Stability Analysis of Network Controlled Temperature Control System with Additive Delays
|
|
|
- Verity Della French
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Copyrigh ech Science Press CMES, vol.4, no., pp.-4, Sabiliy Analysis of Nework Conrolled emperaure Conrol Sysem wih Addiive Delays V. Venkaachalam, * and D. Prabhakaran Absrac: his paper presens, using Lyapunov-Krasovskii funcional echnique combined wih reciprocal convex lemma is considered for a neworked conrol emperaure conrol sysem wih addiive ime-varying-delays. In he sabiliy analysis, a new LK funcional is assumed, and ake he ime-derivaive of he (LK) funcional, using reciprocal convex combinaion echnique was employed o obain less conservaive sabiliy crieria. Finally, he proposed sabiliy analysis culminaes ino a sabiliy crierion in he LMI (linear marix inequaliies) framework. he resuls obained are in accordance wih he heoreically obained in he emperaure conrol sysem and hey are closer o he sandard benchmark emperaure-conrol sysem. Keywords: Delay-dependen sabiliy, ime-varying addiive delays, emperaure conrol, hea exchanger, lyapunov-krasovskii funcional, linear marix inequaliy, reciprocal convex lemma. Inroducion In his paper, sabiliy of nework conrolled hea exchanger sysem, also known as emperaure conrol sysem ha mainains oupu emperaure of a fluid wihin specified limis is analyzed. When hea exchanger is employed for ransfer of hea beween one or more fluids, closed loop conrol is very essenial and sabiliy of he closed loop sysem is significan. he fluids in a ypical hea exchanger sysem may be separaed by a solid wall o preven mixing or hey may be in direc conac also [Kakac and Liu (); Saunders (9)]. he hea exchangers are widely used in space heaing, refrigeraion, air condiioning, power generaions, chemical indusries, perochemical and peroleum indusries, Oil-indusries, gas-indusries and sewage reamen [Kakac and Liu (); Saunders (9); Sephanopoulas ()]. If he hea exchanger sysem is conrolled hrough a maser conrol cener locaed a remoe, hen he feedback loop of he closedloop conrol scheme will be compleed hrough communicaion neworks. Such a ypical nework conrolled emperaure conrol scheme will consis of hea exchanger, sensor, valve, and a regulaor (embedding PI conrol logic) placed a he remoe conrol cener [Sharma, Gupa and Kumar ()]. he emperaure conrol scheme will be pressed ino service in he even of any unexpeced deviaion in he emperaure conrol sysem oupu variable like sudden excessive wihdrawal of seam by oupu loads. Under such Deparmen of Chemical Engineering, Coimbaore Insiue of echnology, Coimbaore-6, India. * Corresponding auhor: V. Venkaachalam. vikranh64@gmail.com. CMES. doi:.97/cmes..4.
2 Copyrigh ech Science Press CMES, vol.4, no., pp.-4, perurbed operaing condiion, he emperaure sensor sense he oupu emperaure. his signal is feedback o he conroller uni hrough a communicaion nework (as digially processed daa packes). In he conroller, he error beween he reference signal and acual signal (delayed by communicaion nework) is compued and processed by proporional-inegral (PI) conrol scheme. he PI conroller subsequenly offers a suiable inpu signal hrough he communicaion nework o he final conrol elemen (he valve) hereby bringing he perurbed hea exchanger erminal emperaure back o he equilibrium condiion. he hear of he hea exchanger conrol scheme, he PI conroller, is designed apriori assuming zero nework delays. However, he use of communicaion nework for daa (signal) ransfer in he closed-loop sysem inroduces ime-delays in he feedback pah. his, in urn, will enable one o achieve opimal performance from he ime-delayed sysem [Baisha and Joa (4)]. Delay dependen sabiliy crieria are employed o compue he sable margin for he nework delays wihin which he emperaure conrol sysem remains asympoically sable. o he bes of auhor s knowledge, he delay-dependen sabiliy of hea exchanger [Yeroglu (5)]. hese wo feedback-loop delays, popularly referred o as nework induced delays, are pracically unavoidable in a disribued conrol sysem scenario where he plan and conroller are conneced hrough a communicaion channel in which he daa (conrol or/and measured) experience buffering, processing and propagaion a various inernodes; refer Zhao e al. [Zhao, Liu and Rees ()]. As a resul, he nework-inroduced wo addiive delays are ime-varying in naure and have dissimilar characerisics [Lam, Goa and Wang (7)]. In general case, hese nework induced delays are ineviably pose serious limiaions o achievable performance of he closed loop sysem, and in some cases, may even lead o desabilizaion of he emperaure conrol sysem. Hence, sable delay margin (i.e. maximum delay bound which he neworked conrolled sysem can accommodae wihou losing asympoic sabiliy) for such emperaure conrol sysem mus be compued for various subses of conroller parameers (proporional gain K p and inegral gain K I ) hrough delay-dependen sabiliy analysis procedure so ha hey serve as a pracical guide-line for fine uning of conroller parameers a he implemenaion sage. Sysem under neworked conrol environmen has no been repored in lieraure so far. In his paper, a generalized crierion (sufficien condiion) is presened for asceraining delay dependen sabiliy of emperaure conrol sysems wih ime-varying addiive feedback loop delays. In he proposed approach, he mahemaical model of he PI conrolled emperaure conrol sysem wih ime-varying feedback loop delays is firs developed as a linear rearded delay-differenial coninuous-ime equaion. his sae-space model is a generalized modelling framework for dynamical sysems wih ime-delays. Subsequenly, based on Lyapunov-Krasovskii funcional approach combined wih Reciprocal convex combinaion [Ko and Park ()], a delay-dependen sabiliy crierion is presened in LMI framework o compue he maximum value bound of he ime-delay wihin which he closed-loop hea exchanger (emperaure conrol) sysem remains asympoically sable in he sense of Lyapunov. he paper concludes wih he presenaion of simulaion resuls of subsaniae he analyical resuls on delay-dependen sabiliy. he proposed sabiliy crierion is expressed as a se of solvable linear marix inequaliies (LMIs) ha
3 Sabiliy Analysis of Nework Conrolled emperaure Conrol Sysem can be solved using sandard numerical packages [Gahine, Nemirovskii, Laub e al. (995)] by casing i as a convex opimizaion problem. hese adequae condiions generally indicaed as sabiliy crieria are expressed as a se of solvable LMI condiions [Xu and Lam ()]. he less conservaism of new delaydependen sabiliy crieria mainly depends on he selecion of he LK funcional used in he analysis, and many useful resuls have been repored in lieraure in recen imes [Lam, Goa and Wang (7); Xu and Lam (); Gao, Chng and Lam (); Wu, Liao, Feng e al. (9); Ramakrishnan and Ray (9, b); Dey, Ray, Ghosh e al. (); Shao and Han (); Shao, Zhu, Zhang e al. (); Li and ian (); Ko, Lee and Park (); Jiao (); Chaibi, isser and Hmamed (); Hamed, Chaabane and Kacem ()]. However, many useful resuls exising in he lieraure, o he bes of our knowledge, here are no resuls available for he delay-dependen sabiliy of emperaure conrol sysem wih addiive ime-varying delays. emperaure conrol model wih addiive ime-varying delays he linear model of emperaure conrol sysem is used o analyze he sysem dynamics and o design a conroller [Sharma, Gupa and Kumar ()]. Fig. shows he block diagram of a emperaure conrol wih including nework-induced ime-delays. Now ha each componen of he sysem namely hea exchanger, sensor, valve, he conroller is modeled by a firs-order ransfer funcion [Sharma, Gupa and Kumar ()]. hey repeaed here for convenience: G V (s) = K V ; G V s+ H(s) = K H ; G H s+ F(s) = K F ; () F s+ where K V, K H and K F are he gains of a valve, hea exchanger and sensor respecively, and V, H and F are he corresponding ime consans. he ransfer funcion of he PI conroller is given below: G C (s) = K P + K I () s where K P and K I are he PI conroller gains respecively; he proporional erm conrols he rae of emperaure rise afer iniial ransiens. he inegral conroller gain adds a pole a he origin and increases he sysem ype by one and hence reduces he seady-sae error [Ramakrishnan and Ray (6)]. he combined effec of he PI conroller gains will srucure he response of he emperaure conrol sysem wih reduced overshoo and faser seling ime.
