ESO201A: Thermodynamics
|
|
|
- Verity Lawrence
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
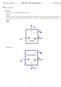
1 ESO201A: Thermodynamics First Semester Mid-Semester Examination Instructor: Sameer Khandekar Time: 120 mins Marks: 250 Solve sub-parts of a question serially. Question #1 (60 marks): One kmol of an ideal gas, initially at T 1, P 1 and V 1 (State #1), is allowed to expand to twice its initial volume in a reversible isothermal process. (a) What is the amount of heat added to the system during this process? Subsequently, the system is brought back to its initial State #1, by first undergoing a constant volume process, followed by a reversible adiabatic process. (b) Will the constant volume process be one of cooling or of heating (give reasons for your answer)? (c) Draw a P-v diagram of the entire cycle. (d) Find the work done by the system in the entire cycle if γ = 2.0. Question #2: 80 marks A nuclear reactor core containing 1 m 3 of saturated water at 20 MPa is enclosed inside a containment room, as shown in the figure. The room is well insulated and evacuated with valve closed. Due to a severe accident, the reactor core ruptures and water fills the containment. Find the containment room volume so that the final pressure is 300 kpa. insulated Containment room (Initially evacuated) valve Question #3: 70 marks Reactor core with 1 m 3 of water An adiabatic air compressor is to be powered by a directcoupled adiabatic steam turbine that is also driving a generator. Steam enters the turbine at 12.5 MPa and 500 C at a rate of 25 kg/s and exits at 10 kpa and a quality of Air enters the compressor at 98 kpa and 295 K at the rate of 10 kg/s and exits at 1 MPa and 620 K. Determine the net power delivered in MW to the generator by the turbine. State all assumptions you have made while solving. (Take C p of air = kj/kgk) 1 MPa 620 K Air Compressor 98 KPa, 295 K 10 kg/s 12.5 MPa, 500 C 25 kg/s Steam Turbine 10 kpa Gen Set
2
3 Question #4: 40 marks (02 marks for the correct answer and -1 mark for the wrong answer.) For the statements below, write /, as the case may be. Solve this question in the regular answer sheet; not here, by clearly writing Answer #1: or, as the case may be. 1. A constant volume ideal gas process is equivalent to a polytropic process with the exponent n (PV n = constant) tending to infinity. 2. For a closed system undergoing a cycle, entire amount of heat supplied can be converted to net work output. 3. For an ideal gas, ( h T ) p ( u T ) v = 0 4. Enthalpy of an ideal gas is a function of temperature only. 5. In general, for all common solids, the term (vdp) is significant. 6. For monoatomic gases, the value of gamma, the specific heat ratio, is equal to The specific heat of gases, for noble gases, such as Ar, He, Ne, Kr, etc., is independent of temperature. 8. For steady incompressible flows, the conservation of volume flow rate is equivalent to conservation of mass flow rate. 9. The exit velocity of a diffuser is usually small as compared with the inlet velocity (for usual engineering systems operating with subsonic flows). 10. A positive Joule-Thomson coefficient indicates that the gas will cool down when it passes through a throttling device. 11. The density ratio ρ vapor / ρ liquid of a pure substance approaches a value equal to unity when approaching the critical conditions. 12. If air pressure is continuously increased inside an adiabatic chamber filled with leafy vegetables, they will eventually cool down. 13. The correction term a/v 2 in the van der Waals equation, accounts for intermolecular forces in real gases. 14. If energy and mass, both cannot cross a system boundary, it is called as a stationary system. 15. A gas turbine produces net work at the expense of the kinetic energy of the working fluid. 16. If the product PV of a gas decreases during a throttling process, its internal energy and temperature will decrease due to throttling. 17. A high temperature (T R > 2), ideal gas behavior can be assumed with good accuracy regardless of pressure (except when P R >> 1) 18. If shear stress exerted by a flowing fluid on the wall is proportional to the velocity gradient at the wall, the SI units of the proportionality constant is (Pa/s) 19. For substances that have a triple point pressure above the atmospheric pressure, sublimation is the only way to change from solid to vapor phase at atmospheric pressure. 20. The principle of corresponding states stipulates that the Z-factor of all the gases is the same at a given reduced pressure and temperature.
