CHEMISTRY CHAPTER- HYDROCARBONS (I PUC) One mark questions
|
|
|
- Gavin Hugh Bishop
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CEMISTRY CAPTER- YDROCARBONS (I PUC) One mark questions 1. What type of structural isomerism is shown by alkanes? 2. Which metal is used in Wurtz reaction? 3. What happens when isopropyl bromide is subjected to Wurtz reaction? 4. What is the nature of mechanism of halogenation of alkanes? 5. Which conformation of ethane is most stable? 6. Can propane show chain isomerism? 7. Why are alkenes reactive in nature? 8. What is the state of hybridization of carbon atoms in ethene? 9. Which of the following show geometrical isomerism? CCl = CCl; C 2 = CCl 2 ; CCl 2 = CCl 10. Name the halogen used o test unsaturation in a hydrocarbon? 11. Is peroxide effect applicable addition of Cl to propene? Give reason. 12. What is Bayer s reagent? 13. What is Lindlar s catalyst? 14. Name the reaction which locates the position of the double bond? 15. Give the tests to show that the given compound is an unsaturated compound. 16. Why alkynes does not show geometrical isomerism? 17. What happens when ethyne is hydrated with dilute solution of gso 4 and 2 SO 4? 18. Name the product formed when vapours of ethyne are passed through Cl solution? 19. Name the product when ethyne is reduced with Na in liquid ammonia? 20. What happens when vapours of ethyne are passed into red hot iron? 21. What is the nature of structure of benzene? 22. Why does benzene resist addition reactions? 23. Which catalyst is used in Friedel,s craft reaction? 24. Name two ortho and two meta directing groups in benzene? 25. What is the nature of substitution in benzene? 26. Who gave the present cyclic structure of benzene? 27. Which electrophile is formed during nitration of benzene? 28. What does LNG stand for? 29. Which hydrocarbon is main constitutent of CNG? Two mark questions 1. What is cracking / pyrolysis? 2. Write a short note on isomerization of alkanes? 3. Identify the products X and Y of the following reactions: Y Na +N 3, heat but-2-yne 2 / Pd/BaSO 4, eat X 1
2 4. ow will you prepare benzene from sodium benzoate? 5. What happens when benzene reacts with acetyl chloride in presence of AlCl 3. Represent in form of chemical reaction. 6. Write the conditions necessary for geometrical isomerism 7. Which one is more polar, cis-but-2-ene or trans-but-2-ene and why? 8. Write the name of ozonolysis products of but-1-ene. 9. What happens when alk.kmno4 is added to ethene? Write the reaction and the use of this reaction. 10. ow is acetylene prepared on commercial scale? 11. Name the functional group of the compound prepared by reaction of propyne with water in presence of mercuric salt and sulphuric acid. 12. State Markovnikov's rule. 13. Name the acid whose sodium salt is required for the preparation of propane? Write chemical equation for the reaction. 14. Explain Wurtz reaction with an example. Where is it used? 15. Define decarboxylation with an example. 16. Name the type of reactions which alkanes undergo. Give one example also. 17. Define conformation. 18. What happens when ethanol is heated with conc.2so4? 19. Define hydrogenation. 20. Draw the Newman s projection of ethane. 21. Benzene despite having 3 double bonds is exceptionally stable. Explain. 22. Benzene undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions easily and nucleophilic substitutions with difficulty. Explain. 23. List the names of Lewis acid other than anhydrous aluminium chloride which can be used during ethylation of benzene. 24. Define hydrocarbons. 25. What do you understand by torsional angle? Which of the conformations of ethane has the maximum and the minimum torsional strain? 26. What are the drawbacks of kekule s structure of benzene? 27. Draw the sawhorse projections of ethane 28. Which is more acidic among the following compounds, benzene, n-hexane and ethyne Arrange them in the decreasing order of acidic behaviour. Also give reason for this behaviour. Three or four mark questions 1) An alkene A on ozonlysis gives a mixture of ethanal and pentan-3-one. Write the structureand IUPAC name of alkene A. 2) Out of benzene, m dinitrobenzene and toluene which will undergo nitration most easily and why? 2
3 3) Why is Wurtz reaction not preferred for the preparation of alkanes containing odd number of carbon atoms? Illustrate your answer by taking one example. 4) State uckel s rule. Draw the structure of Pyridine and Furan. Are these aromatic? 5) Explain the mechanism involved in the chlorination of methane. 6) Explain whether the following systems are aromatic or not? (i) (ii) (iii) 7) Write IUPAC names of the following compounds: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) 8) Addition of Br to propene yields 2-bromopropane, while in the presence of benzoyl peroxide, the same reaction yields 1-bromopropane. Explain and give mechanism. 9) Write chemical reactions for the following conversions: (i) Phenol to benzene (ii) Benzene to ethyl benzene 10) ow do you convert the following? (i) Benzene to p-nitrotoulene (ii) Benzene to acetophenone (iii) Benzene to m-chloronitrobenzene 11) Discuss the orbital structure of benzene. 3
4 CEMISTRY CAPTER- YDROCARBONS (I PUC) Answers : One mark questions: 1) Chain isomerism 2) Sodium 3) 2,3-dimethyl butane 4) Free radical mechanism 5) Staggered conformation 6) No 7) Due to the presence of pi bond in carbon to carbon double bond 8) sp 2 hybridisation 9) CCl = CCl 10) Bromine 11) No. Free radical is not formed due to high bond dissociation energy of Cl 12) Dilute alkaline potassium permanganate solution. 13) Pd supported over barium sulphate or calcium carbonate poisoned with quinoline or sulphur. 14) Ozonolysis 15) a. Bayer s test b. Bromination 16) As they are linear in nature. 17) Ethanal is formed. 18) 1,1-dichloroethane 19) Trans-2-butene 20) Benzene. 21) Planar 22) Due to delocalization of pi electron charge. 23) Anhydrous aluminium chloride 24) Ortho directing groups -- O, N 2 4
5 Meta directing groups --- CO, NO 2 25) Electrophilic substitution 26) Kekule 27) Nitronium ion 28) Liquefied natural gas 29) Methane. Answers: Two mark questions 1) The decomposition of higher alkane into a mixture of lower alkanes, alkenes etc by the application of heat is called pyrolysis / cracking. 2) When unbranched alkanes are heated with anhydrous aluminium chloride and hydrogen chloride isomeric branched alkanes are formed. This process is called isomerization n-butane AlCl 3 / Cl, 570 K 2-methyl-propane 3) X is Cis-but-2-ene ; Y is trans-but-2-ene 4) 5) 5
6 6) Conditions necessary for geometrical isomerism: All compounds containing carbon-carbon double bonds do not show geometrical isomerism. The molecules must contain a double bond. Each of the two carbon atoms of the double bond must have different substituents which may be same or different. 7) Due to the occurrence of both methyl groups on the same side of the C=C bond, the combined effect of the two polar bonds makes cis-but-2-ene much more polar than trans-but-2-ene. 8) 9) 6
7 It is used to test for unsaturation. 10) On commercial scale, acetylene is prepared by reaction of calcium carbide with water. CaC O Ca(O) 2 + C ) Ketone 12) Markovnikov's rule states that, negative part of the addendum (adding molecule) gets attached to that carbon atom which possesses lesser number of hydrogen atoms. 13) Sodium salt of butanoic acid is required for the preparation of propane. C 3 C 2 C 2 COO - Na + + NaO C 3 C 2 C 3 + Na 2 CO 3 14) Alkyl halides on treatment with sodium metal in dry ether solution give higher alkanes. This reaction is known as Wurtz reaction. This reaction is used for the preparation of higher alkanes containing even number of carbon atoms. 15) Sodium salts of carboxylic acids on heating with soda lime (mixture of sodium hydroxide and calcium oxide) give alkanes containing one carbon atom less than the carboxylic acid. This elimination of carbon dioxide from a carboxylic acid is known as decarboxylation. C 3 COO - Na + + NaO C 4 + Na 2 CO 3 7
