NSEP EXAMINATION
|
|
|
- Chloe Edwards
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
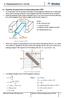
1 NSE 00-0 EXAMINATION CAEE OINT INDIAN ASSOCIATION OF HYSICS TEACHES NATIONAL STANDAD EXAMINATION IN HYSICS 00-0 Tal ie : 0 inues (A-, A- & B) AT - A (Tal Maks : 80) SUB-AT A- Q. Displaceen f an scillaing paicle is gien by y A sin (Bx + C + D). The diensinal fula f [ABCD] is - (A) [M 0 L T 0 ] (B) [M 0 L 0 T ] (C) [M 0 L T ] (D) [M 0 L 0 T 0 ] Apply he ules f diensinal analysis. The quaniy A us hae he diensins f displaceen. The backeed quaniy us be diensinless and hence, B us hae he diensins f ecipcal f displaceen, C us hae he diensins f ecipcal f ie and D us be diensinless. Q. Tw sall sphees f equal asses sa ing in ppsie diecins f a pin A in a hiznal cicula bi wih angenial elciies and especiely. Beween cllisins, he sphees e wih cnsan speeds. The nube f elasic cllisins he sphees will ake befe hey each pin A again is - (A) 4 (B) (C) (D) [C] efe he figue. The fis cllisin will ake place a pin B. Due elasic cllisin, he sphees will exchange hei elciies and cllide a pin C, again hee will be an exchange f elciies and he bdies will ce pin A cllide f he nex ie. A sping balance and disance f hk f he hinge pin f he inclined plane. The gaph ha cecly epesens his aiain is : (A) (C) f f d 4 5 (B) (D) Sping balance d d [A] The eading n he sping balance is he fce equied lif he plane. Since he angula displaceen is he sae eey ie, he wk dne is fixed and hence he que. In he wds he pduc f fce and disance f pin f applicain f fce f he hinge us be cnsan. f f d B C Q. On ne a f an inclined plane 5 hks ae fixed (a he sae sepaain) lif he uppe a elaie he he a kep hiznal as shwn. The hk fixed n he inclined plane is lifed hugh he sae angle wih he help f a sping balance, using hk,,, 4, 5 in de. A gaph is pled beween he eading f Q.4 Idenical pin asses ae placed a (n ) eices f a egula plygn f n sides. The acan eex has a psiin ec a wih espec he cene f he plygn. Theefe, he psiin ec f he cene f ass f he syse is - (A) (n ) a a (B) (C) na (D) (n ) a n CAEE OINT, C Twe, ad N., IIA, Ka (aj.) h.: /
2 NSE 00-0 EXAMINATION CAEE OINT Ne ha he cene f ass will ge shifed in he ppsie diecin wih efeence he psiin ec f he acan eex Q.5 Thee idenical balls ing gehe alng a hiznal line wih elciy cllide wih w siila balls a es alng he sae line. The cllisin is elasic. Afe he cllisin - (A) w balls e wih elciy. (B) w balls e wih elciy (C) hee balls e wih elciy (D) hee balls e wih elciy [C] As pe he law f cnseain f linea enu, he w balls iginally a es alng wih ne f hse aleady in in will e wih elciy. Tw f he hee balls iginally ing will naually ce es. Q.6 A blck is placed n a suface wih eical x css secin gien by he equain y. If 0 he cefficien f ficin is 0.5, he axiu heigh abe he gund a which a blck can be placed wihu slipping is - (A).00 (B).5 (C).50 (D).90 By dawing he usual fee bdy diaga, we can wie, in equilibiu g sin θ µ s N and g cs θ N giing an θ µ s. Bu an dy x x θ. This gies 0.5 dx 0 0 x 5. x Use his alue in he equain y 0 axiu heigh y.5 ge Q.7 Le L be he lengh and d be he diaee f css secin f a wie. Diffeen lenghs f wie f he sae aeial ae subjeced he sae ensin. In which f he fllwing cases will he exensin be axiu? (A) L 00 c, d.0 (B) L 00 c, d 0.5 (C) L 00 c, d 0. (D) L 50 c, d 0.05 [D] L L Exensin l l A. The exensin d is biusly axiu in case f pin (d). Q.8 Cnside an expessin F Ax sin (B) whee F epesens fce, x epesens disance and epesens ie. Diensinally he quaniy AB epesens - (A) enegy (B) suface ensin (C) inensiy f ligh (D) pessue [C] Diensinal analysis suggess ha he quaniy Ax n HS us hae he diensins f fce wheeas B us hae he diensins f ecipcal f ie. Then, he pduc AB will hae he diensins f enegy pe uni aea pe uni ie, he sae as hse f inensiy f ligh. Q.9 Velciy displaceen cue f a paicle ing in a saigh line is as shwn. Line B is nal he cue and line A is nal he X axis. The insananeus acceleain f he paicle a is /s (0, 4) O A(, 0) B(, 0) S (A) /s (B).5 /s (C) /s (D) ze [C] d Acceleain can be wien as an θ ds whee (an θ) is he slpe f he gien cue and he sybls hae hei usual eanings. Since he slpe f B is 4. The slpe f he cue an θ 4. uing hese alues, we ge he acceleain as /s. Q.0 Suppse ha he gaiainal fce aies inesely as he n h pwe f he disance. Then, he peid f a plane in cicula bi f adius aund he sun will be ppinal - n+ (A) (C) n n (B) (D) n/ CAEE OINT, C Twe, ad N., IIA, Ka (aj.) h.: /
3 NSE 00-0 EXAMINATION CAEE OINT [A] In his case we can wie, GM n ω π T 4π T GM This gies he desied esul. n+. Q. In he cicui shwn, he penial diffeences acss C and C ae especiely 400 Ω C 5 µf G 00 Ω Q. A plane f ass es aund he sun f ass M in an ellipical bi. The axiu and iniu disances f he plane f he sun ae and especiely. Theefe, he ie peid f he plane is ppinal - (A) ( + ) (B) ( + ) / (C) ( + ) / (D) ( + ) 4 The sei-aj axis f he ellipical bi f + plane aund he sun is. Wih he sun a he fcus, Keple's law hen gies he ppinaliy. Q. One le f an ideal is aken f an iniial sae A ( 0, V 0 ) a final sae B ( 0, V 0 ) by w diffeen pcesses. () Gas expands isheally duble is lue and hen pessue is dubled a cnsan lue he final sae. () Gas is cpessed isheally unil is pessue is dubled and hen is lue is dubled a cnsan pessue he final sae. The p -V diaga ha cecly epesen he w pcesses is : p 0 B p 0 B (A) p 0 A (B) p 0 A O 0 0 V O 0 0 V p 0 B p 0 B (C) p 0 A (D) p 0 O 0 0 V O 0 0 V [C] Since he fis sep in bh he pcesses is isheal, we hae pv cnsan giing he pv diaga he shape f a ecangula hypebla. This is bseed in pin (C) nly and hence he answe. C 4 µf 500 Ω.0 V (A) l, l (B) l,. l (C) l, l (D) l, l The al cuen in he cicui flws hugh he w esiss and he galanee nly and i is equal A. This pduces a dp f l acss C and a dp f. l acss C. Q.4 A ball is dpped f a heigh h abe a hiznal cncee suface. The cefficien f esiuin f he cllisin inled is e. The ie afe which he ball sps buncing is - (A) h g e (B) h g e h + e h (C) (D) g e g e [C] The ie equied f he fee fall f he ball is h. Then he ie aken f ise and nex fall g h will be (e). The ie aken f ne e g h ise and fall will be (e ) ec. Theefe, g he al ie f which he ball will be in in, will be h h + e( + e + e +.) g g h h h e + e + g g e g e This n siplificain gies he esul. Q.5 A eal blck is esing n a ugh wden suface. A hiznal fce applied he blck is inceased unifly. Which f he fllwing cues cecly epesens elciy f he blck? CAEE OINT, C Twe, ad N., IIA, Ka (aj.) h.: /
4 NSE 00-0 EXAMINATION CAEE OINT (A) (C) (B) (D) [C] Le f µ s N a. Theefe, 0 f <. F > ne fce n he blck k b whee d b µ k N. Theefe, k b d k b A +. Nw, A 0 since 0 a 0. Thus, gaph f agains is a paablic cue as in (c). Q.6 The eah has ass M and adius. Siilaly he sun has ass M and adius. Disance beween hei cenes is. I is knwn ha he cene f ass f he eah-sun syse lies well wihin he sun. Theefe. M M (A) > (B) < M + M M + M (C) M < M (D) M > M Disance f cene f ass f cene f he sun M will be. Since he cene f ass lies M + M wihin he sun esul. M M + M < and hence he Q.7 Cnside a paicle f a igid bdy. Is in can be descibed by ecs, ω, a,a,and α (sybls hae hei usual eanings). Then, which f he fllwing equains is incec? dθ (A) ω (B) ω d (C) ω ( ω ) (D) α a a Vec elain beween linea elciy and angula elciy is ω, s ha pin (b) is incec. Q.8 Thee enegy leels A, B and C in an aic syse ae such ha E A < E B < E C. If he waelenghs cespnding he ansiins C B, B A and C A ae λ, λ and λ especiely, hen (A) λ + λ + λ 0 (B) λ λ + λ (C) λ λ + λ (D) λ [D] λλ λ + λ In es f enegy diffeences, we can wie E CA E CB + E BA. This can fuhe be wien as hc hc hc + and hence he esul. λ λ λ Q.9 The efacing angle f a pis is A and efacie index is c (A/). The angle f iniu deiain is - (A) (80 A) (B) (80 A) (C) (90 A) (D) (90 A) Use he pis fula A + δ sin µ A sin c A A A + δ cs sin A A sin sin A + δ sin A sin A A + δ cs sin. This sugges ha he angles n he w sides ae cpleenay, A A + δ ha is, This can be siplified ge he esul. CAEE OINT, C Twe, ad N., IIA, Ka (aj.) h.: /