4 4 Copyrigh ech Science Press CMES, vol.4, no., pp.-4, ref (s) e (s) Conroller PI Conroller Law Conroller o Acuaor delay k k I ( ) p e s s Valve KV GV ( s) s V Hea Exchanger V (s) K H GH ( s) H (s) s H Sensor o Conroller delay s ( ) e (s) S Sensor K F GF ( s) s F Figure : Block diagram of closed loop emperaure conrol sysem wih addiive imevarying delays In he Fig. τ () porrays sensor o conroller delay (measuring delay) and τ () porrays conroller o acuaor delay (processing delay). Sysem descripion and problem saemen he general sae-space model of he addiive sae-delayed sysem is given by: x () = Ax() + A d x( τ () τ ()) x() = (), [ (τ + τ, )]. () where x() R n is he sae vecor, A R n n are sysem marices, () is he iniial condiion of he sysem for, [ (τ + τ, )]. Consider he sysem () wih he following sysem marices are: K P KV K I KV V V V K H H H A ; Ad K F F F he ime-varying addiive delays τ () and τ () are saisfying he following condiions: τ () τ, τ () τ, (4) τ () μ, τ () μ, (5) where τ and τ are he upper bound of he ime-varying addiive delays τ () and τ (); μ and μ are he derivaives of he delay respecively. o develop a robus sabiliy
5 Sabiliy Analysis of Nework Conrolled emperaure Conrol Sysem 5 crierion in LMI framework o ge o know he delay-dependen sabiliy of he sysem () subjec o he condiion saisfying (4) and (5) using LK funcional approach and reciprocal convex combinaion lemma [Ko and Park ()]. For driving he new sabiliy crierion, following lemmas are of he umos imporance. Lemma [Zhu and Yang ()]: For any posiive symmeric consan marix N R n n, scalars η and η saisfying η < η, a vecor valued funcion ω: [η, η ] R n such ha he inegraion concerned are well defined, hen following inequaliy holds: η ( ω(s)ds) η N η ( η ω(s)ds) η η ω (s)n ω(s)ds η (6) where η = η η Lemma : For a coninuous funcion f(x) and is derivaive f (x) are defined on [a, b], hen b f (x)dx = f(b) f(a). a (7) Lemma [Ko and Park ()]: For any vecors ε, ε, marices P >, Q and real numbers α >, α > wih α + α = saisfying P Q [ Q ], P () he following inequaliy condiion holds: ε α Pε ε α Pε [ ε ε ] [ P Q Q P ] [ε ε ] (9) Proof: he condiion () implies ha α ε α α ε P Q [ α Q P ] α, () ε [ α α ε ] [ α ] which gives α ε α Pε + α ε α Pε ε Qε + ε Qε () By using he relaionship α + α = on () and by rearranging he erms, we deduce he inequaliy condiion (9). 4 Main resuls In his secion, he new sabiliy crierion for he emperaure conrol sysem wih addiive ime-varying delay is presened in he following heorem. heorem: Given non-negaive scalars τ, τ, μ, μ he sysem () saisfying he condiions (4) and (5) is asympoically sable, if here exiss real, posiive, symmeric marices Z, R, Q i, i =,, ; free marices S, S, S of appropriae dimensions such ha following LMI condiions hold:
6 6 Copyrigh ech Science Press CMES, vol.4, no., pp.-4, Z S S [ Z S ] () Z Z >, Q >, Q >, Q >, R > ; () Ξ <, (4) where Ξ = e Pe 5 + e 5 Pe + e (Q + Q + Q )e + e ( Q ( μ ))e + e ( Q ( (e e ) μ))e + e 4 ( Q )e 4 + e 5 Ue 5 [(e e ) ] (e e 4 ) wih e e e e e 4 5 I Ae U Z I where τ = τ + τ and μ = μ + μ. Z S S [ Z S ] (5) Z Proof: consider he LK funcional V() = i= V i () wih V () = x ()Px(), (6) V () = I A I d e,, τ () τ +θ, x (s)q x(s) ds + τ() x (s)q x(s) ds + τ x (s)q x(s) ds, (7) V () = τ x (s)zx (s) dsdθ, () where P, Q i, i =,,, and Z are real symmeric posiive definie marices, and τ() = (τ () + τ ()). Define ( ) x ( ) x ( ) x ( ) x. he ime-derivaive of he funcional V i (), i =,,, is compued along he rajecory of () as follows: he ime-derivaive of V () is given by V () = x ()Px() + x ()Px (),, V () = η ()(e Pe 5 + e 5 Pe )η() (9) he ime-derivaive of V () is given by V () = x ()(Q + Q + Q )x() ( τ ())x ( τ ())Q x( τ ()) ( τ ())x ( τ())q x( τ()) x ( τ )Q x( τ ) () Since in NCSs, τ () μ < and τ () μ <, using Eq. () can be expressed as an inequaliy as follows:
7 Sabiliy Analysis of Nework Conrolled emperaure Conrol Sysem 7 V () x ()(Q + Q + Q )x() ( μ )x ( τ ())Q x( τ ()) ( μ)x ( τ())q x( τ()) x ( τ )Q x( τ ). () In oher words, Eq. () can be revealed in erms of η() as follows: V () η ()(e (Q + Q + Q )e + e ( ( μ )Q )e + e ( ( μ)q )e + e 4 ( Q )e 4 )η() () he ime-derivaive V () is given by V () = x ()τ Zx () τ τ x (s)zx (s)ds. () he Eq. () can be rewrien by expanding he inegral par as follows: V () = η ()(e 5 Ue 5 )η() τ τ τ () x (s)zx (s)ds τ() τ x (s)zx (s)ds τ Which, for applying Lemma, is rewrien on Eq. (4), we ge V () η ()(e 5 Ue 5 )η() τ τ (τ() τ ()) [(τ() τ ()) τ (τ τ()) τ () τ() [(τ τ()) x τ() τ x (s)zx (s)ds] τ () τ() x (s)zx (s)ds (s)zx (s)ds] [(τ τ () ()) x (s)zx (s)ds]. (5) τ () Now, by applying Lemma on Eq. (5), we ge V () η ()(e 5 Ue 5 )η() δ ( δ ( δ ( τ () τ() τ () τ() τ where δ = (τ τ()), δ τ = (τ() τ ()), δ τ = (τ ()) τ Now, we can express Eq. (6) as follows: τ() τ x (s)ds) Z ( x (s)ds) τ () τ() x (s)ds) Z ( x (s)ds) τ () (4) x (s)ds) Z ( x (s)ds) (6) V () η ()(e 5 Ue 5 )η() δ η ()(e e 4 ) Z(e e 4 )η() δ η ()(e e ) Z(e e )η() δ η ()(e e ) Z(e e )η() (7) Since δ + δ + δ =,, he reciprocal convex combinaion echnique of Eq. (7) is deal using Lemma as follows: (e e ) V () η ()(e 5 Ue 5 )η() [(e e ) ] (e e 4 ) Z S S [ Z S Z (e e ) ] [(e e ) ] () (e e 4 ) Provided Z S S [ Z S ] (9) Z holds wih S, S and S being free marices of any dimensions.
8 Copyrigh ech Science Press CMES, vol.4, no., pp.-4, By adding V (), V (), and V () are expressions from (9), () and () respecively, we obain he following quadraic bounding relaion. V () η ()Ξη() () If he condiion Ξ < and relaion (9) holds simulaneously, which he addiive imedelay sysem () wih saisfying he condiion (4) and (5) is asympoically sable. 5 Resuls and discussions In his discussion, he effeciveness of he sabiliy crierion is presened for emperaure conrol sysem wih addiive ime-varying delays is illusraed. he maximum allowable delay margin for addiive ime-varying delays τ and τ for sabiliy for a pick range of PI conroller gains is compued. he gains and ime consans of he emperaure conrol used in he analysis are as follows [Ko and Park ()]. able : Parameer values of emperaure conrol sysem Sysem Gain ime-consan Hea exchanger K H = 4 H = Valve K V =.5 V = Sensor K F =. F = For he aforesaid sysem parameers wih delay free condiion, he conroller capabiliy curve can be obained easily; i is illusraed in Fig.. From he Fig., i is clear ha for all values of K P and K I lying below he conroller capabiliy curve, he closed-loop sysem is asympoically sable. From he curve we choose K P = and K I =.5s, hen he closed loop sysem converges asympoically o equilibrium poin as illusraed in Fig. for a uni sep perurbaion in emperaure conrol sysem oupu variable (from is equilibrium value). Figure : Maximum value of K I for differen values of K P
9 Sabiliy Analysis of Nework Conrolled emperaure Conrol Sysem 9 Figure : Evoluion of θ H () less han zero delay condiion when he nework delay τ is made zero, he sysem Eq. () becomes x () = (A + A d )x() () Now, i is observed ha he Eigenvalues of he sysem sae marix and inpu marix (A + A d ) depend on he conroller parameers K P and K I. ab. given he maximum values of K I (s ) for a fixed value of K P for which he emperaure conrol sysem is on he verge of insabiliy i.e. having one complex conjugae pair of eigenvalues on he jω axis. I is observed from he Fig. ha here is a endency for he curve o decrease gradually wih he increase of K I. able : Maximum inegral conroller gain for a given K P (s ) Eigen values of (A + A d ) ±.9j; -.4; ±.67j; -.5; ±.j; -.645; ±.67j; -.65; ±.5j; -.7; ±.9j; -.76; ±.7j; ; ±.9j; -.6; ±.45j; -.56; -.6 Now, when his PI conroller operaes aop a neworked environmen, he emperaure conrol sysem will be subjeced o addiive nework induced ime-varying delays τ () and τ (). Le he ime-derivaive of he addiive ime-varying delays be bounded as τ () =. and τ () =.. Le choose he conroller parameer K P = and K I =.5s, in he presence of nework induced delays, according o he sabiliy crierion are presened in heorem, he emperaure conrol sysem is sable up o τ = second τ =.5 seconds, and if nework induced delays is increased far beyond his value, he sysem oupu becomes unbounded evoluion. Hence, his analysis clearly brings o he impac of he nework induced delays on sabiliy and performance of he sysem. Le μ =., and μ =.. for differen values of K P and K I, from he capabiliy curve, he
10 Copyrigh ech Science Press CMES, vol.4, no., pp.-4, maximum allowable delay bound τ for a given τ is given in abs. -7. Likewise, abs. - give he maximum allowable delay bound τ for a given τ. From he ables, i is clear ha as he various values of K P and K I, he maximum delay bound ha sysem can accommodae wihou losing sabiliy decreases. he corresponding sabiliy margin presened in Fig. 4 clearly indicaes lessening. able : Maximum allowable delay bound τ for a given τ able 4: Maximum allowable delay bound τ for a given τ able 5: Maximum allowable delay bound τ for a given τ able 6: Maximum allowable delay bound τ for a given τ able 7: Maximum allowable delay bound τ for a given τ able : Maximum allowable delay bound τ for a given τ
11 Sabiliy Analysis of Nework Conrolled emperaure Conrol Sysem able 9: Maximum allowable delay bound τ for a given τ able : Maximum allowable delay bound τ for a given τ - K P K I able : Maximum allowable delay bound τ for a given τ able : Maximum allowable delay bound τ for a given τ -5 K P K I Figure 4: Sabiliy margin for emperaure conrol of hea exchanger Simulaion sudy of he closed-loop emperaure conrol sysem was carried ou for zero nework delay is confined o he sable region shown in Fig. ; i is easy o infer he influence of nework delays on he sabiliy of he sysem. As nework delays increase, he response of he emperaure conrol sysem ges malformed and for higher delays, he closed-loop sysem becomes unsable.
