|
|
|
- Lambert Doyle
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DOI: /ncb2819 Gαi3 / Actin / Acetylated Tubulin Gαi3 / Actin / Acetylated Tubulin a a Gαi3 a Actin Gαi3 WT Gαi3 WT Gαi3 WT b b Gαi3 b Actin Gαi3 KO Gαi3 KO Gαi3 KO # # Figure S1 Loss of protein expression in Gα i3 knockout. Surface views of cochleae from Gnα i3 wild-type (Gα i3 WT) (a a ) and Gnα i3 knockout mice (Gα i3 KO) (b b ). The strong acetylated tubulin between IHCs and OHC1 rows (b) is due to labeling of the inner pillar cell heads. Labeling of (green) is absent from the cochlear epithelium of the knockouts. IHC (#) and OHC (,,). Scale bar: 10 mm (a-b). 1
2 Figure S2 Acetylated tubulin and pericentrin labeling correlates after G- protein signaling disruption. (a-b ) Representative surface views of HCs from mpins Ctrl (a) and mpins KO mice (b) labeled with pericentrin (green), acetylated tubulin (red) and phalloidin (blue), and the corresponding diagram on the right. Kinocilium and pericentrin coordinates were determined according to a grid applied to each HC as depicted on the HC schemes. The Y axis on the histograms correspond to the pericentrin position (x or y coordinates), the X axis correspond to the kinocilium position (x and y coordinates). Scale bar: 2 mm (a-b). (c,d ) Plots illustrating the correlation between the x and y coordinates from the base of the kinocilium and the pericentrin labeling in (c, c ) Gα i3 WT (n = 102 OHCs, n = 42 IHCs) and (d, d ) Gα i3 KO (n = 108 OHCs, n = 35 IHCs) mice. (e,f ) Plots illustrating the correlation between the x and y coordinates in (e, e ) mpins Ctrl (n=77 OHCs, n=34 IHCs) and (f, f ) mpins KO (n=77 OHCs, n=33 IHCs) mice. (g,h ) Plots illustrating the correlation between the x and y coordinates in (g,g ) PTX-untreated (n=101 OHCs, n=30 IHCs) and (h, h ) PTX-treated (n=110 OHCs, n=47 IHCs) cochlear explants. 2
3 Figure S3 Generation of mpins conditional mutant and localisation of apical asymmetrical complexes in the organ of Corti. (a) Schematic representation of the mouse mpins gene targeting strategy. Exons 5, 6, and 7 of the gene were excised following Cre and Flpe-mediated recombination. Regions of homologous recombination are indicated by light gray shading. AseI (A) and SacI (S) and the locations of the probes (5, 3 ) used for Southern blotting analysis are indicated. (b) Southern blot of recombinant ES cells showing homologous integration. (c) PCR genotyping to detect wild-type (170 bp) and targeted (250 bp) alleles. Cre-mediated excision was confirmed in cochlea by the presence of a 300 bp product. (d) Western blotting analysis of the mpins protein (75 kda) in control and mpins cko inner ear. In the cko, the protein levels are strongly reduced. (e-f ) Surface views of cochleae from mpins controls (Ctrl, e-e ) and mpins conditional knockouts (mpins cko, f-f ) from P0/P1 mice processed for immunocytochemistry. Labeling of mpins (green) is absent from the cochlear epithelium of the conditional knockouts.(g,g ) Surface view (g) and Z-stack (g ) confocal cross-section showing the apical localization of Par-6b (green) compared to β-catenin (red). (g ) Lateral view of (g) at the level indicated by the dashed line. (h, h ) Gα i3 (green) is located on the distal-abneural side of the HCs, opposite Vangl2 (red). (h ) High magnification of the inset in h. (i, i ) Gα o (green) labeling reveals weak cytosolic staining in HCs and in the non-sensory region, but no asymmetrical accumulation. Hair bundles and cell junctions were labeled with phalloidin (blue). (j) Representative immunoblot of brain (expressing Gα o ) and liver (not expressing Gα o ) membranes using Gα o antibody. Purified Gα o1 protein served as a positive control. IHC (#) and OHC (,,). Scale bar: 10 mm (e-i). 3
4 Figure S4 Gα i inhibition leads to loss-of-cilium-like morphological defects in the hair bundle. (a) In cultures treated with 5 pg/ml PTX for 48 hours (T3) the distributions of the orientations follow a gradient of severity from OHC1 to OHC3. HCs numbers, out of 2 cochleae per condition, are as follows: PTX T3 (n = 65,68,64 respectively for OHC1, OHC2, OHC3) (b, b ) Vangl2 asymmetry (green) is maintained in mpins cko. (c-d ) In cultures treated with 5 pg/ml PTX for 24 hours (T1), we observe hair bundles exhibiting round (c, c ) or flat shapes (d, d ). (e-f ) The apkc expression domain is more extended at the membrane of HCs in cultures treated with high doses (1 ng/ml) of PTX (f f ) compared to untreated (Unt) cultures (e e ). Note the long cilium in PTX-treated cultures. (g-i) High magnifications of a representative HC from (e) and (f). (h, j) Circular histograms of the distribution of apkc staining in Unt and PTX-treated condition. Each histogram represent data from 30 HCs. Statistical analysis via a two-tailed t test (P< ). Error bars show s.e.m. Scale bars: 10 µm (in b, e-f), 2 µm (in b -d, g -i ). 4
5 Figure S5 Gα i3 is recruited asymmetrically prior to kinocilium migration. (a c ) Luminal surface views of a cochlear epithelium at E15.5 at different locations along the duct. In the apical region of the sensory epithelium, only a few scattered HCs (future IHCs) have started to undergo differentiation, as indicated by MyoVI expression (a, arrowheads) and an apical actin ring (a, arrowheads). (b-b4) In a more basal region of the cochlea, and in the distal-abneural OHC region, Gα i3 starts to accumulate centrally in a few differentiating cells (b, white arrow). In the absence of asymmetrical Gα i3 localization, the kinocilium does not migrate in these cells (b, b1, b2, white arrowhead). By comparison, a line of differentiated IHCs is present, expressing Gα i3 asymmetrically and showing a distal kinocilium (b, b3-b4, yellow arrow and arrowhead). The white lines indicate the relative midline of every HC. (c c ) Luminal surface views of the basal region of cochlear epithelia at E15.5. Gα i3 is asymmetrically localized at the distal-abneural side of IHCs but absent from the prospective OHC region. Insets: higher magnification view of IHCs (yellow arrow) and future OHCs (white arrow) from (c) revealing that the kinocilium is always localized distally in IHCs (yellow arrowhead) but not in future OHCs (white arrowhead). (d-e ) Luminal surface views of the mid-basal to apical region of cochlear epithelia at E16.5 labeled with apkc (d-d ) and Par-6b (e,e ). The proteins are not asymmetrically distributed. (fg) HC differentiation is completed by P0, with every HC expressing MyoVI (f, green), and Gα i3 is asymmetrically localized to the distal-abneural side along with the kinocilium (g and g1-g4, green). Scale bars: 10 µm (in a-f). (h-i ) The asymmetric distribution of mpins (h-h, green) and Par-6B (i, i ) are inverted across the striola in the P0 utricular epithelium (dashed line). β2- spectrin immunostaining labels the cuticular plate (red). Arrows indicate HC polarity with respect to the lateral (Lat) or medial (Med) side of the utricle. (j) Scatter plots of the localization of the kinocilium relative to the center of the Gα i3 expression domain reveals a strong association between Gα i3 and the kinocilium position in wild type (n = 218 OHCs and 68 IHCs), Vangl2 Lp/ Lp (n = 237 OHCs and 73 IHCs) and PTK7 mutants (n = 124 OHCs and 33 IHCs). The dashed line indicates a perfect correlation (r = 1). (k, k ) Ectopic HCs induced by Atoh1-IRES-GFP expression (green) in the non-sensory epithelium display asymmetric cortical apkc (red) localization opposite to the kinocilium side. The dashed line indicates the boundary between the sensory and nonsensory epithelium. (l) Schematic representation of (k). 5
6 Figure S6 Full scans 6
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3267 Supplementary Figure 1 A group of genes required for formation or orientation of annular F-actin bundles and aecm ridges: RNAi phenotypes and their validation by standard mutations.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3267 Supplementary Figure 1 A group of genes required for formation or orientation of annular F-actin bundles and aecm ridges: RNAi phenotypes and their validation by standard mutations.
