GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
|
|
|
- Jacob Ball
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Question Paper & Answer Keys
2 Index 1 Question Paper Analysis 2 Question Paper & Answer keys : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 2
3 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2015 Civil Mathematics 13% Geomatics 6% Transportation 8% General Aptitude 15% Solid Mechanics 3% Structural Analysis 6% Reinforced Cement Concrete 8% Environmental 6% Hydrology & Irrigation 5% Fluid Mechanics 11% Geotechnical 15% Steel Structures 4% : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 3
4 - -Set 1 SUBJECT Mathematics Solid Mechanics Structural Analysis Reinforced Cement Concrete Steel Structures Geotechnical Fluid Mechanics Hydrology & Irrigation Environmental Transportation Geomatics General Aptitude NO OF QUESTION 1M:3 2M:5 1M:1 2M:1 1M:2 2M:2 1M:2 2M:3 1M:0 2M:2 1M:5 2M:5 1M:3 2M:4 1M:1 2M:2 1M:2 2M:2 1M:2 2M:3 1M:2 2M:2 1M:5 2M:5 Topics Asked in Paper Probability and Distribution Calculus; Linear Algebra Numerical Method; Differential Equation Complex Variable Shear Force and Bending Moment Simple Stress & Strain Matrix Method of Structural Analysis Internal Forces in Beams Slope and Deflection Method Trusses and Arches Displacement Method Concrete Technology Analysis of Ultimate Load Capacity Basic Elements of Pre-stressed Concrete Design of Pre-Stressed Concrete Beams Simple Connections Beams; Plastic Analysis Index Properties and Soil Classification Permeability and Seepage Consolidation Surface Investigations Earth Pressure Index Properties and Soil Classification Permeability and Seepage Consolidation; Surface Investigations Hydrology Water Requirements of Crops Hydraulics & Hydraulic Machinery Air Pollution and Noise Pollution Solid Waste Management Quality Standards of Water Domestic Waste Water Treatment Sludge Disposal Geometric Design of Highway Testing and Specifications of Paving Materials Traffic Characteristics Traffic Signs and Signal Design Leveling Theodolite & Traversing Plane Table surveying & Tachometric Corrections Numerical Ability Verbal Ability Total Marks Total : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 4
5 GATE 2015 Examination Civil Section: General Aptitude Q1 to Q 5 carries 1 mark each 1 Which word is not a synonym for the word vernacular? (A) Regional (C) Indigent (B) Indigenous (D) Colloquial [Ans C] 2 Mr Vivek walks 6 meters North-east, then turns and walks 6 meters South-east, both at 60 degrees to east He further moves 2 meters South and 4 meters West What is the straight distance in metres between the point he started from and the point he finally reached? (A) 2 2 (B) 2 [Ans A] (C) 2 (D) Four cards are randomly selected from a pack of 52 cards If the first two cards are kings, what is the probability that the third card is a king? (A) 4/52 (C) (1/52) (1/52) (B) 2/50 (D) (1/52) (1/51) (l/50) [Ans B] 4 Choose the most appropriate word from the options given below to complete the following sentence The official answered that the complaints of the citizen would be looked into (A) Respectably (C) Reputably (B) Respectfully (D) Respectively [Ans B] 5 Choose the statement where underlined word is used correctly (A) The minister insured the victims that everything would be all right (B) He ensured that the company will not have to bear any loss (C) The actor got himself ensured against any accident (D) The teacher insured students of good results [Ans B] Q6 to Q 10 carries 2 marks each 6 How many four digit numbers can be formed with the 10 digits 0, 1, 2, 9 if no number can start with 0 and if repetitions are not allowed? [Ans *] Range: 4536 to 4536 : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 5
6 7 Read the following table giving sales data of five types of batteries for years 2006 to 2012: Year Type I Type II Type III Type IV Type V Out of the following, which type of battery achieved higher growth between the years 2006 and 2012? (A) Type V (B) Type III [Ans D] (C) Type II (D) Type I 8 There are 16 teachers who can teach Thermodynamics (TD) 11 who can teach Electrical Sciences (ES) and 5 who can teach both TD and Mechanics (EM) There are a total of 40 teachers 6 cannot teach any of the three subjects; ie, EM, ES or TD 6 can teach only ES 4 can teach all three subjects, ie, EM, ES and TD 4 can teach ES and TD How many can teach both ES and EM but not TD? (A) 1 (B) 2 [Ans A] (C) 3 (D) 4 9 The word similar in meaning to dreary is (A) Cheerful (B) Dreamy [Ans D] (C) Hard (D) Dismal 10 The given question is followed by two statements: select the most appropriate option that solves the question Capacity of a solution tank A i s 70% of the capacity of tank B How many gallons of solution are in tank A and tank B? Statements: I Tank A is 80% full and tank B is 40% full II Tank A if full contains 14,000 gallons of solution (A) Statement I alone is sufficient (B) Statement II alone is sufficient (C) Either statement I or II alone is sufficient (D) Both the statements I and II together are sufficient [Ans D] : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 6
7 Section: Civil Q1 to Q 25 carries one mark each 1 In friction circle method of slope stability analysis, if r defines the radius of the slip circle, the radius of friction circle is: (A) r sin ϕ (B) r [Ans A] (C) r cos ϕ (D) r tan ϕ 2 Surcharge loading required to be placed on the horizontal backfill of a smooth retaining vertical wall so as to completely eliminate tensile crack is: (A) 2c (C) 2c k a (B) 2c k a (D) 2c k a [Ans D] 3 A groundwater sample was found to contain 500 mg/l total dissolved solids (TDS) TDS (in %) present in the sample is [Ans *] Range: 005 to The relationship between the length scale ratio (L r ) and the velocity scale ratio (V r ) in hydraulic models, in which Froude dynamic similarity is maintained, is: (A) V r = L 15 r (C) V r = L r (B) L r = V r [Ans D] (D) V r = L r 5 Let A = [a ij ], 1 i, j n with n 3 and a ij = i j The rank of A is: (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) n 1 (D) n [Ans B] 6 If the water content of a fully saturated soil mass is 100%, the void ratio of the sample is: (A) Less than specific gravity of soil (C) Greater than specific gravity of soil (B) Equal to specific gravity of soil (D) Independent of specific gravity of soil [Ans B] 7 A superspeedway in New Delhi has among the highest super-elevation rates of any track, on the Indian Grand Prix circuit The track requires drivers to negotiate turns with a radius of 335 m and 33 banking Given this information, the coefficient of side friction required in order to allow a vehicle to travel at 320 km/h along the curve is: (A) 1761 (C) 0253 (B) 0176 (D) 2530 [Ans A] 8 lim x (1 + 1 x )2x is equal to (A) e 2 (B) e (C) 1 (D) e 2 [Ans D] : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 7
8 9 In a leveling work, sum of the Back Sight (BS) and Fore Sight (FS) have been found to be 3085 m and 5645 m respectively If the Reduced Level (RL) of the starting station is m, the RL (in m) of the last station is [Ans *] Range: 9744 to While minimizing the function f(x), necessary and sufficient conditions for a point, x 0 to be a minima are: (A) f (x 0 ) > 0 and f"(x 0 ) = 0 (C) f (x 0 ) = 0 and f"(x 0 ) < 0 (B) f (x 0 ) < 0 and f"(x 0 ) = 0 (D) f (x 0 ) = 0 and f"(x 0 ) > 0 [Ans D] 11 Given, i = 1, the value of the definite integral, x/2 I = o cos x + i sin x cos x i sin x dx is: (A) 1 (B) 1 (C) i (D) i [Ans C] 12 A hydraulic jump takes place in a frictionless rectangular channel The pre-jump depth is y p The alternate and sequent depths corresponding to y p are y a and y s respectively The correct relationship among y p, y a and y s is: (A) y a < y s < y p (B) y p < y s < y a [Ans B] (C) y p < y s = y a (D) y p = y s = y a 13 The relationship between porosity (η) Specific yield (S y ) and specific retention (S t ) of an unconfined aquifer is: (A) S y + S r = η (B) S y + η = S r [Ans A] (C) S r + η = S y (D) S y + S r + η = 1 14 A horizontal beam ABC is loaded as shown in the figure below The distance of the point of contra flexure from end A (in m) is 10 kn 075 m A C B 1 m [Ans *] Range: 025 to Prying forces are: (A) Shearing forces on the bolts because of the joints (B) Tensile forces due to the flexibility of connected parts (C) Bending forces on the bolts because of the joints (D) Forces due the friction between connected parts [Ans B] : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 8
