Soft Carrier Multiplication by Hot Electrons in Graphene
|
|
|
- Charleen Woods
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Soft Carrier Multiplication by Hot Electrons in Graphene Anuj Girdhar 1,3 and J.P. Leburton 1,2,3 1) Department of Physics 2) Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, and 3) Beckman Institute University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Urbana, Il Abstract By using Boltzmann formalism, we show that carrier multiplication by impact ionization can take place at relatively low electric fields during electronic transport in graphene. Because of the absence of energy gap, this effect is not characterized by a field threshold unlike in conventional semiconductors, but is a quadratic function of the electric field. We also show that the resulting current is an increasing function of the electronic temperature, but decreases with increasing carrier concentration. 1
2 In the last decade, owing to its remarkable physical properties, graphene has emerged as a new material for high performance electronic applications [1,2,3,4]. Its strictly two-dimensional (2D) nature consisting of a single sheet of atoms combined with the energy dispersion, linear in the electron momentum, which results in the same velocity v F ~10 8 cm/s for all carriers, is well suited for high speed electronics with planar technology [5,6,7]. Another important feature of graphene is the reduction of energy gap to a single (Dirac) point in k-space, which favors interband processes such as impact ionization or Auger recombination, compared to conventional semiconductors [5]. Recently, the scattering rates for impact ionization and Auger recombination in graphene have been derived for inverted electron-hole populations, for which the scattering times were found longer than 1ps for concentrations less than /cm 2 [8]. This situation is, however, different from electronic transport, where disturbances from equilibrium arises from the external electric field, creating the conditions for interband interaction, which affects the overall transport in graphene at relatively low fields. In this letter we consider the effect of carrier multiplication induced by interband inter-carrier interaction caused by hot electrons transport in mono-layer graphene. We assume carrier populations are away from the intrinsic regime, and the graphene layer is mostly n-type (because of electron-hole symmetry, the p-type case is similar), as achieved in electronic devices. In these conditions, impact ionization with carrier multiplication occurs when a conduction band electron (1) scatters with another electron in the valence band (2), resulting in two secondary electrons in the conduction band (1' and 2'), creating a hole in 2
3 the valence band (Fig. 1). In this inter-electron collision, both momentum and energy are conserved, which around the Dirac point for intra-valley processes yields (1) (2) thereby accounting from the fact that particle 2 is below the gap, so, and dropping the constant factors in these equations. Squaring both equations and taking the difference yields a condition for the relative orientations of the initial and final wavevectors, namely that they all lie on a line. Wavevectors,, and must all be parallel while is antiparallel. Here, only intra-valley scattering events are considered, since the analysis of the scattering matrix element reveals that large momentum-transfer interactions are significantly suppressed. By Fermi's golden rule, the transition probability per unit time is given by ( ) ( ) (3) (4) ( ) where is the scattering matrix element of the screened Coulomb interaction between electrons including the direct and exchange interactions [8,9]. is the effective dielectric constant of single-layer graphene on an SiO 2 substrate, and ( ) is the static screening dielectric function where is, ( ) (5) 3
4 as calculated by Hwang et al. using the random phase approximation, which combines inter and intraband scattering events by use of an effective permittivity which takes both processes into account [10]. Here, is the background dielectric constant due to the substrate. In order to calculate the total scattering rate as a function of electric fields, we assume the electron concentration in the conduction band is high enough, and the fields small enough to justify an electronic temperature model [11]. In these conditions, the distribution function reads ( ) * ( ( ) )+ (6) with, so ( ) is a Fermi-Dirac distribution function displaced in the electric fields with quasi-fermi level and electronic temperature T e. Here we have assumed the field points in the positive direction. is the mean free time as a result of collisions with impurities and phonons [12]. The scattering rate, or the inverse scattering time, is given by ( ) (7) [ ( )][ ( )][ ( )] where S is the probability per unit time defined in eq. 3 and the sum is over all wavevectors 1, 2, and 2 [13]. The exclusion principle is enforced by using the rejection technique after assuming high carrier densities and therefore significant carrier 4
5 degeneracy. We use a Gauss-Kronrod quadrature routine that assumes a linear energy dispersion and includes band degeneracy to compute the integral in eq. 8 [14]. Here we mention the nontrivial transformation of the δ-functions for energy and momentum conservation in the transition probability, ( ) (8) ( ) ( ) [ ( ) ( ) ( )] [ ( )] where θ 1 (θ 2 ) and θ 1 (θ 2 ) are the k 1 (k 2 ) and k 1 (k 2 ) wavevector angles with respect to the field direction. In fig. 2 we show the scattering rate as a function of the initial carrier energy for an electronic temperature T e =1200K and a field of 1kV/cm, which reaches approximately 0.1 ps -1 for carrier energies near ~0.2 ev at a carrier density of /cm 2. The rate decreases by several orders of magnitude for lower energies and higher concentrations. Such strong decrease in the scattering rate is due to the high occupation of low energy states far below the quasi-fermi level. Indeed, the most favorable states for secondary electrons lie in the conduction band at mid-way between k 1 and k 2, which to be empty requires large incident energy E 1, and E 2 close to the Dirac point. The scattering rate is about.2 ps -1 for a carrier energy of ~.5 ev and a carrier concentration of cm -2, increasing by many orders of magnitude for lower energies. These rates are much smaller than those from electron-electron scattering events in the conduction band only (~100 ps -1 at.5 ev for a carrier density of /cm 2 ), as calculated by Li et al, which are due to is the relative availability of states below the Fermi level in intraband scattering events [15]. 5
6 The inset shows the scattering rate variation for different electronic temperature, and for a population of cm -2 (with quasi-fermi level E F =.26 ev). The rate increases rapidly with temperature for incident electrons near the quasi-fermi level, spanning several orders of magnitude between electron temperatures of 300K and 1200K. This is due to the increase of available states below the quasi-fermi level as a result of thermal broadening of the distribution. At incident particle energies much higher than the quasi-fermi level, the scattering rates become independent of temperature since the secondary electrons at mid-way between k 1 and k 2 will always find empty states. The net generation rate per unit area resulting from impact ionization is given by [ ( )][ ( )][ ( )][ ( )] { [ ( )][ ( )][ ( )][ ( )] } (9) where the factor 8 accounts for spin and valley degeneracies, and electron-hole multiplication. Here, the first term corresponds to impact ionization (generation), while the second is the Auger term (recombination), non-negligible at low fields. Figure 3 shows the impact ionization net generation rate as a function of electric fields for three different electronic temperatures. One notices that the generation rate varies by several orders of magnitude for an electronic temperature variation of 300K to 1200K. Again, this is due to the thermal broadening of the distribution, which uncovers available states for secondary electrons just above the Dirac point. Unlike in conventional semiconductors that are characterized by exponential increase of the current, our model shows a power law for the current variation with electric fields that becomes quadratic for low fields. This soft carrier multiplication process is due to the fact that the leading term in the integral in eq. 9 is quadratic in the electric fields. Indeed, using the low-field 6
