Novel robust stability criteria of neutral-type bidirectional associative memory neural networks
|
|
|
- Amos Willis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 0 Novel robus sabiliy crieria of neural-ype bidirecional associaive memory neural neworks Shu-Lian Zhang and Yu-Li Zhang School of Science Dalian Jiaoong Universiy Dalian 608 P. R. China Absrac he exisence uniqueness and global robus exponenial sabiliy is analyzed for a class of uncerain neural-ype bidirecional associaive memory BA neural neworks wih ime-varying delays. Wihou assuming he boundedness of he acivaion funcions by consrucing a novel class of augmened Lyapunov- Krasovskii funcional new relaxed delay-dependen sabiliy crieria of he unique equilibrium poin are presened in erms of linear marix inequaliies LIs. Following he idea of convex combinaion and free-weighing marices mehod less conservaive resuls are obained. wo examples are given o illusrae he effeciveness of our proposed condiions. Keywords: Global robus exponenial sabiliy globally exponenial sabiliy linear marix inequaliyli neural-ype bidirecional associaive memory BA neural nework.. Inroducion Bidirecional associaive memory BA neural neworks which were proposed by Kosko in [0] generalized he single-layer auoassociaive Hebbian correlaor o a wolayer paern-mached heeroassociaive circuis. here are many applicaions for BA neural neworks such as paern recogniion arificial inelligence solving opimizaion problem and auomaic conrol engineering. herefore he BA neural neworks have been one of he mos ineresing research opics and have araced he aenion of many researchers. Up o now many imporan resuls on he sabiliy of BA neural neworks have been repored in he lieraure see e.g. [] [4] [7] [8] [] [5] [9] and references herein. On he oher hand he sabiliy of a neural nework may ofen be desroyed by is unavoidable uncerainies due o he exisence of modeling errors exernal disurbance and parameer flucuaion in he applicaions and designs of neural neworks. herefore he robus sabiliy analysis of neural neworks has gained much research aenion [5] [7] [9] [4] [7]. However he exisence of ime delays in hese DNN models indicaes ha ime delays are dependen on he pas sae. In fac many pracical delay sysems can be modeled as differenial sysems of neural ype whose differenial expression concludes no only he derivaive erm of he curren sae bu also concludes he derivaive erm of he pas sae such as parial elemen equivalen circuis and ransmission lines in elecrical engineering conrolled consrained manipulaors in mechanical engineering populaion dynamics sysem and so on see []. I is naural and imporan ha sysems should conain some informaion abou he derivaive of he pas sae o furher describe and model he dynamics for such complex neural reacions. here have been many resuls abou neural-ype cellular neural neworks bu o he bes of our knowledge few researchers sudied he sabiliy for BA neural neworks which is described by nonlinear delay differenial equaions of he neural ype. By using Jensen inegral inequaliy Liu e al. [] recenly proposed sabiliy condiions of neural-ype BA neural neworks wih consan delays which are expressed in erms of LIs. Based on an inequaliy Park e al. [4] obained a condiion of globally asympoic sabiliy for such sysems also wih consan ime delays. Up o now here are no resuls abou such sysems wih ime varying delays. oivaed by he preceding discussions he aim of his paper is o relax he consrain on he boundedness of he acivaion funcion and sudy he exisence uniqueness and global robus exponenial sabiliy for uncerain neural-ype BA neural neworks wih ime-varying delays. he auhors inroduce a novel form of augmened Lyapunov-Krasovskii funcional ha akes ino accoun k new erms e u Pu and k e v Q v whose derivaives are direcly coupled wih boh neural and rearded sysems. he proposed Lyapunov funcional also includes he erms of cross producs k e u Pu k e v Qv and some inegral erms of cross producs such as ks e u s R g u sd s ks e v s S f v s s d which are no considered in previous resuls. Following he idea of convex combinaion and free-weighing marices mehod [9] we derive several new sufficien Copyrigh c 04 Inernaional Journal of Compuer Science Issues. All Righs Reserved.
2 condiions for he global exponenial sabiliy of BA neural neworks wih ime-varying delays. he derived condiions are expressed in erms of linear marix inequaliies LIs which can be checked numerically very efficienly via he LI oolbox. Some comparisons beween he obained resuls in his paper and previous resuls are made by wo illusraive examples. he res of his paper is organized as follows. In Secion II problem formulaion and preliminaries are given. In Secions IIIIV new delay-dependen condiions are esablished for he exisence uniqueness and exponenial sabiliy. In Secion V he new sabiliy condiions are exended o neural neworks wih normbounded uncer-ainies. Secion VI provides wo illusraive examples. Finally some conclusions are drawn in Secion VII.. Problem descripion Considering he following neural-ype neural neworks wih ime-varying delays: x Ax Bf y Cf y Dx J y Ay Bg x Cg x D y E x x x... x n and y y y... ym are he neural sae vecors JE are he consan exernal inpu vecors. A A A B B B C C C D D D A A A B B B C C C D D D. A diag a a... a n and A diag a a... a m are posiive diagonal marices B b i nm C c i nm D d i nn B bi mn C ci mn D di are mm known consan marices A B C D A B C D are parameric uncerainies 0 0 are he ime-varying delays are posiive consans. f x f y f y... f m ym g x g x... g n xn denoe he neural acivaion funcions. I is assumed ha here exis consans l i l i l l such ha 4 f i s f i s l i l i s s g s g s l l4 s s for any s s R s... ; s i m... n. oreover we assume ha he iniial condiion of neural neworks has he form x yi i [ max 0] i i... m;... n are coninuous funcions. hroughou his paper le y denoe he Euclidean norm n of a vecor yr W W W m W and W W W denoe he ranspose he inverse he larges eigenvalue he smalles eigenvalue and he specral norm of a square marix W respecively. Le W>0<0 denoe a posiive negaive definie symmeric marix I denoe an ideniy marix wih compaible dimension. he definiion of exponenial sabiliy is now given. Definiion [0] he neural nework is said o be globally exponenially sable if here exis consans k 0 and > such ha x y sup x x 0 k sup y y e 0 k is called he exponenial convergence rae. Clearly he equilibrium poin of neural nework is robus sable if and only if he zero soluion of neural nework 4 is robus sable. he ime-varying uncerain marices are defined by: A B C D H0E0 G G G G4 4 A B C D HE G5 G6 G7 G8 H0 H Gi i...8 are known real consan marices wih appropriae dimensions. E 0 E are unknown ime-varying marices saisfying E E I E E I In order o obain he main resuls we need he following lemmas. Lemma see [] Le XY and P be real marices of appropriae dimensions wih P>0. hen for any posiive scalar he following marix inequaliy holds: XYYX XP X YPY. n n Lemma see [7] Coninuous map z : R R is homeomorphic if z is inecive and lim z. z Copyrigh c 04 Inernaional Journal of Compuer Science Issues. All Righs Reserved.
3 Exisence and uniqueness of he equilibrium poin Firsly we consider neural nework wihou uncerainies ha is x Ax Bf y Cf y Dx J 6 y Ay Bg x Cg x Dy E. In order o sudy he exisence and uniqueness of he equilibrium poin we define map H w as H w [ H w H w] [ w x y ] and H w Ax B C f y J H w A y B C g x E. heorem. Under assumpions and given a consan k 0 suppose ha here exis posiive definie symmeric marices P [ Pi ] Q [ Qi ] nonnegaive definie symmeric marices R [ Ri ] S [ Si ] Ui Zi i posiive diagonal marices real marices X Y 4 wih compaible dimensions such ha he following LIs hold i=: i k i e U 0 0 k 0 e U i 44 kp P R A A P R R X X LL4 ki A P X X 4 R AR L L4 6 P R D P 7 AZ P R B P R C k kp e R X X X X L4L4 X X 4 k 5 e R L L4 4 k 6 P D P e R P B P C X X R 46 R D 48 B Q S 49 B Q 4 R B B S 4 R C 44 B Z e R k 55 4 e R C Q S k C Q 5 C S 54 C Z k 66 e R 67 D Z 77 Z Z R U 7 ZB 7 ZC 88 kq Q S A A Q S S Y Y L L 89 ki A Q Y Y 8 S AS L L 8 Q S D Q 84 A Z k 99 kq e S Y Y Y Y L L 90 Y Y4 k 9 e S L L k 9 QD Q e S 00 Y4 Y4 S k S D e S k e S k e S 4 D Z 44 Z Z S U [ X X ] [ 0 X X ] [ Y Y ] [ Y Y ] Li diag li li... lin i 4 and oher parameers 7 i i are all equal o zero's hen neural nework 6 have a unique equilibrium poin. Proof. As done in [6] we will firsly prove ha nm H w H w for any w w w wr. Now suppose H w H w ha is A x x B C f y f y 0 A y y B C g x g x 0. I is easy o see ha [ x x P R P g x g x R] A xx BC f y f y 0 8 [ y y Q S Q f y f y S] A yy B C g x g x 0. 9 By inequaliies and we ge y y L L y y f y f y f y f y y y LL f y f y 0 xx L 4 L4 xx gx gx 4 gx gx xx L L g x g x Copyrigh c 04 Inernaional Journal of Compuer Science Issues. All Righs Reserved.
4 hese ogeher wih Eqs.89 give G 0 0 G G i 44 [ x x g x g x y y f y f y ] G P R P A A P R P L 4 L4 G A R 4 L L4 G4 P R P B C G 4 G B C F4 Q G4 R B C B C S G Q S Q A A Q S Q L L G A S L L \ G On he oher hand one can infer from inequaliy 7 i== ha 0. Le I I I I I B I I I I I 0 0 muliplying by B and B on is lef and righ side respecively we obain I I 0P 0I 0 G k 0 0 Q 0 I I k k e R e S diag 0 I I. 0 0 Noe ha k0 P0 Q0 R0 S00 i i 0 0 hus G<0. Obviously his conradics wih 0. he conradicion implies ha H w H w. Hence map H is inecive. Nex we show ha H w as w. o prove his i suffices o show ha H w H 0 as w. Similar o above proof from Lemma and assumpions we obain [ x P R P g x g0 R] H w H0 [ y Q S Q f y f0 S ] H w H 0 x x g x g0 g x g0 G y y f y f0 f y f0 x x g x g0 g x g0 G y y f y f0 f y f 0 G x x g x g0 g x g0 y y f y f0 f y f0 G x x x x y y y y G x y G w diag... n i max l i li diag ñ... ñn ñi max li l4i i... n. From assumpions and above discussion we have 0 0 G 0. By Schwarz inequaliy and assumpions we have G w [ x P R P g x g0 R] H w H0 [ y Q S Q f y f0 S] H w H0 x P R P g x g0 R H w H0 y Q S Q f y f0 S H w H0 P R P R x H w H0 Q S Q S y H w H0 H w H0 P R P R Q S Q S. ha is w H w H 0 G i i 4. Exponenial sabiliy resul of he equilibrium poin In order o prove he robus sabiliy of he equilibrium * * poin x y of neural nework we will firs simplify * neural nework as follows. Le u x x v * y y hen we have u Au Bf v Cf v Du v Av Bgu Cgu Dv Copyrigh c 04 Inernaional Journal of Compuer Science Issues. All Righs Reserved.
