Title: Closed-form approximations to the Error and Complementary Error Functions and their applications in atmospheric science
|
|
|
- Gavin Ward
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Title: Closed-form approximations to the Error and Complementary Error Functions and their applications in atmospheric science Short title: Closed-form of Error and Complementary Error Functions Authors: C. Ren and A. R. MacKenzie Affiliation: Department of Environmental Sciences Lancaster University, Lancaster LA1 4YQ United Kingdom Corresponding author: C. Ren Address: Department of Environmental Sciences Lancaster University, Lancaster LA1 4YQ United Kingdom Tel: Fax:
2 Abstract The Error function, and related functions, occurs in theoretical aspects of many parts of atmospheric science. This note presents a closed-form approximation for the error, complementary error, and scaled complementary error functions, with maximum relative errors within 0.8%. Unlike other approximate solutions, this single equation gives answers within the stated. The approximation is very useful in solving atmospheric science problems by providing analytical solutions. Examples of the utility of the approximations are: the computation of cirrus cloud physics inside a general circulation model, the cumulative distribution functions of normal and log-normal distributions, and the recurrence period for risk assessment. accuracy for x [ 0 ) Keyword Error function, complementary error function, scaled complementary error function, normal distribution, log-normal distribution, cumulative distribution function, recurrence interval Introduction Error and complementary error functions are extensively used in the fields that employ mathematics and physics, e.g., studies of heat and mass transfer (e.g., Chaudhry and Zubair, 1993; Swartzendruber, 00). In atmospheric science, as elsewhere, the error and complementary error functions occur when normal or lognormal distributions are expressed as cumulative distribution functions. This note presents a close-form approximation for the error, complementary error, and scaled complementary error functions with maximum relative errors within 0.8%. The benefits of using an analytical approximation for error function in atmospheric sciences are demonstrated in some examples. The closed-form approximation of error functions The error function is defined as x t erf ( x) = e dt, (1) 0 and the complementary error function is defined as ( ) ( ) t erfc x 1 erf x = e dt. () x Both functions contain integrals. Sometimes, when one wants to evaluate these functions as accurately as possible, rational Chebyshev approximations (Cody, 1969) can be used. Nowadays, built-in functions are available in several computer languages (Cody, 1990). At other times, however, one may forego some accuracy for the sake of a speedy calculation or in order to gain a clearer insight into the relationships between variables in a problem. Decker (1975) provides and cites approximations that are
3 quick to compute, but all fail to give expressions in closed form. The following achieves closed-form approximations for the error, complementary error, and scaled complementary error functions with maximum relative errors within 0.8%. The complementary error function can be expanded as And erfc n i x ( ) ( x ) x 1 e x = 1 3L i= 0, ( i + 1) i ( 1) 1 3 ( i 1) x < c, (3) n 1 x 1 L erfc( x) = e 1 + x > c i,, (4) x i= 1 ( x ) where c is a positive real number with a value around 1. c increases with the increasing n, and Eq. (3) and (4) diverge when x is near to c. However, from Eq. (3), we know x e x erfc( x) 1, x << 1. (5) Similarly, from Eq. (4), 1 e x erfc( x) x, x >> 1. (6) Both Eq. (5) and (6) suggest that f ( x) = a ( a 1) x + x + a (7) might be a good fit to the scaled complementary error function e erfc( x), since f ( 0 ) = 1 and lim x f ( x) = 1 x. Here, a is an adjustable parameter for (7) to match either (5) or (6). When x + a = a is used for x << 1, the simple match of Eq. (7) to Eq. (5) requires a =. We derive a series of values for a by trial-and-error. These values are given in Table 1, together with their accuracies e x erfc x. when used in Eq. (7) to calculate ( ) The errors introduced by using Eq. (7) to estimate erf ( x) and ( x) erfc are shown in Fig. 1. One can choose a value of a to evaluate the results of the error, complementary error, and scaled complementary error functions easily with a calculator to within the accuracy shown. Table 1 Values of a, errors in erf ( x) and erfc ( x), and advantages of each formulation a a Error in Error in Best choice for erf ( x) erfc ( x) % % errors with known sign % % erf ( x) % % single value of a for
4 both erf ( x) and erfc ( x) % % erfc ( x) % % simple formula Examples of applications in atmospheric science As indicated in Table 1, using a = 3 results in the simplest formula: 3 e x erfc( x) (8) x + x + 9 which is never in error by more than 0.65% for complementary error and scaled complementary error functions, and which provides a neat closed solution that can be incorporated into analytical solutions for a broad range of physical and engineering problems. An example of one such problem, and the driver for the development discussed above, is the nucleation and growth of cirrus cloud particles (Ren and MacKenzie, 005). The approximation allowed us to describe the behaviour of cirrus clouds under all conditions, avoiding an unwieldy and unhelpful description based on asymptotic expansions to both ends when it is, in fact, the middle range that is most interesting (Kärcher and Lohmann, 00; Ren and MacKenzie, 005). The cirrus parameterisations are designed for implementation in global climate models (GCMs) (Lohmann et al., 004), where the error associated with the closed-form approximation is small compared to uncertainty in the model output resulting from missing processes and other simplifications. There are clear advantages in calculation speed and interpretation of results in the use of closed-form approximations to the error and related functions within these very large GCM computer codes. Other examples relate to normal or log-normal distributions. The size distributions of aerosols and clouds, and the parameters of turbulent processes are often log-normally distributed. Shoji and Kitaura (006), for example, found that hourly, daily, and annual precipitation distributions were fitted well with lognormal distributions. The cumulative distribution function, D ( I ) which indicates the probability that rainfall amount, I, will not be exceeded within period of time (hourly, daily, or annual), T can, therefore, be given by λ 1 ln I ln I m 1 ae D( I ) = 1+ erf = 1, (9) lnσ ( a 1) λ + λ + a where I m is the geometric mean of rainfall amount, σ is the ln I ln I m geometric standard deviation of rainfall amounts, and λ = lnσ is a convenient measure of the position of a particular rainfall amount in the rainfall distribution. λ = 1 when I = σi m, λ = when I=σ I m, and so on. You can calculate D(I) with a given λ by a calculator, even by hand.
