Magic. The Lattice Boltzmann Method
|
|
|
- Osborn Bailey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Magic The Lattice Boltzmann Method
2 Lattice Boltzmann: secret ingredients Kn(Ma t f + v x x f + v y y f + v z z f ) = Ω( f ) Analysis Modeling Kn(Ma t π α + x π αx + y π αy + z π αz ) = ω α ( α π α ) ω α : magic relaxation rates α : magic attractors
3 Cumulant method: a magic example 10-1 D3Q27 lattice Magic attractors: relax cumulants Magic relaxation rate: Relative error ER BGK ELB CUM II ω xyz = 2 ω xy L x =L z Error in viscosity Magic cumulant method O(k 4 ) BGK/ELB O(k 2 )
4 From Magic to Science Step 1: Galilean invariance Central moments or cumulants Step 2: Optimize relaxation rates Errors from Taylor analysis still to Find roots of error pre-factors be done
5 Galilean invariance in weak sense Problem: relaxation of (raw) moments with different rates like in MRT method breaks Galilean invariance
6 Galilean invariance in weak sense Regard MRT raw moment equations: Kn(Ma t π xy + x π xxy + y π xyy )=ω xy (π eq xy π xy ) Kn(Ma t π xx + x π xxx + y π xxy )=ω xx (π eq xx π xx ) Kn(Ma t π xxy + x π xxxy + y π xxyy )=ω xxy (π eq xxy π xxy ) Apply Galilean transformation to 3rd eq. π eq xx=π 2 x + 1/3 π eq xy=π x π y π eq xxy=π y /3 π x π x + a π y π y + b π xxy π xxy + bπ xx + 2aπ xy + 2abπ x + a 2 π y + a 2 b rhs xxy +b rhs xx + 2a rhs xy + 2ab rhs x + a 2 rhs y + a 2 b rhs 0 = lhs xxy + b ω xxy ω xx lhs xx + 2a ω xxy ω xy lhs xy Failed!
7 Scattering cascade Non-linear transformation to Galilean invariant variables Central moments Cumulants Back to raw moments n x k x n y k y n z k z vf { f } n x k x n y k y n z k z log(f { f }) n x k x n y k y n z k z F { f } Example 3rd moment ( xxy = 2π x π xy + ω ) xy ( xy π xy ) 2π 2xπ ( y + π y π xx + ω ) xx ( xx π xx ) ω xxy ω xxy
8 in weak sense Galilean invariance at 3rd order moments Perform the Galilean transformation π x π x + a π y π y + b π xxy π xxy + bπ xx + 2aπ xy + 2abπ x + a 2 π y + a 2 b rhs xxy +b rhs xx + 2a rhs xy + 2ab rhs x + a 2 rhs y + a 2 b rhs 0 = lhs xxy + b lhs xx + 2a lhs xy Correct! 3rd order moment now as Galilean invariant as they would be with BGK ansatz
9 Central moments versus cumulants Raw moments: orthogonal decomposition in lattice (=arbitrary) frame of reference Central moments: orthogonal decomposition in frame moving with flow Cumulants or irreducible moments orthogonal decomposition in any frame of reference
10 Equilibrium central moments Transform to raw moments Central moment equilibria polynomials in first order raw moments and monomials in raw moments advection for nonconserved moment! xxyz=2π xyz π x π yz π 2 x + π xxz π y 2π xz π x π y +π xxy π z 2π xy π x π z π xx π y π z + 3π 2 xπ y π z
11 Equilibrium cumulants Transform to raw moments diffusion for nonconserved moment! xxyz= 4π y π x π xz + 2π xz π xy + 2π x π xyz + π yz (π xx 2π 2 x) +π y π xxz + π z (π y (6π 2 x 2π xx ) + π xxy 4π x π xy )) Cumulant equilibria polynomial in all lower order raw moments
12 Test case: 3rd order O(Ma 2 ) Let us investigate: Kn(Ma t π xyy + x π xxyy + y π xyyy + z π xyyz ) = ω xyy ( xyy π xyy ) Assumptions: truncated ( equilibrium state) at 4th order Expansion to low order using π yy = 1/3 +O(Ma 2 ) π xyy =π x /3 +O(Ma 3 ) xyy π xyy =O(Ma 3 )
13 Test case: 3rd order O(Ma 2 ) Note that: Ma t π x = x π xx y π xy z π xz So: x (π xxyy π xx /3) + y (π xyyy π xy /3) + z (π xyyz π xz /3) = O(Ma 4 ) Hence: π xxyy π xx /3 +O(Ma 4 ) π xyyy π xy /3 +O(Ma 4 ) π xyyz π xz /3 +O(Ma 4 )
14 Test case: compare Central moments Cumulants Failed! xxyy=1/9 + π 2 x/3 + π 2 z/3 +O(Ma 4 ) xyyy=π x π y +O(Ma 4 ) xyyz=π x π z /3 +O(Ma 4 ) xxyy=π xx /3 +O(Ma 4 ) xyyy=π xy + π x π y +O(Ma 4 ) xyyz=π xz /3 +O(Ma 4 ) Failed! Failed! Failed!
15 Understand the errors (a research plan) Taylor method (Dubois) a little modified π α + MaKn t π α + = π α Kn( x π αx + y π αy + z π αz) Pre-collision expansion in time = Post-collision expansion in space Expansion in moment form Two scale parameters No generic (acoustic or diffusive) scaling several possibilities Ma & Kn suggested by Asinari
16 Some pitfalls on our way... Expansion parameters ought to be small Not clear for time step expansion Asymptotic order ought to increase with expansion True for Knudsen but false for Mach!
17 Do not forget to scale relaxation rates ν = c 2 s ( 1 ω xy 1 2 O(Ma 2 ) π xy = π eq xy ) O(Kn/Ma) ν Re 1 = Kn Ma 1 = Kn ω xy Ma ( ) 1 1 (Kn x π ω xxy + Kn y π xyy + ) xy O(Ma)!!! O(Ma)!!! diffusive scaling: Ma=Kn better? Be careful using this: π xy = π eq xy +O(Kn) equilibrium as small as reminder!!!
18 Equilibria and their scale in Mach number π eq xy=o(ma 2 ) π eq xx=o(1) π eq xyy=o(ma) π eq xyz=o(ma 3 ) π eq xxyy=o(1) π eq xxyz=o(ma 2 ) π eq xxyyz=o(ma) cyclic repetition of O(Ma), O(Ma 2 ), & O(Ma 3 ) for all higher order moments O(Ma 3 ) is highest order for any moment! no 4th order moment higher than O(Ma 2 ) all odd order moments are at least O(Ma) Convergence completely up to Knudsen number!
19 Magic parameters Analytic solution NSE u y (x,y,z,t = 0)=u 0 sin(2x/l x π)cos(2z/l z π) [ u y (x,y,z,t)=u y (x,y,z,t = 0)e νt ( 2π Lx) 2 +( 2π Lz) 2] L z (" # ") / " ω 4 = ω 5 = ω ! 1 ω 1 = 2 ω 1 = 1 ω 4 = ω 5 = 2 ω 1 ω 1 :viscosity ω 3 = ω 1 :π xxy + π yzz ω 4 :π xxy π yzz ω 5 :π xyz BGK ELB MRT II CLB II CUM II MRT III CLB III CUM III Relative error ER BGK ELB CUM II L x u y BGK & ELB magic cumulants ν = O(h 2 ) O(h 4 ) L x =L z
20 Magic MRT versus magic cumulants 10-1 MRT needs magic parameter for 4th order moment central moments & cumulants Relative error ER BGK ELB CLB * CLB I CLB II MRT I MRT II CUM I CUM II best result: cumulants truncated at 4th order L x =L z use cumulant equilibrium!! strong violations of Galilean invariance in MRT CLB II CUM II MRT II u x O(Ma 2 )!!! this makes the difference! xxyz= 4π y π x π xz + 2π xz π xy + 2π x π xyz + π yz (π xx 2π 2 x) +π y π xxz + π z (π y (6π 2 x 2π xx ) + π xxy 4π x π xy ))
21 Questionnaire Are parameters magic or quadric? Magic! I do not understand them! Do they help us? If they work under general condition, then they are a big leap forward. If not, we might still learn something important from them. We have to understand them! Are cumulants better than moments? Yes! Galilean invariance and stability is improved. Quadric behavior even if we equilibrate 4th cumulants. But they do not solve all problems...
