0.1 MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD ESTIMATION EXPLAINED
|
|
|
- Everett Hunter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 0.1 MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD ESTIMATIO EXPLAIED Maximum likelihood esimaion is a bes-fi saisical mehod for he esimaion of he values of he parameers of a sysem, based on a se of observaions of a random variable ha is relaed o he parameers being esimaed. oe ha he parameers being esimaed are no hemselves random variables. Raher, hey are assumed o be unknon consans. Given a se of observaions X of a random variable X and possibly a se of observaions Y of a condiioning random variable Y, he maximum likelihood esimae of a se of parameers φ is given by φˆ argmax φ { P( X Y; (1.1 here P( X Y; represens he probabiliy ha samples of he random variable X ake he value X, given ha he samples of he random variable Y have aken he value Y. The erms φ and λ afer he semicolon represen he parameers of P( X Y, he disribuion of X condiioned on Y. The erms o he lef of he semicolon are all random variables and he ones o he righ are no random (and have no disribuions associaed ih hem. oe ha in Equaion 1.1 Y and λ are opional. In he simples esimaion here may be no condiioning variables or addiional parameers, and he maximum likelihood esimaor ould simply be given by φ argmax φ { P( X; φ In Equaions 1.1 and 1.2 he probabiliy of X ih respec o φ is maximized. The soluion obained ould be idenical if any monoonically increasing funcion of P( X Y; ere maximized insead of P( X Y;. One paricularly useful monoonic funcion is he logarihm. The logarihm has he simplifying propery ha i ransforms he muliplicaion operaion o an addiion. Thus, if he elemens of he se X ere independen, e ould ge (1.2 log( P( X Y; log( P( X 1, X 2,, X Y; log( P( X 1 Y; P( X 2 Y; P( X Y; log( P( X i Y; (1.3 here X 1, X 2, ec. are elemens of he se X. The maximum likelihood esimaor no becomes φˆ argmax φ log( P( X i Y; (1.4 Maximizaion of Equaion 1.4 is frequenly simpler han maximizaion of Equaion 1.1. The erm log ( P( X Y; is referred o as he log-likelihood of X, or simply as he likelihood of X and is represened as L( X Y;. 1
2 The maximizaion given by Equaion 1.4 resuls in an esimae for he parameer φ such ha he resuling disribuion P( X i Y; is he closes fi o he daa se X. We illusrae his by he folloing example. Example: Consider a given se of seven samples from a random variable X : X { X 1, X 2,, X The random variable is furher assumed o have a Gaussian disribuion ih uni variance. The mean of his disribuion µ is o be esimaed from he sample X. The log-likelihood of any sample X i from a Gaussian disribuion is given by L( X ; µ ( X i µ log e C 2π ( X i µ here C is a consan resuling from he erms no involving µ. To maximize L( X ; µ, e differeniae i ih respec o µ and ge (1.5 leading o 0 d L( X ; µ Xi µ dµ ( X i µ (1.6 µˆ X i hich leads us o he conclusion ha he maximum likelihood esimae of he mean of a Gaussian random variable is merely he average of he observed samples. The maximum likelihood esimaion of he mean of a Gaussian random variable is illusraed picorially by Figure 1.1. In general he maximum likelihood esimae of any parameer of he disribuion of any Random variable resuls in a disribuion ha fis he hisogram of he observed samples mos closely. Thus, he ML esimae is dependen only he observed samples. This can lead o errors in esimaion since he observed samples may no be a fair represenaion of he disribuion of he random variable. This usually occurs hen he number of observed samples is very small. 1.2 HOW HMM-BASED AUTOMATIC SPEECH RECOGITIO (ASR SYS- TEMS FUCTIO ASR sysems are essenially paern classifiers. In any such sysem all uerances of speech are modeled as sequences of sounds. These sounds may eiher be he phonemes in a language, ords in ha language, or larger unis, depending on various facors. The complee se of sounds ha he ASR sysem has o recognize consiues he classes modeled by i. In his discussion, e assume ihou loss of generaliy, ha he (1.7
3 Figure 1.1 Picorial illusraion of ML esimaion of he mean of a Gaussian RV. The hisogram represens he hisogram of he observed samples. The curve in he firs figure represens a Gaussian ih mean µ 1. The curve in he second figure represens a Gaussian hose mean is he average of he observed samples. The hird figure shos a Gaussian ih mean µ 2. Clearly, he Gaussian in he figure o he cener fis he hisogram of he daa mos closely. The mean of his Gaussian is herefore he maximum likelihood esimae of he mean of he RV. sound classes modeled by he sysem are ords. The ASR sysem hen classifies segmens of speech as belonging o one of hese ords, hus idenifying hem. In ASR sysems, classificaion is no performed using he speech signal direcly. Insead, he speech signal is ansformed ino a sequence of feaure vecors, or parameer vecors, and classificaion is performed using hese feaure vecors. The feaure vecors mos idely used used are cepsral coefficiens, or varians of cepsra (such as PLP cepsra derived from poer specra of shor indoed segmens, or frames of speech. Each feaure vecor hus corresponds o a frame of speech. Le S represen he sequence of feaure vecors derived from he uerance being recognized. ASR sysems idenify he sequence of ords in ha uerance using he opimal classifier equaion Ŵ argmax W { P( S WP( W (1.8 here Ŵ is he recognized sequence of ords in ha uerance. P( W is he a priori probabiliy ha he ord sequence W as uered and is usually specified by a language model. For in-deph informaion on language models nd language modeling e refer he reader o [JELIEKS BOOK REF]. P( S W is he likelihood of S given ha he W as he sequence of ords uered. I is ermed as he acousic likelihood of he daa and is obained from he probabiliy disribuion of all sequences feaure vecors ha could represen he sequence of ords W. In HMM-based speech recogniion sysems his probabiliy disribuion of sequences is modeled by an HMM. The folloing secion describes he hidden Markov model in greaer deail. HMM-based modeling of he disribuions of sequences of vecors In HMM-based recogniion sysems he mechanism ha generaes he sequence of feaure vecors represening any ord is modeled by an HMM. When generaing he sequence, he generaor is assumed o be in one of a finie se of saes a any insan of ime. Each sae has a probabiliy disribuion funcion, referred o as he sae disribuion of ha sae, associaed ih i. The hidden Markov modeling paradigm assumes ha o generae he feaure vecor a any insan, he generaor dras a vecor from he sae disribuion of he sae i is in a ha insan. The vecors ha he generaor dras from a sae disribuion are
4 Figure 1.1 Example of a 5 sae HMM ih one non-emiing iniial sae, and a non-emiing erminaing sae. Each of he circles represens a sae. The arros represen valid ransiions from he sae, and he numbers belo he arros represen he probabiliy of ha ransiion. For example, he arros from sae 1 indicae ha if he generaor is in sae 1 a ime, a ime +1 i can be in sae 1 ih probabiliy 0.5, sae 2 ih probabiliy 0.3 and sae 3 ih probabiliy 0.2. The doed arros poin o he sae disribuions associaed ih ha sae. An observaion is dran from his disribuion every ime he generaor visis he sae. The iniial sae (sae 0 and he erminaing sae (sae 4 have no sae disribuions associaed ih hem, and no daa are generaed hen he generaor is in hese saes. oe ha in his figure all ransiions poin lef o righ. In a more generic HMM, ransiions may occur in any direcion, from any sae o any oher sae. said o belong o ha sae. The HMM also has a se of ransiion probabiliies associaed ih each sae. A generaor ha is in sae i a ime and moves o sae j a ime insan + 1 is said o ransi from sae i o sae j a ime insan. The ransiion probabiliies of a sae refer o he probabiliy disribuion of he saes ha he generaor can be in a he nex insan, given ha i is in ha sae a he curren insan. The generaor dras from his disribuion in order o deermine hich sae i ill be in a he nex insan of ime. The ransiion probabiliies and he sae disribuions are all specific o he ord being modeled by