5 NSE 00-0 EXAMINATION CAEE OINT Q.0 efe he aangeen f lgic gaes. F A 0, B 0 and A, B 0, he alues f upu Y ae, especiely - A B Y (A) 0 and (B) and 0 (C) and (D) 0 and 0 efe he uh ables f AND, O and NO gaes f any sandad bk. Q. A plasic ing f adius has a chage + Q disibued unifly alng ne quae f is cicufeence and a chage Q unifly disibued alng he es f he cicufeence. The penial n is axis a a disance f is - (A) Q 4πε 0 (B) 4Q 4πε 0 Q (C) 4πε (D) 0 4πε 0 [C] Using sandad elain, he penial Q Q Q πε which n siplificain gies he answe. Q. The figue shws fu ienains, a angle θ wih a agneic field B, f a agneic diple wih en M. The agniude f que (τ) and penial enegy (U) is bes epesened by 4 θ θ θ θ B Q. A cylindical essel cnains a liquid f densiy p filled up a heigh h. The uppe suface f he liquid is in cnac wih a pisn f ass and aea f css secin A. A sall hle is dilled a he b f he essel. (Neglec he iscus effecs). The speed wih which he liquid ces u f he hle is - (A) gh (B) g h + pa (C) g h + (D) pa g h + pa Use Benulli's hee a he uppe suface and a he sall hle. We ge an equain g pgh + ρ whee is he speed f A efflux. Sling his we ge he expessin f speed g gh + g h +. ρa ρa Q.4 A chaged capaci dischages hugh a esisance. Le U be he enegy sed by he capaci and le be he ae a which enegy ges dissipaed. Then, he ie cnsan is : 4U U U U (A) (B) (C) (D) [C] Take he ai f he enegy sed in he capaci he pwe dissipaed. ha is, CV U C U C. V Q.5 The fllwing figue shws diffeen aangeens f w idenical pieces f plancnex lenses. The efacie index f he liquid used is equal ha f he glass. Then, he effecie fcal lenghs in he hee cases ae elaed as (A) τ τ, τ τ 4 and U U U U 4 (B) τ τ τ τ 4 and U U 4, U U (C) τ τ 4, τ τ and U U U U 4 (D) τ τ τ τ 4 and U U U U 4 Ne ha he agniude f he que acing n he diple is τ MB sin θ and penial enegy is U MB cs θ. f f f liquid (A) f f, f 0 (B) f f f (C) f f > f (D) Nne f he abe CAEE OINT, C Twe, ad N., IIA, Ka (aj.) h.: /
6 NSE 00-0 EXAMINATION CAEE OINT [D] The fcal lenghs f and f ae equal. The aangeen in he hid case is effeciely a plae and hence has an infinie fcal lengh. Q.6 A lng wie caying a cuen A is placed alng he axis f a lng hllw ube f adius 5 c als caying a cuen f A in he sae diecin. The agneic field a a disance f.5 c f he axis is : (A) T (B) T (C) T (D) Ze [A] Ne ha he cuen hugh he wie nly will cnibue he agneic field a a pin inside he hllw ube. Q.7 A Unif slid sphee f ass has a adius. The gaiainal penial a a disance (< ) f he cene f he sphee is : G G (A) ( ) (B) ( ) G G (C) ( ) (D) ( ) [C] The gaiainal penial a a disance <, is ade up f w pas ne due he ass f sphee f adius, say V and ha due he eaining ass, say V. One finds ha GM G V and V ( ), and hen by adding ne ges he esul. efe any sandad bk. Q.8 The fcal lengh f a cncae i is f. An bjec is placed a a disance x f he fcus and fs a eal iage. Theefe, he agnificain (nueically) is : f f x x (A) (B) (C) (D) x x f f [A] Since he iage fed is eal he bjec us be beynd he fcus. Theefe, aking he bjec disance be (f + x) and using i fula, f (f + x) we ge he iage disance as and hen x f he agnificain. u x Q.9 A phn f waelengh λ (less han heshld waelengh λ 0 ) is inciden n a eal suface f wk funcin W 0. The de Bglie waelengh f he ejeced elecn f ass is : hc h (A) h W 0 (B) λ hc W 0 λ h (C) (D) hc hc W 0 h W 0 λ λ [] hc Wih usual nain, E k W0. Als if p is λ p he enu f he phelecn, E k p Ek. Thus, he de Bglie waelengh f he ejeced elecn h h λ which ne subsiuin gies p E k he answe. Q.0 In he fllwing V-T diaga f a pefec gas, he elain beween p and p is : V p T O (A) p p (B) p < p (C) p > p (D) unceain Ne ha he slpe f he V-T diaga is inesely ppinal pessue p. Q. A phgaphic plae placed a a disance f 0 c f a pin suce is expsed f a 4 secnd. If he plae is ed fahe away by 0 c, he ie equied hae he sae expsue (A) 4 secnd (B) 6 secnd (C) 8 secnd (D) 64 secnd Accding he inese squae law, illuinance is inesely ppinal squae f he disance. p CAEE OINT, C Twe, ad N., IIA, Ka (aj.) h.: /
7 NSE 00-0 EXAMINATION CAEE OINT Q. The lage e a cycle aies as π V 0 sin ω f 0 ω π π V 0 sin ω f ω ω The aeage alue f he lage f ne cycle is : V (A) 0 V (B) 0 V (C) ze (D) 0 π [D] The lage epesens he upu f a full wae ecifie whse de cpnen he aeage V alue is 0. π Q. Yung's duble sli expeien is fis pefed in ai and hen by iesing he whle seup in a liquid. The 0 h bigh finge when in liquid is fed a he pin whee 8 h dak finge is lcaed when in ai. The efacie index f he liquid is : (A).5 (B). (C).40 (D).0 λd Finge widh w whee sybls hae hei d usual eanings. Ne ha waelengh λ in ai changes µ λ in a liquid f efacie index µ. Nw, we can wie 0 w liq 7.5 w ai λliqd λaid λai λ ai. d d µ This hen gies µ Q.4 A spheical shell ade f a eal f densiy ρ eains jus belw he suface f a liquid f densiy ρ l. If and ae especiely he inne and he ue adii f he shell, hen, he ai is : (A) ρ (C) ρ l ρ l (B) ρ ρ l ρ ρ (D) l ρ Using he law f flaain, we equae he weigh f he bdy he uphus and ge 4 π( 4 )ρ g π ρ g ρ and he esul fllws. ρ Q.5 A eal sip 6 c lng, 0.6 c wide and 0.7 hick es wih cnsan elciy hugh a unif agneic field f inducin 0.9 T dieced pependicula he sip as shwn. A penial diffeence f.6 µv is induced acss pins M and N f he sip. Theefe, he speed is : M N (A) 0. /s (B) 0. /s (C) 0. /s (D) 0.4 /s [] E in wding, quesin deleed. Q.6 The ai f agneic field a he cene f a cuen caying cicula cil is agneic en is x. If he cuen and he adius bh ae dubled, he alue f his ai wuld be (A) x (B) 4x (C) x/4 (D) x/8 [D] Ne ha agneic field a he cene f a cuen µ ni caying cil is 0 and is agneic en is π nl. Theefe hei ai aies inesely as. Q.7 A cnducing ing f adius is placed in a aying agneic field pependicula he plane f he ing. If he ae a which he agneic field aies is x, he elecic field inensiy a any pin f he ing is - (A) x (B) x/ (C) x (D) 4 /x CAEE OINT, C Twe, ad N., IIA, Ka (aj.) h.: /
8 NSE 00-0 EXAMINATION CAEE OINT Le E be he elecic field inensiy a a pin n he cicufeence f he ing. Then, he ef induced ε E dl f he ing. Since E whee d l is a lengh eleen is cnsan and E dl, he inegal wks u be E (π). Als he induced dφ ef is ε π db π x. Equaing he d d w, we ge he esul. Q.8 Unplaized ligh inensiy f W/ passes hugh hee plaizes. The ansissin axis f he las plaize is cssed wih ha f he fis. If he inensiy f ligh eeging u f he hid plaize is W/, hen he angle beween he ansissin axis f he fis w plaizes is (A) 0 (B) 0 (C) 45 (D) 60 Le he angle beween he axes f he fis w plaizes be θ. The inensiy afe he fis plaize is half f ha inciden n i, ha is 6 W/. The inensiy afe he secnd plaize will be 6 cs θ W/. The inensiy afe he hid plaize can be wien as (6 cs θ) cs (90 θ) since he angle beween he axes f he secnd and he hid plaizes is (90 θ). This gies n siplificain, sin (θ) q 60 θ 0. Q.9 Tw sap bubbles f adii and ae in cnac wih each he. The adius f cuaue f he ineface beween he bubbles is - (A) (B) 6 (C) (D) Excess pessue diffeence acss he ineface is 4T 4T 4T 4T which us be whee is 6 he adius f cuaue a he ineface. This gies 6. Q.40 A adiacie eleen X cnes in anhe sable eleen Y. Half life f X is hs. Iniially nly nuclei f X ae pesen. Afe ie, he ai f nube f nuclei f X ha f Y is fund be : 8. Theefe, (A) 9 hs (B) 6hs (C) 7.5 hs (D) is beween 6 hs and 9 hs [] E in wding, quesin deleed. SUB - AT - A - Q.4 A hp lls dwn an inclined plane wihu slipping. Then, (A) he inclined plane is sh (B) he inclined plane is ugh and sill hee is n lss f echanical enegy (C) he pin f cnac f he hp wih he inclined plane is always a es (D) he linea speeds f diffeen pins n he i f he hp ae diffeen [C, D] efe any sandad bk. Q.4 Which f he fllwing phenena is / ae elaed he aiain in densiy f aspheic ai? (A) iage (B) in wine sund f a whisle f a ailway engine is head a uch lnge disances (C) winkling f a sa (D) isibiliy f sun f se ie afe he sunse [A,B,C,D] All he phenena e due fain f layes f aspheic ai wih diffeen densiies and hence efacie indices. Q.4 The gaph shws he displaceen f a bdy as a funcin f ie. Which f he fllwing is / ae he cnclusin? x (A) The gaph epesens in wih cnsan elciy (B) The gaph epesens acceleaed in (C) The bdy ces es afe a lng ie (D) The gaph epesens a eaded in [C, D] Slpe f he cue a a pin is he elciy which is deceasing in his case and hence he bdy is deceleaing. The gaph is ising expnenially and heefe he bdy will ake a lng ie ce es. CAEE OINT, C Twe, ad N., IIA, Ka (aj.) h.: /
