GATE : , Copyright reserved. Web:
|
|
|
- Tiffany Rice
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GATE-2016 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:
2 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2016 Civil Engineering SOM 5% CMM 6% Mathematics 13% Water Resource Engineering 11% General Aptitude 15% Surveying 5% Environmental Engineering 10% Geotechnical Engineering 15% RCC 5% Transportation Engineering 6% Structural Analysis 3% Steel Structure 3% Mechanics 3% : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 1
3 GATE CE 6-Feb 9 AM-12 PM SUBJECT NO OF QUESTION Topics Asked in Paper Level of Toughness Total Marks Enviormental Engineering Structural Analysis Water Resources Engineering SOM/Solid mechanics R.C.C. Geomatics/Surve -ying Engineering Geotechnical Engineering 1 M: 4 2 M: 3 1 M: 1 2 M: 1 1 M: 3 2 M: 4 1 M: 1 2 M: 2 1 M: 1 2 M: 2 1 M:3 2 M:1 1 M: 3 2 M: 6 BOD,Air Pollution;Sludge Disposal ; Domestic wastewater Moderate Deflection of beam;truess & Strain; Tough 3 Unit hydrographs; flood estimation; fluid routing 10 Easy 11 Struess;Deflection of Beams Easy 5 Concrete Technology;shear; compression and torsion by limit state methods; Leveling;coordinate system; map projections;theodolite traversing; Earth Pressure; Consolidation; Shear Strength;permeability& seepage;compaction; Easy 5 Moderate 5 Moderate 15 Transportation Engineering * Construction Materials and Management Engg. Mechanics Steel Structure 1 M: 2 2 M: 2 1 M: 0 2 M: 3 1 M: 1 2 M: 1 1 M: 1 2 M: 1 Traffic characteristics, Theory of traffic flow; pavements;gis Remote sensing *Construction Management ;Analysis of beam sections at transfer and service loads Trusses and Frames; Kinematics of Rectilinear Motion Plastic Analysis ; Design of Tension Member ;Beams Easy 6 Tough 6 Tough 3 Moderate 3 Engineering 1 M: 5 Numerical Method ;Matrices;Complex Mathematics 2 M: 4 Variable; Probability ; Limit & Continuty. Moderate 13 GA 1 M: 5 Time & Work ; Mixtures,Directions ; Venn 2 M: 5 Diagram ; Mensuration& Area, clock. Easy 15 Total 65 Moderate 100 * Indicates Questions from New Syllabus. Faculty Feedback: Few questions came from New Syllabus; General Ability was pretty easy; many question from Geotechnical Engg,Water Resources Engg, Construction Materials and Management was scoring subject, qualifying is easy but scoring is tough. Practice previous question papers will be beneficial. : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 2
4 GATE-2016 Question Paper & Answer Keys
5 Q.No. 1 Section: General Aptitude [Ans. D] until itself is negative so it can t take one more negative i.e., does not. Hence, Option (D) is the right answer Q.No. 2 [Ans. A] paraphrase means a restatement of a text, passage or a rewording of something written or spoken. Q.No. 3 [Ans. A] figurative means representing by a figure or resemblance or expressing one thing in terms normally denoting another with which it may be regarded as analogous. Q.No. 4 [Ans. C] From given codes Relftaga carefree : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 3
6 Otaga careful Fertaga careless From these codes, clearly known that care means taga, from given alternatives, option C is correct. Q.No. 5 [Ans. D] From given data, 64 cubic blocks of one unit Sizes are formed No. of faces of the Cube is 6 No. of corners of the Cube is 8 After removing one Cubic block from Each corner, The resulting surface area of the body = 6 (4) = 96 sq. Units : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 4
7 Q.No. 6 [Ans. B] Total No. of razors Elegance type from all four quarters = = 10,2510 Total No. of razors of Smooth type from all four quarters = = 8,0059 Total No. of razors of Soft type from all four Quarters = = 7,2186 Total No. of razors of Executive type from all four Quarters = = 3,9286 The revenue of the company in that year of 4 different types of razors Elegance = 10, = 49,20,480 Smooth = 8, = 50,43,717 Soft = 7, = 56,30,508 Executive = 3, = 67,96,132 The Executive of razors contributes the greatest revenue of the company in that year. Q.No. 7 [Ans. D] If seventeen languages were not an indication of the nation s diversity, nothing else is. If nothing else is so the best inference is option D. : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 5
8 Q.No. 8 [Ans. D] Q.No. 9 [Ans. B] f (x) = 2x 7 + 3x 5 for x = 1 the equation is satisfied. The factor is (x 1). Q.No. 10 [Ans. B] load cycles for failure exponentially Eg: load = x Cycles for failure = y x 2 = y2, x 3 = y3, x 4 = y4 By elimination procedure from options, Option (A) Load = 40units, it says that, the load is halved, it takes 10,000 cycles for failure = (100)2 40 units = 10,000 cycles, it is not Option (D) Load = units means it is more than 80 units, so it is not. Option (C) Load = units : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 6
9 3 (80 units) = units 4 From the given relation 3 (80 units) = (10)4 3 = (100) 1 (100) 1/3 = = It is not Option (B) only possible At the load of units, the failure will happen in 5000 cycles. Q.No. 1 Section: Technical [Ans. *] Range: to Q.No. 2 [Ans. C] Q.No. 3 [Ans. D] Q.No. 4 [Ans. A] : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 7
10 Q.No. 5 [Ans. B] Q.No. 6 [Ans. A] ΣF H = 0 H B = D ΣM c = 0 V B 2 L = 0 V B = 0 ΣV = 0 V c = P : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 8
11 Q.No. 7 [Ans. D] Under No circumstances even with the shear reinforcement shall the nominal shear stress, τ V should exceed τ c,max. This prevents the failure of section by diagonal compression Q.No. 8 [Ans. *] Range: 99.9 to As per IS 800, the design bending strength of laterally unsupported beam as governed by lateral torsional buckling is: M d = β b. Z p. f bd β b = Z e Z P ; for semi compact section So, M d = Z e Z P Z P. f bd = Z e. f bd = = 100 kn-m Q.No. 9 [Ans. C] Bull s trench kiln is used to manufacture bricks Q.No. 10 [Ans. B] Tri calcium silicate (C 3 S) hydrates and hardens rapidly and is largely responsible for initial set and early strength : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 9
12 Q.No. 11 [Ans. B] Consolidate undrained test (CU) test, drainage is permitted in consolidation stage. So, pore water pressure = 0. However, in shear stage, No drainage is permitted. So, pore water pressure develops Q.No. 12 [Ans. D] Soil is plastic in range of 26% to 48%. So, plastic limit = 26 %. Liquid limit =48% Since 35% <LL<50%... So, CI. Q.No. 13 [Ans. D] P(a) = Ka. γ. z 2c K a = 0 Z e = QC γ. K a So, max depth of unsupported excavation = 2Z e = 4c γ K a : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 10
13 Q.No. 14 [Ans. *] Range: 21.5 to 21.7 Let area of the catchment be a hectares So, = A A = 21.6 ha Q.No. 15 [Ans. B] : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 11
14 Q.No. 16 [Ans. *] Range: 13.6 to 13.7 F 1 = 10 y 2 y 1 = F 1 2 y 2 = 1 y = Q.No. 17 [Ans. A] Pre-Cursors to photochemical oxidants are NOX, VOCs and sunlight photochemical smooth is formed when pre-cursor pollutants undergo reaction in sunlight Q.No. 18 [Ans. A] Crown corrosion is caused due to H 2 S being released from waste water Q.No. 19 [Ans. B] Given, D= 0.45m, L= 7.5m No. of fabric filter bags, N = A t A b A t = Total area of filter = 300m 2 2 A b = Area of one bag = πdl = π = 10.6 m 2 N = 300 = : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 12
