Taylor Series 6B. lim s x. 1 a We can evaluate the limit directly since there are no singularities: b Again, there are no singularities, so:
|
|
|
- Erick Richard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Taylor Series 6B a We can evaluate the it directly since there are no singularities: b Again, there are no singularities, so: + + c Here we should divide through by in the numerator and denominator and then use the fact that 4 : d Again, dividing through by, we find: a We make use of the Taylor epansion about : 4 sin4 4 sin !! sin4 4 4 b Here we use cos + + to see that:! 4! cos cos + + co s c We use e to see:! 9 e + + 9! e + + e! d We use arctan to see: arctan arctan4 4 Pearson Education Ltd 8. Copying permitted for purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free.
2 a We use the Taylor series for sin about π: sin cosπ( π cosπ( π + 6 sin ( π + ( π + 6 Then we find: π π sin π ( π + 6 b Here we look for a Taylor epansion about for sin( 4: d sin( 4 cos( 4 d sin( 4 sin( 4 sin( + ( + ( + cos( 4 4 4( + ( So we find that: sin( 4 ( 4+ ( a We make use of the Taylor series for ln( + about to deduce that: 4 ln( + + Then we see: ln(+ + b Now we want the Taylor series for ln about given by: Then we note that: ( ( ( + ln ( ( ln ( ( + And observe that in the it as, the second and remaining terms do go to zero, so: ln + Pearson Education Ltd 8. Copying permitted for purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free.
3 4 c We calculate the leading order terms in the denominator and numerator: ( 6 ( e e ( ln( Then we can take the it after dividing through by e e ln( to obtain: d We perform a similar procedure: e sin ( + + ( +! ! ln(+ ( + + Then in the it we have that: 5 e sin ln(+ 6 5 a The first few leading order terms in the Taylor series for sin and 5 sin + +! 5! e + +!! which can be found easily by differentiating the two functions using: d d d sin cos, cos sin, e e d d d e are: Pearson Education Ltd 8. Copying permitted for purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free.
4 5 b Now we compute: e sin sin e sin ( e Plugging in the Taylor epansions: e sin + + +! + sin ( e ( ( ( ( ( Then we can take the it: e sin sin sin ( e e + sin e + 6 a Using: d d,, d d 4 d d d ln,,, d d d we find that the first few leading order terms in the Taylor series for ln and about are given by: ln ( ( + ( +!! ln ( ( + ( + + ( ( + ( +! 4! 8 + ( ( + ( b We have that: + ln ln (ln ( ( + ( ( + + ( 8( + ( + ( ( + + ( ( 8 + ( +, as + ( + Pearson Education Ltd 8. Copying permitted for purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. 4
5 7 a We use d (sinh coshas well as d d d (cosh sinhto write down: 5 sinh where we use sinh,cosh (cosech sinh b Note that cosech sinh, so ( ( (cosech d d d 8 a We compute the necessary derivatives: ( + 4 d! + 4 (+ 4 4( ( ( + 7 b To find the it we can find a finite Taylor series for ( + ( + 8( + ( Then writing + 4 ( ( such that The it is given by: ( ( + 6 Challenge a We do the required differentiation: d dy y (+ 5 y d 5 5 (+ 5 y (+ 5 y dy 4 d ( + 5 y (+ 5 y dy y + 5y 5y 5 y Pearson Education Ltd 8. Copying permitted for purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. 5
6 Challenge b Now we make the substitution y in the epression it as is the same as taking the it as y y y y Then: (( 5y 5y y ( y+ y y and note that taking the Pearson Education Ltd 8. Copying permitted for purchasing institution only. This material is not copyright free. 6
Proof by induction ME 8
 Proof by induction ME 8 n Let f ( n) 9, where n. f () 9 8, which is divisible by 8. f ( n) is divisible by 8 when n =. Assume that for n =, f ( ) 9 is divisible by 8 for. f ( ) 9 9.9 9(9 ) f ( ) f ( )
Proof by induction ME 8 n Let f ( n) 9, where n. f () 9 8, which is divisible by 8. f ( n) is divisible by 8 when n =. Assume that for n =, f ( ) 9 is divisible by 8 for. f ( ) 9 9.9 9(9 ) f ( ) f ( )
Q Scheme Marks AOs Pearson. Notes. Deduces that 21a 168 = 0 and solves to find a = 8 A1* 2.2a
 Further Maths Core Pure (AS/Year 1) Unit Test : Matrices Q Scheme Marks AOs Pearson Finds det M 3 p p 4 p 4 p 6 1 Completes the square to show p 4 p 6 p M1.a Concludes that (p + ) + > 0 for all values
Further Maths Core Pure (AS/Year 1) Unit Test : Matrices Q Scheme Marks AOs Pearson Finds det M 3 p p 4 p 4 p 6 1 Completes the square to show p 4 p 6 p M1.a Concludes that (p + ) + > 0 for all values
Q Scheme Marks AOs Pearson ( ) 2. Notes. Deduces that 21a 168 = 0 and solves to find a = 8 A1* 2.2a
 Further Maths Core Pure (AS/Year 1) Unit Test : Matrices Q Scheme Marks AOs Pearson Finds det M = 3 p p+ 4 = p + 4 p+ 6 1 ( )( ) ( )( ) ( ) Completes the square to show p + 4p+ 6= p+ + M1.a Concludes that
Further Maths Core Pure (AS/Year 1) Unit Test : Matrices Q Scheme Marks AOs Pearson Finds det M = 3 p p+ 4 = p + 4 p+ 6 1 ( )( ) ( )( ) ( ) Completes the square to show p + 4p+ 6= p+ + M1.a Concludes that
Hyperbolic Functions 6D
 Hyperbolic Functions 6D a (sinh cosh b (cosh 5 5sinh 5 c (tanh sech (sinh cosh e f (coth cosech (sech sinh (cosh sinh cosh cosh tanh sech g (e sinh e sinh e + cosh e (cosh sinh h ( cosh cosh + sinh sinh
Hyperbolic Functions 6D a (sinh cosh b (cosh 5 5sinh 5 c (tanh sech (sinh cosh e f (coth cosech (sech sinh (cosh sinh cosh cosh tanh sech g (e sinh e sinh e + cosh e (cosh sinh h ( cosh cosh + sinh sinh
Draft Version 1 Mark scheme Further Maths Core Pure (AS/Year 1) Unit Test 1: Complex numbers 1
 1 w z k k States or implies that 4 i TBC Uses the definition of argument to write 4 k π tan 1 k 4 Makes an attempt to solve for k, for example 4 + k = k is seen. M1.a Finds k = 6 (4 marks) Pearson Education
1 w z k k States or implies that 4 i TBC Uses the definition of argument to write 4 k π tan 1 k 4 Makes an attempt to solve for k, for example 4 + k = k is seen. M1.a Finds k = 6 (4 marks) Pearson Education
Trigonometry and modelling 7E
 Trigonometry and modelling 7E sinq +cosq º sinq cosa + cosq sina Comparing sin : cos Comparing cos : sin Divide the equations: sin tan cos Square and add the equations: cos sin (cos sin ) since cos sin
Trigonometry and modelling 7E sinq +cosq º sinq cosa + cosq sina Comparing sin : cos Comparing cos : sin Divide the equations: sin tan cos Square and add the equations: cos sin (cos sin ) since cos sin
Q Scheme Marks AOs Pearson Progression Step and Progress descriptor. and sin or x 6 16x 6 or x o.e