5 Having derived an analytical expression for the cumulative distribution function, the recurrence interval is then T T λ R ( I ) = = [( a 1) λ + λ + a ] e. (10) 1 D( I ) a This relatively simple expression is much easier to read than the equivalent retaining the error function. For instance, for I = I m, λ = 0 and so R( I m ) = T, which confirms that there is a 50:50 chance that rainfall exceeds the geometric mean, I m. For λ = 1, R(σI m ) 6.3T; for λ =, R(σ I m ) 43.6T. Using Eq. (10), values of λ for the 50-, 100-, and 00-year events are given in Table. This time, a = is used, as this value of a guarantees the approximation having relative errors within 0.8%. Beyond their intrinsic interest, log-normal rainfall statistics also propagate into hydrological theory theoretical treatments of slope stability for example (Iida, 004) and engineering design, where, again, avoiding the use of error functions makes model building and theoretical interpretation easier (Swamee, 00). Table Values of λ for calculating the rainfall amount at a given recurrence interval λ R ( I ) 50yrs 100yrs 00yrs Hourly Daily Annual Conclusion A closed-form approximation for the error, complementary error, and scaled complementary error functions with maximum relative errors within 0.8%. Unlike other approximate solutions, this closed-form equation gives answers within the stated accuracy for x [ 0 ). It is very useful when one wants to gain a clearer insight into the relationships between variables in a problem involving error functions. References Chaudhry AM, Zubair S Analytic study of temperature solutions due to gamma-type moving point-heat source. Int. J. Heat Mass. Transf. 36: Cody WJ Rational chebyshev approximations for the error function. Math. Comp. 3:
6 Cody WJ Performance evaluation of programs for the error and complementary error functions. ACM Trans. Math. Softw. 16: Decker DL Computer evaluation of the complementary error function. Am. J. Phys. 43: Iida, T Theoretical research on the relationship between return period of rainfall and shallow landslides. Hydrological Processes, 18: Kärcher B, Lohmann U. 00. A parameterization of cirrus cloud formation: Homogeneous freezing including effects of aerosol size. J. Geophys. Res. 107(D3): article 4698, doi:10.109/001jd Lohmann U, Kärcher B, Hendricks J Sensitivity studies of cirrus clouds formed by heterogeneous freezing in the ECHAM GCM. J Geophys. Res. 109(D16): D1604, doi:10.109/003jd Ren C, MacKenzie AR Cirrus parameterisation and the role of ice nuclei. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 131: Shoji T, Kitaura H Statistical and geostatistical analysis of rainfall in central Japan. Computers & Geosciences 3: Swamee PK. 00. Near Lognormal Distribution. J. Hydro. Eng. 7: Swartzendruber D. 00. Capillary rise of water into soil as described by a solution of Burger's equation, in Environmental Mechanics, Geophys. Monogr. 19:
7 5 4 for erf(x) for erfc(x), e x erfc(x) Accuracy (% of error) x Figure 1 Relative errors of using Eq. (7) with a = ( ),.7749,.7889,.9110, and 3 to calculate error functions. Each line is for a single value of a. For erf, a increases from bottom up; for erfc, a increases from top down. Errors in erf(x) with a = ( ) and in erfc(x) with a =3 are almost identical when x<1.
Prediction of cirrus clouds in GCMs
 Prediction of cirrus clouds in GCMs Bernd Kärcher, Ulrike Burkhardt, Klaus Gierens, and Johannes Hendricks DLR Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen, 82234 Wessling, Germany bernd.kaercher@dlr.de
Prediction of cirrus clouds in GCMs Bernd Kärcher, Ulrike Burkhardt, Klaus Gierens, and Johannes Hendricks DLR Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen, 82234 Wessling, Germany bernd.kaercher@dlr.de
A Note on the Recursive Calculation of Incomplete Gamma Functions
 A Note on the Recursive Calculation of Incomplete Gamma Functions WALTER GAUTSCHI Purdue University It is known that the recurrence relation for incomplete gamma functions a n, x, 0 a 1, n 0,1,2,..., when
A Note on the Recursive Calculation of Incomplete Gamma Functions WALTER GAUTSCHI Purdue University It is known that the recurrence relation for incomplete gamma functions a n, x, 0 a 1, n 0,1,2,..., when
A world-wide investigation of the probability distribution of daily rainfall
 International Precipitation Conference (IPC10) Coimbra, Portugal, 23 25 June 2010 Topic 1 Extreme precipitation events: Physics- and statistics-based descriptions A world-wide investigation of the probability
International Precipitation Conference (IPC10) Coimbra, Portugal, 23 25 June 2010 Topic 1 Extreme precipitation events: Physics- and statistics-based descriptions A world-wide investigation of the probability
Aerosol Effects on Water and Ice Clouds
 Aerosol Effects on Water and Ice Clouds Ulrike Lohmann Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science, Dalhousie University, Halifax, N. S., Canada Contributions from Johann Feichter, Johannes Hendricks,
Aerosol Effects on Water and Ice Clouds Ulrike Lohmann Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science, Dalhousie University, Halifax, N. S., Canada Contributions from Johann Feichter, Johannes Hendricks,
Klimaänderung. Robert Sausen Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen
 Klimaänderung Robert Sausen Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen Vorlesung WS 2017/18 LMU München 7. Wolken und Aerosole Contents of IPCC 2013 Working
Klimaänderung Robert Sausen Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen Vorlesung WS 2017/18 LMU München 7. Wolken und Aerosole Contents of IPCC 2013 Working
J12.4 SIGNIFICANT IMPACT OF AEROSOLS ON MULTI-YEAR RAIN FREQUENCY AND CLOUD THICKNESS
 J12.4 SIGNIFICANT IMPACT OF AEROSOLS ON MULTI-YEAR RAIN FREQUENCY AND CLOUD THICKNESS Zhanqing Li and F. Niu* University of Maryland College park 1. INTRODUCTION Many observational studies of aerosol indirect
J12.4 SIGNIFICANT IMPACT OF AEROSOLS ON MULTI-YEAR RAIN FREQUENCY AND CLOUD THICKNESS Zhanqing Li and F. Niu* University of Maryland College park 1. INTRODUCTION Many observational studies of aerosol indirect
Why build a climate model
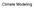 Climate Modeling Why build a climate model Atmosphere H2O vapor and Clouds Absorbing gases CO2 Aerosol Land/Biota Surface vegetation Ice Sea ice Ice sheets (glaciers) Ocean Box Model (0 D) E IN = E OUT
Climate Modeling Why build a climate model Atmosphere H2O vapor and Clouds Absorbing gases CO2 Aerosol Land/Biota Surface vegetation Ice Sea ice Ice sheets (glaciers) Ocean Box Model (0 D) E IN = E OUT
Using Aziz Supercomputer
 The Center of Excellence for Climate Change Research Using Aziz Supercomputer Mansour Almazroui Director, Center of Excellence for Climate Change Research (CECCR) Head, Department of Meteorology King Abdulaziz
The Center of Excellence for Climate Change Research Using Aziz Supercomputer Mansour Almazroui Director, Center of Excellence for Climate Change Research (CECCR) Head, Department of Meteorology King Abdulaziz
Peter Molnar 1 and Paolo Burlando Institute of Environmental Engineering, ETH Zurich, Switzerland
 Hydrology Days 6 Seasonal and regional variability in scaling properties and correlation structure of high resolution precipitation data in a highly heterogeneous mountain environment (Switzerland) Peter
Hydrology Days 6 Seasonal and regional variability in scaling properties and correlation structure of high resolution precipitation data in a highly heterogeneous mountain environment (Switzerland) Peter
REQUEST FOR A SPECIAL PROJECT
 REQUEST FOR A SPECIAL PROJECT 2010 2012 MEMBER STATE: Switzerland Principal Investigator 1 : Affiliation: Prof. Ulrike Lohmann Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science, ETH Zurich Address: Universitaetstrasse
