L p -L q -Time decay estimate for solution of the Cauchy problem for hyperbolic partial differential equations of linear thermoelasticity
|
|
|
- Melissa Harmon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ANNALES POLONICI MATHEMATICI LIV.2 99) L p -L q -Time decay esimae for soluion of he Cauchy problem for hyperbolic parial differenial equaions of linear hermoelasiciy by Jerzy Gawinecki Warszawa) Absrac. We prove he L p -L q -ime decay esimaes for he soluion of he Cauchy problem for he hyperbolic sysem of parial differenial equaions of linear hermoelasiciy. In our proof based on he marix of fundamenal soluions o he sysem we use Srauss Klainerman s approach 2, 5 o he L p -L q -ime decay esimaes. 0. Inroducion. We consider he Cauchy problem for he hyperbolic sysem of parial differenial equaions of linear hermoelasiciy cf. 3): 0.) 0.2) ρ 2 u µ u λ + µ) grad div u + β grad T = 0, β div u + ρτ 2 T k T = 0, wih iniial condiions u+0, x) = u 0 x), 0.3) T +0, x) = T 0 x), u)+0, x) = u x) T )+0, x) = T x) where u = u, u 2, u 3 ) is he displacemen vecor field of he medium, T he emperaure of he medium, 0, x R 3, = /, = 3 j= 2 j ; ρ, µ, λ, β, τ, k are posiive physical consans; u 0, u, T 0, T are given funcions. R e m a r k 0.. The sysem 0.) 0.2) is he principal par of a hyperbolic sysem of parial differenial equaions describing he evoluion of a hermoelasic medium cf. E. S. Suhubi 3, p. 99, formulae )). For he sake of simpliciy we assume in sysem ) ha γ = and T 0 =. Under he assumpion ha he Cauchy daa u 0, u, T 0, T are smooh enough cf. 4, formulae 5.) 5.3)) he soluion of he problem 0.) 0.3) 985 Mahemaics Subjec Classificaion: 35A07, 35A08, 35E05, 35E5, 35L5, 35L40, 35L45, 73B30, 35B40. Key words and phrases: decay esimaes, parial differenial equaions, Cauchy problem, symmeric hyperbolic sysem of firs order, linear hermoelasiciy.
2 36 J. Gawinecki is given by 0.4) U, x) = u, x), T, x)) = H, ) gx) + H, ) hx) where g ) = g ) + D ) h ), gx) = u x), T x)), hx) = u 0 x), T 0 x)), β β D ) = 2, β 3 β β 2 β 3 0 denoes he hree-dimensional convoluion in R 3 and H, x) is he marix of fundamenal soluions of he sysem 0.) 0.2) consruced in 4 of he form 0.5) H jk, x) A = 32π7!ρ 4 τ) {δ jk δ k4 ) A 2 2 x δ x ) B b 2 x δ A3 + δ jk δ k4 x δ x ) A5 x j x k + δ jj δ k4 ) x 3 δ x x δ x b A 4 2 x x x δ ) ) ) x ) A ) 6 x j x k 2 x 3 δ + B x j x k b 2 x 3 δ x ) b δ jj δ k4 ) A 7 x 3 3x ) jx k x 5 ε x ) ε x ) + A 8 x 3 3x ) jx k x 5 ε x ) ε x ) b + A 9 x 3 3x ) jx k x 5 ε x ) ε x ) b x j + A 0 x 3 ε x ) ε x ) δ 4j δ kj ) x j + A 0 x 2 δ x ) δ x ) } δ 4j δ kj ), j, k =, 2, 3, 4, where δ jk denoes he Kronecker symbol, δ ) is Dirac s disribuion, ε ) is Heaviside s funcion { for > 0, ε) = 0 for < 0,
3 L p -L q -Time decay esimae 37 and,, b, A,..., A 0, B are consans. The aim of his paper is o prove he L -L -ime decay esimaes for he soluion of he problem 0.) 0.3) using he formula 0.4), hen o prove he L 2 -L 2 -ime decay esimaes for his soluion applying some heorems of he heory of symmeric firs order hyperbolic sysems cf. Yu. V. Egorov 3, p ) and finally he L p -L q -ime decay esimaes using inerpolaion inequaliies in Sobolev spaces cf. 0, 7, 4). Such L p -L q -ime decay esimaes play an imporan role in he proof of global in ime) exisence of soluion o he Cauchy problem for nonlinear wave equaions cf. 5, 7). Noaion: Besides oher sandard noaion we use he symbol L p,mr 3 ) = W m,p R 3 ) p, m N {0}) for he well-known Sobolev spaces wih norm L p,m R 3 ) = W m,p R 3 ) cf., ); W 0,p R 3 ) = L p R 3 ) wih norm L p R 3 ). We also wrie f = f, x f, x2 f, x3 f) for he space-ime gradien of a funcion f, and Df = x f, x2 f, x3 f) for he space gradien of f. s denoes he smalles ineger larger han or equal o s for s R.. The L -L -ime decay esimaes. We shall prove he following heorem: Theorem. L -L -ime decay esimaes). Le he Cauchy daa u 0, u, T 0, T be funcions vanishing a infiniy. Moreover, le u, Du 0, T, DT 0 ) L R 3 ). Then he soluion u, T ) of he problem 0.) 0.3) given by he formula 0.4) saisfies he following esimaes:.).2) u, ), T, )) L R 3 ) C + ) u, Du 0, T, DT 0 ) L R 3 ), u, ), T, )) L R 3 ) C + ) u, Du 0, T, DT 0 ) L R 3 ) for 0, where C is a consan independen of u 0, u, T 0, T and. P r o o f. We prove.2). The proof of.) runs in he same way. Wriing he soluion U, x) = u, x), T, x)) given by he formula 0.4) in he form.3) U j, x) = H jk, ) g k x) + H jk, ) h k x), k= k=
4 38 J. Gawinecki j =, 2, 3, 4, where U j, x) = u j, x), j =, 2, 3, U 4, x) = T, x), and differeniaing.3) wih respec o and x l for l =, 2, 3) we ge.4).5).6) U j, x) = U 4, x) = l U j, x) = H jk, ) g k x) k= + k= l= k= 3 µ ρ lh jk, ) + λ + µ j H lk, ) ρ β ρ H jk, ) h k j x), j =, 2, 3, H 4k, ) g k x) k= + 3 k= l= 3 k= l= k ρ lh 4k, ) h k l x) β ρ H lk, ) h k l x), l H jk, ) g k x) + k= h k l x) H jk, ) h k l x), l =, 2, 3, j =, 2, 3, 4, h k m = xm hk, m =, 2, 3. We can wrie.4).6) in vecor form as follows: k=.7) V, x) = R, ) V 0 x) where.8) V, x) = u, T ), V 0 x) = u, Du 0, T, DT 0 ) and R, x) is 6 6 marix wih elemens which are linear combinaions of he erms l H jk, x) and H jk, x) cf..3).6)). From.3).6) and.7) i follows ha in order o prove he esimae.2) i is sufficien o prove he following esimaes:.9).0) H jk, ) f L R 3 ) C + ) f L R 3 ), l H jk, ) f L R 3 ) C + ) f L R 3 ) for j, k =, 2, 3, 4 and any scalar funcion fx) saisfying he assumpions of Theorem.. Taking ino accoun he form of he marix H, x) cf. 0.5)) we ge.) H jk, ) fx)
5 = 32π7! ρ 4 τ) {δ A jk δ k4 ) A 2 + δ jk δ k4 A3 L p -L q -Time decay esimae 39 z = fx + z) ds z fx + z) ds z B b b fx + z) ds z z = z =b fx + z) ds z A 4 fx + z) ds z z = z = A5 + δ jj δ k4 ) z jz k a 3 z =a fx + z) ds z A 6 z jz k a 3 fx + z) ds z + B z =a 2 b 2 z =b δ jj δ k4 ) A 7 z 3 3z jz k z 5 z + A 8 z 3 3z ) jz k z 5 fx + z) dz b z b z + A 9 z 3 3z jz k z 5 ) fx + z) dz z j + δ 4j δ kj )A 0 fx + z) dz z 3 a z + δ 4j δ kj )A 0 z j fx + z) ds z z =a z } j fx + z) ds z z =a 2 2 z jz k b 3 fx + z) ds z ) fx + z) dz where ds z is he area elemen of he sphere z = a j, j =, 2, or of z = b. For simpliciy we consider wo ypical inegrals occurring on he righ hand side of.) oher inegrals in.) are esimaed similarly):.2).3) I = I 2 = fx + y) ds y, fx + y) y 3 dy. Differeniaing he inegrals I and I 2 wih respec o and x l l =, 2, 3)
6 40 J. Gawinecki we obain ).4).5).6).7) I = I 2 = I x l = I 2 x l = fx + y) ds y + fx + y) y 3 dy + xl fx + y) ds y, fx + y) ds y, y 3 x l fx + y) dy. Following S. Klainerman cf. 5, pp ) we ge.8).9) fx + y) = = 2 fx + y) = In view of.8),.9) we have.20) I = = s fx + sy) ds = s ) 2 3 s fx + sy) ds, 2 s fx + sy) ds = for > 0. Taking ino accoun ha.2) s 2 3 fx + sy) = s ) 2 s fx + sy) ds ds y j,k= y 3 fx + y) dy, 2 s fx + sy) ds ds y s ) 2 s fx + sy) ds s ) 2 s fx + sy) ds ds y 2 2 s fx + sy) ds ds y s ) 3 s fx + sy) ds. 2 x j x k fx + sy)y j y k 2 b2 D 2 xfx + sy) ) We use he noaion I j = I j, li j = I j x l, j =, 2.