 1a A 45 seen or implied in later working. B1 1.1b 5th Makes an attempt to use the sine rule, for example, writing sin10 sin 45 8x3 4x1 States or implies that sin10 3 and sin 45 A1 1. Solve problems involving
1a A 45 seen or implied in later working. B1 1.1b 5th Makes an attempt to use the sine rule, for example, writing sin10 sin 45 8x3 4x1 States or implies that sin10 3 and sin 45 A1 1. Solve problems involving
Differentiation 9I. 1 a. sin x 0 for 0 x π. So f ( x ) is convex on the interval. [0, π]. f ( x) 6x 6 0 for x 1. So f ( x ) is concave for all x
![Differentiation 9I. 1 a. sin x 0 for 0 x π. So f ( x ) is convex on the interval. [0, π]. f ( x) 6x 6 0 for x 1. So f ( x ) is concave for all x Differentiation 9I. 1 a. sin x 0 for 0 x π. So f ( x ) is convex on the interval. [0, π]. f ( x) 6x 6 0 for x 1. So f ( x ) is concave for all x](/thumbs/87/95085126.jpg) Differentiation 9I a f ( ) f ( ) 6 6 f ( ) 6 ii f ( ) is concave when f ( ) sin for π So f ( ) is concave on the interval [, π]. i f ( ) is conve when f ( ) 6 6 for So f ( ) is conve for all or on the
Differentiation 9I a f ( ) f ( ) 6 6 f ( ) 6 ii f ( ) is concave when f ( ) sin for π So f ( ) is concave on the interval [, π]. i f ( ) is conve when f ( ) 6 6 for So f ( ) is conve for all or on the
Trigonometric Functions Mixed Exercise
 Trigonometric Functions Mied Eercise tan = cot, -80 90 Þ tan = tan Þ tan = Þ tan = ± Calculator value for tan = + is 54.7 ( d.p.) 4 a i cosecq = cotq, 0
Trigonometric Functions Mied Eercise tan = cot, -80 90 Þ tan = tan Þ tan = Þ tan = ± Calculator value for tan = + is 54.7 ( d.p.) 4 a i cosecq = cotq, 0
b UVW is a right-angled triangle, therefore VW is the diameter of the circle. Centre of circle = Midpoint of VW = (8 2) + ( 2 6) = 100
 Circles 6F a U(, 8), V(7, 7) and W(, ) UV = ( x x ) ( y y ) = (7 ) (7 8) = 8 VW = ( 7) ( 7) = 64 UW = ( ) ( 8) = 8 Use Pythagoras' theorem to show UV UW = VW 8 8 = 64 = VW Therefore, UVW is a right-angled
Circles 6F a U(, 8), V(7, 7) and W(, ) UV = ( x x ) ( y y ) = (7 ) (7 8) = 8 VW = ( 7) ( 7) = 64 UW = ( ) ( 8) = 8 Use Pythagoras' theorem to show UV UW = VW 8 8 = 64 = VW Therefore, UVW is a right-angled
9 Mixed Exercise. vector equation is. 4 a
 9 Mixed Exercise a AB r i j k j k c OA AB 7 i j 7 k A7,, and B,,8 8 AB 6 A vector equation is 7 r x 7 y z (i j k) j k a x y z a a 7, Pearson Education Ltd 7. Copying permitted for purchasing institution
9 Mixed Exercise a AB r i j k j k c OA AB 7 i j 7 k A7,, and B,,8 8 AB 6 A vector equation is 7 r x 7 y z (i j k) j k a x y z a a 7, Pearson Education Ltd 7. Copying permitted for purchasing institution
Moments Mixed exercise 4
 Moments Mixed exercise 4 1 a The plank is in equilibrium. Let the reaction forces at the supports be R and R D. Considering moments about point D: R (6 1.5 1) = (100+ 145) (3 1.5) 3.5R = 245 1.5 3.5R =
Moments Mixed exercise 4 1 a The plank is in equilibrium. Let the reaction forces at the supports be R and R D. Considering moments about point D: R (6 1.5 1) = (100+ 145) (3 1.5) 3.5R = 245 1.5 3.5R =
( ) ( ) 2 1 ( ) Conic Sections 1 2E. 1 a. 1 dy. At (16, 8), d y 2 1 Tangent is: dx. Tangent at,8. is 1
 Conic Sections E a y y so At (6, ), d y y ( 6) y 6 y+ 6 y 6+ y+ 6 d y y At, 6 When, y, angent at, is y 6 y 6+ 6+ y 6+ y 6 y y so,, d y At y ( ) y ( ) y y+ y + y+ e 6+ y 6 y 7 7 y 7 so d d y 7 At ( 7, 7),
Conic Sections E a y y so At (6, ), d y y ( 6) y 6 y+ 6 y 6+ y+ 6 d y y At, 6 When, y, angent at, is y 6 y 6+ 6+ y 6+ y 6 y y so,, d y At y ( ) y ( ) y y+ y + y+ e 6+ y 6 y 7 7 y 7 so d d y 7 At ( 7, 7),
( ) Applications of forces 7D. 1 Suppose that the rod has length 2a. Taking moments about A: acos30 3
 Applications of forces 7D Suppose that the rod has length a. Taking moments about A: at 80 acos0 T 80 T 0. 6 N R( ), F T sin0 0 7. N R, T cos0 + R 80 R 80 0 50N In order for the rod to remain in equilibrium,
Applications of forces 7D Suppose that the rod has length a. Taking moments about A: at 80 acos0 T 80 T 0. 6 N R( ), F T sin0 0 7. N R, T cos0 + R 80 R 80 0 50N In order for the rod to remain in equilibrium,
( ) ( ) or ( ) ( ) Review Exercise 1. 3 a 80 Use. 1 a. bc = b c 8 = 2 = 4. b 8. Use = 16 = First find 8 = 1+ = 21 8 = =
 Review Eercise a Use m m a a, so a a a Use c c 6 5 ( a ) 5 a First find Use a 5 m n m n m a m ( a ) or ( a) 5 5 65 m n m a n m a m a a n m or m n (Use a a a ) cancelling y 6 ecause n n ( 5) ( 5)( 5) (
Review Eercise a Use m m a a, so a a a Use c c 6 5 ( a ) 5 a First find Use a 5 m n m n m a m ( a ) or ( a) 5 5 65 m n m a n m a m a a n m or m n (Use a a a ) cancelling y 6 ecause n n ( 5) ( 5)( 5) (
APPM 1350 Final Exam Fall 2017
 APPM 350 Final Exam Fall 207. (26 pts) Evaluate the following. (a) Let g(x) cos 3 (π 2x). Find g (π/3). (b) Let y ( x) x. Find y (4). (c) lim r 0 e /r ln(r) + (a) (9 pt) g (x) 3 cos 2 (π 2x)( sin(π 2x))(
APPM 350 Final Exam Fall 207. (26 pts) Evaluate the following. (a) Let g(x) cos 3 (π 2x). Find g (π/3). (b) Let y ( x) x. Find y (4). (c) lim r 0 e /r ln(r) + (a) (9 pt) g (x) 3 cos 2 (π 2x)( sin(π 2x))(
Solutionbank Edexcel AS and A Level Modular Mathematics
 Page of Exercise A, Question Use the binomial theorem to expand, x
Page of Exercise A, Question Use the binomial theorem to expand, x
2 4 Substituting 2 into gives 2(2) 4. + x + x +...= + + x ! 4! Substituting x= 0 and =1 into (1 + x ) + x = 0, gives 0
 Talor Series 6C 1 Differentiating = +, with respect to, gives = 1+ (1) Differentiating (1) gives = () =, = 1 into = +, gives = + (1), so = 1 1 = into (1) gives =1+ = into gives () = () = = Sousing the
Talor Series 6C 1 Differentiating = +, with respect to, gives = 1+ (1) Differentiating (1) gives = () =, = 1 into = +, gives = + (1), so = 1 1 = into (1) gives =1+ = into gives () = () = = Sousing the
Review exercise 2. 1 The equation of the line is: = 5 a The gradient of l1 is 3. y y x x. So the gradient of l2 is. The equation of line l2 is: y =
 Review exercise The equation of the line is: y y x x y y x x y 8 x+ 6 8 + y 8 x+ 6 y x x + y 0 y ( ) ( x 9) y+ ( x 9) y+ x 9 x y 0 a, b, c Using points A and B: y y x x y y x x y x 0 k 0 y x k ky k x a
Review exercise The equation of the line is: y y x x y y x x y 8 x+ 6 8 + y 8 x+ 6 y x x + y 0 y ( ) ( x 9) y+ ( x 9) y+ x 9 x y 0 a, b, c Using points A and B: y y x x y y x x y x 0 k 0 y x k ky k x a
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Trigonometric ratios 9E. b Using the line of symmetry through A. 1 a. cos 48 = 14.6 So y = 29.