4
5
6
The First Law of Thermodynamics. By: Yidnekachew Messele
 The First Law of Thermodynamics By: Yidnekachew Messele It is the law that relates the various forms of energies for system of different types. It is simply the expression of the conservation of energy
The First Law of Thermodynamics By: Yidnekachew Messele It is the law that relates the various forms of energies for system of different types. It is simply the expression of the conservation of energy
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems
 Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
Chapter 5: The First Law of Thermodynamics: Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics can be simply stated as follows: during an interaction between a system and its surroundings, the amount of energy
first law of ThermodyNamics
 first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
first law of ThermodyNamics First law of thermodynamics - Principle of conservation of energy - Energy can be neither created nor destroyed Basic statement When any closed system is taken through a cycle,
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes. by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes by Asst. Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics:
Chapter 5. Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes
 Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
Chapter 5 Mass and Energy Analysis of Control Volumes Conservation Principles for Control volumes The conservation of mass and the conservation of energy principles for open systems (or control volumes)
CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Lecture slides by Dr. Fawzi Elfghi
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach 8th Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Çengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2015 CHAPTER 5 MASS AND ENERGY ANALYSIS OF CONTROL VOLUMES Lecture slides by Dr. Fawzi Elfghi
5/6/ :41 PM. Chapter 6. Using Entropy. Dr. Mohammad Abuhaiba, PE
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy 1 2 Chapter Objective Means are introduced for analyzing systems from the 2 nd law perspective as they undergo processes that are not necessarily cycles. Objective: introduce entropy
Chapter 7. Entropy. by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn
 Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
Chapter 7 Entropy by Asst.Prof. Dr.Woranee Paengjuntuek and Asst. Prof. Dr.Worarattana Pattaraprakorn Reference: Cengel, Yunus A. and Michael A. Boles, Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 5th ed.,
Thermodynamics ENGR360-MEP112 LECTURE 7
 Thermodynamics ENGR360-MEP11 LECTURE 7 Thermodynamics ENGR360/MEP11 Objectives: 1. Conservation of mass principle.. Conservation of energy principle applied to control volumes (first law of thermodynamics).
Thermodynamics ENGR360-MEP11 LECTURE 7 Thermodynamics ENGR360/MEP11 Objectives: 1. Conservation of mass principle.. Conservation of energy principle applied to control volumes (first law of thermodynamics).
Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002
 16.050 Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002 Do all eight problems. All problems count the same. 1. A system undergoes a reversible cycle while exchanging heat with three thermal reservoirs, as shown below.
16.050 Thermal Energy Final Exam Fall 2002 Do all eight problems. All problems count the same. 1. A system undergoes a reversible cycle while exchanging heat with three thermal reservoirs, as shown below.
Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I
 ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
ME 00 Thermodynamics I Lecture 44: Review Thermodynamics I Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R. China Email : liyo@sjtu.edu.cn
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit.
 I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
I. (20%) Answer the following True (T) or False (F). If false, explain why for full credit. Both the Kelvin and Fahrenheit scales are absolute temperature scales. Specific volume, v, is an intensive property,
Spring_#8. Thermodynamics. Youngsuk Nam
 Spring_#8 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.krac kr Ch.7: Entropy Apply the second law of thermodynamics to processes. Define a new property called entropy to quantify the secondlaw effects. Establish
Spring_#8 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.krac kr Ch.7: Entropy Apply the second law of thermodynamics to processes. Define a new property called entropy to quantify the secondlaw effects. Establish
ENT 254: Applied Thermodynamics
 ENT 54: Applied Thermodynamics Mr. Azizul bin Mohamad Mechanical Engineering Program School of Mechatronic Engineering Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) azizul@unimap.edu.my 019-4747351 04-9798679 Chapter
ENT 54: Applied Thermodynamics Mr. Azizul bin Mohamad Mechanical Engineering Program School of Mechatronic Engineering Universiti Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP) azizul@unimap.edu.my 019-4747351 04-9798679 Chapter
R13. II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) PART- A
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B) 2. Answer
Week 8. Steady Flow Engineering Devices. GENESYS Laboratory
 Week 8. Steady Flow Engineering Devices Objectives 1. Solve energy balance problems for common steady-flow devices such as nozzles, compressors, turbines, throttling valves, mixers, heaters, and heat exchangers
Week 8. Steady Flow Engineering Devices Objectives 1. Solve energy balance problems for common steady-flow devices such as nozzles, compressors, turbines, throttling valves, mixers, heaters, and heat exchangers
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY. Copyright Hany A. Al-Ansary and S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1
 CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
CHAPTER 7 ENTROPY S. I. Abdel-Khalik (2014) 1 ENTROPY The Clausius Inequality The Clausius inequality states that for for all cycles, reversible or irreversible, engines or refrigerators: For internally-reversible
Chapter 4. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems
 Chapter 4 Energy Analysis of Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics is an expression of the conservation of energy principle. Energy can cross the boundaries of a closed system in the form of heat
Chapter 4 Energy Analysis of Closed Systems The first law of thermodynamics is an expression of the conservation of energy principle. Energy can cross the boundaries of a closed system in the form of heat
Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
+ m B1 = 1. u A1. u B1. - m B1 = V A. /v A = , u B1 + V B. = 5.5 kg => = V tot. Table B.1.
