PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com. Question Number 1(a) Answer Additional Guidance Mark. 1. nucleus drawn in the correct position and labelled ;
|
|
|
- Penelope Stevens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1(a) 1. nucleus drawn in the correct position and labelled ; 2. mitochondrion or mitochondria drawn in the correct position and labelled ; 3. flagellum drawn in the correct position and labelled ; 2. N just labelling of the midsection 3. N a single line 4. acrosome drawn in the correct position and labelled ; 4. N a single line across the head region 1(b)(i) for { movement / motility / eq } to reach the { ovum / egg } ; ACCEPT swim or move or propel sperm towards the egg (1) 1(b)(ii) 1. (a obic) respiration ; 2. ference to { energy / ATP } for movement ; 1(b)(iii) 1. contains { enzymes / acrosin / eq } ; 2. digestion of zona pellucida / eq ; 2. ACCE creation of a pathway through the follicle cells
2 2(a)(i) Answer Mark 13.1 ; (1) 2(a)(ii) Answer 16.0 / 16 (%) ; Mark (1) 2(a)(iii) 2(a)(iv) Answer Mark mitochondria / mitochondrion ; (1) 1. idea of more sperm (cells) with defective flagella ; 2. idea that flagella needed to move sperm (cells) ; 1. needs to be comparative ACCEPT only 4% in control 2. ACCEPT swim 3. idea of more sperm (cells) with defective mid-piece ; 4. idea that if mitochondria are affected there is no { respiration / energy / ATP } ( for movement of flagella ) ; 4.ACCEPT damaged or fewer mitochondria ACCEPT less energy, less respiration or less ATP
3 2(b) 1. ( acrosome contains) { acrosin / enzyme / eq } ; 2. Reference to acrosome reaction ; 3. idea that { zona pellucida / jelly layer } needs to be digested ; 3. ACCEPT broken down 4. sperm (cell) needs to { reach / fuse with } cell (surface) membrane of egg / eq ; (3) 2(c) 1. idea that smoking causes {damage to sperm / infertility} ; 2. idea of smoking as a variable to be controlled ; 3. idea of making sure that any effects were due to globozoospermia OR idea of difficulty in distinguishing between genetic and environmental factors ; 3. e.g. difficult to tell if it was due to smoking or disease (3)
4 Answer Additional guidance Mark 3(a) Feature Acrosome Egg cell only Sper m cell only Bot h Neither Cortical granules Flagellu m Haploid nucleus 3(b) Answer Additional guidance Mark 1. (they carry out) (aerobic) respiration ; 2. provide {ATP / energy / eq} ; 3. to { move / drive the / eq } { flagellum / tail } / eq ; 3(c) Answer Additional guidance Mark 1. halves the chromosome number / eq ; 2. to produce a haploid nucleus / eq ; 3. so that at fertilisation the {full complement / diploid number / eq} of chromosomes is restored / eq ; 4. allows genetic variation (in gametes) / eq ; 5. through independent assortment / eq ; 6. through crossing over / eq ;
5 4(a) (QWC Spelling of technical terms must be correct and the answer must be organised in a logical sequence) QWC emphasis is on spelling of technical terms 1. sperm cell {fuses / eq} with egg cell (membrane) ; 1. N the fusion of the nuclei 2. reference to {cortical granules / vesicles / lysosomes} ; 3. idea of (cortical granules) {moving towards / fusing with } egg cell (surface) membrane ; 4. reference to exocytosis (of cortical granules / vesicles / lysosomes) ; 5. idea of contents (of cortical granules) {secreted /released into jelly layer / eq} OR reference to cortical reaction ; 6. idea of { hardening / thickening / eq } of { zona pellucida / jelly layer } OR formation of fertilisation membrane ; 4. N for description of acrosome reaction 5. ACCEPT enzymes / chemicals NOT released into ovum 6. ACCEPT fertilization 7. reference to change in charge across egg cell membrane ;
6 4(b) 1. reference to both { independent / random } assortment and { crossing-over/chiasma(ta) } ; 2. independent assortment gives rise to {new / different / eq} combinations of (paternal and maternal) chromosomes ; 3. crossing over involves swapping of {sections / eq} of {chromatids /chromosomes} ; 3. N swapping genes ACCEPT new combinations of alleles (on a chromosome) / recombinants 4(c)(i) 1. Idea that temperature is a controlled variable e.g. constant temperature removes this variable, so temperature does not affect {results / length of pollen tube} ; 1. CEPT the idea of only changing one variable and keeping all the others constant or so that only methylpurine affecting pollen tubes NOT a control 2. idea that (pollen tube) { growth / enzymes / proteins /eq } affected by temperature ; 3. idea that at this temperature { enzymes / proteins } will not be denatured / pollen not destroyed at this temperature / 22.5 C optimum temperature ; 4. idea that the investigation is valid ; 4. NOT reliable IGNORE fair test, accurate, precise
7 4(c) (ii) 1. idea of { no significant / small / 1mm / eq } increase in { mean length / growth } up to mol dm -3 ; 2. idea of negative correlation described e.g. {decrease in length of / shorter/ reduced growth of} pollen tubes as concentration increased OR over stated range from to 0.01 ; IGNORE units. 2. CCEPT reference to decreases at specific concentrations of methylpurine IGNORE negative correlation unqualified 3. idea of greatest { change / drop / eq } between and mol dm -3 / eq ; 4. credit correct manipulation of the data to illustrate decrease ; 3. NOT references to pid decrease. 4. Some examples given bel Conc. change mp mp3 Difference (mm) (94-28) 66 (95-28) 67 % all decreases 70 / 70.2 % 71 / 70.5 % (95-90) 5 5 / 5.3 % (90-28) / 68.9 % (3) 4(c)(iii) 1. { less / no } transcription / idea of inhibition of RNA polymerase ; 2. { less / no } { translation / protein synthesis/ protein made / eq } ; 3. idea that protein needed for (pollen tube) growth e.g. less protein leads to reduced growth (of pollen tubes) ; 2 & 3 ACCEPT reference to enzyme instead of protein IGNORE repair