8 16) Alkanes undergo free radical substitution. The examples of this category are halogenation, nitration and sulphonation. 17) The spatial arrangements, which are obtained by free rotation around sigma bonds, are called conformation or conformational isomers. 18) Ethene is obtained. C 2 5 O C 2 = C O 19) ydrogenation is a process of adding hydrogen to unsaturated compounds, e.g., vegetable oils are unsaturated compounds which are converted into ghee by hydrogenation. 20) 21) Benzene is exceptionally stable due to resonance. The delocalised electrons cause resonance which in turn makes it stable. 22) Benzene is a planar molecule having delocalized electrons above and below the plane of ring. ence, it is electron-rich. As a result, it is highly attractive to electron deficient species i.e., electrophiles. Therefore, it undergoes electrophilic substitution reactions very easily. Nucleophiles are electron-rich. ence, they are repelled by benzene. ence, benzene undergoes nucleophilic substitutions with difficulty. 8
9 23) Any Lewis acid like anhydrous FeCl 3, SnCl 4, BF 3 etc. can be used during the ethylation of benzene. 24) Organic compounds containing only hydrogen and carbons are called hydrocarbons. 25) The repulsive interaction between the electron clouds, which affects stability of a conformation, is called torsional strain. Magnitude of torsional strain depends upon the angle of rotation about C-C bond. This angle is called dihedral angle or torsional angle. Of all the conformations of ethane, the staggered form has the least torsional strain and the eclipsed form has the maximum torsional strain. 26) a) Unusual stability of benzene. b) According to Kekule, two ortho disubstituted products are possible. But in practice only one ortho disubstituted product is known. c) eat of hydrogenation of benzene is 49.8 kcal/mole, whereas theoretical value of heat of hydrogenation of benzene is 85.8 kcal/mole. It means resonance energy is 36 kcal/mole. d) C - C bond length in benzene are equal, (although it contains 3 double bonds and 3 single bonds) and are 1.39 Å. 27) 28) Eclipsed Staggered 9
10 As the s character increases, the electronegativity of carbon increases and the electrons of C bond pair lie closer to the carbon atom. As a result, partial positive charge of atom increases and + ions are set free. The s character increases in the order: sp 3 < sp 2 < sp. ence, the decreasing order of acidic behaviour is Ethyne > Benzene > exane. Answers: Three marks / four marks questions 1) An alkene A on ozonolysis gives a mixture of ethanal and pentan-3-one. Write structure and IUPAC name of A. During ozonolysis, an ozonide having a cyclic structure is formed as an intermediate which undergoes cleavage to give the final products. Ethanal and pentan-3-one are obtained from the intermediate ozonide. ence, the expected structure of the ozonide is: This ozonide is formed as an addition of ozone to A. The desired structure of A can be obtained by the removal of ozone from the ozonide. ence, the structural formula of A is: The IUPAC name of A is 3-Ethylpent-2-ene. 2) Nitration reactions are examples of electrophilic substitution reactions 10
11 where an electron-rich species is attacked by a nitronium ion (NO + 2 ). Now, C 3 group is electron donating and NO 2 is electron withdrawing. Therefore, toluene will have the maximum electron density among the three compounds followed by benzene. On the other hand, m dinitrobenzene will have the least electron density. ence, it will undergo nitration with difficulty. 3) Wurtz reaction cannot be used for the preparation of unsymmetrical alkanes because if two dissimilar alkyl halides are taken as the reactants, then a mixture of alkanes is obtained as the products. Since the reaction involves free radical species, a side reaction also occurs to produce an alkene. For example, the reaction of bromomethane and iodoethane gives a mixture of alkanes. The boiling points of alkanes (obtained in the mixture) are very close. ence, it becomes difficult to separate them. 4) uckel s rule states that, compounds that have (4n + 2) -electrons, are said to be Aromatic compounds, where n = 1,2,3,4.etc. Pyridine is aromatic because it folllows uckel's rule and has 6 pi electrons where n=1. Furan is also aromatic compound because one of the lone pair of electrons at the oxygen delocalise towards benzene ring and then it follows uckel's rule where n=1. 5) Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the given three steps. 11
12 Step 1: Initiation: The reaction begins with the homolytic cleavage of Cl Cl bond as: Step 2: Propagation: In the second step, chlorine free radicals attack methane molecules and break down the C bond to generate methyl radicals as: These methyl radicals react with other chlorine free radicals to form methyl chloride along with the liberation of a chlorine free radical. ence, methyl free radicals and chlorine free radicals set up a chain reaction. While Cl and C 3 Cl are the major products formed, other higher halogenated compounds are also formed as: Step 3: Termination: Formation of ethane is a result of the termination of chain reactions taking place as a result of the consumption of reactants as: 12
13 6) (i) For the given compound, the number of π-electrons is 6.By uckel s rule, 4n + 2 = 6; 4n = 4; n = 1 For a compound to be aromatic, the value of n must be an integer (n = 0, 1, 2 ). Since the value of n is an integer, the given compound is aromatic in nature. (ii) For the given compound, the number of π-electrons is 4. By uckel s rule, 4n + 2 = 4; 4n = 2 ; For a compound to be aromatic, the value of n must be an integer (n = 0, 1, 2 ), which is not true for the given compound. ence, it is not aromatic in nature. (iii) For the given compound, the number of π-electrons is 8. By uckel s rule, 4n + 2 = 8; 4n = 6; For a compound to be aromatic, the value of n must be an integer (n = 0, 1, 2 ). Since the value of n is not an integer, the given compound is not aromatic in nature. 7) (i) Pen-1-ene-3-yne (ii) Buta-1,3-diene (iii) 4-Phenyl but-1-ene 13
14 (iv) 2-Methyl phenol 8) This reaction follows Markovnikov s rule where the negative part of the addendum is attached to the carbon atom having a lesser number of hydrogen atoms. In the presence of benzoyl peroxide, an addition reaction takes place anti to Markovnikov s rule. The reaction follows a free radical chain mechanism as: 14
15 Secondary free radicals are more stable than primary radicals. ence, the former predominates since it forms at a faster rate. Thus, 1 bromopropane is obtained as the major product. In the presence of peroxide, Br free radical acts as an electrophile. ence, two different products are obtained on addition of Br to propene in the absence and presence of peroxide. 9) (i) Phenol into benzene. (ii)benzene into ethyl benzene. 10) (i)benzene to p-nitro toluene 15
16 (ii) Benzene to acetophenone (iii) Benzene to m-chloronitrobenzene 16
17 11) The structure of benzene molecule is best described in terms of molecular orbital treatment theory. According to this theory, all the C-atoms in benzene are sp 2 - hybridized. Two sp 2 -hybrid orbitals of each C-atom overlap with two sp 2 -hybrid orbital of two other C-atoms to form sigma bonds. In this way there are six sigma bonds are formed between six C-atoms which are 120 o apart. Remaining six sp 2 -orbital of six C- atoms overlap with 1s orbital of six -atoms individually to form six sigma bonds. Since sigma bond results from the overlap of above said planar orbital, all and C atoms are in the same plane and their generate a hexagonal ring of C-atoms. Each C-atom in benzene also has an unhybrid 2pz-orbital containing one electron. These 2pz-orbital are perpendicular to the plane of sigma bonds. These 2pz-orbitals by lateral overlapping form three alternate pi-bonds in benzene ring.there are two possibilities of pi-bond formation in benzene. 17
18 OR Actually these 2pz-orbital produce a pi-molecular orbital containing six electrons. One half of this pi- molecular orbital lies above the plane of hexagonal ring and remaining half below the ring like a sandwich. 18
