In the exam you will be asked to tackle questions such as the one below. Mitosis or meiosis?
|
|
|
- Edwina Maxwell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Get started AO1 Cell division This unit will help you to recognise when cells divide by mitosis and when they divide by meiosis. t will also help you to understand the importance of cell division in the cell cycle. n the exam you will be asked to tackle questions such as the one below. Exam-style question 1 Mitosis and meiosis are types of cell division. 1.1 Complete the table to show which of the features are produced by mitosis and which are produced by meiosis. Feature Mitosis or meiosis? Production of egg cells A lizard growing a new tail Biology Production of pollen in a flower Cells replaced on the skin to heal a cut 1.2 dentify the organs that produce gametes (sex cells) in a man and in a woman. (4 marks) A man A woman 1. Describe two differences between mitosis and meiosis. (2 marks) (2 marks) You will already have done some work on mitosis and meiosis. Before starting the skills boosts, rate your confi dence in each area. Colour in the bars. 1 How can identify the stages in the cell cycle? 2 How can describe situations where mitosis is occurring? How can explain the importance of meiosis? Biology Unit Cell division 17 M0_AQSB_G5_WB_GCSE_8901_B0_ indd 17 18/08/ :51
2 Get started The topic of cell division covers the cell cycle, mitosis and meiosis. Cells divide in a series of stages called the cell cycle. First, a cell grows larger and makes more sub-cellular structures like mitochondria (for energy production) and ribosomes (for making proteins). The cell then makes copies of its chromosomes. One copy moves to each end of the cell, and the nucleus divides. The cell then divides into two new cells. Two cells are produced from one during mitosis. 1 Number these statements (1-) in the order in which they occur in the cell cycle. Stage The cell increases in size and increases the number of sub-cellular structures such as ribosomes and mitochondria. DNA replicates to form two copies of each chromosome. The cytoplasm and cell membrane divide to form two identical, daughter cells. A set of chromosomes moves to each end of the cell and the nucleus divides. Correct order Human body cells have 46 chromosomes. The nucleus of a cell copies the chromosomes to double that number during interphase. The cell then moves a copy to each end of the cell during mitosis. The cell then divides during cytokinesis, making two new cells each with 46 chromosomes. 2 Complete the numbers inside the cells to show what happens to the number of chromosomes during mitosis. Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage a Describe what is happening inside the cell between stages 1 and b Describe what is happening inside the cell between stages 2 and. Meiosis is a different type of cell division where four cells are made from one cell. n females, meiosis takes place in the ovaries, where it produces eggs. n males, meiosis takes place in the testes, where it produces sperm. The four cells that are made from the original parent cell each have a different half set of chromosomes. 4 Complete the numbers inside the cells to show what happens to the number of chromosomes during meiosis. 18 Biology Unit Cell division 2 Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage First meiosis makes two cells, each with a full set of chromosomes. These divide again to make four cells, each with a half set of chromosomes. M0_AQSB_G5_WB_GCSE_8901_B0_ indd 18 18/08/ :51
3 Skills boost 1 How can identify the stages in the cell cycle? Actively dividing cells go through a series of stages called the cell cycle. The first stage is interphase, where the cell makes new components and a copy of each chromosome. Then, during mitosis, the chromosomes move apart and the nucleus divides. The cell cycle ends with cytokinesis (cell division). The two new cells that are produced are genetically identical and are called daughter cells. 1 a Match the overall stages of the cell cycle with the more detailed descriptions. nterphase Mitosis Cytokinesis One set of chromosomes is pulled to each end of the cell, and the nucleus divides. The cell membrane and cytoplasm divide to form two new cells. The cell increases in size and produces more ribosomes and mitochondria. The cell also makes a complete copy of the DNA. b The cell cycle in a tomato plant tip cell lasts 6 hours. i Convert 6 hours to minutes. ii Work out the number of minutes represented by a 1 angle on the pie chart. nterphase Mitosis 20 Cytokinesis Biology iii Use the information in the pie chart to complete the table and calculate the time taken for each stage of the cell cycle. nterphase Mitosis Cytokinesis Angle ( ) Time in minutes Time in hours and minutes How many cells will there be after 6 h? 2 Tomato plants have 10 chromosomes in a normal cell. a How many chromosomes are there in a cell 5 h 20 min after the start of the cell cycle? Look at where the cell cycle will be after 5 h 20 min. b How many chromosomes are there in a cell 6 h after the start of the cell cycle? Look at this graph. t shows the stages of the cell cycle for a different organism over a 10 hour cycle. a Which letter represents the genetic material doubling during interphase? b Which letter represents the genetic material moving apart and the nucleus dividing during mitosis? Amount of DNA in each cell (picograms) X Y Z Time (hours) Biology Unit Cell division 19 M0_AQSB_G5_WB_GCSE_8901_B0_ indd 19 18/08/ :51
4 Skills boost 2 How can describe situations where mitosis is occurring? Mitosis is used for increasing the number of cells during growth, when replacing damaged cells and for asexual reproduction. Mitosis produces genetically identical cells. This means that all cells in the body have exactly the same set of chromosomes. Asexual reproduction leads to offspring produced from only one parent. All the offspring are identical and are known as clones. Genes are sections of DNA found on chromosomes. Humans have 46 chromosomes in the nucleus of normal body cells. The nucleus controls the chemical reactions inside the cell. 1 Look at the diagram and number the parts of the cell in order of size with 1 as the smallest and as the largest. Nucleus Gene Chromosomes nucleus gene chromosome Cell 2 Human skin cells A, B, C and D in the diagram have just been produced to replace some damaged cells. A B C D a Name the type of cell division that has produced these new cells. b What happens to the genetic material before the cell divides? c How many chromosomes will be in cell A? d Why is it important that skin cells can divide? The diagram shows a nucleus just before the nucleus begins to divide during mitosis. Complete the second diagram to show what the nucleus of a cell produced by this mitosis looks like. Remember Mitosis produces identical cells. This means that the cells will have an identical number of chromosomes. You could use this to help you remember what mitosis does. Makes Makes dentical Toes T O Offspring Skin S S S 20 Biology Unit Cell division M0_AQSB_G5_WB_GCSE_8901_B0_ indd 20 18/08/ :51