 5.6 A rigid tank is divided into two rooms by a membrane, both containing water, shown in Fig. P5.6. Room A is at 200 kpa, v = 0.5 m3/kg, VA = m3, and room B contains 3.5 kg at 0.5 MPa, 400 C. The membrane
5.6 A rigid tank is divided into two rooms by a membrane, both containing water, shown in Fig. P5.6. Room A is at 200 kpa, v = 0.5 m3/kg, VA = m3, and room B contains 3.5 kg at 0.5 MPa, 400 C. The membrane
Engineering Thermodynamics. Chapter 6. Entropy: a measure of Disorder 6.1 Introduction
 Engineering hermodynamics AAi Chapter 6 Entropy: a measure of Disorder 6. Introduction he second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of
Engineering hermodynamics AAi Chapter 6 Entropy: a measure of Disorder 6. Introduction he second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of
First Law of Thermodynamics
 CH2303 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics I Unit II First Law of Thermodynamics Dr. M. Subramanian 07-July-2011 Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College
CH2303 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics I Unit II First Law of Thermodynamics Dr. M. Subramanian 07-July-2011 Associate Professor Department of Chemical Engineering Sri Sivasubramaniya Nadar College
Thermodynamics of solids 5. Unary systems. Kwangheon Park Kyung Hee University Department of Nuclear Engineering
 Thermodynamics of solids 5. Unary systems Kwangheon ark Kyung Hee University Department of Nuclear Engineering 5.1. Unary heterogeneous system definition Unary system: one component system. Unary heterogeneous
Thermodynamics of solids 5. Unary systems Kwangheon ark Kyung Hee University Department of Nuclear Engineering 5.1. Unary heterogeneous system definition Unary system: one component system. Unary heterogeneous
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A
 ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A 1. What is meant by thermodynamics system? (A/M 2006) Thermodynamics system is defined as any space or matter or group of matter
ME6301- ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS UNIT I BASIC CONCEPT AND FIRST LAW PART-A 1. What is meant by thermodynamics system? (A/M 2006) Thermodynamics system is defined as any space or matter or group of matter
Basic Thermodynamics Module 1
 Basic Thermodynamics Module 1 Lecture 9: Thermodynamic Properties of Fluids Thermodynamic Properties of fluids Most useful properties: Properties like pressure, volume and temperature which can be measured
Basic Thermodynamics Module 1 Lecture 9: Thermodynamic Properties of Fluids Thermodynamic Properties of fluids Most useful properties: Properties like pressure, volume and temperature which can be measured
Chapter 7. Dr Ali Jawarneh. Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University
 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Objectives Apply the second law of thermodynamics to processes. Define a new property called entropy to quantify
Chapter 7 ENTROPY Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Objectives Apply the second law of thermodynamics to processes. Define a new property called entropy to quantify
ME 354 THERMODYNAMICS 2 MIDTERM EXAMINATION. Instructor: R. Culham. Name: Student ID Number: Instructions
 ME 354 THERMODYNAMICS 2 MIDTERM EXAMINATION February 14, 2011 5:30 pm - 7:30 pm Instructor: R. Culham Name: Student ID Number: Instructions 1. This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. 2. Answer all questions
ME 354 THERMODYNAMICS 2 MIDTERM EXAMINATION February 14, 2011 5:30 pm - 7:30 pm Instructor: R. Culham Name: Student ID Number: Instructions 1. This is a 2 hour, closed-book examination. 2. Answer all questions
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 U N IT - 1 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS 1. 1 kg of gas at 1.1 bar, 27 o C is compressed
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI-621213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 U N IT - 1 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS 1. 1 kg of gas at 1.1 bar, 27 o C is compressed
ME 300 Thermodynamics II
 ME 300 Thermodynamics II Prof. S. H. Frankel Fall 2006 ME 300 Thermodynamics II 1 Week 1 Introduction/Motivation Review Unsteady analysis NEW! ME 300 Thermodynamics II 2 Today s Outline Introductions/motivations
ME 300 Thermodynamics II Prof. S. H. Frankel Fall 2006 ME 300 Thermodynamics II 1 Week 1 Introduction/Motivation Review Unsteady analysis NEW! ME 300 Thermodynamics II 2 Today s Outline Introductions/motivations
Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive
 Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
Unit I Classification following properties of the system in Intensive and Extensive Extensive : mass, weight, volume, potential energy, Kinetic energy, Internal energy, entropy, exergy, energy, magnetization
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics. Chapter 7. KFUPM Housam Binous CHE 303
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Chapter 7 1 Thermodynamics of flow is based on mass, energy and entropy balances Fluid mechanics encompasses the above balances and conservation of momentum
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Chapter 7 1 Thermodynamics of flow is based on mass, energy and entropy balances Fluid mechanics encompasses the above balances and conservation of momentum
ME Thermodynamics I
 Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
Homework - Week 01 HW-01 (25 points) Given: 5 Schematic of the solar cell/solar panel Find: 5 Identify the system and the heat/work interactions associated with it. Show the direction of the interactions.