REQUEST FOR A SPECIAL PROJECT 2010 2012 MEMBER STATE: Switzerland Principal Investigator 1 : Affiliation: Prof. Ulrike Lohmann Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science, ETH Zurich Address: Universitaetstrasse
Effects of stratospheric sulfate aerosol geo-engineering on cirrus clouds
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053797, 2012 Effects of stratospheric sulfate aerosol geo-engineering on cirrus clouds Miriam Kuebbeler, 1 Ulrike Lohmann, 1 and Johann Feichter
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl053797, 2012 Effects of stratospheric sulfate aerosol geo-engineering on cirrus clouds Miriam Kuebbeler, 1 Ulrike Lohmann, 1 and Johann Feichter
Consistent estimates from satellites and models for the first aerosol indirect forcing
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl051870, 2012 Consistent estimates from satellites and models for the first aerosol indirect forcing Joyce E. Penner, 1 Cheng Zhou, 1 and Li Xu
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 39,, doi:10.1029/2012gl051870, 2012 Consistent estimates from satellites and models for the first aerosol indirect forcing Joyce E. Penner, 1 Cheng Zhou, 1 and Li Xu
Regional offline land surface simulations over eastern Canada using CLASS. Diana Verseghy Climate Research Division Environment Canada
 Regional offline land surface simulations over eastern Canada using CLASS Diana Verseghy Climate Research Division Environment Canada The Canadian Land Surface Scheme (CLASS) Originally developed for the
Regional offline land surface simulations over eastern Canada using CLASS Diana Verseghy Climate Research Division Environment Canada The Canadian Land Surface Scheme (CLASS) Originally developed for the
Assessment of the reliability of climate predictions based on comparisons with historical time series
 European Geosciences Union General Assembly 28 Vienna, Austria, 13 18 April 28 Session IS23: Climatic and hydrological perspectives on long term changes Assessment of the reliability of climate predictions
European Geosciences Union General Assembly 28 Vienna, Austria, 13 18 April 28 Session IS23: Climatic and hydrological perspectives on long term changes Assessment of the reliability of climate predictions
Climate impacts of ice nucleation
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012jd017950, 2012 Climate impacts of ice nucleation A. Gettelman, 1,2 X. Liu, 3 D. Barahona, 4,5 U. Lohmann, 2 and C. Chen 1 Received 16 April 2012;
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2012jd017950, 2012 Climate impacts of ice nucleation A. Gettelman, 1,2 X. Liu, 3 D. Barahona, 4,5 U. Lohmann, 2 and C. Chen 1 Received 16 April 2012;
+ ( f o. (t) = f c. f c. )e kt (1)
 CIVE Basic Hydrology Jorge A. Ramírez Computations Example Assume that the time evolution of the infiltration capacity for a given soil is governed by Horton's equation (Note that this equation assumes
CIVE Basic Hydrology Jorge A. Ramírez Computations Example Assume that the time evolution of the infiltration capacity for a given soil is governed by Horton's equation (Note that this equation assumes
Reprinted from MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW, Vol. 109, No. 12, December 1981 American Meteorological Society Printed in I'. S. A.
 Reprinted from MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW, Vol. 109, No. 12, December 1981 American Meteorological Society Printed in I'. S. A. Fitting Daily Precipitation Amounts Using the S B Distribution LLOYD W. SWIFT,
Reprinted from MONTHLY WEATHER REVIEW, Vol. 109, No. 12, December 1981 American Meteorological Society Printed in I'. S. A. Fitting Daily Precipitation Amounts Using the S B Distribution LLOYD W. SWIFT,
Bacteria and fungal spores in the global climate model ECHAM5-HAM
 Bacteria and fungal spores in the global climate model ECHAM5-HAM Ana Sesartic, ETH Zurich, Switzerland Acknowledgements: Ulrike Lohmann, Trude Storelvmo, Sylvaine Ferrachat, Tanja Dallafior, Declan O'Donnell,
Bacteria and fungal spores in the global climate model ECHAM5-HAM Ana Sesartic, ETH Zurich, Switzerland Acknowledgements: Ulrike Lohmann, Trude Storelvmo, Sylvaine Ferrachat, Tanja Dallafior, Declan O'Donnell,
Evaluating parameterisations of subgridscale variability with satellite data
 Evaluating parameterisations of subgridscale variability with satellite data Johannes Quaas Institute for Meteorology University of Leipzig johannes.quaas@uni-leipzig.de www.uni-leipzig.de/~quaas Acknowledgements
Evaluating parameterisations of subgridscale variability with satellite data Johannes Quaas Institute for Meteorology University of Leipzig johannes.quaas@uni-leipzig.de www.uni-leipzig.de/~quaas Acknowledgements
Huw W. Lewis *, Dawn L. Harrison and Malcolm Kitchen Met Office, United Kingdom
 2.6 LOCAL VERTICAL PROFILE CORRECTIONS USING DATA FROM MULTIPLE SCAN ELEVATIONS Huw W. Lewis *, Dawn L. Harrison and Malcolm Kitchen Met Office, United Kingdom 1. INTRODUCTION The variation of reflectivity
2.6 LOCAL VERTICAL PROFILE CORRECTIONS USING DATA FROM MULTIPLE SCAN ELEVATIONS Huw W. Lewis *, Dawn L. Harrison and Malcolm Kitchen Met Office, United Kingdom 1. INTRODUCTION The variation of reflectivity
Supplementary Material for: Scientific Uncertainty and Climate Change: Part I. Uncertainty and Unabated Emissions
 Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Supplementary Material for: Scientific Uncertainty and Climate Change: Part I. Uncertainty and Unabated Emissions Stephan Lewandowsky James S. Risbey
Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) Supplementary Material for: Scientific Uncertainty and Climate Change: Part I. Uncertainty and Unabated Emissions Stephan Lewandowsky James S. Risbey
Computation of the error functions erf and erfc in arbitrary precision with correct rounding
 Computation of the error functions erf and erfc in arbitrary precision with correct rounding Sylvain Chevillard Arenaire, LIP, ENS-Lyon, France Sylvain.Chevillard@ens-lyon.fr Nathalie Revol INRIA, Arenaire,
Computation of the error functions erf and erfc in arbitrary precision with correct rounding Sylvain Chevillard Arenaire, LIP, ENS-Lyon, France Sylvain.Chevillard@ens-lyon.fr Nathalie Revol INRIA, Arenaire,
Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System
 Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System -So far in this class, we ve mostly discussed conceptual models models that qualitatively describe the system example: Daisyworld examined stable and unstable
Chapter 6: Modeling the Atmosphere-Ocean System -So far in this class, we ve mostly discussed conceptual models models that qualitatively describe the system example: Daisyworld examined stable and unstable
Parameterization of the nitric acid effect on CCN activation
 Atmos. Chem. Phys., 5, 879 885, 25 SRef-ID: 168-7324/acp/25-5-879 European Geosciences Union Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Parameterization of the nitric acid effect on CCN activation S. Romakkaniemi,
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 5, 879 885, 25 SRef-ID: 168-7324/acp/25-5-879 European Geosciences Union Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Parameterization of the nitric acid effect on CCN activation S. Romakkaniemi,
Lecture 2 APPLICATION OF EXREME VALUE THEORY TO CLIMATE CHANGE. Rick Katz
 1 Lecture 2 APPLICATION OF EXREME VALUE THEORY TO CLIMATE CHANGE Rick Katz Institute for Study of Society and Environment National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, CO USA email: rwk@ucar.edu Home
1 Lecture 2 APPLICATION OF EXREME VALUE THEORY TO CLIMATE CHANGE Rick Katz Institute for Study of Society and Environment National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, CO USA email: rwk@ucar.edu Home
Interactive comment on The impact of Saharan dust and black carbon on albedo and long-term glacier mass balance by J. Gabbi et al.
