuming for gas R=0.287 kj/kg K and C p =1.005 kj/kg K and inlet conditions to be at 100 kpa and 27 0 C. Determine the power the output of the turbine and the diameter of the inlet pipe. EME-303/ Mr. Arun Sharma,Mr.Ajay Kr.Verma Date:
3 B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1) A vertical piston cylinder assembly that initially has a volume of 0.1m3 is filled with 0.1 kg of nitrogen gas. This is weighted so that the pressure of nitrogen is always maintained at 1.15 bar. Heat transfer is allowed to take place until the volume is reduced to 75% of initial volume. Determine: (i) initial and final temperatures of nitrogen (ii) magnitude and direction of heat transfer. Assume the process to be quasi static and take Cv=0.745kJ/kg K for nitrogen. (Question-11) [5] Q2) A fluid is confined in acylender by a spring loaded frictionless piston so that pressure in the fluid is linear function of volume p=a+bv internal energy of the fluid is given by U= PV where U is in kj,p in kpa and Vin m 3 if the fluid changes from initial states of P 1 =170kPa, P 2 =400kPa, V 1 =0.03m 3 and V 2 =0.06m 3. Find the direction and magnitude of heat and work transfer. (Question-12) [5] Q1) The heat at constant pressure of a certain system is a function of temperature only and may be expressed as C p = / (t+100) J/ 0 C Where t is the temperature of the system in 0 C.The system is heated while it is maintained at pressure of 1 atmosphere until its volume increases from 2000 cm 3 to 2400 cm 3 and its temperature increases from 0 0 C to C. (a) Find the magnitude of the heat interaction. (b) How much does the internal energy of the system. Q2) A blower handles 1 kg of air at 20 0 C and consume a power of 15kW. The inlet and outlet velocities of air are 100 m/s and 150 m/s respectively. Find the exit air temperature, assuming adiabatic condition. Take C p =1.005 kj/kg-k. Q3) In a gas turbine the gas enter at the rate of 5 kg/s with the velocities of 50 m/s and enthalpy of 900 kj/kg and leaves the turbine with a velocities of 150 m/s and enthalpy of 400 kj/kg. The loss of heat from the gases to the surrounding is 25 kj/kg. Assuming for gas R=0.287 kj/kg K and C p =1.005 kj/kg K and inlet conditions to be at 100 kpa and 27 0 C. Determine the power the output of the turbine and the diameter of the inlet pipe. EME-303/ Mr. Arun Sharma,Mr.Ajay Kr.Verma Date:
4 B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1) An insulated rigid pressure vessel divided into two poprtions by a movable partition, one part of vessel is occupied by an ideal gas at pressure P 1 volume V 1 and temperature T 1 the other part is occupied by the same ideal gas but at pressure P 2 and volume V 2 and temperature T 2. The partition is removed and the two portion is mixed adiabatically show that the final pressure and temperature is given by (Question-13) [5] P 3 = (P 1 V 1 +P 2 V 2 )/(V 1 +V 2 ) T 3 = (P 1 V 1 +P 2 V 2 )/ (P 1 V 1 /T 1 +P 2 V 2 /T 2 ) Q2) A spherical balloon of 1m diameter contains a gas at 150 kpa.gas inside the balon is heated until the pressure reaches 450 kpa, During the process of heating pressure of gas pressure of gas inside the balloon is proportional to cube of diameter of balloon. Find the work done by the gas inside the balloon. (Question-4) [5] Q1) The heat at constant pressure of a certain system is a function of temperature only and may be expressed as C p = / (t+100) J/ 0 C Where t is the temperature of the system in 0 C.The system is heated while it is maintained at pressure of 1 atmosphere until its volume increases from 2000 cm 3 to 2400 cm 3 and its temperature increases from 0 0 C to C. (a) Find the magnitude of the heat interaction. (b) How much does the internal energy of the system. Q2) A blower handles 1 kg of air at 20 0 C and consume a power of 15kW. The inlet and outlet velocities of air are 100 m/s and 150 m/s respectively. Find the exit air temperature, assuming adiabatic condition. Take C p =1.005 kj/kg-k. Q3) In a gas turbine the gas enter at the rate of 5 kg/s with the velocities of 50 m/s and enthalpy of 900 kj/kg and leaves the turbine with a velocities of 150 m/s and enthalpy of 400 kj/kg. The loss of heat from the gases to the surrounding is 25 kj/kg. Assuming for gas R=0.287 kj/kg K and C p =1.005 kj/kg K and inlet conditions to be at 100 kpa and 27 0 C. Determine the power the output of the turbine and the diameter of the inlet pipe. EME-303/ Mr. Arun Sharma,Mr.Ajay Kr.Verma Date:
5 B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1). Air is trapped in a piston cylinder machine initially p 1 =100kPa, v 1 =2x10 (-3) m 3. The spring exerts no force on the piston in the initial position. The atmospheric pressure is 100 KPa and the area of the piston is 0.018m 2. The air expands slowly till its volume is v 2 =3x10 (-3) m 3 during the process the spring exerts a force on the piston f=-kx where k=16.2x10 3 N/m Neglecting any friction between the piston and cylinder wall. Determine the final pressure of air and work done by the air on the piston (Question-3) [5] Q2) The Temp. t on a thermometric scale is defined in terms of property k by the relation by the relation Where a and b are the const. The value of K are found to be 1.83 and 6.78 at the ice point and the steam point the temperature of which are assigned the numbers 0 and 100 respectively. Determine the temperature corresponding to of reading of K equal to 2.42 on thermometer. (Question-8) [5] Q1) The heat at constant pressure of a certain system is a function of temperature only and may be expressed as C p = / (t+100) J/ 0 C Where t is the temperature of the system in 0 C.The system is heated while it is maintained at pressure of 1 atmosphere until its volume increases from 2000 cm 3 to 2400 cm 3 and its temperature increases from 0 0 C to C. (a) Find the magnitude of the heat interaction. (b) How much does the internal energy of the system. Q.2) A blower handles 1 kg of air at 20 0 C and consume a power of 15kW. The inlet and outlet velocities of air are 100 m/s and 150 m/s respectively. Find the exit air temperature, assuming adiabatic condition. Take C p =1.005 kj/kg-k. Q.3) In a gas turbine the gas enter at the rate of 5 kg/s with the velocities of 50 m/s and enthalpy of 900 kj/kg and leaves the turbine with a velocities of 150 m/s and enthalpy of 400 kj/kg. The loss of heat from the gases to the surrounding is 25 kj/kg. Assuming for gas R=0.287 kj/kg K and C p =1.005 kj/kg K and inlet conditions to be at 100 kpa and 27 0 C. Determine the power the output of the turbine and the diameter of the inlet pipe. X EME-303/ Mr. Arun Sharma,Mr.Ajay Kr.Verma Date:
6 B.Tech. [SEM III (ME)] QUIZ TEST-2 THERMODYNAMICS Time: 1 hour (EME-303) Max. Marks: 30 Note: All questions are compulsory. Q1. Two kg of water at 80 0 C are mixed adiabatically with 3kg of water at 30 0 C in a constant pressure process of 1 atm. Find the increase in entropy of the total mass of water due to mixing process( C p of water =4.187kJ/kg K) (Q.No.2) [5] Q2. Two kg of air at 500kPa, 80 0 C expands adiabatically in a close system until its volume is doubled and its temp become equal to that of surrounding which is at 100kPa, 5 0 C for this process determine (a) the maximum work (b) the change in availability (c) the irreversibility for air take C v =0.718kJ/kg K, u=c v T where C v is constant, and pv=mrt where p is pressure in kpa and V volume in m 3,m mass in kg and R=0.287kJ/kgK, and T temperature in K. (Q.No.12) [2+2+1] Q.1. Define the term available energy and unavailable energy. M 1 kg of water at T 1 is isobarically and adiabatically mixed with M 2 kg of water at T 2 (T 1 >T 2 ). Show that for equal masses of water, the entropy change of the mixture is given by (ds) universe =2MC p ln[(t 1 +T 2 )/2(T 1 T 2 ) 1/2 and prove that the change is necessarily positive. [3+5] Q2. Find the irreversibility associated with expansion process of air through a very small opening in pipe from pressure and temp of 8 bar and 600K to a pressure of 1.2 bar. Assume air to be an ideal gas and temperature of surroundings to be 298 K. Q.3.A lump of steel of mass 8 Kg at 100 K is dropped in 80 Kg of oil at 300K. Make calculations for the entropy change of steel, the oil and the universe. Take specific heats of steel and oil as 0.5kJ/kgK and 3.5kJ/kgK, respectively. [2+2+2] EME-303/ Mr. Ajay Kr. Verma, Mr. Arun Sharma Date: 18 / 11/ 2013
7 B.Tech. [SEM III (ME)] QUIZ TEST-2 THERMODYNAMICS Time: 1 hour (EME-303) Max. Marks: 30 Note: All questions are compulsory. Q1. A reversible heat engine has heat interaction from three reservoir at 600 K, 700 K and 800 K. the engine rejects 10kJ/s to the sink at 320 K after doing 20 kw of work.the heat supplied by reservoir at 800 K is 70%of the heat supplied by reservoir at 700 K then determine the exact amount of heat interaction with each high temperature reservoir. (Q.No.3) [5] Q2. Find the change in entropy of steam generated at C from 5 kg of water at 27 0 C and atmospheric pressure.take specific heat of water to be 4.2 kj/kg K,Heat of vaporization at c as 2260 kj/kg and specific heat for steam given by: C P =R ( T+0.14T 2 ) (Q.No.1) [5] Q.1. Define the term available energy and unavailable energy. M 1 kg of water at T 1 is isobarically and adiabatically mixed with M 2 kg of water at T 2 (T 1 >T 2 ). Show that for equal masses of water, the entropy change of the mixture is given by (ds) universe=2mc p ln[(t 1 +T 2 )/2(T 1 T 2 ) 1/2 and prove that the change is necessarily positive. [3+5] Q2. Find the irreversibility associated with expansion process of air through a very small opening in pipe from pressure and temp of 8 bar and 600K to a pressure of 1.2 bar. Assume air to be an ideal gas and temperature of surroundings to be 298 K. Q.3.A lump of steel of mass 8 Kg at 100 K is dropped in 80 Kg of oil at 300K. Make calculations for the entropy change of steel, the oil and the universe. Take specific heats of steel and oil as 0.5kJ/kgK and 3.5kJ/kgK, respectively. [2+2+2] EME-303/ Mr. Ajay Kr. Verma, Mr. Arun Sharma Date: 18 / 11/ 2013
8 B.Tech. [SEM III (ME)] QUIZ TEST-2 THERMODYNAMICS Time: 1 hour (EME-303) Max. Marks: 30 Note: All questions are compulsory. Q1. A heat engine receive reversibly 420 kj/ cycle of heat from a source at C and rejects heat reversibly to sink at 27 0 C. There are no other heat transfers. For each of the three hypothetical amount of heat rejected in (a),(b)&(c) below, compute the cyclic integral of dq/t from these results show which case is irreversible, which reversible, and which is impossible: (a) 210 kj/cycle rejected (b) 105kJ/ cycle rejected (c) 315 kj/ cycle rejected. (Q.No.5) [2+2+1=5] Q2. In a certain process, a vapor, while condensing at C, transfer heat to water evaporating at C. The resulting steam is used in power cycle which rejects heat at 35 0 C.What is the fraction of available energy in the heat transferred from the process vapour at C that is lost due to the irreversible heat transfer at C. (Q.No.9) [5] Q.1. Define the term available energy and unavailable energy. M 1 kg of water at T 1 is isobarically and adiabatically mixed with M 2 kg of water at T 2 (T 1 >T 2 ). Show that for equal masses of water, the entropy change of the mixture is given by (ds) universe =2MC p ln[(t 1 +T 2 )/2(T 1 T 2 ) 1/2 and prove that the change is necessarily positive. [3+5] Q2. Find the irreversibility associated with expansion process of air through a very small opening in pipe from pressure and temp of 8 bar and 600K to a pressure of 1.2 bar. Assume air to be an ideal gas and temperature of surroundings to be 298 K. Q.3.A lump of steel of mass 8 Kg at 100 K is dropped in 80 Kg of oil at 300K. Make calculations for the entropy change of steel, the oil and the universe. Take specific heats of steel and oil as 0.5kJ/kgK and 3.5kJ/kgK, respectively. [2+2+2] EME-303/ Mr. Ajay Kr. Verma, Mr. Arun Sharma Date: 18 / 11/ 2013
9 EME-303/ Mr. Ajay Kr. Verma, Mr. Arun Sharma Date: 18 / 11/ 2013 Page-2