15 Q.No. 20 [Ans. A] Biological Nitrogen Removal Nitrifies and Denitrifies Q.No. 21 [Ans. B] Voids filled with bitumen Bitumen content : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 13
16 Q.No. 22 [Ans. *] Range: 1199 to 1201 Flow, q = 3600 = 3600 = 1200 veh/hr t H 3 Q.No. 23 [Ans. C] Min No. of satellites needed for a GPS to determine the position precisely = 4 Q.No. 24 [Ans. C] Passive Remote sensing uses sun as a source of EM energy and records the energy that is naturally radiated or reflected from objects Q.No. 25 [Ans. A] RL of bottom of beam = = m : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 14
17 Q.No. 26 [Ans. A] Q.No. 27 [Ans. B] Q.No. 28 [Ans. B] Q.No. 29 [Ans. C] : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 15
18 Q.No. 30 [Ans. A] Q.No. 31 [Ans. *] 2 x 1 EI. dy dx = 10x2 2 + c 1 0 y 0.5 EI. dy 10 = 10y dx 3 y3 + c 1 a + y = 0.5, dy dx = 0 0 = (0.5)3 + c 1 c 1 = dy dx = dy x=1 dx x=0 5 + c 1 = : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 16
19 C 1 = So, dy dx = C 1 max EI = = Q.No. 32 [Ans. D] By Principal of superposition δ max 1 = δ max 2 and θ max 1 = θ max 2 : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 17
20 Q.No. 33 [Ans. A] At any joint of a truss, if there is no external force, and if two members are collinear then third member carries the zero force So, F = 0 in FT, TG, HU, MP, PL : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 18
21 Q.No. 34 [Ans. D] Taking moments about A = 0 R Bh 8 + P 1.5 = 0 R Bh = 1.5 P 8 ΣF H = 0 R Ah = R Bh = 1.5 P 8 ΣF v = 0 R AV = P : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 19
22 Q.No. 35 [Ans. B] As per IS 456 : 2000, Min tensile reinf, Ast bd = 0.85 f y Ast = 85 bd = f y 415 = mm mm 2 (Ast) max = 0.4 % of bd = = 4000 mm2 100 Q.No. 36 [Ans. *] Range: 9999 to E l = E s 1 + θ Where, E s = 5000 fck = = MPa θ = Creep cofficient = 1.5 E l = = MPa : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 20
23 Q.No. 37 [Ans. B] P L 2 P L 2 MP θ MP L 2 θ = L 2 ϕ θ = ϕ By virtual work method Work done by external force = work done by internal moments M P θ + M P (2θ) = P. L/2θ P U = 6M P L ϕ MP : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 21
24 Q.No. 38 [Ans. B] Max force carried by plates P = A g f y = γ mo 1.1 = kn Load carried by each weld = P = kn 2 For minimum length of weld Strength of weld = Load carried by weld f u l w t = γ mw l w (10 0.7) 410 = l w = mm 105 mm : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 22
25 Q.No. 39 [Ans. *] Range: 37 to E F G H I t E = t O + 4t L + t P 6 E F: t E = F G: t E = G H: t E = H I: t E = = 62 6 = 49 6 = 43 6 = 73 6 t E = = days 6 Q.No. 40 [Ans. *] Range: 41 to 43 n= 0.7, S = 40% V = 100 m 3 n = V v V V v = n v = = 70 m 3 S = V w V v V w = = 28 m 3 V w + V a = V v 28 + V a = 70 V a = 42 m 3 : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 23
26 Q.No. 41 [Ans. A] W Pa P H 3 = 2m 2m K a. γ. H = 40 ka. γ = 40 H So, Pa = 1 2. Ka. γ. H2 = 20 H = 120 kn Taking moment about P = 0 Pa 2 = W 2 Pa = W = 120 kn Ka. γ. H = 40 : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 24
27 Q.No. 42 [Ans. *] Range: 36 to 38 S = C r. H o log σ c 1 + e o σ + C c. H o log σ o + Δσ 1 + e o σ c Where, C r = 0.05, C c = 0.50, H o = 1m Far clay, e o = = σ o = 60 kpa, σ o = ( ) 0.5 = kpa [ γ clay = G + e 1 + e γ w = 10 = kn/m 3 ] Δσ o = = 50 kn/m 2 S = log log = m = m = mm : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 25
28 Q.No. 43 [Ans. *] Range: 65.3 to 65.6 : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 26
29 Q.No. 44 [Ans. *] Range: 100 to 110 CD test: ϕ = 22, C = 15 KPa CU test: σ 1 U = (σ 3 U)tan 2 (45 + ϕ 2 ) + 2c tan (45 + ϕ 2 ) σ = ( ) tan 2 ( ) tan( ) σ = 50 tan tan(56 ) σ = 50 (1.484) σ 1 = = kn/m 2 So, Deviator Stress = σ 1 σ 3 = = kn/m 2 : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 27
30 Q.No. 45 [Ans. *] Range: to m 40 m γ w H 2 = 10 5 = 50 kn/m 2 γ w H 1 = = 650 kn/m 2 γ w H γ w(h 2 H 1 ) = = 250 kn/m2 3 P = 1 2 ( ) ( ) 40 2 = = kn/m : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 28
31 Q.No. 46 [Ans. B] Flow is normal to bedding plane K avg = Στ Σ τ = 1 20 = 2 m/day ki Head difference i = = = 5 Length = 1 12 Seepage discharge q = K avg i A = = 0.5 m 3 /day/m : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 29
32 Q.No. 47 [Ans. B] For Rectangular channel, y c = ( q2 g ) Where, q = Q B = 16 4 = 4 m2 /s y c = [ (4)2 1/3 10 ] = 1.17 m By Manning s method Q = 1 n A (R)2 3 (S) = (4) y n (y n ) 2 3 (0.001) 1 2 y n = 1.28 m y n > y c & s o < s c so mild slope 1 3 : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 30
33 Q.No. 48 [Ans. *] Range: 126 to 128 A 5 m 2. 5 m B m F H = 1 2 C (5)2 = 125 kn 1000 kn F H acts a distance = 5 = 1.67 m from the base 3 F v weight of water enclosed or supported ( actual or imaginary) by the curved surface = ρg volume of portion ABC = [ π ] = [ 25 π ] 6 = : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 31
34 = 22.7 kn F R = F H 2 + F V 2 = (125) 2 + (22.7) 2 =127kN Q.No. 49 [Ans. *] Range: 2.29 to y = 2 m B For hydraulically efficient channel, B = 2 3. y = = 4 3 = 2.31 m Q.No. 50 [Ans. *] Range: 4.4 to 4.6 A P H = 4.2 P OH = 9.8 [OH ] = mol/l B [OH] = mol/l P OH = 9.8 log 10 (2) = 9.5 P H = 4.5 Q.No. 51 [Ans. *] Range: 8000 to 8020 A 1 So, ln(1 η 1 ) = A 2 ln(1 η 2 ) 5600 ln (1 0.96) = A ln (1 0.99) A = m 2 : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 32
35 Q.No. 52 [Ans. *] Range: 0.29 to 0.31 BOD 2 = Lo (1 e k 2 ) 100 = Lo (1 e 2k ) (i) Also 155 = Lo (1 e 4k ) (ii) (i)/(ii) = 1 e 2k 1 e 4k 1 e 4k = e 2k e 4k 1.55 e 2k = 0 let e 2k = x x x = 0 x = 0.55 e 2k = 0.55 K = 0.3 day 1 Q.No. 53 [Ans. B] n. l2 W me,60 = 2R = 2 (5) = 0.5 m W ps = V 9.5 R = = 0.89 m W me,80 = 2 (5) = 0.50 m 80 W ps,80 = = 1.19 m : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 33
36 Q.No. 54 [Ans. *] Range: 2.9 to 3.1 Q.No. 55 [Ans. *] Range: to T R 10.5 S 16.5 T T BM Δ TST, tan 16.5 = T T x (1) ΔTRT, tan(10.5 ) = TT x + 60 = T T + 2 x + 60 From (1) and (2) x tan 16.5 = (x + 10) tan(10.5 ) 2 x = (x + 10) x = m (2) So, T T = = m So, RL of top of tower = = m P Q 60 m x : , info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web: 34
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 016 General Aptitude - GA Set-5 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Out of the following four sentences, select the most suitable sentence with respect to grammar and usage. (A) I will not leave the
GATE 016 General Aptitude - GA Set-5 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Out of the following four sentences, select the most suitable sentence with respect to grammar and usage. (A) I will not leave the
01 Ans: (D) Sol: until itself is negative so it can t take one more negative i.e., does not. Hence, Option (D) is the right answer
 : : GATE_06_CE Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. 0. Out of the following four sentences, select the most suitable sentence with respect to grammar and usage. (A) I will not leave the place until the minister
: : GATE_06_CE Q. Q. 5 carry one mark each. 0. Out of the following four sentences, select the most suitable sentence with respect to grammar and usage. (A) I will not leave the place until the minister
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