9 16 A steel member M has reversal of stress due to live loads, whereas another member N has reversal of stress due to wind load As per IS 800: 2007, the maximum slenderness ratio permitted is: (A) Less for member M than that of member N (B) More for member M than for member N (C) Same for both the members (D) Not specified m the Code [Ans A] 17 In Newton-Raphson iterative method, the initial guess value (x ini ) is considered as zero while finding the roots of the equation: f(x) = 2 + 6x 4x x 3 The correction, Δx, to be added to x ini in the first iteration is [Ans *] Range: 0333 to Net ultimate bearing capacity of a footing embedded in a clay stratum (A) Increases with depth of footing only (B) Increases with size of footing only (C) Increases with depth and size of footing (D) Is independent of depth and size of footing [Ans D] 19 For the plane stress situation shown in the figure, the maximum shear stress and the plane on which it acts are; σ y = 50 MPa y σ x = 50 MPa x σ x = 50 MPa σ y = 50 MPa (A) 50 MPa, on a plane 45 clockwise w r t x axis (B) 50 MPa, on a plane 45 anti clockwise w r t x axis (C) 50 MPa, at all orientations (D) Zero at all orientations [Ans D] 20 SO 2 and CO adversely affect (A) Oxygen carrying capacity of blood and functioning of lungs respectively (B) Functioning of the respiratory system and brain respectively (C) Functioning of the respiratory system and oxygen carrying capacity of blood respectively (D) Functioning of air passages and chest respectively [Ans C] : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 9
10 21 A nozzle is so shaped that the average flow velocity changes linearly from 15 m/s at the beginning to 15 m/s at its end in a distance of 0375 m The magnitude of the convective acceleration (in m s 2 ) at the end of the nozzle is [Ans *] Range: 54 to The following statements are made related to the lengths of turning lanes at signalized intersections: (i) 15 times the average number of vehicles (by vehicle type) that would store in turning lane per cycle during the peak hour (ii) 2 times the average number of vehicle (by vehicle type) that would store in turning lane per cycle during the peak hour (iii) Average number of vehicles (by vehicle type) that would store in the adjacent through lane per cycle during the peak hour (iv) Average number of vehicles (by vehicle type) that would store in all lanes per cycle during the peak hour As per the IRC recommendations, the correct choice for design length of storage lanes is: (A) Maximum of (ii and iii) (C) Average of (i and iii) (B) Maximum of (i and iii) (D) Only (iv) [Ans A] 23 The combined correction due to curvature and refraction (in m) for a distance of 1 km on the surface of Earth is: (A) (C) 763 (B) 0673 (D) 0763 [Ans A] 24 A guided support as shown in the figure below is represented by three springs (horizontal, vertical and rotational) with stiffness k x, k y and k θ respectively The limiting values of k x, k y and k θ are: (A), 0, (B),, [Ans A] (C) 0,, (D),, 0 25 A column of size 450 mm x 600 mm has unsupported length of 30 m and is braced against side sway in both directions According to IS 456: 2000, the minimum eccentricities (in mm) with respect to major and minor principal axis are (A) 200 and 200 (B) 260 and 210 [Ans B] (C) 260 and 200 (D) 210 and 150 : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 10
11 Q26 to Q 55 carries 2 marks each 26 A 4m thick layer of normally consolidated clay has an average void ratio of 130 Its compression index is 06 and coefficient of consolidation is 1 m 2 y r If the increase in vertical pressure due to foundation load on the clay layer is equal to the existing effective overburden pressure, the change in the thickness of the clay layer is mm [Ans *] Range: 314 to The average surface area of a reservoir in the month of June is 20 km 2 In the same month, the average rate of inflow is 10 m 3 s outflow rate is 15 m 3 s monthly rainfall is 10 cm monthly seepage loss is 18 cm and the storage change is 16 million m 3 The evaporation (in cm) in that month is: (A) 468 (C) 136 (B) 1360 (D) 234 [Ans B] 28 A landfill is to be designed to serve a population of for a period of 25 years The solid waste (SW) generation is 2 kg/person/day The density of the un-compacted SW is 100 kg/m 3 and a compaction ratio of 4 is suggested The ratio of compacted fill (ie, SW + cover) to compacted SW is 15 The landfill volume (in million m 3 ) required is [Ans *]Range: 219 to In a wastewater treatment plant, primary sedimentation tank (PST) designed at an overflow rate of 325 m 3 /day/m 2 is 325 m long, 80 m wide and liquid depth of 225 m If the length of the weir is 75 m the weir loading rate (in m 3 /day/m) is [Ans *] Range: to Stress path equation for tri-axial test upon application of deviatric stress is, q = p The respective values of cohesion, c (in kpa) and angle of internal friction, ϕ are: (A) 20 and 20 (C) 30 and 30 (B) 20 and 30 (D) 30 and 20 [Ans B] 31 A simply supported beam AB of span L = 24 m is subjected to two wheel loads acting at a distance d = 5 m apart as shown in the figure below Each wheel transmits a load P = 3 kn and may occupy any position along the beam If the beam is an I-section having section modulus, S = 162 cm 3, the maximum bending stress (in GPa) due to the wheel loads is P P A B d L [Ans *] Range: to : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 11
12 32 The velocity components of a two dimensional plane motion of a fluid are: u = y x x2 y and v = xy 2 2y x3 3 The correct statement is: (A) Fluid is incompressible and flow is irrotational (B) Fluid is incompressible and flow is rotational (C) Fluid is compressible and flow is irrotational (D) Fluid is compressible and flow is rotational [Ans A] 33 A 588 cm 3 volume of moist sand weighs 1010 gm Its dry weight is 918 gm and specific gravity of solids, G is 267 Assuming density of water as 1 gm/cm 3, the void ratio is [Ans *] Range: 071 to The relation between speed u (m km/h) and density k (number of vehicles/km) for a traffic stream on a road is u = k The capacity on this road is vph (vehicles/hour) [Ans *] Range: 175 to Match the information related to tests on aggregates given in Group-I with that in Group-II Group-I Group-II P Resistance to impact 1 Hardness Q Resistance to wear 2 Strength R Resistance to weathering action 3 Toughness S Resistance to crushing 4 Soundness (A) P-1, Q-3, R-4, S-2 (B) P-3, Q-1, R-4, S-2 (C) P-4, Q-l, R-3, S-2 (D) P-3, Q-4, R-2, S-l [Ans B] 36 A pile of diameter 04 m is fully embedded in a clay stratum having 5 layers, each 5 m thick as shown in the figure below Assume a constant unit weight of soil as I8 kn/m 3 for all the layers Using λ-method (λ = 015 for 25 m embedment length) and neglecting the end bearing component, the ultimate pile capacity (in kn) is G S γ = 18 kn m 3 for all layers 5 m c = 40 kpa Pile Dia = 04m, L = 25m 5 m c = 50 kpa 5 m c = 60 kpa 5 m c = 70 kpa 5 m c = 80 kpa [Ans *] Range: to The bearings of two inaccessible stations S 1 (Easting 500 m, Northing 500 m) and S 2 (Easting 600 m, Northing 450 m) from a station S 3 were observed as 225 and ' respectively The independent Easting (in m) of station S 3 is: (A) (B) [Ans C] (C) (D) : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 12
