Deutscher Wetterdienst
|
|
|
- Laura Bond
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Deutscher Wetterdienst Small scales do not forget! Axel Seifert Hans-Ertel Centre for Weather Research Max Planck Institute, Hamburg Deutscher Wetterdienst, Offenbach with Carmen Köhler (DWD), Claudia Frick (ETH Zürich), Bjorn Stevens (MPI-M Hamburg) and others.
2 Overview è Recent work on microphysics parameterizations è Prognostic cirrus microphysics è Prognostic melting scheme for snow è Two-moment microphysics for deep convection è Some thougths on sub-grid precipitation è Autoconversion è Convective precipitation è PDF-based vs stochastic schemes è Conclusions
3 Parameterization of cirrus clouds: Multiple ice modes è Heterogeneous and homogeneous nucleation produce very different number concentration, and compete with each other è To properly describe this system we use a twomoment two-mode cloud ice scheme with a onemoment snow class Heterogeneous Homogeneous Prognostic ice variables: q hom, N hom, q het, N het, q s è Depositional growth can then be parameterized by a multi-timescale relaxation approach (e.g. Morrison et al. 2005)
4 Parameterization of cirrus clouds: Multiple ice modes è Idealized simulations of orographic cirrus clouds
5 Parameterization of cirrus clouds: Multiple ice modes è Idealized simulations of orographic cirrus clouds è Impact on radiation?
6 Homogeneous nucleation: è Timescale of nucleation and depositional growth S i i +1 Large-scale models: τ freez <τ dep t S cr Fully-resolved (large-eddy) model: i i +2 t τ freez <τ dep t cr τ freez τ dep Current NWP models: t τ freez <τ dep t time/s
7 Explicit snow melting model: The problem è In current microphysics schemes meltwater contributes to rain, i.e., external instead of internal mixture. è This leads to unphysical behavior, e.g., rain/meltwater may have a much higher fall speed, but fall speed of snow is always assumed as,dry snow. è In most NWP models snow melts too fast leading to problems in the forecasts of precipitation phase and wet snow. è This can be a serious forecast problem! A series of power line towers which snapped off during the wet snowfall event in November 2005 in Germany (picture by Sven Lüke,
8 Explicit snow melting model: Prognostic melt water è Parameterization concept follows Szyrmer and Zawadzki (1999, JAS) è Snowflakes below a critical size D* have melted completely è Larger snowflakes are partially melted with LWF ~ 1/D s è Instead of predicting q s and D* we use mixing ratios of ice and liquid part L s,i = L s,w = D m i (D s )f m (D s,)dd s D m w (D s )f m (D s,)dd s. and diagnose D* each time step. f(d s ) melted snow transformed to rain ice part of melting snowflakes melt water on snowflakes D* D s
9 Explicit snow melting model: a case study è Stratiform precipitation over Germany on 16 Nov 2010 Lindenberg cloud radar LDR
10 Explicit snow melting model: a case study è Stratiform precipitation over Germany on 16 Nov 2010 Lindenberg cloud radar LDR
11 The Seifert and Beheng two-moment scheme: Extended version by Blahak, Noppel, Beheng and Seifert Number and mass concentrations of six different species cloud droplets rain drops cloud ice snow graupel hail (including wet growth) Process parameterizations: Drop activation/nucleation scheme using Segal&Khain (2006). Homogeneous ice nucleation based on Kärcher et al. (2008). Heterogeneous ice nucleation using the empirical scheme of Phillips et al. (2008). 12 prognostic variables compared to five of the operational one-moment microphysics.
12 Diurnal cycle of precipitation (space-time averaged) è Diurnal cycle of hourly precipitation averaged over the evaluation domain. è Two-moment scheme (colored lines) gives a better representation of the diurnal cycles compare to the operational one-moment scheme è Currently the two-moment scheme is too expensive for operations, and the actual skill scores are only marginally improved. Fig. 7. Time series of hourly rain rate averaged over the (a) the sout the radar data, the six two-moment microphysics experiments, and th
13 Advanced microphysics needs memory è For a better representation of microphysical processes we tend to add more prognostic variables, e.g., è More moments of the particle size distribution, e.g., number and mass density or even a,radar reflectivityʻ (2nd moment w.r.t. mass) è Additional particle types like graupel, hail, drizzle or various ice modes è Variable for meltwater on particles or rimed mass on snowflakes etc. è Some variables to track available CCN and IN, i.e., a simple aerosol model. è Additional prognostic variables become necessary when we start to resolve the spatial and temporal scales of the individual processes. è Prognostic variables provide memory only for resolved processes. è Do we need memory for sub-grid parameterizations?
14 Does autoconversion need memory? Collision-coalescence of droplets is a key process for rain formation. Bulk schemes usually rely on autoconversion schemes. The time evolution of the cloud droplet size distribution (CSD) leads to a memory effect: Within the lifetime of a cloud parcels the CSD broadens (becomes positively skewed) which is crucial for autoconversion. Schemes with no explicit assumptions about the evolution of the CSD: - All Kessler- and Sundquist-type schemes including Liu and Daum (2004) - Berry and Reinhardt (1974) - Khairoutdinov and Kogan (2000) Schemes with explicit parameterization of the evolution of the CSD: - Lüpckes et al. (1989): Three drop classes including two cloud categories with explicit size distributions. - Seifert and Beheng (2001): Dynamics similarity using rain water as a proxy for large cloud droplets. - Sant et al. (2012, submitted): Similar to Lüpckes et al. approach, but drizzle class instead of 2nd cloud mode. è More advanced schemes include memory to represent the broading of the cloud size distribution.
15 Does convection need memory? è è è Convective clouds have a pronounced lifecycle Usually they need at least 15 min to develop precipitation. The precipitation efficiency of warm shallow clouds shows a dependency on cloud lifetime (Seifert and Stevens 2010, JAS). A simple kinematic 1D cloud model: from Golding (2000) è The lack of a representation of the cloud lifecycle, i.e., the lack of memory in current convection schemes makes a physically-based parameterization of convective precipitation very difficult.
16 Statistical physics point of view... Recently Wouters and Lucarini (2012, J. Stat. Mech., P03003) have shown that a systematic coarsegraining (using Ruelle response theory) of two weakly coupled nonlinear dynamical systems with slow variables X and fast variables Y leads to the following parameterized dynamics of X Ẋ(s) =F X (X(s)) + M 1 + σ(s)+ 0 dτ h(s τ,x (t τ)). which are the original dynamics of X and three parameterization of the dynamics of Y: a constant drift term, an additive noise term, and a memory term. Due to the memory term the system does in general show non-markovian behavior: Fig. 2 of WL12: Fluctuation of Y affecting the slow variables X (,stochastic term ). Fig. 3 of WL12: Memory effect describing how X affects itself through the lagged-response of Y. è Large-scale forcing leads to the formation of clouds at the small scales, but their response back to the large scale is delayed, i.e., the small scales have memory and depend not only on the current large-scale state but also on previous large-scale states.
17 PDF-based vs stochastic schemes PDF-based subgrid scheme: can represent spatial heterogeneity can be used to achieve consistency between different parameterizations well established in the parameterization community prognostic schemes can provide largescale memory scale adaptivity can be included, but is challenging. Small scale spatial or temporal correlations cannot easily be included, i.e., lack of small-scale memory. Stochastic parameterization: can represent spatial and temporal variability. can maybe be used to achieve consistency between different parameterizations. not well established in the parameterization community, but well established in theoretical physics and ensemble forecasting. scale adaptivity is, to some extent, intrinsic in the scheme. Small scale temporal correlations and memory can be represented. (A stochastic scheme is actually sampling a much more complicated PDF than the ones assumed in current explicit PDF schemes.)