he HMM. Figure 1.1 shos an example of an HMM ih 5 saes. The HMM in his figure only permis ransiions in one direcion. Transiions ih probabiliy 0 are no shon. This HMM has a non-emiing iniial sae and a non-emiing erminaing sae. on-emiing saes are saes ih hich here are no probabiliy disribuions associaed - he generaor does no generae observaions hen i is in hese saes. The non-emiing iniial sae in figure 1.1 implies ha a 0, i.e. jus before he generaor begins generaing vecors, i is in he iniial sae here i does no generae any observaions. Similarly, if he generaor eners he erminaing sae i can no longer ransi o any of he oher saes in he HMM, nor can i generae any more observaions. Thus, o generae a sequence of vecors for he ord, he generaor is assumed o ransi hrough a sequence of + 2 saes in he HMM, beginning ih he non-emiing iniial sae and erminaing in he non-emiing final, or absorbing sae. A each ime insan i dras observaions from he sae disribuion of he sae i is in a ha ime insan. The sequence of vecors so generaed is said o be generaed by he HMM. The model for he generaing mechanism for a sequence of ords is also an HMM and easily consruced by concaenaing HMMs for individual ords. Figure 1.2 shos an example here he HMMs for hree ords have been concaenaed o obain an HMM modeling a sequence of hree ords. The saisical parameers of he HMM represening a sequence of ords W are he se of ransiion probabiliies, represened as a marix A W, and he se of sae probabiliy disribuion funcions. The marix A W consiss of elemens a ( i, j, each of hich represens he probabiliy ha he generaor ill be in sae j in he nex ime insan, given ha i is currenly in sae i. Thus, for an HMM ih K saes, e have
5 K a ( i, j 1.0 j 1 (1.9 The sae disribuion of he k h sae is represened by P W, k ( X, here X represens any feaure vecor ha belongs o ha sae. In speech recogniion sysems he various sae disribuions are usually modeled as Gaussians or mixures of Gaussians. Typically, for compuaional efficiency, hese Gaussians are assumed o have diagonal covariance marices, i.e. covariance marices here he off-diagonal elemens are all 0. For simpliciy e represen he sae disribuion of he k h sae as P W, k ( X M( X; φ k (1.10 here M( X; φ k denoes a Gaussian mixure disribuion corresponding o he kh sae of he HMM represening he ord sequence W and represens he se of parameers associaed ih i. We denoe he se of φ k for all he saes in he HMM for W as λ W. A W and λ W represen he complee se of parameers needed o uniquely idenify he HMM modeling W. φ k The probabiliy of any vecor sequence S ha is generaed by he HMM for W is no given by P( S W P( S, s W s Ξ s Ξ P( s WP( S s (1.11 here s represens any sae sequence ha he generaor can follo hen generaing S, and Ξ represens he se of all possible sae sequences. The sae sequence s is, quie lierally, a sequence of saes, one for every feaure vecor in S. Tha is, s [ s 1, s 2, s 3,, s ] (1.12 here is he sae associaed ih S(, he h vecor in S, and is he oal number of vecors in he s sequence S. The probabiliy erms in he righ hand side of Equaion (1.11 can no be rien as WORD 1 WORD 2 WORD 3 Figure 1.2 Example of consrucing he HMM for a sequence of ords from he HMMs of individual ords. The non-emiing erminaing sae of any ord is merged ih he non-emiing iniial sae of he nex ord. The merged sae is no longer an iniial sae or a erminaing sae. Hoever, i remains non-emiing, and no sae disribuion is associaed ih i. The resuling HMM has a non-emiing iniial sae, a non-emiing erminaing sae and several inermediae non-emiing saes as ell.
6 P( S s M( S( ; φ s P( s W a( 0, s 1 a( s, s + 1 (1.13 here a( 0, s represens he probabiliy of ransiing from he h 1 0 sae (i.e he iniial non-emiing sae of he HMM for W o he firs sae in he sae sequence s, and a( s, s + 1 represens he probabiliy of ransiing from sae s o sae s + 1. Equaion (1.11 can no be rerien as P( S W a( 0, s 1 a( s, s + 1 s Ξ, p Ideally, recogniion ould be performed as M( S( ; φ s (1.14 Ŵ argmax W P( W P( s WP( S s s Ξ (1.15 Hoever, for easy implemenaion, HMM based speech recogniion sysems usually esimae no jus he bes ord sequence, bu also he bes sae sequence associaed ih he ord sequence. i.e. recogniion is performed as: Ŵ argmax W, s { P( WP( S, s W Using Equaion (1.13, his can be furher expanded ino arg max W, s { P( WP( s WP( S s (1.16 Ŵ argmax W, s P( W a( 0, s 1 a( s, s + 1 M( S( ; φ s (1.17 In order o evaluae Equaion (1.17 fully, he erm ihin he braces ould have o be compued for every possible ord sequence in he language. This ould be impracical. In pracice, dynamic programming mehods are used o obain locally opimal esimaes for Ŵ. There, is hoever, furher refinemen possiblein HMM-based sysems. The CMU Sphinx-III HMM based recogniion sysem, for example, is a phone-based recogniion sysem in hich ords are furher decomposed ino sequences of phoneic unis and he HMMs for ords are buil by concaenaing he HMMs modeling hese phoenic unis. In order o reduce he oal number of parameers needed o consruc HMMs for all he phoneic unis modeled by he sysem, he sae disribuions of he HMMs of he various phoneic unis are shared, i.e. he same disribuion is used by he saes of he HMMs of several phoneic unis. In he nex secion e ill explain he precise manner in hich he Sphinx (or any oher HMM-based sysem models any given lanugage and learns he parameers of he models used o represen he basic sound unis of he language.
Vehicle Arrival Models : Headway
 Chaper 12 Vehicle Arrival Models : Headway 12.1 Inroducion Modelling arrival of vehicle a secion of road is an imporan sep in raffic flow modelling. I has imporan applicaion in raffic flow simulaion where
Chaper 12 Vehicle Arrival Models : Headway 12.1 Inroducion Modelling arrival of vehicle a secion of road is an imporan sep in raffic flow modelling. I has imporan applicaion in raffic flow simulaion where
10. State Space Methods
 . Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
. Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
State-Space Models. Initialization, Estimation and Smoothing of the Kalman Filter
 Sae-Space Models Iniializaion, Esimaion and Smoohing of he Kalman Filer Iniializaion of he Kalman Filer The Kalman filer shows how o updae pas predicors and he corresponding predicion error variances when
Sae-Space Models Iniializaion, Esimaion and Smoohing of he Kalman Filer Iniializaion of he Kalman Filer The Kalman filer shows how o updae pas predicors and he corresponding predicion error variances when
Object tracking: Using HMMs to estimate the geographical location of fish
 Objec racking: Using HMMs o esimae he geographical locaion of fish 02433 - Hidden Markov Models Marin Wæver Pedersen, Henrik Madsen Course week 13 MWP, compiled June 8, 2011 Objecive: Locae fish from agging
Objec racking: Using HMMs o esimae he geographical locaion of fish 02433 - Hidden Markov Models Marin Wæver Pedersen, Henrik Madsen Course week 13 MWP, compiled June 8, 2011 Objecive: Locae fish from agging
Diebold, Chapter 7. Francis X. Diebold, Elements of Forecasting, 4th Edition (Mason, Ohio: Cengage Learning, 2006). Chapter 7. Characterizing Cycles
 Diebold, Chaper 7 Francis X. Diebold, Elemens of Forecasing, 4h Ediion (Mason, Ohio: Cengage Learning, 006). Chaper 7. Characerizing Cycles Afer compleing his reading you should be able o: Define covariance
Diebold, Chaper 7 Francis X. Diebold, Elemens of Forecasing, 4h Ediion (Mason, Ohio: Cengage Learning, 006). Chaper 7. Characerizing Cycles Afer compleing his reading you should be able o: Define covariance
Math 315: Linear Algebra Solutions to Assignment 6
 Mah 35: Linear Algebra s o Assignmen 6 # Which of he following ses of vecors are bases for R 2? {2,, 3, }, {4,, 7, 8}, {,,, 3}, {3, 9, 4, 2}. Explain your answer. To generae he whole R 2, wo linearly independen
Mah 35: Linear Algebra s o Assignmen 6 # Which of he following ses of vecors are bases for R 2? {2,, 3, }, {4,, 7, 8}, {,,, 3}, {3, 9, 4, 2}. Explain your answer. To generae he whole R 2, wo linearly independen
) were both constant and we brought them from under the integral.