13 38 A water treatment plant of capacity, 1 m 3 s has filter boxes of dimensions 6 m 10 m Loading rate to the filters is 120 m 3 /day/m 2 When two of the filters are out of service for back washing, the loading rate (in m 3 /day/m 2 ) is [Ans *] Range: 144 to A simply supported reinforced concrete beam of length 10 m sags while undergoing shrinkage Assuming a uniform curvature of 0004 m 1 along the span, the maximum deflection (in m) of the beam at mid-span is [Ans *] Range: to: According to the concept of Limit State Design as per IS 456:2000 The probability of failure of a structure is [Ans *] Range: to A field channel has cultivable commanded area of 2000 hectares The intensities of irrigation for gram and wheat are 30% and 50% respectively Gram has a kor period of 18 days, kor depth of 12 cm, while wheat has a kor period of 18 days and a kor depth of 15 cm The discharge (in m 3 s) required in the field channel to supply water to the commanded area during the kor period is [Ans *] Range: 1427 to In Marshall method of mix design, the coarse aggregate, fine aggregate, fines and bitumen having respective values of specific gravity , 265 and 101 are mixed in the relative proportions (% by weight) of and 55 respectively The theoretical specific gravity of the mix and the effective specific gravity of the aggregates in the mix respectively are (A) 242 and 263 (C) 242 and 2 93 (B) 242 and 278 (D) 264 and 278 [Ans A] 43 A triangular gate with a base width of 2 m and a height of 15 m lies in a vertical plane The top vertex of the gate is 15 m below the surface of a tank which contains oil of specific gravity 08 Considering the density of water and acceleration due to gravity to be 1000 kg m 3 and 981 m s 2 respectively, the hydrostatic force (in kn) exerted by the oil on the gate is [Ans *] Range: 2943 to Two Pegs A and B were fixed on opposite banks of a 50 m wide river The level was set up at A and the staff readings on Pegs A and B were observed as 1350 m and 1550 m respectively Thereafter the instrument was shifted and set up at B The staff readings on Pegs B and A were observed as 0750 m and 0550 m, respectively If the RL of Peg A is m, the RL (in m) of Peg B is [Ans *] Range: 100 to The two Eigen values of the matrix [ 2 1 ] have a ratio of 3:1 for p = 2 What is another value 1 p of p for which the Eigen values have the same ratio of 3:1? (A) 2 (C) 7/3 (B) 1 (D) 14/3 [Ans D] : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 13
14 46 For step-size, Δx = 04, the value of following integral using Simpson s 1/3 rule is 08 ( x 200x x 3 900x x 5 ) dx 0 [Ans *] Range: to Consider the following second order linear differential equation d 2 y dx 2 = 12x2 + 24x 20 The boundary conditions are: at x = 0, y = 5 and at x = 2, y = 21 The value of y at x = 1 is [Ans *] Range: 2 to 2 48 A fixed end beam is subjected to a load, W at l/3rd span from the left support as shown in the figure The collapse load of the beam is: W X L/3 2M p Y M p Z L/2 L/2 (A) 165 M P L (B) 155 M P L [Ans C] (C) 150 M P L (D) 160 M P L 49 A 6 m high retaining wall having a smooth vertical back face retains a layered horizontal backfill Top 3 m thick layer of the backfill is sand having an angle of internal friction, ϕ = 30 while the bottom layer is 3 m thick clay with cohesion, c = 20 kpa Assume unit weight for both sand and clay as 18 kn m 3 The total active earth pressure per unit length of the wall (in kn/m) is: (A) 150 (B) 216 (C) 156 (D) 196 [Ans A] 50 In a pre-stressed concrete beam section shown in the figure, the net loss is 10% and the final pre-stressing force applied at X is 750 kn The initial fiber stresses (in N mm 2 ) at the top and bottom of the beam were: b d 1 d 1 X b = 250 mm d 1 = 200 mm d 2 = 100 mm d 2 (A) 4166 and (B) 4166 and [Ans D] (C) and (D) 4166 and : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 14
15 51 Ultimate BOD of a river water sample is 20 mg/l BOD rate constant (natural log) is 015 day 1 The respective values of BOD (in %) exerted and remaining after 7 days are: (A) 45 and 55 (C) 65 and 35 (B) 55 and 45 (D) 75 and 25 [Ans C] 52 A pipe of 07 m diameter has a length of 6 km and connects two reservoirs A and B The water level m reservoir A is at an elevation 30m above the water level in reservoir B Halfway along the pipe line, there is a branch through which water can be supplied to a third reservoir C The friction factor of the pipe is 0024 The quantity of water discharged into reservoir C is 015m 3 s Considering the acceleration due to gravity as 981 m s 2 and neglecting minor losses, the discharge (mm 3 s) into the reservoir B is [Ans *] Range: to A steel strip of length L = 200 mm is fixed at end A and rests at B on a vertical spring of stiffness k = 2 N/mm The steel strip is 5 mm wide and 10 mm thick A vertical load, P = 50 N is applied at B, as shown in the figure Considering E = 200 GPa, the force (in N) developed in the spring is P A B k L [Ans *] Range: 3 to 3 54 The probability density function of a random variable, x is f(x) = x 4 (4 x2 ) fo 0 x 2 = 0 otherwise The mean, μ x of the random variable is [Ans *] Range: to In a system, two connected rigid bars AC and BC are of identical length, L with pin supports at A and B The bars are interconnected at C by a frictionless hinge The rotation of the hinge is restrained by a rotational spring of stiffness, k The system initially assumes a straight line configuration, ACB Assuming both the bars as weightless, the rotation at supports, A and B, due to a transverse load, P applied at C is: (A) PL 4k (C) P 4k (B) PL 2k (D) Pk 4L [Ans A] : , info@thegateacademycom Copyright reserved Web:wwwthegateacademycom 15
NODIA AND COMPANY. GATE SOLVED PAPER Civil Engineering Copyright By NODIA & COMPANY
 No part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any form or any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, or otherwise without the prior permission of the author. GATE SOLVED PAPER Civil
No part of this publication may be reproduced or distributed in any form or any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, or otherwise without the prior permission of the author. GATE SOLVED PAPER Civil
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown.
 D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
GATE : , Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
 GATE-2016 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2016 Civil Engineering
GATE-2016 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2016 Civil Engineering
Entrance exam Master Course
 - 1 - Guidelines for completion of test: On each page, fill in your name and your application code Each question has four answers while only one answer is correct. o Marked correct answer means 4 points
- 1 - Guidelines for completion of test: On each page, fill in your name and your application code Each question has four answers while only one answer is correct. o Marked correct answer means 4 points
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 2018 General Aptitude (GA) Set-7 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The driver applied the as soon as she approached the hotel where she wanted to take a. The words that best fill the blanks in the
GATE 2018 General Aptitude (GA) Set-7 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The driver applied the as soon as she approached the hotel where she wanted to take a. The words that best fill the blanks in the
SEM-2016(01HI CIVIL ENGINEERING. Paper Answer all questions. Question No. 1 does not have internal choice,
 Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 5 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(01HI CIVIL ENGINEERING Paper - 11 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 300 Instructions to
Roll No. Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 5 No. of Printed Pages : 8 SEM-2016(01HI CIVIL ENGINEERING Paper - 11 Time : 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 300 Instructions to
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
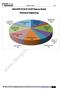 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
1. Two forces P and Q are acting at an angle as shown in the figure. In terms of these quantities, what are values of R and respectively?
 1. Two forces P and Q are acting at an angle as shown in the figure. In terms of these quantities, what are values of R and respectively? Q R P a) Qsin P Q PQ cos and tan 1 P Q cos b) Qsin P Q PQ cos and
1. Two forces P and Q are acting at an angle as shown in the figure. In terms of these quantities, what are values of R and respectively? Q R P a) Qsin P Q PQ cos and tan 1 P Q cos b) Qsin P Q PQ cos and
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each.
 GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
Introduction to Soil Mechanics
 Introduction to Soil Mechanics Sela Sode and Colin Jones WILEY Blackwell Contents Preface Dedication and Acknowledgments List of Symbols Soil Structure 1.1 Volume relationships 1.1.1 Voids ratio (e) 1.1.2
Introduction to Soil Mechanics Sela Sode and Colin Jones WILEY Blackwell Contents Preface Dedication and Acknowledgments List of Symbols Soil Structure 1.1 Volume relationships 1.1.1 Voids ratio (e) 1.1.2
GATE SOLUTIONS E N G I N E E R I N G
 GATE SOLUTIONS C I V I L E N G I N E E R I N G From (1987-018) Office : F-16, (Lower Basement), Katwaria Sarai, New Delhi-110016 Phone : 011-65064 Mobile : 81309090, 9711853908 E-mail: info@iesmasterpublications.com,
GATE SOLUTIONS C I V I L E N G I N E E R I N G From (1987-018) Office : F-16, (Lower Basement), Katwaria Sarai, New Delhi-110016 Phone : 011-65064 Mobile : 81309090, 9711853908 E-mail: info@iesmasterpublications.com,
Structural Analysis. For. Civil Engineering.
 Structural Analysis For Civil Engineering By www.thegateacademy.com ` Syllabus for Structural Analysis Syllabus Statically Determinate and Indeterminate Structures by Force/ Energy Methods; Method of Superposition;
Structural Analysis For Civil Engineering By www.thegateacademy.com ` Syllabus for Structural Analysis Syllabus Statically Determinate and Indeterminate Structures by Force/ Energy Methods; Method of Superposition;
1.The number of simultaneous equations to be solved in the slope deflection method,
 EXAM-1 1.The number of simultaneous equations to be solved in the slope deflection method, is equal to : A. the degree of statistical indeterminacy B. the degree of kinematic indeterminacy C. the number
EXAM-1 1.The number of simultaneous equations to be solved in the slope deflection method, is equal to : A. the degree of statistical indeterminacy B. the degree of kinematic indeterminacy C. the number
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 GATE-2015 Question Paper & Answer Keys GATE-2015 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
GATE-2015 Question Paper & Answer Keys GATE-2015 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
Reinforced Soil Structures Reinforced Soil Walls. Prof K. Rajagopal Department of Civil Engineering IIT Madras, Chennai
 Geosynthetics and Reinforced Soil Structures Reinforced Soil Walls continued Prof K. Rajagopal Department of Civil Engineering IIT Madras, Chennai e-mail: gopalkr@iitm.ac.inac in Outline of the Lecture
Geosynthetics and Reinforced Soil Structures Reinforced Soil Walls continued Prof K. Rajagopal Department of Civil Engineering IIT Madras, Chennai e-mail: gopalkr@iitm.ac.inac in Outline of the Lecture
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 General ptitude G Set-8 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The chairman requested the aggrieved shareholders to him. () bare with () bore with (C) bear with (D) bare Q.2 Identify the correct spelling out
General ptitude G Set-8 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 The chairman requested the aggrieved shareholders to him. () bare with () bore with (C) bear with (D) bare Q.2 Identify the correct spelling out
Theory of Shear Strength
 SKAA 1713 SOIL MECHANICS Theory of Shear Strength Prepared by, Dr. Hetty 1 SOIL STRENGTH DEFINITION Shear strength of a soil is the maximum internal resistance to applied shearing forces The maximum or
SKAA 1713 SOIL MECHANICS Theory of Shear Strength Prepared by, Dr. Hetty 1 SOIL STRENGTH DEFINITION Shear strength of a soil is the maximum internal resistance to applied shearing forces The maximum or
DESIGN AND DETAILING OF COUNTERFORT RETAINING WALL
 DESIGN AND DETAILING OF COUNTERFORT RETAINING WALL When the height of the retaining wall exceeds about 6 m, the thickness of the stem and heel slab works out to be sufficiently large and the design becomes
DESIGN AND DETAILING OF COUNTERFORT RETAINING WALL When the height of the retaining wall exceeds about 6 m, the thickness of the stem and heel slab works out to be sufficiently large and the design becomes
Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad. Chapter (7)
 Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad Chapter (7) 2017-2016 Soil Properties Physical Properties Mechanical Properties Gradation and Structure Compressibility Soil-Water Relationships Shear Strength Bearing Capacity
Instructor : Dr. Jehad Hamad Chapter (7) 2017-2016 Soil Properties Physical Properties Mechanical Properties Gradation and Structure Compressibility Soil-Water Relationships Shear Strength Bearing Capacity
CE : CIVIL ENGINEERING
 2009 CE : CIVIL ENGINEERING Duration : Three Hours Read the following instructions carefully. l. This question paper contains 16 printed pages including pages for rough work. Please check all pages and
2009 CE : CIVIL ENGINEERING Duration : Three Hours Read the following instructions carefully. l. This question paper contains 16 printed pages including pages for rough work. Please check all pages and
SN QUESTION YEAR MARK 1. State and prove the relationship between shearing stress and rate of change of bending moment at a section in a loaded beam.
 ALPHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (21000) ASSIGNMENT 1 SIMPLE STRESSES AND STRAINS SN QUESTION YEAR MARK 1 State and prove the relationship
ALPHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (21000) ASSIGNMENT 1 SIMPLE STRESSES AND STRAINS SN QUESTION YEAR MARK 1 State and prove the relationship
GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING ECG 503 LECTURE NOTE ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF RETAINING STRUCTURES
 GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING ECG 503 LECTURE NOTE 07 3.0 ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF RETAINING STRUCTURES LEARNING OUTCOMES Learning outcomes: At the end of this lecture/week the students would be able to: Understand
GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING ECG 503 LECTURE NOTE 07 3.0 ANALYSIS AND DESIGN OF RETAINING STRUCTURES LEARNING OUTCOMES Learning outcomes: At the end of this lecture/week the students would be able to: Understand
SECTION A. 8 kn/m. C 3 m 3m
 SECTION Question 1 150 m 40 kn 5 kn 8 kn/m C 3 m 3m D 50 ll dimensions in mm 15 15 Figure Q1(a) Figure Q1(b) The horizontal beam CD shown in Figure Q1(a) has a uniform cross-section as shown in Figure
SECTION Question 1 150 m 40 kn 5 kn 8 kn/m C 3 m 3m D 50 ll dimensions in mm 15 15 Figure Q1(a) Figure Q1(b) The horizontal beam CD shown in Figure Q1(a) has a uniform cross-section as shown in Figure
7 STATICALLY DETERMINATE PLANE TRUSSES
 7 STATICALLY DETERMINATE PLANE TRUSSES OBJECTIVES: This chapter starts with the definition of a truss and briefly explains various types of plane truss. The determinancy and stability of a truss also will
7 STATICALLY DETERMINATE PLANE TRUSSES OBJECTIVES: This chapter starts with the definition of a truss and briefly explains various types of plane truss. The determinancy and stability of a truss also will
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS. Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola
 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola Mechanics of materials branch of mechanics that studies the internal effects of stress and strain in a solid body. stress is associated with the
MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Prepared by Engr. John Paul Timola Mechanics of materials branch of mechanics that studies the internal effects of stress and strain in a solid body. stress is associated with the
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK. Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Subject code/name: ME2254/STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Year/Sem:II / IV UNIT I STRESS, STRAIN DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART A (2 MARKS)
INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA
 EGC373 (F) / Page 1 of 5 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA UK DEGREE TRANSFER PROGRAMME INTI ADELAIDE TRANSFER PROGRAMME EGC 373: FOUNDATION ENGINEERING FINAL EXAMINATION : AUGUST 00 SESSION This paper consists of
EGC373 (F) / Page 1 of 5 INTI COLLEGE MALAYSIA UK DEGREE TRANSFER PROGRAMME INTI ADELAIDE TRANSFER PROGRAMME EGC 373: FOUNDATION ENGINEERING FINAL EXAMINATION : AUGUST 00 SESSION This paper consists of
Sabah Shawkat Cabinet of Structural Engineering Walls carrying vertical loads should be designed as columns. Basically walls are designed in
 Sabah Shawkat Cabinet of Structural Engineering 17 3.6 Shear walls Walls carrying vertical loads should be designed as columns. Basically walls are designed in the same manner as columns, but there are
Sabah Shawkat Cabinet of Structural Engineering 17 3.6 Shear walls Walls carrying vertical loads should be designed as columns. Basically walls are designed in the same manner as columns, but there are
CHAPTER 4: BENDING OF BEAMS
 (74) CHAPTER 4: BENDING OF BEAMS This chapter will be devoted to the analysis of prismatic members subjected to equal and opposite couples M and M' acting in the same longitudinal plane. Such members are
(74) CHAPTER 4: BENDING OF BEAMS This chapter will be devoted to the analysis of prismatic members subjected to equal and opposite couples M and M' acting in the same longitudinal plane. Such members are
PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM - 613 403 - THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub : Strength of Materials Year / Sem: II / III Sub Code : MEB 310
PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM - 613 403 - THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub : Strength of Materials Year / Sem: II / III Sub Code : MEB 310
Soil Mechanics Prof. B.V.S. Viswanathan Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture 51 Earth Pressure Theories II
 Soil Mechanics Prof. B.V.S. Viswanathan Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture 51 Earth Pressure Theories II Welcome to lecture number two on earth pressure theories.