 Trigonometric ratios 9E a b Using the line of symmetry through A y cos.6 So y 9. cos 9. s.f. Using sin x sin 6..7.sin 6 sin x.7.sin 6 x sin.7 7.6 x 7.7 s.f. So y 0 6+ 7.7 6. y 6. s.f. b a Using sin sin
Trigonometric ratios 9E a b Using the line of symmetry through A y cos.6 So y 9. cos 9. s.f. Using sin x sin 6..7.sin 6 sin x.7.sin 6 x sin.7 7.6 x 7.7 s.f. So y 0 6+ 7.7 6. y 6. s.f. b a Using sin sin
6675/01 Edexcel GCE Pure Mathematics P5 Further Mathematics FP2 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary
 6675/1 Edecel GCE Pure Mathematics P5 Further Mathematics FP Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Monday June 5 Morning Time: 1 hour 3 minutes 1 1. (a) Find d. (1 4 ) (b) Find, to 3 decimal places, the value of.3
6675/1 Edecel GCE Pure Mathematics P5 Further Mathematics FP Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Monday June 5 Morning Time: 1 hour 3 minutes 1 1. (a) Find d. (1 4 ) (b) Find, to 3 decimal places, the value of.3
Review exercise
 Review eercise y cos sin When : 8 y and 8 gradient of normal is 8 y When : 9 y and 8 Equation of normal is y 8 8 y8 8 8 8y 8 8 8 8y 8 8 8 8y 8 8 8 y e ln( ) e ln e When : y e ln and e Equation of tangent
Review eercise y cos sin When : 8 y and 8 gradient of normal is 8 y When : 9 y and 8 Equation of normal is y 8 8 y8 8 8 8y 8 8 8 8y 8 8 8 8y 8 8 8 y e ln( ) e ln e When : y e ln and e Equation of tangent
Finds the value of θ: θ = ( ). Accept awrt θ = 77.5 ( ). A1 ft 1.1b
 1a States that a = 4. 6 + a = 0 may be seen. B1 1.1b 4th States that b = 5. 4 + 9 + b = 0 may be seen. B1 1.1b () Understand Newton s first law and the concept of equilibrium. 1b States that R = i 9j (N).
1a States that a = 4. 6 + a = 0 may be seen. B1 1.1b 4th States that b = 5. 4 + 9 + b = 0 may be seen. B1 1.1b () Understand Newton s first law and the concept of equilibrium. 1b States that R = i 9j (N).
Trigonometric Functions 6C
 Trigonometric Functions 6C a b c d e sin 3 q æ ö ø 4 tan 6 q 4 æ ö tanq ø cos q æ ö ø 3 cosec 3 q - sin q sin q cos q sin q (using sin q + cos q ) So - sin q sin q æ ö ø 6 4cot 6 q sec q cot q secq cos
Trigonometric Functions 6C a b c d e sin 3 q æ ö ø 4 tan 6 q 4 æ ö tanq ø cos q æ ö ø 3 cosec 3 q - sin q sin q cos q sin q (using sin q + cos q ) So - sin q sin q æ ö ø 6 4cot 6 q sec q cot q secq cos
Mark scheme Mechanics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 7: Kinematics 1 (constant acceleration)
 1a Figure 1 General shape of the graph is correct. i.e. horizontal line, followed by negative gradient, followed by a positive gradient. Vertical axis labelled correctly. Horizontal axis labelled correctly.
1a Figure 1 General shape of the graph is correct. i.e. horizontal line, followed by negative gradient, followed by a positive gradient. Vertical axis labelled correctly. Horizontal axis labelled correctly.
Constant acceleration, Mixed Exercise 9
 Constant acceleration, Mixed Exercise 9 a 45 000 45 km h = m s 3600 =.5 m s 3 min = 80 s b s= ( a+ bh ) = (60 + 80).5 = 5 a The distance from A to B is 5 m. b s= ( a+ bh ) 5 570 = (3 + 3 + T ) 5 ( T +
Constant acceleration, Mixed Exercise 9 a 45 000 45 km h = m s 3600 =.5 m s 3 min = 80 s b s= ( a+ bh ) = (60 + 80).5 = 5 a The distance from A to B is 5 m. b s= ( a+ bh ) 5 570 = (3 + 3 + T ) 5 ( T +
Integration Exercises - Part 3 (Sol'ns) (Hyperbolic Functions) (12 pages; 6/2/18) (The constant of integration has been omitted throughout.
 Integration Eercises - Part (Sol'ns) (Hyperbolic Functions) ( pages; 6//8) (The constant of integration has been omitted throughout.) () cosech Given that d tanh = sech, we could investigate d coth = d
Integration Eercises - Part (Sol'ns) (Hyperbolic Functions) ( pages; 6//8) (The constant of integration has been omitted throughout.) () cosech Given that d tanh = sech, we could investigate d coth = d
Q Scheme Marks AOs. 1a States or uses I = F t M1 1.2 TBC. Notes
 Q Scheme Marks AOs Pearson 1a States or uses I = F t M1 1.2 TBC I = 5 0.4 = 2 N s Answer must include units. 1b 1c Starts with F = m a and v = u + at Substitutes to get Ft = m(v u) Cue ball begins at rest
Q Scheme Marks AOs Pearson 1a States or uses I = F t M1 1.2 TBC I = 5 0.4 = 2 N s Answer must include units. 1b 1c Starts with F = m a and v = u + at Substitutes to get Ft = m(v u) Cue ball begins at rest
( 2) ( ) Hyperbolic Functions 6E. cosh d (cosh sech ) d sinh tanh. cosh. x x x x x x C. x 1 x. 2 a. x x x = + = + cosh dx sinh C 3sinh C.
 Hyperolic Functions 6E a (sinh+ cosh ) cosh+ sinh+ + cosh cosh (cosh sech ) sinh tanh sinh sinh sechtanh sech+ cosh cosh cosh c a a sinh cosh+ cosh sinh sinh + + ( ) + + ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) arcosh + ( ) +
Hyperolic Functions 6E a (sinh+ cosh ) cosh+ sinh+ + cosh cosh (cosh sech ) sinh tanh sinh sinh sechtanh sech+ cosh cosh cosh c a a sinh cosh+ cosh sinh sinh + + ( ) + + ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) arcosh + ( ) +
h (1- sin 2 q)(1+ tan 2 q) j sec 4 q - 2sec 2 q tan 2 q + tan 4 q 2 cosec x =
 Trigonometric Functions 6D a Use + tan q sec q with q replaced with q + tan q ( ) sec ( q ) b (secq -)(secq +) sec q - (+ tan q) - tan q c tan q(cosec q -) ( ) tan q (+ cot q) - tan q cot q tan q d (sec
Trigonometric Functions 6D a Use + tan q sec q with q replaced with q + tan q ( ) sec ( q ) b (secq -)(secq +) sec q - (+ tan q) - tan q c tan q(cosec q -) ( ) tan q (+ cot q) - tan q cot q tan q d (sec
Mark scheme Pure Mathematics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 2: Coordinate geometry in the (x, y) plane
 Mark scheme Pure Mathematics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test : Coordinate in the (x, y) plane Q Scheme Marks AOs Pearson 1a Use of the gradient formula to begin attempt to find k. k 1 ( ) or 1 (k 4) ( k 1) (i.e.