7 approximation for the distribution one can be split into an even zero-field component and an odd term proportional to the field F ( ) ( ) ( ) (10) ( ) ( ) ( ) (11) Then, the product of the distribution functions can be expressed as a sum of powers of the fields, the odd terms vanish once the angular integral is performed since they are also odd in powers of. The zero-order term vanishes due to detailed balance, which results in a quadratic dependence of the current density on applied field for small fields. However, the exponent of the power law decreases with increasing field as a result of the sign of contributing higher-order terms in the expansion of the distribution function. This power law appears to be in good agreement with the model in ref. [16] that uses the quadratic term for the upkick current at low biases in G-FET devices. Typical impact ionization and Auger recombination rates for hot electrons are strongly dependent on temperature and range from ~10 17 s -1 cm -2 to ~10 23 s -1 cm -2 for temperatures varying between 300K and 1200K at a field of 10 kv/cm. When compared to values obtained by Meric et al for a G-FET device, we obtain a corresponding current of ~0.3 ma comparable to the experimental data, by assuming that impact ionization takes place over 0.1um range on the drain side for electronic temperatures of 1200K and carrier densities of ~ cm -2, suggesting that carrier multiplication and Auger recombination events are important processes in such devices [17]. 7
8 In conclusion, we proposed a model for hot carrier impact ionization and Auger recombination depending on the electronic temperatures and carrier concentrations in graphene. These processes are strongly dependent on the availability of states near the Fermi-level, as shown by large variations in response to thermal broadening and shifting of the Fermi energy, which results in a power law of the multiplication current with electric field. The power law dependence of the current density on applied field is in agreement with current upkick observed in graphene FET devices at low gate bias. References [1] M. Wilson, Phys. Today 59 (1), 21 (2006). [2] Y. Zhang, Y. W. Tan, H. L. Stormer, and P. Kim, Nature 438, 201 (2005). [3] C. Berger, Z. Song, X. Li, X. Wu, N. Brown, C. Naud, D. Mayou, T. Li, J. Hass, A. N. Marchenkov, E. H. Conrad, P. N. First, and W. A. de Heer, Science 312, 1191 (2006). [4] A. Akturk and N. Goldsman, J. Appl. Phys. 103, (2008). [5] P. R. Wallace, Phys. Rev. 71, 622 (1947). [6] X. F. Wang and T. Chakraborty, Phys. Rev. B 75, (2007). [7] G. W. Semenoff, Phys. Rev. Lett. 53, 2449 (1984). [8] F. Rana, Phys. Rev. B 76, (2007). [9] A. Mošková and M. Moško, Phys. Rev. B 49, 7443 (1994). [10] E. H. Hwang and S. Das Sarma, Phys. Rev. B 75, (2007). [11] G. Bauer, Determination of Electron Temperatures and of Hot Electron Distribution Functions in Semiconductors, (Springer, Berlin, 1974). 8
9 [12] O. Madelung, Introduction to Solid-State Theory, edited by M. Cardona, P. Fulde, and H.-J. Queisser, (Springer-Verlag, Marburg, 1978), pp [13] K. Hess, Advanced Theory of Semiconductor Devices, edited by N. Holonyak, Jr., (Prentice Hall, New Jersey, 1988), pp [14] A. S. Kronrod, Doklady Akad. Nauk SSSR 154, 283 (1964). [15] X. Li, E. A. Barry, J. M. Zavada, M. Buongiorno Nardelli, and K. W. Kim, Appl. Phys. Lett. 97, (2010). [16] B. Scott and J. P. Leburton (Unpublished). [17] I. Meric, M. Y. Han, A. F. Young, B. Ozyilmaz, P. Kim, and K. L. Shepard, Nature Nanotech. 3, 654 (2008). 9
10 10
11 11
12 12
13 Figure Captions: 1. Schematic of a carrier multiplication scattering event in the Dirac cone in graphene. Conduction electron 1 scatters with valence electron 2, creating two conduction electrons 1 and 2 in addition to a valence hole. The reverse event is Auger recombination. 2. Electron-electron scattering rate for carrier multiplication as a function of the energy of the incident electron (particle 1) for various carrier concentrations at an electronic temperature of 1200 K, electric field of 1 kv/cm, and mean free time of 30 fs [17]. The inset shows the scattering rate for a carrier concentration of /cm 2 for electron temperatures varying between 300K to 1200K. 3. Current density as a function of applied fields for temperatures 300K to 1200K at various carrier concentrations and mean free time of 30 fs [17]. The same symbols as figure 2 are used for different carrier concentrations. 13
Low Bias Transport in Graphene: An Introduction
 Lecture Notes on Low Bias Transport in Graphene: An Introduction Dionisis Berdebes, Tony Low, and Mark Lundstrom Network for Computational Nanotechnology Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University West
Lecture Notes on Low Bias Transport in Graphene: An Introduction Dionisis Berdebes, Tony Low, and Mark Lundstrom Network for Computational Nanotechnology Birck Nanotechnology Center Purdue University West
Summary lecture VI. with the reduced mass and the dielectric background constant
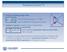 Summary lecture VI Excitonic binding energy reads with the reduced mass and the dielectric background constant Δ Statistical operator (density matrix) characterizes quantum systems in a mixed state and
Summary lecture VI Excitonic binding energy reads with the reduced mass and the dielectric background constant Δ Statistical operator (density matrix) characterizes quantum systems in a mixed state and
Nonlinear optical conductance in a graphene pn junction in the terahertz regime
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2010 Nonlinear optical conductance in a graphene pn junction in the terahertz
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Engineering - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Engineering and Information Sciences 2010 Nonlinear optical conductance in a graphene pn junction in the terahertz
Ultrafast Optical-Pump Terahertz-Probe Spectroscopy of the Carrier Relaxation and Recombination Dynamics in Epitaxial Graphene
 Letter Subscriber access provided by CORNELL UNIV Ultrafast Optical-Pump Terahertz-Probe Spectroscopy of the Carrier Relaxation and Recombination Dynamics in Epitaxial Graphene Paul A. George, Jared Strait,
Letter Subscriber access provided by CORNELL UNIV Ultrafast Optical-Pump Terahertz-Probe Spectroscopy of the Carrier Relaxation and Recombination Dynamics in Epitaxial Graphene Paul A. George, Jared Strait,
Supplementary Figure 2 Photoluminescence in 1L- (black line) and 7L-MoS 2 (red line) of the Figure 1B with illuminated wavelength of 543 nm.
 PL (normalized) Intensity (arb. u.) 1 1 8 7L-MoS 1L-MoS 6 4 37 38 39 4 41 4 Raman shift (cm -1 ) Supplementary Figure 1 Raman spectra of the Figure 1B at the 1L-MoS area (black line) and 7L-MoS area (red
PL (normalized) Intensity (arb. u.) 1 1 8 7L-MoS 1L-MoS 6 4 37 38 39 4 41 4 Raman shift (cm -1 ) Supplementary Figure 1 Raman spectra of the Figure 1B at the 1L-MoS area (black line) and 7L-MoS area (red
arxiv: v3 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 22 Jul 2008
![arxiv: v3 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 22 Jul 2008 arxiv: v3 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 22 Jul 2008](/thumbs/83/88787233.jpg) Ultrafast Optical-Pump Terahertz-Probe Spectroscopy of the Carrier Relaxation and Recombination Dynamics in Epitaxial Graphene Paul A. George, Jared Strait, Jahan Dawlaty, Shriram Shivaraman, Mvs Chandrashekhar,
Ultrafast Optical-Pump Terahertz-Probe Spectroscopy of the Carrier Relaxation and Recombination Dynamics in Epitaxial Graphene Paul A. George, Jared Strait, Jahan Dawlaty, Shriram Shivaraman, Mvs Chandrashekhar,
Highly Confined Tunable Mid-Infrared Plasmonics in Graphene Nanoresonators
 Supplementary Information for Highly Confined Tunable Mid-Infrared Plasmonics in Graphene Nanoresonators by Victor W. Brar, Min Seok Jang, Michelle Sherrott, Josue J. Lopez and Harry Atwater 1 Approximating
Supplementary Information for Highly Confined Tunable Mid-Infrared Plasmonics in Graphene Nanoresonators by Victor W. Brar, Min Seok Jang, Michelle Sherrott, Josue J. Lopez and Harry Atwater 1 Approximating
Reduction of Fermi velocity in folded graphene observed by resonance Raman spectroscopy
 Reduction of Fermi velocity in folded graphene observed by resonance Raman spectroscopy Zhenhua Ni, Yingying Wang, Ting Yu, Yumeng You, and Zexiang Shen* Division of Physics and Applied Physics, School
Reduction of Fermi velocity in folded graphene observed by resonance Raman spectroscopy Zhenhua Ni, Yingying Wang, Ting Yu, Yumeng You, and Zexiang Shen* Division of Physics and Applied Physics, School
3D Weyl metallic states realized in the Bi 1-x Sb x alloy and BiTeI. Heon-Jung Kim Department of Physics, Daegu University, Korea
 3D Weyl metallic states realized in the Bi 1-x Sb x alloy and BiTeI Heon-Jung Kim Department of Physics, Daegu University, Korea Content 3D Dirac metals Search for 3D generalization of graphene Bi 1-x
3D Weyl metallic states realized in the Bi 1-x Sb x alloy and BiTeI Heon-Jung Kim Department of Physics, Daegu University, Korea Content 3D Dirac metals Search for 3D generalization of graphene Bi 1-x
Semiconductor device structures are traditionally divided into homojunction devices
 0. Introduction: Semiconductor device structures are traditionally divided into homojunction devices (devices consisting of only one type of semiconductor material) and heterojunction devices (consisting
0. Introduction: Semiconductor device structures are traditionally divided into homojunction devices (devices consisting of only one type of semiconductor material) and heterojunction devices (consisting
Supplementary Figure 1: The effect of relaxation times on the sideband. spectrum of a THz driven bi-layer graphene. Contour plot of the sideband
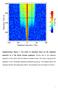 Supplementary Figure 1: The effect of relaxation times on the sideband spectrum of a THz driven bi-layer graphene. Contour plot of the sideband spectrum of THz driven BLG for different relaxation times.