18 PDF-based vs stochastic schemes PDF-based subgrid scheme: can represent spatial heterogeneity can be used to achieve consistency between different parameterizations well established in the parameterization community prognostic schemes can provide largescale memory scale adaptivity can be included, but is challenging. Small scale spatial or temporal correlations cannot easily be included, i.e., lack of small-scale memory. Stochastic parameterization: can represent spatial and temporal variability. can maybe be used to achieve consistency between different parameterizations. not well established in the parameterization community, but well established in theoretical physics and ensemble forecasting. scale adaptivity is, to some extent, intrinsic in the scheme. Small scale temporal correlations and memory can be represented. (A stochastic scheme is actually sampling a much more complicated PDF than the ones assumed in current explicit PDF schemes.) Mixed scheme with PDF-based large-scale state and a stochastic scheme sampling the small-scale variability including lifecycle and memory effects.
19 Summary and conclusions è High resolution NWP needs a more detailed representation of cloud microphysics. è This can be achieved be more sophisticated parameterizations which have additional prognostic variables. è This allows us to choose the appropriate microphysics scheme for a certain scale, but unstructured grids with varying grid-spacing would still be challenging. è In sub-grid parameterizations, e.g., convection schemes, the microphysics is often treated quite poorly. è PDF-based schemes are attractive for parameterizations, but lack the small-scale correlations or memory. è Therefore stochastic schemes with an explicit representation of cloud lifecycles might be an interesting extension of currently available parameterizations.
20 In large-scale models parameterization are built upon τ process t but now we have to deal with t τ process and this maybe even for spatially sub-grid processes with l process x i.e., even sub-grid processes can have memory.
A hierarchy of one- and two-moment microphysical parameterizations in the COSMO model
 Deutscher Wetterdienst GB Forschung und Entwicklung A hierarchy of one- and two-moment microphysical parameterizations in the COSMO model Axel Seifert German Weather Service Offenbach, Germany Ulrich Blahak
Deutscher Wetterdienst GB Forschung und Entwicklung A hierarchy of one- and two-moment microphysical parameterizations in the COSMO model Axel Seifert German Weather Service Offenbach, Germany Ulrich Blahak
Parametrizing cloud and precipitation in today s NWP and climate models. Richard Forbes
 Parametrizing cloud and precipitation in today s NWP and climate models Richard Forbes (ECMWF) with thanks to Peter Bechtold and Martin Köhler RMetS National Meeting on Clouds and Precipitation, 16 Nov
Parametrizing cloud and precipitation in today s NWP and climate models Richard Forbes (ECMWF) with thanks to Peter Bechtold and Martin Köhler RMetS National Meeting on Clouds and Precipitation, 16 Nov
CONVECTIVE CLOUD MICROPHYSICS IN A HIGH-RESOLUTION NWP MODEL
 CONVECTIVE CLOUD MICROPHYSICS IN A HIGH-RESOLUTION NWP MODEL J. Trentmann 1, A. Seifert 2, H. Wernli 1 1 Institute for Atmospheric Physics, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany 2 German Weather
CONVECTIVE CLOUD MICROPHYSICS IN A HIGH-RESOLUTION NWP MODEL J. Trentmann 1, A. Seifert 2, H. Wernli 1 1 Institute for Atmospheric Physics, Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz, Germany 2 German Weather
A Revised Version of the Cloud Microphysical Parameterization of COSMO-LME
 A Revised Version of the Cloud Microphysical Parameterization of COSMO-LME Axel Seifert DWD, Offenbach -1- Motivation: Well known problems of COSMO-LME regards wintertime precipitation: Overestimation
A Revised Version of the Cloud Microphysical Parameterization of COSMO-LME Axel Seifert DWD, Offenbach -1- Motivation: Well known problems of COSMO-LME regards wintertime precipitation: Overestimation
ECMWF Workshop on "Parametrization of clouds and precipitation across model resolutions
 ECMWF Workshop on "Parametrization of clouds and precipitation across model resolutions Themes: 1. Parametrization of microphysics 2. Representing sub-grid cloud variability 3. Constraining cloud and precipitation
ECMWF Workshop on "Parametrization of clouds and precipitation across model resolutions Themes: 1. Parametrization of microphysics 2. Representing sub-grid cloud variability 3. Constraining cloud and precipitation
Assimilation of radar reflectivity
 Assimilation of radar reflectivity Axel Seifert Deutscher Wetterdienst, Offenbach, Germany Convective-scale NWP at DWD: Plans for 2020 Storm-scale ICON-RUC-EPS: hourly 12h ensemble forecasts based on short
Assimilation of radar reflectivity Axel Seifert Deutscher Wetterdienst, Offenbach, Germany Convective-scale NWP at DWD: Plans for 2020 Storm-scale ICON-RUC-EPS: hourly 12h ensemble forecasts based on short
Modeling of cloud microphysics: from simple concepts to sophisticated parameterizations. Part I: warm-rain microphysics
 Modeling of cloud microphysics: from simple concepts to sophisticated parameterizations. Part I: warm-rain microphysics Wojciech Grabowski National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado parameterization
Modeling of cloud microphysics: from simple concepts to sophisticated parameterizations. Part I: warm-rain microphysics Wojciech Grabowski National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado parameterization
HIERARCHY OF MICROPHYSICAL PARAMETERIZATIONS SUITABLE FOR CLOUD AND MESOSCALE MODELS.
 HIERARCHY OF MICROPHYSICAL PARAMETERIZATIONS SUITABLE FOR CLOUD AND MESOSCALE MODELS. William D. Hall, Roy M. Rasmussen, and Gregory Thompson National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado
HIERARCHY OF MICROPHYSICAL PARAMETERIZATIONS SUITABLE FOR CLOUD AND MESOSCALE MODELS. William D. Hall, Roy M. Rasmussen, and Gregory Thompson National Center for Atmospheric Research, Boulder, Colorado
Chapter 7 Precipitation Processes
 Chapter 7 Precipitation Processes Chapter overview: Supersaturation and water availability Nucleation of liquid droplets and ice crystals Liquid droplet and ice growth by diffusion Collision and collection
Chapter 7 Precipitation Processes Chapter overview: Supersaturation and water availability Nucleation of liquid droplets and ice crystals Liquid droplet and ice growth by diffusion Collision and collection
Role of atmospheric aerosol concentration on deep convective precipitation: Cloud-resolving model simulations
 Role of atmospheric aerosol concentration on deep convective precipitation: Cloud-resolving model simulations Wei-Kuo Tao,1 Xiaowen Li,1,2 Alexander Khain,3 Toshihisa Matsui,1,2 Stephen Lang,4 and Joanne
Role of atmospheric aerosol concentration on deep convective precipitation: Cloud-resolving model simulations Wei-Kuo Tao,1 Xiaowen Li,1,2 Alexander Khain,3 Toshihisa Matsui,1,2 Stephen Lang,4 and Joanne
A Novel Approach for Representing Ice Microphysics in Models: Description and Tests Using a Kinematic Framework
 1528 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 65 A Novel Approach for Representing Ice Microphysics in Models: Description and Tests Using a Kinematic Framework HUGH MORRISON
1528 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 65 A Novel Approach for Representing Ice Microphysics in Models: Description and Tests Using a Kinematic Framework HUGH MORRISON