7 L p -L q -Time decay esimae 4 for y = b and s ) s 2, 2 s 2 for 0 s we ge.22) I b 2 s 2 Dxfx 2 + sy) ds ds y. Using he spherical coordinaes we have.23) I b D 2 xf L R 3 ) for > 0. Acing in he same way we ge.24) Ix l = Since s xl fx + sy) = we have.25) Similarly.26).27) s xl fx + sy) ds ds y. 3 x 2 l x j fx + sy)y j b D 2 x fx + sy) j= I x l b I 2 b 3 b 3 s 2 D 2 xfx + sy) ds ds y D 2 xf L R 3 ) for > 0. fx + y) dy + fx + y) dy + a I 2 x l b 3 fx + y) dy D xfx + y) dy. for y = b Dxfx + y) dy, Changing he variable y o z in he above inegrals we derive.28) I 2 b 3 3 fx + z) dz.29) + a 2 b z a b z a Dxfx + z) dz b 3 3 f L R 3 ) + a 2 D xf L R 3 ) I 2 x l b 3 2 b z a, Dxfx + z) dz b 3 2 D xf L R 3 ).
8 42 J. Gawinecki Noing ha / 3 / 2 / for we ge.30) I 2 + I 2 x l C D xf L R 3 ) for. From.23),.25),.30) we obain.3) H jk, ) f ) L R 3 ) C f L,2 R 3 ) for 0 and j, k =, 2, 3, 4. In order o obain an esimae analogous o.30) for 0 we proceed as above expressing he inegrals I and I 2 cf..8),.9)) in he following form:.32).33) I = 2 I x l = + Afer some calculaions we ge s ) 2 3 s fx + sy) ds ds y s ) 3 s fx + sy) ds ds y, s ) 2 s xl fx + sy) ds ds y..34) I + I x l C f L R 3 ) for 0. I is easy o see ha for 0 fx + y).35) y 3 dy b 3 b 3 f L R 3 ), fx + y) dy.36) fx + y) y 3 dy b 3 j= 3 xj fx + y)y j dy b 3 a D xf L R 3 ),.37) y 3 x l fx + y) dy b 3 xl fx + y) dy b 3 D xf L R 3 ).
9 L p -L q -Time decay esimae 43 Hence.38) I 2 + I 2 x l C f L, R 3 ) for 0. Thus from.38) and.34) we obain.39) H jk, ) f ) L R 3 ) C f L R 3 ) for 0. Now, in view of 2 + ) for 0 and 2 + ) for and aking ino accoun.3),.39) we conclude ha.40) H jk, ) f ) L R 3 ) C + ) f L R 3 ) for The L 2 -L 2 -ime decay esimaes. We derive he L 2 -L 2 -ime decay esimaes for soluion of he Cauchy problem 0.) 0.3). More precisely, we formulae he following heorem: Theorem 2. L 2 -L 2 -ime decay esimaes). Le he Cauchy daa u 0, u, T 0, T be funcions vanishing a infiniy. Moreover, le u, Du 0, T, DT 0 ) L 2 R 3 ). Then he soluion u, T ) of he problem 0.) 0.3) given by he formula 0.4) saisfies he following esimaes: 2.) 2.2) u, ), T, )) L2 R 3 ) u, ), T, )) L 2 R 3 ) C u, Du 0, T, DT 0 ) L 2 R 3 ) for 0, C u, Du 0, T, DT 0 ) L 2 R 3 ) for 0, where C is consan independen of u 0, u, T 0, T and. S k e c h o f p r o o f. Following Yu. V. Egorov cf. 3, pp , ) we reduce he Cauchy problem 0.) 0.3) o an equivalen Cauchy problem for a linear symmeric hyperbolic sysem of firs order. Nex, applying he exisence and uniqueness heorems cf. 3, Theorem 3.2, p. 329) we obain he esimaes 2.), 2.2). 3. The L p -L q -ime decay esimaes. In his secion we express he L p -L q -ime decay esimaes for soluions of he Cauchy problem 0.) 0.3) in erms of heir gradien. We consider he operaor Π defined as follows: 3.) Π fx) = R, ) fx) for any funcion fx) saisfying he assumpions of Theorems. and 2., where R, x) is defined by.7).
10 44 J. Gawinecki 3.2) 3.3) From Theorems. and 2. i follows ha Π 0 :L R 3 ) L R 3 ), Π 0 C + ), Π : L 2 R 3 ) L 2 R 3 ), Π C. By inerpolaion cf. J. Shaah 0, S. Klainerman and G. Ponce 7) we have 3.4) Π θ : L, L 2 θ L, L 2 θ, Π θ = Π 0 θ Π θ wih 0 θ, where X, Y θ 0 θ ) denoes he complex inerpolaion space cf. 8, 4) wih respec o X and Y. In order o obain he L p -L q -ime decay esimaes where q = 2α + 2, p = 2α + 2)/2α + ), /p + /q =, α is a nonnegaive ineger) we noice ha for θ = /α + ) 3α 3.5) L, L 2 /α+) = L p,s 0 where s 0 =, p = 2α + 2 α + 2α +, 3.6) Hence, we have 3.7) 3.8) L, L 2 /α+) = L 2α+2. Π α) : L p,s 0 R 3 ) L 2α+2 R 3 ), Π α) = Π 0 /α+) Π /α+) C + ) α/α+). So, we have proved he following heorem: Theorem 3. L p -L q -ime decay esimaes). Le he Cauchy daa u 0, u, T 0, T be funcions vanishing a infiniy. Moreover, le u, Du 0, T, DT 0 ) L p,s 0 R 3 ) for p = 2α + 2 2α +, s 0 = 3α/α + ) and α a nonnegaive ineger. Then he soluion of he problem 0.) 0.3) given by he formula 0.4) saisfies he following esimaes: 3.9) u, ), T, )) L 2α+2 R 3 ) C + ) α/α+) u, Du 0, T, DT 0 ) L p,s0 R 3 ) for 0 where C is a consan independen of u 0, u, T 0, T and. R e m a r k 3.. In a subsequen paper, we shall apply Theorem 3. in he proof of global in ime) exisence of soluion of he Cauchy problem for he nonlinear hyperbolic sysem of parial differenial equaions describing a hermoelasic medium.
11 L p -L q -Time decay esimae 45 References R. Adams, Sobolev Spaces, Academic Press, New York K. O. Friedrichs, Symmeric hyperbolic linear differenial equaions, Comm. Pure Appl. Mah ), Yu. V. Egorov, Linear Differenial Equaions of Principal Type, Nauka, Moscow 984 in Russian). 4 J. G a w i n e c k i, Marix of fundamenal soluions for he sysem of equaions of hyperbolic hermoelasiciy wih wo relaxaion imes and soluion of he Cauchy problem, Bull. Acad. Polon. Sci., Sér. Sci. Techn. 988 in prin). 5 S. Klainerman, Global exisence for nonlinear wave equaions, Comm. Pure Appl. Mah ), , Long-ime behaviour of soluions o nonlinear evoluion equaions, Arch. Raional Mech. Anal ), S. Klainerman and G. Ponce, Global, small ampliude soluions o nonlinear evoluion equaions, Comm. Pure Appl. Mah ), J. L. Lions e E. Magenes, Problèmes aux limies non homogènes e applicaions, Dunod, Paris A. Piskorek, Fourier and Laplace ransformaion wih heir applicaions, Warsaw Universiy, 988 in Polish). 0 J. Shaah, Global exisence of small soluions o nonlinear evoluion equaions, J. Differenial Equaions ), S. L. S o b o l e v, Applicaions of Funcional Analysis in Mahemaical Physics, 3h ed. Nauka, Moscow 988 in Russian). 2 W. A. S r a u s s, Nonlinear scaering heory a low energy, J. Func. Anal. 4 98), E. S. Suhubi, Thermoelasic solids, in: Coninuum Physics, A. C. Eringen ed.), Academic Press, New York H. T r i e b e l, Inerpolaion Theory, Funcion Spaces, Differenial Operaors, Deuscher Verlag der Wissenschafen, Berlin 978. DEPARTMENT OF MATHEMATICS MILITARY TECHNICAL ACADEMY S. KALISKIEGO WARSZAWA, POLAND Reçu par la Rédacion le Révisé le
Ann. Funct. Anal. 2 (2011), no. 2, A nnals of F unctional A nalysis ISSN: (electronic) URL:
 Ann. Func. Anal. 2 2011, no. 2, 34 41 A nnals of F uncional A nalysis ISSN: 2008-8752 elecronic URL: www.emis.de/journals/afa/ CLASSIFICAION OF POSIIVE SOLUIONS OF NONLINEAR SYSEMS OF VOLERRA INEGRAL EQUAIONS
Ann. Func. Anal. 2 2011, no. 2, 34 41 A nnals of F uncional A nalysis ISSN: 2008-8752 elecronic URL: www.emis.de/journals/afa/ CLASSIFICAION OF POSIIVE SOLUIONS OF NONLINEAR SYSEMS OF VOLERRA INEGRAL EQUAIONS
Properties Of Solutions To A Generalized Liénard Equation With Forcing Term
 Applied Mahemaics E-Noes, 8(28), 4-44 c ISSN 67-25 Available free a mirror sies of hp://www.mah.nhu.edu.w/ amen/ Properies Of Soluions To A Generalized Liénard Equaion Wih Forcing Term Allan Kroopnick
Applied Mahemaics E-Noes, 8(28), 4-44 c ISSN 67-25 Available free a mirror sies of hp://www.mah.nhu.edu.w/ amen/ Properies Of Soluions To A Generalized Liénard Equaion Wih Forcing Term Allan Kroopnick
On Gronwall s Type Integral Inequalities with Singular Kernels
 Filoma 31:4 (217), 141 149 DOI 1.2298/FIL17441A Published by Faculy of Sciences and Mahemaics, Universiy of Niš, Serbia Available a: hp://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filoma On Gronwall s Type Inegral Inequaliies