 YIELD-PER-RECRUIT (coninued The yield-per-recrui model applies o a cohor, bu we saw in he Age Disribuions lecure ha he properies of a cohor do no apply in general o a collecion of cohors, which is wha
YIELD-PER-RECRUIT (coninued The yield-per-recrui model applies o a cohor, bu we saw in he Age Disribuions lecure ha he properies of a cohor do no apply in general o a collecion of cohors, which is wha
STATE-SPACE MODELLING. A mass balance across the tank gives:
 B. Lennox and N.F. Thornhill, 9, Sae Space Modelling, IChemE Process Managemen and Conrol Subjec Group Newsleer STE-SPACE MODELLING Inroducion: Over he pas decade or so here has been an ever increasing
B. Lennox and N.F. Thornhill, 9, Sae Space Modelling, IChemE Process Managemen and Conrol Subjec Group Newsleer STE-SPACE MODELLING Inroducion: Over he pas decade or so here has been an ever increasing
Hidden Markov Models
 Hidden Markov Models Probabilisic reasoning over ime So far, we ve mosly deal wih episodic environmens Excepions: games wih muliple moves, planning In paricular, he Bayesian neworks we ve seen so far describe
Hidden Markov Models Probabilisic reasoning over ime So far, we ve mosly deal wih episodic environmens Excepions: games wih muliple moves, planning In paricular, he Bayesian neworks we ve seen so far describe
Speaker Adaptation Techniques For Continuous Speech Using Medium and Small Adaptation Data Sets. Constantinos Boulis
 Speaker Adapaion Techniques For Coninuous Speech Using Medium and Small Adapaion Daa Ses Consaninos Boulis Ouline of he Presenaion Inroducion o he speaker adapaion problem Maximum Likelihood Sochasic Transformaions
Speaker Adapaion Techniques For Coninuous Speech Using Medium and Small Adapaion Daa Ses Consaninos Boulis Ouline of he Presenaion Inroducion o he speaker adapaion problem Maximum Likelihood Sochasic Transformaions
Zürich. ETH Master Course: L Autonomous Mobile Robots Localization II
 Roland Siegwar Margaria Chli Paul Furgale Marco Huer Marin Rufli Davide Scaramuzza ETH Maser Course: 151-0854-00L Auonomous Mobile Robos Localizaion II ACT and SEE For all do, (predicion updae / ACT),
Roland Siegwar Margaria Chli Paul Furgale Marco Huer Marin Rufli Davide Scaramuzza ETH Maser Course: 151-0854-00L Auonomous Mobile Robos Localizaion II ACT and SEE For all do, (predicion updae / ACT),
20. Applications of the Genetic-Drift Model
 0. Applicaions of he Geneic-Drif Model 1) Deermining he probabiliy of forming any paricular combinaion of genoypes in he nex generaion: Example: If he parenal allele frequencies are p 0 = 0.35 and q 0
0. Applicaions of he Geneic-Drif Model 1) Deermining he probabiliy of forming any paricular combinaion of genoypes in he nex generaion: Example: If he parenal allele frequencies are p 0 = 0.35 and q 0
Georey E. Hinton. University oftoronto. Technical Report CRG-TR February 22, Abstract
 Parameer Esimaion for Linear Dynamical Sysems Zoubin Ghahramani Georey E. Hinon Deparmen of Compuer Science Universiy oftorono 6 King's College Road Torono, Canada M5S A4 Email: zoubin@cs.orono.edu Technical
Parameer Esimaion for Linear Dynamical Sysems Zoubin Ghahramani Georey E. Hinon Deparmen of Compuer Science Universiy oftorono 6 King's College Road Torono, Canada M5S A4 Email: zoubin@cs.orono.edu Technical
t is a basis for the solution space to this system, then the matrix having these solutions as columns, t x 1 t, x 2 t,... x n t x 2 t...
 Mah 228- Fri Mar 24 5.6 Marix exponenials and linear sysems: The analogy beween firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions (Chaper 5) and scalar linear differenial equaions (Chaper ) is much sronger
Mah 228- Fri Mar 24 5.6 Marix exponenials and linear sysems: The analogy beween firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions (Chaper 5) and scalar linear differenial equaions (Chaper ) is much sronger
Kriging Models Predicting Atrazine Concentrations in Surface Water Draining Agricultural Watersheds
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Kriging Models Predicing Arazine Concenraions in Surface Waer Draining Agriculural Waersheds Paul L. Mosquin, Jeremy Aldworh, Wenlin Chen Supplemenal Maerial Number
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Kriging Models Predicing Arazine Concenraions in Surface Waer Draining Agriculural Waersheds Paul L. Mosquin, Jeremy Aldworh, Wenlin Chen Supplemenal Maerial Number
CHERNOFF DISTANCE AND AFFINITY FOR TRUNCATED DISTRIBUTIONS *
 haper 5 HERNOFF DISTANE AND AFFINITY FOR TRUNATED DISTRIBUTIONS * 5. Inroducion In he case of disribuions ha saisfy he regulariy condiions, he ramer- Rao inequaliy holds and he maximum likelihood esimaor
haper 5 HERNOFF DISTANE AND AFFINITY FOR TRUNATED DISTRIBUTIONS * 5. Inroducion In he case of disribuions ha saisfy he regulariy condiions, he ramer- Rao inequaliy holds and he maximum likelihood esimaor
Authors. Introduction. Introduction
 Auhors Hidden Applied in Agriculural Crops Classificaion Caholic Universiy of Rio de Janeiro (PUC-Rio Paula B. C. Leie Raul Q. Feiosa Gilson A. O. P. Cosa Hidden Applied in Agriculural Crops Classificaion
Auhors Hidden Applied in Agriculural Crops Classificaion Caholic Universiy of Rio de Janeiro (PUC-Rio Paula B. C. Leie Raul Q. Feiosa Gilson A. O. P. Cosa Hidden Applied in Agriculural Crops Classificaion
Solutions from Chapter 9.1 and 9.2
 Soluions from Chaper 9 and 92 Secion 9 Problem # This basically boils down o an exercise in he chain rule from calculus We are looking for soluions of he form: u( x) = f( k x c) where k x R 3 and k is
Soluions from Chaper 9 and 92 Secion 9 Problem # This basically boils down o an exercise in he chain rule from calculus We are looking for soluions of he form: u( x) = f( k x c) where k x R 3 and k is
Optimal Paired Choice Block Designs. Supplementary Material
 Saisica Sinica: Supplemen Opimal Paired Choice Block Designs Rakhi Singh 1, Ashish Das 2 and Feng-Shun Chai 3 1 IITB-Monash Research Academy, Mumbai, India 2 Indian Insiue of Technology Bombay, Mumbai,
Saisica Sinica: Supplemen Opimal Paired Choice Block Designs Rakhi Singh 1, Ashish Das 2 and Feng-Shun Chai 3 1 IITB-Monash Research Academy, Mumbai, India 2 Indian Insiue of Technology Bombay, Mumbai,
Matlab and Python programming: how to get started
 Malab and Pyhon programming: how o ge sared Equipping readers he skills o wrie programs o explore complex sysems and discover ineresing paerns from big daa is one of he main goals of his book. In his chaper,
Malab and Pyhon programming: how o ge sared Equipping readers he skills o wrie programs o explore complex sysems and discover ineresing paerns from big daa is one of he main goals of his book. In his chaper,
Modal identification of structures from roving input data by means of maximum likelihood estimation of the state space model
 Modal idenificaion of srucures from roving inpu daa by means of maximum likelihood esimaion of he sae space model J. Cara, J. Juan, E. Alarcón Absrac The usual way o perform a forced vibraion es is o fix
Modal idenificaion of srucures from roving inpu daa by means of maximum likelihood esimaion of he sae space model J. Cara, J. Juan, E. Alarcón Absrac The usual way o perform a forced vibraion es is o fix
Asymptotic Equipartition Property - Seminar 3, part 1
 Asympoic Equipariion Propery - Seminar 3, par 1 Ocober 22, 2013 Problem 1 (Calculaion of ypical se) To clarify he noion of a ypical se A (n) ε and he smalles se of high probabiliy B (n), we will calculae
Asympoic Equipariion Propery - Seminar 3, par 1 Ocober 22, 2013 Problem 1 (Calculaion of ypical se) To clarify he noion of a ypical se A (n) ε and he smalles se of high probabiliy B (n), we will calculae
GMM - Generalized Method of Moments
 GMM - Generalized Mehod of Momens Conens GMM esimaion, shor inroducion 2 GMM inuiion: Maching momens 2 3 General overview of GMM esimaion. 3 3. Weighing marix...........................................
GMM - Generalized Mehod of Momens Conens GMM esimaion, shor inroducion 2 GMM inuiion: Maching momens 2 3 General overview of GMM esimaion. 3 3. Weighing marix...........................................