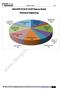 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 2018 General Aptitude (GA) Set-7 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The driver applied the as soon as she approached the hotel where she wanted to take a. The words that best fill the blanks in the
GATE 2018 General Aptitude (GA) Set-7 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The driver applied the as soon as she approached the hotel where she wanted to take a. The words that best fill the blanks in the
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1 Question Paper Analysis 2 Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 2 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2015
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1 Question Paper Analysis 2 Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 2 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2015
1.5 STRESS-PATH METHOD OF SETTLEMENT CALCULATION 1.5 STRESS-PATH METHOD OF SETTLEMENT CALCULATION
 Module 6 Lecture 40 Evaluation of Soil Settlement - 6 Topics 1.5 STRESS-PATH METHOD OF SETTLEMENT CALCULATION 1.5.1 Definition of Stress Path 1.5. Stress and Strain Path for Consolidated Undrained Undrained
Module 6 Lecture 40 Evaluation of Soil Settlement - 6 Topics 1.5 STRESS-PATH METHOD OF SETTLEMENT CALCULATION 1.5.1 Definition of Stress Path 1.5. Stress and Strain Path for Consolidated Undrained Undrained
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
GATE SOLUTIONS E N G I N E E R I N G
 GATE SOLUTIONS C I V I L E N G I N E E R I N G From (1987-018) Office : F-16, (Lower Basement), Katwaria Sarai, New Delhi-110016 Phone : 011-65064 Mobile : 81309090, 9711853908 E-mail: info@iesmasterpublications.com,
GATE SOLUTIONS C I V I L E N G I N E E R I N G From (1987-018) Office : F-16, (Lower Basement), Katwaria Sarai, New Delhi-110016 Phone : 011-65064 Mobile : 81309090, 9711853908 E-mail: info@iesmasterpublications.com,
Design of Beams (Unit - 8)
 Design of Beams (Unit - 8) Contents Introduction Beam types Lateral stability of beams Factors affecting lateral stability Behaviour of simple and built - up beams in bending (Without vertical stiffeners)
Design of Beams (Unit - 8) Contents Introduction Beam types Lateral stability of beams Factors affecting lateral stability Behaviour of simple and built - up beams in bending (Without vertical stiffeners)
External Work. When a force F undergoes a displacement dx in the same direction i as the force, the work done is
 Structure Analysis I Chapter 9 Deflection Energy Method External Work Energy Method When a force F undergoes a displacement dx in the same direction i as the force, the work done is du e = F dx If the
Structure Analysis I Chapter 9 Deflection Energy Method External Work Energy Method When a force F undergoes a displacement dx in the same direction i as the force, the work done is du e = F dx If the
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SEMESTER: III SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A
 DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
CHAPTER 4. Design of R C Beams
 CHAPTER 4 Design of R C Beams Learning Objectives Identify the data, formulae and procedures for design of R C beams Design simply-supported and continuous R C beams by integrating the following processes
CHAPTER 4 Design of R C Beams Learning Objectives Identify the data, formulae and procedures for design of R C beams Design simply-supported and continuous R C beams by integrating the following processes
Structural Analysis. For. Civil Engineering.
 Structural Analysis For Civil Engineering By www.thegateacademy.com ` Syllabus for Structural Analysis Syllabus Statically Determinate and Indeterminate Structures by Force/ Energy Methods; Method of Superposition;
Structural Analysis For Civil Engineering By www.thegateacademy.com ` Syllabus for Structural Analysis Syllabus Statically Determinate and Indeterminate Structures by Force/ Energy Methods; Method of Superposition;
Chapter. Materials. 1.1 Notations Used in This Chapter
 Chapter 1 Materials 1.1 Notations Used in This Chapter A Area of concrete cross-section C s Constant depending on the type of curing C t Creep coefficient (C t = ε sp /ε i ) C u Ultimate creep coefficient
Chapter 1 Materials 1.1 Notations Used in This Chapter A Area of concrete cross-section C s Constant depending on the type of curing C t Creep coefficient (C t = ε sp /ε i ) C u Ultimate creep coefficient
CE5510 Advanced Structural Concrete Design - Design & Detailing of Openings in RC Flexural Members-
 CE5510 Advanced Structural Concrete Design - Design & Detailing Openings in RC Flexural Members- Assoc Pr Tan Kiang Hwee Department Civil Engineering National In this lecture DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING
CE5510 Advanced Structural Concrete Design - Design & Detailing Openings in RC Flexural Members- Assoc Pr Tan Kiang Hwee Department Civil Engineering National In this lecture DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING
7.3 Design of members subjected to combined forces
 7.3 Design of members subjected to combined forces 7.3.1 General In the previous chapters of Draft IS: 800 LSM version, we have stipulated the codal provisions for determining the stress distribution in
7.3 Design of members subjected to combined forces 7.3.1 General In the previous chapters of Draft IS: 800 LSM version, we have stipulated the codal provisions for determining the stress distribution in
GATE : , Copyright reserved. Web:
 GATE-2016 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2016 Mechanical Engineering
GATE-2016 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2016 Mechanical Engineering
1.The number of simultaneous equations to be solved in the slope deflection method,
 EXAM-1 1.The number of simultaneous equations to be solved in the slope deflection method, is equal to : A. the degree of statistical indeterminacy B. the degree of kinematic indeterminacy C. the number
EXAM-1 1.The number of simultaneous equations to be solved in the slope deflection method, is equal to : A. the degree of statistical indeterminacy B. the degree of kinematic indeterminacy C. the number
Entrance exam Master Course
 - 1 - Guidelines for completion of test: On each page, fill in your name and your application code Each question has four answers while only one answer is correct. o Marked correct answer means 4 points
- 1 - Guidelines for completion of test: On each page, fill in your name and your application code Each question has four answers while only one answer is correct. o Marked correct answer means 4 points
Solution: The moment of inertia for the cross-section is: ANS: ANS: Problem 15.6 The material of the beam in Problem
 Problem 15.4 The beam consists of material with modulus of elasticity E 14x10 6 psi and is subjected to couples M 150, 000 in lb at its ends. (a) What is the resulting radius of curvature of the neutral
Problem 15.4 The beam consists of material with modulus of elasticity E 14x10 6 psi and is subjected to couples M 150, 000 in lb at its ends. (a) What is the resulting radius of curvature of the neutral
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK. Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
Part 1 is to be completed without notes, beam tables or a calculator. DO NOT turn Part 2 over until you have completed and turned in Part 1.