Soil Mechanics Prof. B.V.S. Viswanathan Department of Civil Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture 51 Earth Pressure Theories II Welcome to lecture number two on earth pressure theories.
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
Chapter 7: Bending and Shear in Simple Beams
 Chapter 7: Bending and Shear in Simple Beams Introduction A beam is a long, slender structural member that resists loads that are generally applied transverse (perpendicular) to its longitudinal axis.
Chapter 7: Bending and Shear in Simple Beams Introduction A beam is a long, slender structural member that resists loads that are generally applied transverse (perpendicular) to its longitudinal axis.
Downloaded from Downloaded from / 1
 PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY III SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2002 LEVEL : B. E. (Civil) SUBJECT: BEG256CI, Strength of Material Full Marks: 80 TIME: 03:00 hrs Pass marks: 32 Candidates are required to give their
PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY III SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2002 LEVEL : B. E. (Civil) SUBJECT: BEG256CI, Strength of Material Full Marks: 80 TIME: 03:00 hrs Pass marks: 32 Candidates are required to give their
8.1. What is meant by the shear strength of soils? Solution 8.1 Shear strength of a soil is its internal resistance to shearing stresses.
 8.1. What is meant by the shear strength of soils? Solution 8.1 Shear strength of a soil is its internal resistance to shearing stresses. 8.2. Some soils show a peak shear strength. Why and what type(s)
8.1. What is meant by the shear strength of soils? Solution 8.1 Shear strength of a soil is its internal resistance to shearing stresses. 8.2. Some soils show a peak shear strength. Why and what type(s)
SRI CHANDRASEKHARENDRA SARASWATHI VISWA MAHAVIDHYALAYA
 SRI CHANDRASEKHARENDRA SARASWATHI VISWA MAHAVIDHYALAYA (Declared as Deemed-to-be University under Section 3 of the UGC Act, 1956, Vide notification No.F.9.9/92-U-3 dated 26 th May 1993 of the Govt. of
SRI CHANDRASEKHARENDRA SARASWATHI VISWA MAHAVIDHYALAYA (Declared as Deemed-to-be University under Section 3 of the UGC Act, 1956, Vide notification No.F.9.9/92-U-3 dated 26 th May 1993 of the Govt. of
UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define stress. When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation.
 UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define stress. When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The magnitude
UNIT 1 STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define stress. When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The magnitude
ME3560 Tentative Schedule Spring 2019
 ME3560 Tentative Schedule Spring 2019 Week Number Date Lecture Topics Covered Prior to Lecture Read Section Assignment Prep Problems for Prep Probs. Must be Solved by 1 Monday 1/7/2019 1 Introduction to
ME3560 Tentative Schedule Spring 2019 Week Number Date Lecture Topics Covered Prior to Lecture Read Section Assignment Prep Problems for Prep Probs. Must be Solved by 1 Monday 1/7/2019 1 Introduction to
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SEMESTER: III SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A
 DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
Theory of Shear Strength
 MAJ 1013 ADVANCED SOIL MECHANICS Theory of Shear Strength Prepared by, Dr. Hetty 1 Strength of different materials Steel Concrete Soil Tensile strength Compressive strength Shear strength Complex behavior
MAJ 1013 ADVANCED SOIL MECHANICS Theory of Shear Strength Prepared by, Dr. Hetty 1 Strength of different materials Steel Concrete Soil Tensile strength Compressive strength Shear strength Complex behavior
Civil Engineering Design (1) Design of Reinforced Concrete Columns 2006/7
 Civil Engineering Design (1) Design of Reinforced Concrete Columns 2006/7 Dr. Colin Caprani, Chartered Engineer 1 Contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 Background... 3 1.2 Failure Modes... 5 1.3 Design Aspects...
Civil Engineering Design (1) Design of Reinforced Concrete Columns 2006/7 Dr. Colin Caprani, Chartered Engineer 1 Contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 Background... 3 1.2 Failure Modes... 5 1.3 Design Aspects...
GATE-2014 Exam Solutions Civil Engineering (Evening Session)
 GATE-01 Exam Solutions Page 1 Section - I (Civil Engineering) One Mark Questions Q.1 If G s.7%, n 0%, w 0% then the degree of saturation is. Se wg n and e 0.67 1 n S.71 0 0.67 81.% Q. The determinant of
GATE-01 Exam Solutions Page 1 Section - I (Civil Engineering) One Mark Questions Q.1 If G s.7%, n 0%, w 0% then the degree of saturation is. Se wg n and e 0.67 1 n S.71 0 0.67 81.% Q. The determinant of
Roadway Grade = m, amsl HWM = Roadway grade dictates elevation of superstructure and not minimum free board requirement.
 Example on Design of Slab Bridge Design Data and Specifications Chapter 5 SUPERSTRUCTURES Superstructure consists of 10m slab, 36m box girder and 10m T-girder all simply supported. Only the design of Slab
Example on Design of Slab Bridge Design Data and Specifications Chapter 5 SUPERSTRUCTURES Superstructure consists of 10m slab, 36m box girder and 10m T-girder all simply supported. Only the design of Slab
9.5 Compression Members
 9.5 Compression Members This section covers the following topics. Introduction Analysis Development of Interaction Diagram Effect of Prestressing Force 9.5.1 Introduction Prestressing is meaningful when
9.5 Compression Members This section covers the following topics. Introduction Analysis Development of Interaction Diagram Effect of Prestressing Force 9.5.1 Introduction Prestressing is meaningful when
Rigid pavement design
 Rigid pavement design Lecture Notes in Transportation Systems Engineering Prof. Tom V. Mathew Contents 1 Overview 1 1.1 Modulus of sub-grade reaction.......................... 2 1.2 Relative stiffness
Rigid pavement design Lecture Notes in Transportation Systems Engineering Prof. Tom V. Mathew Contents 1 Overview 1 1.1 Modulus of sub-grade reaction.......................... 2 1.2 Relative stiffness
 QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE / Name: CE 2251 / SOIL MECHANICS SEMESTER: IV UNIT 1- INTRODUCTION PART - A (2 marks) 1. Distinguish between Residual and Transported soil. (AUC May/June 2012)
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE / Name: CE 2251 / SOIL MECHANICS SEMESTER: IV UNIT 1- INTRODUCTION PART - A (2 marks) 1. Distinguish between Residual and Transported soil. (AUC May/June 2012)
Chapter (11) Pile Foundations
 Chapter (11) Introduction Piles are structural members that are made of steel, concrete, or timber. They are used to build pile foundations (classified as deep foundations) which cost more than shallow
Chapter (11) Introduction Piles are structural members that are made of steel, concrete, or timber. They are used to build pile foundations (classified as deep foundations) which cost more than shallow
Design of RC Retaining Walls
 Lecture - 09 Design of RC Retaining Walls By: Prof Dr. Qaisar Ali Civil Engineering Department UET Peshawar www.drqaisarali.com 1 Topics Retaining Walls Terms Related to Retaining Walls Types of Retaining
Lecture - 09 Design of RC Retaining Walls By: Prof Dr. Qaisar Ali Civil Engineering Department UET Peshawar www.drqaisarali.com 1 Topics Retaining Walls Terms Related to Retaining Walls Types of Retaining
18.Define the term modulus of resilience. May/June Define Principal Stress. 20. Define Hydrostatic Pressure.
