16.1 Draw Newman projections for these staggered and three eclipsed conformations of 1, 2 - dichlorobutane as viewed downt he central C-C bond.
|
|
|
- Jemima Melton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CAPTER 16 Practice Exercises 16.1 Draw Newman projections for these staggered and three eclipsed conformations of 1, 2 - dichlorobutane as viewed downt he central C-C bond (a) The more stable conformation is the one with the t-b-tyl substituent equatorial and the methyl substituent axial. The more stable conformation is the one with both t-butyl subsittuents equatorial and the methyl substituent axial. The more stable conformation is the one with the two ADJACENT methyl substituents equatorial and the other methyl substituent axial (a) 2,2-dimethylpropane < 2-methylbutane < pentane (bp 9.5 C) (bp 28 C) (bp 36 C) 2,2,4-trimethylhexane < 3,3-dimethylheptane < nonane (bp 112 C) (bp 137 C) (bp 151 C) 16.7 (a) cis-4-methyl-2-pentene trans-2,2-dimethyl-3-hexane 16.9 (a) 1-isopropyl-4-methyl-cyclohexene 4-methyleyelooctene 4-tert-butylcyclohexene The given alcohol has two double bonds, indicated by an asterisk. The number of possible stereoisomers is 2 n, where n = the number of double bonds. Thus, there are 4 possible cis-trans isomers.
2 C=CC 2 C 2 C=CC 2 C 2 C=CC 2 * * The order of increasing stability of carbocations is: methyl < primary < secondary < tertiary C 2 < < (a) 2-methyl-2-butanol 2-methyl-2-butanol (a) CC=C 2 2 C CC 2 C 2 2 C 2 2 C22 C Step 1: Generation of the S 3 electrophile: S S S S S 3 - Step 2: Nucleophilic attack of benzene on S 3 electrophile:
3 Step 3: Loss of proton to regenerate aromatic ring (benzenesulfonic acid) and sulfuric acid: S 3 S 3 S 2 S 4 Review Questions 16.1 A hydrocarbon is a compound composed only of hydrogen and carbon atoms In saturated hydrocarbons, each carbon is bonded to four other atoms, either hydrogen or carbon atoms. Unsaturated hydrocarbons have carbon atoms that have a double or triple bond to another carbon atom (a) (d) (e) (f)
4 16.7 (C 2 ) 2 (a) (C 2 ) 4 C( ) 2 (C 2 ) 2 C(C 2 ) 2 (C 2 ) 2 (C 2 ) 2 C(C 2 ) (a) different compounds constitutional isomers constitutional isomers (d) different compounds (e) constitutional isomers (f) constitutional isomers (a) 2-methylpentane 2,5-dimethylhexane 3-ethyloctane (d) 2,2,3-trimethylbutane (e) isobutylcyclopentane (f) 1-tert-butyl-2,4-dimethyl-cyclohexane (a) 1,3-dimethylbutane The longest chain is pentane. The IUPAC name is 2-methylpentane. 4-methylpentane The pentane chain is numbered incorrectly. The IUPAC name is 2-methylpentane. 2,2-diethylbutane The longest chain in pentane. The IUPAC name is 3-ethyl-3-methylpentane. (d) 2-ethyl-3-methylpentane The longest chain is hexane. The IUPAC name is 3,4-dimethylhexane.
5 (e) 2-propylpentane The longest chain is heptane. The IUPAC name is 4-methylheptane. (f) 2,2-diethylheptane The longest chain is octane. The IUPAC name is 3-ethyl-3-methyloctane. (g) 2,2-dimethylcyclopropane The ring is numbered incorrectly. The IUPAC name is 1,1-dimethylcyclopropane. (h) 1-ethyl-5-methylcyclohexane The ring is numbered incorrectly. The IUPAC name is 1-ethyl-3-methylcyclohexane No, because alkanes do not have rings or C C double bonds and so all conformations are usually interconvertable by rotation about a C C single bond. owever, there are some extremely crowded molecules which are locked into specific conformers. These are called conformational isomers or locked conformational isomers and are not correctly defined by cistrans nomenclature There are two enantiomers of the trans-1,2-dimethylcyclopropane.. C 2 cyclopentane methylcyclobutane ethylcyclopropane
6 trans-1,2-dimethylcyclopropane 1,1-dimethylcyclopropane cis-1,2-dimethylcyclopropane (a) trans-2-methylhex-3-ene 2-methyl-3-hex-3-yne 2-methylbut-1-ene (d) 3-ethyl-3-methylpent-1-yne (e) 2,3-dimethylbut-2-ene (f) cis-pent-2-ene (a) 2-isobutylhept-1-ene 1,4,4-trimethylcyclopentene 1,3-cyclopentadiene (d) 3,3-dimethylbut-1-yne (e) 2,4-dimethylpent-2-ene (f) oct-1-yne (g) 2,2,5-dimethylhex-3-yne (h) 3-methylpent-1-yne (a) 2,2-dimethylhex-3-yne oct-2,5-diyne 3,6-dimethylhept-2-ene-4-yne (d) hept-1,4-diyne (a) Correct name: but-2-ene.you must select the longest carbon chain containing the ene functional group but-2-ene 4 Not: 2 3 C methylpropene Correct name: pent-2-ene. You must number the chain to give the first carbon of the double bond the lowest possible number.
7 Not: pent-2-ene pent-3-ene Correct name: 1-methylcyclohexene. By default, the first carbon of the double bond in a ring is given the number 1. In this case, this can also be the ring carbon with the methyl group attached. 1-methylcyclohexene 1 2 Not: 2-methylcyclohexene 2 1 (d) (e) (f) This name is not incorrect even though there is no indication of where the double bond is positioned. The indication of the two methyls on the third carbon means that the double bond is attached to the first carbon. Technically, the correct name is 3,3-dimethylpent-1- ene. Correct name: 4-hexyne. As with the chain carbons are numbered to give the first carbon of the double bond the lowest possible number C 3 C 2 C 2 C C C 2 C 3 Correct name: 2-isopropyl-2-butene. The longest chain containing the function group is a pentene (a) No Yes Yes (d) No (e) Yes (f) No
8 (e) For alkenes to exist as a pair of cis-trans isomers, both carbons of the double bond must have two different substituents. Thus, only and (d) can exist as a cis or trans isomer. 3 C cis-bromoprop-1-ene 3 C trans-bromoprop-1-ene (d) 16.31Molecules (a) and do not show cis-trans isomerism. (d) (a) Alkenes that do not show cis-trans isomerism are: pent-1-ene 2-methylbut-2-ene 3-methylbut-1-ene 2-methylbut-1-ene Alkenes that do show cis-trans isomerism are: trans-pent-2-ene cis-pent-2-ene Cycloalkanes that do not show cis-trans isomerism are:
9 C 2 C3 3 C cyclopentane methylcyclobutane ethylcyclopropane 1,1-dimethyl cyclopropane (d) Cycloalkanes that do show cis-trans isomerism are: 3 C 3 C cis-1,2-dimethylcyclopropane trans-1,2-dimethylcyclopropane (a) C C C is more stable. C 3 3 C 3 C C C is more stable C=C C Ni C C S 4 C 2 2 C=C 2 C 2 2 (d) 2 C C 2 C 2 C 2 (e) 2 C C 2 C 2
10 / Pd/C 2 Lindlar catalyst 2 Na/N (a) 1-bromo-2-chloro-4-ethylbenzene 4-iodo-1,2-dimethylbenzene I 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (d) 4-phenylpentan-2-ol 2 N N 2 N 2 (e) p-cresol (f) 2,4-dichlorophenol
11 (g) 1-phenylcyclopropanol (h) styrene (phenylethene) (i) m-bromophenol (j) 2,4-dibromoaniline N 2 (k) isobutylbenzene (l) m-xylene isopropylbenzene
