Supplementary Materials for
|
|
|
- Suzanna Taylor
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/1/eaau413/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Structure and dynamics conspire in the evolution of affinity between intrinsically disordered proteins Per Jemth*, Elin Karlsson, Beat Vögeli, Brenda Guzovsky, Eva Andersson, Greta Hultqvist, Jakob Dogan, Peter Güntert, Roland Riek, Celestine N. Chi* *Corresponding author. (C.N.C.); (P.J.) The PDF file includes: Published 24 October 218, Sci. Adv. 4, eaau413 (218) DOI: /sciadv.aau413 Fig. S1. Structural changes taking place and chemical shift restraints. Fig. S2. Strips from [ 1 H- 1 H]-NOESY-[ 1 H- 15 N]-HSQC spectra showing resonances emanating from residues 174 and 175 of the respective CID domains. Fig. S3. Strips from [ 1 H- 1 H]-NOESY [ 1 H- 15 N]-HSQC spectra showing resonances emanating from residues 176 and 177 of the CID domains. Fig. S4. 15 N relaxation data for the bound CID and NCBD domains and amide secondary chemical shifts of the complexes. Fig. S5. Backbone subnanosecond motions and ΔCp for the three CID/NCBD complexes. Fig. S6. Frustration in the CID/NCBD complexes without electrostatics. Fig. S7. [ 1 H- 15 N]-HSQC correlation spectra for bound and free CID and NCBD domains and the number of restraints in the structure determination as a function of amino acid residue. Fig. S8. Restraints used for structure calculations and refinement. Fig. S9. Urea and temperature denaturation experiments and Coulomb surfaces of the ancestral and extant CID/NCBD complexes. Legend for table S1 Other Supplementary Material for this manuscript includes the following: (available at advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/1/eaau413/dc1) Table S1 (Microsoft Excel format). ITC parameters and intermolecular NOEs.
2 a C b C N 1 N 2 N 3 18 c N d N C C e ( 13 C ) (ppm) g 1-1 CID N f ( 13 C ) (ppm) h N NCBD ( 13 C ) (ppm) i ( 13 C ) (ppm) j ( 13 C ) (ppm) ( 13 C ) (ppm)
3 Fig. S1. Structural changes taking place and chemical shift restraints. (a) Overlay of the most ancient Cambrian-like D/P NCBD (red), Ordovician-Silurian 1R/2R NCBD (blue) and extant human CREBBP NCBD (magenta) domains in complex with CID domains (1R CID for the older complexes and human NCOA3 CID for extant human, respectively). (b) The structures are reoriented by 18 to show the displacement of N 3 in the most ancient complex. Also shown is the slight tilting of the N 1 of human CREBBP NCBD as compared to the older NCBD domains. The orientations of the helices are also reflected in the RDCs (fig. S2). (c) Overlay of the most ancient Cambrian-like complex with the Ordovician-Silurian 1R/2R complex and (d) the 1R/2R complex with the extant human complex. (e to j) Plots of the difference of experimental C shifts to those of random coil values as a function of the amino acid sequences for ancestral and modern CID domains (e) and NCBD domains (f). Note the different scales on the y-axes in the different panels.
4 Fig. S2. Strips from [ 1 H- 1 H]-NOESY-[ 1 H- 15 N]-HSQC spectra showing resonances emanating from residues 174 and 175 of the respective CID domains. Cross peaks arising from inter- and intra-molecular contacts are shown. New contacts appear in the evolutionarily younger complexes. Note that human NCOA3 has a proline at position 174 and thus contains no H-N.
5 Fig. S3. Strips from [ 1 H- 1 H]-NOESY [ 1 H- 15 N]-HSQC spectra showing resonances emanating from residues 176 and 177 of the CID domains. Cross peaks arising from inter- and intra-molecular contacts are shown. New contacts appear in the evolutionarily younger complexes.
6
7 Fig. S4. 15 N relaxation data for the bound CID and NCBD domains and amide secondary chemical shifts of the complexes. Relaxation rates plotted versus amino acid sequence for the CID domains (a to f) and NCBD domains (h to m) for the three complexes. (a to c) the most ancient Cambrian-like complex. (a) Transverse 15 N R 2 derived from R 1 and R 1 relaxation rates plotted as a function of the amino acid sequence. The spectra were recorded with a spin lock frequency of 2 khz, thus the contributions of all exchange processes slower than 8 s (present in R 2 ) were suppressed. (b) Longitudinal 15 N R 1 relaxation rate (reports on ps-ns motions) plotted as a function of the amino acid sequence. (c and d) The Ordovician-Silurain 1R/2R complex; see legend (a and b). (e and f) The extant human complex; see legend for (ab). The experiments depicted in (a to f) were performed with labeled CID domains. In panels (h to n) similar experiments as in panels (a to f) were performed with labeled NCBD domains. Errors are propagated errors from single exponential fits. (o) and (p) Amide secondary chemical shifts of the complexes are indicative of bent helices. The differences of experimental amide shift from the random coil value ( H N ) are plotted against the amino acid sequence for the respective CID/NCBD complexes. Red, blue and magenta connected dots are for the most ancient Cambrian-like, Ordovician-Silurian 1R/2R and extant human complex, respectively. The black lines symbolize the wave-like pattern of the helices. The positive shifts are a result of short hydrogen bonds at the concave side while the negative shifts are from long hydrogen bonds on the convex side. There are 3-4 residues per repeat giving the wave-like signature which is characteristic of bent helices. The grey shading shows regions of increased bending seen in the structure, indicating that the bending is not an artefact from calculation. Also indicated are the positions of Pro and aromatic residues, since the ring current from these residues can change amid proton shifts
8
9 Fig. S5. Backbone subnanosecond motions and ΔC p for the three CID/NCBD complexes. Ratio of transverse and longitudinal relaxation rates plotted versus amino acid sequence for the CID domains (a to c) and NCBD domains (f and g) for the three complexes. Free (red) and bound (light-blue) for the (a) Cambrian-like complex, (b) the Ordovician-Silurian 1R/2R complex, and (c) the extant human complex. Data for CID-bound NCBD domains are shown in (e, f and g). (d to h) [ 1 H]- 15 N heteronuclear NOE rates. Negative and zero values indicate large H-N bond amplitudes of motions faster than 1 ns. Errors are propagated errors from single exponential fits. H was measured at different temperatures and the slope corresponds to C p. (i) ph 6.5 and (j) ph 7.5.
10 Fig. S6. Frustration in the CID/NCBD complexes without electrostatics. Mutational frustration for each complex, calculated using electrostatics=. Left panel: CID/NCBD backbones are displayed as grey ribbons (darkest grey is NCBD), the direct contacts with solid lines and the water-mediated interactions with dashed lines. Minimally frustrated interactions are shown in green, highly frustrated contacts in red, and neutral contacts are not drawn. Middle and Right panel: Histograms of local frustration plotted as a function of amino acid sequence. The proportion of contacts within 5 Å of the Cα atom of each residue is plotted, classified according to their frustration index. (a) The Cambrian-like complex contains the 1R CID (middle panel) and D/P NCBD (right panel) domain. (b) The Ordovician-Silurian complex contains 1R CID (middle panel) and 1R/2R NCBD (right panel) domain. (c) The Extant human complex contains NCOA3 CID (middle panel) and CREBBP NCBD (right panel) domain.