Generalized Local Equilibrium in the Cascaded Lattice Boltzmann Method. Abstract
 Accepted for publication on Physical Review E (R), code ERR1034 Generalized Local Equilibrium in the Cascaded Lattice Boltzmann Method Pietro Asinari Department of Energetics, Politecnico di Torino, Corso
Accepted for publication on Physical Review E (R), code ERR1034 Generalized Local Equilibrium in the Cascaded Lattice Boltzmann Method Pietro Asinari Department of Energetics, Politecnico di Torino, Corso
2x (x 2 + y 2 + 1) 2 2y. (x 2 + y 2 + 1) 4. 4xy. (1, 1)(x 1) + (1, 1)(y + 1) (1, 1)(x 1)(y + 1) 81 x y y + 7.
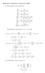 Homework 8 Solutions, November 007. (1 We calculate some derivatives: f x = f y = x (x + y + 1 y (x + y + 1 x = (x + y + 1 4x (x + y + 1 4 y = (x + y + 1 4y (x + y + 1 4 x y = 4xy (x + y + 1 4 Substituting
Homework 8 Solutions, November 007. (1 We calculate some derivatives: f x = f y = x (x + y + 1 y (x + y + 1 x = (x + y + 1 4x (x + y + 1 4 y = (x + y + 1 4y (x + y + 1 4 x y = 4xy (x + y + 1 4 Substituting
Analysis of the Lattice Boltzmann Method by the Truncated Moment System
 by the Truncated Moment System Pietro Asinari, PhD Department of Energetics, Politecnico di Torino, Torino 10129, Italy, pietro.asinari@polito.it http://staff.polito.it/pietro.asinari Lab for Simulation,
by the Truncated Moment System Pietro Asinari, PhD Department of Energetics, Politecnico di Torino, Torino 10129, Italy, pietro.asinari@polito.it http://staff.polito.it/pietro.asinari Lab for Simulation,
1. A polynomial p(x) in one variable x is an algebraic expression in x of the form
 POLYNOMIALS Important Points 1. A polynomial p(x) in one variable x is an algebraic expression in x of the form p(x) = a nx n +a n-1x n-1 + a 2x 2 +a 1x 1 +a 0x 0 where a 0, a 1, a 2 a n are constants
POLYNOMIALS Important Points 1. A polynomial p(x) in one variable x is an algebraic expression in x of the form p(x) = a nx n +a n-1x n-1 + a 2x 2 +a 1x 1 +a 0x 0 where a 0, a 1, a 2 a n are constants
Question: 1. Use suitable identities to find the following products:
 CH-2 Polynomial Question: 1. Use suitable identities to find the following products: (i) (x + 4) (x + 10) Solution:- (x+4)(x+10) = x 2 +10x+4x+4 x 10 = x 2 +14x+40 (ii) (x + 8) (x 10) Solution: x 2-10x+8x-80
CH-2 Polynomial Question: 1. Use suitable identities to find the following products: (i) (x + 4) (x + 10) Solution:- (x+4)(x+10) = x 2 +10x+4x+4 x 10 = x 2 +14x+40 (ii) (x + 8) (x 10) Solution: x 2-10x+8x-80
Lattice Boltzmann Method for Moving Boundaries
 Lattice Boltzmann Method for Moving Boundaries Hans Groot March 18, 2009 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Moving Boundary Conditions 3 Cylinder in Transient Couette Flow 4 Collision-Advection Process for Moving
Lattice Boltzmann Method for Moving Boundaries Hans Groot March 18, 2009 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Moving Boundary Conditions 3 Cylinder in Transient Couette Flow 4 Collision-Advection Process for Moving
On the stability of a relative velocity lattice Boltzmann scheme for compressible Navier-Stokes equations
 On the stability of a relative velocity lattice Boltzmann scheme for compressible Navier-Stokes equations François Dubois, Tony Fevrier, Benjamin Graille To cite this version: François Dubois, Tony Fevrier,
On the stability of a relative velocity lattice Boltzmann scheme for compressible Navier-Stokes equations François Dubois, Tony Fevrier, Benjamin Graille To cite this version: François Dubois, Tony Fevrier,
Hong Zhou, Guang-Xiang Liu,* Xiao-Feng Wang and Yan Wang * Supporting Information
 Three cobalt(ii) coordination polymers based on V-shaped aromatic polycarboxylates and rigid bis(imidazole) ligand: Syntheses, crystal structures, physical properties and theoretical studies Hong Zhou,
Three cobalt(ii) coordination polymers based on V-shaped aromatic polycarboxylates and rigid bis(imidazole) ligand: Syntheses, crystal structures, physical properties and theoretical studies Hong Zhou,
arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 26 May 2015
![arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 26 May 2015 arxiv: v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 26 May 2015](/thumbs/77/76344468.jpg) Increasing stability and accuracy of the lattice Boltzmann scheme: recursivity and regularization arxiv:1505.06900v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 26 May 2015 Orestis Malaspinas a,b a Institut Jean le Rond d Alembert,
Increasing stability and accuracy of the lattice Boltzmann scheme: recursivity and regularization arxiv:1505.06900v1 [physics.flu-dyn] 26 May 2015 Orestis Malaspinas a,b a Institut Jean le Rond d Alembert,
Lattice Boltzmann methods Summer term Cumulant-based LBM. 25. July 2017
 Cumulant-based LBM Prof. B. Wohlmuth Markus Muhr 25. July 2017 1. Repetition: LBM and notation Discretization SRT-equation Content 2. MRT-model Basic idea Moments and moment-transformation 3. Cumulant-based
Cumulant-based LBM Prof. B. Wohlmuth Markus Muhr 25. July 2017 1. Repetition: LBM and notation Discretization SRT-equation Content 2. MRT-model Basic idea Moments and moment-transformation 3. Cumulant-based
Some aspects of consistency and stability for lattice Boltzmann methods
 Some aspects of consistency and stability for lattice Boltzmann methods Workshop Lattice Boltzmann schemes Methods and Applications 5 December 28, Cemagref Antony, France Martin Rheinländer Arbeitsgruppe
Some aspects of consistency and stability for lattice Boltzmann methods Workshop Lattice Boltzmann schemes Methods and Applications 5 December 28, Cemagref Antony, France Martin Rheinländer Arbeitsgruppe
Equivalence between kinetic method for fluid-dynamic equation and macroscopic finite-difference scheme
 Equivalence between kinetic method for fluid-dynamic equation and macroscopic finite-difference scheme Pietro Asinari (1), Taku Ohwada (2) (1) Department of Energetics, Politecnico di Torino, Torino 10129,
Equivalence between kinetic method for fluid-dynamic equation and macroscopic finite-difference scheme Pietro Asinari (1), Taku Ohwada (2) (1) Department of Energetics, Politecnico di Torino, Torino 10129,
arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.comp-ph] 2 Nov 2006
![arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.comp-ph] 2 Nov 2006 arxiv:physics/ v1 [physics.comp-ph] 2 Nov 2006](/thumbs/72/66778042.jpg) Three-Dimensional Multi-Relaxation Time arxiv:physics/0611016v1 [physics.comp-ph] 2 Nov 2006 (MRT) Lattice-Boltzmann Models for Multiphase Flow Kannan N. Premnath, John Abraham M.J. Zucrow Labs., School
Three-Dimensional Multi-Relaxation Time arxiv:physics/0611016v1 [physics.comp-ph] 2 Nov 2006 (MRT) Lattice-Boltzmann Models for Multiphase Flow Kannan N. Premnath, John Abraham M.J. Zucrow Labs., School
A DARK GREY P O N T, with a Switch Tail, and a small Star on the Forehead. Any