 The Cryosphere Discuss., 9, C553 C564, 2015 www.the-cryosphere-discuss.net/9/c553/2015/ Author(s) 2015. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribute 3.0 License. The Cryosphere Discussions
The Cryosphere Discuss., 9, C553 C564, 2015 www.the-cryosphere-discuss.net/9/c553/2015/ Author(s) 2015. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribute 3.0 License. The Cryosphere Discussions
Modelling aerosol-cloud interations in GCMs
 Modelling aerosol-cloud interations in GCMs Ulrike Lohmann ETH Zurich Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science Reading, 13.11.2006 Acknowledgements: Sylvaine Ferrachat, Corinna Hoose, Erich Roeckner,
Modelling aerosol-cloud interations in GCMs Ulrike Lohmann ETH Zurich Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science Reading, 13.11.2006 Acknowledgements: Sylvaine Ferrachat, Corinna Hoose, Erich Roeckner,
Do aerosols affect lightning?: A global study of a relation between aerosol optical depth and cloud to ground lightning
 Do aerosols affect lightning?: A global study of a relation between aerosol optical depth and cloud to ground lightning Beata Kucienska 1,*, G. B. Raga 1, Ilan Koren 2, Orit Altaratz 2 1. Centro de Ciencias
Do aerosols affect lightning?: A global study of a relation between aerosol optical depth and cloud to ground lightning Beata Kucienska 1,*, G. B. Raga 1, Ilan Koren 2, Orit Altaratz 2 1. Centro de Ciencias
Drought Monitoring with Hydrological Modelling
 st Joint EARS/JRC International Drought Workshop, Ljubljana,.-5. September 009 Drought Monitoring with Hydrological Modelling Stefan Niemeyer IES - Institute for Environment and Sustainability Ispra -
st Joint EARS/JRC International Drought Workshop, Ljubljana,.-5. September 009 Drought Monitoring with Hydrological Modelling Stefan Niemeyer IES - Institute for Environment and Sustainability Ispra -
Leo Donner GFDL/NOAA, Princeton University. EGU, Vienna, 18 April 2016
 Cloud Dynamical Controls on Climate Forcing by Aerosol-Cloud Interactions: New Insights from Observations, High- Resolution Models, and Parameterizations Leo Donner GFDL/NOAA, Princeton University EGU,
Cloud Dynamical Controls on Climate Forcing by Aerosol-Cloud Interactions: New Insights from Observations, High- Resolution Models, and Parameterizations Leo Donner GFDL/NOAA, Princeton University EGU,
Evaluation of cloud thermodynamic phase parametrizations in the LMDZ GCM by using POLDER satellite data
 GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L06126, doi:10.1029/2003gl019095, 2004 Evaluation of cloud thermodynamic phase parametrizations in the LMDZ GCM by using POLDER satellite data M. Doutriaux-Boucher
GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 31, L06126, doi:10.1029/2003gl019095, 2004 Evaluation of cloud thermodynamic phase parametrizations in the LMDZ GCM by using POLDER satellite data M. Doutriaux-Boucher
Changes to Extreme Precipitation Events: What the Historical Record Shows and What It Means for Engineers
 Changes to Extreme Precipitation Events: What the Historical Record Shows and What It Means for Engineers Geoffrey M Bonnin National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration National Weather Service Office
Changes to Extreme Precipitation Events: What the Historical Record Shows and What It Means for Engineers Geoffrey M Bonnin National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration National Weather Service Office
FUTURE PROJECTIONS OF PRECIPITATION CHARACTERISTICS IN ASIA
 FUTURE PROJECTIONS OF PRECIPITATION CHARACTERISTICS IN ASIA AKIO KITOH, MASAHIRO HOSAKA, YUKIMASA ADACHI, KENJI KAMIGUCHI Meteorological Research Institute Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0052, Japan It is anticipated
FUTURE PROJECTIONS OF PRECIPITATION CHARACTERISTICS IN ASIA AKIO KITOH, MASAHIRO HOSAKA, YUKIMASA ADACHI, KENJI KAMIGUCHI Meteorological Research Institute Tsukuba, Ibaraki 305-0052, Japan It is anticipated
Understanding land-surfaceatmosphere. observations and models
 Understanding land-surfaceatmosphere coupling in observations and models Alan K. Betts Atmospheric Research akbetts@aol.com MERRA Workshop AMS Conference, Phoenix January 11, 2009 Land-surface-atmosphere
Understanding land-surfaceatmosphere coupling in observations and models Alan K. Betts Atmospheric Research akbetts@aol.com MERRA Workshop AMS Conference, Phoenix January 11, 2009 Land-surface-atmosphere
Notes on Ewald summation techniques
 February 3, 011 Notes on Ewald summation techniques Adapted from similar presentation in PHY 71 he total electrostatic potential energy of interaction between point charges {q i } at the positions {r i
February 3, 011 Notes on Ewald summation techniques Adapted from similar presentation in PHY 71 he total electrostatic potential energy of interaction between point charges {q i } at the positions {r i
Updated H 2 SO 4 -H 2 O binary homogeneous nucleation look-up tables
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2008jd010527, 2008 Updated H 2 SO 4 -H 2 O binary homogeneous nucleation look-up tables Fangqun Yu 1 Received 2 June
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2008jd010527, 2008 Updated H 2 SO 4 -H 2 O binary homogeneous nucleation look-up tables Fangqun Yu 1 Received 2 June
Shape of the return probability density function and extreme value statistics
 Shape of the return probability density function and extreme value statistics 13/09/03 Int. Workshop on Risk and Regulation, Budapest Overview I aim to elucidate a relation between one field of research
Shape of the return probability density function and extreme value statistics 13/09/03 Int. Workshop on Risk and Regulation, Budapest Overview I aim to elucidate a relation between one field of research
Storm rainfall. Lecture content. 1 Analysis of storm rainfall 2 Predictive model of storm rainfall for a given
 Storm rainfall Lecture content 1 Analysis of storm rainfall 2 Predictive model of storm rainfall for a given max rainfall depth 1 rainfall duration and return period à Depth-Duration-Frequency curves 2
Storm rainfall Lecture content 1 Analysis of storm rainfall 2 Predictive model of storm rainfall for a given max rainfall depth 1 rainfall duration and return period à Depth-Duration-Frequency curves 2
Aerosol Dynamics. Antti Lauri NetFAM Summer School Zelenogorsk, 9 July 2008
 Aerosol Dynamics Antti Lauri NetFAM Summer School Zelenogorsk, 9 July 2008 Department of Physics, Division of Atmospheric Sciences and Geophysics, University of Helsinki Aerosol Dynamics: What? A way to
Aerosol Dynamics Antti Lauri NetFAM Summer School Zelenogorsk, 9 July 2008 Department of Physics, Division of Atmospheric Sciences and Geophysics, University of Helsinki Aerosol Dynamics: What? A way to
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Sullivan et al..73/pnas.54393 Temporal Averaging and Integration Time Step Effects on Attribution Metrics An important consideration in the attribution analysis is the effect of
Supporting Information Sullivan et al..73/pnas.54393 Temporal Averaging and Integration Time Step Effects on Attribution Metrics An important consideration in the attribution analysis is the effect of