12 (1) /Al 3 (2) / 2 S 4 (3) / 2 S 4 Review Problems (1) Alkanes are less dense than water. (2) As alkane molar mass increases, density increases. (3) Constitutional isomers have similar densities Boiling points of unbranched alkanes are related to their surface area: the larger the surface area, the greater the strength of the dispersion forces and the higher the boiling point. The relative increase in molecular size per C 2 group is greatest between C 4 and and becomes progressively smaller as molecular mass increases. Therefore, the increase in boiling point per C 2 group is greatest between C 4 and, and becomes progressively smaller for the higher alkanes (a) No, alkanes are too non-polar to dissolve in a very polar solvent such as water. Yes, dodecane is non-polar and dissolves in a non-polar solvent such as hexane. Yes, alkanes burn when ignited in the presence of oxygen to produce water and carbon dioxide. (d) It is a liquid. Alkanes containing 5 to 17 carbon atoms are colourless liquids. (e) It is less dense than water. All liquid and solid alkanes are less dense than water (1.0 g/ml) The three structures with molecular formula C22 are 1,1-dibromoethane, cis-1,2- dibromoethane and trans-1,2-dibromoethane. The dipole moment of the C bond is shown in the structures below by a solid arrow. trans-1,2-dibromoethane has no dipole moment because the two C dipoles point in opposite directions and therefore cancel each other out. owever, 1,1- dibromoethane and cis-1,2-dibromoethane both have a net dipole moment (in the direction shown by the dotted arrow) since the two C dipoles do not point in opposite directions. C C C C C C No dipole moment 1,1-dibromoethane cis-1,2-dibromoethane trans-1,2-dibromoethane (a)
13 C C C cis-4-methylpent-2-ene C C C trans-4-methylpent-2-ene CC 2 C C 2 4-methylpent-1-ene (a) 2,2-dichlorobutane butan-2-ol
14 2,2,3,3-tetrabromobutane (a) 3 carbocation 2 carbocation formed more readily 2 carbocation 2 carbocation Both carbocations are of equal stability and formed at approximately equal rates. 3 carbocation 2 carbocation formed more readily (d) 3 carbocation 1 carbocation formed more readily
15 16.65 (a) 2 2 S 4 I I (d) (e) 2 2S 4 (f) 2 2 S alogens undergo anti addition to alkenes. In cycloalkenes, anti addition results in trans dihalides. (a) 2 2
16 16.69 (a) (a) or (a) C 2 C CC S 4 C 2 CC 2 C 2 or C S 4
17 2 2 C CC 2 or C C CC 2 2 S 4 (d) C C S 4 C (a) Add water to each double bond by regioselective protonation of the double bond to form a 3 carbocation (Markovnikov s rule). Reaction of each carbocation with water and the loss of a proton yields terpin. Note that the reactions do not necessarily proceed in the order shown. Both carbon-carbon double bonds react at similar rates because in each case, a tertiary carbocation is formed. 2 - Limonene Terpin Two cis-trans isomers are possible: The mechanism for this reaction is similar to that proposed in problem except for a different starting alkene.
18 1-methylcyclohexene methanol 2 S 4 C 8 16 Step 1: C3 Step 2: 3 C Step 3: 3 C C The key to solving the problem is recognising that the skeleton of the alkenes must be the same with only the position of the double bond being different. 2 or Pt Structures A and B
19 16.81 (a) 2 Ni 2 2 S 4 (d) Resonance accounts for the two equivalent structures of benzene: N Resonance accounts for the four equivalent structures of anthracene: N Cyclopentadiene: Cyclopentane: resonance stabilised cyclopentadienyl anion
20 The conjugate base of cyclopentadiene is a highly stable six electron aromatic anion with five resonance structures delocalising the negative charge over five different carbons. The cyclopentyl anion, a conjugate base of cyclopentane, has the negative charge on one carbon, making it a much stronger conjugate base than the resonance stabilised aromatic cyclopentadienyl anion. As a negatively charged conjugate base becomes more stable though delocalisation and resonance, its base strength becomes weaker. (Acid strengths are inversely proportional to their conjugate base strengths.) Step 1: Formation of Lewis acid-lewis base complex: Al Al Step 2: Formation of the tert-butyl cation: Al Al Step 3: Electrophilic attack on the benzene ring to form a resonance-stabilised carbocation intermediate with three resonance structures: Step 4: Proton transfer to regenerate the aromatic ring: Al Al
21 16.91 (a) C C 2 C 2 C C 2 C 2 S 4 C C 2 2 Ni C 2 Additional Exercises Both carbons in ethane have four electron pairs (all bonding pairs) surrounding each carbon atom. A tetrahedral arrangement of bonding pairs with bond angles of o minimises electron pair repulsions. In ethene, both carbons have three regions of electron density surrounding each carbon atom. A trigonal planar arrangement of three regions of electron density with bond angles of 120 o minimises repulsions sp 3-1s sp 3 -sp 3 sp 2 -sp 3 (a) sp 2 -sp 3 C 2 2p-2p sp 2-1s 2p-2p sp 2 -sp 2 sp 2 -sp 2 sp-sp 2 sp-sp sp 2 -sp 2 sp 2 -sp 2 sp 2 -sp 3 C C-C=C 2 (d) sp 2 -sp 2 2 x 2p-2p 2p-2p 2p-2p sp 3-1s sp 2 -sp 3 sp 3 -sp 3 (a) sp 3-1s 2p-2p sp 2 -sp 2 sp 2 -sp 3 sp 3 -sp 3 2p-2p sp 2 -sp 2 sp 2-1s sp 3 -sp 3
22 sp-sp 3 sp-sp sp 3 -sp 3 sp 3-1s sp 3 -sp 3 sp 3 -sp 3 2 x 2p-2p (d) sp 3-1s sp 3 -sp (a) The positive charge is delocalised over carbon and oxygen atoms via two resonance structures. The resonance structure on the right is especially stable because both these atoms have filled octets:. The positive charge is delocalised between two carbon atoms via two equivalent resonance structures: The positive charge is delocalised over four carbon atoms via five resonance structures: (a) 3 C 2 Pt C 2 C 2 Same molecule results from either top or bottom attack
23 Two different molecules are formed which are non-superimposable and are mirror images of each other and are therefore enantiomers.
CHAPTER 15. Practice exercises 15.1
 CAPTER 15 Practice exercises 15.1 15.3 (a) C 9 18 : isobutylcyclopentane C 11 22 : sec-butylcycloheptane C 6 2 : 1-ethyl-1-methylcyclopropane 15.5 (a) 3,3-dimethyl-1-pentene 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene 3,3-dimethyl-1-butyne
CAPTER 15 Practice exercises 15.1 15.3 (a) C 9 18 : isobutylcyclopentane C 11 22 : sec-butylcycloheptane C 6 2 : 1-ethyl-1-methylcyclopropane 15.5 (a) 3,3-dimethyl-1-pentene 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene 3,3-dimethyl-1-butyne
BRCC CHM 102 Class Notes Chapter 11 Page 1 of 9
 BRCC CHM 102 Class Notes Chapter 11 Page 1 of 9 Chapter 11 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes hydrocarbons compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen * 4 families: 1) alkanes only single bonds (includes cycloalkanes)
BRCC CHM 102 Class Notes Chapter 11 Page 1 of 9 Chapter 11 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes hydrocarbons compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen * 4 families: 1) alkanes only single bonds (includes cycloalkanes)
A. They all have a benzene ring structure in the molecule. B. They all have the same molecular formula. C. They all have carbon and hydrogen only
 Ch 21 G12 CoreI- Choose the best answer, then transfer your answers to page (1) [32 marks; 2 each] 1. What characteristic do all aromatic hydrocarbons share? A. They all have a benzene ring structure in
Ch 21 G12 CoreI- Choose the best answer, then transfer your answers to page (1) [32 marks; 2 each] 1. What characteristic do all aromatic hydrocarbons share? A. They all have a benzene ring structure in
1. How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane?
 1. How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? The formation of ethane is due to the side reaction in termination step by the combination of two CH 3 free radicals. 2.