 NAME CM 3505 Fall 06 Test 2 Part 1 is to be completed without notes, beam tables or a calculator. Part 2 is to be completed after turning in Part 1. DO NOT turn Part 2 over until you have completed and
NAME CM 3505 Fall 06 Test 2 Part 1 is to be completed without notes, beam tables or a calculator. Part 2 is to be completed after turning in Part 1. DO NOT turn Part 2 over until you have completed and
Review Lecture. AE1108-II: Aerospace Mechanics of Materials. Dr. Calvin Rans Dr. Sofia Teixeira De Freitas
 Review Lecture AE1108-II: Aerospace Mechanics of Materials Dr. Calvin Rans Dr. Sofia Teixeira De Freitas Aerospace Structures & Materials Faculty of Aerospace Engineering Analysis of an Engineering System
Review Lecture AE1108-II: Aerospace Mechanics of Materials Dr. Calvin Rans Dr. Sofia Teixeira De Freitas Aerospace Structures & Materials Faculty of Aerospace Engineering Analysis of an Engineering System
SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL
 SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL Necessity of studying Shear Strength of soils : Soil failure usually occurs in the form of shearing along internal surface within the soil. Shear Strength: Thus, structural strength
SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL Necessity of studying Shear Strength of soils : Soil failure usually occurs in the form of shearing along internal surface within the soil. Shear Strength: Thus, structural strength
For publication information, visit
 CIVIL ENGINEERING 017 By Engineers Institute of India ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. No part of this work covered by the copyright herein may be reproduced, transmitted, stored or used in any form or by any means
CIVIL ENGINEERING 017 By Engineers Institute of India ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. No part of this work covered by the copyright herein may be reproduced, transmitted, stored or used in any form or by any means
D1. A normally consolidated clay has the following void ratio e versus effective stress σ relationship obtained in an oedometer test.
 (d) COMPRESSIBILITY AND CONSOLIDATION D1. A normally consolidated clay has the following void ratio e versus effective stress σ relationship obtained in an oedometer test. (a) Plot the e - σ curve. (b)
(d) COMPRESSIBILITY AND CONSOLIDATION D1. A normally consolidated clay has the following void ratio e versus effective stress σ relationship obtained in an oedometer test. (a) Plot the e - σ curve. (b)
Design of Reinforced Concrete Beam for Shear
 Lecture 06 Design of Reinforced Concrete Beam for Shear By: Prof Dr. Qaisar Ali Civil Engineering Department UET Peshawar drqaisarali@uetpeshawar.edu.pk 1 Topics Addressed Shear Stresses in Rectangular
Lecture 06 Design of Reinforced Concrete Beam for Shear By: Prof Dr. Qaisar Ali Civil Engineering Department UET Peshawar drqaisarali@uetpeshawar.edu.pk 1 Topics Addressed Shear Stresses in Rectangular
Prof. B V S Viswanadham, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay
 51 Module 4: Lecture 2 on Stress-strain relationship and Shear strength of soils Contents Stress state, Mohr s circle analysis and Pole, Principal stressspace, Stress pathsin p-q space; Mohr-coulomb failure
51 Module 4: Lecture 2 on Stress-strain relationship and Shear strength of soils Contents Stress state, Mohr s circle analysis and Pole, Principal stressspace, Stress pathsin p-q space; Mohr-coulomb failure
14. *14.8 CASTIGLIANO S THEOREM
 *14.8 CASTIGLIANO S THEOREM Consider a body of arbitrary shape subjected to a series of n forces P 1, P 2, P n. Since external work done by forces is equal to internal strain energy stored in body, by
*14.8 CASTIGLIANO S THEOREM Consider a body of arbitrary shape subjected to a series of n forces P 1, P 2, P n. Since external work done by forces is equal to internal strain energy stored in body, by
CIV100 Mechanics. Module 5: Internal Forces and Design. by: Jinyue Zhang. By the end of this Module you should be able to:
 CIV100 Mechanics Module 5: Internal Forces and Design by: Jinyue Zhang Module Objective By the end of this Module you should be able to: Find internal forces of any structural members Understand how Shear
CIV100 Mechanics Module 5: Internal Forces and Design by: Jinyue Zhang Module Objective By the end of this Module you should be able to: Find internal forces of any structural members Understand how Shear
Buckling of slender piles in soft soils. Large scale loading tests and introduction of a simple calculation scheme
 Dipl.-Ing. Stefan Vogt Zentrum Geotechnik, Technische Universität München Buckling of slender piles in soft soils Large scale loading tests and introduction of a simple calculation scheme Research work
Dipl.-Ing. Stefan Vogt Zentrum Geotechnik, Technische Universität München Buckling of slender piles in soft soils Large scale loading tests and introduction of a simple calculation scheme Research work
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown.
 D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
CHAPTER 5 Statically Determinate Plane Trusses
 CHAPTER 5 Statically Determinate Plane Trusses TYPES OF ROOF TRUSS TYPES OF ROOF TRUSS ROOF TRUSS SETUP ROOF TRUSS SETUP OBJECTIVES To determine the STABILITY and DETERMINACY of plane trusses To analyse
CHAPTER 5 Statically Determinate Plane Trusses TYPES OF ROOF TRUSS TYPES OF ROOF TRUSS ROOF TRUSS SETUP ROOF TRUSS SETUP OBJECTIVES To determine the STABILITY and DETERMINACY of plane trusses To analyse
ENG1001 Engineering Design 1
 ENG1001 Engineering Design 1 Structure & Loads Determine forces that act on structures causing it to deform, bend, and stretch Forces push/pull on objects Structures are loaded by: > Dead loads permanent
ENG1001 Engineering Design 1 Structure & Loads Determine forces that act on structures causing it to deform, bend, and stretch Forces push/pull on objects Structures are loaded by: > Dead loads permanent
CHAPTER 5 Statically Determinate Plane Trusses TYPES OF ROOF TRUSS
 CHAPTER 5 Statically Determinate Plane Trusses TYPES OF ROOF TRUSS 1 TYPES OF ROOF TRUSS ROOF TRUSS SETUP 2 ROOF TRUSS SETUP OBJECTIVES To determine the STABILITY and DETERMINACY of plane trusses To analyse
CHAPTER 5 Statically Determinate Plane Trusses TYPES OF ROOF TRUSS 1 TYPES OF ROOF TRUSS ROOF TRUSS SETUP 2 ROOF TRUSS SETUP OBJECTIVES To determine the STABILITY and DETERMINACY of plane trusses To analyse
Name :. Roll No. :... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.TECH (CE-NEW)/SEM-3/CE-301/ SOLID MECHANICS
 Name :. Roll No. :..... Invigilator s Signature :.. 2011 SOLID MECHANICS Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates are required to give their answers
Name :. Roll No. :..... Invigilator s Signature :.. 2011 SOLID MECHANICS Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates are required to give their answers
Mechanics of Materials Primer
 Mechanics of Materials rimer Notation: A = area (net = with holes, bearing = in contact, etc...) b = total width of material at a horizontal section d = diameter of a hole D = symbol for diameter E = modulus
Mechanics of Materials rimer Notation: A = area (net = with holes, bearing = in contact, etc...) b = total width of material at a horizontal section d = diameter of a hole D = symbol for diameter E = modulus