11
12 Fig. S7. [ 1 H- 15 N]-HSQC correlation spectra for bound and free CID and NCBD domains and the number of restraints in the structure determination as a function of amino acid residue. (a) Most ancient Cambrian-like complex: 15 N- labeled 1R CID bound to unlabeled D/P NCBD. (b) Ordovician-Silurian complex: 15 N-labeled 1R CID bound to unlabeled 1R/2R NCBD. (c) extant human complex: 15 N-labeled NCOA3 CID bound to unlabeled human CREBBP NCBD. (d) Most ancient Cambrian-like complex: 15 N-labeled D/P NCBD bound to unlabeled 1R CID. (e) Ordovician-Silurian complex: 15 N-labeled 1R/2R NCBD bound to unlabeled 1R CID. (f) extant human complex: 15 N-labeled human CREBBP NCBD bound to unlabeled human NCOA3 CID. (g) 15 N-labeled 1R CID. (h) 15 N-labeled NCOA3 CID. (i) 15 N-labeled D/P NCBD. (j) 15 N-labeled CREBBP NCBD. (k) The most ancient Cambrian-like complex, (l) the Ordovician-Silurian 1R/2R complex and (m) the extant human complex. Sequential (white), medium (grey) and long range (black) distances.
13 3J HNHA(Hz) b C 1 RDC (Hz) 1 14 RDC (Hz) measured C 1 1 R=.97 R=.99 h N N N 2 N C 2 R=.56 R=.56 R=.91 R= R=.97 R= RDC (Hz) extracted from structure C 2 C 1 C C C i j k l m n R=.76 R= C 1 C g 2 N R=.82 R=.67 N 1 N 3 N N f 2 N N 1 e d c C 3 N C 2 2 RDC (Hz) 3J HNHA(Hz) a
14 Fig. S8. Restraints used for structure calculations and refinement. Three bond HNHA couplings were determined as described in the methods section, for (a) the CID domain and (b) the NCBD domain for most ancient Cambrian-like (red), Ordovician-Silurian 1R/2R (blue) and extant human (magenta) CID/NCBD complexes. The coupling constants were then converted into φ dihedral angles following the relationship described by Vuister and Bax 1. All three helices for the NCBD and the first two helices of the CID domains showed the characteristic small couplings (1-4 Hz) associated with helices. The loop regions as well as the C 3 showed higher values (5-1 Hz). For the RDC measurements, the CID/NCBD complexes were aligned in pf1 phage and 1 D H-N RDCs were determined in an IPAP manner as described in the method section. RDCs for the most ancient Cambrian-like complex (c), Ordovician-Silurian 1R/2R complex (d) and human extant complex (e). In the top row, RDCs as function of residue number for the NCBD domains are shown, while in the bottom row are those for the CID domains. For structural refinement, RDCs were extracted from the structures that were calculated without RDCs (x-axis) and plotted against the measured RDCs (y-axis) (top panels). The RDCs were then included in the structure calculations and the RDCs from these structures were later extracted and plotted against the measured RDCs (bottom panel). The R-value (indicated) shows how well the extracted values agree with the measured values. (f) Most ancient Cambrian-like complex, (g) Ordovician-Silurian 1R/2R complex and (h) extant human complex. Blue are RDCs for the NCBD domain and red for the CID domain (note that the alignment in the pf1 phages were much stronger for the NCBD than for the CID domains). (i to n) Representation of the complexes calculated without (light grey) and with RDCs (colored) for (i and l) most ancient Cambrian-like complex (j and m) Ordovician-Silurian 1R/2R complex and (k and f) extant human complex. For clarity, only two of the structures are shown in (l-f).
15
16 Fig. S9. Urea and temperature denaturation experiments and Coulomb surfaces of the ancestral and extant CID/NCBD complexes. The Molar ellipticity is plotted as function of (a) urea concentration in units of molar (M) and (b) temperature in Kelvin (K) for the Cambrian-like (red), Ordovician-Silurian (blue) and extant human (magenta) CID/NCBD complexes, at 4 M CID and 15 M NCBD, respectively. The data were fitted to the standard chemical and thermal denaturation equations, respectively, for global two-state unfolding. The cooperativity of the urea denaturation curves denoted the md-n value is similar for all three complexes within error (.95.4, and kcal mol -1 M -1, respectively). The urea midpoint was lower for the Cambrian-like (2.9.4 M), compared to the Ordovician-Silurian ( M) and the human (3.5.9 M) complexes. These results were also mirrored in the thermal denaturation experiments with Tm values of 325 K, 344 K and 34 K, respectively. Coulomb surfaces color code: red < -1 kcal/(mol)(e), blue >+1 kcal/(mol)(e). In (c), (d) and (e) the NCBD domains are displayed in grey cartoons while the CID domains are shown as surfaces. In (f), (g) and (h) the CID domains are displayed in grey cartoons and the NCBD domains as surfaces. Panels (i), (j) and (k) are as (f), (g) and (h) but the complexes are reoriented to show the C 3 helix of the CID domains. Table S1. ITC parameters and intermolecular NOEs. Tab 1. ph dependence, Tab 2 temperature variation at ph 7.5, Tab 3 temperature variation at ph 6.5 and Tab 4 intermolecular NOEs. Extra intermolecular NOEs, which are not present in the Cambrian-like complex are highlighted in yellow.
Introduction solution NMR
 2 NMR journey Introduction solution NMR Alexandre Bonvin Bijvoet Center for Biomolecular Research with thanks to Dr. Klaartje Houben EMBO Global Exchange course, IHEP, Beijing April 28 - May 5, 20 3 Topics
2 NMR journey Introduction solution NMR Alexandre Bonvin Bijvoet Center for Biomolecular Research with thanks to Dr. Klaartje Houben EMBO Global Exchange course, IHEP, Beijing April 28 - May 5, 20 3 Topics
Table S1. Primers used for the constructions of recombinant GAL1 and λ5 mutants. GAL1-E74A ccgagcagcgggcggctgtctttcc ggaaagacagccgcccgctgctcgg
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Table S1. Primers used for the constructions of recombinant GAL1 and λ5 mutants Sense primer (5 to 3 ) Anti-sense primer (5 to 3 ) GAL1 mutants GAL1-E74A ccgagcagcgggcggctgtctttcc ggaaagacagccgcccgctgctcgg
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Table S1. Primers used for the constructions of recombinant GAL1 and λ5 mutants Sense primer (5 to 3 ) Anti-sense primer (5 to 3 ) GAL1 mutants GAL1-E74A ccgagcagcgggcggctgtctttcc ggaaagacagccgcccgctgctcgg
Magnetic Resonance Lectures for Chem 341 James Aramini, PhD. CABM 014A
 Magnetic Resonance Lectures for Chem 341 James Aramini, PhD. CABM 014A jma@cabm.rutgers.edu " J.A. 12/11/13 Dec. 4 Dec. 9 Dec. 11" " Outline" " 1. Introduction / Spectroscopy Overview 2. NMR Spectroscopy
Magnetic Resonance Lectures for Chem 341 James Aramini, PhD. CABM 014A jma@cabm.rutgers.edu " J.A. 12/11/13 Dec. 4 Dec. 9 Dec. 11" " Outline" " 1. Introduction / Spectroscopy Overview 2. NMR Spectroscopy
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 5 N 4 8 20 22 24 2 28 4 8 20 22 24 2 28 a b 0 9 8 7 H c (kda) 95 0 57 4 28 2 5.5 Precipitate before NMR expt. Supernatant before NMR expt. Precipitate after hrs NMR expt. Supernatant after hrs NMR expt.
5 N 4 8 20 22 24 2 28 4 8 20 22 24 2 28 a b 0 9 8 7 H c (kda) 95 0 57 4 28 2 5.5 Precipitate before NMR expt. Supernatant before NMR expt. Precipitate after hrs NMR expt. Supernatant after hrs NMR expt.