5 Skills boost How can explain the importance of meiosis? Meiosis is the type of cell division that makes sperm cells and eggs. Meiosis involves two divisions. First, two cells are made with full sets of chromosomes. These two cells then divide to make four non-identical cells which can be used in sexual reproduction. Each gamete contains half of the chromosomes needed to make a full set. They join together during fertilisation to form a zygote. Gamete A sex cell such as egg or sperm. Gametes are formed by meiosis. 1 Which diagram represents cell division by meiosis? Circle A one letter. A B C 2 Name an organ where meiosis takes place. You could use this to help you remember what meiosis does. Makes Eggs O Sperm S Alleles are different versions of the same gene. For example, one chromosome could carry the allele for blue eyes and the other chromosome could carry the allele for brown eyes. Biology n this diagram the top cell contains two alleles for two different genes. B is the gene for brown eyes and b the gene for blue eyes. F is the gene for brown hair and f is the gene for blond hair. Write the letters in the boxes to make four different combinations of alleles from these two genes, just like during meiosis. BbFf The diploid number in human cells is 46 chromosomes. The haploid number is 2. Most body cells contain 46 chromosomes, but eggs or sperm cells only contain 2 chromosomes. Diploid comes from the Greek for double and haploid means half. 4 Circle A the correct keywords in this passage. Meiosis doubles / halves / triples the number of chromosomes and leads to identical / non-identical / cloned cells. n meiosis the cell divides twice. The first division produces two cells with the same number of chromosomes as in the original full set in the parent cell (called the triploid / diploid / haploid number). The second division divides those two cells and reduces the number of chromosomes to half the number in the original parent cell. The four cells now have the triploid / diploid / haploid number of chromosomes. This reduction is essential for sexual / asexual reproduction and increases / maintains / decreases genetic variety. Biology Unit Cell division 21 M0_AQSB_G5_WB_GCSE_8901_B0_ indd 21 18/08/ :51
6 Sample response Get back on track Your understanding of mitosis, meiosis and the cell cycle will often be tested in the context of living things. Read this question carefully, use your knowledge and consider your response. Look at this exam-style question and the answers given by a student. Exam-style question 1.1 Mitosis and meiosis are types of cell division. Complete the table below to show whether mitosis or meiosis is being described. Place one tick in each row. Example of cell division Mitosis Meiosis Gametes made in the testes Growth of an embryo A yeast cell budding to produce offspring Non identical cells are produced (4 marks) 1.2 The diagram shows a cell dividing. Division 1 Division 2 pair of chromosomes DNA replication dentify the type of cell division shown. Give three reasons for your decision. Meiosis because the cell divides twice to produce four cells. 1. Growth involves mitosis. Explain why growth does not involve meiosis. Meiosis produces cells that are not identical. The cells produced do not have ( marks) the same genes and therefore they are not the same. The original cell has 46 chromosomes but the cells produced by meiosis have only 2 chromosomes, and the chromosomes are all different. ( marks) 1 Give two reasons why this student did not get all four marks for How could the student have achieved more marks for 1.2? The student scored 2 marks for 1.. What extra response could have achieved the third mark for 1.? 22 Biology Unit Cell division M0_AQSB_G5_WB_GCSE_8901_B0_ indd 22 18/08/ :51
7 Your turn! Get back on track Now use what you have learned to answer this question. Remember to read the question thoroughly, looking for clues. Make good use of your knowledge. Read each feature carefully, use the additional guidance below and apply your knowledge from other areas of biology. Exam-style question 1 Mitosis and meiosis are types of cell division. 1.1 Complete the table to show which of the features are produced by mitosis and which are produced by meiosis. Feature Mitosis or meiosis? Production of egg cells A lizard growing a new tail Production of pollen in a flower Cells replaced on the skin to heal a cut Eggs need to contain only half the genetic information; this is the haploid number. Some animals can grow new body parts identical to the original one. Pollen in plants is similar to sperm in animals. Lots of new cells are made on both sides of a cut until they meet in the middle. (4 marks) Biology 1.2 dentify the organs that produce gametes (sex cells) in a man and in a woman. Think about which organs make sperm and eggs. A man A woman 1. Describe two differences between mitosis and meiosis. (2 marks) What type of cells are made? Where are they made? How many are made? What are the cells used for? (2 marks) Biology Unit Cell division 2 M0_AQSB_G5_WB_GCSE_8901_B0_ indd 2 18/08/ :51
8 Get back on track Need more practice? You need to be able to recognise where mitosis and meiosis are occurring in a given situation. Often, you will be tested on your understanding of both types of cell division in the same question. Have a go at this exam-style question. Exam-style question 1 The diagram shows two types of cell division. W X Cell division type A Y Z Cell division type B 1.1 Give the name for the type of cell division labelled type A in the diagram. 1.2 Give the name for the type of cell division labelled type B in the diagram. 1. What is the name given to cell Y? Cell W contains 8 picograms of DNA. (1 picogram = grams) 1.4 How many picograms of DNA are there in cell X? (1 mark) (1 mark) (1 mark) (1 mark) Boost your grade To improve your grade, make sure you can: understand the overall stages of the cell cycle recognise and describe mitosis occurring in different situations explain that meiosis halves the number of chromosomes but fertilisation restores a full set. How confi dent do you feel about each of these skills? Colour in the bars. 1 How can identify the stages in the cell cycle? 2 How can describe situations where mitosis is occurring? How can explain the importance of meiosis? 24 Biology Unit Cell division M0_AQSB_G5_WB_GCSE_8901_B0_ indd 24 18/08/ :51
Purposes of Cell Division
 Purposes of Cell Division Increase the number of cells for growth and repair of worn out tissues What examples in the human body can you think of? Transmit genetic information to later generations Why
Purposes of Cell Division Increase the number of cells for growth and repair of worn out tissues What examples in the human body can you think of? Transmit genetic information to later generations Why
Meiosis. Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and meiosis II
 Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
#2 How do organisms grow?