Filoma 31:4 (217), 141 149 DOI 1.2298/FIL17441A Published by Faculy of Sciences and Mahemaics, Universiy of Niš, Serbia Available a: hp://www.pmf.ni.ac.rs/filoma On Gronwall s Type Inegral Inequaliies
Differential Equations
 Mah 21 (Fall 29) Differenial Equaions Soluion #3 1. Find he paricular soluion of he following differenial equaion by variaion of parameer (a) y + y = csc (b) 2 y + y y = ln, > Soluion: (a) The corresponding
Mah 21 (Fall 29) Differenial Equaions Soluion #3 1. Find he paricular soluion of he following differenial equaion by variaion of parameer (a) y + y = csc (b) 2 y + y y = ln, > Soluion: (a) The corresponding
CONTRIBUTION TO IMPULSIVE EQUATIONS
 European Scienific Journal Sepember 214 /SPECIAL/ ediion Vol.3 ISSN: 1857 7881 (Prin) e - ISSN 1857-7431 CONTRIBUTION TO IMPULSIVE EQUATIONS Berrabah Faima Zohra, MA Universiy of sidi bel abbes/ Algeria
European Scienific Journal Sepember 214 /SPECIAL/ ediion Vol.3 ISSN: 1857 7881 (Prin) e - ISSN 1857-7431 CONTRIBUTION TO IMPULSIVE EQUATIONS Berrabah Faima Zohra, MA Universiy of sidi bel abbes/ Algeria
CERTAIN CLASSES OF SOLUTIONS OF LAGERSTROM EQUATIONS
 SARAJEVO JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol.10 (22 (2014, 67 76 DOI: 10.5644/SJM.10.1.09 CERTAIN CLASSES OF SOLUTIONS OF LAGERSTROM EQUATIONS ALMA OMERSPAHIĆ AND VAHIDIN HADŽIABDIĆ Absrac. This paper presens sufficien
SARAJEVO JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS Vol.10 (22 (2014, 67 76 DOI: 10.5644/SJM.10.1.09 CERTAIN CLASSES OF SOLUTIONS OF LAGERSTROM EQUATIONS ALMA OMERSPAHIĆ AND VAHIDIN HADŽIABDIĆ Absrac. This paper presens sufficien
Convergence of the Neumann series in higher norms
 Convergence of he Neumann series in higher norms Charles L. Epsein Deparmen of Mahemaics, Universiy of Pennsylvania Version 1.0 Augus 1, 003 Absrac Naural condiions on an operaor A are given so ha he Neumann
Convergence of he Neumann series in higher norms Charles L. Epsein Deparmen of Mahemaics, Universiy of Pennsylvania Version 1.0 Augus 1, 003 Absrac Naural condiions on an operaor A are given so ha he Neumann
DISCRETE GRONWALL LEMMA AND APPLICATIONS
 DISCRETE GRONWALL LEMMA AND APPLICATIONS JOHN M. HOLTE MAA NORTH CENTRAL SECTION MEETING AT UND 24 OCTOBER 29 Gronwall s lemma saes an inequaliy ha is useful in he heory of differenial equaions. Here is
DISCRETE GRONWALL LEMMA AND APPLICATIONS JOHN M. HOLTE MAA NORTH CENTRAL SECTION MEETING AT UND 24 OCTOBER 29 Gronwall s lemma saes an inequaliy ha is useful in he heory of differenial equaions. Here is
ODEs II, Lecture 1: Homogeneous Linear Systems - I. Mike Raugh 1. March 8, 2004
 ODEs II, Lecure : Homogeneous Linear Sysems - I Mike Raugh March 8, 4 Inroducion. In he firs lecure we discussed a sysem of linear ODEs for modeling he excreion of lead from he human body, saw how o ransform
ODEs II, Lecure : Homogeneous Linear Sysems - I Mike Raugh March 8, 4 Inroducion. In he firs lecure we discussed a sysem of linear ODEs for modeling he excreion of lead from he human body, saw how o ransform
Vanishing Viscosity Method. There are another instructive and perhaps more natural discontinuous solutions of the conservation law
 Vanishing Viscosiy Mehod. There are anoher insrucive and perhaps more naural disconinuous soluions of he conservaion law (1 u +(q(u x 0, he so called vanishing viscosiy mehod. This mehod consiss in viewing
Vanishing Viscosiy Mehod. There are anoher insrucive and perhaps more naural disconinuous soluions of he conservaion law (1 u +(q(u x 0, he so called vanishing viscosiy mehod. This mehod consiss in viewing
Sobolev-type Inequality for Spaces L p(x) (R N )
 In. J. Conemp. Mah. Sciences, Vol. 2, 27, no. 9, 423-429 Sobolev-ype Inequaliy for Spaces L p(x ( R. Mashiyev and B. Çekiç Universiy of Dicle, Faculy of Sciences and Ars Deparmen of Mahemaics, 228-Diyarbakir,
In. J. Conemp. Mah. Sciences, Vol. 2, 27, no. 9, 423-429 Sobolev-ype Inequaliy for Spaces L p(x ( R. Mashiyev and B. Çekiç Universiy of Dicle, Faculy of Sciences and Ars Deparmen of Mahemaics, 228-Diyarbakir,
The Asymptotic Behavior of Nonoscillatory Solutions of Some Nonlinear Dynamic Equations on Time Scales
 Advances in Dynamical Sysems and Applicaions. ISSN 0973-5321 Volume 1 Number 1 (2006, pp. 103 112 c Research India Publicaions hp://www.ripublicaion.com/adsa.hm The Asympoic Behavior of Nonoscillaory Soluions
Advances in Dynamical Sysems and Applicaions. ISSN 0973-5321 Volume 1 Number 1 (2006, pp. 103 112 c Research India Publicaions hp://www.ripublicaion.com/adsa.hm The Asympoic Behavior of Nonoscillaory Soluions
Existence of positive solution for a third-order three-point BVP with sign-changing Green s function
 Elecronic Journal of Qualiaive Theory of Differenial Equaions 13, No. 3, 1-11; hp://www.mah.u-szeged.hu/ejqde/ Exisence of posiive soluion for a hird-order hree-poin BVP wih sign-changing Green s funcion
Elecronic Journal of Qualiaive Theory of Differenial Equaions 13, No. 3, 1-11; hp://www.mah.u-szeged.hu/ejqde/ Exisence of posiive soluion for a hird-order hree-poin BVP wih sign-changing Green s funcion
Existence of positive solutions for second order m-point boundary value problems
 ANNALES POLONICI MATHEMATICI LXXIX.3 (22 Exisence of posiive soluions for second order m-poin boundary value problems by Ruyun Ma (Lanzhou Absrac. Le α, β, γ, δ and ϱ := γβ + αγ + αδ >. Le ψ( = β + α,
ANNALES POLONICI MATHEMATICI LXXIX.3 (22 Exisence of posiive soluions for second order m-poin boundary value problems by Ruyun Ma (Lanzhou Absrac. Le α, β, γ, δ and ϱ := γβ + αγ + αδ >. Le ψ( = β + α,
An Introduction to Malliavin calculus and its applications
 An Inroducion o Malliavin calculus and is applicaions Lecure 5: Smoohness of he densiy and Hörmander s heorem David Nualar Deparmen of Mahemaics Kansas Universiy Universiy of Wyoming Summer School 214
An Inroducion o Malliavin calculus and is applicaions Lecure 5: Smoohness of he densiy and Hörmander s heorem David Nualar Deparmen of Mahemaics Kansas Universiy Universiy of Wyoming Summer School 214
Monotonic Solutions of a Class of Quadratic Singular Integral Equations of Volterra type
 In. J. Conemp. Mah. Sci., Vol. 2, 27, no. 2, 89-2 Monoonic Soluions of a Class of Quadraic Singular Inegral Equaions of Volerra ype Mahmoud M. El Borai Deparmen of Mahemaics, Faculy of Science, Alexandria
In. J. Conemp. Mah. Sci., Vol. 2, 27, no. 2, 89-2 Monoonic Soluions of a Class of Quadraic Singular Inegral Equaions of Volerra ype Mahmoud M. El Borai Deparmen of Mahemaics, Faculy of Science, Alexandria
THE WAVE EQUATION. part hand-in for week 9 b. Any dilation v(x, t) = u(λx, λt) of u(x, t) is also a solution (where λ is constant).
 THE WAVE EQUATION 43. (S) Le u(x, ) be a soluion of he wave equaion u u xx = 0. Show ha Q43(a) (c) is a. Any ranslaion v(x, ) = u(x + x 0, + 0 ) of u(x, ) is also a soluion (where x 0, 0 are consans).
THE WAVE EQUATION 43. (S) Le u(x, ) be a soluion of he wave equaion u u xx = 0. Show ha Q43(a) (c) is a. Any ranslaion v(x, ) = u(x + x 0, + 0 ) of u(x, ) is also a soluion (where x 0, 0 are consans).
