Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology - II Week 1; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Review of Early Development of Humans.
|
|
|
- Ruth Lora Lane
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology - II Week 1; Lecture 1; Monday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Review of Early Development of Humans Special Senses
2 Review: Historical and Developmental Perspectives Ontogeny Early embryological development Cross-section of the body Chordate features dorsal hollow nerve cord, notochord, gut tube, certain blood vessels, muscle blocks, and coelom.
3
4 Concurrent events: Neural folds to Neural Groove
5
6 Mesodermal structures Paraxial mesoderm Lateral mesoderm Intermediate mesoderm Somites Segmental structures - how many in the head, neck, thorax, abdomen, pelvis, and in what remains of the tail. What is the total number of of segments in the body?
7 Early Development Continued: Dorsal hollow nerve tube Neural crest Further differentiation of the mesoderm
8 Neural Crest Development
9
10 Structures Visible in the Basic Cross-Section of the Body (Embryo or Adult!) Coelom Somatopleure Splanchnopleure Parietal Peritoneum Visceral Peritoneum Dorsal mesentery Ventral mesentery
11
12
13
14
15
16
17 Trans-segmental structures versus Segmental structures
18
19
20
21 Gill slits / Gill pouches
22 Further endodermal development: Lateral folds Oropharyngeal membrane Embryonic foregut Embryonic hindgut
23
24
25 Special Senses
26 See in Chapter ½ of your Laboratory Manual...
27 See in Chapter 1/2 of your Laboratory Manual...
28 Special Sense: Smell
29 Hard and Soft Palate(s) separate nasal pharynx from oral pharynx. Right and left sides separated by nasal septum (made up of vomer and perpendicular plate of ethmoid). Free-floating nasal conchae held in place by connective tissue. -Increase surface area. Sensory innervation of nasal cavity by Olfactory Nerve, Cranial nerve I.
30
31 Special Sense: Vision
32 Eye starts out as photosensitive lobe of brain underlying surface of skin. Lobe eventually becomes two-layered cup = retina. Connected to brain by stalk that is the OPITC NERVE (cranial nerve II). Lens from ectodermal placode. Marginal cells of retina become specialized as MUSCLE CELLS that regulate opening of pupil: Sphinctor pupillae (parasympathetically regulated) Dilator pupillae (sympathetically regulated)
33
34 Developing Retina Developing Lens
35 Cells derived from NEURAL CREST condense around retina: CHOROID vascular layer lying directly up against retina. Superficial, more fibrous layer clear in front = CORNEA; white-pigmented remainder = SCLERA.
36
37 Aqueous Chamber Of Eye Vitreous Chamber Of Eye
38 Iris Ciliary Body Choroid Retina Sclera
39 FOCUSING: Distance focus need FLATTER LENS less curvature, greater focal length. Normally, lens is held somewhat flat by taut ligaments. Close-up focus ciliary muscles contract, relieve tension on ligaments, allow lens to get more spherical. Greater curvature, lesser focal length. With age, lens hardens, so even with ciliary muscle action, it can t change shape.
40 Aqueous Chamber Of Eye Vitreous Chamber Of Eye
41 PHOTORECEPTION: Light hits rods (simply light-sensitive) and cones (specifically color-sensitive). Pigments (light sensitive proteins) abosrb light, and change configuration. This changes permiability of cell. (However) When light is absorbed by a photosensitive cell, it is NOT depolarized. It is HYPERPOLARIZED. Once signal gets to optic nerve, it travels as a normal nerve would. Usually takes multiple cells being stimulated to sense light.
42
43 EYEBALL MOVING MUSCLES: Rectus Muscles Superior rectus - III Inferior rectus - III Lateral rectus - VI Medial rectus - III Oblique muscles Superior oblique - IV Inferior oblique - III Lavator palpebrae superioris - III
44
45
46 Special Sense: Hearing & Balance
47 Otic Vesicle
48 Early Development of the Ear
49 Middle Ear Ossicles
50
51
52 Sense of Hearing: Pressure waves in inner ear distort sensory hair cells. Distortion changes membrane. Membrane permiability changes Sodium ions flood in. Depolarization of cell. Action potential.
53
Identify the structure labelled 1.
 Identify the structure labelled 1. Identify the structure labelled 1. Cornea Identify the structure labelled 2. Identify the structure labelled 2. Sclera 1 2 Identify the structure labelled 1. Pupil Identify
Identify the structure labelled 1. Identify the structure labelled 1. Cornea Identify the structure labelled 2. Identify the structure labelled 2. Sclera 1 2 Identify the structure labelled 1. Pupil Identify
Mesoderm Development
 Quiz rules: Spread out across available tables No phones, text books, or (lecture) notes on your desks No consultation with your colleagues No websites open other than the Quiz page No screen snap shots
Quiz rules: Spread out across available tables No phones, text books, or (lecture) notes on your desks No consultation with your colleagues No websites open other than the Quiz page No screen snap shots
Mesoderm Divided into three main types - Paraxial (somite) - Intermediate - Lateral (somatic and splanchnic)
 Mesoderm Divided into three main types - Paraxial (somite) - Intermediate - Lateral (somatic and splanchnic) Fates of Mesoderm Paraxial - Dermis of skin - Axial Skeleton - Axial and limb muscles/tendons
Mesoderm Divided into three main types - Paraxial (somite) - Intermediate - Lateral (somatic and splanchnic) Fates of Mesoderm Paraxial - Dermis of skin - Axial Skeleton - Axial and limb muscles/tendons
Developmental Zoology. Ectodermal derivatives (ZOO ) Developmental Stages. Developmental Stages
 Developmental Zoology (ZOO 228.1.0) Ectodermal derivatives 1 Developmental Stages Ø Early Development Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Neurulation Ø Later Development Organogenesis Larval molts Metamorphosis
Developmental Zoology (ZOO 228.1.0) Ectodermal derivatives 1 Developmental Stages Ø Early Development Fertilization Cleavage Gastrulation Neurulation Ø Later Development Organogenesis Larval molts Metamorphosis
Gut Tube Development. For it s rare that a man thinks of anything so seriously as his dinner!