SENSITIVITY OF IDEALIZED SQUALL LINE SIMULATIONS TO THE LEVEL OF COMPLEXITY USED IN TWO-MOMENT BULK MICROPHYSICS SCHEMES
 BNL-95332-2011-JA SENSITIVITY OF IDEALIZED SQUALL LINE SIMULATIONS TO THE LEVEL OF COMPLEXITY USED IN TWO-MOMENT BULK MICROPHYSICS SCHEMES K. Van Weverberg 1, A. M. Vogelmann 1, H. Morrison 2, and J. Milbrandt
BNL-95332-2011-JA SENSITIVITY OF IDEALIZED SQUALL LINE SIMULATIONS TO THE LEVEL OF COMPLEXITY USED IN TWO-MOMENT BULK MICROPHYSICS SCHEMES K. Van Weverberg 1, A. M. Vogelmann 1, H. Morrison 2, and J. Milbrandt
Parameterization of Cumulus Convective Cloud Systems in Mesoscale Forecast Models
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Parameterization of Cumulus Convective Cloud Systems in Mesoscale Forecast Models Yefim L. Kogan Cooperative Institute
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A. Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Parameterization of Cumulus Convective Cloud Systems in Mesoscale Forecast Models Yefim L. Kogan Cooperative Institute
The Purdue Lin Microphysics Scheme in WRF. Russ Schumacher AT 730 Final Project 26 April 2006
 The Purdue Lin Microphysics Scheme in WRF Russ Schumacher AT 730 Final Project 26 April 2006 Overview Introduction to microphysics schemes Introduction to the Purdue Lin scheme Tunable coefficients, inputs
The Purdue Lin Microphysics Scheme in WRF Russ Schumacher AT 730 Final Project 26 April 2006 Overview Introduction to microphysics schemes Introduction to the Purdue Lin scheme Tunable coefficients, inputs
The New Thompson Microphysical Scheme in WRF
 The New Thompson Microphysical Scheme in WRF by W.D. Hall, Roy M. Rasmussen, and Gregory Thompson RAL, National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, CO 80307 Work funded by the FAA AWRP program Introduction
The New Thompson Microphysical Scheme in WRF by W.D. Hall, Roy M. Rasmussen, and Gregory Thompson RAL, National Center for Atmospheric Research Boulder, CO 80307 Work funded by the FAA AWRP program Introduction
Collision and Coalescence 3/3/2010. ATS 351 Lab 7 Precipitation. Droplet Growth by Collision and Coalescence. March 7, 2006
 ATS 351 Lab 7 Precipitation March 7, 2006 Droplet Growth by Collision and Coalescence Growth by condensation alone takes too long ( 15 C -) Occurs in clouds with tops warmer than 5 F Greater the speed
ATS 351 Lab 7 Precipitation March 7, 2006 Droplet Growth by Collision and Coalescence Growth by condensation alone takes too long ( 15 C -) Occurs in clouds with tops warmer than 5 F Greater the speed
Kinematic Modelling: How sensitive are aerosol-cloud interactions to microphysical representation
 Kinematic Modelling: How sensitive are aerosol-cloud interactions to microphysical representation Adrian Hill Co-authors: Ben Shipway, Ian Boutle, Ryo Onishi UK Met Office Abstract This work discusses
Kinematic Modelling: How sensitive are aerosol-cloud interactions to microphysical representation Adrian Hill Co-authors: Ben Shipway, Ian Boutle, Ryo Onishi UK Met Office Abstract This work discusses
Ice multiplication in clouds: modeling new processes
 Ice multiplication in clouds: modeling new processes VAUGHAN PHILLIPS DEPT OF PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY AND ECO. SCIENCE, LUND UNIVERSITY, 25 OCT 2017 Acknowledgements: E. WILLIAMS MIT, USA M. FORMENTON, I. KUDZOTSA
Ice multiplication in clouds: modeling new processes VAUGHAN PHILLIPS DEPT OF PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY AND ECO. SCIENCE, LUND UNIVERSITY, 25 OCT 2017 Acknowledgements: E. WILLIAMS MIT, USA M. FORMENTON, I. KUDZOTSA
Aerosol Effects on Water and Ice Clouds
 Aerosol Effects on Water and Ice Clouds Ulrike Lohmann Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science, Dalhousie University, Halifax, N. S., Canada Contributions from Johann Feichter, Johannes Hendricks,
Aerosol Effects on Water and Ice Clouds Ulrike Lohmann Department of Physics and Atmospheric Science, Dalhousie University, Halifax, N. S., Canada Contributions from Johann Feichter, Johannes Hendricks,
Warm Rain Precipitation Processes
 Warm Rain Precipitation Processes Cloud and Precipitation Systems November 16, 2005 Jonathan Wolfe 1. Introduction Warm and cold precipitation formation processes are fundamentally different in a variety
Warm Rain Precipitation Processes Cloud and Precipitation Systems November 16, 2005 Jonathan Wolfe 1. Introduction Warm and cold precipitation formation processes are fundamentally different in a variety
National Center for Atmospheric Research,* Boulder, Colorado. (Manuscript received 18 June 2007, in final form 4 January 2008) ABSTRACT
 3642 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 21 A New Two-Moment Bulk Stratiform Cloud Microphysics Scheme in the Community Atmosphere Model, Version 3 (CAM3). Part I: Description and Numerical Tests HUGH
3642 J O U R N A L O F C L I M A T E VOLUME 21 A New Two-Moment Bulk Stratiform Cloud Microphysics Scheme in the Community Atmosphere Model, Version 3 (CAM3). Part I: Description and Numerical Tests HUGH
Real case simulations using spectral bin cloud microphysics: Remarks on precedence research and future activity
 Real case simulations using spectral bin cloud microphysics: Remarks on precedence research and future activity Takamichi Iguchi 1,2 (takamichi.iguchi@nasa.gov) 1 Earth System Science Interdisciplinary
Real case simulations using spectral bin cloud microphysics: Remarks on precedence research and future activity Takamichi Iguchi 1,2 (takamichi.iguchi@nasa.gov) 1 Earth System Science Interdisciplinary
Modeling multiscale interactions in the climate system
 Modeling multiscale interactions in the climate system Christopher S. Bretherton Atmospheric Sciences and Applied Mathematics University of Washington 08.09.2017 Aqua Worldview Motivation Weather and climate
Modeling multiscale interactions in the climate system Christopher S. Bretherton Atmospheric Sciences and Applied Mathematics University of Washington 08.09.2017 Aqua Worldview Motivation Weather and climate
Uncertainty and complexity in cloud microphysics
 Uncertainty and complexity in cloud microphysics Axel Seifert Deutscher Wetterdienst Offenbach, Germany E-mail: axel.seifert@dwd.de 1 Introduction The parameterization of cloud microphysical processes
Uncertainty and complexity in cloud microphysics Axel Seifert Deutscher Wetterdienst Offenbach, Germany E-mail: axel.seifert@dwd.de 1 Introduction The parameterization of cloud microphysical processes
An improvement of the SBU-YLIN microphysics scheme in squall line simulation
 1 An improvement of the SBU-YLIN microphysics scheme in squall line simulation Qifeng QIAN* 1, and Yanluan Lin 1 ABSTRACT The default SBU-YLIN scheme in Weather Research and Forecasting Model (WRF) is
1 An improvement of the SBU-YLIN microphysics scheme in squall line simulation Qifeng QIAN* 1, and Yanluan Lin 1 ABSTRACT The default SBU-YLIN scheme in Weather Research and Forecasting Model (WRF) is
Chapter 8 - Precipitation. Rain Drops, Cloud Droplets, and CCN
 Chapter 8 - Precipitation Rain Drops, Cloud Droplets, and CCN Recall the relative sizes of rain drops, cloud drops, and CCN: raindrops - 2000 μ m = 2 mm fall at a speed of 4-5 ms -1 cloud drops - 20 μ
Chapter 8 - Precipitation Rain Drops, Cloud Droplets, and CCN Recall the relative sizes of rain drops, cloud drops, and CCN: raindrops - 2000 μ m = 2 mm fall at a speed of 4-5 ms -1 cloud drops - 20 μ
4.4 DRIZZLE-INDUCED MESOSCALE VARIABILITY OF BOUNDARY LAYER CLOUDS IN A REGIONAL FORECAST MODEL. David B. Mechem and Yefim L.