Supplementary Figure 1: The effect of relaxation times on the sideband spectrum of a THz driven bi-layer graphene. Contour plot of the sideband spectrum of THz driven BLG for different relaxation times.
Minimal Update of Solid State Physics
 Minimal Update of Solid State Physics It is expected that participants are acquainted with basics of solid state physics. Therefore here we will refresh only those aspects, which are absolutely necessary
Minimal Update of Solid State Physics It is expected that participants are acquainted with basics of solid state physics. Therefore here we will refresh only those aspects, which are absolutely necessary
GRAPHENE is a single two-dimensional (2-D) atomic
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NANOTECHNOLOGY, VOL. 7, NO. 1, JANUARY 2008 91 Graphene Terahertz Plasmon Oscillators Farhan Rana Abstract In this paper we propose and discuss coherent terahertz sources based on
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NANOTECHNOLOGY, VOL. 7, NO. 1, JANUARY 2008 91 Graphene Terahertz Plasmon Oscillators Farhan Rana Abstract In this paper we propose and discuss coherent terahertz sources based on
Electric Field-Dependent Charge-Carrier Velocity in Semiconducting Carbon. Nanotubes. Yung-Fu Chen and M. S. Fuhrer
 Electric Field-Dependent Charge-Carrier Velocity in Semiconducting Carbon Nanotubes Yung-Fu Chen and M. S. Fuhrer Department of Physics and Center for Superconductivity Research, University of Maryland,
Electric Field-Dependent Charge-Carrier Velocity in Semiconducting Carbon Nanotubes Yung-Fu Chen and M. S. Fuhrer Department of Physics and Center for Superconductivity Research, University of Maryland,
Computational Model of Edge Effects in Graphene Nanoribbon Transistors
 Nano Res (2008) 1: 395 402 DOI 10.1007/s12274-008-8039-y Research Article 00395 Computational Model of Edge Effects in Graphene Nanoribbon Transistors Pei Zhao 1, Mihir Choudhury 2, Kartik Mohanram 2,
Nano Res (2008) 1: 395 402 DOI 10.1007/s12274-008-8039-y Research Article 00395 Computational Model of Edge Effects in Graphene Nanoribbon Transistors Pei Zhao 1, Mihir Choudhury 2, Kartik Mohanram 2,
Electrical Transport. Ref. Ihn Ch. 10 YC, Ch 5; BW, Chs 4 & 8
 Electrical Transport Ref. Ihn Ch. 10 YC, Ch 5; BW, Chs 4 & 8 Electrical Transport The study of the transport of electrons & holes (in semiconductors) under various conditions. A broad & somewhat specialized
Electrical Transport Ref. Ihn Ch. 10 YC, Ch 5; BW, Chs 4 & 8 Electrical Transport The study of the transport of electrons & holes (in semiconductors) under various conditions. A broad & somewhat specialized
Density of states for electrons and holes. Distribution function. Conduction and valence bands
 Intrinsic Semiconductors In the field of semiconductors electrons and holes are usually referred to as free carriers, or simply carriers, because it is these particles which are responsible for carrying
Intrinsic Semiconductors In the field of semiconductors electrons and holes are usually referred to as free carriers, or simply carriers, because it is these particles which are responsible for carrying
Appendix 1: List of symbols
 Appendix 1: List of symbols Symbol Description MKS Units a Acceleration m/s 2 a 0 Bohr radius m A Area m 2 A* Richardson constant m/s A C Collector area m 2 A E Emitter area m 2 b Bimolecular recombination
Appendix 1: List of symbols Symbol Description MKS Units a Acceleration m/s 2 a 0 Bohr radius m A Area m 2 A* Richardson constant m/s A C Collector area m 2 A E Emitter area m 2 b Bimolecular recombination
Review of Optical Properties of Materials
 Review of Optical Properties of Materials Review of optics Absorption in semiconductors: qualitative discussion Derivation of Optical Absorption Coefficient in Direct Semiconductors Photons When dealing
Review of Optical Properties of Materials Review of optics Absorption in semiconductors: qualitative discussion Derivation of Optical Absorption Coefficient in Direct Semiconductors Photons When dealing
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig S1: Multilayer MoS 2 FETs on SiO2/Si substrates, and contact resistance effects. (Left): Transfer curves and effective mobility of multilayer
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Fig S1: Multilayer MoS 2 FETs on SiO2/Si substrates, and contact resistance effects. (Left): Transfer curves and effective mobility of multilayer
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures 8 6 Energy (ev 4 2 2 4 Γ M K Γ Supplementary Figure : Energy bands of antimonene along a high-symmetry path in the Brillouin zone, including spin-orbit coupling effects. Empty circles
Supplementary Figures 8 6 Energy (ev 4 2 2 4 Γ M K Γ Supplementary Figure : Energy bands of antimonene along a high-symmetry path in the Brillouin zone, including spin-orbit coupling effects. Empty circles
Basic Principles of Light Emission in Semiconductors
 Basic Principles of Light Emission in Semiconductors Class: Integrated Photonic Devices Time: Fri. 8:00am ~ 11:00am. Classroom: 資電 06 Lecturer: Prof. 李明昌 (Ming-Chang Lee) Model for Light Generation and
Basic Principles of Light Emission in Semiconductors Class: Integrated Photonic Devices Time: Fri. 8:00am ~ 11:00am. Classroom: 資電 06 Lecturer: Prof. 李明昌 (Ming-Chang Lee) Model for Light Generation and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Dirac cones reshaped by interaction effects in suspended graphene D. C. Elias et al #1. Experimental devices Graphene monolayers were obtained by micromechanical cleavage of graphite on top of an oxidized
Dirac cones reshaped by interaction effects in suspended graphene D. C. Elias et al #1. Experimental devices Graphene monolayers were obtained by micromechanical cleavage of graphite on top of an oxidized
arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 15 Apr 2007
![arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 15 Apr 2007 arxiv: v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 15 Apr 2007](/thumbs/80/82131568.jpg) Non-linear electromagnetic response of graphene S. A. Mikhailov Institute for Theoretical Physics II, University of Augsburg, D-86135 Augsburg, Germany (Dated: May 31, 218) arxiv:74.199v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall]
Non-linear electromagnetic response of graphene S. A. Mikhailov Institute for Theoretical Physics II, University of Augsburg, D-86135 Augsburg, Germany (Dated: May 31, 218) arxiv:74.199v1 [cond-mat.mes-hall]
Chapter 3 Properties of Nanostructures
 Chapter 3 Properties of Nanostructures In Chapter 2, the reduction of the extent of a solid in one or more dimensions was shown to lead to a dramatic alteration of the overall behavior of the solids. Generally,