10 B.Tech. [SEM III (ME)] QUIZ TEST-2 THERMODYNAMICS Time: 1 hour (EME-303) Max. Marks: 30 Note: All questions are compulsory. Q1. A system has a heat capacity at const. volume C v =AT 2 where A = J/K 3 The system is originally at 200 K, and a thermal reservoir at 100 K is available.what is the maximum amount of work that can be recovered as a system is cooled down to the temperature of the reservoir. (Q.No.7) [5] Q2. A quantity of air initially at 1bar 300K undergoes two types of interactions : (a) it is brought to a final temperature of 500 K adiabatically by paddle wheel work transfer,(b) the same temperature rise is brought about by heat transfer from a thermal reservoir at 600 K. Take T 0 =300K, p 0 =1 atm. Determine the irreversibility (in kj/kg) in each case and comment on the results. (Q.No.13) [ =5] Q.1. Define the term available energy and unavailable energy. M 1 kg of water at T 1 is isobarically and adiabatically mixed with M 2 kg of water at T 2 (T 1 >T 2 ). Show that for equal masses of water, the entropy change of the mixture is given by (ds) universe =2MC p ln[(t 1 +T 2 )/2(T 1 T 2 ) 1/2 and prove that the change is necessarily positive. [3+5] Q2. Find the irreversibility associated with expansion process of air through a very small opening in pipe from pressure and temp of 8 bar and 600K to a pressure of 1.2 bar. Assume air to be an ideal gas and temperature of surroundings to be 298 K. Q.3.A lump of steel of mass 8 Kg at 100 K is dropped in 80 Kg of oil at 300K. Make calculations for the entropy change of steel, the oil and the universe. Take specific heats of steel and oil as 0.5kJ/kgK and 3.5kJ/kgK, respectively. [2+2+2] EME-303/ Mr. Ajay Kr. Verma, Mr. Arun Sharma Date: 18 / 11/ 2013
11 EME-303/ Mr. Ajay Kr. Verma, Mr. Arun Sharma Date: 18 / 11/ 2013 Page-2
12 B.Tech. [SEM III (ME)] QUIZ TEST-2 THERMODYNAMICS Time: 1 hour (EME-303) Max. Marks: 30 Note: All questions are compulsory. Q1. Water is heated at constant pressure of 0.7 MPa. The boiling point is C. The initial temperature of water is 0 0 C. The latent heat of evaporation is kJ/kg. Find the increase of entropy of water, if the final state is steam. (Q.No.11) [5] Q2. A heat engine is working between starting temperature limit of T 1 and T 2 of two bodies. Working fluid flows at rate m kg/s and has specific heat at constant pressure as C P.determine the maximum obtainable work from engine. (Q.No.4) [5] Q.1. Define the term available energy and unavailable energy. M 1 kg of water at T 1 is isobarically and adiabatically mixed with M 2 kg of water at T 2 (T 1 >T 2 ). Show that for equal masses of water, the entropy change of the mixture is given by (ds) universe =2MC p ln[(t 1 +T 2 )/2(T 1 T 2 ) 1/2 and prove that the change is necessarily positive. [3+5] Q2. Find the irreversibility associated with expansion process of air through a very small opening in pipe from pressure and temp of 8 bar and 600K to a pressure of 1.2 bar. Assume air to be an ideal gas and temperature of surroundings to be 298 K. Q.3.A lump of steel of mass 8 Kg at 100 K is dropped in 80 Kg of oil at 300K. Make calculations for the entropy change of steel, the oil and the universe. Take specific heats of steel and oil as 0.5kJ/kgK and 3.5kJ/kgK, respectively. [2+2+2] EME-303/ Mr. Ajay Kr. Verma, Mr. Arun Sharma Date: 18 / 11/ 2013
13 B.Tech. [SEM III (ME)] SPECIAL QUIZ THERMODYNAMICS Time: 1 hour (EME-303) Max. marks : 30 Note: All questions are compulsory. Q1. A system undergoes a process as : 1-2 isobaric,2-3 polytropic where n=1.4 and 3-1 isothermal where pv=c. Find the v 2 and Net Work.(p 1 =400kPa,p 2 =100kPa,V 1 =0.1m 3 ) (Q.No.5) [2+3] Q2. The properties of certain fluid are related as follows U= t, p.v=0.287(t+273) Where u is the specific internal energy (kj/kg), t is in C, p is pressure (kn/m2) and v is specific volume (m3/kg). For this fluid find C v and C p. (Q.No.1) [2.5=2.5=5] Q.1.. A gas contained in a cylinder is compressed from 1 MPa and 0.05m 3 to 2MPa. Compression is governed by pv 1.4 =constant.internal energy of a gas is given by : U=7.5pV-425 kj Where p is pressure in kpa and V is volume in m 3 Determine the heat, work, and change in internal energy assuming compression process is isentropic. [3+3+2=8] Q2. In isentropic flow through nozzle, air flows at the rate of 600 kg/hr. at inlet to the nozzle, pressure is 2MPa and temperature is C. The exit pressure is 0.5 MPa. Initial air velocity is 300 m/s. determines (i) exit velocity of air (ii) inlet and exit area of nozzle. [3+3=6] Q3.Explain the free expansion process and PMM-I EME-303 / Mr. Ajay Kr. Verma Date:
14 B.Tech. [SEM III (ME)] SPECIAL QUIZ THERMODYNAMICS Time: 1 hour (EME-303) Max. marks : 30 Note: All questions are compulsory. Q1. Air initially at 60kPa pressure, 800K temperature and occupying a volume of 0.1 m 3 is compressed isothermally until the volume is halved and subsequently it goes further compression at constant pressure till the volume is halved again. Sketch the process on p-v plot and make calculations for the total work done and total heat interaction for the two processes. Assume ideal gas behavior for air and take C p = 1.005kJ/kg K. (Q.No.2) [3+2=5] Q2. A thermocouple with test junction at t 0 C on gas thermometer scale and reference junction at ice point gives the e.m.f. as mv The mill voltmeter is calibrated at ice and steam point.what will be the reading of this thermometer when the gas thermometer reads 70 0 C. (Q.No.7) [5] Q.1. A compressor is required to provide air at 0.5 MPa and C for a stationary power plant. The air intake is at 0.1MPa and 20 0 C.The out let velocity is 25 m/s.(a) Find the work per unit mass needed for an adiabatic compressor.(b) if the air flow is 0.62 kg /s find the capacity of the motor connected to compressor assuming compressor mechanical efficiency [4+4=8] Q2. Determine the heat transfer and its direction for a system in which a perfect gas having molecular weight of 16 is compressed from kpa,20 0 C to a pressure of 600 kpa following the law pv 1.3 =constant.take specific heat at constant pressure of gas as 1.7 kj/kg K. [3+3=6] Q3. Explain the macroscopic and microscopic approach and quasi-static process. [2+2+2=6] EME-303 / Mr. Ajay Kr. Verma, Mr. Arun Sharma Date:
QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION. 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance in thermodynamics.
 QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION 1. What do you mean by thermodynamic equilibrium? How does it differ from thermal equilibrium? [05 Marks, June-2015] 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance
QUESTION BANK UNIT-1 INTRODUCTION 1. What do you mean by thermodynamic equilibrium? How does it differ from thermal equilibrium? [05 Marks, June-2015] 2. State zeroth law of thermodynamics? Write its importance
UNIT I Basic concepts and Work & Heat Transfer
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW SVCET
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
Two mark questions and answers UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW 1. What do you understand by pure substance? A pure substance is defined as one that is homogeneous and invariable in chemical composition
R13 SET - 1 '' ''' '' ' '''' Code No RT21033
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
 BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
5/6/ :41 PM. Chapter 6. Using Entropy. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Chapter 7. Entropy. by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS. B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A
 UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
Where F1 is the force and dl1 is the infinitesimal displacement, but F1 = p1a1
 In order to force the fluid to flow across the boundary of the system against a pressure p1, work is done on the boundary of the system. The amount of work done is dw = - F1.dl1, Where F1 is the force
In order to force the fluid to flow across the boundary of the system against a pressure p1, work is done on the boundary of the system. The amount of work done is dw = - F1.dl1, Where F1 is the force
Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive
 Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
First Law of Thermodynamics
 CH2303 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics I Unit II First Law of Thermodynamics Dr. M. Subramanian 07-July-2011 Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College
CH2303 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics I Unit II First Law of Thermodynamics Dr. M. Subramanian 07-July-2011 Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College
R13. II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) PART- A
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems
 Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES. The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial.
 THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 2 THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES SAE
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 2 THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES SAE
Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002
 16.050 Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002 Do all eight problems. All problems count the same. 1. A system undergoes a reversible cycle while exchanging heat with three thermal reservoirs, as shown below.
16.050 Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002 Do all eight problems. All problems count the same. 1. A system undergoes a reversible cycle while exchanging heat with three thermal reservoirs, as shown below.
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit.
 I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Paper II. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
 We RoU No. 700095 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time ; 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 0 Instructions
We RoU No. 700095 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time ; 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 0 Instructions
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A
 ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A 1. What is meant by thermodynamics system? (A/M 2006) Thermodynamics system is defined as any space or matter or group of matter
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A 1. What is meant by thermodynamics system? (A/M 2006) Thermodynamics system is defined as any space or matter or group of matter
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY. Copyright Hany A. Al-Ansary and S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1
 CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 U N IT - 1 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS 1. 1 kg of gas at 1.1 bar, 27 o C is compressed
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 U N IT - 1 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS 1. 1 kg of gas at 1.1 bar, 27 o C is compressed
first law of ThermodyNamics
 first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
20 m neon m propane. g 20. Problems with solutions:
 Problems with solutions:. A -m tank is filled with a gas at room temperature 0 C and pressure 00 Kpa. How much mass is there if the gas is a) Air b) Neon, or c) Propane? Given: T7K; P00KPa; M air 9; M
Problems with solutions:. A -m tank is filled with a gas at room temperature 0 C and pressure 00 Kpa. How much mass is there if the gas is a) Air b) Neon, or c) Propane? Given: T7K; P00KPa; M air 9; M
Content. Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas.
 Entropy Content Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas. Entropy Entropy can be viewed as a measure of molecular disorder, or molecular randomness. As a system becomes
Entropy Content Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas. Entropy Entropy can be viewed as a measure of molecular disorder, or molecular randomness. As a system becomes
(1)5. Which of the following equations is always valid for a fixed mass system undergoing an irreversible or reversible process:
 Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
THERMODYNAMICS SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION MECHANICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL THERMODYNAMICS THERMODYNAMICS THERMODYNAMICS
 1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION MECHANICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL 2 Syllabus: Thermal Engineering (Thermodynamics) Properties of Pure Substances : p-v & P-T diagrams of pure substance like H 2
1 SSC-JE STAFF SELECTION COMMISSION MECHANICAL ENGINEERING STUDY MATERIAL 2 Syllabus: Thermal Engineering (Thermodynamics) Properties of Pure Substances : p-v & P-T diagrams of pure substance like H 2
Dishwasher. Heater. Homework Solutions ME Thermodynamics I Spring HW-1 (25 points)
 HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
ME Thermodynamics I
 Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems
 First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems Content The First Law of Thermodynamics Energy Balance Energy Change of a System Mechanisms of Energy Transfer First Law of Thermodynamics in Closed Systems Moving
First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems Content The First Law of Thermodynamics Energy Balance Energy Change of a System Mechanisms of Energy Transfer First Law of Thermodynamics in Closed Systems Moving
In the next lecture...
 16 1 In the next lecture... Solve problems from Entropy Carnot cycle Exergy Second law efficiency 2 Problem 1 A heat engine receives reversibly 420 kj/cycle of heat from a source at 327 o C and rejects
16 1 In the next lecture... Solve problems from Entropy Carnot cycle Exergy Second law efficiency 2 Problem 1 A heat engine receives reversibly 420 kj/cycle of heat from a source at 327 o C and rejects
+ m B1 = 1. u A1. u B1. - m B1 = V A. /v A = , u B1 + V B. = 5.5 kg => = V tot. Table B.1.