Class XI Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons Chemistry
 Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
1. How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane?
 1. How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? The formation of ethane is due to the side reaction in termination step by the combination of two CH 3 free radicals. 2.
1. How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? The formation of ethane is due to the side reaction in termination step by the combination of two CH 3 free radicals. 2.
DAV CENTENARY PUBLIC SCHOOL, PASCHIM ENCLAVE, NEW DELHI - 87
 HYDROCARBONS 1. Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain. 2. Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia
HYDROCARBONS 1. Why do alkenes prefer to undergo electrophilic addition reaction while arenes prefer electrophilic substitution reactions? Explain. 2. Alkynes on reduction with sodium in liquid ammonia
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)
 Unit 13 HYDROCARBONS I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Arrange the following in decreasing order of their boiling points. (A) n butane (B) 2 methylbutane (C) n-pentane (D) 2,2 dimethylpropane A
Unit 13 HYDROCARBONS I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Arrange the following in decreasing order of their boiling points. (A) n butane (B) 2 methylbutane (C) n-pentane (D) 2,2 dimethylpropane A
CHAPTER HYDROCARBONS. Chapterwise Previous year Qs. (a) Na (b) HCl in H2O (c) KOH in C2H5OH (d) Zn in alcohol. Ans: (c)
 122 CHAPTER HYDROCARBONS 1. Acetylenic hydrogens are acidic because [1989] Sigma electron density of C Hbond in acetylene is nearer to carbon, which has 50% s- character Acetylene has only open hydrogen
122 CHAPTER HYDROCARBONS 1. Acetylenic hydrogens are acidic because [1989] Sigma electron density of C Hbond in acetylene is nearer to carbon, which has 50% s- character Acetylene has only open hydrogen
ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE (AUTONOMOUS) ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE ROAD, CUDDALORE CH101T ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I (SEMESTER-I)
 UNIT I 1. The hybridization involved in the formation of acetylene is a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) sp 3 d 2. The IUPAC name of is 1. 3-hexene b) 4-hexene c) 3-hexyne d) 4-hexyne 3. -------- is the type of
UNIT I 1. The hybridization involved in the formation of acetylene is a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) sp 3 d 2. The IUPAC name of is 1. 3-hexene b) 4-hexene c) 3-hexyne d) 4-hexyne 3. -------- is the type of
Downloaded from
 1 Class XI Chemistry Ch 13: Hydrocarbons TOP Concepts: 1. Alkanes: General formula: C n H 2n+2 2. Preparation of alkanes: 3. Kolbe s electrolytic method: Alkali metal salts of carboxylic acids undergo
1 Class XI Chemistry Ch 13: Hydrocarbons TOP Concepts: 1. Alkanes: General formula: C n H 2n+2 2. Preparation of alkanes: 3. Kolbe s electrolytic method: Alkali metal salts of carboxylic acids undergo
 1 TOP Concepts: Class XI Chemistry Ch 13: Hydrocarbons 1. Alkanes: General formula: C n H 2n+2 2. Preparation of alkanes: 3. Kolbe s electrolytic method: Alkali metal salts of carboxylic acids undergo
1 TOP Concepts: Class XI Chemistry Ch 13: Hydrocarbons 1. Alkanes: General formula: C n H 2n+2 2. Preparation of alkanes: 3. Kolbe s electrolytic method: Alkali metal salts of carboxylic acids undergo
Organic Mechanisms 1
 Organic Mechanisms 1 Concepts The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page Chemical properties of alkanes 314 Chemical properties of alkenes 318 Bonding in alkenes 320 Bonding
Organic Mechanisms 1 Concepts The key ideas required to understand this section are: Concept Book page Chemical properties of alkanes 314 Chemical properties of alkenes 318 Bonding in alkenes 320 Bonding
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 3. AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS Aromatic
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 3. AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS Aromatic
Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes. Excluded sections 3.15&3.16
 Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes Excluded sections 3.15&3.16 3.1 Definition and Classification Alkene: a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carboncarbon double bonds. ethylene is the simplest alkene. Alkyne:
Chapter 3 Alkenes and Alkynes Excluded sections 3.15&3.16 3.1 Definition and Classification Alkene: a hydrocarbon that contains one or more carboncarbon double bonds. ethylene is the simplest alkene. Alkyne:
Chapter 12: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
 Chapter 12: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS contain carbon-carbon multiple bonds. Alkenes C=C double bonds Alkynes triple bonds Aromatics benzene rings 1 2 NAMING ALKENES Step 1: Name
Chapter 12: Unsaturated Hydrocarbons UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS contain carbon-carbon multiple bonds. Alkenes C=C double bonds Alkynes triple bonds Aromatics benzene rings 1 2 NAMING ALKENES Step 1: Name
Chapter 17. Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic system, they are available to attack a strong electrophile to give
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic system, they are available to attack a strong electrophile to give
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 201/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry CHE1502/201/1/2016
 CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS
 BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS The discovery of benzene: 1825 - Michael Faraday, empirical formula of C 1834 - Eilhard Mitscherlich synthesized benzin from gum benzoin, empirical formula C Aromatic The
BENZENE AND AROMATIC COMPOUNDS The discovery of benzene: 1825 - Michael Faraday, empirical formula of C 1834 - Eilhard Mitscherlich synthesized benzin from gum benzoin, empirical formula C Aromatic The
Chem 145 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Alkynes
 Dr. Seham ALTERARY Chem 145 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Alkynes Chapter 4 1434-1435 2013-2014 2 st semester By the end of this chapter you should be familiar with: Definition for Alkynes. Nomenclature of
Dr. Seham ALTERARY Chem 145 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Alkynes Chapter 4 1434-1435 2013-2014 2 st semester By the end of this chapter you should be familiar with: Definition for Alkynes. Nomenclature of
1. CONCEPTS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2. SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 3. ISOMERISM II 4. HYDROCARBONS II 5. HALOALKANES. Vikasana - CET 2012
 CET OBJECTIVE QUESTION ON 1. CONCEPTS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2. SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 3. ISOMERISM II 4. HYDROCARBONS II 5. HALOALKANES 1.The inductive effect a. Implies the atoms ability to cause
CET OBJECTIVE QUESTION ON 1. CONCEPTS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2. SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 3. ISOMERISM II 4. HYDROCARBONS II 5. HALOALKANES 1.The inductive effect a. Implies the atoms ability to cause
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 RGANIC CEMISTRY Short Answer Questions: 1. Explain the following with suitable examples? a) Wurtz Reaction. b) Kolbe s Electrolysis. c) Friedal Craft s Alkylation Ans. a) Wurtz Reaction: Alkyl halides