12 Copyrigh ech Science Press CMES, vol.4, no., pp.-4, 6 Conclusion In his research, he problem of delay-dependen sabiliy of emperaure conrol sysems wih addiive ime-varying delay has been addressed using Lyapunov-Krasovskii funcional echnique. In he sabiliy analysis, he emperaure conrol sysem is mahemaically modeled in erms of sae space model, and reciprocal convex combinaion echnique is employed in he sabiliy analysis o make i less number of decision variables. he proposed resuls are validaed benchmark emperaure conrol sysem wih ime-varying addiive delays. he deduced resuls of his paper impar more realisic operaing condiion in a real-ime emperaure conrol sysem. Acknowledgemen: One of he auhors (Dr. D. Prabhakaran) is graeful o All India Council for echnical Educaion (AICE), New Delhi, India for financial suppor (File No. /AICE/RFD/RPS (Policy-II) /-6). he auhors would like o express heir sincere hanks o Dr. S. R. K. Prasad (Corresponden, CI), Dr. R. Prabhakar (Secreary, CI), Dr. V. Selladurai (Principal, CI), Dr. M. hirumarimugan (Head of he Deparmen of Chemical Engineering, CI) for heir useful discussions and encouragemen during he course of work. Also, we like o acknowledgmen Dr.. Venkaachalam (Associae Professor of Physics, Coimbaore Insiue of echnology, Coimbaore, India) for heir valuable help in sudying dynamical sysem wih ime delays. References Baisha, A. P.; Joa, F. G. (4): Effecs of ime delay saisical parameers on he mos likely regions of sabiliy in an NCS. Conrol Engineering and Applied Informaics, vol. 6, pp. -. Chaibi, N.; isser, E. H.; Hmamed, A. (): Delay-dependen robus sabiliy of singular sysems wih addiive ime-varying delays. Inernaional Journal of Auomaion and Compuing, vol., no., pp Dey, R.; Ray, G.; Ghosh, S.; Rakshi, A. (): Sabiliy analysis for coninuous sysem wih addiive ime-varying delays: a less conservaive resul. Applied Mahemaics and Compuaion, vol. 5, no., pp Gahine, P.; Nemirovskii, A.; Laub, A. J.; Chilali, M. (995): Conrol oolbox for use wih Malab. Mahworks, Naick. Gao, H.; Chng,.; Lam, J. (): A new delay sysem approach o nework-based conrol. Auomaica, vol., no., pp Hamed, B. B.; Chaabane, M.; Kacem, W. (): Absolue sabiliy of nonlinear sysems wih wo addiive ime-varying delay componens. Inernaional Journal of Auomaion and Compuing, vol., no., pp Jiao, J. M. (): A sabiliy crierion for singular sysems wih wo addiive imevarying delay componens. Inernaional Journal of Auomaica, vol., no., pp Kakac, S.; Liu, H. (): Hea exchangers: selecion, raing and hermal design (nd ediion). CRC Press.
13 Sabiliy Analysis of Nework Conrolled emperaure Conrol Sysem Ko, J. W.; Lee, W. I.; Park, P. G. (): Delayed sysem approach o he sabiliy of neworked conrol sysems. Inernaional Muli conference of Engineers and Compuer Scieniss, vol., pp. 6-. Ko, J. W.; Park, P. G. (): Reciprocally convex approach for he sabiliy of neworked conrol sysems. Inelligen Conrol and Innovaive Compuing, vol., pp. -9. Lam, J.; Goa, H.; Wang, C. (7): Sabiliy analysis for coninuous sysems wih wo addiive ime-varying delay componens. Sysem and Conrol Leers, vol. 56, no., pp Li,.; ian, J. (): Convex polyhedron mehod o sabiliy of coninuous sysems wih wo addiive ime-varying delay componens. Journal of Applied Mahemaics. Ramakrishnan, K.; Ray, G. (9): Delay-dependen sabiliy analysis of linear sysems wih addiive ime-varying delays. 5h Annual IEEE Conference on Auomaion Science and Engineering, Bangalore, India, pp. -6. Ramakrishnan, K.; Ray, G. (b): Sabiliy crieria wih less LMI variables for linear sysem wih addiive ime-delays. Journal of Applied Mahemaics and Compuing, vol. 6, no. -, pp Ramakrishnan, K.; Ray, G. (6): Sabiliy crierion for neworked conrol sysems wih addiive ime-varying sae-delays and bounded nonlineariy. Inernaional Journal of Sysems, Conrol and Communicaions, vol. 7, no., pp. 6-. Saunders, E. A. (9): Hea exchanges: selecion, design and consrucion. Longman Scienific and echnical, New York. Shao, H.; Han, Q. L. (): On sabilizaion for sysems wih wo addiive ime-varying inpu delays arising from neworked conrol sysems. Journal of he Franklin Insiue, vol. 49, no. 6, pp Shao, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhong, G. (): Delay-dependen H conrol for sysems wih wo addiive ime-vary delays. Journal of Conrol Engineering and echnology, vol., no., pp Sharma, C.; Gupa, S.; Kumar, V. (): Modeling and simulaion of hea exchanger used in soda recovery. Proceedings of he World Congress on Engineering, vol.. Sephanopoulas, G. (): Chemical process conrol. Prenice-Hall of India Privae Limied, pp. 9-. Wu, H.; Liao, X.; Feng, W.; Guo, S.; Zhang, W. (9): Robus sabiliy analysis of uncerain sysems wih wo addiive ime-varying delay componens. Applied Mahemaical Modelling, vol., no., pp Xu, S.; Lam, J. (): A survey of linear marix inequaliy echniques in sabiliy analysis of delay sysems. Inernaional Journal of Sysems Science, vol. 9, no., pp Yeroglu, C. (5): Robus sabilizing PID conrollers for muliple ime delay sysems wih parameric uncerainy. Conrol Engineering and Applied Informaics, vol. 7, pp. -9. Zhao, Y.; Liu, G.; Rees, D. (): Packe-based dead-band conrol for inerne-based neworked conrol sysem. IEEE ransacions on Conrol Sysems echnology, vol., no. 5, pp
14 4 Copyrigh ech Science Press CMES, vol.4, no., pp.-4, Zhu, X. L.; Yang, G. H. (): Jensen inegral inequaliy approach o sabiliy analysis of coninuous-ime sysems wih ime-varying delay. IE Conrol heory and Applicaions, vol., no. 6, pp
Mean-square Stability Control for Networked Systems with Stochastic Time Delay
 JOURNAL OF SIMULAION VOL. 5 NO. May 7 Mean-square Sabiliy Conrol for Newored Sysems wih Sochasic ime Delay YAO Hejun YUAN Fushun School of Mahemaics and Saisics Anyang Normal Universiy Anyang Henan. 455
JOURNAL OF SIMULAION VOL. 5 NO. May 7 Mean-square Sabiliy Conrol for Newored Sysems wih Sochasic ime Delay YAO Hejun YUAN Fushun School of Mahemaics and Saisics Anyang Normal Universiy Anyang Henan. 455
A DELAY-DEPENDENT STABILITY CRITERIA FOR T-S FUZZY SYSTEM WITH TIME-DELAYS
 A DELAY-DEPENDENT STABILITY CRITERIA FOR T-S FUZZY SYSTEM WITH TIME-DELAYS Xinping Guan ;1 Fenglei Li Cailian Chen Insiue of Elecrical Engineering, Yanshan Universiy, Qinhuangdao, 066004, China. Deparmen
A DELAY-DEPENDENT STABILITY CRITERIA FOR T-S FUZZY SYSTEM WITH TIME-DELAYS Xinping Guan ;1 Fenglei Li Cailian Chen Insiue of Elecrical Engineering, Yanshan Universiy, Qinhuangdao, 066004, China. Deparmen
Sliding Mode Controller for Unstable Systems
 S. SIVARAMAKRISHNAN e al., Sliding Mode Conroller for Unsable Sysems, Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 22 (1) 41 47 (28) 41 Sliding Mode Conroller for Unsable Sysems S. Sivaramakrishnan, A. K. Tangirala, and M.
S. SIVARAMAKRISHNAN e al., Sliding Mode Conroller for Unsable Sysems, Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 22 (1) 41 47 (28) 41 Sliding Mode Conroller for Unsable Sysems S. Sivaramakrishnan, A. K. Tangirala, and M.