UNIT I Basic concepts and Work & Heat Transfer
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
20 m neon m propane. g 20. Problems with solutions:
 Problems with solutions:. A -m tank is filled with a gas at room temperature 0 C and pressure 00 Kpa. How much mass is there if the gas is a) Air b) Neon, or c) Propane? Given: T7K; P00KPa; M air 9; M
Problems with solutions:. A -m tank is filled with a gas at room temperature 0 C and pressure 00 Kpa. How much mass is there if the gas is a) Air b) Neon, or c) Propane? Given: T7K; P00KPa; M air 9; M
1 st Law Analysis of Control Volume (open system) Chapter 6
 1 st Law Analysis of Control Volume (open system) Chapter 6 In chapter 5, we did 1st law analysis for a control mass (closed system). In this chapter the analysis of the 1st law will be on a control volume
1 st Law Analysis of Control Volume (open system) Chapter 6 In chapter 5, we did 1st law analysis for a control mass (closed system). In this chapter the analysis of the 1st law will be on a control volume
S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks : 100
 Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4162]-189 S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks
Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4162]-189 S.E. (Chemical Engineering) (Second Semester)EXAMINATION, 2012 THERMODYNAMICS-I (2008 PATTERN) Time : Three Hours Maximum Marks
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES. The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial.
 THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 2 THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES SAE
THERMODYNAMICS, FLUID AND PLANT PROCESSES The tutorials are drawn from other subjects so the solutions are identified by the appropriate tutorial. THERMODYNAMICS TUTORIAL 2 THERMODYNAMIC PRINCIPLES SAE
R13 SET - 1 '' ''' '' ' '''' Code No RT21033
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, June - 2015 THERMODYNAMICS (Com. to ME, AE, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
(1)5. Which of the following equations is always valid for a fixed mass system undergoing an irreversible or reversible process:
 Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
Last Name First Name ME 300 Engineering Thermodynamics Exam #2 Spring 2008 March 28, 2008 Form A Note : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) Closed book, closed notes; one 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed. 60 points total; 60 minutes;
Chapter 2: The Physical Properties of Pure Compounds
 Chapter 2: The Physical Properties of Pure Compounds 2-10. The boiler is an important unit operation in the Rankine cycle. This problem further explores the phenomenon of boiling. A. When you are heating
Chapter 2: The Physical Properties of Pure Compounds 2-10. The boiler is an important unit operation in the Rankine cycle. This problem further explores the phenomenon of boiling. A. When you are heating
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS. B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A
 UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
UBMCC11 - THERMODYNAMICS B.E (Marine Engineering) B 16 UNIT I BASIC CONCEPTS AND FIRST LAW PART- A 1. What do you understand by pure substance? 2. Define thermodynamic system. 3. Name the different types
Unified Quiz: Thermodynamics
 Unified Quiz: Thermodynamics October 14, 2005 Calculators allowed. No books or notes allowed. A list of equations is provided. Put your ID number on each page of the exam. Read all questions carefully.
Unified Quiz: Thermodynamics October 14, 2005 Calculators allowed. No books or notes allowed. A list of equations is provided. Put your ID number on each page of the exam. Read all questions carefully.
FINAL EXAM. ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW:
 ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
ME 200 Thermodynamics I, Spring 2013 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: Div. 5 7:30 am Div. 2 10:30 am Div. 4 12:30 am Prof. Naik Prof. Braun Prof. Bae Div. 3 2:30 pm Div. 1 4:30 pm Div. 6 4:30 pm Prof. Chen Prof.
Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts
 Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts 1-1 Thermodynamics and Energy Application Areas of Thermodynamics 1-2 Importance of Dimensions and Units Some SI and English Units Dimensional Homogeneity Unity
Chapter 1 Introduction and Basic Concepts 1-1 Thermodynamics and Energy Application Areas of Thermodynamics 1-2 Importance of Dimensions and Units Some SI and English Units Dimensional Homogeneity Unity
Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S.K Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S.K Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 17 Properties of Pure Substances-I Good morning to all of you. We were discussing
Basic Thermodynamics Prof. S.K Som Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 17 Properties of Pure Substances-I Good morning to all of you. We were discussing
7. Development of the 2nd Law
 7-1 7. Development of the 2nd Law 7.1 1st Law Limitations The 1 st Law describes energy accounting. Once we have a process (or string of processes) we can calculate the relevant energy interactions. The
7-1 7. Development of the 2nd Law 7.1 1st Law Limitations The 1 st Law describes energy accounting. Once we have a process (or string of processes) we can calculate the relevant energy interactions. The
First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems
 First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems Content The First Law of Thermodynamics Energy Balance Energy Change of a System Mechanisms of Energy Transfer First Law of Thermodynamics in Closed Systems Moving
First Law of Thermodynamics Closed Systems Content The First Law of Thermodynamics Energy Balance Energy Change of a System Mechanisms of Energy Transfer First Law of Thermodynamics in Closed Systems Moving
 CHAPTER INTRODUCTION AND BASIC PRINCIPLES. (Tutorial). Determine if the following properties of the system are intensive or extensive properties: Property Intensive Extensive Volume Density Conductivity
CHAPTER INTRODUCTION AND BASIC PRINCIPLES. (Tutorial). Determine if the following properties of the system are intensive or extensive properties: Property Intensive Extensive Volume Density Conductivity
The exergy of asystemis the maximum useful work possible during a process that brings the system into equilibrium with aheat reservoir. (4.