 #2 How do organisms grow? Why doesn t a cell keep growing larger and larger? The larger a cell becomes the more demands the cell places on its DNA. The cell also has trouble moving enough nutrients and
#2 How do organisms grow? Why doesn t a cell keep growing larger and larger? The larger a cell becomes the more demands the cell places on its DNA. The cell also has trouble moving enough nutrients and
Lesson Overview Meiosis
 11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
11.4 THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
What is a sex cell? How are sex cells made? How does meiosis help explain Mendel s results?
 CHAPTER 6 3 Meiosis SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a sex cell? How are sex cells made? How does meiosis help explain
CHAPTER 6 3 Meiosis SECTION Heredity BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is a sex cell? How are sex cells made? How does meiosis help explain
Q1. The diagram shows some of the cell divisions that occur during human reproduction.
 Q. The diagram shows some of the cell divisions that occur during human reproduction. (a) (i) Name the type of cell division that produces cell D from cell B. () Which organ in the male body produces cell
Q. The diagram shows some of the cell divisions that occur during human reproduction. (a) (i) Name the type of cell division that produces cell D from cell B. () Which organ in the male body produces cell
Sexual Reproduction. The two parent cells needed for sexual reproduction are called gametes. They are formed during a process known as meiosis.
 Sexual Reproduction Recall that asexual reproduction involves only one parent cell. This parent cell divides to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent. Sexual reproduction,
Sexual Reproduction Recall that asexual reproduction involves only one parent cell. This parent cell divides to produce two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent. Sexual reproduction,
Meiosis. Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and meiosis II
 Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
Meiosis A process in which the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half through the separation of homologous chromosomes to form gametes, or sex cells Two distinct divisions, called meiosis I and
10.2 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis
 10.2 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis There are thousands of different species of organisms. Each species produces more of its own. A species of bacteria splits to make two identical bacteria. A eucalyptus
10.2 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis There are thousands of different species of organisms. Each species produces more of its own. A species of bacteria splits to make two identical bacteria. A eucalyptus
Lesson 1 Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis
 Lesson 1 Name Date Class A. What is sexual reproduction? 1. produces an offspring when genetic materials from two different sex cells combine. a. The female sex cell, a(n), forms in an ovary. b. The male
Lesson 1 Name Date Class A. What is sexual reproduction? 1. produces an offspring when genetic materials from two different sex cells combine. a. The female sex cell, a(n), forms in an ovary. b. The male
Cell Division: the process of copying and dividing entire cells The cell grows, prepares for division, and then divides to form new daughter cells.
 Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
THINK ABOUT IT. Lesson Overview. Meiosis. As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located.
 Notes THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
Notes THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures?
MGC New Life Christian Academy
 A. Meiosis Main Idea: Meiosis produces haploid gametes. Key Concept: Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent. Sexual
A. Meiosis Main Idea: Meiosis produces haploid gametes. Key Concept: Asexual reproduction involves one parent and produces offspring that are genetically identical to each other and to the parent. Sexual
Unit 6 : Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction
 Unit 6 : Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction 2006-2007 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same number of chromosomes
Unit 6 : Meiosis & Sexual Reproduction 2006-2007 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same number of chromosomes
Reproduction and Meiosis. Reproduction
 Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Chapter Wrap-Up Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Asexual Reproduction Digital Vision Ltd./SuperStock Why do living things reproduce? What do you think? Before you
Chapter Introduction Lesson 1 Lesson 2 Chapter Wrap-Up Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis Asexual Reproduction Digital Vision Ltd./SuperStock Why do living things reproduce? What do you think? Before you
Lesson Overview 11.4 Meiosis
 Lesson Overview 11.4 Meiosis THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the
Lesson Overview 11.4 Meiosis THINK ABOUT IT As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the
Name Class Date. Term Definition How I m Going to Remember the Meaning
 11.4 Meiosis Lesson Objectives Contrast the number of chromosomes in body cells and in gametes. Summarize the events of meiosis. Contrast meiosis and mitosis. Describe how alleles from different genes
11.4 Meiosis Lesson Objectives Contrast the number of chromosomes in body cells and in gametes. Summarize the events of meiosis. Contrast meiosis and mitosis. Describe how alleles from different genes
Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Name: AP Biology Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Define the following terms: gene locus gamete male gamete female gamete
Name: AP Biology Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles 13.1 Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes 1. Define the following terms: gene locus gamete male gamete female gamete
Cell division / Asexual reproduction
 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produces cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes same genetic information Asexual
Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produces cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA same number of chromosomes same genetic information Asexual
Lesson Overview Meiosis
 11.4 As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures? What cellular
11.4 As geneticists in the early 1900s applied Mendel s laws, they wondered where genes might be located. They expected genes to be carried on structures inside the cell, but which structures? What cellular
Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle
 Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Name Date Class Mrs. Knight Biology EHS Unit 6 Test: The Cell Cycle 1. What are the four main stages of the cell cycle (correct order)? A. G 1, S, G 0, M C. G 2, S, G 1, M B. G 1, S, G 2, M D. M, G 2,
Science 9 Unit 2 pack: Reproduction
 Science 9 Unit 2 pack: Reproduction Name Ch 4: The Nucleus Ch 5: Mitosis Ch 6: Meiosis Students will develop an understanding of the processes of cell division as they pertain to reproduction. 0 Section
Science 9 Unit 2 pack: Reproduction Name Ch 4: The Nucleus Ch 5: Mitosis Ch 6: Meiosis Students will develop an understanding of the processes of cell division as they pertain to reproduction. 0 Section
T R L J. Version 2, 2018 NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MEIOSIS WORKBOOK
 NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MEIOSIS WORKBOOK 1 STUDY CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Instructions Regular revision throughout the year is essential. It s vital you keep a track of what you understand
NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MEIOSIS WORKBOOK 1 STUDY CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Instructions Regular revision throughout the year is essential. It s vital you keep a track of what you understand
Learning Objectives:
 Review! Why is cell division important?! What are the different types of cell division?! What are these useful for?! What are the products?! What is a somatic cell?! What is a sex cell?! What is a haploid
Review! Why is cell division important?! What are the different types of cell division?! What are these useful for?! What are the products?! What is a somatic cell?! What is a sex cell?! What is a haploid
What is mitosis? -Process in which a cell divides, creating TWO complete Sets of the original cell with the same EXACT genetic Material (DNA)
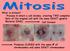 What is mitosis? -Process in which a cell divides, creating TWO complete Sets of the original cell with the same EXACT genetic Material (DNA) Cell Division Produces CLONES with the same # of chromosomes
What is mitosis? -Process in which a cell divides, creating TWO complete Sets of the original cell with the same EXACT genetic Material (DNA) Cell Division Produces CLONES with the same # of chromosomes
Why do cells divide? Why do cells divide? What would happen if they didn t?