Mark scheme Pure Mathematics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test : Coordinate in the (x, y) plane Q Scheme Marks AOs Pearson 1a Use of the gradient formula to begin attempt to find k. k 1 ( ) or 1 (k 4) ( k 1) (i.e.
Differentiation 9F. tan 3x. Using the result. The first term is a product with. 3sec 3. 2 x and sec x. Using the product rule for the first term: then
 Differentiation 9F a tan Using the reslt tan k k sec k sec 4tan Let tan ; then 4 sec and sec tan sec d tan tan The first term is a proct with and v tan and sec Using the proct rle for the first term: sec
Differentiation 9F a tan Using the reslt tan k k sec k sec 4tan Let tan ; then 4 sec and sec tan sec d tan tan The first term is a proct with and v tan and sec Using the proct rle for the first term: sec
A level Exam-style practice
 A level Exam-style practice 1 a e 0 b Using conservation of momentum for the system : 6.5 40 10v 15 10v 15 3 v 10 v 1.5 m s 1 c Kinetic energy lost = initial kinetic energy final kinetic energy 1 1 6.5
A level Exam-style practice 1 a e 0 b Using conservation of momentum for the system : 6.5 40 10v 15 10v 15 3 v 10 v 1.5 m s 1 c Kinetic energy lost = initial kinetic energy final kinetic energy 1 1 6.5
i j k i j k i j k
 Vectors D a The equation of the line is (r a) b0 r ba b. This gives: r (i+j k)(i+j+k) (i+j k) r (i+j k) i+0j k b The equation of the line is (r a) b0 r ba b. This gives: r ( i+ j+ k) (i k) ( i+ j+ k) 0
Vectors D a The equation of the line is (r a) b0 r ba b. This gives: r (i+j k)(i+j+k) (i+j k) r (i+j k) i+0j k b The equation of the line is (r a) b0 r ba b. This gives: r ( i+ j+ k) (i k) ( i+ j+ k) 0
90 Chapter 5 Logarithmic, Exponential, and Other Transcendental Functions. Name Class. (a) (b) ln x (c) (a) (b) (c) 1 x. y e (a) 0 (b) y.
 90 Chapter 5 Logarithmic, Eponential, and Other Transcendental Functions Test Form A Chapter 5 Name Class Date Section. Find the derivative: f ln. 6. Differentiate: y. ln y y y y. Find dy d if ey y. y
90 Chapter 5 Logarithmic, Eponential, and Other Transcendental Functions Test Form A Chapter 5 Name Class Date Section. Find the derivative: f ln. 6. Differentiate: y. ln y y y y. Find dy d if ey y. y
Circles, Mixed Exercise 6
 Circles, Mixed Exercise 6 a QR is the diameter of the circle so the centre, C, is the midpoint of QR ( 5) 0 Midpoint = +, + = (, 6) C(, 6) b Radius = of diameter = of QR = of ( x x ) + ( y y ) = of ( 5
Circles, Mixed Exercise 6 a QR is the diameter of the circle so the centre, C, is the midpoint of QR ( 5) 0 Midpoint = +, + = (, 6) C(, 6) b Radius = of diameter = of QR = of ( x x ) + ( y y ) = of ( 5
The gradient of the radius from the centre of the circle ( 1, 6) to (2, 3) is: ( 6)
 Circles 6E a (x + ) + (y + 6) = r, (, ) Substitute x = and y = into the equation (x + ) + (y + 6) = r + + + 6 = r ( ) ( ) 9 + 8 = r r = 90 = 0 b The line has equation x + y = 0 y = x + y = x + The gradient
Circles 6E a (x + ) + (y + 6) = r, (, ) Substitute x = and y = into the equation (x + ) + (y + 6) = r + + + 6 = r ( ) ( ) 9 + 8 = r r = 90 = 0 b The line has equation x + y = 0 y = x + y = x + The gradient
( y) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Trigonometric ratios, Mixed Exercise 9. 2 b. Using the sine rule. a Using area of ABC = sin x sin80. So 10 = 24sinθ.
 Trigonometric ratios, Mixed Exercise 9 b a Using area of ABC acsin B 0cm 6 8 sinθ cm So 0 4sinθ So sinθ 0 4 θ 4.6 or 3 s.f. (.) As θ is obtuse, ABC 3 s.f b Using the cosine rule b a + c ac cos B AC 8 +
Trigonometric ratios, Mixed Exercise 9 b a Using area of ABC acsin B 0cm 6 8 sinθ cm So 0 4sinθ So sinθ 0 4 θ 4.6 or 3 s.f. (.) As θ is obtuse, ABC 3 s.f b Using the cosine rule b a + c ac cos B AC 8 +
Mark Scheme (Results) June GCE Further Pure FP3 (6669) Paper 1
 Mark (Results) June 0 GCE Further Pure FP (6669) Paper Edexcel is one of the leading examining and awarding bodies in the UK and throughout the world. We provide a wide range of qualifications including
Mark (Results) June 0 GCE Further Pure FP (6669) Paper Edexcel is one of the leading examining and awarding bodies in the UK and throughout the world. We provide a wide range of qualifications including
Elastic collisions in two dimensions 5C
 Elastic collisions in two dimensions 5C 1 No change in component of velocity perpendicular to line of centres. So component of velocity for A=6sin10 Since B is stationary before impact, it will be moving
Elastic collisions in two dimensions 5C 1 No change in component of velocity perpendicular to line of centres. So component of velocity for A=6sin10 Since B is stationary before impact, it will be moving
Hyperbolic Functions Mixed Exercise 6
 Hyprbolic Functions Mid Ercis 6 a b c ln ln sinh(ln ) ln ln + cosh(ln ) + ln tanh ln ln + ( 6 ) ( + ) 6 7 ln ln ln,and ln ln ln,and ln ln 6 artanh artanhy + + y ln ln y + y ln + y + y y ln + y y + y y
Hyprbolic Functions Mid Ercis 6 a b c ln ln sinh(ln ) ln ln + cosh(ln ) + ln tanh ln ln + ( 6 ) ( + ) 6 7 ln ln ln,and ln ln ln,and ln ln 6 artanh artanhy + + y ln ln y + y ln + y + y y ln + y y + y y
Math 181, Exam 2, Study Guide 2 Problem 1 Solution. 1 + dx. 1 + (cos x)2 dx. 1 + cos2 xdx. = π ( 1 + cos π 2
 Math 8, Exam, Study Guide Problem Solution. Use the trapezoid rule with n to estimate the arc-length of the curve y sin x between x and x π. Solution: The arclength is: L b a π π + ( ) dy + (cos x) + cos
Math 8, Exam, Study Guide Problem Solution. Use the trapezoid rule with n to estimate the arc-length of the curve y sin x between x and x π. Solution: The arclength is: L b a π π + ( ) dy + (cos x) + cos
FUNCTIONS OF ONE VARIABLE FUNCTION DEFINITIONS
 Page of 6 FUNCTIONS OF ONE VARIABLE FUNCTION DEFINITIONS 6. HYPERBOLIC FUNCTIONS These functions which are defined in terms of e will be seen later to be related to the trigonometic functions via comple
Page of 6 FUNCTIONS OF ONE VARIABLE FUNCTION DEFINITIONS 6. HYPERBOLIC FUNCTIONS These functions which are defined in terms of e will be seen later to be related to the trigonometic functions via comple
Calculus for Engineers II - Sample Problems on Integrals Manuela Kulaxizi
 Calculus for Engineers II - Sample Problems on Integrals Manuela Kulaxizi Question : Solve the following integrals:. π sin x. x 4 3. 4. sinh 8 x cosh x sin x cos 7 x 5. x 5 ln x 6. 8x + 6 3x + x 7. 8..