 CE6306 STREGNTH OF MATERIALS Question Bank Unit-I STRESS, STRAIN, DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART-A 1. Define Poison s Ratio May/June 2009 2. What is thermal stress? May/June 2009 3. Estimate the load carried
CE6306 STREGNTH OF MATERIALS Question Bank Unit-I STRESS, STRAIN, DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART-A 1. Define Poison s Ratio May/June 2009 2. What is thermal stress? May/June 2009 3. Estimate the load carried
Name :. Roll No. :... Invigilator s Signature :.. CS/B.TECH (CE-NEW)/SEM-3/CE-301/ SOLID MECHANICS
 Name :. Roll No. :..... Invigilator s Signature :.. 2011 SOLID MECHANICS Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates are required to give their answers
Name :. Roll No. :..... Invigilator s Signature :.. 2011 SOLID MECHANICS Time Allotted : 3 Hours Full Marks : 70 The figures in the margin indicate full marks. Candidates are required to give their answers
MECHANICS OF STRUCTURES SCI 1105 COURSE MATERIAL UNIT - I
 MECHANICS OF STRUCTURES SCI 1105 COURSE MATERIAL UNIT - I Engineering Mechanics Branch of science which deals with the behavior of a body with the state of rest or motion, subjected to the action of forces.
MECHANICS OF STRUCTURES SCI 1105 COURSE MATERIAL UNIT - I Engineering Mechanics Branch of science which deals with the behavior of a body with the state of rest or motion, subjected to the action of forces.
SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL. Chapter 10: Sections Chapter 12: All sections except
 SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL Chapter 10: Sections 10. 10.3 Chapter 1: All sections ecept 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.17 1.18 TOPICS Introduction Components of Shear Strength of Soils Normal and Shear Stresses on a Plane
SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL Chapter 10: Sections 10. 10.3 Chapter 1: All sections ecept 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.17 1.18 TOPICS Introduction Components of Shear Strength of Soils Normal and Shear Stresses on a Plane
GATE question paper Civil Engineering (CE) 2005
 GATE question paper Civil Engineering (CE) 005 GATE question paper Civil Engineering 005 Q.1- Q.30 Carry One Mark Each. 1. Consider the matrices X (4 3) Y (4-3) and P ( 3). The order of [P(X T Y) -1 P
GATE question paper Civil Engineering (CE) 005 GATE question paper Civil Engineering 005 Q.1- Q.30 Carry One Mark Each. 1. Consider the matrices X (4 3) Y (4-3) and P ( 3). The order of [P(X T Y) -1 P
Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures (II)
 Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures (II) Discussion Eng. Mohammed R. Kuheil Review The thickness of one-way ribbed slabs After finding the value of total load (Dead and live loads), the elements are
Design of Reinforced Concrete Structures (II) Discussion Eng. Mohammed R. Kuheil Review The thickness of one-way ribbed slabs After finding the value of total load (Dead and live loads), the elements are
STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS
 1 UNIT I STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define: Stress When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The
1 UNIT I STRESS STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS, STATES OF STRESS 1. Define: Stress When an external force acts on a body, it undergoes deformation. At the same time the body resists deformation. The
FE Fluids Review March 23, 2012 Steve Burian (Civil & Environmental Engineering)
 Topic: Fluid Properties 1. If 6 m 3 of oil weighs 47 kn, calculate its specific weight, density, and specific gravity. 2. 10.0 L of an incompressible liquid exert a force of 20 N at the earth s surface.
Topic: Fluid Properties 1. If 6 m 3 of oil weighs 47 kn, calculate its specific weight, density, and specific gravity. 2. 10.0 L of an incompressible liquid exert a force of 20 N at the earth s surface.
BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS)
 BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS) All questions carry equal marks(10 marks) Q.1 (a) Write the SI units of following quantities and also mention whether it is scalar or vector: (i)
BE Semester- I ( ) Question Bank (MECHANICS OF SOLIDS) All questions carry equal marks(10 marks) Q.1 (a) Write the SI units of following quantities and also mention whether it is scalar or vector: (i)
[8] Bending and Shear Loading of Beams
![[8] Bending and Shear Loading of Beams [8] Bending and Shear Loading of Beams](/thumbs/92/110949676.jpg) [8] Bending and Shear Loading of Beams Page 1 of 28 [8] Bending and Shear Loading of Beams [8.1] Bending of Beams (will not be covered in class) [8.2] Bending Strain and Stress [8.3] Shear in Straight
[8] Bending and Shear Loading of Beams Page 1 of 28 [8] Bending and Shear Loading of Beams [8.1] Bending of Beams (will not be covered in class) [8.2] Bending Strain and Stress [8.3] Shear in Straight
Purpose of this Guide: To thoroughly prepare students for the exact types of problems that will be on Exam 3.
 ES230 STRENGTH OF MTERILS Exam 3 Study Guide Exam 3: Wednesday, March 8 th in-class Updated 3/3/17 Purpose of this Guide: To thoroughly prepare students for the exact types of problems that will be on
ES230 STRENGTH OF MTERILS Exam 3 Study Guide Exam 3: Wednesday, March 8 th in-class Updated 3/3/17 Purpose of this Guide: To thoroughly prepare students for the exact types of problems that will be on
PLATE GIRDERS II. Load. Web plate Welds A Longitudinal elevation. Fig. 1 A typical Plate Girder
 16 PLATE GIRDERS II 1.0 INTRODUCTION This chapter describes the current practice for the design of plate girders adopting meaningful simplifications of the equations derived in the chapter on Plate Girders
16 PLATE GIRDERS II 1.0 INTRODUCTION This chapter describes the current practice for the design of plate girders adopting meaningful simplifications of the equations derived in the chapter on Plate Girders
ME3560 Tentative Schedule Fall 2018
 ME3560 Tentative Schedule Fall 2018 Week Number 1 Wednesday 8/29/2018 1 Date Lecture Topics Covered Introduction to course, syllabus and class policies. Math Review. Differentiation. Prior to Lecture Read
ME3560 Tentative Schedule Fall 2018 Week Number 1 Wednesday 8/29/2018 1 Date Lecture Topics Covered Introduction to course, syllabus and class policies. Math Review. Differentiation. Prior to Lecture Read
UNIT-I STRESS, STRAIN. 1. A Member A B C D is subjected to loading as shown in fig determine the total elongation. Take E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2
 UNIT-I STRESS, STRAIN 1. A Member A B C D is subjected to loading as shown in fig determine the total elongation. Take E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2 Young s modulus E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2 Area1=900mm 2 Area2=400mm 2 Area3=625mm
UNIT-I STRESS, STRAIN 1. A Member A B C D is subjected to loading as shown in fig determine the total elongation. Take E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2 Young s modulus E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2 Area1=900mm 2 Area2=400mm 2 Area3=625mm
Only for Reference Page 1 of 18
 Only for Reference www.civilpddc2013.weebly.com Page 1 of 18 Seat No.: Enrolment No. GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY PDDC - SEMESTER II EXAMINATION WINTER 2013 Subject Code: X20603 Date: 26-12-2013 Subject