Timescales of Protein Dynamics
 Timescales of Protein Dynamics From Henzler-Wildman and Kern, Nature 2007 Dynamics from NMR Show spies Amide Nitrogen Spies Report On Conformational Dynamics Amide Hydrogen Transverse Relaxation Ensemble
Timescales of Protein Dynamics From Henzler-Wildman and Kern, Nature 2007 Dynamics from NMR Show spies Amide Nitrogen Spies Report On Conformational Dynamics Amide Hydrogen Transverse Relaxation Ensemble
Supporting Protocol This protocol describes the construction and the force-field parameters of the non-standard residue for the Ag + -site using CNS
 Supporting Protocol This protocol describes the construction and the force-field parameters of the non-standard residue for the Ag + -site using CNS CNS input file generatemetal.inp: remarks file generate/generatemetal.inp
Supporting Protocol This protocol describes the construction and the force-field parameters of the non-standard residue for the Ag + -site using CNS CNS input file generatemetal.inp: remarks file generate/generatemetal.inp
Timescales of Protein Dynamics
 Timescales of Protein Dynamics From Henzler-Wildman and Kern, Nature 2007 Summary of 1D Experiment time domain data Fourier Transform (FT) frequency domain data or Transverse Relaxation Ensemble of Nuclear
Timescales of Protein Dynamics From Henzler-Wildman and Kern, Nature 2007 Summary of 1D Experiment time domain data Fourier Transform (FT) frequency domain data or Transverse Relaxation Ensemble of Nuclear
NMR in Structural Biology
 NMR in Structural Biology Exercise session 2 1. a. List 3 NMR observables that report on structure. b. Also indicate whether the information they give is short/medium or long-range, or perhaps all three?
NMR in Structural Biology Exercise session 2 1. a. List 3 NMR observables that report on structure. b. Also indicate whether the information they give is short/medium or long-range, or perhaps all three?
Presenter: She Zhang
 Presenter: She Zhang Introduction Dr. David Baker Introduction Why design proteins de novo? It is not clear how non-covalent interactions favor one specific native structure over many other non-native
Presenter: She Zhang Introduction Dr. David Baker Introduction Why design proteins de novo? It is not clear how non-covalent interactions favor one specific native structure over many other non-native
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11524 Supplementary discussion Functional analysis of the sugar porter family (SP) signature motifs. As seen in Fig. 5c, single point mutation of the conserved
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11524 Supplementary discussion Functional analysis of the sugar porter family (SP) signature motifs. As seen in Fig. 5c, single point mutation of the conserved
Resonance assignments in proteins. Christina Redfield
 Resonance assignments in proteins Christina Redfield 1. Introduction The assignment of resonances in the complex NMR spectrum of a protein is the first step in any study of protein structure, function
Resonance assignments in proteins Christina Redfield 1. Introduction The assignment of resonances in the complex NMR spectrum of a protein is the first step in any study of protein structure, function
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Micelle-Triggered b-hairpin to a-helix Transition in a 14-Residue Peptide from a Choline-Binding Repeat of the Pneumococcal Autolysin LytA HØctor Zamora-Carreras, [a] Beatriz Maestro,
Supporting Information Micelle-Triggered b-hairpin to a-helix Transition in a 14-Residue Peptide from a Choline-Binding Repeat of the Pneumococcal Autolysin LytA HØctor Zamora-Carreras, [a] Beatriz Maestro,
Useful background reading
 Overview of lecture * General comment on peptide bond * Discussion of backbone dihedral angles * Discussion of Ramachandran plots * Description of helix types. * Description of structures * NMR patterns
Overview of lecture * General comment on peptide bond * Discussion of backbone dihedral angles * Discussion of Ramachandran plots * Description of helix types. * Description of structures * NMR patterns
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.1299 Protein fold determined by paramagnetic magic-angle spinning solid-state NMR spectroscopy Ishita Sengupta 1, Philippe S. Nadaud 1, Jonathan J. Helmus 1, Charles D. Schwieters 2
DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.1299 Protein fold determined by paramagnetic magic-angle spinning solid-state NMR spectroscopy Ishita Sengupta 1, Philippe S. Nadaud 1, Jonathan J. Helmus 1, Charles D. Schwieters 2
I690/B680 Structural Bioinformatics Spring Protein Structure Determination by NMR Spectroscopy
 I690/B680 Structural Bioinformatics Spring 2006 Protein Structure Determination by NMR Spectroscopy Suggested Reading (1) Van Holde, Johnson, Ho. Principles of Physical Biochemistry, 2 nd Ed., Prentice
I690/B680 Structural Bioinformatics Spring 2006 Protein Structure Determination by NMR Spectroscopy Suggested Reading (1) Van Holde, Johnson, Ho. Principles of Physical Biochemistry, 2 nd Ed., Prentice
Interpreting and evaluating biological NMR in the literature. Worksheet 1
 Interpreting and evaluating biological NMR in the literature Worksheet 1 1D NMR spectra Application of RF pulses of specified lengths and frequencies can make certain nuclei detectable We can selectively
Interpreting and evaluating biological NMR in the literature Worksheet 1 1D NMR spectra Application of RF pulses of specified lengths and frequencies can make certain nuclei detectable We can selectively
Filtered/edited NOESY spectra
 Filtered/edited NOESY spectra NMR Seminar HS 207 Nina Ripin 22..7 Overview NMR of biomolecular complexes Problems and Solutions Filtered/edited nomenclature Experimental elements NOESY vs filtered pulse
Filtered/edited NOESY spectra NMR Seminar HS 207 Nina Ripin 22..7 Overview NMR of biomolecular complexes Problems and Solutions Filtered/edited nomenclature Experimental elements NOESY vs filtered pulse
Molecular Modeling lecture 2
 Molecular Modeling 2018 -- lecture 2 Topics 1. Secondary structure 3. Sequence similarity and homology 2. Secondary structure prediction 4. Where do protein structures come from? X-ray crystallography
Molecular Modeling 2018 -- lecture 2 Topics 1. Secondary structure 3. Sequence similarity and homology 2. Secondary structure prediction 4. Where do protein structures come from? X-ray crystallography
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.3194
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mass spectrometry and solution NMR data for -syn samples used in this study. (a) Matrix-assisted laser-desorption and ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrum of uniformly-
Supplementary Figure 1 Mass spectrometry and solution NMR data for -syn samples used in this study. (a) Matrix-assisted laser-desorption and ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrum of uniformly-
Supplementary Figure 1.
 a b c d e f g 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of unfolded regions in the Chz1-H2A.Z-H2B complex and structure and dynamics of Chz.core-sH2B_H2A.Z. (a) 1 H- 15 N HSQC spectrum of Chz1. All backbone
a b c d e f g 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of unfolded regions in the Chz1-H2A.Z-H2B complex and structure and dynamics of Chz.core-sH2B_H2A.Z. (a) 1 H- 15 N HSQC spectrum of Chz1. All backbone
HSQC spectra for three proteins
 HSQC spectra for three proteins SH3 domain from Abp1p Kinase domain from EphB2 apo Calmodulin What do the spectra tell you about the three proteins? HSQC spectra for three proteins Small protein Big protein
HSQC spectra for three proteins SH3 domain from Abp1p Kinase domain from EphB2 apo Calmodulin What do the spectra tell you about the three proteins? HSQC spectra for three proteins Small protein Big protein
BMB/Bi/Ch 173 Winter 2018
 BMB/Bi/Ch 173 Winter 2018 Homework Set 8.1 (100 Points) Assigned 2-27-18, due 3-6-18 by 10:30 a.m. TA: Rachael Kuintzle. Office hours: SFL 220, Friday 3/2 4:00-5:00pm and SFL 229, Monday 3/5 4:00-5:30pm.
