Mechanical Engineering Excerise 1
|
|
|
- Corey Harmon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Mechanical Engineering Excerise 1 1. Given that the determinant of the matrix the matrix is is 12, the determinant of (A) 96 (B) 24 (C) 24 (D) x sin x Lt 1 cosx x 0 is (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) 3 (D) not defined 3. The argument of the complex number 1 + i 1 i, wherei = 1, is (A) π (B) π π (C) 2 2 (D) π dx 4. The matrix form of the linear system 3x 5y dt = and dy 4 x 8 y dt = + is (A) d x 3 5 x = dt y 4 8 y (B) d x 3 8 x = dt y 4 5 y (C) d x 4 5 x = dt y 3 8 y (D) d x 4 8 x = dt y 3 5 y 5. Which one of the following describes the relationship among the three vectors, i+ j+ k,2 i+ 3 j+ k and5 i+ 6 j+ 4 k?
2 (A) The vectors are mutually perpendicular (B) The vectors are linearly dependent (C) The vectors are linearly independent (D) The vectors are unit vectors 6. A circular rod of length L and area of cross section A has a modulus of elasticity E and coefficient of thermal expansion α. One end of the rod is fixed and other end is free. If the temperature of the rod is increased by ΔT, then (A) stress developed in the rod is E α ΔT and strain developed in the rod is α ΔT (B) both stress and strain developed in the rod are zero (C) stress developed in the rod is zero and strain developed in the rod is α ΔT (D) stress developed in the rod is E α ΔT and strain developed in the rod is zero 7. A metallic rod of 500 mm length and 50 mm diameter, when subjected to a tensile force of 100 kn at the ends, experiences an increase in its length by 0.5 mm and a reduction in its diameter by mm. The Poisson s ratio of the rod material is 8. Critical damping is the (A) (B) (C) Largest amount of damping for which no oscillation occurs in free vibration Smallest amount of damping for which no oscillation occurs in free vibration largest amount of damping for which the motion is simple harmonic in free vibration
3 (D) Smallest amount of damping for which the motion is simple harmonic in free vibration 9. A circular object of radius r rolls without slipping on a horizontal level floor with the center having velocity V. The velocity at the point of contact between the object and the floor is (A) zero ( B) V in the direction of motion (C) V opposite to the direction of motion ( D) V vertically upward from the floor 10. For the given statements: I. Mating spur gear teeth is an example of higher pair II. A revolute joint is an example of lower pair Indicate the correct answer. (A) Both I and II are false (C) I is false and II is true (B) I is true and II is false (D) Both I and II are true 11. A rigid link PQ is 2 m long and oriented at 20o to the horizontal as shown in the figure. The magnitude and direction of velocity V Q, and the direction of velocity V P are given. The magnitude of V P (in m/s) at this instant is
4 (A) 2.14 (B) 1.89 (C) (D) Biot number signifies the ratio of (A) convective resistance in the fluid to conductive resistance in the solid (B) conductive resistance in the solid to convective resistance in the fluid (C) inertia force to viscous force in the fluid (D) buoyancy force to viscous force in the fluid 13. The maximum theoretical work obtainable, when a system interacts to equilibrium with a reference environment, is called (A) Entropy (B) Enthalpy (C) Exergy (D) Rothalpy 14. Consider a two dimensional laminar flow over a long cylinder as shown in the figure below. The free stream velocity is U and the free stream temperaturee T is lower than the cylinder surface temperature T s. The local heat transfer coefficient is minimum at point (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) For a completely submerged body with centree of gravity G and centre of buoyancy B, the condition of stability will be
5 (A) G is located below B (B) G is located above B (C) G and B are coincident (D) independent of the locations of G and B 16. In a power plant, water (density = 1000 kg/m 3 ) is pumped from 80 kpa to 3 MPa. The pump has an isentropic efficiency of Assuming that the temperature of the water remains the same, the specific work (in kj/kg) supplied to the pump is (A) 0.34 (B) 2.48 (C) 2.92 (D) Which one of the following is a CFC refrigerant? (A) R744 (B) R290 (C) R502 (D) R The jobs arrive at a facility, for service, in a random manner. The probability distribution of number of arrivals of jobs in a fixed time interval is (A) Normal (B) Poisson (C) Erlang (D) Beta 19. In exponential smoothening method, which one of the following is true? (A) 0 α 1 and high value of a is used for stable demand (B) 0 α 1 and high value of a is used for unstable demand (C) α 1 and high value of a is used for stable demand (D) α 0 and high value of a is used for unstable demand 20. For machining a rectangular island represented by coordinates P(0,0), Q(100,0), R(100,50) and S(0,50) on a casting using CNC milling machine, an end mill with a diameter of 16 mm is used. The trajectory of the cutter centre to machine the island PQRS is (A) ( 8, 8), (108, 8), (108,58), ( 8,58), ( 8, 8)
6 (B) (8,8), (94,8), (94,44), (8,44), (8,8) (C) ( 8,8), (94,0), (94,44), (8,44), ( 8,8) (D) (0,0), (100,0), (100,50), (50,0), (0,0) 21. Which one of the following instruments is widely used to check and calibrate geometric features of machine tools during their assembly? (A) Ultrasonic probe (C) Laser interferometer (B) Coordinate Measuring Machine (CMM) (D) Vernier calipers 22. The major difficulty during welding of aluminium is due to its (A) high tendency of oxidation (C) low melting point (B) high thermal conductivity (D) low density 23. The main cutting force acting on a tool during the turning (orthogonal cutting) operation of a metal is 400 N. The turning was performed using 2 mm depth of cut and 0.1 mm/rev feed rate. The specific cutting pressure (in N/mm 2 ) is (A) 1000 (B) 2000 (C) 3000 (D) The process of reheating the martensitic steel to reduce its brittleness without any significant loss in its hardness is (A) normalising (B) annealing (C) quenching (D) tempering 25. In solid state welding, the contamination layers between the surfaces to be welded are removed by (A) alcohol (C) water jet (B) plastic deformation (D) sand blasting
7 26. The integral C ( ydx xdy ) is evaluated along the circle counter clockwise direction. The integral is equal to 2 x + y 2 1 = traversed in 4 (A) 0 π (B) 4 (C) π 2 π (D) If y = f(x) is the solution of 2 d y 0 2 dx = dy dx = 2 at x = 10, f(15) = with the boundary conditions y = 5 at x = 0, and 28. In the following table, x is a discrete random variable and p(x) density. The standard deviation of x is is the probability (A) 0.18 (B) 0.36 (C) 0.54 (D) Using the trapezoidal rule, and dividing the interval of integration into three equal subintervals, the definite integral + 1 x dx is The state of stress at a point is given by σ x = 6 MPa, σ y = 4 MPa, and τ xy = 8 MPa. The maximum tensile stress (in MPa) at the point is 31. A block R of mass 100 kg is placed on a block S of mass 150 kg as shown in the figure. Block R is tied to the wall by a mass less and inextensible string PQ. If the coefficient of static friction for all surfaces is 0.4, the minimum force F (in kn) needed to move the block S is