RGANIC CEMISTRY Short Answer Questions: 1. Explain the following with suitable examples? a) Wurtz Reaction. b) Kolbe s Electrolysis. c) Friedal Craft s Alkylation Ans. a) Wurtz Reaction: Alkyl halides
Detailed Course Content
 Detailed Course Content Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds The Structural Theory of Organic Chemistry 4 Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule 6 Lewis Structures 8 Formal Charge 11 Resonance 14 Quantum
Detailed Course Content Chapter 1: Carbon Compounds and Chemical Bonds The Structural Theory of Organic Chemistry 4 Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule 6 Lewis Structures 8 Formal Charge 11 Resonance 14 Quantum
Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds. Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons
 Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons Reactions of Alkanes Single bonds (C-C) are strong and very hard to break, therefore these compounds are relatively unreactive
Chapter 1 Reactions of Organic Compounds Reactions Involving Hydrocarbons Reactions of Alkanes Single bonds (C-C) are strong and very hard to break, therefore these compounds are relatively unreactive
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 203/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry
 E1502/203/1/2016 Tutorial letter 203/1/2016 General hemistry 1B E1502 Semester 1 Department of hemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 3. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY T
E1502/203/1/2016 Tutorial letter 203/1/2016 General hemistry 1B E1502 Semester 1 Department of hemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 3. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY T
Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry The study of carbon compounds constitutes a separate branch of chemistry known as organic chemistry The
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry The study of carbon compounds constitutes a separate branch of chemistry known as organic chemistry The
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Chem 263 ct. 8, 2013 lectrophilic Aromatic Substitution Benzene appears to be a remarkably stable and unreactive compared to alkenes, such as cyclohexene or ethylene, or even alkanes, such as cyclohexane
Chem 263 ct. 8, 2013 lectrophilic Aromatic Substitution Benzene appears to be a remarkably stable and unreactive compared to alkenes, such as cyclohexene or ethylene, or even alkanes, such as cyclohexane
1. CONCEPTS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2. SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 3. ISOMERISM II 4. HYDROCARBONS II 5. HALOALKANES. Vikasana - CET 2012
 CET OBJECTIVE QUESTION ON 1. CONCEPTS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2. SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 3. ISOMERISM II 4. HYDROCARBONS II 5. HALOALKANES 1.The inductive effect a. Implies the atoms ability to cause
CET OBJECTIVE QUESTION ON 1. CONCEPTS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2. SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 3. ISOMERISM II 4. HYDROCARBONS II 5. HALOALKANES 1.The inductive effect a. Implies the atoms ability to cause
Mechanisms. . CCl2 F + Cl.
 Mechanisms 1) Free radical substitution Alkane à halogenoalkane Initiation: Propagation: Termination: Overall: 2) Ozone depletion UV light breaks the C Cl bond releasing chlorine radical CFCl 3 F à. CCl2
Mechanisms 1) Free radical substitution Alkane à halogenoalkane Initiation: Propagation: Termination: Overall: 2) Ozone depletion UV light breaks the C Cl bond releasing chlorine radical CFCl 3 F à. CCl2
Organic Chemistry. February 18, 2014
 Organic Chemistry February 18, 2014 What does organic mean? Organic Describes products Grown through natural biological process Without synthetic materials In the 18 th century Produced by a living system
Organic Chemistry February 18, 2014 What does organic mean? Organic Describes products Grown through natural biological process Without synthetic materials In the 18 th century Produced by a living system
Organic Chemistry SL IB CHEMISTRY SL
 Organic Chemistry SL IB CHEMISTRY SL 10.1 Fundamentals of organic chemistry Understandings: A homologous series is a series of compounds of the same family, with the same general formula, which differ
Organic Chemistry SL IB CHEMISTRY SL 10.1 Fundamentals of organic chemistry Understandings: A homologous series is a series of compounds of the same family, with the same general formula, which differ
Chapter 4: Aromatic Compounds. Bitter almonds are the source of the aromatic compound benzaldehyde
 Chapter 4: Aromatic Compounds Bitter almonds are the source of the aromatic compound benzaldehyde Sources of Benzene Benzene, C 6 H 6, is the parent hydrocarbon of the especially stable compounds known
Chapter 4: Aromatic Compounds Bitter almonds are the source of the aromatic compound benzaldehyde Sources of Benzene Benzene, C 6 H 6, is the parent hydrocarbon of the especially stable compounds known
Benzene and Aromatic Compounds
 1 Background Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Benzene has four degrees of unsaturation, making it a highly unsaturated hydrocarbon. Whereas
1 Background Benzene and Aromatic Compounds Benzene (C 6 H 6 ) is the simplest aromatic hydrocarbon (or arene). Benzene has four degrees of unsaturation, making it a highly unsaturated hydrocarbon. Whereas
Alkenes. Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents
 Alkenes Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents Alkenes Family of hydrocarbons, the alkenes, which contain less hydrogen, carbon for carbon, than the alkanes Structure of ethylene, The carbon-carbon
Alkenes Dr. Munther A. M-Ali For 1 st Stage Setudents Alkenes Family of hydrocarbons, the alkenes, which contain less hydrogen, carbon for carbon, than the alkanes Structure of ethylene, The carbon-carbon
Organic Chemistry Worksheets
 Highlight the single longest, continuous carbon-carbon chain. Note the alkyl branches that are connected to the root chain. Count the carbons in the root chain, starting from the end closest to the alkyl
Highlight the single longest, continuous carbon-carbon chain. Note the alkyl branches that are connected to the root chain. Count the carbons in the root chain, starting from the end closest to the alkyl
2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Isolated and Conjugated Dienes
 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Isolated and Conjugated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Reactions of Isolated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. The Mechanism Double Bonds can have Different Reactivities
2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Isolated and Conjugated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. Reactions of Isolated Dienes 2016 Pearson Education, Inc. The Mechanism Double Bonds can have Different Reactivities
Arrange the following alkene in increasing order of their enthalpy of hydrogenation ( )
 Q.1. Which of the statements is correct? (I) Melting point of alkane increases with increase of C atoms and with increase in branching. (II) Boiling point of alkane increases with increase of C atoms but
Q.1. Which of the statements is correct? (I) Melting point of alkane increases with increase of C atoms and with increase in branching. (II) Boiling point of alkane increases with increase of C atoms but