Fig. S1. Proliferation and cell cycle exit are affected by the med mutation. (A,B) M-phase nuclei are visualized by a-ph3 labeling in wild-type (A)
 Fig. S1. Proliferation and cell cycle exit are affected by the med mutation. (A,B) M-phase nuclei are visualized by a-ph3 labeling in wild-type (A) and mutant (B) 4 dpf retinae. The central retina of the
Fig. S1. Proliferation and cell cycle exit are affected by the med mutation. (A,B) M-phase nuclei are visualized by a-ph3 labeling in wild-type (A) and mutant (B) 4 dpf retinae. The central retina of the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 GP2 Type I-piliated bacteria FAE M cell M cell pocket idc T cell mdc Generation of antigenspecific T cells Induction of antigen-specific mucosal immune response Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic diagram
GP2 Type I-piliated bacteria FAE M cell M cell pocket idc T cell mdc Generation of antigenspecific T cells Induction of antigen-specific mucosal immune response Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic diagram
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11419 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of innate immune signaling pathways induced by intracellular Salmonella in cultured macrophages. a, During the infection Salmonella
doi:10.1038/nature11419 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of innate immune signaling pathways induced by intracellular Salmonella in cultured macrophages. a, During the infection Salmonella
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/301/ra98/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Epithelial Morphogenesis by the G Protein Coupled Receptor Mist and Its Ligand Fog Alyssa J. Manning,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/301/ra98/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Regulation of Epithelial Morphogenesis by the G Protein Coupled Receptor Mist and Its Ligand Fog Alyssa J. Manning,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb97 P ( μm, hours) 1 2 4 P DMSO Figure S1 unningham et al. E 97 65 27 MFN1 GFP-Parkin Opa1 ctin GPDH HEK293 GFP-Parkin 19 115 97 65 27 Mitochondrial Fraction SH-SY5Y GFP-Parkin Mito DMSO Mito
DOI:.38/ncb97 P ( μm, hours) 1 2 4 P DMSO Figure S1 unningham et al. E 97 65 27 MFN1 GFP-Parkin Opa1 ctin GPDH HEK293 GFP-Parkin 19 115 97 65 27 Mitochondrial Fraction SH-SY5Y GFP-Parkin Mito DMSO Mito
Supplementary Figure 1. Real time in vivo imaging of SG secretion. (a) SGs from Drosophila third instar larvae that express Sgs3-GFP (green) and
 Supplementary Figure 1. Real time in vivo imaging of SG secretion. (a) SGs from Drosophila third instar larvae that express Sgs3-GFP (green) and Lifeact-Ruby (red) were imaged in vivo to visualize secretion
Supplementary Figure 1. Real time in vivo imaging of SG secretion. (a) SGs from Drosophila third instar larvae that express Sgs3-GFP (green) and Lifeact-Ruby (red) were imaged in vivo to visualize secretion
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2215 Figure S1 Number of egfp-vps4a bursts versus cellular expression levels. The total number of egfp-vps4a bursts, counted at the end of each movie (frame 2000, after 1h 28 min) are plotted
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2215 Figure S1 Number of egfp-vps4a bursts versus cellular expression levels. The total number of egfp-vps4a bursts, counted at the end of each movie (frame 2000, after 1h 28 min) are plotted
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2647 Figure S1 Other Rab GTPases do not co-localize with the ER. a, Cos-7 cells cotransfected with an ER luminal marker (either KDEL-venus or mch-kdel) and mch-tagged human Rab5 (mch-rab5,
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2647 Figure S1 Other Rab GTPases do not co-localize with the ER. a, Cos-7 cells cotransfected with an ER luminal marker (either KDEL-venus or mch-kdel) and mch-tagged human Rab5 (mch-rab5,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12791 Supplementary Figure 1 (1/3) WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 (2/3) 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE SUPPLEMENTARY
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12791 Supplementary Figure 1 (1/3) WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 RESEARCH SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 (2/3) 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE SUPPLEMENTARY
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. NAD + -related genes expression in mouse tissues and in cells overexpressing NRK1. mrna (a) and protein (b) levels of NRK1, NRK2 and other enzymes involved
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. NAD + -related genes expression in mouse tissues and in cells overexpressing NRK1. mrna (a) and protein (b) levels of NRK1, NRK2 and other enzymes involved
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2362 Figure S1 CYLD and CASPASE 8 genes are co-regulated. Analysis of gene expression across 79 tissues was carried out as described previously [Ref: PMID: 18636086]. Briefly, microarray
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2362 Figure S1 CYLD and CASPASE 8 genes are co-regulated. Analysis of gene expression across 79 tissues was carried out as described previously [Ref: PMID: 18636086]. Briefly, microarray
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2662
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlastin phylogeny and homology. (a) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on 18 Atlastin-1 sequences using the program Quicktree. Numbers at internal nodes correspond to bootstrap
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlastin phylogeny and homology. (a) Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on 18 Atlastin-1 sequences using the program Quicktree. Numbers at internal nodes correspond to bootstrap
Supplemental Data. Perrella et al. (2013). Plant Cell /tpc
 Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity 150 50 150 0 10 20 50 C 150 0 10 20 50 D 0 10 20 Distance (μm) 50 20 40 E 50 F 0 10 20 50 0 15 30 Distance (μm) Supplemental Figure 1: Co-localization
Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity Intensity 150 50 150 0 10 20 50 C 150 0 10 20 50 D 0 10 20 Distance (μm) 50 20 40 E 50 F 0 10 20 50 0 15 30 Distance (μm) Supplemental Figure 1: Co-localization
Supplementary Figure 1: To test the role of mir-17~92 in orthologous genetic model of ADPKD, we generated Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F (Pkd1-KO) and Ksp/Cre;Pkd1
 Supplementary Figure 1: To test the role of mir-17~92 in orthologous genetic model of ADPKD, we generated Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F (Pkd1-KO) and Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F ;mir-17~92 F/F (Pkd1-miR-17~92KO) mice. (A) Q-PCR