Reading from Young & Freedman: For this topic, read sections 25.4 & 25.5, the introduction to chapter 26 and sections 26.1 to 26.2 & 26.4.
 PHY1 Elecriciy Topic 7 (Lecures 1 & 11) Elecric Circuis n his opic, we will cover: 1) Elecromoive Force (EMF) ) Series and parallel resisor combinaions 3) Kirchhoff s rules for circuis 4) Time dependence
PHY1 Elecriciy Topic 7 (Lecures 1 & 11) Elecric Circuis n his opic, we will cover: 1) Elecromoive Force (EMF) ) Series and parallel resisor combinaions 3) Kirchhoff s rules for circuis 4) Time dependence
Testing the Random Walk Model. i.i.d. ( ) r
 he random walk heory saes: esing he Random Walk Model µ ε () np = + np + Momen Condiions where where ε ~ i.i.d he idea here is o es direcly he resricions imposed by momen condiions. lnp lnp µ ( lnp lnp
he random walk heory saes: esing he Random Walk Model µ ε () np = + np + Momen Condiions where where ε ~ i.i.d he idea here is o es direcly he resricions imposed by momen condiions. lnp lnp µ ( lnp lnp
Notes on Kalman Filtering
 Noes on Kalman Filering Brian Borchers and Rick Aser November 7, Inroducion Daa Assimilaion is he problem of merging model predicions wih acual measuremens of a sysem o produce an opimal esimae of he curren
Noes on Kalman Filering Brian Borchers and Rick Aser November 7, Inroducion Daa Assimilaion is he problem of merging model predicions wih acual measuremens of a sysem o produce an opimal esimae of he curren
Bias in Conditional and Unconditional Fixed Effects Logit Estimation: a Correction * Tom Coupé
 Bias in Condiional and Uncondiional Fixed Effecs Logi Esimaion: a Correcion * Tom Coupé Economics Educaion and Research Consorium, Naional Universiy of Kyiv Mohyla Academy Address: Vul Voloska 10, 04070
Bias in Condiional and Uncondiional Fixed Effecs Logi Esimaion: a Correcion * Tom Coupé Economics Educaion and Research Consorium, Naional Universiy of Kyiv Mohyla Academy Address: Vul Voloska 10, 04070
Designing Information Devices and Systems I Spring 2019 Lecture Notes Note 17
 EES 16A Designing Informaion Devices and Sysems I Spring 019 Lecure Noes Noe 17 17.1 apaciive ouchscreen In he las noe, we saw ha a capacior consiss of wo pieces on conducive maerial separaed by a nonconducive
EES 16A Designing Informaion Devices and Sysems I Spring 019 Lecure Noes Noe 17 17.1 apaciive ouchscreen In he las noe, we saw ha a capacior consiss of wo pieces on conducive maerial separaed by a nonconducive
Concourse Math Spring 2012 Worked Examples: Matrix Methods for Solving Systems of 1st Order Linear Differential Equations
 Concourse Mah 80 Spring 0 Worked Examples: Marix Mehods for Solving Sysems of s Order Linear Differenial Equaions The Main Idea: Given a sysem of s order linear differenial equaions d x d Ax wih iniial
Concourse Mah 80 Spring 0 Worked Examples: Marix Mehods for Solving Sysems of s Order Linear Differenial Equaions The Main Idea: Given a sysem of s order linear differenial equaions d x d Ax wih iniial
Robust estimation based on the first- and third-moment restrictions of the power transformation model
 h Inernaional Congress on Modelling and Simulaion, Adelaide, Ausralia, 6 December 3 www.mssanz.org.au/modsim3 Robus esimaion based on he firs- and hird-momen resricions of he power ransformaion Nawaa,
h Inernaional Congress on Modelling and Simulaion, Adelaide, Ausralia, 6 December 3 www.mssanz.org.au/modsim3 Robus esimaion based on he firs- and hird-momen resricions of he power ransformaion Nawaa,
Analyze patterns and relationships. 3. Generate two numerical patterns using AC
 envision ah 2.0 5h Grade ah Curriculum Quarer 1 Quarer 2 Quarer 3 Quarer 4 andards: =ajor =upporing =Addiional Firs 30 Day 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 andards: Operaions and Algebraic Thinking
envision ah 2.0 5h Grade ah Curriculum Quarer 1 Quarer 2 Quarer 3 Quarer 4 andards: =ajor =upporing =Addiional Firs 30 Day 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 andards: Operaions and Algebraic Thinking
Section 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equations; Method of Undetermined Coefficients
 Secion 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equaions; Mehod of Undeermined Coefficiens Key Terms/Ideas: Linear Differenial operaor Nonlinear operaor Second order homogeneous DE Second order nonhomogeneous DE Soluion o homogeneous
Secion 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equaions; Mehod of Undeermined Coefficiens Key Terms/Ideas: Linear Differenial operaor Nonlinear operaor Second order homogeneous DE Second order nonhomogeneous DE Soluion o homogeneous
Math 334 Fall 2011 Homework 11 Solutions
 Dec. 2, 2 Mah 334 Fall 2 Homework Soluions Basic Problem. Transform he following iniial value problem ino an iniial value problem for a sysem: u + p()u + q() u g(), u() u, u () v. () Soluion. Le v u. Then
Dec. 2, 2 Mah 334 Fall 2 Homework Soluions Basic Problem. Transform he following iniial value problem ino an iniial value problem for a sysem: u + p()u + q() u g(), u() u, u () v. () Soluion. Le v u. Then
Errata (1 st Edition)
 P Sandborn, os Analysis of Elecronic Sysems, s Ediion, orld Scienific, Singapore, 03 Erraa ( s Ediion) S K 05D Page 8 Equaion (7) should be, E 05D E Nu e S K he L appearing in he equaion in he book does
P Sandborn, os Analysis of Elecronic Sysems, s Ediion, orld Scienific, Singapore, 03 Erraa ( s Ediion) S K 05D Page 8 Equaion (7) should be, E 05D E Nu e S K he L appearing in he equaion in he book does
Isolated-word speech recognition using hidden Markov models
 Isolaed-word speech recogniion using hidden Markov models Håkon Sandsmark December 18, 21 1 Inroducion Speech recogniion is a challenging problem on which much work has been done he las decades. Some of
Isolaed-word speech recogniion using hidden Markov models Håkon Sandsmark December 18, 21 1 Inroducion Speech recogniion is a challenging problem on which much work has been done he las decades. Some of
Some Basic Information about M-S-D Systems
 Some Basic Informaion abou M-S-D Sysems 1 Inroducion We wan o give some summary of he facs concerning unforced (homogeneous) and forced (non-homogeneous) models for linear oscillaors governed by second-order,
Some Basic Informaion abou M-S-D Sysems 1 Inroducion We wan o give some summary of he facs concerning unforced (homogeneous) and forced (non-homogeneous) models for linear oscillaors governed by second-order,
Math 10B: Mock Mid II. April 13, 2016
 Name: Soluions Mah 10B: Mock Mid II April 13, 016 1. ( poins) Sae, wih jusificaion, wheher he following saemens are rue or false. (a) If a 3 3 marix A saisfies A 3 A = 0, hen i canno be inverible. True.
Name: Soluions Mah 10B: Mock Mid II April 13, 016 1. ( poins) Sae, wih jusificaion, wheher he following saemens are rue or false. (a) If a 3 3 marix A saisfies A 3 A = 0, hen i canno be inverible. True.