Only for Reference www.civilpddc2013.weebly.com Page 1 of 18 Seat No.: Enrolment No. GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY PDDC - SEMESTER II EXAMINATION WINTER 2013 Subject Code: X20603 Date: 26-12-2013 Subject
NCEES Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Examination CIVIL EXAM SPECIFICATIONS
 NCEES Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Examination CIVIL EXAM SPECIFICATIONS Effective Beginning with the April 2009 Examinations The FE examination is an 8-hour supplied-reference examination: 120 questions
NCEES Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) Examination CIVIL EXAM SPECIFICATIONS Effective Beginning with the April 2009 Examinations The FE examination is an 8-hour supplied-reference examination: 120 questions
Influence of residual stresses in the structural behavior of. tubular columns and arches. Nuno Rocha Cima Gomes
 October 2014 Influence of residual stresses in the structural behavior of Abstract tubular columns and arches Nuno Rocha Cima Gomes Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal Contact:
October 2014 Influence of residual stresses in the structural behavior of Abstract tubular columns and arches Nuno Rocha Cima Gomes Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Portugal Contact:
PRINCIPLES OF GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING
 PRINCIPLES OF GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING Fourth Edition BRAJA M. DAS California State University, Sacramento I(T)P Boston Albany Bonn Cincinnati London Madrid Melbourne Mexico City New York Paris San Francisco
PRINCIPLES OF GEOTECHNICAL ENGINEERING Fourth Edition BRAJA M. DAS California State University, Sacramento I(T)P Boston Albany Bonn Cincinnati London Madrid Melbourne Mexico City New York Paris San Francisco
14. *14.8 CASTIGLIANO S THEOREM
 *14.8 CASTIGLIANO S THEOREM Consider a body of arbitrary shape subjected to a series of n forces P 1, P 2, P n. Since external work done by forces is equal to internal strain energy stored in body, by
*14.8 CASTIGLIANO S THEOREM Consider a body of arbitrary shape subjected to a series of n forces P 1, P 2, P n. Since external work done by forces is equal to internal strain energy stored in body, by
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -00 04 CIVIL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : STRENGTH OF MATERIALS II Course Code : A404 Class : II B. Tech II Semester Section
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad -00 04 CIVIL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Course Name : STRENGTH OF MATERIALS II Course Code : A404 Class : II B. Tech II Semester Section
Structural Steelwork Eurocodes Development of A Trans-national Approach
 Structural Steelwork Eurocodes Development of A Trans-national Approach Course: Eurocode Module 7 : Worked Examples Lecture 0 : Simple braced frame Contents: 1. Simple Braced Frame 1.1 Characteristic Loads
Structural Steelwork Eurocodes Development of A Trans-national Approach Course: Eurocode Module 7 : Worked Examples Lecture 0 : Simple braced frame Contents: 1. Simple Braced Frame 1.1 Characteristic Loads
Lesson 6 Review of fundamentals: Fluid flow
 Lesson 6 Review of fundamentals: Fluid flow The specific objective of this lesson is to conduct a brief review of the fundamentals of fluid flow and present: A general equation for conservation of mass
Lesson 6 Review of fundamentals: Fluid flow The specific objective of this lesson is to conduct a brief review of the fundamentals of fluid flow and present: A general equation for conservation of mass
Full Length Test Civil Engineering
 Full ength Test ivil Engineering nswer Keys and Explanations 1 [ns ] Green s theorem and stokes theorem convert line integral to surface integral and vice versa Whereas Gauss s Divergence theorem converts
Full ength Test ivil Engineering nswer Keys and Explanations 1 [ns ] Green s theorem and stokes theorem convert line integral to surface integral and vice versa Whereas Gauss s Divergence theorem converts
Chapter 12: Lateral Earth Pressure
 Part 4: Lateral Earth Pressure and Earth-Retaining Structures Chapter 12: Lateral Earth Pressure Introduction Vertical or near-vertical slopes of soil are supported by retaining walls, cantilever sheetpile
Part 4: Lateral Earth Pressure and Earth-Retaining Structures Chapter 12: Lateral Earth Pressure Introduction Vertical or near-vertical slopes of soil are supported by retaining walls, cantilever sheetpile
Chapter 12. Static Equilibrium and Elasticity
 Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Static Equilibrium Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial
Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Static Equilibrium Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial
Mechanics of Structure
 S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CE/CS/CR/CV] Mechanics of Structure Time: Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 70 Q.1(a) Attempt any SIX of the following. [1] Q.1(a) Define moment of Inertia. State MI
S.Y. Diploma : Sem. III [CE/CS/CR/CV] Mechanics of Structure Time: Hrs.] Prelim Question Paper Solution [Marks : 70 Q.1(a) Attempt any SIX of the following. [1] Q.1(a) Define moment of Inertia. State MI
PES Institute of Technology
 PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
SERVICEABILITY OF BEAMS AND ONE-WAY SLABS
 CHAPTER REINFORCED CONCRETE Reinforced Concrete Design A Fundamental Approach - Fifth Edition Fifth Edition SERVICEABILITY OF BEAMS AND ONE-WAY SLABS A. J. Clark School of Engineering Department of Civil
CHAPTER REINFORCED CONCRETE Reinforced Concrete Design A Fundamental Approach - Fifth Edition Fifth Edition SERVICEABILITY OF BEAMS AND ONE-WAY SLABS A. J. Clark School of Engineering Department of Civil
CIVIL DEPARTMENT MECHANICS OF STRUCTURES- ASSIGNMENT NO 1. Brach: CE YEAR:
 MECHANICS OF STRUCTURES- ASSIGNMENT NO 1 SEMESTER: V 1) Find the least moment of Inertia about the centroidal axes X-X and Y-Y of an unequal angle section 125 mm 75 mm 10 mm as shown in figure 2) Determine
MECHANICS OF STRUCTURES- ASSIGNMENT NO 1 SEMESTER: V 1) Find the least moment of Inertia about the centroidal axes X-X and Y-Y of an unequal angle section 125 mm 75 mm 10 mm as shown in figure 2) Determine
A. V T = 1 B. Ms = 1 C. Vs = 1 D. Vv = 1
 Geology and Soil Mechanics 55401 /1A (2002-2003) Mark the best answer on the multiple choice answer sheet. 1. Soil mechanics is the application of hydraulics, geology and mechanics to problems relating
Geology and Soil Mechanics 55401 /1A (2002-2003) Mark the best answer on the multiple choice answer sheet. 1. Soil mechanics is the application of hydraulics, geology and mechanics to problems relating
RAMWALL DESIGN METHODOLOGY
 RAMWALL DESIGN METHODOLOGY Submitted by:. June 005 CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION 1 Page. REFERENCED DOCUMENTS & ABBREVIATIONS 1 3 DESIGN METHODOLOGY / THEORY 3.1 General 3. Internal Analysis 4 3.3 External
RAMWALL DESIGN METHODOLOGY Submitted by:. June 005 CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION 1 Page. REFERENCED DOCUMENTS & ABBREVIATIONS 1 3 DESIGN METHODOLOGY / THEORY 3.1 General 3. Internal Analysis 4 3.3 External
Geology and Soil Mechanics /1A ( ) Mark the best answer on the multiple choice answer sheet.