9 NSE 00-0 EXAMINATION CAEE OINT Q.44 A ansis is cnneced in cn eie de. The cllec supply is 0 l and lage dp acss esis f kω in he cllec cicui is 0.5 l. If he cuen gain is β is 49, hen (A) he base cuen is 50 µa (B) cuen gain α is (C) he eie cuen is abu 50 µa (D) he base cuen is 0 µa [B, C] 0.5 The cllec cuen is biusly A. use he sandad elains f he cuen gains α, β and he elain beween he α β. Als ne ha I E I B + I C. α Q.45 The aiain f gaiainal field inensiy wih disance f he cene f a bdy is shwn in he gaph f which ne can cnclude ha E g [A, B, C] Since in case f a esis he lage and he cuen ae in phase, pin (d) is n pssible. Due eacie cpnen capaci he pins gien ae pssible. Q.47 A pesn is siing in a ing ain and is facing he engine. He sses up a cin which falls behind hi. He cncludes ha he ain is ing - (A) fwad wih inceasing speed (B) fwad wih deceasing speed (C) backwad wih inceasing speed (D) backwad wih deceasing speed [A, D] Only in case f fwad acceleain and backwad deceleain is he gien bseain pssible. Q.48 F an LC cicui A B C E g 4 O (A) aiain f gaiainal field inensiy is due he spheical ass bdy f adius (B) E g f < (C) he sepaain f w pins and is 9/4 (D) he sepaain f w pins and is /4 [A, B] efe any sandad bk. Q.46 When an alenaing cuen flws hugh a cicui cnsising f a esis in seies wih a capaci, duing he cycle a se insan i is pssible hae - (A) lage acss he cicui ze bu cuen hugh i n ze (B) cuen hugh he cicui ze bu he lage acss i n ze (C) cuen hugh he capaci n ze bu he lage acss i ze (D) cuen hugh he esis n ze bu he lage acss i ze D O ω ω (A) A and B epesen and Z especiely (B) A and B epesen Z and especiely (C) A, B, C and D epesen Z, X, and X C especiely (D) f ω ω, he phase diffeence beween cuen and lage beces ze [C, D] Ne ha is independen f ω, X L diecly ppinal ω and X C inesely ppinal ω. Again Z has a axiu a iniu alue a ω ω a which he lage and he cuen ae in phase. Q.49 A funace has a w layeed wall as shwn scheaically. Each laye has he sae aea f css secin. The epeaue θ a he ineface f w layes can be educed by l i l 0 inne laye ue laye 800 C 80 C k i θ C k 0 CAEE OINT, C Twe, ad N., IIA, Ka (aj.) h.: /
10 NSE 00-0 EXAMINATION CAEE OINT (A) inceasing he heal cnduciiy f ue laye (B) deceasing he heal cnduciiy f inne laye (C) by inceasing he hickness f inne laye (D) by deceasing he hickness f ue laye [A, B, C, D] ae f hea flw H which l l + 0 KA K 0A 800 θ is als equal. Using hese w l KA 70 elains we ge, θ 800. Thus K l + 0 K 0 l ne can educe he epeaue a he ineface by any f he fu pins gien. Q.50 Siple pendulus and hae lenghs l 80 c and l 00 c especiely. The bbs ae f asses and. Iniially bh ae a es in equilibiu psiin. If each f he bbs is gien a displaceen f c, he wk dne is W and W especiely. Then (A) W > W if (B) W < W if 5 (C) W W if 4 4 (D) W W if 5 [A, D] Wih usual nain, he heigh hugh which he θ bb falls is h l( csθ) l sin θ l since θ is sall. Theefe, we can wie 4 h lθ l a l.e. gh a. Thus, he wk dne W l ga W l l AT B Maks : 60 * All quesins ae cpulsy. * All quesins cay equal aks Q.5 Assue ha a cnsan pwe is supplied an elecic ain and i is fully used in acceleaing he ain. Obain elain giing he elciy f he ain and disance aeled by i as funcins f ie. we cnsan, heefe F F d d. Inegaing his we ge dx. Wiing he elciy as and d fuhe inegaing, we ge he expessin f he disance x Q.5 A blck f ass.5 kg ess n a ugh hiznal suface. A hiznal fce applied he blck inceases unifly f 0 5 N in 5 secnd. Deeine elciy and displaceen f he blck afe 5 secnd. Use µ s 0.6 and µ k 0.5 and g 0 /s. Wih usual nain, F s µ s N 9N and F k µ k N 7.5 N. Applied fce ises F s 9 N a s. Theefe, f s, 0 and s 0. F s, ne fce n he blck is ( 7.5), d d ha is d d 5 + A. Hee.5 kg. Nw, a s, 0, gies A 6. Wih his we ge f s, Theefe, a 5 s, 6 /s. F ds he equain f, we ge s d B. Again a s, s 0, giing 9 B. Wih his we ge, s 5 4 s Hence a 5 s, CAEE OINT, C Twe, ad N., IIA, Ka (aj.) h.: /
11 NSE 00-0 EXAMINATION CAEE OINT Q.5 A we used f pwe ansissin leaks a cuen in he gund. Assue ha he cuen speads unifly (heispheically) in he gund. Le p be he esisiiy f he gund and be he disance f he cene f he we (assued be d). The lwe end f he d is spheical wih adius b. Deeine () cuen densiy as a funcin f, () agniude f elecic field a a disance. and () penial diffeence beween he lwe end f he d and a pin disance. we efe he figue. Wih usual nain, we hae qv qv. Again, qb. Eliinaing f he w qb elains, we ge V. Nw, sin θ B q l q lb. Subsiuing he alues gies V sinθ θ 0 O b Use I J da inside gund whee cuen densiy ec J is paallel he aea eleen da f he heispheical suface. When inegaed, he aea ces u be π. This gies he cuen I densiy dieced adially uwad a any π pin. Using icscpic f f Oh's law J σ E whee s is he cnduciiy, we ge he agniude f J I elecic field E ρ whee we hae used σ π J ρ. Nw, deeine he penial σ dv diffeence we use he elain E dv d Ed. Subsiuing he alue f E and inegaing beween he liis b and, we ge he Iρ penial diffeence π b Q.54 An alpha paicle is acceleaed hugh a penial diffeence f 0 kv. Then i enes in a egin f ansese agneic field f inducin 0.0 T exended up a disance f 0.0. Deeine he angle hugh which he alpha paicle deiaes. (ass f he alpha paicle kg) q θ l Q.55 A hin plancnex lens f fcal lengh f is cu alng he axis in w hales. The w hales ae placed a a disance d f each he as shwn. The iages fed by he w hales lie in he sae plane. The disance beween he bjec plane and he iage plane is.8. The agnificain pduced by ne f he hales is. Deeine f, d and he agnificain pduced by he he half. Obiusly L fs an iage wih agnificain s ha u. Again u +.8 u giing u 0.6 and.. Using lens fula we ge f 0.4. Nw, f lens L, u d and. d. Using hese alues and als f 0.4, we ge d (d 0.6) 0 d 0.6. Fuhe he agnificain pduced by L is bjec plane d L L θ iage plane CAEE OINT, C Twe, ad N., IIA, Ka (aj.) h.: /
11. HAFAT İş-Enerji Power of a force: Power in the ability of a force to do work
 MÜHENDİSLİK MEKNİĞİ. HFT İş-Eneji Pwe f a fce: Pwe in he abiliy f a fce d wk F: The fce applied n paicle Q P = F v = Fv cs( θ ) F Q v θ Pah f Q v: The velciy f Q ÖRNEK: İŞ-ENERJİ ω µ k v Calculae he pwe
MÜHENDİSLİK MEKNİĞİ. HFT İş-Eneji Pwe f a fce: Pwe in he abiliy f a fce d wk F: The fce applied n paicle Q P = F v = Fv cs( θ ) F Q v θ Pah f Q v: The velciy f Q ÖRNEK: İŞ-ENERJİ ω µ k v Calculae he pwe
INDIAN ASSOCIATION OF PHYSICS TEACHERS NATIONAL STANDARD EXAMINATION IN PHYSICS
 INDIAN ASSOCIATION OF HYSICS TEACHES NATIONAL STANDAD EXAMINATION IN HYSICS 00-0 Tal ie : 0 inues (A-, A- & ) AT - A (Tal Marks : 80) SU-AT A- Q. Displaceen f an scillaing paricle is gien by y = A sin
INDIAN ASSOCIATION OF HYSICS TEACHES NATIONAL STANDAD EXAMINATION IN HYSICS 00-0 Tal ie : 0 inues (A-, A- & ) AT - A (Tal Marks : 80) SU-AT A- Q. Displaceen f an scillaing paricle is gien by y = A sin
A) N B) 0.0 N C) N D) N E) N
 Cdinat: H Bahluli Sunday, Nvembe, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Five identical pint chages each with chage =10 nc ae lcated at the cnes f a egula hexagn, as shwn in Figue 1. Find the magnitude f the net electic fce
Cdinat: H Bahluli Sunday, Nvembe, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Five identical pint chages each with chage =10 nc ae lcated at the cnes f a egula hexagn, as shwn in Figue 1. Find the magnitude f the net electic fce
Example
 hapte Exaple.6-3. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5 A single hllw fibe is placed within a vey lage glass tube. he hllw fibe is 0 c in length and has a
hapte Exaple.6-3. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 5 A single hllw fibe is placed within a vey lage glass tube. he hllw fibe is 0 c in length and has a
ÖRNEK 1: THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MOMENTUM RELATION Calculate the linear momentum of a particle of mass m=10 kg which has a. kg m s
 MÜHENDİSLİK MEKANİĞİ. HAFTA İMPULS- MMENTUM-ÇARPIŞMA Linea oenu of a paicle: The sybol L denoes he linea oenu and is defined as he ass ies he elociy of a paicle. L ÖRNEK : THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MMENTUM RELATIN
MÜHENDİSLİK MEKANİĞİ. HAFTA İMPULS- MMENTUM-ÇARPIŞMA Linea oenu of a paicle: The sybol L denoes he linea oenu and is defined as he ass ies he elociy of a paicle. L ÖRNEK : THE LINEAR IMPULSE-MMENTUM RELATIN
A) (0.46 î ) N B) (0.17 î ) N
 Phys10 Secnd Maj-14 Ze Vesin Cdinat: xyz Thusday, Apil 3, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Thee chages, 1 = =.0 μc and Q = 4.0 μc, ae fixed in thei places as shwn in Figue 1. Find the net electstatic fce n Q due t 1 and.
Phys10 Secnd Maj-14 Ze Vesin Cdinat: xyz Thusday, Apil 3, 015 Page: 1 Q1. Thee chages, 1 = =.0 μc and Q = 4.0 μc, ae fixed in thei places as shwn in Figue 1. Find the net electstatic fce n Q due t 1 and.
2. The units in which the rate of a chemical reaction in solution is measured are (could be); 4rate. sec L.sec
 Kineic Pblem Fm Ramnd F. X. Williams. Accding he equain, NO(g + B (g NOB(g In a ceain eacin miue he ae f fmain f NOB(g was fund be 4.50 0-4 ml L - s -. Wha is he ae f cnsumpin f B (g, als in ml L - s -?
Kineic Pblem Fm Ramnd F. X. Williams. Accding he equain, NO(g + B (g NOB(g In a ceain eacin miue he ae f fmain f NOB(g was fund be 4.50 0-4 ml L - s -. Wha is he ae f cnsumpin f B (g, als in ml L - s -?