1. How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? The formation of ethane is due to the side reaction in termination step by the combination of two CH 3 free radicals. 2.
unsaturated (one or more pi bonds) alkanes alkenes alkynes benzene naming alkanes C 4 H 10 C 5 H 12 C 6 H 14 C 7 H 16 C 8 H 18 C 9 H 20 C 10 H 22
 hapter 4: Alkanes and ycloalkanes [Sections: 4.1-4.14] Basic Organic ompound Nomenclature hydrocarbons: comprised of just carbon and hydrogen saturated (no pi bonds) unsaturated (one or more pi bonds)
hapter 4: Alkanes and ycloalkanes [Sections: 4.1-4.14] Basic Organic ompound Nomenclature hydrocarbons: comprised of just carbon and hydrogen saturated (no pi bonds) unsaturated (one or more pi bonds)
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 201/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry CHE1502/201/1/2016
 CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
CE1502/201/1/2016 Tutorial letter 201/1/2016 General Chemistry 1B CE1502 Semester 1 Department of Chemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 1. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY
Summary Chapter General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith
 Summary Chapter 11-12 General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith Organic Chem Review: Valence Electrons Example: Determine the valence electrons of Selenium (Se): 1. Find Se on the
Summary Chapter 11-12 General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith Organic Chem Review: Valence Electrons Example: Determine the valence electrons of Selenium (Se): 1. Find Se on the
CHEM 241 ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES CHAP 3 ASSIGN H H
 CEM 241 ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES CAP 3 ASSIGN COMFORMATIONS AND cis-trans STEREOISOMERS 1. trans-1,2-dibromocyclohexane is represented by structure(s): D. II and III E. I and II 2. cis-1,3-dibromocyclohexane
CEM 241 ALKANES AND CYCLOALKANES CAP 3 ASSIGN COMFORMATIONS AND cis-trans STEREOISOMERS 1. trans-1,2-dibromocyclohexane is represented by structure(s): D. II and III E. I and II 2. cis-1,3-dibromocyclohexane
Class XI Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons Chemistry
 Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
Question 13.1: How do you account for the formation of ethane during chlorination of methane? Chlorination of methane proceeds via a free radical chain mechanism. The whole reaction takes place in the
Unit 2, Review for Quiz #1: Hydrocarbons
 Unit 2, Review for Quiz #1: Hydrocarbons 1. What is the simplest organic molecule? a) CH 4 c) HCN b) CO 2 d) HC CH 2. Which of the following molecules would be classified as organic? I) CaCO 3 II) C 2
Unit 2, Review for Quiz #1: Hydrocarbons 1. What is the simplest organic molecule? a) CH 4 c) HCN b) CO 2 d) HC CH 2. Which of the following molecules would be classified as organic? I) CaCO 3 II) C 2
Chapter 3 AN INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC COMPOUNDS NOMENCLATURE, PHYSICAL PROPERTIES, REPRESENTATION OF STRUCTURE AND
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY, 2 ND EDITION PAULA YURKANIS BRUICE Chapter 3 AN INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC COMPOUNDS NOMENCLATURE, PHYSICAL PROPERTIES, AND REPRESENTATION OF STRUCTURE RAED M. AL-ZOUBI, ASSISTANT PROFESSOR
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY, 2 ND EDITION PAULA YURKANIS BRUICE Chapter 3 AN INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC COMPOUNDS NOMENCLATURE, PHYSICAL PROPERTIES, AND REPRESENTATION OF STRUCTURE RAED M. AL-ZOUBI, ASSISTANT PROFESSOR
CHAPTER 12: SATURATED HYDROCARBONS
 CHAPTER 12: SATURATED HYDROCARBONS MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following statements concerning organic compounds is correct? Organic compounds are found only in non-living systems. b. Organic compounds
CHAPTER 12: SATURATED HYDROCARBONS MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following statements concerning organic compounds is correct? Organic compounds are found only in non-living systems. b. Organic compounds
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Alkanes molecules consisting of carbons and hydrogens in the following ratio: C n H 2n+2 Therefore, an alkane having 4 carbons would have 2(4) + 2 hydrogens, which equals 10 hydrogens.
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Alkanes molecules consisting of carbons and hydrogens in the following ratio: C n H 2n+2 Therefore, an alkane having 4 carbons would have 2(4) + 2 hydrogens, which equals 10 hydrogens.
1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound?
 CEM 331: Chapter 1/2: Structures (Atoms, Molecules, Bonding) 1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound? N C 2 C N C 2 C N 1 2 3 4 1: three sigma bonds and
CEM 331: Chapter 1/2: Structures (Atoms, Molecules, Bonding) 1. What are the respective hybridizations of the atoms numbered 1 to 4 in this compound? N C 2 C N C 2 C N 1 2 3 4 1: three sigma bonds and
Organic Chemistry. A. Introduction
 Organic Chemistry A. Introduction 1. Organic chemistry is defined as the chemistry of CARBON compounds. There are a huge number of organic compounds. This results from the fact that carbon forms chains
Organic Chemistry A. Introduction 1. Organic chemistry is defined as the chemistry of CARBON compounds. There are a huge number of organic compounds. This results from the fact that carbon forms chains
ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE OF ARTS & SCIENCE (AUTONOMOUS) ST. JOSEPH S COLLEGE ROAD, CUDDALORE CH101T ORGANIC CHEMISTRY I (SEMESTER-I)
 UNIT I 1. The hybridization involved in the formation of acetylene is a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) sp 3 d 2. The IUPAC name of is 1. 3-hexene b) 4-hexene c) 3-hexyne d) 4-hexyne 3. -------- is the type of
UNIT I 1. The hybridization involved in the formation of acetylene is a) sp b) sp 2 c) sp 3 d) sp 3 d 2. The IUPAC name of is 1. 3-hexene b) 4-hexene c) 3-hexyne d) 4-hexyne 3. -------- is the type of
Chemistry 110. Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell. Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes.
 Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes Chapter 12 Alkenes are hydrocarbons which have one or more
Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes Chapter 12 Alkenes are hydrocarbons which have one or more
Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes
 Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes Chapter 12 Alkenes are hydrocarbons which have one or more
Chemistry 110 Bettelheim, Brown, Campbell & Farrell Ninth Edition Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry Chapter 12 Alkenes & Alkynes Chapter 12 Alkenes are hydrocarbons which have one or more
Alkanes 3/27/17. Hydrocarbons: Compounds made of hydrogen and carbon only. Aliphatic (means fat ) - Open chain Aromatic - ring. Alkane Alkene Alkyne
 Alkanes EQ 1. How will I define Hydrocarbons? 2. Compare and contrast the 3 types of hydrocarbons (Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes). Hydrocarbons: Compounds made of hydrogen and carbon only. Aliphatic (means
Alkanes EQ 1. How will I define Hydrocarbons? 2. Compare and contrast the 3 types of hydrocarbons (Alkanes, alkenes, alkynes). Hydrocarbons: Compounds made of hydrogen and carbon only. Aliphatic (means
Chapter 4: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
 1. Nomenclature hapter 4: lkanes and ycloalkanes hydrocarbons: comprised of just carbon and hydrogen saturated (no pi bonds) [Sections: 4.1-4.14] unsaturated (one or more pi bonds) alkanes alkenes alkynes
1. Nomenclature hapter 4: lkanes and ycloalkanes hydrocarbons: comprised of just carbon and hydrogen saturated (no pi bonds) [Sections: 4.1-4.14] unsaturated (one or more pi bonds) alkanes alkenes alkynes
Chapter 3: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
 Chapter 3: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes 55 Chapter 3: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Problems 3.1 Do the structural formulas in each pair represent the same compound or constitutional isomers? Constitutional isomers
Chapter 3: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes 55 Chapter 3: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Problems 3.1 Do the structural formulas in each pair represent the same compound or constitutional isomers? Constitutional isomers
Chapter 2: Hydrocarbon Frameworks - Alkanes
 Chapter 2: Hydrocarbon Frameworks - Alkanes 1. Alkanes are characterized by the general molecular formula: A) C n H 2n-2 B) C n H 2n C) C n H 2n+2 D) C n H 2n+4 2. Cycloalkanes are characterized by the
Chapter 2: Hydrocarbon Frameworks - Alkanes 1. Alkanes are characterized by the general molecular formula: A) C n H 2n-2 B) C n H 2n C) C n H 2n+2 D) C n H 2n+4 2. Cycloalkanes are characterized by the
Chapter 4 Alkanes: Nomenclature, Conformational Analysis, and an Introduction to Synthesis"
 Chapter 4 Alkanes: Nomenclature, Conformational Analysis, and an Introduction to Synthesis" Alkanes = saturated hydrocarbons" Simplest alkane = methane C 4" " We can build additional alkanes by adding
Chapter 4 Alkanes: Nomenclature, Conformational Analysis, and an Introduction to Synthesis" Alkanes = saturated hydrocarbons" Simplest alkane = methane C 4" " We can build additional alkanes by adding
CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Text Sections (N0 1.9, 9-11) Homework: Chapter 1:
 CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Atomic Structure - Valence Electrons Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule - Ionic bond - Covalent bond How to write Lewis
CHEM 261 HOME WORK Lecture Topics: MODULE 1: The Basics: Bonding and Molecular Structure Atomic Structure - Valence Electrons Chemical Bonds: The Octet Rule - Ionic bond - Covalent bond How to write Lewis
UNIT (7) ORGANIC COMPOUNDS: HYDROCARBONS
 UNIT (7) RGANI MPUNDS: YDRARBNS rganic chemistry is the study carbon containing compounds. 7.1 Bonding in rganic ompounds rganic compounds are made up of only a few elements and the bonding is almost entirely
UNIT (7) RGANI MPUNDS: YDRARBNS rganic chemistry is the study carbon containing compounds. 7.1 Bonding in rganic ompounds rganic compounds are made up of only a few elements and the bonding is almost entirely
Chapter 2: Alkanes MULTIPLE CHOICE
 Chapter 2: Alkanes MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following orbitals is properly described as an antibonding orbital? a. sp + 1s d. sp 2 1s b. sp 2 + 1s e. sp 2 + sp 2 sp 3 + 1s D DIF: Easy REF: 2.2 2.
Chapter 2: Alkanes MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following orbitals is properly described as an antibonding orbital? a. sp + 1s d. sp 2 1s b. sp 2 + 1s e. sp 2 + sp 2 sp 3 + 1s D DIF: Easy REF: 2.2 2.
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
 Chapter 3 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Two types Saturated hydrocarbons Unsaturated hydrocarbons 3.1 Alkanes Also referred as aliphatic hydrocarbons General formula: CnH2n+2 (straight chain) and CnH2n (cyclic)
Chapter 3 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Two types Saturated hydrocarbons Unsaturated hydrocarbons 3.1 Alkanes Also referred as aliphatic hydrocarbons General formula: CnH2n+2 (straight chain) and CnH2n (cyclic)
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Families of Organic Compounds Organic compounds can be grouped into families by their common structural features We shall survey the nature of the compounds in a tour of the families
Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Families of Organic Compounds Organic compounds can be grouped into families by their common structural features We shall survey the nature of the compounds in a tour of the families
Organic Chemistry. A brief introduction
 Organic Chemistry A brief introduction Organic Chemistry the study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties excluding: CO, CO 2, CS 2, carbonates and cyanides eight million known organic compounds
Organic Chemistry A brief introduction Organic Chemistry the study of carbon-containing compounds and their properties excluding: CO, CO 2, CS 2, carbonates and cyanides eight million known organic compounds
Unsaturated hydrocarbons. Chapter 13
 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Chapter 13 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons which contain at least one C-C multiple (double or triple) bond. The multiple bond is a site for chemical reactions in these molecules.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons Chapter 13 Unsaturated hydrocarbons Hydrocarbons which contain at least one C-C multiple (double or triple) bond. The multiple bond is a site for chemical reactions in these molecules.
1. Multiple Choice Questions (15 points) Please circle the best answer to each question. Lone pairs are generally not shown.
 Page 2 Name _ANSWER KEY_ 1. Multiple Choice Questions (15 points) Please circle the best answer to each question. Lone pairs are generally not shown. (i) The formal charges on the nitrogen and oxygen atoms
Page 2 Name _ANSWER KEY_ 1. Multiple Choice Questions (15 points) Please circle the best answer to each question. Lone pairs are generally not shown. (i) The formal charges on the nitrogen and oxygen atoms
CHE 321 Summer 2010 Exam 2 Form Choose the structure(s) that represent cis-1-sec-butyl-4-methylcyclohexane. I II III
 CE 321 Summer 2010 Exam 2 orm 2 Multiple Choice Questions: 60 points 1. Choose the structure(s) that represent cis-1-sec-butyl-4-methylcyclohexane. I II III (A) I only (B) II only (C) I and II only II
CE 321 Summer 2010 Exam 2 orm 2 Multiple Choice Questions: 60 points 1. Choose the structure(s) that represent cis-1-sec-butyl-4-methylcyclohexane. I II III (A) I only (B) II only (C) I and II only II
An alkane homolog differs only in the number of CH 2 groups. Example: butane: CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 and pentane CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 are homolgs.
 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes Reading: Wade chapter 3, sections 3-1- 3-9 Study Problems: 3-33, 3-37, 3-39, 3-40, 3-42 Key Concepts and Skills: Explain and predict trends in the physical properties
Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes Reading: Wade chapter 3, sections 3-1- 3-9 Study Problems: 3-33, 3-37, 3-39, 3-40, 3-42 Key Concepts and Skills: Explain and predict trends in the physical properties
Unit 5: Organic Chemistry
 Unit 5: Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry: discipline in chemistry focussing strictly on the study of hydrocarbons compounds made up of carbon & hydrogen Organic compounds can contain other elements
Unit 5: Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry: discipline in chemistry focussing strictly on the study of hydrocarbons compounds made up of carbon & hydrogen Organic compounds can contain other elements
Vision. Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. How rods work H 3 C CH 3. Protein opsin. 11-cis-retinal. Opsin. Rhodopsin.