 4.4 DRIZZLE-INDUCED MESOSCALE VARIABILITY OF BOUNDARY LAYER CLOUDS IN A REGIONAL FORECAST MODEL David B. Mechem and Yefim L. Kogan Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological Studies University
4.4 DRIZZLE-INDUCED MESOSCALE VARIABILITY OF BOUNDARY LAYER CLOUDS IN A REGIONAL FORECAST MODEL David B. Mechem and Yefim L. Kogan Cooperative Institute for Mesoscale Meteorological Studies University
Future directions for parametrization of cloud and precipitation microphysics
 Future directions for parametrization of cloud and precipitation microphysics Richard Forbes (ECMWF) ECMWF-JCSDA Workshop, 15-17 June 2010 Cloud and Precipitation Microphysics A Complex System! Ice Nucleation
Future directions for parametrization of cloud and precipitation microphysics Richard Forbes (ECMWF) ECMWF-JCSDA Workshop, 15-17 June 2010 Cloud and Precipitation Microphysics A Complex System! Ice Nucleation
ERAD THE EIGHTH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON RADAR IN METEOROLOGY AND HYDROLOGY
 Discrimination Between Winter Precipitation Types Based on Explicit Microphysical Modeling of Melting and Refreezing in the Polarimetric Hydrometeor Classification Algorithm 1 Introduction The winter weather
Discrimination Between Winter Precipitation Types Based on Explicit Microphysical Modeling of Melting and Refreezing in the Polarimetric Hydrometeor Classification Algorithm 1 Introduction The winter weather
MESO-NH cloud forecast verification with satellite observation
 MESO-NH cloud forecast verification with satellite observation Jean-Pierre CHABOUREAU Laboratoire d Aérologie, University of Toulouse and CNRS, France http://mesonh.aero.obs-mip.fr/chaboureau/ DTC Verification
MESO-NH cloud forecast verification with satellite observation Jean-Pierre CHABOUREAU Laboratoire d Aérologie, University of Toulouse and CNRS, France http://mesonh.aero.obs-mip.fr/chaboureau/ DTC Verification
1. describe the two methods by which cloud droplets can grow to produce precipitation (pp );
 10 Precipitation Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe the two methods by which cloud droplets can grow to produce precipitation (pp. 232 236); 2. distinguish
10 Precipitation Learning Goals After studying this chapter, students should be able to: 1. describe the two methods by which cloud droplets can grow to produce precipitation (pp. 232 236); 2. distinguish
PUBLICATIONS. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems. Recirculation and growth of raindrops in simulated shallow cumulus
 PUBLICATIONS Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems RESEARCH ARTICLE 10.1002/2016MS000631 Key Points: Raindrop growth in a field of shallow cumuli is simulated with a Lagrangian drop model Recirculating
PUBLICATIONS Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems RESEARCH ARTICLE 10.1002/2016MS000631 Key Points: Raindrop growth in a field of shallow cumuli is simulated with a Lagrangian drop model Recirculating
1 INTRODUCTION 2 MODEL SETUP
 8.1 INFLUENCE OF AMBIENT ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS AND OROGRAPHY ON THE CHARACTERISTICS OF DEEP CONVECTIVE CELLS AS SIMULATED WITH A SOPHISTICATED TWO-MOMENT (BULK) MICROPHYSICAL SCHEME Ulrich Blahak, H.
8.1 INFLUENCE OF AMBIENT ENVIRONMENTAL CONDITIONS AND OROGRAPHY ON THE CHARACTERISTICS OF DEEP CONVECTIVE CELLS AS SIMULATED WITH A SOPHISTICATED TWO-MOMENT (BULK) MICROPHYSICAL SCHEME Ulrich Blahak, H.
Microphysics. Improving QPF and much more. Greg Thompson. Research Applications Laboratory Nat l Center for Atmospheric Research
 Microphysics Improving QPF and much more Greg Thompson Research Applications Laboratory Nat l Center for Atmospheric Research Outline Background Tests Results Applications Future Goals: NCAR-RAL microphysics
Microphysics Improving QPF and much more Greg Thompson Research Applications Laboratory Nat l Center for Atmospheric Research Outline Background Tests Results Applications Future Goals: NCAR-RAL microphysics
Physical Processes & Issues
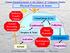 Physical Processes & Issues Radiative Transfer Climate VIS IR Cloud Drops & Ice Aerosol Processing Air quality Condensation Droplets & Xtals Cloud Dynamics Collection Aerosol Activation Hydrological Cycle
Physical Processes & Issues Radiative Transfer Climate VIS IR Cloud Drops & Ice Aerosol Processing Air quality Condensation Droplets & Xtals Cloud Dynamics Collection Aerosol Activation Hydrological Cycle
PALM - Cloud Physics. Contents. PALM group. last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015
 PALM - Cloud Physics PALM group Institute of Meteorology and Climatology, Leibniz Universität Hannover last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015 PALM group PALM Seminar 1 / 16 Contents Motivation Approach
PALM - Cloud Physics PALM group Institute of Meteorology and Climatology, Leibniz Universität Hannover last update: Monday 21 st September, 2015 PALM group PALM Seminar 1 / 16 Contents Motivation Approach
NATS 1750 Lecture. Wednesday 28 th November Pearson Education, Inc.