Lecture 3. Electrostatics
 Lecue lecsics In his lecue yu will len: Thee wys slve pblems in elecsics: ) Applicin f he Supepsiin Pinciple (SP) b) Applicin f Guss Lw in Inegl Fm (GLIF) c) Applicin f Guss Lw in Diffeenil Fm (GLDF) C
Lecue lecsics In his lecue yu will len: Thee wys slve pblems in elecsics: ) Applicin f he Supepsiin Pinciple (SP) b) Applicin f Guss Lw in Inegl Fm (GLIF) c) Applicin f Guss Lw in Diffeenil Fm (GLDF) C
MEAN GRAVITY ALONG PLUMBLINE. University of New Brunswick, Department of Geodesy and Geomatics Engineering, Fredericton, N.B.
 MEA GRAVITY ALG PLUMBLIE Beh-Anne Main 1, Chis MacPhee, Rbe Tenze 1, Pe Vaníek 1 and Macel Sans 1 1. Inducin 1 Univesiy f ew Bunswick, Depamen f Gedesy and Gemaics Engineeing, Fedeicn,.B., E3B 5A3, Canada
MEA GRAVITY ALG PLUMBLIE Beh-Anne Main 1, Chis MacPhee, Rbe Tenze 1, Pe Vaníek 1 and Macel Sans 1 1. Inducin 1 Univesiy f ew Bunswick, Depamen f Gedesy and Gemaics Engineeing, Fedeicn,.B., E3B 5A3, Canada
The Components of Vector B. The Components of Vector B. Vector Components. Component Method of Vector Addition. Vector Components
 Upcming eens in PY05 Due ASAP: PY05 prees n WebCT. Submiing i ges yu pin ward yur 5-pin Lecure grade. Please ake i seriusly, bu wha cuns is wheher r n yu submi i, n wheher yu ge hings righ r wrng. Due
Upcming eens in PY05 Due ASAP: PY05 prees n WebCT. Submiing i ges yu pin ward yur 5-pin Lecure grade. Please ake i seriusly, bu wha cuns is wheher r n yu submi i, n wheher yu ge hings righ r wrng. Due
Maxwell Equations. Dr. Ray Kwok sjsu
 Maxwell quains. Ray Kwk sjsu eeence: lecmagneic Fields and Waves, Lain & Csn (Feeman) Inducin lecdynamics,.. Giihs (Penice Hall) Fundamenals ngineeing lecmagneics,.k. Cheng (Addisn Wesley) Maxwell quains.
Maxwell quains. Ray Kwk sjsu eeence: lecmagneic Fields and Waves, Lain & Csn (Feeman) Inducin lecdynamics,.. Giihs (Penice Hall) Fundamenals ngineeing lecmagneics,.k. Cheng (Addisn Wesley) Maxwell quains.
CHAPTER 24 GAUSS LAW
 CHAPTR 4 GAUSS LAW LCTRIC FLUX lectic flux is a measue f the numbe f electic filed lines penetating sme suface in a diectin pependicula t that suface. Φ = A = A csθ with θ is the angle between the and
CHAPTR 4 GAUSS LAW LCTRIC FLUX lectic flux is a measue f the numbe f electic filed lines penetating sme suface in a diectin pependicula t that suface. Φ = A = A csθ with θ is the angle between the and
β A Constant-G m Biasing
 p 2002 EE 532 Anal IC Des II Pae 73 Cnsan-G Bas ecall ha us a PTAT cuen efeence (see p f p. 66 he nes) bas a bpla anss pes cnsan anscnucance e epeaue (an als epenen f supply lae an pcess). Hw h we achee
p 2002 EE 532 Anal IC Des II Pae 73 Cnsan-G Bas ecall ha us a PTAT cuen efeence (see p f p. 66 he nes) bas a bpla anss pes cnsan anscnucance e epeaue (an als epenen f supply lae an pcess). Hw h we achee
1. Show that if the angular momentum of a boby is determined with respect to an arbitrary point A, then. r r r. H r A can be expressed by H r r r r
 1. Shw that if the angula entu f a bb is deteined with espect t an abita pint, then H can be epessed b H = ρ / v + H. This equies substituting ρ = ρ + ρ / int H = ρ d v + ρ ( ω ρ ) d and epanding, nte
1. Shw that if the angula entu f a bb is deteined with espect t an abita pint, then H can be epessed b H = ρ / v + H. This equies substituting ρ = ρ + ρ / int H = ρ d v + ρ ( ω ρ ) d and epanding, nte
CHAPTER GAUSS'S LAW
 lutins--ch 14 (Gauss's Law CHAPTE 14 -- GAU' LAW 141 This pblem is ticky An electic field line that flws int, then ut f the cap (see Figue I pduces a negative flux when enteing and an equal psitive flux
lutins--ch 14 (Gauss's Law CHAPTE 14 -- GAU' LAW 141 This pblem is ticky An electic field line that flws int, then ut f the cap (see Figue I pduces a negative flux when enteing and an equal psitive flux
Notes on Inductance and Circuit Transients Joe Wolfe, Physics UNSW. Circuits with R and C. τ = RC = time constant
 Nes n Inducance and cu Tansens Je Wlfe, Physcs UNSW cus wh and - Wha happens when yu clse he swch? (clse swch a 0) - uen flws ff capac, s d Acss capac: Acss ess: c d s d d ln + cns. 0, ln cns. ln ln ln
Nes n Inducance and cu Tansens Je Wlfe, Physcs UNSW cus wh and - Wha happens when yu clse he swch? (clse swch a 0) - uen flws ff capac, s d Acss capac: Acss ess: c d s d d ln + cns. 0, ln cns. ln ln ln
Part 2 KINEMATICS Motion in One and Two Dimensions Projectile Motion Circular Motion Kinematics Problems
 Pa 2 KINEMATICS Min in One and Tw Dimensins Pjecile Min Cicula Min Kinemaics Pblems KINEMATICS The Descipin f Min Physics is much me han jus he descipin f min. Bu being able descibe he min f an bjec mahemaically
Pa 2 KINEMATICS Min in One and Tw Dimensins Pjecile Min Cicula Min Kinemaics Pblems KINEMATICS The Descipin f Min Physics is much me han jus he descipin f min. Bu being able descibe he min f an bjec mahemaically
A) 100 K B) 150 K C) 200 K D) 250 K E) 350 K
 Phys10 Secnd Maj-09 Ze Vesin Cdinat: k Wednesday, May 05, 010 Page: 1 Q1. A ht bject and a cld bject ae placed in themal cntact and the cmbinatin is islated. They tansfe enegy until they each a final equilibium
Phys10 Secnd Maj-09 Ze Vesin Cdinat: k Wednesday, May 05, 010 Page: 1 Q1. A ht bject and a cld bject ae placed in themal cntact and the cmbinatin is islated. They tansfe enegy until they each a final equilibium
Today - Lecture 13. Today s lecture continue with rotations, torque, Note that chapters 11, 12, 13 all involve rotations
 Today - Lecue 13 Today s lecue coninue wih oaions, oque, Noe ha chapes 11, 1, 13 all inole oaions slide 1 eiew Roaions Chapes 11 & 1 Viewed fom aboe (+z) Roaional, o angula elociy, gies angenial elociy
Today - Lecue 13 Today s lecue coninue wih oaions, oque, Noe ha chapes 11, 1, 13 all inole oaions slide 1 eiew Roaions Chapes 11 & 1 Viewed fom aboe (+z) Roaional, o angula elociy, gies angenial elociy
 WORK POWER AND ENERGY Consevaive foce a) A foce is said o be consevaive if he wok done by i is independen of pah followed by he body b) Wok done by a consevaive foce fo a closed pah is zeo c) Wok done
WORK POWER AND ENERGY Consevaive foce a) A foce is said o be consevaive if he wok done by i is independen of pah followed by he body b) Wok done by a consevaive foce fo a closed pah is zeo c) Wok done
AP Physics 1 MC Practice Kinematics 1D
 AP Physics 1 MC Pracice Kinemaics 1D Quesins 1 3 relae w bjecs ha sar a x = 0 a = 0 and mve in ne dimensin independenly f ne anher. Graphs, f he velciy f each bjec versus ime are shwn belw Objec A Objec
AP Physics 1 MC Pracice Kinemaics 1D Quesins 1 3 relae w bjecs ha sar a x = 0 a = 0 and mve in ne dimensin independenly f ne anher. Graphs, f he velciy f each bjec versus ime are shwn belw Objec A Objec
Electric Charge. Electric charge is quantized. Electric charge is conserved
 lectstatics lectic Chage lectic chage is uantized Chage cmes in incements f the elementay chage e = ne, whee n is an intege, and e =.6 x 0-9 C lectic chage is cnseved Chage (electns) can be mved fm ne
lectstatics lectic Chage lectic chage is uantized Chage cmes in incements f the elementay chage e = ne, whee n is an intege, and e =.6 x 0-9 C lectic chage is cnseved Chage (electns) can be mved fm ne
FARADAY'S LAW dt
 FAADAY'S LAW 31.1 Faaday's Law of Induction In the peious chapte we leaned that electic cuent poduces agnetic field. Afte this ipotant discoey, scientists wondeed: if electic cuent poduces agnetic field,
FAADAY'S LAW 31.1 Faaday's Law of Induction In the peious chapte we leaned that electic cuent poduces agnetic field. Afte this ipotant discoey, scientists wondeed: if electic cuent poduces agnetic field,
4. Fundamental of A.C. Circuit
 4. Fundaenal of A.. icui 4. Equaion fo geneaion of alenaing induce EMF An A geneao uses he pinciple of Faaday s elecoagneic inducion law. saes ha when cuen caying conduco cu he agneic field hen ef induced
4. Fundaenal of A.. icui 4. Equaion fo geneaion of alenaing induce EMF An A geneao uses he pinciple of Faaday s elecoagneic inducion law. saes ha when cuen caying conduco cu he agneic field hen ef induced
Physics Courseware Physics I Constant Acceleration