1. What is the letter designation given to dumbbell shaped orbitals like the one depicted below?
 1. What is the letter designation given to dumbbell shaped orbitals like the one depicted below? 2. Which of the following does not have an octet of electrons surrounding the central atom? A. B 3 B. C
1. What is the letter designation given to dumbbell shaped orbitals like the one depicted below? 2. Which of the following does not have an octet of electrons surrounding the central atom? A. B 3 B. C
Q.1 Draw out suitable structures which fit the molecular formula C 6 H 6
 Aromatic compounds 2814 1 BENZENE Structure Primary analysis revealed benzene had an... empirical formula of and a molecular formula of 6 6 Q.1 Draw out suitable structures which fit the molecular formula
Aromatic compounds 2814 1 BENZENE Structure Primary analysis revealed benzene had an... empirical formula of and a molecular formula of 6 6 Q.1 Draw out suitable structures which fit the molecular formula
Chapter 5. Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 5. Aromatic Compounds 5.1 Structure of Benzene: The Kekule Proposal Mid-1800s, benzene was known to have the molecular formula C 6 6. Benzene reacts with 2 in the presence of iron to give substitution
Chapter 5. Aromatic Compounds 5.1 Structure of Benzene: The Kekule Proposal Mid-1800s, benzene was known to have the molecular formula C 6 6. Benzene reacts with 2 in the presence of iron to give substitution
Assignment - 3. Organic Chemistry
 Assignment - 3 Organic hemistry 85 ORGANI EMISTRY Assignment Sheet 1. (a) For each of the compounds : (i) Ethane (ii) Vinegar, (iii) Marsh gas, draw the relevant structural formula. (b) (i) What words
Assignment - 3 Organic hemistry 85 ORGANI EMISTRY Assignment Sheet 1. (a) For each of the compounds : (i) Ethane (ii) Vinegar, (iii) Marsh gas, draw the relevant structural formula. (b) (i) What words
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY- 1
 ORGANIC CEMISTRY- 1 ALKENES Alkenes are also called Olefins (C n 2n ) unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes occur abundantly in nature. Ethylene ( 2 C=C 2 ) is a plant hormone that induces ripening in fruit.
ORGANIC CEMISTRY- 1 ALKENES Alkenes are also called Olefins (C n 2n ) unsaturated hydrocarbons. Alkenes occur abundantly in nature. Ethylene ( 2 C=C 2 ) is a plant hormone that induces ripening in fruit.
Part Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital of an atom overlaps with p orbital of another atoms]
![Part Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital of an atom overlaps with p orbital of another atoms] Part Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital of an atom overlaps with p orbital of another atoms]](/thumbs/89/100347388.jpg) Program Name B.Sc. (Chemistry) B.Sc. - Part I Paper Code CH- 02 (Organic chemistry) Section A (Very Short Answer Questions 2 Each Question Carries 2 Marks Part -1 1. Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital
Program Name B.Sc. (Chemistry) B.Sc. - Part I Paper Code CH- 02 (Organic chemistry) Section A (Very Short Answer Questions 2 Each Question Carries 2 Marks Part -1 1. Define s-p overlapping. [When s orbital
Chapter 3. Alkenes And Alkynes
 Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
Class XII - Chemistry Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acid Chapter-wise Problems
 Class XII - Chemistry Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acid Chapter-wise Problems I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Addition of water to alkynes occurs in acidic medium and in the presence of Hg
Class XII - Chemistry Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acid Chapter-wise Problems I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Addition of water to alkynes occurs in acidic medium and in the presence of Hg
1. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy of activation?.
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy of activation?. A) +. +. B) + +. C) +.. + D) +.. + E) +.. + 2. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy of activation?. A) +. +. B) + +. C) +.. + D) +.. + E) +.. + 2. Which of the following reactions would have the smallest energy
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Chem 263 Sept 29, 2016 lectrophilic Aromatic Substitution Benzene appears to be a remarkably stable (36 kcal/mole more) and unreactive compared to alkenes, such as cyclohexene or ethylene, or even alkanes,
Chem 263 Sept 29, 2016 lectrophilic Aromatic Substitution Benzene appears to be a remarkably stable (36 kcal/mole more) and unreactive compared to alkenes, such as cyclohexene or ethylene, or even alkanes,
Organic Chemistry. Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon.
 Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon. In this chapter we will discuss the structural features of organic molecules, nomenclature, and a
Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon. In this chapter we will discuss the structural features of organic molecules, nomenclature, and a
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition
 16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Substitution Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives Benzene is aromatic: a cyclic conjugated
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition Substitution Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives Benzene is aromatic: a cyclic conjugated
Chapter 8: Chemistry of Alkynes (C n H 2n-2 )
 hapter 8: hemistry of Alkynes ( n 2n-2 ) Bonding & hybridization Both are sp-hybridized Bond angles = 180 o 1 σ + 2 π bonds Linear around lassification R R R' σ bond energy: 88 kcal/mol π bond energy:
hapter 8: hemistry of Alkynes ( n 2n-2 ) Bonding & hybridization Both are sp-hybridized Bond angles = 180 o 1 σ + 2 π bonds Linear around lassification R R R' σ bond energy: 88 kcal/mol π bond energy:
Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing.
 Chapter 21 Lecture Notes Organic Chemistry Intro Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing. The Bonding of Carbon Because carbon has four valence electrons, it can form covalent bonds.
Chapter 21 Lecture Notes Organic Chemistry Intro Organic Chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing. The Bonding of Carbon Because carbon has four valence electrons, it can form covalent bonds.
SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 1. The credit for synthesizing first organic compound in the laboratory went to a) Berzelius b) Wohler c) Kolbe d) Berthelot Ans : b) Wohler [Note : (i) N H 4 Cl+KCNO NH 4 CNO
SYNTHETIC ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 1. The credit for synthesizing first organic compound in the laboratory went to a) Berzelius b) Wohler c) Kolbe d) Berthelot Ans : b) Wohler [Note : (i) N H 4 Cl+KCNO NH 4 CNO
Plymstock School. Arenes. P.J.McCormack
 Plymstock School 1 A2 Chemistry F324: Rings, Polymers & Analysis 4.1.1 - Arenes Arenes P.J.McCormack 2 4.1.1 Arenes Objective Checklist Draw the structure of benzene Explain the terms arene and aromatic
Plymstock School 1 A2 Chemistry F324: Rings, Polymers & Analysis 4.1.1 - Arenes Arenes P.J.McCormack 2 4.1.1 Arenes Objective Checklist Draw the structure of benzene Explain the terms arene and aromatic
Chapter 16 Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 16 Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Paul D. Adams University of Arkansas Substitution Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives
John E. McMurry www.cengage.com/chemistry/mcmurry Chapter 16 Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Paul D. Adams University of Arkansas Substitution Reactions of Benzene and Its Derivatives
Chapter 9 Alkynes. Introduction
 hapter 9 Alkynes Introduction Alkynes contain a triple bond. General formula is n 2n-2. Two elements of unsaturation for each triple bond. MST reactions are like alkenes: addition and oxidation. Some reactions
hapter 9 Alkynes Introduction Alkynes contain a triple bond. General formula is n 2n-2. Two elements of unsaturation for each triple bond. MST reactions are like alkenes: addition and oxidation. Some reactions
Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Why this Chapter? Continuation of coverage of aromatic compounds in preceding chapter focus shift to understanding reactions Examine relationship
Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Why this Chapter? Continuation of coverage of aromatic compounds in preceding chapter focus shift to understanding reactions Examine relationship
Chapter 9 Alkynes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 9 Alkynes Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 9.1 Sources of Alkynes Acetylene Industrial preparation of acetylene is by dehydrogenation of
Chapter 9 Alkynes Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 9.1 Sources of Alkynes Acetylene Industrial preparation of acetylene is by dehydrogenation of
CHAPTER 3 ALKENES, ALKYNES & CONJUGATE DIENES
 CHEM 244 PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERING STUDENTS, COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING PRE-REQUISITES COURSE; CHEM 101 CREDIT HOURS; 2 (2+0) Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College
CHEM 244 PRINCIPLES OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I FOR CHEMICAL ENGINEERING STUDENTS, COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING PRE-REQUISITES COURSE; CHEM 101 CREDIT HOURS; 2 (2+0) Dr. Mohamed El-Newehy Chemistry Department, College
Organic Chemistry, 7 L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter , Prentice Hall
 Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds 2010, Prentice Hall Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although h benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic
Organic Chemistry, 7 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds 2010, Prentice Hall Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Although h benzene s pi electrons are in a stable aromatic
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution
 Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophile substitutes for a hydrogen on the benzene ring. Chapter 17: Aromatics 2-Reactions Slide 17-2 1 Mechanism Step
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Electrophile substitutes for a hydrogen on the benzene ring. Chapter 17: Aromatics 2-Reactions Slide 17-2 1 Mechanism Step
Alkanes 3/27/17. Hydrocarbons: Compounds made of hydrogen and carbon only. Aliphatic (means fat ) - Open chain Aromatic - ring. Alkane Alkene Alkyne
 Alkanes EQ 1. How will I define Hydrocarbons? 2. Compare and contrast the 3 types of hydrocarbons (Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes). Hydrocarbons: Compounds made of hydrogen and carbon only. Aliphatic (means
Alkanes EQ 1. How will I define Hydrocarbons? 2. Compare and contrast the 3 types of hydrocarbons (Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes). Hydrocarbons: Compounds made of hydrogen and carbon only. Aliphatic (means
AP Chemistry Chapter 22 - Organic and Biological Molecules
 AP Chemistry Chapter - Organic and Biological Molecules.1 Alkanes: Saturated Hydrocarbons A. Straight-chain Hydrocarbons 1. Straight-chain alkanes have the formula C n H n+. Carbons are sp hybridized The
AP Chemistry Chapter - Organic and Biological Molecules.1 Alkanes: Saturated Hydrocarbons A. Straight-chain Hydrocarbons 1. Straight-chain alkanes have the formula C n H n+. Carbons are sp hybridized The
An alkane homolog differs only in the number of CH 2 groups. Example: butane: CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 and pentane CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 are homolgs.
 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes Reading: Wade chapter 3, sections 3-1- 3-9 Study Problems: 3-33, 3-37, 3-39, 3-40, 3-42 Key Concepts and Skills: Explain and predict trends in the physical properties
Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes Reading: Wade chapter 3, sections 3-1- 3-9 Study Problems: 3-33, 3-37, 3-39, 3-40, 3-42 Key Concepts and Skills: Explain and predict trends in the physical properties
Chem101 General Chemistry. Lecture 11 Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
 hem101 General hemistry Lecture 11 Unsaturated ydrocarbons Unsaturated ydrocarbons ontain one or more double or triple carbon-carbon bond. University of Wisconsin-Eau laire hem101 - Lecture 11 2 Unsaturated
hem101 General hemistry Lecture 11 Unsaturated ydrocarbons Unsaturated ydrocarbons ontain one or more double or triple carbon-carbon bond. University of Wisconsin-Eau laire hem101 - Lecture 11 2 Unsaturated
N.b. A catalyst is a species which speeds up a chemical reaction but which remains chemically unchanged. Reverse process of dehydration of an alcohol
 An Introduction to Organic hemistry N.b. A catalyst is a species which speeds up a chemical reaction but which remains chemically unchanged. ydration (Addition) Reverse process of dehydration of an alcohol
An Introduction to Organic hemistry N.b. A catalyst is a species which speeds up a chemical reaction but which remains chemically unchanged. ydration (Addition) Reverse process of dehydration of an alcohol
Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
 5 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes APTER SUMMARY Addition is the characteristic reaction of alkenes and alkynes. Since the carbons of a double or triple bond do not have the maximum number
5 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes APTER SUMMARY Addition is the characteristic reaction of alkenes and alkynes. Since the carbons of a double or triple bond do not have the maximum number
Q1. Which one of the following is least likely to occur in the reaction between methane and chlorine?
 Q1. Which one of the following is least likely to occur in the reaction between methane and chlorine? A B C D C 4 + Cl C 3 + Cl C 3 + Cl C 3 Cl + C 3 + Cl 2 C 3 Cl + Cl C 3 Cl + Cl C 2 Cl + Cl (Total 1
Q1. Which one of the following is least likely to occur in the reaction between methane and chlorine? A B C D C 4 + Cl C 3 + Cl C 3 + Cl C 3 Cl + C 3 + Cl 2 C 3 Cl + Cl C 3 Cl + Cl C 2 Cl + Cl (Total 1
Halo Alkanes and Halo Arenes
 alo Alkanes and alo Arenes Short Answer Questions: **1. Write the isomers of the compound having formula C 4 9 Br? Sol. There are five isomers of C 4 9 Br. These are: 2-bromobutane is expected to exhibit
alo Alkanes and alo Arenes Short Answer Questions: **1. Write the isomers of the compound having formula C 4 9 Br? Sol. There are five isomers of C 4 9 Br. These are: 2-bromobutane is expected to exhibit
UNIT.10 HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
 UNIT.10 ALOALKANES AND ALOARENES ONE MARKS QUESTIONS 1. What are haloalkanes? aloalkane is a derivative obtained by replacing hydrogen atom of alkane by halogen atom. 2. What is the hybridization of the
UNIT.10 ALOALKANES AND ALOARENES ONE MARKS QUESTIONS 1. What are haloalkanes? aloalkane is a derivative obtained by replacing hydrogen atom of alkane by halogen atom. 2. What is the hybridization of the
Introduction to Organic Chemistry. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Introduction to Organic Chemistry Copyright The McGraw-ill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Common Elements in Organic Compounds 2 Classification of ydrocarbons ydrocarbons
Introduction to Organic Chemistry Copyright The McGraw-ill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Common Elements in Organic Compounds 2 Classification of ydrocarbons ydrocarbons
240 Chem. Aromatic Compounds. Chapter 6
 240 Chem Aromatic Compounds Chapter 6 1 The expressing aromatic compounds came to mean benzene and derivatives of benzene. Structure of Benzene: Resonance Description C 6 H 6 1.It contains a six-membered
240 Chem Aromatic Compounds Chapter 6 1 The expressing aromatic compounds came to mean benzene and derivatives of benzene. Structure of Benzene: Resonance Description C 6 H 6 1.It contains a six-membered
Unsaturated hydrocarbons. Chapter 13
 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Chapter 13 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons which contain at least one C-C multiple (double or triple) bond. The multiple bond is a site for chemical reactions in these molecules.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons Chapter 13 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons which contain at least one C-C multiple (double or triple) bond. The multiple bond is a site for chemical reactions in these molecules.
