Basic Principles of Tracer Kinetic Modelling
|
|
|
- Peregrine Robinson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Spectrum of Medical Imaging Basic Principles of Tracer Kinetic Modelling Adriaan A. Lammertsma Structure X-ray/CT/MRI Physiology US, SPECT, PET, MRI/S Metabolism PET, MRS Drug distribution PET Molecular pathways PET Molecular targets PET, SPECT Department of Nuclear Medicine & PET Research, VU University Medical Center, Amsterdam, The Netherlands PET: Quantitative Picomolar Sensitivity Jones, 1996 PET Diagnosis [ 11 C]PIB Uptake Inject Scan 1.4 Control 1.4 AD Wait Increased uptake: Increased binding Increased flow and/or extraction Increased delivery Qualitative PET sufficient for diagnosis (sensitivity/specificity) Quantitative PET needed for monitoring disease progression and response to therapy Data Tolboom, Ossenkoppele, et al. [ 11 C]R116301: NK1 Receptor Ligand Principles of Modelling base-line post-aprepitant Summed image BP ND = / Data Wolfensberger et al.
2 Tracer Model PET scanner Measurement Radioactivity Principles of Modelling Tracer Model Quantitative Evaluation Physiological Parameter Tracer Kinetic Modelling Compartment Models Tracer Model: Purpose: Method: Mathematical description of the fate of the tracer in the human body, in particular in the organ under study To quantify functional entities given the distribution of radioactivity Divide possible distribution of tracer in a limited number of discrete compartments volume tracer Free Bound Glucose metabolism Receptor ligand flow tracer scanning Delivery through arterial blood Input function Nomenclature Consensus nomenclature for in vivo imaging of reversibly binding radioligands Flow Innis RB, Cunningham VJ, Delforge J, Fujita M, Gjedde A, Gunn RN, Holden J, Houle S, Huang SC, Ichise M, Iida H, Ito H, Kimura Y, Koeppe RA, Knudsen GM, Knuuti J, Lammertsma AA, Laruelle M, Logan J, Maguire RP, Mintun MA, Morris ED, Parsey R, Price JC, Slifstein M, Sossi V, Suhara T, Votaw JR, Wong DF, Carson RE J Cereb Flow Metab (2007) 27: 33 39
3 H 2 O as Perfusion Tracer Single Compartment Model Advantages Freely diffusible Metabolically inert Simple kinetics Short half life (2 min) Repeat measurements Disadvantages Short half life On-site cyclotron C A d /dt = C A - = E F; H 2 O: E = 1 = F V T = / = /V T ; H 2 O: =F/V T H 2 O Compartment Model H 2 O Time-Activity Curves C A F F/V T C A F (t) = F C A(t) e -(F/VT)t Non-linear regression F/V T d /dt = F C A -(F/V T ) Solution: (t) = F C A (t) e -(F/V T)t History Delay and dispersion Lammertsma et al. (1990) J Cereb Flow Metab 10: Parametric Images Volume of Distribution CBF Equilibrium - partition coefficient d (t)/dt = 0; dc P (t)/dt=0 V T = /C P Non-equilibrium V T = / C P C P d/dt = C P V T Single tissue compartment model d (t)/dt = C P (t) - (t) At equilibrium: C P (t) - (t) = 0 V T = /C P = / Data Rijbroek, Boellaard, et al.
4 Receptor Ligand Uptake Receptor Studies Three Compartment Model Two Compartment Model C P C F C S metabolites k 5 k 6 metabolites Whole blood C NS PET PET Exchange between C F and C NS fast C ND = C F + C NS Receptor Ligand Model Quantitative PET Study Injection of positron emitting tracer Measurement of time-activity curves Input: plasma (C P ) + whole blood (C WB ) Response: Ideal: tissue ( ) Actual: PET (C PET ) Solution C PET = f (C P, C WB, parameters)
5 PET Receptor Studies PET Receptor Studies PET measurement C PET (t) = (1-V B ) (t) + V B C WB (t) (t) = C ND (t) + C S (t) Relationship with pharmacological parameters = f ND k on (B avail -C S (t)/sa) = k off Note: B avail = B max -B occ (e.g. endogenous ligand) Differential equations V B dc ND (t)/dt = C P (t) - C ND (t) - C ND (t) + C S (t) dc S (t)/dt = C ND (t) - C S (t) Tracer alone = f ND k on B avail = k off K D = k off /k on BP ND = / =f ND B avail /K D Receptor Studies Receptor Studies Parameter of interest Binding Potential: BP ND = / Parameters of interest Tracer alone BP ND = f ND B avail / K D Multiple studies in same subject Separate assessment B avail and K D Binding Potential: BP ND = / Reflects specific binding Tracer alone: BP ND = f ND B avail /K D Volume of distribution: V T = / (1+ / ) Contains non-displaceable component Volume of Distribution Single tissue compartment model At equilibrium: V T = /C P = / C P d/dt = C P Two tissue compartment model At equilibrium: dc ND (t)/dt = dc S (t)/dt = 0 dc S /dt = C ND - C S = 0 C S = ( / ) C ND V T = /C P = (C ND +C S )/C P =(1+ / ) C ND /C P dc ND /dt+dc S /dt = C P - C ND = 0 C ND = ( / ) C P V T = / (1+ / ) Binding Potential input model Direct BP ND = / But: often unstable Indirect Target tissue: V T = / (1+ / ) Reference tissue: V T ' = '/ ' = / BP ND = (V T -V T ')/V T But: reference tissue required Reference tissue model
6 Time after injection (min) Binding Potential Definitions Relative to non-displaceable concentration: BP ND = f ND B avail /K D = (V T -V ND )/V ND = / Overview Kinetic Analysis Process Relative to total plasma concentration: BP P = f P B avail /K D = V T -V ND = / Relative to free plasma concentration: BP F = B avail /K D = (V T -V ND )/f P = /f P Overview kinetic analysis Dynamic PET scan Kinetic model Activity (kbq/ml) Input function Limitations V B Fitting routine time-activity curve Ac (kbq/cc) Tijd (min) Kinetic parameters Limitations Tracer Procedures Model Simplifications Theoretical Model simplifications Complexity physiological process Practical Performance scanner Imperfect implementation Complexity procedure Measurement of blood volume using C O sample: 100% blood, concentration C A PET scanner: tissue concentration concentration is constant: tissue BV = / C A
7 Model Simplifications Pathophysiology C O is a red cell marker Capillary haematocrit < large vessel hematocrit Whole blood concentration is not constant Correction for haematocrit difference required Separate haematocrit measurement Alternative: fixed haematocrit ratio Assumed haematocrit ratio to be checked in pathology A tracer procedure should be reassessed for each new pathophysiological condition Possible breakdown of the model should be considered in interpreting clinical data Limitations Tracer Procedures Complexity Physiological Process Theoretical Model simplifications Complexity physiological process Practical Performance scanner Imperfect implementation Complexity procedure Tracer Metabolite Questions
Using mathematical models & approaches to quantify BRAIN (dynamic) Positron Emission Tomography (PET) data
 Using mathematical models & approaches to quantify BRAIN (dynamic) Positron Emission Tomography (PET) data Imaging Seminars Series Stony Brook University, Health Science Center Stony Brook, NY - January