Mark Scheme (RESULTS) January 2009
 Scheme (RESULTS) January 2009 GCE GCE Biology (6BI02/01) Edexcel Limited. Registered in England and Wales No. 4496750 Registered Office: One90 High Holborn, London WC1V 7BH 1(a) 1. {one / few / similar}
Scheme (RESULTS) January 2009 GCE GCE Biology (6BI02/01) Edexcel Limited. Registered in England and Wales No. 4496750 Registered Office: One90 High Holborn, London WC1V 7BH 1(a) 1. {one / few / similar}
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer Pearson Edexcel GCE in Biology (6BI02) Paper 01 Development, Plants and the Environment
 Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2016 Pearson Edexcel GCE in Biology (6BI02) Paper 01 Development, Plants and the Environment Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications are awarded by
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2016 Pearson Edexcel GCE in Biology (6BI02) Paper 01 Development, Plants and the Environment Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications are awarded by
Edexcel (A) Biology A-level
 Edexcel (A) Biology A-level Topic 3: Voice of the Genome Notes Cell Structure All living organisms are made of cells and share some common features. In multicellular organisms, cells are organised into
Edexcel (A) Biology A-level Topic 3: Voice of the Genome Notes Cell Structure All living organisms are made of cells and share some common features. In multicellular organisms, cells are organised into
PMT. Mark Scheme (Results) January Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Subsidiary Level in Biology (WBI02) Paper 01
 Mark Scheme (Results) January 2015 Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Subsidiary Level in Biology (WBI02) Paper 01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications are awarded by Pearson,
Mark Scheme (Results) January 2015 Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Subsidiary Level in Biology (WBI02) Paper 01 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications are awarded by Pearson,
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com. Question Number 1(a) sclerenchyma B ; xylem - D ; Answer Additional Guidance Mark. Allow lower case b and d (2)
 1(a) sclerenchyma B ; xylem - D ; Allow lower case b and d (2) 1(b) Statement True False Both tissues have a structural function Both tissues have a transport function End plates are missing in xylem vessels
1(a) sclerenchyma B ; xylem - D ; Allow lower case b and d (2) 1(b) Statement True False Both tissues have a structural function Both tissues have a transport function End plates are missing in xylem vessels
Mark Scheme (Results) January International Advanced Level Biology (WBI02) Unit 2: Development, Plants and the Environment
 Mark Scheme (Results) January 2014 International Advanced Level Biology (WBI02) Unit 2: Development, Plants and the Environment Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from
Mark Scheme (Results) January 2014 International Advanced Level Biology (WBI02) Unit 2: Development, Plants and the Environment Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer Pearson Edexcel GCE in Biology (6BI02) Paper 01 Development, Plants and the Environment
 Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2015 Pearson Edexcel GCE in Biology (6BI02) Paper 01 Development, Plants and the Environment Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications are awarded by
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2015 Pearson Edexcel GCE in Biology (6BI02) Paper 01 Development, Plants and the Environment Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications are awarded by
2. idea that acid destroys bacteria ; 3. reference to {low / no} oxygen ; 4. reference to using anaerobic respiration ;
 1(a)(i) C hydrolysis ; (1) Question 1(a)(ii) C glucose ; (1) Question 1(b) 1. reference to {low ph / (hydrochloric) acid / HCl / eq} ; 2. idea that acid destroys bacteria ; 3. reference to {low / no} oxygen
1(a)(i) C hydrolysis ; (1) Question 1(a)(ii) C glucose ; (1) Question 1(b) 1. reference to {low ph / (hydrochloric) acid / HCl / eq} ; 2. idea that acid destroys bacteria ; 3. reference to {low / no} oxygen
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer GCE Biology (6BI02) Paper 01R. Unit 2: Development, Plants and Environment
 Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2014 GCE Biology (6BI02) Paper 01R Unit 2: Development, Plants and Environment Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2014 GCE Biology (6BI02) Paper 01R Unit 2: Development, Plants and Environment Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world
2. small / 70s ribosomes box; (2) Feature also present ( ) or absent ( ) in chloroplasts
 1(a)(i) 1. circular DNA box ; 2. small / 70s ribosomes box; (2) 1(a)(ii) Features present in mitochondria Surrounded by a double membrane Feature also present () or absent () in chloroplasts Crista present
1(a)(i) 1. circular DNA box ; 2. small / 70s ribosomes box; (2) 1(a)(ii) Features present in mitochondria Surrounded by a double membrane Feature also present () or absent () in chloroplasts Crista present
Mark Scheme (Results) October Pearson Edexcel International GCE in Biology (WBI02) Paper 1
 Mark Scheme (Results) October 2016 Pearson Edexcel International GCE in Biology (WBI02) Paper 1 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world s leading learning
Mark Scheme (Results) October 2016 Pearson Edexcel International GCE in Biology (WBI02) Paper 1 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world s leading learning