 NATS 1750 Lecture Wednesday 28 th November 2012 Processes that lift air Orographic lifting Elevated terrains act as barriers Result can be a rainshadow desert Frontal wedging Cool air acts as a barrier
NATS 1750 Lecture Wednesday 28 th November 2012 Processes that lift air Orographic lifting Elevated terrains act as barriers Result can be a rainshadow desert Frontal wedging Cool air acts as a barrier
Effects of aerosols on the dynamics and microphysics of squall lines simulated by spectral bin and bulk parameterization schemes
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2009jd011902, 2009 Effects of aerosols on the dynamics and microphysics of squall lines simulated by spectral bin and bulk parameterization schemes
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 114,, doi:10.1029/2009jd011902, 2009 Effects of aerosols on the dynamics and microphysics of squall lines simulated by spectral bin and bulk parameterization schemes
Performance of a Triclass Parameterization for the Collision Coalescence Process in Shallow Clouds
 1744 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 70 Performance of a Triclass Parameterization for the Collision Coalescence Process in Shallow Clouds VIVEK SANT AND ULRIKE LOHMANN
1744 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 70 Performance of a Triclass Parameterization for the Collision Coalescence Process in Shallow Clouds VIVEK SANT AND ULRIKE LOHMANN
FREEZING CONTAMINATION : AIRCRAFT ICING
 FREEZING CONTAMINATION : AIRCRAFT ICING FORECASTING METHODS Extrapolation of observational icing data Looking for icing scenarios Using numerical model outputs Crossing observations with model outputs
FREEZING CONTAMINATION : AIRCRAFT ICING FORECASTING METHODS Extrapolation of observational icing data Looking for icing scenarios Using numerical model outputs Crossing observations with model outputs
Developments at DWD: Integrated water vapour (IWV) from ground-based GPS
 1 Working Group on Data Assimilation 2 Developments at DWD: Integrated water vapour (IWV) from ground-based Christoph Schraff, Maria Tomassini, and Klaus Stephan Deutscher Wetterdienst, Frankfurter Strasse
1 Working Group on Data Assimilation 2 Developments at DWD: Integrated water vapour (IWV) from ground-based Christoph Schraff, Maria Tomassini, and Klaus Stephan Deutscher Wetterdienst, Frankfurter Strasse
Microphysics Schemes in EMC s Operational Hurricane Models
 Microphysics Schemes in EMC s Operational Hurricane Models Brad Ferrier, Weiguo Wang, Eric Aligo 1,2 1 Environment Modeling Center (EMC)/NCEP/NWS 2 I.M. Systems Group, Inc. HFIP Physics Workshop 9 11 August
Microphysics Schemes in EMC s Operational Hurricane Models Brad Ferrier, Weiguo Wang, Eric Aligo 1,2 1 Environment Modeling Center (EMC)/NCEP/NWS 2 I.M. Systems Group, Inc. HFIP Physics Workshop 9 11 August
A critical review of the design, execution and evaluation of cloud seeding experiments
 A critical review of the design, execution and evaluation of cloud seeding experiments Roelof T. Bruintjes WMA Meeting September 2013, Santiago Research Applications Program, National Center for Atmospheric
A critical review of the design, execution and evaluation of cloud seeding experiments Roelof T. Bruintjes WMA Meeting September 2013, Santiago Research Applications Program, National Center for Atmospheric
Chapter 7: Precipitation Processes. ESS5 Prof. Jin-Yi Yu
 Chapter 7: Precipitation Processes From: Introduction to Tropical Meteorology, 1st Edition, Version 1.1.2, Produced by the COMET Program Copyright 2007-2008, 2008, University Corporation for Atmospheric
Chapter 7: Precipitation Processes From: Introduction to Tropical Meteorology, 1st Edition, Version 1.1.2, Produced by the COMET Program Copyright 2007-2008, 2008, University Corporation for Atmospheric
MICROPHYSICAL AND PRECIPITATION FORMATION PROCESSES AND RADAR SIGNATURES
 MICROPHYSICAL AND PRECIPITATION FORMATION PROCESSES AND RADAR SIGNATURES 4 TH International Workshop on Weather Modification 3 rd Workshop on Cloud Physics 21-22 October 2010 Daegu, Korea Projects Current
MICROPHYSICAL AND PRECIPITATION FORMATION PROCESSES AND RADAR SIGNATURES 4 TH International Workshop on Weather Modification 3 rd Workshop on Cloud Physics 21-22 October 2010 Daegu, Korea Projects Current
Multi-Scale Modeling of Turbulence and Microphysics in Clouds. Steven K. Krueger University of Utah
 Multi-Scale Modeling of Turbulence and Microphysics in Clouds Steven K. Krueger University of Utah 10,000 km Scales of Atmospheric Motion 1000 km 100 km 10 km 1 km 100 m 10 m 1 m 100 mm 10 mm 1 mm Planetary
Multi-Scale Modeling of Turbulence and Microphysics in Clouds Steven K. Krueger University of Utah 10,000 km Scales of Atmospheric Motion 1000 km 100 km 10 km 1 km 100 m 10 m 1 m 100 mm 10 mm 1 mm Planetary
Operational and research activities at ECMWF now and in the future
 Operational and research activities at ECMWF now and in the future Sarah Keeley Education Officer Erland Källén Director of Research ECMWF An independent intergovernmental organisation established in 1975
Operational and research activities at ECMWF now and in the future Sarah Keeley Education Officer Erland Källén Director of Research ECMWF An independent intergovernmental organisation established in 1975
Diagnosing Model Systematic Error for Clouds and Precipitation
 Diagnosing Model Systematic Error for Clouds and Precipitation Richard Forbes (ECMWF) With Thanks to Maike Ahlgrimm, Peter Bechtold, Martin Köhler and ECMWF colleagues, and Graeme Stephens (CSU), Julien
Diagnosing Model Systematic Error for Clouds and Precipitation Richard Forbes (ECMWF) With Thanks to Maike Ahlgrimm, Peter Bechtold, Martin Köhler and ECMWF colleagues, and Graeme Stephens (CSU), Julien
Understanding macrophysical outcomes of microphysical choices in simulations of shallow cumulus convection
 Understanding macrophysical outcomes of microphysical choices in simulations of shallow cumulus convection BJORN STEVENS, Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Univ. of California Los Angeles
Understanding macrophysical outcomes of microphysical choices in simulations of shallow cumulus convection BJORN STEVENS, Department of Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Univ. of California Los Angeles
AEROSOL-CLOUD INTERACTIONS AND PRECIPITATION IN A GLOBAL SCALE. SAHEL Conference April 2007 CILSS Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso
 AEROSOL-CLOUD INTERACTIONS AND PRECIPITATION IN A GLOBAL SCALE SAHEL Conference 2007 2-6 April 2007 CILSS Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso The aerosol/precipitation connection Aerosol environment has changed
AEROSOL-CLOUD INTERACTIONS AND PRECIPITATION IN A GLOBAL SCALE SAHEL Conference 2007 2-6 April 2007 CILSS Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso The aerosol/precipitation connection Aerosol environment has changed
The convection-permitting COSMO-DE-EPS and PEPS at DWD
 Deutscher Wetterdienst The convection-permitting COSMO-DE-EPS and PEPS at DWD Detlev Majewski based on Chr. Gebhardt, S. Theis, M. Paulat, M. Buchhold and M. Denhard Deutscher Wetterdienst The model COSMO-DE
Deutscher Wetterdienst The convection-permitting COSMO-DE-EPS and PEPS at DWD Detlev Majewski based on Chr. Gebhardt, S. Theis, M. Paulat, M. Buchhold and M. Denhard Deutscher Wetterdienst The model COSMO-DE
Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17
 Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Changes of state of water, H 2 O Water is the only substance in atmosphere that exists
Moisture, Clouds, and Precipitation Earth Science, 13e Chapter 17 Stanley C. Hatfield Southwestern Illinois College Changes of state of water, H 2 O Water is the only substance in atmosphere that exists
Modeling Challenges At High Latitudes. Judith Curry Georgia Institute of Technology
 Modeling Challenges At High Latitudes Judith Curry Georgia Institute of Technology Physical Process Parameterizations Radiative transfer Surface turbulent fluxes Cloudy boundary layer Cloud microphysics
Modeling Challenges At High Latitudes Judith Curry Georgia Institute of Technology Physical Process Parameterizations Radiative transfer Surface turbulent fluxes Cloudy boundary layer Cloud microphysics
Climate Modeling Issues at GFDL on the Eve of AR5
 Climate Modeling Issues at GFDL on the Eve of AR5 Leo Donner, Chris Golaz, Yi Ming, Andrew Wittenberg, Bill Stern, Ming Zhao, Paul Ginoux, Jeff Ploshay, S.J. Lin, Charles Seman CPPA PI Meeting, 29 September
Climate Modeling Issues at GFDL on the Eve of AR5 Leo Donner, Chris Golaz, Yi Ming, Andrew Wittenberg, Bill Stern, Ming Zhao, Paul Ginoux, Jeff Ploshay, S.J. Lin, Charles Seman CPPA PI Meeting, 29 September
Snow Microphysics and the Top-Down Approach to Forecasting Winter Weather Precipitation Type
 Roger Vachalek Journey Forecaster National Weather Service Des Moines, Iowa www.snowcrystals.com Why is Snow Microphysics Important? Numerical Prediction Models better forecast areas of large scale forcing
Roger Vachalek Journey Forecaster National Weather Service Des Moines, Iowa www.snowcrystals.com Why is Snow Microphysics Important? Numerical Prediction Models better forecast areas of large scale forcing
Key Laboratory of Mesoscale Severe Weather, Ministry of Education, School of Atmospheric Sciences, Nanjing University
 Modeling Rapid Intensification of Typhoon Saomai (2006) with the Weather Research and Forecasting Model and Sensitivity to Cloud Microphysical Parameterizations Jie Ming and Yuan Wang Key Laboratory of
Modeling Rapid Intensification of Typhoon Saomai (2006) with the Weather Research and Forecasting Model and Sensitivity to Cloud Microphysical Parameterizations Jie Ming and Yuan Wang Key Laboratory of
Where does the memory of convection stem from? Why can it be useful for parameterizations?