Use Hooke s Law (as it applies in the uniaxial direction),
 0.6 STRSS-STRAIN RLATIONSHIP Use the principle of superposition Use Poisson s ratio, v lateral longitudinal Use Hooke s Law (as it applies in the uniaxial direction), x x v y z, y y vx z, z z vx y Copyright
0.6 STRSS-STRAIN RLATIONSHIP Use the principle of superposition Use Poisson s ratio, v lateral longitudinal Use Hooke s Law (as it applies in the uniaxial direction), x x v y z, y y vx z, z z vx y Copyright
3.032 Problem Set 1 Fall 2007 Due: Start of Lecture,
 3.032 Problem Set 1 Fall 2007 Due: Start of Lecture, 09.14.07 1. The I35 bridge in Minneapolis collapsed in Summer 2007. The failure apparently occurred at a pin in the gusset plate of the truss supporting
3.032 Problem Set 1 Fall 2007 Due: Start of Lecture, 09.14.07 1. The I35 bridge in Minneapolis collapsed in Summer 2007. The failure apparently occurred at a pin in the gusset plate of the truss supporting
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 GATE-2015 Question Paper & Answer Keys GATE-2015 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
GATE-2015 Question Paper & Answer Keys GATE-2015 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
Slenderness Effects for Concrete Columns in Sway Frame - Moment Magnification Method (CSA A )
 Slenderness Effects for Concrete Columns in Sway Frame - Moment Magnification Method (CSA A23.3-94) Slender Concrete Column Design in Sway Frame Buildings Evaluate slenderness effect for columns in a
Slenderness Effects for Concrete Columns in Sway Frame - Moment Magnification Method (CSA A23.3-94) Slender Concrete Column Design in Sway Frame Buildings Evaluate slenderness effect for columns in a
Philadelphia University Faculty of Engineering
 Final Exam, Second Semester: 2015/2016 Civil Engineering Department Course Title: SOIL MECHANICS Date: 9/6/2016 Course No: 0670331 Time: 2 hours Lecturer: Dr. Mohammed Mustafa Al-Iessa No. of pages: 9
Final Exam, Second Semester: 2015/2016 Civil Engineering Department Course Title: SOIL MECHANICS Date: 9/6/2016 Course No: 0670331 Time: 2 hours Lecturer: Dr. Mohammed Mustafa Al-Iessa No. of pages: 9
P.E. Civil Exam Review:
 P.E. Civil Exam Review: Structural Analysis J.P. Mohsen Email: jpm@louisville.edu Structures Determinate Indeterminate STATICALLY DETERMINATE STATICALLY INDETERMINATE Stability and Determinacy of Trusses
P.E. Civil Exam Review: Structural Analysis J.P. Mohsen Email: jpm@louisville.edu Structures Determinate Indeterminate STATICALLY DETERMINATE STATICALLY INDETERMINATE Stability and Determinacy of Trusses
CIVIL ENGINEERING
 CIVIL ENGINEERING ESE SUBJECTWISE CONVENTIONAL SOLVED PAPER-I 1995-018 Office: F-16, (Lower Basement), Katwaria Sarai, New Delhi-110 016 Phone: 011-65 064 Mobile: 81309 090, 97118 53908 Email: info@iesmasterpublications.com,
CIVIL ENGINEERING ESE SUBJECTWISE CONVENTIONAL SOLVED PAPER-I 1995-018 Office: F-16, (Lower Basement), Katwaria Sarai, New Delhi-110 016 Phone: 011-65 064 Mobile: 81309 090, 97118 53908 Email: info@iesmasterpublications.com,
DESIGN AND DETAILING OF COUNTERFORT RETAINING WALL
 DESIGN AND DETAILING OF COUNTERFORT RETAINING WALL When the height of the retaining wall exceeds about 6 m, the thickness of the stem and heel slab works out to be sufficiently large and the design becomes
DESIGN AND DETAILING OF COUNTERFORT RETAINING WALL When the height of the retaining wall exceeds about 6 m, the thickness of the stem and heel slab works out to be sufficiently large and the design becomes
ME Final Exam. PROBLEM NO. 4 Part A (2 points max.) M (x) y. z (neutral axis) beam cross-sec+on. 20 kip ft. 0.2 ft. 10 ft. 0.1 ft.
 ME 323 - Final Exam Name December 15, 2015 Instructor (circle) PROEM NO. 4 Part A (2 points max.) Krousgrill 11:30AM-12:20PM Ghosh 2:30-3:20PM Gonzalez 12:30-1:20PM Zhao 4:30-5:20PM M (x) y 20 kip ft 0.2
ME 323 - Final Exam Name December 15, 2015 Instructor (circle) PROEM NO. 4 Part A (2 points max.) Krousgrill 11:30AM-12:20PM Ghosh 2:30-3:20PM Gonzalez 12:30-1:20PM Zhao 4:30-5:20PM M (x) y 20 kip ft 0.2
Bending Stress. Sign convention. Centroid of an area
 Bending Stress Sign convention The positive shear force and bending moments are as shown in the figure. Centroid of an area Figure 40: Sign convention followed. If the area can be divided into n parts
Bending Stress Sign convention The positive shear force and bending moments are as shown in the figure. Centroid of an area Figure 40: Sign convention followed. If the area can be divided into n parts
- Rectangular Beam Design -
 Semester 1 2016/2017 - Rectangular Beam Design - Department of Structures and Material Engineering Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Introduction The purposes
Semester 1 2016/2017 - Rectangular Beam Design - Department of Structures and Material Engineering Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering University Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Introduction The purposes
 UNIT III DEFLECTION OF BEAMS 1. What are the methods for finding out the slope and deflection at a section? The important methods used for finding out the slope and deflection at a section in a loaded
UNIT III DEFLECTION OF BEAMS 1. What are the methods for finding out the slope and deflection at a section? The important methods used for finding out the slope and deflection at a section in a loaded
ESE TOPICWISE OBJECTIVE SOLVED PAPER I
 C I V I L E N G I N E E R I N G ESE TOPICWISE OBJECTIVE SOLVED PAPER I FROM 1995-018 UPSC Engineering Services Eamination, State Engineering Service Eamination & Public Sector Eamination. Regd. office
C I V I L E N G I N E E R I N G ESE TOPICWISE OBJECTIVE SOLVED PAPER I FROM 1995-018 UPSC Engineering Services Eamination, State Engineering Service Eamination & Public Sector Eamination. Regd. office
Design of Reinforced Concrete Beam for Shear
 Lecture 06 Design of Reinforced Concrete Beam for Shear By: Civil Engineering Department UET Peshawar drqaisarali@uetpeshawar.edu.pk Topics Addressed Shear Stresses in Rectangular Beams Diagonal Tension
Lecture 06 Design of Reinforced Concrete Beam for Shear By: Civil Engineering Department UET Peshawar drqaisarali@uetpeshawar.edu.pk Topics Addressed Shear Stresses in Rectangular Beams Diagonal Tension
CHAPTER 4. Stresses in Beams
 CHAPTER 4 Stresses in Beams Problem 1. A rolled steel joint (RSJ) of -section has top and bottom flanges 150 mm 5 mm and web of size 00 mm 1 mm. t is used as a simply supported beam over a span of 4 m
CHAPTER 4 Stresses in Beams Problem 1. A rolled steel joint (RSJ) of -section has top and bottom flanges 150 mm 5 mm and web of size 00 mm 1 mm. t is used as a simply supported beam over a span of 4 m
Stress Analysis Lecture 4 ME 276 Spring Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy
 Stress Analysis Lecture 4 ME 76 Spring 017-018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Shear and Moment Diagrams Beam Sign Convention The positive directions are as follows: The internal shear force causes a
Stress Analysis Lecture 4 ME 76 Spring 017-018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Shear and Moment Diagrams Beam Sign Convention The positive directions are as follows: The internal shear force causes a