 1 of 41 Boardworks Ltd 2007 2 of 41 Boardworks Ltd 2007 Why do cells divide? 3 of 41 Boardworks Ltd 2007 Why do cells divide? What would happen if they didn t? Organisms would only ever exist as single
1 of 41 Boardworks Ltd 2007 2 of 41 Boardworks Ltd 2007 Why do cells divide? 3 of 41 Boardworks Ltd 2007 Why do cells divide? What would happen if they didn t? Organisms would only ever exist as single
Science Unit Learning Summary
 Learning Summary Inheritance, variation and evolution Content Sexual and asexual reproduction. Meiosis leads to non-identical cells being formed while mitosis leads to identical cells being formed. In
Learning Summary Inheritance, variation and evolution Content Sexual and asexual reproduction. Meiosis leads to non-identical cells being formed while mitosis leads to identical cells being formed. In
9-4 Meiosis Meiosis. Slide 1 of 35
 9-4 Meiosis 11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 11-4 Meiosis Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that
9-4 Meiosis 11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 11-4 Meiosis Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that
Mitosis & Meiosis. PPT Questions. 4. Why must each new cell get a complete copy of the original cell s DNA?
 1. From where do new cells arise? Mitosis & Meiosis PPT Questions 2. Why does the body constantly make new cells? 3. Is cell division the same in all cells? Explain. 4. Why must each new cell get a complete
1. From where do new cells arise? Mitosis & Meiosis PPT Questions 2. Why does the body constantly make new cells? 3. Is cell division the same in all cells? Explain. 4. Why must each new cell get a complete
Binary fission occurs in prokaryotes. parent cell. DNA duplicates. cell begins to divide. daughter cells
 Chapter 11 Chapter 11 Some eukaryotes reproduce through mitosis. Binary fission is similar in function to mitosis. Asexual reproduction is the creation of offspring from a single parent. Binary fission
Chapter 11 Chapter 11 Some eukaryotes reproduce through mitosis. Binary fission is similar in function to mitosis. Asexual reproduction is the creation of offspring from a single parent. Binary fission
11-4 Meiosis Meiosis. Slide 1 of 35. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with
11-4 Meiosis 1 of 35 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with
Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction. What is Cellular Reproduction?
 Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction What is Cellular Reproduction? Answer: The division of a parent cell into two daughter cells Requirements of Each Daughter Cell: 1) Necessary genomic
Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction What is Cellular Reproduction? Answer: The division of a parent cell into two daughter cells Requirements of Each Daughter Cell: 1) Necessary genomic
CELL DIVISION: MEIOSIS
 CELL DIVISION: MEIOSIS How do Organisms Reproduce? Option 1: Asexual Reproduction Can be done by a single organism without the involvement of gametes (sperm or egg) Offspring are clones of the parent,
CELL DIVISION: MEIOSIS How do Organisms Reproduce? Option 1: Asexual Reproduction Can be done by a single organism without the involvement of gametes (sperm or egg) Offspring are clones of the parent,
Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction
 Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction Chapter 11: Cellular Reproduction What is Cellular Reproduction? Answer: The division of a parent cell into two daughter cells Requirements of
Chapter 11: The Continuity of Life: Cellular Reproduction Chapter 11: Cellular Reproduction What is Cellular Reproduction? Answer: The division of a parent cell into two daughter cells Requirements of
Title: WS CH 18.1 (see p ) Unit: Heredity (7.4.1) 18.1 Reading Outline p Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis
 Title: WS CH 18.1 (see p.612-625) Unit: Heredity (7.4.1) 18.1 Reading Outline p. 612-625 NPD A. What is sexual reproduction? (p615) 1. _ produces an offspring when genetic materials from two different
Title: WS CH 18.1 (see p.612-625) Unit: Heredity (7.4.1) 18.1 Reading Outline p. 612-625 NPD A. What is sexual reproduction? (p615) 1. _ produces an offspring when genetic materials from two different
Genetics word list. the molecule which contains genes. This will be looked at in more detail. it is shaped in a double helix (spiral)
 Genetics word list DNA the molecule which contains genes. This will be looked at in more detail. it is shaped in a double helix (spiral) Chromosomes X-shaped objects found in the nucleus of a cell. The
Genetics word list DNA the molecule which contains genes. This will be looked at in more detail. it is shaped in a double helix (spiral) Chromosomes X-shaped objects found in the nucleus of a cell. The
Sexual Reproduction and Genetics
 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics section 1 Meiosis Before You Read Think about the traits that make people unique. Some people are tall, while others are short. People can have brown, blue, or green
10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics section 1 Meiosis Before You Read Think about the traits that make people unique. Some people are tall, while others are short. People can have brown, blue, or green
Meiosis. Activity. Procedure Part I:
 Activity The purpose of meiosis, a cell division process, is to create gametes with genetic variability for use in sexual reproduction. These gametes, or the sperm and egg, are then used in the process
Activity The purpose of meiosis, a cell division process, is to create gametes with genetic variability for use in sexual reproduction. These gametes, or the sperm and egg, are then used in the process
WarmUp 1. C. a phosphate group is removed
 WarmUp 1 1. Energy is released from ATP when C. a phosphate group is removed 2. During normal mitotic cell division, a parent cell with four chromosomes will produce two daughter cells, each containing-
WarmUp 1 1. Energy is released from ATP when C. a phosphate group is removed 2. During normal mitotic cell division, a parent cell with four chromosomes will produce two daughter cells, each containing-
Warm-Up Questions. 1. What are the stages of mitosis in order? 2. The diagram represents a cell process.