CHAPTER 10 VALIDATION OF TEST WITH ARTIFICAL NEURAL NETWORK
 175 CHAPTER 10 VALIDATION OF TEST WITH ARTIFICAL NEURAL NETWORK 10.1 INTRODUCTION Amongs he research work performed, he bes resuls of experimenal work are validaed wih Arificial Neural Nework. From he
175 CHAPTER 10 VALIDATION OF TEST WITH ARTIFICAL NEURAL NETWORK 10.1 INTRODUCTION Amongs he research work performed, he bes resuls of experimenal work are validaed wih Arificial Neural Nework. From he
d 1 = c 1 b 2 - b 1 c 2 d 2 = c 1 b 3 - b 1 c 3
 and d = c b - b c c d = c b - b c c This process is coninued unil he nh row has been compleed. The complee array of coefficiens is riangular. Noe ha in developing he array an enire row may be divided or
and d = c b - b c c d = c b - b c c This process is coninued unil he nh row has been compleed. The complee array of coefficiens is riangular. Noe ha in developing he array an enire row may be divided or
Stability and Bifurcation in a Neural Network Model with Two Delays
 Inernaional Mahemaical Forum, Vol. 6, 11, no. 35, 175-1731 Sabiliy and Bifurcaion in a Neural Nework Model wih Two Delays GuangPing Hu and XiaoLing Li School of Mahemaics and Physics, Nanjing Universiy
Inernaional Mahemaical Forum, Vol. 6, 11, no. 35, 175-1731 Sabiliy and Bifurcaion in a Neural Nework Model wih Two Delays GuangPing Hu and XiaoLing Li School of Mahemaics and Physics, Nanjing Universiy
On Robust Stability of Uncertain Neutral Systems with Discrete and Distributed Delays
 009 American Conrol Conference Hya Regency Riverfron S. Louis MO USA June 0-009 FrC09.5 On Robus Sabiliy of Uncerain Neural Sysems wih Discree and Disribued Delays Jian Sun Jie Chen G.P. Liu Senior Member
009 American Conrol Conference Hya Regency Riverfron S. Louis MO USA June 0-009 FrC09.5 On Robus Sabiliy of Uncerain Neural Sysems wih Discree and Disribued Delays Jian Sun Jie Chen G.P. Liu Senior Member
LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION
 CHBE320 LECTURE V LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dep. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 5-1 Road Map of he Lecure V Laplace Transform and Transfer funcions
CHBE320 LECTURE V LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dep. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 5-1 Road Map of he Lecure V Laplace Transform and Transfer funcions
Optimal Control of Dc Motor Using Performance Index of Energy
 American Journal of Engineering esearch AJE 06 American Journal of Engineering esearch AJE e-issn: 30-0847 p-issn : 30-0936 Volume-5, Issue-, pp-57-6 www.ajer.org esearch Paper Open Access Opimal Conrol
American Journal of Engineering esearch AJE 06 American Journal of Engineering esearch AJE e-issn: 30-0847 p-issn : 30-0936 Volume-5, Issue-, pp-57-6 www.ajer.org esearch Paper Open Access Opimal Conrol
STATE-SPACE MODELLING. A mass balance across the tank gives:
 B. Lennox and N.F. Thornhill, 9, Sae Space Modelling, IChemE Process Managemen and Conrol Subjec Group Newsleer STE-SPACE MODELLING Inroducion: Over he pas decade or so here has been an ever increasing
B. Lennox and N.F. Thornhill, 9, Sae Space Modelling, IChemE Process Managemen and Conrol Subjec Group Newsleer STE-SPACE MODELLING Inroducion: Over he pas decade or so here has been an ever increasing
Pade and Laguerre Approximations Applied. to the Active Queue Management Model. of Internet Protocol
 Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 7, 013, no. 16, 663-673 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikari.com hp://dx.doi.org/10.1988/ams.013.39499 Pade and Laguerre Approximaions Applied o he Acive Queue Managemen Model of Inerne
Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 7, 013, no. 16, 663-673 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikari.com hp://dx.doi.org/10.1988/ams.013.39499 Pade and Laguerre Approximaions Applied o he Acive Queue Managemen Model of Inerne
A DELAY-DEPENDENT APPROACH TO ROBUST STABILITY FOR UNCERTAIN STOCHASTIC NEURAL NETWORKS WITH TIME-VARYING DELAY
 Journal of Marine Science and echnology Vol. 8 No. pp. 77-83 (00) 77 A DELAY-DEPENDEN APPROACH O ROBUS SABILIY FOR UNCERAIN SOCHASIC NEURAL NEWORKS WIH IME-VARYING DELAY Chien-Yu Lu* Chin-Wen Liao* Koan-Yuh
Journal of Marine Science and echnology Vol. 8 No. pp. 77-83 (00) 77 A DELAY-DEPENDEN APPROACH O ROBUS SABILIY FOR UNCERAIN SOCHASIC NEURAL NEWORKS WIH IME-VARYING DELAY Chien-Yu Lu* Chin-Wen Liao* Koan-Yuh
Bifurcation Analysis of a Stage-Structured Prey-Predator System with Discrete and Continuous Delays
 Applied Mahemaics 4 59-64 hp://dx.doi.org/.46/am..4744 Published Online July (hp://www.scirp.org/ournal/am) Bifurcaion Analysis of a Sage-Srucured Prey-Predaor Sysem wih Discree and Coninuous Delays Shunyi
Applied Mahemaics 4 59-64 hp://dx.doi.org/.46/am..4744 Published Online July (hp://www.scirp.org/ournal/am) Bifurcaion Analysis of a Sage-Srucured Prey-Predaor Sysem wih Discree and Coninuous Delays Shunyi
Physics 235 Chapter 2. Chapter 2 Newtonian Mechanics Single Particle
 Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
( ) ( ) if t = t. It must satisfy the identity. So, bulkiness of the unit impulse (hyper)function is equal to 1. The defining characteristic is
 UNIT IMPULSE RESPONSE, UNIT STEP RESPONSE, STABILITY. Uni impulse funcion (Dirac dela funcion, dela funcion) rigorously defined is no sricly a funcion, bu disribuion (or measure), precise reamen requires
UNIT IMPULSE RESPONSE, UNIT STEP RESPONSE, STABILITY. Uni impulse funcion (Dirac dela funcion, dela funcion) rigorously defined is no sricly a funcion, bu disribuion (or measure), precise reamen requires
arxiv: v1 [math.gm] 4 Nov 2018
![arxiv: v1 [math.gm] 4 Nov 2018 arxiv: v1 [math.gm] 4 Nov 2018](/thumbs/91/104887155.jpg) Unpredicable Soluions of Linear Differenial Equaions Mara Akhme 1,, Mehme Onur Fen 2, Madina Tleubergenova 3,4, Akylbek Zhamanshin 3,4 1 Deparmen of Mahemaics, Middle Eas Technical Universiy, 06800, Ankara,
Unpredicable Soluions of Linear Differenial Equaions Mara Akhme 1,, Mehme Onur Fen 2, Madina Tleubergenova 3,4, Akylbek Zhamanshin 3,4 1 Deparmen of Mahemaics, Middle Eas Technical Universiy, 06800, Ankara,
The motions of the celt on a horizontal plane with viscous friction
 The h Join Inernaional Conference on Mulibody Sysem Dynamics June 8, 18, Lisboa, Porugal The moions of he cel on a horizonal plane wih viscous fricion Maria A. Munisyna 1 1 Moscow Insiue of Physics and
The h Join Inernaional Conference on Mulibody Sysem Dynamics June 8, 18, Lisboa, Porugal The moions of he cel on a horizonal plane wih viscous fricion Maria A. Munisyna 1 1 Moscow Insiue of Physics and
Lecture 20: Riccati Equations and Least Squares Feedback Control
 34-5 LINEAR SYSTEMS Lecure : Riccai Equaions and Leas Squares Feedback Conrol 5.6.4 Sae Feedback via Riccai Equaions A recursive approach in generaing he marix-valued funcion W ( ) equaion for i for he
34-5 LINEAR SYSTEMS Lecure : Riccai Equaions and Leas Squares Feedback Conrol 5.6.4 Sae Feedback via Riccai Equaions A recursive approach in generaing he marix-valued funcion W ( ) equaion for i for he
Novel robust stability criteria of neutral-type bidirectional associative memory neural networks
 www.ijcsi.org 0 Novel robus sabiliy crieria of neural-ype bidirecional associaive memory neural neworks Shu-Lian Zhang and Yu-Li Zhang School of Science Dalian Jiaoong Universiy Dalian 608 P. R. China
www.ijcsi.org 0 Novel robus sabiliy crieria of neural-ype bidirecional associaive memory neural neworks Shu-Lian Zhang and Yu-Li Zhang School of Science Dalian Jiaoong Universiy Dalian 608 P. R. China
SUFFICIENT CONDITIONS FOR EXISTENCE SOLUTION OF LINEAR TWO-POINT BOUNDARY PROBLEM IN MINIMIZATION OF QUADRATIC FUNCTIONAL
 HE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF HE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Series A, OF HE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volume, Number 4/200, pp 287 293 SUFFICIEN CONDIIONS FOR EXISENCE SOLUION OF LINEAR WO-POIN BOUNDARY PROBLEM IN
HE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF HE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Series A, OF HE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volume, Number 4/200, pp 287 293 SUFFICIEN CONDIIONS FOR EXISENCE SOLUION OF LINEAR WO-POIN BOUNDARY PROBLEM IN
Anti-Disturbance Control for Multiple Disturbances
 Workshop a 3 ACC Ani-Disurbance Conrol for Muliple Disurbances Lei Guo (lguo@buaa.edu.cn) Naional Key Laboraory on Science and Technology on Aircraf Conrol, Beihang Universiy, Beijing, 9, P.R. China. Presened
Workshop a 3 ACC Ani-Disurbance Conrol for Muliple Disurbances Lei Guo (lguo@buaa.edu.cn) Naional Key Laboraory on Science and Technology on Aircraf Conrol, Beihang Universiy, Beijing, 9, P.R. China. Presened
Ordinary Differential Equations
 Ordinary Differenial Equaions 5. Examples of linear differenial equaions and heir applicaions We consider some examples of sysems of linear differenial equaions wih consan coefficiens y = a y +... + a
Ordinary Differenial Equaions 5. Examples of linear differenial equaions and heir applicaions We consider some examples of sysems of linear differenial equaions wih consan coefficiens y = a y +... + a
di Bernardo, M. (1995). A purely adaptive controller to synchronize and control chaotic systems.