 Y Y Y X X «/ YY Y Y ««Y x ) & \ & & } # Y \#$& / Y Y X» \\ / X X X x & Y Y X «q «z \x» = q Y # % \ & [ & Z \ & { + % ) / / «q zy» / & / / / & x x X / % % ) Y x X Y $ Z % Y Y x x } / % «] «] # z» & Y X»
Y Y Y X X «/ YY Y Y ««Y x ) & \ & & } # Y \#$& / Y Y X» \\ / X X X x & Y Y X «q «z \x» = q Y # % \ & [ & Z \ & { + % ) / / «q zy» / & / / / & x x X / % % ) Y x X Y $ Z % Y Y x x } / % «] «] # z» & Y X»
Taylor Expansions in 2d
 Taylor Expansions in 2 In your irst year Calculus course you evelope a amily o ormulae or approximating a unction F(t) or t near any ixe point t 0. The cruest approximation was just a constant. F(t 0 +
Taylor Expansions in 2 In your irst year Calculus course you evelope a amily o ormulae or approximating a unction F(t) or t near any ixe point t 0. The cruest approximation was just a constant. F(t 0 +
MANY BILLS OF CONCERN TO PUBLIC
 - 6 8 9-6 8 9 6 9 XXX 4 > -? - 8 9 x 4 z ) - -! x - x - - X - - - - - x 00 - - - - - x z - - - x x - x - - - - - ) x - - - - - - 0 > - 000-90 - - 4 0 x 00 - -? z 8 & x - - 8? > 9 - - - - 64 49 9 x - -
- 6 8 9-6 8 9 6 9 XXX 4 > -? - 8 9 x 4 z ) - -! x - x - - X - - - - - x 00 - - - - - x z - - - x x - x - - - - - ) x - - - - - - 0 > - 000-90 - - 4 0 x 00 - -? z 8 & x - - 8? > 9 - - - - 64 49 9 x - -
The lattice Boltzmann equation: background and boundary conditions
 The lattice Boltzmann equation: background and boundary conditions Tim Reis Department of Mathematics Sciences University of Greenwich Leslie Comrie Seminar Series November 2016 Acknowledgements: P. Dellar
The lattice Boltzmann equation: background and boundary conditions Tim Reis Department of Mathematics Sciences University of Greenwich Leslie Comrie Seminar Series November 2016 Acknowledgements: P. Dellar
Lecture 5: Kinetic theory of fluids
 Lecture 5: Kinetic theory of fluids September 21, 2015 1 Goal 2 From atoms to probabilities Fluid dynamics descrines fluids as continnum media (fields); however under conditions of strong inhomogeneities
Lecture 5: Kinetic theory of fluids September 21, 2015 1 Goal 2 From atoms to probabilities Fluid dynamics descrines fluids as continnum media (fields); however under conditions of strong inhomogeneities
Chapter 7: Exponents
 Chapter 7: Exponents Algebra 1 Chapter 7 Notes Name: Algebra Homework: Chapter 7 (Homework is listed by date assigned; homework is due the following class period) HW# Date In-Class Homework Section 7.:
Chapter 7: Exponents Algebra 1 Chapter 7 Notes Name: Algebra Homework: Chapter 7 (Homework is listed by date assigned; homework is due the following class period) HW# Date In-Class Homework Section 7.:
Lattice Boltzmann Method
 3 Lattice Boltzmann Method 3.1 Introduction The lattice Boltzmann method is a discrete computational method based upon the lattice gas automata - a simplified, fictitious molecular model. It consists of
3 Lattice Boltzmann Method 3.1 Introduction The lattice Boltzmann method is a discrete computational method based upon the lattice gas automata - a simplified, fictitious molecular model. It consists of
Matrix lattice Boltzmann reloaded
 Matrix lattice Boltzmann reloaded By Ilya Karlin,2, Pietro Asinari 3, Sauro Succi 4,5 Aerothermochemistry and Combustion Systems Lab, ETH Zurich, 8092 Zurich, Switzerland 2 School of Engineering Sciences,
Matrix lattice Boltzmann reloaded By Ilya Karlin,2, Pietro Asinari 3, Sauro Succi 4,5 Aerothermochemistry and Combustion Systems Lab, ETH Zurich, 8092 Zurich, Switzerland 2 School of Engineering Sciences,
OWELL WEEKLY JOURNAL
 Y \»< - } Y Y Y & #»»» q ] q»»»>) & - - - } ) x ( - { Y» & ( x - (» & )< - Y X - & Q Q» 3 - x Q Y 6 \Y > Y Y X 3 3-9 33 x - - / - -»- --
Y \»< - } Y Y Y & #»»» q ] q»»»>) & - - - } ) x ( - { Y» & ( x - (» & )< - Y X - & Q Q» 3 - x Q Y 6 \Y > Y Y X 3 3-9 33 x - - / - -»- --
Realizations of Loops and Groups defined by short identities
 Comment.Math.Univ.Carolin. 50,3(2009) 373 383 373 Realizations of Loops and Groups defined by short identities A.D. Keedwell Abstract. In a recent paper, those quasigroup identities involving at most three
Comment.Math.Univ.Carolin. 50,3(2009) 373 383 373 Realizations of Loops and Groups defined by short identities A.D. Keedwell Abstract. In a recent paper, those quasigroup identities involving at most three
1 Partial differentiation and the chain rule
 1 Partial differentiation and the chain rule In this section we review and discuss certain notations and relations involving partial derivatives. The more general case can be illustrated by considering
1 Partial differentiation and the chain rule In this section we review and discuss certain notations and relations involving partial derivatives. The more general case can be illustrated by considering
Math 192r, Problem Set #3: Solutions
 Math 192r Problem Set #3: Solutions 1. Let F n be the nth Fibonacci number as Wilf indexes them (with F 0 F 1 1 F 2 2 etc.). Give a simple homogeneous linear recurrence relation satisfied by the sequence
Math 192r Problem Set #3: Solutions 1. Let F n be the nth Fibonacci number as Wilf indexes them (with F 0 F 1 1 F 2 2 etc.). Give a simple homogeneous linear recurrence relation satisfied by the sequence
Unit 3 Factors & Products
 1 Unit 3 Factors & Products General Outcome: Develop algebraic reasoning and number sense. Specific Outcomes: 3.1 Demonstrate an understanding of factors of whole number by determining the: o prime factors
1 Unit 3 Factors & Products General Outcome: Develop algebraic reasoning and number sense. Specific Outcomes: 3.1 Demonstrate an understanding of factors of whole number by determining the: o prime factors
Demonstration of the Coupled Evolution Rules 163 APPENDIX F: DEMONSTRATION OF THE COUPLED EVOLUTION RULES
 Demonstration of the Coupled Evolution Rules 163 APPENDIX F: DEMONSTRATION OF THE COUPLED EVOLUTION RULES Before going into the demonstration we need to point out two limitations: a. It assumes I=1/2 for
Demonstration of the Coupled Evolution Rules 163 APPENDIX F: DEMONSTRATION OF THE COUPLED EVOLUTION RULES Before going into the demonstration we need to point out two limitations: a. It assumes I=1/2 for
Semi-implicit-linearized Multiple-relaxation-time formulation of Lattice Boltzmann Schemes for Mixture Modeling. Abstract
 Accepted for publication on Physical Review E Semi-implicit-linearized Multiple-relaxation-time formulation of Lattice Boltzmann Schemes for Mixture Modeling Pietro Asinari Department of Energetics, Politecnico
Accepted for publication on Physical Review E Semi-implicit-linearized Multiple-relaxation-time formulation of Lattice Boltzmann Schemes for Mixture Modeling Pietro Asinari Department of Energetics, Politecnico
Lattice Boltzmann Methods for Fluid Dynamics
 Lattice Boltzmann Methods for Fluid Dynamics Steven Orszag Department of Mathematics Yale University In collaboration with Hudong Chen, Isaac Goldhirsch, and Rick Shock Transient flow around a car LBGK