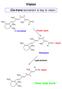 Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
Vision Cis-trans isomerism is key to vision. 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C O C 3 11-cis-retinal Protein opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 3 C N Opsin C 3 Rhodopsin Light photons 3 C N Opsin 3 C 11 12 3 C C 3 C 3 ow rods
Alkanes. Introduction
 Introduction Alkanes Recall that alkanes are aliphatic hydrocarbons having C C and C H bonds. They can be categorized as acyclic or cyclic. Acyclic alkanes have the molecular formula C n H 2n+2 (where
Introduction Alkanes Recall that alkanes are aliphatic hydrocarbons having C C and C H bonds. They can be categorized as acyclic or cyclic. Acyclic alkanes have the molecular formula C n H 2n+2 (where
National 5 Chemistry. Unit 2 Nature s Chemistry Summary Notes
 National 5 Chemistry Unit 2 Nature s Chemistry Summary Notes Success Criteria I am confident that I understand this and I can apply this to problems? I have some understanding but I need to revise this
National 5 Chemistry Unit 2 Nature s Chemistry Summary Notes Success Criteria I am confident that I understand this and I can apply this to problems? I have some understanding but I need to revise this
CHE1502. Tutorial letter 203/1/2016. General Chemistry 1B. Semester 1. Department of Chemistry
 E1502/203/1/2016 Tutorial letter 203/1/2016 General hemistry 1B E1502 Semester 1 Department of hemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 3. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY T
E1502/203/1/2016 Tutorial letter 203/1/2016 General hemistry 1B E1502 Semester 1 Department of hemistry This tutorial letter contains the answers to the questions in assignment 3. FIRST SEMESTER: KEY T
STRUCTURE. Dr. Sheppard CHEM 2411 Spring 2015
 STRUCTURE Dr. Sheppard CHEM 2411 Spring 2015 Klein (2nd ed.) sections 1.8-1.10, 1.12-1.13, 2.7-2.12, 3.2, 3.4-3.5, 3.8-3.9, 4.6-4.13, 4.14, 8.5, 15.16, 21.3 Topics Structure Physical Properties Hybridization
STRUCTURE Dr. Sheppard CHEM 2411 Spring 2015 Klein (2nd ed.) sections 1.8-1.10, 1.12-1.13, 2.7-2.12, 3.2, 3.4-3.5, 3.8-3.9, 4.6-4.13, 4.14, 8.5, 15.16, 21.3 Topics Structure Physical Properties Hybridization
Organic Chemistry 17.1
 Organic Chemistry 17.1 Introduction to Organic Compounds Naming Alkanes Isomers of Alkanes Naming Cycloalkanes What are Organic Compounds? (1807) The term organic compound originated Meant compounds derived
Organic Chemistry 17.1 Introduction to Organic Compounds Naming Alkanes Isomers of Alkanes Naming Cycloalkanes What are Organic Compounds? (1807) The term organic compound originated Meant compounds derived
4. A sample of 0.200g of an organic compound was subjected to combustion analysis and
 1. A sample of 0.205g of an organic compound was subjected to combustion analysis and produced 0.660g of carbon dioxide, 0.225g of water and nothing else. Its RMM is 82. 2. A sample of 0.400g of an organic
1. A sample of 0.205g of an organic compound was subjected to combustion analysis and produced 0.660g of carbon dioxide, 0.225g of water and nothing else. Its RMM is 82. 2. A sample of 0.400g of an organic
Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons
 Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons Chapter 12 Chapter 12 12.1 Organic Compounds 12.2 Alkanes 12.3 Alkanes with Substituents 12.4 Properties of Alkanes 12.5 Alkenes and Alkynes 12.6 Cis-Trans
Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons Chapter 12 Chapter 12 12.1 Organic Compounds 12.2 Alkanes 12.3 Alkanes with Substituents 12.4 Properties of Alkanes 12.5 Alkenes and Alkynes 12.6 Cis-Trans
Organic Compounds. Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons. also contain other nonmetals such as oxygen, nitrogen,
 Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons Chapter 12 12.1 Organic Compounds Identify properties characteristic of organic or inorganic compounds. Chapter 12 12.1 Organic Compounds 12.2 Alkanes 12.3
Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons Chapter 12 12.1 Organic Compounds Identify properties characteristic of organic or inorganic compounds. Chapter 12 12.1 Organic Compounds 12.2 Alkanes 12.3
Chapter 3. Alkenes And Alkynes
 Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
Chapter 3 Alkenes And Alkynes Alkenes ydrocarbons containing double bonds C C double bond the functional group center of reactivity Molecular Formula of Alkene Acyclic alkene: C n 2n Cyclic alkene: C n
Chemistry 20 Chapters 2 Alkanes
 Chemistry 20 Chapters 2 Alkanes ydrocarbons: a large family of organic compounds and they contain only carbon and hydrogen. ydrocarbons are divided into two groups: 1. Saturated hydrocarbon: a hydrocarbon
Chemistry 20 Chapters 2 Alkanes ydrocarbons: a large family of organic compounds and they contain only carbon and hydrogen. ydrocarbons are divided into two groups: 1. Saturated hydrocarbon: a hydrocarbon
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions
 Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
Structure and Preparation of Alkenes: Elimination Reactions Alkene Nomenclature First identify the longest continuous chain that includes the double bond. Replace the -ane ending of the corresponding unbranched
Full file at
 Chapter 2 - Alkanes: The Nature of Organic Compounds 1. Which of the following functional group classifications do not contain oxygen? A. ether B. thiol C. aldehyde D. ester E. amide 2. To which functional
Chapter 2 - Alkanes: The Nature of Organic Compounds 1. Which of the following functional group classifications do not contain oxygen? A. ether B. thiol C. aldehyde D. ester E. amide 2. To which functional
Chapter 3. Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry
 Chapter 3. Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry Functional Group: Be able to identify and name any of the functional groups listed on Table 3.1, pages 76-77. Summary of important functional
Chapter 3. Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Their Stereochemistry Functional Group: Be able to identify and name any of the functional groups listed on Table 3.1, pages 76-77. Summary of important functional
Exam Analysis: Organic Chemistry, Midterm 1
 Exam Analysis: Organic Chemistry, Midterm 1 1) TEST BREAK DOWN: There are three independent topics covered in the first midterm, which are hybridization, structure and isomerism, and resonance. The test
Exam Analysis: Organic Chemistry, Midterm 1 1) TEST BREAK DOWN: There are three independent topics covered in the first midterm, which are hybridization, structure and isomerism, and resonance. The test
Unit 7 Part 1 Introduction to Organic Chemistry Nomenclature and Isomerism in Simple Organic Compounds UNIT 7 INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 Unit 7 Part 1 Introduction to Organic hemistry Nomenclature and Isomerism in Simple Organic ompounds UNIT 7 INTRODUTION TO ORGANI EMISTRY PART 1 NOMENLATURE AND ISOMERISM IN SIMPLE ORGANI MOLEULES ontents
Unit 7 Part 1 Introduction to Organic hemistry Nomenclature and Isomerism in Simple Organic ompounds UNIT 7 INTRODUTION TO ORGANI EMISTRY PART 1 NOMENLATURE AND ISOMERISM IN SIMPLE ORGANI MOLEULES ontents
MOLECULER MODELS/ISOMERS ORGANIC STRUCTURES AND NAMING
 REVISED 10/14 EMISTRY 1101L MOLEULER MODELS/ISOMERS ORGANI STRUTURES AND NAMING NOTE: This lab does not require safety glasses or lab coats. INTRODUTION Electron Dot Structures: Electron dot structures,
REVISED 10/14 EMISTRY 1101L MOLEULER MODELS/ISOMERS ORGANI STRUTURES AND NAMING NOTE: This lab does not require safety glasses or lab coats. INTRODUTION Electron Dot Structures: Electron dot structures,
Chapter 2: Hydrocarbon Frameworks Alkanes
 1. Alkanes are characterized by the general molecular formula: A) CnH2n-2 B) CnH2n C) CnH2n+2 D) CnH2n+4 2. Cycloalkanes are characterized by the general molecular formula: A) CnH2n-2 B) CnH2n C) CnH2n+2
1. Alkanes are characterized by the general molecular formula: A) CnH2n-2 B) CnH2n C) CnH2n+2 D) CnH2n+4 2. Cycloalkanes are characterized by the general molecular formula: A) CnH2n-2 B) CnH2n C) CnH2n+2
Chapter 2 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes: Introduction to Hydrocarbons
 Chapter 2 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes: Introduction to ydrocarbons Copyright The McGraw-ill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 2.1 Classes of ydrocarbons ydrocarbons Aliphatic
Chapter 2 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes: Introduction to ydrocarbons Copyright The McGraw-ill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 2.1 Classes of ydrocarbons ydrocarbons Aliphatic
Chapter 4 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes.! Structure, Nomenclature and Conformations
 hapter 4 Alkanes and ycloalkanes Structure, Nomenclature and onformations arbon Bonding Structural Representation of Simple Alkanes Name Kekule structure ondensed structure Model methane ethane propane
hapter 4 Alkanes and ycloalkanes Structure, Nomenclature and onformations arbon Bonding Structural Representation of Simple Alkanes Name Kekule structure ondensed structure Model methane ethane propane
CHAPTER 4 HW: ALKANES
 CAPTER 4 W: ALKANES CLASSES OF CARBON 1. assify each carbon atom pointed to below as 1, 2, 3 or 4. 2. Draw an alkane that contains only: 1 and 4 carbon atoms 2 carbon atoms 1 and 2 carbon atoms 1 and 3
CAPTER 4 W: ALKANES CLASSES OF CARBON 1. assify each carbon atom pointed to below as 1, 2, 3 or 4. 2. Draw an alkane that contains only: 1 and 4 carbon atoms 2 carbon atoms 1 and 2 carbon atoms 1 and 3
3. Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
 3. Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition, Chapter 3 2003 Ronald Kluger Department of Chemistry University of Toronto 1 Families of Organic Compounds!
3. Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 6 th edition, Chapter 3 2003 Ronald Kluger Department of Chemistry University of Toronto 1 Families of Organic Compounds!
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I)
 Unit 13 HYDROCARBONS I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Arrange the following in decreasing order of their boiling points. (A) n butane (B) 2 methylbutane (C) n-pentane (D) 2,2 dimethylpropane A
Unit 13 HYDROCARBONS I. Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I) 1. Arrange the following in decreasing order of their boiling points. (A) n butane (B) 2 methylbutane (C) n-pentane (D) 2,2 dimethylpropane A
Introduction to Organic Chemistry. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Introduction to Organic Chemistry Copyright The McGraw-ill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Common Elements in Organic Compounds 2 Classification of ydrocarbons ydrocarbons
Introduction to Organic Chemistry Copyright The McGraw-ill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Common Elements in Organic Compounds 2 Classification of ydrocarbons ydrocarbons
Unit 2, Lesson 01: Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Hydrocarbons
 Unit 2, Lesson 01: Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Hydrocarbons Organic Chemistry: is the branch of chemistry that deals with carbon-based covalent compounds. living organisms are made up of a huge
Unit 2, Lesson 01: Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Hydrocarbons Organic Chemistry: is the branch of chemistry that deals with carbon-based covalent compounds. living organisms are made up of a huge
CHEM120 - ORGANIC CHEMISTRY WORKSHEET 1
 EM120 - RGANI EMISTRY WRKSEET 1 Some of the objectives To understand and know the hybridization concept Be able to distinguish different geometries, including basic bond lengths and angles within organic
EM120 - RGANI EMISTRY WRKSEET 1 Some of the objectives To understand and know the hybridization concept Be able to distinguish different geometries, including basic bond lengths and angles within organic
CHAPTER 4 HW SOLUTIONS: ALKANES
 CAPTER W SOLUTONS: ALKANES CATEGORZATONS. assify each carbon atom pointed to below as,, or.. Draw an alkane that contains only: and carbon atoms carbon atoms and carbon atoms and carbon atoms or or or
CAPTER W SOLUTONS: ALKANES CATEGORZATONS. assify each carbon atom pointed to below as,, or.. Draw an alkane that contains only: and carbon atoms carbon atoms and carbon atoms and carbon atoms or or or
Ch09. Alkenes & Alkynes. Unsaturated hydrocarbons. Double and triple bonds in our carbon backbone. version 1.0
 Ch09 Alkenes & Alkynes Unsaturated hydrocarbons. Double and triple bonds in our carbon backbone. version 1.0 Nick DeMello, PhD. 2007-2015 Ch09 Alkenes & Alkynes Alkenes & Alkynes Definition and bond angles.
Ch09 Alkenes & Alkynes Unsaturated hydrocarbons. Double and triple bonds in our carbon backbone. version 1.0 Nick DeMello, PhD. 2007-2015 Ch09 Alkenes & Alkynes Alkenes & Alkynes Definition and bond angles.
Chapter 3: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
 Brown 5e ISV SM 3-1 Chapter 3: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Problems 3.1 Do the structural formulas in each pair represent the same compound or constitutional isomers? Constitutional isomers have the same
Brown 5e ISV SM 3-1 Chapter 3: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Problems 3.1 Do the structural formulas in each pair represent the same compound or constitutional isomers? Constitutional isomers have the same
1.8. Organic Chemistry. Practice Exam Organic Chem. System LENGTH: VOLUME MASS Temperature. 1 gal = 4 qt. 1 lb = 16 oz.
 rganic hemistry Practice Exam rganic hem Name (last) (First) Read all questions before you start. Show all work and explain your answers to receive full credit. Report all numerical answers to the proper
rganic hemistry Practice Exam rganic hem Name (last) (First) Read all questions before you start. Show all work and explain your answers to receive full credit. Report all numerical answers to the proper
12.01 Organic Chemistry
 12.01 rganic hemistry hemistry of arbon An Introduction to nomenclatures, structures and reactions Dr. Fred mega Garces hemistry 100 Miramar ollege 1 rganic hemistry What is rganic hemistry? rganic hemistry:
12.01 rganic hemistry hemistry of arbon An Introduction to nomenclatures, structures and reactions Dr. Fred mega Garces hemistry 100 Miramar ollege 1 rganic hemistry What is rganic hemistry? rganic hemistry:
Test Bank for Organic Chemistry 8th Edition by Wade
 Test Bank for Organic Chemistry 8th Edition by Wade Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bankfororganic-chemistry-8th-edition-by-wade/ Organic Chemistry 8th Edition Test Bank Wade
Test Bank for Organic Chemistry 8th Edition by Wade Link download full: https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bankfororganic-chemistry-8th-edition-by-wade/ Organic Chemistry 8th Edition Test Bank Wade
Summary Chapter 13-14
 Summary Chapter 1-1 Nomenclature 1 prefix + + prefix,- dimethyl 1,5- First give locajon and type of subsjtuents Second give locajon of double bond How many carbons in longest chain? How many of the funcjonal
Summary Chapter 1-1 Nomenclature 1 prefix + + prefix,- dimethyl 1,5- First give locajon and type of subsjtuents Second give locajon of double bond How many carbons in longest chain? How many of the funcjonal
INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: ALKANES
 P a g e 1 Chapter 12 INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: ALKANES Organic chemistry: The study of carbon compounds. Carbon is tetravalent; it always forms four bonds. Organic molecules have covalent bonds.
P a g e 1 Chapter 12 INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: ALKANES Organic chemistry: The study of carbon compounds. Carbon is tetravalent; it always forms four bonds. Organic molecules have covalent bonds.