5 4 * * f v f v y f y g u * * i i i i i i i g u x g x wih f 0 g 0 0 i... m;... n. By assumpions and we can see ha fi s fi s l i li s s l i g s g s l. 4 s s Nex we consider neural nework wihou uncerainies ha is u Au B f v C f v Du 4 v Av Bgu Cgu Dv. heorem. he unique equilibrium poin of neural nework 4 is sable wih exponenial convergence rae k if he condiions of heorem are saisfied. Proof. Consider he following Lyapunov-Krasovskii funcional: V u V u 5 i wih k k V u e P e Q ks d V u e s R s s ks e s S sd s ks ks V u s e u s U u sds s e v s U v sd s [ u u ] [ v v ] s [ u s g u s u s] s [ v s f v s v s]. For convenience we denoe u u v v. he ime derivaive of funcional 5 along he raecories of neural nework 4 is obained as follows: k V u e k P P k Q Q k V u e R S k e R k e S i V u e u U u v U v k k s d k s e u s U u s s e v s U v sd s. Based on Leibniz-Newon formula for any real marix X i i...4 wih compaible dimensions we ge k 0 e u X u X u u u sd s 6 k 0 e u X u X 4 k 0 e v Y v Y u u u sd s 7 v v v sd s 8 k 0 e v Y v Y4 v v v s d s. 9 I is easy o ge he following inequaliies by using Lemma : u X u X u sds k e u s U u sds k e U 0 u X u X u sds 4 k e u s Uu sds k e U v Y v Y v sds k e v s U v sds k e U 4 vy v Y vs ds k e v s U v sds k e U [ u u u g u g u u u v v v f v f v v v ]. On he oher hand one can infer from inequaliies ha he following marix inequaliies hold for any Copyrigh c 04 Inernaional Journal of Compuer Science Issues. All Righs Reserved.
6 5 posiive diagonal marices i i 4 wih compaible dimensions k 0 e v L L v f v f v v L L f v 4 k 0 e v LLv f v f v v L L f v 5 k 0 e u L4Lu g u g u u L L g u 6 4 k 0 e u LLu g u g u u L L g u o ge less conservaive crierion we inroduce he following equaliies for any real marices Z Z wih compaible dimensions 0 u Z u Au B f v C f v D u 8 0 v Z v A v B g u C g u D v. 9 From 5-9 we obain k k V u e e U k e U k e U k e U. Noe ha 0 0 so k k e U e U k e U k e U 0 holds if and only if he following four inequaliies k k e U e U 0 0 k k e U e U 0 k k e U e U 0 k k e U e U 0 are rue. From he well-known Schur complemen inequaliies 0- are equivalen o 7 wih i= respecively hus Vu 0 holds if 7 i= are rue. Furhermore following he similar line in [7] from Lemma we have V u0 x sup u * 0 * 4 0 y sup v 4 P R R U 4 Q S 4 S U max l l max l l. and i n i 4 i i n i i eanwhile k V u e * P x Q m m * y min k e m P m Q x y * * by Lyapunov sabiliy heory he proof of heorem is compleed. Remark. One can noice ha he augmened Lyapunov funcional approach of his paper is quie differen from k previous ones. New erms e u Pu and k e v Qv are used o augmen he Lyapunov funcional whose derivaives are direcly coupled wih boh neural and rearded sysems. herefore he augmened Lyapunov funcional can lead o an reduce in he conservaiveness of he resuls which will be illusraed by hree examples. Remark. he proposed Lyapunov funcional also includes he erms of cross producs k k e u Pu e v Qv and some inegral erms of cross producs such as ks ks e u s R gd u s s e v s S fd v s s which are no considered in previous resuls. his approach provides a quasi-full-size Lyapunov funcional hrough augmenaion. oreover he se of Lyapunov- Krasovskii funcional inroduced in Park e al. [4] is us reduced form of he one proposed in his paper. I is well known ha as he Lyapunov funcional is reduced he corresponding resuls become more conservaive. herefore he proposed novel augmened Lyapunov funcional can yield less conservaive resuls han he exising mehods. Remark. I should be poined ou ha he condiion of heorem in [4] needs o be revised. In he proof one Copyrigh c 04 Inernaional Journal of Compuer Science Issues. All Righs Reserved.
7 6 key sep is he following proposiion see inequaliy 4 in Page 79 of [4]: Proposiion. Le L L 4. he following inequaliy holds for any given L4 0 posiive definie marices Z: g y Zg y y L ZL y Unforunaely he above Proposiion is no valid in general his fac can be illusraed by he following example: Example.. Obviously g s g s s s saisfy condiions wih L 4 I. Se y [ ] hen g y [ ]. Furher se Z 5 we have g y Zg y y LZLy i.e. inequaliy 4 is false. 4 4 Based on above analysis he LIs of heorem in [4] may no be sufficien condiions assumed ha Z is a posiive definie marix. In fac if Z is revised o be a posiive scalar marix hen he above Proposiion and heorem in [4] are sill valid. Remark 4. If any of are unknown or any of are no differeniable by seing Pi Qi 0 i R S 0 in funcional 5 and adding he following zero equaions o he ime derivaive along he raecories of neural nework 4: 0 u K u Au B f v C f v D u 0 v K v A v B g u Cg u Dv Ki i are any real marices wih compaible dimensions. Following he similar line in heorem we can obain a sabiliy crierion similar o LIs 7. Remark 5. In erms of LIs heorem and Remark 4 provide a sufficien condiion for he global exponenial sabiliy of he delayed neural-ype neural nework in 4. One of he advanages of he LI approach is ha he LI condiion can be checked numerically very efficienly by using he inerior-poin algorihms which have been developed recenly in solving LIs []. Nex consider sysem 4 wih D D 0 ha is u Au Bf v Cf v 5 v Av Bgu Cgu. I is easy o see he following resul holds from heorem. Corollary. Under assumpions and given a consan k 0 suppose ha here exis posiive definie symmeric marices PQ nonnegaive definie symmeric marices RSZ i Ui i posiive diagonal marices real marices X Y 4 wih compaible dimensions such ha he LIs 7 i= wih D D 0 hold hen he equilibrium poin of neural nework 5 is exponenial sable. Remark 6. In Corollary by seing Pi Qi 0 i R S 0 we can employ his crierion o analyze he sabiliy of neural nework 5 when any of are unknown or any of are no differeniable. 5. Robus exponenial sabiliy resuls of uncerain delayed neural nework Now based on Lemma we invesigae he robus exponenial sabiliy condiion for neural nework wih uncerainies saisfying 4 and 5. Firsly by using he same funcional as in heorem we can easily obain he following resul. heorem. Under assumpions -5 and given a consan k 0 suppose ha here exis posiive scalars 0 posiive definie symmeric marices PQ nonnegaive definie symmeric marices RSZ i Ui i posiive diagonal marices real marices X Y 4 wih compaible dimensions such ha he following LIs hold i=: 0H0 H i H00 0I H 0 I k i 0 0 e U 0 k e U [ G 0000 \ G 0000G G 00] 0 4 [ G 0000 \ G 0000G G 00] 4 Copyrigh c 04 Inernaional Journal of Compuer Science Issues. All Righs Reserved.
8 7 [0 0 0 G6 G7 0 0 G5 \ 0 0 \ 0 0 G8 0] [0 0 0 G G 0 0 G \ G 0] PR P R \ Z QS \ Q S Z [ ] [ ] and oher parameers are all defined in heorem hen he equilibrium poin of neural nework is robus exponenial sable Remark 7. Similar o Remark 4 if any of are no differeniable or any of are unknown by seing Pi Qi 0 i RS 0 in funcional 5 and adding he following zero equaions 0 u K u Au B f v C f v D u 0 v K v A v B g u C g u D v o he ime derivaive along he raecories of neural nework following he similar line in heorem we can obain a sabiliy crierion similar o LIs 6. Now consider sysem wih D D 0 ha is u Au Bf v Cf v v Av Bgu Cgu. I is easy o see he following resul holds from heorem. Corollary. Under assumpions and given a consan k 0 suppose ha here exis posiive scalars 0 posiive definie symmeric marices PQ nonnegaive definie symmeric marices RSU i i posiive diagonal marices real marices X Y 4 wih compaible dimensions such ha he LIs 6 wih D D 0 hold hen he equilibrium poin of neural nework 7 is robus exponenial sable. Remark 8. In Corollary by seing Pi Qi 0 i R S 0 we can employ his crierion o analyze he sabiliy of neural nework 7 when any of are unknown or any of are no differeniable. 6. Comparison and Illusraive Examples Nex we provide wo numerical examples o demonsrae he effeciveness and less conservaiveness of our delaydependen sabiliy crieria over some recen resuls in he lieraure. Example 5.. Consider neural nework 5 wih A I A 4 I B B C C L L 0 L L4 I. his model was sudied in [7] [8]. For his neural nework i is verified in [8] ha he resuls given in [] [] fail o ascerain he sabiliy for any ime delay. Furhermore if we se exponenial convergence rae k be fixed as 0.5 none of he crieria of [4] [9] can guaranee he sabiliy for any ime delay wih 0or 0. Se 0.50 all of he crieria given in [8] [7] fail o verify he sabiliy for any ime delay he allowable ime delay upper bound obained by Gau e al. [7] is 0.50 while our mehod shows ha he equilibrium poin of his neural nework is exponenially sable for any ime delay wih.06. his is much larger han he one of [7] which shows he less conservaiveness of our developed mehod. Example 5.. Consider neural nework 6 wih A diag.5 A diag B B c 0 C C c c c D D E J 6 4 f s f s g s g s 0.5 s s. Obviously he acivaion funcions saisfy assumpions and wih L L 0 L L4 I. Obviously none of he resuls in [] [4] [7] [8] [] [5] and [9] can be applied o verify he sabiliy of his model. However if we se 0.5 from heorems and we can conclude ha his neural nework has a unique equilibrium poin Copyrigh c 04 Inernaional Journal of Compuer Science Issues. All Righs Reserved.