 Where does the memory of convection stem from? Why can it be useful for parameterizations? D'où vient la mémoire de la convection? En quoi cela peut-il être utile pour les paramétrisations? Maxime Colin,
Where does the memory of convection stem from? Why can it be useful for parameterizations? D'où vient la mémoire de la convection? En quoi cela peut-il être utile pour les paramétrisations? Maxime Colin,
Precipitation Processes. Precipitation Processes 2/24/11. Two Mechanisms that produce raindrops:
 Precipitation is any form of water that falls from a cloud and reaches the ground. How do cloud drops grow? Chapter 7 When air is saturated with respect to a flat surface it is unsaturated with respect
Precipitation is any form of water that falls from a cloud and reaches the ground. How do cloud drops grow? Chapter 7 When air is saturated with respect to a flat surface it is unsaturated with respect
Precipitations. Terminal Velocity. Chapter 7: Precipitation Processes. Growth of Cloud Droplet Forms of Precipitations Cloud Seeding
 Chapter 7: Precipitation Processes Precipitations Water Vapor Saturated Need cloud nuclei Cloud Droplet formed around Cloud Nuclei Growth of Cloud Droplet Forms of Precipitations Cloud Seeding Precipitation
Chapter 7: Precipitation Processes Precipitations Water Vapor Saturated Need cloud nuclei Cloud Droplet formed around Cloud Nuclei Growth of Cloud Droplet Forms of Precipitations Cloud Seeding Precipitation
STEPHEN M. SALEEBY AND WILLIAM R. COTTON
 18 JOURNAL OF APPLIED METEOROLOGY VOLUME 43 A Large-Droplet Mode and Prognostic Number Concentration of Cloud Droplets in the Colorado State University Regional Atmospheric Modeling System (RAMS). Part
18 JOURNAL OF APPLIED METEOROLOGY VOLUME 43 A Large-Droplet Mode and Prognostic Number Concentration of Cloud Droplets in the Colorado State University Regional Atmospheric Modeling System (RAMS). Part
Modelling aerosol-cloud interations in GCMs
 Modelling aerosol-cloud interations in GCMs Ulrike Lohmann ETH Zurich Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science Reading, 13.11.2006 Acknowledgements: Sylvaine Ferrachat, Corinna Hoose, Erich Roeckner,
Modelling aerosol-cloud interations in GCMs Ulrike Lohmann ETH Zurich Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science Reading, 13.11.2006 Acknowledgements: Sylvaine Ferrachat, Corinna Hoose, Erich Roeckner,
4/25/18. Precipitation and Radar GEF4310 Cloud Physics. Schedule, Spring Global precipitation patterns
 Precipitation and Radar GEF4310 Cloud Physics Trude Storelvmo, Dept. of Geoscience, U. of Oslo Spring 2018 Schedule, Spring 2018 Week # Monday (exercises) Wednesday (lectures) 3 (15/1) No class (17/1)
Precipitation and Radar GEF4310 Cloud Physics Trude Storelvmo, Dept. of Geoscience, U. of Oslo Spring 2018 Schedule, Spring 2018 Week # Monday (exercises) Wednesday (lectures) 3 (15/1) No class (17/1)
Mystery of ice multiplication in warm based precipitating shallow cumulus clouds
 Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl042440, 2010 Mystery of ice multiplication in warm based precipitating shallow cumulus clouds Jiming Sun, 1,2 Parisa
Click Here for Full Article GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH LETTERS, VOL. 37,, doi:10.1029/2010gl042440, 2010 Mystery of ice multiplication in warm based precipitating shallow cumulus clouds Jiming Sun, 1,2 Parisa
Precipitation Processes METR σ is the surface tension, ρ l is the water density, R v is the Gas constant for water vapor, T is the air
 Precipitation Processes METR 2011 Introduction In order to grow things on earth, they need water. The way that the earth naturally irrigates is through snowfall and rainfall. Therefore, it is important
Precipitation Processes METR 2011 Introduction In order to grow things on earth, they need water. The way that the earth naturally irrigates is through snowfall and rainfall. Therefore, it is important
A Stochastic Parameterization for Deep Convection
 A Stochastic Parameterization for Deep Convection EGU Assembly 7th April 2006 Bob Plant 1, George Craig 2 and Christian Keil 2 1: Department of Meteorology, University of Reading, UK 2: DLR-Institut fuer
A Stochastic Parameterization for Deep Convection EGU Assembly 7th April 2006 Bob Plant 1, George Craig 2 and Christian Keil 2 1: Department of Meteorology, University of Reading, UK 2: DLR-Institut fuer
Exploring stochastic model uncertainty representations
 Exploring stochastic model uncertainty representations with relevance to the greyzone Sarah-Jane Lock, Martin Leutbecher, Peter Bechtold, Richard Forbes Research Department, ECMWF ECMWF November 15, 2017
Exploring stochastic model uncertainty representations with relevance to the greyzone Sarah-Jane Lock, Martin Leutbecher, Peter Bechtold, Richard Forbes Research Department, ECMWF ECMWF November 15, 2017
Precipitation AOSC 200 Tim Canty. Cloud Development: Orographic Lifting
 Precipitation AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Precipitation formation Rain Ice Lecture 14 Oct 11 2018 1 Cloud Development: Orographic Lifting
Precipitation AOSC 200 Tim Canty Class Web Site: http://www.atmos.umd.edu/~tcanty/aosc200 Topics for today: Precipitation formation Rain Ice Lecture 14 Oct 11 2018 1 Cloud Development: Orographic Lifting
A brief overview of the scheme is given below, taken from the whole description available in Lopez (2002).
 Towards an operational implementation of Lopez s prognostic large scale cloud and precipitation scheme in ARPEGE/ALADIN NWP models F.Bouyssel, Y.Bouteloup, P. Marquet Météo-France, CNRM/GMAP, 42 av. G.
Towards an operational implementation of Lopez s prognostic large scale cloud and precipitation scheme in ARPEGE/ALADIN NWP models F.Bouyssel, Y.Bouteloup, P. Marquet Météo-France, CNRM/GMAP, 42 av. G.