Supplementary Figure 1: To test the role of mir-17~92 in orthologous genetic model of ADPKD, we generated Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F (Pkd1-KO) and Ksp/Cre;Pkd1 F/F ;mir-17~92 F/F (Pkd1-miR-17~92KO) mice. (A) Q-PCR
downstream (0.8 kb) homologous sequences to the genomic locus of DIC. A DIC mutant strain (ro- 6
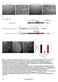 A B C D ts Figure S1 Generation of DIC- mcherry expressing N.crassa strain. A. N. crassa colony morphology. When a cot1 (top, left panel) strain is grown at permissive temperature (25 C), it exhibits straight
A B C D ts Figure S1 Generation of DIC- mcherry expressing N.crassa strain. A. N. crassa colony morphology. When a cot1 (top, left panel) strain is grown at permissive temperature (25 C), it exhibits straight
Hair Cells: The Sensory Transducers of the Inner Ear
 Chapter 1 Hair Cells: The Sensory Transducers of the Inner Ear Hair cells are specialized cells that transform a mechanical motion into changes in membrane potential. Such changes, whereby one form of
Chapter 1 Hair Cells: The Sensory Transducers of the Inner Ear Hair cells are specialized cells that transform a mechanical motion into changes in membrane potential. Such changes, whereby one form of
Supplemental Data. Wang et al. (2014). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Figure1: Mock and NPA-treated tomato plants. (A) NPA treated tomato (cv. Moneymaker) developed a pin-like inflorescence (arrowhead). (B) Comparison of first and second leaves from mock and
Supplemental Figure1: Mock and NPA-treated tomato plants. (A) NPA treated tomato (cv. Moneymaker) developed a pin-like inflorescence (arrowhead). (B) Comparison of first and second leaves from mock and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11589 Supplementary Figure 1 Ciona intestinalis and Petromyzon marinus neural crest expression domain comparison. Cartoon shows dorsal views of Ciona mid gastrula (left) and Petromyzon
doi:10.1038/nature11589 Supplementary Figure 1 Ciona intestinalis and Petromyzon marinus neural crest expression domain comparison. Cartoon shows dorsal views of Ciona mid gastrula (left) and Petromyzon
Role of Mitochondrial Remodeling in Programmed Cell Death in
 Developmental Cell, Vol. 12 Supplementary Data Role of Mitochondrial Remodeling in Programmed Cell Death in Drosophila melanogaster Gaurav Goyal, Brennan Fell, Apurva Sarin, Richard J. Youle, V. Sriram.
Developmental Cell, Vol. 12 Supplementary Data Role of Mitochondrial Remodeling in Programmed Cell Death in Drosophila melanogaster Gaurav Goyal, Brennan Fell, Apurva Sarin, Richard J. Youle, V. Sriram.
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles
 Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
Illegitimate translation causes unexpected gene expression from on-target out-of-frame alleles created by CRISPR-Cas9 Shigeru Makino, Ryutaro Fukumura, Yoichi Gondo* Mutagenesis and Genomics Team, RIKEN
Auditory Hair Cell Centrioles Undergo Confined Brownian Motion Throughout the Developmental Migration of the Kinocilium
 48 Biophysical Journal Volume 105 July 2013 48 58 Auditory Hair Cell Centrioles Undergo Confined Brownian Motion Throughout the Developmental Migration of the Kinocilium Léa Lepelletier, k ** 6 Jacques
48 Biophysical Journal Volume 105 July 2013 48 58 Auditory Hair Cell Centrioles Undergo Confined Brownian Motion Throughout the Developmental Migration of the Kinocilium Léa Lepelletier, k ** 6 Jacques
Supplemental Information. The Mitochondrial Fission Receptor MiD51. Requires ADP as a Cofactor
 Structure, Volume 22 Supplemental Information The Mitochondrial Fission Receptor MiD51 Requires ADP as a Cofactor Oliver C. Losón, Raymond Liu, Michael E. Rome, Shuxia Meng, Jens T. Kaiser, Shu-ou Shan,
Structure, Volume 22 Supplemental Information The Mitochondrial Fission Receptor MiD51 Requires ADP as a Cofactor Oliver C. Losón, Raymond Liu, Michael E. Rome, Shuxia Meng, Jens T. Kaiser, Shu-ou Shan,
Dishevelled genes mediate a conserved mammalian PCP pathway to regulate convergent extension during neurulation
 RESEARCH ARTICLE 1767 Development 133, 1767-1778 (2006) doi:10.1242/dev.02347 Dishevelled genes mediate a conserved mammalian PCP pathway to regulate convergent extension during neurulation Jianbo Wang
RESEARCH ARTICLE 1767 Development 133, 1767-1778 (2006) doi:10.1242/dev.02347 Dishevelled genes mediate a conserved mammalian PCP pathway to regulate convergent extension during neurulation Jianbo Wang
Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice Supplementary Figure 2.
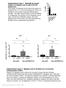 Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice. Percentage of marginal zone B cells in the spleen of wild-type mice (+/+), mice homozygous for cpm or pri
Supplementary Figure 1. Markedly decreased numbers of marginal zone B cells in DOCK8 mutant mice. Percentage of marginal zone B cells in the spleen of wild-type mice (+/+), mice homozygous for cpm or pri
Article. PTK7 Regulates Myosin II Activity to Orient Planar Polarity in the Mammalian Auditory Epithelium
 Current Biology 22, 956 966, June 5, 2012 ª2012 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2012.03.068 PTK7 Regulates Myosin II Activity to Orient Planar Polarity in the Mammalian Auditory Epithelium
Current Biology 22, 956 966, June 5, 2012 ª2012 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2012.03.068 PTK7 Regulates Myosin II Activity to Orient Planar Polarity in the Mammalian Auditory Epithelium
FSC-W FSC-H CD4 CD62-L
 Supplementary Fig. 1 a SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H CD4 CD62-L b SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-A FSC-A 7-AAD FSC-A CD4 IL-9 CD4 c SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H 7-AAD KI67 Annexin-V 7-AAD d I L -5
Supplementary Fig. 1 a SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H CD4 CD62-L b SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-A FSC-A 7-AAD FSC-A CD4 IL-9 CD4 c SSC-A FSC-A FSC-W FSC-H SSC-W SSC-H 7-AAD KI67 Annexin-V 7-AAD d I L -5
Heather Currinn, Benjamin Guscott, Zita Balklava, Alice Rothnie and Thomas Wassmer*
 Online Resources APP controls the formation of PI(3,5)P 2 vesicles through its binding of the PIKfyve complex. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences Heather Currinn, Benjamin Guscott, Zita Balklava, Alice
Online Resources APP controls the formation of PI(3,5)P 2 vesicles through its binding of the PIKfyve complex. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences Heather Currinn, Benjamin Guscott, Zita Balklava, Alice