The parameterization of cloud cover
 vailable online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 57 (24 ) 293 298 23 ISES Solar World Congress The parameterization of cloud cover Heinrich Morf* Senior Member ISES, Buechraiweg 47,
vailable online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Energy Procedia 57 (24 ) 293 298 23 ISES Solar World Congress The parameterization of cloud cover Heinrich Morf* Senior Member ISES, Buechraiweg 47,
An Alternative Temporal Rainfall Distribution for Hydrologic Analysis and Design
 An Alternative Temporal Rainfall Distribution for Hydrologic Analysis and Design Joseph P. Wilson, PE, PH Wilson Hydro, LLC PhD Candidate Missouri University of Science Technology Rolla, Missouri Sorry
An Alternative Temporal Rainfall Distribution for Hydrologic Analysis and Design Joseph P. Wilson, PE, PH Wilson Hydro, LLC PhD Candidate Missouri University of Science Technology Rolla, Missouri Sorry
R.Garçon, F.Garavaglia, J.Gailhard, E.Paquet, F.Gottardi EDF-DTG
 Homogeneous samples and reliability of probabilistic models : using an atmospheric circulation patterns sampling for a better estimation of extreme rainfall probability R.Garçon, F.Garavaglia, J.Gailhard,
Homogeneous samples and reliability of probabilistic models : using an atmospheric circulation patterns sampling for a better estimation of extreme rainfall probability R.Garçon, F.Garavaglia, J.Gailhard,
Intensity-Duration-Frequency (IDF) Curves Example
 Intensity-Duration-Frequency (IDF) Curves Example Intensity-Duration-Frequency (IDF) curves describe the relationship between rainfall intensity, rainfall duration, and return period (or its inverse, probability
Intensity-Duration-Frequency (IDF) Curves Example Intensity-Duration-Frequency (IDF) curves describe the relationship between rainfall intensity, rainfall duration, and return period (or its inverse, probability
5. General Circulation Models
 5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
5. General Circulation Models I. 3-D Climate Models (General Circulation Models) To include the full three-dimensional aspect of climate, including the calculation of the dynamical transports, requires
Precipitation in climate modeling for the Mediterranean region
 Precipitation in climate modeling for the Mediterranean region Simon Krichak Dept. of Geophysics Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences, Tel Aviv University, Israel Concepts for Convective Parameterizations
Precipitation in climate modeling for the Mediterranean region Simon Krichak Dept. of Geophysics Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences, Tel Aviv University, Israel Concepts for Convective Parameterizations
Beyond Wiener Askey Expansions: Handling Arbitrary PDFs
 Journal of Scientific Computing, Vol. 27, Nos. 1 3, June 2006 ( 2005) DOI: 10.1007/s10915-005-9038-8 Beyond Wiener Askey Expansions: Handling Arbitrary PDFs Xiaoliang Wan 1 and George Em Karniadakis 1
Journal of Scientific Computing, Vol. 27, Nos. 1 3, June 2006 ( 2005) DOI: 10.1007/s10915-005-9038-8 Beyond Wiener Askey Expansions: Handling Arbitrary PDFs Xiaoliang Wan 1 and George Em Karniadakis 1
CIVE322 BASIC HYDROLOGY
 CIVE322 BASIC HYDROLOGY Homework No.3 Solution 1. The coordinates of four precipitation gauging stations are A = (3,4), B = (9,4), C = (3,12), and D = (9,12). The observed precipitation amounts at these
CIVE322 BASIC HYDROLOGY Homework No.3 Solution 1. The coordinates of four precipitation gauging stations are A = (3,4), B = (9,4), C = (3,12), and D = (9,12). The observed precipitation amounts at these
Climate Change: the Uncertainty of Certainty
 Climate Change: the Uncertainty of Certainty Reinhard Furrer, UZH JSS, Geneva Oct. 30, 2009 Collaboration with: Stephan Sain - NCAR Reto Knutti - ETHZ Claudia Tebaldi - Climate Central Ryan Ford, Doug
Climate Change: the Uncertainty of Certainty Reinhard Furrer, UZH JSS, Geneva Oct. 30, 2009 Collaboration with: Stephan Sain - NCAR Reto Knutti - ETHZ Claudia Tebaldi - Climate Central Ryan Ford, Doug
CONVECTIVE CLOUD MICROPHYSICS IN A HIGH-RESOLUTION NWP MODEL
 CONVECTIVE CLOUD MICROPHYSICS IN A HIGH-RESOLUTION NWP MODEL J. Trentmann 1, A. Seifert 2, H. Wernli 1 1 Institute for Atmospheric Physics, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany 2 German Weather
CONVECTIVE CLOUD MICROPHYSICS IN A HIGH-RESOLUTION NWP MODEL J. Trentmann 1, A. Seifert 2, H. Wernli 1 1 Institute for Atmospheric Physics, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany 2 German Weather
8 Mechanisms for tropical rainfall responses to equatorial
 8 Mechanisms for tropical rainfall responses to equatorial heating More reading: 1. Hamouda, M. and Kucharski, F. (2019) Ekman pumping Mechanism driving Precipitation anomalies in Response to Equatorial
8 Mechanisms for tropical rainfall responses to equatorial heating More reading: 1. Hamouda, M. and Kucharski, F. (2019) Ekman pumping Mechanism driving Precipitation anomalies in Response to Equatorial
Using statistical methods to analyse environmental extremes.
 Using statistical methods to analyse environmental extremes. Emma Eastoe Department of Mathematics and Statistics Lancaster University December 16, 2008 Focus of talk Discuss statistical models used to
Using statistical methods to analyse environmental extremes. Emma Eastoe Department of Mathematics and Statistics Lancaster University December 16, 2008 Focus of talk Discuss statistical models used to
Statistical Seismic Landslide Hazard Analysis: an Example from Taiwan
 Statistical Seismic Landslide Hazard Analysis: an Example from Taiwan Chyi-Tyi Lee Graduate Institute of Applied Geology, National Central University, Taiwan Seismology Forum 27: Natural Hazards and Surface
Statistical Seismic Landslide Hazard Analysis: an Example from Taiwan Chyi-Tyi Lee Graduate Institute of Applied Geology, National Central University, Taiwan Seismology Forum 27: Natural Hazards and Surface
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model
 The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
The PRECIS Regional Climate Model General overview (1) The regional climate model (RCM) within PRECIS is a model of the atmosphere and land surface, of limited area and high resolution and locatable over
SEISMIC HAZARD CHARACTERIZATION AND RISK EVALUATION USING GUMBEL S METHOD OF EXTREMES (G1 AND G3) AND G-R FORMULA FOR IRAQ
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 2898 SEISMIC HAZARD CHARACTERIZATION AND RISK EVALUATION USING GUMBEL S METHOD OF EXTREMES (G1 AND G3)
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 2004 Paper No. 2898 SEISMIC HAZARD CHARACTERIZATION AND RISK EVALUATION USING GUMBEL S METHOD OF EXTREMES (G1 AND G3)
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System
 An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
An Introduction to Coupled Models of the Atmosphere Ocean System Jonathon S. Wright jswright@tsinghua.edu.cn Atmosphere Ocean Coupling 1. Important to climate on a wide range of time scales Diurnal to
Appendix 1: UK climate projections
 Appendix 1: UK climate projections The UK Climate Projections 2009 provide the most up-to-date estimates of how the climate may change over the next 100 years. They are an invaluable source of information