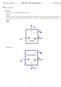
 5.6 A rigid tank is divided into two rooms by a membrane, both containing water, shown in Fig. P5.6. Room A is at 200 kpa, v = 0.5 m3/kg, VA = m3, and room B contains 3.5 kg at 0.5 MPa, 400 C. The membrane
5.6 A rigid tank is divided into two rooms by a membrane, both containing water, shown in Fig. P5.6. Room A is at 200 kpa, v = 0.5 m3/kg, VA = m3, and room B contains 3.5 kg at 0.5 MPa, 400 C. The membrane
 CHAPTER INTRODUCTION AND BASIC PRINCIPLES. (Tutorial). Determine if the following properties of the system are intensive or extensive properties: Property Intensive Extensive Volume Density Conductivity
CHAPTER INTRODUCTION AND BASIC PRINCIPLES. (Tutorial). Determine if the following properties of the system are intensive or extensive properties: Property Intensive Extensive Volume Density Conductivity
MARIA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 MARIA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY ATTOOR ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (TWO MARK QUESTION BANK) UNIT 1 (BASIC COMCEPTS AND FIRST LAW) 1. Define the term thermal engineering. Thermal engineering
MARIA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY ATTOOR ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (TWO MARK QUESTION BANK) UNIT 1 (BASIC COMCEPTS AND FIRST LAW) 1. Define the term thermal engineering. Thermal engineering
Chapter 7. Entropy: A Measure of Disorder
 Chapter 7 Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Entropy and the Clausius Inequality The second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of microscopic
Chapter 7 Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Entropy and the Clausius Inequality The second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of microscopic
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 04 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : THERMODYNAMICS Course Code : AME00 Regulation : IARE - R1 Year
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 04 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name : THERMODYNAMICS Course Code : AME00 Regulation : IARE - R1 Year
II/IV B.Tech (Regular) DEGREE EXAMINATION. (1X12 = 12 Marks) Answer ONE question from each unit.
 Page 1 of 8 Hall Ticket Number: 14CH 404 II/IV B.Tech (Regular) DEGREE EXAMINATION June, 2016 Chemical Engineering Fourth Semester Engineering Thermodynamics Time: Three Hours Maximum : 60 Marks Answer
Page 1 of 8 Hall Ticket Number: 14CH 404 II/IV B.Tech (Regular) DEGREE EXAMINATION June, 2016 Chemical Engineering Fourth Semester Engineering Thermodynamics Time: Three Hours Maximum : 60 Marks Answer
Chapter 7. Dr Ali Jawarneh. Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University
 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Objectives Apply the second law of thermodynamics to processes. Define a new property called entropy to quantify
Chapter 7 ENTROPY Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Objectives Apply the second law of thermodynamics to processes. Define a new property called entropy to quantify
7. Development of the 2nd Law
 7-1 7. Development of the 2nd Law 7.1 1st Law Limitations The 1 st Law describes energy accounting. Once we have a process (or string of processes) we can calculate the relevant energy interactions. The
7-1 7. Development of the 2nd Law 7.1 1st Law Limitations The 1 st Law describes energy accounting. Once we have a process (or string of processes) we can calculate the relevant energy interactions. The
Lecture 29-30: Closed system entropy balance
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 2016 Lecture 29-30: Closed system entropy balance Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 200240, P.
ME 200 Thermodynamics I Spring 2016 Lecture 29-30: Closed system entropy balance Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 200240, P.
Thermodynamics I Spring 1432/1433H (2011/2012H) Saturday, Wednesday 8:00am - 10:00am & Monday 8:00am - 9:00am MEP 261 Class ZA
 Thermodynamics I Spring 1432/1433H (2011/2012H) Saturday, Wednesday 8:00am - 10:00am & Monday 8:00am - 9:00am MEP 261 Class ZA Dr. Walid A. Aissa Associate Professor, Mech. Engg. Dept. Faculty of Engineering
Thermodynamics I Spring 1432/1433H (2011/2012H) Saturday, Wednesday 8:00am - 10:00am & Monday 8:00am - 9:00am MEP 261 Class ZA Dr. Walid A. Aissa Associate Professor, Mech. Engg. Dept. Faculty of Engineering
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes. by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems. Temperature, Heat & The First Law of Thermodynamics
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 18 Temperature, Heat & The First Law of Thermodynamics Equilibrium & temperature scales Thermal expansion Exchange of heat First law of thermodynamics Heat conduction
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 18 Temperature, Heat & The First Law of Thermodynamics Equilibrium & temperature scales Thermal expansion Exchange of heat First law of thermodynamics Heat conduction
ME Thermodynamics I. Lecture Notes and Example Problems
 ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 621 213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS UNIT-I Basic Concept and First Law 1. What do you understand
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 621 213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS UNIT-I Basic Concept and First Law 1. What do you understand
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED HEAT
 SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED HEAT LIST OF TOPICS A B C D E F G H I J K Pressure, Temperature, Energy Heat Transfer Internal Energy, Thermodynamic systems. First Law of Thermodynamics Gas Laws, Displacement
SECOND ENGINEER REG. III/2 APPLIED HEAT LIST OF TOPICS A B C D E F G H I J K Pressure, Temperature, Energy Heat Transfer Internal Energy, Thermodynamic systems. First Law of Thermodynamics Gas Laws, Displacement
PTT 277/3 APPLIED THERMODYNAMICS SEM 1 (2013/2014)
 PTT 77/3 APPLIED THERMODYNAMICS SEM 1 (013/014) 1 Energy can exist in numerous forms: Thermal Mechanical Kinetic Potential Electric Magnetic Chemical Nuclear The total energy of a system on a unit mass:
PTT 77/3 APPLIED THERMODYNAMICS SEM 1 (013/014) 1 Energy can exist in numerous forms: Thermal Mechanical Kinetic Potential Electric Magnetic Chemical Nuclear The total energy of a system on a unit mass:
Chapter 1: Basic Definitions, Terminologies and Concepts
 Chapter : Basic Definitions, Terminologies and Concepts ---------------------------------------. UThermodynamics:U It is a basic science that deals with: -. Energy transformation from one form to another..
Chapter : Basic Definitions, Terminologies and Concepts ---------------------------------------. UThermodynamics:U It is a basic science that deals with: -. Energy transformation from one form to another..