 Warm-Up Questions 1. What are the stages of mitosis in order? 2. The diagram represents a cell process. Which statement regarding this process is true? A. Cell B contains the same genetic information that
Warm-Up Questions 1. What are the stages of mitosis in order? 2. The diagram represents a cell process. Which statement regarding this process is true? A. Cell B contains the same genetic information that
CELL DIVISION IN EUKARYOTES. Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 CELL DIVISION IN EUKARYOTES Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. PURPOSE: Reproduction of new cells from previously existing cells 2 of Genetically Identical
CELL DIVISION IN EUKARYOTES Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. PURPOSE: Reproduction of new cells from previously existing cells 2 of Genetically Identical
Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1
 Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1 How does a child inherit one copy of each gene from each parent? Compare what you already know with this flowchart. 1. Fill in each blank
Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1 How does a child inherit one copy of each gene from each parent? Compare what you already know with this flowchart. 1. Fill in each blank
Reproduction of Organisms
 Reproduction of Organisms Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
Reproduction of Organisms Sexual Reproduction and Meiosis What do you think? Read the three statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree
biology Slide 1 of 35 End Show Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 biology 1 of 35 Do Now: Turn in mitosis worksheet Write down your homework http://www.richannel.org/collection s/2013/chromosome#/chromosome -2 http://www.richannel.org/collection s/2013/chromosome#/chromosome
biology 1 of 35 Do Now: Turn in mitosis worksheet Write down your homework http://www.richannel.org/collection s/2013/chromosome#/chromosome -2 http://www.richannel.org/collection s/2013/chromosome#/chromosome
THE PROCESS OF LIVING THINGS CREATING OFFSPRING.
 REPRODUCTION 1 THE PROCESS OF LIVING THINGS CREATING OFFSPRING. Offspring are the next generation. It happens on multiple levels for multicellular organisms 2 SPECIES SURVIVAL Think back to 7th grade Organisms
REPRODUCTION 1 THE PROCESS OF LIVING THINGS CREATING OFFSPRING. Offspring are the next generation. It happens on multiple levels for multicellular organisms 2 SPECIES SURVIVAL Think back to 7th grade Organisms
Cell Cycle and Cell Division
 Cell Cycle and Cell Division The Cell Cycle is the series of events that take place in the cell from one cell division to another. Cell Cycle includes: 1-Interphase 2-Mitosis 3-Cytokinesis Phases of the
Cell Cycle and Cell Division The Cell Cycle is the series of events that take place in the cell from one cell division to another. Cell Cycle includes: 1-Interphase 2-Mitosis 3-Cytokinesis Phases of the
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 11. Reproduction Section 1
 Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 11 Reproduction Section 1 Reproduction Key Idea: An individual formed by asexual reproduction is genetically identical to its parent. Asexual Reproduction In asexual
Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction Chapter 11 Reproduction Section 1 Reproduction Key Idea: An individual formed by asexual reproduction is genetically identical to its parent. Asexual Reproduction In asexual
CHAPTER 3 VOCABULARY (for now)
 3.1 Meiosis CHAPTER 3 VOCABULARY (for now) VOCABULARY WORD VOCABULARY WORD diploid number Independent assortment haploid number gametes homologous chromosomes zygote genetic diversity Crossing over Sexual
3.1 Meiosis CHAPTER 3 VOCABULARY (for now) VOCABULARY WORD VOCABULARY WORD diploid number Independent assortment haploid number gametes homologous chromosomes zygote genetic diversity Crossing over Sexual
Cell Division: the process of copying and dividing entire cells The cell grows, prepares for division, and then divides to form new daughter cells.
 Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Question #1 What must occur in order for Mendel s principles to hold true?
 11.4 Question #1 What must occur in order for Mendel s principles to hold true? An organism with two parents must inherit a single copy of every gene from each parent When that organism produces gametes,
11.4 Question #1 What must occur in order for Mendel s principles to hold true? An organism with two parents must inherit a single copy of every gene from each parent When that organism produces gametes,
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION. Chapter 10
 CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION Chapter 10 Cell division = The formation of 2 daughter cells from a single parent cell Increases ratio of surface area to volume for each cell Allows for more efficient exchange
11-4 Meiosis Chromosome Number Slide 1 of 35
 Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with just one set. Chromosome
Each organism must inherit a single copy of every gene from each of its parents. Gametes are formed by a process that separates the two sets of genes so that each gamete ends up with just one set. Chromosome
biology Slide 1 of 35 End Show Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 biology 1 of 35 Why do you look a little like your mom and your dad? Why do you look a little like your grandma but your brother or sister looks a little like your grandpa? How is the way you look and
biology 1 of 35 Why do you look a little like your mom and your dad? Why do you look a little like your grandma but your brother or sister looks a little like your grandpa? How is the way you look and
Bio 105: Cell Division
 Cell Division Bio 105: Cell Division Starts with DNA Replication Laboratory 8 DNA Replication When does DNA replicate? Just prior to cell division Multicellular Organisms Grow Replace old cells Unicellular
Cell Division Bio 105: Cell Division Starts with DNA Replication Laboratory 8 DNA Replication When does DNA replicate? Just prior to cell division Multicellular Organisms Grow Replace old cells Unicellular
Cell Cycle (mitosis and meiosis) Test Review
 Cell Cycle (mitosis and meiosis) Test Review Name: Chapter 10 1. What problems are caused when a cell becomes too large? When a cell becomes too large the cell is strained and has a hard time moving enough
Cell Cycle (mitosis and meiosis) Test Review Name: Chapter 10 1. What problems are caused when a cell becomes too large? When a cell becomes too large the cell is strained and has a hard time moving enough
Cell Division THE MAJOR STEPS OF CELL DIVISION: 10/28/2013. When does DNA replicate? The first step of cell division is DNA replication:
 Cell Division Biology 105 Laboratory 8 THE MAJOR STEPS OF CELL DIVISION: When does DNA replicate? The first step of cell division is DNA replication: This occurs just prior to cell division. Cells need
Cell Division Biology 105 Laboratory 8 THE MAJOR STEPS OF CELL DIVISION: When does DNA replicate? The first step of cell division is DNA replication: This occurs just prior to cell division. Cells need
The Cell Cycle. The Cell Cycle
 The Cell Cycle Cells divide by Mitosis or Meiosis. Mitosis allows the organism to replace cells that have died or aren't working, and is how living things grow. It makes an exact copy of the parent cell.