Mechanics of Structure
 S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CE/CS/CR/CV] Mechanics of Structure Time: Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 70 Q.1(a) Attempt any SIX of the following. [1] Q.1(a) Define moment of Inertia. State MI
S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CE/CS/CR/CV] Mechanics of Structure Time: Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 70 Q.1(a) Attempt any SIX of the following. [1] Q.1(a) Define moment of Inertia. State MI
CRACK FORMATION AND CRACK PROPAGATION INTO THE COMPRESSION ZONE ON REINFORCED CONCRETE BEAM STRUCTURES
 S. Kakay et al. Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas. Vol. 5 No. (017) 116 14 CRACK FORMATION AND CRACK PROPAGATION INTO THE COMPRESSION ZONE ON REINFORCED CONCRETE BEAM STRUCTURES SAMDAR KAKAY DANIEL BÅRDSEN
S. Kakay et al. Int. J. Comp. Meth. and Exp. Meas. Vol. 5 No. (017) 116 14 CRACK FORMATION AND CRACK PROPAGATION INTO THE COMPRESSION ZONE ON REINFORCED CONCRETE BEAM STRUCTURES SAMDAR KAKAY DANIEL BÅRDSEN
ε t increases from the compressioncontrolled Figure 9.15: Adjusted interaction diagram
 CHAPTER NINE COLUMNS 4 b. The modified axial strength in compression is reduced to account for accidental eccentricity. The magnitude of axial force evaluated in step (a) is multiplied by 0.80 in case
CHAPTER NINE COLUMNS 4 b. The modified axial strength in compression is reduced to account for accidental eccentricity. The magnitude of axial force evaluated in step (a) is multiplied by 0.80 in case
Only for Reference Page 1 of 18
 Only for Reference www.civilpddc2013.weebly.com Page 1 of 18 Seat No.: Enrolment No. GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY PDDC - SEMESTER II EXAMINATION WINTER 2013 Subject Code: X20603 Date: 26-12-2013 Subject
Only for Reference www.civilpddc2013.weebly.com Page 1 of 18 Seat No.: Enrolment No. GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY PDDC - SEMESTER II EXAMINATION WINTER 2013 Subject Code: X20603 Date: 26-12-2013 Subject
[8] Bending and Shear Loading of Beams
![[8] Bending and Shear Loading of Beams [8] Bending and Shear Loading of Beams](/thumbs/92/110949676.jpg) [8] Bending and Shear Loading of Beams Page 1 of 28 [8] Bending and Shear Loading of Beams [8.1] Bending of Beams (will not be covered in class) [8.2] Bending Strain and Stress [8.3] Shear in Straight
[8] Bending and Shear Loading of Beams Page 1 of 28 [8] Bending and Shear Loading of Beams [8.1] Bending of Beams (will not be covered in class) [8.2] Bending Strain and Stress [8.3] Shear in Straight
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each.
 GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
Lecture-04 Design of RC Members for Shear and Torsion
 Lecture-04 Design of RC Members for Shear and Torsion By: Prof. Dr. Qaisar Ali Civil Engineering Department UET Peshawar drqaisarali@uetpeshawar.edu.pk www.drqaisarali.com 1 Topics Addressed Design of
Lecture-04 Design of RC Members for Shear and Torsion By: Prof. Dr. Qaisar Ali Civil Engineering Department UET Peshawar drqaisarali@uetpeshawar.edu.pk www.drqaisarali.com 1 Topics Addressed Design of
Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad. Chapter (7)
 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad Chapter (7) 2017-2016 Soil Properties Physical Properties Mechanical Properties Gradation and Structure Compressibility Soil-Water Relationships Shear Strength Bearing Capacity
Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad Chapter (7) 2017-2016 Soil Properties Physical Properties Mechanical Properties Gradation and Structure Compressibility Soil-Water Relationships Shear Strength Bearing Capacity
Fundamentals of Structural Design Part of Steel Structures
 Fundamentals of Structural Design Part of Steel Structures Civil Engineering for Bachelors 133FSTD Teacher: Zdeněk Sokol Office number: B619 1 Syllabus of lectures 1. Introduction, history of steel structures,
Fundamentals of Structural Design Part of Steel Structures Civil Engineering for Bachelors 133FSTD Teacher: Zdeněk Sokol Office number: B619 1 Syllabus of lectures 1. Introduction, history of steel structures,
Mechanics of Materials CIVL 3322 / MECH 3322
 Mechanics of Materials CIVL 3322 / MECH 3322 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 A Quiz 11 A Quiz 12 A Quiz 13 A Quiz 14 A Quiz 15 A Quiz 16 In Statics, we spent most of our time looking at reactions at supports Two variations
Mechanics of Materials CIVL 3322 / MECH 3322 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 A Quiz 11 A Quiz 12 A Quiz 13 A Quiz 14 A Quiz 15 A Quiz 16 In Statics, we spent most of our time looking at reactions at supports Two variations
7 STATICALLY DETERMINATE PLANE TRUSSES
 7 STATICALLY DETERMINATE PLANE TRUSSES OBJECTIVES: This chapter starts with the definition of a truss and briefly explains various types of plane truss. The determinancy and stability of a truss also will
7 STATICALLY DETERMINATE PLANE TRUSSES OBJECTIVES: This chapter starts with the definition of a truss and briefly explains various types of plane truss. The determinancy and stability of a truss also will
Civil Engineering Design (1) Design of Reinforced Concrete Columns 2006/7
 Civil Engineering Design (1) Design of Reinforced Concrete Columns 2006/7 Dr. Colin Caprani, Chartered Engineer 1 Contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 Background... 3 1.2 Failure Modes... 5 1.3 Design Aspects...
Civil Engineering Design (1) Design of Reinforced Concrete Columns 2006/7 Dr. Colin Caprani, Chartered Engineer 1 Contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 Background... 3 1.2 Failure Modes... 5 1.3 Design Aspects...
V Predicted Weldment Fatigue Behavior AM 11/03 1
 V Predicted Weldment Fatigue Behavior AM 11/03 1 Outline Heavy and Light Industry weldments The IP model Some predictions of the IP model AM 11/03 2 Heavy industry AM 11/03 3 Heavy industry AM 11/03 4
V Predicted Weldment Fatigue Behavior AM 11/03 1 Outline Heavy and Light Industry weldments The IP model Some predictions of the IP model AM 11/03 2 Heavy industry AM 11/03 3 Heavy industry AM 11/03 4
Strength of Materials (15CV 32)
 Strength of Materials (15CV 32) Module 1 : Simple Stresses and Strains Dr. H. Ananthan, Professor, VVIET,MYSURU 8/21/2017 Introduction, Definition and concept and of stress and strain. Hooke s law, Stress-Strain
Strength of Materials (15CV 32) Module 1 : Simple Stresses and Strains Dr. H. Ananthan, Professor, VVIET,MYSURU 8/21/2017 Introduction, Definition and concept and of stress and strain. Hooke s law, Stress-Strain
STRUCTURAL SURFACES & FLOOR GRILLAGES
 STRUCTURAL SURFACES & FLOOR GRILLAGES INTRODUCTION Integral car bodies are 3D structures largely composed of approximately subassemblies- SSS Planar structural subassemblies can be grouped into two categories
STRUCTURAL SURFACES & FLOOR GRILLAGES INTRODUCTION Integral car bodies are 3D structures largely composed of approximately subassemblies- SSS Planar structural subassemblies can be grouped into two categories
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
MAAE 2202 A. Come to the PASS workshop with your mock exam complete. During the workshop you can work with other students to review your work.