Straight. C C bonds are sp 3 hybridized. Butane, C 4 H 10 H 3 C
 Hydrocarbons Straight Chain Alkanes aren t Straight C C bonds are sp 3 hybridized Butane, C 4 H 10 Structural Shorthand Explicit hydrogens (those required to complete carbon s valence) are usually left
Hydrocarbons Straight Chain Alkanes aren t Straight C C bonds are sp 3 hybridized Butane, C 4 H 10 Structural Shorthand Explicit hydrogens (those required to complete carbon s valence) are usually left
1) (100 pts) 5) (20 pts) 3) (35 pts) 4) (25pts. Total (200 pts) More Tutorial at
 Name: Perm number: Question 1) (100 pts) 2) (20 pts) 3) (35 pts) 4) (25pts 5) (20 pts) Total (200 pts) Your score 1. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers
Name: Perm number: Question 1) (100 pts) 2) (20 pts) 3) (35 pts) 4) (25pts 5) (20 pts) Total (200 pts) Your score 1. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers
CHEM J-10 June The structure of ( )-linalool, a commonly occurring natural product, is shown below.
 CEM1102 2014-J-10 June 2014 The structure of ( )-linalool, a commonly occurring natural product, is shown below. 4 What is the molecular formula of ( )-linalool? C 10 18 O Which of the following best describes
CEM1102 2014-J-10 June 2014 The structure of ( )-linalool, a commonly occurring natural product, is shown below. 4 What is the molecular formula of ( )-linalool? C 10 18 O Which of the following best describes
ALKANES STRUCTURE, PROPERTIES, AND SYNTHESIS A STUDENT WHO HAS MASTERED THE MATERIAL IN THIS SECTION SHOULD BE ABLE TO:
 ALKANES STRUCTURE, PROPERTIES, AND SYNTESIS A STUDENT WO AS MASTERED TE MATERIAL IN TIS SECTION SOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Predict relative boiling points of alkanes, in comparison with other alkanes and with
ALKANES STRUCTURE, PROPERTIES, AND SYNTESIS A STUDENT WO AS MASTERED TE MATERIAL IN TIS SECTION SOULD BE ABLE TO: 1. Predict relative boiling points of alkanes, in comparison with other alkanes and with
NAME PER DATE DUE ACTIVE LEARNING IN CHEMISTRY EDUCATION CHAPTER 25 INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC COMPOUNDS. (Part 1) , A.J.
 NAME PER DATE DUE ACTIVE LEARNING IN CHEMISTRY EDUCATION CHAPTER 25 INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC COMPOUNDS (Part 1) 25-1 1997, A.J. Girondi NOTICE OF RIGHTS All rights reserved. No part of this document may
NAME PER DATE DUE ACTIVE LEARNING IN CHEMISTRY EDUCATION CHAPTER 25 INTRODUCTION TO ORGANIC COMPOUNDS (Part 1) 25-1 1997, A.J. Girondi NOTICE OF RIGHTS All rights reserved. No part of this document may
Organic Chemistry. February 18, 2014
 Organic Chemistry February 18, 2014 What does organic mean? Organic Describes products Grown through natural biological process Without synthetic materials In the 18 th century Produced by a living system
Organic Chemistry February 18, 2014 What does organic mean? Organic Describes products Grown through natural biological process Without synthetic materials In the 18 th century Produced by a living system
CHAPTER 2. Structure and Reactivity: Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar Molecules
 CHAPTER 2 Structure and Reactivity: Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar Molecules 2-1 Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Simple Chemical Processes Chemical thermodynamics: Is concerned with the extent that
CHAPTER 2 Structure and Reactivity: Acids and Bases, Polar and Nonpolar Molecules 2-1 Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Simple Chemical Processes Chemical thermodynamics: Is concerned with the extent that
Chapter 4. An Introduction to Organic Compounds
 Chapter 4 An Introduction to Organic Compounds Chapter 4 Educational Goals 1. Given the formula of a molecule, the student will be able to draw the line bond structure. 2. Understand and construct condensed
Chapter 4 An Introduction to Organic Compounds Chapter 4 Educational Goals 1. Given the formula of a molecule, the student will be able to draw the line bond structure. 2. Understand and construct condensed
Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
 Unsaturated ydrocarbons hemical Formulas and Unsaturation n n 2n n 2n+2 n 2n+2 hemical Formulas and Unsaturation n n n n 2n n 2n hemical Formulas and Unsaturation ydrocarbons Saturated ydrocarbons Unsaturated
Unsaturated ydrocarbons hemical Formulas and Unsaturation n n 2n n 2n+2 n 2n+2 hemical Formulas and Unsaturation n n n n 2n n 2n hemical Formulas and Unsaturation ydrocarbons Saturated ydrocarbons Unsaturated
Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry
 Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry The study of carbon compounds constitutes a separate branch of chemistry known as organic chemistry The
Chemistry: The Central Science Chapter 25: The Chemistry of Life: Organic and Biological Chemistry The study of carbon compounds constitutes a separate branch of chemistry known as organic chemistry The
Departmental Final Examination. Organic Chemistry I Caffein
 Departmental Final Examination rganic Chemistry I 2423 Caffein Name CEMISTRY 2423 FINAL EXAM FALL, 2005 DIRECTINS: A periodic table is attached at the end of this exam. Please answer all questions as completely
Departmental Final Examination rganic Chemistry I 2423 Caffein Name CEMISTRY 2423 FINAL EXAM FALL, 2005 DIRECTINS: A periodic table is attached at the end of this exam. Please answer all questions as completely