 Energy Equation Entropy equation in Chapter 4: control mass approach The second law of thermodynamics Availability (exergy) The exergy of asystemis the maximum useful work possible during a process that
Energy Equation Entropy equation in Chapter 4: control mass approach The second law of thermodynamics Availability (exergy) The exergy of asystemis the maximum useful work possible during a process that
ESO 201A Thermodynamics
 ESO 201A Thermodynamics Instructor: Sameer Khandekar Tutorial 9 [7-27] A completely reversible heat pump produces heat at arate of 300 kw to warm a house maintained at 24 C. Theexterior air, which is at
ESO 201A Thermodynamics Instructor: Sameer Khandekar Tutorial 9 [7-27] A completely reversible heat pump produces heat at arate of 300 kw to warm a house maintained at 24 C. Theexterior air, which is at
ME 200 Final Exam December 12, :00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m.
 CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 1:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. Mongia Abraham Sojka Bae Naik ME 200 Final Exam December 12, 2011 8:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m. INSTRUCTIONS
CIRCLE YOUR LECTURE BELOW: First Name Last Name 7:30 a.m. 8:30 a.m. 10:30 a.m. 1:30 p.m. 3:30 p.m. Mongia Abraham Sojka Bae Naik ME 200 Final Exam December 12, 2011 8:00 a.m. to 10:00 a.m. INSTRUCTIONS
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011.
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Mehmet Kanoglu University of Gaziantep Copyright The McGraw-Hill
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Mehmet Kanoglu University of Gaziantep Copyright The McGraw-Hill
Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle
 ME 00 Thermodynamics I Spring 015 Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R.
ME 00 Thermodynamics I Spring 015 Lecture 35: Vapor power systems, Rankine cycle Yong Li Shanghai Jiao Tong University Institute of Refrigeration and Cryogenics 800 Dong Chuan Road Shanghai, 0040, P. R.
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, Chapter 7 ENTROPY
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
MAE 320 HW 7B. 1e. For an isolated system, please circle the parameter which will change with time. (a) Total energy;
 MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
MAE 320 HW 7B his comprehensive homework is due Monday, December 5 th, 206. Each problem is worth the points indicated. Copying of the solution from another is not acceptable. Multi-choice, multi-answer
Chapter 1: Basic Definitions, Terminologies and Concepts
 Chapter : Basic Definitions, Terminologies and Concepts ---------------------------------------. UThermodynamics:U It is a basic science that deals with: -. Energy transformation from one form to another..
Chapter : Basic Definitions, Terminologies and Concepts ---------------------------------------. UThermodynamics:U It is a basic science that deals with: -. Energy transformation from one form to another..
ME 201 Thermodynamics
 Spring 01 ME 01 Thermodynamics Property Evaluation Practice Problems II Solutions 1. Air at 100 K and 1 MPa goes to MPa isenthapically. Determine the entropy change. Substance Type: Ideal Gas (air) Process:
Spring 01 ME 01 Thermodynamics Property Evaluation Practice Problems II Solutions 1. Air at 100 K and 1 MPa goes to MPa isenthapically. Determine the entropy change. Substance Type: Ideal Gas (air) Process:
Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Spring 2002
 10.213 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Spring 2002 Test 2 Solution Problem 1 (35 points) High pressure steam (stream 1) at a rate of 1000 kg/h initially at 3.5 MPa and 350 ºC is expanded in a turbine
10.213 Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics Spring 2002 Test 2 Solution Problem 1 (35 points) High pressure steam (stream 1) at a rate of 1000 kg/h initially at 3.5 MPa and 350 ºC is expanded in a turbine
ENTROPY. Chapter 7. Mehmet Kanoglu. Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition. Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles.