Solutions from Chapter 9.1 and 9.2
 Soluions from Chaper 9 and 92 Secion 9 Problem # This basically boils down o an exercise in he chain rule from calculus We are looking for soluions of he form: u( x) = f( k x c) where k x R 3 and k is
Soluions from Chaper 9 and 92 Secion 9 Problem # This basically boils down o an exercise in he chain rule from calculus We are looking for soluions of he form: u( x) = f( k x c) where k x R 3 and k is
Oscillation of an Euler Cauchy Dynamic Equation S. Huff, G. Olumolode, N. Pennington, and A. Peterson
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE FOURTH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS May 4 7, 00, Wilmingon, NC, USA pp 0 Oscillaion of an Euler Cauchy Dynamic Equaion S Huff, G Olumolode,
PROCEEDINGS OF THE FOURTH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON DYNAMICAL SYSTEMS AND DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS May 4 7, 00, Wilmingon, NC, USA pp 0 Oscillaion of an Euler Cauchy Dynamic Equaion S Huff, G Olumolode,
t 2 B F x,t n dsdt t u x,t dxdt
 Evoluion Equaions For 0, fixed, le U U0, where U denoes a bounded open se in R n.suppose ha U is filled wih a maerial in which a conaminan is being ranspored by various means including diffusion and convecion.
Evoluion Equaions For 0, fixed, le U U0, where U denoes a bounded open se in R n.suppose ha U is filled wih a maerial in which a conaminan is being ranspored by various means including diffusion and convecion.
On a Fractional Stochastic Landau-Ginzburg Equation
 Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 4, 1, no. 7, 317-35 On a Fracional Sochasic Landau-Ginzburg Equaion Nguyen Tien Dung Deparmen of Mahemaics, FPT Universiy 15B Pham Hung Sree, Hanoi, Vienam dungn@fp.edu.vn
Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 4, 1, no. 7, 317-35 On a Fracional Sochasic Landau-Ginzburg Equaion Nguyen Tien Dung Deparmen of Mahemaics, FPT Universiy 15B Pham Hung Sree, Hanoi, Vienam dungn@fp.edu.vn
On the Fourier Transform for Heat Equation
 Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 8, 24, no. 82, 463-467 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikari.com hp://dx.doi.org/.2988/ams.24.45355 On he Fourier Transform for Hea Equaion P. Haarsa and S. Poha 2 Deparmen of Mahemaics,
Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 8, 24, no. 82, 463-467 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikari.com hp://dx.doi.org/.2988/ams.24.45355 On he Fourier Transform for Hea Equaion P. Haarsa and S. Poha 2 Deparmen of Mahemaics,
Math 334 Fall 2011 Homework 11 Solutions
 Dec. 2, 2 Mah 334 Fall 2 Homework Soluions Basic Problem. Transform he following iniial value problem ino an iniial value problem for a sysem: u + p()u + q() u g(), u() u, u () v. () Soluion. Le v u. Then
Dec. 2, 2 Mah 334 Fall 2 Homework Soluions Basic Problem. Transform he following iniial value problem ino an iniial value problem for a sysem: u + p()u + q() u g(), u() u, u () v. () Soluion. Le v u. Then
Lecture 20: Riccati Equations and Least Squares Feedback Control
 34-5 LINEAR SYSTEMS Lecure : Riccai Equaions and Leas Squares Feedback Conrol 5.6.4 Sae Feedback via Riccai Equaions A recursive approach in generaing he marix-valued funcion W ( ) equaion for i for he
34-5 LINEAR SYSTEMS Lecure : Riccai Equaions and Leas Squares Feedback Conrol 5.6.4 Sae Feedback via Riccai Equaions A recursive approach in generaing he marix-valued funcion W ( ) equaion for i for he
New effective moduli of isotropic viscoelastic composites. Part I. Theoretical justification
 IOP Conference Series: Maerials Science and Engineering PAPE OPEN ACCESS New effecive moduli of isoropic viscoelasic composies. Par I. Theoreical jusificaion To cie his aricle: A A Sveashkov and A A akurov
IOP Conference Series: Maerials Science and Engineering PAPE OPEN ACCESS New effecive moduli of isoropic viscoelasic composies. Par I. Theoreical jusificaion To cie his aricle: A A Sveashkov and A A akurov
BOUNDEDNESS OF MAXIMAL FUNCTIONS ON NON-DOUBLING MANIFOLDS WITH ENDS
 BOUNDEDNESS OF MAXIMAL FUNCTIONS ON NON-DOUBLING MANIFOLDS WITH ENDS XUAN THINH DUONG, JI LI, AND ADAM SIKORA Absrac Le M be a manifold wih ends consruced in [2] and be he Laplace-Belrami operaor on M
BOUNDEDNESS OF MAXIMAL FUNCTIONS ON NON-DOUBLING MANIFOLDS WITH ENDS XUAN THINH DUONG, JI LI, AND ADAM SIKORA Absrac Le M be a manifold wih ends consruced in [2] and be he Laplace-Belrami operaor on M
arxiv: v1 [math.pr] 19 Feb 2011
![arxiv: v1 [math.pr] 19 Feb 2011 arxiv: v1 [math.pr] 19 Feb 2011](/thumbs/92/110849938.jpg) A NOTE ON FELLER SEMIGROUPS AND RESOLVENTS VADIM KOSTRYKIN, JÜRGEN POTTHOFF, AND ROBERT SCHRADER ABSTRACT. Various equivalen condiions for a semigroup or a resolven generaed by a Markov process o be of
A NOTE ON FELLER SEMIGROUPS AND RESOLVENTS VADIM KOSTRYKIN, JÜRGEN POTTHOFF, AND ROBERT SCHRADER ABSTRACT. Various equivalen condiions for a semigroup or a resolven generaed by a Markov process o be of
Chapter 2. First Order Scalar Equations
 Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
Chaper. Firs Order Scalar Equaions We sar our sudy of differenial equaions in he same way he pioneers in his field did. We show paricular echniques o solve paricular ypes of firs order differenial equaions.
Section 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equations; Method of Undetermined Coefficients
 Secion 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equaions; Mehod of Undeermined Coefficiens Key Terms/Ideas: Linear Differenial operaor Nonlinear operaor Second order homogeneous DE Second order nonhomogeneous DE Soluion o homogeneous
Secion 3.5 Nonhomogeneous Equaions; Mehod of Undeermined Coefficiens Key Terms/Ideas: Linear Differenial operaor Nonlinear operaor Second order homogeneous DE Second order nonhomogeneous DE Soluion o homogeneous
Stability and Bifurcation in a Neural Network Model with Two Delays
 Inernaional Mahemaical Forum, Vol. 6, 11, no. 35, 175-1731 Sabiliy and Bifurcaion in a Neural Nework Model wih Two Delays GuangPing Hu and XiaoLing Li School of Mahemaics and Physics, Nanjing Universiy
Inernaional Mahemaical Forum, Vol. 6, 11, no. 35, 175-1731 Sabiliy and Bifurcaion in a Neural Nework Model wih Two Delays GuangPing Hu and XiaoLing Li School of Mahemaics and Physics, Nanjing Universiy
Differential Harnack Estimates for Parabolic Equations
 Differenial Harnack Esimaes for Parabolic Equaions Xiaodong Cao and Zhou Zhang Absrac Le M,g be a soluion o he Ricci flow on a closed Riemannian manifold In his paper, we prove differenial Harnack inequaliies
Differenial Harnack Esimaes for Parabolic Equaions Xiaodong Cao and Zhou Zhang Absrac Le M,g be a soluion o he Ricci flow on a closed Riemannian manifold In his paper, we prove differenial Harnack inequaliies
Mapping Properties Of The General Integral Operator On The Classes R k (ρ, b) And V k (ρ, b)
 Applied Mahemaics E-Noes, 15(215), 14-21 c ISSN 167-251 Available free a mirror sies of hp://www.mah.nhu.edu.w/ amen/ Mapping Properies Of The General Inegral Operaor On The Classes R k (ρ, b) And V k
Applied Mahemaics E-Noes, 15(215), 14-21 c ISSN 167-251 Available free a mirror sies of hp://www.mah.nhu.edu.w/ amen/ Mapping Properies Of The General Inegral Operaor On The Classes R k (ρ, b) And V k
On the probabilistic stability of the monomial functional equation
 Available online a www.jnsa.com J. Nonlinear Sci. Appl. 6 (013), 51 59 Research Aricle On he probabilisic sabiliy of he monomial funcional equaion Claudia Zaharia Wes Universiy of Timişoara, Deparmen of
Available online a www.jnsa.com J. Nonlinear Sci. Appl. 6 (013), 51 59 Research Aricle On he probabilisic sabiliy of he monomial funcional equaion Claudia Zaharia Wes Universiy of Timişoara, Deparmen of
THE GENERALIZED PASCAL MATRIX VIA THE GENERALIZED FIBONACCI MATRIX AND THE GENERALIZED PELL MATRIX
 J Korean Mah Soc 45 008, No, pp 479 49 THE GENERALIZED PASCAL MATRIX VIA THE GENERALIZED FIBONACCI MATRIX AND THE GENERALIZED PELL MATRIX Gwang-yeon Lee and Seong-Hoon Cho Reprined from he Journal of he
J Korean Mah Soc 45 008, No, pp 479 49 THE GENERALIZED PASCAL MATRIX VIA THE GENERALIZED FIBONACCI MATRIX AND THE GENERALIZED PELL MATRIX Gwang-yeon Lee and Seong-Hoon Cho Reprined from he Journal of he
Asymptotic instability of nonlinear differential equations
 Elecronic Journal of Differenial Equaions, Vol. 1997(1997), No. 16, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: hp://ejde.mah.sw.edu or hp://ejde.mah.un.edu fp (login: fp) 147.26.13.11 or 129.12.3.113 Asympoic insabiliy
Elecronic Journal of Differenial Equaions, Vol. 1997(1997), No. 16, pp. 1 7. ISSN: 172-6691. URL: hp://ejde.mah.sw.edu or hp://ejde.mah.un.edu fp (login: fp) 147.26.13.11 or 129.12.3.113 Asympoic insabiliy
The L p -Version of the Generalized Bohl Perron Principle for Vector Equations with Infinite Delay
 Advances in Dynamical Sysems and Applicaions ISSN 973-5321, Volume 6, Number 2, pp. 177 184 (211) hp://campus.ms.edu/adsa The L p -Version of he Generalized Bohl Perron Principle for Vecor Equaions wih
Advances in Dynamical Sysems and Applicaions ISSN 973-5321, Volume 6, Number 2, pp. 177 184 (211) hp://campus.ms.edu/adsa The L p -Version of he Generalized Bohl Perron Principle for Vecor Equaions wih
Lecture 10: The Poincaré Inequality in Euclidean space
 Deparmens of Mahemaics Monana Sae Universiy Fall 215 Prof. Kevin Wildrick n inroducion o non-smooh analysis and geomery Lecure 1: The Poincaré Inequaliy in Euclidean space 1. Wha is he Poincaré inequaliy?