 di ernardo, M. (995). A purely adapive conroller o synchronize and conrol chaoic sysems. hps://doi.org/.6/375-96(96)8-x Early version, also known as pre-prin Link o published version (if available):.6/375-96(96)8-x
di ernardo, M. (995). A purely adapive conroller o synchronize and conrol chaoic sysems. hps://doi.org/.6/375-96(96)8-x Early version, also known as pre-prin Link o published version (if available):.6/375-96(96)8-x
Chapter 5 Digital PID control algorithm. Hesheng Wang Department of Automation,SJTU 2016,03
 Chaper 5 Digial PID conrol algorihm Hesheng Wang Deparmen of Auomaion,SJTU 216,3 Ouline Absrac Quasi-coninuous PID conrol algorihm Improvemen of sandard PID algorihm Choosing parameer of PID regulaor Brief
Chaper 5 Digial PID conrol algorihm Hesheng Wang Deparmen of Auomaion,SJTU 216,3 Ouline Absrac Quasi-coninuous PID conrol algorihm Improvemen of sandard PID algorihm Choosing parameer of PID regulaor Brief
Research Article Modified Function Projective Synchronization between Different Dimension Fractional-Order Chaotic Systems
 Absrac and Applied Analysis Volume 212, Aricle ID 862989, 12 pages doi:1.1155/212/862989 Research Aricle Modified Funcion Projecive Synchronizaion beween Differen Dimension Fracional-Order Chaoic Sysems
Absrac and Applied Analysis Volume 212, Aricle ID 862989, 12 pages doi:1.1155/212/862989 Research Aricle Modified Funcion Projecive Synchronizaion beween Differen Dimension Fracional-Order Chaoic Sysems
Existence Theory of Second Order Random Differential Equations
 Global Journal of Mahemaical Sciences: Theory and Pracical. ISSN 974-32 Volume 4, Number 3 (22), pp. 33-3 Inernaional Research Publicaion House hp://www.irphouse.com Exisence Theory of Second Order Random
Global Journal of Mahemaical Sciences: Theory and Pracical. ISSN 974-32 Volume 4, Number 3 (22), pp. 33-3 Inernaional Research Publicaion House hp://www.irphouse.com Exisence Theory of Second Order Random
10. State Space Methods
 . Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
. Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
Global Synchronization of Directed Networks with Fast Switching Topologies
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 52 (2009) pp. 1019 1924 c Chinese Physical Sociey and IOP Publishing Ld Vol. 52, No. 6, December 15, 2009 Global Synchronizaion of Direced Neworks wih Fas Swiching
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 52 (2009) pp. 1019 1924 c Chinese Physical Sociey and IOP Publishing Ld Vol. 52, No. 6, December 15, 2009 Global Synchronizaion of Direced Neworks wih Fas Swiching
POSITIVE SOLUTIONS OF NEUTRAL DELAY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION
 Novi Sad J. Mah. Vol. 32, No. 2, 2002, 95-108 95 POSITIVE SOLUTIONS OF NEUTRAL DELAY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION Hajnalka Péics 1, János Karsai 2 Absrac. We consider he scalar nonauonomous neural delay differenial
Novi Sad J. Mah. Vol. 32, No. 2, 2002, 95-108 95 POSITIVE SOLUTIONS OF NEUTRAL DELAY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION Hajnalka Péics 1, János Karsai 2 Absrac. We consider he scalar nonauonomous neural delay differenial
(1) (2) Differentiation of (1) and then substitution of (3) leads to. Therefore, we will simply consider the second-order linear system given by (4)
 Phase Plane Analysis of Linear Sysems Adaped from Applied Nonlinear Conrol by Sloine and Li The general form of a linear second-order sysem is a c b d From and b bc d a Differeniaion of and hen subsiuion
Phase Plane Analysis of Linear Sysems Adaped from Applied Nonlinear Conrol by Sloine and Li The general form of a linear second-order sysem is a c b d From and b bc d a Differeniaion of and hen subsiuion
Sliding Mode Extremum Seeking Control for Linear Quadratic Dynamic Game
 Sliding Mode Exremum Seeking Conrol for Linear Quadraic Dynamic Game Yaodong Pan and Ümi Özgüner ITS Research Group, AIST Tsukuba Eas Namiki --, Tsukuba-shi,Ibaraki-ken 5-856, Japan e-mail: pan.yaodong@ais.go.jp
Sliding Mode Exremum Seeking Conrol for Linear Quadraic Dynamic Game Yaodong Pan and Ümi Özgüner ITS Research Group, AIST Tsukuba Eas Namiki --, Tsukuba-shi,Ibaraki-ken 5-856, Japan e-mail: pan.yaodong@ais.go.jp
Research Article Further Stability Analysis of Time-Delay Systems with Nonlinear Perturbations
 Hindawi Mahemaical Problems in Engineering Volume 7, Aricle ID 594757, pages hps://doi.org/.55/7/594757 Research Aricle Furher Sabiliy Analysis of Time-Delay Sysems wih Nonlinear Perurbaions Jie Sun andjingzhang,3
Hindawi Mahemaical Problems in Engineering Volume 7, Aricle ID 594757, pages hps://doi.org/.55/7/594757 Research Aricle Furher Sabiliy Analysis of Time-Delay Sysems wih Nonlinear Perurbaions Jie Sun andjingzhang,3
Embedded Systems and Software. A Simple Introduction to Embedded Control Systems (PID Control)
 Embedded Sysems and Sofware A Simple Inroducion o Embedded Conrol Sysems (PID Conrol) Embedded Sysems and Sofware, ECE:3360. The Universiy of Iowa, 2016 Slide 1 Acknowledgemens The maerial in his lecure
Embedded Sysems and Sofware A Simple Inroducion o Embedded Conrol Sysems (PID Conrol) Embedded Sysems and Sofware, ECE:3360. The Universiy of Iowa, 2016 Slide 1 Acknowledgemens The maerial in his lecure
Vehicle Arrival Models : Headway
 Chaper 12 Vehicle Arrival Models : Headway 12.1 Inroducion Modelling arrival of vehicle a secion of road is an imporan sep in raffic flow modelling. I has imporan applicaion in raffic flow simulaion where
Chaper 12 Vehicle Arrival Models : Headway 12.1 Inroducion Modelling arrival of vehicle a secion of road is an imporan sep in raffic flow modelling. I has imporan applicaion in raffic flow simulaion where
Variational Iteration Method for Solving System of Fractional Order Ordinary Differential Equations
 IOSR Journal of Mahemaics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 2278-5728, p-issn: 2319-765X. Volume 1, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov - Dec. 214), PP 48-54 Variaional Ieraion Mehod for Solving Sysem of Fracional Order Ordinary Differenial
IOSR Journal of Mahemaics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 2278-5728, p-issn: 2319-765X. Volume 1, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov - Dec. 214), PP 48-54 Variaional Ieraion Mehod for Solving Sysem of Fracional Order Ordinary Differenial
INVERSE RESPONSE COMPENSATION BY ESTIMATING PARAMETERS OF A PROCESS COMPRISING OF TWO FIRST ORDER SYSTEMS
 Inernaional Journal of Informaion Technology and nowledge Managemen July-December 0, Volume 5, No., pp. 433-438 INVERSE RESPONSE COMPENSATION BY ESTIMATING PARAMETERS OF A PROCESS COMPRISING OF TWO FIRST
Inernaional Journal of Informaion Technology and nowledge Managemen July-December 0, Volume 5, No., pp. 433-438 INVERSE RESPONSE COMPENSATION BY ESTIMATING PARAMETERS OF A PROCESS COMPRISING OF TWO FIRST
Sub Module 2.6. Measurement of transient temperature
 Mechanical Measuremens Prof. S.P.Venkaeshan Sub Module 2.6 Measuremen of ransien emperaure Many processes of engineering relevance involve variaions wih respec o ime. The sysem properies like emperaure,
Mechanical Measuremens Prof. S.P.Venkaeshan Sub Module 2.6 Measuremen of ransien emperaure Many processes of engineering relevance involve variaions wih respec o ime. The sysem properies like emperaure,
Dynamic Effects of Feedback Control!
 Dynamic Effecs of Feedback Conrol! Rober Sengel! Roboics and Inelligen Sysems MAE 345, Princeon Universiy, 2017 Inner, Middle, and Ouer Feedback Conrol Loops Sep Response of Linear, Time- Invarian (LTI)
Dynamic Effecs of Feedback Conrol! Rober Sengel! Roboics and Inelligen Sysems MAE 345, Princeon Universiy, 2017 Inner, Middle, and Ouer Feedback Conrol Loops Sep Response of Linear, Time- Invarian (LTI)
Module 4: Time Response of discrete time systems Lecture Note 2
 Module 4: Time Response of discree ime sysems Lecure Noe 2 1 Prooype second order sysem The sudy of a second order sysem is imporan because many higher order sysem can be approimaed by a second order model
Module 4: Time Response of discree ime sysems Lecure Noe 2 1 Prooype second order sysem The sudy of a second order sysem is imporan because many higher order sysem can be approimaed by a second order model
Robust and Learning Control for Complex Systems
 Robus and Learning Conrol for Complex Sysems Peer M. Young Sepember 13, 2007 & Talk Ouline Inroducion Robus Conroller Analysis and Design Theory Experimenal Applicaions Overview MIMO Robus HVAC Conrol
Robus and Learning Conrol for Complex Sysems Peer M. Young Sepember 13, 2007 & Talk Ouline Inroducion Robus Conroller Analysis and Design Theory Experimenal Applicaions Overview MIMO Robus HVAC Conrol
4. Advanced Stability Theory
 Applied Nonlinear Conrol Nguyen an ien - 4 4 Advanced Sabiliy heory he objecive of his chaper is o presen sabiliy analysis for non-auonomous sysems 41 Conceps of Sabiliy for Non-Auonomous Sysems Equilibrium
Applied Nonlinear Conrol Nguyen an ien - 4 4 Advanced Sabiliy heory he objecive of his chaper is o presen sabiliy analysis for non-auonomous sysems 41 Conceps of Sabiliy for Non-Auonomous Sysems Equilibrium
Improved Approximate Solutions for Nonlinear Evolutions Equations in Mathematical Physics Using the Reduced Differential Transform Method
 Journal of Applied Mahemaics & Bioinformaics, vol., no., 01, 1-14 ISSN: 179-660 (prin), 179-699 (online) Scienpress Ld, 01 Improved Approimae Soluions for Nonlinear Evoluions Equaions in Mahemaical Physics
Journal of Applied Mahemaics & Bioinformaics, vol., no., 01, 1-14 ISSN: 179-660 (prin), 179-699 (online) Scienpress Ld, 01 Improved Approimae Soluions for Nonlinear Evoluions Equaions in Mahemaical Physics
Delay and Its Time-Derivative Dependent Stable Criterion for Differential-Algebraic Systems
 Applied Maemaics 6 7 4- Publised Online June 6 in SciRes p://wwwscirporg/journal/am p://dxdoiorg/46/am67 Delay and Is ime-derivaive Dependen Sable Crierion for Differenial-Algebraic Sysems Hui Liu Yucai
Applied Maemaics 6 7 4- Publised Online June 6 in SciRes p://wwwscirporg/journal/am p://dxdoiorg/46/am67 Delay and Is ime-derivaive Dependen Sable Crierion for Differenial-Algebraic Sysems Hui Liu Yucai
Navneet Saini, Mayank Goyal, Vishal Bansal (2013); Term Project AML310; Indian Institute of Technology Delhi
 Creep in Viscoelasic Subsances Numerical mehods o calculae he coefficiens of he Prony equaion using creep es daa and Herediary Inegrals Mehod Navnee Saini, Mayank Goyal, Vishal Bansal (23); Term Projec