8 (A) 0.69 (B) 0.88 (C) 0.98 (D) A pair of spur gears with module 5 mm and a center distance of 450 mm is used for a speed reduction of 5:1. The number of teeth on pinionn is 33. Consider a cantilever beam, having negligible mass and uniform flexural rigidity, with length 0.01 m. The frequency of vibration of the beam, with a 0.5 kg mass attached at the free tip, is 100 Hz. The flexural rigidity (in N.m 2 ) of the beam is 34. An ideal water jet with volume flow rate of 0.05 m 3 /s strikes a flat plate placed normal to its path and exerts a force of 1000 N. Considering the density of water as 1000 kg/m 3, the diameter (in mm) of the water jet is 35. A block weighing 200 N is in contact with a level plane whose coefficients of static and kinetic friction are 0.4 and 0.2, respectively. The block is acted upon by a horizontal force (in newton) P = 10t, wheree t denotes the time in seconds. The velocity (in m/s) of the block attained after 10 seconds is 36. A slider crank mechanism m has slider mass of 10 kg, stroke of 0.2 m and rotates with a uniform angular velocity of 10 rad/s. The primary inertia forces of the slider are partially balanced by a revolving mass of 6 kg at the crank, placed at a distance equal to crank radius. Neglect the mass of connecting rod and crank. When the
9 crank angle (with respect to slider axis) is 30, the unbalanced normal to the slider axis is force (in newton) 37. An offset slider crank mechanism is shown in the figure at an instant. Conventionally, the Quick Return Ratio (QRR) is considered to be greater than one. The value of QRR is 38. A rigid uniform rod AB of length L and mass m is hinged at C such that AC = L/3, CB = 2L/ /3. Ends A and B are supported by springs of spring constant k. The natural frequency of the system is given by (A) k 2m (B) k m (C) 2k m (D) 5k m 39. A hydrodynamic journal bearing is subject to 2000 N load at a rotational speed of 2000 rpm. Both bearing bore diameter and length are 40 mm. If radial clearance is 20 µm and bearing is lubricated with an oil having viscosity 0.03 Pa.s, the Sommerfeld number of the bearing is
10 40. A 200 mm long, stresss free rod at room temperature is held between two immovable rigid walls. The temperature of the rod is uniformly raised by 250 C. If the Young s modulus and coefficient of thermal expansion are 200 GPa and / C, respectively, the magnitude of the longitudinal stress (in MPa) developed in the rod is kg of water is in saturated liquid state at 2 bar (v f = m 3 /kg, u f = kj/kg, h f = 505 kj/kg). Heat is added in a constant pressuree process till the temperature of water reaches 400 C (v = m 3 /kg, u = kj/ /kg, h = kj/kg). The heat added (in kj) in the process is 42. Consider one dimensiona al steady state heat conduction across a wall (as shown in figure below) of thickness 30 mm and thermal conductivity 15 W/m.K. At x = 0, a constant heat flux, q" = W/m 2 is applied. On the other side of the wall, heat is removed from the wall by convection with a fluid at 25 C and heat transfer coefficient of 250 W/m 2.K. The temperature (in C), at x = 0 is
11 43. Water flows through a pipe having an inner radius of 10 mm at the rate of 36 kg/hr at 25 C. The viscosity of water at 25 C is kg/m.s. The Reynolds number of the flow is 44. For a fully developed flow of water in a pipe having diameter 10 cm, velocity 0.1 m/s and kinematic viscosity 10 5 m 2 /s, the value of Darcy friction factor is 45. In a simple concentric shaft bearing arrangement, the lubricant flows in the 2 mm gap between the shaft and the bearing. The flow may be assumed to be a plane Couette flow with zero pressure gradient. The diameter of the shaft is 100 mm and its tangential speed is 10 m/s. The dynamic viscosity of the lubricant is 0.1 kg/m.s. The frictional resisting force (in newton) per 100 mm length of the bearing is 46. The non dimensional fluid temperature profile near the surface of a convectively TW T y y cooled flat plate is given by = a+ b + c T T L L W 2, where y is measured perpendicular to the plate, L is the plate length, and a, b and c are arbitrary constants. T W and T are wall and ambient temperatures, respectively. If the thermal conductivity of the fluid is k and the wall heat flux is q", the Nusselt number q" L Nu =. is equal to T T k W (A) a (B) b (C) 2c (D) (b + 2c) 47. In an air standard Otto cycle, air is supplied at 0.1 MPa and 308 K. The ratio of the specific heats (γ) and the specific gas constant (R) of air are 1.4 and J/kg.K, respectively. If the compression ratio is 8 and the maximum temperature in the cycle is 2660 K, the heat (in kj/kg) supplied to the engine is
12 48. A reversible heat enginee receives 2 kj of heat from a reservoirr at 1000 K and a certain amount of heat from a reservoir at 800 K. It rejects 1 kj of heat to a reservoir at 4000 K. The net work output (in kj) of the cycle is (A) 0.8 (B) 1.0 (C) 1.4 (D) An ideal reheat Rankine cycle operates between the pressure limits of 10 kpa and 8 MPa, with reheat being done at 4 MPa. The temperature of steam at the inlets of both turbines is 500 C and the enthalpy of steam is 3185 kj/kg at the exit of the high pressure turbine and 2247 kj/kg at the exit of low pressure turbine. The enthalpy of water at the exit from the pumpp is 191 kj/kg. Use the following table for relevant data. Disregarding the pump work, the cycle efficiency (in percentage) is 50. Jobs arrive at a facility at an average rate of 5 in an 8 hour shift. The arrival of the jobs follows Poisson distribution. The averagee service time of a job on the facility is 40 minutes. The service time follows exponential distribution. Idle time (in hours) at the facility per shift will be (A) 5 7 (B) 14 3 (C) 7 5 (D) A metal rod of initial length L 0 is subjected to a drawing process. The length of the rod at any instant is given by the expression, L(t) = L 0 (1 + t 2 ), where t is the time in minutes. The true strain rate (in min 1 ) at the end of one minute is
13 52. During pure orthogonal turning operation of a hollow cylindrical pipe, it is found that the thickness of the chip produced is 0.5 mm. The feed given to the zero degree rake angle tool is 0.2 mm/rev. The shear strain produced during the operation is 53. For the given assembly: 25 H7/g8, match Group A with Group B (A) P I, Q III, R IV, S II (C) P II, Q III, R IV, S I (B) P I, Q IV, R III, S II (D) P II, Q IV, R III, S I 54. If the Taylor s tool life exponent n is 0.2, and the tool changing time is 1.5 min, then the tool life (in min) for maximum production rate is 55. An aluminium alloy (density 2600 kg/m 3 ) casting is to be produced. A cylindrical hole of 100 mmm diameter and 1000 mm length is made in the casting using sand core (density 1600 kg/m 3 ). The net buoyancy force (in newton) acting on the core is
14 Key for Excerise 1 Q.NO Key/ Range 1 A 2 A 3 C 4 A 5 B 6 C to B 9 A 10 D 11 D 12 B 13 C 14 B 15 A 16 D 17 C 18 B 19 B 20 A 21 C 22 A 23 B 24 A 25 B 26 C to D to to D to to to to to to D to to to to to to to B to C to B to to D to to 8
Set 2 (d) 150 C (a) 0.45 (d) can be positive, negative or zero (C) 8.5 J/K (a) 0.1
 Set 2 1. In a new temperature scale say o p, the boiling and freezing points of water at one atmosphere are 100 p and 300 p respectively. Correlate this scale with the Centigrade scale. The reading of