Lattice Boltzmann Methods for Fluid Dynamics Steven Orszag Department of Mathematics Yale University In collaboration with Hudong Chen, Isaac Goldhirsch, and Rick Shock Transient flow around a car LBGK
. p.1/31. Department Mathematics and Statistics Arizona State University. Don Jones
 Modified-Truncation Finite Difference Schemes. p.1/31 Department Mathematics and Statistics Arizona State University Don Jones dajones@math.asu.edu . p.2/31 Heat Equation t u = λu xx + f . p.2/31 Heat
Modified-Truncation Finite Difference Schemes. p.1/31 Department Mathematics and Statistics Arizona State University Don Jones dajones@math.asu.edu . p.2/31 Heat Equation t u = λu xx + f . p.2/31 Heat
LATTICE BOLTZMANN MODELLING OF PULSATILE FLOW USING MOMENT BOUNDARY CONDITIONS
 6th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM 6) 7th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ECFD 7) 5 June 28, Glasgow, UK LATTICE BOLTZMANN MODELLING OF PULSATILE FLOW USING MOMENT
6th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM 6) 7th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ECFD 7) 5 June 28, Glasgow, UK LATTICE BOLTZMANN MODELLING OF PULSATILE FLOW USING MOMENT
Painlevé Test for the Certain (2+1)-Dimensional Nonlinear Evolution Equations. Abstract
 Painlevé Test for the Certain (2+1)-Dimensional Nonlinear Evolution Equations T. Alagesan and Y. Chung Department of Information and Communications, Kwangju Institute of Science and Technology, 1 Oryong-dong,
Painlevé Test for the Certain (2+1)-Dimensional Nonlinear Evolution Equations T. Alagesan and Y. Chung Department of Information and Communications, Kwangju Institute of Science and Technology, 1 Oryong-dong,
Numerical Algorithms for Visual Computing 2008/09 Example Solutions for Assignment 4. Problem 1 (Shift invariance of the Laplace operator)
 Numercal Algorthms for Vsual Computng 008/09 Example Solutons for Assgnment 4 Problem (Shft nvarance of the Laplace operator The Laplace equaton s shft nvarant,.e., nvarant under translatons x x + a, y
Numercal Algorthms for Vsual Computng 008/09 Example Solutons for Assgnment 4 Problem (Shft nvarance of the Laplace operator The Laplace equaton s shft nvarant,.e., nvarant under translatons x x + a, y
Multi species Lattice Boltzmann Models and Applications to Sustainable Energy Systems
 Multi species Lattice Boltzmann Models and Applications to Sustainable Energy Systems Pietro Asinari, PhD Dipartimento di Energetica (DENER), Politecnico di Torino (POLITO), Torino 10129, Italy e-mail:
Multi species Lattice Boltzmann Models and Applications to Sustainable Energy Systems Pietro Asinari, PhD Dipartimento di Energetica (DENER), Politecnico di Torino (POLITO), Torino 10129, Italy e-mail:
Relativistic Electrodynamics
 Relativistic Electrodynamics Notes (I will try to update if typos are found) June 1, 2009 1 Dot products The Pythagorean theorem says that distances are given by With time as a fourth direction, we find
Relativistic Electrodynamics Notes (I will try to update if typos are found) June 1, 2009 1 Dot products The Pythagorean theorem says that distances are given by With time as a fourth direction, we find
BOOLEAN ALGEBRA TRUTH TABLE
 BOOLEAN ALGEBRA TRUTH TABLE Truth table is a table which represents all the possible values of logical variables / statements along with all the possible results of the given combinations of values. Eg:
BOOLEAN ALGEBRA TRUTH TABLE Truth table is a table which represents all the possible values of logical variables / statements along with all the possible results of the given combinations of values. Eg:
Cumulant-based LBM. Repetition: LBM and notation. Content. Computational Fluid Dynamics. 1. Repetition: LBM and notation Discretization SRT-equation
 Content Cumulant-based LBM Prof B Wohlmuth Markus Muhr 25 July 2017 1 epetition: LBM and notation Discretiation ST-equation 2 MT-model Basic idea Moments and moment-transformation 3 Cumulant-based LBM
Content Cumulant-based LBM Prof B Wohlmuth Markus Muhr 25 July 2017 1 epetition: LBM and notation Discretiation ST-equation 2 MT-model Basic idea Moments and moment-transformation 3 Cumulant-based LBM
6.4 Directional derivatives
 103 6.5 First order gauge coordinates for rotation in this way means something different than a rotation of the image. There would be no way otherwise to recognize rotated images from non-rotated ones!
103 6.5 First order gauge coordinates for rotation in this way means something different than a rotation of the image. There would be no way otherwise to recognize rotated images from non-rotated ones!
Consider the function f(x, y). Recall that we can approximate f(x, y) with a linear function in x and y:
 Taylor s Formula Consider the unction (x, y). Recall that we can approximate (x, y) with a linear unction in x and y: (x, y) (a, b)+ x (a, b)(x a)+ y (a, b)(y b) Notice that again this is just a linear
Taylor s Formula Consider the unction (x, y). Recall that we can approximate (x, y) with a linear unction in x and y: (x, y) (a, b)+ x (a, b)(x a)+ y (a, b)(y b) Notice that again this is just a linear
3 Applications of partial differentiation
 Advanced Calculus Chapter 3 Applications of partial differentiation 37 3 Applications of partial differentiation 3.1 Stationary points Higher derivatives Let U R 2 and f : U R. The partial derivatives
Advanced Calculus Chapter 3 Applications of partial differentiation 37 3 Applications of partial differentiation 3.1 Stationary points Higher derivatives Let U R 2 and f : U R. The partial derivatives
MATH443 PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Second Midterm Exam-Solutions. December 6, 2017, Wednesday 10:40-12:30, SA-Z02
 1 MATH443 PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Second Midterm Exam-Solutions December 6 2017 Wednesday 10:40-12:30 SA-Z02 QUESTIONS: Solve any four of the following five problems [25]1. Solve the initial and
1 MATH443 PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS Second Midterm Exam-Solutions December 6 2017 Wednesday 10:40-12:30 SA-Z02 QUESTIONS: Solve any four of the following five problems [25]1. Solve the initial and
Physical Modeling of Multiphase flow. Boltzmann method
 with lattice Boltzmann method Exa Corp., Burlington, MA, USA Feburary, 2011 Scope Scope Re-examine the non-ideal gas model in [Shan & Chen, Phys. Rev. E, (1993)] from the perspective of kinetic theory
with lattice Boltzmann method Exa Corp., Burlington, MA, USA Feburary, 2011 Scope Scope Re-examine the non-ideal gas model in [Shan & Chen, Phys. Rev. E, (1993)] from the perspective of kinetic theory
Chapter 7: Exponents
 Chapter : Exponents Algebra Chapter Notes Name: Algebra Homework: Chapter (Homework is listed by date assigned; homework is due the following class period) HW# Date In-Class Homework M / Review of Sections.-.