T H E R M O D Y N A M I C S M E
 T H E R M O D Y N A M I C S M E THERMODYNAMICS CONTENTS 1 BASIC CONCEPTS IN THERMODYNAMICS 2 TEMPERATURE 3 WORK AND HEAT TRANSFER Thermodynamic system, surroundings, universe, system boundary Types of
T H E R M O D Y N A M I C S M E THERMODYNAMICS CONTENTS 1 BASIC CONCEPTS IN THERMODYNAMICS 2 TEMPERATURE 3 WORK AND HEAT TRANSFER Thermodynamic system, surroundings, universe, system boundary Types of
CHAPTER 2 ENERGY INTERACTION (HEAT AND WORK)
 CHATER ENERGY INTERACTION (HEAT AND WORK) Energy can cross the boundary of a closed system in two ways: Heat and Work. WORK The work is done by a force as it acts upon a body moving in direction of force.
CHATER ENERGY INTERACTION (HEAT AND WORK) Energy can cross the boundary of a closed system in two ways: Heat and Work. WORK The work is done by a force as it acts upon a body moving in direction of force.
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ESE TOPIC WISE OBJECTIVE SOLVED PAPER-I FROM (1995-2017) UPSC Engineering Services Examination State Engineering Service Examination & Public Sector Examination. IES MASTER PUBLICATION
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ESE TOPIC WISE OBJECTIVE SOLVED PAPER-I FROM (1995-2017) UPSC Engineering Services Examination State Engineering Service Examination & Public Sector Examination. IES MASTER PUBLICATION
Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I
 ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
Chapter One Reviews of Thermodynamics Update on 2013/9/13
 Chapter One Reviews of Thermodynamics Update on 2013/9/13 (1.1). Thermodynamic system An isolated system is a system that exchanges neither mass nor energy with its environment. An insulated rigid tank
Chapter One Reviews of Thermodynamics Update on 2013/9/13 (1.1). Thermodynamic system An isolated system is a system that exchanges neither mass nor energy with its environment. An insulated rigid tank
This follows from the Clausius inequality as a consequence of the second law of thermodynamics. Therefore. (for reversible process only) (22.
 Entropy Clausius inequality can be used to analyze the cyclic process in a quantitative manner. The second law became a law of wider applicability when Clausius introduced the property called entropy.
Entropy Clausius inequality can be used to analyze the cyclic process in a quantitative manner. The second law became a law of wider applicability when Clausius introduced the property called entropy.
Exergy and the Dead State
 EXERGY The energy content of the universe is constant, just as its mass content is. Yet at times of crisis we are bombarded with speeches and articles on how to conserve energy. As engineers, we know that
EXERGY The energy content of the universe is constant, just as its mass content is. Yet at times of crisis we are bombarded with speeches and articles on how to conserve energy. As engineers, we know that
1. Basic state values of matter
 1. Basic state values of matter Example 1.1 The pressure inside a boiler is p p = 115.10 5 Pa and p v = 9.44.10 4 Pa inside a condenser. Calculate the absolute pressure inside the boiler and condenser
1. Basic state values of matter Example 1.1 The pressure inside a boiler is p p = 115.10 5 Pa and p v = 9.44.10 4 Pa inside a condenser. Calculate the absolute pressure inside the boiler and condenser
Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 20 Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy gases Entropy solids & liquids Heat engines Refrigerators Second law of thermodynamics 1. The efficiency of
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 20 Entropy & the Second Law of Thermodynamics Entropy gases Entropy solids & liquids Heat engines Refrigerators Second law of thermodynamics 1. The efficiency of
ME 200 Final Exam December 14, :00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m.
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 11:30 a.m. Boregowda Boregowda Braun Bae 2:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Meyer Naik Hess ME 200 Final Exam December 14, 2015
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 11:30 a.m. Boregowda Boregowda Braun Bae 2:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. 4:30 p.m. Meyer Naik Hess ME 200 Final Exam December 14, 2015
S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100
 Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4162]-189 S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks
Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4162]-189 S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks
Thermodynamics I Chapter 2 Properties of Pure Substances
 Thermodynamics I Chapter 2 Properties of Pure Substances Mohsin Mohd Sies Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Properties of Pure Substances (Motivation) To quantify the changes
Thermodynamics I Chapter 2 Properties of Pure Substances Mohsin Mohd Sies Fakulti Kejuruteraan Mekanikal, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Properties of Pure Substances (Motivation) To quantify the changes
Thermodynamic Systems
 Thermodynamic Systems For purposes of analysis we consider two types of Thermodynamic Systems: Closed System - usually referred to as a System or a Control Mass. This type of system is separated from its
Thermodynamic Systems For purposes of analysis we consider two types of Thermodynamic Systems: Closed System - usually referred to as a System or a Control Mass. This type of system is separated from its
MAE 320 HW 7B. 1e. For an isolated system, please circle the parameter which will change with time. (a) Total energy;
 MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
Consequences of Second Law of Thermodynamics. Entropy. Clausius Inequity
 onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology New Delhi II Semester MEL 140 ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS
 PROBLEM SET 1: Review of Basics Problem 1: Define Work. Explain how the force is generated in an automobile. Problem 2: Define and classify Energy and explain the relation between a body and energy. Problem
PROBLEM SET 1: Review of Basics Problem 1: Define Work. Explain how the force is generated in an automobile. Problem 2: Define and classify Energy and explain the relation between a body and energy. Problem
Basic thermodynamics. heat to the high temperature reservoir.
 Consider a heat engine that is operating in a cyclic process takes heat (QH) from a high temperature reservoir & converts completely into work (W), violating the Kelvin Planck statement. Let the work W,
Consider a heat engine that is operating in a cyclic process takes heat (QH) from a high temperature reservoir & converts completely into work (W), violating the Kelvin Planck statement. Let the work W,
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
IS A PARTICULAR PROCESS / REACTION FEASIBLE? TO WHAT EXTENT DOES THE PROCESS / REACTION PROCEED?