Creep in Viscoelasic Subsances Numerical mehods o calculae he coefficiens of he Prony equaion using creep es daa and Herediary Inegrals Mehod Navnee Saini, Mayank Goyal, Vishal Bansal (23); Term Projec
Application of a Stochastic-Fuzzy Approach to Modeling Optimal Discrete Time Dynamical Systems by Using Large Scale Data Processing
 Applicaion of a Sochasic-Fuzzy Approach o Modeling Opimal Discree Time Dynamical Sysems by Using Large Scale Daa Processing AA WALASZE-BABISZEWSA Deparmen of Compuer Engineering Opole Universiy of Technology
Applicaion of a Sochasic-Fuzzy Approach o Modeling Opimal Discree Time Dynamical Sysems by Using Large Scale Daa Processing AA WALASZE-BABISZEWSA Deparmen of Compuer Engineering Opole Universiy of Technology
A NEW TECHNOLOGY FOR SOLVING DIFFUSION AND HEAT EQUATIONS
 THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 7, Vol., No. A, pp. 33-4 33 A NEW TECHNOLOGY FOR SOLVING DIFFUSION AND HEAT EQUATIONS by Xiao-Jun YANG a and Feng GAO a,b * a School of Mechanics and Civil Engineering, China Universiy
THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 7, Vol., No. A, pp. 33-4 33 A NEW TECHNOLOGY FOR SOLVING DIFFUSION AND HEAT EQUATIONS by Xiao-Jun YANG a and Feng GAO a,b * a School of Mechanics and Civil Engineering, China Universiy
Linear Response Theory: The connection between QFT and experiments
 Phys540.nb 39 3 Linear Response Theory: The connecion beween QFT and experimens 3.1. Basic conceps and ideas Q: How do we measure he conduciviy of a meal? A: we firs inroduce a weak elecric field E, and
Phys540.nb 39 3 Linear Response Theory: The connecion beween QFT and experimens 3.1. Basic conceps and ideas Q: How do we measure he conduciviy of a meal? A: we firs inroduce a weak elecric field E, and
Signal and System (Chapter 3. Continuous-Time Systems)
 Signal and Sysem (Chaper 3. Coninuous-Time Sysems) Prof. Kwang-Chun Ho kwangho@hansung.ac.kr Tel: 0-760-453 Fax:0-760-4435 1 Dep. Elecronics and Informaion Eng. 1 Nodes, Branches, Loops A nework wih b
Signal and Sysem (Chaper 3. Coninuous-Time Sysems) Prof. Kwang-Chun Ho kwangho@hansung.ac.kr Tel: 0-760-453 Fax:0-760-4435 1 Dep. Elecronics and Informaion Eng. 1 Nodes, Branches, Loops A nework wih b
Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering
 Srucural Dynamics and Earhquae Engineering Course 1 Inroducion. Single degree of freedom sysems: Equaions of moion, problem saemen, soluion mehods. Course noes are available for download a hp://www.c.up.ro/users/aurelsraan/
Srucural Dynamics and Earhquae Engineering Course 1 Inroducion. Single degree of freedom sysems: Equaions of moion, problem saemen, soluion mehods. Course noes are available for download a hp://www.c.up.ro/users/aurelsraan/
Recursive Least-Squares Fixed-Interval Smoother Using Covariance Information based on Innovation Approach in Linear Continuous Stochastic Systems
 8 Froniers in Signal Processing, Vol. 1, No. 1, July 217 hps://dx.doi.org/1.2266/fsp.217.112 Recursive Leas-Squares Fixed-Inerval Smooher Using Covariance Informaion based on Innovaion Approach in Linear
8 Froniers in Signal Processing, Vol. 1, No. 1, July 217 hps://dx.doi.org/1.2266/fsp.217.112 Recursive Leas-Squares Fixed-Inerval Smooher Using Covariance Informaion based on Innovaion Approach in Linear
Modified Projective Synchronization of Different Hyperchaotic Systems
 ISSN 76-7659, England, UK Journal of Informaion and Compuing Science Vol., No., 009, pp. 033-00 Modified Projecive Synchronizaion of Differen Hyperchaoic Sysems HongLan Zhu, +, XueBing Zhang Huaiyin Insiue
ISSN 76-7659, England, UK Journal of Informaion and Compuing Science Vol., No., 009, pp. 033-00 Modified Projecive Synchronizaion of Differen Hyperchaoic Sysems HongLan Zhu, +, XueBing Zhang Huaiyin Insiue
Modal identification of structures from roving input data by means of maximum likelihood estimation of the state space model
 Modal idenificaion of srucures from roving inpu daa by means of maximum likelihood esimaion of he sae space model J. Cara, J. Juan, E. Alarcón Absrac The usual way o perform a forced vibraion es is o fix
Modal idenificaion of srucures from roving inpu daa by means of maximum likelihood esimaion of he sae space model J. Cara, J. Juan, E. Alarcón Absrac The usual way o perform a forced vibraion es is o fix
Stabilization of NCSs: Asynchronous Partial Transfer Approach
 25 American Conrol Conference June 8-, 25 Porland, OR, USA WeC3 Sabilizaion of NCSs: Asynchronous Parial Transfer Approach Guangming Xie, Long Wang Absrac In his paper, a framework for sabilizaion of neworked
25 American Conrol Conference June 8-, 25 Porland, OR, USA WeC3 Sabilizaion of NCSs: Asynchronous Parial Transfer Approach Guangming Xie, Long Wang Absrac In his paper, a framework for sabilizaion of neworked
Research Article Dual Synchronization of Fractional-Order Chaotic Systems via a Linear Controller
 The Scienific World Journal Volume 213, Aricle ID 159194, 6 pages hp://dx.doi.org/1155/213/159194 Research Aricle Dual Synchronizaion of Fracional-Order Chaoic Sysems via a Linear Conroller Jian Xiao,
The Scienific World Journal Volume 213, Aricle ID 159194, 6 pages hp://dx.doi.org/1155/213/159194 Research Aricle Dual Synchronizaion of Fracional-Order Chaoic Sysems via a Linear Conroller Jian Xiao,
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 10, October ISSN
 Inernaional Journal of Scienific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 10, Ocober-2013 900 FUZZY MEAN RESIDUAL LIFE ORDERING OF FUZZY RANDOM VARIABLES J. EARNEST LAZARUS PIRIYAKUMAR 1, A. YAMUNA 2 1.
Inernaional Journal of Scienific & Engineering Research, Volume 4, Issue 10, Ocober-2013 900 FUZZY MEAN RESIDUAL LIFE ORDERING OF FUZZY RANDOM VARIABLES J. EARNEST LAZARUS PIRIYAKUMAR 1, A. YAMUNA 2 1.
THE FOURIER-YANG INTEGRAL TRANSFORM FOR SOLVING THE 1-D HEAT DIFFUSION EQUATION. Jian-Guo ZHANG a,b *
 Zhang, J.-G., e al.: The Fourier-Yang Inegral Transform for Solving he -D... THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 07, Vol., Suppl., pp. S63-S69 S63 THE FOURIER-YANG INTEGRAL TRANSFORM FOR SOLVING THE -D HEAT DIFFUSION
Zhang, J.-G., e al.: The Fourier-Yang Inegral Transform for Solving he -D... THERMAL SCIENCE: Year 07, Vol., Suppl., pp. S63-S69 S63 THE FOURIER-YANG INTEGRAL TRANSFORM FOR SOLVING THE -D HEAT DIFFUSION
Modeling the Dynamics of an Ice Tank Carriage
 Modeling he Dynamics of an Ice Tank Carriage The challenge: To model he dynamics of an Ice Tank Carriage and idenify a mechanism o alleviae he backlash inheren in he design of he gearbox. Maplesof, a division
Modeling he Dynamics of an Ice Tank Carriage The challenge: To model he dynamics of an Ice Tank Carriage and idenify a mechanism o alleviae he backlash inheren in he design of he gearbox. Maplesof, a division
Matrix Versions of Some Refinements of the Arithmetic-Geometric Mean Inequality
 Marix Versions of Some Refinemens of he Arihmeic-Geomeric Mean Inequaliy Bao Qi Feng and Andrew Tonge Absrac. We esablish marix versions of refinemens due o Alzer ], Carwrigh and Field 4], and Mercer 5]
Marix Versions of Some Refinemens of he Arihmeic-Geomeric Mean Inequaliy Bao Qi Feng and Andrew Tonge Absrac. We esablish marix versions of refinemens due o Alzer ], Carwrigh and Field 4], and Mercer 5]
CONTRIBUTION TO IMPULSIVE EQUATIONS
 European Scienific Journal Sepember 214 /SPECIAL/ ediion Vol.3 ISSN: 1857 7881 (Prin) e - ISSN 1857-7431 CONTRIBUTION TO IMPULSIVE EQUATIONS Berrabah Faima Zohra, MA Universiy of sidi bel abbes/ Algeria
European Scienific Journal Sepember 214 /SPECIAL/ ediion Vol.3 ISSN: 1857 7881 (Prin) e - ISSN 1857-7431 CONTRIBUTION TO IMPULSIVE EQUATIONS Berrabah Faima Zohra, MA Universiy of sidi bel abbes/ Algeria
An Introduction to Malliavin calculus and its applications
 An Inroducion o Malliavin calculus and is applicaions Lecure 5: Smoohness of he densiy and Hörmander s heorem David Nualar Deparmen of Mahemaics Kansas Universiy Universiy of Wyoming Summer School 214
An Inroducion o Malliavin calculus and is applicaions Lecure 5: Smoohness of he densiy and Hörmander s heorem David Nualar Deparmen of Mahemaics Kansas Universiy Universiy of Wyoming Summer School 214
Class Meeting # 10: Introduction to the Wave Equation
 MATH 8.5 COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # 0 8.5 Inroducion o PDEs, Fall 0 Professor: Jared Speck Class Meeing # 0: Inroducion o he Wave Equaion. Wha is he wave equaion? The sandard wave equaion for a funcion
MATH 8.5 COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # 0 8.5 Inroducion o PDEs, Fall 0 Professor: Jared Speck Class Meeing # 0: Inroducion o he Wave Equaion. Wha is he wave equaion? The sandard wave equaion for a funcion
Probabilistic Models for Reliability Analysis of a System with Three Consecutive Stages of Deterioration
 Yusuf I., Gaawa R.I. Volume, December 206 Probabilisic Models for Reliabiliy Analysis of a Sysem wih Three Consecuive Sages of Deerioraion Ibrahim Yusuf Deparmen of Mahemaical Sciences, Bayero Universiy,
Yusuf I., Gaawa R.I. Volume, December 206 Probabilisic Models for Reliabiliy Analysis of a Sysem wih Three Consecuive Sages of Deerioraion Ibrahim Yusuf Deparmen of Mahemaical Sciences, Bayero Universiy,
Simulation-Solving Dynamic Models ABE 5646 Week 2, Spring 2010
 Simulaion-Solving Dynamic Models ABE 5646 Week 2, Spring 2010 Week Descripion Reading Maerial 2 Compuer Simulaion of Dynamic Models Finie Difference, coninuous saes, discree ime Simple Mehods Euler Trapezoid
Simulaion-Solving Dynamic Models ABE 5646 Week 2, Spring 2010 Week Descripion Reading Maerial 2 Compuer Simulaion of Dynamic Models Finie Difference, coninuous saes, discree ime Simple Mehods Euler Trapezoid
Solutions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Math 246, Spring 2011, Professor David Levermore
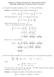 Soluions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Mah 6, Spring, Professor David Levermore Compue he Laplace ransform of f e from is definiion Soluion The definiion of he Laplace ransform gives L[f]s
Soluions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Mah 6, Spring, Professor David Levermore Compue he Laplace ransform of f e from is definiion Soluion The definiion of he Laplace ransform gives L[f]s
Positive continuous solution of a quadratic integral equation of fractional orders
 Mah. Sci. Le., No., 9-7 (3) 9 Mahemaical Sciences Leers An Inernaional Journal @ 3 NSP Naural Sciences Publishing Cor. Posiive coninuous soluion of a quadraic inegral equaion of fracional orders A. M.