Calculus for Engineers II - Sample Problems on Integrals Manuela Kulaxizi Question : Solve the following integrals:. π sin x. x 4 3. 4. sinh 8 x cosh x sin x cos 7 x 5. x 5 ln x 6. 8x + 6 3x + x 7. 8..
Completion Date: Monday February 11, 2008
 MATH 4 (R) Winter 8 Intermediate Calculus I Solutions to Problem Set #4 Completion Date: Monday February, 8 Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta Question. [Sec..9,
MATH 4 (R) Winter 8 Intermediate Calculus I Solutions to Problem Set #4 Completion Date: Monday February, 8 Department of Mathematical and Statistical Sciences University of Alberta Question. [Sec..9,
CHAPTER 23 MACLAURIN S SERIES
 EXERCISE 97 Page 9 CHAPTER MACLAURIN S SERIES. Determine the irst our terms o the power series or sin using Maclaurin s series. Let () sin () sin () cos () cos () sin () sin () 8 cos () 8 cos 8 i( ) 6
EXERCISE 97 Page 9 CHAPTER MACLAURIN S SERIES. Determine the irst our terms o the power series or sin using Maclaurin s series. Let () sin () sin () cos () cos () sin () sin () 8 cos () 8 cos 8 i( ) 6
2 a Substituting (1,4,7) and the coefficients. c The normal vector of the plane
 Exam-style practice: Paper 1 1 a First we find y and d x. y t t ( = + y = t t + 1 1 y t t t t = + + 1. x= t+ t = 1+ t. We now find the limits in terms of t. x= t = x=.75= t+ t t t +.75= 1± 1+ 15 t = We
Exam-style practice: Paper 1 1 a First we find y and d x. y t t ( = + y = t t + 1 1 y t t t t = + + 1. x= t+ t = 1+ t. We now find the limits in terms of t. x= t = x=.75= t+ t t t +.75= 1± 1+ 15 t = We
Draft Version 1 Mark scheme Further Maths Core Pure (AS/Year 1) Unit Test 5: Algebra and Functions. Q Scheme Marks AOs. Notes
 1 b Uses α + β = to write 4p = 6 a TBC Solves to find 3 p = Uses c αβ = to write a 30 3p = k Solves to find k = 40 9 (4) (4 marks) Education Ltd 018. Copying permitted for purchasing institution only.
1 b Uses α + β = to write 4p = 6 a TBC Solves to find 3 p = Uses c αβ = to write a 30 3p = k Solves to find k = 40 9 (4) (4 marks) Education Ltd 018. Copying permitted for purchasing institution only.
MATH 1220 Midterm 1 Thurs., Sept. 20, 2007
 MATH 220 Midterm Thurs., Sept. 20, 2007 Write your name and ID number at the top of this page. Show all your work. You may refer to one double-sided sheet of notes during the eam and nothing else. Calculators
MATH 220 Midterm Thurs., Sept. 20, 2007 Write your name and ID number at the top of this page. Show all your work. You may refer to one double-sided sheet of notes during the eam and nothing else. Calculators
= + then for all n N. n= is true, now assume the statement is. ) clearly the base case 1 ( ) ( ) ( )( ) θ θ θ θ ( θ θ θ θ)
 Complex numbers mixed exercise i a We have e cos + isin hence i i ( e + e ) ( cos + isin + cos + isin ) ( cos + isin + cos sin) cos Where we have used the fact that cos cos sin sin b We have ia ia ib ib
Complex numbers mixed exercise i a We have e cos + isin hence i i ( e + e ) ( cos + isin + cos + isin ) ( cos + isin + cos sin) cos Where we have used the fact that cos cos sin sin b We have ia ia ib ib
Pre-Calculus Mathematics Limit Process Calculus
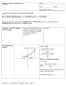 NOTES : LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES Name: Date: Period: Mrs. Nguyen s Initial: LESSON.1 THE TANGENT AND VELOCITY PROBLEMS Pre-Calculus Mathematics Limit Process Calculus The type of it that is used to find
NOTES : LIMITS AND DERIVATIVES Name: Date: Period: Mrs. Nguyen s Initial: LESSON.1 THE TANGENT AND VELOCITY PROBLEMS Pre-Calculus Mathematics Limit Process Calculus The type of it that is used to find
Solutionbank Edexcel AS and A Level Modular Mathematics
 Page of Exercise A, Question The curve C, with equation y = x ln x, x > 0, has a stationary point P. Find, in terms of e, the coordinates of P. (7) y = x ln x, x > 0 Differentiate as a product: = x + x
Page of Exercise A, Question The curve C, with equation y = x ln x, x > 0, has a stationary point P. Find, in terms of e, the coordinates of P. (7) y = x ln x, x > 0 Differentiate as a product: = x + x
2016 FAMAT Convention Mu Integration 1 = 80 0 = 80. dx 1 + x 2 = arctan x] k2
![2016 FAMAT Convention Mu Integration 1 = 80 0 = 80. dx 1 + x 2 = arctan x] k2 2016 FAMAT Convention Mu Integration 1 = 80 0 = 80. dx 1 + x 2 = arctan x] k2](/thumbs/96/127235785.jpg) 6 FAMAT Convention Mu Integration. A. 3 3 7 6 6 3 ] 3 6 6 3. B. For quadratic functions, Simpson s Rule is eact. Thus, 3. D.. B. lim 5 3 + ) 3 + ] 5 8 8 cot θ) dθ csc θ ) dθ cot θ θ + C n k n + k n lim
6 FAMAT Convention Mu Integration. A. 3 3 7 6 6 3 ] 3 6 6 3. B. For quadratic functions, Simpson s Rule is eact. Thus, 3. D.. B. lim 5 3 + ) 3 + ] 5 8 8 cot θ) dθ csc θ ) dθ cot θ θ + C n k n + k n lim
Paper Reference. Further Pure Mathematics FP3 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary. Monday 24 June 2013 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 6669/01 Edexcel GCE Further Pure Mathematics FP3 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Monday 24 June 2013 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes This is
Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 6669/01 Edexcel GCE Further Pure Mathematics FP3 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Monday 24 June 2013 Afternoon Time: 1 hour 30 minutes This is
Math 1B Final Exam, Solution. Prof. Mina Aganagic Lecture 2, Spring (6 points) Use substitution and integration by parts to find:
 Math B Final Eam, Solution Prof. Mina Aganagic Lecture 2, Spring 20 The eam is closed book, apart from a sheet of notes 8. Calculators are not allowed. It is your responsibility to write your answers clearly..
Math B Final Eam, Solution Prof. Mina Aganagic Lecture 2, Spring 20 The eam is closed book, apart from a sheet of notes 8. Calculators are not allowed. It is your responsibility to write your answers clearly..