9 which is exponenial sable for any c wih 0 c Conclusion In his paper we have invesigaed he global robus sabiliy problem of uncerain BA neural neworks of neural-ype. By employing new Lyapunov-Krasovskii funcional we proposed several novel sabiliy crieria for he considered neural neworks. he obained resuls are all in he form of LI which can be easily opimized. Finally hree examples are given o show he superioriy of our proposed sabiliy condiions o some exising ones. References [] S. Boyd L. E.I. Ghaoui E. Feron V. Balakrishnan Linear arix Inequaliy in Sysem and Conrol heory SIA Philadelphia PA 994. [] J. Cao L. Wang Exponenial sabiliy and periodic oscillaory soluion in BA neworks wih delays IEEE rans. Neural New. 00: [] J. Cao. Dong Exponenial sabiliy of delayed bidirecional associaive memory neworks Appl. ah. Compu.005:05-. [4] J. Cao D.W.C. Ho X. Huang LI-based crieria for global robus sabiliy of bidirecional associaive memory neworks wih ime delay Nonl. Anal : [5] A. Chen L. Huang J. Cao Exponenial sabiliy of delayed bidirecional associaive memory neural neworks wih reacion diffusion erms In. J. Sysems Science 00785: 4-4. [6] L. Chen H. Zhao New LI condiions for global exponenial sabiliy of cellular neural neworks wih delays Nonl. Anal.: Real World Appl. 0090: [7] Gau R.S. Hsieh J.G. Lien C.H. Global exponenial sabiliy for uncerain bidirecional associaive memory neural neworks wih muliple ime-varying delays via LI approach In. J. Circ. heor. Appl. 0086: [8] X. Huang J. Cao D.S. Huang LI-based approach for delay-dependen exponenial sabiliy analysis of BA neural neworks Chaos Solions Fracals 0054: [9] Y. He G.P. Liu D. Rees and. Wu Sabiliy analysis for neural neworks wih ime-varying inerval delay IEEE rans. Neural New : [0] B. Kosko Adapive bidirecional associaive memories Applied Opics 9876: [] B. Kosko Bidirecional associaive memories IEEE rans. Sysems an Cybernaics 9888: [] J. Liu G. Zong New delay-dependen asympoic sabiliy condiions concerning BA neural neworks of neural ype Neurocompuing 0097: [] H. ai X. Liao C. Li A semi-free weighing marices approach for neural-ype delayed neural neworks J. Compu. Appl. ah. 0095: [4] J. H. Park C. H. Park O.. Kwon S.. Lee A new sabiliy crierion for bidirecional associaive memory neural neworks of neural-ype Appl. ah. Compu : [5] J. H. Park Robus sabiliy of bidirecional associaive memory neural neworks wih delays Physics Leers A 00649: [6] S. Senan S. Arik Global robus sabiliy of bidirecional associaive memory neural neworks wih muliple ime delays IEEE rans. Sys. an Cybern. B 00705: [7] L. Sheng H. Yang Novel global robus exponenial sabiliy crierion for uncerain BA neural neworks wih ime-varying delays Chaos Solions Fracals 00940: 0-. [8] Z. Wang H. Zhang Sabiliy analysis of BA neural neworks wih ime-varying delays Progress in Naural Science 0077: 06-. [9] Z. Wang H. Zhang W. Yu Robus exponenial sabiliy analysis of neural neworks wih muliple ime delays Neurocompuing 00770: [0] S. Xu J. Lam D. W.C. Ho Y. Zou Delay-dependen exponenial sabiliy for a class of neural neworks wih ime delays" J. Compu. Appl. ah. 0058:6-8. [] Z. Zeng and J. Wang Improved condiions for global exponenial sabiliy of recurren neural neworks wih imevarying delays IEEE rans. Neural New. 0067:6-65. [] H. Zhang and Z. Wang Global asympoic sabiliy of delayed cellular neural neworks IEEE rans. Neural New. 0078: [] H. Zhang Z. Wang and D. Liu Global asympoic sabiliy of recurren neural neworks wih muliple imevarying delays IEEE rans. Neural New : [4] H. Zhang Z. Wang D. Liu Robus sabiliy analysis for inerval Cohen-Grossberg neural neworks wih unknown ime-varying delays IEEE rans. Neural New : [5] H. Zhang Z. Wang D. Liu Robus exponenial sabiliy of cellular neural neworks wih muliple ime varying delays IEEE rans. Circuis Sys. II : [6] H. Zhang Z. Wang and D. Liu Global asympoic sabiliy and robus sabiliy of a class of Cohen-Grossberg neural neworks wih mixed delays IEEE rans. Circuis Sys. I 00956: [7] C.D. Zheng H. Zhang and Z. Wang Novel delaydependen crieria for global robus exponenial sabiliy of delayed cellular neural neworks wih norm-bounded uncerainies Neurocompuing : Firs Auhor was born in Liaoning China in 96. She Graduaed from Dalian Universiy of echnology and oined he Deparmen of ahemaics Dalian Jiaoong Universiy China as Associae Professor in 00. Yu-Li Zhang was born in Jiangsu China in 978. She received he aser Degree in mahemaics from China Universiy of ining and echnology in 00 and hen oined he Deparmen of ahemaics Dalian Jiaoong Universiy China. Copyrigh c 04 Inernaional Journal of Compuer Science Issues. All Righs Reserved.
A DELAY-DEPENDENT STABILITY CRITERIA FOR T-S FUZZY SYSTEM WITH TIME-DELAYS
 A DELAY-DEPENDENT STABILITY CRITERIA FOR T-S FUZZY SYSTEM WITH TIME-DELAYS Xinping Guan ;1 Fenglei Li Cailian Chen Insiue of Elecrical Engineering, Yanshan Universiy, Qinhuangdao, 066004, China. Deparmen
A DELAY-DEPENDENT STABILITY CRITERIA FOR T-S FUZZY SYSTEM WITH TIME-DELAYS Xinping Guan ;1 Fenglei Li Cailian Chen Insiue of Elecrical Engineering, Yanshan Universiy, Qinhuangdao, 066004, China. Deparmen
Stability and Bifurcation in a Neural Network Model with Two Delays
 Inernaional Mahemaical Forum, Vol. 6, 11, no. 35, 175-1731 Sabiliy and Bifurcaion in a Neural Nework Model wih Two Delays GuangPing Hu and XiaoLing Li School of Mahemaics and Physics, Nanjing Universiy
Inernaional Mahemaical Forum, Vol. 6, 11, no. 35, 175-1731 Sabiliy and Bifurcaion in a Neural Nework Model wih Two Delays GuangPing Hu and XiaoLing Li School of Mahemaics and Physics, Nanjing Universiy
On Robust Stability of Uncertain Neutral Systems with Discrete and Distributed Delays
 009 American Conrol Conference Hya Regency Riverfron S. Louis MO USA June 0-009 FrC09.5 On Robus Sabiliy of Uncerain Neural Sysems wih Discree and Disribued Delays Jian Sun Jie Chen G.P. Liu Senior Member
009 American Conrol Conference Hya Regency Riverfron S. Louis MO USA June 0-009 FrC09.5 On Robus Sabiliy of Uncerain Neural Sysems wih Discree and Disribued Delays Jian Sun Jie Chen G.P. Liu Senior Member
The Asymptotic Behavior of Nonoscillatory Solutions of Some Nonlinear Dynamic Equations on Time Scales
 Advances in Dynamical Sysems and Applicaions. ISSN 0973-5321 Volume 1 Number 1 (2006, pp. 103 112 c Research India Publicaions hp://www.ripublicaion.com/adsa.hm The Asympoic Behavior of Nonoscillaory Soluions
Advances in Dynamical Sysems and Applicaions. ISSN 0973-5321 Volume 1 Number 1 (2006, pp. 103 112 c Research India Publicaions hp://www.ripublicaion.com/adsa.hm The Asympoic Behavior of Nonoscillaory Soluions
STABILITY OF NONLINEAR NEUTRAL DELAY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS WITH VARIABLE DELAYS
 Elecronic Journal of Differenial Equaions, Vol. 217 217, No. 118, pp. 1 14. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: hp://ejde.mah.xsae.edu or hp://ejde.mah.un.edu STABILITY OF NONLINEAR NEUTRAL DELAY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
Elecronic Journal of Differenial Equaions, Vol. 217 217, No. 118, pp. 1 14. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: hp://ejde.mah.xsae.edu or hp://ejde.mah.un.edu STABILITY OF NONLINEAR NEUTRAL DELAY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
Mean-square Stability Control for Networked Systems with Stochastic Time Delay
 JOURNAL OF SIMULAION VOL. 5 NO. May 7 Mean-square Sabiliy Conrol for Newored Sysems wih Sochasic ime Delay YAO Hejun YUAN Fushun School of Mahemaics and Saisics Anyang Normal Universiy Anyang Henan. 455
JOURNAL OF SIMULAION VOL. 5 NO. May 7 Mean-square Sabiliy Conrol for Newored Sysems wih Sochasic ime Delay YAO Hejun YUAN Fushun School of Mahemaics and Saisics Anyang Normal Universiy Anyang Henan. 455
Ann. Funct. Anal. 2 (2011), no. 2, A nnals of F unctional A nalysis ISSN: (electronic) URL:
 Ann. Func. Anal. 2 2011, no. 2, 34 41 A nnals of F uncional A nalysis ISSN: 2008-8752 elecronic URL: www.emis.de/journals/afa/ CLASSIFICAION OF POSIIVE SOLUIONS OF NONLINEAR SYSEMS OF VOLERRA INEGRAL EQUAIONS
Ann. Func. Anal. 2 2011, no. 2, 34 41 A nnals of F uncional A nalysis ISSN: 2008-8752 elecronic URL: www.emis.de/journals/afa/ CLASSIFICAION OF POSIIVE SOLUIONS OF NONLINEAR SYSEMS OF VOLERRA INEGRAL EQUAIONS
A DELAY-DEPENDENT APPROACH TO ROBUST STABILITY FOR UNCERTAIN STOCHASTIC NEURAL NETWORKS WITH TIME-VARYING DELAY
 Journal of Marine Science and echnology Vol. 8 No. pp. 77-83 (00) 77 A DELAY-DEPENDEN APPROACH O ROBUS SABILIY FOR UNCERAIN SOCHASIC NEURAL NEWORKS WIH IME-VARYING DELAY Chien-Yu Lu* Chin-Wen Liao* Koan-Yuh
Journal of Marine Science and echnology Vol. 8 No. pp. 77-83 (00) 77 A DELAY-DEPENDEN APPROACH O ROBUS SABILIY FOR UNCERAIN SOCHASIC NEURAL NEWORKS WIH IME-VARYING DELAY Chien-Yu Lu* Chin-Wen Liao* Koan-Yuh
10. State Space Methods
 . Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
. Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
Matrix Versions of Some Refinements of the Arithmetic-Geometric Mean Inequality