ERAD 2012 Toulouse, France 26 June 2012
 Taking the Microphysical Fingerprints of Storms with Dual-Polarization Radar Matthew R. Kumjian 1, Alexander V. Ryzhkov 1, Silke Trömel 2, and Clemens Simmer 2 1. Cooperative Institute for MesoscaleMeteorological
Taking the Microphysical Fingerprints of Storms with Dual-Polarization Radar Matthew R. Kumjian 1, Alexander V. Ryzhkov 1, Silke Trömel 2, and Clemens Simmer 2 1. Cooperative Institute for MesoscaleMeteorological
Representing sub-grid heterogeneity of cloud and precipitation across scales
 Representing sub-grid heterogeneity of cloud and precipitation across scales ECMWF Seminar, September 2015 Richard Forbes, Maike Ahlgrimm (European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts) Thanks to
Representing sub-grid heterogeneity of cloud and precipitation across scales ECMWF Seminar, September 2015 Richard Forbes, Maike Ahlgrimm (European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts) Thanks to
High-resolution simulations of winter precipitation over the Colorado Rockies
 High-resolution simulations of winter precipitation over the Colorado Rockies Gregory Thompson Research Applications Laboratory, National Center for Atmospheric Research Abstract: The Weather Research
High-resolution simulations of winter precipitation over the Colorado Rockies Gregory Thompson Research Applications Laboratory, National Center for Atmospheric Research Abstract: The Weather Research
A Numerical Study of Urban Aerosol Impacts on Clouds and Precipitation
 504 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 69 A Numerical Study of Urban Aerosol Impacts on Clouds and Precipitation JI-YOUNG HAN AND JONG-JIN BAIK School of Earth and Environmental
504 J O U R N A L O F T H E A T M O S P H E R I C S C I E N C E S VOLUME 69 A Numerical Study of Urban Aerosol Impacts on Clouds and Precipitation JI-YOUNG HAN AND JONG-JIN BAIK School of Earth and Environmental
Verification of in-flight icing forecasts and diagnoses over Europe using ADWICE compared to PIREPS
 Verification of in-flight icing forecasts and diagnoses over Europe using ADWICE compared to PIREPS 16th Aviation, Range and Aerospace Meteorology Conference, 7 January 2013, Austin, TX Frank Kalinka Research
Verification of in-flight icing forecasts and diagnoses over Europe using ADWICE compared to PIREPS 16th Aviation, Range and Aerospace Meteorology Conference, 7 January 2013, Austin, TX Frank Kalinka Research
Development of an Effective Double-Moment Cloud Microphysics Scheme with Prognostic Cloud Condensation Nuclei (CCN) for Weather and Climate Models
 MAY 2010 L I M A N D H O N G 1587 Development of an Effective Double-Moment loud Microphysics Scheme with Prognostic loud ondensation Nuclei (N) for Weather and limate Models KYO-SUN SUNNY LIM AND SONG-YOU
MAY 2010 L I M A N D H O N G 1587 Development of an Effective Double-Moment loud Microphysics Scheme with Prognostic loud ondensation Nuclei (N) for Weather and limate Models KYO-SUN SUNNY LIM AND SONG-YOU
Prediction of cirrus clouds in GCMs
 Prediction of cirrus clouds in GCMs Bernd Kärcher, Ulrike Burkhardt, Klaus Gierens, and Johannes Hendricks DLR Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen, 82234 Wessling, Germany bernd.kaercher@dlr.de
Prediction of cirrus clouds in GCMs Bernd Kärcher, Ulrike Burkhardt, Klaus Gierens, and Johannes Hendricks DLR Institut für Physik der Atmosphäre Oberpfaffenhofen, 82234 Wessling, Germany bernd.kaercher@dlr.de
Cloud parameterization and cloud prediction scheme in Eta numerical weather model
 Cloud parameterization and cloud prediction scheme in Eta numerical weather model Belgrade, 10th September, 2018 Ivan Ristić, CEO at Weather2 Ivana Kordić, meteorologist at Weather2 Introduction Models
Cloud parameterization and cloud prediction scheme in Eta numerical weather model Belgrade, 10th September, 2018 Ivan Ristić, CEO at Weather2 Ivana Kordić, meteorologist at Weather2 Introduction Models
The prognostic deep convection parametrization for operational forecast in horizontal resolutions of 8, 4 and 2 km
 The prognostic deep convection parametrization for operational forecast in horizontal resolutions of 8, 4 and 2 km Martina Tudor, Stjepan Ivatek-Šahdan and Antonio Stanešić tudor@cirus.dhz.hr Croatian
The prognostic deep convection parametrization for operational forecast in horizontal resolutions of 8, 4 and 2 km Martina Tudor, Stjepan Ivatek-Šahdan and Antonio Stanešić tudor@cirus.dhz.hr Croatian
RAINFALL ENHANCEMENT PROGRAMS AND NEED FOR TRAINING. SAHEL Conference April 2007 CILSS Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso
 RAINFALL ENHANCEMENT PROGRAMS AND NEED FOR TRAINING SAHEL Conference 2007 2-6 April 2007 CILSS Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso Fundamentals What are clouds made of? Cloud droplets Condensation on hygroscopic
RAINFALL ENHANCEMENT PROGRAMS AND NEED FOR TRAINING SAHEL Conference 2007 2-6 April 2007 CILSS Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso Fundamentals What are clouds made of? Cloud droplets Condensation on hygroscopic
WRF Model Simulated Proxy Datasets Used for GOES-R Research Activities
 WRF Model Simulated Proxy Datasets Used for GOES-R Research Activities Jason Otkin Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies Space Science and Engineering Center University of Wisconsin
WRF Model Simulated Proxy Datasets Used for GOES-R Research Activities Jason Otkin Cooperative Institute for Meteorological Satellite Studies Space Science and Engineering Center University of Wisconsin
models Cumulus congestus. Sønderjylland, Foto: Flemming Byg. B. H. Sass NetFam course at DMI January 2009
 Prediction of clouds and precipitation in atmospheric models Cumulus congestus. Sønderjylland, 2002. Foto: Flemming Byg. B. H. Sass NetFam course at DMI January 2009 outline Basic definitions and characteristics
Prediction of clouds and precipitation in atmospheric models Cumulus congestus. Sønderjylland, 2002. Foto: Flemming Byg. B. H. Sass NetFam course at DMI January 2009 outline Basic definitions and characteristics
Kessler warm rain microphysics scheme. Haifan Yan
 Kessler warm rain microphysics scheme Haifan Yan INTRODUCTION One moment scheme,and many available bulk schemes have followed the approach of Kessler The purpose of the scheme is to increase understanding
Kessler warm rain microphysics scheme Haifan Yan INTRODUCTION One moment scheme,and many available bulk schemes have followed the approach of Kessler The purpose of the scheme is to increase understanding
Precipitation Processes
 Precipitation Processes Dave Rahn Precipitation formation processes may be classified into two categories. These are cold and warm processes, where cold processes can only occur below 0 C and warm processes
Precipitation Processes Dave Rahn Precipitation formation processes may be classified into two categories. These are cold and warm processes, where cold processes can only occur below 0 C and warm processes
REPRESENTING CLOUD AND PRECIPITATION IN NWP MODELS IN CANADA. Environment Canada [RPN], Dorval, Canada
![REPRESENTING CLOUD AND PRECIPITATION IN NWP MODELS IN CANADA. Environment Canada [RPN], Dorval, Canada REPRESENTING CLOUD AND PRECIPITATION IN NWP MODELS IN CANADA. Environment Canada [RPN], Dorval, Canada](/thumbs/82/86396255.jpg) REPRESENTING CLOUD AND PRECIPITATION IN NWP MODELS IN CANADA. (Peter) M.K. Yau 1 and Jason Milbrandt 2 1 McGill University, Montreal, Canada 2 Environment Canada [RPN], Dorval, Canada Environment Canada's
REPRESENTING CLOUD AND PRECIPITATION IN NWP MODELS IN CANADA. (Peter) M.K. Yau 1 and Jason Milbrandt 2 1 McGill University, Montreal, Canada 2 Environment Canada [RPN], Dorval, Canada Environment Canada's
Parametrizing Cloud Cover in Large-scale Models
 Parametrizing Cloud Cover in Large-scale Models Stephen A. Klein Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Ming Zhao Princeton University Robert Pincus Earth System Research Laboratory November 14, 006 European
Parametrizing Cloud Cover in Large-scale Models Stephen A. Klein Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Ming Zhao Princeton University Robert Pincus Earth System Research Laboratory November 14, 006 European