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Mehmet Kanoglu Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 7 ENTROPY Mehmet Kanoglu Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required
Thermodynamics II. Week 9
 hermodynamics II Week 9 Example Oxygen gas in a piston cylinder at 300K, 00 kpa with volume o. m 3 is compressed in a reversible adiabatic process to a final temperature of 700K. Find the final pressure
hermodynamics II Week 9 Example Oxygen gas in a piston cylinder at 300K, 00 kpa with volume o. m 3 is compressed in a reversible adiabatic process to a final temperature of 700K. Find the final pressure
Dishwasher. Heater. Homework Solutions ME Thermodynamics I Spring HW-1 (25 points)
 HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
HW-1 (25 points) (a) Given: 1 for writing given, find, EFD, etc., Schematic of a household piping system Find: Identify system and location on the system boundary where the system interacts with the environment
Thermodynamics I. Properties of Pure Substances
 Thermodynamics I Properties of Pure Substances Dr.-Eng. Zayed Al-Hamamre 1 Content Pure substance Phases of a pure substance Phase-change processes of pure substances o Compressed liquid, Saturated liquid,
Thermodynamics I Properties of Pure Substances Dr.-Eng. Zayed Al-Hamamre 1 Content Pure substance Phases of a pure substance Phase-change processes of pure substances o Compressed liquid, Saturated liquid,
Thermodynamics I Spring 1432/1433H (2011/2012H) Saturday, Wednesday 8:00am - 10:00am & Monday 8:00am - 9:00am MEP 261 Class ZA
 Thermodynamics I Spring 1432/1433H (2011/2012H) Saturday, Wednesday 8:00am - 10:00am & Monday 8:00am - 9:00am MEP 261 Class ZA Dr. Walid A. Aissa Associate Professor, Mech. Engg. Dept. Faculty of Engineering
Thermodynamics I Spring 1432/1433H (2011/2012H) Saturday, Wednesday 8:00am - 10:00am & Monday 8:00am - 9:00am MEP 261 Class ZA Dr. Walid A. Aissa Associate Professor, Mech. Engg. Dept. Faculty of Engineering
T098. c Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq (BUET) First Law of Thermodynamics ME 201 (2012) 2 / 26
 Conservation of Energy for a Closed System Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET Dhaka-, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Conservation of Energy for a Closed System Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET Dhaka-, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
 Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Two mark questions and answers UNIT II SECOND LAW 1. Define Clausius statement. It is impossible for a self-acting machine working in a cyclic process, to transfer heat from a body at lower temperature
Engineering Thermodynamics
 David Ng Summer 2017 Contents 1 July 5, 2017 3 1.1 Thermodynamics................................ 3 2 July 7, 2017 3 2.1 Properties.................................... 3 3 July 10, 2017 4 3.1 Systems.....................................
David Ng Summer 2017 Contents 1 July 5, 2017 3 1.1 Thermodynamics................................ 3 2 July 7, 2017 3 2.1 Properties.................................... 3 3 July 10, 2017 4 3.1 Systems.....................................
Chapter 7. Entropy: A Measure of Disorder
 Chapter 7 Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Entropy and the Clausius Inequality The second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of microscopic
Chapter 7 Entropy: A Measure of Disorder Entropy and the Clausius Inequality The second law of thermodynamics leads to the definition of a new property called entropy, a quantitative measure of microscopic
This follows from the Clausius inequality as a consequence of the second law of thermodynamics. Therefore. (for reversible process only) (22.
 Entropy Clausius inequality can be used to analyze the cyclic process in a quantitative manner. The second law became a law of wider applicability when Clausius introduced the property called entropy.
Entropy Clausius inequality can be used to analyze the cyclic process in a quantitative manner. The second law became a law of wider applicability when Clausius introduced the property called entropy.
PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES. Chapter 3. Mehmet Kanoglu. Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition. Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A.
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES Mehmet Kanoglu Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach, 6 th Edition Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2008 Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES Mehmet Kanoglu Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
ME Thermodynamics I. Lecture Notes and Example Problems
 ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
ME 227.3 Thermodynamics I Lecture Notes and Example Problems James D. Bugg September 2018 Department of Mechanical Engineering Introduction Part I: Lecture Notes This part contains handout versions of
SHRI RAMSWAROOP MEMORIAL COLLEGE OF ENGG. & MANAGEMENT
 B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1) 2 kg of an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically from pressure
B.Tech. [SEM III (ME-31, 32, 33,34,35 & 36)] QUIZ TEST-1 Time: 1 Hour THERMODYNAMICS Max. Marks: 30 (EME-303) Note: Attempt All Questions. Q1) 2 kg of an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically from pressure
Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy
 Definition of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy - Some definitions. - The zeroth law. - Properties of pure substances. - Ideal gas law. - Entropy and the second law. Some
Definition of Thermodynamics: Thermodynamics is the Science of Energy and Entropy - Some definitions. - The zeroth law. - Properties of pure substances. - Ideal gas law. - Entropy and the second law. Some
c Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq (BUET) Thermodynamic Processes & Efficiency ME 6101 (2017) 2 / 25 T145 = Q + W cv + i h 2 = h (V2 1 V 2 2)
 Thermodynamic Processes & Isentropic Efficiency Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
Thermodynamic Processes & Isentropic Efficiency Dr. Md. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh zahurul@me.buet.ac.bd
SKMM 2413 Thermodynamics
 SKMM 2413 Thermodynamics Md. Mizanur Rahman, PhD Department of Thermo-Fluids Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia UTM Office: C23-228 mizanur@fkm.utm.my Semester I, 2016-2017
SKMM 2413 Thermodynamics Md. Mizanur Rahman, PhD Department of Thermo-Fluids Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Universiti Teknologi Malaysia UTM Office: C23-228 mizanur@fkm.utm.my Semester I, 2016-2017
Spring_#7. Thermodynamics. Youngsuk Nam.