BMB/Bi/Ch 173 Winter 2018 Homework Set 8.1 (100 Points) Assigned 2-27-18, due 3-6-18 by 10:30 a.m. TA: Rachael Kuintzle. Office hours: SFL 220, Friday 3/2 4:00-5:00pm and SFL 229, Monday 3/5 4:00-5:30pm.
NMR in Medicine and Biology
 NMR in Medicine and Biology http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/nmr_spectroscopy MRI- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (water) In-vivo spectroscopy (metabolites) Solid-state t NMR (large structures) t Solution NMR
NMR in Medicine and Biology http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/nmr_spectroscopy MRI- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (water) In-vivo spectroscopy (metabolites) Solid-state t NMR (large structures) t Solution NMR
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1. Secondary structure of CAP (in the camp 2 -bound state) 10. α-helices are shown as cylinders and β- strands as arrows. Labeling of secondary structure is indicated. CDB, DBD and the hinge are
Figure S1. Secondary structure of CAP (in the camp 2 -bound state) 10. α-helices are shown as cylinders and β- strands as arrows. Labeling of secondary structure is indicated. CDB, DBD and the hinge are
Supplemental data for
 Supplemental data for A Real-Time Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Assay using NMR: Activation of RhoA by PDZ- RhoGEF. Geneviève M.C. Gasmi-Seabrook 1,3, Christopher B. Marshall 1,3, Melissa Cheung 1,3, Bryan
Supplemental data for A Real-Time Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Assay using NMR: Activation of RhoA by PDZ- RhoGEF. Geneviève M.C. Gasmi-Seabrook 1,3, Christopher B. Marshall 1,3, Melissa Cheung 1,3, Bryan
PROTEIN NMR SPECTROSCOPY
 List of Figures List of Tables xvii xxvi 1. NMR SPECTROSCOPY 1 1.1 Introduction to NMR Spectroscopy 2 1.2 One Dimensional NMR Spectroscopy 3 1.2.1 Classical Description of NMR Spectroscopy 3 1.2.2 Nuclear
List of Figures List of Tables xvii xxvi 1. NMR SPECTROSCOPY 1 1.1 Introduction to NMR Spectroscopy 2 1.2 One Dimensional NMR Spectroscopy 3 1.2.1 Classical Description of NMR Spectroscopy 3 1.2.2 Nuclear
Basic principles of multidimensional NMR in solution
 Basic principles of multidimensional NMR in solution 19.03.2008 The program 2/93 General aspects Basic principles Parameters in NMR spectroscopy Multidimensional NMR-spectroscopy Protein structures NMR-spectra
Basic principles of multidimensional NMR in solution 19.03.2008 The program 2/93 General aspects Basic principles Parameters in NMR spectroscopy Multidimensional NMR-spectroscopy Protein structures NMR-spectra
Supplementary Figures
 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Type I FGFR1 inhibitors (a) Chemical structures of a pyrazolylaminopyrimidine inhibitor (henceforth referred to as PAPI; PDB-code of the FGFR1-PAPI complex:
1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Type I FGFR1 inhibitors (a) Chemical structures of a pyrazolylaminopyrimidine inhibitor (henceforth referred to as PAPI; PDB-code of the FGFR1-PAPI complex:
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information German Edition: DOI: Sampling of Glycan-Bound Conformers by the Anti-HIV Lectin Oscillatoria agardhii agglutinin in the Absence of Sugar** Marta G. Carneiro, Leonardus M. I. Koharudin,
Supporting Information German Edition: DOI: Sampling of Glycan-Bound Conformers by the Anti-HIV Lectin Oscillatoria agardhii agglutinin in the Absence of Sugar** Marta G. Carneiro, Leonardus M. I. Koharudin,
Supplemental Information
 Supplemental Information Combinatorial Readout of Unmodified H3R2 and Acetylated H3K14 by the Tandem PHD Finger of MOZ Reveals a Regulatory Mechanism for HOXA9 Transcription Yu Qiu 1, Lei Liu 1, Chen Zhao
Supplemental Information Combinatorial Readout of Unmodified H3R2 and Acetylated H3K14 by the Tandem PHD Finger of MOZ Reveals a Regulatory Mechanism for HOXA9 Transcription Yu Qiu 1, Lei Liu 1, Chen Zhao
Jeff Grinstead SB 2006/2007. NMR Spectroscopy. NMR Spectroscopy JG/1 07
 NMR Spectroscopy Jeff Grinstead NMR Spectroscopy NMR for structural biology Challenges for determining protein structures using NMR Proteins have thousands of signals Assign the specific signal for each
NMR Spectroscopy Jeff Grinstead NMR Spectroscopy NMR for structural biology Challenges for determining protein structures using NMR Proteins have thousands of signals Assign the specific signal for each
NMR Assay of Purity and Folding
 NMR Assay of Purity and Folding Don t Need Resonance Assignments or Labeling 1D requires only 10-50 µm protein concentration 2D Provides A More Detailed Assay 15 N- 1 H HSQC 1 H COSY 13 C HSQC also! Analyze
NMR Assay of Purity and Folding Don t Need Resonance Assignments or Labeling 1D requires only 10-50 µm protein concentration 2D Provides A More Detailed Assay 15 N- 1 H HSQC 1 H COSY 13 C HSQC also! Analyze
Sequential resonance assignments in (small) proteins: homonuclear method 2º structure determination
 Lecture 9 M230 Feigon Sequential resonance assignments in (small) proteins: homonuclear method 2º structure determination Reading resources v Roberts NMR of Macromolecules, Chap 4 by Christina Redfield
Lecture 9 M230 Feigon Sequential resonance assignments in (small) proteins: homonuclear method 2º structure determination Reading resources v Roberts NMR of Macromolecules, Chap 4 by Christina Redfield
The wonderful world of NUCLEIC ACID NMR!