KEY. Math 334 Midterm III Winter 2008 section 002 Instructor: Scott Glasgow
 KEY Mah 334 Miderm III Winer 008 secion 00 Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his exam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on your own paper, preferably engineering
KEY Mah 334 Miderm III Winer 008 secion 00 Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his exam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on your own paper, preferably engineering
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 0.038/NCLIMATE893 Temporal resoluion and DICE * Supplemenal Informaion Alex L. Maren and Sephen C. Newbold Naional Cener for Environmenal Economics, US Environmenal Proecion
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 0.038/NCLIMATE893 Temporal resoluion and DICE * Supplemenal Informaion Alex L. Maren and Sephen C. Newbold Naional Cener for Environmenal Economics, US Environmenal Proecion
References are appeared in the last slide. Last update: (1393/08/19)
 SYSEM IDEIFICAIO Ali Karimpour Associae Professor Ferdowsi Universi of Mashhad References are appeared in he las slide. Las updae: 0..204 393/08/9 Lecure 5 lecure 5 Parameer Esimaion Mehods opics o be
SYSEM IDEIFICAIO Ali Karimpour Associae Professor Ferdowsi Universi of Mashhad References are appeared in he las slide. Las updae: 0..204 393/08/9 Lecure 5 lecure 5 Parameer Esimaion Mehods opics o be
Differential Equations
 Mah 21 (Fall 29) Differenial Equaions Soluion #3 1. Find he paricular soluion of he following differenial equaion by variaion of parameer (a) y + y = csc (b) 2 y + y y = ln, > Soluion: (a) The corresponding
Mah 21 (Fall 29) Differenial Equaions Soluion #3 1. Find he paricular soluion of he following differenial equaion by variaion of parameer (a) y + y = csc (b) 2 y + y y = ln, > Soluion: (a) The corresponding
Hamilton- J acobi Equation: Explicit Formulas In this lecture we try to apply the method of characteristics to the Hamilton-Jacobi equation: u t
 M ah 5 2 7 Fall 2 0 0 9 L ecure 1 0 O c. 7, 2 0 0 9 Hamilon- J acobi Equaion: Explici Formulas In his lecure we ry o apply he mehod of characerisics o he Hamilon-Jacobi equaion: u + H D u, x = 0 in R n
M ah 5 2 7 Fall 2 0 0 9 L ecure 1 0 O c. 7, 2 0 0 9 Hamilon- J acobi Equaion: Explici Formulas In his lecure we ry o apply he mehod of characerisics o he Hamilon-Jacobi equaion: u + H D u, x = 0 in R n
Chapter 2. First Order Scalar Equations
 Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
Time series model fitting via Kalman smoothing and EM estimation in TimeModels.jl
 Time series model fiing via Kalman smoohing and EM esimaion in TimeModels.jl Gord Sephen Las updaed: January 206 Conens Inroducion 2. Moivaion and Acknowledgemens....................... 2.2 Noaion......................................
Time series model fiing via Kalman smoohing and EM esimaion in TimeModels.jl Gord Sephen Las updaed: January 206 Conens Inroducion 2. Moivaion and Acknowledgemens....................... 2.2 Noaion......................................
Non-uniform circular motion *
 OpenSax-CNX module: m14020 1 Non-uniform circular moion * Sunil Kumar Singh This work is produced by OpenSax-CNX and licensed under he Creaive Commons Aribuion License 2.0 Wha do we mean by non-uniform
OpenSax-CNX module: m14020 1 Non-uniform circular moion * Sunil Kumar Singh This work is produced by OpenSax-CNX and licensed under he Creaive Commons Aribuion License 2.0 Wha do we mean by non-uniform
Sensors, Signals and Noise
 Sensors, Signals and Noise COURSE OUTLINE Inroducion Signals and Noise: 1) Descripion Filering Sensors and associaed elecronics rv 2017/02/08 1 Noise Descripion Noise Waveforms and Samples Saisics of Noise
Sensors, Signals and Noise COURSE OUTLINE Inroducion Signals and Noise: 1) Descripion Filering Sensors and associaed elecronics rv 2017/02/08 1 Noise Descripion Noise Waveforms and Samples Saisics of Noise
Online Appendix to Solution Methods for Models with Rare Disasters
 Online Appendix o Soluion Mehods for Models wih Rare Disasers Jesús Fernández-Villaverde and Oren Levinal In his Online Appendix, we presen he Euler condiions of he model, we develop he pricing Calvo block,
Online Appendix o Soluion Mehods for Models wih Rare Disasers Jesús Fernández-Villaverde and Oren Levinal In his Online Appendix, we presen he Euler condiions of he model, we develop he pricing Calvo block,
Application of a Stochastic-Fuzzy Approach to Modeling Optimal Discrete Time Dynamical Systems by Using Large Scale Data Processing
 Applicaion of a Sochasic-Fuzzy Approach o Modeling Opimal Discree Time Dynamical Sysems by Using Large Scale Daa Processing AA WALASZE-BABISZEWSA Deparmen of Compuer Engineering Opole Universiy of Technology
Applicaion of a Sochasic-Fuzzy Approach o Modeling Opimal Discree Time Dynamical Sysems by Using Large Scale Daa Processing AA WALASZE-BABISZEWSA Deparmen of Compuer Engineering Opole Universiy of Technology
Module 2 F c i k c s la l w a s o s f dif di fusi s o i n
 Module Fick s laws of diffusion Fick s laws of diffusion and hin film soluion Adolf Fick (1855) proposed: d J α d d d J (mole/m s) flu (m /s) diffusion coefficien and (mole/m 3 ) concenraion of ions, aoms
Module Fick s laws of diffusion Fick s laws of diffusion and hin film soluion Adolf Fick (1855) proposed: d J α d d d J (mole/m s) flu (m /s) diffusion coefficien and (mole/m 3 ) concenraion of ions, aoms
Solutions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Math 246, Spring 2011, Professor David Levermore
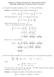 Soluions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Mah 6, Spring, Professor David Levermore Compue he Laplace ransform of f e from is definiion Soluion The definiion of he Laplace ransform gives L[f]s
Soluions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Mah 6, Spring, Professor David Levermore Compue he Laplace ransform of f e from is definiion Soluion The definiion of he Laplace ransform gives L[f]s
Vectorautoregressive Model and Cointegration Analysis. Time Series Analysis Dr. Sevtap Kestel 1
 Vecorauoregressive Model and Coinegraion Analysis Par V Time Series Analysis Dr. Sevap Kesel 1 Vecorauoregression Vecor auoregression (VAR) is an economeric model used o capure he evoluion and he inerdependencies
Vecorauoregressive Model and Coinegraion Analysis Par V Time Series Analysis Dr. Sevap Kesel 1 Vecorauoregression Vecor auoregression (VAR) is an economeric model used o capure he evoluion and he inerdependencies
Robert Kollmann. 6 September 2017
 Appendix: Supplemenary maerial for Tracable Likelihood-Based Esimaion of Non- Linear DSGE Models Economics Leers (available online 6 Sepember 207) hp://dx.doi.org/0.06/j.econle.207.08.027 Rober Kollmann
Appendix: Supplemenary maerial for Tracable Likelihood-Based Esimaion of Non- Linear DSGE Models Economics Leers (available online 6 Sepember 207) hp://dx.doi.org/0.06/j.econle.207.08.027 Rober Kollmann
WEEK-3 Recitation PHYS 131. of the projectile s velocity remains constant throughout the motion, since the acceleration a x
 WEEK-3 Reciaion PHYS 131 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. Problems 9, 37, 41 & 71 and Ch. 4: FOC 1, 3, 5, 8. Problems 3, 5 & 16. Feb 8, 018 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. 1. (a) The horizonal componen of he projecile
WEEK-3 Reciaion PHYS 131 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. Problems 9, 37, 41 & 71 and Ch. 4: FOC 1, 3, 5, 8. Problems 3, 5 & 16. Feb 8, 018 Ch. 3: FOC 1, 3, 4, 6, 14. 1. (a) The horizonal componen of he projecile
Testing for a Single Factor Model in the Multivariate State Space Framework
 esing for a Single Facor Model in he Mulivariae Sae Space Framework Chen C.-Y. M. Chiba and M. Kobayashi Inernaional Graduae School of Social Sciences Yokohama Naional Universiy Japan Faculy of Economics
esing for a Single Facor Model in he Mulivariae Sae Space Framework Chen C.-Y. M. Chiba and M. Kobayashi Inernaional Graduae School of Social Sciences Yokohama Naional Universiy Japan Faculy of Economics
Two Coupled Oscillators / Normal Modes
 Lecure 3 Phys 3750 Two Coupled Oscillaors / Normal Modes Overview and Moivaion: Today we ake a small, bu significan, sep owards wave moion. We will no ye observe waves, bu his sep is imporan in is own
Lecure 3 Phys 3750 Two Coupled Oscillaors / Normal Modes Overview and Moivaion: Today we ake a small, bu significan, sep owards wave moion. We will no ye observe waves, bu his sep is imporan in is own
IMPACT OF AN OBLIQUE BREAKING WAVE ON A WALL
 Source: Physics of Fluids Vol 6 No pp 6-64 4 DOI: 6/64445 IMPACT OF AN OIQUE REAKING WAVE ON A WA Jian-Jun SHU School of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering Nanyang Technological Universiy 5 Nanyang Avenue
Source: Physics of Fluids Vol 6 No pp 6-64 4 DOI: 6/64445 IMPACT OF AN OIQUE REAKING WAVE ON A WA Jian-Jun SHU School of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering Nanyang Technological Universiy 5 Nanyang Avenue
Article from. Predictive Analytics and Futurism. July 2016 Issue 13
 Aricle from Predicive Analyics and Fuurism July 6 Issue An Inroducion o Incremenal Learning By Qiang Wu and Dave Snell Machine learning provides useful ools for predicive analyics The ypical machine learning
Aricle from Predicive Analyics and Fuurism July 6 Issue An Inroducion o Incremenal Learning By Qiang Wu and Dave Snell Machine learning provides useful ools for predicive analyics The ypical machine learning
PENALIZED LEAST SQUARES AND PENALIZED LIKELIHOOD
 PENALIZED LEAST SQUARES AND PENALIZED LIKELIHOOD HAN XIAO 1. Penalized Leas Squares Lasso solves he following opimizaion problem, ˆβ lasso = arg max β R p+1 1 N y i β 0 N x ij β j β j (1.1) for some 0.