 Marix Versions of Some Refinemens of he Arihmeic-Geomeric Mean Inequaliy Bao Qi Feng and Andrew Tonge Absrac. We esablish marix versions of refinemens due o Alzer ], Carwrigh and Field 4], and Mercer 5]
Marix Versions of Some Refinemens of he Arihmeic-Geomeric Mean Inequaliy Bao Qi Feng and Andrew Tonge Absrac. We esablish marix versions of refinemens due o Alzer ], Carwrigh and Field 4], and Mercer 5]
Lecture 20: Riccati Equations and Least Squares Feedback Control
 34-5 LINEAR SYSTEMS Lecure : Riccai Equaions and Leas Squares Feedback Conrol 5.6.4 Sae Feedback via Riccai Equaions A recursive approach in generaing he marix-valued funcion W ( ) equaion for i for he
34-5 LINEAR SYSTEMS Lecure : Riccai Equaions and Leas Squares Feedback Conrol 5.6.4 Sae Feedback via Riccai Equaions A recursive approach in generaing he marix-valued funcion W ( ) equaion for i for he
On Oscillation of a Generalized Logistic Equation with Several Delays
 Journal of Mahemaical Analysis and Applicaions 253, 389 45 (21) doi:1.16/jmaa.2.714, available online a hp://www.idealibrary.com on On Oscillaion of a Generalized Logisic Equaion wih Several Delays Leonid
Journal of Mahemaical Analysis and Applicaions 253, 389 45 (21) doi:1.16/jmaa.2.714, available online a hp://www.idealibrary.com on On Oscillaion of a Generalized Logisic Equaion wih Several Delays Leonid
Fractional Method of Characteristics for Fractional Partial Differential Equations
 Fracional Mehod of Characerisics for Fracional Parial Differenial Equaions Guo-cheng Wu* Modern Teile Insiue, Donghua Universiy, 188 Yan-an ilu Road, Shanghai 51, PR China Absrac The mehod of characerisics
Fracional Mehod of Characerisics for Fracional Parial Differenial Equaions Guo-cheng Wu* Modern Teile Insiue, Donghua Universiy, 188 Yan-an ilu Road, Shanghai 51, PR China Absrac The mehod of characerisics
An Introduction to Malliavin calculus and its applications
 An Inroducion o Malliavin calculus and is applicaions Lecure 5: Smoohness of he densiy and Hörmander s heorem David Nualar Deparmen of Mahemaics Kansas Universiy Universiy of Wyoming Summer School 214
An Inroducion o Malliavin calculus and is applicaions Lecure 5: Smoohness of he densiy and Hörmander s heorem David Nualar Deparmen of Mahemaics Kansas Universiy Universiy of Wyoming Summer School 214
CONTRIBUTION TO IMPULSIVE EQUATIONS
 European Scienific Journal Sepember 214 /SPECIAL/ ediion Vol.3 ISSN: 1857 7881 (Prin) e - ISSN 1857-7431 CONTRIBUTION TO IMPULSIVE EQUATIONS Berrabah Faima Zohra, MA Universiy of sidi bel abbes/ Algeria
European Scienific Journal Sepember 214 /SPECIAL/ ediion Vol.3 ISSN: 1857 7881 (Prin) e - ISSN 1857-7431 CONTRIBUTION TO IMPULSIVE EQUATIONS Berrabah Faima Zohra, MA Universiy of sidi bel abbes/ Algeria
t is a basis for the solution space to this system, then the matrix having these solutions as columns, t x 1 t, x 2 t,... x n t x 2 t...
 Mah 228- Fri Mar 24 5.6 Marix exponenials and linear sysems: The analogy beween firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions (Chaper 5) and scalar linear differenial equaions (Chaper ) is much sronger
Mah 228- Fri Mar 24 5.6 Marix exponenials and linear sysems: The analogy beween firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions (Chaper 5) and scalar linear differenial equaions (Chaper ) is much sronger
POSITIVE SOLUTIONS OF NEUTRAL DELAY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION
 Novi Sad J. Mah. Vol. 32, No. 2, 2002, 95-108 95 POSITIVE SOLUTIONS OF NEUTRAL DELAY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION Hajnalka Péics 1, János Karsai 2 Absrac. We consider he scalar nonauonomous neural delay differenial
Novi Sad J. Mah. Vol. 32, No. 2, 2002, 95-108 95 POSITIVE SOLUTIONS OF NEUTRAL DELAY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION Hajnalka Péics 1, János Karsai 2 Absrac. We consider he scalar nonauonomous neural delay differenial
Existence of positive solution for a third-order three-point BVP with sign-changing Green s function
 Elecronic Journal of Qualiaive Theory of Differenial Equaions 13, No. 3, 1-11; hp://www.mah.u-szeged.hu/ejqde/ Exisence of posiive soluion for a hird-order hree-poin BVP wih sign-changing Green s funcion
Elecronic Journal of Qualiaive Theory of Differenial Equaions 13, No. 3, 1-11; hp://www.mah.u-szeged.hu/ejqde/ Exisence of posiive soluion for a hird-order hree-poin BVP wih sign-changing Green s funcion
Chapter 2. First Order Scalar Equations
 Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 15 Nov 2016
![arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 15 Nov 2016 arxiv: v1 [math.ca] 15 Nov 2016](/thumbs/90/102217337.jpg) arxiv:6.599v [mah.ca] 5 Nov 26 Counerexamples on Jumarie s hree basic fracional calculus formulae for non-differeniable coninuous funcions Cheng-shi Liu Deparmen of Mahemaics Norheas Peroleum Universiy
arxiv:6.599v [mah.ca] 5 Nov 26 Counerexamples on Jumarie s hree basic fracional calculus formulae for non-differeniable coninuous funcions Cheng-shi Liu Deparmen of Mahemaics Norheas Peroleum Universiy
Sliding Mode Extremum Seeking Control for Linear Quadratic Dynamic Game
 Sliding Mode Exremum Seeking Conrol for Linear Quadraic Dynamic Game Yaodong Pan and Ümi Özgüner ITS Research Group, AIST Tsukuba Eas Namiki --, Tsukuba-shi,Ibaraki-ken 5-856, Japan e-mail: pan.yaodong@ais.go.jp
Sliding Mode Exremum Seeking Conrol for Linear Quadraic Dynamic Game Yaodong Pan and Ümi Özgüner ITS Research Group, AIST Tsukuba Eas Namiki --, Tsukuba-shi,Ibaraki-ken 5-856, Japan e-mail: pan.yaodong@ais.go.jp
t 2 B F x,t n dsdt t u x,t dxdt
 Evoluion Equaions For 0, fixed, le U U0, where U denoes a bounded open se in R n.suppose ha U is filled wih a maerial in which a conaminan is being ranspored by various means including diffusion and convecion.
Evoluion Equaions For 0, fixed, le U U0, where U denoes a bounded open se in R n.suppose ha U is filled wih a maerial in which a conaminan is being ranspored by various means including diffusion and convecion.
TO our knowledge, most exciting results on the existence
 IAENG Inernaional Journal of Applied Mahemaics, 42:, IJAM_42 2 Exisence and Uniqueness of a Periodic Soluion for hird-order Delay Differenial Equaion wih wo Deviaing Argumens A. M. A. Abou-El-Ela, A. I.
IAENG Inernaional Journal of Applied Mahemaics, 42:, IJAM_42 2 Exisence and Uniqueness of a Periodic Soluion for hird-order Delay Differenial Equaion wih wo Deviaing Argumens A. M. A. Abou-El-Ela, A. I.
EXISTENCE OF NON-OSCILLATORY SOLUTIONS TO FIRST-ORDER NEUTRAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 Elecronic Journal of Differenial Equaions, Vol. 206 (206, No. 39, pp.. ISSN: 072-669. URL: hp://ejde.mah.xsae.edu or hp://ejde.mah.un.edu fp ejde.mah.xsae.edu EXISTENCE OF NON-OSCILLATORY SOLUTIONS TO
Elecronic Journal of Differenial Equaions, Vol. 206 (206, No. 39, pp.. ISSN: 072-669. URL: hp://ejde.mah.xsae.edu or hp://ejde.mah.un.edu fp ejde.mah.xsae.edu EXISTENCE OF NON-OSCILLATORY SOLUTIONS TO
STATE-SPACE MODELLING. A mass balance across the tank gives:
 B. Lennox and N.F. Thornhill, 9, Sae Space Modelling, IChemE Process Managemen and Conrol Subjec Group Newsleer STE-SPACE MODELLING Inroducion: Over he pas decade or so here has been an ever increasing
B. Lennox and N.F. Thornhill, 9, Sae Space Modelling, IChemE Process Managemen and Conrol Subjec Group Newsleer STE-SPACE MODELLING Inroducion: Over he pas decade or so here has been an ever increasing
DISCRETE GRONWALL LEMMA AND APPLICATIONS
 DISCRETE GRONWALL LEMMA AND APPLICATIONS JOHN M. HOLTE MAA NORTH CENTRAL SECTION MEETING AT UND 24 OCTOBER 29 Gronwall s lemma saes an inequaliy ha is useful in he heory of differenial equaions. Here is
DISCRETE GRONWALL LEMMA AND APPLICATIONS JOHN M. HOLTE MAA NORTH CENTRAL SECTION MEETING AT UND 24 OCTOBER 29 Gronwall s lemma saes an inequaliy ha is useful in he heory of differenial equaions. Here is
Supplement for Stochastic Convex Optimization: Faster Local Growth Implies Faster Global Convergence
 Supplemen for Sochasic Convex Opimizaion: Faser Local Growh Implies Faser Global Convergence Yi Xu Qihang Lin ianbao Yang Proof of heorem heorem Suppose Assumpion holds and F (w) obeys he LGC (6) Given
Supplemen for Sochasic Convex Opimizaion: Faser Local Growh Implies Faser Global Convergence Yi Xu Qihang Lin ianbao Yang Proof of heorem heorem Suppose Assumpion holds and F (w) obeys he LGC (6) Given
Bifurcation Analysis of a Stage-Structured Prey-Predator System with Discrete and Continuous Delays
 Applied Mahemaics 4 59-64 hp://dx.doi.org/.46/am..4744 Published Online July (hp://www.scirp.org/ournal/am) Bifurcaion Analysis of a Sage-Srucured Prey-Predaor Sysem wih Discree and Coninuous Delays Shunyi
Applied Mahemaics 4 59-64 hp://dx.doi.org/.46/am..4744 Published Online July (hp://www.scirp.org/ournal/am) Bifurcaion Analysis of a Sage-Srucured Prey-Predaor Sysem wih Discree and Coninuous Delays Shunyi
di Bernardo, M. (1995). A purely adaptive controller to synchronize and control chaotic systems.