Chapter 3 Properties of Nanostructures In Chapter 2, the reduction of the extent of a solid in one or more dimensions was shown to lead to a dramatic alteration of the overall behavior of the solids. Generally,
Section 12: Intro to Devices
 Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Silicon
Section 12: Intro to Devices Extensive reading materials on reserve, including Robert F. Pierret, Semiconductor Device Fundamentals Bond Model of Electrons and Holes Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Si Silicon
ESE 372 / Spring 2013 / Lecture 5 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor
 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor V G V G 1 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor We will need to understand how this current flows through Si What is electric current? 2 Back
Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor V G V G 1 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor We will need to understand how this current flows through Si What is electric current? 2 Back
Impact of Calcium on Transport Property of Graphene. Jyoti Katoch and Masa Ishigami*
 Impact of Calcium on Transport Property of Graphene Jyoti Katoch and Masa Ishigami* Department of Physics and Nanoscience Technology Center, University of Central Florida, Orlando, FL, 32816 *Corresponding
Impact of Calcium on Transport Property of Graphene Jyoti Katoch and Masa Ishigami* Department of Physics and Nanoscience Technology Center, University of Central Florida, Orlando, FL, 32816 *Corresponding
Classification of Solids
 Classification of Solids Classification by conductivity, which is related to the band structure: (Filled bands are shown dark; D(E) = Density of states) Class Electron Density Density of States D(E) Examples
Classification of Solids Classification by conductivity, which is related to the band structure: (Filled bands are shown dark; D(E) = Density of states) Class Electron Density Density of States D(E) Examples
Application II: The Ballistic Field-E ect Transistor
 Chapter 1 Application II: The Ballistic Field-E ect Transistor 1.1 Introduction In this chapter, we apply the formalism we have developed for charge currents to understand the output characteristics of
Chapter 1 Application II: The Ballistic Field-E ect Transistor 1.1 Introduction In this chapter, we apply the formalism we have developed for charge currents to understand the output characteristics of
Spin Lifetime Enhancement by Shear Strain in Thin Silicon-on-Insulator Films. Dmitry Osintsev, Viktor Sverdlov, and Siegfried Selberherr
 10.1149/05305.0203ecst The Electrochemical Society Spin Lifetime Enhancement by Shear Strain in Thin Silicon-on-Insulator Films Dmitry Osintsev, Viktor Sverdlov, and Siegfried Selberherr Institute for
10.1149/05305.0203ecst The Electrochemical Society Spin Lifetime Enhancement by Shear Strain in Thin Silicon-on-Insulator Films Dmitry Osintsev, Viktor Sverdlov, and Siegfried Selberherr Institute for
Summary lecture VII. Boltzmann scattering equation reads in second-order Born-Markov approximation
 Summary lecture VII Boltzmann scattering equation reads in second-order Born-Markov approximation and describes time- and momentum-resolved electron scattering dynamics in non-equilibrium Markov approximation
Summary lecture VII Boltzmann scattering equation reads in second-order Born-Markov approximation and describes time- and momentum-resolved electron scattering dynamics in non-equilibrium Markov approximation
Supplementary Information
 Ultrafast Dynamics of Defect-Assisted Electron-Hole Recombination in Monolayer MoS Haining Wang, Changjian Zhang, and Farhan Rana School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University, Ithaca,
Ultrafast Dynamics of Defect-Assisted Electron-Hole Recombination in Monolayer MoS Haining Wang, Changjian Zhang, and Farhan Rana School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University, Ithaca,
B12: Semiconductor Devices
 B12: Semiconductor Devices Example Sheet 2: Solutions Question 1 To get from eq. (5.70) of the notes to the expression given in the examples sheet, we simply invoke the relations n 0 p 0, n 0 n 0. In this
B12: Semiconductor Devices Example Sheet 2: Solutions Question 1 To get from eq. (5.70) of the notes to the expression given in the examples sheet, we simply invoke the relations n 0 p 0, n 0 n 0. In this
Nonlinear Electrodynamics and Optics of Graphene
 Nonlinear Electrodynamics and Optics of Graphene S. A. Mikhailov and N. A. Savostianova University of Augsburg, Institute of Physics, Universitätsstr. 1, 86159 Augsburg, Germany E-mail: sergey.mikhailov@physik.uni-augsburg.de
Nonlinear Electrodynamics and Optics of Graphene S. A. Mikhailov and N. A. Savostianova University of Augsburg, Institute of Physics, Universitätsstr. 1, 86159 Augsburg, Germany E-mail: sergey.mikhailov@physik.uni-augsburg.de
Gate Carrier Injection and NC-Non- Volatile Memories
 Gate Carrier Injection and NC-Non- Volatile Memories Jean-Pierre Leburton Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering and Beckman Institute University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Urbana, IL 61801,
Gate Carrier Injection and NC-Non- Volatile Memories Jean-Pierre Leburton Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering and Beckman Institute University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Urbana, IL 61801,
In recent years, graphene has gathered much interest for electrical
 pubs.acs.org/nanolett Very Slow Cooling Dynamics of Photoexcited Carriers in Graphene Observed by Optical-Pump Terahertz-Probe Spectroscopy Jared H. Strait,* Haining Wang, Shriram Shivaraman, Virgil Shields,
pubs.acs.org/nanolett Very Slow Cooling Dynamics of Photoexcited Carriers in Graphene Observed by Optical-Pump Terahertz-Probe Spectroscopy Jared H. Strait,* Haining Wang, Shriram Shivaraman, Virgil Shields,
Time Resolved Pump-Probe Reflectivity in GaAs and GaN
 Time Resolved Pump-Probe Reflectivity in GaAs and GaN S. S. Prabhu * and A. S. Vengurlekar Department of Condensed Matter Physics and Material Science, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Homi Bhabha
Time Resolved Pump-Probe Reflectivity in GaAs and GaN S. S. Prabhu * and A. S. Vengurlekar Department of Condensed Matter Physics and Material Science, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Homi Bhabha
Impact Ionization Can Explain Carrier Multiplication in PbSe Quantum Dots
 Impact Ionization Can Explain Carrier Multiplication in PbSe Quantum Dots A. Franceschetti,* J. M. An, and A. Zunger National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, Colorado 8040 Received May 3, 2006; Revised
Impact Ionization Can Explain Carrier Multiplication in PbSe Quantum Dots A. Franceschetti,* J. M. An, and A. Zunger National Renewable Energy Laboratory, Golden, Colorado 8040 Received May 3, 2006; Revised
Graphene: massless electrons in flatland.