Deparmens of Mahemaics Monana Sae Universiy Fall 215 Prof. Kevin Wildrick n inroducion o non-smooh analysis and geomery Lecure 1: The Poincaré Inequaliy in Euclidean space 1. Wha is he Poincaré inequaliy?
ENGI 9420 Engineering Analysis Assignment 2 Solutions
 ENGI 940 Engineering Analysis Assignmen Soluions 0 Fall [Second order ODEs, Laplace ransforms; Secions.0-.09]. Use Laplace ransforms o solve he iniial value problem [0] dy y, y( 0) 4 d + [This was Quesion
ENGI 940 Engineering Analysis Assignmen Soluions 0 Fall [Second order ODEs, Laplace ransforms; Secions.0-.09]. Use Laplace ransforms o solve he iniial value problem [0] dy y, y( 0) 4 d + [This was Quesion
Positive continuous solution of a quadratic integral equation of fractional orders
 Mah. Sci. Le., No., 9-7 (3) 9 Mahemaical Sciences Leers An Inernaional Journal @ 3 NSP Naural Sciences Publishing Cor. Posiive coninuous soluion of a quadraic inegral equaion of fracional orders A. M.
Mah. Sci. Le., No., 9-7 (3) 9 Mahemaical Sciences Leers An Inernaional Journal @ 3 NSP Naural Sciences Publishing Cor. Posiive coninuous soluion of a quadraic inegral equaion of fracional orders A. M.
SUFFICIENT CONDITIONS FOR EXISTENCE SOLUTION OF LINEAR TWO-POINT BOUNDARY PROBLEM IN MINIMIZATION OF QUADRATIC FUNCTIONAL
 HE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF HE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Series A, OF HE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volume, Number 4/200, pp 287 293 SUFFICIEN CONDIIONS FOR EXISENCE SOLUION OF LINEAR WO-POIN BOUNDARY PROBLEM IN
HE PUBLISHING HOUSE PROCEEDINGS OF HE ROMANIAN ACADEMY, Series A, OF HE ROMANIAN ACADEMY Volume, Number 4/200, pp 287 293 SUFFICIEN CONDIIONS FOR EXISENCE SOLUION OF LINEAR WO-POIN BOUNDARY PROBLEM IN
On the Stability of the n-dimensional Quadratic and Additive Functional Equation in Random Normed Spaces via Fixed Point Method
 In. Journal of Mah. Analysis, Vol. 7, 013, no. 49, 413-48 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikari.com hp://d.doi.org/10.1988/ijma.013.36165 On he Sabiliy of he n-dimensional Quadraic and Addiive Funcional Equaion in Random
In. Journal of Mah. Analysis, Vol. 7, 013, no. 49, 413-48 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikari.com hp://d.doi.org/10.1988/ijma.013.36165 On he Sabiliy of he n-dimensional Quadraic and Addiive Funcional Equaion in Random
Improved Approximate Solutions for Nonlinear Evolutions Equations in Mathematical Physics Using the Reduced Differential Transform Method
 Journal of Applied Mahemaics & Bioinformaics, vol., no., 01, 1-14 ISSN: 179-660 (prin), 179-699 (online) Scienpress Ld, 01 Improved Approimae Soluions for Nonlinear Evoluions Equaions in Mahemaical Physics
Journal of Applied Mahemaics & Bioinformaics, vol., no., 01, 1-14 ISSN: 179-660 (prin), 179-699 (online) Scienpress Ld, 01 Improved Approimae Soluions for Nonlinear Evoluions Equaions in Mahemaical Physics
Research Article Existence and Uniqueness of Periodic Solution for Nonlinear Second-Order Ordinary Differential Equations
 Hindawi Publishing Corporaion Boundary Value Problems Volume 11, Aricle ID 19156, 11 pages doi:1.1155/11/19156 Research Aricle Exisence and Uniqueness of Periodic Soluion for Nonlinear Second-Order Ordinary
Hindawi Publishing Corporaion Boundary Value Problems Volume 11, Aricle ID 19156, 11 pages doi:1.1155/11/19156 Research Aricle Exisence and Uniqueness of Periodic Soluion for Nonlinear Second-Order Ordinary
Class Meeting # 10: Introduction to the Wave Equation
 MATH 8.5 COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # 0 8.5 Inroducion o PDEs, Fall 0 Professor: Jared Speck Class Meeing # 0: Inroducion o he Wave Equaion. Wha is he wave equaion? The sandard wave equaion for a funcion
MATH 8.5 COURSE NOTES - CLASS MEETING # 0 8.5 Inroducion o PDEs, Fall 0 Professor: Jared Speck Class Meeing # 0: Inroducion o he Wave Equaion. Wha is he wave equaion? The sandard wave equaion for a funcion
System of Linear Differential Equations
 Sysem of Linear Differenial Equaions In "Ordinary Differenial Equaions" we've learned how o solve a differenial equaion for a variable, such as: y'k5$e K2$x =0 solve DE yx = K 5 2 ek2 x C_C1 2$y''C7$y
Sysem of Linear Differenial Equaions In "Ordinary Differenial Equaions" we've learned how o solve a differenial equaion for a variable, such as: y'k5$e K2$x =0 solve DE yx = K 5 2 ek2 x C_C1 2$y''C7$y
GRADIENT ESTIMATES FOR A SIMPLE PARABOLIC LICHNEROWICZ EQUATION. Osaka Journal of Mathematics. 51(1) P.245-P.256
 Tile Auhor(s) GRADIENT ESTIMATES FOR A SIMPLE PARABOLIC LICHNEROWICZ EQUATION Zhao, Liang Ciaion Osaka Journal of Mahemaics. 51(1) P.45-P.56 Issue Dae 014-01 Tex Version publisher URL hps://doi.org/10.18910/9195
Tile Auhor(s) GRADIENT ESTIMATES FOR A SIMPLE PARABOLIC LICHNEROWICZ EQUATION Zhao, Liang Ciaion Osaka Journal of Mahemaics. 51(1) P.45-P.56 Issue Dae 014-01 Tex Version publisher URL hps://doi.org/10.18910/9195
t is a basis for the solution space to this system, then the matrix having these solutions as columns, t x 1 t, x 2 t,... x n t x 2 t...
 Mah 228- Fri Mar 24 5.6 Marix exponenials and linear sysems: The analogy beween firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions (Chaper 5) and scalar linear differenial equaions (Chaper ) is much sronger
Mah 228- Fri Mar 24 5.6 Marix exponenials and linear sysems: The analogy beween firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions (Chaper 5) and scalar linear differenial equaions (Chaper ) is much sronger
Finish reading Chapter 2 of Spivak, rereading earlier sections as necessary. handout and fill in some missing details!
 MAT 257, Handou 6: Ocober 7-2, 20. I. Assignmen. Finish reading Chaper 2 of Spiva, rereading earlier secions as necessary. handou and fill in some missing deails! II. Higher derivaives. Also, read his
MAT 257, Handou 6: Ocober 7-2, 20. I. Assignmen. Finish reading Chaper 2 of Spiva, rereading earlier secions as necessary. handou and fill in some missing deails! II. Higher derivaives. Also, read his
arxiv:math/ v1 [math.nt] 3 Nov 2005
![arxiv:math/ v1 [math.nt] 3 Nov 2005 arxiv:math/ v1 [math.nt] 3 Nov 2005](/thumbs/71/66009857.jpg) arxiv:mah/0511092v1 [mah.nt] 3 Nov 2005 A NOTE ON S AND THE ZEROS OF THE RIEMANN ZETA-FUNCTION D. A. GOLDSTON AND S. M. GONEK Absrac. Le πs denoe he argumen of he Riemann zea-funcion a he poin 1 + i. Assuming
arxiv:mah/0511092v1 [mah.nt] 3 Nov 2005 A NOTE ON S AND THE ZEROS OF THE RIEMANN ZETA-FUNCTION D. A. GOLDSTON AND S. M. GONEK Absrac. Le πs denoe he argumen of he Riemann zea-funcion a he poin 1 + i. Assuming
Theory of! Partial Differential Equations!
 hp://www.nd.edu/~gryggva/cfd-course/! Ouline! Theory o! Parial Dierenial Equaions! Gréar Tryggvason! Spring 011! Basic Properies o PDE!! Quasi-linear Firs Order Equaions! - Characerisics! - Linear and
hp://www.nd.edu/~gryggva/cfd-course/! Ouline! Theory o! Parial Dierenial Equaions! Gréar Tryggvason! Spring 011! Basic Properies o PDE!! Quasi-linear Firs Order Equaions! - Characerisics! - Linear and
TO our knowledge, most exciting results on the existence
 IAENG Inernaional Journal of Applied Mahemaics, 42:, IJAM_42 2 Exisence and Uniqueness of a Periodic Soluion for hird-order Delay Differenial Equaion wih wo Deviaing Argumens A. M. A. Abou-El-Ela, A. I.