 For it s rare that a man thinks of anything so seriously as his dinner! Ben Johnson Gut Tube Development This chapter will follow the development of the embryonic gut caudal to the developing pharynx,
For it s rare that a man thinks of anything so seriously as his dinner! Ben Johnson Gut Tube Development This chapter will follow the development of the embryonic gut caudal to the developing pharynx,
Head and Face Development
 Head and Face Development Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ Larsen s Human Embryology The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical Sciences,
Head and Face Development Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ Larsen s Human Embryology The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical Sciences,
BIOLOGY 340 Exam Study Guide All Exams Comparative Embryology Dr. Stuart S. Sumida California State University San Bernardino; Department of Biology
 BIOLOGY 340 Exam Study Guide All Exams Comparative Embryology Dr. Stuart S. Sumida California State University San Bernardino; Department of Biology Midterm and final exams may include materials studied
BIOLOGY 340 Exam Study Guide All Exams Comparative Embryology Dr. Stuart S. Sumida California State University San Bernardino; Department of Biology Midterm and final exams may include materials studied
SENSORY PROCESSES PROVIDE INFORMATION ON ANIMALS EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT AND INTERNAL STATUS 34.4
 SENSORY PROCESSES PROVIDE INFORMATION ON ANIMALS EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT AND INTERNAL STATUS 34.4 INTRODUCTION Animals need information about their external environments to move, locate food, find mates,
SENSORY PROCESSES PROVIDE INFORMATION ON ANIMALS EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT AND INTERNAL STATUS 34.4 INTRODUCTION Animals need information about their external environments to move, locate food, find mates,
Introduction to Animals
 Introduction to Animals Characteristics of Animals multicellular Except for sponges, animal cells are arranged into tissues. Tissues are necessary to produce organs and organ systems. Tissues, organs,
Introduction to Animals Characteristics of Animals multicellular Except for sponges, animal cells are arranged into tissues. Tissues are necessary to produce organs and organ systems. Tissues, organs,
Kingdom Animalia. Zoology the study of animals
 Kingdom Animalia Zoology the study of animals Summary Animals are multicellular and eukaryotic. consume and digest organic materials thereby being heterotrophs. Most are motile at some time in their lives.
Kingdom Animalia Zoology the study of animals Summary Animals are multicellular and eukaryotic. consume and digest organic materials thereby being heterotrophs. Most are motile at some time in their lives.
Developmental Biology Biology Ectodermal Organs. November 22, 2005
 Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Ectodermal Organs November 22, 2005 Germinal neuroepithelium external limiting membrane neural tube neuroepithelium (stem cells) Figure 13.3 Figure 13.4 Neuroepithelial
Developmental Biology Biology 4361 Ectodermal Organs November 22, 2005 Germinal neuroepithelium external limiting membrane neural tube neuroepithelium (stem cells) Figure 13.3 Figure 13.4 Neuroepithelial
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.32 - OVERVIEW OF ANIMALS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes that feed by ingesting their food Most animals are diploid, and produce gametes produced directly by meiosis Animals lack cell
!! www.clutchprep.com Animals are multicellular, heterotrophic eukaryotes that feed by ingesting their food Most animals are diploid, and produce gametes produced directly by meiosis Animals lack cell
Folding of the embryo.. the embryo is becoming a tube like structure
 The embryo is a Folding of the embryo.. the embryo is becoming a tube like structure WEEK 4 EMBRYO General features Primordia of the brain Somites Primordia of the heart Branchial arches Primordia
The embryo is a Folding of the embryo.. the embryo is becoming a tube like structure WEEK 4 EMBRYO General features Primordia of the brain Somites Primordia of the heart Branchial arches Primordia
The Radiata-Bilateria split. Second branching in the evolutionary tree
 The Radiata-Bilateria split Second branching in the evolutionary tree Two very important characteristics are used to distinguish between the second bifurcation of metazoans Body symmetry Germinal layers
The Radiata-Bilateria split Second branching in the evolutionary tree Two very important characteristics are used to distinguish between the second bifurcation of metazoans Body symmetry Germinal layers
Detailed Learning Outcomes
 Detailed Learning Outcomes Following lectures, workshops and directed study activities, students should: 1. Understand the principles behind the study of bioscience in relation to the profession of SLT
Detailed Learning Outcomes Following lectures, workshops and directed study activities, students should: 1. Understand the principles behind the study of bioscience in relation to the profession of SLT
Lesson 16. References: Chapter: 9: Reading for Next Lesson: Chapter: 9:
 Lesson 16 Lesson Outline: The Skull o Neurocranium, Form and Function o Dermatocranium, Form and Function o Splanchnocranium, Form and Function Evolution and Design of Jaws Fate of the Splanchnocranium
Lesson 16 Lesson Outline: The Skull o Neurocranium, Form and Function o Dermatocranium, Form and Function o Splanchnocranium, Form and Function Evolution and Design of Jaws Fate of the Splanchnocranium
Sensory Systems (con t)
 10 th or 11 th Lecture Fri/Mon 06/09 Feb 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh Sensory Processing II Chapter 13 Housekeeping, Fri 06
10 th or 11 th Lecture Fri/Mon 06/09 Feb 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh Sensory Processing II Chapter 13 Housekeeping, Fri 06
Sensory Processing II Chapter 13
 10 th or 11 th Lecture Fri/Mon 06/09 Feb 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh Sensory Processing II Chapter 13 1 Housekeeping, Fri
10 th or 11 th Lecture Fri/Mon 06/09 Feb 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh Sensory Processing II Chapter 13 1 Housekeeping, Fri
Sensory Processing II
 10 th or 11 th Lecture Fri/Mon 06/09 Feb 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh Sensory Processing II Chapter 13 1 Housekeeping, Fri
10 th or 11 th Lecture Fri/Mon 06/09 Feb 2009 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (MCB/VetSci 437) Univ. of Arizona, spring 2009 Kevin Bonine & Kevin Oh Sensory Processing II Chapter 13 1 Housekeeping, Fri
Introduction to Embryology. He who sees things grow from the beginning will have the finest view of them.