PENALIZED LEAST SQUARES AND PENALIZED LIKELIHOOD HAN XIAO 1. Penalized Leas Squares Lasso solves he following opimizaion problem, ˆβ lasso = arg max β R p+1 1 N y i β 0 N x ij β j β j (1.1) for some 0.
Class Meeting # 10: Introduction to the Wave Equation
 MATH 8.5 COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # 0 8.5 Inroducion o PDEs, Fall 0 Professor: Jared Speck Class Meeing # 0: Inroducion o he Wave Equaion. Wha is he wave equaion? The sandard wave equaion for a funcion
MATH 8.5 COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # 0 8.5 Inroducion o PDEs, Fall 0 Professor: Jared Speck Class Meeing # 0: Inroducion o he Wave Equaion. Wha is he wave equaion? The sandard wave equaion for a funcion
Lecture 33: November 29
 36-705: Inermediae Saisics Fall 2017 Lecurer: Siva Balakrishnan Lecure 33: November 29 Today we will coninue discussing he boosrap, and hen ry o undersand why i works in a simple case. In he las lecure
36-705: Inermediae Saisics Fall 2017 Lecurer: Siva Balakrishnan Lecure 33: November 29 Today we will coninue discussing he boosrap, and hen ry o undersand why i works in a simple case. In he las lecure
Physics 127b: Statistical Mechanics. Fokker-Planck Equation. Time Evolution
 Physics 7b: Saisical Mechanics Fokker-Planck Equaion The Langevin equaion approach o he evoluion of he velociy disribuion for he Brownian paricle migh leave you uncomforable. A more formal reamen of his
Physics 7b: Saisical Mechanics Fokker-Planck Equaion The Langevin equaion approach o he evoluion of he velociy disribuion for he Brownian paricle migh leave you uncomforable. A more formal reamen of his
SEIF, EnKF, EKF SLAM. Pieter Abbeel UC Berkeley EECS
 SEIF, EnKF, EKF SLAM Pieer Abbeel UC Berkeley EECS Informaion Filer From an analyical poin of view == Kalman filer Difference: keep rack of he inverse covariance raher han he covariance marix [maer of
SEIF, EnKF, EKF SLAM Pieer Abbeel UC Berkeley EECS Informaion Filer From an analyical poin of view == Kalman filer Difference: keep rack of he inverse covariance raher han he covariance marix [maer of
The Rosenblatt s LMS algorithm for Perceptron (1958) is built around a linear neuron (a neuron with a linear
 In The name of God Lecure4: Percepron and AALIE r. Majid MjidGhoshunih Inroducion The Rosenbla s LMS algorihm for Percepron 958 is buil around a linear neuron a neuron ih a linear acivaion funcion. Hoever,
In The name of God Lecure4: Percepron and AALIE r. Majid MjidGhoshunih Inroducion The Rosenbla s LMS algorihm for Percepron 958 is buil around a linear neuron a neuron ih a linear acivaion funcion. Hoever,
Modeling Economic Time Series with Stochastic Linear Difference Equations
 A. Thiemer, SLDG.mcd, 6..6 FH-Kiel Universiy of Applied Sciences Prof. Dr. Andreas Thiemer e-mail: andreas.hiemer@fh-kiel.de Modeling Economic Time Series wih Sochasic Linear Difference Equaions Summary:
A. Thiemer, SLDG.mcd, 6..6 FH-Kiel Universiy of Applied Sciences Prof. Dr. Andreas Thiemer e-mail: andreas.hiemer@fh-kiel.de Modeling Economic Time Series wih Sochasic Linear Difference Equaions Summary:
CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIRCUITS
 CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS 257 12.1 RESISTORS IN SERIES AND IN PARALLEL When wo resisors are conneced ogeher as shown in Figure 12.1 we said ha hey are conneced in series. As
CHAPTER 12 DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS DIRECT CURRENT CIUITS 257 12.1 RESISTORS IN SERIES AND IN PARALLEL When wo resisors are conneced ogeher as shown in Figure 12.1 we said ha hey are conneced in series. As
STRUCTURAL CHANGE IN TIME SERIES OF THE EXCHANGE RATES BETWEEN YEN-DOLLAR AND YEN-EURO IN
 Inernaional Journal of Applied Economerics and Quaniaive Sudies. Vol.1-3(004) STRUCTURAL CHANGE IN TIME SERIES OF THE EXCHANGE RATES BETWEEN YEN-DOLLAR AND YEN-EURO IN 001-004 OBARA, Takashi * Absrac The
Inernaional Journal of Applied Economerics and Quaniaive Sudies. Vol.1-3(004) STRUCTURAL CHANGE IN TIME SERIES OF THE EXCHANGE RATES BETWEEN YEN-DOLLAR AND YEN-EURO IN 001-004 OBARA, Takashi * Absrac The
R t. C t P t. + u t. C t = αp t + βr t + v t. + β + w t
 Exercise 7 C P = α + β R P + u C = αp + βr + v (a) (b) C R = α P R + β + w (c) Assumpions abou he disurbances u, v, w : Classical assumions on he disurbance of one of he equaions, eg. on (b): E(v v s P,
Exercise 7 C P = α + β R P + u C = αp + βr + v (a) (b) C R = α P R + β + w (c) Assumpions abou he disurbances u, v, w : Classical assumions on he disurbance of one of he equaions, eg. on (b): E(v v s P,
How to Deal with Structural Breaks in Practical Cointegration Analysis
 How o Deal wih Srucural Breaks in Pracical Coinegraion Analysis Roselyne Joyeux * School of Economic and Financial Sudies Macquarie Universiy December 00 ABSTRACT In his noe we consider he reamen of srucural
How o Deal wih Srucural Breaks in Pracical Coinegraion Analysis Roselyne Joyeux * School of Economic and Financial Sudies Macquarie Universiy December 00 ABSTRACT In his noe we consider he reamen of srucural
Echocardiography Project and Finite Fourier Series
 Echocardiography Projec and Finie Fourier Series 1 U M An echocardiagram is a plo of how a porion of he hear moves as he funcion of ime over he one or more hearbea cycles If he hearbea repeas iself every
Echocardiography Projec and Finie Fourier Series 1 U M An echocardiagram is a plo of how a porion of he hear moves as he funcion of ime over he one or more hearbea cycles If he hearbea repeas iself every
Generalized Least Squares
 Generalized Leas Squares Augus 006 1 Modified Model Original assumpions: 1 Specificaion: y = Xβ + ε (1) Eε =0 3 EX 0 ε =0 4 Eεε 0 = σ I In his secion, we consider relaxing assumpion (4) Insead, assume
Generalized Leas Squares Augus 006 1 Modified Model Original assumpions: 1 Specificaion: y = Xβ + ε (1) Eε =0 3 EX 0 ε =0 4 Eεε 0 = σ I In his secion, we consider relaxing assumpion (4) Insead, assume
Mathematical Theory and Modeling ISSN (Paper) ISSN (Online) Vol 3, No.3, 2013
 Mahemaical Theory and Modeling ISSN -580 (Paper) ISSN 5-05 (Online) Vol, No., 0 www.iise.org The ffec of Inverse Transformaion on he Uni Mean and Consan Variance Assumpions of a Muliplicaive rror Model
Mahemaical Theory and Modeling ISSN -580 (Paper) ISSN 5-05 (Online) Vol, No., 0 www.iise.org The ffec of Inverse Transformaion on he Uni Mean and Consan Variance Assumpions of a Muliplicaive rror Model
Basic Circuit Elements Professor J R Lucas November 2001
 Basic Circui Elemens - J ucas An elecrical circui is an inerconnecion of circui elemens. These circui elemens can be caegorised ino wo ypes, namely acive and passive elemens. Some Definiions/explanaions
Basic Circui Elemens - J ucas An elecrical circui is an inerconnecion of circui elemens. These circui elemens can be caegorised ino wo ypes, namely acive and passive elemens. Some Definiions/explanaions