Using mathematical models & approaches to quantify BRAIN (dynamic) Positron Emission Tomography (PET) data Imaging Seminars Series Stony Brook University, Health Science Center Stony Brook, NY - January
Journal of Biomedical Research, 2012, 26(2): Review. PET imaging for receptor occupancy: meditations on calculation and simplification
 Journal of Biomedical Research, 2012, 26(2): 69-76 JBR Review PET imaging for receptor occupancy: meditations on calculation and simplification Yumin Zhang *, Gerard B. Fox Translational Sciences, Global
Journal of Biomedical Research, 2012, 26(2): 69-76 JBR Review PET imaging for receptor occupancy: meditations on calculation and simplification Yumin Zhang *, Gerard B. Fox Translational Sciences, Global
PET Tracer Kinetic Modeling In Drug
 PET Tracer Kinetic Modeling In Drug Discovery Research Applications Sandra M. Sanabria-Bohórquez Imaging Merck & Co., Inc. Positron Emission Tomography - PET PET is an advanced d imaging i technique permitting
PET Tracer Kinetic Modeling In Drug Discovery Research Applications Sandra M. Sanabria-Bohórquez Imaging Merck & Co., Inc. Positron Emission Tomography - PET PET is an advanced d imaging i technique permitting
Positron Emission Tomography Compartmental Models: A Basis Pursuit Strategy for Kinetic Modelling
 Positron Emission Tomography Compartmental Models: A Basis Pursuit Strategy for Kinetic Modelling Roger N. Gunn, Steve R. Gunn, Federico E. Turkheimer, John A. D. Aston, and Vincent J. Cunningham McConnell
Positron Emission Tomography Compartmental Models: A Basis Pursuit Strategy for Kinetic Modelling Roger N. Gunn, Steve R. Gunn, Federico E. Turkheimer, John A. D. Aston, and Vincent J. Cunningham McConnell
Tomography is imaging by sections. 1
 Tomography is imaging by sections. 1 It is a technique used in clinical medicine and biomedical research to create images that show how certain tissues are performing their physiological functions. 1 Conversely,
Tomography is imaging by sections. 1 It is a technique used in clinical medicine and biomedical research to create images that show how certain tissues are performing their physiological functions. 1 Conversely,
Introduction to SPECT & PET TBMI02 - Medical Image Analysis 2017
 Introduction to SPECT & PET TBMI02 - Medical Image Analysis 2017 Marcus Ressner, PhD, Medical Radiation Physicist, Linköping University Hospital Content What is Nuclear medicine? Basic principles of Functional
Introduction to SPECT & PET TBMI02 - Medical Image Analysis 2017 Marcus Ressner, PhD, Medical Radiation Physicist, Linköping University Hospital Content What is Nuclear medicine? Basic principles of Functional
Parameter identification in medical imaging
 Trabalho apresentado no XXXVII CNMAC, S.J. dos Campos - SP, 017. Proceeding Series of the Brazilian Society of Computational and Applied Mathematics Parameter identification in medical imaging Louise Reips
Trabalho apresentado no XXXVII CNMAC, S.J. dos Campos - SP, 017. Proceeding Series of the Brazilian Society of Computational and Applied Mathematics Parameter identification in medical imaging Louise Reips
Parametric [ 11 C]flumazenil images. Ursula MH Klumpers, Ronald Boellaard, Dick J Veltman, Reina W Kloet, Witte JG Hoogendijk, Adriaan A Lammertsma
![Parametric [ 11 C]flumazenil images. Ursula MH Klumpers, Ronald Boellaard, Dick J Veltman, Reina W Kloet, Witte JG Hoogendijk, Adriaan A Lammertsma Parametric [ 11 C]flumazenil images. Ursula MH Klumpers, Ronald Boellaard, Dick J Veltman, Reina W Kloet, Witte JG Hoogendijk, Adriaan A Lammertsma](/thumbs/81/84602235.jpg) 3 Parametric [ 11 C]flumazenil images Ursula MH Klumpers, Ronald Boellaard, Dick J Veltman, Reina W Kloet, Witte JG Hoogendijk, Adriaan A Lammertsma 50 Chapter 3 ABSTRACT Objective: This [ 11 C]flumazenil
3 Parametric [ 11 C]flumazenil images Ursula MH Klumpers, Ronald Boellaard, Dick J Veltman, Reina W Kloet, Witte JG Hoogendijk, Adriaan A Lammertsma 50 Chapter 3 ABSTRACT Objective: This [ 11 C]flumazenil
Spectral analysis: principle and clinical applications
 REVIEW Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 17, No. 6, 427 434, 2003 Spectral analysis: principle and clinical applications Kenya MURASE Department of Medical Physics and Engineering, Division of Medical Technology
REVIEW Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 17, No. 6, 427 434, 2003 Spectral analysis: principle and clinical applications Kenya MURASE Department of Medical Physics and Engineering, Division of Medical Technology
Introduction to the Course and the Techniques. Jeffry R. Alger, PhD Ahmanson-Lovelace Brain Mapping Center Department of Neurology
 Introduction to the Course and the Techniques Jeffry R. Alger, PhD Ahmanson-Lovelace Brain Mapping Center Department of Neurology (jralger@ucla.edu) CTSI Neuroimaging April 2013 Rationale for the Course
Introduction to the Course and the Techniques Jeffry R. Alger, PhD Ahmanson-Lovelace Brain Mapping Center Department of Neurology (jralger@ucla.edu) CTSI Neuroimaging April 2013 Rationale for the Course
Outline Chapter 14 Nuclear Medicine
 Outline Chapter 14 uclear Medicine Radiation Dosimetry I Text: H.E Johns and J.R. Cunningham, The physics of radiology, 4 th ed. http://www.utoledo.edu/med/depts/radther Introduction Detectors for nuclear
Outline Chapter 14 uclear Medicine Radiation Dosimetry I Text: H.E Johns and J.R. Cunningham, The physics of radiology, 4 th ed. http://www.utoledo.edu/med/depts/radther Introduction Detectors for nuclear
 www.aask24.com www.aask24.com www.aask24.com P=Positron E= Emission T=Tomography Positron emission or beta plus decay (+ ) is a particular type of radioactive decay, in which a proton inside a radionuclide
www.aask24.com www.aask24.com www.aask24.com P=Positron E= Emission T=Tomography Positron emission or beta plus decay (+ ) is a particular type of radioactive decay, in which a proton inside a radionuclide
Bioimage Informatics. Lecture 23, Spring Emerging Applications: Molecular Imaging
 Bioimage Informatics Lecture 23, Spring 2012 Emerging Applications: Molecular Imaging Lecture 23 April 25, 2012 1 Outline Overview of molecular imaging Molecular imaging modalities Molecular imaging applications
Bioimage Informatics Lecture 23, Spring 2012 Emerging Applications: Molecular Imaging Lecture 23 April 25, 2012 1 Outline Overview of molecular imaging Molecular imaging modalities Molecular imaging applications
Graphical Evaluation of Blood-to-Brain Transfer Constants from Multiple-T ime Uptake Data. Generalizations
 Journal o/cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 5:584-590 1985 Raven Press, New York Graphical Evaluation of Blood-to-Brain Transfer Constants from Multiple-T ime Uptake Data. Generalizations Clifford S.