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1 Sns and Duf co-localise in embryonic nephrocytes a-c, Wild-type stage 11 (a),14 (b) and 16 (c) embryos stained with anti-duf (green) and anti-sns (red). Higher magnification images
Supplementary Figure 1 Sns and Duf co-localise in embryonic nephrocytes a-c, Wild-type stage 11 (a),14 (b) and 16 (c) embryos stained with anti-duf (green) and anti-sns (red). Higher magnification images
Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods Modeling of magnetic field In this study, the magnetic field was generated with N52 grade nickel-plated neodymium block magnets (K&J Magnetics). The residual flux density of the magnets
Supplementary Methods Modeling of magnetic field In this study, the magnetic field was generated with N52 grade nickel-plated neodymium block magnets (K&J Magnetics). The residual flux density of the magnets
Supplemental material
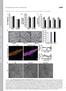 Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Mourier et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201411100/dc1 Figure S1. Size and mitochondrial content in Mfn1 and Mfn2 knockout hearts. (A) Body
Supplemental material THE JOURNAL OF CELL BIOLOGY Mourier et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201411100/dc1 Figure S1. Size and mitochondrial content in Mfn1 and Mfn2 knockout hearts. (A) Body
Mitochondrial Dynamics Is a Distinguishing Feature of Skeletal Muscle Fiber Types and Regulates Organellar Compartmentalization
 Cell Metabolism Supplemental Information Mitochondrial Dynamics Is a Distinguishing Feature of Skeletal Muscle Fiber Types and Regulates Organellar Compartmentalization Prashant Mishra, Grigor Varuzhanyan,
Cell Metabolism Supplemental Information Mitochondrial Dynamics Is a Distinguishing Feature of Skeletal Muscle Fiber Types and Regulates Organellar Compartmentalization Prashant Mishra, Grigor Varuzhanyan,
Fluid Flow and Interlinked Feedback Loops Establish Left-Right Asymmetric Decay of Cerl2 mrna in the Mouse Embryo
 Fluid Flow and Interlinked Feedback Loops Establish Left-Right Asymmetric Decay of Cerl2 mrna in the Mouse Embryo Tetsuya Nakamura, 1 Daisuke Saito, 2 Aiko Kawasumi, 1 Kyosuke Shinohara, 1 Yasuko Asai,
Fluid Flow and Interlinked Feedback Loops Establish Left-Right Asymmetric Decay of Cerl2 mrna in the Mouse Embryo Tetsuya Nakamura, 1 Daisuke Saito, 2 Aiko Kawasumi, 1 Kyosuke Shinohara, 1 Yasuko Asai,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Cao et al. 10.1073/pnas.1306220110 Gram - bacteria Hemolymph Cytoplasm PGRP-LC TAK1 signalosome Imd dfadd Dredd Dnr1 Ikk signalosome P Relish Nucleus AMP and effector genes Fig.
Supporting Information Cao et al. 10.1073/pnas.1306220110 Gram - bacteria Hemolymph Cytoplasm PGRP-LC TAK1 signalosome Imd dfadd Dredd Dnr1 Ikk signalosome P Relish Nucleus AMP and effector genes Fig.
Intravital Imaging Reveals Ghost Fibers as Architectural Units Guiding Myogenic Progenitors during Regeneration
 Cell Stem Cell Supplemental Information Intravital Imaging Reveals Ghost Fibers as Architectural Units Guiding Myogenic Progenitors during Regeneration Micah T. Webster, Uri Manor, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz,
Cell Stem Cell Supplemental Information Intravital Imaging Reveals Ghost Fibers as Architectural Units Guiding Myogenic Progenitors during Regeneration Micah T. Webster, Uri Manor, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz,
Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell /tpc
 Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.109.071837 1 C Total 5 kg 20 kg 100 kg Transmission Image 100 kg soluble pdtpi-gfp Plastid (PDH-alpha) Mito (PDH-alpha) GFP Image vector
Supplemental Data. Chen and Thelen (2010). Plant Cell 10.1105/tpc.109.071837 1 C Total 5 kg 20 kg 100 kg Transmission Image 100 kg soluble pdtpi-gfp Plastid (PDH-alpha) Mito (PDH-alpha) GFP Image vector
Actions of auxin. Hormones: communicating with chemicals History: Discovery of a growth substance (hormone- auxin)
 Hormones: communicating with chemicals History- discovery of plant hormone. Auxin Concepts of hormones Auxin levels are regulated by synthesis/degradation, transport, compartmentation, conjugation. Polar
Hormones: communicating with chemicals History- discovery of plant hormone. Auxin Concepts of hormones Auxin levels are regulated by synthesis/degradation, transport, compartmentation, conjugation. Polar
TNFα 18hr. Control. CHX 18hr. TNFα+ CHX 18hr. TNFα: 18 18hr (KDa) PARP. Cleaved. Cleaved. Cleaved. Caspase3. Pellino3 shrna. Control shrna.
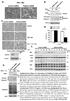 Survival ( %) a. TNFα 18hr b. Control sirna Pellino3 sirna TNFα: 18 18hr c. Control shrna Pellino3 shrna Caspase3 Actin Control d. Control shrna Pellino3 shrna *** 100 80 60 CHX 18hr 40 TNFα+ CHX 18hr
Survival ( %) a. TNFα 18hr b. Control sirna Pellino3 sirna TNFα: 18 18hr c. Control shrna Pellino3 shrna Caspase3 Actin Control d. Control shrna Pellino3 shrna *** 100 80 60 CHX 18hr 40 TNFα+ CHX 18hr
Super-resolution microscopy reveals a LINC complex recruitment at nuclear indentation sites
 Supplementary Information Super-resolution microscopy reveals a LINC complex recruitment at nuclear indentation sites Marie Versaevel 1, Jean-Baptiste Braquenier 2, Maryam Riaz 1, Thomas Grevesse 1, Joséphine
Supplementary Information Super-resolution microscopy reveals a LINC complex recruitment at nuclear indentation sites Marie Versaevel 1, Jean-Baptiste Braquenier 2, Maryam Riaz 1, Thomas Grevesse 1, Joséphine
Lipid transfer proteins confer resistance to trichothecenes
 Lipid transfer proteins confer resistance to trichothecenes John McLaughlin and Anwar Bin-Umer Tumer Laboratory National Fusarium Head Blight Forum December 6th, 2012 FY09-11: Identify trichothecene resistance
Lipid transfer proteins confer resistance to trichothecenes John McLaughlin and Anwar Bin-Umer Tumer Laboratory National Fusarium Head Blight Forum December 6th, 2012 FY09-11: Identify trichothecene resistance
Supplementary Figure 1. AnnexinV FITC and Sytox orange staining in wild type, Nlrp3 /, ASC / and casp1/11 / TEC treated with TNF /CHX.
 Supplementary Figure 1. AnnexinV FITC and Sytox orange staining in wild type, Nlrp3 /, ASC / and casp1/11 / TEC treated with TNF /CHX. Phase contrast and widefield fluorescence microscopy (20x magnification).
Supplementary Figure 1. AnnexinV FITC and Sytox orange staining in wild type, Nlrp3 /, ASC / and casp1/11 / TEC treated with TNF /CHX. Phase contrast and widefield fluorescence microscopy (20x magnification).
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. In vitro screening of recombinant R-CaMP2 variants.