IAENG Inernaional Journal of Applied Mahemaics, 42:, IJAM_42 2 Exisence and Uniqueness of a Periodic Soluion for hird-order Delay Differenial Equaion wih wo Deviaing Argumens A. M. A. Abou-El-Ela, A. I.
2. Nonlinear Conservation Law Equations
 . Nonlinear Conservaion Law Equaions One of he clear lessons learned over recen years in sudying nonlinear parial differenial equaions is ha i is generally no wise o ry o aack a general class of nonlinear
. Nonlinear Conservaion Law Equaions One of he clear lessons learned over recen years in sudying nonlinear parial differenial equaions is ha i is generally no wise o ry o aack a general class of nonlinear
10. State Space Methods
 . Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
. Sae Space Mehods. Inroducion Sae space modelling was briefly inroduced in chaper. Here more coverage is provided of sae space mehods before some of heir uses in conrol sysem design are covered in he
Lecture 10: Wave equation, solution by spherical means
 Lecure : Wave equaion, soluion by spherical means Physical modeling eample: Elasodynamics u (; ) displacemen vecor in elasic body occupying a domain U R n, U, The posiion of he maerial poin siing a U in
Lecure : Wave equaion, soluion by spherical means Physical modeling eample: Elasodynamics u (; ) displacemen vecor in elasic body occupying a domain U R n, U, The posiion of he maerial poin siing a U in
Average Number of Lattice Points in a Disk
 Average Number of Laice Poins in a Disk Sujay Jayakar Rober S. Sricharz Absrac The difference beween he number of laice poins in a disk of radius /π and he area of he disk /4π is equal o he error in he
Average Number of Laice Poins in a Disk Sujay Jayakar Rober S. Sricharz Absrac The difference beween he number of laice poins in a disk of radius /π and he area of he disk /4π is equal o he error in he
STABILITY OF PEXIDERIZED QUADRATIC FUNCTIONAL EQUATION IN NON-ARCHIMEDEAN FUZZY NORMED SPASES
 Novi Sad J. Mah. Vol. 46, No. 1, 2016, 15-25 STABILITY OF PEXIDERIZED QUADRATIC FUNCTIONAL EQUATION IN NON-ARCHIMEDEAN FUZZY NORMED SPASES N. Eghbali 1 Absrac. We deermine some sabiliy resuls concerning
Novi Sad J. Mah. Vol. 46, No. 1, 2016, 15-25 STABILITY OF PEXIDERIZED QUADRATIC FUNCTIONAL EQUATION IN NON-ARCHIMEDEAN FUZZY NORMED SPASES N. Eghbali 1 Absrac. We deermine some sabiliy resuls concerning
Endpoint Strichartz estimates
 Endpoin Sricharz esimaes Markus Keel and Terence Tao (Amer. J. Mah. 10 (1998) 955 980) Presener : Nobu Kishimoo (Kyoo Universiy) 013 Paricipaing School in Analysis of PDE 013/8/6 30, Jeju 1 Absrac of he
Endpoin Sricharz esimaes Markus Keel and Terence Tao (Amer. J. Mah. 10 (1998) 955 980) Presener : Nobu Kishimoo (Kyoo Universiy) 013 Paricipaing School in Analysis of PDE 013/8/6 30, Jeju 1 Absrac of he
Recursive Least-Squares Fixed-Interval Smoother Using Covariance Information based on Innovation Approach in Linear Continuous Stochastic Systems
 8 Froniers in Signal Processing, Vol. 1, No. 1, July 217 hps://dx.doi.org/1.2266/fsp.217.112 Recursive Leas-Squares Fixed-Inerval Smooher Using Covariance Informaion based on Innovaion Approach in Linear
8 Froniers in Signal Processing, Vol. 1, No. 1, July 217 hps://dx.doi.org/1.2266/fsp.217.112 Recursive Leas-Squares Fixed-Inerval Smooher Using Covariance Informaion based on Innovaion Approach in Linear
Variational Iteration Method for Solving System of Fractional Order Ordinary Differential Equations
 IOSR Journal of Mahemaics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 2278-5728, p-issn: 2319-765X. Volume 1, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov - Dec. 214), PP 48-54 Variaional Ieraion Mehod for Solving Sysem of Fracional Order Ordinary Differenial
IOSR Journal of Mahemaics (IOSR-JM) e-issn: 2278-5728, p-issn: 2319-765X. Volume 1, Issue 6 Ver. II (Nov - Dec. 214), PP 48-54 Variaional Ieraion Mehod for Solving Sysem of Fracional Order Ordinary Differenial
The expectation value of the field operator.
 The expecaion value of he field operaor. Dan Solomon Universiy of Illinois Chicago, IL dsolom@uic.edu June, 04 Absrac. Much of he mahemaical developmen of quanum field heory has been in suppor of deermining
The expecaion value of he field operaor. Dan Solomon Universiy of Illinois Chicago, IL dsolom@uic.edu June, 04 Absrac. Much of he mahemaical developmen of quanum field heory has been in suppor of deermining
Some New Uniqueness Results of Solutions to Nonlinear Fractional Integro-Differential Equations
 Annals of Pure and Applied Mahemaics Vol. 6, No. 2, 28, 345-352 ISSN: 2279-87X (P), 2279-888(online) Published on 22 February 28 www.researchmahsci.org DOI: hp://dx.doi.org/.22457/apam.v6n2a Annals of
Annals of Pure and Applied Mahemaics Vol. 6, No. 2, 28, 345-352 ISSN: 2279-87X (P), 2279-888(online) Published on 22 February 28 www.researchmahsci.org DOI: hp://dx.doi.org/.22457/apam.v6n2a Annals of
Theory of! Partial Differential Equations-I!
 hp://users.wpi.edu/~grear/me61.hml! Ouline! Theory o! Parial Dierenial Equaions-I! Gréar Tryggvason! Spring 010! Basic Properies o PDE!! Quasi-linear Firs Order Equaions! - Characerisics! - Linear and
hp://users.wpi.edu/~grear/me61.hml! Ouline! Theory o! Parial Dierenial Equaions-I! Gréar Tryggvason! Spring 010! Basic Properies o PDE!! Quasi-linear Firs Order Equaions! - Characerisics! - Linear and
Math-Net.Ru All Russian mathematical portal
 Mah-NeRu All Russian mahemaical poral Roman Popovych, On elemens of high order in general finie fields, Algebra Discree Mah, 204, Volume 8, Issue 2, 295 300 Use of he all-russian mahemaical poral Mah-NeRu
Mah-NeRu All Russian mahemaical poral Roman Popovych, On elemens of high order in general finie fields, Algebra Discree Mah, 204, Volume 8, Issue 2, 295 300 Use of he all-russian mahemaical poral Mah-NeRu
Chapter 3 Boundary Value Problem
 Chaper 3 Boundary Value Problem A boundary value problem (BVP) is a problem, ypically an ODE or a PDE, which has values assigned on he physical boundary of he domain in which he problem is specified. Le
Chaper 3 Boundary Value Problem A boundary value problem (BVP) is a problem, ypically an ODE or a PDE, which has values assigned on he physical boundary of he domain in which he problem is specified. Le
Generalized Chebyshev polynomials
 Generalized Chebyshev polynomials Clemene Cesarano Faculy of Engineering, Inernaional Telemaic Universiy UNINETTUNO Corso Viorio Emanuele II, 39 86 Roma, Ialy email: c.cesarano@unineunouniversiy.ne ABSTRACT
Generalized Chebyshev polynomials Clemene Cesarano Faculy of Engineering, Inernaional Telemaic Universiy UNINETTUNO Corso Viorio Emanuele II, 39 86 Roma, Ialy email: c.cesarano@unineunouniversiy.ne ABSTRACT
Math Week 14 April 16-20: sections first order systems of linear differential equations; 7.4 mass-spring systems.