 It is most beneficial to you to write this mock final exam UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the exam in 3 hours. Work on your own. Keep your textbook closed. Attempt every question. After the
It is most beneficial to you to write this mock final exam UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the exam in 3 hours. Work on your own. Keep your textbook closed. Attempt every question. After the
Pre-stressed concrete = Pre-compression concrete Pre-compression stresses is applied at the place when tensile stress occur Concrete weak in tension
 Pre-stressed concrete = Pre-compression concrete Pre-compression stresses is applied at the place when tensile stress occur Concrete weak in tension but strong in compression Steel tendon is first stressed
Pre-stressed concrete = Pre-compression concrete Pre-compression stresses is applied at the place when tensile stress occur Concrete weak in tension but strong in compression Steel tendon is first stressed
MECE 3321 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS CHAPTER 3
 MECE 3321 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS CHAPTER 3 Samantha Ramirez TENSION AND COMPRESSION TESTS Tension and compression tests are used primarily to determine the relationship between σ avg and ε avg in any material.
MECE 3321 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS CHAPTER 3 Samantha Ramirez TENSION AND COMPRESSION TESTS Tension and compression tests are used primarily to determine the relationship between σ avg and ε avg in any material.
U V603 Pages: 5. 6 In an isometric projection all horizontal lines of the object are represented by lines inclined
 Reg No.: Name: APJ ABDUL KALAM TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SIXTH SEMESTER B.TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION, APRIL 2018 Course Code: CE352 Course Name: COMPREHENSIVE EXAM (CE) Max. Marks: 50 Duration: 1 Hour Instructions
Reg No.: Name: APJ ABDUL KALAM TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SIXTH SEMESTER B.TECH DEGREE EXAMINATION, APRIL 2018 Course Code: CE352 Course Name: COMPREHENSIVE EXAM (CE) Max. Marks: 50 Duration: 1 Hour Instructions
Ch 4a Stress, Strain and Shearing
 Ch. 4a - Stress, Strain, Shearing Page 1 Ch 4a Stress, Strain and Shearing Reading Assignment Ch. 4a Lecture Notes Sections 4.1-4.3 (Salgado) Other Materials Handout 4 Homework Assignment 3 Problems 4-13,
Ch. 4a - Stress, Strain, Shearing Page 1 Ch 4a Stress, Strain and Shearing Reading Assignment Ch. 4a Lecture Notes Sections 4.1-4.3 (Salgado) Other Materials Handout 4 Homework Assignment 3 Problems 4-13,
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS. Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola
 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola Mechanics of materials branch of mechanics that studies the internal effects of stress and strain in a solid body. stress is associated with the
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola Mechanics of materials branch of mechanics that studies the internal effects of stress and strain in a solid body. stress is associated with the
Sabah Shawkat Cabinet of Structural Engineering Walls carrying vertical loads should be designed as columns. Basically walls are designed in
 Sabah Shawkat Cabinet of Structural Engineering 17 3.6 Shear walls Walls carrying vertical loads should be designed as columns. Basically walls are designed in the same manner as columns, but there are
Sabah Shawkat Cabinet of Structural Engineering 17 3.6 Shear walls Walls carrying vertical loads should be designed as columns. Basically walls are designed in the same manner as columns, but there are
Design of a Multi-Storied RC Building
 Design of a Multi-Storied RC Building 16 14 14 3 C 1 B 1 C 2 B 2 C 3 B 3 C 4 13 B 15 (S 1 ) B 16 (S 2 ) B 17 (S 3 ) B 18 7 B 4 B 5 B 6 B 7 C 5 C 6 C 7 C 8 C 9 7 B 20 B 22 14 B 19 (S 4 ) C 10 C 11 B 23
Design of a Multi-Storied RC Building 16 14 14 3 C 1 B 1 C 2 B 2 C 3 B 3 C 4 13 B 15 (S 1 ) B 16 (S 2 ) B 17 (S 3 ) B 18 7 B 4 B 5 B 6 B 7 C 5 C 6 C 7 C 8 C 9 7 B 20 B 22 14 B 19 (S 4 ) C 10 C 11 B 23
NAME: Given Formulae: Law of Cosines: Law of Sines:
 NME: Given Formulae: Law of Cosines: EXM 3 PST PROBLEMS (LESSONS 21 TO 28) 100 points Thursday, November 16, 2017, 7pm to 9:30, Room 200 You are allowed to use a calculator and drawing equipment, only.
NME: Given Formulae: Law of Cosines: EXM 3 PST PROBLEMS (LESSONS 21 TO 28) 100 points Thursday, November 16, 2017, 7pm to 9:30, Room 200 You are allowed to use a calculator and drawing equipment, only.
Chapter (5) Allowable Bearing Capacity and Settlement
 Chapter (5) Allowable Bearing Capacity and Settlement Introduction As we discussed previously in Chapter 3, foundations should be designed for both shear failure and allowable settlement. So the allowable
Chapter (5) Allowable Bearing Capacity and Settlement Introduction As we discussed previously in Chapter 3, foundations should be designed for both shear failure and allowable settlement. So the allowable
Module 11 Design of Joints for Special Loading. Version 2 ME, IIT Kharagpur
 Module 11 Design of Joints for Special Loading Version ME, IIT Kharagpur Lesson Design of Eccentrically Loaded Welded Joints Version ME, IIT Kharagpur Instructional Objectives: At the end of this lesson,
Module 11 Design of Joints for Special Loading Version ME, IIT Kharagpur Lesson Design of Eccentrically Loaded Welded Joints Version ME, IIT Kharagpur Instructional Objectives: At the end of this lesson,
CITY AND GUILDS 9210 UNIT 135 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS Level 6 TUTORIAL 5A - MOMENT DISTRIBUTION METHOD
 Outcome 1 The learner can: CITY AND GUIDS 910 UNIT 15 ECHANICS OF SOIDS evel 6 TUTORIA 5A - OENT DISTRIBUTION ETHOD Calculate stresses, strain and deflections in a range of components under various load
Outcome 1 The learner can: CITY AND GUIDS 910 UNIT 15 ECHANICS OF SOIDS evel 6 TUTORIA 5A - OENT DISTRIBUTION ETHOD Calculate stresses, strain and deflections in a range of components under various load
Full Length Test Civil Engineering
 Full ength Test ivil Engineering nswer Keys and Explanations 1 [ns ] Green s theorem and stokes theorem convert line integral to surface integral and vice versa Whereas Gauss s Divergence theorem converts
Full ength Test ivil Engineering nswer Keys and Explanations 1 [ns ] Green s theorem and stokes theorem convert line integral to surface integral and vice versa Whereas Gauss s Divergence theorem converts
BOOK OF COURSE WORKS ON STRENGTH OF MATERIALS FOR THE 2 ND YEAR STUDENTS OF THE UACEG
 BOOK OF COURSE WORKS ON STRENGTH OF MATERIALS FOR THE ND YEAR STUDENTS OF THE UACEG Assoc.Prof. Dr. Svetlana Lilkova-Markova, Chief. Assist. Prof. Dimitar Lolov Sofia, 011 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS GENERAL
BOOK OF COURSE WORKS ON STRENGTH OF MATERIALS FOR THE ND YEAR STUDENTS OF THE UACEG Assoc.Prof. Dr. Svetlana Lilkova-Markova, Chief. Assist. Prof. Dimitar Lolov Sofia, 011 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS GENERAL
Chapter Objectives. Design a beam to resist both bendingand shear loads
 Chapter Objectives Design a beam to resist both bendingand shear loads A Bridge Deck under Bending Action Castellated Beams Post-tensioned Concrete Beam Lateral Distortion of a Beam Due to Lateral Load
Chapter Objectives Design a beam to resist both bendingand shear loads A Bridge Deck under Bending Action Castellated Beams Post-tensioned Concrete Beam Lateral Distortion of a Beam Due to Lateral Load
Jeff Brown Hope College, Department of Engineering, 27 Graves Pl., Holland, Michigan, USA UNESCO EOLSS
 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Jeff Brown Hope College, Department of Engineering, 27 Graves Pl., Holland, Michigan, USA Keywords: Solid mechanics, stress, strain, yield strength Contents 1. Introduction 2. Stress
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Jeff Brown Hope College, Department of Engineering, 27 Graves Pl., Holland, Michigan, USA Keywords: Solid mechanics, stress, strain, yield strength Contents 1. Introduction 2. Stress
Supplement: Statically Indeterminate Trusses and Frames
 : Statically Indeterminate Trusses and Frames Approximate Analysis - In this supplement, we consider an approximate method of solving statically indeterminate trusses and frames subjected to lateral loads
: Statically Indeterminate Trusses and Frames Approximate Analysis - In this supplement, we consider an approximate method of solving statically indeterminate trusses and frames subjected to lateral loads
1. Two forces P and Q are acting at an angle as shown in the figure. In terms of these quantities, what are values of R and respectively?