Journal o/cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 5:584-590 1985 Raven Press, New York Graphical Evaluation of Blood-to-Brain Transfer Constants from Multiple-T ime Uptake Data. Generalizations Clifford S.
Nuclear Medicine RADIOPHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY
 Nuclear Medicine RADIOPHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY An alpha particle consists of two protons and two neutrons Common alpha-particle emitters Radon-222 gas in the environment Uranium-234 and -238) in the environment
Nuclear Medicine RADIOPHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY An alpha particle consists of two protons and two neutrons Common alpha-particle emitters Radon-222 gas in the environment Uranium-234 and -238) in the environment
Strategies to Improve Neuroreceptor Parameter Estimation by Linear Regression Analysis
 Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism 22:1271 1281 22 he International Society for Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism Published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Strategies to
Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism 22:1271 1281 22 he International Society for Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism Published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Strategies to
Measuring cerebral blood flow and other haemodynamic parameters using Arterial Spin Labelling MRI. David Thomas
 Measuring cerebral blood flow and other haemodynamic parameters using Arterial Spin Labelling MRI David Thomas Principal Research Associate in MR Physics Leonard Wolfson Experimental Neurology Centre UCL
Measuring cerebral blood flow and other haemodynamic parameters using Arterial Spin Labelling MRI David Thomas Principal Research Associate in MR Physics Leonard Wolfson Experimental Neurology Centre UCL
Functional Neuroimaging with PET
 Functional Neuroimaging with PET Terry Oakes troakes@wisc.edu W.M.Keck Lab for Functional Brain Imaging and Behavior Seeing the Brain Just look at it! Anatomic Images (MRI) Functional Images PET fmri (Just
Functional Neuroimaging with PET Terry Oakes troakes@wisc.edu W.M.Keck Lab for Functional Brain Imaging and Behavior Seeing the Brain Just look at it! Anatomic Images (MRI) Functional Images PET fmri (Just
Dynamic Contrast Enhance (DCE)-MRI
 Dynamic Contrast Enhance (DCE)-MRI contrast enhancement in ASL: labeling of blood (endogenous) for this technique: usage of a exogenous contras agent typically based on gadolinium molecules packed inside
Dynamic Contrast Enhance (DCE)-MRI contrast enhancement in ASL: labeling of blood (endogenous) for this technique: usage of a exogenous contras agent typically based on gadolinium molecules packed inside
On the Undecidability Among Kinetic Models: From Model Selection to Model Averaging
 Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism 23:490 498 2003 The International Society for Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism Published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia On the Undecidability
Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism 23:490 498 2003 The International Society for Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism Published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia On the Undecidability
Physics in Nuclear Medicine
 SIMON R. CHERRY, PH.D. Professor Department of Biomedical Engineering University of California-Davis Davis, California JAMES A. SORENSON, PH.D. Emeritus Professor of Medical Physics University of Wisconsin-Madison
SIMON R. CHERRY, PH.D. Professor Department of Biomedical Engineering University of California-Davis Davis, California JAMES A. SORENSON, PH.D. Emeritus Professor of Medical Physics University of Wisconsin-Madison
Nuclear Medicine Intro & Physics from Medical Imaging Signals and Systems, Chapter 7, by Prince and Links
 Nuclear Medicine Intro & Physics from Medical Imaging Signals and Systems, Chapter 7, by Prince and Links NM - introduction Relies on EMISSION of photons from body (versus transmission of photons through
Nuclear Medicine Intro & Physics from Medical Imaging Signals and Systems, Chapter 7, by Prince and Links NM - introduction Relies on EMISSION of photons from body (versus transmission of photons through
CLINICALLY USEFUL RADIONUCLIDES:
 INTRODUCTION It is important that Nuclear Medicine Technologists be familiar with the imaging properties of all commonly used radionuclides to insure correct choice of isotope for a particular study as
INTRODUCTION It is important that Nuclear Medicine Technologists be familiar with the imaging properties of all commonly used radionuclides to insure correct choice of isotope for a particular study as
The ASL signal. Parenchy mal signal. Venous signal. Arterial signal. Input Function (Label) Dispersion: (t e -kt ) Relaxation: (e -t/t1a )
 Lecture Goals Other non-bold techniques (T2 weighted, Mn contrast agents, SSFP, Dynamic Diffusion, ASL) Understand Basic Principles in Spin labeling : spin inversion, flow vs. perfusion ASL variations
Lecture Goals Other non-bold techniques (T2 weighted, Mn contrast agents, SSFP, Dynamic Diffusion, ASL) Understand Basic Principles in Spin labeling : spin inversion, flow vs. perfusion ASL variations
EL-GY 6813/BE-GY 6203 Medical Imaging, Fall 2016 Final Exam
 EL-GY 6813/BE-GY 6203 Medical Imaging, Fall 2016 Final Exam (closed book, 1 sheets of notes double sided allowed, no calculator or other electronic devices allowed) 1. Ultrasound Physics (15 pt) A) (9
EL-GY 6813/BE-GY 6203 Medical Imaging, Fall 2016 Final Exam (closed book, 1 sheets of notes double sided allowed, no calculator or other electronic devices allowed) 1. Ultrasound Physics (15 pt) A) (9
Radiochemistry in nuclear medicine
 Lecce, Jan 14 2011 Radiochemistry in nuclear medicine Giancarlo Pascali, PhD radiochemist IFC-CNR, Pisa pascali@ifc.cnr.it Do not say contrast media (but Contrast media Mainly anatomical High injected
Lecce, Jan 14 2011 Radiochemistry in nuclear medicine Giancarlo Pascali, PhD radiochemist IFC-CNR, Pisa pascali@ifc.cnr.it Do not say contrast media (but Contrast media Mainly anatomical High injected
Technical University of Denmark
 Technical University of Denmark Page 1 of 10 pages Written test, 12 December 2012 Course name: Introduction to medical imaging Course no. 31540 Aids allowed: None. Pocket calculator not allowed "Weighting":
Technical University of Denmark Page 1 of 10 pages Written test, 12 December 2012 Course name: Introduction to medical imaging Course no. 31540 Aids allowed: None. Pocket calculator not allowed "Weighting":
Nuclear Medicine Treatments and Clinical Applications
 INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 243- LECTURE 2 Nuclear Medicine Treatments and Clinical Applications DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM Next Lectures Outlines Introduction to Nuclear Physics Physics of Radioactivity
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 243- LECTURE 2 Nuclear Medicine Treatments and Clinical Applications DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM Next Lectures Outlines Introduction to Nuclear Physics Physics of Radioactivity
Low Energy Medical Isotope Production. Naomi Ratcliffe IIAA, University of Huddersfield UK
 Low Energy Medical Isotope Production Naomi Ratcliffe naomi.ratcliffe@hud.ac.uk IIAA, University of Huddersfield UK Overview: Nuclear Medicine Cover the use of radioactive isotopes for diagnostic and therapy
Low Energy Medical Isotope Production Naomi Ratcliffe naomi.ratcliffe@hud.ac.uk IIAA, University of Huddersfield UK Overview: Nuclear Medicine Cover the use of radioactive isotopes for diagnostic and therapy
Metabolic system dynamics: lumped and distributed models
 Metabolic system dynamics: lumped and distributed models G.M. Saidel 1,2, J.A. DiBella II 1 & M.E. Cabrera 1,2,3 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Case Western Reserve University Cleveland, OH, USA
Metabolic system dynamics: lumped and distributed models G.M. Saidel 1,2, J.A. DiBella II 1 & M.E. Cabrera 1,2,3 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Case Western Reserve University Cleveland, OH, USA