 Geology and Soil Mechanics 55401 /1A (2003-2004) Mark the best answer on the multiple choice answer sheet. 1. Soil mechanics is the application of hydraulics, geology and mechanics to problems relating
Geology and Soil Mechanics 55401 /1A (2003-2004) Mark the best answer on the multiple choice answer sheet. 1. Soil mechanics is the application of hydraulics, geology and mechanics to problems relating
*** ***! " " ) * % )!( & ' % # $. 0 1 %./ +, - 7 : %8% 9 ) 7 / ( * 7 : %8% 9 < ;14. " > /' ;-,=. / ١
 ١ ******!" #$ % & '!( ) % * ") +,-./ % 01. 3 ( 4 56 7/4 ) 8%9 % : 7 ;14 < 8%9 % : *7./ = ;-, >/'." Soil Permeability & Seepage ٢ Soil Permeability- Definition ٣ What is Permeability? Permeability is the
١ ******!" #$ % & '!( ) % * ") +,-./ % 01. 3 ( 4 56 7/4 ) 8%9 % : 7 ;14 < 8%9 % : *7./ = ;-, >/'." Soil Permeability & Seepage ٢ Soil Permeability- Definition ٣ What is Permeability? Permeability is the
Chapter (6) Geometric Design of Shallow Foundations
 Chapter (6) Geometric Design of Shallow Foundations Introduction As we stated in Chapter 3, foundations are considered to be shallow if if [D (3 4)B]. Shallow foundations have several advantages: minimum
Chapter (6) Geometric Design of Shallow Foundations Introduction As we stated in Chapter 3, foundations are considered to be shallow if if [D (3 4)B]. Shallow foundations have several advantages: minimum
EVALUATION OF BENDING LOAD IN BATTER PILES SET IN SOFT CLAY
 EVALUATION OF BENDING LOAD IN BATTER PILES SET IN SOFT CLAY Tetsuya KOHNO 1, Hiroyuki TANAKA 2, Masahiro SHIRATO 3 and Shoichi NAKATANI 4 Abstract In this study, we conducted centrifuge tests to evaluate
EVALUATION OF BENDING LOAD IN BATTER PILES SET IN SOFT CLAY Tetsuya KOHNO 1, Hiroyuki TANAKA 2, Masahiro SHIRATO 3 and Shoichi NAKATANI 4 Abstract In this study, we conducted centrifuge tests to evaluate
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION
 Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION 1-1 The Fluid. 1-2 Dimensions. 1-3 Units. 1-4 Fluid Properties. 1 1-1 The Fluid: It is the substance that deforms continuously when subjected to a shear stress. Matter Solid Fluid
Chapter 1 INTRODUCTION 1-1 The Fluid. 1-2 Dimensions. 1-3 Units. 1-4 Fluid Properties. 1 1-1 The Fluid: It is the substance that deforms continuously when subjected to a shear stress. Matter Solid Fluid
UNIT II SHALLOW FOUNDATION
 Introduction UNIT II SHALLOW FOUNDATION A foundation is a integral part of the structure which transfer the load of the superstructure to the soil. A foundation is that member which provides support for
Introduction UNIT II SHALLOW FOUNDATION A foundation is a integral part of the structure which transfer the load of the superstructure to the soil. A foundation is that member which provides support for
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING SUBJECT CODE : CE6405 YEAR : II SUBJECT NAME : SOIL MECHANICS SEM : IV QUESTION BANK (As per Anna University 2013 regulation) UNIT 1- SOIL
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING SUBJECT CODE : CE6405 YEAR : II SUBJECT NAME : SOIL MECHANICS SEM : IV QUESTION BANK (As per Anna University 2013 regulation) UNIT 1- SOIL
CHAPTER 5 Statically Determinate Plane Trusses
 CHAPTER 5 Statically Determinate Plane Trusses TYPES OF ROOF TRUSS TYPES OF ROOF TRUSS ROOF TRUSS SETUP ROOF TRUSS SETUP OBJECTIVES To determine the STABILITY and DETERMINACY of plane trusses To analyse
CHAPTER 5 Statically Determinate Plane Trusses TYPES OF ROOF TRUSS TYPES OF ROOF TRUSS ROOF TRUSS SETUP ROOF TRUSS SETUP OBJECTIVES To determine the STABILITY and DETERMINACY of plane trusses To analyse
Foundation Analysis LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE
 Foundation Analysis LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE INTRODUCTION Vertical or near-vertical slopes of soil are supported by retaining walls, cantilever sheet-pile walls, sheet-pile bulkheads, braced cuts, and other
Foundation Analysis LATERAL EARTH PRESSURE INTRODUCTION Vertical or near-vertical slopes of soil are supported by retaining walls, cantilever sheet-pile walls, sheet-pile bulkheads, braced cuts, and other
ENG1001 Engineering Design 1
 ENG1001 Engineering Design 1 Structure & Loads Determine forces that act on structures causing it to deform, bend, and stretch Forces push/pull on objects Structures are loaded by: > Dead loads permanent
ENG1001 Engineering Design 1 Structure & Loads Determine forces that act on structures causing it to deform, bend, and stretch Forces push/pull on objects Structures are loaded by: > Dead loads permanent
two structural analysis (statics & mechanics) APPLIED ACHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: DR. ANNE NICHOLS SPRING 2017 lecture STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS AND SYSTEMS
 APPLIED ACHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS AND SYSTEMS DR. ANNE NICHOLS SPRING 2017 lecture two structural analysis (statics & mechanics) Analysis 1 Structural Requirements strength serviceability
APPLIED ACHITECTURAL STRUCTURES: STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS AND SYSTEMS DR. ANNE NICHOLS SPRING 2017 lecture two structural analysis (statics & mechanics) Analysis 1 Structural Requirements strength serviceability
CHAPTER 5 Statically Determinate Plane Trusses TYPES OF ROOF TRUSS
 CHAPTER 5 Statically Determinate Plane Trusses TYPES OF ROOF TRUSS 1 TYPES OF ROOF TRUSS ROOF TRUSS SETUP 2 ROOF TRUSS SETUP OBJECTIVES To determine the STABILITY and DETERMINACY of plane trusses To analyse
CHAPTER 5 Statically Determinate Plane Trusses TYPES OF ROOF TRUSS 1 TYPES OF ROOF TRUSS ROOF TRUSS SETUP 2 ROOF TRUSS SETUP OBJECTIVES To determine the STABILITY and DETERMINACY of plane trusses To analyse
STRENGTH OF MATERIALS-I. Unit-1. Simple stresses and strains
 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS-I Unit-1 Simple stresses and strains 1. What is the Principle of surveying 2. Define Magnetic, True & Arbitrary Meridians. 3. Mention different types of chains 4. Differentiate between
STRENGTH OF MATERIALS-I Unit-1 Simple stresses and strains 1. What is the Principle of surveying 2. Define Magnetic, True & Arbitrary Meridians. 3. Mention different types of chains 4. Differentiate between
FLEXIBILITY METHOD FOR INDETERMINATE FRAMES
 UNIT - I FLEXIBILITY METHOD FOR INDETERMINATE FRAMES 1. What is meant by indeterminate structures? Structures that do not satisfy the conditions of equilibrium are called indeterminate structure. These
UNIT - I FLEXIBILITY METHOD FOR INDETERMINATE FRAMES 1. What is meant by indeterminate structures? Structures that do not satisfy the conditions of equilibrium are called indeterminate structure. These
CE5510 Advanced Structural Concrete Design - Design & Detailing of Openings in RC Flexural Members-
 CE5510 Advanced Structural Concrete Design - Design & Detailing Openings in RC Flexural Members- Assoc Pr Tan Kiang Hwee Department Civil Engineering National In this lecture DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING
CE5510 Advanced Structural Concrete Design - Design & Detailing Openings in RC Flexural Members- Assoc Pr Tan Kiang Hwee Department Civil Engineering National In this lecture DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING
Engineering Mechanics. Friction in Action
 Engineering Mechanics Friction in Action What is friction? Friction is a retarding force that opposes motion. Friction types: Static friction Kinetic friction Fluid friction Sources of dry friction Dry
Engineering Mechanics Friction in Action What is friction? Friction is a retarding force that opposes motion. Friction types: Static friction Kinetic friction Fluid friction Sources of dry friction Dry
R13. II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) PART-A
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL
 Soil Failure Criteria SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL Knowledge about the shear strength of soil important for the analysis of: Bearing capacity of foundations, Slope stability, Lateral pressure on retaining structures,
Soil Failure Criteria SHEAR STRENGTH OF SOIL Knowledge about the shear strength of soil important for the analysis of: Bearing capacity of foundations, Slope stability, Lateral pressure on retaining structures,
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK : AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING.
 Course Name Course Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 0 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING : Mechanics of Fluids : A00 : II-I- B. Tech Year : 0 0 Course Coordinator
Course Name Course Code Class Branch INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING Dundigal, Hyderabad - 00 0 AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING : Mechanics of Fluids : A00 : II-I- B. Tech Year : 0 0 Course Coordinator
[5] Stress and Strain
![[5] Stress and Strain [5] Stress and Strain](/thumbs/95/123344550.jpg) [5] Stress and Strain Page 1 of 34 [5] Stress and Strain [5.1] Internal Stress of Solids [5.2] Design of Simple Connections (will not be covered in class) [5.3] Deformation and Strain [5.4] Hooke s Law
[5] Stress and Strain Page 1 of 34 [5] Stress and Strain [5.1] Internal Stress of Solids [5.2] Design of Simple Connections (will not be covered in class) [5.3] Deformation and Strain [5.4] Hooke s Law