Appendix 1: UK climate projections The UK Climate Projections 2009 provide the most up-to-date estimates of how the climate may change over the next 100 years. They are an invaluable source of information
Climate Change and Predictability of the Indian Summer Monsoon
 Climate Change and Predictability of the Indian Summer Monsoon B. N. Goswami (goswami@tropmet.res.in) Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune Annual mean Temp. over India 1875-2004 Kothawale, Roopakum
Climate Change and Predictability of the Indian Summer Monsoon B. N. Goswami (goswami@tropmet.res.in) Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology, Pune Annual mean Temp. over India 1875-2004 Kothawale, Roopakum
NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE The Skillful Time Scale of Climate Models
 Journal January of 2016 the Meteorological Society of Japan, I. TAKAYABU Vol. 94A, pp. and 191 197, K. HIBINO 2016 191 DOI:10.2151/jmsj.2015-038 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE The Skillful Time Scale of Climate
Journal January of 2016 the Meteorological Society of Japan, I. TAKAYABU Vol. 94A, pp. and 191 197, K. HIBINO 2016 191 DOI:10.2151/jmsj.2015-038 NOTES AND CORRESPONDENCE The Skillful Time Scale of Climate
Climate Change Models: The Cyprus Case
 Climate Change Models: The Cyprus Case M. Petrakis, C. Giannakopoulos, G. Lemesios National Observatory of Athens AdaptToClimate 2014, Nicosia Cyprus Climate Research (1) Climate is one of the most challenging
Climate Change Models: The Cyprus Case M. Petrakis, C. Giannakopoulos, G. Lemesios National Observatory of Athens AdaptToClimate 2014, Nicosia Cyprus Climate Research (1) Climate is one of the most challenging
Comparison of Convection Characteristics at the Tropical Western Pacific Darwin Site Between Observation and Global Climate Models Simulations
 Comparison of Convection Characteristics at the Tropical Western Pacific Darwin Site Between Observation and Global Climate Models Simulations G.J. Zhang Center for Atmospheric Sciences Scripps Institution
Comparison of Convection Characteristics at the Tropical Western Pacific Darwin Site Between Observation and Global Climate Models Simulations G.J. Zhang Center for Atmospheric Sciences Scripps Institution
Deutscher Wetterdienst
 Deutscher Wetterdienst Small scales do not forget! Axel Seifert Hans-Ertel Centre for Weather Research Max Planck Institute, Hamburg Deutscher Wetterdienst, Offenbach with Carmen Köhler (DWD), Claudia
Deutscher Wetterdienst Small scales do not forget! Axel Seifert Hans-Ertel Centre for Weather Research Max Planck Institute, Hamburg Deutscher Wetterdienst, Offenbach with Carmen Köhler (DWD), Claudia
9 Condensation. Learning Goals. After studying this chapter, students should be able to:
 9 Condensation Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. explain the microphysical processes that operate in clouds to influence the formation and growth of cloud droplets
9 Condensation Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. explain the microphysical processes that operate in clouds to influence the formation and growth of cloud droplets
Model Systems at MPI-M. Marco Giorgetta
 Model Systems at MPI-M Marco Giorgetta Content What is a model in climate research as used here for IPCC? What is a model? Components of the climate system Climate models What is inside? Climate models
Model Systems at MPI-M Marco Giorgetta Content What is a model in climate research as used here for IPCC? What is a model? Components of the climate system Climate models What is inside? Climate models
Regional climate modelling in the future. Ralf Döscher, SMHI, Sweden
 Regional climate modelling in the future Ralf Döscher, SMHI, Sweden The chain Global H E H E C ( m 3/s ) Regional downscaling 120 adam 3 C HAM 4 adam 3 C HAM 4 trl A2 A2 B2 B2 80 40 0 J F M A M J J A S
Regional climate modelling in the future Ralf Döscher, SMHI, Sweden The chain Global H E H E C ( m 3/s ) Regional downscaling 120 adam 3 C HAM 4 adam 3 C HAM 4 trl A2 A2 B2 B2 80 40 0 J F M A M J J A S
MEASUREMENTS IN LOW LATITUDE HIGH ALTITUDE CIRRUS
 MEASUREMENTS IN LOW LATITUDE HIGH ALTITUDE CIRRUS 1. INTRODUCTION Andrew J. Heymsfield, Carl Schmitt and Aaron Bansemer National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado According to the ISCCP
MEASUREMENTS IN LOW LATITUDE HIGH ALTITUDE CIRRUS 1. INTRODUCTION Andrew J. Heymsfield, Carl Schmitt and Aaron Bansemer National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, Colorado According to the ISCCP
Climate Risk Profile for Samoa
 Climate Risk Profile for Samoa Report Prepared by Wairarapa J. Young Samoa Meteorology Division March, 27 Summary The likelihood (i.e. probability) components of climate-related risks in Samoa are evaluated
Climate Risk Profile for Samoa Report Prepared by Wairarapa J. Young Samoa Meteorology Division March, 27 Summary The likelihood (i.e. probability) components of climate-related risks in Samoa are evaluated
MATH115. Infinite Series. Paolo Lorenzo Bautista. July 17, De La Salle University. PLBautista (DLSU) MATH115 July 17, / 43
 MATH115 Infinite Series Paolo Lorenzo Bautista De La Salle University July 17, 2014 PLBautista (DLSU) MATH115 July 17, 2014 1 / 43 Infinite Series Definition If {u n } is a sequence and s n = u 1 + u 2
MATH115 Infinite Series Paolo Lorenzo Bautista De La Salle University July 17, 2014 PLBautista (DLSU) MATH115 July 17, 2014 1 / 43 Infinite Series Definition If {u n } is a sequence and s n = u 1 + u 2
Final report for Project Dynamical downscaling for SEACI. Principal Investigator: John McGregor
 Final report for Project 1.3.6 1.3.6 Dynamical downscaling for SEACI Principal Investigator: John McGregor CSIRO Marine and Atmospheric Research, john.mcgregor@csiro.au, Tel: 03 9239 4400, Fax: 03 9239
Final report for Project 1.3.6 1.3.6 Dynamical downscaling for SEACI Principal Investigator: John McGregor CSIRO Marine and Atmospheric Research, john.mcgregor@csiro.au, Tel: 03 9239 4400, Fax: 03 9239
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Effect of remote sea surface temperature change on tropical cyclone potential intensity Gabriel A. Vecchi Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory NOAA Brian J. Soden Rosenstiel School for Marine and Atmospheric
Effect of remote sea surface temperature change on tropical cyclone potential intensity Gabriel A. Vecchi Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory NOAA Brian J. Soden Rosenstiel School for Marine and Atmospheric
Parameterization of cirrus cloud formation in large-scale models: Homogeneous nucleation
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jd009355, 2008 Parameterization of cirrus cloud formation in large-scale models: Homogeneous nucleation Donifan Barahona
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 113,, doi:10.1029/2007jd009355, 2008 Parameterization of cirrus cloud formation in large-scale models: Homogeneous nucleation Donifan Barahona
3B.3: Climate Controls on the Extreme Rainstorms in the Contiguous US:
 97 th AMS Annual Meeting 3B.3: Climate Controls on the Extreme Rainstorms in the Contiguous US: 1979-2015 Xiaodong Chen and Faisal Hossain Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of