Chapter : Exponents Algebra Chapter Notes Name: Algebra Homework: Chapter (Homework is listed by date assigned; homework is due the following class period) HW# Date In-Class Homework M / Review of Sections.-.
EJL R Sβ. sum. General objective: Reduce the complexity of the analysis by exploiting symmetry. Garth J. Simpson
 e sum = EJL R Sβ General objective: Reduce the complexity of the analysis by exploiting symmetry. Specific Objectives: 1. The molecular symmetry matrix S. How to populate it.. Relationships between the
e sum = EJL R Sβ General objective: Reduce the complexity of the analysis by exploiting symmetry. Specific Objectives: 1. The molecular symmetry matrix S. How to populate it.. Relationships between the
On the Comparison Between Lattice Boltzmann Methods and Spectral Methods for DNS of Incompressible Turbulent Channel Flows on Small Domain Size
 Advances in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics Adv. Appl. Math. Mech., Vol. 11, No. 3, pp. 598-67 DOI: 1.428/aamm.218.s4 June 219 On the Comparison Between Lattice Boltzmann Methods and Spectral Methods
Advances in Applied Mathematics and Mechanics Adv. Appl. Math. Mech., Vol. 11, No. 3, pp. 598-67 DOI: 1.428/aamm.218.s4 June 219 On the Comparison Between Lattice Boltzmann Methods and Spectral Methods
Theorem (4.11). Let M be a closed subspace of a Hilbert space H. For any x, y E, the parallelogram law applied to x/2 and y/2 gives.
 Math 641 Lecture #19 4.11, 4.12, 4.13 Inner Products and Linear Functionals (Continued) Theorem (4.10). Every closed, convex set E in a Hilbert space H contains a unique element of smallest norm, i.e.,
Math 641 Lecture #19 4.11, 4.12, 4.13 Inner Products and Linear Functionals (Continued) Theorem (4.10). Every closed, convex set E in a Hilbert space H contains a unique element of smallest norm, i.e.,
Factorisation CHAPTER Introduction
 FACTORISATION 217 Factorisation CHAPTER 14 14.1 Introduction 14.1.1 Factors of natural numbers You will remember what you learnt about factors in Class VI. Let us take a natural number, say 30, and write
FACTORISATION 217 Factorisation CHAPTER 14 14.1 Introduction 14.1.1 Factors of natural numbers You will remember what you learnt about factors in Class VI. Let us take a natural number, say 30, and write
Molecular Vibrations C. David Sherrill School of Chemistry and Biochemistry Georgia Institute of Technology
 Molecular Vibrations C. David Sherrill School of Chemistry and Biochemistry Georgia Institute of Technology Why Estimate Molecular Vibrations? Simulation of vibrational spectrum (identification of molecules)
Molecular Vibrations C. David Sherrill School of Chemistry and Biochemistry Georgia Institute of Technology Why Estimate Molecular Vibrations? Simulation of vibrational spectrum (identification of molecules)
8.5 Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials
 8.5. Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials www.ck12.org 8.5 Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials Learning Objectives Write a polynomial expression in standard form. Classify polynomial expression
8.5. Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials www.ck12.org 8.5 Addition and Subtraction of Polynomials Learning Objectives Write a polynomial expression in standard form. Classify polynomial expression
M E M P H I S, T E N N., S A T U E D A Y, OCTOBER 8, 1870.
 5 L V 8 5 x - L : L Q ) L - \ \ Q Q - V 84 z < L L 4 Y z ( (
5 L V 8 5 x - L : L Q ) L - \ \ Q Q - V 84 z < L L 4 Y z ( (
Definition: Let f(x) be a function of one variable with continuous derivatives of all orders at a the point x 0, then the series.
 2.4 Local properties o unctions o several variables In this section we will learn how to address three kinds o problems which are o great importance in the ield o applied mathematics: how to obtain the
2.4 Local properties o unctions o several variables In this section we will learn how to address three kinds o problems which are o great importance in the ield o applied mathematics: how to obtain the
13. LECTURE 13. Objectives
 13. LECTURE 13 Objectives I can use Clairaut s Theorem to make my calculations easier. I can take higher derivatives. I can check if a function is a solution to a partial differential equation. Higher
13. LECTURE 13 Objectives I can use Clairaut s Theorem to make my calculations easier. I can take higher derivatives. I can check if a function is a solution to a partial differential equation. Higher
Simplified Analytical Model of a Six-Degree-of-Freedom Large-Gap Magnetic Suspension System
 NASA Technical Memorandum 112868 Simplified Analytical Model of a Six-Degree-of-Freedom Large-Gap Magnetic Suspension System Nelson J. Groom Langley Research Center, Hampton, Virginia June 1997 National
NASA Technical Memorandum 112868 Simplified Analytical Model of a Six-Degree-of-Freedom Large-Gap Magnetic Suspension System Nelson J. Groom Langley Research Center, Hampton, Virginia June 1997 National
Algebra I Lesson 6 Monomials and Polynomials (Grades 9-12) Instruction 6-1 Multiplying Polynomials
 In algebra, we deal with different types of expressions. Grouping them helps us to learn rules and concepts easily. One group of expressions is called polynomials. In a polynomial, the powers are whole
In algebra, we deal with different types of expressions. Grouping them helps us to learn rules and concepts easily. One group of expressions is called polynomials. In a polynomial, the powers are whole
Polynomials. In many problems, it is useful to write polynomials as products. For example, when solving equations: Example:
 Polynomials Monomials: 10, 5x, 3x 2, x 3, 4x 2 y 6, or 5xyz 2. A monomial is a product of quantities some of which are unknown. Polynomials: 10 + 5x 3x 2 + x 3, or 4x 2 y 6 + 5xyz 2. A polynomial is a
Polynomials Monomials: 10, 5x, 3x 2, x 3, 4x 2 y 6, or 5xyz 2. A monomial is a product of quantities some of which are unknown. Polynomials: 10 + 5x 3x 2 + x 3, or 4x 2 y 6 + 5xyz 2. A polynomial is a
Chapter 11. Taylor Series. Josef Leydold Mathematical Methods WS 2018/19 11 Taylor Series 1 / 27
 Chapter 11 Taylor Series Josef Leydold Mathematical Methods WS 2018/19 11 Taylor Series 1 / 27 First-Order Approximation We want to approximate function f by some simple function. Best possible approximation
Chapter 11 Taylor Series Josef Leydold Mathematical Methods WS 2018/19 11 Taylor Series 1 / 27 First-Order Approximation We want to approximate function f by some simple function. Best possible approximation
Divergence of the gradient expansion and the applicability of fluid dynamics Gabriel S. Denicol (IF-UFF)
 Divergence of the gradient expansion and the applicability of fluid dynamics Gabriel S. Denicol (IF-UFF) arxiv:1608.07869, arxiv:1711.01657, arxiv:1709.06644 Frankfurt University 1.February.2018 Preview
Divergence of the gradient expansion and the applicability of fluid dynamics Gabriel S. Denicol (IF-UFF) arxiv:1608.07869, arxiv:1711.01657, arxiv:1709.06644 Frankfurt University 1.February.2018 Preview
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 19: Least squares problems (continued). Norms and inner products.
 MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 19: Least squares problems (continued). Norms and inner products. Orthogonal projection Theorem 1 Let V be a subspace of R n. Then any vector x R n is uniquely represented
MATH 304 Linear Algebra Lecture 19: Least squares problems (continued). Norms and inner products. Orthogonal projection Theorem 1 Let V be a subspace of R n. Then any vector x R n is uniquely represented
Factorisation. Learn and Remember. Sol. Let the duration of each period be x. Period 8 9. Duration of period 45 x (min.)
 246 MATHEMATICS-I Sol. Let the duration of each period be x. Period 8 9 Duration of period 45 x (min.) If the period increases then the duration of period decreases. So, it is a case of inverse proportion...
246 MATHEMATICS-I Sol. Let the duration of each period be x. Period 8 9 Duration of period 45 x (min.) If the period increases then the duration of period decreases. So, it is a case of inverse proportion...
Contents. Chapter 2 Digital Circuits Page 1 of 30
 Chapter 2 Digital Circuits Page 1 of 30 Contents Contents... 1 2 Digital Circuits... 2 2.1 Binary Numbers... 2 2.2 Binary Switch... 4 2.3 Basic Logic Operators and Logic Expressions... 5 2.4 Truth Tables...
Chapter 2 Digital Circuits Page 1 of 30 Contents Contents... 1 2 Digital Circuits... 2 2.1 Binary Numbers... 2 2.2 Binary Switch... 4 2.3 Basic Logic Operators and Logic Expressions... 5 2.4 Truth Tables...
3.5 Quadratic Approximation and Convexity/Concavity
 3.5 Quadratic Approximation and Convexity/Concavity 55 3.5 Quadratic Approximation and Convexity/Concavity Overview: Second derivatives are useful for understanding how the linear approximation varies
3.5 Quadratic Approximation and Convexity/Concavity 55 3.5 Quadratic Approximation and Convexity/Concavity Overview: Second derivatives are useful for understanding how the linear approximation varies
Relativistic Viscous Hydrodynamics for Multi-Component Systems with Multiple Conserved Currents
 Reference: AM and T. Hirano, arxiv:1003:3087 Relativistic Viscous Hydrodynamics for Multi-Component Systems with Multiple Conserved Currents Akihiko Monnai Department of Physics, The University of Tokyo
Reference: AM and T. Hirano, arxiv:1003:3087 Relativistic Viscous Hydrodynamics for Multi-Component Systems with Multiple Conserved Currents Akihiko Monnai Department of Physics, The University of Tokyo
Section 14.8 Maxima & minima of functions of two variables. Learning outcomes. After completing this section, you will inshaallah be able to
 Section 14.8 Maxima & minima of functions of two variables 14.8 1 Learning outcomes After completing this section, you will inshaallah be able to 1. explain what is meant by relative maxima or relative
Section 14.8 Maxima & minima of functions of two variables 14.8 1 Learning outcomes After completing this section, you will inshaallah be able to 1. explain what is meant by relative maxima or relative
Chapter-2 BOOLEAN ALGEBRA
 Chapter-2 BOOLEAN ALGEBRA Introduction: An algebra that deals with binary number system is called Boolean Algebra. It is very power in designing logic circuits used by the processor of computer system.
Chapter-2 BOOLEAN ALGEBRA Introduction: An algebra that deals with binary number system is called Boolean Algebra. It is very power in designing logic circuits used by the processor of computer system.
100 CHAPTER 4. SYSTEMS AND ADAPTIVE STEP SIZE METHODS APPENDIX
 100 CHAPTER 4. SYSTEMS AND ADAPTIVE STEP SIZE METHODS APPENDIX.1 Norms If we have an approximate solution at a given point and we want to calculate the absolute error, then we simply take the magnitude
100 CHAPTER 4. SYSTEMS AND ADAPTIVE STEP SIZE METHODS APPENDIX.1 Norms If we have an approximate solution at a given point and we want to calculate the absolute error, then we simply take the magnitude
Algebraic Expressions
 Algebraic Expressions 1. Expressions are formed from variables and constants. 2. Terms are added to form expressions. Terms themselves are formed as product of factors. 3. Expressions that contain exactly
Algebraic Expressions 1. Expressions are formed from variables and constants. 2. Terms are added to form expressions. Terms themselves are formed as product of factors. 3. Expressions that contain exactly
The lattice Boltzmann equation (LBE) has become an alternative method for solving various fluid dynamic
 36th AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference and Exhibit 5-8 June 2006, San Francisco, California AIAA 2006-3904 Direct and Large-Eddy Simulation of Decaying and Forced Isotropic Turbulence Using Lattice Boltzmann
36th AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference and Exhibit 5-8 June 2006, San Francisco, California AIAA 2006-3904 Direct and Large-Eddy Simulation of Decaying and Forced Isotropic Turbulence Using Lattice Boltzmann
Fluid Equations for Rarefied Gases
 1 Fluid Equations for Rarefied Gases Jean-Luc Thiffeault Department of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics Columbia University http://plasma.ap.columbia.edu/~jeanluc 23 March 2001 with E. A. Spiegel
1 Fluid Equations for Rarefied Gases Jean-Luc Thiffeault Department of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics Columbia University http://plasma.ap.columbia.edu/~jeanluc 23 March 2001 with E. A. Spiegel
LOWELL WEEKLY JOURNAL
 Y G y G Y 87 y Y 8 Y - $ X ; ; y y q 8 y $8 $ $ $ G 8 q < 8 6 4 y 8 7 4 8 8 < < y 6 $ q - - y G y G - Y y y 8 y y y Y Y 7-7- G - y y y ) y - y y y y - - y - y 87 7-7- G G < G y G y y 6 X y G y y y 87 G
Y G y G Y 87 y Y 8 Y - $ X ; ; y y q 8 y $8 $ $ $ G 8 q < 8 6 4 y 8 7 4 8 8 < < y 6 $ q - - y G y G - Y y y 8 y y y Y Y 7-7- G - y y y ) y - y y y y - - y - y 87 7-7- G G < G y G y y 6 X y G y y y 87 G
Pietro Asinari Department of Energetics, Politecnico di Torino, Corso Duca degli Abruzzi 24, Torino, Italy. (Dated: September 25, 2009) Abstract
 Submitted for publication to Physical Review E, code EL10375, version Ge Lattice Boltzmann scheme for mixture modeling: analysis of the continuum diffusion regimes recovering Maxwell Stefan model and incompressible
Submitted for publication to Physical Review E, code EL10375, version Ge Lattice Boltzmann scheme for mixture modeling: analysis of the continuum diffusion regimes recovering Maxwell Stefan model and incompressible
REGULAR IDENTITIES IN LATTICES
 TRANSACTIONS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 158, Number 1, July 1971 REGULAR IDENTITIES IN LATTICES BY R. PADMANABHANC) Abstract. An algebraic system 3i = is called a quasilattice
TRANSACTIONS OF THE AMERICAN MATHEMATICAL SOCIETY Volume 158, Number 1, July 1971 REGULAR IDENTITIES IN LATTICES BY R. PADMANABHANC) Abstract. An algebraic system 3i = is called a quasilattice
Answers and Solutions to Section 13.3 Homework Problems 1-23 (odd) and S. F. Ellermeyer. f dr
 Answers and Solutions to Section 13.3 Homework Problems 1-23 (odd) and 29-33 S. F. Ellermeyer 1. By looking at the picture in the book, we see that f dr 5 1 4. 3. For the vector field Fx,y 6x 5yi 5x 4yj,
Answers and Solutions to Section 13.3 Homework Problems 1-23 (odd) and 29-33 S. F. Ellermeyer 1. By looking at the picture in the book, we see that f dr 5 1 4. 3. For the vector field Fx,y 6x 5yi 5x 4yj,
LESSON 7.1 FACTORING POLYNOMIALS I
 LESSON 7.1 FACTORING POLYNOMIALS I LESSON 7.1 FACTORING POLYNOMIALS I 293 OVERVIEW Here s what you ll learn in this lesson: Greatest Common Factor a. Finding the greatest common factor (GCF) of a set of
LESSON 7.1 FACTORING POLYNOMIALS I LESSON 7.1 FACTORING POLYNOMIALS I 293 OVERVIEW Here s what you ll learn in this lesson: Greatest Common Factor a. Finding the greatest common factor (GCF) of a set of
Polynomials. Math 4800/6080 Project Course
 Polynomials. Math 4800/6080 Project Course 2. Algebraic Curves. Everyone knows what a curve is, until he has studied enough mathematics to become confused through the countless number of possible exceptions.