Chapter 22. Organic and Biological Molecules
 Chapter 22 Organic and Biological Molecules The Bonding of Carbon Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon. Because carbon can form single, double, and triple bonds, the following
Chapter 22 Organic and Biological Molecules The Bonding of Carbon Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon. Because carbon can form single, double, and triple bonds, the following
1. Which compound would you expect to have the lowest boiling point? A) NH 2 B) NH 2
 MULTIPLE CICE QUESTINS Topic: Intermolecular forces 1. Which compound would you expect to have the lowest boiling point? A) N 2 B) N 2 C) N D) E) N Ans: : N 2 D Topic: Molecular geometry, dipole moment
MULTIPLE CICE QUESTINS Topic: Intermolecular forces 1. Which compound would you expect to have the lowest boiling point? A) N 2 B) N 2 C) N D) E) N Ans: : N 2 D Topic: Molecular geometry, dipole moment
Organic Chemistry. Second Edition. Chapter 19 Aromatic Substitution Reactions. David Klein. Klein, Organic Chemistry 2e
 Organic Chemistry Second Edition David Klein Chapter 19 Aromatic Substitution Reactions Copyright 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Klein, Organic Chemistry 2e 19.1 Introduction to Electrophilic
Organic Chemistry Second Edition David Klein Chapter 19 Aromatic Substitution Reactions Copyright 2015 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. Klein, Organic Chemistry 2e 19.1 Introduction to Electrophilic
Chapter 3. Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry
 Chapter 3. Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry Functional Group: Be able to identify and name any of the functional groups listed on Table 3.1, pages 76-77. Summary of important functional
Chapter 3. Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry Functional Group: Be able to identify and name any of the functional groups listed on Table 3.1, pages 76-77. Summary of important functional
Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes & Aromatic Compounds
 Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes & Aromatic Compounds Chapter Outline 13.1 Alkenes and Alkynes 13.2 Nomenclature of Alkenes and Alkynes 13.3 Cis Trans Isomers 13.4 Alkenes in Food and Medicine 13.6 Reactions
Chapter 13 Alkenes and Alkynes & Aromatic Compounds Chapter Outline 13.1 Alkenes and Alkynes 13.2 Nomenclature of Alkenes and Alkynes 13.3 Cis Trans Isomers 13.4 Alkenes in Food and Medicine 13.6 Reactions
Page (Extra space) (4) Benzene can be converted into amine U by the two-step synthesis shown below.
 Q1. The hydrocarbons benzene and cyclohexene are both unsaturated compounds. Benzene normally undergoes substitution reactions, but cyclohexene normally undergoes addition reactions. (a) The molecule cyclohexatriene
Q1. The hydrocarbons benzene and cyclohexene are both unsaturated compounds. Benzene normally undergoes substitution reactions, but cyclohexene normally undergoes addition reactions. (a) The molecule cyclohexatriene
Organic Chemistry. Why are these compounds called Organic. What is a Hydrocarbon? Questions: P167 Read
 Organic Chemistry The fact that carbon can form a wide variety of relatively stable long chain molecules results in this very important branch of Chemistry: Organics. Carbon forms strong covalent bonds
Organic Chemistry The fact that carbon can form a wide variety of relatively stable long chain molecules results in this very important branch of Chemistry: Organics. Carbon forms strong covalent bonds
Alkanes and Alkenes. The Alkanes
 Alkanes and Alkenes The Alkanes Alkanes are hydrocarbons (i.e. compounds of carbon and hydrogen only). They are called saturated hydrocarbons because they contain no double bonds, and so cannot undergo
Alkanes and Alkenes The Alkanes Alkanes are hydrocarbons (i.e. compounds of carbon and hydrogen only). They are called saturated hydrocarbons because they contain no double bonds, and so cannot undergo
3 free radical is most stable. Q.5. A + Cl 2 hv monochloro product To maximize the yield of monochloro product in the above reaction? Cl 2 must be add
 Q.1. I II III IV IV III II I I III II IV IV II III I I II III IV The decreasing order of the anti knocking value of octane number of the following is: (I) CH 4 (II) C 2 H 6 (III) C 3 H 8 (IV) C 4 H 10
Q.1. I II III IV IV III II I I III II IV IV II III I I II III IV The decreasing order of the anti knocking value of octane number of the following is: (I) CH 4 (II) C 2 H 6 (III) C 3 H 8 (IV) C 4 H 10
CHEMISTRY - TRO 4E CH.21 - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY.