97 th AMS Annual Meeting 3B.3: Climate Controls on the Extreme Rainstorms in the Contiguous US: 1979-2015 Xiaodong Chen and Faisal Hossain Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering University of
Analysis of Cloud-Radiation Interactions Using ARM Observations and a Single-Column Model
 Analysis of Cloud-Radiation Interactions Using ARM Observations and a Single-Column Model S. F. Iacobellis, R. C. J. Somerville, D. E. Lane, and J. Berque Scripps Institution of Oceanography University
Analysis of Cloud-Radiation Interactions Using ARM Observations and a Single-Column Model S. F. Iacobellis, R. C. J. Somerville, D. E. Lane, and J. Berque Scripps Institution of Oceanography University
Forecasts for the Future: Understanding Climate Models and Climate Projections for the 21 st Century
 Forecasts for the Future: Understanding Climate Models and Climate Projections for the 21 st Century Linda E. Sohl NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies and the Center for Climate Systems Reseearch
Forecasts for the Future: Understanding Climate Models and Climate Projections for the 21 st Century Linda E. Sohl NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies and the Center for Climate Systems Reseearch
EVA Tutorial #2 PEAKS OVER THRESHOLD APPROACH. Rick Katz
 1 EVA Tutorial #2 PEAKS OVER THRESHOLD APPROACH Rick Katz Institute for Mathematics Applied to Geosciences National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, CO USA email: rwk@ucar.edu Home page: www.isse.ucar.edu/staff/katz/
1 EVA Tutorial #2 PEAKS OVER THRESHOLD APPROACH Rick Katz Institute for Mathematics Applied to Geosciences National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, CO USA email: rwk@ucar.edu Home page: www.isse.ucar.edu/staff/katz/
Chapter 3 Single Random Variables and Probability Distributions (Part 1)
 Chapter 3 Single Random Variables and Probability Distributions (Part 1) Contents What is a Random Variable? Probability Distribution Functions Cumulative Distribution Function Probability Density Function
Chapter 3 Single Random Variables and Probability Distributions (Part 1) Contents What is a Random Variable? Probability Distribution Functions Cumulative Distribution Function Probability Density Function
A climate model study of indirect radiative forcing by anthropogenic sulfate aerosols
 A climate model study of indirect radiative forcing by anthropogenic sulfate aerosols A. Jones, D.L. Roberts & A. Slingo Hadley Centre for Climate Prediction and Research, Meteorological Office, London
A climate model study of indirect radiative forcing by anthropogenic sulfate aerosols A. Jones, D.L. Roberts & A. Slingo Hadley Centre for Climate Prediction and Research, Meteorological Office, London
Combining Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods to Produce Gridded Climatologies
 Combining Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods to Produce Gridded Climatologies Michael Squires Alan McNab National Climatic Data Center (NCDC - NOAA) Asheville, NC Abstract There are nearly 8,000 sites
Combining Deterministic and Probabilistic Methods to Produce Gridded Climatologies Michael Squires Alan McNab National Climatic Data Center (NCDC - NOAA) Asheville, NC Abstract There are nearly 8,000 sites
Cloud Brightening and Climate Change
 Cloud Brightening and Climate Change 89 Hannele Korhonen and Antti-Ilari Partanen Contents Definitions... 778 Aerosols and Cloud Albedo... 778 Cloud Brightening with Sea-Salt Aerosol... 779 Climate Effects
Cloud Brightening and Climate Change 89 Hannele Korhonen and Antti-Ilari Partanen Contents Definitions... 778 Aerosols and Cloud Albedo... 778 Cloud Brightening with Sea-Salt Aerosol... 779 Climate Effects
The Comparison Test & Limit Comparison Test
 The Comparison Test & Limit Comparison Test Math4 Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky February 5, 207 Math4 Lecture 3 / 3 Summary of (some of) what we have learned about series... Math4 Lecture
The Comparison Test & Limit Comparison Test Math4 Department of Mathematics, University of Kentucky February 5, 207 Math4 Lecture 3 / 3 Summary of (some of) what we have learned about series... Math4 Lecture
TREND AND VARIABILITY ANALYSIS OF RAINFALL SERIES AND THEIR EXTREME
 TREND AND VARIABILITY ANALYSIS OF RAINFALL SERIES AND THEIR EXTREME EVENTS J. Abaurrea, A. C. Cebrián. Dpto. Métodos Estadísticos. Universidad de Zaragoza. Abstract: Rainfall series and their corresponding
TREND AND VARIABILITY ANALYSIS OF RAINFALL SERIES AND THEIR EXTREME EVENTS J. Abaurrea, A. C. Cebrián. Dpto. Métodos Estadísticos. Universidad de Zaragoza. Abstract: Rainfall series and their corresponding
Parameterizing the competition between homogeneous and heterogeneous freezing in ice cloud formation polydisperse ice nuclei
 Atmos. Chem. Phys., 9, 5933 5948, 009 www.atmos-chem-phys.net/9/5933/009/ Author(s) 009. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Parameterizing
Atmos. Chem. Phys., 9, 5933 5948, 009 www.atmos-chem-phys.net/9/5933/009/ Author(s) 009. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Parameterizing
Consistent changes in twenty-first century daily precipitation from regional climate simulations for Korea using two convection parameterizations
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L14706, doi:10.1029/2008gl034126, 2008 Consistent changes in twenty-first century daily precipitation from regional climate simulations
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 35, L14706, doi:10.1029/2008gl034126, 2008 Consistent changes in twenty-first century daily precipitation from regional climate simulations
Diagnosis of Relative Humidity Changes in a Warmer Climate Using Tracers of Last Saturation
 Diagnosis of Relative Humidity Changes in a Warmer Climate Using Tracers of Last Saturation 8 March, 2011 Jonathon Wright Department of Applied Mathematics & Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge
Diagnosis of Relative Humidity Changes in a Warmer Climate Using Tracers of Last Saturation 8 March, 2011 Jonathon Wright Department of Applied Mathematics & Theoretical Physics University of Cambridge
[1] Emissions of CO 2 and other GHGs are increasing
![[1] Emissions of CO 2 and other GHGs are increasing [1] Emissions of CO 2 and other GHGs are increasing](/thumbs/81/84565805.jpg) The science and policy of climate change is based on four major pieces of evidence [1] Emissions of CO 2 and other GHGs are increasing 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 195 1953 1956 1959 1962 1965 1968 1971 1974 1977 198
The science and policy of climate change is based on four major pieces of evidence [1] Emissions of CO 2 and other GHGs are increasing 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 195 1953 1956 1959 1962 1965 1968 1971 1974 1977 198
Simulations of contrail-to-cirrus transition: Study of the radiative impact on contrail evolution S. Unterstraßer, K. Gierens
 Simulations of contrail-to-cirrus transition: Study of the radiative impact on contrail evolution S. Unterstraßer, K. Gierens Folie 1 Standardfoliensatz >24.4.2006 Personal Introduction Simon Unterstrasser