 Supplementary Figure 1 In vitro screening of recombinant R-CaMP2 variants. Baseline fluorescence compared to R-CaMP1.07 at nominally zero calcium plotted versus dynamic range ( F/F) for 150 recombinant
Supplementary Figure 1 In vitro screening of recombinant R-CaMP2 variants. Baseline fluorescence compared to R-CaMP1.07 at nominally zero calcium plotted versus dynamic range ( F/F) for 150 recombinant
Functional interactions between Fat family cadherins in tissue morphogenesis and planar polarity
 1806 RESEARCH ARTICLE Development 139, 1806-1820 (2012) doi:10.1242/dev.077461 2012. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Functional interactions between Fat family cadherins in tissue morphogenesis
1806 RESEARCH ARTICLE Development 139, 1806-1820 (2012) doi:10.1242/dev.077461 2012. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Functional interactions between Fat family cadherins in tissue morphogenesis
Transitivity-dependent and transitivity-independent cell-to-cell movement of RNA
 Himber et al. Transitivity-dependent and transitivity-independent cell-to-cell movement of RNA silencing SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental material 1. Short-range movement of GFP silencing affects a nearly
Himber et al. Transitivity-dependent and transitivity-independent cell-to-cell movement of RNA silencing SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental material 1. Short-range movement of GFP silencing affects a nearly
Neurite formation & neuronal polarization
 Neurite formation & neuronal polarization Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 An immature neuron in cell culture first sprouts
Neurite formation & neuronal polarization Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 An immature neuron in cell culture first sprouts
Turing at 100: Legacy of a universal mind
 Turing at 100: Legacy a universal mind Nature 23 february 2012 Turing instability u t = au+ bv+ D u xxu u 3 dv dt = cu+ dv+ D v xxv Above threshold Below threshold Turing instability : a simple non linear
Turing at 100: Legacy a universal mind Nature 23 february 2012 Turing instability u t = au+ bv+ D u xxu u 3 dv dt = cu+ dv+ D v xxv Above threshold Below threshold Turing instability : a simple non linear
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10923 Supplementary Figure 1 Ten-a and Ten-m antibody and cell type specificities. a c, Representative single confocal sections of a Drosophila NMJ stained with antibodies to Ten-a (red),
doi:10.1038/nature10923 Supplementary Figure 1 Ten-a and Ten-m antibody and cell type specificities. a c, Representative single confocal sections of a Drosophila NMJ stained with antibodies to Ten-a (red),
Three Myosins Contribute Uniquely to the Assembly and Constriction of the Fission Yeast Cytokinetic Contractile Ring
 Current Biology Supplemental Information Three Myosins Contribute Uniquely to the Assembly and Constriction of the Fission Yeast Cytokinetic Contractile Ring Caroline Laplante, Julien Berro, Erdem Karatekin,
Current Biology Supplemental Information Three Myosins Contribute Uniquely to the Assembly and Constriction of the Fission Yeast Cytokinetic Contractile Ring Caroline Laplante, Julien Berro, Erdem Karatekin,
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterisation of IHG-1 overexpressing and knockdown cell lines. (A) Total cellular RNA was prepared from HeLa cells stably overexpressing IHG-1 or mts-ihg-1. IHG-1 mrna was quantified
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterisation of IHG-1 overexpressing and knockdown cell lines. (A) Total cellular RNA was prepared from HeLa cells stably overexpressing IHG-1 or mts-ihg-1. IHG-1 mrna was quantified
Fig. S1. Expression pattern of moody-gal4 in third instar. Maximum projection illustrating a dissected moody-gal4>ngfp L3 larva stained for Repo
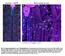 Fig. S1. Expression pattern of moody-gal4 in third instar. Maximum projection illustrating a dissected moody-gal4>ngfp L3 larva stained for Repo (magenta), Fas2 (blue) and GFP (green) in overview (A) and
Fig. S1. Expression pattern of moody-gal4 in third instar. Maximum projection illustrating a dissected moody-gal4>ngfp L3 larva stained for Repo (magenta), Fas2 (blue) and GFP (green) in overview (A) and
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. The phenotypes of PI , BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions.
 Supplementary Figure 1 The phenotypes of PI 159925, BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions. (a) Plant height. (b) Number of branches. (c) Average internode length. (d) Number of nodes. (e) Pods
Supplementary Figure 1 The phenotypes of PI 159925, BR121, and Harosoy under short-day conditions. (a) Plant height. (b) Number of branches. (c) Average internode length. (d) Number of nodes. (e) Pods
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005
 7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
7.06 Problem Set #4, Spring 2005 1. You re doing a mutant hunt in S. cerevisiae (budding yeast), looking for temperaturesensitive mutants that are defective in the cell cycle. You discover a mutant strain
Supplementary Figure 1. CoMIC in 293T, HeLa, and HepG2 cells. (a) Mitochondrial morphology in 293T, HeLa and HepG2 cells. Cells were transfected with
 Supplementary Figure 1. CoMIC in 293T, HeLa, and HepG2 cells. (a) Mitochondrial morphology in 293T, HeLa and HepG2 cells. Cells were transfected with DsRed-mito. Right panels are time-course enlarged images
Supplementary Figure 1. CoMIC in 293T, HeLa, and HepG2 cells. (a) Mitochondrial morphology in 293T, HeLa and HepG2 cells. Cells were transfected with DsRed-mito. Right panels are time-course enlarged images
Table S1 List of primers used for genotyping and qrt-pcr.
 Table S1 List of primers used for genotyping and qrt-pcr. genotyping! allele! ligomer*! 5'-sequence-3'! rice! d10-2! F! TTGGCTTTGCCTCGTTTC!!! R! AGCCTCCACTTGTACTGTG! Arabidopsis! max2-3, max2-4! F! ACTCTCTCCGACCTCCCTGACG!!!
Table S1 List of primers used for genotyping and qrt-pcr. genotyping! allele! ligomer*! 5'-sequence-3'! rice! d10-2! F! TTGGCTTTGCCTCGTTTC!!! R! AGCCTCCACTTGTACTGTG! Arabidopsis! max2-3, max2-4! F! ACTCTCTCCGACCTCCCTGACG!!!
Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell
 Supplemental Materials Molecular iology of the Cell Figure S1 Krüger et al. Arabidopsis Plasmodium H. sapiens* 1) Xenopus* 1) Drosophila C.elegans S.cerevisae S.pombe L.major T.cruzi T.brucei DCP5 CITH
Supplemental Materials Molecular iology of the Cell Figure S1 Krüger et al. Arabidopsis Plasmodium H. sapiens* 1) Xenopus* 1) Drosophila C.elegans S.cerevisae S.pombe L.major T.cruzi T.brucei DCP5 CITH
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of beige fat and cells and characteristics of exosome release, related to Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of beige fat and cells and characteristics of exosome release, related to Figure 1 (a) Fold-change in UCP-1 mrna abundance in white adipocytes upon β-adrenergic stimulation
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of beige fat and cells and characteristics of exosome release, related to Figure 1 (a) Fold-change in UCP-1 mrna abundance in white adipocytes upon β-adrenergic stimulation
Actinobacteria Relative abundance (%) Co-housed CD300f WT. CD300f KO. Colon length (cm) Day 9. Microscopic inflammation score
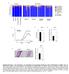 y groups y individuals 9 Actinobacteria Relative abundance (%) acteroidetes Cyanobacteria Deferribacteres Firmicutes Proteobacteria TM Tenericutes Unclassified CDf CDf Co-housed CDf Co-housed CDf CDf CDf
y groups y individuals 9 Actinobacteria Relative abundance (%) acteroidetes Cyanobacteria Deferribacteres Firmicutes Proteobacteria TM Tenericutes Unclassified CDf CDf Co-housed CDf Co-housed CDf CDf CDf
Neurite formation & neuronal polarization. The cytoskeletal components of neurons have characteristic distributions and associations
 Mechanisms of neuronal migration & Neurite formation & neuronal polarization Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 The cytoskeletal
Mechanisms of neuronal migration & Neurite formation & neuronal polarization Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 The cytoskeletal
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Figure S1. Mitochondrial morphology in Fis1-null, Mff-null and Fis1/Mff-null MEF cells. (A) Western blotting of lysates from Fis1-null, Mff-null and Fis1/Mff-null cells. Lysates were
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Figure S1. Mitochondrial morphology in Fis1-null, Mff-null and Fis1/Mff-null MEF cells. (A) Western blotting of lysates from Fis1-null, Mff-null and Fis1/Mff-null cells. Lysates were
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/281/ra51/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Rapgef2 Connects GPCR-Mediated camp Signals to ERK Activation in Neuronal and Endocrine Cells Andrew C. Emery, Maribeth
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/281/ra51/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Rapgef2 Connects GPCR-Mediated camp Signals to ERK Activation in Neuronal and Endocrine Cells Andrew C. Emery, Maribeth
Biological Roles of Cytokinins
 Direct Control of Shoot Meristem Activity by a Cytokinin-Activating Enzyme By Kurakawa et. Al. Published in Nature Presented by Boyana Grigorova Biological Roles of Cytokinins Cytokinins are positive regulators
Direct Control of Shoot Meristem Activity by a Cytokinin-Activating Enzyme By Kurakawa et. Al. Published in Nature Presented by Boyana Grigorova Biological Roles of Cytokinins Cytokinins are positive regulators
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. HSP21 expression in 35S:HSP21 and hsp21 knockdown plants. (a) Since no T- DNA insertion line for HSP21 is available in the publicly available T-DNA collections,
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. HSP21 expression in 35S:HSP21 and hsp21 knockdown plants. (a) Since no T- DNA insertion line for HSP21 is available in the publicly available T-DNA collections,
Isoform-specific functions of Mud/NuMA mediate binucleation of Drosophila male accessory gland cells
 Taniguchi et al. BMC Developmental Biology (2014) 14:46 DOI 10.1186/s12861-014-0046-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Isoform-specific functions of Mud/NuMA mediate binucleation of Drosophila male accessory
Taniguchi et al. BMC Developmental Biology (2014) 14:46 DOI 10.1186/s12861-014-0046-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Isoform-specific functions of Mud/NuMA mediate binucleation of Drosophila male accessory
Distinct capacity for differentiation to inner ear cell types by progenitor cells of the cochlea and vestibular organs
 First posted online on 27 October 2016 as 10.1242/dev.139840 Access the most recent version at http://dev.biologists.org/lookup/doi/10.1242/dev.139840 Distinct capacity for differentiation to inner ear
First posted online on 27 October 2016 as 10.1242/dev.139840 Access the most recent version at http://dev.biologists.org/lookup/doi/10.1242/dev.139840 Distinct capacity for differentiation to inner ear
Tissue/planar cell polarity in vertebrates: new insights and new questions
 REVIEW 647 Development 134, 647-658 (2007) doi:10.1242/dev.02772 Tissue/planar cell polarity in vertebrates: new insights and new questions Yanshu Wang 1 and Jeremy Nathans 1,2 This review focuses on the
REVIEW 647 Development 134, 647-658 (2007) doi:10.1242/dev.02772 Tissue/planar cell polarity in vertebrates: new insights and new questions Yanshu Wang 1 and Jeremy Nathans 1,2 This review focuses on the
Hair Cell Generation by Notch Inhibition in the Adult Mammalian Cristae
 JARO 14: 813 828 (2013) DOI: 10.1007/s10162-013-0414-z D 2013 Association for Research in Otolaryngology Research Article JARO Journal of the Association for Research in Otolaryngology Hair Cell Generation
JARO 14: 813 828 (2013) DOI: 10.1007/s10162-013-0414-z D 2013 Association for Research in Otolaryngology Research Article JARO Journal of the Association for Research in Otolaryngology Hair Cell Generation
Retinoic acid signalling regulates the development of tonotopically patterned hair cells in the chicken cochlea
 Received 23 Sep 2013 Accepted 8 Apr 2014 Published 20 May 2014 DOI: 10.1038/ncomms4840 Retinoic acid signalling regulates the development of tonotopically patterned hair cells in the chicken cochlea Benjamin
Received 23 Sep 2013 Accepted 8 Apr 2014 Published 20 May 2014 DOI: 10.1038/ncomms4840 Retinoic acid signalling regulates the development of tonotopically patterned hair cells in the chicken cochlea Benjamin
Baz, Par-6 and apkc are not required for axon or dendrite specification in Drosophila
 Baz, Par-6 and apkc are not required for axon or dendrite specification in Drosophila Melissa M. Rolls and Chris Q. Doe, Inst. Neurosci and Inst. Mol. Biol., HHMI, Univ. Oregon, Eugene, Oregon 97403 Correspondence
Baz, Par-6 and apkc are not required for axon or dendrite specification in Drosophila Melissa M. Rolls and Chris Q. Doe, Inst. Neurosci and Inst. Mol. Biol., HHMI, Univ. Oregon, Eugene, Oregon 97403 Correspondence
Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of REF52-hE2F1p::4NLS-d4Venus reporter cells and characterization of E2F dynamics. (a) Alignment of E2F dynamics
 Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of REF52-hE2F1p::4NLS-d4Venus reporter cells and characterization of E2F dynamics. (a) Alignment of E2F dynamics trajectories to endogenous E2F1 mrna expression. Gray
Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of REF52-hE2F1p::4NLS-d4Venus reporter cells and characterization of E2F dynamics. (a) Alignment of E2F dynamics trajectories to endogenous E2F1 mrna expression. Gray
Frequency (Hz) Amplitude (pa) D1 WT D1 KO D2 WT D2 KO D1 WT D1 KO D2 WT D2 KO
 A D1 MSNs B D2 MSNs C Frequency (Hz) 4 3 2 1 D Amplitude (pa) 5 4 3 2 1 D1 D1 D2 D2 D1 D1 D2 D2 Supplemental Figure 1. B deletion did not alter GABA-mIPSCs in D1 or D2 MSNs. (A,B) Representative recording
A D1 MSNs B D2 MSNs C Frequency (Hz) 4 3 2 1 D Amplitude (pa) 5 4 3 2 1 D1 D1 D2 D2 D1 D1 D2 D2 Supplemental Figure 1. B deletion did not alter GABA-mIPSCs in D1 or D2 MSNs. (A,B) Representative recording