 Physics Curseware Physics I Cnsan Accelerain Equains fr cnsan accelerain in dimensin x + a + a + ax + x Prblem.- In he 00-m race an ahlee acceleraes unifrmly frm res his p speed f 0m/s in he firs x5m as
Physics Curseware Physics I Cnsan Accelerain Equains fr cnsan accelerain in dimensin x + a + a + ax + x Prblem.- In he 00-m race an ahlee acceleraes unifrmly frm res his p speed f 0m/s in he firs x5m as
March 15. Induction and Inductance Chapter 31
 Mach 15 Inductin and Inductance Chapte 31 > Fces due t B fields Lentz fce τ On a mving chage F B On a cuent F il B Cuent caying cil feels a tque = µ B Review > Cuents geneate B field Bit-Savat law = qv
Mach 15 Inductin and Inductance Chapte 31 > Fces due t B fields Lentz fce τ On a mving chage F B On a cuent F il B Cuent caying cil feels a tque = µ B Review > Cuents geneate B field Bit-Savat law = qv
dm dt = 1 V The number of moles in any volume is M = CV, where C = concentration in M/L V = liters. dcv v
 Mg: Pcess Aalyss: Reac ae s defed as whee eac ae elcy lue M les ( ccea) e. dm he ube f les ay lue s M, whee ccea M/L les. he he eac ae beces f a hgeeus eac, ( ) d Usually s csa aqueus eeal pcesses eac,
Mg: Pcess Aalyss: Reac ae s defed as whee eac ae elcy lue M les ( ccea) e. dm he ube f les ay lue s M, whee ccea M/L les. he he eac ae beces f a hgeeus eac, ( ) d Usually s csa aqueus eeal pcesses eac,
Rotational Motion and the Law of Gravity
 Chape 7 7 Roaional Moion and he Law of Gaiy PROBLEM SOLUTIONS 7.1 (a) Eah oaes adians (360 ) on is axis in 1 day. Thus, ad 1 day 5 7.7 10 ad s 4 1 day 8.64 10 s Because of is oaion abou is axis, Eah bulges
Chape 7 7 Roaional Moion and he Law of Gaiy PROBLEM SOLUTIONS 7.1 (a) Eah oaes adians (360 ) on is axis in 1 day. Thus, ad 1 day 5 7.7 10 ad s 4 1 day 8.64 10 s Because of is oaion abou is axis, Eah bulges
Chapter 7. Interference
 Chape 7 Inefeence Pa I Geneal Consideaions Pinciple of Supeposiion Pinciple of Supeposiion When wo o moe opical waves mee in he same locaion, hey follow supeposiion pinciple Mos opical sensos deec opical
Chape 7 Inefeence Pa I Geneal Consideaions Pinciple of Supeposiion Pinciple of Supeposiion When wo o moe opical waves mee in he same locaion, hey follow supeposiion pinciple Mos opical sensos deec opical
r r r r r EE334 Electromagnetic Theory I Todd Kaiser
 334 lecoagneic Theoy I Todd Kaise Maxwell s quaions: Maxwell s equaions wee developed on expeienal evidence and have been found o goven all classical elecoagneic phenoena. They can be wien in diffeenial
334 lecoagneic Theoy I Todd Kaise Maxwell s quaions: Maxwell s equaions wee developed on expeienal evidence and have been found o goven all classical elecoagneic phenoena. They can be wien in diffeenial
FARADAY'S LAW. dates : No. of lectures allocated. Actual No. of lectures 3 9/5/09-14 /5/09
 FARADAY'S LAW No. of lectues allocated Actual No. of lectues dates : 3 9/5/09-14 /5/09 31.1 Faaday's Law of Induction In the pevious chapte we leaned that electic cuent poduces agnetic field. Afte this
FARADAY'S LAW No. of lectues allocated Actual No. of lectues dates : 3 9/5/09-14 /5/09 31.1 Faaday's Law of Induction In the pevious chapte we leaned that electic cuent poduces agnetic field. Afte this
Physics 207 Lecture 13
 Physics 07 Lecue 3 Physics 07, Lecue 3, Oc. 8 Agenda: Chape 9, finish, Chape 0 Sa Chape 9: Moenu and Collision Ipulse Cene of ass Chape 0: oaional Kineaics oaional Enegy Moens of Ineia Paallel axis heoe
Physics 07 Lecue 3 Physics 07, Lecue 3, Oc. 8 Agenda: Chape 9, finish, Chape 0 Sa Chape 9: Moenu and Collision Ipulse Cene of ass Chape 0: oaional Kineaics oaional Enegy Moens of Ineia Paallel axis heoe
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION PREVIOUS EAMCET BITS
 P P Methd EECTOMAGNETIC INDUCTION PEVIOUS EAMCET BITS [ENGINEEING PAPE]. A cnduct d f length tates with angula speed ω in a unifm magnetic field f inductin B which is pependicula t its mtin. The induced
P P Methd EECTOMAGNETIC INDUCTION PEVIOUS EAMCET BITS [ENGINEEING PAPE]. A cnduct d f length tates with angula speed ω in a unifm magnetic field f inductin B which is pependicula t its mtin. The induced
PHYS PRACTICE EXAM 2
 PHYS 1800 PRACTICE EXAM Pa I Muliple Choice Quesions [ ps each] Diecions: Cicle he one alenaive ha bes complees he saemen o answes he quesion. Unless ohewise saed, assume ideal condiions (no ai esisance,
PHYS 1800 PRACTICE EXAM Pa I Muliple Choice Quesions [ ps each] Diecions: Cicle he one alenaive ha bes complees he saemen o answes he quesion. Unless ohewise saed, assume ideal condiions (no ai esisance,
5/20/2011. HITT An electron moves from point i to point f, in the direction of a uniform electric field. During this displacement:
 5/0/011 Chapte 5 In the last lectue: CapacitanceII we calculated the capacitance C f a system f tw islated cnducts. We als calculated the capacitance f sme simple gemeties. In this chapte we will cve the
5/0/011 Chapte 5 In the last lectue: CapacitanceII we calculated the capacitance C f a system f tw islated cnducts. We als calculated the capacitance f sme simple gemeties. In this chapte we will cve the
WYSE Academic Challenge Sectional Mathematics 2006 Solution Set
 WYSE Academic Challenge Sectinal 006 Slutin Set. Cect answe: e. mph is 76 feet pe minute, and 4 mph is 35 feet pe minute. The tip up the hill takes 600/76, 3.4 minutes, and the tip dwn takes 600/35,.70
WYSE Academic Challenge Sectinal 006 Slutin Set. Cect answe: e. mph is 76 feet pe minute, and 4 mph is 35 feet pe minute. The tip up the hill takes 600/76, 3.4 minutes, and the tip dwn takes 600/35,.70
i-clicker Question lim Physics 123 Lecture 2 1 Dimensional Motion x 1 x 2 v is not constant in time v = v(t) acceleration lim Review:
 Reiew: Physics 13 Lecure 1 Dimensinal Min Displacemen: Dx = x - x 1 (If Dx < 0, he displacemen ecr pins he lef.) Aerage elciy: (N he same as aerage speed) a slpe = a x x 1 1 Dx D x 1 x Crrecin: Calculus
Reiew: Physics 13 Lecure 1 Dimensinal Min Displacemen: Dx = x - x 1 (If Dx < 0, he displacemen ecr pins he lef.) Aerage elciy: (N he same as aerage speed) a slpe = a x x 1 1 Dx D x 1 x Crrecin: Calculus
Lecture 4 ( ) Some points of vertical motion: Here we assumed t 0 =0 and the y axis to be vertical.
 Sme pins f erical min: Here we assumed and he y axis be erical. ( ) y g g y y y y g dwnwards 9.8 m/s g Lecure 4 Accelerain The aerage accelerain is defined by he change f elciy wih ime: a ; In analgy,
Sme pins f erical min: Here we assumed and he y axis be erical. ( ) y g g y y y y g dwnwards 9.8 m/s g Lecure 4 Accelerain The aerage accelerain is defined by he change f elciy wih ime: a ; In analgy,
Example 11: The man shown in Figure (a) pulls on the cord with a force of 70
 Chapte Tw ce System 35.4 α α 100 Rx cs 0.354 R 69.3 35.4 β β 100 Ry cs 0.354 R 111 Example 11: The man shwn in igue (a) pulls n the cd with a fce f 70 lb. Repesent this fce actin n the suppt A as Catesian
Chapte Tw ce System 35.4 α α 100 Rx cs 0.354 R 69.3 35.4 β β 100 Ry cs 0.354 R 111 Example 11: The man shwn in igue (a) pulls n the cd with a fce f 70 lb. Repesent this fce actin n the suppt A as Catesian
Lecture 3: Resistive forces, and Energy
 Lecure 3: Resisive frces, and Energy Las ie we fund he velciy f a prjecile ving wih air resisance: g g vx ( ) = vx, e vy ( ) = + v + e One re inegrain gives us he psiin as a funcin f ie: dx dy g g = vx,
Lecure 3: Resisive frces, and Energy Las ie we fund he velciy f a prjecile ving wih air resisance: g g vx ( ) = vx, e vy ( ) = + v + e One re inegrain gives us he psiin as a funcin f ie: dx dy g g = vx,
3. No. The relationship between the parts of a non-rigid object can change. Different parts of the object may have different values of ω.
 CHAPTE : ainal Min Answers Quesins. The deer will regiser a disance greaer han he disance acually raveled. The deer cuns he nuber f revluins and he calibrain gives he disance raveled per revluin (πr).
CHAPTE : ainal Min Answers Quesins. The deer will regiser a disance greaer han he disance acually raveled. The deer cuns he nuber f revluins and he calibrain gives he disance raveled per revluin (πr).
Chapter 2. Kinematics in One Dimension. Kinematics deals with the concepts that are needed to describe motion.