 Lecture 12 M230 Feigon Sequential resonance assignments in DNA (and RNA): homonuclear method 2 structure determination Reading resources Evans Chap 9 The wonderful world of NUCLEIC ACID NMR! Catalytically
Lecture 12 M230 Feigon Sequential resonance assignments in DNA (and RNA): homonuclear method 2 structure determination Reading resources Evans Chap 9 The wonderful world of NUCLEIC ACID NMR! Catalytically
Protein Structure Determination Using NMR Restraints BCMB/CHEM 8190
 Protein Structure Determination Using NMR Restraints BCMB/CHEM 8190 Programs for NMR Based Structure Determination CNS - Brünger, A. T.; Adams, P. D.; Clore, G. M.; DeLano, W. L.; Gros, P.; Grosse-Kunstleve,
Protein Structure Determination Using NMR Restraints BCMB/CHEM 8190 Programs for NMR Based Structure Determination CNS - Brünger, A. T.; Adams, P. D.; Clore, G. M.; DeLano, W. L.; Gros, P.; Grosse-Kunstleve,
SUPPLEMENTARY ONLINE DATA
 SUPPLEMENTARY ONLINE DATA Secreted Isoform of Human Lynx1 (SLURP-2): Spatial Structure and Pharmacology of Interaction with Different Types of Acetylcholine Receptors E.N. Lyukmanova 1,2,*, M.A. Shulepko
SUPPLEMENTARY ONLINE DATA Secreted Isoform of Human Lynx1 (SLURP-2): Spatial Structure and Pharmacology of Interaction with Different Types of Acetylcholine Receptors E.N. Lyukmanova 1,2,*, M.A. Shulepko
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Resonance assignment and NMR spectra for hairpin and duplex A 6 constructs. (a) 2D HSQC spectra of hairpin construct (hp-a 6 -RNA) with labeled assignments. (b) 2D HSQC or SOFAST-HMQC
Supplementary Figure 1 Resonance assignment and NMR spectra for hairpin and duplex A 6 constructs. (a) 2D HSQC spectra of hairpin construct (hp-a 6 -RNA) with labeled assignments. (b) 2D HSQC or SOFAST-HMQC
Theory and Applications of Residual Dipolar Couplings in Biomolecular NMR
 Theory and Applications of Residual Dipolar Couplings in Biomolecular NMR Residual Dipolar Couplings (RDC s) Relatively new technique ~ 1996 Nico Tjandra, Ad Bax- NIH, Jim Prestegard, UGA Combination of
Theory and Applications of Residual Dipolar Couplings in Biomolecular NMR Residual Dipolar Couplings (RDC s) Relatively new technique ~ 1996 Nico Tjandra, Ad Bax- NIH, Jim Prestegard, UGA Combination of
Structure and evolution of the spliceosomal peptidyl-prolyl cistrans isomerase Cwc27
 Acta Cryst. (2014). D70, doi:10.1107/s1399004714021695 Supporting information Volume 70 (2014) Supporting information for article: Structure and evolution of the spliceosomal peptidyl-prolyl cistrans isomerase
Acta Cryst. (2014). D70, doi:10.1107/s1399004714021695 Supporting information Volume 70 (2014) Supporting information for article: Structure and evolution of the spliceosomal peptidyl-prolyl cistrans isomerase
NB-DNJ/GCase-pH 7.4 NB-DNJ+/GCase-pH 7.4 NB-DNJ+/GCase-pH 4.5
 SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Suppl. Table 1. Protonation states at ph 7.4 and 4.5. Protonation states of titratable residues in GCase at ph 7.4 and 4.5. Histidine: HID, H at δ-nitrogen; HIE, H at ε-nitrogen; HIP,
SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES Suppl. Table 1. Protonation states at ph 7.4 and 4.5. Protonation states of titratable residues in GCase at ph 7.4 and 4.5. Histidine: HID, H at δ-nitrogen; HIE, H at ε-nitrogen; HIP,
PROTEIN'STRUCTURE'DETERMINATION'
 PROTEIN'STRUCTURE'DETERMINATION' USING'NMR'RESTRAINTS' BCMB/CHEM'8190' Programs for NMR Based Structure Determination CNS - Brünger, A. T.; Adams, P. D.; Clore, G. M.; DeLano, W. L.; Gros, P.; Grosse-Kunstleve,
PROTEIN'STRUCTURE'DETERMINATION' USING'NMR'RESTRAINTS' BCMB/CHEM'8190' Programs for NMR Based Structure Determination CNS - Brünger, A. T.; Adams, P. D.; Clore, G. M.; DeLano, W. L.; Gros, P.; Grosse-Kunstleve,
Protein-protein interactions and NMR: G protein/effector complexes
 Protein-protein interactions and NMR: G protein/effector complexes Helen Mott 5th CCPN Annual Conference, August 2005 Department of Biochemistry University of Cambridge Fast k on,off >> (ν free - ν bound
Protein-protein interactions and NMR: G protein/effector complexes Helen Mott 5th CCPN Annual Conference, August 2005 Department of Biochemistry University of Cambridge Fast k on,off >> (ν free - ν bound
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.2720 1 2 3 Tuning underwater adhesion with cation-π interactions Matthew A. Gebbie, Wei Wei, Alex M. Schrader,
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 10.1038/NCHEM.2720 1 2 3 Tuning underwater adhesion with cation-π interactions Matthew A. Gebbie, Wei Wei, Alex M. Schrader,
NMR Spectroscopy: A Quantum Phenomena
 NMR Spectroscopy: A Quantum Phenomena Pascale Legault Département de Biochimie Université de Montréal Outline 1) Energy Diagrams and Vector Diagrams 2) Simple 1D Spectra 3) Beyond Simple 1D Spectra 4)
NMR Spectroscopy: A Quantum Phenomena Pascale Legault Département de Biochimie Université de Montréal Outline 1) Energy Diagrams and Vector Diagrams 2) Simple 1D Spectra 3) Beyond Simple 1D Spectra 4)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11054 Supplementary Fig. 1 Sequence alignment of Na v Rh with NaChBac, Na v Ab, and eukaryotic Na v and Ca v homologs. Secondary structural elements of Na v Rh are indicated above the
doi:10.1038/nature11054 Supplementary Fig. 1 Sequence alignment of Na v Rh with NaChBac, Na v Ab, and eukaryotic Na v and Ca v homologs. Secondary structural elements of Na v Rh are indicated above the
Structural characterization of NiV N 0 P in solution and in crystal.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Structural characterization of NiV N 0 P in solution and in crystal. (a) SAXS analysis of the N 32-383 0 -P 50 complex. The Guinier plot for complex concentrations of 0.55, 1.1,
Supplementary Figure 1 Structural characterization of NiV N 0 P in solution and in crystal. (a) SAXS analysis of the N 32-383 0 -P 50 complex. The Guinier plot for complex concentrations of 0.55, 1.1,
1) NMR is a method of chemical analysis. (Who uses NMR in this way?) 2) NMR is used as a method for medical imaging. (called MRI )
 Uses of NMR: 1) NMR is a method of chemical analysis. (Who uses NMR in this way?) 2) NMR is used as a method for medical imaging. (called MRI ) 3) NMR is used as a method for determining of protein, DNA,
Uses of NMR: 1) NMR is a method of chemical analysis. (Who uses NMR in this way?) 2) NMR is used as a method for medical imaging. (called MRI ) 3) NMR is used as a method for determining of protein, DNA,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Dph2 SeMet (iron-free) # Dph2 (iron-free) Dph2-[4Fe-4S] Data collection Space group P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 Cell dimensions a, b, c (Å) 58.26, 82.08, 160.42 58.74, 81.87, 160.01 55.70, 80.53,
Dph2 SeMet (iron-free) # Dph2 (iron-free) Dph2-[4Fe-4S] Data collection Space group P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 P2 1 2 1 2 1 Cell dimensions a, b, c (Å) 58.26, 82.08, 160.42 58.74, 81.87, 160.01 55.70, 80.53,
NMR, X-ray Diffraction, Protein Structure, and RasMol
 NMR, X-ray Diffraction, Protein Structure, and RasMol Introduction So far we have been mostly concerned with the proteins themselves. The techniques (NMR or X-ray diffraction) used to determine a structure
NMR, X-ray Diffraction, Protein Structure, and RasMol Introduction So far we have been mostly concerned with the proteins themselves. The techniques (NMR or X-ray diffraction) used to determine a structure
Supplementary Figure S1. Urea-mediated buffering mechanism of H. pylori. Gastric urea is funneled to a cytoplasmic urease that is presumably attached
 Supplementary Figure S1. Urea-mediated buffering mechanism of H. pylori. Gastric urea is funneled to a cytoplasmic urease that is presumably attached to HpUreI. Urea hydrolysis products 2NH 3 and 1CO 2
Supplementary Figure S1. Urea-mediated buffering mechanism of H. pylori. Gastric urea is funneled to a cytoplasmic urease that is presumably attached to HpUreI. Urea hydrolysis products 2NH 3 and 1CO 2
NMR Characterization of Partially Folded and Unfolded Conformational Ensembles of Proteins
 Elisar Barbar Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Ohio University, Athens, OH 45701 NMR Characterization of Partially Folded and Unfolded Conformational Ensembles of Proteins Abstract: Studies of
Elisar Barbar Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Ohio University, Athens, OH 45701 NMR Characterization of Partially Folded and Unfolded Conformational Ensembles of Proteins Abstract: Studies of
Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the
 Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the interaction of OPTN and TBK1. (a) Analytical gel filtration chromatography analysis of the interaction between TBK1 CTD and OPTN(1-119).
Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the interaction of OPTN and TBK1. (a) Analytical gel filtration chromatography analysis of the interaction between TBK1 CTD and OPTN(1-119).
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Arai et al. 10.1073/pnas.15179911 SI Text Protein Expression and Purification. Myb3 (mouse, residues 84 315) was expressed in Escherichia coli as a fusion with the B1 domain of protein
Supporting Information Arai et al. 10.1073/pnas.15179911 SI Text Protein Expression and Purification. Myb3 (mouse, residues 84 315) was expressed in Escherichia coli as a fusion with the B1 domain of protein
Bulk behaviour. Alanine. FIG. 1. Chemical structure of the RKLPDA peptide. Numbers on the left mark alpha carbons.
 Bulk behaviour To characterise the conformational behaviour of the peptide, first we looked at the statistics of alpha carbons and the torsion angles. Then they were correlated with positions of positively
Bulk behaviour To characterise the conformational behaviour of the peptide, first we looked at the statistics of alpha carbons and the torsion angles. Then they were correlated with positions of positively
An engineered scorpion toxin analogue with improved Kv1.3 selectivity displays reduced conformational flexibility
 An engineered scorpion toxin analogue with improved Kv1.3 selectivity displays reduced conformational flexibility Adam Bartok a,#, Krisztina Fehér b,c,#,, Andrea Bodor d, Kinga Rákosi e, Gábor K. Tóth
An engineered scorpion toxin analogue with improved Kv1.3 selectivity displays reduced conformational flexibility Adam Bartok a,#, Krisztina Fehér b,c,#,, Andrea Bodor d, Kinga Rákosi e, Gábor K. Tóth
Using NMR to study Macromolecular Interactions. John Gross, BP204A UCSF. Nov 27, 2017
 Using NMR to study Macromolecular Interactions John Gross, BP204A UCSF Nov 27, 2017 Outline Review of basic NMR experiment Multidimensional NMR Monitoring ligand binding Structure Determination Review:
Using NMR to study Macromolecular Interactions John Gross, BP204A UCSF Nov 27, 2017 Outline Review of basic NMR experiment Multidimensional NMR Monitoring ligand binding Structure Determination Review:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10657 Supplementary Text Introduction. All retroviruses contain three genes: namely, gag, pol and env, which code for structural, enzymatic and glycoprotein receptor proteins, respectively.
doi:10.1038/nature10657 Supplementary Text Introduction. All retroviruses contain three genes: namely, gag, pol and env, which code for structural, enzymatic and glycoprotein receptor proteins, respectively.
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Resveratrol Serves as a Protein-Substrate Interaction Stabilizer in Human SIRT1 Activation Xuben Hou,, David Rooklin, Hao Fang *,,, Yingkai Zhang Department of Medicinal Chemistry
Supplementary Information Resveratrol Serves as a Protein-Substrate Interaction Stabilizer in Human SIRT1 Activation Xuben Hou,, David Rooklin, Hao Fang *,,, Yingkai Zhang Department of Medicinal Chemistry
Acta Crystallographica Section D
 Supporting information Acta Crystallographica Section D Volume 70 (2014) Supporting information for article: Structural basis of the heterodimerization of the MST and RASSF SARAH domains in the Hippo signalling
Supporting information Acta Crystallographica Section D Volume 70 (2014) Supporting information for article: Structural basis of the heterodimerization of the MST and RASSF SARAH domains in the Hippo signalling
Protein dynamics from NMR Relaxation data
 Protein dynamics from NMR Relaxation data Clubb 3/15/17 (S f2 ) ( e ) Nitrogen-15 relaxation ZZ-exchange R 1 = 1/T 1 Longitudinal relaxation (decay back to z-axis) R 2 = 1/T 2 Spin-spin relaxation (dephasing
Protein dynamics from NMR Relaxation data Clubb 3/15/17 (S f2 ) ( e ) Nitrogen-15 relaxation ZZ-exchange R 1 = 1/T 1 Longitudinal relaxation (decay back to z-axis) R 2 = 1/T 2 Spin-spin relaxation (dephasing
1. 3-hour Open book exam. No discussion among yourselves.
 Lecture 13 Review 1. 3-hour Open book exam. No discussion among yourselves. 2. Simple calculations. 3. Terminologies. 4. Decriptive questions. 5. Analyze a pulse program using density matrix approach (omonuclear
Lecture 13 Review 1. 3-hour Open book exam. No discussion among yourselves. 2. Simple calculations. 3. Terminologies. 4. Decriptive questions. 5. Analyze a pulse program using density matrix approach (omonuclear
NMR BMB 173 Lecture 16, February
 NMR The Structural Biology Continuum Today s lecture: NMR Lots of slides adapted from Levitt, Spin Dynamics; Creighton, Proteins; And Andy Rawlinson There are three types of particles in the universe Quarks
NMR The Structural Biology Continuum Today s lecture: NMR Lots of slides adapted from Levitt, Spin Dynamics; Creighton, Proteins; And Andy Rawlinson There are three types of particles in the universe Quarks
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Ottmann et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907587106 Fig. S1. Primary structure alignment of SBT3 with C5 peptidase from Streptococcus pyogenes. The Matchmaker tool in UCSF Chimera (http:// www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera)
Supporting Information Ottmann et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907587106 Fig. S1. Primary structure alignment of SBT3 with C5 peptidase from Streptococcus pyogenes. The Matchmaker tool in UCSF Chimera (http:// www.cgl.ucsf.edu/chimera)
Name: BCMB/CHEM 8190, BIOMOLECULAR NMR FINAL EXAM-5/5/10
 Name: BCMB/CHEM 8190, BIOMOLECULAR NMR FINAL EXAM-5/5/10 Instructions: This is an open book, limited time, exam. You may use notes you have from class and any text book you find useful. You may also use
Name: BCMB/CHEM 8190, BIOMOLECULAR NMR FINAL EXAM-5/5/10 Instructions: This is an open book, limited time, exam. You may use notes you have from class and any text book you find useful. You may also use
Sensitive NMR Approach for Determining the Binding Mode of Tightly Binding Ligand Molecules to Protein Targets
 Supporting information Sensitive NMR Approach for Determining the Binding Mode of Tightly Binding Ligand Molecules to Protein Targets Wan-Na Chen, Christoph Nitsche, Kala Bharath Pilla, Bim Graham, Thomas
Supporting information Sensitive NMR Approach for Determining the Binding Mode of Tightly Binding Ligand Molecules to Protein Targets Wan-Na Chen, Christoph Nitsche, Kala Bharath Pilla, Bim Graham, Thomas
Solid-state NMR and proteins : basic concepts (a pictorial introduction) Barth van Rossum,
 Solid-state NMR and proteins : basic concepts (a pictorial introduction) Barth van Rossum, 16.02.2009 Solid-state and solution NMR spectroscopy have many things in common Several concepts have been/will
Solid-state NMR and proteins : basic concepts (a pictorial introduction) Barth van Rossum, 16.02.2009 Solid-state and solution NMR spectroscopy have many things in common Several concepts have been/will
Orientational degeneracy in the presence of one alignment tensor.