 Limitations of First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics is a law of conservation of energy. It does not specify the direction of the process. All spontaneous processes processed in one
Limitations of First Law of Thermodynamics The first law of thermodynamics is a law of conservation of energy. It does not specify the direction of the process. All spontaneous processes processed in one
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : THERMODYNAMICS Code : A30306 Class : II B. Tech I Semester Branch :
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -500 043 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : THERMODYNAMICS Code : A30306 Class : II B. Tech I Semester Branch :
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ME6301-ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS
 SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE (Approved by the AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Tamilnadu and Affiliated to Anna University, chennai) Established in 1998 - An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution Dr. E.M.Abdullah
SYED AMMAL ENGINEERING COLLEGE (Approved by the AICTE, New Delhi, Govt. of Tamilnadu and Affiliated to Anna University, chennai) Established in 1998 - An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Institution Dr. E.M.Abdullah
1. INTRODUCTION TO REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITION
 CHAPTER ONE 1. INTRODUCTION TO REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITION Refrigeration may be defined as the process of reducing and maintaining a temperature of a space or material below that of the surroundings.
CHAPTER ONE 1. INTRODUCTION TO REFRIGERATION AND AIR CONDITION Refrigeration may be defined as the process of reducing and maintaining a temperature of a space or material below that of the surroundings.
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore (21301jtsizemore) 1
 Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
Version 001 HW 15 Thermodynamics C&J sizemore 21301jtsizemore 1 This print-out should have 38 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering.
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ESE TOPICWISE OBJECTIVE SOLVED PAPER-I FROM (1995-2018) UPSC Engineering Services Examination State Engineering Service Examination & Public Sector Examination. IES MASTER PUBLICATION
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ESE TOPICWISE OBJECTIVE SOLVED PAPER-I FROM (1995-2018) UPSC Engineering Services Examination State Engineering Service Examination & Public Sector Examination. IES MASTER PUBLICATION
CHAPTER 8 ENTROPY. Blank
 CHAPER 8 ENROPY Blank SONNAG/BORGNAKKE SUDY PROBLEM 8-8. A heat engine efficiency from the inequality of Clausius Consider an actual heat engine with efficiency of η working between reservoirs at and L.
CHAPER 8 ENROPY Blank SONNAG/BORGNAKKE SUDY PROBLEM 8-8. A heat engine efficiency from the inequality of Clausius Consider an actual heat engine with efficiency of η working between reservoirs at and L.
Name: I have observed the honor code and have neither given nor received aid on this exam.
 ME 235 FINAL EXAM, ecember 16, 2011 K. Kurabayashi and. Siegel, ME ept. Exam Rules: Open Book and one page of notes allowed. There are 4 problems. Solve each problem on a separate page. Name: I have observed
ME 235 FINAL EXAM, ecember 16, 2011 K. Kurabayashi and. Siegel, ME ept. Exam Rules: Open Book and one page of notes allowed. There are 4 problems. Solve each problem on a separate page. Name: I have observed
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER. 13 June 2007
 ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 13 June 2007 Midterm Examination R. Culham This is a 2 hour, open-book examination. You are permitted to use: course text book calculator There are
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 13 June 2007 Midterm Examination R. Culham This is a 2 hour, open-book examination. You are permitted to use: course text book calculator There are
ME 2202 ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS TWO MARKS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW
 ME 2202 ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS TWO MARKS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW 1. What is thermodynamics? It is a basic science that deals with energy and its transformations. The
ME 2202 ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS TWO MARKS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW 1. What is thermodynamics? It is a basic science that deals with energy and its transformations. The
The first law of thermodynamics. U = internal energy. Q = amount of heat energy transfer
 Thermodynamics Investigation of the energy transfer by heat and work and how natural systems behave (Q) Heat transfer of energy due to temp differences. (W) Work transfer of energy through mechanical means.
Thermodynamics Investigation of the energy transfer by heat and work and how natural systems behave (Q) Heat transfer of energy due to temp differences. (W) Work transfer of energy through mechanical means.
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON. University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS. For The Following Qualifications:-
 UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS For The Following Qualifications:- B.Sc. M.Sci. Physics 1B28: Thermal Physics COURSE CODE : PHYSIB28 UNIT VALUE : 0.50 DATE
UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LONDON University of London EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS For The Following Qualifications:- B.Sc. M.Sci. Physics 1B28: Thermal Physics COURSE CODE : PHYSIB28 UNIT VALUE : 0.50 DATE
Topics to be covered. Fundamental Concepts & Definitions: Thermodynamics; definition and scope. Microscopic
 time Class No Text/ Reference page Topics to be covered Fundamental Concepts & Definitions: Thermodynamics; definition and scope. Microscopic 1 and Macroscopic approaches. Engineering Thermodynamics Definition,,
time Class No Text/ Reference page Topics to be covered Fundamental Concepts & Definitions: Thermodynamics; definition and scope. Microscopic 1 and Macroscopic approaches. Engineering Thermodynamics Definition,,
Spring_#7. Thermodynamics. Youngsuk Nam.
 Spring_#7 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.kr You can t connect the dots looking forward; you can only connect them looking backwards. So you have to trust that the dots will somehow connect in
Spring_#7 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.kr You can t connect the dots looking forward; you can only connect them looking backwards. So you have to trust that the dots will somehow connect in
Physics 5D PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Fall 2013
 Print your name: Physics 5D PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Fall 2013 Real Exam is Wednesday December 11 Thimann Lecture 3 4:00-7:00 pm Closed book exam two 8.5x11 sheets of notes ok Note: Avogadro s number N A =
Print your name: Physics 5D PRACTICE FINAL EXAM Fall 2013 Real Exam is Wednesday December 11 Thimann Lecture 3 4:00-7:00 pm Closed book exam two 8.5x11 sheets of notes ok Note: Avogadro s number N A =
THERMODYNAMICS NOTES. These notes give a brief overview of engineering thermodynamics. They are based on the thermodynamics text by Black & Hartley.