 Chpe Kinemic in One Dimenin Kinemic del wih he cncep h e needed decibe min. Dynmic del wih he effec h fce he n min. Tgehe, kinemic nd dynmic fm he bnch f phyic knwn Mechnic.. Diplcemen. Diplcemen.0 m 5.0
Chpe Kinemic in One Dimenin Kinemic del wih he cncep h e needed decibe min. Dynmic del wih he effec h fce he n min. Tgehe, kinemic nd dynmic fm he bnch f phyic knwn Mechnic.. Diplcemen. Diplcemen.0 m 5.0
Announcements Candidates Visiting Next Monday 11 12:20 Class 4pm Research Talk Opportunity to learn a little about what physicists do
 Wed., /11 Thus., /1 Fi., /13 Mn., /16 Tues., /17 Wed., /18 Thus., /19 Fi., / 17.7-9 Magnetic Field F Distibutins Lab 5: Bit-Savat B fields f mving chages (n quiz) 17.1-11 Pemanent Magnets 18.1-3 Mic. View
Wed., /11 Thus., /1 Fi., /13 Mn., /16 Tues., /17 Wed., /18 Thus., /19 Fi., / 17.7-9 Magnetic Field F Distibutins Lab 5: Bit-Savat B fields f mving chages (n quiz) 17.1-11 Pemanent Magnets 18.1-3 Mic. View
Magnetism. Chapter 21
 1.1 Magnetic Fields Chapte 1 Magnetism The needle f a cmpass is pemanent magnet that has a nth magnetic ple (N) at ne end and a suth magnetic ple (S) at the the. 1.1 Magnetic Fields 1.1 Magnetic Fields
1.1 Magnetic Fields Chapte 1 Magnetism The needle f a cmpass is pemanent magnet that has a nth magnetic ple (N) at ne end and a suth magnetic ple (S) at the the. 1.1 Magnetic Fields 1.1 Magnetic Fields
Fig. 1S. The antenna construction: (a) main geometrical parameters, (b) the wire support pillar and (c) the console link between wire and coaxial
 a b c Fig. S. The anenna consucion: (a) ain geoeical paaees, (b) he wie suppo pilla and (c) he console link beween wie and coaial pobe. Fig. S. The anenna coss-secion in he y-z plane. Accoding o [], he
a b c Fig. S. The anenna consucion: (a) ain geoeical paaees, (b) he wie suppo pilla and (c) he console link beween wie and coaial pobe. Fig. S. The anenna coss-secion in he y-z plane. Accoding o [], he
The Production of Polarization
 Physics 36: Waves Lecue 13 3/31/211 The Poducion of Polaizaion Today we will alk abou he poducion of polaized ligh. We aleady inoduced he concep of he polaizaion of ligh, a ansvese EM wave. To biefly eview
Physics 36: Waves Lecue 13 3/31/211 The Poducion of Polaizaion Today we will alk abou he poducion of polaized ligh. We aleady inoduced he concep of he polaizaion of ligh, a ansvese EM wave. To biefly eview
Prerna Tower, Road No 2, Contractors Area, Bistupur, Jamshedpur , Tel (0657) , PART A PHYSICS
 Pena Towe, oad No, Conacos Aea, isupu, Jamshedpu 83, Tel (657)89, www.penaclasses.com AIEEE PAT A PHYSICS Physics. Two elecic bulbs maked 5 W V and W V ae conneced in seies o a 44 V supply. () W () 5 W
Pena Towe, oad No, Conacos Aea, isupu, Jamshedpu 83, Tel (657)89, www.penaclasses.com AIEEE PAT A PHYSICS Physics. Two elecic bulbs maked 5 W V and W V ae conneced in seies o a 44 V supply. () W () 5 W
Lecture 22 Electromagnetic Waves
 Lecue Elecomagneic Waves Pogam: 1. Enegy caied by he wave (Poyning veco).. Maxwell s equaions and Bounday condiions a inefaces. 3. Maeials boundaies: eflecion and efacion. Snell s Law. Quesions you should
Lecue Elecomagneic Waves Pogam: 1. Enegy caied by he wave (Poyning veco).. Maxwell s equaions and Bounday condiions a inefaces. 3. Maeials boundaies: eflecion and efacion. Snell s Law. Quesions you should
Ch23. Introduction to Analytical Separations
 Ch3. Inoducion o Analyical Sepaaions 3. Medical Issue : Measuing Silicones Leaking fo Beas Iplans High olecula ass poly(diehylsiloane), PDMS, [(CH 3 ) SiO] n : Used as GC saionay phase, gels in beas iplans
Ch3. Inoducion o Analyical Sepaaions 3. Medical Issue : Measuing Silicones Leaking fo Beas Iplans High olecula ass poly(diehylsiloane), PDMS, [(CH 3 ) SiO] n : Used as GC saionay phase, gels in beas iplans
Chapter 31 Faraday s Law
 Chapte 31 Faaday s Law Change oving --> cuent --> agnetic field (static cuent --> static agnetic field) The souce of agnetic fields is cuent. The souce of electic fields is chage (electic onopole). Altenating
Chapte 31 Faaday s Law Change oving --> cuent --> agnetic field (static cuent --> static agnetic field) The souce of agnetic fields is cuent. The souce of electic fields is chage (electic onopole). Altenating
Fri. 10/23 (C14) Linear Dielectrics (read rest at your discretion) Mon. (C 17) , E to B; Lorentz Force Law: fields
 Fi. 0/23 (C4) 4.4. Linea ielectics (ead est at yu discetin) Mn. (C 7) 2..-..2, 2.3. t B; 5..-..2 Lentz Fce Law: fields Wed. and fces Thus. (C 7) 5..3 Lentz Fce Law: cuents Fi. (C 7) 5.2 Bit-Savat Law HW6
Fi. 0/23 (C4) 4.4. Linea ielectics (ead est at yu discetin) Mn. (C 7) 2..-..2, 2.3. t B; 5..-..2 Lentz Fce Law: fields Wed. and fces Thus. (C 7) 5..3 Lentz Fce Law: cuents Fi. (C 7) 5.2 Bit-Savat Law HW6
Kinematics Review Outline
 Kinemaics Review Ouline 1.1.0 Vecrs and Scalars 1.1 One Dimensinal Kinemaics Vecrs have magniude and direcin lacemen; velciy; accelerain sign indicaes direcin + is nrh; eas; up; he righ - is suh; wes;
Kinemaics Review Ouline 1.1.0 Vecrs and Scalars 1.1 One Dimensinal Kinemaics Vecrs have magniude and direcin lacemen; velciy; accelerain sign indicaes direcin + is nrh; eas; up; he righ - is suh; wes;
Always solve problems by writing a logical and. Under what conditions they are useful. Under what conditions they are true
 Aleady accmplished Read Te Chape Read Te Chape Read Te Chape 3 Read CPS (Cmpeen Pblem Sle) Chap. 3 Wked Te Pblems Chap. - 3 Wked CPS Pblems Chap. 3 Pblems m Lab I & Ne Weeks Cnnec Min (Chape & 3) wih Ineacins
Aleady accmplished Read Te Chape Read Te Chape Read Te Chape 3 Read CPS (Cmpeen Pblem Sle) Chap. 3 Wked Te Pblems Chap. - 3 Wked CPS Pblems Chap. 3 Pblems m Lab I & Ne Weeks Cnnec Min (Chape & 3) wih Ineacins
06 - ROTATIONAL MOTION Page 1 ( Answers at the end of all questions )
 06 - ROTATIONAL MOTION Page ) A body A of mass M while falling vetically downwads unde gavity beaks into two pats, a body B of mass ( / ) M and a body C of mass ( / ) M. The cente of mass of bodies B and
06 - ROTATIONAL MOTION Page ) A body A of mass M while falling vetically downwads unde gavity beaks into two pats, a body B of mass ( / ) M and a body C of mass ( / ) M. The cente of mass of bodies B and
Relative and Circular Motion
 Relaie and Cicula Moion a) Relaie moion b) Cenipeal acceleaion Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 1 Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 2 Time on Video Pelecue Looks like mosly eeyone hee has iewed enie pelecue GOOD! Thank you
Relaie and Cicula Moion a) Relaie moion b) Cenipeal acceleaion Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 1 Mechanics Lecue 3 Slide 2 Time on Video Pelecue Looks like mosly eeyone hee has iewed enie pelecue GOOD! Thank you
Electric Fields and Electric Forces
 Cpyight, iley 006 (Cutnell & Jhnsn 9. Ptential Enegy Chapte 9 mgh mgh GPE GPE Electic Fields and Electic Fces 9. Ptential Enegy 9. Ptential Enegy 9. The Electic Ptential Diffeence 9. The Electic Ptential
Cpyight, iley 006 (Cutnell & Jhnsn 9. Ptential Enegy Chapte 9 mgh mgh GPE GPE Electic Fields and Electic Fces 9. Ptential Enegy 9. Ptential Enegy 9. The Electic Ptential Diffeence 9. The Electic Ptential
(Sample 3) Exam 1 - Physics Patel SPRING 1998 FORM CODE - A (solution key at end of exam)
 (Sample 3) Exam 1 - Physics 202 - Patel SPRING 1998 FORM CODE - A (solution key at end of exam) Be sue to fill in you student numbe and FORM lette (A, B, C) on you answe sheet. If you foget to include
(Sample 3) Exam 1 - Physics 202 - Patel SPRING 1998 FORM CODE - A (solution key at end of exam) Be sue to fill in you student numbe and FORM lette (A, B, C) on you answe sheet. If you foget to include
Phy 213: General Physics III
 Phy 1: Geneal Physics III Chapte : Gauss Law Lectue Ntes E Electic Flux 1. Cnside a electic field passing thugh a flat egin in space w/ aea=a. The aea vect ( A ) with a magnitude f A and is diected nmal
Phy 1: Geneal Physics III Chapte : Gauss Law Lectue Ntes E Electic Flux 1. Cnside a electic field passing thugh a flat egin in space w/ aea=a. The aea vect ( A ) with a magnitude f A and is diected nmal
Circular Motion. Radians. One revolution is equivalent to which is also equivalent to 2π radians. Therefore we can.
 1 Cicula Moion Radians One evoluion is equivalen o 360 0 which is also equivalen o 2π adians. Theefoe we can say ha 360 = 2π adians, 180 = π adians, 90 = π 2 adians. Hence 1 adian = 360 2π Convesions Rule
1 Cicula Moion Radians One evoluion is equivalen o 360 0 which is also equivalen o 2π adians. Theefoe we can say ha 360 = 2π adians, 180 = π adians, 90 = π 2 adians. Hence 1 adian = 360 2π Convesions Rule
Physics 2212 GH Quiz #2 Solutions Spring 2016
 Physics 2212 GH Quiz #2 Solutions Sping 216 I. 17 points) Thee point chages, each caying a chage Q = +6. nc, ae placed on an equilateal tiangle of side length = 3. mm. An additional point chage, caying
Physics 2212 GH Quiz #2 Solutions Sping 216 I. 17 points) Thee point chages, each caying a chage Q = +6. nc, ae placed on an equilateal tiangle of side length = 3. mm. An additional point chage, caying
PHYSICS. Time allowed: 90 minutes. Section A is a set of questions on data analysis. It requires work on graph paper.