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Level in Biology (WBI02) Paper 01 Development, Plants and the Environment
 Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2017 Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Level in Biology (WBI02) Paper 01 Development, Plants and the Environment Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2017 Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Level in Biology (WBI02) Paper 01 Development, Plants and the Environment Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications
Answer Additional Guidance Mark. Answer Additional Guidance Mark
 1(a) 1. cellulose (molecule) is a { polymer / chain / eq } of β-glucose / eq ; 1. CCEPT many β-glucose 2. cellulose molecules held together { by hydrogen bonds / as microfibrils } ; 3. idea of arrangement
1(a) 1. cellulose (molecule) is a { polymer / chain / eq } of β-glucose / eq ; 1. CCEPT many β-glucose 2. cellulose molecules held together { by hydrogen bonds / as microfibrils } ; 3. idea of arrangement
Genetics word list. the molecule which contains genes. This will be looked at in more detail. it is shaped in a double helix (spiral)
 Genetics word list DNA the molecule which contains genes. This will be looked at in more detail. it is shaped in a double helix (spiral) Chromosomes X-shaped objects found in the nucleus of a cell. The
Genetics word list DNA the molecule which contains genes. This will be looked at in more detail. it is shaped in a double helix (spiral) Chromosomes X-shaped objects found in the nucleus of a cell. The
Cherry Hill Tuition A Level Biology (Salters). Paper 15 Mark Scheme Page 1 of 16. GCE Biology (6BI02) Paper 01 Development, Plants & Environment
 Cherry Hill Tuition A Level Biology (Salters). Paper 15 Scheme Page 1 of 16 Scheme (Results) January 2013 GCE Biology (6BI02) Paper 01 Development, Plants & Environment Cherry Hill Tuition A Level Biology
Cherry Hill Tuition A Level Biology (Salters). Paper 15 Scheme Page 1 of 16 Scheme (Results) January 2013 GCE Biology (6BI02) Paper 01 Development, Plants & Environment Cherry Hill Tuition A Level Biology
D leaf palisade cell (1) Answer Acceptable answers Mark. through (partially permeable) membrane (2) Answer Acceptable answers Mark
 1(a) D leaf palisade cell 1(b) An explanation linking two of the following: by osmosis Ignore references to diffusion reject active transport from an area of high water concentration to an area of low
1(a) D leaf palisade cell 1(b) An explanation linking two of the following: by osmosis Ignore references to diffusion reject active transport from an area of high water concentration to an area of low
Why do cells divide? Why do cells divide? What would happen if they didn t?
 1 of 41 Boardworks Ltd 2007 2 of 41 Boardworks Ltd 2007 Why do cells divide? 3 of 41 Boardworks Ltd 2007 Why do cells divide? What would happen if they didn t? Organisms would only ever exist as single
1 of 41 Boardworks Ltd 2007 2 of 41 Boardworks Ltd 2007 Why do cells divide? 3 of 41 Boardworks Ltd 2007 Why do cells divide? What would happen if they didn t? Organisms would only ever exist as single
Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division. Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms
 Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms Genes DNA Chromatin fiber Chromosomes Fig. 9.6 Genes, the segments of DNA, are part of chromatin fiber
Cellular Reproduction = Cell Division Passes on Genes from Cells to Cells Reproduction of Organisms Genes DNA Chromatin fiber Chromosomes Fig. 9.6 Genes, the segments of DNA, are part of chromatin fiber
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction
 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Single parent produces offspring All offspring are genetically identical to one another and to parent Produces identical somatic (body) cells Sexual
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Single parent produces offspring All offspring are genetically identical to one another and to parent Produces identical somatic (body) cells Sexual
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level. Published
 Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level BIOLOGY 5090/ Paper Theory MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and candidates,
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge Ordinary Level BIOLOGY 5090/ Paper Theory MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 80 Published This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and candidates,
Mark Scheme (Results) January 2017
 Mark Scheme (Results) January 2017 Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Subsidiary Level in Biology (WBI02) Paper 01 Development, Plants and the Environment Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and
Mark Scheme (Results) January 2017 Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Subsidiary Level in Biology (WBI02) Paper 01 Development, Plants and the Environment Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and
Review of Terms. Haploid cells (1n) with one copy of each chromosome. Diploid cells (2n) with two copies of each chromosome
 Review of Terms Haploid cells (1n) with one copy of each chromosome Diploid cells (2n) with two copies of each chromosome Somatic non-germline cells Gametes sex cells (eggs and sperm) Reductional division
Review of Terms Haploid cells (1n) with one copy of each chromosome Diploid cells (2n) with two copies of each chromosome Somatic non-germline cells Gametes sex cells (eggs and sperm) Reductional division
1(a)(i) nucleus (1) (1) Answer Acceptable answers Mark. Answer Acceptable answers Mark. Answer Acceptable answers Mark