 Mah 2250-004 Week 4 April 6-20 secions 7.-7.3 firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions; 7.4 mass-spring sysems. Mon Apr 6 7.-7.2 Sysems of differenial equaions (7.), and he vecor Calculus we need
Mah 2250-004 Week 4 April 6-20 secions 7.-7.3 firs order sysems of linear differenial equaions; 7.4 mass-spring sysems. Mon Apr 6 7.-7.2 Sysems of differenial equaions (7.), and he vecor Calculus we need
Dynamical systems method for solving linear ill-posed problems
 ANNALES POLONICI MATHEMATICI * (2*) Dynamical sysems mehod for solving linear ill-posed problems by A. G. Ramm (Manhaan, KS) Absrac. Various versions of he Dynamical Sysems Mehod (DSM) are proposed for
ANNALES POLONICI MATHEMATICI * (2*) Dynamical sysems mehod for solving linear ill-posed problems by A. G. Ramm (Manhaan, KS) Absrac. Various versions of he Dynamical Sysems Mehod (DSM) are proposed for
Two Coupled Oscillators / Normal Modes
 Lecure 3 Phys 3750 Two Coupled Oscillaors / Normal Modes Overview and Moivaion: Today we ake a small, bu significan, sep owards wave moion. We will no ye observe waves, bu his sep is imporan in is own
Lecure 3 Phys 3750 Two Coupled Oscillaors / Normal Modes Overview and Moivaion: Today we ake a small, bu significan, sep owards wave moion. We will no ye observe waves, bu his sep is imporan in is own
A Note on the Equivalence of Fractional Relaxation Equations to Differential Equations with Varying Coefficients
 mahemaics Aricle A Noe on he Equivalence of Fracional Relaxaion Equaions o Differenial Equaions wih Varying Coefficiens Francesco Mainardi Deparmen of Physics and Asronomy, Universiy of Bologna, and he
mahemaics Aricle A Noe on he Equivalence of Fracional Relaxaion Equaions o Differenial Equaions wih Varying Coefficiens Francesco Mainardi Deparmen of Physics and Asronomy, Universiy of Bologna, and he
Concourse Math Spring 2012 Worked Examples: Matrix Methods for Solving Systems of 1st Order Linear Differential Equations
 Concourse Mah 80 Spring 0 Worked Examples: Marix Mehods for Solving Sysems of s Order Linear Differenial Equaions The Main Idea: Given a sysem of s order linear differenial equaions d x d Ax wih iniial
Concourse Mah 80 Spring 0 Worked Examples: Marix Mehods for Solving Sysems of s Order Linear Differenial Equaions The Main Idea: Given a sysem of s order linear differenial equaions d x d Ax wih iniial
Ordinary Differential Equations
 Ordinary Differenial Equaions 5. Examples of linear differenial equaions and heir applicaions We consider some examples of sysems of linear differenial equaions wih consan coefficiens y = a y +... + a
Ordinary Differenial Equaions 5. Examples of linear differenial equaions and heir applicaions We consider some examples of sysems of linear differenial equaions wih consan coefficiens y = a y +... + a
QUANTITATIVE DECAY FOR NONLINEAR WAVE EQUATIONS
 QUANTITATIVE DECAY FOR NONLINEAR WAVE EQUATIONS SPUR FINAL PAPER, SUMMER 08 CALVIN HSU MENTOR: RUOXUAN YANG PROJECT SUGGESTED BY: ANDREW LAWRIE Augus, 08 Absrac. In his paper, we discuss he decay rae for
QUANTITATIVE DECAY FOR NONLINEAR WAVE EQUATIONS SPUR FINAL PAPER, SUMMER 08 CALVIN HSU MENTOR: RUOXUAN YANG PROJECT SUGGESTED BY: ANDREW LAWRIE Augus, 08 Absrac. In his paper, we discuss he decay rae for
EXISTENCE OF NON-OSCILLATORY SOLUTIONS TO FIRST-ORDER NEUTRAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 Elecronic Journal of Differenial Equaions, Vol. 206 (206, No. 39, pp.. ISSN: 072-669. URL: hp://ejde.mah.xsae.edu or hp://ejde.mah.un.edu fp ejde.mah.xsae.edu EXISTENCE OF NON-OSCILLATORY SOLUTIONS TO
Elecronic Journal of Differenial Equaions, Vol. 206 (206, No. 39, pp.. ISSN: 072-669. URL: hp://ejde.mah.xsae.edu or hp://ejde.mah.un.edu fp ejde.mah.xsae.edu EXISTENCE OF NON-OSCILLATORY SOLUTIONS TO
Existence Theory of Second Order Random Differential Equations
 Global Journal of Mahemaical Sciences: Theory and Pracical. ISSN 974-32 Volume 4, Number 3 (22), pp. 33-3 Inernaional Research Publicaion House hp://www.irphouse.com Exisence Theory of Second Order Random
Global Journal of Mahemaical Sciences: Theory and Pracical. ISSN 974-32 Volume 4, Number 3 (22), pp. 33-3 Inernaional Research Publicaion House hp://www.irphouse.com Exisence Theory of Second Order Random
A NOTE ON S(t) AND THE ZEROS OF THE RIEMANN ZETA-FUNCTION
 Bull. London Mah. Soc. 39 2007 482 486 C 2007 London Mahemaical Sociey doi:10.1112/blms/bdm032 A NOTE ON S AND THE ZEROS OF THE RIEMANN ZETA-FUNCTION D. A. GOLDSTON and S. M. GONEK Absrac Le πs denoe he
Bull. London Mah. Soc. 39 2007 482 486 C 2007 London Mahemaical Sociey doi:10.1112/blms/bdm032 A NOTE ON S AND THE ZEROS OF THE RIEMANN ZETA-FUNCTION D. A. GOLDSTON and S. M. GONEK Absrac Le πs denoe he
KEY. Math 334 Midterm III Fall 2008 sections 001 and 003 Instructor: Scott Glasgow
 KEY Mah 334 Miderm III Fall 28 secions and 3 Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his exam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on your own paper, preferably engineering
KEY Mah 334 Miderm III Fall 28 secions and 3 Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his exam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on your own paper, preferably engineering
KEY. Math 334 Midterm III Winter 2008 section 002 Instructor: Scott Glasgow
 KEY Mah 334 Miderm III Winer 008 secion 00 Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his exam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on your own paper, preferably engineering
KEY Mah 334 Miderm III Winer 008 secion 00 Insrucor: Sco Glasgow Please do NOT wrie on his exam. No credi will be given for such work. Raher wrie in a blue book, or on your own paper, preferably engineering
Omega-limit sets and bounded solutions
 arxiv:3.369v [mah.gm] 3 May 6 Omega-limi ses and bounded soluions Dang Vu Giang Hanoi Insiue of Mahemaics Vienam Academy of Science and Technology 8 Hoang Quoc Vie, 37 Hanoi, Vienam e-mail: dangvugiang@yahoo.com
arxiv:3.369v [mah.gm] 3 May 6 Omega-limi ses and bounded soluions Dang Vu Giang Hanoi Insiue of Mahemaics Vienam Academy of Science and Technology 8 Hoang Quoc Vie, 37 Hanoi, Vienam e-mail: dangvugiang@yahoo.com
An Invariance for (2+1)-Extension of Burgers Equation and Formulae to Obtain Solutions of KP Equation
 Commun Theor Phys Beijing, China 43 2005 pp 591 596 c Inernaional Academic Publishers Vol 43, No 4, April 15, 2005 An Invariance for 2+1-Eension of Burgers Equaion Formulae o Obain Soluions of KP Equaion
Commun Theor Phys Beijing, China 43 2005 pp 591 596 c Inernaional Academic Publishers Vol 43, No 4, April 15, 2005 An Invariance for 2+1-Eension of Burgers Equaion Formulae o Obain Soluions of KP Equaion
Math 221: Mathematical Notation
 Mah 221: Mahemaical Noaion Purpose: One goal in any course is o properly use he language o ha subjec. These noaions summarize some o he major conceps and more diicul opics o he uni. Typing hem helps you
Mah 221: Mahemaical Noaion Purpose: One goal in any course is o properly use he language o ha subjec. These noaions summarize some o he major conceps and more diicul opics o he uni. Typing hem helps you
CHARACTERIZATION OF REARRANGEMENT INVARIANT SPACES WITH FIXED POINTS FOR THE HARDY LITTLEWOOD MAXIMAL OPERATOR
 Annales Academiæ Scieniarum Fennicæ Mahemaica Volumen 31, 2006, 39 46 CHARACTERIZATION OF REARRANGEMENT INVARIANT SPACES WITH FIXED POINTS FOR THE HARDY LITTLEWOOD MAXIMAL OPERATOR Joaquim Marín and Javier
Annales Academiæ Scieniarum Fennicæ Mahemaica Volumen 31, 2006, 39 46 CHARACTERIZATION OF REARRANGEMENT INVARIANT SPACES WITH FIXED POINTS FOR THE HARDY LITTLEWOOD MAXIMAL OPERATOR Joaquim Marín and Javier
A Necessary and Sufficient Condition for the Solutions of a Functional Differential Equation to Be Oscillatory or Tend to Zero
 JOURNAL OF MAEMAICAL ANALYSIS AND APPLICAIONS 24, 7887 1997 ARICLE NO. AY965143 A Necessary and Sufficien Condiion for he Soluions of a Funcional Differenial Equaion o Be Oscillaory or end o Zero Piambar
JOURNAL OF MAEMAICAL ANALYSIS AND APPLICAIONS 24, 7887 1997 ARICLE NO. AY965143 A Necessary and Sufficien Condiion for he Soluions of a Funcional Differenial Equaion o Be Oscillaory or end o Zero Piambar
23.2. Representing Periodic Functions by Fourier Series. Introduction. Prerequisites. Learning Outcomes
 Represening Periodic Funcions by Fourier Series 3. Inroducion In his Secion we show how a periodic funcion can be expressed as a series of sines and cosines. We begin by obaining some sandard inegrals
Represening Periodic Funcions by Fourier Series 3. Inroducion In his Secion we show how a periodic funcion can be expressed as a series of sines and cosines. We begin by obaining some sandard inegrals
EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS THEOREMS ON CERTAIN DIFFERENCE-DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
 Elecronic Journal of Differenial Equaions, Vol. 29(29), No. 49, pp. 2. ISSN: 72-669. URL: hp://ejde.mah.xsae.edu or hp://ejde.mah.un.edu fp ejde.mah.xsae.edu EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS THEOREMS ON CERTAIN
Elecronic Journal of Differenial Equaions, Vol. 29(29), No. 49, pp. 2. ISSN: 72-669. URL: hp://ejde.mah.xsae.edu or hp://ejde.mah.un.edu fp ejde.mah.xsae.edu EXISTENCE AND UNIQUENESS THEOREMS ON CERTAIN
Vehicle Arrival Models : Headway
 Chaper 12 Vehicle Arrival Models : Headway 12.1 Inroducion Modelling arrival of vehicle a secion of road is an imporan sep in raffic flow modelling. I has imporan applicaion in raffic flow simulaion where
Chaper 12 Vehicle Arrival Models : Headway 12.1 Inroducion Modelling arrival of vehicle a secion of road is an imporan sep in raffic flow modelling. I has imporan applicaion in raffic flow simulaion where
f(s)dw Solution 1. Approximate f by piece-wise constant left-continuous non-random functions f n such that (f(s) f n (s)) 2 ds 0.