 He who sees things grow from the beginning will have the finest view of them. Aristotle 384 322 B.C. Introduction to Embryology This lecture will introduce you to the science of developmental biology or
He who sees things grow from the beginning will have the finest view of them. Aristotle 384 322 B.C. Introduction to Embryology This lecture will introduce you to the science of developmental biology or
Pamela E. Knapp, Ph.D. Dept. of Anatomy & Neurobiology DEVELOPMENT OF THE PHARYNGEAL (BRANCHIAL) ARCHES
 Embryology Pamela E. Knapp, Ph.D. Dept. of Anatomy & Neurobiology DEVELOPMENT OF THE PHARYNGEAL (BRANCHIAL) ARCHES READING: Larsen, 4 th Edition, Chapter 16; or, Langman, 8 th Edition, pp. 345-365 OBJECTIVES:
Embryology Pamela E. Knapp, Ph.D. Dept. of Anatomy & Neurobiology DEVELOPMENT OF THE PHARYNGEAL (BRANCHIAL) ARCHES READING: Larsen, 4 th Edition, Chapter 16; or, Langman, 8 th Edition, pp. 345-365 OBJECTIVES:
Name. Biology Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2013 KEY. Midterm 3
 Name 100 Total Points Open Book Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2013 KEY Midterm 3 Read the Following Instructions: * Answer 20 questions (5 points each) out of the available 25 questions
Name 100 Total Points Open Book Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2013 KEY Midterm 3 Read the Following Instructions: * Answer 20 questions (5 points each) out of the available 25 questions
Lecture 2 - Making babies: Organ formation in the Ectoderm, Mesoderm, Endoderm and Neural Crest. Outline August 15, 2016 Eddy De Robertis, M.D., Ph.D.
 Lecture 2 - Making babies: Organ formation in the Ectoderm, Mesoderm, Endoderm and Neural Crest Lecture Objectives Outline August 15, 2016, M.D., Ph.D. - To examine how the main organ systems are formed
Lecture 2 - Making babies: Organ formation in the Ectoderm, Mesoderm, Endoderm and Neural Crest Lecture Objectives Outline August 15, 2016, M.D., Ph.D. - To examine how the main organ systems are formed
Chapter 9. Benefits of Being Large. Levels of Organization in Organismal Complexity. Hierarchical Organization of Animal Complexity. Fig. 9.
 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 9 Architectural Pattern of an Animal Levels of Organization in Organismal Complexity Zoologists recognize
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 9 Architectural Pattern of an Animal Levels of Organization in Organismal Complexity Zoologists recognize
Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 4 Dr. Stuart Sumida. Overview of Pre-Metazoan. and Protostome Development (Insects)
 Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 4 Dr. Stuart Sumida Overview of Pre-Metazoan and Protostome Development (Insects) Plants Fungi Animals In1998 fossilized animal embryos were reported from the
Biology 340 Comparative Embryology Lecture 4 Dr. Stuart Sumida Overview of Pre-Metazoan and Protostome Development (Insects) Plants Fungi Animals In1998 fossilized animal embryos were reported from the
Revision Based on Chapter 25 Grade 11
 Revision Based on Chapter 25 Grade 11 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Revision Based on Chapter 25 Grade 11 Biology Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
18. Which body system is needed for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide? A. Respiratory B. Integumentary C. Digestive D. Urinary 19.
 1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT a part of the study of anatomy? A. The structure of body parts B. Predicting the body's responses to stimuli C. Microscopic organization D. The relationship
1 Student: 1. Which of the following is NOT a part of the study of anatomy? A. The structure of body parts B. Predicting the body's responses to stimuli C. Microscopic organization D. The relationship
Section 4 Professor Donald McFarlane
 Characteristics Section 4 Professor Donald McFarlane Lecture 11 Animals: Origins and Bauplans Multicellular heterotroph Cells lack cell walls Most have nerves, muscles, capacity to move at some point in
Characteristics Section 4 Professor Donald McFarlane Lecture 11 Animals: Origins and Bauplans Multicellular heterotroph Cells lack cell walls Most have nerves, muscles, capacity to move at some point in
Chapter 1. The Human Organism 1-1
 Chapter 1 The Human Organism 1-1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: Scientific discipline that investigates the body s structure Physiology: Scientific investigation of the processes or functions
Chapter 1 The Human Organism 1-1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: Scientific discipline that investigates the body s structure Physiology: Scientific investigation of the processes or functions
2. Examine the external anatomy of the squid and identify the following structures: tentacles, arms, fins, siphon, mantle, eyes and collar.
 Cephalopod Anatomy As their name implies, members of the class Cephalopoda have modified head-foot which bears an array of prehensile tentacles and arms at the cranial end of the body. The visceral mass
Cephalopod Anatomy As their name implies, members of the class Cephalopoda have modified head-foot which bears an array of prehensile tentacles and arms at the cranial end of the body. The visceral mass
INVERTEBRATE DIVERSITY
 INVERTEBRATE DIVERSITY 1 INVERTEBRATES Animals that lack a backbone Invertebrates 2 1 ANIMAL DEVELOPMENT Meiosis Egg Sperm Zygote Adult Blastula hollow ball of cells in a developing animal Gastrula Stage
INVERTEBRATE DIVERSITY 1 INVERTEBRATES Animals that lack a backbone Invertebrates 2 1 ANIMAL DEVELOPMENT Meiosis Egg Sperm Zygote Adult Blastula hollow ball of cells in a developing animal Gastrula Stage
Today: Animal Body Plans. Animal Body Plans: The Gut. The Animal Kingdom- General Characteristics: Animal Body Plans: Symmetry
 Today: Exploring the Animal Kingdom Introduction to Ecology The Animal Kingdom- General Characteristics: Multicellular Heterotrophic (via ingestion) Eukaryotes Require Oxygen for aerobic respiration Reproduce
Today: Exploring the Animal Kingdom Introduction to Ecology The Animal Kingdom- General Characteristics: Multicellular Heterotrophic (via ingestion) Eukaryotes Require Oxygen for aerobic respiration Reproduce
Comparative Anatomy Biology 440 Fall semester
 Comparative Anatomy Biology 440 Fall semester TuTh 10:00 11:15 G23 Lab at 1:00 in 3106 or 3108 Comparative Anatomy Biology 440 Spring semester TuTh 11:30-12:45 G23 Lab at 2:00 in either 3108 or 3106 Dr.