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer GCE Further Pure Mathematics 3 (6669/01R)
 Mark (Results) Summer 03 GCE Further Pure Mathematics 3 (6669/0R) Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world s leading learning company. We provide a wide
Mark (Results) Summer 03 GCE Further Pure Mathematics 3 (6669/0R) Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world s leading learning company. We provide a wide
Elastic collisions in one dimension 4D
 Elastic collisions in one dimension 4D 1 a First collision (between A and B) 5+ 1 1= u+ v u+ v= 11 (1) 1 v u e= = 5 1 v u= () Subtracting equation () from equation (1) gives: 3u=9 u=3 Substituting into
Elastic collisions in one dimension 4D 1 a First collision (between A and B) 5+ 1 1= u+ v u+ v= 11 (1) 1 v u e= = 5 1 v u= () Subtracting equation () from equation (1) gives: 3u=9 u=3 Substituting into
Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules (continued)
 Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules (continued) Sec 3.5: Implicit Differentiation (continued) Implicit Differentiation What if you want to find the slope of the tangent line to a curve that is not the graph
Chapter 3 Differentiation Rules (continued) Sec 3.5: Implicit Differentiation (continued) Implicit Differentiation What if you want to find the slope of the tangent line to a curve that is not the graph
( ) Trigonometric identities and equations, Mixed exercise 10
 Trigonometric identities and equations, Mixed exercise 0 a is in the third quadrant, so cos is ve. The angle made with the horizontal is. So cos cos a cos 0 0 b sin sin ( 80 + 4) sin 4 b is in the fourth
Trigonometric identities and equations, Mixed exercise 0 a is in the third quadrant, so cos is ve. The angle made with the horizontal is. So cos cos a cos 0 0 b sin sin ( 80 + 4) sin 4 b is in the fourth
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer GCE Further Pure FP3 (6669) Paper 1
 Mark (Results) Summer 1 GCE Further Pure FP3 (6669) Paper 1 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world s leading learning company. We provide a wide range
Mark (Results) Summer 1 GCE Further Pure FP3 (6669) Paper 1 Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications come from Pearson, the world s leading learning company. We provide a wide range
Elastic collisions in two dimensions 5B
 Elastic collisions in two dimensions 5B a First collision: e=0.5 cos α = cos30 () sin α = 0.5 sin30 () Squaring and adding equations () and () gies: cos α+ sin α = 4cos 30 + sin 30 (cos α+ sin α)= 4 3
Elastic collisions in two dimensions 5B a First collision: e=0.5 cos α = cos30 () sin α = 0.5 sin30 () Squaring and adding equations () and () gies: cos α+ sin α = 4cos 30 + sin 30 (cos α+ sin α)= 4 3
Quality of tests Mixed exercise 8
 Quality of tests Mixed exercise 8 1 a H :p=.35 H 1 :p>.35 Assume H, so that X B(15,.35) Significance level 5%, so require c such that P( Xc)
Quality of tests Mixed exercise 8 1 a H :p=.35 H 1 :p>.35 Assume H, so that X B(15,.35) Significance level 5%, so require c such that P( Xc)
Version 1.0. General Certificate of Education (A-level) January 2011 MFP2. Mathematics. (Specification 6360) Further Pure 2.
 Version.0 General Certificate of Education (A-level) January 0 Mathematics MFP (Specification 660) Further Pure Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Eaminer and considered, together with
Version.0 General Certificate of Education (A-level) January 0 Mathematics MFP (Specification 660) Further Pure Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Eaminer and considered, together with
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER DIFFERENTIATION 4 (Products and quotients) & (Logarithmic differentiation) A.J.Hobson
 JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 104 DIFFERENTIATION 4 (Products and quotients) & (Logarithmic differentiation) by AJHobson 1041 Products 1042 Quotients 1043 Logarithmic differentiation 1044 Exercises 1045 Answers
JUST THE MATHS UNIT NUMBER 104 DIFFERENTIATION 4 (Products and quotients) & (Logarithmic differentiation) by AJHobson 1041 Products 1042 Quotients 1043 Logarithmic differentiation 1044 Exercises 1045 Answers
Mark scheme Pure Mathematics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 8: Exponentials and Logarithms
 a Substitutes (, 00) into the equation. Substitutes (5, 50) into the equation. Makes an attempt to solve the expressions by division. For 3 example, b (or equivalent) seen. 8 00 ab 6th 5 50 ab Solves for
a Substitutes (, 00) into the equation. Substitutes (5, 50) into the equation. Makes an attempt to solve the expressions by division. For 3 example, b (or equivalent) seen. 8 00 ab 6th 5 50 ab Solves for
Mark scheme Pure Mathematics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 8: Exponentials and Logarithms
 Mark scheme Pure Mathematics Year (AS) Unit Test 8: Exponentials and Logarithms a Substitutes (, 00) into the equation. Substitutes (5, 50) into the equation. Makes an attempt to solve the expressions
Mark scheme Pure Mathematics Year (AS) Unit Test 8: Exponentials and Logarithms a Substitutes (, 00) into the equation. Substitutes (5, 50) into the equation. Makes an attempt to solve the expressions
Review Exercise 2. 1 a Chemical A 5x+ Chemical B 2x+ 2y12 [ x+ Chemical C [ 4 12]
![Review Exercise 2. 1 a Chemical A 5x+ Chemical B 2x+ 2y12 [ x+ Chemical C [ 4 12] Review Exercise 2. 1 a Chemical A 5x+ Chemical B 2x+ 2y12 [ x+ Chemical C [ 4 12]](/thumbs/82/84751684.jpg) Review Exercise a Chemical A 5x+ y 0 Chemical B x+ y [ x+ y 6] b Chemical C 6 [ ] x+ y x+ y x, y 0 c T = x+ y d ( x, y) = (, ) T = Pearson Education Ltd 08. Copying permitted for purchasing institution
Review Exercise a Chemical A 5x+ y 0 Chemical B x+ y [ x+ y 6] b Chemical C 6 [ ] x+ y x+ y x, y 0 c T = x+ y d ( x, y) = (, ) T = Pearson Education Ltd 08. Copying permitted for purchasing institution
Systems of Linear Equations
 4 Systems of Linear Equations Copyright 2014, 2010, 2006 Pearson Education, Inc. Section 4.1, Slide 1 1-1 4.1 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables R.1 Fractions Objectives 1. Decide whether an
4 Systems of Linear Equations Copyright 2014, 2010, 2006 Pearson Education, Inc. Section 4.1, Slide 1 1-1 4.1 Systems of Linear Equations in Two Variables R.1 Fractions Objectives 1. Decide whether an
Q Scheme Marks AOs. Notes. Ignore any extra columns with 0 probability. Otherwise 1 for each. If 4, 5 or 6 missing B0B0.
 1a k(16 9) + k(25 9) + k(36 9) (or 7k + 16k + 27k). M1 2.1 4th = 1 M1 Þ k = 1 50 (answer given). * Model simple random variables as probability (3) 1b x 4 5 6 P(X = x) 7 50 16 50 27 50 Note: decimal values
1a k(16 9) + k(25 9) + k(36 9) (or 7k + 16k + 27k). M1 2.1 4th = 1 M1 Þ k = 1 50 (answer given). * Model simple random variables as probability (3) 1b x 4 5 6 P(X = x) 7 50 16 50 27 50 Note: decimal values
Solutions to Problem Sheet for Week 6
 THE UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS Solutions to Problem Sheet for Week 6 MATH90: Differential Calculus (Advanced) Semester, 07 Web Page: sydney.edu.au/science/maths/u/ug/jm/math90/
THE UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY SCHOOL OF MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS Solutions to Problem Sheet for Week 6 MATH90: Differential Calculus (Advanced) Semester, 07 Web Page: sydney.edu.au/science/maths/u/ug/jm/math90/
UC Merced: MATH 21 Final Exam 16 May 2006
 UC Merced: MATH 2 Final Eam 6 May 2006 On the front of your bluebook print () your name, (2) your student ID number, (3) your instructor s name (Bianchi) and () a grading table. Show all work in your bluebook
UC Merced: MATH 2 Final Eam 6 May 2006 On the front of your bluebook print () your name, (2) your student ID number, (3) your instructor s name (Bianchi) and () a grading table. Show all work in your bluebook
Pure Mathematics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 1: Algebra and Functions
 Pure Mathematics Year (AS) Unit Test : Algebra and Functions Simplify 6 4, giving your answer in the form p 8 q, where p and q are positive rational numbers. f( x) x ( k 8) x (8k ) a Find the discriminant
Pure Mathematics Year (AS) Unit Test : Algebra and Functions Simplify 6 4, giving your answer in the form p 8 q, where p and q are positive rational numbers. f( x) x ( k 8) x (8k ) a Find the discriminant
The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part question. The total number of marks for this paper is 72.