 1(a)(i) nucleus 1(a)(ii) C In DNA, the bases A - T are complementary 1(b) A definition including two of the following: a sperm fuses with egg / penetrates the egg nuclei/genetic information fuses /combines
1(a)(i) nucleus 1(a)(ii) C In DNA, the bases A - T are complementary 1(b) A definition including two of the following: a sperm fuses with egg / penetrates the egg nuclei/genetic information fuses /combines
Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13. The Eukaryotic Genome. The Eukaryotic Genome. The Eukaryotic Genome
 Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13 The Eukaryotic Genome pp. 244-245,268-269 Genome All of the genes in a cell. Eukaryotic cells contain their DNA in long linear pieces. In prokaryotic cells, there is
Topic 8 Mitosis & Meiosis Ch.12 & 13 The Eukaryotic Genome pp. 244-245,268-269 Genome All of the genes in a cell. Eukaryotic cells contain their DNA in long linear pieces. In prokaryotic cells, there is
Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Chapter Questions 1) What is a genome? A) the complete complement of an organism's genes B) a specific sequence of polypeptides within
Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Chapter Questions 1) What is a genome? A) the complete complement of an organism's genes B) a specific sequence of polypeptides within
Fertilization. Key Concepts. Introduction. Activation Changes Juxtaposition Acrosome Syngamy Membrane Potential Cortical Reaction Electrophysiology
 Fertilization 1 Activation Changes Juxtaposition Acrosome Syngamy Membrane Potential Cortical Reaction Electrophysiology Key Concepts 2 Sexual Reproduction Fertilization Syngamy Conjugation Parthenogenesis
Fertilization 1 Activation Changes Juxtaposition Acrosome Syngamy Membrane Potential Cortical Reaction Electrophysiology Key Concepts 2 Sexual Reproduction Fertilization Syngamy Conjugation Parthenogenesis
Cell Division Mark Scheme
 Cell Division Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Topic Sub Topic Booklet Edexcel Biology GCSE(9-1) Cells and Control Cell Division Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 41 minutes Score: /34 Percentage: /100 1(a)
Cell Division Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Topic Sub Topic Booklet Edexcel Biology GCSE(9-1) Cells and Control Cell Division Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 41 minutes Score: /34 Percentage: /100 1(a)
02/02/ Living things are organized. Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures. Learning Outcome B1
 Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures Learning Outcome B1 Describe the following cell structures and their functions: Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Golgi
Analyze the functional inter-relationship of cell structures Learning Outcome B1 Describe the following cell structures and their functions: Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Cytoskeleton Cytoplasm Golgi
X-Sheet 3 Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis
 X-Sheet 3 Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis 13 Key Concepts In this session we will focus on summarising what you need to know about: Revise Mitosis (Grade 11), the process of meiosis, First Meiotic division,
X-Sheet 3 Cell Division: Mitosis and Meiosis 13 Key Concepts In this session we will focus on summarising what you need to know about: Revise Mitosis (Grade 11), the process of meiosis, First Meiotic division,
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics Mitosis is a form of asexual reproduction This means that it only requires 1 organism (ex. Skin cells dividing) For growth and repair in somatic (body) cells! Results
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics Mitosis is a form of asexual reproduction This means that it only requires 1 organism (ex. Skin cells dividing) For growth and repair in somatic (body) cells! Results
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction. Chapter 9
 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 9 9.1 Genes and Alleles Genes Sequences of DNA that encode heritable traits Alleles Slightly different forms of the same gene Each specifies a different version
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 9 9.1 Genes and Alleles Genes Sequences of DNA that encode heritable traits Alleles Slightly different forms of the same gene Each specifies a different version
Biology. Chapter 12. Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction. Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr. Cengage Learning 2015
 Biology Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr Chapter 12 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction 12.1 Why Sex? In asexual reproduction, a single individual gives rise to offspring that are identical to
Biology Concepts and Applications 9e Starr Evers Starr Chapter 12 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction 12.1 Why Sex? In asexual reproduction, a single individual gives rise to offspring that are identical to
The Cell Cycle. The Basis for Heritability: Mitosis and Meiosis. Let s start with a banana.
 The Basis for Heritability: Mitosis and Meiosis Ch. 11: 222-223, 227-231 Ch. 12: less emphasis on 249-50 I. Overview A. What Darwin didn t know B. Getting cells from cells II. Mitosis A. The bottom line
The Basis for Heritability: Mitosis and Meiosis Ch. 11: 222-223, 227-231 Ch. 12: less emphasis on 249-50 I. Overview A. What Darwin didn t know B. Getting cells from cells II. Mitosis A. The bottom line
Lesson Overview Meiosis
 11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
Cells. Unit Review: Cells MEIOSIS. TECHBOOK UNIT 0 Views. Essential Questions and Answers for Review Sheet. What is meiosis?