 di ernardo, M. (995). A purely adapive conroller o synchronize and conrol chaoic sysems. hps://doi.org/.6/375-96(96)8-x Early version, also known as pre-prin Link o published version (if available):.6/375-96(96)8-x
di ernardo, M. (995). A purely adapive conroller o synchronize and conrol chaoic sysems. hps://doi.org/.6/375-96(96)8-x Early version, also known as pre-prin Link o published version (if available):.6/375-96(96)8-x
arxiv: v1 [math.gm] 4 Nov 2018
![arxiv: v1 [math.gm] 4 Nov 2018 arxiv: v1 [math.gm] 4 Nov 2018](/thumbs/91/104887155.jpg) Unpredicable Soluions of Linear Differenial Equaions Mara Akhme 1,, Mehme Onur Fen 2, Madina Tleubergenova 3,4, Akylbek Zhamanshin 3,4 1 Deparmen of Mahemaics, Middle Eas Technical Universiy, 06800, Ankara,
Unpredicable Soluions of Linear Differenial Equaions Mara Akhme 1,, Mehme Onur Fen 2, Madina Tleubergenova 3,4, Akylbek Zhamanshin 3,4 1 Deparmen of Mahemaics, Middle Eas Technical Universiy, 06800, Ankara,
Chapter 6. Systems of First Order Linear Differential Equations
 Chaper 6 Sysems of Firs Order Linear Differenial Equaions We will only discuss firs order sysems However higher order sysems may be made ino firs order sysems by a rick shown below We will have a sligh
Chaper 6 Sysems of Firs Order Linear Differenial Equaions We will only discuss firs order sysems However higher order sysems may be made ino firs order sysems by a rick shown below We will have a sligh
(1) (2) Differentiation of (1) and then substitution of (3) leads to. Therefore, we will simply consider the second-order linear system given by (4)
 Phase Plane Analysis of Linear Sysems Adaped from Applied Nonlinear Conrol by Sloine and Li The general form of a linear second-order sysem is a c b d From and b bc d a Differeniaion of and hen subsiuion
Phase Plane Analysis of Linear Sysems Adaped from Applied Nonlinear Conrol by Sloine and Li The general form of a linear second-order sysem is a c b d From and b bc d a Differeniaion of and hen subsiuion
A Primal-Dual Type Algorithm with the O(1/t) Convergence Rate for Large Scale Constrained Convex Programs
 PROC. IEEE CONFERENCE ON DECISION AND CONTROL, 06 A Primal-Dual Type Algorihm wih he O(/) Convergence Rae for Large Scale Consrained Convex Programs Hao Yu and Michael J. Neely Absrac This paper considers
PROC. IEEE CONFERENCE ON DECISION AND CONTROL, 06 A Primal-Dual Type Algorihm wih he O(/) Convergence Rae for Large Scale Consrained Convex Programs Hao Yu and Michael J. Neely Absrac This paper considers
Boundedness and Exponential Asymptotic Stability in Dynamical Systems with Applications to Nonlinear Differential Equations with Unbounded Terms
 Advances in Dynamical Sysems and Applicaions. ISSN 0973-531 Volume Number 1 007, pp. 107 11 Research India Publicaions hp://www.ripublicaion.com/adsa.hm Boundedness and Exponenial Asympoic Sabiliy in Dynamical
Advances in Dynamical Sysems and Applicaions. ISSN 0973-531 Volume Number 1 007, pp. 107 11 Research India Publicaions hp://www.ripublicaion.com/adsa.hm Boundedness and Exponenial Asympoic Sabiliy in Dynamical
CERTAIN CLASSES OF SOLUTIONS OF LAGERSTROM EQUATIONS
 SARAJEVO JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol.10 (22 (2014, 67 76 DOI: 10.5644/SJM.10.1.09 CERTAIN CLASSES OF SOLUTIONS OF LAGERSTROM EQUATIONS ALMA OMERSPAHIĆ AND VAHIDIN HADŽIABDIĆ Absrac. This paper presens sufficien
SARAJEVO JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol.10 (22 (2014, 67 76 DOI: 10.5644/SJM.10.1.09 CERTAIN CLASSES OF SOLUTIONS OF LAGERSTROM EQUATIONS ALMA OMERSPAHIĆ AND VAHIDIN HADŽIABDIĆ Absrac. This paper presens sufficien
Chapter 3 Boundary Value Problem
 Chaper 3 Boundary Value Problem A boundary value problem (BVP) is a problem, ypically an ODE or a PDE, which has values assigned on he physical boundary of he domain in which he problem is specified. Le
Chaper 3 Boundary Value Problem A boundary value problem (BVP) is a problem, ypically an ODE or a PDE, which has values assigned on he physical boundary of he domain in which he problem is specified. Le
Ordinary Differential Equations
 Ordinary Differenial Equaions 5. Examples of linear differenial equaions and heir applicaions We consider some examples of sysems of linear differenial equaions wih consan coefficiens y = a y +... + a
Ordinary Differenial Equaions 5. Examples of linear differenial equaions and heir applicaions We consider some examples of sysems of linear differenial equaions wih consan coefficiens y = a y +... + a
Multi-component Levi Hierarchy and Its Multi-component Integrable Coupling System
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 44 (2005) pp. 990 996 c Inernaional Academic Publishers Vol. 44, No. 6, December 5, 2005 uli-componen Levi Hierarchy and Is uli-componen Inegrable Coupling Sysem XIA
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 44 (2005) pp. 990 996 c Inernaional Academic Publishers Vol. 44, No. 6, December 5, 2005 uli-componen Levi Hierarchy and Is uli-componen Inegrable Coupling Sysem XIA
4. Advanced Stability Theory
 Applied Nonlinear Conrol Nguyen an ien - 4 4 Advanced Sabiliy heory he objecive of his chaper is o presen sabiliy analysis for non-auonomous sysems 41 Conceps of Sabiliy for Non-Auonomous Sysems Equilibrium
Applied Nonlinear Conrol Nguyen an ien - 4 4 Advanced Sabiliy heory he objecive of his chaper is o presen sabiliy analysis for non-auonomous sysems 41 Conceps of Sabiliy for Non-Auonomous Sysems Equilibrium
Hamilton- J acobi Equation: Weak S olution We continue the study of the Hamilton-Jacobi equation:
 M ah 5 7 Fall 9 L ecure O c. 4, 9 ) Hamilon- J acobi Equaion: Weak S oluion We coninue he sudy of he Hamilon-Jacobi equaion: We have shown ha u + H D u) = R n, ) ; u = g R n { = }. ). In general we canno
M ah 5 7 Fall 9 L ecure O c. 4, 9 ) Hamilon- J acobi Equaion: Weak S oluion We coninue he sudy of he Hamilon-Jacobi equaion: We have shown ha u + H D u) = R n, ) ; u = g R n { = }. ). In general we canno
Variational Iteration Method for Solving System of Fractional Order Ordinary Differential Equations
 IOSR Journal of Mahemaics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 2278-5728, p-issn: 2319-765X. Volume 1, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov - Dec. 214), PP 48-54 Variaional Ieraion Mehod for Solving Sysem of Fracional Order Ordinary Differenial
IOSR Journal of Mahemaics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 2278-5728, p-issn: 2319-765X. Volume 1, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov - Dec. 214), PP 48-54 Variaional Ieraion Mehod for Solving Sysem of Fracional Order Ordinary Differenial
u(x) = e x 2 y + 2 ) Integrate and solve for x (1 + x)y + y = cos x Answer: Divide both sides by 1 + x and solve for y. y = x y + cos x
 . 1 Mah 211 Homework #3 February 2, 2001 2.4.3. y + (2/x)y = (cos x)/x 2 Answer: Compare y + (2/x) y = (cos x)/x 2 wih y = a(x)x + f(x)and noe ha a(x) = 2/x. Consequenly, an inegraing facor is found wih
. 1 Mah 211 Homework #3 February 2, 2001 2.4.3. y + (2/x)y = (cos x)/x 2 Answer: Compare y + (2/x) y = (cos x)/x 2 wih y = a(x)x + f(x)and noe ha a(x) = 2/x. Consequenly, an inegraing facor is found wih
Course Notes for EE227C (Spring 2018): Convex Optimization and Approximation
 Course Noes for EE7C Spring 018: Convex Opimizaion and Approximaion Insrucor: Moriz Hard Email: hard+ee7c@berkeley.edu Graduae Insrucor: Max Simchowiz Email: msimchow+ee7c@berkeley.edu Ocober 15, 018 3
Course Noes for EE7C Spring 018: Convex Opimizaion and Approximaion Insrucor: Moriz Hard Email: hard+ee7c@berkeley.edu Graduae Insrucor: Max Simchowiz Email: msimchow+ee7c@berkeley.edu Ocober 15, 018 3
On Gronwall s Type Integral Inequalities with Singular Kernels
 Filoma 31:4 (217), 141 149 DOI 1.2298/FIL17441A Published by Faculy of Sciences and Mahemaics, Universiy of Niš, Serbia Available a: hp://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filoma On Gronwall s Type Inegral Inequaliies
Filoma 31:4 (217), 141 149 DOI 1.2298/FIL17441A Published by Faculy of Sciences and Mahemaics, Universiy of Niš, Serbia Available a: hp://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filoma On Gronwall s Type Inegral Inequaliies
Undetermined coefficients for local fractional differential equations
 Available online a www.isr-publicaions.com/jmcs J. Mah. Compuer Sci. 16 (2016), 140 146 Research Aricle Undeermined coefficiens for local fracional differenial equaions Roshdi Khalil a,, Mohammed Al Horani
Available online a www.isr-publicaions.com/jmcs J. Mah. Compuer Sci. 16 (2016), 140 146 Research Aricle Undeermined coefficiens for local fracional differenial equaions Roshdi Khalil a,, Mohammed Al Horani
Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics. Stability in cellular neural networks with a piecewise constant argument
 Journal of Compuaional and Applied Mahemaics 33 (00 365 373 Conens liss available a ScienceDirec Journal of Compuaional and Applied Mahemaics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locae/cam Sabiliy in cellular
Journal of Compuaional and Applied Mahemaics 33 (00 365 373 Conens liss available a ScienceDirec Journal of Compuaional and Applied Mahemaics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locae/cam Sabiliy in cellular