6: Positron Emission Tomography
 6: Positron Emission Tomography. What is the principle of PET imaging? Positron annihilation Electronic collimation coincidence detection. What is really measured by the PET camera? True, scatter and random
6: Positron Emission Tomography. What is the principle of PET imaging? Positron annihilation Electronic collimation coincidence detection. What is really measured by the PET camera? True, scatter and random
A New Approach of Weighted Integration Technique Based on Accumulated Images Using Dynamic PET and H 50
 Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 11:492-501 1991 The International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism Published by Raven Press, Ltd., New York A New Approach of Weighted Integration
Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 11:492-501 1991 The International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism Published by Raven Press, Ltd., New York A New Approach of Weighted Integration
Best MeV. Best , 25 MeV
 Best 15 15 MeV 400 µa Best 25 20, 25 MeV 400 µa Best 28u/35 20, 28 35 15 MeV 400 1000 µa Best 70 70 35 MeV 700 µa 2014 Best Cyclotron Systems Best Cyclotron Systems 8765 Ash St., Unit 7, Vancouver, BC
Best 15 15 MeV 400 µa Best 25 20, 25 MeV 400 µa Best 28u/35 20, 28 35 15 MeV 400 1000 µa Best 70 70 35 MeV 700 µa 2014 Best Cyclotron Systems Best Cyclotron Systems 8765 Ash St., Unit 7, Vancouver, BC
Historical Perspective - Radiotracing -
 Historical Perspective - Radiotracing - 1911, first radiotracer experiment: 1943 Nobel Prize One of the first radiotracer experiments was an experiment in gastronomy. George de Hevesy, one of the most
Historical Perspective - Radiotracing - 1911, first radiotracer experiment: 1943 Nobel Prize One of the first radiotracer experiments was an experiment in gastronomy. George de Hevesy, one of the most
1st Faculty of Medicine, Charles University in Prague Center for Advanced Preclinical Imaging (CAPI)
 Radioation Resolution and Sensitivity Nuclear Imaging PET + SPECT Radioactive Decay (EC,Ɣ), (β -,Ɣ), (I.T.,Ɣ) β + Projection imaging collimator needed one angular view Projection imaging coincidence imaging,
Radioation Resolution and Sensitivity Nuclear Imaging PET + SPECT Radioactive Decay (EC,Ɣ), (β -,Ɣ), (I.T.,Ɣ) β + Projection imaging collimator needed one angular view Projection imaging coincidence imaging,
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Phys Med Biol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 September 21.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Phys Med Biol. 2012 September 21; 57(18): 5809 5821. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/57/18/5809. Kinetic Parameter Estimation Using a Closed-Form
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Phys Med Biol. 2012 September 21; 57(18): 5809 5821. doi:10.1088/0031-9155/57/18/5809. Kinetic Parameter Estimation Using a Closed-Form
Revision checklist. Step Learning outcome Had a look Nearly there Nailed it!
 Radioactivity a Atomic models Describe the structure of an atom (in terms of nucleus and electrons). State where most of the mass of an atom is found. State the sizes of atoms and small molecules. Describe
Radioactivity a Atomic models Describe the structure of an atom (in terms of nucleus and electrons). State where most of the mass of an atom is found. State the sizes of atoms and small molecules. Describe
This Week. 3/23/2017 Physics 214 Summer
 This Week Atoms and nuclei What are we made of? The periodic table Why does it stop? How were the elements made? Radioactive decay Useful but can be toxic Discovery of X Rays: Cathode Rays and TV sets
This Week Atoms and nuclei What are we made of? The periodic table Why does it stop? How were the elements made? Radioactive decay Useful but can be toxic Discovery of X Rays: Cathode Rays and TV sets
The general concept of pharmacokinetics
 The general concept of pharmacokinetics Hartmut Derendorf, PhD University of Florida Pharmacokinetics the time course of drug and metabolite concentrations in the body Pharmacokinetics helps to optimize
The general concept of pharmacokinetics Hartmut Derendorf, PhD University of Florida Pharmacokinetics the time course of drug and metabolite concentrations in the body Pharmacokinetics helps to optimize
Differentiating Chemical Reactions from Nuclear Reactions
 Differentiating Chemical Reactions from Nuclear Reactions 1 CHEMICAL Occurs when bonds are broken or formed. Atoms remained unchanged, though may be rearranged. Involves valence electrons Small energy
Differentiating Chemical Reactions from Nuclear Reactions 1 CHEMICAL Occurs when bonds are broken or formed. Atoms remained unchanged, though may be rearranged. Involves valence electrons Small energy
Nuclear Radiation. Natural Radioactivity. A person working with radioisotopes wears protective clothing and gloves and stands behind a shield.
 Nuclear Radiation Natural Radioactivity A person working with radioisotopes wears protective clothing and gloves and stands behind a shield. 1 Radioactive Isotopes A radioactive isotope has an unstable
Nuclear Radiation Natural Radioactivity A person working with radioisotopes wears protective clothing and gloves and stands behind a shield. 1 Radioactive Isotopes A radioactive isotope has an unstable
MEDICAL EQUIPMENT: NUCLEAR MEDICINE. Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah
 MEDICAL EQUIPMENT: NUCLEAR MEDICINE Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah www.k-space.org Recommended Textbook Introduction to Medical Imaging: Physics, Engineering and Clinical Applications, by Nadine Barrie Smith
MEDICAL EQUIPMENT: NUCLEAR MEDICINE Prof. Yasser Mostafa Kadah www.k-space.org Recommended Textbook Introduction to Medical Imaging: Physics, Engineering and Clinical Applications, by Nadine Barrie Smith
Radioisotopes in action. Diagnostic application of radioisotopes. Steps of diagnostic procedure. Information from various medical imaging techniques
 Radioisotopes in action Diagnostic application of radioisotopes Steps of diagnostic procedure - Radioactive material introduced into the patient - Distribution and alteration of activity is detected -
Radioisotopes in action Diagnostic application of radioisotopes Steps of diagnostic procedure - Radioactive material introduced into the patient - Distribution and alteration of activity is detected -
ADME studies with radiolabeled compounds. Biomedical Applications of Radioisotopes and Pharmacokinetics Unit
 ADME studies with radiolabeled compounds Miguel Ángel Morcillo Alonso Biomedical Applications of Radioisotopes and Pharmacokinetics Unit CIEMAT (Centro de Investigaciones Energéticas, Medioambientales
ADME studies with radiolabeled compounds Miguel Ángel Morcillo Alonso Biomedical Applications of Radioisotopes and Pharmacokinetics Unit CIEMAT (Centro de Investigaciones Energéticas, Medioambientales
Essentials of nuclear medicine
 Essentials of nuclear medicine Medical imaging CT Rtg X- rays usg Ultrasound MR Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Nuclear Medicine SPECT PET A conventional radiological, ultrasound and magnetic resonance diagnostics
Essentials of nuclear medicine Medical imaging CT Rtg X- rays usg Ultrasound MR Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Nuclear Medicine SPECT PET A conventional radiological, ultrasound and magnetic resonance diagnostics
Radioisotopes and PET
 Radioisotopes and PET 1 Radioisotopes Elements are defined by their number of protons, but there is some variation in the number of neutrons. Atoms resulting from this variation are called isotopes. Consider
Radioisotopes and PET 1 Radioisotopes Elements are defined by their number of protons, but there is some variation in the number of neutrons. Atoms resulting from this variation are called isotopes. Consider
RADIOPHARMACEUTICALS
 RADIOPHARMACEUTICALS Samy Sadek, Ph.D. Associate Professor, New York Medical College. Radiopharmaceutical Chemist, St. Vincent's Hospital- Manhattan. 1 X-Ray Discovery: Roentgen Wilhelm Roentgen ca. 1895.