Non-parametric techniques. Instance Based Learning. NN Decision Boundaries. Nearest Neighbor Algorithm. Distance metric important
 on-parameric echniques Insance Based Learning AKA: neares neighbor mehods, non-parameric, lazy, memorybased, or case-based learning Copyrigh 2005 by David Helmbold 1 Do no fi a model (as do LTU, decision
on-parameric echniques Insance Based Learning AKA: neares neighbor mehods, non-parameric, lazy, memorybased, or case-based learning Copyrigh 2005 by David Helmbold 1 Do no fi a model (as do LTU, decision
On a Discrete-In-Time Order Level Inventory Model for Items with Random Deterioration
 Journal of Agriculure and Life Sciences Vol., No. ; June 4 On a Discree-In-Time Order Level Invenory Model for Iems wih Random Deerioraion Dr Biswaranjan Mandal Associae Professor of Mahemaics Acharya
Journal of Agriculure and Life Sciences Vol., No. ; June 4 On a Discree-In-Time Order Level Invenory Model for Iems wih Random Deerioraion Dr Biswaranjan Mandal Associae Professor of Mahemaics Acharya
Navneet Saini, Mayank Goyal, Vishal Bansal (2013); Term Project AML310; Indian Institute of Technology Delhi
 Creep in Viscoelasic Subsances Numerical mehods o calculae he coefficiens of he Prony equaion using creep es daa and Herediary Inegrals Mehod Navnee Saini, Mayank Goyal, Vishal Bansal (23); Term Projec
Creep in Viscoelasic Subsances Numerical mehods o calculae he coefficiens of he Prony equaion using creep es daa and Herediary Inegrals Mehod Navnee Saini, Mayank Goyal, Vishal Bansal (23); Term Projec
Math 333 Problem Set #2 Solution 14 February 2003
 Mah 333 Problem Se #2 Soluion 14 February 2003 A1. Solve he iniial value problem dy dx = x2 + e 3x ; 2y 4 y(0) = 1. Soluion: This is separable; we wrie 2y 4 dy = x 2 + e x dx and inegrae o ge The iniial
Mah 333 Problem Se #2 Soluion 14 February 2003 A1. Solve he iniial value problem dy dx = x2 + e 3x ; 2y 4 y(0) = 1. Soluion: This is separable; we wrie 2y 4 dy = x 2 + e x dx and inegrae o ge The iniial
Robotics I. April 11, The kinematics of a 3R spatial robot is specified by the Denavit-Hartenberg parameters in Tab. 1.
 Roboics I April 11, 017 Exercise 1 he kinemaics of a 3R spaial robo is specified by he Denavi-Harenberg parameers in ab 1 i α i d i a i θ i 1 π/ L 1 0 1 0 0 L 3 0 0 L 3 3 able 1: able of DH parameers of
Roboics I April 11, 017 Exercise 1 he kinemaics of a 3R spaial robo is specified by he Denavi-Harenberg parameers in ab 1 i α i d i a i θ i 1 π/ L 1 0 1 0 0 L 3 0 0 L 3 3 able 1: able of DH parameers of
On Boundedness of Q-Learning Iterates for Stochastic Shortest Path Problems
 MATHEMATICS OF OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 38, No. 2, May 2013, pp. 209 227 ISSN 0364-765X (prin) ISSN 1526-5471 (online) hp://dx.doi.org/10.1287/moor.1120.0562 2013 INFORMS On Boundedness of Q-Learning Ieraes
MATHEMATICS OF OPERATIONS RESEARCH Vol. 38, No. 2, May 2013, pp. 209 227 ISSN 0364-765X (prin) ISSN 1526-5471 (online) hp://dx.doi.org/10.1287/moor.1120.0562 2013 INFORMS On Boundedness of Q-Learning Ieraes
A Bayesian Approach to Spectral Analysis
 Chirped Signals A Bayesian Approach o Specral Analysis Chirped signals are oscillaing signals wih ime variable frequencies, usually wih a linear variaion of frequency wih ime. E.g. f() = A cos(ω + α 2
Chirped Signals A Bayesian Approach o Specral Analysis Chirped signals are oscillaing signals wih ime variable frequencies, usually wih a linear variaion of frequency wih ime. E.g. f() = A cos(ω + α 2
2. Nonlinear Conservation Law Equations
 . Nonlinear Conservaion Law Equaions One of he clear lessons learned over recen years in sudying nonlinear parial differenial equaions is ha i is generally no wise o ry o aack a general class of nonlinear
. Nonlinear Conservaion Law Equaions One of he clear lessons learned over recen years in sudying nonlinear parial differenial equaions is ha i is generally no wise o ry o aack a general class of nonlinear
DYNAMIC ECONOMETRIC MODELS vol NICHOLAS COPERNICUS UNIVERSITY - TORUŃ Józef Stawicki and Joanna Górka Nicholas Copernicus University
 DYNAMIC ECONOMETRIC MODELS vol.. - NICHOLAS COPERNICUS UNIVERSITY - TORUŃ 996 Józef Sawicki and Joanna Górka Nicholas Copernicus Universiy ARMA represenaion for a sum of auoregressive processes In he ime
DYNAMIC ECONOMETRIC MODELS vol.. - NICHOLAS COPERNICUS UNIVERSITY - TORUŃ 996 Józef Sawicki and Joanna Górka Nicholas Copernicus Universiy ARMA represenaion for a sum of auoregressive processes In he ime
5. Stochastic processes (1)
 Lec05.pp S-38.45 - Inroducion o Teleraffic Theory Spring 2005 Conens Basic conceps Poisson process 2 Sochasic processes () Consider some quaniy in a eleraffic (or any) sysem I ypically evolves in ime randomly
Lec05.pp S-38.45 - Inroducion o Teleraffic Theory Spring 2005 Conens Basic conceps Poisson process 2 Sochasic processes () Consider some quaniy in a eleraffic (or any) sysem I ypically evolves in ime randomly
Presentation Overview
 Acion Refinemen in Reinforcemen Learning by Probabiliy Smoohing By Thomas G. Dieerich & Didac Busques Speaer: Kai Xu Presenaion Overview Bacground The Probabiliy Smoohing Mehod Experimenal Sudy of Acion
Acion Refinemen in Reinforcemen Learning by Probabiliy Smoohing By Thomas G. Dieerich & Didac Busques Speaer: Kai Xu Presenaion Overview Bacground The Probabiliy Smoohing Mehod Experimenal Sudy of Acion
Financial Econometrics Kalman Filter: some applications to Finance University of Evry - Master 2
 Financial Economerics Kalman Filer: some applicaions o Finance Universiy of Evry - Maser 2 Eric Bouyé January 27, 2009 Conens 1 Sae-space models 2 2 The Scalar Kalman Filer 2 21 Presenaion 2 22 Summary
Financial Economerics Kalman Filer: some applicaions o Finance Universiy of Evry - Maser 2 Eric Bouyé January 27, 2009 Conens 1 Sae-space models 2 2 The Scalar Kalman Filer 2 21 Presenaion 2 22 Summary
STAD57 Time Series Analysis. Lecture 14
 STAD57 Time Series Analysis Lecure 14 1 Maximum Likelihood AR(p) Esimaion Insead of Yule-Walker (MM) for AR(p) model, can use Maximum Likelihood (ML) esimaion Likelihood is join densiy of daa {x 1,,x n
STAD57 Time Series Analysis Lecure 14 1 Maximum Likelihood AR(p) Esimaion Insead of Yule-Walker (MM) for AR(p) model, can use Maximum Likelihood (ML) esimaion Likelihood is join densiy of daa {x 1,,x n
Supplementary Document
 Saisica Sinica (2013): Preprin 1 Supplemenary Documen for Funcional Linear Model wih Zero-value Coefficien Funcion a Sub-regions Jianhui Zhou, Nae-Yuh Wang, and Naisyin Wang Universiy of Virginia, Johns
Saisica Sinica (2013): Preprin 1 Supplemenary Documen for Funcional Linear Model wih Zero-value Coefficien Funcion a Sub-regions Jianhui Zhou, Nae-Yuh Wang, and Naisyin Wang Universiy of Virginia, Johns