 PHYSICS EXAMIATIO FOR ETRACE SCHOLARSHIPS JAUARY 7 Tie allowed: 9 inutes Section A is a set of questions on data analysis. It equies wok on gaph pape. Section B consists of nine questions. Attept as any
PHYSICS EXAMIATIO FOR ETRACE SCHOLARSHIPS JAUARY 7 Tie allowed: 9 inutes Section A is a set of questions on data analysis. It equies wok on gaph pape. Section B consists of nine questions. Attept as any
Lecture 17: Kinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System:
 Lecue 17: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: descipion of diffusion flux acoss he α/ ineface Today s opics Majo asks of oday s Lecue: how o deive he diffusion flux of aoms. Once an incipien
Lecue 17: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: descipion of diffusion flux acoss he α/ ineface Today s opics Majo asks of oday s Lecue: how o deive he diffusion flux of aoms. Once an incipien
3 ) = 10(1-3t)e -3t A
 haper 6, Sluin. d i ( e 6 e ) 0( - )e - A p i 0(-)e - e - 0( - )e -6 W haper 6, Sluin. w w (40)(80 (40)(0) ) ( ) w w w 0 0 80 60 kw haper 6, Sluin. i d 80 60 40x0 480 ma haper 6, Sluin 4. i (0) 6sin 4-0.7
haper 6, Sluin. d i ( e 6 e ) 0( - )e - A p i 0(-)e - e - 0( - )e -6 W haper 6, Sluin. w w (40)(80 (40)(0) ) ( ) w w w 0 0 80 60 kw haper 6, Sluin. i d 80 60 40x0 480 ma haper 6, Sluin 4. i (0) 6sin 4-0.7
Niraj Sir. circular motion;; SOLUTIONS TO CONCEPTS CHAPTER 7
 SOLUIONS O CONCEPS CHAPE 7 cicula otion;;. Distance between Eath & Moon.85 0 5 k.85 0 8 7. days 4 600 (7.) sec.6 0 6 sec.4.85 0 v 6.6 0 8 05.4/sec v (05.4) a 0.007/sec.7 0 /sec 8.85 0. Diaete of eath 800k
SOLUIONS O CONCEPS CHAPE 7 cicula otion;;. Distance between Eath & Moon.85 0 5 k.85 0 8 7. days 4 600 (7.) sec.6 0 6 sec.4.85 0 v 6.6 0 8 05.4/sec v (05.4) a 0.007/sec.7 0 /sec 8.85 0. Diaete of eath 800k
5.1 Angles and Their Measure
 5. Angles and Their Measure Secin 5. Nes Page This secin will cver hw angles are drawn and als arc lengh and rains. We will use (hea) represen an angle s measuremen. In he figure belw i describes hw yu
5. Angles and Their Measure Secin 5. Nes Page This secin will cver hw angles are drawn and als arc lengh and rains. We will use (hea) represen an angle s measuremen. In he figure belw i describes hw yu
Mass Linear Momentum Moment of Momentum Energy Putting it all together!
 inie Cnrl lue nalsis vin fr a Sse a inie Cnrl lue a Linear enu en f enu Ener Puin i all eer! D Cnservain f a B = Tal aun f a in e e b = a er uni a = DB ˆ b b n ˆ n ˆ equain Bu D / =! Cninui Equain a leavin
inie Cnrl lue nalsis vin fr a Sse a inie Cnrl lue a Linear enu en f enu Ener Puin i all eer! D Cnservain f a B = Tal aun f a in e e b = a er uni a = DB ˆ b b n ˆ n ˆ equain Bu D / =! Cninui Equain a leavin
Exam 3, vers Physics Spring, 2003
 1 of 9 Exam 3, ves. 0001 - Physics 1120 - Sping, 2003 NAME Signatue Student ID # TA s Name(Cicle one): Michael Scheffestein, Chis Kelle, Paisa Seelungsawat Stating time of you Tues ecitation (wite time
1 of 9 Exam 3, ves. 0001 - Physics 1120 - Sping, 2003 NAME Signatue Student ID # TA s Name(Cicle one): Michael Scheffestein, Chis Kelle, Paisa Seelungsawat Stating time of you Tues ecitation (wite time
, on the power of the transmitter P t fed to it, and on the distance R between the antenna and the observation point as. r r t
 Lecue 6: Fiis Tansmission Equaion and Rada Range Equaion (Fiis equaion. Maximum ange of a wieless link. Rada coss secion. Rada equaion. Maximum ange of a ada. 1. Fiis ansmission equaion Fiis ansmission
Lecue 6: Fiis Tansmission Equaion and Rada Range Equaion (Fiis equaion. Maximum ange of a wieless link. Rada coss secion. Rada equaion. Maximum ange of a ada. 1. Fiis ansmission equaion Fiis ansmission
ELECTRIC & MAGNETIC FIELDS I (STATIC FIELDS) ELC 205A
 LCTRIC & MAGNTIC FILDS I (STATIC FILDS) LC 05A D. Hanna A. Kils Assciate Pfess lectnics & Cmmnicatins ngineeing Depatment Faclty f ngineeing Cai Univesity Fall 0 f Static lecticity lectic & Magnetic Fields
LCTRIC & MAGNTIC FILDS I (STATIC FILDS) LC 05A D. Hanna A. Kils Assciate Pfess lectnics & Cmmnicatins ngineeing Depatment Faclty f ngineeing Cai Univesity Fall 0 f Static lecticity lectic & Magnetic Fields
CHAPTER 5: Circular Motion; Gravitation
 CHAPER 5: Cicula Motion; Gavitation Solution Guide to WebAssign Pobles 5.1 [1] (a) Find the centipetal acceleation fo Eq. 5-1.. a R v ( 1.5 s) 1.10 1.4 s (b) he net hoizontal foce is causing the centipetal
CHAPER 5: Cicula Motion; Gavitation Solution Guide to WebAssign Pobles 5.1 [1] (a) Find the centipetal acceleation fo Eq. 5-1.. a R v ( 1.5 s) 1.10 1.4 s (b) he net hoizontal foce is causing the centipetal
Torque, Angular Momentum and Rotational Kinetic Energy
 Toque, Angula Moentu and Rotational Kinetic Enegy In ou peious exaples that inoled a wheel, like fo exaple a pulley we wee always caeful to specify that fo the puposes of the poble it would be teated as
Toque, Angula Moentu and Rotational Kinetic Enegy In ou peious exaples that inoled a wheel, like fo exaple a pulley we wee always caeful to specify that fo the puposes of the poble it would be teated as
Physics 111. Exam #1. September 28, 2018
 Physics xam # Sepember 8, 08 ame Please read and fllw hese insrucins carefully: Read all prblems carefully befre aemping slve hem. Yur wrk mus be legible, and he rganizain clear. Yu mus shw all wrk, including
Physics xam # Sepember 8, 08 ame Please read and fllw hese insrucins carefully: Read all prblems carefully befre aemping slve hem. Yur wrk mus be legible, and he rganizain clear. Yu mus shw all wrk, including
Introduction. Electrostatics
 UNIVESITY OF TECHNOLOGY, SYDNEY FACULTY OF ENGINEEING 4853 Electmechanical Systems Electstatics Tpics t cve:. Culmb's Law 5. Mateial Ppeties. Electic Field Stength 6. Gauss' Theem 3. Electic Ptential 7.
UNIVESITY OF TECHNOLOGY, SYDNEY FACULTY OF ENGINEEING 4853 Electmechanical Systems Electstatics Tpics t cve:. Culmb's Law 5. Mateial Ppeties. Electic Field Stength 6. Gauss' Theem 3. Electic Ptential 7.
Two-dimensional Effects on the CSR Interaction Forces for an Energy-Chirped Bunch. Rui Li, J. Bisognano, R. Legg, and R. Bosch
 Two-dimensional Effecs on he CS Ineacion Foces fo an Enegy-Chiped Bunch ui Li, J. Bisognano,. Legg, and. Bosch Ouline 1. Inoducion 2. Pevious 1D and 2D esuls fo Effecive CS Foce 3. Bunch Disibuion Vaiaion
Two-dimensional Effecs on he CS Ineacion Foces fo an Enegy-Chiped Bunch ui Li, J. Bisognano,. Legg, and. Bosch Ouline 1. Inoducion 2. Pevious 1D and 2D esuls fo Effecive CS Foce 3. Bunch Disibuion Vaiaion
Charged particle motion in magnetic field
 Chaged paticle otion in agnetic field Paticle otion in cued agnetic fieldlines We diide the equation of otion into a elocity coponent along the agnetic field and pependicula to the agnetic field. Suppose
Chaged paticle otion in agnetic field Paticle otion in cued agnetic fieldlines We diide the equation of otion into a elocity coponent along the agnetic field and pependicula to the agnetic field. Suppose
Lecture 18: Kinetics of Phase Growth in a Two-component System: general kinetics analysis based on the dilute-solution approximation
 Lecue 8: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: geneal kineics analysis based on he dilue-soluion appoximaion Today s opics: In he las Lecues, we leaned hee diffeen ways o descibe he diffusion
Lecue 8: Kineics of Phase Gowh in a Two-componen Sysem: geneal kineics analysis based on he dilue-soluion appoximaion Today s opics: In he las Lecues, we leaned hee diffeen ways o descibe he diffusion
Gauss s Law Simulation Activities
 Gauss s Law Simulation Activities Name: Backgound: The electic field aound a point chage is found by: = kq/ 2 If thee ae multiple chages, the net field at any point is the vecto sum of the fields. Fo a
Gauss s Law Simulation Activities Name: Backgound: The electic field aound a point chage is found by: = kq/ 2 If thee ae multiple chages, the net field at any point is the vecto sum of the fields. Fo a
Lecture #2 : Impedance matching for narrowband block
 Lectue # : Ipedance atching f nawband blck ichad Chi-Hsi Li Telephne : 817-788-848 (UA) Cellula phne: 13917441363 (C) Eail : chihsili@yah.c.cn 1. Ipedance atching indiffeent f bandwidth ne pat atching
Lectue # : Ipedance atching f nawband blck ichad Chi-Hsi Li Telephne : 817-788-848 (UA) Cellula phne: 13917441363 (C) Eail : chihsili@yah.c.cn 1. Ipedance atching indiffeent f bandwidth ne pat atching
Work, Energy, and Power. AP Physics C
 k, Eneg, and Pwe AP Phsics C Thee ae man diffeent TYPES f Eneg. Eneg is expessed in JOULES (J) 4.19 J = 1 calie Eneg can be expessed me specificall b using the tem ORK() k = The Scala Dt Pduct between
k, Eneg, and Pwe AP Phsics C Thee ae man diffeent TYPES f Eneg. Eneg is expessed in JOULES (J) 4.19 J = 1 calie Eneg can be expessed me specificall b using the tem ORK() k = The Scala Dt Pduct between
The 37th International Physics Olympiad Singapore. Experimental Competition. Wednesday, 12 July, Sample Solution
 The 37h Inernainal Physics Olypiad Singapre Experienal Cpeiin Wednesday, July, 006 Saple Sluin Par a A skech f he experienal seup (n required) Receiver Raing able Gnieer Fixed ar Bea splier Gnieer Mvable
The 37h Inernainal Physics Olypiad Singapre Experienal Cpeiin Wednesday, July, 006 Saple Sluin Par a A skech f he experienal seup (n required) Receiver Raing able Gnieer Fixed ar Bea splier Gnieer Mvable
Announcements. Formulas Review. Exam format
 Annuncemens 1. N hmewrk due mrrw! a. Wuld be an ecellen eening sud fr and/r ake he eam. Eam 1 sars da! a. Aailable in Tesing Cener frm Tues, Sep. 16 10:15 am, up Mnda, Sep, clsing ime i. If u pick up ur