Mah. Sci. Le., No., 9-7 (3) 9 Mahemaical Sciences Leers An Inernaional Journal @ 3 NSP Naural Sciences Publishing Cor. Posiive coninuous soluion of a quadraic inegral equaion of fracional orders A. M.
Hopf Bifurcation and Stability Analysis of a Business Cycle Model With Time-Delayed Feedback
 Hopf Bifurcaion and Sabiliy Analysis of a Business Cycle Model Wih ime-delayed Feedback Lei Peng #, Yanhui Zhai # Suden, School of Science, ianjin Polyechnic Universiy, ianjin 3387, China Professor, School
Hopf Bifurcaion and Sabiliy Analysis of a Business Cycle Model Wih ime-delayed Feedback Lei Peng #, Yanhui Zhai # Suden, School of Science, ianjin Polyechnic Universiy, ianjin 3387, China Professor, School
Georey E. Hinton. University oftoronto. Technical Report CRG-TR February 22, Abstract
 Parameer Esimaion for Linear Dynamical Sysems Zoubin Ghahramani Georey E. Hinon Deparmen of Compuer Science Universiy oftorono 6 King's College Road Torono, Canada M5S A4 Email: zoubin@cs.orono.edu Technical
Parameer Esimaion for Linear Dynamical Sysems Zoubin Ghahramani Georey E. Hinon Deparmen of Compuer Science Universiy oftorono 6 King's College Road Torono, Canada M5S A4 Email: zoubin@cs.orono.edu Technical
MATH 5720: Gradient Methods Hung Phan, UMass Lowell October 4, 2018
 MATH 5720: Gradien Mehods Hung Phan, UMass Lowell Ocober 4, 208 Descen Direcion Mehods Consider he problem min { f(x) x R n}. The general descen direcions mehod is x k+ = x k + k d k where x k is he curren
MATH 5720: Gradien Mehods Hung Phan, UMass Lowell Ocober 4, 208 Descen Direcion Mehods Consider he problem min { f(x) x R n}. The general descen direcions mehod is x k+ = x k + k d k where x k is he curren
CONTROL SYSTEMS, ROBOTICS AND AUTOMATION Vol. XI Control of Stochastic Systems - P.R. Kumar
 CONROL OF SOCHASIC SYSEMS P.R. Kumar Deparmen of Elecrical and Compuer Engineering, and Coordinaed Science Laboraory, Universiy of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign, USA. Keywords: Markov chains, ransiion probabiliies,
CONROL OF SOCHASIC SYSEMS P.R. Kumar Deparmen of Elecrical and Compuer Engineering, and Coordinaed Science Laboraory, Universiy of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign, USA. Keywords: Markov chains, ransiion probabiliies,
Theory of! Partial Differential Equations-I!
 hp://users.wpi.edu/~grear/me61.hml! Ouline! Theory o! Parial Dierenial Equaions-I! Gréar Tryggvason! Spring 010! Basic Properies o PDE!! Quasi-linear Firs Order Equaions! - Characerisics! - Linear and
hp://users.wpi.edu/~grear/me61.hml! Ouline! Theory o! Parial Dierenial Equaions-I! Gréar Tryggvason! Spring 010! Basic Properies o PDE!! Quasi-linear Firs Order Equaions! - Characerisics! - Linear and
Open Access Finite-time Stabilization for a Class of Networked Systems with Delay
 Send Orders for Reprins o reprins@benhamscience.ae The Open Auomaion and Conrol Sysems Journal, 214, 6, 1779-1784 1779 Open Access Finie-ime Sabilizaion for a Class of Neworked Sysems wih Delay Hejun Yao
Send Orders for Reprins o reprins@benhamscience.ae The Open Auomaion and Conrol Sysems Journal, 214, 6, 1779-1784 1779 Open Access Finie-ime Sabilizaion for a Class of Neworked Sysems wih Delay Hejun Yao
An recursive analytical technique to estimate time dependent physical parameters in the presence of noise processes
 WHAT IS A KALMAN FILTER An recursive analyical echnique o esimae ime dependen physical parameers in he presence of noise processes Example of a ime and frequency applicaion: Offse beween wo clocks PREDICTORS,
WHAT IS A KALMAN FILTER An recursive analyical echnique o esimae ime dependen physical parameers in he presence of noise processes Example of a ime and frequency applicaion: Offse beween wo clocks PREDICTORS,
Random Walk with Anti-Correlated Steps
 Random Walk wih Ani-Correlaed Seps John Noga Dirk Wagner 2 Absrac We conjecure he expeced value of random walks wih ani-correlaed seps o be exacly. We suppor his conjecure wih 2 plausibiliy argumens and
Random Walk wih Ani-Correlaed Seps John Noga Dirk Wagner 2 Absrac We conjecure he expeced value of random walks wih ani-correlaed seps o be exacly. We suppor his conjecure wih 2 plausibiliy argumens and
Electrical and current self-induction
 Elecrical and curren self-inducion F. F. Mende hp://fmnauka.narod.ru/works.hml mende_fedor@mail.ru Absrac The aricle considers he self-inducance of reacive elemens. Elecrical self-inducion To he laws of
Elecrical and curren self-inducion F. F. Mende hp://fmnauka.narod.ru/works.hml mende_fedor@mail.ru Absrac The aricle considers he self-inducance of reacive elemens. Elecrical self-inducion To he laws of
Optimal Path Planning for Flexible Redundant Robot Manipulators
 25 WSEAS In. Conf. on DYNAMICAL SYSEMS and CONROL, Venice, Ialy, November 2-4, 25 (pp363-368) Opimal Pah Planning for Flexible Redundan Robo Manipulaors H. HOMAEI, M. KESHMIRI Deparmen of Mechanical Engineering
25 WSEAS In. Conf. on DYNAMICAL SYSEMS and CONROL, Venice, Ialy, November 2-4, 25 (pp363-368) Opimal Pah Planning for Flexible Redundan Robo Manipulaors H. HOMAEI, M. KESHMIRI Deparmen of Mechanical Engineering
The Asymptotic Behavior of Nonoscillatory Solutions of Some Nonlinear Dynamic Equations on Time Scales
 Advances in Dynamical Sysems and Applicaions. ISSN 0973-5321 Volume 1 Number 1 (2006, pp. 103 112 c Research India Publicaions hp://www.ripublicaion.com/adsa.hm The Asympoic Behavior of Nonoscillaory Soluions
Advances in Dynamical Sysems and Applicaions. ISSN 0973-5321 Volume 1 Number 1 (2006, pp. 103 112 c Research India Publicaions hp://www.ripublicaion.com/adsa.hm The Asympoic Behavior of Nonoscillaory Soluions
Problemas das Aulas Práticas
 Mesrado Inegrado em Engenharia Elecroécnica e de Compuadores Conrolo em Espaço de Esados Problemas das Aulas Práicas J. Miranda Lemos Fevereiro de 3 Translaed o English by José Gaspar, 6 J. M. Lemos, IST
Mesrado Inegrado em Engenharia Elecroécnica e de Compuadores Conrolo em Espaço de Esados Problemas das Aulas Práicas J. Miranda Lemos Fevereiro de 3 Translaed o English by José Gaspar, 6 J. M. Lemos, IST
Robust Learning Control with Application to HVAC Systems
 Robus Learning Conrol wih Applicaion o HVAC Sysems Naional Science Foundaion & Projec Invesigaors: Dr. Charles Anderson, CS Dr. Douglas Hile, ME Dr. Peer Young, ECE Mechanical Engineering Compuer Science
Robus Learning Conrol wih Applicaion o HVAC Sysems Naional Science Foundaion & Projec Invesigaors: Dr. Charles Anderson, CS Dr. Douglas Hile, ME Dr. Peer Young, ECE Mechanical Engineering Compuer Science
On a Fractional Stochastic Landau-Ginzburg Equation
 Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 4, 1, no. 7, 317-35 On a Fracional Sochasic Landau-Ginzburg Equaion Nguyen Tien Dung Deparmen of Mahemaics, FPT Universiy 15B Pham Hung Sree, Hanoi, Vienam dungn@fp.edu.vn
Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 4, 1, no. 7, 317-35 On a Fracional Sochasic Landau-Ginzburg Equaion Nguyen Tien Dung Deparmen of Mahemaics, FPT Universiy 15B Pham Hung Sree, Hanoi, Vienam dungn@fp.edu.vn
DIRECTIONAL CHANGE IN A PRIORI ANTI-WINDUP COMPENSATORS VS. PREDICTION HORIZON
 DIRECTIONAL CHANGE IN A PRIORI ANTI-WINDUP COMPENSATORS VS. PREDICTION HORIZON Dariusz Horla Poznan Universiy of Technology, Insiue of Conrol and Informaion Engineering Division of Conrol and Roboics,
DIRECTIONAL CHANGE IN A PRIORI ANTI-WINDUP COMPENSATORS VS. PREDICTION HORIZON Dariusz Horla Poznan Universiy of Technology, Insiue of Conrol and Informaion Engineering Division of Conrol and Roboics,
MATH 128A, SUMMER 2009, FINAL EXAM SOLUTION
 MATH 28A, SUMME 2009, FINAL EXAM SOLUTION BENJAMIN JOHNSON () (8 poins) [Lagrange Inerpolaion] (a) (4 poins) Le f be a funcion defined a some real numbers x 0,..., x n. Give a defining equaion for he Lagrange
MATH 28A, SUMME 2009, FINAL EXAM SOLUTION BENJAMIN JOHNSON () (8 poins) [Lagrange Inerpolaion] (a) (4 poins) Le f be a funcion defined a some real numbers x 0,..., x n. Give a defining equaion for he Lagrange
Notes on Kalman Filtering
 Noes on Kalman Filering Brian Borchers and Rick Aser November 7, Inroducion Daa Assimilaion is he problem of merging model predicions wih acual measuremens of a sysem o produce an opimal esimae of he curren
Noes on Kalman Filering Brian Borchers and Rick Aser November 7, Inroducion Daa Assimilaion is he problem of merging model predicions wih acual measuremens of a sysem o produce an opimal esimae of he curren
FAULT DETECTION FOR NONLINEAR SYSTEMS WITH MULTIPLE PERIODIC INPUTS. Z. Y. Yang and C. W. Chan
 FAULT DETECTION FOR NONLINEAR SYSTES WITH ULTIPLE PERIODIC INPUTS Z. Y. Yang and C. W. Chan Dep. of echanical Engineering, Univ. of Hong Kong, Pokfulam Road, Hong Kong Absrac: Faul diagnosis is imporan