 Spring_#7 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.kr You can t connect the dots looking forward; you can only connect them looking backwards. So you have to trust that the dots will somehow connect in
Spring_#7 Thermodynamics Youngsuk Nam ysnam1@khu.ac.kr You can t connect the dots looking forward; you can only connect them looking backwards. So you have to trust that the dots will somehow connect in
Where F1 is the force and dl1 is the infinitesimal displacement, but F1 = p1a1
 In order to force the fluid to flow across the boundary of the system against a pressure p1, work is done on the boundary of the system. The amount of work done is dw = - F1.dl1, Where F1 is the force
In order to force the fluid to flow across the boundary of the system against a pressure p1, work is done on the boundary of the system. The amount of work done is dw = - F1.dl1, Where F1 is the force
Readings for this homework assignment and upcoming lectures
 Homework #3 (group) Tuesday, February 13 by 4:00 pm 5290 exercises (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm extra credit (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm Readings for this homework assignment
Homework #3 (group) Tuesday, February 13 by 4:00 pm 5290 exercises (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm extra credit (individual) Thursday, February 15 by 4:00 pm Readings for this homework assignment
Week 5. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems. GENESYS Laboratory
 Week 5. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems Objectives 1. Examine the moving boundary work or PdV work commonly encountered in reciprocating devices such as automotive engines and compressors 2. Identify
Week 5. Energy Analysis of Closed Systems Objectives 1. Examine the moving boundary work or PdV work commonly encountered in reciprocating devices such as automotive engines and compressors 2. Identify
Chapter 6. Using Entropy
 Chapter 6 Using Entropy Learning Outcomes Demonstrate understanding of key concepts related to entropy and the second law... including entropy transfer, entropy production, and the increase in entropy
Chapter 6 Using Entropy Learning Outcomes Demonstrate understanding of key concepts related to entropy and the second law... including entropy transfer, entropy production, and the increase in entropy
Dr Ali Jawarneh. Hashemite University
 Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Examine the moving boundary work or P d work commonly encountered in reciprocating devices such as automotive engines and compressors.
Dr Ali Jawarneh Department of Mechanical Engineering Hashemite University Examine the moving boundary work or P d work commonly encountered in reciprocating devices such as automotive engines and compressors.
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
 BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER. 12 June 2006
 ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 1 June 006 Midterm Examination R. Culham This is a hour, closed-book examination. You are permitted to use one 8.5 in. 11 in. crib sheet (one side
ECE309 INTRODUCTION TO THERMODYNAMICS & HEAT TRANSFER 1 June 006 Midterm Examination R. Culham This is a hour, closed-book examination. You are permitted to use one 8.5 in. 11 in. crib sheet (one side
Eng Thermodynamics I conservation of mass; 2. conservation of energy (1st Law of Thermodynamics); and 3. the 2nd Law of Thermodynamics.
 Eng3901 - Thermodynamics I 1 1 Introduction 1.1 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics is the study of the relationships between heat transfer, work interactions, kinetic and potential energies, and the properties
Eng3901 - Thermodynamics I 1 1 Introduction 1.1 Thermodynamics Thermodynamics is the study of the relationships between heat transfer, work interactions, kinetic and potential energies, and the properties
Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
 Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach Seventh Edition in SI Units Yunus A. Cengel, Michael A. Boles McGraw-Hill, 2011 Chapter 3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
ME 2322 Thermodynamics I PRE-LECTURE Lesson 10 Complete the items below Name:
 Lesson 10 1. (5 pt) If P > P sat (T), the phase is a subcooled liquid. 2. (5 pt) if P < P sat (T), the phase is superheated vapor. 3. (5 pt) if T > T sat (P), the phase is superheated vapor. 4. (5 pt)
Lesson 10 1. (5 pt) If P > P sat (T), the phase is a subcooled liquid. 2. (5 pt) if P < P sat (T), the phase is superheated vapor. 3. (5 pt) if T > T sat (P), the phase is superheated vapor. 4. (5 pt)
Objectives. Conservation of mass principle: Mass Equation The Bernoulli equation Conservation of energy principle: Energy equation
 Objectives Conservation of mass principle: Mass Equation The Bernoulli equation Conservation of energy principle: Energy equation Conservation of Mass Conservation of Mass Mass, like energy, is a conserved
Objectives Conservation of mass principle: Mass Equation The Bernoulli equation Conservation of energy principle: Energy equation Conservation of Mass Conservation of Mass Mass, like energy, is a conserved
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 621 213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS UNIT-I Basic Concept and First Law 1. What do you understand
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE TIRUCHIRAPALLI 621 213. Department: Mechanical Subject Code: ME2202 Semester: III Subject Name: ENGG. THERMODYNAMICS UNIT-I Basic Concept and First Law 1. What do you understand
KNOWN: Pressure, temperature, and velocity of steam entering a 1.6-cm-diameter pipe.