 Cells TECHBOOK UNIT 0 Views Unit Review: Cells MEIOSIS Essential Questions and Answers for Review Sheet What is meiosis? Answer: Meiosis is the process by which specialized cells called gametes form in
Cells TECHBOOK UNIT 0 Views Unit Review: Cells MEIOSIS Essential Questions and Answers for Review Sheet What is meiosis? Answer: Meiosis is the process by which specialized cells called gametes form in
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Level In Biology (WBI02) Development, Plants and the Environment
 Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2018 Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Level In Biology (WBI02) Development, Plants and the Environment Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2018 Pearson Edexcel International Advanced Level In Biology (WBI02) Development, Plants and the Environment Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications
Ch. 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 Introduction Ch. 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles 2004-05 Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. -Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less closely
Introduction Ch. 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles 2004-05 Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. -Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less closely
Human biology Laboratory. Cell division. Lecturer Maysam A Mezher
 Human biology Laboratory Cell division Lecturer Maysam A Mezher CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact
Human biology Laboratory Cell division Lecturer Maysam A Mezher CHROMOSOME STRUCTURE 1. During nuclear division, the DNA (as chromatin) in a Eukaryotic cell's nucleus is coiled into very tight compact
Almost all human cells contain 46 chromosomes, and are diploid (2n). Q: If a sperm cell has 46 chromosomes (2n) & an egg cell has 46 chromosomes
 Almost all human cells contain 46 chromosomes, and are diploid (2n). Q: If a sperm cell has 46 chromosomes (2n) & an egg cell has 46 chromosomes (2n), when they combine during fertilization, how many chromosomes
Almost all human cells contain 46 chromosomes, and are diploid (2n). Q: If a sperm cell has 46 chromosomes (2n) & an egg cell has 46 chromosomes (2n), when they combine during fertilization, how many chromosomes
MEIOSIS C H A P T E R 1 3
 MEIOSIS CHAPTER 13 CENTRAL DOGMA OF BIOLOGY DNA RNA Protein OFFSPRING ACQUIRE GENES FROM PARENTS Genes are segments of DNA that program specific traits. Genetic info is transmitted as specific sequences
MEIOSIS CHAPTER 13 CENTRAL DOGMA OF BIOLOGY DNA RNA Protein OFFSPRING ACQUIRE GENES FROM PARENTS Genes are segments of DNA that program specific traits. Genetic info is transmitted as specific sequences
CHAPTER 6. Chromosomes and Meiosis
 CHAPTER 6 Chromosomes and Meiosis CHROMOSOMES DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a long, thin molecule that directs cellular functions and heredity. DNA contains information that is encoded in segments called
CHAPTER 6 Chromosomes and Meiosis CHROMOSOMES DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a long, thin molecule that directs cellular functions and heredity. DNA contains information that is encoded in segments called
A. mitosis. B. endocytosis. C. exocytosis. D. meiosis. Section of mrna G U C C A A A C G
 Directions: For each of the following questions, decide which of the choices is best and fill in the corresponding space on the answer document. 1. 2. The table below shows the genetic code. Below the
Directions: For each of the following questions, decide which of the choices is best and fill in the corresponding space on the answer document. 1. 2. The table below shows the genetic code. Below the
Overview. Overview: Variations on a Theme. Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes. Inheritance of Genes
 Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview I. Cell Types II. Meiosis I. Meiosis I II. Meiosis II III. Genetic Variation IV. Reproduction Overview: Variations on a Theme Figure 13.1 Living organisms
Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview I. Cell Types II. Meiosis I. Meiosis I II. Meiosis II III. Genetic Variation IV. Reproduction Overview: Variations on a Theme Figure 13.1 Living organisms
CELL REPRODUCTION. Unit 20 LEARNING OBJECTIVES:
 Unit 20 CELL REPRODUCTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Be able to distinguish the differences between mitotic and meiotic cell division. 2. Learn the role that both mitotic and meiotic types of cell division
Unit 20 CELL REPRODUCTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES: 1. Be able to distinguish the differences between mitotic and meiotic cell division. 2. Learn the role that both mitotic and meiotic types of cell division
Meiosis and Life Cycles - 1
 Meiosis and Life Cycles - 1 We have just finished looking at the process of mitosis, a process that produces cells genetically identical to the original cell. Mitosis ensures that each cell of an organism
Meiosis and Life Cycles - 1 We have just finished looking at the process of mitosis, a process that produces cells genetically identical to the original cell. Mitosis ensures that each cell of an organism
Q1. The diagram shows some of the cell divisions that occur during human reproduction.
 Q. The diagram shows some of the cell divisions that occur during human reproduction. (a) (i) Name the type of cell division that produces cell D from cell B. () Which organ in the male body produces cell
Q. The diagram shows some of the cell divisions that occur during human reproduction. (a) (i) Name the type of cell division that produces cell D from cell B. () Which organ in the male body produces cell
For a species to survive, it must REPRODUCE! Ch 13 NOTES Meiosis. Genetics Terminology: Homologous chromosomes
 For a species to survive, it must REPRODUCE! Ch 13 NOTES Meiosis Genetics Terminology: Autosomes Somatic cell Gamete Karyotype Homologous chromosomes Meiosis Sex chromosomes Diploid Haploid Zygote Synapsis
For a species to survive, it must REPRODUCE! Ch 13 NOTES Meiosis Genetics Terminology: Autosomes Somatic cell Gamete Karyotype Homologous chromosomes Meiosis Sex chromosomes Diploid Haploid Zygote Synapsis
Chapter 6: Cell Growth and Reproduction Lesson 6.3: Meiosis and Reproduction
 Chapter 6: Cell Growth and Reproduction Lesson 6.3: Meiosis and Reproduction One parent or two? That is the main difference between sexual and asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction just means combining
Chapter 6: Cell Growth and Reproduction Lesson 6.3: Meiosis and Reproduction One parent or two? That is the main difference between sexual and asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction just means combining
Chapter 13. Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction. AP Biology
 Chapter 13. Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of
Chapter 13. Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of
Cell Organelles Tutorial
 1 Name: Cell Organelles Tutorial TEK 7.12D: Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast,
1 Name: Cell Organelles Tutorial TEK 7.12D: Differentiate between structure and function in plant and animal cell organelles, including cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondrion, chloroplast,
In the exam you will be asked to tackle questions such as the one below. Mitosis or meiosis?
 Get started AO1 Cell division This unit will help you to recognise when cells divide by mitosis and when they divide by meiosis. t will also help you to understand the importance of cell division in the
Get started AO1 Cell division This unit will help you to recognise when cells divide by mitosis and when they divide by meiosis. t will also help you to understand the importance of cell division in the
Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction. AP Biology
 Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction Cell division / Asexual reproduction! Mitosis " produce cells with same information! identical daughter cells " exact copies! clones " same amount of DNA! same number of chromosomes!
Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction Cell division / Asexual reproduction! Mitosis " produce cells with same information! identical daughter cells " exact copies! clones " same amount of DNA! same number of chromosomes!
Meiosis. Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and meiosis II
 Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction. AP Biology 2/27/15
 Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction 2/27/15 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis u produce cells with same information identical daughter cells u exact copies clones u same amount of DNA same number
Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction 2/27/15 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis u produce cells with same information identical daughter cells u exact copies clones u same amount of DNA same number
Photosynthesis and Photosynthesis Pigments
 Photosynthesis & Photosynthesis Pigments Scheme 2 Level A Level Subject Biology Exam Board Edexcel Topic Energy of Biological Processes Sub Topic Photosynthesis and Photosynthesis Pigments Booklet Scheme
Photosynthesis & Photosynthesis Pigments Scheme 2 Level A Level Subject Biology Exam Board Edexcel Topic Energy of Biological Processes Sub Topic Photosynthesis and Photosynthesis Pigments Booklet Scheme
Sexual Reproduction. The two parent cells needed for sexual reproduction are called gametes. They are formed during a process known as meiosis.
 Sexual Reproduction Recall that asexual reproduction involves only one parent cell. This parent cell divides to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent. Sexual reproduction,
Sexual Reproduction Recall that asexual reproduction involves only one parent cell. This parent cell divides to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent. Sexual reproduction,
Cell division and multiplication
 CELL DIVISION Cell division and multiplication As we already mentioned, the genetic information contained in the nucleus is hereditary Meaning it is passed on from cell to cell; from parent to child This
CELL DIVISION Cell division and multiplication As we already mentioned, the genetic information contained in the nucleus is hereditary Meaning it is passed on from cell to cell; from parent to child This
Cell Structure and Function
 Quarter 2 Review Biology Cell Structure and Function Identify the organelles AND give function of each. 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. 3. 4. 4. 5. Looking at the above diagram, what does the structure labeled 1 do? Why
Quarter 2 Review Biology Cell Structure and Function Identify the organelles AND give function of each. 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. 3. 4. 4. 5. Looking at the above diagram, what does the structure labeled 1 do? Why
2. Cellular and Molecular Biology
 2. Cellular and Molecular Biology 2.1 Cell Structure 2.2 Transport Across Cell Membranes 2.3 Cellular Metabolism 2.4 DNA Replication 2.5 Cell Division 2.6 Biosynthesis 2.1 Cell Structure What is a cell?
2. Cellular and Molecular Biology 2.1 Cell Structure 2.2 Transport Across Cell Membranes 2.3 Cellular Metabolism 2.4 DNA Replication 2.5 Cell Division 2.6 Biosynthesis 2.1 Cell Structure What is a cell?
Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction
 Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction 2007-2008 Turn in warm ups to basket! Prepare for your test! Get out your mitosis/meiosis foldable After the test: New vocabulary! 2/23/17 Draw and label the parts of the
Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction 2007-2008 Turn in warm ups to basket! Prepare for your test! Get out your mitosis/meiosis foldable After the test: New vocabulary! 2/23/17 Draw and label the parts of the
Cell Reproduction Mitosis & Meiosis
 Cell Reproduction Mitosis & Meiosis Outcomes 1. Describe mitosis in detail (460-465) interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis (the cell cycle) explain the importance of maintaining chromosome number through
Cell Reproduction Mitosis & Meiosis Outcomes 1. Describe mitosis in detail (460-465) interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis (the cell cycle) explain the importance of maintaining chromosome number through
Meiosis vs Mitosis. How many times did it go through prophase-metaphase-anaphase-telophase?
 Meiosis vs Mitosis Mitosis produces identical copies of cells for growth or repair. Meiosis produces egg cells or sperm cells. Look at the diagram of meiosis: What happened during prophase I? How many
Meiosis vs Mitosis Mitosis produces identical copies of cells for growth or repair. Meiosis produces egg cells or sperm cells. Look at the diagram of meiosis: What happened during prophase I? How many
Cell Division: the process of copying and dividing entire cells The cell grows, prepares for division, and then divides to form new daughter cells.
 Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
2. Next, try to describe the cell cycle as follows: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis
 1. First, tell me something exciting you did over spring break! 2. Next, try to describe the cell cycle as follows: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis *Reminder*-Thursday
1. First, tell me something exciting you did over spring break! 2. Next, try to describe the cell cycle as follows: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis *Reminder*-Thursday
The division of a unicellular organism reproduces an entire organism, increasing the population. Here s one amoeba dividing into 2.
 1. Cell division functions in 3 things : reproduction, growth, and repair The division of a unicellular organism reproduces an entire organism, increasing the population. Here s one amoeba dividing into
1. Cell division functions in 3 things : reproduction, growth, and repair The division of a unicellular organism reproduces an entire organism, increasing the population. Here s one amoeba dividing into
Biology Kevin Dees. Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Reproduction Characteristic of all living things Reproduction also involves the transmission of traits from one generation to the next; inheritance Heredity Latin
Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Reproduction Characteristic of all living things Reproduction also involves the transmission of traits from one generation to the next; inheritance Heredity Latin
Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles. Reproduction
 Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Reproduction Characteristic of all living things Reproduction also involves the transmission of traits from one generation to the next; inheritance Heredity Latin
Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Reproduction Characteristic of all living things Reproduction also involves the transmission of traits from one generation to the next; inheritance Heredity Latin
Cell division / Asexual reproduction
 Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction 2007-2008 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes
Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction 2007-2008 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes
Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis
 Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis 1. In mitosis, if a parent cell has 16 chromosomes, each daughter cell will have how many chromosomes? a. 64 b. 32 c. 16 d. 8 e. 4 2. Chromatids that are
Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis 1. In mitosis, if a parent cell has 16 chromosomes, each daughter cell will have how many chromosomes? a. 64 b. 32 c. 16 d. 8 e. 4 2. Chromatids that are
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: HUHE.CUMM Summarize the three phases of the cell cycle: interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis.