Simulations of contrail-to-cirrus transition: Study of the radiative impact on contrail evolution S. Unterstraßer, K. Gierens Folie 1 Standardfoliensatz >24.4.2006 Personal Introduction Simon Unterstrasser
Uncertainty and Risk in Foundation Design
 2.1 Classify the uncertainty associated with following items as either aleatory or epistemic and explain your reason for your classification: average wind speed over a 30 day period, location of a certain
2.1 Classify the uncertainty associated with following items as either aleatory or epistemic and explain your reason for your classification: average wind speed over a 30 day period, location of a certain
Heavier summer downpours with climate change revealed by weather forecast resolution model
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2258 Heavier summer downpours with climate change revealed by weather forecast resolution model Number of files = 1 File #1 filename: kendon14supp.pdf File
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCLIMATE2258 Heavier summer downpours with climate change revealed by weather forecast resolution model Number of files = 1 File #1 filename: kendon14supp.pdf File
Estimating Probable Maximum Precipitation for Linau River Basin in Sarawak
 Estimating Probable Maximum Precipitation for Linau River Basin in Sarawak M. Hussain, S. Nadya and F.J. Chia Hydropower Development Division, Sarawak Energy Berhad, 93050, Kuching, Sarawak, Malaysia Date
Estimating Probable Maximum Precipitation for Linau River Basin in Sarawak M. Hussain, S. Nadya and F.J. Chia Hydropower Development Division, Sarawak Energy Berhad, 93050, Kuching, Sarawak, Malaysia Date
Climate Change and Water Cycle: Effect to Water Resources and their Utilization in Finland (CLIMWATER)
 Climate Change and Water Cycle: Effect to Water Resources and their Utilization in Finland (CLIMWATER) Final Seminar of the Ficca Programme 2.12.2014 J. Pulliainen (FMI), L. Backman, J. Kaurola, T. Olsson,
Climate Change and Water Cycle: Effect to Water Resources and their Utilization in Finland (CLIMWATER) Final Seminar of the Ficca Programme 2.12.2014 J. Pulliainen (FMI), L. Backman, J. Kaurola, T. Olsson,
J. Schneider & Chr. Voigt - Physics and Chemistry of Aerosols and Ice Clouds
 Chapter 8 Contrails and contrail cirrus 8.1 Introduction - Terminology 8.2 Contrail formation conditions 8.3 Heterogeneous nucleation on volatile aerosol and soot 8.4 Indirect effect of soot on cirrus
Chapter 8 Contrails and contrail cirrus 8.1 Introduction - Terminology 8.2 Contrail formation conditions 8.3 Heterogeneous nucleation on volatile aerosol and soot 8.4 Indirect effect of soot on cirrus
CURRENT AND FUTURE TROPICAL CYCLONE RISK IN THE SOUTH PACIFIC
 CURRENT AND FUTURE TROPICAL CYCLONE RISK IN THE SOUTH PACIFIC COUNTRY RISK PROFILE: SAMOA JUNE 2013 Samoa has been affected by devastating cyclones on multiple occasions, e.g. tropical cyclones Ofa and
CURRENT AND FUTURE TROPICAL CYCLONE RISK IN THE SOUTH PACIFIC COUNTRY RISK PROFILE: SAMOA JUNE 2013 Samoa has been affected by devastating cyclones on multiple occasions, e.g. tropical cyclones Ofa and
2. There may be large uncertainties in the dating of materials used to draw timelines for paleo records.
 Limitations of Paleo Data A Discussion: Although paleoclimatic information may be used to construct scenarios representing future climate conditions, there are limitations associated with this approach.
Limitations of Paleo Data A Discussion: Although paleoclimatic information may be used to construct scenarios representing future climate conditions, there are limitations associated with this approach.
Annex I to Resolution 6.2/2 (Cg-XVI) Approved Text to replace Chapter B.4 of WMO Technical Regulations (WMO-No. 49), Vol. I
 Annex I to Resolution 6.2/2 (Cg-XVI) Approved Text to replace Chapter B.4 of WMO Technical Regulations (WMO-No. 49), Vol. I TECHNICAL REGULATIONS VOLUME I General Meteorological Standards and Recommended
Annex I to Resolution 6.2/2 (Cg-XVI) Approved Text to replace Chapter B.4 of WMO Technical Regulations (WMO-No. 49), Vol. I TECHNICAL REGULATIONS VOLUME I General Meteorological Standards and Recommended
A. Parodi 1, (1) CIMA Research Foundation, Italy. in cooperation with: K. A. Emanuel 2, and E. Foufoula-Georgiou 3 (2) EAPS, MIT, USA
 Spatial and temporal evolution of deep moist convective processes: the role of microphysics A. Parodi 1, (1) CIMA Research Foundation, Italy in cooperation with: K. A. Emanuel 2, and E. Foufoula-Georgiou
Spatial and temporal evolution of deep moist convective processes: the role of microphysics A. Parodi 1, (1) CIMA Research Foundation, Italy in cooperation with: K. A. Emanuel 2, and E. Foufoula-Georgiou
Thessaloniki, Greece
 9th International Conference on Urban Drainage Modelling Effects of Climate Change on the Estimation of Intensity-Duration- Frequency (IDF) curves for, Greece, Greece G. Terti, P. Galiatsatou, P. Prinos
9th International Conference on Urban Drainage Modelling Effects of Climate Change on the Estimation of Intensity-Duration- Frequency (IDF) curves for, Greece, Greece G. Terti, P. Galiatsatou, P. Prinos
IYGB Mathematical Methods 1
 IYGB Mathematical Methods Practice Paper A Time: 3 hours Candidates may use any non programmable, non graphical calculator which does not have the capability of storing data or manipulating algebraic expressions
IYGB Mathematical Methods Practice Paper A Time: 3 hours Candidates may use any non programmable, non graphical calculator which does not have the capability of storing data or manipulating algebraic expressions
WRF MODEL STUDY OF TROPICAL INERTIA GRAVITY WAVES WITH COMPARISONS TO OBSERVATIONS. Stephanie Evan, Joan Alexander and Jimy Dudhia.
 WRF MODEL STUDY OF TROPICAL INERTIA GRAVITY WAVES WITH COMPARISONS TO OBSERVATIONS. Stephanie Evan, Joan Alexander and Jimy Dudhia. Background Small-scale Gravity wave Inertia Gravity wave Mixed RossbyGravity
WRF MODEL STUDY OF TROPICAL INERTIA GRAVITY WAVES WITH COMPARISONS TO OBSERVATIONS. Stephanie Evan, Joan Alexander and Jimy Dudhia. Background Small-scale Gravity wave Inertia Gravity wave Mixed RossbyGravity
EFFECTS OF GLOBAL WARMING ON LANDSLIDE FREQUENCIES IN RATNAPURA DISTRICT, SRI LANKA- 2011
 EFFECTS OF GLOBAL WARMING ON LANDSLIDE FREQUENCIES IN RATNAPURA DISTRICT, SRI LANKA- 2011 T. D. Rathnaweera, Student, (Email: tdr19862142@gmail.com) U. P. Nawagamuwa,Senior Lecturer, (Email: udeni@uom.lk)
EFFECTS OF GLOBAL WARMING ON LANDSLIDE FREQUENCIES IN RATNAPURA DISTRICT, SRI LANKA- 2011 T. D. Rathnaweera, Student, (Email: tdr19862142@gmail.com) U. P. Nawagamuwa,Senior Lecturer, (Email: udeni@uom.lk)
Potential impacts of aerosol and dust pollution acting as cloud nucleating aerosol on water resources in the Colorado River Basin
 Potential impacts of aerosol and dust pollution acting as cloud nucleating aerosol on water resources in the Colorado River Basin Vandana Jha, W. R. Cotton, and G. G. Carrio Colorado State University,
Potential impacts of aerosol and dust pollution acting as cloud nucleating aerosol on water resources in the Colorado River Basin Vandana Jha, W. R. Cotton, and G. G. Carrio Colorado State University,