14 Autoregressive Moving Average Models
 14 Auoregressive Moving Average Models In his chaper an imporan parameric family of saionary ime series is inroduced, he family of he auoregressive moving average, or ARMA, processes. For a large class
14 Auoregressive Moving Average Models In his chaper an imporan parameric family of saionary ime series is inroduced, he family of he auoregressive moving average, or ARMA, processes. For a large class
Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Additional materials (enclosed):
 ADVANCED GCE 78/0 MATHEMATICS (MEI) Differenial Equaions THURSDAY JANUARY 008 Morning Time: hour 30 minues Addiional maerials (enclosed): None Addiional maerials (required): Answer Bookle (8 pages) Graph
ADVANCED GCE 78/0 MATHEMATICS (MEI) Differenial Equaions THURSDAY JANUARY 008 Morning Time: hour 30 minues Addiional maerials (enclosed): None Addiional maerials (required): Answer Bookle (8 pages) Graph
Online Convex Optimization Example And Follow-The-Leader
 CSE599s, Spring 2014, Online Learning Lecure 2-04/03/2014 Online Convex Opimizaion Example And Follow-The-Leader Lecurer: Brendan McMahan Scribe: Sephen Joe Jonany 1 Review of Online Convex Opimizaion
CSE599s, Spring 2014, Online Learning Lecure 2-04/03/2014 Online Convex Opimizaion Example And Follow-The-Leader Lecurer: Brendan McMahan Scribe: Sephen Joe Jonany 1 Review of Online Convex Opimizaion
2.160 System Identification, Estimation, and Learning. Lecture Notes No. 8. March 6, 2006
 2.160 Sysem Idenificaion, Esimaion, and Learning Lecure Noes No. 8 March 6, 2006 4.9 Eended Kalman Filer In many pracical problems, he process dynamics are nonlinear. w Process Dynamics v y u Model (Linearized)
2.160 Sysem Idenificaion, Esimaion, and Learning Lecure Noes No. 8 March 6, 2006 4.9 Eended Kalman Filer In many pracical problems, he process dynamics are nonlinear. w Process Dynamics v y u Model (Linearized)
d 1 = c 1 b 2 - b 1 c 2 d 2 = c 1 b 3 - b 1 c 3
 and d = c b - b c c d = c b - b c c This process is coninued unil he nh row has been compleed. The complee array of coefficiens is riangular. Noe ha in developing he array an enire row may be divided or
and d = c b - b c c d = c b - b c c This process is coninued unil he nh row has been compleed. The complee array of coefficiens is riangular. Noe ha in developing he array an enire row may be divided or
Problemas das Aulas Práticas
 Mesrado Inegrado em Engenharia Elecroécnica e de Compuadores Conrolo em Espaço de Esados Problemas das Aulas Práicas J. Miranda Lemos Fevereiro de 3 Translaed o English by José Gaspar, 6 J. M. Lemos, IST
Mesrado Inegrado em Engenharia Elecroécnica e de Compuadores Conrolo em Espaço de Esados Problemas das Aulas Práicas J. Miranda Lemos Fevereiro de 3 Translaed o English by José Gaspar, 6 J. M. Lemos, IST
Chapter 2. Models, Censoring, and Likelihood for Failure-Time Data
 Chaper 2 Models, Censoring, and Likelihood for Failure-Time Daa William Q. Meeker and Luis A. Escobar Iowa Sae Universiy and Louisiana Sae Universiy Copyrigh 1998-2008 W. Q. Meeker and L. A. Escobar. Based
Chaper 2 Models, Censoring, and Likelihood for Failure-Time Daa William Q. Meeker and Luis A. Escobar Iowa Sae Universiy and Louisiana Sae Universiy Copyrigh 1998-2008 W. Q. Meeker and L. A. Escobar. Based
CONFIDENCE INTERVAL FOR THE DIFFERENCE IN BINOMIAL PROPORTIONS FROM STRATIFIED 2X2 SAMPLES
 Proceedings of he Annual Meeing of he American Saisical Associaion Augus 5-9 00 CONFIDENCE INTERVAL FOR TE DIFFERENCE IN BINOMIAL PROPORTIONS FROM STRATIFIED X SAMPLES Peng-Liang Zhao John. Troxell ui
Proceedings of he Annual Meeing of he American Saisical Associaion Augus 5-9 00 CONFIDENCE INTERVAL FOR TE DIFFERENCE IN BINOMIAL PROPORTIONS FROM STRATIFIED X SAMPLES Peng-Liang Zhao John. Troxell ui
3.1.3 INTRODUCTION TO DYNAMIC OPTIMIZATION: DISCRETE TIME PROBLEMS. A. The Hamiltonian and First-Order Conditions in a Finite Time Horizon
 3..3 INRODUCION O DYNAMIC OPIMIZAION: DISCREE IME PROBLEMS A. he Hamilonian and Firs-Order Condiions in a Finie ime Horizon Define a new funcion, he Hamilonian funcion, H. H he change in he oal value of
3..3 INRODUCION O DYNAMIC OPIMIZAION: DISCREE IME PROBLEMS A. he Hamilonian and Firs-Order Condiions in a Finie ime Horizon Define a new funcion, he Hamilonian funcion, H. H he change in he oal value of
ODEs II, Lecture 1: Homogeneous Linear Systems - I. Mike Raugh 1. March 8, 2004
 ODEs II, Lecure : Homogeneous Linear Sysems - I Mike Raugh March 8, 4 Inroducion. In he firs lecure we discussed a sysem of linear ODEs for modeling he excreion of lead from he human body, saw how o ransform
ODEs II, Lecure : Homogeneous Linear Sysems - I Mike Raugh March 8, 4 Inroducion. In he firs lecure we discussed a sysem of linear ODEs for modeling he excreion of lead from he human body, saw how o ransform
Math Week 14 April 16-20: sections first order systems of linear differential equations; 7.4 mass-spring systems.
 Mah 2250-004 Week 4 April 6-20 secions 7.-7.3 firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions; 7.4 mass-spring sysems. Mon Apr 6 7.-7.2 Sysems of differenial equaions (7.), and he vecor Calculus we need
Mah 2250-004 Week 4 April 6-20 secions 7.-7.3 firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions; 7.4 mass-spring sysems. Mon Apr 6 7.-7.2 Sysems of differenial equaions (7.), and he vecor Calculus we need
BU Macro BU Macro Fall 2008, Lecture 4
 Dynamic Programming BU Macro 2008 Lecure 4 1 Ouline 1. Cerainy opimizaion problem used o illusrae: a. Resricions on exogenous variables b. Value funcion c. Policy funcion d. The Bellman equaion and an
Dynamic Programming BU Macro 2008 Lecure 4 1 Ouline 1. Cerainy opimizaion problem used o illusrae: a. Resricions on exogenous variables b. Value funcion c. Policy funcion d. The Bellman equaion and an
KEY. Math 334 Midterm I Fall 2008 sections 001 and 003 Instructor: Scott Glasgow
 1 KEY Mah 4 Miderm I Fall 8 secions 1 and Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his eam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on our own paper, preferabl engineering
1 KEY Mah 4 Miderm I Fall 8 secions 1 and Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his eam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on our own paper, preferabl engineering
T L. t=1. Proof of Lemma 1. Using the marginal cost accounting in Equation(4) and standard arguments. t )+Π RB. t )+K 1(Q RB
 Elecronic Companion EC.1. Proofs of Technical Lemmas and Theorems LEMMA 1. Le C(RB) be he oal cos incurred by he RB policy. Then we have, T L E[C(RB)] 3 E[Z RB ]. (EC.1) Proof of Lemma 1. Using he marginal
Elecronic Companion EC.1. Proofs of Technical Lemmas and Theorems LEMMA 1. Le C(RB) be he oal cos incurred by he RB policy. Then we have, T L E[C(RB)] 3 E[Z RB ]. (EC.1) Proof of Lemma 1. Using he marginal