 Orientational degeneracy in the presence of one alignment tensor. Rotation about the x, y and z axes can be performed in the aligned mode of the program to examine the four degenerate orientations of two
Orientational degeneracy in the presence of one alignment tensor. Rotation about the x, y and z axes can be performed in the aligned mode of the program to examine the four degenerate orientations of two
Nitrogenase MoFe protein from Clostridium pasteurianum at 1.08 Å resolution: comparison with the Azotobacter vinelandii MoFe protein
 Acta Cryst. (2015). D71, 274-282, doi:10.1107/s1399004714025243 Supporting information Volume 71 (2015) Supporting information for article: Nitrogenase MoFe protein from Clostridium pasteurianum at 1.08
Acta Cryst. (2015). D71, 274-282, doi:10.1107/s1399004714025243 Supporting information Volume 71 (2015) Supporting information for article: Nitrogenase MoFe protein from Clostridium pasteurianum at 1.08
Introduction to biomolecular NMR spectroscopy
 Oct 2002 Introduction to biomolecular NMR spectroscopy Michael Sattler, Structural & Computational Biology EMBL Heidelberg Contents Introduction...2 History... 3 Methodological developments for structure
Oct 2002 Introduction to biomolecular NMR spectroscopy Michael Sattler, Structural & Computational Biology EMBL Heidelberg Contents Introduction...2 History... 3 Methodological developments for structure
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Table of Contents Page Supplementary Table 1. Diffraction data collection statistics 2 Supplementary Table 2. Crystallographic refinement statistics 3 Supplementary Fig. 1. casic1mfc packing in the R3
Table of Contents Page Supplementary Table 1. Diffraction data collection statistics 2 Supplementary Table 2. Crystallographic refinement statistics 3 Supplementary Fig. 1. casic1mfc packing in the R3
A Combined Optical and EPR Spectroscopy Study: Azobenzene-Based Biradicals as Reversible Molecular Photoswitches
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2017 A Combined Optical and EPR Spectroscopy Study: Azobenzene-Based Biradicals as Reversible
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. This journal is the Owner Societies 2017 A Combined Optical and EPR Spectroscopy Study: Azobenzene-Based Biradicals as Reversible
Supplementary Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Probing the excited-state chemical shifts and exchange
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supplementary Information Probing the excited-state chemical shifts and exchange
Deuteration: Structural Studies of Larger Proteins
 Deuteration: Structural Studies of Larger Proteins Problems with larger proteins Impact of deuteration on relaxation rates Approaches to structure determination Practical aspects of producing deuterated
Deuteration: Structural Studies of Larger Proteins Problems with larger proteins Impact of deuteration on relaxation rates Approaches to structure determination Practical aspects of producing deuterated
Residual Dipolar Couplings BCMB/CHEM 8190
 Residual Dipolar Couplings BCMB/CHEM 8190 Recent Reviews Prestegard, A-Hashimi & Tolman, Quart. Reviews Biophys. 33, 371-424 (2000). Bax, Kontaxis & Tjandra, Methods in Enzymology, 339, 127-174 (2001)
Residual Dipolar Couplings BCMB/CHEM 8190 Recent Reviews Prestegard, A-Hashimi & Tolman, Quart. Reviews Biophys. 33, 371-424 (2000). Bax, Kontaxis & Tjandra, Methods in Enzymology, 339, 127-174 (2001)
Supplementary Information. Overlap between folding and functional energy landscapes for. adenylate kinase conformational change
 Supplementary Information Overlap between folding and functional energy landscapes for adenylate kinase conformational change by Ulrika Olsson & Magnus Wolf-Watz Contents: 1. Supplementary Note 2. Supplementary
Supplementary Information Overlap between folding and functional energy landscapes for adenylate kinase conformational change by Ulrika Olsson & Magnus Wolf-Watz Contents: 1. Supplementary Note 2. Supplementary
Triple Resonance Experiments For Proteins
 Triple Resonance Experiments For Proteins Limitations of homonuclear ( 1 H) experiments for proteins -the utility of homonuclear methods drops quickly with mass (~10 kda) -severe spectral degeneracy -decreased
Triple Resonance Experiments For Proteins Limitations of homonuclear ( 1 H) experiments for proteins -the utility of homonuclear methods drops quickly with mass (~10 kda) -severe spectral degeneracy -decreased
Structurele Biologie NMR
 MR journey Structurele Biologie MR 5 /3C 3 /65 MR & Structural biology course setup lectures - Sprangers R & Kay LE ature (27) basics of MR (Klaartje ouben: k.houben@uu.nl; 4/2) from peaks to data (ans
MR journey Structurele Biologie MR 5 /3C 3 /65 MR & Structural biology course setup lectures - Sprangers R & Kay LE ature (27) basics of MR (Klaartje ouben: k.houben@uu.nl; 4/2) from peaks to data (ans
Three-dimensional structure of a viral genome-delivery portal vertex
 Three-dimensional structure of a viral genome-delivery portal vertex Adam S. Olia 1, Peter E. Prevelige Jr. 2, John E. Johnson 3 and Gino Cingolani 4 1 Department of Biological Sciences, Purdue University,
Three-dimensional structure of a viral genome-delivery portal vertex Adam S. Olia 1, Peter E. Prevelige Jr. 2, John E. Johnson 3 and Gino Cingolani 4 1 Department of Biological Sciences, Purdue University,
CHAPTER 29 HW: AMINO ACIDS + PROTEINS
 CAPTER 29 W: AMI ACIDS + PRTEIS For all problems, consult the table of 20 Amino Acids provided in lecture if an amino acid structure is needed; these will be given on exams. Use natural amino acids (L)
CAPTER 29 W: AMI ACIDS + PRTEIS For all problems, consult the table of 20 Amino Acids provided in lecture if an amino acid structure is needed; these will be given on exams. Use natural amino acids (L)
Principles of NMR Protein Spectroscopy. 2) Assignment of chemical shifts in a protein ( 1 H, 13 C, 15 N) 3) Three dimensional structure determination
 1) Protein preparation (>50 aa) 2) Assignment of chemical shifts in a protein ( 1 H, 13 C, 15 N) 3) Three dimensional structure determination Protein Expression overexpression in E. coli - BL21(DE3) 1
1) Protein preparation (>50 aa) 2) Assignment of chemical shifts in a protein ( 1 H, 13 C, 15 N) 3) Three dimensional structure determination Protein Expression overexpression in E. coli - BL21(DE3) 1
Magic-Angle Spinning (MAS) drive bearing
 Magic-Angle Spinning (MAS) magic-angle spinning is done pneumatically spinning frequency can be stabilized within a few Hz Magic-Angle Spinning (MAS) drive bearing Magic-Angle Spinning (MAS) Maximum spinning
Magic-Angle Spinning (MAS) magic-angle spinning is done pneumatically spinning frequency can be stabilized within a few Hz Magic-Angle Spinning (MAS) drive bearing Magic-Angle Spinning (MAS) Maximum spinning
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Crystallization. a, Crystallization constructs of the ET B receptor are shown, with all of the modifications to the human wild-type the ET B receptor indicated. Residues interacting
Supplementary Figure 1 Crystallization. a, Crystallization constructs of the ET B receptor are shown, with all of the modifications to the human wild-type the ET B receptor indicated. Residues interacting
A.D.J. van Dijk "Modelling of biomolecular complexes by data-driven docking"
 Chapter 3. Various strategies of using Residual Dipolar Couplings in NMRdriven protein docking: application to Lys48-linked di-ubiquitin and validation against 15 N-relaxation data. Aalt D.J. van Dijk,
Chapter 3. Various strategies of using Residual Dipolar Couplings in NMRdriven protein docking: application to Lys48-linked di-ubiquitin and validation against 15 N-relaxation data. Aalt D.J. van Dijk,
Protein-protein interactions by NMR
 Protein-protein interactions by NMR Fast k on,off >> (ν free - ν bound ) A + B k on k off AB k on,off ~ (ν free - ν bound ) Slow k on,off
Protein-protein interactions by NMR Fast k on,off >> (ν free - ν bound ) A + B k on k off AB k on,off ~ (ν free - ν bound ) Slow k on,off
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1 Protein sequence alignment of Vibrionaceae with either a 40-residue insertion or a 44-residue insertion. Identical residues are indicated by red background.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1 Protein sequence alignment of Vibrionaceae with either a 40-residue insertion or a 44-residue insertion. Identical residues are indicated by red background.