A Necessary and Sufficient Condition for the Solutions of a Functional Differential Equation to Be Oscillatory or Tend to Zero
 JOURNAL OF MAEMAICAL ANALYSIS AND APPLICAIONS 24, 7887 1997 ARICLE NO. AY965143 A Necessary and Sufficien Condiion for he Soluions of a Funcional Differenial Equaion o Be Oscillaory or end o Zero Piambar
JOURNAL OF MAEMAICAL ANALYSIS AND APPLICAIONS 24, 7887 1997 ARICLE NO. AY965143 A Necessary and Sufficien Condiion for he Soluions of a Funcional Differenial Equaion o Be Oscillaory or end o Zero Piambar
Predator - Prey Model Trajectories and the nonlinear conservation law
 Predaor - Prey Model Trajecories and he nonlinear conservaion law James K. Peerson Deparmen of Biological Sciences and Deparmen of Mahemaical Sciences Clemson Universiy Ocober 28, 213 Ouline Drawing Trajecories
Predaor - Prey Model Trajecories and he nonlinear conservaion law James K. Peerson Deparmen of Biological Sciences and Deparmen of Mahemaical Sciences Clemson Universiy Ocober 28, 213 Ouline Drawing Trajecories
Global Synchronization of Directed Networks with Fast Switching Topologies
 Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 52 (2009) pp. 1019 1924 c Chinese Physical Sociey and IOP Publishing Ld Vol. 52, No. 6, December 15, 2009 Global Synchronizaion of Direced Neworks wih Fas Swiching
Commun. Theor. Phys. (Beijing, China) 52 (2009) pp. 1019 1924 c Chinese Physical Sociey and IOP Publishing Ld Vol. 52, No. 6, December 15, 2009 Global Synchronizaion of Direced Neworks wih Fas Swiching
Optimality Conditions for Unconstrained Problems
 62 CHAPTER 6 Opimaliy Condiions for Unconsrained Problems 1 Unconsrained Opimizaion 11 Exisence Consider he problem of minimizing he funcion f : R n R where f is coninuous on all of R n : P min f(x) x
62 CHAPTER 6 Opimaliy Condiions for Unconsrained Problems 1 Unconsrained Opimizaion 11 Exisence Consider he problem of minimizing he funcion f : R n R where f is coninuous on all of R n : P min f(x) x
The Existence, Uniqueness and Stability of Almost Periodic Solutions for Riccati Differential Equation
 ISSN 1749-3889 (prin), 1749-3897 (online) Inernaional Journal of Nonlinear Science Vol.5(2008) No.1,pp.58-64 The Exisence, Uniqueness and Sailiy of Almos Periodic Soluions for Riccai Differenial Equaion
ISSN 1749-3889 (prin), 1749-3897 (online) Inernaional Journal of Nonlinear Science Vol.5(2008) No.1,pp.58-64 The Exisence, Uniqueness and Sailiy of Almos Periodic Soluions for Riccai Differenial Equaion
Oscillation of an Euler Cauchy Dynamic Equation S. Huff, G. Olumolode, N. Pennington, and A. Peterson
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE FOURTH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS May 4 7, 00, Wilmingon, NC, USA pp 0 Oscillaion of an Euler Cauchy Dynamic Equaion S Huff, G Olumolode,
PROCEEDINGS OF THE FOURTH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS May 4 7, 00, Wilmingon, NC, USA pp 0 Oscillaion of an Euler Cauchy Dynamic Equaion S Huff, G Olumolode,
Chapter 8 The Complete Response of RL and RC Circuits
 Chaper 8 The Complee Response of RL and RC Circuis Seoul Naional Universiy Deparmen of Elecrical and Compuer Engineering Wha is Firs Order Circuis? Circuis ha conain only one inducor or only one capacior
Chaper 8 The Complee Response of RL and RC Circuis Seoul Naional Universiy Deparmen of Elecrical and Compuer Engineering Wha is Firs Order Circuis? Circuis ha conain only one inducor or only one capacior
Existence of multiple positive periodic solutions for functional differential equations
 J. Mah. Anal. Appl. 325 (27) 1378 1389 www.elsevier.com/locae/jmaa Exisence of muliple posiive periodic soluions for funcional differenial equaions Zhijun Zeng a,b,,libi a, Meng Fan a a School of Mahemaics
J. Mah. Anal. Appl. 325 (27) 1378 1389 www.elsevier.com/locae/jmaa Exisence of muliple posiive periodic soluions for funcional differenial equaions Zhijun Zeng a,b,,libi a, Meng Fan a a School of Mahemaics
The L p -Version of the Generalized Bohl Perron Principle for Vector Equations with Infinite Delay
 Advances in Dynamical Sysems and Applicaions ISSN 973-5321, Volume 6, Number 2, pp. 177 184 (211) hp://campus.ms.edu/adsa The L p -Version of he Generalized Bohl Perron Principle for Vecor Equaions wih
Advances in Dynamical Sysems and Applicaions ISSN 973-5321, Volume 6, Number 2, pp. 177 184 (211) hp://campus.ms.edu/adsa The L p -Version of he Generalized Bohl Perron Principle for Vecor Equaions wih
MATH 5720: Gradient Methods Hung Phan, UMass Lowell October 4, 2018
 MATH 5720: Gradien Mehods Hung Phan, UMass Lowell Ocober 4, 208 Descen Direcion Mehods Consider he problem min { f(x) x R n}. The general descen direcions mehod is x k+ = x k + k d k where x k is he curren
MATH 5720: Gradien Mehods Hung Phan, UMass Lowell Ocober 4, 208 Descen Direcion Mehods Consider he problem min { f(x) x R n}. The general descen direcions mehod is x k+ = x k + k d k where x k is he curren
Research Article Further Stability Analysis of Time-Delay Systems with Nonlinear Perturbations
 Hindawi Mahemaical Problems in Engineering Volume 7, Aricle ID 594757, pages hps://doi.org/.55/7/594757 Research Aricle Furher Sabiliy Analysis of Time-Delay Sysems wih Nonlinear Perurbaions Jie Sun andjingzhang,3
Hindawi Mahemaical Problems in Engineering Volume 7, Aricle ID 594757, pages hps://doi.org/.55/7/594757 Research Aricle Furher Sabiliy Analysis of Time-Delay Sysems wih Nonlinear Perurbaions Jie Sun andjingzhang,3
L p -L q -Time decay estimate for solution of the Cauchy problem for hyperbolic partial differential equations of linear thermoelasticity
 ANNALES POLONICI MATHEMATICI LIV.2 99) L p -L q -Time decay esimae for soluion of he Cauchy problem for hyperbolic parial differenial equaions of linear hermoelasiciy by Jerzy Gawinecki Warszawa) Absrac.
ANNALES POLONICI MATHEMATICI LIV.2 99) L p -L q -Time decay esimae for soluion of he Cauchy problem for hyperbolic parial differenial equaions of linear hermoelasiciy by Jerzy Gawinecki Warszawa) Absrac.
d 1 = c 1 b 2 - b 1 c 2 d 2 = c 1 b 3 - b 1 c 3
 and d = c b - b c c d = c b - b c c This process is coninued unil he nh row has been compleed. The complee array of coefficiens is riangular. Noe ha in developing he array an enire row may be divided or
and d = c b - b c c d = c b - b c c This process is coninued unil he nh row has been compleed. The complee array of coefficiens is riangular. Noe ha in developing he array an enire row may be divided or
Technical Report Doc ID: TR March-2013 (Last revision: 23-February-2016) On formulating quadratic functions in optimization models.
 Technical Repor Doc ID: TR--203 06-March-203 (Las revision: 23-Februar-206) On formulaing quadraic funcions in opimizaion models. Auhor: Erling D. Andersen Convex quadraic consrains quie frequenl appear
Technical Repor Doc ID: TR--203 06-March-203 (Las revision: 23-Februar-206) On formulaing quadraic funcions in opimizaion models. Auhor: Erling D. Andersen Convex quadraic consrains quie frequenl appear
ODEs II, Lecture 1: Homogeneous Linear Systems - I. Mike Raugh 1. March 8, 2004
 ODEs II, Lecure : Homogeneous Linear Sysems - I Mike Raugh March 8, 4 Inroducion. In he firs lecure we discussed a sysem of linear ODEs for modeling he excreion of lead from he human body, saw how o ransform
ODEs II, Lecure : Homogeneous Linear Sysems - I Mike Raugh March 8, 4 Inroducion. In he firs lecure we discussed a sysem of linear ODEs for modeling he excreion of lead from he human body, saw how o ransform
An Introduction to Backward Stochastic Differential Equations (BSDEs) PIMS Summer School 2016 in Mathematical Finance.
 1 An Inroducion o Backward Sochasic Differenial Equaions (BSDEs) PIMS Summer School 2016 in Mahemaical Finance June 25, 2016 Chrisoph Frei cfrei@ualbera.ca This inroducion is based on Touzi [14], Bouchard
1 An Inroducion o Backward Sochasic Differenial Equaions (BSDEs) PIMS Summer School 2016 in Mahemaical Finance June 25, 2016 Chrisoph Frei cfrei@ualbera.ca This inroducion is based on Touzi [14], Bouchard
LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION
 CHBE320 LECTURE V LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dep. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 5-1 Road Map of he Lecure V Laplace Transform and Transfer funcions
CHBE320 LECTURE V LAPLACE TRANSFORM AND TRANSFER FUNCTION Professor Dae Ryook Yang Spring 2018 Dep. of Chemical and Biological Engineering 5-1 Road Map of he Lecure V Laplace Transform and Transfer funcions
dt = C exp (3 ln t 4 ). t 4 W = C exp ( ln(4 t) 3) = C(4 t) 3.
 Mah Rahman Exam Review Soluions () Consider he IVP: ( 4)y 3y + 4y = ; y(3) = 0, y (3) =. (a) Please deermine he longes inerval for which he IVP is guaraneed o have a unique soluion. Soluion: The disconinuiies
Mah Rahman Exam Review Soluions () Consider he IVP: ( 4)y 3y + 4y = ; y(3) = 0, y (3) =. (a) Please deermine he longes inerval for which he IVP is guaraneed o have a unique soluion. Soluion: The disconinuiies
Positive continuous solution of a quadratic integral equation of fractional orders
 Mah. Sci. Le., No., 9-7 (3) 9 Mahemaical Sciences Leers An Inernaional Journal @ 3 NSP Naural Sciences Publishing Cor. Posiive coninuous soluion of a quadraic inegral equaion of fracional orders A. M.