Set 2 1. In a new temperature scale say o p, the boiling and freezing points of water at one atmosphere are 100 p and 300 p respectively. Correlate this scale with the Centigrade scale. The reading of
Set 1. a. 100 kj/kg b. 110 kj/kg c. 140 kj/kg d. 150 kj/kg
 Set 1 1. Two blocks which are at different states are brought into contact with each other and allowed to reach a final state of thermal equilibrium. The final temperature attained is specified by the
Set 1 1. Two blocks which are at different states are brought into contact with each other and allowed to reach a final state of thermal equilibrium. The final temperature attained is specified by the
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 At least one eigenvalue of a singular matrix is (A) positive (B) zero (C) negative (D) imaginary Q. At x = 0, the function f( x) = x has (A) a minimum (C) a point of
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 At least one eigenvalue of a singular matrix is (A) positive (B) zero (C) negative (D) imaginary Q. At x = 0, the function f( x) = x has (A) a minimum (C) a point of
PES Institute of Technology
 PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
PES Institute of Technology Bangalore south campus, Bangalore-5460100 Department of Mechanical Engineering Faculty name : Madhu M Date: 29/06/2012 SEM : 3 rd A SEC Subject : MECHANICS OF MATERIALS Subject
This equation of motion may be solved either by differential equation method or by graphical method as discussed below:
 2.15. Frequency of Under Damped Forced Vibrations Consider a system consisting of spring, mass and damper as shown in Fig. 22. Let the system is acted upon by an external periodic (i.e. simple harmonic)
2.15. Frequency of Under Damped Forced Vibrations Consider a system consisting of spring, mass and damper as shown in Fig. 22. Let the system is acted upon by an external periodic (i.e. simple harmonic)
LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR.
 LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR. IBIKUNLE ROTIMI ADEDAYO SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION. Introduction Consider
LANMARK UNIVERSITY OMU-ARAN, KWARA STATE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MECHANICS OF MACHINE (MCE 322). LECTURER: ENGR. IBIKUNLE ROTIMI ADEDAYO SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION. Introduction Consider
General Aptitude (GA) Set-1. The words that best fill the blanks in the above sentence are.
 GATE 2018 General Aptitude (GA) Set-1 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Going by the that many hands make light work, the school involved all the students in the task. The words that best fill the blanks
GATE 2018 General Aptitude (GA) Set-1 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Going by the that many hands make light work, the school involved all the students in the task. The words that best fill the blanks
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering 6% 15% 13% 3% 8% Engineering Mathematics Engineering Mechanics Mechanics of Materials Theory Of Machines Machine Design Fluid Mechanics 19% 8%
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 For the given fluctuating fatigue load, the values of stress amplitude and stress ratio are respectively MPa 250 200 150 100 50 0 Time (A) 100 MPa and 5 (B) 250 MPa
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 For the given fluctuating fatigue load, the values of stress amplitude and stress ratio are respectively MPa 250 200 150 100 50 0 Time (A) 100 MPa and 5 (B) 250 MPa
R13. II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) PART-A
 SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SET - 1 II B. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, Jan - 2015 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, AE, MTE) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Note: 1. Question Paper consists of two parts (Part-A and Part-B)
SRI CHANDRASEKHARENDRA SARASWATHI VISWA MAHAVIDHYALAYA
 SRI CHANDRASEKHARENDRA SARASWATHI VISWA MAHAVIDHYALAYA (Declared as Deemed-to-be University under Section 3 of the UGC Act, 1956, Vide notification No.F.9.9/92-U-3 dated 26 th May 1993 of the Govt. of
SRI CHANDRASEKHARENDRA SARASWATHI VISWA MAHAVIDHYALAYA (Declared as Deemed-to-be University under Section 3 of the UGC Act, 1956, Vide notification No.F.9.9/92-U-3 dated 26 th May 1993 of the Govt. of
Downloaded from Downloaded from / 1
 PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY III SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2002 LEVEL : B. E. (Civil) SUBJECT: BEG256CI, Strength of Material Full Marks: 80 TIME: 03:00 hrs Pass marks: 32 Candidates are required to give their
PURWANCHAL UNIVERSITY III SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2002 LEVEL : B. E. (Civil) SUBJECT: BEG256CI, Strength of Material Full Marks: 80 TIME: 03:00 hrs Pass marks: 32 Candidates are required to give their
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical Engineering
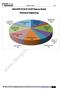 ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
ANALYSIS OF GATE 2018*(Memory Based) Mechanical ME Industrial 4% General Aptitude 15% Mathematics 14% Mechanics 4% Manufacturing 14% Mechanics of Materials 14% Thermodynamics 10% Heat Transfer 2% Fluid
Figure 1 Answer: = m
 Q1. Figure 1 shows a solid cylindrical steel rod of length =.0 m and diameter D =.0 cm. What will be increase in its length when m = 80 kg block is attached to its bottom end? (Young's modulus of steel
Q1. Figure 1 shows a solid cylindrical steel rod of length =.0 m and diameter D =.0 cm. What will be increase in its length when m = 80 kg block is attached to its bottom end? (Young's modulus of steel
If there is convective heat transfer from outer surface to fluid maintained at T W.
 Heat Transfer 1. What are the different modes of heat transfer? Explain with examples. 2. State Fourier s Law of heat conduction? Write some of their applications. 3. State the effect of variation of temperature
Heat Transfer 1. What are the different modes of heat transfer? Explain with examples. 2. State Fourier s Law of heat conduction? Write some of their applications. 3. State the effect of variation of temperature
AE302,ME302,DAE14,DME14
 AE302,ME302,DAE14,DME14 III SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION, JANUARY-2013 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY-I Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 75 GROUP A : Answer any three questions. (Question No. 1 is compulsory) Q.1 What
AE302,ME302,DAE14,DME14 III SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION, JANUARY-2013 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY-I Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 75 GROUP A : Answer any three questions. (Question No. 1 is compulsory) Q.1 What
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS
 BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
BME-A PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTIONS CREDITS CHANGE ACCHA HAI TEAM UNIT-1 Introduction: Introduction to Thermodynamics, Concepts of systems, control volume, state, properties, equilibrium, quasi-static process,
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown.