![The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part question. The total number of marks for this paper is 72. The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part question. The total number of marks for this paper is 72.](/thumbs/95/124097068.jpg) ADVANCED GCE UNIT / MATHEMATICS (MEI Further Methods for Advanced Mathematics (FP THURSDAY JUNE Additional materials: Answer booklet (8 pages Graph paper MEI Eamination Formulae and Tables (MF Morning
ADVANCED GCE UNIT / MATHEMATICS (MEI Further Methods for Advanced Mathematics (FP THURSDAY JUNE Additional materials: Answer booklet (8 pages Graph paper MEI Eamination Formulae and Tables (MF Morning
Problem Set 9 Solutions
 8.4 Problem Set 9 Solutions Total: 4 points Problem : Integrate (a) (b) d. ( 4 + 4)( 4 + 5) d 4. Solution (4 points) (a) We use the method of partial fractions to write A B (C + D) = + +. ( ) ( 4 + 5)
8.4 Problem Set 9 Solutions Total: 4 points Problem : Integrate (a) (b) d. ( 4 + 4)( 4 + 5) d 4. Solution (4 points) (a) We use the method of partial fractions to write A B (C + D) = + +. ( ) ( 4 + 5)
13 Lecture 13 L Hospital s Rule and Taylor s Theorem
 3 Lecture 3 L Hospital s Rule and Taylor s Theorem 3 L Hospital s Rule Theorem 3 L Hospital s Rule) Let a R or a = and functions f,g : a,b) R satisfy the following properties ) f,g are differentiable on
3 Lecture 3 L Hospital s Rule and Taylor s Theorem 3 L Hospital s Rule Theorem 3 L Hospital s Rule) Let a R or a = and functions f,g : a,b) R satisfy the following properties ) f,g are differentiable on
2 nd ORDER O.D.E.s SUBSTITUTIONS
 nd ORDER O.D.E.s SUBSTITUTIONS Question 1 (***+) d y y 8y + 16y = d d d, y 0, Find the general solution of the above differential equation by using the transformation equation t = y. Give the answer in
nd ORDER O.D.E.s SUBSTITUTIONS Question 1 (***+) d y y 8y + 16y = d d d, y 0, Find the general solution of the above differential equation by using the transformation equation t = y. Give the answer in
FURTHER MATHEMATICS A2/FM/CP1 A LEVEL CORE PURE 1
 Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Centre Number Candidate Number Examiner Comments Total Marks FURTHER MATHEMATICS A LEVEL CORE PURE 1 CM Bronze Set B (Edexcel Version) Time allowed: 1 hour and 30
Surname Other Names Candidate Signature Centre Number Candidate Number Examiner Comments Total Marks FURTHER MATHEMATICS A LEVEL CORE PURE 1 CM Bronze Set B (Edexcel Version) Time allowed: 1 hour and 30
a b = a a a and that has been used here. ( )
 Review Eercise ( i j+ k) ( i+ j k) i j k = = i j+ k (( ) ( ) ) (( ) ( ) ) (( ) ( ) ) = i j+ k = ( ) i ( ( )) j+ ( ) k = j k Hence ( ) ( i j+ k) ( i+ j k) = ( ) + ( ) = 8 = Formulae for finding the vector
Review Eercise ( i j+ k) ( i+ j k) i j k = = i j+ k (( ) ( ) ) (( ) ( ) ) (( ) ( ) ) = i j+ k = ( ) i ( ( )) j+ ( ) k = j k Hence ( ) ( i j+ k) ( i+ j k) = ( ) + ( ) = 8 = Formulae for finding the vector
Mark scheme. Statistics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 5: Statistical Hypothesis Testing. Pearson Progression Step and Progress descriptor. Q Scheme Marks AOs
 1a Two from: Each bolt is either faulty or not faulty. The probability of a bolt being faulty (or not) may be assumed constant. Whether one bolt is faulty (or not) may be assumed to be independent (or
1a Two from: Each bolt is either faulty or not faulty. The probability of a bolt being faulty (or not) may be assumed constant. Whether one bolt is faulty (or not) may be assumed to be independent (or
Version 1.0. General Certificate of Education (A-level) June 2012 MPC4. Mathematics. (Specification 6360) Pure Core 4. Mark Scheme
 Version.0 General Certificate of Education (A-level) June 0 Mathematics MPC (Specification 660) Pure Core Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Eaminer and considered, together with the
Version.0 General Certificate of Education (A-level) June 0 Mathematics MPC (Specification 660) Pure Core Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Principal Eaminer and considered, together with the
Differential Equations DIRECT INTEGRATION. Graham S McDonald
 Differential Equations DIRECT INTEGRATION Graham S McDonald A Tutorial Module introducing ordinary differential equations and the method of direct integration Table of contents Begin Tutorial c 2004 g.s.mcdonald@salford.ac.uk
Differential Equations DIRECT INTEGRATION Graham S McDonald A Tutorial Module introducing ordinary differential equations and the method of direct integration Table of contents Begin Tutorial c 2004 g.s.mcdonald@salford.ac.uk
Paper Reference. Further Pure Mathematics FP3 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary. Monday 22 June 2015 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes
 Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 6669/01 Edexcel GCE Further Pure Mathematics FP3 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Monday 22 June 2015 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials
Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 6669/01 Edexcel GCE Further Pure Mathematics FP3 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Monday 22 June 2015 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com. Paper Reference. Further Pure Mathematics FP3 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary
 Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 6669/01 Edexcel GCE Further Pure Mathematics FP3 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Monday 22 June 2015 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials
Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 6669/01 Edexcel GCE Further Pure Mathematics FP3 Advanced/Advanced Subsidiary Monday 22 June 2015 Morning Time: 1 hour 30 minutes Materials
Elastic strings and springs Mixed exercise 3
 Elastic strings and springs Mixed exercise ( )T cosθ mg By Hooke s law 5mgx T 6a a sinθ a + x () () () a 4 5mg Ifcos θ, T from () 5 8 5mg 5mgx so, from () 8 6a a x 4 If cos θ, then sinθ 5 5 a sinθ from
Elastic strings and springs Mixed exercise ( )T cosθ mg By Hooke s law 5mgx T 6a a sinθ a + x () () () a 4 5mg Ifcos θ, T from () 5 8 5mg 5mgx so, from () 8 6a a x 4 If cos θ, then sinθ 5 5 a sinθ from
a k 0, then k + 1 = 2 lim 1 + 1
 Math 7 - Midterm - Form A - Page From the desk of C. Davis Buenger. https://people.math.osu.edu/buenger.8/ Problem a) [3 pts] If lim a k = then a k converges. False: The divergence test states that if
Math 7 - Midterm - Form A - Page From the desk of C. Davis Buenger. https://people.math.osu.edu/buenger.8/ Problem a) [3 pts] If lim a k = then a k converges. False: The divergence test states that if
Math 122 Test 3. April 17, 2018
 SI: Math Test 3 April 7, 08 EF: 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Total Name Directions:. No books, notes or April showers. You may use a calculator to do routine arithmetic computations. You may not use your calculator
SI: Math Test 3 April 7, 08 EF: 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Total Name Directions:. No books, notes or April showers. You may use a calculator to do routine arithmetic computations. You may not use your calculator