Comparative Anatomy Biology 440 Fall semester TuTh 10:00 11:15 G23 Lab at 1:00 in 3106 or 3108 Comparative Anatomy Biology 440 Spring semester TuTh 11:30-12:45 G23 Lab at 2:00 in either 3108 or 3106 Dr.
Introduction to Animal Kingdom. Invertebrates and Vertebrates
 Introduction to Animal Kingdom Invertebrates and Vertebrates Introduction To Animals Vertebrate animal with a backbone. Invertebrate animal without a backbone; includes more than 95% of all animal species
Introduction to Animal Kingdom Invertebrates and Vertebrates Introduction To Animals Vertebrate animal with a backbone. Invertebrate animal without a backbone; includes more than 95% of all animal species
Architectural Pattern of an animal. Chapter 9
 Architectural Pattern of an animal Chapter 9 What is an animal? Levels of organization and organismal complexity 5 major levels of complexity Unicellular Metazoan? Tissue Organ Organ systems Levels of
Architectural Pattern of an animal Chapter 9 What is an animal? Levels of organization and organismal complexity 5 major levels of complexity Unicellular Metazoan? Tissue Organ Organ systems Levels of
THE PROBLEMS OF DEVELOPMENT. Cell differentiation. Cell determination
 We emphasize these points from Kandel in Bi/CNS 150 Bi/CNS/NB 150: Neuroscience Read Lecture Lecture Friday, October 2, 2015 Development 1: pp 5-10 Introduction Brains evolved All higher animals have brains
We emphasize these points from Kandel in Bi/CNS 150 Bi/CNS/NB 150: Neuroscience Read Lecture Lecture Friday, October 2, 2015 Development 1: pp 5-10 Introduction Brains evolved All higher animals have brains
PSYCHOSOMATICS COURSE PSYCHOSOMATICS MANUAL. Section E DEVELOPMENTAL ISSUES WORK IN PROGRESS - DO NOT COPY - FOR CORE ENERGETICS TRAINING USE, ONLY!
 PSYCHOSOMATICS MANUAL Section E DEVELOPMENTAL ISSUES 1 DEVELOPMENTAL ISSUES IN HEALTH AND ILLNESS TISSUE LAYERS, ENERGETIC BLUE PRINT and PSYCHOSOMATIC UNITY Understanding the basic function of the tissue
PSYCHOSOMATICS MANUAL Section E DEVELOPMENTAL ISSUES 1 DEVELOPMENTAL ISSUES IN HEALTH AND ILLNESS TISSUE LAYERS, ENERGETIC BLUE PRINT and PSYCHOSOMATIC UNITY Understanding the basic function of the tissue
Chapter 32. Objectives. Table of Contents. Characteristics. Characteristics, continued. Section 1 The Nature of Animals
 Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Objectives Identify four important characteristics of animals. List two kinds of tissues found only in animals. Explain how the first animals may have evolved
Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Objectives Identify four important characteristics of animals. List two kinds of tissues found only in animals. Explain how the first animals may have evolved
Organization of Vertebrate Body. Organization of Vertebrate Body
 The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation Chapter 43 There are four levels of organization: 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems Bodies of vertebrates are composed of different cell types
The Animal Body and Principles of Regulation Chapter 43 There are four levels of organization: 1. Cells 2. Tissues 3. Organs 4. Organ systems Bodies of vertebrates are composed of different cell types
HUMAN EYE AND THE COLOURFUL WORLD
 HUMAN EYE AND THE COLOURFUL WORLD Class: 10 (Boys) Sub: PHYSICS NOTES The Human Eye: The human eye is a sensitive sense organ and acts like a camera, which enable us to capture the colourful picture of
HUMAN EYE AND THE COLOURFUL WORLD Class: 10 (Boys) Sub: PHYSICS NOTES The Human Eye: The human eye is a sensitive sense organ and acts like a camera, which enable us to capture the colourful picture of
Name KEY. Biology Developmental Biology Winter Quarter Midterm 3 KEY
 Name KEY 100 Total Points Open Book Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2009 Midterm 3 KEY All of the 25 multi-choice questions are single-answer. Choose the best answer. (4 pts each) Place
Name KEY 100 Total Points Open Book Biology 411 - Developmental Biology Winter Quarter 2009 Midterm 3 KEY All of the 25 multi-choice questions are single-answer. Choose the best answer. (4 pts each) Place
Animal Origins and Evolution
 Animal Origins and Evolution Common Features of Animals multicellular heterotrophic motile Sexual reproduction, embryo Evolution of Animals All animals are multicellular and heterotrophic, which means
Animal Origins and Evolution Common Features of Animals multicellular heterotrophic motile Sexual reproduction, embryo Evolution of Animals All animals are multicellular and heterotrophic, which means
v Scientists have identified 1.3 million living species of animals v The definition of an animal
 Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements BIOSC 041 v Genetics review: group problem sets Groups of 3-4 Correct answer presented to class = 2 pts extra credit Incorrect attempt = 1 pt extra credit v Lecture: Animal
Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements BIOSC 041 v Genetics review: group problem sets Groups of 3-4 Correct answer presented to class = 2 pts extra credit Incorrect attempt = 1 pt extra credit v Lecture: Animal
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 6, 2007 Mesoderm Formation Chick Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of
Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 6, 2007 Mesoderm Formation Chick Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of
12-The Nervous System. Taft College Human Physiology
 12-The Nervous System Taft College Human Physiology Introduction To The Nervous System The nervous system is a wired system with discrete pathways (nerves) and local actions. The effects of nervous stimulation
12-The Nervous System Taft College Human Physiology Introduction To The Nervous System The nervous system is a wired system with discrete pathways (nerves) and local actions. The effects of nervous stimulation
Are these organisms. animals or not?