 4.3 Steam enters a.6-cm-diameter pipe at 80 bar and 600 o C with a velocity of 50 m/s. Determine the mass flow rate, in kg/s. KNOWN: Pressure, temperature, and velocity of steam entering a.6-cm-diameter
4.3 Steam enters a.6-cm-diameter pipe at 80 bar and 600 o C with a velocity of 50 m/s. Determine the mass flow rate, in kg/s. KNOWN: Pressure, temperature, and velocity of steam entering a.6-cm-diameter
CLASS Fourth Units (Second part)
 CLASS Fourth Units (Second part) Energy analysis of closed systems Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. MOVING BOUNDARY WORK Moving boundary work (P
CLASS Fourth Units (Second part) Energy analysis of closed systems Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. MOVING BOUNDARY WORK Moving boundary work (P
Applied Thermodynamics for Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Applied Thermodynamics for Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No - 03 First Law of Thermodynamics (Open System) Good afternoon,
Applied Thermodynamics for Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No - 03 First Law of Thermodynamics (Open System) Good afternoon,
University of Engineering & Technology Lahore. (KSK Campus)
 Course File Session-2015 Semester: Fall 2016 MT-24: Thermodynamics for Technologists Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Engineering & Technology Lahore. (KSK Campus) Course File Contents
Course File Session-2015 Semester: Fall 2016 MT-24: Thermodynamics for Technologists Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Engineering & Technology Lahore. (KSK Campus) Course File Contents
Unified Quiz: Thermodynamics
 Fall 004 Unified Quiz: Thermodynamics November 1, 004 Calculators allowed. No books allowed. A list of equations is provided. Put your name on each page of the exam. Read all questions carefully. Do all
Fall 004 Unified Quiz: Thermodynamics November 1, 004 Calculators allowed. No books allowed. A list of equations is provided. Put your name on each page of the exam. Read all questions carefully. Do all
Pure Substance. Properties of Pure Substances & Equations of State. Vapour-Liquid-Solid Phase Equilibrium
 Pure Substance Properties of Pure Substances & Equations of State Dr. d. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of echanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET) Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh
Pure Substance Properties of Pure Substances & Equations of State Dr. d. Zahurul Haq Professor Department of echanical Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology (BUET) Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh
ME 201 Thermodynamics
 ME 0 Thermodynamics Solutions First Law Practice Problems. Consider a balloon that has been blown up inside a building and has been allowed to come to equilibrium with the inside temperature of 5 C and
ME 0 Thermodynamics Solutions First Law Practice Problems. Consider a balloon that has been blown up inside a building and has been allowed to come to equilibrium with the inside temperature of 5 C and
Non-Newtonian fluids is the fluids in which shear stress is not directly proportional to deformation rate, such as toothpaste,
 CHAPTER1: Basic Definitions, Zeroth, First, and Second Laws of Thermodynamics 1.1. Definitions What does thermodynamic mean? It is a Greeks word which means a motion of the heat. Water is a liquid substance
CHAPTER1: Basic Definitions, Zeroth, First, and Second Laws of Thermodynamics 1.1. Definitions What does thermodynamic mean? It is a Greeks word which means a motion of the heat. Water is a liquid substance
Content. Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas.
 Entropy Content Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas. Entropy Entropy can be viewed as a measure of molecular disorder, or molecular randomness. As a system becomes
Entropy Content Entropy and principle of increasing entropy. Change of entropy in an ideal gas. Entropy Entropy can be viewed as a measure of molecular disorder, or molecular randomness. As a system becomes
Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall 2006
 FINAL EXAM Date: Thursday, December 21, 2006, 9 am 12 am Examiner: Prof. E. Timofeev Associate Examiner: Prof. D. Frost READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU PROCEED: Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall
FINAL EXAM Date: Thursday, December 21, 2006, 9 am 12 am Examiner: Prof. E. Timofeev Associate Examiner: Prof. D. Frost READ CAREFULLY BEFORE YOU PROCEED: Course: MECH-341 Thermodynamics II Semester: Fall
CM 3230 Thermodynamics, Fall 2016 Lecture 16
 CM 3230 Thermodynamics, Fall 2016 Lecture 16 1. Joule-Thomsom Expansion - For a substance flowing adiabatically through a throttle (valve or pourous plug): in > out and negligible change in kinetic and
CM 3230 Thermodynamics, Fall 2016 Lecture 16 1. Joule-Thomsom Expansion - For a substance flowing adiabatically through a throttle (valve or pourous plug): in > out and negligible change in kinetic and
10 minutes reading time is allowed for this paper.
 EGT1 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IB Tuesday 31 May 2016 2 to 4 Paper 4 THERMOFLUID MECHANICS Answer not more than four questions. Answer not more than two questions from each section. All questions carry the
EGT1 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IB Tuesday 31 May 2016 2 to 4 Paper 4 THERMOFLUID MECHANICS Answer not more than four questions. Answer not more than two questions from each section. All questions carry the
1. (10) Calorically perfect ideal air at 300 K, 100 kpa, 1000 m/s, is brought to rest isentropically. Determine its final temperature.
 AME 5053 Intermediate Thermodynamics Examination Prof J M Powers 30 September 0 0 Calorically perfect ideal air at 300 K, 00 kpa, 000 m/s, is brought to rest isentropically Determine its final temperature
AME 5053 Intermediate Thermodynamics Examination Prof J M Powers 30 September 0 0 Calorically perfect ideal air at 300 K, 00 kpa, 000 m/s, is brought to rest isentropically Determine its final temperature