 True / False 1. Mitotic divisions reduce the number of chromosomes found in daughter cells. False LEARNING OBJECTIVES: HUHE.CUMM.16.2-4-1 - Summarize the three phases of the cell cycle: interphase, mitosis,
True / False 1. Mitotic divisions reduce the number of chromosomes found in daughter cells. False LEARNING OBJECTIVES: HUHE.CUMM.16.2-4-1 - Summarize the three phases of the cell cycle: interphase, mitosis,
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 5: Chromosomes and Inheritance
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 5: Chromosomes and Inheritance Chromosomes and Inheritance Learning Outcomes 5.1 Differentiate between sexual and asexual reproduction in terms of the genetic variation of the offspring.
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 5: Chromosomes and Inheritance Chromosomes and Inheritance Learning Outcomes 5.1 Differentiate between sexual and asexual reproduction in terms of the genetic variation of the offspring.
Meiosis. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Meiosis Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction requires fertilization, a union of two cells from two individual organisms. If those two cells each contain one set of chromosomes, then the resulting cell
Meiosis Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Sexual reproduction requires fertilization, a union of two cells from two individual organisms. If those two cells each contain one set of chromosomes, then the resulting cell
CELL BIOLOGY. Which of the following cell structures does not have membranes? A. Ribosomes B. Mitochondria C. Chloroplasts D.
 1 CELL BIOLOGY PROKARYOTIC and EUKARYOTIC SP/1. SP/2. SP/4. Plant and animal cells both have A. ribosomes, cell walls and mitochondria. B. Golgi apparatus, chromosomes and mitochondria. C. Golgi apparatus,
1 CELL BIOLOGY PROKARYOTIC and EUKARYOTIC SP/1. SP/2. SP/4. Plant and animal cells both have A. ribosomes, cell walls and mitochondria. B. Golgi apparatus, chromosomes and mitochondria. C. Golgi apparatus,
Cell Reproduction Review
 Name Date Period Cell Reproduction Review Explain what is occurring in each part of the cell cycle --- G 0, G1, S, G2, and M. 1 CELL DIVISION Label all parts of each cell in the cell cycle and explain
Name Date Period Cell Reproduction Review Explain what is occurring in each part of the cell cycle --- G 0, G1, S, G2, and M. 1 CELL DIVISION Label all parts of each cell in the cell cycle and explain
KARYOTYPE. An organism s complete set of chromosomes
 CH. 9-3 MEIOSIS 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES You should be able to: Determine haploid and diploid numbers. Define homologous chromosomes. Distinguish between autosomes/sex chromosomes. Identify and draw stages
CH. 9-3 MEIOSIS 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES You should be able to: Determine haploid and diploid numbers. Define homologous chromosomes. Distinguish between autosomes/sex chromosomes. Identify and draw stages
Chapter 03. Lecture and Animation Outline
 Chapter 03 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Chapter 03 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION & MEIOSIS
 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION & MEIOSIS Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less closely related individuals of the
SEXUAL REPRODUCTION & MEIOSIS Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. Offspring resemble their parents more than they do less closely related individuals of the
Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction
 Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction 2007-2008 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis u produce cells with same information identical daughter cells u exact copies clones u same amount of DNA same number
Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction 2007-2008 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis u produce cells with same information identical daughter cells u exact copies clones u same amount of DNA same number
Name Chapter 10: Chromosomes, Mitosis, and Meiosis Mrs. Laux Take home test #7 DUE: MONDAY, NOVEMBER 16, 2009 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A bacterial chromosome consists of: A. a linear DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. B. a circular DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. C. a circular DNA
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. A bacterial chromosome consists of: A. a linear DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. B. a circular DNA molecule many times larger than the cell. C. a circular DNA
Meiosis. Introduction. A life cycle is the generation-to-generation sequence of stages in the reproductive history of an organism.