 !! www.clutchprep.com TOPI: ORGANI EMISTRY Organic hemistry is the study of carbon and the other common nonmetals it is connected to:,, &. Some organic molecules are made of just carbons and hydrogens
!! www.clutchprep.com TOPI: ORGANI EMISTRY Organic hemistry is the study of carbon and the other common nonmetals it is connected to:,, &. Some organic molecules are made of just carbons and hydrogens
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution جانشینی الکتروندوستی آروماتیک شیمی آلی 2
 16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution جانشینی الکتروندوستی آروماتیک شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution جانشینی الکتروندوستی آروماتیک شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution جانشینی الکتروندوستی آروماتیک شیمی آلی 2
 16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution جانشینی الکتروندوستی آروماتیک شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based
16. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution جانشینی الکتروندوستی آروماتیک شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based
15.1: Hydrocarbon Reactions
 15.1: Hydrocarbon Reactions Halogenation An alkane will react with a halogen to produce a halalkane and the corresponding hydrogen halide. The catalyst is ultraviolet radiation. Reaction 1 methane chlorine
15.1: Hydrocarbon Reactions Halogenation An alkane will react with a halogen to produce a halalkane and the corresponding hydrogen halide. The catalyst is ultraviolet radiation. Reaction 1 methane chlorine
Chemistry 1110 Exam 4 Study Guide
 Chapter 10 Chemistry 1110 Exam 4 Study Guide 10.1 Know that unstable nuclei can undergo radioactive decay. Identify alpha particles, beta particles, and/or gamma rays based on physical properties such
Chapter 10 Chemistry 1110 Exam 4 Study Guide 10.1 Know that unstable nuclei can undergo radioactive decay. Identify alpha particles, beta particles, and/or gamma rays based on physical properties such
Lecture Topics: I. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution (EAS)
 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Reading: Wade chapter 17, sections 17-1- 17-15 Study Problems: 17-44, 17-46, 17-47, 17-48, 17-51, 17-52, 17-53, 17-59, 17-61 Key Concepts and Skills: Predict and propose
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Reading: Wade chapter 17, sections 17-1- 17-15 Study Problems: 17-44, 17-46, 17-47, 17-48, 17-51, 17-52, 17-53, 17-59, 17-61 Key Concepts and Skills: Predict and propose
CHAPTER 16 - CHEMISTRY OF BENZENE: ELECTROPHILIC AROMATIC SUBSTITUTION
 CAPTR 16 - CMISTRY F BNZN: LCTRPILIC ARMATIC SUBSTITUTIN As stated in the previous chapter, benzene and other aromatic rings do not undergo electrophilic addition reactions of the simple alkenes but rather
CAPTR 16 - CMISTRY F BNZN: LCTRPILIC ARMATIC SUBSTITUTIN As stated in the previous chapter, benzene and other aromatic rings do not undergo electrophilic addition reactions of the simple alkenes but rather
Organic Chemistry. M. R. Naimi-Jamal. Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology
 Organic Chemistry M. R. Naimi-Jamal Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology Chapter 5-2. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry,
Organic Chemistry M. R. Naimi-Jamal Faculty of Chemistry Iran University of Science & Technology Chapter 5-2. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry,
Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
 rganic Chemistry, 6 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District 2006, Prentice all Electrophilic
rganic Chemistry, 6 th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Chapter 17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District 2006, Prentice all Electrophilic
Unit 12 Organic Chemistry
 Unit 12 Organic Chemistry Day 138 5/5/14 QOD: What is Organic Chemistry? Do Now: True or false? 1. Electrochemical cells generate electricity. 2. Electrons flow from left to right in a battery. 3. Redox
Unit 12 Organic Chemistry Day 138 5/5/14 QOD: What is Organic Chemistry? Do Now: True or false? 1. Electrochemical cells generate electricity. 2. Electrons flow from left to right in a battery. 3. Redox
Aromatic Compounds II
 2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 2 Aromatic Compounds II Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 17 in Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition, L.
2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 2 Aromatic Compounds II Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 17 in Organic Chemistry, 8 th Edition, L.
Vision. Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. How rods work H 3 C CH 3. Protein opsin. 11-cis-retinal. Opsin. Rhodopsin.
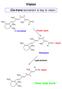 Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
Chapter 15. Reactions of Aromatic Compounds. Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution on Arenes. The first step is the slow, rate-determining step
 Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution on Arenes Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds The characteristic reaction of aromatic rings is substitution initiated by an electrophile halogenation nitration
Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution on Arenes Chapter 15 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds The characteristic reaction of aromatic rings is substitution initiated by an electrophile halogenation nitration
Treatment of cyclooctatetrene with potassium gives you a dianion. Classify the starting material and product as aromatic, antiaromatic or
 Treatment of cyclooctatetrene with potassium gives you a dianion. Classify the starting material and product as aromatic, antiaromatic or nonaromatic? 1 2 Classify cyclononatetrene and it s various ions
Treatment of cyclooctatetrene with potassium gives you a dianion. Classify the starting material and product as aromatic, antiaromatic or nonaromatic? 1 2 Classify cyclononatetrene and it s various ions
These are aliphatic hydrocarbons in which carbons atoms are joined by single covalent bonds. These are saturated organic compounds.
 These are aliphatic hydrocarbons in which carbons atoms are joined by single covalent bonds. These are saturated organic compounds. C n H 2n+2 The part of an Alkane obtained after the removing the one
These are aliphatic hydrocarbons in which carbons atoms are joined by single covalent bonds. These are saturated organic compounds. C n H 2n+2 The part of an Alkane obtained after the removing the one
Aryl Halides. Structure
 Aryl Halides Structure Aryl halides are compounds containing halogen attached directly to an aromatic ring. They have the general formula ArX, where Ar is phenyl, substituted phenyl. X= F,Cl,Br,I An aryl
Aryl Halides Structure Aryl halides are compounds containing halogen attached directly to an aromatic ring. They have the general formula ArX, where Ar is phenyl, substituted phenyl. X= F,Cl,Br,I An aryl
08. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution. Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition, Chapter 16
 08. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition, Chapter 16 Benzene is a nucleophile p electrons make benzene nucleophile, like alkenes.
08. Chemistry of Benzene: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition, Chapter 16 Benzene is a nucleophile p electrons make benzene nucleophile, like alkenes.
ALKYNE, AROMATIC HYDROCARBONS OR ARENES ALKYNES. Alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbon with at least one triple bond between two carbon atoms ( C = C)
 ALKYNES Alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbon with at least one triple bond between two carbon atoms ( C = C) Their general formula is Cn H2n-2 They are also called as a acetylenes STRUCTURE OF ALKYNES Each
ALKYNES Alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbon with at least one triple bond between two carbon atoms ( C = C) Their general formula is Cn H2n-2 They are also called as a acetylenes STRUCTURE OF ALKYNES Each
Just Chemistry Department Organic Chemistry 217
 Part 2 Just Chemistry Department Organic Chemistry 217 Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes كيمياء عضوية ك 217 د. حسين المغيض Dr. Hussein Al-Mughaid Direct hydration: Addition of H 2 O (Acid-catalyzed hydration)
Part 2 Just Chemistry Department Organic Chemistry 217 Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes كيمياء عضوية ك 217 د. حسين المغيض Dr. Hussein Al-Mughaid Direct hydration: Addition of H 2 O (Acid-catalyzed hydration)
What is the major product of the following reaction?
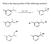 What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
What is the major product of the following reaction? Predict the major product of the following reaction: 2-methylbutane + Br 2 /light energy? A) 1-bromo-2-methylbutane B) 2-bromo-2-methylbutane C) 2-bromo-3-methylbutane
Organic Chemistry. REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling
 Organic Chemistry REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS This is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms Substitution
Organic Chemistry REACTIONS Grade 12 Physical Science Mrs KL Faling SUBSTITUTION REACTIONS This is a reaction where an atom or group of atoms is replaced by another atom or group of atoms Substitution
Chapter 2: Alkanes MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Chapter 2: Alkanes MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following orbitals is properly described as an antibonding orbital? a. sp + 1s d. sp 2 1s b. sp 2 + 1s e. sp 2 + sp 2 sp 3 + 1s D DIF: Easy REF: 2.2 2.
Chapter 2: Alkanes MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following orbitals is properly described as an antibonding orbital? a. sp + 1s d. sp 2 1s b. sp 2 + 1s e. sp 2 + sp 2 sp 3 + 1s D DIF: Easy REF: 2.2 2.
75. A This is a Markovnikov addition reaction. In these reactions, the pielectrons in the alkene act as a nucleophile. The strongest electrophile will
 71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
71. B SN2 stands for substitution nucleophilic bimolecular. This means that there is a bimolecular rate-determining step. Therefore, the reaction will follow second-order kinetics based on the collision