Mah. Sci. Le., No., 9-7 (3) 9 Mahemaical Sciences Leers An Inernaional Journal @ 3 NSP Naural Sciences Publishing Cor. Posiive coninuous soluion of a quadraic inegral equaion of fracional orders A. M.
Research Article Existence and Uniqueness of Periodic Solution for Nonlinear Second-Order Ordinary Differential Equations
 Hindawi Publishing Corporaion Boundary Value Problems Volume 11, Aricle ID 19156, 11 pages doi:1.1155/11/19156 Research Aricle Exisence and Uniqueness of Periodic Soluion for Nonlinear Second-Order Ordinary
Hindawi Publishing Corporaion Boundary Value Problems Volume 11, Aricle ID 19156, 11 pages doi:1.1155/11/19156 Research Aricle Exisence and Uniqueness of Periodic Soluion for Nonlinear Second-Order Ordinary
Intermittent Impulsive Synchronization of Chaotic Delayed Neural Networks
 Differ Equ Dyn Sys (Jan&Apr ) 9(&):9 69 DOI.7/s59--8-8 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Inermien Impulsive Synchronizaion of Chaoic Delayed Neural Neworks Xinzhi Liu Xuemin Shen Hongao Zhang Published online: April Foundaion
Differ Equ Dyn Sys (Jan&Apr ) 9(&):9 69 DOI.7/s59--8-8 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Inermien Impulsive Synchronizaion of Chaoic Delayed Neural Neworks Xinzhi Liu Xuemin Shen Hongao Zhang Published online: April Foundaion
Anti-Disturbance Control for Multiple Disturbances
 Workshop a 3 ACC Ani-Disurbance Conrol for Muliple Disurbances Lei Guo (lguo@buaa.edu.cn) Naional Key Laboraory on Science and Technology on Aircraf Conrol, Beihang Universiy, Beijing, 9, P.R. China. Presened
Workshop a 3 ACC Ani-Disurbance Conrol for Muliple Disurbances Lei Guo (lguo@buaa.edu.cn) Naional Key Laboraory on Science and Technology on Aircraf Conrol, Beihang Universiy, Beijing, 9, P.R. China. Presened
SUFFICIENT CONDITIONS FOR EXISTENCE SOLUTION OF LINEAR TWO-POINT BOUNDARY PROBLEM IN MINIMIZATION OF QUADRATIC FUNCTIONAL
 HE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF HE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Series A, OF HE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volume, Number 4/200, pp 287 293 SUFFICIEN CONDIIONS FOR EXISENCE SOLUION OF LINEAR WO-POIN BOUNDARY PROBLEM IN
HE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF HE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Series A, OF HE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volume, Number 4/200, pp 287 293 SUFFICIEN CONDIIONS FOR EXISENCE SOLUION OF LINEAR WO-POIN BOUNDARY PROBLEM IN
Solutions to Assignment 1
 MA 2326 Differenial Equaions Insrucor: Peronela Radu Friday, February 8, 203 Soluions o Assignmen. Find he general soluions of he following ODEs: (a) 2 x = an x Soluion: I is a separable equaion as we
MA 2326 Differenial Equaions Insrucor: Peronela Radu Friday, February 8, 203 Soluions o Assignmen. Find he general soluions of he following ODEs: (a) 2 x = an x Soluion: I is a separable equaion as we
THE GENERALIZED PASCAL MATRIX VIA THE GENERALIZED FIBONACCI MATRIX AND THE GENERALIZED PELL MATRIX
 J Korean Mah Soc 45 008, No, pp 479 49 THE GENERALIZED PASCAL MATRIX VIA THE GENERALIZED FIBONACCI MATRIX AND THE GENERALIZED PELL MATRIX Gwang-yeon Lee and Seong-Hoon Cho Reprined from he Journal of he
J Korean Mah Soc 45 008, No, pp 479 49 THE GENERALIZED PASCAL MATRIX VIA THE GENERALIZED FIBONACCI MATRIX AND THE GENERALIZED PELL MATRIX Gwang-yeon Lee and Seong-Hoon Cho Reprined from he Journal of he
Math 334 Fall 2011 Homework 11 Solutions
 Dec. 2, 2 Mah 334 Fall 2 Homework Soluions Basic Problem. Transform he following iniial value problem ino an iniial value problem for a sysem: u + p()u + q() u g(), u() u, u () v. () Soluion. Le v u. Then
Dec. 2, 2 Mah 334 Fall 2 Homework Soluions Basic Problem. Transform he following iniial value problem ino an iniial value problem for a sysem: u + p()u + q() u g(), u() u, u () v. () Soluion. Le v u. Then
6.2 Transforms of Derivatives and Integrals.
 SEC. 6.2 Transforms of Derivaives and Inegrals. ODEs 2 3 33 39 23. Change of scale. If l( f ()) F(s) and c is any 33 45 APPLICATION OF s-shifting posiive consan, show ha l( f (c)) F(s>c)>c (Hin: In Probs.
SEC. 6.2 Transforms of Derivaives and Inegrals. ODEs 2 3 33 39 23. Change of scale. If l( f ()) F(s) and c is any 33 45 APPLICATION OF s-shifting posiive consan, show ha l( f (c)) F(s>c)>c (Hin: In Probs.
Section 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equations; Method of Undetermined Coefficients
 Secion 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equaions; Mehod of Undeermined Coefficiens Key Terms/Ideas: Linear Differenial operaor Nonlinear operaor Second order homogeneous DE Second order nonhomogeneous DE Soluion o homogeneous
Secion 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equaions; Mehod of Undeermined Coefficiens Key Terms/Ideas: Linear Differenial operaor Nonlinear operaor Second order homogeneous DE Second order nonhomogeneous DE Soluion o homogeneous
Delay and Its Time-Derivative Dependent Stable Criterion for Differential-Algebraic Systems
 Applied Maemaics 6 7 4- Publised Online June 6 in SciRes p://wwwscirporg/journal/am p://dxdoiorg/46/am67 Delay and Is ime-derivaive Dependen Sable Crierion for Differenial-Algebraic Sysems Hui Liu Yucai
Applied Maemaics 6 7 4- Publised Online June 6 in SciRes p://wwwscirporg/journal/am p://dxdoiorg/46/am67 Delay and Is ime-derivaive Dependen Sable Crierion for Differenial-Algebraic Sysems Hui Liu Yucai
arxiv: v1 [math.fa] 9 Dec 2018
![arxiv: v1 [math.fa] 9 Dec 2018 arxiv: v1 [math.fa] 9 Dec 2018](/thumbs/95/124071290.jpg) AN INVERSE FUNCTION THEOREM CONVERSE arxiv:1812.03561v1 [mah.fa] 9 Dec 2018 JIMMIE LAWSON Absrac. We esablish he following converse of he well-known inverse funcion heorem. Le g : U V and f : V U be inverse
AN INVERSE FUNCTION THEOREM CONVERSE arxiv:1812.03561v1 [mah.fa] 9 Dec 2018 JIMMIE LAWSON Absrac. We esablish he following converse of he well-known inverse funcion heorem. Le g : U V and f : V U be inverse
Solutions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Math 246, Spring 2011, Professor David Levermore
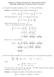 Soluions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Mah 6, Spring, Professor David Levermore Compue he Laplace ransform of f e from is definiion Soluion The definiion of he Laplace ransform gives L[f]s
Soluions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Mah 6, Spring, Professor David Levermore Compue he Laplace ransform of f e from is definiion Soluion The definiion of he Laplace ransform gives L[f]s
2. Nonlinear Conservation Law Equations
 . Nonlinear Conservaion Law Equaions One of he clear lessons learned over recen years in sudying nonlinear parial differenial equaions is ha i is generally no wise o ry o aack a general class of nonlinear
. Nonlinear Conservaion Law Equaions One of he clear lessons learned over recen years in sudying nonlinear parial differenial equaions is ha i is generally no wise o ry o aack a general class of nonlinear
An Invariance for (2+1)-Extension of Burgers Equation and Formulae to Obtain Solutions of KP Equation
 Commun Theor Phys Beijing, China 43 2005 pp 591 596 c Inernaional Academic Publishers Vol 43, No 4, April 15, 2005 An Invariance for 2+1-Eension of Burgers Equaion Formulae o Obain Soluions of KP Equaion
Commun Theor Phys Beijing, China 43 2005 pp 591 596 c Inernaional Academic Publishers Vol 43, No 4, April 15, 2005 An Invariance for 2+1-Eension of Burgers Equaion Formulae o Obain Soluions of KP Equaion
Physics 235 Chapter 2. Chapter 2 Newtonian Mechanics Single Particle
 Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Chaper 2 Newonian Mechanics Single Paricle In his Chaper we will review wha Newon s laws of mechanics ell us abou he moion of a single paricle. Newon s laws are only valid in suiable reference frames,
Pade and Laguerre Approximations Applied. to the Active Queue Management Model. of Internet Protocol
 Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 7, 013, no. 16, 663-673 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikari.com hp://dx.doi.org/10.1988/ams.013.39499 Pade and Laguerre Approximaions Applied o he Acive Queue Managemen Model of Inerne
Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 7, 013, no. 16, 663-673 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikari.com hp://dx.doi.org/10.1988/ams.013.39499 Pade and Laguerre Approximaions Applied o he Acive Queue Managemen Model of Inerne
Properties Of Solutions To A Generalized Liénard Equation With Forcing Term
 Applied Mahemaics E-Noes, 8(28), 4-44 c ISSN 67-25 Available free a mirror sies of hp://www.mah.nhu.edu.w/ amen/ Properies Of Soluions To A Generalized Liénard Equaion Wih Forcing Term Allan Kroopnick
Applied Mahemaics E-Noes, 8(28), 4-44 c ISSN 67-25 Available free a mirror sies of hp://www.mah.nhu.edu.w/ amen/ Properies Of Soluions To A Generalized Liénard Equaion Wih Forcing Term Allan Kroopnick
Sliding Mode Controller for Unstable Systems
 S. SIVARAMAKRISHNAN e al., Sliding Mode Conroller for Unsable Sysems, Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 22 (1) 41 47 (28) 41 Sliding Mode Conroller for Unsable Sysems S. Sivaramakrishnan, A. K. Tangirala, and M.
S. SIVARAMAKRISHNAN e al., Sliding Mode Conroller for Unsable Sysems, Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 22 (1) 41 47 (28) 41 Sliding Mode Conroller for Unsable Sysems S. Sivaramakrishnan, A. K. Tangirala, and M.