Spin Relaxation and NOEs BCMB/CHEM 8190
 Spin Relaxation and NOEs BCMB/CHEM 8190 T 1, T 2 (reminder), NOE T 1 is the time constant for longitudinal relaxation - the process of re-establishing the Boltzmann distribution of the energy level populations
Spin Relaxation and NOEs BCMB/CHEM 8190 T 1, T 2 (reminder), NOE T 1 is the time constant for longitudinal relaxation - the process of re-establishing the Boltzmann distribution of the energy level populations
Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling. Chapter 4 Part I
 Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling Chapter 4 Part I 1 Information on Proteins Each modeling study depends on the quality of the known experimental data. Basis of the model Search in the literature
Introduction to Comparative Protein Modeling Chapter 4 Part I 1 Information on Proteins Each modeling study depends on the quality of the known experimental data. Basis of the model Search in the literature
Electrostatic properties of the structure of the docking and dimerization domain of protein kinase A IIa
 Eur. J. Biochem. 269, 2040 2051 (2002) Ó FEBS 2002 doi:10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.02852.x Electrostatic properties of the structure of the docking and dimerization domain of protein kinase A IIa Dimitrios
Eur. J. Biochem. 269, 2040 2051 (2002) Ó FEBS 2002 doi:10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.02852.x Electrostatic properties of the structure of the docking and dimerization domain of protein kinase A IIa Dimitrios
Labelling strategies in the NMR structure determination of larger proteins
 Labelling strategies in the NMR structure determination of larger proteins - Difficulties of studying larger proteins - The effect of deuteration on spectral complexity and relaxation rates - NMR expts
Labelling strategies in the NMR structure determination of larger proteins - Difficulties of studying larger proteins - The effect of deuteration on spectral complexity and relaxation rates - NMR expts
Supplementary Figures:
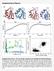 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure 1: The two strings converge to two qualitatively different pathways. A) Models of active (red) and inactive (blue) states used as end points for the string calculations
Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure 1: The two strings converge to two qualitatively different pathways. A) Models of active (red) and inactive (blue) states used as end points for the string calculations
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Results DNA binding property of the SRA domain was examined by an electrophoresis mobility shift assay (EMSA) using synthesized 12-bp oligonucleotide duplexes containing unmodified, hemi-methylated,
Supplementary Results DNA binding property of the SRA domain was examined by an electrophoresis mobility shift assay (EMSA) using synthesized 12-bp oligonucleotide duplexes containing unmodified, hemi-methylated,
CN NC. dha-7. dha-6 R' R. E-vhf (s-trans) E-vhf (s-cis) R CN. Z-vhf (s-cis) Z-vhf (s-trans) R = AcS R' = AcS
 R' R R' R dha-6 dha-7 R' R R' R E-vhf (s-cis) E-vhf (s-trans) R R' R R' Z-vhf (s-cis) Z-vhf (s-trans) R = R' = Supplementary Figure 1 Nomenclature of compounds. Supplementary Figure 2 500 MHz 1 H NMR spectrum
R' R R' R dha-6 dha-7 R' R R' R E-vhf (s-cis) E-vhf (s-trans) R R' R R' Z-vhf (s-cis) Z-vhf (s-trans) R = R' = Supplementary Figure 1 Nomenclature of compounds. Supplementary Figure 2 500 MHz 1 H NMR spectrum
A prevalent intraresidue hydrogen bond stabilizes proteins
 Supplementary Information A prevalent intraresidue hydrogen bond stabilizes proteins Robert W. Newberry 1 & Ronald T. Raines 1,2 * 1 Department of Chemistry and 2 Department of Biochemistry, University
Supplementary Information A prevalent intraresidue hydrogen bond stabilizes proteins Robert W. Newberry 1 & Ronald T. Raines 1,2 * 1 Department of Chemistry and 2 Department of Biochemistry, University
Biology Chemistry & Physics of Biomolecules. Examination #1. Proteins Module. September 29, Answer Key
 Biology 5357 Chemistry & Physics of Biomolecules Examination #1 Proteins Module September 29, 2017 Answer Key Question 1 (A) (5 points) Structure (b) is more common, as it contains the shorter connection
Biology 5357 Chemistry & Physics of Biomolecules Examination #1 Proteins Module September 29, 2017 Answer Key Question 1 (A) (5 points) Structure (b) is more common, as it contains the shorter connection
Sequential Assignment Strategies in Proteins
 Sequential Assignment Strategies in Proteins NMR assignments in order to determine a structure by traditional, NOE-based 1 H- 1 H distance-based methods, the chemical shifts of the individual 1 H nuclei
Sequential Assignment Strategies in Proteins NMR assignments in order to determine a structure by traditional, NOE-based 1 H- 1 H distance-based methods, the chemical shifts of the individual 1 H nuclei
NMR course at the FMP: NMR of organic compounds and small biomolecules - II -
 NMR course at the FMP: NMR of organic compounds and small biomolecules - II - 16.03.2009 The program 2/76 CW vs. FT NMR What is a pulse? Vectormodel Water-flip-back 3/76 CW vs. FT CW vs. FT 4/76 Two methods
NMR course at the FMP: NMR of organic compounds and small biomolecules - II - 16.03.2009 The program 2/76 CW vs. FT NMR What is a pulse? Vectormodel Water-flip-back 3/76 CW vs. FT CW vs. FT 4/76 Two methods
Supplementary Figures. Measuring Similarity Between Dynamic Ensembles of Biomolecules
 Supplementary Figures Measuring Similarity Between Dynamic Ensembles of Biomolecules Shan Yang, Loïc Salmon 2, and Hashim M. Al-Hashimi 3*. Department of Chemistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI,
Supplementary Figures Measuring Similarity Between Dynamic Ensembles of Biomolecules Shan Yang, Loïc Salmon 2, and Hashim M. Al-Hashimi 3*. Department of Chemistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI,
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb
 Supplementary Table 1 Mean inclination angles a of wild-type and mutant K10 RNAs Base pair K10-wt K10-au-up K10-2gc-up K10-2gc-low K10-A-low 1-44 2.8 ± 0.7 4.8 ± 0.8 3.2 ± 0.6 4.3 ± 1.9 12.5 ± 0.4 2 43-2.5
Supplementary Table 1 Mean inclination angles a of wild-type and mutant K10 RNAs Base pair K10-wt K10-au-up K10-2gc-up K10-2gc-low K10-A-low 1-44 2.8 ± 0.7 4.8 ± 0.8 3.2 ± 0.6 4.3 ± 1.9 12.5 ± 0.4 2 43-2.5
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Ellena et al. 10.1073/pnas.0908317106 SI Experimental Procedures Protein Expression and Sample Preparation. Syb(1 96) and Syb(1 116) from Rattus norvegicus were expressed in BL21(DE3)
Supporting Information Ellena et al. 10.1073/pnas.0908317106 SI Experimental Procedures Protein Expression and Sample Preparation. Syb(1 96) and Syb(1 116) from Rattus norvegicus were expressed in BL21(DE3)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Parallel Allostery by camp and PDE Coordinates Activation and Termination Phases in camp Signaling Srinath Krishnamurthy, 1 Nikhil Kumar Tulsian, 1 Arun Chandramohan, 1 and Ganesh S. Anand 1, * 1 Department
Parallel Allostery by camp and PDE Coordinates Activation and Termination Phases in camp Signaling Srinath Krishnamurthy, 1 Nikhil Kumar Tulsian, 1 Arun Chandramohan, 1 and Ganesh S. Anand 1, * 1 Department