FAULT DETECTION FOR NONLINEAR SYSTES WITH ULTIPLE PERIODIC INPUTS Z. Y. Yang and C. W. Chan Dep. of echanical Engineering, Univ. of Hong Kong, Pokfulam Road, Hong Kong Absrac: Faul diagnosis is imporan
Robust estimation based on the first- and third-moment restrictions of the power transformation model
 h Inernaional Congress on Modelling and Simulaion, Adelaide, Ausralia, 6 December 3 www.mssanz.org.au/modsim3 Robus esimaion based on he firs- and hird-momen resricions of he power ransformaion Nawaa,
h Inernaional Congress on Modelling and Simulaion, Adelaide, Ausralia, 6 December 3 www.mssanz.org.au/modsim3 Robus esimaion based on he firs- and hird-momen resricions of he power ransformaion Nawaa,
STABILITY OF RESET SWITCHING SYSTEMS
 STABILITY OF RESET SWITCHING SYSTEMS J.P. Paxman,G.Vinnicombe Cambridge Universiy Engineering Deparmen, UK, jpp7@cam.ac.uk Keywords: Sabiliy, swiching sysems, bumpless ransfer, conroller realizaion. Absrac
STABILITY OF RESET SWITCHING SYSTEMS J.P. Paxman,G.Vinnicombe Cambridge Universiy Engineering Deparmen, UK, jpp7@cam.ac.uk Keywords: Sabiliy, swiching sysems, bumpless ransfer, conroller realizaion. Absrac
Homotopy Perturbation Method for Solving Some Initial Boundary Value Problems with Non Local Conditions
 Proceedings of he World Congress on Engineering and Compuer Science 23 Vol I WCECS 23, 23-25 Ocober, 23, San Francisco, USA Homoopy Perurbaion Mehod for Solving Some Iniial Boundary Value Problems wih
Proceedings of he World Congress on Engineering and Compuer Science 23 Vol I WCECS 23, 23-25 Ocober, 23, San Francisco, USA Homoopy Perurbaion Mehod for Solving Some Iniial Boundary Value Problems wih
A New Perturbative Approach in Nonlinear Singularity Analysis
 Journal of Mahemaics and Saisics 7 (: 49-54, ISSN 549-644 Science Publicaions A New Perurbaive Approach in Nonlinear Singulariy Analysis Ta-Leung Yee Deparmen of Mahemaics and Informaion Technology, The
Journal of Mahemaics and Saisics 7 (: 49-54, ISSN 549-644 Science Publicaions A New Perurbaive Approach in Nonlinear Singulariy Analysis Ta-Leung Yee Deparmen of Mahemaics and Informaion Technology, The
CERTAIN CLASSES OF SOLUTIONS OF LAGERSTROM EQUATIONS
 SARAJEVO JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol.10 (22 (2014, 67 76 DOI: 10.5644/SJM.10.1.09 CERTAIN CLASSES OF SOLUTIONS OF LAGERSTROM EQUATIONS ALMA OMERSPAHIĆ AND VAHIDIN HADŽIABDIĆ Absrac. This paper presens sufficien
SARAJEVO JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol.10 (22 (2014, 67 76 DOI: 10.5644/SJM.10.1.09 CERTAIN CLASSES OF SOLUTIONS OF LAGERSTROM EQUATIONS ALMA OMERSPAHIĆ AND VAHIDIN HADŽIABDIĆ Absrac. This paper presens sufficien
An introduction to the theory of SDDP algorithm
 An inroducion o he heory of SDDP algorihm V. Leclère (ENPC) Augus 1, 2014 V. Leclère Inroducion o SDDP Augus 1, 2014 1 / 21 Inroducion Large scale sochasic problem are hard o solve. Two ways of aacking
An inroducion o he heory of SDDP algorihm V. Leclère (ENPC) Augus 1, 2014 V. Leclère Inroducion o SDDP Augus 1, 2014 1 / 21 Inroducion Large scale sochasic problem are hard o solve. Two ways of aacking
Stable block Toeplitz matrix for the processing of multichannel seismic data
 Indian Journal of Marine Sciences Vol. 33(3), Sepember 2004, pp. 215-219 Sable block Toepliz marix for he processing of mulichannel seismic daa Kiri Srivasava* & V P Dimri Naional Geophysical Research
Indian Journal of Marine Sciences Vol. 33(3), Sepember 2004, pp. 215-219 Sable block Toepliz marix for he processing of mulichannel seismic daa Kiri Srivasava* & V P Dimri Naional Geophysical Research
Analytical Solutions of an Economic Model by the Homotopy Analysis Method
 Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol., 26, no. 5, 2483-249 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikari.com hp://dx.doi.org/.2988/ams.26.6688 Analyical Soluions of an Economic Model by he Homoopy Analysis Mehod Jorge Duare ISEL-Engineering
Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol., 26, no. 5, 2483-249 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikari.com hp://dx.doi.org/.2988/ams.26.6688 Analyical Soluions of an Economic Model by he Homoopy Analysis Mehod Jorge Duare ISEL-Engineering
Stochastic Model for Cancer Cell Growth through Single Forward Mutation
 Journal of Modern Applied Saisical Mehods Volume 16 Issue 1 Aricle 31 5-1-2017 Sochasic Model for Cancer Cell Growh hrough Single Forward Muaion Jayabharahiraj Jayabalan Pondicherry Universiy, jayabharahi8@gmail.com
Journal of Modern Applied Saisical Mehods Volume 16 Issue 1 Aricle 31 5-1-2017 Sochasic Model for Cancer Cell Growh hrough Single Forward Muaion Jayabharahiraj Jayabalan Pondicherry Universiy, jayabharahi8@gmail.com
Bias in Conditional and Unconditional Fixed Effects Logit Estimation: a Correction * Tom Coupé
 Bias in Condiional and Uncondiional Fixed Effecs Logi Esimaion: a Correcion * Tom Coupé Economics Educaion and Research Consorium, Naional Universiy of Kyiv Mohyla Academy Address: Vul Voloska 10, 04070
Bias in Condiional and Uncondiional Fixed Effecs Logi Esimaion: a Correcion * Tom Coupé Economics Educaion and Research Consorium, Naional Universiy of Kyiv Mohyla Academy Address: Vul Voloska 10, 04070
arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 15 Nov 2016
![arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 15 Nov 2016 arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 15 Nov 2016](/thumbs/90/102217337.jpg) arxiv:6.599v [mah.ca] 5 Nov 26 Counerexamples on Jumarie s hree basic fracional calculus formulae for non-differeniable coninuous funcions Cheng-shi Liu Deparmen of Mahemaics Norheas Peroleum Universiy
arxiv:6.599v [mah.ca] 5 Nov 26 Counerexamples on Jumarie s hree basic fracional calculus formulae for non-differeniable coninuous funcions Cheng-shi Liu Deparmen of Mahemaics Norheas Peroleum Universiy
Failure of the work-hamiltonian connection for free energy calculations. Abstract
 Failure of he work-hamilonian connecion for free energy calculaions Jose M. G. Vilar 1 and J. Miguel Rubi 1 Compuaional Biology Program, Memorial Sloan-Keering Cancer Cener, 175 York Avenue, New York,
Failure of he work-hamilonian connecion for free energy calculaions Jose M. G. Vilar 1 and J. Miguel Rubi 1 Compuaional Biology Program, Memorial Sloan-Keering Cancer Cener, 175 York Avenue, New York,
3.1.3 INTRODUCTION TO DYNAMIC OPTIMIZATION: DISCRETE TIME PROBLEMS. A. The Hamiltonian and First-Order Conditions in a Finite Time Horizon
 3..3 INRODUCION O DYNAMIC OPIMIZAION: DISCREE IME PROBLEMS A. he Hamilonian and Firs-Order Condiions in a Finie ime Horizon Define a new funcion, he Hamilonian funcion, H. H he change in he oal value of
3..3 INRODUCION O DYNAMIC OPIMIZAION: DISCREE IME PROBLEMS A. he Hamilonian and Firs-Order Condiions in a Finie ime Horizon Define a new funcion, he Hamilonian funcion, H. H he change in he oal value of
Asymptotic instability of nonlinear differential equations
 Elecronic Journal of Differenial Equaions, Vol. 1997(1997), No. 16, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: hp://ejde.mah.sw.edu or hp://ejde.mah.un.edu fp (login: fp) 147.26.13.11 or 129.12.3.113 Asympoic insabiliy
Elecronic Journal of Differenial Equaions, Vol. 1997(1997), No. 16, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: hp://ejde.mah.sw.edu or hp://ejde.mah.un.edu fp (login: fp) 147.26.13.11 or 129.12.3.113 Asympoic insabiliy
TO our knowledge, most exciting results on the existence
 IAENG Inernaional Journal of Applied Mahemaics, 42:, IJAM_42 2 Exisence and Uniqueness of a Periodic Soluion for hird-order Delay Differenial Equaion wih wo Deviaing Argumens A. M. A. Abou-El-Ela, A. I.
IAENG Inernaional Journal of Applied Mahemaics, 42:, IJAM_42 2 Exisence and Uniqueness of a Periodic Soluion for hird-order Delay Differenial Equaion wih wo Deviaing Argumens A. M. A. Abou-El-Ela, A. I.
Dual synchronization of chaotic and hyperchaotic systems
 Available online a www.jnsa.com J. Nonlinear Sci. Appl. 9 (1), 77 Research Aricle Dual synchronizaion of chaoic and hyperchaoic sysems A. Almaroud Ohman a, M. S. M. Noorani a, M. Mossa Al-Sawalha b, a
Available online a www.jnsa.com J. Nonlinear Sci. Appl. 9 (1), 77 Research Aricle Dual synchronizaion of chaoic and hyperchaoic sysems A. Almaroud Ohman a, M. S. M. Noorani a, M. Mossa Al-Sawalha b, a
The field of mathematics has made tremendous impact on the study of
 A Populaion Firing Rae Model of Reverberaory Aciviy in Neuronal Neworks Zofia Koscielniak Carnegie Mellon Universiy Menor: Dr. G. Bard Ermenrou Universiy of Pisburgh Inroducion: The field of mahemaics
A Populaion Firing Rae Model of Reverberaory Aciviy in Neuronal Neworks Zofia Koscielniak Carnegie Mellon Universiy Menor: Dr. G. Bard Ermenrou Universiy of Pisburgh Inroducion: The field of mahemaics