 Meiosis The pomegranate (Punica granatum) is believed to have originated near Iran and southern Afghanistan. The flowers are bright red with five petals. After the flower is fertilized with pollen the
Meiosis The pomegranate (Punica granatum) is believed to have originated near Iran and southern Afghanistan. The flowers are bright red with five petals. After the flower is fertilized with pollen the
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell The cell is the basic unit of life Although cells differ substantially from one another, they all share certain characteristics that reflect a common ancestry and remind us
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell The cell is the basic unit of life Although cells differ substantially from one another, they all share certain characteristics that reflect a common ancestry and remind us
CHAPTER 9 MEIOSIS AND SEXUAL REPRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 9 MEIOSIS AND SEXUAL REPRODUCTION 9.1 INTRODUCING ALLELES When an orchid or aphid reproduces all by it self, what sort of offspring does it get? By the process of asexual reproduction, one alone
CHAPTER 9 MEIOSIS AND SEXUAL REPRODUCTION 9.1 INTRODUCING ALLELES When an orchid or aphid reproduces all by it self, what sort of offspring does it get? By the process of asexual reproduction, one alone
Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division
 Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The process of meiosis results in. A. the production of four identical cells B. no change in chromosome number from parental cells C. a doubling of
Chapter 2 Cells and Cell Division MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The process of meiosis results in. A. the production of four identical cells B. no change in chromosome number from parental cells C. a doubling of
Chapter 11 - Concept Mapping
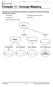 Chapter 11 - Concept Mapping Using the terms and phrases provided below, complete the concept map showing the process of meiosis. chromatids crossing-over haploid sperm and ovum homologous chromosomes
Chapter 11 - Concept Mapping Using the terms and phrases provided below, complete the concept map showing the process of meiosis. chromatids crossing-over haploid sperm and ovum homologous chromosomes
Benchmark Clarification for SC.912.L.16.17
 Benchmark Clarification for SC.912.L.16.17 Students will: Differentiate the process of meiosis and meiosis Describe the role of mitosis in asexual reproduction, and/or the role of meiosis in sexual reproduction,
Benchmark Clarification for SC.912.L.16.17 Students will: Differentiate the process of meiosis and meiosis Describe the role of mitosis in asexual reproduction, and/or the role of meiosis in sexual reproduction,
Dr. Ramesh U4L3 Meiosis
 Dr. Ramesh U4L3 Meiosis The Cell Cycle and Cell Division: MEIOSIS The Cell Cycle and Cell Division KEY CONCEPT: Meiosis Halves the Nuclear Chromosome Content and Generates Diversity Organisms have two
Dr. Ramesh U4L3 Meiosis The Cell Cycle and Cell Division: MEIOSIS The Cell Cycle and Cell Division KEY CONCEPT: Meiosis Halves the Nuclear Chromosome Content and Generates Diversity Organisms have two
Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll
 Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll Learning Objectives: The student is able to construct an explanation, using visual representations or narratives, as to how DNA in chromosomes is transmitted
Ladies and Gentlemen.. The King of Rock and Roll Learning Objectives: The student is able to construct an explanation, using visual representations or narratives, as to how DNA in chromosomes is transmitted
Intitial Question: How can the mathematically impossible become the biologically possiblenamely,
 Intitial Question: How can the mathematically impossible become the biologically possiblenamely, a cell with 46 chromosomes splits to form tow cells each with 46 chromosomes/ This means 46 divided by 2
Intitial Question: How can the mathematically impossible become the biologically possiblenamely, a cell with 46 chromosomes splits to form tow cells each with 46 chromosomes/ This means 46 divided by 2
3.2 Cell Organelles. KEY CONCEPT Eukaryotic cells share many similarities.
 KEY CONCEPT Eukaryotic cells share many similarities. ! Cells have an internal structure. ! Cells have an internal structure. The cytoskeleton has many functions. ! Cells have an internal structure. The
KEY CONCEPT Eukaryotic cells share many similarities. ! Cells have an internal structure. ! Cells have an internal structure. The cytoskeleton has many functions. ! Cells have an internal structure. The
Biology I Level - 2nd Semester Final Review
 Biology I Level - 2nd Semester Final Review The 2 nd Semester Final encompasses all material that was discussed during second semester. It s important that you review ALL notes and worksheets from the
Biology I Level - 2nd Semester Final Review The 2 nd Semester Final encompasses all material that was discussed during second semester. It s important that you review ALL notes and worksheets from the
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell What jobs do cells have to do for an organism to live Gas exchange CO 2 & O 2 Eat (take in & digest food) Make energy ATP Build
Cell Structure and Function Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial cell What jobs do cells have to do for an organism to live Gas exchange CO 2 & O 2 Eat (take in & digest food) Make energy ATP Build
0610 BIOLOGY. Mark schemes should be read in conjunction with the question paper and the Principal Examiner Report for Teachers.
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 01 series 010 BIOLOGY 010/1 Paper (Extended Theory), maximum raw mark 0 This mark
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education MARK SCHEME for the May/June 01 series 010 BIOLOGY 010/1 Paper (Extended Theory), maximum raw mark 0 This mark
Cell Structure and Cell Cycle
 E X E R C I S E 4 Cell Structure and Cell Cycle Materials model or diagram of a cell compound microscopes and lens paper prepared slides of human skeletal muscle cells, pseudostratified ciliated columnar
E X E R C I S E 4 Cell Structure and Cell Cycle Materials model or diagram of a cell compound microscopes and lens paper prepared slides of human skeletal muscle cells, pseudostratified ciliated columnar
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 10 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 10 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Variations on a Theme Living
13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Variations on a Theme Living
Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction (Ch. 13)
 Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction (Ch. 13) Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes
Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction (Ch. 13) Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION. Chapter 10
 CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Outline Overview: Variations on a Theme Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. Offspring resemble their parents
Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Lecture Outline Overview: Variations on a Theme Living organisms are distinguished by their ability to reproduce their own kind. Offspring resemble their parents
Purposes of Cell Division
 Purposes of Cell Division Increase the number of cells for growth and repair of worn out tissues What examples in the human body can you think of? Transmit genetic information to later generations Why
Purposes of Cell Division Increase the number of cells for growth and repair of worn out tissues What examples in the human body can you think of? Transmit genetic information to later generations Why
Lesson Overview Meiosis
 11.4 As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures? What cellular
11.4 As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures? What cellular