 Graphene: massless electrons in flatland. Enrico Rossi Work supported by: University of Chile. Oct. 24th 2008 Collaorators CMTC, University of Maryland Sankar Das Sarma Shaffique Adam Euyuong Hwang Roman
Graphene: massless electrons in flatland. Enrico Rossi Work supported by: University of Chile. Oct. 24th 2008 Collaorators CMTC, University of Maryland Sankar Das Sarma Shaffique Adam Euyuong Hwang Roman
Electro-Thermal Transport in Silicon and Carbon Nanotube Devices E. Pop, D. Mann, J. Rowlette, K. Goodson and H. Dai
 Electro-Thermal Transport in Silicon and Carbon Nanotube Devices E. Pop, D. Mann, J. Rowlette, K. Goodson and H. Dai E. Pop, 1,2 D. Mann, 1 J. Rowlette, 2 K. Goodson 2 and H. Dai 1 Dept. of 1 Chemistry
Electro-Thermal Transport in Silicon and Carbon Nanotube Devices E. Pop, D. Mann, J. Rowlette, K. Goodson and H. Dai E. Pop, 1,2 D. Mann, 1 J. Rowlette, 2 K. Goodson 2 and H. Dai 1 Dept. of 1 Chemistry
Journal of Atoms and Molecules
 Research article Journal of Atoms and Molecules An International Online Journal ISSN 77 147 Hot Electron Transport in Polar Semiconductor at Low Lattice Temperature A. K. Ghorai Physics Department, Kalimpong
Research article Journal of Atoms and Molecules An International Online Journal ISSN 77 147 Hot Electron Transport in Polar Semiconductor at Low Lattice Temperature A. K. Ghorai Physics Department, Kalimpong
L5: Surface Recombination, Continuity Equation & Extended Topics tanford University
 L5: Surface Recombination, Continuity Equation & Extended Topics EE 216 : Aneesh Nainani 1 Announcements Project Select topic by Jan 29 (Tuesday) 9 topics, maximum 4 students per topic Quiz Thursday (Jan
L5: Surface Recombination, Continuity Equation & Extended Topics EE 216 : Aneesh Nainani 1 Announcements Project Select topic by Jan 29 (Tuesday) 9 topics, maximum 4 students per topic Quiz Thursday (Jan
2005 EDP Sciences. Reprinted with permission.
 H. Holmberg, N. Lebedeva, S. Novikov, J. Ikonen, P. Kuivalainen, M. Malfait, and V. V. Moshchalkov, Large magnetoresistance in a ferromagnetic GaMnAs/GaAs Zener diode, Europhysics Letters 71 (5), 811 816
H. Holmberg, N. Lebedeva, S. Novikov, J. Ikonen, P. Kuivalainen, M. Malfait, and V. V. Moshchalkov, Large magnetoresistance in a ferromagnetic GaMnAs/GaAs Zener diode, Europhysics Letters 71 (5), 811 816
Detectors of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search: Charge Transport and Phonon Emission in Ge 100 Crystals at 40 mk
 J Low Temp Phys (2008) 151: 443 447 DOI 10.1007/s10909-007-9666-5 Detectors of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search: Charge Transport and Phonon Emission in Ge 100 Crystals at 40 mk K.M. Sundqvist B. Sadoulet
J Low Temp Phys (2008) 151: 443 447 DOI 10.1007/s10909-007-9666-5 Detectors of the Cryogenic Dark Matter Search: Charge Transport and Phonon Emission in Ge 100 Crystals at 40 mk K.M. Sundqvist B. Sadoulet
Electron Spectroscopy
 Electron Spectroscopy Photoelectron spectroscopy is based upon a single photon in/electron out process. The energy of a photon is given by the Einstein relation : E = h ν where h - Planck constant ( 6.62
Electron Spectroscopy Photoelectron spectroscopy is based upon a single photon in/electron out process. The energy of a photon is given by the Einstein relation : E = h ν where h - Planck constant ( 6.62
Self-Consistent Drift-Diffusion Analysis of Intermediate Band Solar Cell (IBSC): Effect of Energetic Position of IB on Conversion Efficiency
 Self-onsistent Drift-Diffusion Analysis of ntermediate Band Solar ell (BS): Effect of Energetic Position of B on onversion Efficiency Katsuhisa Yoshida 1,, Yoshitaka Okada 1,, and Nobuyuki Sano 3 1 raduate
Self-onsistent Drift-Diffusion Analysis of ntermediate Band Solar ell (BS): Effect of Energetic Position of B on onversion Efficiency Katsuhisa Yoshida 1,, Yoshitaka Okada 1,, and Nobuyuki Sano 3 1 raduate
(a) (b) Supplementary Figure 1. (a) (b) (a) Supplementary Figure 2. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e)
 (a) (b) Supplementary Figure 1. (a) An AFM image of the device after the formation of the contact electrodes and the top gate dielectric Al 2 O 3. (b) A line scan performed along the white dashed line
(a) (b) Supplementary Figure 1. (a) An AFM image of the device after the formation of the contact electrodes and the top gate dielectric Al 2 O 3. (b) A line scan performed along the white dashed line
arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 7 Dec 2009
![arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 7 Dec 2009 arxiv: v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 7 Dec 2009](/thumbs/85/91574443.jpg) First Principles Analysis of Electron-Phonon Interactions in Graphene K. M. Borysenko, 1 J. T. Mullen, 2 E. A. Barry, 1 S. Paul, 2 Y. G. arxiv:0912.0562v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 7 Dec 2009 Semenov, 1 J. M.
First Principles Analysis of Electron-Phonon Interactions in Graphene K. M. Borysenko, 1 J. T. Mullen, 2 E. A. Barry, 1 S. Paul, 2 Y. G. arxiv:0912.0562v2 [cond-mat.mes-hall] 7 Dec 2009 Semenov, 1 J. M.
Lecture 4 - Carrier generation and recombination. February 12, 2007
 6.720J/3.43J - Integrated Microelectronic Devices - Spring 2007 Lecture 4-1 Contents: Lecture 4 - Carrier generation and recombination 1. G&R mechanisms February 12, 2007 2. Thermal equilibrium: principle
6.720J/3.43J - Integrated Microelectronic Devices - Spring 2007 Lecture 4-1 Contents: Lecture 4 - Carrier generation and recombination 1. G&R mechanisms February 12, 2007 2. Thermal equilibrium: principle
1 Name: Student number: DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND. Fall :00-11:00
 1 Name: DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Final Exam Physics 3000 December 11, 2012 Fall 2012 9:00-11:00 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Answer all seven (7) questions.
1 Name: DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS AND PHYSICAL OCEANOGRAPHY MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Final Exam Physics 3000 December 11, 2012 Fall 2012 9:00-11:00 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Answer all seven (7) questions.
Electron Interactions and Nanotube Fluorescence Spectroscopy C.L. Kane & E.J. Mele
 Electron Interactions and Nanotube Fluorescence Spectroscopy C.L. Kane & E.J. Mele Large radius theory of optical transitions in semiconducting nanotubes derived from low energy theory of graphene Phys.
Electron Interactions and Nanotube Fluorescence Spectroscopy C.L. Kane & E.J. Mele Large radius theory of optical transitions in semiconducting nanotubes derived from low energy theory of graphene Phys.