PRECIPITATION PROCESSES
 PRECIPITATION PROCESSES Loknath Adhikari This summary deals with the mechanisms of warm rain processes and tries to summarize the factors affecting the rapid growth of hydrometeors in clouds from (sub)
PRECIPITATION PROCESSES Loknath Adhikari This summary deals with the mechanisms of warm rain processes and tries to summarize the factors affecting the rapid growth of hydrometeors in clouds from (sub)
Investigating the simulation of cloud microphysical processes in numerical models using a one-dimensional dynamical framework
 ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE LETTERS Atmos. Sci. Let. 10: 207 21 (2009) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).239 Investigating the simulation of cloud microphysical processes in numerical
ATMOSPHERIC SCIENCE LETTERS Atmos. Sci. Let. 10: 207 21 (2009) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com).239 Investigating the simulation of cloud microphysical processes in numerical
In this chapter we explain the processes by which nonprecipitating cloud droplets and ice crystals grow large enough to fall as precipitation
 Goals for today: 19 Oct., 2011 Ch 7, Precipitation Processes In this chapter we explain the processes by which nonprecipitating cloud droplets and ice crystals grow large enough to fall as precipitation
Goals for today: 19 Oct., 2011 Ch 7, Precipitation Processes In this chapter we explain the processes by which nonprecipitating cloud droplets and ice crystals grow large enough to fall as precipitation
14B.1 Evaluating cloud microphysics schemes in nested NMMB forecasts
 14B.1 Evaluating cloud microphysics schemes in nested NMMB forecasts Brad Ferrier1,2 Weiguo Wang1,2 Edward Colón1,2 NOAA/NWS/NCEP Environmental Modeling Center (EMC) 2 IM Systems Group, Inc. (IMSG) 1 1
14B.1 Evaluating cloud microphysics schemes in nested NMMB forecasts Brad Ferrier1,2 Weiguo Wang1,2 Edward Colón1,2 NOAA/NWS/NCEP Environmental Modeling Center (EMC) 2 IM Systems Group, Inc. (IMSG) 1 1
Representation of model error for data assimilation on convective scale
 Representation of model error for data assimilation on convective scale Yuefei Zenga,b, Tijana Janjicb, Alberto de Lozarc, Ulrich Blahakc, Hendrik Reichc, Axel Seifertc, Stephan Raspa, George Craiga a)
Representation of model error for data assimilation on convective scale Yuefei Zenga,b, Tijana Janjicb, Alberto de Lozarc, Ulrich Blahakc, Hendrik Reichc, Axel Seifertc, Stephan Raspa, George Craiga a)
Evaluating parameterisations of subgridscale variability with satellite data
 Evaluating parameterisations of subgridscale variability with satellite data Johannes Quaas Institute for Meteorology University of Leipzig johannes.quaas@uni-leipzig.de www.uni-leipzig.de/~quaas Acknowledgements
Evaluating parameterisations of subgridscale variability with satellite data Johannes Quaas Institute for Meteorology University of Leipzig johannes.quaas@uni-leipzig.de www.uni-leipzig.de/~quaas Acknowledgements
Introduction. Effect of aerosols on precipitation: - challenging problem - no agreement between the results (quantitative and qualitative)
 Introduction Atmospheric aerosols affect the cloud mycrophysical structure & formation (observations, numerical studies) An increase of the aerosol particles: - increases CCN concentrations - decreases
Introduction Atmospheric aerosols affect the cloud mycrophysical structure & formation (observations, numerical studies) An increase of the aerosol particles: - increases CCN concentrations - decreases
Parameterization of Cloud Microphysics Based on the Prediction of Bulk Ice Particle Properties. Part III: Introduction of Multiple Free Categories
 MARCH 2016 M I L B R A N D T A N D M O R R I S O N 975 Parameterization of Cloud Microphysics Based on the Prediction of Bulk Ice Particle Properties. Part III: Introduction of Multiple Free Categories
MARCH 2016 M I L B R A N D T A N D M O R R I S O N 975 Parameterization of Cloud Microphysics Based on the Prediction of Bulk Ice Particle Properties. Part III: Introduction of Multiple Free Categories
From small-scale turbulence to large-scale convection: a unified scale-adaptive EDMF parameterization
 From small-scale turbulence to large-scale convection: a unified scale-adaptive EDMF parameterization Kay Sušelj 1, Joao Teixeira 1 and Marcin Kurowski 1,2 1 JET PROPULSION LABORATORY/CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE
From small-scale turbulence to large-scale convection: a unified scale-adaptive EDMF parameterization Kay Sušelj 1, Joao Teixeira 1 and Marcin Kurowski 1,2 1 JET PROPULSION LABORATORY/CALIFORNIA INSTITUTE
Prediction of clouds and precipitation in atmospheric models
 Prediction of clouds and precipitation in atmospheric models Cumulus congestus. Sønderjylland, 2002. Foto: Flemming Byg. B. H. Sass NetFam Summer School July 2008 outline Basic definitions and characteristics
Prediction of clouds and precipitation in atmospheric models Cumulus congestus. Sønderjylland, 2002. Foto: Flemming Byg. B. H. Sass NetFam Summer School July 2008 outline Basic definitions and characteristics
Short Term forecasts along the GCSS Pacific Cross-section: Evaluating new Parameterizations in the Community Atmospheric Model
 Short Term forecasts along the GCSS Pacific Cross-section: Evaluating new Parameterizations in the Community Atmospheric Model Cécile Hannay, Dave Williamson, Jerry Olson, Rich Neale, Andrew Gettelman,
Short Term forecasts along the GCSS Pacific Cross-section: Evaluating new Parameterizations in the Community Atmospheric Model Cécile Hannay, Dave Williamson, Jerry Olson, Rich Neale, Andrew Gettelman,
Nathan Hosannah. Advisor Professor J. E. Gonzalez
 Nathan Hosannah nhosannah@gmail.com Advisor Professor J. E. Gonzalez Department of Mechanical Engineering, NOAA CREST Center CCNY / Graduate-Center, CUNY This study was supported and monitored National
Nathan Hosannah nhosannah@gmail.com Advisor Professor J. E. Gonzalez Department of Mechanical Engineering, NOAA CREST Center CCNY / Graduate-Center, CUNY This study was supported and monitored National
Future work on explicit convection
 Future work on explicit convection Humphrey Lean et al MetOffice@Reading, Reading, UK Cascade Downstream meeting, Oct 2014 Thanks to many colleagues Introduction Convection permitting models have provided
Future work on explicit convection Humphrey Lean et al MetOffice@Reading, Reading, UK Cascade Downstream meeting, Oct 2014 Thanks to many colleagues Introduction Convection permitting models have provided
Tue 3/29/2016. Representation of clouds and precipitation:
 Tue 3/29/2016 Representation of clouds and precipitation: - Case study example of microphysics test - Bulk parameterizations: Process listing - WRF scheme options Convective parameterization paper summaries
Tue 3/29/2016 Representation of clouds and precipitation: - Case study example of microphysics test - Bulk parameterizations: Process listing - WRF scheme options Convective parameterization paper summaries
Utilization of spectral bin microphysics and bulk parameterization schemes to simulate the cloud structure and precipitation in a mesoscale rain event
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2007jd008475, 2007 Utilization of spectral bin microphysics and bulk parameterization schemes to simulate the cloud structure and precipitation in
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 112,, doi:10.1029/2007jd008475, 2007 Utilization of spectral bin microphysics and bulk parameterization schemes to simulate the cloud structure and precipitation in
CONSTRAIN proposal for grey zone model comparison case. Adrian Hill, Paul Field, Adrian Lock, Thomas Frederikse, Stephan de Roode, Pier Siebesma
 CONSTRAIN proposal for grey zone model comparison case Adrian Hill, Paul Field, Adrian Lock, Thomas Frederikse, Stephan de Roode, Pier Siebesma Contents Introduction CONSTRAIN Overview of UM Limited Area
CONSTRAIN proposal for grey zone model comparison case Adrian Hill, Paul Field, Adrian Lock, Thomas Frederikse, Stephan de Roode, Pier Siebesma Contents Introduction CONSTRAIN Overview of UM Limited Area