1. What is the letter designation given to dumbbell shaped orbitals like the one depicted below?
 1. What is the letter designation given to dumbbell shaped orbitals like the one depicted below? 2. Which of the following does not have an octet of electrons surrounding the central atom? A. B 3 B. C
1. What is the letter designation given to dumbbell shaped orbitals like the one depicted below? 2. Which of the following does not have an octet of electrons surrounding the central atom? A. B 3 B. C
Isomerism in Alkanes, Haloalkanes, and Alkenes using Molecular Models
 EXPERIMENT 1 Isomerism in Alkanes, aloalkanes, and Alkenes using Molecular Models Materials Needed - Molecular model kit Relevant Textbook Reading Denniston, chap 11.2-11.4, 12.1-12.3 Background In uncharged,
EXPERIMENT 1 Isomerism in Alkanes, aloalkanes, and Alkenes using Molecular Models Materials Needed - Molecular model kit Relevant Textbook Reading Denniston, chap 11.2-11.4, 12.1-12.3 Background In uncharged,
HYDROCARBON COMPOUNDS
 YDROARBON OMPOUNDS hapter Quiz lassify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 1. ydrocarbons are unsaturated. 22.2 2. The IUPA name for 3(2)33 is butane. 22.1
YDROARBON OMPOUNDS hapter Quiz lassify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. 1. ydrocarbons are unsaturated. 22.2 2. The IUPA name for 3(2)33 is butane. 22.1
CHEM Week 2 notes
 EM1002 2011 Week 2 notes Unless otherwise stated, all images in this file have been reproduced from: Blackman, Bottle, Schmid, Mocerino and Wille, hemistry, 2007 (John Wiley) ISBN: 9 78047081 0866 You
EM1002 2011 Week 2 notes Unless otherwise stated, all images in this file have been reproduced from: Blackman, Bottle, Schmid, Mocerino and Wille, hemistry, 2007 (John Wiley) ISBN: 9 78047081 0866 You
STRUCTURE, ISOMERISM AND NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
 II STRUCTURE, ISOMERISM AND NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS I. OBJECTIVES AND BACKGROUND This exercise will give you an opportunity to experience the three-dimensional nature of molecules and to visualize
II STRUCTURE, ISOMERISM AND NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS I. OBJECTIVES AND BACKGROUND This exercise will give you an opportunity to experience the three-dimensional nature of molecules and to visualize
Organic Nomenclature
 University of Puget Sound Department of Chemistry Chem 111 Spring, 2010 Organic Nomenclature LEARNING GOALS AND ASSESSMENTS 1. Be familiar with the structure and nomenclature of organic compounds. a. Identify
University of Puget Sound Department of Chemistry Chem 111 Spring, 2010 Organic Nomenclature LEARNING GOALS AND ASSESSMENTS 1. Be familiar with the structure and nomenclature of organic compounds. a. Identify
Unit 12 Organic Chemistry
 Unit 12 Organic Chemistry Day 138 5/5/14 QOD: What is Organic Chemistry? Do Now: True or false? 1. Electrochemical cells generate electricity. 2. Electrons flow from left to right in a battery. 3. Redox
Unit 12 Organic Chemistry Day 138 5/5/14 QOD: What is Organic Chemistry? Do Now: True or false? 1. Electrochemical cells generate electricity. 2. Electrons flow from left to right in a battery. 3. Redox
Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons
 Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons Chapter 12 Chapter 12 12.1 Organic Compounds 12.2 Alkanes 12.3 Alkanes with Substituents 12.4 Properties of Alkanes 12.5 Alkenes and Alkynes 12.6 Cis-Trans
Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons Chapter 12 Chapter 12 12.1 Organic Compounds 12.2 Alkanes 12.3 Alkanes with Substituents 12.4 Properties of Alkanes 12.5 Alkenes and Alkynes 12.6 Cis-Trans
12.1 Organic Compounds
 Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons Chapter 12 12.1 Organic Compounds Identify properties characteristic of organic or inorganic compounds. Chapter 12 12.1 Organic Compounds 12.2 Alkanes 12.3
Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons Chapter 12 12.1 Organic Compounds Identify properties characteristic of organic or inorganic compounds. Chapter 12 12.1 Organic Compounds 12.2 Alkanes 12.3
Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons
 Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons Chapter 12 Chapter 12 12.1 Organic Compounds 12.2 Alkanes 12.3 Alkanes with Substituents 12.4 Properties of Alkanes 12.5 Alkenes and Alkynes 12.6 Cis-Trans
Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Hydrocarbons Chapter 12 Chapter 12 12.1 Organic Compounds 12.2 Alkanes 12.3 Alkanes with Substituents 12.4 Properties of Alkanes 12.5 Alkenes and Alkynes 12.6 Cis-Trans
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is a tertiary amine? 1) A) B) C) D) E) D 2) There are 8 isomers that have
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is a tertiary amine? 1) A) B) C) D) E) D 2) There are 8 isomers that have
HYDROCARBONS. Types of Hydrocarbons HYDROCARBONS. Question 2.2. Question 2.1. Chapter 2. What is the hybridization of the starred carbon of geraniol?
 hapter 2 Introduction to ydrocabons arbon Backbone, Nomenclature, Physical & hemical Properties YDROARBONS ompounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen atoms (, ). Each carbon has 4 bonds. They represent
hapter 2 Introduction to ydrocabons arbon Backbone, Nomenclature, Physical & hemical Properties YDROARBONS ompounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen atoms (, ). Each carbon has 4 bonds. They represent
Study Union: CHM 2210 Final Exam Review 1. The following molecules are related in what manner?
 Study Union: CHM 2210 Final Exam Review 1. The following molecules are related in what manner? A) They are isotopes B) They are constitutional isomers C) They are the same structure D) They are composed
Study Union: CHM 2210 Final Exam Review 1. The following molecules are related in what manner? A) They are isotopes B) They are constitutional isomers C) They are the same structure D) They are composed
Chapter 2. Alkanes and Cycloalkanes; Conformational and Geometrical Isomerism
 Chapter 2 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes; Conformational and Geometrical Isomerism Hydrocarbons are compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen. There are three main classes of hydrocarbons, based on the
Chapter 2 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes; Conformational and Geometrical Isomerism Hydrocarbons are compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen. There are three main classes of hydrocarbons, based on the
Chapter 22. Organic and Biological Molecules
 Chapter 22 Organic and Biological Molecules The Bonding of Carbon Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon. Because carbon can form single, double, and triple bonds, the following
Chapter 22 Organic and Biological Molecules The Bonding of Carbon Organic chemistry is the chemistry of compounds containing carbon. Because carbon can form single, double, and triple bonds, the following
Chemistry 3719, Fall 2003 Exam 1 Name:
 Chemistry 3719, Fall 2003 Exam 1 Name: This exam is worth 100 points out of a total of 600 points for Chemistry 3719/3719L. You have 50 minutes to complete the exam and you may use molecular models as
Chemistry 3719, Fall 2003 Exam 1 Name: This exam is worth 100 points out of a total of 600 points for Chemistry 3719/3719L. You have 50 minutes to complete the exam and you may use molecular models as
REVIEW PROBLEMS Key. 1. Draw a complete orbital picture for the molecule shown below. Is this molecule chiral? Explain. H H.
 rganic hemistry II (E325) REVIEW PRBLEMS Key 1. Draw a complete orbital picture for the molecule shown below. Is this molecule chiral? Explain. 3 3 sp3 orbital p orbital sp2 orbital s orbital molecule
rganic hemistry II (E325) REVIEW PRBLEMS Key 1. Draw a complete orbital picture for the molecule shown below. Is this molecule chiral? Explain. 3 3 sp3 orbital p orbital sp2 orbital s orbital molecule
Chapter 2: An Introduction to Organic Compounds
 Chapter : An Introduction to Organic Compounds I. FUNCTIONAL GROUPS: Functional groups with similar structure/reactivity may be "grouped" together. A. Functional Groups With Carbon-Carbon Multiple Bonds.
Chapter : An Introduction to Organic Compounds I. FUNCTIONAL GROUPS: Functional groups with similar structure/reactivity may be "grouped" together. A. Functional Groups With Carbon-Carbon Multiple Bonds.
1. True or false: In a molecule, carbon always forms bonds with four other elements. 5. An unsaturated hydrocarbon must contain a or bond.
 APTER 20 Organic hemistry 1. True or false: In a molecule, carbon always forms bonds with four other elements. False 2. A triple bond involves sharing electrons. a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 5 e. 6 e. 6 3. ydrocarbons
APTER 20 Organic hemistry 1. True or false: In a molecule, carbon always forms bonds with four other elements. False 2. A triple bond involves sharing electrons. a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 5 e. 6 e. 6 3. ydrocarbons
Study Union: CHM 2210 Final Exam Review 1. The following molecules are related in what manner?
 Study Union: CHM 2210 Final Exam Review 1. The following molecules are related in what manner? A) They are isotopes B) They are constitutional isomers C) They are the same structure D) They are composed
Study Union: CHM 2210 Final Exam Review 1. The following molecules are related in what manner? A) They are isotopes B) They are constitutional isomers C) They are the same structure D) They are composed
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: SATURATED HYDROCARBONS
 19 09/16/2013 13:54:37 Page 283 APTER 19 ORGANI EMISTRY: SATURATED YDROARBONS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Two of the major reasons for the large number of organic compounds is the ability of carbon
19 09/16/2013 13:54:37 Page 283 APTER 19 ORGANI EMISTRY: SATURATED YDROARBONS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS 1. Two of the major reasons for the large number of organic compounds is the ability of carbon