 1 2 3 4 5 Are these organisms 6 7 8 animals or not? 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Typical Animal Characteristics Eukaryotic Multicellular Ability to move Reproduce Obtain food (heterotrophic)
1 2 3 4 5 Are these organisms 6 7 8 animals or not? 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Typical Animal Characteristics Eukaryotic Multicellular Ability to move Reproduce Obtain food (heterotrophic)
Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements
 Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements v Genetics review: group problem sets Groups of 3-4 Correct answer presented to class = 2 pts extra credit Incorrect attempt = 1 pt extra credit v Lecture: Animal Body Plans
Biosc 41 9/10 Announcements v Genetics review: group problem sets Groups of 3-4 Correct answer presented to class = 2 pts extra credit Incorrect attempt = 1 pt extra credit v Lecture: Animal Body Plans
Bio Section III Organogenesis. The Neural Crest and Axonal Specification. Student Learning Objectives. Student Learning Objectives
 Bio 127 - Section III Organogenesis The Neural Crest and Axonal Specification Gilbert 9e Chapter 10 Student Learning Objectives 1. You should understand that the neural crest is an evolutionary advancement
Bio 127 - Section III Organogenesis The Neural Crest and Axonal Specification Gilbert 9e Chapter 10 Student Learning Objectives 1. You should understand that the neural crest is an evolutionary advancement
Theory of colour measurement Contemporary wool dyeing and finishing
 Theory of colour measurement Contemporary wool dyeing and finishing Dr Rex Brady Deakin University Colour measurement theory Topics 1. How we see colour 2. Generation of colours 3. Measurement of colour
Theory of colour measurement Contemporary wool dyeing and finishing Dr Rex Brady Deakin University Colour measurement theory Topics 1. How we see colour 2. Generation of colours 3. Measurement of colour
Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos
 Ectoderm Germ Layer Frog Fate Map Frog Fate Map Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos Organizer forms three distinct regions Notochord formation in chick Beta-catenin localization How does beta-catenin
Ectoderm Germ Layer Frog Fate Map Frog Fate Map Role of Organizer Chages in Late Frog Embryos Organizer forms three distinct regions Notochord formation in chick Beta-catenin localization How does beta-catenin
Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm
 Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 7, 2006 Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of BMPs more lateral mesoderm
Biology 4361 Paraxial and Intermediate Mesoderm December 7, 2006 Major Mesoderm Lineages Mesodermal subdivisions are specified along a mediolateral axis by increasing amounts of BMPs more lateral mesoderm
Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The anatomic term means toward the midline. a. anterior b. posterior c. medial d. cranial The term medial indicates an anatomic direction
Chapter 1: Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The anatomic term means toward the midline. a. anterior b. posterior c. medial d. cranial The term medial indicates an anatomic direction
Outline. v Definition and major characteristics of animals v Dividing animals into groups based on: v Animal Phylogeny
 BIOSC 041 Overview of Animal Diversity: Animal Body Plans Reference: Chapter 32 Outline v Definition and major characteristics of animals v Dividing animals into groups based on: Body symmetry Tissues
BIOSC 041 Overview of Animal Diversity: Animal Body Plans Reference: Chapter 32 Outline v Definition and major characteristics of animals v Dividing animals into groups based on: Body symmetry Tissues
Superphylum Deuterostomia
 Superphylum Deuterostomia Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The phyla Echinodermata and Chordata (the phylum in which humans are placed) both belong to the superphylum Deuterostomia. Recall that protostome and deuterostomes
Superphylum Deuterostomia Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The phyla Echinodermata and Chordata (the phylum in which humans are placed) both belong to the superphylum Deuterostomia. Recall that protostome and deuterostomes
BIO 115 SP 2012 Homework 1: Introduction to A&P and Chemistry Please note that this is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 115 SP 2012 Homework 1: Introduction to A&P and Chemistry Please note that this is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. When a body is in the anatomical position, it is A. Standing erect,
BIO 115 SP 2012 Homework 1: Introduction to A&P and Chemistry Please note that this is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. When a body is in the anatomical position, it is A. Standing erect,
Broken Arrow Public Schools Physiology Objectives
 1 st six weeks 1 Define anatomy and physiology. 2 Compare and contrast levels of structural organization. 3 Identify necessary life functions and essential needs and how they are related to homeostasis.
1 st six weeks 1 Define anatomy and physiology. 2 Compare and contrast levels of structural organization. 3 Identify necessary life functions and essential needs and how they are related to homeostasis.
Lecture 07, 13 Sept 2005 Chapters 12 and 13. Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005
 Lecture 07, 13 Sept 2005 Chapters 12 and 13 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Kristen Potter Vertebrate Physiology 437 Chapter
Lecture 07, 13 Sept 2005 Chapters 12 and 13 Vertebrate Physiology ECOL 437 (aka MCB 437, VetSci 437) University of Arizona Fall 2005 instr: Kevin Bonine t.a.: Kristen Potter Vertebrate Physiology 437 Chapter
4: Eating Big, Ugly, Scary Words for Lunch
 4: Eating Big, Ugly, Scary Words for Lunch Today s Subject: As suggested by the title, students will learn not to fear large, technical words, but to rather pause to understand them and add them to their
4: Eating Big, Ugly, Scary Words for Lunch Today s Subject: As suggested by the title, students will learn not to fear large, technical words, but to rather pause to understand them and add them to their
Introduction Chpt 1. Study Slides
 Introduction Chpt 1 Study Slides A group of molecules working together toward a common function is a: A. Cell B. Atom C. Organelle D. Tissue E. Organ ANSWER A group of molecules working together toward
Introduction Chpt 1 Study Slides A group of molecules working together toward a common function is a: A. Cell B. Atom C. Organelle D. Tissue E. Organ ANSWER A group of molecules working together toward
What defines the zygote, the blastula, and the gastrula? Draw pictures.