Intensity / a.u. 2 theta / deg. MAPbI 3. 1:1 MaPbI 3-x. Cl x 3:1. Supplementary figures
 Intensity / a.u. Supplementary figures 110 MAPbI 3 1:1 MaPbI 3-x Cl x 3:1 220 330 0 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 2 theta / deg Supplementary Fig. 1 X-ray Diffraction (XRD) patterns of MAPbI3 and MAPbI 3-x Cl
Intensity / a.u. Supplementary figures 110 MAPbI 3 1:1 MaPbI 3-x Cl x 3:1 220 330 0 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 2 theta / deg Supplementary Fig. 1 X-ray Diffraction (XRD) patterns of MAPbI3 and MAPbI 3-x Cl
Effects of Finite Layer Thickness on the Differential Capacitance of Electron Bilayers
 Effects of Finite Layer Thickness on the Differential Capacitance of Electron Bilayers J.J. Durrant: McNair Scholar Dr. Charles Hanna: Mentor Physics Abstract We have calculated the effects of finite thickness
Effects of Finite Layer Thickness on the Differential Capacitance of Electron Bilayers J.J. Durrant: McNair Scholar Dr. Charles Hanna: Mentor Physics Abstract We have calculated the effects of finite thickness
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/NNANO.211.214 Control over topological insulator photocurrents with light polarization J.W. McIver*, D. Hsieh*, H. Steinberg, P. Jarillo-Herrero and N. Gedik SI I. Materials and device fabrication
DOI: 1.138/NNANO.211.214 Control over topological insulator photocurrents with light polarization J.W. McIver*, D. Hsieh*, H. Steinberg, P. Jarillo-Herrero and N. Gedik SI I. Materials and device fabrication
Introduction to Sources: Radiative Processes and Population Inversion in Atoms, Molecules, and Semiconductors Atoms and Molecules
 OPTI 500 DEF, Spring 2012, Lecture 2 Introduction to Sources: Radiative Processes and Population Inversion in Atoms, Molecules, and Semiconductors Atoms and Molecules Energy Levels Every atom or molecule
OPTI 500 DEF, Spring 2012, Lecture 2 Introduction to Sources: Radiative Processes and Population Inversion in Atoms, Molecules, and Semiconductors Atoms and Molecules Energy Levels Every atom or molecule
Carbon based Nanoscale Electronics
 Carbon based Nanoscale Electronics 09 02 200802 2008 ME class Outline driving force for the carbon nanomaterial electronic properties of fullerene exploration of electronic carbon nanotube gold rush of
Carbon based Nanoscale Electronics 09 02 200802 2008 ME class Outline driving force for the carbon nanomaterial electronic properties of fullerene exploration of electronic carbon nanotube gold rush of
Summary lecture II. Graphene exhibits a remarkable linear and gapless band structure
 Summary lecture II Bloch theorem: eigen functions of an electron in a perfectly periodic potential have the shape of plane waves modulated with a Bloch factor that possess the periodicity of the potential
Summary lecture II Bloch theorem: eigen functions of an electron in a perfectly periodic potential have the shape of plane waves modulated with a Bloch factor that possess the periodicity of the potential
Understanding the effect of n-type and p-type doping in the channel of graphene nanoribbon transistor
 Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 39, No. 5, September 2016, pp. 1303 1309. DOI 10.1007/s12034-016-1277-9 c Indian Academy of Sciences. Understanding the effect of n-type and p-type doping in the channel of graphene
Bull. Mater. Sci., Vol. 39, No. 5, September 2016, pp. 1303 1309. DOI 10.1007/s12034-016-1277-9 c Indian Academy of Sciences. Understanding the effect of n-type and p-type doping in the channel of graphene
Bilayer GNR Mobility Model in Ballistic Transport Limit
 ilayer GNR Mobility Model in allistic Transport Limit S. Mahdi Mousavi, M.Taghi Ahmadi, Hatef Sadeghi, and Razali Ismail Computational Nanoelectronics (CoNE) Research Group, Electrical Engineering Faculty,
ilayer GNR Mobility Model in allistic Transport Limit S. Mahdi Mousavi, M.Taghi Ahmadi, Hatef Sadeghi, and Razali Ismail Computational Nanoelectronics (CoNE) Research Group, Electrical Engineering Faculty,
Microscopic Modelling of the Optical Properties of Quantum-Well Semiconductor Lasers
 Microscopic Modelling of the Optical Properties of Quantum-Well Semiconductor Lasers Stephan W. Koch Department of Physics Philipps University, Marburg/Germany OVERVIEW - Outline of Theory - Gain/Absorption
Microscopic Modelling of the Optical Properties of Quantum-Well Semiconductor Lasers Stephan W. Koch Department of Physics Philipps University, Marburg/Germany OVERVIEW - Outline of Theory - Gain/Absorption
Hybrid Surface-Phonon-Plasmon Polariton Modes in Graphene /
 Supplementary Information: Hybrid Surface-Phonon-Plasmon Polariton Modes in Graphene / Monolayer h-bn stacks Victor W. Brar 1,2, Min Seok Jang 3,, Michelle Sherrott 1, Seyoon Kim 1, Josue J. Lopez 1, Laura
Supplementary Information: Hybrid Surface-Phonon-Plasmon Polariton Modes in Graphene / Monolayer h-bn stacks Victor W. Brar 1,2, Min Seok Jang 3,, Michelle Sherrott 1, Seyoon Kim 1, Josue J. Lopez 1, Laura
MTLE-6120: Advanced Electronic Properties of Materials. Intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors. Reading: Kasap:
 MTLE-6120: Advanced Electronic Properties of Materials 1 Intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors Reading: Kasap: 5.1-5.6 Band structure and conduction 2 Metals: partially filled band(s) i.e. bands cross
MTLE-6120: Advanced Electronic Properties of Materials 1 Intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors Reading: Kasap: 5.1-5.6 Band structure and conduction 2 Metals: partially filled band(s) i.e. bands cross
Landau Bogolubov Energy Spectrum of Superconductors
 Landau Bogolubov Energy Spectrum of Superconductors L.N. Tsintsadze 1 and N.L. Tsintsadze 1,2 1. Department of Plasma Physics, E. Andronikashvili Institute of Physics, Tbilisi 0128, Georgia 2. Faculty
Landau Bogolubov Energy Spectrum of Superconductors L.N. Tsintsadze 1 and N.L. Tsintsadze 1,2 1. Department of Plasma Physics, E. Andronikashvili Institute of Physics, Tbilisi 0128, Georgia 2. Faculty
Supplementary Figure 1. Selected area electron diffraction (SAED) of bilayer graphene and tblg. (a) AB
 Supplementary Figure 1. Selected area electron diffraction (SAED) of bilayer graphene and tblg. (a) AB stacked bilayer graphene (b), (c), (d), (e), and (f) are twisted bilayer graphene with twist angle
Supplementary Figure 1. Selected area electron diffraction (SAED) of bilayer graphene and tblg. (a) AB stacked bilayer graphene (b), (c), (d), (e), and (f) are twisted bilayer graphene with twist angle
Black phosphorus field-effect transistors
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2014.35 Black phosphorus field-effect transistors Likai Li, Yijun Yu, Guo Jun Ye, Qingqin Ge, Xuedong Ou, Hua Wu, Donglai Feng, Xian Hui Chen and Yuanbo Zhang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NNANO.2014.35 Black phosphorus field-effect transistors Likai Li, Yijun Yu, Guo Jun Ye, Qingqin Ge, Xuedong Ou, Hua Wu, Donglai Feng, Xian Hui Chen and Yuanbo Zhang
Tunneling Spectroscopy of Disordered Two-Dimensional Electron Gas in the Quantum Hall Regime
 Tunneling Spectroscopy of Disordered Two-Dimensional Electron Gas in the Quantum Hall Regime The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Tunneling Spectroscopy of Disordered Two-Dimensional Electron Gas in the Quantum Hall Regime The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Time resolved ultrafast ARPES for the study of topological insulators: The case of Bi 2 Te 3
 Eur. Phys. J. Special Topics 222, 1271 1275 (2013) EDP Sciences, Springer-Verlag 2013 DOI: 10.1140/epjst/e2013-01921-1 THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL SPECIAL TOPICS Regular Article Time resolved ultrafast
Eur. Phys. J. Special Topics 222, 1271 1275 (2013) EDP Sciences, Springer-Verlag 2013 DOI: 10.1140/epjst/e2013-01921-1 THE EUROPEAN PHYSICAL JOURNAL SPECIAL TOPICS Regular Article Time resolved ultrafast
SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION. Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course. Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS
 2753 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2011 Wednesday, 22 June, 9.30 am 12.30
2753 SECOND PUBLIC EXAMINATION Honour School of Physics Part C: 4 Year Course Honour School of Physics and Philosophy Part C C3: CONDENSED MATTER PHYSICS TRINITY TERM 2011 Wednesday, 22 June, 9.30 am 12.30
Electrical Characteristics of MOS Devices
 Electrical Characteristics of MOS Devices The MOS Capacitor Voltage components Accumulation, Depletion, Inversion Modes Effect of channel bias and substrate bias Effect of gate oide charges Threshold-voltage
Electrical Characteristics of MOS Devices The MOS Capacitor Voltage components Accumulation, Depletion, Inversion Modes Effect of channel bias and substrate bias Effect of gate oide charges Threshold-voltage
PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS AND THEIR HETEROSTRUCTURES
 PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS AND THEIR HETEROSTRUCTURES Jasprit Singh University of Michigan McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Caracas Lisbon London Madrid Mexico Milan Montreal
PHYSICS OF SEMICONDUCTORS AND THEIR HETEROSTRUCTURES Jasprit Singh University of Michigan McGraw-Hill, Inc. New York St. Louis San Francisco Auckland Bogota Caracas Lisbon London Madrid Mexico Milan Montreal
Semiconductor Devices and Circuits Fall Midterm Exam. Instructor: Dr. Dietmar Knipp, Professor of Electrical Engineering. Name: Mat. -Nr.