 D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
D : SOLID MECHANICS Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. Q.1 Find the force (in kn) in the member BH of the truss shown. Q.2 Consider the forces of magnitude F acting on the sides of the regular hexagon having
SILVER OAK COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY ADITYA SILVER OAK INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
 SUBJECT: ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (2131905) (ME) DATE: 11-08-2017 TIME: 10:00 am to 11:30 am TOTAL MARKS: 40 Q.1 (a) Answer following questions in short/brief: 1. Energy of an isolated system is always
SUBJECT: ENGINEERING THERMODYNAMICS (2131905) (ME) DATE: 11-08-2017 TIME: 10:00 am to 11:30 am TOTAL MARKS: 40 Q.1 (a) Answer following questions in short/brief: 1. Energy of an isolated system is always
UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL 4.1 INTRODUCTION 4.2 DYNAMICALLY EQUIVALENT SYSTEM. Structure. Objectives. 4.1 Introduction
 UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4. Dynamically Equivalent System 4.3 Turning Moment Diagram 4.3.1 Turning Moment Diagram of a Single Cylinder 4-storke IC Engine 4.3. Turning Moment
UNIT 4 FLYWHEEL Structure 4.1 Introduction Objectives 4. Dynamically Equivalent System 4.3 Turning Moment Diagram 4.3.1 Turning Moment Diagram of a Single Cylinder 4-storke IC Engine 4.3. Turning Moment
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State Hooke s law. 3. Define modular ratio,
D : SOLID MECHANICS. Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each.
 GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
GTE 2016 Q. 1 Q. 9 carry one mark each. D : SOLID MECHNICS Q.1 single degree of freedom vibrating system has mass of 5 kg, stiffness of 500 N/m and damping coefficient of 100 N-s/m. To make the system
SN QUESTION YEAR MARK 1. State and prove the relationship between shearing stress and rate of change of bending moment at a section in a loaded beam.
 ALPHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (21000) ASSIGNMENT 1 SIMPLE STRESSES AND STRAINS SN QUESTION YEAR MARK 1 State and prove the relationship
ALPHA COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (21000) ASSIGNMENT 1 SIMPLE STRESSES AND STRAINS SN QUESTION YEAR MARK 1 State and prove the relationship
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5
 COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPICS PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4017 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/WEEK : 6 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 108 CREDITS : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPICS PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
Answers to questions in each section should be tied together and handed in separately.
 EGT0 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IA Wednesday 4 June 014 9 to 1 Paper 1 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Answer all questions. The approximate number of marks allocated to each part of a question is indicated in the
EGT0 ENGINEERING TRIPOS PART IA Wednesday 4 June 014 9 to 1 Paper 1 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Answer all questions. The approximate number of marks allocated to each part of a question is indicated in the
Tuesday, February 11, Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis. Dr. Mohammad Suliman Abuhaiba, PE
 1 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Chapter Outline Equilibrium & Free-Body Diagrams Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Singularity Functions Stress Cartesian Stress Components Mohr s Circle for
1 Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2 Chapter Outline Equilibrium & Free-Body Diagrams Shear Force and Bending Moments in Beams Singularity Functions Stress Cartesian Stress Components Mohr s Circle for
Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics
 1896 1920 1987 2006 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA235) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & Civil Engineering First Assignment The first
1896 1920 1987 2006 Introduction to Marine Hydrodynamics (NA235) Department of Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering School of Naval Architecture, Ocean & Civil Engineering First Assignment The first
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy
 Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
Stress Analysis Lecture 3 ME 276 Spring 2017-2018 Dr./ Ahmed Mohamed Nagib Elmekawy Axial Stress 2 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 3 Beam under the action of two tensile forces 4 Shear Stress
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 009 Mechanical
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 009 Mechanical
The University of Melbourne Engineering Mechanics
 The University of Melbourne 436-291 Engineering Mechanics Tutorial Four Poisson s Ratio and Axial Loading Part A (Introductory) 1. (Problem 9-22 from Hibbeler - Statics and Mechanics of Materials) A short
The University of Melbourne 436-291 Engineering Mechanics Tutorial Four Poisson s Ratio and Axial Loading Part A (Introductory) 1. (Problem 9-22 from Hibbeler - Statics and Mechanics of Materials) A short
QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SEMESTER: III SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A
 DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
DEPARTMENT: CIVIL SUBJECT CODE: CE2201 QUESTION BANK SEMESTER: III SUBJECT NAME: MECHANICS OF SOLIDS UNIT 1- STRESS AND STRAIN PART A (2 Marks) 1. Define longitudinal strain and lateral strain. 2. State
Figure 3: Problem 7. (a) 0.9 m (b) 1.8 m (c) 2.7 m (d) 3.6 m
 1. For the manometer shown in figure 1, if the absolute pressure at point A is 1.013 10 5 Pa, the absolute pressure at point B is (ρ water =10 3 kg/m 3, ρ Hg =13.56 10 3 kg/m 3, ρ oil = 800kg/m 3 ): (a)
1. For the manometer shown in figure 1, if the absolute pressure at point A is 1.013 10 5 Pa, the absolute pressure at point B is (ρ water =10 3 kg/m 3, ρ Hg =13.56 10 3 kg/m 3, ρ oil = 800kg/m 3 ): (a)
2014 MECHANICS OF MATERIALS
 R10 SET - 1 II. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, March 2014 MEHNIS OF MTERILS (ivil Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 nswer any FIVE Questions ll Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
R10 SET - 1 II. Tech I Semester Regular Examinations, March 2014 MEHNIS OF MTERILS (ivil Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 nswer any FIVE Questions ll Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
ME3560 Tentative Schedule Spring 2019
 ME3560 Tentative Schedule Spring 2019 Week Number Date Lecture Topics Covered Prior to Lecture Read Section Assignment Prep Problems for Prep Probs. Must be Solved by 1 Monday 1/7/2019 1 Introduction to
ME3560 Tentative Schedule Spring 2019 Week Number Date Lecture Topics Covered Prior to Lecture Read Section Assignment Prep Problems for Prep Probs. Must be Solved by 1 Monday 1/7/2019 1 Introduction to
Sub. Code:
 Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. ) The model answer and the answer written by candidate may
Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. ) The model answer and the answer written by candidate may
1. Choose answer and indicate by writing only the corresponding capital letter (A, B, C, D) as the case may be).
 1. Choose answer and indicate by writing only the corresponding capital letter (A, B, C, D) as the case may be). 1.1 The manufacturing area of a plat is divided into four quadrants. Four machines have
1. Choose answer and indicate by writing only the corresponding capital letter (A, B, C, D) as the case may be). 1.1 The manufacturing area of a plat is divided into four quadrants. Four machines have
9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
 9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Deforming force Deforming force is the force which changes the shape or size of a body. Restoring force Restoring force is the internal force developed inside the body
9 MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS Deforming force Deforming force is the force which changes the shape or size of a body. Restoring force Restoring force is the internal force developed inside the body
UNIT-I STRESS, STRAIN. 1. A Member A B C D is subjected to loading as shown in fig determine the total elongation. Take E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2
 UNIT-I STRESS, STRAIN 1. A Member A B C D is subjected to loading as shown in fig determine the total elongation. Take E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2 Young s modulus E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2 Area1=900mm 2 Area2=400mm 2 Area3=625mm
UNIT-I STRESS, STRAIN 1. A Member A B C D is subjected to loading as shown in fig determine the total elongation. Take E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2 Young s modulus E= 2 x10 5 N/mm 2 Area1=900mm 2 Area2=400mm 2 Area3=625mm
ME3560 Tentative Schedule Fall 2018
 ME3560 Tentative Schedule Fall 2018 Week Number 1 Wednesday 8/29/2018 1 Date Lecture Topics Covered Introduction to course, syllabus and class policies. Math Review. Differentiation. Prior to Lecture Read
ME3560 Tentative Schedule Fall 2018 Week Number 1 Wednesday 8/29/2018 1 Date Lecture Topics Covered Introduction to course, syllabus and class policies. Math Review. Differentiation. Prior to Lecture Read
The problem of transmitting a torque or rotary motion from one plane to another is frequently encountered in machine design.