RADIOPHARMACEUTICALS Samy Sadek, Ph.D. Associate Professor, New York Medical College. Radiopharmaceutical Chemist, St. Vincent's Hospital- Manhattan. 1 X-Ray Discovery: Roentgen Wilhelm Roentgen ca. 1895.
Statistical estimation with Kronecker products in positron emission tomography
 Linear Algebra and its Applications 398 (2005) 25 36 www.elsevier.com/locate/laa Statistical estimation with Kronecker products in positron emission tomography John A.D. Aston a, Roger N. Gunn b,,1 a Statistical
Linear Algebra and its Applications 398 (2005) 25 36 www.elsevier.com/locate/laa Statistical estimation with Kronecker products in positron emission tomography John A.D. Aston a, Roger N. Gunn b,,1 a Statistical
Lesson 14. Radiotracers
 Lesson 14 Radiotracers Introduction Basic principle: All isotopes of a given element will behave identically in most physical, environmental and biological environments. Ea sier to detect radioactive atoms
Lesson 14 Radiotracers Introduction Basic principle: All isotopes of a given element will behave identically in most physical, environmental and biological environments. Ea sier to detect radioactive atoms
( t) ASL Modelling and Quantification. David Thomas. Overview of talk. Brief review of ASL. ASL CBF quantification model. ASL CBF quantification model
 verview of talk AL Modelling and Quantification David homas CL nstitute of Neurology Queen quare, London, K d.thomas@ucl.ac.uk Brief review of AL Descrie the 2 main AL quantification models model General
verview of talk AL Modelling and Quantification David homas CL nstitute of Neurology Queen quare, London, K d.thomas@ucl.ac.uk Brief review of AL Descrie the 2 main AL quantification models model General
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, 44 Binney Street, Boston, MA 02115, USA ramsey
 SPECIAL FEATURE: MEDICAL PHYSICS www.iop.org/journals/physed Nuclear medicine Ramsey D Badawi Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, 44 Binney Street, Boston, MA 02115, USA E-mail: ramsey badawi@dfci.harvard.edu
SPECIAL FEATURE: MEDICAL PHYSICS www.iop.org/journals/physed Nuclear medicine Ramsey D Badawi Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, 44 Binney Street, Boston, MA 02115, USA E-mail: ramsey badawi@dfci.harvard.edu
Welcome to MR! CT PET (with FDG) MRI (T2 w.) MR Image types: T2 weighted T1 weighted Sequence parameters FLAIR Diffusion
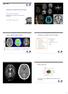 Phsics Images Welcome to R! Introduction to agnetic Resonance Imaging Adam Espe Hansen, PET/R-phsicist Department of Clinical Phsiolog, Nuclear medicine & PET Rigshospitalet Basic Kinetic odeling in olecular
Phsics Images Welcome to R! Introduction to agnetic Resonance Imaging Adam Espe Hansen, PET/R-phsicist Department of Clinical Phsiolog, Nuclear medicine & PET Rigshospitalet Basic Kinetic odeling in olecular
This Week. 7/20/2016 Physics 214 Spring
 This Week Atoms and nuclei What are we made of? The periodic table Why does it stop? How were the elements made? Radioactive decay Useful but can be toxic Discovery of X Rays: Cathode Rays and TV sets
This Week Atoms and nuclei What are we made of? The periodic table Why does it stop? How were the elements made? Radioactive decay Useful but can be toxic Discovery of X Rays: Cathode Rays and TV sets
Isotope Production for Nuclear Medicine
 Isotope Production for Nuclear Medicine Eva Birnbaum Isotope Program Manager February 26 th, 2016 LA-UR-16-21119 Isotopes for Nuclear Medicine More than 20 million nuclear medicine procedures are performed
Isotope Production for Nuclear Medicine Eva Birnbaum Isotope Program Manager February 26 th, 2016 LA-UR-16-21119 Isotopes for Nuclear Medicine More than 20 million nuclear medicine procedures are performed
Sodium isotopes in biology
 Stable Relative Mole isotope atomic mass fraction 23 Na 22.989 769 28 1 Sodium isotopes in biology Both 22 Na and 24 Na can be used as radioactive tracers to study electrolytes in the human body [102-104].
Stable Relative Mole isotope atomic mass fraction 23 Na 22.989 769 28 1 Sodium isotopes in biology Both 22 Na and 24 Na can be used as radioactive tracers to study electrolytes in the human body [102-104].
Chemical Exchange. Spin-interactions External interactions Magnetic field Bo, RF field B1
 Chemical Exchange Spin-interactions External interactions Magnetic field Bo, RF field B1 Internal Interactions Molecular motions Chemical shifts J-coupling Chemical Exchange 1 Outline Motional time scales
Chemical Exchange Spin-interactions External interactions Magnetic field Bo, RF field B1 Internal Interactions Molecular motions Chemical shifts J-coupling Chemical Exchange 1 Outline Motional time scales
Radiation Detectors. How do we detect ionizing radiation? What are these effects? Types of Ionizing Radiation Detectors
 Radiation Detectors 1 How do we detect ionizing radiation? Indirectly, by its effects as it traverses matter? What are these effects? Ionization and excitation of the atoms and molecules Heat 2 Types of
Radiation Detectors 1 How do we detect ionizing radiation? Indirectly, by its effects as it traverses matter? What are these effects? Ionization and excitation of the atoms and molecules Heat 2 Types of
An Input Function Estimation Method for. FDG-PET Human Brain Studies 1
 An Input Function Estimation Method for FDG-PET Human Brain Studies 1 Hongbin Guo,2 Rosemary A Renaut 2 Kewei Chen 3 Abbreviated Title: Input Function Estimation for FDG-PET Abstract Introduction: A new
An Input Function Estimation Method for FDG-PET Human Brain Studies 1 Hongbin Guo,2 Rosemary A Renaut 2 Kewei Chen 3 Abbreviated Title: Input Function Estimation for FDG-PET Abstract Introduction: A new
Laboratory 3: Kit Preparation and Chromatography. Design Considerations for a Radiopharmaceutical
 Laboratory 3: Kit Preparation and Chromatography PART 1: KIT PREPARATION Introduction In nuclear medicine, radionuclides are rarely used in their simplest chemical form. Instead they are incorporated into
Laboratory 3: Kit Preparation and Chromatography PART 1: KIT PREPARATION Introduction In nuclear medicine, radionuclides are rarely used in their simplest chemical form. Instead they are incorporated into
ELG7173 Topics in signal Processing II Computational Techniques in Medical Imaging
 ELG7173 Topics in signal Processing II Computational Techniques in Medical Imaging Topic #1: Intro to medical imaging Medical Imaging Classifications n Measurement physics Send Energy into body Send stuff
ELG7173 Topics in signal Processing II Computational Techniques in Medical Imaging Topic #1: Intro to medical imaging Medical Imaging Classifications n Measurement physics Send Energy into body Send stuff
Unit 12: Nuclear Chemistry
 Unit 12: Nuclear Chemistry 1. Stability of isotopes is based on the ratio of neutrons and protons in its nucleus. Although most nuclei are stable, some are unstable and spontaneously decay, emitting radiation.