The Cell Cycle Cells divide by Mitosis or Meiosis. Mitosis allows the organism to replace cells that have died or aren't working, and is how living things grow. It makes an exact copy of the parent cell.
Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis
 Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis 1. In mitosis, if a parent cell has 16 chromosomes, each daughter cell will have how many chromosomes? a. 64 b. 32 c. 16 d. 8 e. 4 2. Chromatids that are
Honors Biology Test Chapter 8 Mitosis and Meiosis 1. In mitosis, if a parent cell has 16 chromosomes, each daughter cell will have how many chromosomes? a. 64 b. 32 c. 16 d. 8 e. 4 2. Chromatids that are
Meiosis produces haploid gametes.
 Section 1: produces haploid gametes. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? What are the stages of
Section 1: produces haploid gametes. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions How does the reduction in chromosome number occur during meiosis? What are the stages of
Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology
 Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology by Mark Anestis Practice problems for these concepts can be found at : Cell Division Review Questions for AP Biology Mitosis During mitosis, the fourth stage of the cell
Mitosis and Meiosis for AP Biology by Mark Anestis Practice problems for these concepts can be found at : Cell Division Review Questions for AP Biology Mitosis During mitosis, the fourth stage of the cell
True or false? Comprehension Section The nucleolus directs and controls all of the cell s activities.
 Use with textbook pages 131 132. True or false? Comprehension Section 4.1 Read the statements given below. If the statement is true, write T on the line in front of the statement. If it is false, write
Use with textbook pages 131 132. True or false? Comprehension Section 4.1 Read the statements given below. If the statement is true, write T on the line in front of the statement. If it is false, write
Anaphase, Telophase. Animal cells divide their cytoplasm by forming? Cleavage furrow. Bacteria, Paramecium, Amoeba, etc. reproduce by...
 The 4 phases of mitosis Animal cells divide their cytoplasm by forming? Bacteria, Paramecium, Amoeba, etc. reproduce by... Cell which after division is identical to the original is called a Prophase, Metaphase,
The 4 phases of mitosis Animal cells divide their cytoplasm by forming? Bacteria, Paramecium, Amoeba, etc. reproduce by... Cell which after division is identical to the original is called a Prophase, Metaphase,
6-10 Sexual reproduction requires special cells (gametes) made by meiosis.
 Do Now Answer the following questions: For every cell undergoing mitosis, how many cells are created? For a cell with 6 chromosomes, how many chromosomes are in the daughter cells? Why are daughter cells
Do Now Answer the following questions: For every cell undergoing mitosis, how many cells are created? For a cell with 6 chromosomes, how many chromosomes are in the daughter cells? Why are daughter cells
MEIOSIS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU
 MEIOSIS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes such as animals, plants and fungi The number of sets of chromosomes
MEIOSIS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU Meiosis is a special type of cell division necessary for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes such as animals, plants and fungi The number of sets of chromosomes
Cell Division: the process of copying and dividing entire cells The cell grows, prepares for division, and then divides to form new daughter cells.
 Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
Mitosis & Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences for genetic variation. 1. Students will describe
5.3 Reproduction and Meiosis
 5.3 Reproduction and Meiosis Lesson Objectives Compare and contrast asexual and sexual reproduction. Give an overview of sexual reproduction, and outline the phases of meiosis. Explain why sexual reproduction
5.3 Reproduction and Meiosis Lesson Objectives Compare and contrast asexual and sexual reproduction. Give an overview of sexual reproduction, and outline the phases of meiosis. Explain why sexual reproduction
Agenda. 1. Lesson Learning Goals 2. Meiosis 3. Meiosis Bingo
 Meiosis SBI 3U Agenda 1. Lesson Learning Goals 2. Meiosis 3. Meiosis Bingo Learning Goals By the end of today s lesson, you will be able: To use proper vocabulary related to this unit, including meiosis,
Meiosis SBI 3U Agenda 1. Lesson Learning Goals 2. Meiosis 3. Meiosis Bingo Learning Goals By the end of today s lesson, you will be able: To use proper vocabulary related to this unit, including meiosis,
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Q2 (4.6) Put the following in order from biggest to smallest: Gene DNA Cell Chromosome Nucleus. Q8 (Biology) (4.6)
 Q1 (4.6) What is variation? Q2 (4.6) Put the following in order from biggest to smallest: Gene DNA Cell Chromosome Nucleus Q3 (4.6) What are genes? Q4 (4.6) What sort of reproduction produces genetically
Q1 (4.6) What is variation? Q2 (4.6) Put the following in order from biggest to smallest: Gene DNA Cell Chromosome Nucleus Q3 (4.6) What are genes? Q4 (4.6) What sort of reproduction produces genetically
KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions.
 5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle Why must cells divide? Growth and Repair -
5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 5.1 10.1 The Cell Cell Growth Cycle Why must cells divide? Growth and Repair -
= Sexual Reproduction. 2 Types of Reproduction. Key Terms Gonads- sex organs (testes, ovaries) Sexual Reproduction. What is Meiosis?
 Sexual And Meiosis 2 Types of Asexual Sexual Sexual Increases survival for both plants and animals by passing genetic material within generations. Creates VARIETY in a species by the reassortment (mixing)
Sexual And Meiosis 2 Types of Asexual Sexual Sexual Increases survival for both plants and animals by passing genetic material within generations. Creates VARIETY in a species by the reassortment (mixing)
Overview. Overview: Variations on a Theme. Offspring acquire genes from parents by inheriting chromosomes. Inheritance of Genes
 Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview I. Cell Types II. Meiosis I. Meiosis I II. Meiosis II III. Genetic Variation IV. Reproduction Overview: Variations on a Theme Figure 13.1 Living organisms
Chapter 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Overview I. Cell Types II. Meiosis I. Meiosis I II. Meiosis II III. Genetic Variation IV. Reproduction Overview: Variations on a Theme Figure 13.1 Living organisms
Gametes are the reproductive cells - the egg or the sperm. Gametes.