Polynomials. Math 4800/6080 Project Course 2. Algebraic Curves. Everyone knows what a curve is, until he has studied enough mathematics to become confused through the countless number of possible exceptions.
Polynomials and Polynomial Equations
 Polynomials and Polynomial Equations A Polynomial is any expression that has constants, variables and exponents, and can be combined using addition, subtraction, multiplication and division, but: no division
Polynomials and Polynomial Equations A Polynomial is any expression that has constants, variables and exponents, and can be combined using addition, subtraction, multiplication and division, but: no division
Robot Control Basics CS 685
 Robot Control Basics CS 685 Control basics Use some concepts from control theory to understand and learn how to control robots Control Theory general field studies control and understanding of behavior
Robot Control Basics CS 685 Control basics Use some concepts from control theory to understand and learn how to control robots Control Theory general field studies control and understanding of behavior
FUZZY BCK-FILTERS INDUCED BY FUZZY SETS
 Scientiae Mathematicae Japonicae Online, e-2005, 99 103 99 FUZZY BCK-FILTERS INDUCED BY FUZZY SETS YOUNG BAE JUN AND SEOK ZUN SONG Received January 23, 2005 Abstract. We give the definition of fuzzy BCK-filter
Scientiae Mathematicae Japonicae Online, e-2005, 99 103 99 FUZZY BCK-FILTERS INDUCED BY FUZZY SETS YOUNG BAE JUN AND SEOK ZUN SONG Received January 23, 2005 Abstract. We give the definition of fuzzy BCK-filter
Quantum Information & Quantum Computing
 Math 478, Phys 478, CS4803, February 9, 006 1 Georgia Tech Math, Physics & Computing Math 478, Phys 478, CS4803 Quantum Information & Quantum Computing Problems Set 1 Due February 9, 006 Part I : 1. Read
Math 478, Phys 478, CS4803, February 9, 006 1 Georgia Tech Math, Physics & Computing Math 478, Phys 478, CS4803 Quantum Information & Quantum Computing Problems Set 1 Due February 9, 006 Part I : 1. Read
Fluid Equations for Rarefied Gases
 1 Fluid Equations for Rarefied Gases Jean-Luc Thiffeault Department of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics Columbia University http://plasma.ap.columbia.edu/~jeanluc 21 May 2001 with E. A. Spiegel
1 Fluid Equations for Rarefied Gases Jean-Luc Thiffeault Department of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics Columbia University http://plasma.ap.columbia.edu/~jeanluc 21 May 2001 with E. A. Spiegel
POLYNOMIAL EXPRESSIONS PART 1
 POLYNOMIAL EXPRESSIONS PART 1 A polynomial is an expression that is a sum of one or more terms. Each term consists of one or more variables multiplied by a coefficient. Coefficients can be negative, so
POLYNOMIAL EXPRESSIONS PART 1 A polynomial is an expression that is a sum of one or more terms. Each term consists of one or more variables multiplied by a coefficient. Coefficients can be negative, so
Neatest and Promptest Manner. E d i t u r ami rul)lihher. FOIt THE CIIILDIIES'. Trifles.
 » ~ $ ) 7 x X ) / ( 8 2 X 39 ««x» ««! «! / x? \» «({? «» q «(? (?? x! «? 8? ( z x x q? ) «q q q ) x z x 69 7( X X ( 3»«! ( ~«x ««x ) (» «8 4 X «4 «4 «8 X «x «(» X) ()»» «X «97 X X X 4 ( 86) x) ( ) z z
» ~ $ ) 7 x X ) / ( 8 2 X 39 ««x» ««! «! / x? \» «({? «» q «(? (?? x! «? 8? ( z x x q? ) «q q q ) x z x 69 7( X X ( 3»«! ( ~«x ««x ) (» «8 4 X «4 «4 «8 X «x «(» X) ()»» «X «97 X X X 4 ( 86) x) ( ) z z
Grad s approximation for missing data in lattice Boltzmann simulations
 Europhysics Letters PREPRINT Grad s approximation for missing data in lattice Boltzmann simulations S. Ansumali 2, S. S. Chikatamarla 1 and I. V. Karlin 1 1 Aerothermochemistry and Combustion Systems Laboratory,
Europhysics Letters PREPRINT Grad s approximation for missing data in lattice Boltzmann simulations S. Ansumali 2, S. S. Chikatamarla 1 and I. V. Karlin 1 1 Aerothermochemistry and Combustion Systems Laboratory,
CS205B / CME306 Homework 3. R n+1 = R n + tω R n. (b) Show that the updated rotation matrix computed from this update is not orthogonal.
 CS205B / CME306 Homework 3 Rotation Matrices 1. The ODE that describes rigid body evolution is given by R = ω R. (a) Write down the forward Euler update for this equation. R n+1 = R n + tω R n (b) Show
CS205B / CME306 Homework 3 Rotation Matrices 1. The ODE that describes rigid body evolution is given by R = ω R. (a) Write down the forward Euler update for this equation. R n+1 = R n + tω R n (b) Show
Manipulator Dynamics 2. Instructor: Jacob Rosen Advanced Robotic - MAE 263D - Department of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering - UCLA
 Manipulator Dynamics 2 Forward Dynamics Problem Given: Joint torques and links geometry, mass, inertia, friction Compute: Angular acceleration of the links (solve differential equations) Solution Dynamic
Manipulator Dynamics 2 Forward Dynamics Problem Given: Joint torques and links geometry, mass, inertia, friction Compute: Angular acceleration of the links (solve differential equations) Solution Dynamic
( ) R kj. = y k y j. y A ( ) z A. y a. z a. Derivatives of the second order electrostatic tensor with respect to the translation of ( ) δ yβ.