Unit 12: Nuclear Chemistry 1. Stability of isotopes is based on the ratio of neutrons and protons in its nucleus. Although most nuclei are stable, some are unstable and spontaneously decay, emitting radiation.
Study of the feasibility of a compact gamma camera for real-time cancer assessment
 Study of the feasibility of a compact gamma camera for real-time cancer assessment L. Caballero Instituto de Física Corpuscular - CSIC - University of Valencia; C/Catedrático José Beltrán, 2; E-46980;
Study of the feasibility of a compact gamma camera for real-time cancer assessment L. Caballero Instituto de Física Corpuscular - CSIC - University of Valencia; C/Catedrático José Beltrán, 2; E-46980;
2015 U N I V E R S I T I T E K N O L O G I P E T R O N A S
 Multi-Modality based Diagnosis: A way forward by Hafeez Ullah Amin Centre for Intelligent Signal and Imaging Research (CISIR) Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering 2015 U N I V E R S I T I
Multi-Modality based Diagnosis: A way forward by Hafeez Ullah Amin Centre for Intelligent Signal and Imaging Research (CISIR) Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering 2015 U N I V E R S I T I
The Impact of Nuclear Science on Life Science. Introduction
 The Impact of Nuclear Science on Life Science Introduction G. Kraft GSI, Biophysik, Darmstadt, Germany The development of life science was always strongly interconnected with physical sciences. This interaction
The Impact of Nuclear Science on Life Science Introduction G. Kraft GSI, Biophysik, Darmstadt, Germany The development of life science was always strongly interconnected with physical sciences. This interaction
β and γ decays, Radiation Therapies and Diagnostic, Fusion and Fission Final Exam Surveys New material Example of β-decay Beta decay Y + e # Y'+e +
 β and γ decays, Radiation Therapies and Diagnostic, Fusion and Fission Last Lecture: Radioactivity, Nuclear decay Radiation damage This lecture: nuclear physics in medicine and fusion and fission Final
β and γ decays, Radiation Therapies and Diagnostic, Fusion and Fission Last Lecture: Radioactivity, Nuclear decay Radiation damage This lecture: nuclear physics in medicine and fusion and fission Final
Schémata zpracovalo Servisní středisko pro e-learning na MU
 Schémata zpracovalo Servisní středisko pro e-learning na MU http://is.muni.cz/stech/ Life is a dynamic system with focused behavior, with autoreproduction, characterized by flow of substrates, energies
Schémata zpracovalo Servisní středisko pro e-learning na MU http://is.muni.cz/stech/ Life is a dynamic system with focused behavior, with autoreproduction, characterized by flow of substrates, energies
PANEL DISCUSSION. Radionuclides and Health A promising future! OCTOBER 14-16, 2014 PARIS LE BOURGET FRANCE
 PANEL DISCUSSION Radionuclides and Health A promising future! Hosted by Richard Zimmermann, Chrysalium Consulting Discussion coordinated by François Sarkozy, President of FSNB Health & Care Speakers: Remigiusz
PANEL DISCUSSION Radionuclides and Health A promising future! Hosted by Richard Zimmermann, Chrysalium Consulting Discussion coordinated by François Sarkozy, President of FSNB Health & Care Speakers: Remigiusz
Radiopharmacy. Prof. Roger Schibli Department of Chemistry and Applied Biosciences ETHZ Center for Radiopharmaceutical Science ETH-PSI-USZ
 Wider Horizons for Pharmacists Radiopharmacy Prof. Roger Schibli Department of Chemistry and Applied Biosciences ETHZ Center for Radiopharmaceutical Science ETH-PSI-USZ Radiopharmacy? 7.12.2012 Institute
Wider Horizons for Pharmacists Radiopharmacy Prof. Roger Schibli Department of Chemistry and Applied Biosciences ETHZ Center for Radiopharmaceutical Science ETH-PSI-USZ Radiopharmacy? 7.12.2012 Institute
Faculty of Sciences. Analysis of Positron Emission Tomography data: A comparison between approaches for linearized time-activity curves.
 Faculty of Sciences Analysis of Positron Emission Tomography data: A comparison between approaches for linearized time-activity curves Bart de Laat Master dissertation submitted to obtain the degree of
Faculty of Sciences Analysis of Positron Emission Tomography data: A comparison between approaches for linearized time-activity curves Bart de Laat Master dissertation submitted to obtain the degree of
22.56J Noninvasive Imaging in Biology and Medicine Instructor: Prof. Alan Jasanoff Fall 2005, TTh 1-2:30
 22.56J Noninvasive Imaging in Biology and Medicine Instructor: Prof. Alan Jasanoff Fall 2005, TTh 1-2:30 Sample problems HW1 1. Look up (e.g. in the CRC Manual of Chemistry and Physics www.hbcpnetbase.com)
22.56J Noninvasive Imaging in Biology and Medicine Instructor: Prof. Alan Jasanoff Fall 2005, TTh 1-2:30 Sample problems HW1 1. Look up (e.g. in the CRC Manual of Chemistry and Physics www.hbcpnetbase.com)
Nuclear Chemistry. Background Radiation. Three-fourths of all exposure to radiation comes from background radiation.
 Chapter 11 Nuclear Chemistry Background Radiation Three-fourths of all exposure to radiation comes from background radiation. Most of the remaining one-fourth comes from medical irradiation such as X-rays.
Chapter 11 Nuclear Chemistry Background Radiation Three-fourths of all exposure to radiation comes from background radiation. Most of the remaining one-fourth comes from medical irradiation such as X-rays.