 Meiosis Meiosis is the type of cell division for that produces the cells ( ) which are also known as gametes. Two important characteristics of meiosis is that it reduces the number of chromosomes to half
Meiosis Meiosis is the type of cell division for that produces the cells ( ) which are also known as gametes. Two important characteristics of meiosis is that it reduces the number of chromosomes to half
Chapter 11 - Concept Mapping
 Chapter 11 - Concept Mapping Using the terms and phrases provided below, complete the concept map showing the process of meiosis. chromatids crossing-over haploid sperm and ovum homologous chromosomes
Chapter 11 - Concept Mapping Using the terms and phrases provided below, complete the concept map showing the process of meiosis. chromatids crossing-over haploid sperm and ovum homologous chromosomes
Cellular Reproduction. MXMS 7th Grade Science
 Cellular Reproduction MXMS 7th Grade Science What is cell division? 2 primary methods allow for cells to divide and reproduce themselves: A. Mitosis: produces identical offspring B. Meiosis: produces genetically
Cellular Reproduction MXMS 7th Grade Science What is cell division? 2 primary methods allow for cells to divide and reproduce themselves: A. Mitosis: produces identical offspring B. Meiosis: produces genetically
1. The process in which ( ) are produced. 2. Males produce cells and females produce cells through meiosis
 Name: Aim 35: What is Meiosis? Date: I. What is Meiosis? What is Meiosis? Which organisms undergo Meiosis? Where does Meiosis occur? What does Meiosis produce? What is Meiosis also known as? 1. The process
Name: Aim 35: What is Meiosis? Date: I. What is Meiosis? What is Meiosis? Which organisms undergo Meiosis? Where does Meiosis occur? What does Meiosis produce? What is Meiosis also known as? 1. The process
Name: Period: EOC Review Part F Outline
 Name: Period: EOC Review Part F Outline Mitosis and Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences
Name: Period: EOC Review Part F Outline Mitosis and Meiosis SC.912.L.16.17 Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis and relate to the processes of sexual and asexual reproduction and their consequences
Chapter 10.2 Notes. Genes don t exist free in the nucleus but lined up on a. In the body cells of animals and most plants, chromosomes occur in
 Chapter 10.2 Notes NAME Honors Biology Organisms have tens of thousands of genes that determine individual traits Genes don t exist free in the nucleus but lined up on a Diploid and Haploid Cells In the
Chapter 10.2 Notes NAME Honors Biology Organisms have tens of thousands of genes that determine individual traits Genes don t exist free in the nucleus but lined up on a Diploid and Haploid Cells In the
Biology Notes 2. Mitosis vs Meiosis
 Biology Notes 2 Mitosis vs Meiosis Diagram Booklet Cell Cycle (bottom corner draw cell in interphase) Mitosis Meiosis l Meiosis ll Cell Cycle Interphase Cell spends the majority of its life in this phase
Biology Notes 2 Mitosis vs Meiosis Diagram Booklet Cell Cycle (bottom corner draw cell in interphase) Mitosis Meiosis l Meiosis ll Cell Cycle Interphase Cell spends the majority of its life in this phase
CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES
 CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION The adult human body produces roughly cells every day. WHY DO CELLS REPRODUCE? So that the organism can and As multicellular organisms grow larger, its
CELL REPRODUCTION NOTES CELL GROWTH AND DIVISION The adult human body produces roughly cells every day. WHY DO CELLS REPRODUCE? So that the organism can and As multicellular organisms grow larger, its
Meiosis. The sexy shuffling machine. LO: Describe the events of meiosis Explain how meiosis creates uniqueness Compare & contrast mitosis & meiosis
 Meiosis The sexy shuffling machine LO: Describe the events of meiosis Explain how meiosis creates uniqueness Compare & contrast mitosis & meiosis http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kvmb4js99ta Meiosis Intro
Meiosis The sexy shuffling machine LO: Describe the events of meiosis Explain how meiosis creates uniqueness Compare & contrast mitosis & meiosis http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kvmb4js99ta Meiosis Intro
Ch. 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics. p
 Ch. 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics p. 270 - 10.1 Meiosis p. 270-276 Essential Question Main Idea! Meiosis produces haploid gametes Where are the instructions for each trait located in a cell?! On
Ch. 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics p. 270 - 10.1 Meiosis p. 270-276 Essential Question Main Idea! Meiosis produces haploid gametes Where are the instructions for each trait located in a cell?! On
Cell division and multiplication
 CELL DIVISION Cell division and multiplication As we already mentioned, the genetic information contained in the nucleus is hereditary Meaning it is passed on from cell to cell; from parent to child This
CELL DIVISION Cell division and multiplication As we already mentioned, the genetic information contained in the nucleus is hereditary Meaning it is passed on from cell to cell; from parent to child This
GENES, ALLELES, AND CHROMOSOMES All living things carry their genetic information in DNA Sections of DNA with instructions for making proteins are
 GENES, ALLELES, AND CHROMOSOMES All living things carry their genetic information in DNA Sections of DNA with instructions for making proteins are called genes DNA coils up to form structures called chromosomes
GENES, ALLELES, AND CHROMOSOMES All living things carry their genetic information in DNA Sections of DNA with instructions for making proteins are called genes DNA coils up to form structures called chromosomes
Mitosis & Meiosis Practice Test
 Name: DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST Class: ALL ID: A Mitosis & Meiosis Practice Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make
Name: DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST Class: ALL ID: A Mitosis & Meiosis Practice Test Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make
Cells. Unit Review: Cells MEIOSIS. TECHBOOK UNIT 0 Views. Essential Questions and Answers for Review Sheet. What is meiosis?