 What makes a multicellular organism multicellular? a) Multiple cells b) Multiple cells that work together c) Specialized cells d) Multiple specialized cells that work together What defines the zygote,
What makes a multicellular organism multicellular? a) Multiple cells b) Multiple cells that work together c) Specialized cells d) Multiple specialized cells that work together What defines the zygote,
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY Revised 11/2010 DESCRIPTION OF COURSE: Covers the basics of human anatomy and physiology including anatomical terminology, basic biochemistry, cells and tissues, and the integumentary,
ANIMAL DIVERSITY AND THE EVOLUTION OF BODY PLANS
 ANIMAL DIVERSITY AND THE EVOLUTION OF BODY PLANS GENERAL FEATURES OF ANIMALS Heterotrophy - obtain energy and organic molecules by ingesting other organisms Multicellularity - Many have complex bodies
ANIMAL DIVERSITY AND THE EVOLUTION OF BODY PLANS GENERAL FEATURES OF ANIMALS Heterotrophy - obtain energy and organic molecules by ingesting other organisms Multicellularity - Many have complex bodies
Langara College Spring archived
 Instructor: Office: COMPARATIVE VERTEBRATE ANATOMY Anoush Dadgar A303k Office Phone: 604-323-5236 Email: Office Hours: Lab Instructor: adadgar@langara.bc.ca 10:30 M, T, W & Th or by appointment Sandy Connors
Instructor: Office: COMPARATIVE VERTEBRATE ANATOMY Anoush Dadgar A303k Office Phone: 604-323-5236 Email: Office Hours: Lab Instructor: adadgar@langara.bc.ca 10:30 M, T, W & Th or by appointment Sandy Connors
PHYSICS & BIOLOGY IN MEDICINE 218 RADIOLOGIC FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY. Fall 2017
 PHYSICS & BIOLOGY IN MEDICINE 218 RADIOLOGIC FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY Fall 2017 INSTRUCTORS Allan MacKenzie-Graham, PhD Jeff Alger, PhD Neuroscience Research Building 225Z 635 Charles Young Drive Email: amg@ucla.edu
PHYSICS & BIOLOGY IN MEDICINE 218 RADIOLOGIC FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY Fall 2017 INSTRUCTORS Allan MacKenzie-Graham, PhD Jeff Alger, PhD Neuroscience Research Building 225Z 635 Charles Young Drive Email: amg@ucla.edu
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body NOTES
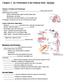 Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body NOTES Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body NOTES Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable
Biology 11. The Kingdom Animalia
 Biology 11 The Kingdom Animalia Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: Describe the 5 ways we classify animals Symmetry Germ layers Body plan Segmentation Animal Evolution Hank Video
Biology 11 The Kingdom Animalia Objectives By the end of the lesson you should be able to: Describe the 5 ways we classify animals Symmetry Germ layers Body plan Segmentation Animal Evolution Hank Video
Some sensory receptors are specialized neurons while others are specialized cells that regulate neurons Figure 50.4
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Sensory and Motor Mechanisms Chapter 50 Sensory receptors transduce stimulus energy and transmit signals to the central nervous system Sensory Pathways Sensory pathways have four basic
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Sensory and Motor Mechanisms Chapter 50 Sensory receptors transduce stimulus energy and transmit signals to the central nervous system Sensory Pathways Sensory pathways have four basic
Applegate: The Anatomy and Physiology Learning System, 3 rd Edition
 Applegate: The Anatomy and Physiology Learning System, 3 rd Edition Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body TRUE/FALSE 1. The cell is the simplest living unit of organization within the human body. T
Applegate: The Anatomy and Physiology Learning System, 3 rd Edition Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body TRUE/FALSE 1. The cell is the simplest living unit of organization within the human body. T
Cells to systems. 1) Chemical Level All matter is a combination of atoms: - Oxygen - Carbon - Nitrogen - Hydrogen Make up 96% of total body chemistry
 Cells to systems Organisation of the Human body: 1. Chemical level 2. Cellular level 3. Tissue level 4. Organ level 5. Body system level 6. Organism level 1) Chemical Level All matter is a combination
Cells to systems Organisation of the Human body: 1. Chemical level 2. Cellular level 3. Tissue level 4. Organ level 5. Body system level 6. Organism level 1) Chemical Level All matter is a combination
Resources. Visual Concepts. Chapter Presentation. Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
 Chapter Presentation Visual Concepts Transparencies Standardized Test Prep Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Section 2 Animal Body Systems Objectives Identify the features that animals have in
Chapter Presentation Visual Concepts Transparencies Standardized Test Prep Introduction to Animals Table of Contents Section 2 Animal Body Systems Objectives Identify the features that animals have in
MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning
 MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning Learning Goals for Lecture 29 4.1 Describe the contributions of early developmental events in the embryo to the formation
MCDB 4777/5777 Molecular Neurobiology Lecture 29 Neural Development- In the beginning Learning Goals for Lecture 29 4.1 Describe the contributions of early developmental events in the embryo to the formation
Essential Question Content Skills Assessment Standards. Anatomical terms. Homeostatic mechanisms. Characteristics of Life. Requirements for life
 Honors Anatomy & Physiology 2012 Michael Harshaw, Melissa Castone Essential Question Content Skills Assessment Standards Month Introduction September- 1.5 weeks How do Anatomy and Physiology relate to
Honors Anatomy & Physiology 2012 Michael Harshaw, Melissa Castone Essential Question Content Skills Assessment Standards Month Introduction September- 1.5 weeks How do Anatomy and Physiology relate to
9/4/2015 INDUCTION CHAPTER 1. Neurons are similar across phyla Thus, many different model systems are used in developmental neurobiology. Fig 1.