 CHAPER ORSION ORSION orsion refers to the twisting of a structural member when it is loaded by moments/torques that produce rotation about the longitudinal axis of the member he problem of transmitting
CHAPER ORSION ORSION orsion refers to the twisting of a structural member when it is loaded by moments/torques that produce rotation about the longitudinal axis of the member he problem of transmitting
3 Hours/100 Marks Seat No.
 *17304* 17304 14115 3 Hours/100 Marks Seat No. Instructions : (1) All questions are compulsory. (2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (3) Figures to the right indicate full
*17304* 17304 14115 3 Hours/100 Marks Seat No. Instructions : (1) All questions are compulsory. (2) Illustrate your answers with neat sketches wherever necessary. (3) Figures to the right indicate full
NAME: Given Formulae: Law of Cosines: Law of Sines:
 NME: Given Formulae: Law of Cosines: EXM 3 PST PROBLEMS (LESSONS 21 TO 28) 100 points Thursday, November 16, 2017, 7pm to 9:30, Room 200 You are allowed to use a calculator and drawing equipment, only.
NME: Given Formulae: Law of Cosines: EXM 3 PST PROBLEMS (LESSONS 21 TO 28) 100 points Thursday, November 16, 2017, 7pm to 9:30, Room 200 You are allowed to use a calculator and drawing equipment, only.
: APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE
 COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
COURSE TITLE : APPLIED MECHANICS & STRENGTH OF MATERIALS COURSE CODE : 4021 COURSE CATEGORY : A PERIODS/ WEEK : 5 PERIODS/ SEMESTER : 75 CREDIT : 5 TIME SCHEDULE MODULE TOPIC PERIODS 1 Simple stresses
PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [ ] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics
![PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [ ] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [ ] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics](/thumbs/92/109382806.jpg) Page1 PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [2910601] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics 1. Differentiate between Scalar and Vector quantity. Write S.I.
Page1 PDDC 1 st Semester Civil Engineering Department Assignments of Mechanics of Solids [2910601] Introduction, Fundamentals of Statics 1. Differentiate between Scalar and Vector quantity. Write S.I.
Grade XI. Physics Exam Preparation Booklet. Chapter-wise Important Questions. #GrowWithGreen
 Grade XI Physics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter-wise Important Questions #GrowWithGreen Units and Measurements Q1. After reading the physics book, Anamika recalled and noted down the expression for the
Grade XI Physics Exam Preparation Booklet Chapter-wise Important Questions #GrowWithGreen Units and Measurements Q1. After reading the physics book, Anamika recalled and noted down the expression for the
MARKS DISTRIBUTION AS PER CHAPTER (QUESTION ASKED IN GTU EXAM) Name Of Chapter. Applications of. Friction. Centroid & Moment.
 Introduction Fundamentals of statics Applications of fundamentals of statics Friction Centroid & Moment of inertia Simple Stresses & Strain Stresses in Beam Torsion Principle Stresses DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL
Introduction Fundamentals of statics Applications of fundamentals of statics Friction Centroid & Moment of inertia Simple Stresses & Strain Stresses in Beam Torsion Principle Stresses DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL
[5] Stress and Strain
![[5] Stress and Strain [5] Stress and Strain](/thumbs/95/123344550.jpg) [5] Stress and Strain Page 1 of 34 [5] Stress and Strain [5.1] Internal Stress of Solids [5.2] Design of Simple Connections (will not be covered in class) [5.3] Deformation and Strain [5.4] Hooke s Law
[5] Stress and Strain Page 1 of 34 [5] Stress and Strain [5.1] Internal Stress of Solids [5.2] Design of Simple Connections (will not be covered in class) [5.3] Deformation and Strain [5.4] Hooke s Law
1. What would be the value of F1 to balance the system if F2=20N? 20cm T =? 20kg
 1. What would be the value of F1 to balance the system if F2=20N? F2 5cm 20cm F1 (a) 3 N (b) 5 N (c) 4N (d) None of the above 2. The stress in a wire of diameter 2 mm, if a load of 100 gram is applied
1. What would be the value of F1 to balance the system if F2=20N? F2 5cm 20cm F1 (a) 3 N (b) 5 N (c) 4N (d) None of the above 2. The stress in a wire of diameter 2 mm, if a load of 100 gram is applied
MAAE 2202 A. Come to the PASS workshop with your mock exam complete. During the workshop you can work with other students to review your work.
 It is most beneficial to you to write this mock final exam UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the exam in 3 hours. Work on your own. Keep your textbook closed. Attempt every question. After the
It is most beneficial to you to write this mock final exam UNDER EXAM CONDITIONS. This means: Complete the exam in 3 hours. Work on your own. Keep your textbook closed. Attempt every question. After the
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 231) Problems on Heat Transfer
 Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 1) Problems on Heat Transfer 1. What is the thermal conductivity of a material 8 cm thick if the temperature at one end of the product is 0 C and the temperature
Principles of Food and Bioprocess Engineering (FS 1) Problems on Heat Transfer 1. What is the thermal conductivity of a material 8 cm thick if the temperature at one end of the product is 0 C and the temperature
2012 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS
 R10 SET - 1 II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
R10 SET - 1 II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, April 2012 MECHANICS OF SOLIDS (Com. to ME, AME, MM) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
DYNAMICS ME HOMEWORK PROBLEM SETS
 DYNAMICS ME 34010 HOMEWORK PROBLEM SETS Mahmoud M. Safadi 1, M.B. Rubin 2 1 safadi@technion.ac.il, 2 mbrubin@technion.ac.il Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology Spring
DYNAMICS ME 34010 HOMEWORK PROBLEM SETS Mahmoud M. Safadi 1, M.B. Rubin 2 1 safadi@technion.ac.il, 2 mbrubin@technion.ac.il Faculty of Mechanical Engineering Technion Israel Institute of Technology Spring
Class XI Physics Syllabus One Paper Three Hours Max Marks: 70
 Class XI Physics Syllabus 2013 One Paper Three Hours Max Marks: 70 Class XI Weightage Unit I Physical World & Measurement 03 Unit II Kinematics 10 Unit III Laws of Motion 10 Unit IV Work, Energy & Power
Class XI Physics Syllabus 2013 One Paper Three Hours Max Marks: 70 Class XI Weightage Unit I Physical World & Measurement 03 Unit II Kinematics 10 Unit III Laws of Motion 10 Unit IV Work, Energy & Power
EMA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 3 Torsion
 EMA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 3 Torsion Introduction Stress and strain in components subjected to torque T Circular Cross-section shape Material Shaft design Non-circular
EMA 3702 Mechanics & Materials Science (Mechanics of Materials) Chapter 3 Torsion Introduction Stress and strain in components subjected to torque T Circular Cross-section shape Material Shaft design Non-circular
FE Fluids Review March 23, 2012 Steve Burian (Civil & Environmental Engineering)
 Topic: Fluid Properties 1. If 6 m 3 of oil weighs 47 kn, calculate its specific weight, density, and specific gravity. 2. 10.0 L of an incompressible liquid exert a force of 20 N at the earth s surface.