 Cells TECHBOOK UNIT 0 Views Unit Review: Cells MEIOSIS Essential Questions and Answers for Review Sheet What is meiosis? Answer: Meiosis is the process by which specialized cells called gametes form in
Cells TECHBOOK UNIT 0 Views Unit Review: Cells MEIOSIS Essential Questions and Answers for Review Sheet What is meiosis? Answer: Meiosis is the process by which specialized cells called gametes form in
The Cell Cycle & Cell Division
 The Cell Cycle & Cell Division http://www.nobel.se/medicine/laureates/2001/press.html The Cell Cycle Animated Cycle http://www.cellsalive.com/cell_cycle.htm MITOSIS Mitosis The process of cell division
The Cell Cycle & Cell Division http://www.nobel.se/medicine/laureates/2001/press.html The Cell Cycle Animated Cycle http://www.cellsalive.com/cell_cycle.htm MITOSIS Mitosis The process of cell division
7th 4.2 review. 1. Chromosomes line up single file at the middle of the cell. 2. Two identical nuclei form. 3. Sister chromatids separate.
 Match each activity to the correct phase of mitosis. You may use the same answer more than once. a. prophase b. metaphase c. anaphase d. telophase 1. Chromosomes line up single file at the middle of the
Match each activity to the correct phase of mitosis. You may use the same answer more than once. a. prophase b. metaphase c. anaphase d. telophase 1. Chromosomes line up single file at the middle of the
Cancer: DNA Synthesis, Mitosis, and Meiosis
 Chapter 5 Cancer: DNA Synthesis, Mitosis, and Meiosis Copyright 2007 Pearson Copyright Prentice Hall, 2007 Inc. Pearson Prentice Hall, Inc. 1 5.6 Meiosis Another form of cell division, meiosis, occurs
Chapter 5 Cancer: DNA Synthesis, Mitosis, and Meiosis Copyright 2007 Pearson Copyright Prentice Hall, 2007 Inc. Pearson Prentice Hall, Inc. 1 5.6 Meiosis Another form of cell division, meiosis, occurs
CH 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 CH 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles AP Biology 2005-2006 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA
CH 13 Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles AP Biology 2005-2006 Cell division / Asexual reproduction Mitosis produce cells with same information identical daughter cells exact copies clones same amount of DNA
Labs 7 and 8: Mitosis, Meiosis, Gametes and Genetics
 Biology 107 General Biology Labs 7 and 8: Mitosis, Meiosis, Gametes and Genetics In Biology 107, our discussion of the cell has focused on the structure and function of subcellular organelles. The next
Biology 107 General Biology Labs 7 and 8: Mitosis, Meiosis, Gametes and Genetics In Biology 107, our discussion of the cell has focused on the structure and function of subcellular organelles. The next
Sexual Reproduction ( Cell Division ) - Chromosome # s
 Sexual Reproduction ( Cell Division ) - Chromosome # s somatic cells: all the cells in the body except for specialized sex cells each somatic cell has a specific # of chromosomes - ( humans have 46, 23
Sexual Reproduction ( Cell Division ) - Chromosome # s somatic cells: all the cells in the body except for specialized sex cells each somatic cell has a specific # of chromosomes - ( humans have 46, 23
Reinforcement Unit 3 Resource Book. Meiosis and Mendel KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have.
 6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. Your body is made of two basic cell types. One basic type are somatic cells, also called body cells,
6.1 CHROMOSOMES AND MEIOSIS KEY CONCEPT Gametes have half the number of chromosomes that body cells have. Your body is made of two basic cell types. One basic type are somatic cells, also called body cells,
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles
 Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Chapter 13: Meiosis & Sexual Life Cycles What you must know The difference between asexual and sexual reproduction. The role of meiosis and fertilization in sexually reproducing organisms. The importance
Chapter 5: Mitosis is the Basis of Asexual Reproduction
 Chapter 5: Mitosis is the Basis of Asexual Reproduction Section 5.1: The Cell Cycle and Mitosis Living things must be able to reproduce. For unicellular organisms, cell reproduction is necessary to maintain
Chapter 5: Mitosis is the Basis of Asexual Reproduction Section 5.1: The Cell Cycle and Mitosis Living things must be able to reproduce. For unicellular organisms, cell reproduction is necessary to maintain
Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles
 Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Chapter Questions 1) What is a genome? A) the complete complement of an organism's genes B) a specific sequence of polypeptides within
Biology, 7e (Campbell) Chapter 13: Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycles Chapter Questions 1) What is a genome? A) the complete complement of an organism's genes B) a specific sequence of polypeptides within
Cellular Growth & Reproduction. Biology 1B Ms. Morris
 Cellular Growth & Reproduction Biology 1B Ms. Morris Friday, February 7, 2014 Warm Up: Look around at the other people in the classroom. What types of variation (differences) do you see? What similarities
Cellular Growth & Reproduction Biology 1B Ms. Morris Friday, February 7, 2014 Warm Up: Look around at the other people in the classroom. What types of variation (differences) do you see? What similarities
Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1
 Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1 Almost all the cells in your body were produced by mitosis. The only exceptions are the gametes sperm or eggs which are produced by a different
Meiosis and Fertilization Understanding How Genes Are Inherited 1 Almost all the cells in your body were produced by mitosis. The only exceptions are the gametes sperm or eggs which are produced by a different
This is DUE: Come prepared to share your findings with your group.
 Biology 160 NAME: Reading Guide 11: Population Dynamics, Humans, Part I This is DUE: Come prepared to share your findings with your group. *As before, please turn in only the Critical Thinking questions
Biology 160 NAME: Reading Guide 11: Population Dynamics, Humans, Part I This is DUE: Come prepared to share your findings with your group. *As before, please turn in only the Critical Thinking questions
2 points: Easy - Chromosomes. 2 points: Easy - Chromosomes. 2 points: Easy - Chromosomes. 2 points: Easy - Chromosomes. 2 points: Easy - Chromosomes
 the cell cycle are these cells in? Be sure to hide the Interphase What are the two Chromatids halves of a called? By definition, which cells have ½ the total number of s? Haploid the cell cycle is this
the cell cycle are these cells in? Be sure to hide the Interphase What are the two Chromatids halves of a called? By definition, which cells have ½ the total number of s? Haploid the cell cycle is this