 THERMODYNAMICS NOTES These notes give a brief overview of engineering thermodynamics. They are based on the thermodynamics text by Black & Hartley. Topics covered include: concepts; properties; conservation
THERMODYNAMICS NOTES These notes give a brief overview of engineering thermodynamics. They are based on the thermodynamics text by Black & Hartley. Topics covered include: concepts; properties; conservation
HEAT- I Part - A C D A B. Te m p. Heat input
 e m p HE- I Part -. solid material is supplied with heat at a constant rate. he temperature of the material is changing with heat input as shown in the graph. Study the graph carefully and answer the following
e m p HE- I Part -. solid material is supplied with heat at a constant rate. he temperature of the material is changing with heat input as shown in the graph. Study the graph carefully and answer the following
ME Thermodynamics I
 HW-03 (25 points) i) Given: for writing Given, Find, Basic equations Rigid tank containing nitrogen gas in two sections initially separated by a membrane. Find: Initial density (kg/m3) of nitrogen gas
HW-03 (25 points) i) Given: for writing Given, Find, Basic equations Rigid tank containing nitrogen gas in two sections initially separated by a membrane. Find: Initial density (kg/m3) of nitrogen gas
Consequences of Second Law of Thermodynamics. Entropy. Clausius Inequity
 onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
ESO201A: Thermodynamics
 ESO201A: Thermodynamics First Semester 2015-2016 Mid-Semester Examination Instructor: Sameer Khandekar Time: 120 mins Marks: 250 Solve sub-parts of a question serially. Question #1 (60 marks): One kmol
ESO201A: Thermodynamics First Semester 2015-2016 Mid-Semester Examination Instructor: Sameer Khandekar Time: 120 mins Marks: 250 Solve sub-parts of a question serially. Question #1 (60 marks): One kmol
Dr Ali Jawarneh. Hashemite University
 Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Examine the moving boundary work or P d work commonly encountered in reciprocating devices such as automotive engines and compressors.
Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Examine the moving boundary work or P d work commonly encountered in reciprocating devices such as automotive engines and compressors.
Unified Quiz: Thermodynamics
 Unified Quiz: Thermodynamics October 14, 2005 Calculators allowed. No books or notes allowed. A list of equations is provided. Put your ID number on each page of the exam. Read all questions carefully.
Unified Quiz: Thermodynamics October 14, 2005 Calculators allowed. No books or notes allowed. A list of equations is provided. Put your ID number on each page of the exam. Read all questions carefully.
Engineering Thermodynamics Solutions Manual
 Engineering Thermodynamics Solutions Manual Prof. T.T. Al-Shemmeri Download free books at Prof. T.T. Al-Shemmeri Engineering Thermodynamics Solutions Manual 2 2012 Prof. T.T. Al-Shemmeri & bookboon.com
Engineering Thermodynamics Solutions Manual Prof. T.T. Al-Shemmeri Download free books at Prof. T.T. Al-Shemmeri Engineering Thermodynamics Solutions Manual 2 2012 Prof. T.T. Al-Shemmeri & bookboon.com
Spring_#8. Thermodynamics. Youngsuk Nam
 Spring_#8 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.krac kr Ch.7: Entropy Apply the second law of thermodynamics to processes. Define a new property called entropy to quantify the secondlaw effects. Establish
Spring_#8 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.krac kr Ch.7: Entropy Apply the second law of thermodynamics to processes. Define a new property called entropy to quantify the secondlaw effects. Establish
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics. Chapter 7. KFUPM Housam Binous CHE 303
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Chapter 7 1 Thermodynamics of flow is based on mass, energy and entropy balances Fluid mechanics encompasses the above balances and conservation of momentum
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Chapter 7 1 Thermodynamics of flow is based on mass, energy and entropy balances Fluid mechanics encompasses the above balances and conservation of momentum
The First Law of Thermodynamics. By: Yidnekachew Messele
 The First Law of Thermodynamics By: Yidnekachew Messele It is the law that relates the various forms of energies for system of different types. It is simply the expression of the conservation of energy
The First Law of Thermodynamics By: Yidnekachew Messele It is the law that relates the various forms of energies for system of different types. It is simply the expression of the conservation of energy
S6. (a) State what is meant by an ideal gas...
 IB PHYSICS Name: DEVIL PHYSICS Period: Date: BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS TSOKOS CHAPTER 3 TEST REVIEW S1. Thermal energy is transferred through the glass windows of a house mainly by A. conduction. B. radiation.
IB PHYSICS Name: DEVIL PHYSICS Period: Date: BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS TSOKOS CHAPTER 3 TEST REVIEW S1. Thermal energy is transferred through the glass windows of a house mainly by A. conduction. B. radiation.
Readings for this homework assignment and upcoming lectures
 Homework #3 (group) Tuesday, February 13 by 4:00 pm 5290 exercises (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm extra credit (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm Readings for this homework assignment
Homework #3 (group) Tuesday, February 13 by 4:00 pm 5290 exercises (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm extra credit (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm Readings for this homework assignment
Chapter 6. Using Entropy
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy Learning Outcomes Demonstrate understanding of key concepts related to entropy and the second law... including entropy transfer, entropy production, and the increase in entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy Learning Outcomes Demonstrate understanding of key concepts related to entropy and the second law... including entropy transfer, entropy production, and the increase in entropy
Physics 202 Homework 5
 Physics 202 Homework 5 Apr 29, 2013 1. A nuclear-fueled electric power plant utilizes a so-called boiling water reac- 5.8 C tor. In this type of reactor, nuclear energy causes water under pressure to boil
Physics 202 Homework 5 Apr 29, 2013 1. A nuclear-fueled electric power plant utilizes a so-called boiling water reac- 5.8 C tor. In this type of reactor, nuclear energy causes water under pressure to boil
SEM-2016(03)-II MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Paper -11. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before. attempting questions.
 Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(03)-II MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper -11 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 300 Instructions
Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(03)-II MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper -11 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 300 Instructions
CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS. Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola
 CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS Science that involves design and analysis of devices and systems for energy conversion Deals with heat and work and
CONCEPTS AND DEFINITIONS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS Science that involves design and analysis of devices and systems for energy conversion Deals with heat and work and
c Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq (BUET) Entropy ME 203 (2017) 2 / 27 T037
 onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
onsequences of Second Law of hermodynamics Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & echnology BUE Dhaka-000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
The Kinetic Theory of Gases
 PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 19 The Kinetic Theory of Gases Ideal gas RMS speed Internal energy Isothermal process Isobaric process Isochoric process Adiabatic process General process 1. Figure
PHYS102 Previous Exam Problems CHAPTER 19 The Kinetic Theory of Gases Ideal gas RMS speed Internal energy Isothermal process Isobaric process Isochoric process Adiabatic process General process 1. Figure
Chapter 4. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems
 Chapter 4 Energy Analysis of Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics is an expression of the conservation of energy principle. Energy can cross the boundaries of a closed system in the form of heat
Chapter 4 Energy Analysis of Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics is an expression of the conservation of energy principle. Energy can cross the boundaries of a closed system in the form of heat