12/1/17 OUTLINE KEY POINTS ELEMENTS WITH UNSTABLE NUCLEI Radioisotopes and Nuclear Reactions 16.2 Biological Effects of Nuclear Radiation
 OUTLINE 16.1 Radioisotopes and Nuclear Reactions 16.2 Biological Effects of Nuclear Radiation PET scan X-ray technology CT scan 2009 W.H. Freeman KEY POINTS Radioactivity is the consequence of an unstable
OUTLINE 16.1 Radioisotopes and Nuclear Reactions 16.2 Biological Effects of Nuclear Radiation PET scan X-ray technology CT scan 2009 W.H. Freeman KEY POINTS Radioactivity is the consequence of an unstable
Properties of the nucleus. 8.2 Nuclear Physics. Isotopes. Stable Nuclei. Size of the nucleus. Size of the nucleus
 Properties of the nucleus 8. Nuclear Physics Properties of nuclei Binding Energy Radioactive decay Natural radioactivity Consists of protons and neutrons Z = no. of protons (Atomic number) N = no. of neutrons
Properties of the nucleus 8. Nuclear Physics Properties of nuclei Binding Energy Radioactive decay Natural radioactivity Consists of protons and neutrons Z = no. of protons (Atomic number) N = no. of neutrons
Basic physics of nuclear medicine
 Basic physics of nuclear medicine Nuclear structure Atomic number (Z): the number of protons in a nucleus; defines the position of an element in the periodic table. Mass number (A) is the number of nucleons
Basic physics of nuclear medicine Nuclear structure Atomic number (Z): the number of protons in a nucleus; defines the position of an element in the periodic table. Mass number (A) is the number of nucleons
69 Ga Ga
 Stable isotope Relative atomic mass Mole fraction 69 Ga 68.925 574 0.601 08 71 Ga 70.924 703 0.398 92 Gallium isotopes in medicine 68 Ga is a radioactive isotope that emits positrons, which are used to
Stable isotope Relative atomic mass Mole fraction 69 Ga 68.925 574 0.601 08 71 Ga 70.924 703 0.398 92 Gallium isotopes in medicine 68 Ga is a radioactive isotope that emits positrons, which are used to
Year 12 Notes Radioactivity 1/5
 Year Notes Radioactivity /5 Radioactivity Stable and Unstable Nuclei Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration of certain nuclei, a random process in which particles and/or high-energy photons are
Year Notes Radioactivity /5 Radioactivity Stable and Unstable Nuclei Radioactivity is the spontaneous disintegration of certain nuclei, a random process in which particles and/or high-energy photons are
Positron Emission Tomography
 Positron Emission Tomography CERN Accelerator School Small Accelerators Zeegse, the Netherlands A.M.J. Paans Nuclear Medicine & Molecular Imaging UMC Groningen Elements of Life PET-nuclide Hydrogen Carbon
Positron Emission Tomography CERN Accelerator School Small Accelerators Zeegse, the Netherlands A.M.J. Paans Nuclear Medicine & Molecular Imaging UMC Groningen Elements of Life PET-nuclide Hydrogen Carbon
Medical Biophysics II. Final exam theoretical questions 2013.
 Medical Biophysics II. Final exam theoretical questions 2013. 1. Early atomic models. Rutherford-experiment. Franck-Hertz experiment. Bohr model of atom. 2. Quantum mechanical atomic model. Quantum numbers.
Medical Biophysics II. Final exam theoretical questions 2013. 1. Early atomic models. Rutherford-experiment. Franck-Hertz experiment. Bohr model of atom. 2. Quantum mechanical atomic model. Quantum numbers.
Medical Applications of Nuclear Radiation and Isotopes
 Mitglied der Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft Medical Applications of Nuclear Radiation and Isotopes Syed M. Qaim Forschungszentrum Jülich and Universität zu Köln, Germany E-mail: s.m.qaim@fz-juelich.de Lecture
Mitglied der Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft Medical Applications of Nuclear Radiation and Isotopes Syed M. Qaim Forschungszentrum Jülich and Universität zu Köln, Germany E-mail: s.m.qaim@fz-juelich.de Lecture
PRODUCTION OF RADIOISOTOPES FOR IMAGING AND THERAPY AT LOW ENERGY
 PRODUCTION OF RADIOISOTOPES FOR IMAGING AND THERAPY AT LOW ENERGY THOMAS J. RUTH TRIUMF Vancouver, BC, Canada truth@triumf.ca 1 Introduction The production of radioisotopes for use in biomedical procedures
PRODUCTION OF RADIOISOTOPES FOR IMAGING AND THERAPY AT LOW ENERGY THOMAS J. RUTH TRIUMF Vancouver, BC, Canada truth@triumf.ca 1 Introduction The production of radioisotopes for use in biomedical procedures
Mayneord-Phillips Summer School St Edmund Hall, University of Oxford July Proton decays to n, e +, ν
 Positron Emission Tomography Physics & Instrumentation Dimitra G. Darambara, Ph.D Multimodality Molecular Imaging Joint Department of Physics RMH/ICR Outline Introduction PET Physics overview Types of
Positron Emission Tomography Physics & Instrumentation Dimitra G. Darambara, Ph.D Multimodality Molecular Imaging Joint Department of Physics RMH/ICR Outline Introduction PET Physics overview Types of
Outline. Superconducting magnet. Magnetic properties of blood. Physiology BOLD-MRI signal. Magnetic properties of blood
 Magnetic properties of blood Physiology BOLD-MRI signal Aart Nederveen Department of Radiology AMC a.j.nederveen@amc.nl Outline Magnetic properties of blood Moses Blood oxygenation BOLD fmri Superconducting
Magnetic properties of blood Physiology BOLD-MRI signal Aart Nederveen Department of Radiology AMC a.j.nederveen@amc.nl Outline Magnetic properties of blood Moses Blood oxygenation BOLD fmri Superconducting
Blood Water Dynamics
 Bioengineering 208 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Winter 2007 Lecture 8 Arterial Spin Labeling ASL Basics ASL for fmri Velocity Selective ASL Vessel Encoded ASL Blood Water Dynamics Tissue Water Perfusion:
Bioengineering 208 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Winter 2007 Lecture 8 Arterial Spin Labeling ASL Basics ASL for fmri Velocity Selective ASL Vessel Encoded ASL Blood Water Dynamics Tissue Water Perfusion:
PHARMACOKINETIC DERIVATION OF RATES AND ORDERS OF REACTIONS IN MULTI- COMPARTMENT MODEL USING MATLAB
 IJPSR (2016), Vol. 7, Issue 11 (Research Article) Received on 29 May, 2016; received in revised form, 07 July, 2016; accepted, 27 July, 2016; published 01 November, 2016 PHARMACOKINETIC DERIVATION OF RATES
IJPSR (2016), Vol. 7, Issue 11 (Research Article) Received on 29 May, 2016; received in revised form, 07 July, 2016; accepted, 27 July, 2016; published 01 November, 2016 PHARMACOKINETIC DERIVATION OF RATES
Positron Emission Tomography Basics: Radiochemistry. N. Scott Mason, Ph.D. Radiochemist University of Pittsburgh PET Facility
 Positron Emission Tomography Basics: Radiochemistry. Scott Mason, Ph.D. Radiochemist PET Facility What is PET? Positron Emission Tomography In-Vivo Imaging and Quantification of rgan/tissue Function Uses
Positron Emission Tomography Basics: Radiochemistry. Scott Mason, Ph.D. Radiochemist PET Facility What is PET? Positron Emission Tomography In-Vivo Imaging and Quantification of rgan/tissue Function Uses
PET scan simulation. Meysam Dadgar. UMSU, Iran. IFMP, Elbasan, Fig 1: PET camera simulation in gate by cylindrical phantom
 PET scan simulation Meysam Dadgar UMSU, Iran IFMP, Elbasan, 2016 Meysamdadgar10@gmail.com 1 Fig 1: PET camera simulation in gate by cylindrical phantom 2 What is PET? Positron emission tomography (PET),
PET scan simulation Meysam Dadgar UMSU, Iran IFMP, Elbasan, 2016 Meysamdadgar10@gmail.com 1 Fig 1: PET camera simulation in gate by cylindrical phantom 2 What is PET? Positron emission tomography (PET),
Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology
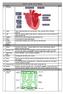 Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
Week 1: 1. The Heart Science Year 10 Unit 1 Biology RAG 2. Artery Takes oxygenated blood away from the heart. Thick, muscular walls to withstand pressure. 3. Vein Takes deoxygenated blood towards the heart.