Topic: Fluid Properties 1. If 6 m 3 of oil weighs 47 kn, calculate its specific weight, density, and specific gravity. 2. 10.0 L of an incompressible liquid exert a force of 20 N at the earth s surface.
NORMAL STRESS. The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts.
 NORMAL STRESS The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts. σ = force/area = P/A where σ = the normal stress P = the centric
NORMAL STRESS The simplest form of stress is normal stress/direct stress, which is the stress perpendicular to the surface on which it acts. σ = force/area = P/A where σ = the normal stress P = the centric
ROTATING RING. Volume of small element = Rdθbt if weight density of ring = ρ weight of small element = ρrbtdθ. Figure 1 Rotating ring
 ROTATIONAL STRESSES INTRODUCTION High centrifugal forces are developed in machine components rotating at a high angular speed of the order of 100 to 500 revolutions per second (rps). High centrifugal force
ROTATIONAL STRESSES INTRODUCTION High centrifugal forces are developed in machine components rotating at a high angular speed of the order of 100 to 500 revolutions per second (rps). High centrifugal force
SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. Paper II. Please read each of the following instructions carefully before attempting questions.
 We RoU No. 700095 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time ; 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 0 Instructions
We RoU No. 700095 Candidate should write his/her Roll No. here. Total No. of Questions : 7 No. of Printed Pages : 7 SEM-2017(03HI MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Paper II Time ; 3 Hours ] [ Total Marks : 0 Instructions
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING BRANCH: MECHANICAL YEAR / SEMESTER: I / II UNIT 1 PART- A 1. State Newton's three laws of motion? 2.
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING BRANCH: MECHANICAL YEAR / SEMESTER: I / II UNIT 1 PART- A 1. State Newton's three laws of motion? 2.
3. Kinetics of Particles
 3. Kinetics of Particles 3.1 Force, Mass and Acceleration 3.3 Impulse and Momentum 3.4 Impact 1 3.1 Force, Mass and Acceleration We draw two important conclusions from the results of the experiments. First,
3. Kinetics of Particles 3.1 Force, Mass and Acceleration 3.3 Impulse and Momentum 3.4 Impact 1 3.1 Force, Mass and Acceleration We draw two important conclusions from the results of the experiments. First,
ISHIK UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING
 ISHIK UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK FOR THE MECHANICS OF MATERIALS-I 1. A rod 150 cm long and of diameter 2.0 cm is subjected to an axial pull of 20 kn. If the modulus
ISHIK UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF MECHATRONICS ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK FOR THE MECHANICS OF MATERIALS-I 1. A rod 150 cm long and of diameter 2.0 cm is subjected to an axial pull of 20 kn. If the modulus
Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each.
 GATE 2016 General Aptitude GA Set-7 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 If I were you, I that laptop. It s much too expensive. (A) won t buy (C) wouldn t buy (B) shan t buy (D) would buy Q.2 He turned a
GATE 2016 General Aptitude GA Set-7 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 If I were you, I that laptop. It s much too expensive. (A) won t buy (C) wouldn t buy (B) shan t buy (D) would buy Q.2 He turned a
STRESS, STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS
 VELAMMAL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, MADURAI 625009 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING CE8301 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS I -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
VELAMMAL COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, MADURAI 625009 DEPARTMENT OF CIVIL ENGINEERING CE8301 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS I -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Physics 201 Midterm Exam 3
 Physics 201 Midterm Exam 3 Information and Instructions Student ID Number: Section Number: TA Name: Please fill in all the information above. Please write and bubble your Name and Student Id number on
Physics 201 Midterm Exam 3 Information and Instructions Student ID Number: Section Number: TA Name: Please fill in all the information above. Please write and bubble your Name and Student Id number on
GATE 2009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper
 GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper. For a matrix [M]= x [M]. The value of x is given by GATE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING 009 (ME) GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper Q. No. 0 Carry One
GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper. For a matrix [M]= x [M]. The value of x is given by GATE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING 009 (ME) GATE 009 Mechanical Engineering Question Paper Q. No. 0 Carry One
Structural Analysis I Chapter 4 - Torsion TORSION
 ORSION orsional stress results from the action of torsional or twisting moments acting about the longitudinal axis of a shaft. he effect of the application of a torsional moment, combined with appropriate
ORSION orsional stress results from the action of torsional or twisting moments acting about the longitudinal axis of a shaft. he effect of the application of a torsional moment, combined with appropriate
cos(θ)sin(θ) Alternative Exercise Correct Correct θ = 0 skiladæmi 10 Part A Part B Part C Due: 11:59pm on Wednesday, November 11, 2015
 skiladæmi 10 Due: 11:59pm on Wednesday, November 11, 015 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due Grading Policy Alternative Exercise 1115 A bar with cross sectional
skiladæmi 10 Due: 11:59pm on Wednesday, November 11, 015 You will receive no credit for items you complete after the assignment is due Grading Policy Alternative Exercise 1115 A bar with cross sectional
1. Replace the given system of forces acting on a body as shown in figure 1 by a single force and couple acting at the point A.
 Code No: Z0321 / R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech - Regular Examinations, June 2009 CLASSICAL MECHANICS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile
Code No: Z0321 / R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech - Regular Examinations, June 2009 CLASSICAL MECHANICS ( Common to Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Mechatronics, Production Engineering and Automobile
(Following Paper ID and Roll No. to be filled in your Answer Book) I I I I I. B.Tech. SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION,
 - Printed Pages - 6 TME - 201 (Following Paper ID and Roll No. to be filled in your Answer Book) I I I I I Roll No. B.Tech. SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION, 2005-2006 '-" Time: 3 Hours oa:::::t U') om (D om
- Printed Pages - 6 TME - 201 (Following Paper ID and Roll No. to be filled in your Answer Book) I I I I I Roll No. B.Tech. SECOND SEMESTER EXAMINATION, 2005-2006 '-" Time: 3 Hours oa:::::t U') om (D om
General Aptitude - GA Set-3. Q.1 Based on the given statements, select the appropriate option with respect to grammar and usage.
 GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-3 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Based on the given statements, select the appropriate option with respect to grammar and usage. Statements (i) (ii) The height of
GATE 2016 General Aptitude - GA Set-3 Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Based on the given statements, select the appropriate option with respect to grammar and usage. Statements (i) (ii) The height of
Civil Services Examination-1989
 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PAPER I Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum marks: 300 INSTRUCTIONS Each question is printed both in Hindi and in English. Answers must be written in the, medium specified in the Admission.
MECHANICAL ENGINEERING PAPER I Time allowed: 3 hours Maximum marks: 300 INSTRUCTIONS Each question is printed both in Hindi and in English. Answers must be written in the, medium specified in the Admission.
(48) CHAPTER 3: TORSION
 (48) CHAPTER 3: TORSION Introduction: In this chapter structural members and machine parts that are in torsion will be considered. More specifically, you will analyze the stresses and strains in members
(48) CHAPTER 3: TORSION Introduction: In this chapter structural members and machine parts that are in torsion will be considered. More specifically, you will analyze the stresses and strains in members
C7047. PART A Answer all questions, each carries 5 marks.
 7047 Reg No.: Total Pages: 3 Name: Max. Marks: 100 PJ DUL KLM TEHNOLOGIL UNIVERSITY FIRST SEMESTER.TEH DEGREE EXMINTION, DEEMER 2017 ourse ode: E100 ourse Name: ENGINEERING MEHNIS PRT nswer all questions,
7047 Reg No.: Total Pages: 3 Name: Max. Marks: 100 PJ DUL KLM TEHNOLOGIL UNIVERSITY FIRST SEMESTER.TEH DEGREE EXMINTION, DEEMER 2017 ourse ode: E100 ourse Name: ENGINEERING MEHNIS PRT nswer all questions,
DIVIDED SYLLABUS ( ) - CLASS XI PHYSICS (CODE 042) COURSE STRUCTURE APRIL
 DIVIDED SYLLABUS (2015-16 ) - CLASS XI PHYSICS (CODE 042) COURSE STRUCTURE APRIL Unit I: Physical World and Measurement Physics Need for measurement: Units of measurement; systems of units; SI units, fundamental
DIVIDED SYLLABUS (2015-16 ) - CLASS XI PHYSICS (CODE 042) COURSE STRUCTURE APRIL Unit I: Physical World and Measurement Physics Need for measurement: Units of measurement; systems of units; SI units, fundamental
18.Define the term modulus of resilience. May/June Define Principal Stress. 20. Define Hydrostatic Pressure.
 CE6306 STREGNTH OF MATERIALS Question Bank Unit-I STRESS, STRAIN, DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART-A 1. Define Poison s Ratio May/June 2009 2. What is thermal stress? May/June 2009 3. Estimate the load carried
CE6306 STREGNTH OF MATERIALS Question Bank Unit-I STRESS, STRAIN, DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS PART-A 1. Define Poison s Ratio May/June 2009 2. What is thermal stress? May/June 2009 3. Estimate the load carried
Chapter 12. Static Equilibrium and Elasticity
 Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Static Equilibrium Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial
Chapter 12 Static Equilibrium and Elasticity Static Equilibrium Equilibrium implies that the object moves with both constant velocity and constant angular velocity relative to an observer in an inertial
Strength of Material. Shear Strain. Dr. Attaullah Shah
 Strength of Material Shear Strain Dr. Attaullah Shah Shear Strain TRIAXIAL DEFORMATION Poisson's Ratio Relationship Between E, G, and ν BIAXIAL DEFORMATION Bulk Modulus of Elasticity or Modulus of Volume
Strength of Material Shear Strain Dr. Attaullah Shah Shear Strain TRIAXIAL DEFORMATION Poisson's Ratio Relationship Between E, G, and ν BIAXIAL DEFORMATION Bulk Modulus of Elasticity or Modulus of Volume
Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section at C of the beam shown in Fig. 1 4a.
 E X M P L E 1.1 Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section at of the beam shown in Fig. 1 a. 70 N/m m 6 m Fig. 1 Support Reactions. This problem can be solved in the most direct
E X M P L E 1.1 Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross section at of the beam shown in Fig. 1 a. 70 N/m m 6 m Fig. 1 Support Reactions. This problem can be solved in the most direct
Strength of Materials (15CV 32)
 Strength of Materials (15CV 32) Module 1 : Simple Stresses and Strains Dr. H. Ananthan, Professor, VVIET,MYSURU 8/21/2017 Introduction, Definition and concept and of stress and strain. Hooke s law, Stress-Strain
Strength of Materials (15CV 32) Module 1 : Simple Stresses and Strains Dr. H. Ananthan, Professor, VVIET,MYSURU 8/21/2017 Introduction, Definition and concept and of stress and strain. Hooke s law, Stress-Strain
CIVL222 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS. Chapter 6. Torsion
 CIVL222 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Chapter 6 Torsion Definition Torque is a moment that tends to twist a member about its longitudinal axis. Slender members subjected to a twisting load are said to be in torsion.
CIVL222 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Chapter 6 Torsion Definition Torque is a moment that tends to twist a member about its longitudinal axis. Slender members subjected to a twisting load are said to be in torsion.
UNIT I Basic concepts and Work & Heat Transfer
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Engineering Thermodynamics (16ME307) Year & Sem: II-B. Tech & II-Sem
[7] Torsion. [7.1] Torsion. [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion. [7] Torsion Page 1 of 21
![[7] Torsion. [7.1] Torsion. [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion. [7] Torsion Page 1 of 21 [7] Torsion. [7.1] Torsion. [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion. [7] Torsion Page 1 of 21](/thumbs/88/115835122.jpg) [7] Torsion Page 1 of 21 [7] Torsion [7.1] Torsion [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion [7] Torsion Page 2 of 21 [7.1] Torsion SHEAR STRAIN DUE TO TORSION 1) A shaft with a circular cross section is
[7] Torsion Page 1 of 21 [7] Torsion [7.1] Torsion [7.2] Statically Indeterminate Torsion [7] Torsion Page 2 of 21 [7.1] Torsion SHEAR STRAIN DUE TO TORSION 1) A shaft with a circular cross section is
Sliding Contact Bearings
 Sliding Contact Bearings Classification of Bearings 1. According to the direction of load to be supported. The bearings under this group are classified as: (a) Radial bearings (b) Thrust bearings. In radial
Sliding Contact Bearings Classification of Bearings 1. According to the direction of load to be supported. The bearings under this group are classified as: (a) Radial bearings (b) Thrust bearings. In radial
Principles of Convection
 Principles of Convection Point Conduction & convection are similar both require the presence of a material medium. But convection requires the presence of fluid motion. Heat transfer through the: Solid
Principles of Convection Point Conduction & convection are similar both require the presence of a material medium. But convection requires the presence of fluid motion. Heat transfer through the: Solid
Direct and Shear Stress
 Direct and Shear Stress 1 Direct & Shear Stress When a body is pulled by a tensile force or crushed by a compressive force, the loading is said to be direct. Direct stresses are also found to arise when
Direct and Shear Stress 1 Direct & Shear Stress When a body is pulled by a tensile force or crushed by a compressive force, the loading is said to be direct. Direct stresses are also found to arise when
Heat Transfer Analysis of Machine Tool Main Spindle
 Technical Paper Heat Transfer Analysis of Machine Tool Main Spindle oshimitsu HIRASAWA Yukimitsu YAMAMOTO CAE analysis is very useful for shortening development time and reducing the need for development
Technical Paper Heat Transfer Analysis of Machine Tool Main Spindle oshimitsu HIRASAWA Yukimitsu YAMAMOTO CAE analysis is very useful for shortening development time and reducing the need for development
Consider a control volume in the form of a straight section of a streamtube ABCD.