Annuncemens 1. N hmewrk due mrrw! a. Wuld be an ecellen eening sud fr and/r ake he eam. Eam 1 sars da! a. Aailable in Tesing Cener frm Tues, Sep. 16 10:15 am, up Mnda, Sep, clsing ime i. If u pick up ur
EM-2. 1 Coulomb s law, electric field, potential field, superposition q. Electric field of a point charge (1)
 EM- Coulomb s law, electic field, potential field, supeposition q ' Electic field of a point chage ( ') E( ) kq, whee k / 4 () ' Foce of q on a test chage e at position is ee( ) Electic potential O kq
EM- Coulomb s law, electic field, potential field, supeposition q ' Electic field of a point chage ( ') E( ) kq, whee k / 4 () ' Foce of q on a test chage e at position is ee( ) Electic potential O kq
Physics 2001/2051 Moments of Inertia Experiment 1
 Physics 001/051 Momens o Ineia Expeimen 1 Pelab 1 Read he ollowing backgound/seup and ensue you ae amilia wih he heoy equied o he expeimen. Please also ill in he missing equaions 5, 7 and 9. Backgound/Seup
Physics 001/051 Momens o Ineia Expeimen 1 Pelab 1 Read he ollowing backgound/seup and ensue you ae amilia wih he heoy equied o he expeimen. Please also ill in he missing equaions 5, 7 and 9. Backgound/Seup
ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes]
![ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes] ENGI 4430 Advanced Calculus for Engineering Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Problem Set 9 Solutions [Theorems of Gauss and Stokes]](/thumbs/91/106162145.jpg) ENGI 44 Avance alculus fo Engineeing Faculy of Engineeing an Applie cience Poblem e 9 oluions [Theoems of Gauss an okes]. A fla aea A is boune by he iangle whose veices ae he poins P(,, ), Q(,, ) an R(,,
ENGI 44 Avance alculus fo Engineeing Faculy of Engineeing an Applie cience Poblem e 9 oluions [Theoems of Gauss an okes]. A fla aea A is boune by he iangle whose veices ae he poins P(,, ), Q(,, ) an R(,,
Transient Radial Flow Toward a Well Aquifer Equation, based on assumptions becomes a 1D PDE for h(r,t) : Transient Radial Flow Toward a Well
 ansien Radial Flw wad a Well Aqife Eqain, based n assmpins becmes a D PDE f h(,) : -ansien flw in a hmgenes, ispic aqife -flly peneaing pmping well & infinie, hiznal, cnfined aqife f nifm hickness, hs
ansien Radial Flw wad a Well Aqife Eqain, based n assmpins becmes a D PDE f h(,) : -ansien flw in a hmgenes, ispic aqife -flly peneaing pmping well & infinie, hiznal, cnfined aqife f nifm hickness, hs
PHYS 1444 Lecture #5
 Shot eview Chapte 24 PHYS 1444 Lectue #5 Tuesday June 19, 212 D. Andew Bandt Capacitos and Capacitance 1 Coulom s Law The Fomula QQ Q Q F 1 2 1 2 Fomula 2 2 F k A vecto quantity. Newtons Diection of electic
Shot eview Chapte 24 PHYS 1444 Lectue #5 Tuesday June 19, 212 D. Andew Bandt Capacitos and Capacitance 1 Coulom s Law The Fomula QQ Q Q F 1 2 1 2 Fomula 2 2 F k A vecto quantity. Newtons Diection of electic
CHE CHAPTER 11 Spring 2005 GENERAL 2ND ORDER REACTION IN TURBULENT TUBULAR REACTORS
 CHE 52 - CHPTE Sping 2005 GENEL 2ND ODE ECTION IN TUULENT TUUL ECTOS Vassilats & T, IChEJ. (4), 666 (965) Cnside the fllwing stichiety: a + b = P The ass cnsevatin law f species i yields Ci + vci =. Di
CHE 52 - CHPTE Sping 2005 GENEL 2ND ODE ECTION IN TUULENT TUUL ECTOS Vassilats & T, IChEJ. (4), 666 (965) Cnside the fllwing stichiety: a + b = P The ass cnsevatin law f species i yields Ci + vci =. Di
Field due to a collection of N discrete point charges: r is in the direction from
 Physcs 46 Fomula Shee Exam Coulomb s Law qq Felec = k ˆ (Fo example, f F s he elecc foce ha q exes on q, hen ˆ s a un veco n he decon fom q o q.) Elecc Feld elaed o he elecc foce by: Felec = qe (elecc
Physcs 46 Fomula Shee Exam Coulomb s Law qq Felec = k ˆ (Fo example, f F s he elecc foce ha q exes on q, hen ˆ s a un veco n he decon fom q o q.) Elecc Feld elaed o he elecc foce by: Felec = qe (elecc
1 2 U CV. K dq I dt J nqv d J V IR P VI
 o 5 o T C T F 9 T K T o C 7.5 L L T V VT Q mct nct Q F V ml F V dq A H k TH TC dt L pv nt Kt nt CV ideal monatomic gas 5 CV ideal diatomic gas w/o vibation V W pdv V U Q W W Q e Q Q e Canot H C T T S C
o 5 o T C T F 9 T K T o C 7.5 L L T V VT Q mct nct Q F V ml F V dq A H k TH TC dt L pv nt Kt nt CV ideal monatomic gas 5 CV ideal diatomic gas w/o vibation V W pdv V U Q W W Q e Q Q e Canot H C T T S C
Fundamental Vehicle Loads & Their Estimation
 Fundaenal Vehicle Loads & Thei Esiaion The silified loads can only be alied in he eliinay design sage when he absence of es o siulaion daa They should always be qualified and udaed as oe infoaion becoes
Fundaenal Vehicle Loads & Thei Esiaion The silified loads can only be alied in he eliinay design sage when he absence of es o siulaion daa They should always be qualified and udaed as oe infoaion becoes
Rotational Motion: Statics and Dynamics
 Physics 07 Lectue 17 Goals: Lectue 17 Chapte 1 Define cente of mass Analyze olling motion Intoduce and analyze toque Undestand the equilibium dynamics of an extended object in esponse to foces Employ consevation
Physics 07 Lectue 17 Goals: Lectue 17 Chapte 1 Define cente of mass Analyze olling motion Intoduce and analyze toque Undestand the equilibium dynamics of an extended object in esponse to foces Employ consevation
Physics 111. Exam #1. January 26, 2018
 Physics xam # Januay 6, 08 ame Please ead and fllw these instuctins caefully: Read all pblems caefully befe attempting t slve them. Yu wk must be legible, and the ganizatin clea. Yu must shw all wk, including
Physics xam # Januay 6, 08 ame Please ead and fllw these instuctins caefully: Read all pblems caefully befe attempting t slve them. Yu wk must be legible, and the ganizatin clea. Yu must shw all wk, including
Motion Along a Straight Line
 PH 1-3A Fall 010 Min Alng a Sraigh Line Lecure Chaper (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamenals f Physics 8 h ediin) Min alng a sraigh line Sudies he min f bdies Deals wih frce as he cause f changes in min
PH 1-3A Fall 010 Min Alng a Sraigh Line Lecure Chaper (Halliday/Resnick/Walker, Fundamenals f Physics 8 h ediin) Min alng a sraigh line Sudies he min f bdies Deals wih frce as he cause f changes in min
Unit 6 Practice Test. Which vector diagram correctly shows the change in velocity Δv of the mass during this time? (1) (1) A. Energy KE.
 Unit 6 actice Test 1. Which one of the following gaphs best epesents the aiation of the kinetic enegy, KE, and of the gaitational potential enegy, GE, of an obiting satellite with its distance fom the
Unit 6 actice Test 1. Which one of the following gaphs best epesents the aiation of the kinetic enegy, KE, and of the gaitational potential enegy, GE, of an obiting satellite with its distance fom the
Application of Fractional Calculus in Food Rheology E. Vozáry, Gy. Csima, L. Csapó, F. Mohos
 Applicain f Facinal Calculus in F Rhelgy Szen Isán Uniesiy, Depamen f Physics an Cnl Vzay.sze@ek.szie.hu Keyws: facinal calculus, iscelasic, f, ceep, ecey Absac. In facinal calculus he e (β) f iffeeniain
Applicain f Facinal Calculus in F Rhelgy Szen Isán Uniesiy, Depamen f Physics an Cnl Vzay.sze@ek.szie.hu Keyws: facinal calculus, iscelasic, f, ceep, ecey Absac. In facinal calculus he e (β) f iffeeniain
Heat transfer between shell and rigid body through the thin heat-conducting layer taking into account mechanical contact
 Advanced Cmpuainal Meds in Hea Tansfe X 8 Hea ansfe beween sell and igid bdy ug e in ea-cnducing laye aking in accun mecanical cnac V. V. Zzulya Cen de Invesigación Cienífica de Yucaán, Méida, Yucaán,
Advanced Cmpuainal Meds in Hea Tansfe X 8 Hea ansfe beween sell and igid bdy ug e in ea-cnducing laye aking in accun mecanical cnac V. V. Zzulya Cen de Invesigación Cienífica de Yucaán, Méida, Yucaán,
Phys102 Second Major-182 Zero Version Monday, March 25, 2019 Page: 1
 Monday, Mach 5, 019 Page: 1 Q1. Figue 1 shows thee pais of identical conducting sphees that ae to be touched togethe and then sepaated. The initial chages on them befoe the touch ae indicated. Rank the
Monday, Mach 5, 019 Page: 1 Q1. Figue 1 shows thee pais of identical conducting sphees that ae to be touched togethe and then sepaated. The initial chages on them befoe the touch ae indicated. Rank the
51. Elektrijada, Kopaonik
 may 11. 51. Elekrijada Kpanik Tes in Physics 1. A mbile is frmed by suppring fur meal buerflies f equal mass m frm a sring f lengh L. The pins f suppr are evenly spaced a disance l apar as shwn in Figure
may 11. 51. Elekrijada Kpanik Tes in Physics 1. A mbile is frmed by suppring fur meal buerflies f equal mass m frm a sring f lengh L. The pins f suppr are evenly spaced a disance l apar as shwn in Figure
Sections 3.1 and 3.4 Exponential Functions (Growth and Decay)
 Secions 3.1 and 3.4 Eponenial Funcions (Gowh and Decay) Chape 3. Secions 1 and 4 Page 1 of 5 Wha Would You Rahe Have... $1million, o double you money evey day fo 31 days saing wih 1cen? Day Cens Day Cens
Secions 3.1 and 3.4 Eponenial Funcions (Gowh and Decay) Chape 3. Secions 1 and 4 Page 1 of 5 Wha Would You Rahe Have... $1million, o double you money evey day fo 31 days saing wih 1cen? Day Cens Day Cens
Sharif University of Technology - CEDRA By: Professor Ali Meghdari
 Shaif Univesiy of echnology - CEDRA By: Pofesso Ali Meghai Pupose: o exen he Enegy appoach in eiving euaions of oion i.e. Lagange s Meho fo Mechanical Syses. opics: Genealize Cooinaes Lagangian Euaion
Shaif Univesiy of echnology - CEDRA By: Pofesso Ali Meghai Pupose: o exen he Enegy appoach in eiving euaions of oion i.e. Lagange s Meho fo Mechanical Syses. opics: Genealize Cooinaes Lagangian Euaion