Dosimetry of patients injected with tracers Ga-68, Zr-89 and Lu-177. Bruno Vanderlinden
 Dosimetry of patients injected with tracers Ga-68, Zr-89 and Lu-177 Bruno Vanderlinden What is NM speciality? Imaging radiology Physics Diagnostic Treatment assessment Clinical pathology Biological marker
Dosimetry of patients injected with tracers Ga-68, Zr-89 and Lu-177 Bruno Vanderlinden What is NM speciality? Imaging radiology Physics Diagnostic Treatment assessment Clinical pathology Biological marker
Radioisotopes in action. Diagnostic application of radioisotopes. Steps of diagnostic procedure. Information from various medical imaging techniques
 Radioisotopes in action Diagnostic application of radioisotopes Steps of diagnostic procedure - Radioactive material introduced into the patient - Distribution and alteration of activity is detected -Monitoring
Radioisotopes in action Diagnostic application of radioisotopes Steps of diagnostic procedure - Radioactive material introduced into the patient - Distribution and alteration of activity is detected -Monitoring
A Neurosurgeon s Perspectives of Diffusion Tensor Imaging(DTI) Diffusion Tensor MRI (DTI) Background and Relevant Physics.
 A Neurosurgeon s Perspectives of Diffusion Tensor Imaging(DTI) Kalai Arasu Muthusamy, D.Phil(Oxon) Senior Lecturer & Consultant Neurosurgeon. Division of Neurosurgery. University Malaya Medical Centre.
A Neurosurgeon s Perspectives of Diffusion Tensor Imaging(DTI) Kalai Arasu Muthusamy, D.Phil(Oxon) Senior Lecturer & Consultant Neurosurgeon. Division of Neurosurgery. University Malaya Medical Centre.
Technical University of Denmark
 Technical University of Denmark Page 1 of 11 pages Written test, 9 December 2010 Course name: Introduction to medical imaging Course no. 31540 Aids allowed: none. "Weighting": All problems weight equally.
Technical University of Denmark Page 1 of 11 pages Written test, 9 December 2010 Course name: Introduction to medical imaging Course no. 31540 Aids allowed: none. "Weighting": All problems weight equally.
HY Ιατρική Απεικόνιση. Διδάσκων: Kώστας Μαριάς
 HY 571 - Ιατρική Απεικόνιση Διδάσκων: Kώστας Μαριάς 11. MRI Τ1,Τ2, PD and physiological parameter imaging Summary and Clarifications Resonance is referred to as the property of an atom to absorb energy
HY 571 - Ιατρική Απεικόνιση Διδάσκων: Kώστας Μαριάς 11. MRI Τ1,Τ2, PD and physiological parameter imaging Summary and Clarifications Resonance is referred to as the property of an atom to absorb energy
Bases of radioisotope diagnostic methods
 Medical, pharmaceutical applications of radioisotopes Bases of radioisotope diagnostic methods Dr. István Voszka Basis of application: radioisotopes have identical behavior in the organism to corresponding
Medical, pharmaceutical applications of radioisotopes Bases of radioisotope diagnostic methods Dr. István Voszka Basis of application: radioisotopes have identical behavior in the organism to corresponding
Radionuclide Imaging MII Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
 Radionuclide Imaging MII 3073 Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Positron (β + ) emission Positron is an electron with positive charge. Positron-emitting radionuclides are most commonly produced in cyclotron
Radionuclide Imaging MII 3073 Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Positron (β + ) emission Positron is an electron with positive charge. Positron-emitting radionuclides are most commonly produced in cyclotron
11/10/2014. Chapter 1: Introduction to Medical Imaging. Projection (Transmission) vs. Emission Imaging. Emission Imaging
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Medical Imaging Overview of Modalities Properties of an Image: Limitations on Information Content Contrast (both object & image): Brightness difference Sharpness (blur): Smallest
Chapter 1: Introduction to Medical Imaging Overview of Modalities Properties of an Image: Limitations on Information Content Contrast (both object & image): Brightness difference Sharpness (blur): Smallest
Chapter 2 PET Imaging Basics
 Chapter 2 PET Imaging Basics Timothy G. Turkington PET Radiotracers Positron emission tomography (PET) imaging is the injection (or inhalation) of a substance containing a positron emitter, the subsequent
Chapter 2 PET Imaging Basics Timothy G. Turkington PET Radiotracers Positron emission tomography (PET) imaging is the injection (or inhalation) of a substance containing a positron emitter, the subsequent
Imaging Brain Structure and Function
 Imaging Brain Structure and Function Thomas J. Grabowski, Jr., MD Professor, Radiology and Neurology (joint) Director, UW Integrated Brain Imaging Center Director, UW Alzheimer s Disease Research Center
Imaging Brain Structure and Function Thomas J. Grabowski, Jr., MD Professor, Radiology and Neurology (joint) Director, UW Integrated Brain Imaging Center Director, UW Alzheimer s Disease Research Center
Medical Physics. Nuclear Medicine Principles and Applications
 Medical Physics Nuclear Medicine Principles and Applications Dr Roger Fulton Department of PET & Nuclear Medicine Royal Prince Alfred Hospital Sydney Email: rfulton@mail.usyd.edu.au Lectures: http://www-personal.usyd.edu.au/~rfulton/medical_physics
Medical Physics Nuclear Medicine Principles and Applications Dr Roger Fulton Department of PET & Nuclear Medicine Royal Prince Alfred Hospital Sydney Email: rfulton@mail.usyd.edu.au Lectures: http://www-personal.usyd.edu.au/~rfulton/medical_physics
Units and Definition
 RADIATION SOURCES Units and Definition Activity (Radioactivity) Definition Activity: Rate of decay (transformation or disintegration) is described by its activity Activity = number of atoms that decay
RADIATION SOURCES Units and Definition Activity (Radioactivity) Definition Activity: Rate of decay (transformation or disintegration) is described by its activity Activity = number of atoms that decay
Imaging: PET and SPECT
 Imaging: PET and SPECT Positron Emission Tomography Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography PET and SPECT Properties of ideal imaging nuclides, biological, chemical, physical Production of radionuclides
Imaging: PET and SPECT Positron Emission Tomography Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography PET and SPECT Properties of ideal imaging nuclides, biological, chemical, physical Production of radionuclides