MTH 3311 Test #1. order 3, linear. The highest order of derivative of y is 2. Furthermore, y and its derivatives are all raised to the
 MTH 3311 Test #1 F 018 Pat Rossi Name Show CLEARLY how you arrive at your answers. 1. Classify the following according to order and linearity. If an equation is not linear, eplain why. (a) y + y y = 4
MTH 3311 Test #1 F 018 Pat Rossi Name Show CLEARLY how you arrive at your answers. 1. Classify the following according to order and linearity. If an equation is not linear, eplain why. (a) y + y y = 4
Applications of forces 7C
 Applications of forces 7C 1 Let the normal reaction be R N, the friction force be F N and the coefficient of friction be µ. Resolve horizontally to find F, vertically to find R and use F µr to find µ:
Applications of forces 7C 1 Let the normal reaction be R N, the friction force be F N and the coefficient of friction be µ. Resolve horizontally to find F, vertically to find R and use F µr to find µ:
PMT. Mark Scheme (Results) Summer Pearson Edexcel GCE in Further Pure Mathematics FP3 (6669/01)
 Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 4 Pearson Edecel GCE in Further Pure Mathematics FP3 (6669/) Edecel and BTEC Qualifications Edecel and BTEC qualifications are awarded by Pearson, the UK s largest awarding
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 4 Pearson Edecel GCE in Further Pure Mathematics FP3 (6669/) Edecel and BTEC Qualifications Edecel and BTEC qualifications are awarded by Pearson, the UK s largest awarding
Section 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models. Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved
 Section 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 3 8 ( ) = + (a) f x 3x 4x x (b) ( ) g x 2 x + 3 = x 1 (a) f is a polynomial of degree 8. (b) g is
Section 4.1 Polynomial Functions and Models Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved 3 8 ( ) = + (a) f x 3x 4x x (b) ( ) g x 2 x + 3 = x 1 (a) f is a polynomial of degree 8. (b) g is
Suggested Homework Solutions
 Suggested Homework Solutions Chapter Fourteen Section #9: Real and Imaginary parts of /z: z = x + iy = x + iy x iy ( ) x iy = x #9: Real and Imaginary parts of ln z: + i ( y ) ln z = ln(re iθ ) = ln r
Suggested Homework Solutions Chapter Fourteen Section #9: Real and Imaginary parts of /z: z = x + iy = x + iy x iy ( ) x iy = x #9: Real and Imaginary parts of ln z: + i ( y ) ln z = ln(re iθ ) = ln r
! " k x 2k$1 # $ k x 2k. " # p $ 1! px! p " p 1 # !"#$%&'"()'*"+$",&-('./&-/. !"#$%&'()"*#%+!'",' -./#")'.,&'+.0#.1)2,'!%)2%! !"#$%&'"%(")*$+&#,*$,#
 "#$%&'()"*#%+'",' -./#")'.,&'+.0#.1)2,' %)2% "#$%&'"()'*"+$",&-('./&-/. Taylor Series o a unction at x a is " # a k " # " x a# k k0 k It is a Power Series centered at a. Maclaurin Series o a unction is
"#$%&'()"*#%+'",' -./#")'.,&'+.0#.1)2,' %)2% "#$%&'"()'*"+$",&-('./&-/. Taylor Series o a unction at x a is " # a k " # " x a# k k0 k It is a Power Series centered at a. Maclaurin Series o a unction is
CHAPTER 1. DIFFERENTIATION 18. As x 1, f(x). At last! We are now in a position to sketch the curve; see Figure 1.4.
 CHAPTER. DIFFERENTIATION 8 and similarly for x, As x +, fx), As x, fx). At last! We are now in a position to sketch the curve; see Figure.4. Figure.4: A sketch of the function y = fx) =/x ). Observe the
CHAPTER. DIFFERENTIATION 8 and similarly for x, As x +, fx), As x, fx). At last! We are now in a position to sketch the curve; see Figure.4. Figure.4: A sketch of the function y = fx) =/x ). Observe the
The normal distribution Mixed exercise 3
 The normal distribution Mixed exercise 3 ~ N(78, 4 ) a Using the normal CD function, P( 85).459....4 (4 d.p.) b Using the normal CD function, P( 8).6946... The probability that three men, selected at random,
The normal distribution Mixed exercise 3 ~ N(78, 4 ) a Using the normal CD function, P( 85).459....4 (4 d.p.) b Using the normal CD function, P( 8).6946... The probability that three men, selected at random,
Mark Scheme Summer 2009
 Mark Summer 009 GCE GCE Mathematics (6668/0) Edecel is one of the leading eamining and awarding bodies in the UK and throughout the world. We provide a wide range of qualifications including academic,
Mark Summer 009 GCE GCE Mathematics (6668/0) Edecel is one of the leading eamining and awarding bodies in the UK and throughout the world. We provide a wide range of qualifications including academic,
Questions. x 2 e x dx. Use Part 1 of the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus to find the derivative of the functions g(x) = x cost2 dt.
 Questions. Evaluate the Riemann sum for f() =,, with four subintervals, taking the sample points to be right endpoints. Eplain, with the aid of a diagram, what the Riemann sum represents.. If f() = ln,
Questions. Evaluate the Riemann sum for f() =,, with four subintervals, taking the sample points to be right endpoints. Eplain, with the aid of a diagram, what the Riemann sum represents.. If f() = ln,
Calculus 1 - Lab ) f(x) = 1 x. 3.8) f(x) = arcsin( x+1., prove the equality cosh 2 x sinh 2 x = 1. Calculus 1 - Lab ) lim. 2.
 ) Solve the following inequalities.) ++.) 4 >.) Calculus - Lab { + > + 5 + < +. ) Graph the functions f() =, g() = + +, h() = cos( ), r() = +. ) Find the domain of the following functions.) f() = +.) f()
) Solve the following inequalities.) ++.) 4 >.) Calculus - Lab { + > + 5 + < +. ) Graph the functions f() =, g() = + +, h() = cos( ), r() = +. ) Find the domain of the following functions.) f() = +.) f()
1a States correct answer: 5.3 (m s 1 ) B1 2.2a 4th Understand the difference between a scalar and a vector. Notes
 1a States correct answer: 5.3 (m s 1 ) B1.a 4th Understand the difference between a scalar and a vector. 1b States correct answer: 4.8 (m s 1 ) B1.a 4th Understand the difference between a scalar and a
1a States correct answer: 5.3 (m s 1 ) B1.a 4th Understand the difference between a scalar and a vector. 1b States correct answer: 4.8 (m s 1 ) B1.a 4th Understand the difference between a scalar and a
Mat104 Fall 2002, Improper Integrals From Old Exams
 Mat4 Fall 22, Improper Integrals From Old Eams For the following integrals, state whether they are convergent or divergent, and give your reasons. () (2) (3) (4) (5) converges. Break it up as 3 + 2 3 +
Mat4 Fall 22, Improper Integrals From Old Eams For the following integrals, state whether they are convergent or divergent, and give your reasons. () (2) (3) (4) (5) converges. Break it up as 3 + 2 3 +
Math 122 Test 3. April 15, 2014
 SI: Math 1 Test 3 April 15, 014 EF: 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 Total Name Directions: 1. No books, notes or 6 year olds with ear infections. You may use a calculator to do routine arithmetic computations. You may not
SI: Math 1 Test 3 April 15, 014 EF: 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 Total Name Directions: 1. No books, notes or 6 year olds with ear infections. You may use a calculator to do routine arithmetic computations. You may not