 INDUCTION CHAPTER 1 Neurons are similar across phyla Thus, many different model systems are used in developmental neurobiology Fig 1.1 1 EVOLUTION OF METAZOAN BRAINS GASTRULATION MAKING THE 3 RD GERM LAYER
INDUCTION CHAPTER 1 Neurons are similar across phyla Thus, many different model systems are used in developmental neurobiology Fig 1.1 1 EVOLUTION OF METAZOAN BRAINS GASTRULATION MAKING THE 3 RD GERM LAYER
Developmental Biology 3230 Midterm Exam 1 March 2006
 Name Developmental Biology 3230 Midterm Exam 1 March 2006 1. (20pts) Regeneration occurs to some degree to most metazoans. When you remove the head of a hydra a new one regenerates. Graph the inhibitor
Name Developmental Biology 3230 Midterm Exam 1 March 2006 1. (20pts) Regeneration occurs to some degree to most metazoans. When you remove the head of a hydra a new one regenerates. Graph the inhibitor
1/30/2009. Copyright The McGraw Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 CHAPTER 9 Architectural Pattern of an Animal New Designs for Living Zoologists recognize 34 major phyla of living multicellular animals Survivors of around 100 phyla that appeared 600 million years ago
CHAPTER 9 Architectural Pattern of an Animal New Designs for Living Zoologists recognize 34 major phyla of living multicellular animals Survivors of around 100 phyla that appeared 600 million years ago
Introduction to Animal Diversity. Chapter 23.1, 23.2 and additional
 Introduction to Animal Diversity Chapter 23.1, 23.2 and additional 1 Think of an Animal... Does your choice have hair or fur? Does it have a skeleton? Over a million species of animals described 95% have
Introduction to Animal Diversity Chapter 23.1, 23.2 and additional 1 Think of an Animal... Does your choice have hair or fur? Does it have a skeleton? Over a million species of animals described 95% have
Journal #1: How might an Anatomist and Physiologist see a computer differently?
 Journal #1: How might an Anatomist and Physiologist see a computer differently? Objective #1: Define Anatomy and Physiology and describe various specialties of each discipline. Identify the major levels
Journal #1: How might an Anatomist and Physiologist see a computer differently? Objective #1: Define Anatomy and Physiology and describe various specialties of each discipline. Identify the major levels
Developmental Biology Lecture Outlines
 Developmental Biology Lecture Outlines Lecture 01: Introduction Course content Developmental Biology Obsolete hypotheses Current theory Lecture 02: Gametogenesis Spermatozoa Spermatozoon function Spermatozoon
Developmental Biology Lecture Outlines Lecture 01: Introduction Course content Developmental Biology Obsolete hypotheses Current theory Lecture 02: Gametogenesis Spermatozoa Spermatozoon function Spermatozoon
Cell-Cell Communication in Development
 Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development October 2, 2007 Cell-Cell Communication - Topics Induction and competence Paracrine factors inducer molecules Signal transduction
Biology 4361 - Developmental Biology Cell-Cell Communication in Development October 2, 2007 Cell-Cell Communication - Topics Induction and competence Paracrine factors inducer molecules Signal transduction
Neural development its all connected
 Neural development its all connected How do you build a complex nervous system? How do you build a complex nervous system? 1. Learn how tissue is instructed to become nervous system. Neural induction 2.
Neural development its all connected How do you build a complex nervous system? How do you build a complex nervous system? 1. Learn how tissue is instructed to become nervous system. Neural induction 2.
Chapter 32 Intro to Animals. Image from:
 Chapter 32 Intro to Animals Image from: http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/index.html Animals Invertebrates (animals without a backbone) Porifera Cnidaria Worms Mollusks Echinoderms Arthropods Animals
Chapter 32 Intro to Animals Image from: http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/index.html Animals Invertebrates (animals without a backbone) Porifera Cnidaria Worms Mollusks Echinoderms Arthropods Animals
Biology. Part I
 Biology Part I 2014-03 www.u5d.net Part I Mostly humnn biology CONTENT Page Embryology 1 Levels in an organism and systems at large 17 Glands 24 Blood system 27 Muscles 35 Skeleton 45 Åsa Wohlin 1 Embryology
Biology Part I 2014-03 www.u5d.net Part I Mostly humnn biology CONTENT Page Embryology 1 Levels in an organism and systems at large 17 Glands 24 Blood system 27 Muscles 35 Skeleton 45 Åsa Wohlin 1 Embryology
HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY STRUCTURE 30
 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY STRUCTURE 30 Description This second-year course in biology emphasizes the workings of the human body. The course is offered in the fall semester and meets six (6) periods per
HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY STRUCTURE 30 Description This second-year course in biology emphasizes the workings of the human body. The course is offered in the fall semester and meets six (6) periods per
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Prepared by Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar
The Human Body: An Orientation Prepared by Dr. Naim Kittana Dr. Suhaib Hattab Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University 1 Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar
An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology
 C h a p t e r 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris 1-1 The common functions of all living things include responsiveness,
C h a p t e r 1 An Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris 1-1 The common functions of all living things include responsiveness,
Life Sciences For NET & SLET Exams Of UGC-CSIR. Section B and C. Volume-08. Contents A. BASIC CONCEPT OF DEVELOPMENT 1
 Section B and C Volume-08 Contents 5. DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY A. BASIC CONCEPT OF DEVELOPMENT 1 B. GAMETOGENESIS, FERTILIZATION AND EARLY DEVELOPMENT 23 C. MORPHOGENESIS AND ORGANOGENESIS IN ANIMALS 91 0
Section B and C Volume-08 Contents 5. DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY A. BASIC CONCEPT OF DEVELOPMENT 1 B. GAMETOGENESIS, FERTILIZATION AND EARLY DEVELOPMENT 23 C. MORPHOGENESIS AND ORGANOGENESIS IN ANIMALS 91 0
Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition
 Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following describes anatomy? a. Using devices to investigate parameters such as heart rate
Chapter 01: Organization of the Body Patton: Anatomy and Physiology, 9th Edition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Which of the following describes anatomy? a. Using devices to investigate parameters such as heart rate
Chapter 8-9 Intro to Animals. Image from:
 Chapter 8-9 Intro to Animals Image from: http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/index.html Zoology Definition: the scientific study of the behavior, structure, physiology, classification, and distribution
Chapter 8-9 Intro to Animals Image from: http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/index.html Zoology Definition: the scientific study of the behavior, structure, physiology, classification, and distribution
Review sheet for exam III
 Review sheet for exam III WARNING: I have tried to be complete, but I may have missed something. You are responsible for all the material discussed in class. This is only a guide. NOTE: the extra material
Review sheet for exam III WARNING: I have tried to be complete, but I may have missed something. You are responsible for all the material discussed in class. This is only a guide. NOTE: the extra material
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 211 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. 4 Credit Hours. Prepared by: Deborah Allen. Revised date: July, 2014
 JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 211 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Deborah Allen Revised date: July, 2014 Linda Abernathy, Division Chair for Math, Science, and Business Shirley
JEFFERSON COLLEGE COURSE SYLLABUS BIO 211 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 4 Credit Hours Prepared by: Deborah Allen Revised date: July, 2014 Linda Abernathy, Division Chair for Math, Science, and Business Shirley
Introduction to Animal Diversity Lecture 7 Winter 2014
 Introduction to Animal Diversity Lecture 7 Winter 2014 Evolution of Animals 1 Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Prokaryotes No nucleus Nucleoid region Simple No membrane bound organelles Smaller (1-5 nm) Evolutionarily
Introduction to Animal Diversity Lecture 7 Winter 2014 Evolution of Animals 1 Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Prokaryotes No nucleus Nucleoid region Simple No membrane bound organelles Smaller (1-5 nm) Evolutionarily
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
A. Incorrect! Sponges are mostly marine animals. This is a feature of sponges.
 College Biology - Problem Drill 15: The Evolution of Animal Diversity Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which is not a feature of the phyla porifera- sponges? Question #01 (A) Most are marine animals. (B) They have
College Biology - Problem Drill 15: The Evolution of Animal Diversity Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which is not a feature of the phyla porifera- sponges? Question #01 (A) Most are marine animals. (B) They have
Grade 9 Science Review
 G r a d e 9 S c i e n c e R e v i e w E n d o f Y e a r 2 0 1 6 P a g e 1 Grade 9 Science Review Chapter 1 - Organisation of matter 1. Find the density of a mysterious liquid with a mass of 4.5 grams and
G r a d e 9 S c i e n c e R e v i e w E n d o f Y e a r 2 0 1 6 P a g e 1 Grade 9 Science Review Chapter 1 - Organisation of matter 1. Find the density of a mysterious liquid with a mass of 4.5 grams and
Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy Specific Objectives
 Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy Specific Objectives Page 1 General Information A course in Comparative Morphology can be approached from a number of different directions. In my opinion, the important aspects
Comparative Vertebrate Anatomy Specific Objectives Page 1 General Information A course in Comparative Morphology can be approached from a number of different directions. In my opinion, the important aspects
Grade 5, Unit C, Physical Science, Chapter 14, Changing Forms of Energy. How Does sound Behave? Sound Transmits Energy
 Pearson Scott Foresman CORRELATION TO CONNECTICUT SCIENCE FRAMEWORK Grade 5 Core Themes, Content Standards and Expected Performances (User Note: In addition to the student text there are Leveled Readers
Pearson Scott Foresman CORRELATION TO CONNECTICUT SCIENCE FRAMEWORK Grade 5 Core Themes, Content Standards and Expected Performances (User Note: In addition to the student text there are Leveled Readers
Visual pigments. Neuroscience, Biochemistry Dr. Mamoun Ahram Third year, 2019
 Visual pigments Neuroscience, Biochemistry Dr. Mamoun Ahram Third year, 2019 References Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/nbk11522/#a 127) The
Visual pigments Neuroscience, Biochemistry Dr. Mamoun Ahram Third year, 2019 References Webvision: The Organization of the Retina and Visual System (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/nbk11522/#a 127) The
An Episode in the Ancestry of Vertebrates: From Mitrate to Crown-Group Craniate
 A R T I C L E S I N T E G R A T I V E B I O L O G Y 115 A R T I C L E S An Episode in the Ancestry of Vertebrates: From Mitrate to Crown-Group Craniate R. P. S. JEFFERIES AND A. G. JACOBSON Human beings
A R T I C L E S I N T E G R A T I V E B I O L O G Y 115 A R T I C L E S An Episode in the Ancestry of Vertebrates: From Mitrate to Crown-Group Craniate R. P. S. JEFFERIES AND A. G. JACOBSON Human beings
Lesson 10. References: Chapter 8: Reading for Next Lesson: Chapter 8:
 Lesson 10 Lesson Outline: General Features of the Skeletal System Axial Skeleton (Vertebral Column) Ontogenetic Origins (Morphogenesis) of the Skeletal System Functions of the Axial Skeleton Phylogenetic
Lesson 10 Lesson Outline: General Features of the Skeletal System Axial Skeleton (Vertebral Column) Ontogenetic Origins (Morphogenesis) of the Skeletal System Functions of the Axial Skeleton Phylogenetic
Questions in developmental biology. Differentiation Morphogenesis Growth/apoptosis Reproduction Evolution Environmental integration
 Questions in developmental biology Differentiation Morphogenesis Growth/apoptosis Reproduction Evolution Environmental integration Representative cell types of a vertebrate zygote => embryo => adult differentiation
Questions in developmental biology Differentiation Morphogenesis Growth/apoptosis Reproduction Evolution Environmental integration Representative cell types of a vertebrate zygote => embryo => adult differentiation