 Supporting information Derivatives of R with respect to the translation of fragment along the y and z axis: y = y k y j (S1) z ( = z z k j) (S2) Derivatives of S with respect to the translation of fragment
Supporting information Derivatives of R with respect to the translation of fragment along the y and z axis: y = y k y j (S1) z ( = z z k j) (S2) Derivatives of S with respect to the translation of fragment
On the classification of certain curves up to projective tranformations
 On the classification of certain curves up to projective tranformations Mehdi Nadjafikhah Abstract The purpose of this paper is to classify the curves in the form y 3 = c 3 x 3 +c 2 x 2 + c 1x + c 0, with
On the classification of certain curves up to projective tranformations Mehdi Nadjafikhah Abstract The purpose of this paper is to classify the curves in the form y 3 = c 3 x 3 +c 2 x 2 + c 1x + c 0, with
QR Decomposition. When solving an overdetermined system by projection (or a least squares solution) often the following method is used:
 (In practice not Gram-Schmidt, but another process Householder Transformations are used.) QR Decomposition When solving an overdetermined system by projection (or a least squares solution) often the following
(In practice not Gram-Schmidt, but another process Householder Transformations are used.) QR Decomposition When solving an overdetermined system by projection (or a least squares solution) often the following
Lattice Bhatnagar Gross Krook model for the Lorenz attractor
 Physica D 154 (2001) 43 50 Lattice Bhatnagar Gross Krook model for the Lorenz attractor Guangwu Yan a,b,,liyuan a a LSEC, Institute of Computational Mathematics, Academy of Mathematics and System Sciences,
Physica D 154 (2001) 43 50 Lattice Bhatnagar Gross Krook model for the Lorenz attractor Guangwu Yan a,b,,liyuan a a LSEC, Institute of Computational Mathematics, Academy of Mathematics and System Sciences,
A LATTICE BOLTZMANN SCHEME WITH A THREE DIMENSIONAL CUBOID LATTICE. Haoda Min
 A LATTICE BOLTZMANN SCHEME WITH A THREE DIMENSIONAL CUBOID LATTICE by Haoda Min A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
A LATTICE BOLTZMANN SCHEME WITH A THREE DIMENSIONAL CUBOID LATTICE by Haoda Min A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree
Ph.D. Katarína Bellová Page 1 Mathematics 2 (10-PHY-BIPMA2) EXAM - Solutions, 20 July 2017, 10:00 12:00 All answers to be justified.
 PhD Katarína Bellová Page 1 Mathematics 2 (10-PHY-BIPMA2 EXAM - Solutions, 20 July 2017, 10:00 12:00 All answers to be justified Problem 1 [ points]: For which parameters λ R does the following system
PhD Katarína Bellová Page 1 Mathematics 2 (10-PHY-BIPMA2 EXAM - Solutions, 20 July 2017, 10:00 12:00 All answers to be justified Problem 1 [ points]: For which parameters λ R does the following system
review To find the coefficient of all the terms in 15ab + 60bc 17ca: Coefficient of ab = 15 Coefficient of bc = 60 Coefficient of ca = -17
 1. Revision Recall basic terms of algebraic expressions like Variable, Constant, Term, Coefficient, Polynomial etc. The coefficients of the terms in 4x 2 5xy + 6y 2 are Coefficient of 4x 2 is 4 Coefficient
1. Revision Recall basic terms of algebraic expressions like Variable, Constant, Term, Coefficient, Polynomial etc. The coefficients of the terms in 4x 2 5xy + 6y 2 are Coefficient of 4x 2 is 4 Coefficient
Schemes for Mixture Modeling
 DEPARTMENT OF ENERGETICS Consistency of Multiplerelaxation-time Lattice Boltzmann Schemes for Mixture Modeling Invited Talk (Prof. Taku Ohwada) Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics Graduate School
DEPARTMENT OF ENERGETICS Consistency of Multiplerelaxation-time Lattice Boltzmann Schemes for Mixture Modeling Invited Talk (Prof. Taku Ohwada) Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics Graduate School
Chapter 7: Exponents
 Chapter : Exponents Algebra Chapter Notes Name: Notes #: Sections.. Section.: Review Simplify; leave all answers in positive exponents:.) m -.) y -.) m 0.) -.) -.) - -.) (m ) 0.) 0 x y Evaluate if a =
Chapter : Exponents Algebra Chapter Notes Name: Notes #: Sections.. Section.: Review Simplify; leave all answers in positive exponents:.) m -.) y -.) m 0.) -.) -.) - -.) (m ) 0.) 0 x y Evaluate if a =
SEMICLASSICAL LATTICE BOLTZMANN EQUATION HYDRODYNAMICS
 The Seventh Nobeyama Workshop on CFD: To the Memory of Prof. Kuwahara Sanjo Kaikan, the University of Tokyo, Japan, September. 23-24, 2009 SEMICLASSICAL LATTICE BOLTZMANN EQUATION HYDRODYNAMICS Jaw-Yen
The Seventh Nobeyama Workshop on CFD: To the Memory of Prof. Kuwahara Sanjo Kaikan, the University of Tokyo, Japan, September. 23-24, 2009 SEMICLASSICAL LATTICE BOLTZMANN EQUATION HYDRODYNAMICS Jaw-Yen
Lattice Boltzmann Simulations of 2D Laminar Flows past Two Tandem Cylinders
 Lattice Boltzmann Simulations of 2D Laminar Flows past Two Tandem Cylinders Alberto Mussa a, Pietro Asinari a,, and Li-Shi Luo b a Department of Energetics, Politecnico di Torino, Torino 10129, Italy Tel.:
Lattice Boltzmann Simulations of 2D Laminar Flows past Two Tandem Cylinders Alberto Mussa a, Pietro Asinari a,, and Li-Shi Luo b a Department of Energetics, Politecnico di Torino, Torino 10129, Italy Tel.:
Contents. 2 Partial Derivatives. 2.1 Limits and Continuity. Calculus III (part 2): Partial Derivatives (by Evan Dummit, 2017, v. 2.
 Calculus III (part 2): Partial Derivatives (by Evan Dummit, 2017, v 260) Contents 2 Partial Derivatives 1 21 Limits and Continuity 1 22 Partial Derivatives 5 23 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient
Calculus III (part 2): Partial Derivatives (by Evan Dummit, 2017, v 260) Contents 2 Partial Derivatives 1 21 Limits and Continuity 1 22 Partial Derivatives 5 23 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient
Numerical Simulation of Rarefied Gases using Hyperbolic Moment Equations in Partially-Conservative Form
 Numerical Simulation of Rarefied Gases using Hyperbolic Moment Equations in Partially-Conservative Form Julian Koellermeier, Manuel Torrilhon May 18th, 2017 FU Berlin J. Koellermeier 1 / 52 Partially-Conservative
Numerical Simulation of Rarefied Gases using Hyperbolic Moment Equations in Partially-Conservative Form Julian Koellermeier, Manuel Torrilhon May 18th, 2017 FU Berlin J. Koellermeier 1 / 52 Partially-Conservative
The Lattice Boltzmann method for hyperbolic systems. Benjamin Graille. October 19, 2016
 The Lattice Boltzmann method for hyperbolic systems Benjamin Graille October 19, 2016 Framework The Lattice Boltzmann method 1 Description of the lattice Boltzmann method Link with the kinetic theory Classical
The Lattice Boltzmann method for hyperbolic systems Benjamin Graille October 19, 2016 Framework The Lattice Boltzmann method 1 Description of the lattice Boltzmann method Link with the kinetic theory Classical
Gas Turbine Technologies Torino (Italy) 26 January 2006
 Pore Scale Mesoscopic Modeling of Reactive Mixtures in the Porous Media for SOFC Application: Physical Model, Numerical Code Development and Preliminary Validation Michele CALI, Pietro ASINARI Dipartimento
Pore Scale Mesoscopic Modeling of Reactive Mixtures in the Porous Media for SOFC Application: Physical Model, Numerical Code Development and Preliminary Validation Michele CALI, Pietro ASINARI Dipartimento
Welcome to Math Video Lessons. Stanley Ocken. Department of Mathematics The City College of New York Fall 2013
 Welcome to Math 19500 Video Lessons Prof. Department of Mathematics The City College of New York Fall 2013 An important feature of the following Beamer slide presentations is that you, the reader, move
Welcome to Math 19500 Video Lessons Prof. Department of Mathematics The City College of New York Fall 2013 An important feature of the following Beamer slide presentations is that you, the reader, move