 1. Two forces P and Q are acting at an angle as shown in the figure. In terms of these quantities, what are values of R and respectively? Q R P a) Qsin P Q PQ cos and tan 1 P Q cos b) Qsin P Q PQ cos and
1. Two forces P and Q are acting at an angle as shown in the figure. In terms of these quantities, what are values of R and respectively? Q R P a) Qsin P Q PQ cos and tan 1 P Q cos b) Qsin P Q PQ cos and
The objective of this experiment is to investigate the behavior of steel specimen under a tensile test and to determine it's properties.
 Objective: The objective of this experiment is to investigate the behavior of steel specimen under a tensile test and to determine it's properties. Introduction: Mechanical testing plays an important role
Objective: The objective of this experiment is to investigate the behavior of steel specimen under a tensile test and to determine it's properties. Introduction: Mechanical testing plays an important role
UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define stress. When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation.
 UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define stress. When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The magnitude
UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define stress. When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The magnitude
JUT!SI I I I TO BE RETURNED AT THE END OF EXAMINATION. THIS PAPER MUST NOT BE REMOVED FROM THE EXAM CENTRE. SURNAME: FIRST NAME: STUDENT NUMBER:
 JUT!SI I I I TO BE RETURNED AT THE END OF EXAMINATION. THIS PAPER MUST NOT BE REMOVED FROM THE EXAM CENTRE. SURNAME: FIRST NAME: STUDENT NUMBER: COURSE: Tutor's name: Tutorial class day & time: SPRING
JUT!SI I I I TO BE RETURNED AT THE END OF EXAMINATION. THIS PAPER MUST NOT BE REMOVED FROM THE EXAM CENTRE. SURNAME: FIRST NAME: STUDENT NUMBER: COURSE: Tutor's name: Tutorial class day & time: SPRING
Theory of Shear Strength
 SKAA 1713 SOIL MECHANICS Theory of Shear Strength Prepared by, Dr. Hetty 1 SOIL STRENGTH DEFINITION Shear strength of a soil is the maximum internal resistance to applied shearing forces The maximum or
SKAA 1713 SOIL MECHANICS Theory of Shear Strength Prepared by, Dr. Hetty 1 SOIL STRENGTH DEFINITION Shear strength of a soil is the maximum internal resistance to applied shearing forces The maximum or
Soil strength. the strength depends on the applied stress. water pressures are required
 Soil Strength Soil strength u Soils are essentially frictional materials the strength depends on the applied stress u Strength is controlled by effective stresses water pressures are required u Soil strength
Soil Strength Soil strength u Soils are essentially frictional materials the strength depends on the applied stress u Strength is controlled by effective stresses water pressures are required u Soil strength
BTECH MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS. Level 3 Unit 5
 BTECH MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS Level 3 Unit 5 FORCES AS VECTORS Vectors have a magnitude (amount) and a direction. Forces are vectors FORCES AS VECTORS (2 FORCES) Forces F1 and F2 are in
BTECH MECHANICAL PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS Level 3 Unit 5 FORCES AS VECTORS Vectors have a magnitude (amount) and a direction. Forces are vectors FORCES AS VECTORS (2 FORCES) Forces F1 and F2 are in
Theory of Shear Strength
 MAJ 1013 ADVANCED SOIL MECHANICS Theory of Shear Strength Prepared by, Dr. Hetty 1 Strength of different materials Steel Concrete Soil Tensile strength Compressive strength Shear strength Complex behavior
MAJ 1013 ADVANCED SOIL MECHANICS Theory of Shear Strength Prepared by, Dr. Hetty 1 Strength of different materials Steel Concrete Soil Tensile strength Compressive strength Shear strength Complex behavior
EN Eurocode 7. Section 3 Geotechnical Data Section 6 Spread Foundations. Trevor L.L. Orr Trinity College Dublin Ireland.
 EN 1997 1: Sections 3 and 6 Your logo Brussels, 18-20 February 2008 Dissemination of information workshop 1 EN 1997-1 Eurocode 7 Section 3 Geotechnical Data Section 6 Spread Foundations Trevor L.L. Orr
EN 1997 1: Sections 3 and 6 Your logo Brussels, 18-20 February 2008 Dissemination of information workshop 1 EN 1997-1 Eurocode 7 Section 3 Geotechnical Data Section 6 Spread Foundations Trevor L.L. Orr
Physics 8 Monday, November 23, 2015
 Physics 8 Monday, November 23, 2015 Handing out HW11, due Friday, December 4. One or two more beam-related examples, then we ll move on to oscillations ( periodic motion ). This week s reading is Mazur
Physics 8 Monday, November 23, 2015 Handing out HW11, due Friday, December 4. One or two more beam-related examples, then we ll move on to oscillations ( periodic motion ). This week s reading is Mazur
NCEES Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Examination CIVIL EXAM SPECIFICATIONS
 NCEES Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Examination CIVIL EXAM SPECIFICATIONS Effective Beginning with the April 2009 Examinations The FE examination is an 8-hour supplied-reference examination: 120 questions
NCEES Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Examination CIVIL EXAM SPECIFICATIONS Effective Beginning with the April 2009 Examinations The FE examination is an 8-hour supplied-reference examination: 120 questions
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich
 UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS For Marker s Use Only LAST NAME (printed): FIRST
UNIVERSITY OF SASKATCHEWAN ME 313.3 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS I FINAL EXAM DECEMBER 13, 2008 Professor A. Dolovich A CLOSED BOOK EXAMINATION TIME: 3 HOURS For Marker s Use Only LAST NAME (printed): FIRST
OUTCOME 1 - TUTORIAL 3 BENDING MOMENTS. You should judge your progress by completing the self assessment exercises. CONTENTS
 Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 15 Engineering Science L/601/1404 OUTCOME 1 - TUTORIAL 3 BENDING MOMENTS 1. Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements of static engineering
Unit 2: Unit code: QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 15 Engineering Science L/601/1404 OUTCOME 1 - TUTORIAL 3 BENDING MOMENTS 1. Be able to determine the behavioural characteristics of elements of static engineering
Chapter 8. Shear and Diagonal Tension
 Chapter 8. and Diagonal Tension 8.1. READING ASSIGNMENT Text Chapter 4; Sections 4.1-4.5 Code Chapter 11; Sections 11.1.1, 11.3, 11.5.1, 11.5.3, 11.5.4, 11.5.5.1, and 11.5.6 8.2. INTRODUCTION OF SHEAR
Chapter 8. and Diagonal Tension 8.1. READING ASSIGNMENT Text Chapter 4; Sections 4.1-4.5 Code Chapter 11; Sections 11.1.1, 11.3, 11.5.1, 11.5.3, 11.5.4, 11.5.5.1, and 11.5.6 8.2. INTRODUCTION OF SHEAR