The retinoblastoma gene pathway regulates the postmitotic state of hair cells of the mouse inner ear
 Research article 2377 The retinoblastoma gene pathway regulates the postmitotic state of hair cells of the mouse inner ear Johanna Mantela 1, Zhe Jiang 2, Jukka Ylikoski 1, Bernd Fritzsch 3, Eldad Zacksenhaus
Research article 2377 The retinoblastoma gene pathway regulates the postmitotic state of hair cells of the mouse inner ear Johanna Mantela 1, Zhe Jiang 2, Jukka Ylikoski 1, Bernd Fritzsch 3, Eldad Zacksenhaus
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals unique sets of neuropeptides, transcription factors and receptors in specific types of sympathetic neurons (a) Dissection of paravertebral SGs
Supplementary Figure 1 Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals unique sets of neuropeptides, transcription factors and receptors in specific types of sympathetic neurons (a) Dissection of paravertebral SGs
targets. clustering show that different complex pathway
 Supplementary Figure 1. CLICR allows clustering and activation of cytoplasmic protein targets. (a, b) Upon light activation, the Cry2 (red) and LRP6c (green) components co-cluster due to the heterodimeric
Supplementary Figure 1. CLICR allows clustering and activation of cytoplasmic protein targets. (a, b) Upon light activation, the Cry2 (red) and LRP6c (green) components co-cluster due to the heterodimeric
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES AND THEIR LEGENDS. Transient infection of the zebrafish notochord triggers chronic inflammation
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES AND THEIR LEGENDS Transient infection of the zebrafish notochord triggers chronic inflammation Mai Nguyen-Chi 1,2,5, Quang Tien Phan 1,2,5, Catherine Gonzalez 1,2, Jean-François
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES AND THEIR LEGENDS Transient infection of the zebrafish notochord triggers chronic inflammation Mai Nguyen-Chi 1,2,5, Quang Tien Phan 1,2,5, Catherine Gonzalez 1,2, Jean-François
Hes5. Hes Relative mrna levels
 A a Absolute mrna levels 6 5 4 3 2 1 hjag1 EP cdl1 EP Jag1 E2+1 b d m Hey1 c e EP Hey1 Dl1 E2+1 f h m Hey1 g i EP Hey1 1 a Hes5 Hes5 a Hes5 Hes5 B a b EP e 1.4 1.2 EP GFP GFP E2+1 c m Hey1 d Hey1 Relative
A a Absolute mrna levels 6 5 4 3 2 1 hjag1 EP cdl1 EP Jag1 E2+1 b d m Hey1 c e EP Hey1 Dl1 E2+1 f h m Hey1 g i EP Hey1 1 a Hes5 Hes5 a Hes5 Hes5 B a b EP e 1.4 1.2 EP GFP GFP E2+1 c m Hey1 d Hey1 Relative
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 med!1,2 Wild-type (N2) end!3 elt!2 5 1 15 Time (minutes) 5 1 15 Time (minutes) med!1,2 end!3 5 1 15 Time (minutes) elt!2 5 1 15 Time (minutes) Supplementary Figure 1: Number of med-1,2, end-3, end-1 and
med!1,2 Wild-type (N2) end!3 elt!2 5 1 15 Time (minutes) 5 1 15 Time (minutes) med!1,2 end!3 5 1 15 Time (minutes) elt!2 5 1 15 Time (minutes) Supplementary Figure 1: Number of med-1,2, end-3, end-1 and
Anisotropy of Crumbs and apkc Drives Myosin Cable Assembly during Tube Formation
 Article Anisotropy of Crumbs and apkc Drives Myosin Cable Assembly during Tube Formation Katja Röper 1, * 1 MRC-Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Cambridge CB2 0QH, UK *Correspondence: kroeper@mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk
Article Anisotropy of Crumbs and apkc Drives Myosin Cable Assembly during Tube Formation Katja Röper 1, * 1 MRC-Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Cambridge CB2 0QH, UK *Correspondence: kroeper@mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk
The Role of GRASP65 in Golgi Cisternal Stacking and Cell Cycle Progression
 Traffic 2010; 11: 827 842 2010 John Wiley & Sons A/S doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01055.x The Role of GRASP65 in Golgi Cisternal Stacking and Cell Cycle Progression Danming Tang, Hebao Yuan and Yanzhuang
Traffic 2010; 11: 827 842 2010 John Wiley & Sons A/S doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2010.01055.x The Role of GRASP65 in Golgi Cisternal Stacking and Cell Cycle Progression Danming Tang, Hebao Yuan and Yanzhuang
CILIA are multifunctional organelles that form on the. Unexpected Roles for Ciliary Kinesins and Intraflagellar Transport Proteins
 HIGHLIGHTED ARTICLE INVESTIGATION Unexpected Roles for Ciliary Kinesins and Intraflagellar Transport Proteins Niedharsan Pooranachandran and Jarema J. Malicki 1 Bateson Centre and the Department of Biomedical
HIGHLIGHTED ARTICLE INVESTIGATION Unexpected Roles for Ciliary Kinesins and Intraflagellar Transport Proteins Niedharsan Pooranachandran and Jarema J. Malicki 1 Bateson Centre and the Department of Biomedical
NOVA regulates Dcc alternative splicing during neuronal migration and axon guidance in the spinal cord.
 University of Colorado, Boulder CU Scholar Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology Faculty Contributions Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology 5-25-2016 NOVA regulates Dcc alternative splicing
University of Colorado, Boulder CU Scholar Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology Faculty Contributions Molecular, Cellular, and Developmental Biology 5-25-2016 NOVA regulates Dcc alternative splicing
Developmental Biology
 Developmental Biology 334 (2009) 161 173 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Developmental Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Wingless signaling and the control of cell
Developmental Biology 334 (2009) 161 173 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Developmental Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Wingless signaling and the control of cell
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
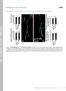 Supplemental material Kasprowicz et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201310090/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. NMJ morphology of shi 12-12B ; shi-4c not treated
Supplemental material Kasprowicz et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201310090/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. NMJ morphology of shi 12-12B ; shi-4c not treated
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. ssp mutant phenotypes in a functional SP background.
 Supplementary Figure 1 ssp mutant phenotypes in a functional SP background. (a,b) Statistical comparisons of primary and sympodial shoot flowering times as determined by mean values for leaf number on
Supplementary Figure 1 ssp mutant phenotypes in a functional SP background. (a,b) Statistical comparisons of primary and sympodial shoot flowering times as determined by mean values for leaf number on
Ordered patterns of cell shape and orientational correlation during spontaneous cell migration. Supplementary information
 Ordered patterns of cell shape and orientational correlation during spontaneous cell migration Supplementary information Yusuke T. Maeda*, Junya Inose, Miki Y. Matsuo, Suguru Iwaya and Masaki Sano Department
Ordered patterns of cell shape and orientational correlation during spontaneous cell migration Supplementary information Yusuke T. Maeda*, Junya Inose, Miki Y. Matsuo, Suguru Iwaya and Masaki Sano Department
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Statistical organelle dissection of Arabidopsis guard cells using image database LIPS Takumi Higaki *, Natsumaro Kutsuna, Yoichiroh Hosokawa, Kae Akita, Kazuo Ebine, Takashi Ueda,
Supplementary information Statistical organelle dissection of Arabidopsis guard cells using image database LIPS Takumi Higaki *, Natsumaro Kutsuna, Yoichiroh Hosokawa, Kae Akita, Kazuo Ebine, Takashi Ueda,
Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the
 Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the interaction of OPTN and TBK1. (a) Analytical gel filtration chromatography analysis of the interaction between TBK1 CTD and OPTN(1-119).