MATH 128A, SUMMER 2009, FINAL EXAM SOLUTION
 MATH 28A, SUMME 2009, FINAL EXAM SOLUTION BENJAMIN JOHNSON () (8 poins) [Lagrange Inerpolaion] (a) (4 poins) Le f be a funcion defined a some real numbers x 0,..., x n. Give a defining equaion for he Lagrange
MATH 28A, SUMME 2009, FINAL EXAM SOLUTION BENJAMIN JOHNSON () (8 poins) [Lagrange Inerpolaion] (a) (4 poins) Le f be a funcion defined a some real numbers x 0,..., x n. Give a defining equaion for he Lagrange
POSITIVE AND MONOTONE SYSTEMS IN A PARTIALLY ORDERED SPACE
 Urainian Mahemaical Journal, Vol. 55, No. 2, 2003 POSITIVE AND MONOTONE SYSTEMS IN A PARTIALLY ORDERED SPACE A. G. Mazo UDC 517.983.27 We invesigae properies of posiive and monoone differenial sysems wih
Urainian Mahemaical Journal, Vol. 55, No. 2, 2003 POSITIVE AND MONOTONE SYSTEMS IN A PARTIALLY ORDERED SPACE A. G. Mazo UDC 517.983.27 We invesigae properies of posiive and monoone differenial sysems wih
Robust Stability and Stabilization for Singular Systems With State Delay and Parameter Uncertainty
 11 IEEE RANSACIONS ON AUOMAIC CONROL, VOL. 47, NO. 7, JULY Now, we choose 8= 1; ; 1 9= 19; 5 5; 7 he corresponding Riccai equaion (13) admis he maximal soluion 5= 1; ; 7 : By heorem 2, all opimal conrols
11 IEEE RANSACIONS ON AUOMAIC CONROL, VOL. 47, NO. 7, JULY Now, we choose 8= 1; ; 1 9= 19; 5 5; 7 he corresponding Riccai equaion (13) admis he maximal soluion 5= 1; ; 7 : By heorem 2, all opimal conrols
Differential Harnack Estimates for Parabolic Equations
 Differenial Harnack Esimaes for Parabolic Equaions Xiaodong Cao and Zhou Zhang Absrac Le M,g be a soluion o he Ricci flow on a closed Riemannian manifold In his paper, we prove differenial Harnack inequaliies
Differenial Harnack Esimaes for Parabolic Equaions Xiaodong Cao and Zhou Zhang Absrac Le M,g be a soluion o he Ricci flow on a closed Riemannian manifold In his paper, we prove differenial Harnack inequaliies
T L. t=1. Proof of Lemma 1. Using the marginal cost accounting in Equation(4) and standard arguments. t )+Π RB. t )+K 1(Q RB
 Elecronic Companion EC.1. Proofs of Technical Lemmas and Theorems LEMMA 1. Le C(RB) be he oal cos incurred by he RB policy. Then we have, T L E[C(RB)] 3 E[Z RB ]. (EC.1) Proof of Lemma 1. Using he marginal
Elecronic Companion EC.1. Proofs of Technical Lemmas and Theorems LEMMA 1. Le C(RB) be he oal cos incurred by he RB policy. Then we have, T L E[C(RB)] 3 E[Z RB ]. (EC.1) Proof of Lemma 1. Using he marginal
Hyperchaos Synchronization Between two Different Hyperchaotic Systems
 ISSN 76-769, England, UK Journal of Informaion and Compuing Science Vo3, No., 8, pp. 73-8 Hperchaos Snchroniaion Beween wo Differen Hperchaoic Ssems Qiang Jia + Facul of Science, Jiangsu Universi, Zhenjiang,
ISSN 76-769, England, UK Journal of Informaion and Compuing Science Vo3, No., 8, pp. 73-8 Hperchaos Snchroniaion Beween wo Differen Hperchaoic Ssems Qiang Jia + Facul of Science, Jiangsu Universi, Zhenjiang,
Essential Maps and Coincidence Principles for General Classes of Maps
 Filoma 31:11 (2017), 3553 3558 hps://doi.org/10.2298/fil1711553o Published by Faculy of Sciences Mahemaics, Universiy of Niš, Serbia Available a: hp://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filoma Essenial Maps Coincidence
Filoma 31:11 (2017), 3553 3558 hps://doi.org/10.2298/fil1711553o Published by Faculy of Sciences Mahemaics, Universiy of Niš, Serbia Available a: hp://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filoma Essenial Maps Coincidence
An introduction to the theory of SDDP algorithm
 An inroducion o he heory of SDDP algorihm V. Leclère (ENPC) Augus 1, 2014 V. Leclère Inroducion o SDDP Augus 1, 2014 1 / 21 Inroducion Large scale sochasic problem are hard o solve. Two ways of aacking
An inroducion o he heory of SDDP algorihm V. Leclère (ENPC) Augus 1, 2014 V. Leclère Inroducion o SDDP Augus 1, 2014 1 / 21 Inroducion Large scale sochasic problem are hard o solve. Two ways of aacking
EXERCISES FOR SECTION 1.5
 1.5 Exisence and Uniqueness of Soluions 43 20. 1 v c 21. 1 v c 1 2 4 6 8 10 1 2 2 4 6 8 10 Graph of approximae soluion obained using Euler s mehod wih = 0.1. Graph of approximae soluion obained using Euler
1.5 Exisence and Uniqueness of Soluions 43 20. 1 v c 21. 1 v c 1 2 4 6 8 10 1 2 2 4 6 8 10 Graph of approximae soluion obained using Euler s mehod wih = 0.1. Graph of approximae soluion obained using Euler
Solution of Integro-Differential Equations by Using ELzaki Transform
 Global Journal of Mahemaical Sciences: Theory and Pracical. Volume, Number (), pp. - Inernaional Research Publicaion House hp://www.irphouse.com Soluion of Inegro-Differenial Equaions by Using ELzaki Transform
Global Journal of Mahemaical Sciences: Theory and Pracical. Volume, Number (), pp. - Inernaional Research Publicaion House hp://www.irphouse.com Soluion of Inegro-Differenial Equaions by Using ELzaki Transform
Example on p. 157
 Example 2.5.3. Le where BV [, 1] = Example 2.5.3. on p. 157 { g : [, 1] C g() =, g() = g( + ) [, 1), var (g) = sup g( j+1 ) g( j ) he supremum is aken over all he pariions of [, 1] (1) : = < 1 < < n =
Example 2.5.3. Le where BV [, 1] = Example 2.5.3. on p. 157 { g : [, 1] C g() =, g() = g( + ) [, 1), var (g) = sup g( j+1 ) g( j ) he supremum is aken over all he pariions of [, 1] (1) : = < 1 < < n =
Finish reading Chapter 2 of Spivak, rereading earlier sections as necessary. handout and fill in some missing details!
 MAT 257, Handou 6: Ocober 7-2, 20. I. Assignmen. Finish reading Chaper 2 of Spiva, rereading earlier secions as necessary. handou and fill in some missing deails! II. Higher derivaives. Also, read his
MAT 257, Handou 6: Ocober 7-2, 20. I. Assignmen. Finish reading Chaper 2 of Spiva, rereading earlier secions as necessary. handou and fill in some missing deails! II. Higher derivaives. Also, read his
EECE251. Circuit Analysis I. Set 4: Capacitors, Inductors, and First-Order Linear Circuits
 EEE25 ircui Analysis I Se 4: apaciors, Inducors, and Firs-Order inear ircuis Shahriar Mirabbasi Deparmen of Elecrical and ompuer Engineering Universiy of Briish olumbia shahriar@ece.ubc.ca Overview Passive
EEE25 ircui Analysis I Se 4: apaciors, Inducors, and Firs-Order inear ircuis Shahriar Mirabbasi Deparmen of Elecrical and ompuer Engineering Universiy of Briish olumbia shahriar@ece.ubc.ca Overview Passive
Orthogonal Rational Functions, Associated Rational Functions And Functions Of The Second Kind
 Proceedings of he World Congress on Engineering 2008 Vol II Orhogonal Raional Funcions, Associaed Raional Funcions And Funcions Of The Second Kind Karl Deckers and Adhemar Bulheel Absrac Consider he sequence
Proceedings of he World Congress on Engineering 2008 Vol II Orhogonal Raional Funcions, Associaed Raional Funcions And Funcions Of The Second Kind Karl Deckers and Adhemar Bulheel Absrac Consider he sequence
OSCILLATION OF SECOND-ORDER DELAY AND NEUTRAL DELAY DYNAMIC EQUATIONS ON TIME SCALES
 Dynamic Sysems and Applicaions 6 (2007) 345-360 OSCILLATION OF SECOND-ORDER DELAY AND NEUTRAL DELAY DYNAMIC EQUATIONS ON TIME SCALES S. H. SAKER Deparmen of Mahemaics and Saisics, Universiy of Calgary,
Dynamic Sysems and Applicaions 6 (2007) 345-360 OSCILLATION OF SECOND-ORDER DELAY AND NEUTRAL DELAY DYNAMIC EQUATIONS ON TIME SCALES S. H. SAKER Deparmen of Mahemaics and Saisics, Universiy of Calgary,
GRADIENT ESTIMATES FOR A SIMPLE PARABOLIC LICHNEROWICZ EQUATION. Osaka Journal of Mathematics. 51(1) P.245-P.256
 Tile Auhor(s) GRADIENT ESTIMATES FOR A SIMPLE PARABOLIC LICHNEROWICZ EQUATION Zhao, Liang Ciaion Osaka Journal of Mahemaics. 51(1) P.45-P.56 Issue Dae 014-01 Tex Version publisher URL hps://doi.org/10.18910/9195
Tile Auhor(s) GRADIENT ESTIMATES FOR A SIMPLE PARABOLIC LICHNEROWICZ EQUATION Zhao, Liang Ciaion Osaka Journal of Mahemaics. 51(1) P.45-P.56 Issue Dae 014-01 Tex Version publisher URL hps://doi.org/10.18910/9195
Recursive Least-Squares Fixed-Interval Smoother Using Covariance Information based on Innovation Approach in Linear Continuous Stochastic Systems
 8 Froniers in Signal Processing, Vol. 1, No. 1, July 217 hps://dx.doi.org/1.2266/fsp.217.112 Recursive Leas-Squares Fixed-Inerval Smooher Using Covariance Informaion based on Innovaion Approach in Linear
8 Froniers in Signal Processing, Vol. 1, No. 1, July 217 hps://dx.doi.org/1.2266/fsp.217.112 Recursive Leas-Squares Fixed-Inerval Smooher Using Covariance Informaion based on Innovaion Approach in Linear