 Semiconductor Devices and Circuits Fall 2003 Midterm Exam Instructor: Dr. Dietmar Knipp, Professor of Electrical Engineering Name: Mat. -Nr.: Guidelines: Duration of the Midterm: 1 hour The exam is a closed
Semiconductor Devices and Circuits Fall 2003 Midterm Exam Instructor: Dr. Dietmar Knipp, Professor of Electrical Engineering Name: Mat. -Nr.: Guidelines: Duration of the Midterm: 1 hour The exam is a closed
Self-Doping Effects in Epitaxially-Grown Graphene. Abstract
 Self-Doping Effects in Epitaxially-Grown Graphene D.A.Siegel, 1,2 S.Y.Zhou, 1,2 F.ElGabaly, 3 A.V.Fedorov, 4 A.K.Schmid, 3 anda.lanzara 1,2 1 Department of Physics, University of California, Berkeley,
Self-Doping Effects in Epitaxially-Grown Graphene D.A.Siegel, 1,2 S.Y.Zhou, 1,2 F.ElGabaly, 3 A.V.Fedorov, 4 A.K.Schmid, 3 anda.lanzara 1,2 1 Department of Physics, University of California, Berkeley,
Numerical calculation of the electron mobility in ZnS and ZnSe semiconductors using the iterative method
 International Journal o the Physical Sciences Vol. 5(11), pp. 1752-1756, 18 September, 21 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ijps ISSN 1992-195 21 Academic Journals Full Length Research
International Journal o the Physical Sciences Vol. 5(11), pp. 1752-1756, 18 September, 21 Available online at http://www.academicjournals.org/ijps ISSN 1992-195 21 Academic Journals Full Length Research
Nonlinear resistance of two-dimensional electrons in crossed electric and magnetic fields
 Nonlinear resistance of two-dimensional electrons in crossed electric and magnetic fields Jing Qiao Zhang and Sergey Vitkalov* Department of Physics, City College of the City University of New York, New
Nonlinear resistance of two-dimensional electrons in crossed electric and magnetic fields Jing Qiao Zhang and Sergey Vitkalov* Department of Physics, City College of the City University of New York, New
2 Fundamentals of Flash Lamp Annealing of Shallow Boron-Doped Silicon
 2 Fundamentals of Flash Lamp Annealing of Shallow Boron-Doped Silicon MSA of semiconductors is usually performed using flash lamps. It has been shown that FLA holds the balance between effective dopant
2 Fundamentals of Flash Lamp Annealing of Shallow Boron-Doped Silicon MSA of semiconductors is usually performed using flash lamps. It has been shown that FLA holds the balance between effective dopant
Observation of topological surface state quantum Hall effect in an intrinsic three-dimensional topological insulator
 Observation of topological surface state quantum Hall effect in an intrinsic three-dimensional topological insulator Authors: Yang Xu 1,2, Ireneusz Miotkowski 1, Chang Liu 3,4, Jifa Tian 1,2, Hyoungdo
Observation of topological surface state quantum Hall effect in an intrinsic three-dimensional topological insulator Authors: Yang Xu 1,2, Ireneusz Miotkowski 1, Chang Liu 3,4, Jifa Tian 1,2, Hyoungdo
Semiconductor Physics and Devices Chapter 3.
 Introduction to the Quantum Theory of Solids We applied quantum mechanics and Schrödinger s equation to determine the behavior of electrons in a potential. Important findings Semiconductor Physics and
Introduction to the Quantum Theory of Solids We applied quantum mechanics and Schrödinger s equation to determine the behavior of electrons in a potential. Important findings Semiconductor Physics and
Graphene-based long-wave infrared TM surface plasmon modulator
 Graphene-based long-wave infrared TM surface plasmon modulator David R. Andersen 1, 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Department of Physics and Astronomy, The University of Iowa, Iowa
Graphene-based long-wave infrared TM surface plasmon modulator David R. Andersen 1, 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Department of Physics and Astronomy, The University of Iowa, Iowa
Electronic and Optoelectronic Properties of Semiconductor Structures
 Electronic and Optoelectronic Properties of Semiconductor Structures Jasprit Singh University of Michigan, Ann Arbor CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS PREFACE INTRODUCTION xiii xiv 1.1 SURVEY OF ADVANCES
Electronic and Optoelectronic Properties of Semiconductor Structures Jasprit Singh University of Michigan, Ann Arbor CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS CONTENTS PREFACE INTRODUCTION xiii xiv 1.1 SURVEY OF ADVANCES
Studying of the Dipole Characteristic of THz from Photoconductors
 PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 4, NO. 3, 8 386 Studying of the Dipole Characteristic of THz from Photoconductors Hong Liu, Weili Ji, and Wei Shi School of Automation and Information Engineering, Xi an University of
PIERS ONLINE, VOL. 4, NO. 3, 8 386 Studying of the Dipole Characteristic of THz from Photoconductors Hong Liu, Weili Ji, and Wei Shi School of Automation and Information Engineering, Xi an University of
Theory of spin-polarized transport in photoexcited semiconductor/ferromagnet tunnel junctions
 PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 57, NUMBER 7 15 FEBRUARY 1998-I Theory of spin-polarized transport in photoexcited semiconductor/ferromagnet tunnel junctions R. Jansen,* M. W. J. Prins, and H. van Kempen Research
PHYSICAL REVIEW B VOLUME 57, NUMBER 7 15 FEBRUARY 1998-I Theory of spin-polarized transport in photoexcited semiconductor/ferromagnet tunnel junctions R. Jansen,* M. W. J. Prins, and H. van Kempen Research
Before we go to the topic of hole, we discuss this important topic. The effective mass m is defined as. 2 dk 2
 Notes for Lecture 7 Holes, Electrons In the previous lecture, we learned how electrons move in response to an electric field to generate current. In this lecture, we will see why the hole is a natural
Notes for Lecture 7 Holes, Electrons In the previous lecture, we learned how electrons move in response to an electric field to generate current. In this lecture, we will see why the hole is a natural
Monte Carlo Based Calculation of Electron Transport Properties in Bulk InAs, AlAs and InAlAs
 Bulg. J. Phys. 37 (2010) 215 222 Monte Carlo Based Calculation of Electron Transport Properties in Bulk InAs, AlAs and InAlAs H. Arabshahi 1, S. Golafrooz 2 1 Department of Physics, Ferdowsi University
Bulg. J. Phys. 37 (2010) 215 222 Monte Carlo Based Calculation of Electron Transport Properties in Bulk InAs, AlAs and InAlAs H. Arabshahi 1, S. Golafrooz 2 1 Department of Physics, Ferdowsi University
Graphite, graphene and relativistic electrons
 Graphite, graphene and relativistic electrons Introduction Physics of E. graphene Y. Andrei Experiments Rutgers University Transport electric field effect Quantum Hall Effect chiral fermions STM Dirac
Graphite, graphene and relativistic electrons Introduction Physics of E. graphene Y. Andrei Experiments Rutgers University Transport electric field effect Quantum Hall Effect chiral fermions STM Dirac
Non-equilibrium Green s functions: Rough interfaces in THz quantum cascade lasers
 Non-equilibrium Green s functions: Rough interfaces in THz quantum cascade lasers Tillmann Kubis, Gerhard Klimeck Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana
Non-equilibrium Green s functions: Rough interfaces in THz quantum cascade lasers Tillmann Kubis, Gerhard Klimeck Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Purdue University, West Lafayette, Indiana
ELECTRONIC TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE
 ELECTRONIC TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE J. González Instituto de Estructura de la Materia, CSIC, Spain 1985 1991 4 ELECTRONIC TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE Graphene has opened the way to understand the behaior of an
ELECTRONIC TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE J. González Instituto de Estructura de la Materia, CSIC, Spain 1985 1991 4 ELECTRONIC TRANSPORT IN GRAPHENE Graphene has opened the way to understand the behaior of an
Supplementary Figure 1: A potential scheme to electrically gate the graphene-based metamaterial. Here density. The voltage equals, where is the DC
 Supplementary Figure 1: A potential scheme to electrically gate the graphene-based metamaterial. Here density. The voltage equals, where is the DC permittivity of the dielectric. is the surface charge
Supplementary Figure 1: A potential scheme to electrically gate the graphene-based metamaterial. Here density. The voltage equals, where is the DC permittivity of the dielectric. is the surface charge
Controlling Graphene Ultrafast Hot Carrier Response from Metal-like. to Semiconductor-like by Electrostatic Gating
 Controlling Graphene Ultrafast Hot Carrier Response from Metal-like to Semiconductor-like by Electrostatic Gating S.-F. Shi, 1,2* T.-T. Tang, 1 B. Zeng, 1 L. Ju, 1 Q. Zhou, 1 A. Zettl, 1,2,3 F. Wang 1,2,3
Controlling Graphene Ultrafast Hot Carrier Response from Metal-like to Semiconductor-like by Electrostatic Gating S.-F. Shi, 1,2* T.-T. Tang, 1 B. Zeng, 1 L. Ju, 1 Q. Zhou, 1 A. Zettl, 1,2,3 F. Wang 1,2,3
Radiation Detection for the Beta- Delayed Alpha and Gamma Decay of 20 Na. Ellen Simmons
 Radiation Detection for the Beta- Delayed Alpha and Gamma Decay of 20 Na Ellen Simmons 1 Contents Introduction Review of the Types of Radiation Charged Particle Radiation Detection Review of Semiconductor
Radiation Detection for the Beta- Delayed Alpha and Gamma Decay of 20 Na Ellen Simmons 1 Contents Introduction Review of the Types of Radiation Charged Particle Radiation Detection Review of Semiconductor
Ambipolar Graphene Field Effect Transistors by Local Metal Side Gates USA. Indiana 47907, USA. Abstract
 Ambipolar Graphene Field Effect Transistors by Local Metal Side Gates J. F. Tian *, a, b, L. A. Jauregui c, b, G. Lopez c, b, H. Cao a, b *, a, b, c, and Y. P. Chen a Department of Physics, Purdue University,
Ambipolar Graphene Field Effect Transistors by Local Metal Side Gates J. F. Tian *, a, b, L. A. Jauregui c, b, G. Lopez c, b, H. Cao a, b *, a, b, c, and Y. P. Chen a Department of Physics, Purdue University,
Lecture 7: Extrinsic semiconductors - Fermi level
 Lecture 7: Extrinsic semiconductors - Fermi level Contents 1 Dopant materials 1 2 E F in extrinsic semiconductors 5 3 Temperature dependence of carrier concentration 6 3.1 Low temperature regime (T < T
Lecture 7: Extrinsic semiconductors - Fermi level Contents 1 Dopant materials 1 2 E F in extrinsic semiconductors 5 3 Temperature dependence of carrier concentration 6 3.1 Low temperature regime (T < T
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits. Lecture 03: MOS Transistor
 CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
CMPEN 411 VLSI Digital Circuits Lecture 03: MOS Transistor Kyusun Choi [Adapted from Rabaey s Digital Integrated Circuits, Second Edition, 2003 J. Rabaey, A. Chandrakasan, B. Nikolic] CMPEN 411 L03 S.1
Raman Imaging and Electronic Properties of Graphene
 Raman Imaging and Electronic Properties of Graphene F. Molitor, D. Graf, C. Stampfer, T. Ihn, and K. Ensslin Laboratory for Solid State Physics, ETH Zurich, 8093 Zurich, Switzerland ensslin@phys.ethz.ch
Raman Imaging and Electronic Properties of Graphene F. Molitor, D. Graf, C. Stampfer, T. Ihn, and K. Ensslin Laboratory for Solid State Physics, ETH Zurich, 8093 Zurich, Switzerland ensslin@phys.ethz.ch
Out-of-equilibrium electron dynamics in photoexcited topological insulators studied by TR-ARPES
 Cliquez et modifiez le titre Out-of-equilibrium electron dynamics in photoexcited topological insulators studied by TR-ARPES Laboratoire de Physique des Solides Orsay, France June 15, 2016 Workshop Condensed
Cliquez et modifiez le titre Out-of-equilibrium electron dynamics in photoexcited topological insulators studied by TR-ARPES Laboratoire de Physique des Solides Orsay, France June 15, 2016 Workshop Condensed
Particle Monte Carlo simulation of quantum phenomena in semiconductor nanostructures
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 89 NUMBER 7 APRIL 00 Particle Monte Carlo simulation of quantum phenomena in semiconductor nanostructures Hideaki Tsuchiya and Umberto Ravaioli a) Beckman Institute University
JOURNAL OF APPLIED PHYSICS VOLUME 89 NUMBER 7 APRIL 00 Particle Monte Carlo simulation of quantum phenomena in semiconductor nanostructures Hideaki Tsuchiya and Umberto Ravaioli a) Beckman Institute University
Ultrafast study of Dirac fermions in out of equilibrium Topological Insulators
 Ultrafast study of Dirac fermions in out of equilibrium Topological Insulators Marino Marsi Laboratoire de Physique des Solides CNRS Univ. Paris-Sud - Université Paris-Saclay IMPACT, Cargèse, August 26
Ultrafast study of Dirac fermions in out of equilibrium Topological Insulators Marino Marsi Laboratoire de Physique des Solides CNRS Univ. Paris-Sud - Université Paris-Saclay IMPACT, Cargèse, August 26
Note that it is traditional to draw the diagram for semiconductors rotated 90 degrees, i.e. the version on the right above.
 5 Semiconductors The nearly free electron model applies equally in the case where the Fermi level lies within a small band gap (semiconductors), as it does when the Fermi level lies within a band (metal)
5 Semiconductors The nearly free electron model applies equally in the case where the Fermi level lies within a small band gap (semiconductors), as it does when the Fermi level lies within a band (metal)
Optical Properties of Lattice Vibrations
 Optical Properties of Lattice Vibrations For a collection of classical charged Simple Harmonic Oscillators, the dielectric function is given by: Where N i is the number of oscillators with frequency ω
Optical Properties of Lattice Vibrations For a collection of classical charged Simple Harmonic Oscillators, the dielectric function is given by: Where N i is the number of oscillators with frequency ω
THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES. SCHOOL OF PHYSICS FINAL EXAMI NATIO N june, 2010
 THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES SCHOOL OF PHYSICS FINAL EXAMI NATIO N june, 2010 PHYS3080 Solid State Physics Time Allowed - 2 hours Total number of questions - 5 Answer ALL questions All questions are
THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW SOUTH WALES SCHOOL OF PHYSICS FINAL EXAMI NATIO N june, 2010 PHYS3080 Solid State Physics Time Allowed - 2 hours Total number of questions - 5 Answer ALL questions All questions are