 Advanced Financial Models Example shee 3 - Michaelmas 217 Michael Tehranchi Problem 1. Le f : [, R be a coninuous (non-random funcion and W a Brownian moion, and le σ 2 = f(s 2 ds and assume σ 2
Advanced Financial Models Example shee 3 - Michaelmas 217 Michael Tehranchi Problem 1. Le f : [, R be a coninuous (non-random funcion and W a Brownian moion, and le σ 2 = f(s 2 ds and assume σ 2
POSITIVE SOLUTIONS OF NEUTRAL DELAY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION
 Novi Sad J. Mah. Vol. 32, No. 2, 2002, 95-108 95 POSITIVE SOLUTIONS OF NEUTRAL DELAY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION Hajnalka Péics 1, János Karsai 2 Absrac. We consider he scalar nonauonomous neural delay differenial
Novi Sad J. Mah. Vol. 32, No. 2, 2002, 95-108 95 POSITIVE SOLUTIONS OF NEUTRAL DELAY DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION Hajnalka Péics 1, János Karsai 2 Absrac. We consider he scalar nonauonomous neural delay differenial
Second quantization and gauge invariance.
 1 Second quanizaion and gauge invariance. Dan Solomon Rauland-Borg Corporaion Moun Prospec, IL Email: dsolom@uic.edu June, 1. Absrac. I is well known ha he single paricle Dirac equaion is gauge invarian.
1 Second quanizaion and gauge invariance. Dan Solomon Rauland-Borg Corporaion Moun Prospec, IL Email: dsolom@uic.edu June, 1. Absrac. I is well known ha he single paricle Dirac equaion is gauge invarian.
MA 214 Calculus IV (Spring 2016) Section 2. Homework Assignment 1 Solutions
 MA 14 Calculus IV (Spring 016) Secion Homework Assignmen 1 Soluions 1 Boyce and DiPrima, p 40, Problem 10 (c) Soluion: In sandard form he given firs-order linear ODE is: An inegraing facor is given by
MA 14 Calculus IV (Spring 016) Secion Homework Assignmen 1 Soluions 1 Boyce and DiPrima, p 40, Problem 10 (c) Soluion: In sandard form he given firs-order linear ODE is: An inegraing facor is given by
Dual Representation as Stochastic Differential Games of Backward Stochastic Differential Equations and Dynamic Evaluations
 arxiv:mah/0602323v1 [mah.pr] 15 Feb 2006 Dual Represenaion as Sochasic Differenial Games of Backward Sochasic Differenial Equaions and Dynamic Evaluaions Shanjian Tang Absrac In his Noe, assuming ha he
arxiv:mah/0602323v1 [mah.pr] 15 Feb 2006 Dual Represenaion as Sochasic Differenial Games of Backward Sochasic Differenial Equaions and Dynamic Evaluaions Shanjian Tang Absrac In his Noe, assuming ha he
Hamilton- J acobi Equation: Weak S olution We continue the study of the Hamilton-Jacobi equation:
 M ah 5 7 Fall 9 L ecure O c. 4, 9 ) Hamilon- J acobi Equaion: Weak S oluion We coninue he sudy of he Hamilon-Jacobi equaion: We have shown ha u + H D u) = R n, ) ; u = g R n { = }. ). In general we canno
M ah 5 7 Fall 9 L ecure O c. 4, 9 ) Hamilon- J acobi Equaion: Weak S oluion We coninue he sudy of he Hamilon-Jacobi equaion: We have shown ha u + H D u) = R n, ) ; u = g R n { = }. ). In general we canno
Solutions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Math 246, Spring 2011, Professor David Levermore
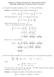 Soluions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Mah 6, Spring, Professor David Levermore Compue he Laplace ransform of f e from is definiion Soluion The definiion of he Laplace ransform gives L[f]s
Soluions of Sample Problems for Third In-Class Exam Mah 6, Spring, Professor David Levermore Compue he Laplace ransform of f e from is definiion Soluion The definiion of he Laplace ransform gives L[f]s
arxiv: v1 [math.pr] 21 May 2010
![arxiv: v1 [math.pr] 21 May 2010 arxiv: v1 [math.pr] 21 May 2010](/thumbs/85/92939918.jpg) ON SCHRÖDINGER S EQUATION, 3-DIMENSIONAL BESSEL BRIDGES, AND PASSAGE TIME PROBLEMS arxiv:15.498v1 [mah.pr 21 May 21 GERARDO HERNÁNDEZ-DEL-VALLE Absrac. In his work we relae he densiy of he firs-passage
ON SCHRÖDINGER S EQUATION, 3-DIMENSIONAL BESSEL BRIDGES, AND PASSAGE TIME PROBLEMS arxiv:15.498v1 [mah.pr 21 May 21 GERARDO HERNÁNDEZ-DEL-VALLE Absrac. In his work we relae he densiy of he firs-passage
Pade and Laguerre Approximations Applied. to the Active Queue Management Model. of Internet Protocol
 Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 7, 013, no. 16, 663-673 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikari.com hp://dx.doi.org/10.1988/ams.013.39499 Pade and Laguerre Approximaions Applied o he Acive Queue Managemen Model of Inerne
Applied Mahemaical Sciences, Vol. 7, 013, no. 16, 663-673 HIKARI Ld, www.m-hikari.com hp://dx.doi.org/10.1988/ams.013.39499 Pade and Laguerre Approximaions Applied o he Acive Queue Managemen Model of Inerne
SELBERG S CENTRAL LIMIT THEOREM ON THE CRITICAL LINE AND THE LERCH ZETA-FUNCTION. II
 SELBERG S CENRAL LIMI HEOREM ON HE CRIICAL LINE AND HE LERCH ZEA-FUNCION. II ANDRIUS GRIGUIS Deparmen of Mahemaics Informaics Vilnius Universiy, Naugarduko 4 035 Vilnius, Lihuania rius.griguis@mif.vu.l
SELBERG S CENRAL LIMI HEOREM ON HE CRIICAL LINE AND HE LERCH ZEA-FUNCION. II ANDRIUS GRIGUIS Deparmen of Mahemaics Informaics Vilnius Universiy, Naugarduko 4 035 Vilnius, Lihuania rius.griguis@mif.vu.l
Solution of Integro-Differential Equations by Using ELzaki Transform
 Global Journal of Mahemaical Sciences: Theory and Pracical. Volume, Number (), pp. - Inernaional Research Publicaion House hp://www.irphouse.com Soluion of Inegro-Differenial Equaions by Using ELzaki Transform
Global Journal of Mahemaical Sciences: Theory and Pracical. Volume, Number (), pp. - Inernaional Research Publicaion House hp://www.irphouse.com Soluion of Inegro-Differenial Equaions by Using ELzaki Transform
On Oscillation of a Generalized Logistic Equation with Several Delays
 Journal of Mahemaical Analysis and Applicaions 253, 389 45 (21) doi:1.16/jmaa.2.714, available online a hp://www.idealibrary.com on On Oscillaion of a Generalized Logisic Equaion wih Several Delays Leonid
Journal of Mahemaical Analysis and Applicaions 253, 389 45 (21) doi:1.16/jmaa.2.714, available online a hp://www.idealibrary.com on On Oscillaion of a Generalized Logisic Equaion wih Several Delays Leonid
Finite Element Analysis of Structures
 KAIT OE5 Finie Elemen Analysis of rucures Mid-erm Exam, Fall 9 (p) m. As shown in Fig., we model a russ srucure of uniform area (lengh, Area Am ) subjeced o a uniform body force ( f B e x N / m ) using
KAIT OE5 Finie Elemen Analysis of rucures Mid-erm Exam, Fall 9 (p) m. As shown in Fig., we model a russ srucure of uniform area (lengh, Area Am ) subjeced o a uniform body force ( f B e x N / m ) using
Some Regularity Properties of Three Dimensional Incompressible Magnetohydrodynamic Flows
 Global Journal of Pure and Applied Mahemaics. ISSN 973-78 Volume 3, Number 7 (7), pp. 339-335 Research India Publicaions hp://www.ripublicaion.com Some Regulariy Properies of Three Dimensional Incompressible
Global Journal of Pure and Applied Mahemaics. ISSN 973-78 Volume 3, Number 7 (7), pp. 339-335 Research India Publicaions hp://www.ripublicaion.com Some Regulariy Properies of Three Dimensional Incompressible
Chapter 6. Systems of First Order Linear Differential Equations
 Chaper 6 Sysems of Firs Order Linear Differenial Equaions We will only discuss firs order sysems However higher order sysems may be made ino firs order sysems by a rick shown below We will have a sligh
Chaper 6 Sysems of Firs Order Linear Differenial Equaions We will only discuss firs order sysems However higher order sysems may be made ino firs order sysems by a rick shown below We will have a sligh