 6 MOMENTUM EQUATION 6.1 Momentum and Fluid Flow In mechanics, the momentum of a particle or object is defined as the product of its mass m and its velocity v: Momentum = mv The particles of a fluid stream
6 MOMENTUM EQUATION 6.1 Momentum and Fluid Flow In mechanics, the momentum of a particle or object is defined as the product of its mass m and its velocity v: Momentum = mv The particles of a fluid stream
PHYSICS. Course Structure. Unit Topics Marks. Physical World and Measurement. 1 Physical World. 2 Units and Measurements.
 PHYSICS Course Structure Unit Topics Marks I Physical World and Measurement 1 Physical World 2 Units and Measurements II Kinematics 3 Motion in a Straight Line 23 4 Motion in a Plane III Laws of Motion
PHYSICS Course Structure Unit Topics Marks I Physical World and Measurement 1 Physical World 2 Units and Measurements II Kinematics 3 Motion in a Straight Line 23 4 Motion in a Plane III Laws of Motion
Entrance exam Master Course
 - 1 - Guidelines for completion of test: On each page, fill in your name and your application code Each question has four answers while only one answer is correct. o Marked correct answer means 4 points
- 1 - Guidelines for completion of test: On each page, fill in your name and your application code Each question has four answers while only one answer is correct. o Marked correct answer means 4 points
1. A pure shear deformation is shown. The volume is unchanged. What is the strain tensor.
 Elasticity Homework Problems 2014 Section 1. The Strain Tensor. 1. A pure shear deformation is shown. The volume is unchanged. What is the strain tensor. 2. Given a steel bar compressed with a deformation
Elasticity Homework Problems 2014 Section 1. The Strain Tensor. 1. A pure shear deformation is shown. The volume is unchanged. What is the strain tensor. 2. Given a steel bar compressed with a deformation
MULTIPLE-CHOICE PROBLEMS:(Two marks per answer) (Circle the Letter Beside the Most Correct Answer in the Questions Below.)
 MULTIPLE-CHOICE PROLEMS:(Two marks per answer) (Circle the Letter eside the Most Correct Answer in the Questions elow.) 1. The absolute viscosity µ of a fluid is primarily a function of: a. Density. b.
MULTIPLE-CHOICE PROLEMS:(Two marks per answer) (Circle the Letter eside the Most Correct Answer in the Questions elow.) 1. The absolute viscosity µ of a fluid is primarily a function of: a. Density. b.
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-67 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2007
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-67 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2007
WORK SHEET FOR MEP311
 EXPERIMENT II-1A STUDY OF PRESSURE DISTRIBUTIONS IN LUBRICATING OIL FILMS USING MICHELL TILTING PAD APPARATUS OBJECTIVE To study generation of pressure profile along and across the thick fluid film (converging,
EXPERIMENT II-1A STUDY OF PRESSURE DISTRIBUTIONS IN LUBRICATING OIL FILMS USING MICHELL TILTING PAD APPARATUS OBJECTIVE To study generation of pressure profile along and across the thick fluid film (converging,
Chapter 3. Load and Stress Analysis. Lecture Slides
 Lecture Slides Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2015 by McGraw Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner.
Lecture Slides Chapter 3 Load and Stress Analysis 2015 by McGraw Hill Education. This is proprietary material solely for authorized instructor use. Not authorized for sale or distribution in any manner.
SECTION A. 8 kn/m. C 3 m 3m
 SECTION Question 1 150 m 40 kn 5 kn 8 kn/m C 3 m 3m D 50 ll dimensions in mm 15 15 Figure Q1(a) Figure Q1(b) The horizontal beam CD shown in Figure Q1(a) has a uniform cross-section as shown in Figure
SECTION Question 1 150 m 40 kn 5 kn 8 kn/m C 3 m 3m D 50 ll dimensions in mm 15 15 Figure Q1(a) Figure Q1(b) The horizontal beam CD shown in Figure Q1(a) has a uniform cross-section as shown in Figure
Answer Key. Mechanical Engineering GATE Afternoon Session 1st Feb, Write us at Phone: ,
 Answer Key of Shared on QualifyGate.com Mechanical Engineering GATE-2015 Afternoon Session 1st Feb, 2015 Write us at info@madeeasy.in Phone: 011-45124612, 9958995830 www.madeeasy.in 1 Section - I (General
Answer Key of Shared on QualifyGate.com Mechanical Engineering GATE-2015 Afternoon Session 1st Feb, 2015 Write us at info@madeeasy.in Phone: 011-45124612, 9958995830 www.madeeasy.in 1 Section - I (General
Rutgers University Department of Physics & Astronomy. 01:750:271 Honors Physics I Fall Lecture 19. Home Page. Title Page. Page 1 of 36.
 Rutgers University Department of Physics & Astronomy 01:750:271 Honors Physics I Fall 2015 Lecture 19 Page 1 of 36 12. Equilibrium and Elasticity How do objects behave under applied external forces? Under
Rutgers University Department of Physics & Astronomy 01:750:271 Honors Physics I Fall 2015 Lecture 19 Page 1 of 36 12. Equilibrium and Elasticity How do objects behave under applied external forces? Under
N = Shear stress / Shear strain
 UNIT - I 1. What is meant by factor of safety? [A/M-15] It is the ratio between ultimate stress to the working stress. Factor of safety = Ultimate stress Permissible stress 2. Define Resilience. [A/M-15]
UNIT - I 1. What is meant by factor of safety? [A/M-15] It is the ratio between ultimate stress to the working stress. Factor of safety = Ultimate stress Permissible stress 2. Define Resilience. [A/M-15]
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS
 Chapter Nine MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS MCQ I 9.1 Modulus of rigidity of ideal liquids is (a) infinity. (b) zero. (c) unity. (d) some finite small non-zero constant value. 9. The maximum load a wire
Chapter Nine MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS MCQ I 9.1 Modulus of rigidity of ideal liquids is (a) infinity. (b) zero. (c) unity. (d) some finite small non-zero constant value. 9. The maximum load a wire
PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM - 613 403 - THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub : Strength of Materials Year / Sem: II / III Sub Code : MEB 310
PERIYAR CENTENARY POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE PERIYAR NAGAR - VALLAM - 613 403 - THANJAVUR. DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK Sub : Strength of Materials Year / Sem: II / III Sub Code : MEB 310