Supplementary Figure 1. Biochemical and sequence alignment analyses the interaction of OPTN and TBK1. (a) Analytical gel filtration chromatography analysis of the interaction between TBK1 CTD and OPTN(1-119).
4) Please cite Dagda et al J Biol Chem 284: , for any publications or presentations resulting from use or modification of the macro.
 Supplement Figure S1. Algorithmic quantification of mitochondrial morphology in SH- SY5Y cells treated with known fission/fusion mediators. Parental SH-SY5Y cells were transiently transfected with an empty
Supplement Figure S1. Algorithmic quantification of mitochondrial morphology in SH- SY5Y cells treated with known fission/fusion mediators. Parental SH-SY5Y cells were transiently transfected with an empty
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/11/eaao4709/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Pushing the limits of photoreception in twilight conditions: The rod-like cone retina of the deep-sea pearlsides Fanny
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/11/eaao4709/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Pushing the limits of photoreception in twilight conditions: The rod-like cone retina of the deep-sea pearlsides Fanny
Gipc1 has a dual role in Vangl2 trafficking and hair bundle integrity in the inner ear
 RESEARCH ARTICLE 3775 Development 139, 3775-3785 (2012) doi:10.1242/dev.074229 2012. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Gipc1 has a dual role in Vangl2 trafficking and hair bundle integrity in
RESEARCH ARTICLE 3775 Development 139, 3775-3785 (2012) doi:10.1242/dev.074229 2012. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Gipc1 has a dual role in Vangl2 trafficking and hair bundle integrity in
23-. Shoot and root development depend on ratio of IAA/CK
 Balance of Hormones regulate growth and development Environmental factors regulate hormone levels light- e.g. phototropism gravity- e.g. gravitropism temperature Mode of action of each hormone 1. Signal
Balance of Hormones regulate growth and development Environmental factors regulate hormone levels light- e.g. phototropism gravity- e.g. gravitropism temperature Mode of action of each hormone 1. Signal
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information MAP2/Hoechst Hyp.-AP ph 6.5 Hyp.-SD ph 7.2 Norm.-SD ph 7.2 Supplementary Figure 1. Mitochondrial elongation in cortical neurons by acidosis. Representative images of neuronal
Supplementary Information MAP2/Hoechst Hyp.-AP ph 6.5 Hyp.-SD ph 7.2 Norm.-SD ph 7.2 Supplementary Figure 1. Mitochondrial elongation in cortical neurons by acidosis. Representative images of neuronal
The Role of Inorganic Carbon Transport and Accumulation in the CO 2 -Concentrating Mechanism and CO 2 Assimilation in Chlamydomonas
 The Role of Inorganic Carbon Transport and Accumulation in the CO 2 -Concentrating Mechanism and CO 2 Assimilation in Chlamydomonas Is there a Role for the CCM in Increasing Biological CO 2 Capture? Generalized
The Role of Inorganic Carbon Transport and Accumulation in the CO 2 -Concentrating Mechanism and CO 2 Assimilation in Chlamydomonas Is there a Role for the CCM in Increasing Biological CO 2 Capture? Generalized
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/9/e1500511/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Contractility parameters of human -cardiac myosin with the hypertrophic cardiomyopathy mutation R403Q show loss of
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/9/e1500511/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Contractility parameters of human -cardiac myosin with the hypertrophic cardiomyopathy mutation R403Q show loss of
Supporting Information
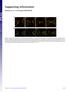 Supporting Information Fleissner et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907039106 Fig. S1. (A) MAK-2-GFP localized to CATs tips is not bound by membrane. his-3::pccg1 mak-2-gfp; mak-2 strain labeled with membrane dye FM4
Supporting Information Fleissner et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907039106 Fig. S1. (A) MAK-2-GFP localized to CATs tips is not bound by membrane. his-3::pccg1 mak-2-gfp; mak-2 strain labeled with membrane dye FM4
Micro-Flow in a bundle of micro-pillars. A. Keißner, Ch. Brücker
 Micro-Flow in a bundle of micro-pillars A. Keißner, Ch. Brücker Institute of Mechanics and Fluid Dynamics, University of Freiberg, TU Freiberg, Germany, Email: armin.keissner@imfd.tu-freiberg.de Abstract
Micro-Flow in a bundle of micro-pillars A. Keißner, Ch. Brücker Institute of Mechanics and Fluid Dynamics, University of Freiberg, TU Freiberg, Germany, Email: armin.keissner@imfd.tu-freiberg.de Abstract
Chapter 4 Evaluating a potential interaction between deltex and git in Drosophila: genetic interaction, gene overexpression and cell biology assays.
 Evaluating a potential interaction between deltex and git in Drosophila: genetic interaction, gene overexpression and cell biology assays. The data described in chapter 3 presented evidence that endogenous
Evaluating a potential interaction between deltex and git in Drosophila: genetic interaction, gene overexpression and cell biology assays. The data described in chapter 3 presented evidence that endogenous
Genetically Modified Human Renal Proximal Tubule Epithelial Cells (RPTEC/TERT1) A New Model for Drug Toxicity Studies
 Genetically Modified Human Renal Proximal Tubule Epithelial Cells (RPTEC/TERT1) A New Model for Drug Toxicity Studies Chaozhong Zou, Ph.D. Senior Scientist, ATCC About ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit
Genetically Modified Human Renal Proximal Tubule Epithelial Cells (RPTEC/TERT1) A New Model for Drug Toxicity Studies Chaozhong Zou, Ph.D. Senior Scientist, ATCC About ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit
Supplementary Figure 1-10 with Figure legends
 332 coordinates mechanotransduction and growth cone bifurcation in sensory neurons Li Yang Chiang 1, Kate Poole, Beatriz E. Oliveira, Neuza Duarte,Yinth Andrea Bernal Sierra, Leena Bruckner Tuderman, Manuel
332 coordinates mechanotransduction and growth cone bifurcation in sensory neurons Li Yang Chiang 1, Kate Poole, Beatriz E. Oliveira, Neuza Duarte,Yinth Andrea Bernal Sierra, Leena Bruckner Tuderman, Manuel
Supplementary Information. In colloidal drop drying processes, multi-ring depositions are formed due to the stick-slip
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI for Soft Matter. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 14 Supplementary Information A1. Contact line receding velocity of an evaporating drop In colloidal
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI for Soft Matter. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 14 Supplementary Information A1. Contact line receding velocity of an evaporating drop In colloidal
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Different crystal forms obtained for Sky
 Supplementary Figure 1 Different crystal forms obtained for Sky 1 353. (a) Crystal form 1 obtained in the presence of 20% PEG 3350 and 0.2 M ammonium citrate tribasic ph 7.0. (b) Crystal form 1 of the
Supplementary Figure 1 Different crystal forms obtained for Sky 1 353. (a) Crystal form 1 obtained in the presence of 20% PEG 3350 and 0.2 M ammonium citrate tribasic ph 7.0. (b) Crystal form 1 of the
